Neodymium iron boron magnet surface anti-corrosion treatment method
An anti-corrosion treatment, NdFeB technology, applied in the direction of surface pretreatment, machine tools for surface polishing, devices for coating liquid on the surface, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient surface treatment of NdFeB magnets before anti-corrosion, and improve the appearance of inconsistency Phenomenon, reduce uncontrollable factors, high cleanliness effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-1
[0049] A method for anticorrosion treatment of the surface of an NdFeB magnet, the steps of which are:
[0050](1) Put the NdFeB product into a vibrating finishing machine for dry grinding. The abrasive is resin abrasive M1 doped with silicon carbide. The frequency of the equipment is 50Hz. Abrasive: product = 6:1 (weight ratio), and the time is 40min , the product roughness after grinding is 0.2μm;
[0051] (2) After the treatment in (1), the product is phosphated by dipping method. The phosphating time is 5 minutes, and the temperature of the phosphating solution is 50°C. After phosphating, the product is washed, dried, and dried to obtain product A01.
Embodiment 1-2
[0053] A method for anticorrosion treatment of the surface of an NdFeB magnet, the steps of which are:
[0054] (1) Put the NdFeB product into a vibrating finishing machine for dry grinding. The abrasive is resin abrasive M1 doped with silicon carbide. The frequency of the equipment is 50Hz. Abrasive: product = 6:1 (weight ratio), and the time is 30min , the product roughness after grinding is 0.8μm;
[0055] (2) After the treatment in (1), the product is phosphated by dipping method. The phosphating time is 5 minutes, and the temperature of the phosphating solution is 50°C. After phosphating, the product is washed, dried, and dried to obtain product A02.
Embodiment 1
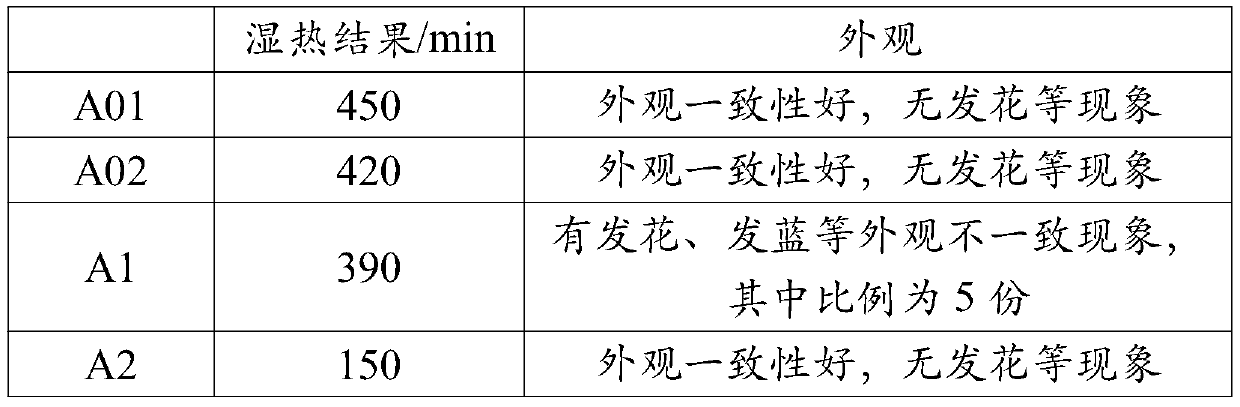
[0068] The whole process of embodiment 1 (A01 and A02) and comparative example 1 (A1) has no loss of base material, but the pretreatment process of comparative example 2 (A2) can cause the loss of each 0.01mm of product length, width and thickness, making the cost increase high. Namely: Embodiments A01 and A02 and the NdFeB magnet surface anticorrosion treatment process using abrasive M1 replace the degreasing-water washing-(pickling-water washing) process, simplify the process flow, and have no substrate loss and consistent appearance Good performance and lower cost.
[0069] And Example 1-1 is compared with 1-2, the appearance results are consistent, but the roughness of the ground product has a slight impact on the heat and humidity resistance of the magnet, that is, the product with a roughness of 0.8 μm after grinding is better than the product after grinding For products with a roughness of 0.2 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com