Heat-resistant magnesium alloy and preparation method thereof
A magnesium alloy, heat-resistant technology, applied in the field of new material preparation, can solve the problem that the alloy is not suitable for large-scale commercial use, achieve high market value, improve heat resistance, and reduce costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] This embodiment provides a heat-resistant magnesium alloy, the composition of which is: zinc Zn0.7Wt.%, zirconium Zr0.5Wt.%, rare earth neodymium Nd1.0Wt.%, rare earth yttrium Y2.3Wt.%, metal cobalt Co0.2Wt .%, metal molybdenum Mo0.2Wt.%, metal vanadium V0.5Wt.%; alkaline earth calcium Ca2.0Wt.%, alkaline earth strontium Sr0.2Wt.%, and the balance of Mg and unavoidable impurities in the casting process and / or modifying elements.
[0041] The preparation steps of the heat-resistant magnesium alloy are:
[0042] (1) Add Nd, Y, Ca, Sr and Mg to the smelting furnace respectively according to the composition and melt to prepare master alloys Mg-Ca, Mg-Sr, Mg-Nd and Mg-Y;
[0043] (2) Heat the crucible resistance furnace to 750-780°C, use graphite or stainless steel crucible to melt the magnesium ingot under the cover agent, and then add Mg-Ca, Mg-Sr, Mg-Nd, Mg-Y, Zn, Zr, Co, Mo and V, heat preservation at 750-780°C for ten minutes, pay attention to stirring the melt duri...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the composition of the heat-resistant magnesium alloy is: zinc Zn0.5Wt.%, zirconium Zr0.6Wt.%, rare earth neodymium Nd1.3Wt.%, rare earth yttrium Y2.5Wt.%, metal Cobalt Co0.2Wt.%, metal molybdenum Mo0.2Wt.%, metal vanadium V0.5Wt.%; alkaline earth calcium Ca2.0Wt.%, alkaline earth strontium Sr0.2Wt.%, and the balance of Mg and unavoidable in the casting process impurities and / or modifying elements. The magnesium alloy ingot (without any treatment) prepared by the gas shielded melting casting method was subjected to a mechanical test, and the obtained mechanical performance indexes are shown in Table 2.
[0051] Table 2
[0052] Temperature T(°C) Yield strength σ s (MPa)
[0053] There is no obvious difference between Example 1 and Example 2 in room temperature and high temperature performance, the difference is that the content of rare earth Nd and rare earth Y in Example 1 is reduced, and th...
Embodiment 3
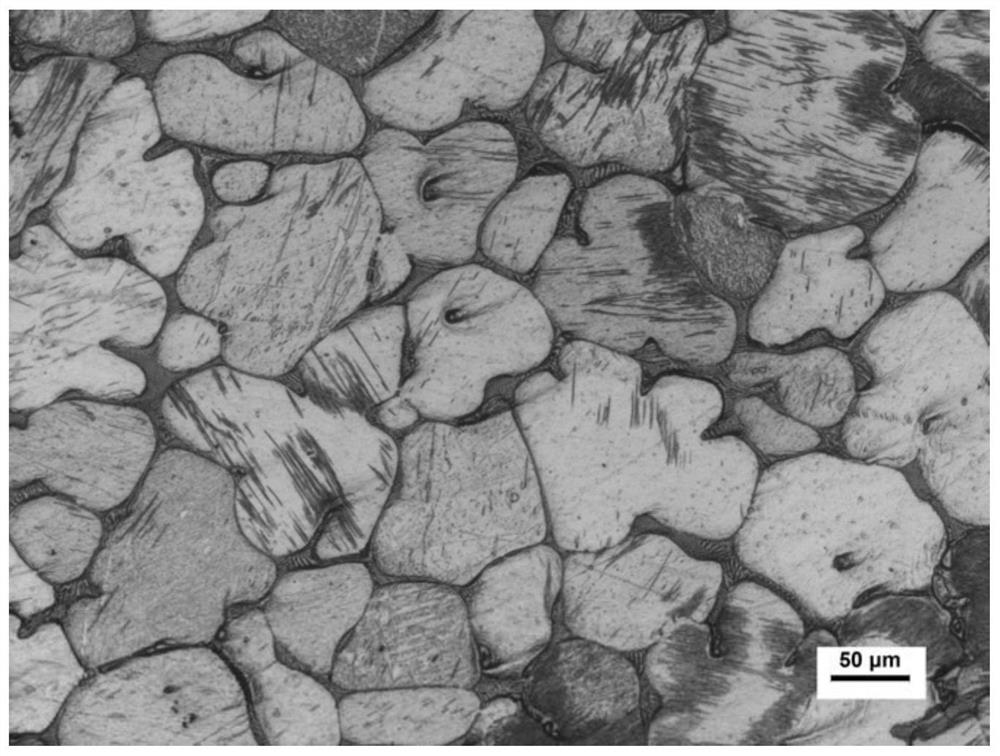
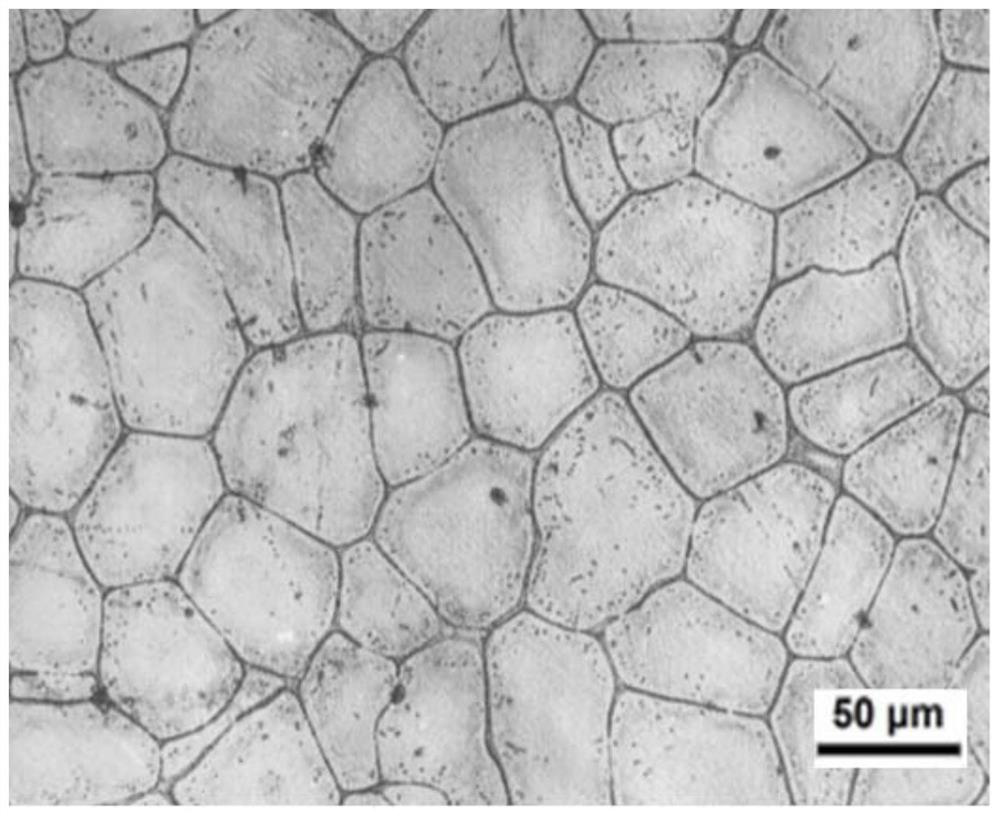
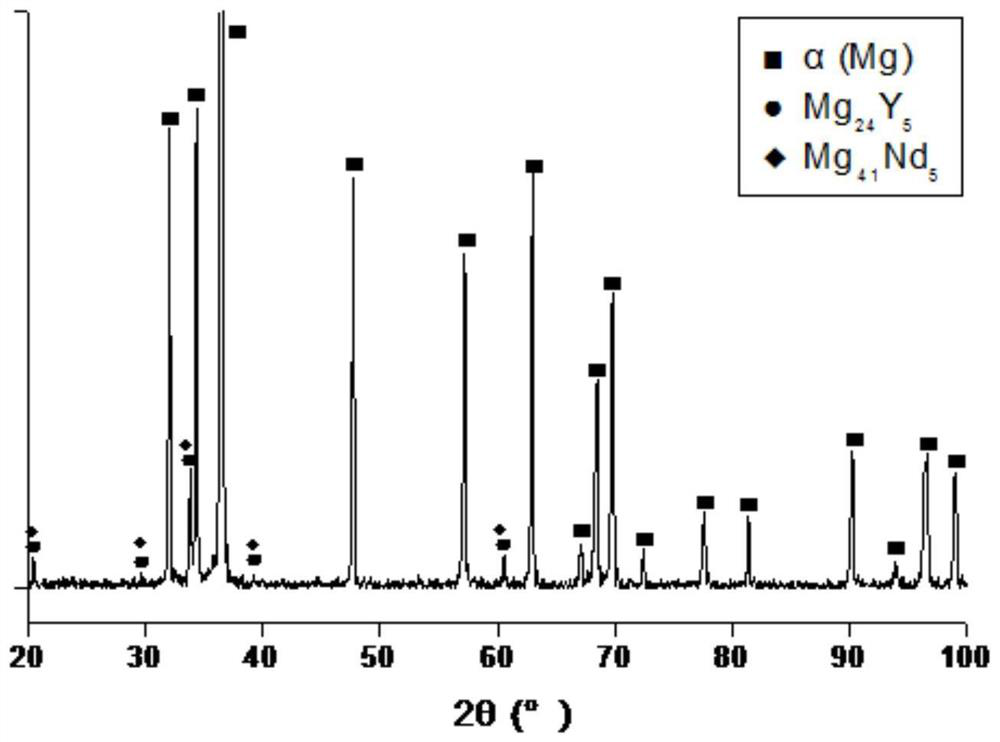
[0055] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that the composition of the heat-resistant magnesium alloy is: zinc Zn0.7Wt.%, zirconium Zr0.6Wt.%, rare earth neodymium Nd2.0Wt.%, rare earth yttrium Y2.2Wt.%, metal Cobalt Co0.2Wt.%, metal molybdenum Mo0.2Wt.%, metal vanadium V0.5Wt.%; alkaline earth calcium Ca2.0Wt.%, alkaline earth strontium Sr0.2Wt.%, and the balance of Mg and unavoidable in the casting process impurities and / or modifying elements. The magnesium alloy ingot (without any treatment) prepared by the gas shielded melting casting method was subjected to a mechanical test, and the obtained mechanical properties are shown in Table 3, and the enlarged microstructure is shown in image 3 and Figure 4 , showing that after the appropriate increase of rare earth neodymium Nd and rare earth yttrium Y, the tensile strength at room temperature and high temperature has increased.
[0056] table 3
[0057] Temperature T(°C) Yield strength σ ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com