Clostridium modified by kinase gene with phosphorylation function and application of clostridium
A technology of genetic modification and phosphorylation, applied in the field of microbial engineering, can solve problems such as affecting the synthesis of Clostridium metabolites
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0027] (1) Vector construction
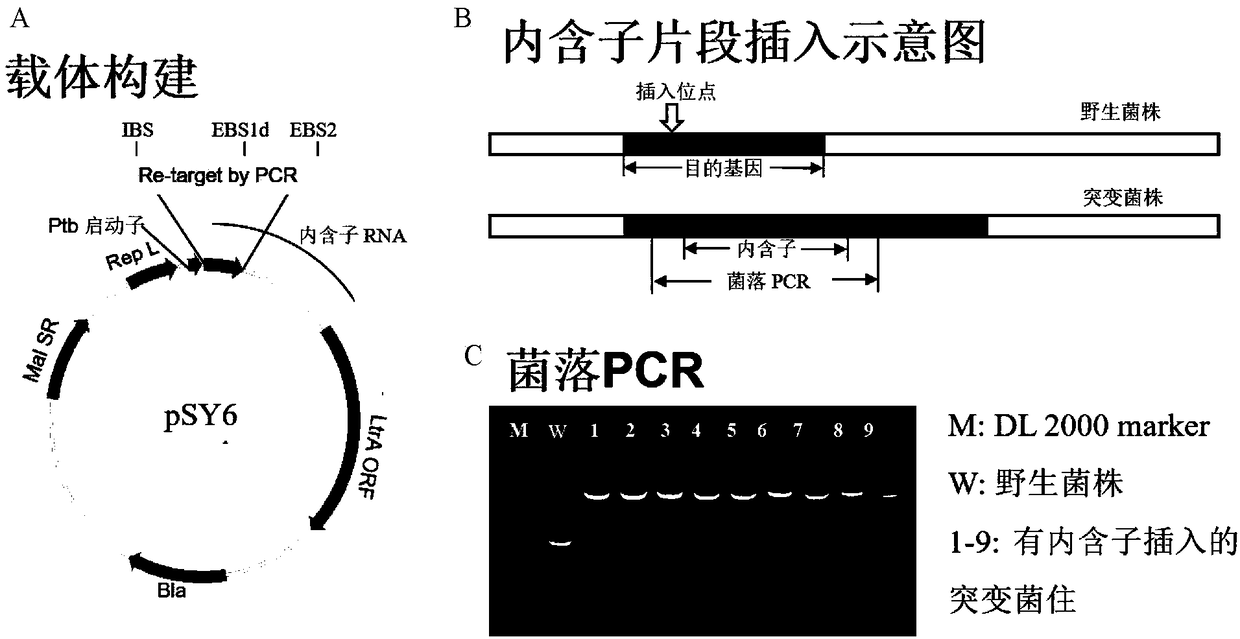
[0028] Gene knockout: use the pSY6 plasmid containing class II intron as the vector, such as figure 1 A. The intron fragment is modified by overlap extension PCR to make it have the function of specifically recognizing the target gene, and insert the target site to block the expression of the target gene, as shown in the illustration figure 1 b. Overlap extension PCR primers were designed through the "Clostron" website (www.clostron.com), and the insertion site in the gene to be knocked out was predicted according to the algorithm published in the literature (Journal of Molecular Biology, 2004, 336:421-439). The sequence is shown in Table 1. In the first round of PCR, primers IBS and EBSuniversal were used to amplify intron fragment 1, and primers EBS1d and EBS2 were used to amplify intron fragment 2. The reaction system and reaction conditions were shown in Table 2. In the second round ...
Embodiment 2
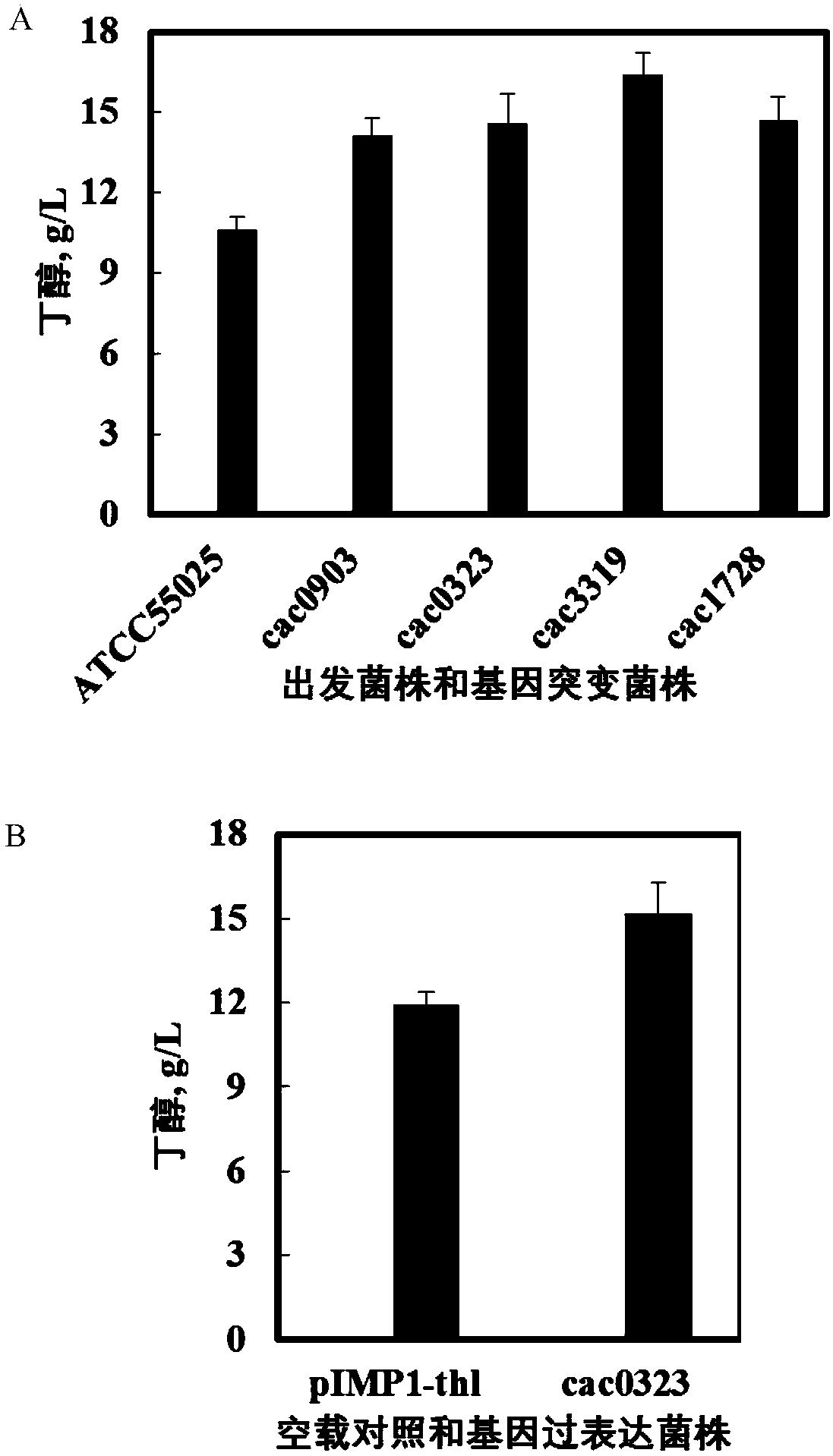
[0048] Fermentative production of butanol by a kinase-inactive strain with phosphorylation function
[0049] This example mainly includes the following steps: the seed medium used is CGM medium, and the CGM medium is deoxygenated by nitrogen gas for 20 minutes before use, then sterilized at 121°C for 15 minutes, cooled to room temperature, and inserted into 2 mL of -80°C refrigerator. Histidine kinase inactivated bacteria. After culturing at 37°C for 16-20 hours, insert the P2 fermentation medium and carry out anaerobic fermentation in the fermenter. After the liquid pH is lower than 5.0, the fermentation pH is controlled to be maintained above 5.0 by automatically feeding 50% (v / v) ammonia water. Samples were taken regularly to detect the bacterial concentration and solvent content.
[0050] CGM medium: every liter of medium contains glucose 20g, yeast powder 2g, tryptone 4g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.5g, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.5g, ammonium acetate 2.2g and...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Cell Morphology Detection of Kinase-inactive Strain with Phosphorylation Function
[0056] The cell morphological changes of the starting strain ATCC55025, cac3319 knockout bacteria and cac0437 knockout bacteria were observed by scanning electron microscope. The specific steps include: taking materials: during the acidogenic period (8h), the acidogenic to solventogenic transition period (16h), the solventogenic period (32h) and the decay period (72h), take 4mL of fermentation broth and centrifuge at 8000rpm for 5min, discard the supernatant , wash with 0.1mol / L PBS for 10min, repeat 3 times; fix: after washing, centrifuge and discard the supernatant, immediately add 2.5% glutaraldehyde to fix for more than 2h; wash: wash with 0.1mol / L PBS for 10min, repeat this step 3 times Dehydration: use 50%, 70%, 90%, 95% tert-butanol to process the sample step by step for each 10min and then use pure tert-butanol to process the sample for 10min, this step is repeated 3 times; Put ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com