Mixed transition metal borate negative electrode material and preparation method thereof
A technology of transition metal and negative electrode material, applied in the field of mixed transition metal borate negative electrode material and its preparation, can solve the problems of high redox potential of lithium metal, low energy density of negative electrode, internal short circuit, etc. Chemical activity, avoiding the slow reaction rate of the product, and avoiding the effect of lithium precipitation in the negative electrode
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
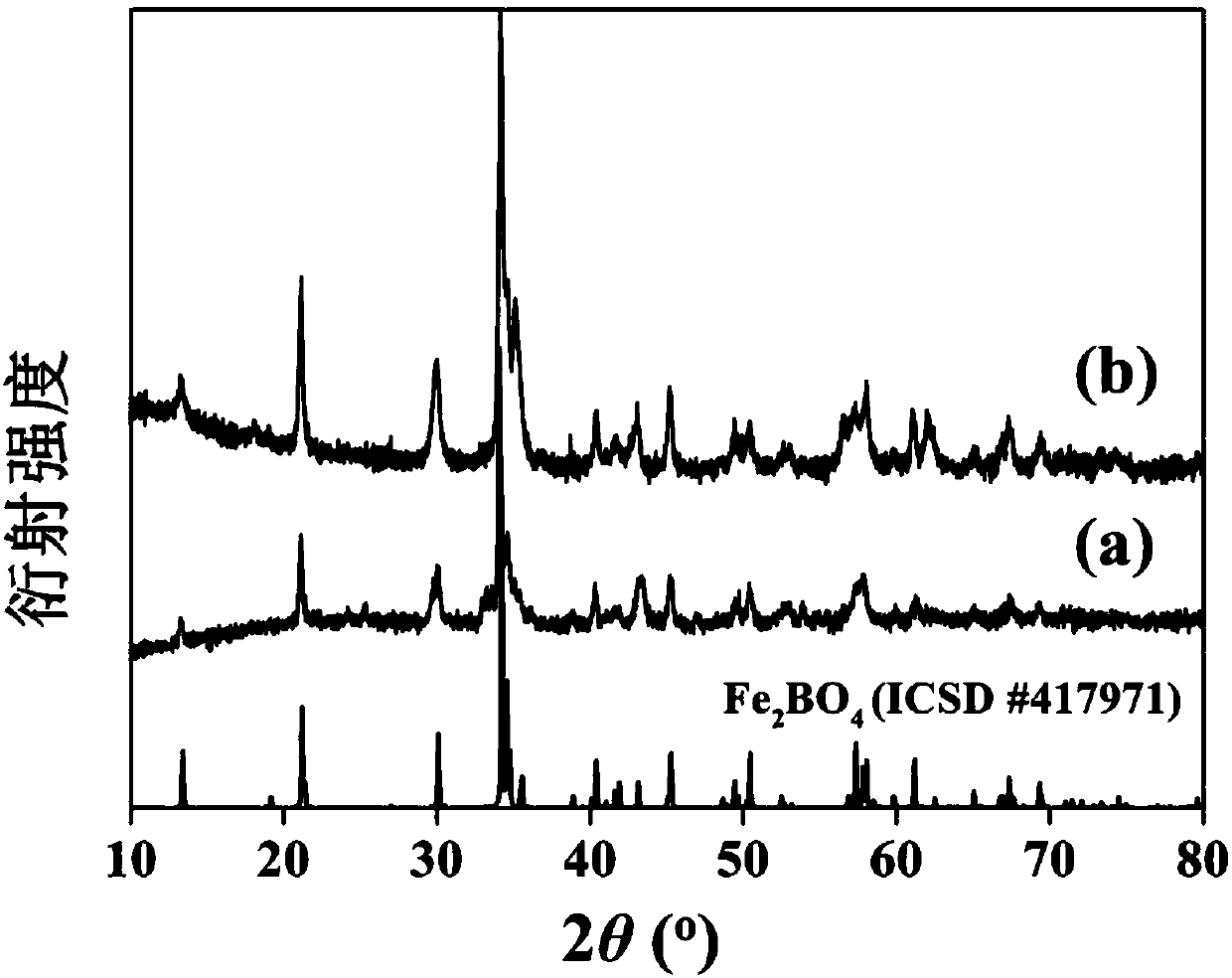
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] A kind of mixed transition metal borate FeVBO of the present embodiment 4 The preparation method of the negative electrode material, the specific preparation steps are as follows:
[0039] (1) Liquid phase mixing: mix 4.986g iron sulfate (FeSO 4 ) and 2.985g vanadium pentoxide (V 2 o 5 ) into 200mL deionized water, heated to 40°C and stirred for 20 min to dissolve, then added 2.029g boric acid (H 3 BO 3 ) stirred for 30 min to dissolve, and finally added 3.153g citric acid (C 6 h 8 o 7 ) as a chelating agent, heated to 70°C and continuously stirred, evaporated excess water to form a sol;
[0040] (2) Aging process: heat and age the sol obtained in step (1) in an oven at 80°C for 24 hours to obtain a dry gel-like precursor mixture;
[0041] (3) Pre-fired curing: The precursor mixture in step (2) was fired at 500°C for 10 hours in an air atmosphere to form a fully cured carbon-free intermediate reaction product;
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2 A mixed transition metal borate FeVBO of this example 4 The preparation method of the negative electrode material, the specific preparation steps are as follows:
[0045] (1) Liquid phase mixing: 5.975 g ferric citrate and 2.854 g ammonium metavanadate (NH 4 VO 3 ) into 300mL of deionized water, heated to 50°C and stirred for 50 min to dissolve, then added 1.171 g of ammonium pentaborate (NH 4 B 5 o 8 ) stirred for 20 min to dissolve, and finally added 4.395 g glucose (C 6 h 12 o 6 ) as a chelating agent, heated to 80°C and continuously stirred to evaporate excess water to form a sol;
[0046] (2) Aging process: heat and age the sol obtained in step (1) in an oven at 100°C for 12 h to obtain a dry gel-like precursor mixture;
[0047] (3) Pre-fired curing: the precursor mixture in step (2) was fired at 600°C for 2 hours in an air atmosphere to form a fully cured carbon-free intermediate reaction product;
Embodiment 3
[0051] A kind of carbon composite material FeVBO of mixed transition metal borate of the present embodiment 4 The preparation method of / C negative electrode material, concrete preparation steps are as follows:
[0052] (1) Liquid phase mixing: 2.626g ferrous oxalate (FeC 2 o 4 ) and 6.357g vanadium acetylacetonate (C 15 h 21 o 6 V), added to 250ml of deionized water, heated to 60°C and stirred for 120 minutes to dissolve, then added 1.017g of boron oxide (B 2 o 3 ), stirred for 10 minutes to dissolve, and finally added 6.577g of sucrose as a carbon source and chelating agent, heated to 90°C and continued to stir, evaporated excess water and finally formed a sol;
[0053] (2) Aging process: heat and age the sol obtained in step (1) in an oven at 90°C for 36 h to obtain a dry gel-like precursor mixture;
[0054] (3) Pre-fired curing: the precursor mixture in step (2) was heated in N 2 -H 2 Mixed gas atmosphere (95% N 2 + 5%H 2 ) at 400°C for 6 h to form a fully soli...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com