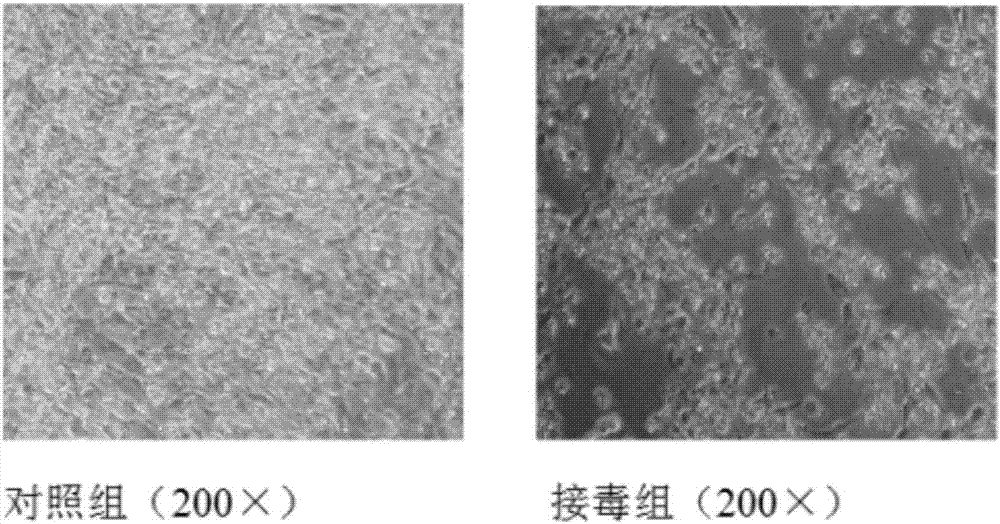
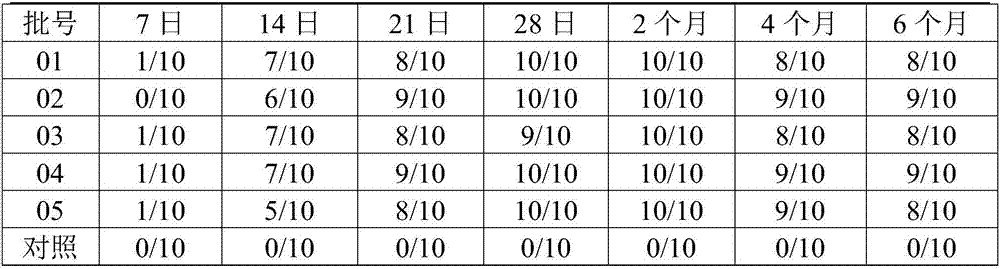
Duck adenovirus type 2 strain
An adenovirus and disease technology, applied in the field of duck adenovirus type 2 strains, can solve the problem of lack of prevention, and achieve the effects of good safety, good commercial development prospects, and effective immune protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] Isolation and identification of GD strain
[0014] 1. Epidemiological investigation Since 2014, a group I duck type 2 adenovirus disease with high mortality has appeared in some muscovy ducks in Guangdong, Zhejiang and other regions. After the autopsy of the muscovy duck that died of illness, the main pathological changes were as follows: hepatomegaly, hepatic necrosis, splenomegaly, hemorrhagic spots, pancreas necrosis and other diseases characterized by multiple organ lesions. After clinical investigation and laboratory testing, the preliminary diagnosis was Group I duck adenovirus type 2. In 2015, the inventor successfully isolated a virus from ducks in a duck farm in Guangdong.
[0015] 2. Virus isolation Take 50-100 g of liver, spleen, pericardial fluid, pancreas, and bursa of the diseased duck, grind the tissue with a mortar, and add liquid nitrogen continuously until it is ground into powder (no obvious visible particles) Homogenize with sterile normal saline a...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Preparation of GD Strain Virus Seeds
[0032] Select the duck embryo fibroblasts that have grown into a single layer, discard the original culture medium, add serum-free M199 maintenance solution with a final concentration of 1% virus seed (the third generation of the original virus strain of GD strain), and culture at 37°C for 60~ After 78 hours, obvious cytopathy can appear, and harvest when the cytopathy reaches more than 80%. According to this method, 10 generations were passed continuously, which were respectively marked as C3-C10 generations. The virus content of each passage was determined. Will test for sterility and virus content ≥10 6.0 TCID 50 The virus solution is mixed, quantitatively divided, and stored in a freeze-dried manner.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Preparation of GD strain antigen
[0035] 1 Material selection for seedling preparation Duck embryo fibroblasts and preparation of GD strain virus liquid.
[0036] 2. Cell preparation Take 11-13 day-old SPF duck embryos, digest them with 0.25% trypsin, add an appropriate amount of M199 culture medium containing 10% serum for culture.
[0037] 3 Inoculation of virus Select the duck embryo fibroblasts that have grown to a single layer, discard the original culture medium, add the maintenance solution with a final concentration of 1% virus species, and place in a 37°C incubator to continue culturing.
[0038] 4 Harvesting After inoculation, observe twice a day and record the cell lesions. Harvest when the cytopathic rate reaches more than 80%, freeze and thaw twice, and store the harvested cytotoxicity at -20°C before inactivation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com