Preparation method of xanthan gum nano microgel
A technology of microgel and xanthan gum, applied in the field of natural polymers in biomedical materials, to achieve the effects of improving therapeutic effect, improving bioavailability, good biocompatibility and biodegradability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
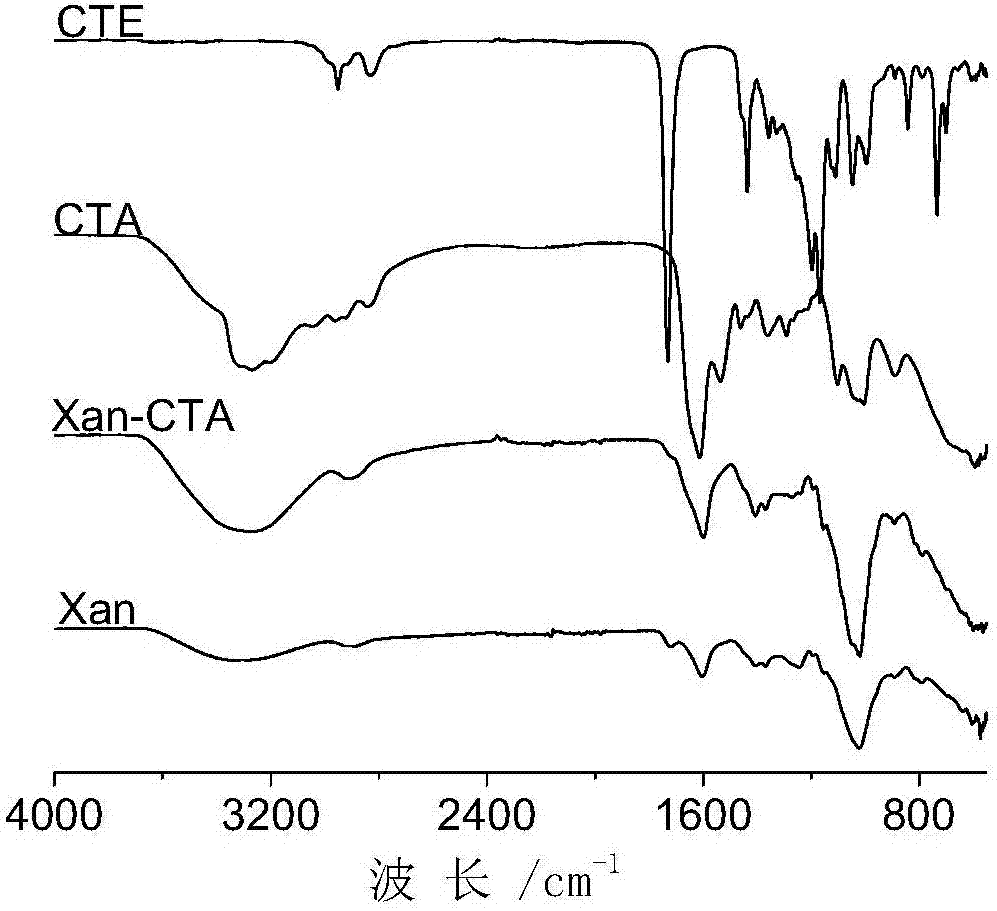
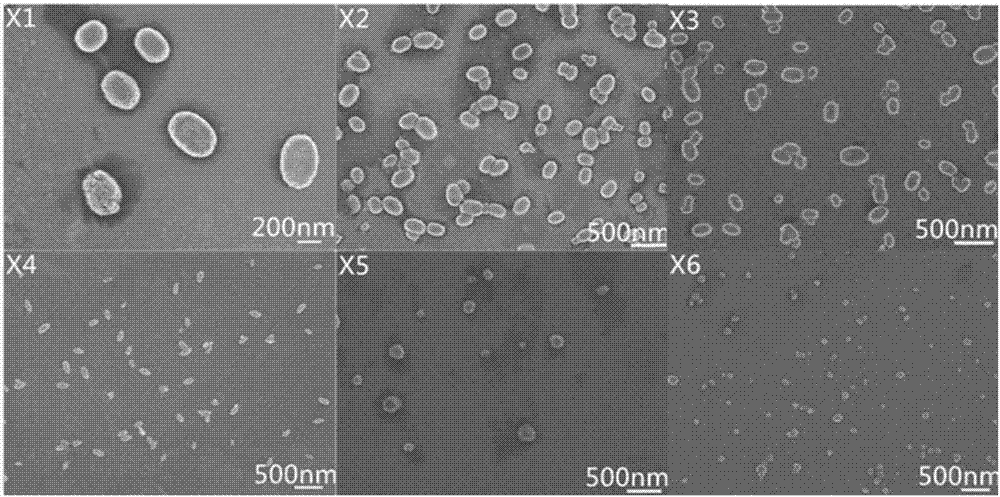
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
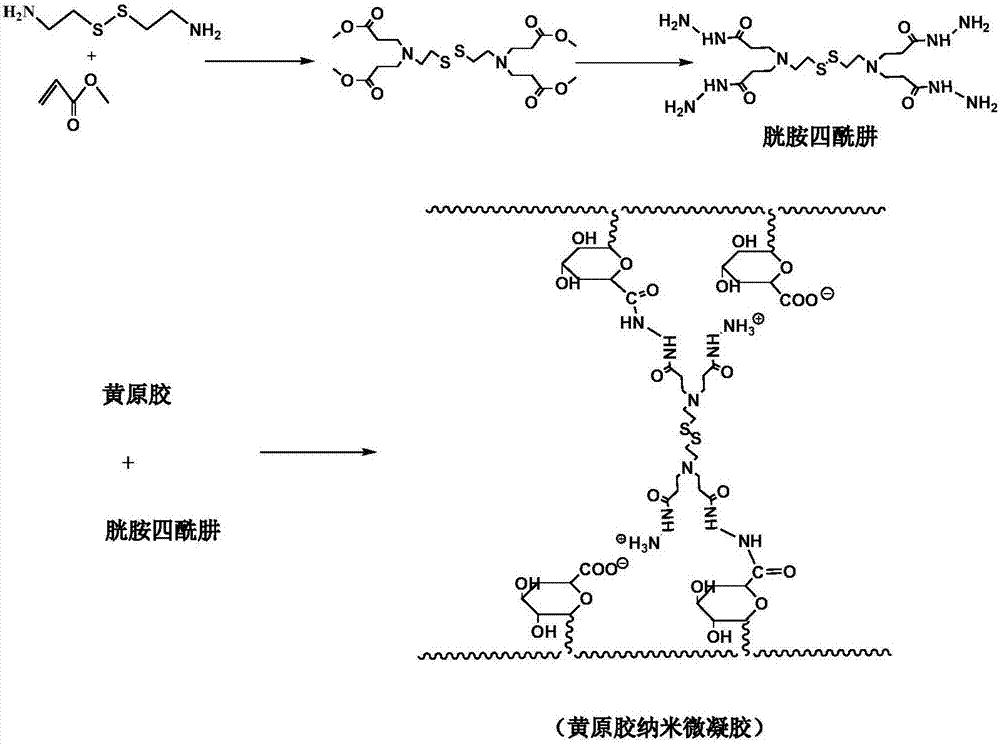
[0029] 1) Synthesis of cystamine tetramethyl ester and cystamine tetrahydrazide:
[0030] Dissolve 4.68g of cystamine dihydrochloride and 7.86g of methyl acrylate in 50mL of anhydrous methanol, stir to dissolve completely, add 4.2g of triethylamine, and react with magnetic stirring at room temperature for 24 hours under nitrogen atmosphere. After the reaction was completed, the crude product was dissolved in 150mL of dichloromethane, washed three times with 50mL of ultrapure water, once with 50mL of saturated sodium chloride solution, and finally dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate and suction filtered. After the filtrate was concentrated by rotary evaporation, A yellow liquid was obtained. The crude product was separated and purified by silica gel chromatography to obtain CTE as a colorless liquid. Dissolve 2.81g of tetramethyl cystamine in 20mL of anhydrous methanol, add 2.4g of anhydrous hydrazine after complete dissolution, and react under nitrogen protection under reflux...
Embodiment 2
[0035] pH Sensitivity of Xanthan Gum Nanogels:
[0036] With the 0.01mg / mL xanthan gum nano-microgel obtained in Example 1, get 20mL nano-microgel solution, and adjust the pH value of the nano-microgel solution to be 3, 5, 6.5, 7.4 with 0.1M HCl and 0.1M NaOH , 10. Observe the particle size and zata potential of xanthan gum nanoparticles changing with pH, and detect the change of microgel particle size with pH value by dynamic laser light scattering system to reflect the pH sensitivity of microgel. The results are from Figure 5 It can be seen from the left figure that the particle size of xanthan gum nanoparticles generally increases with the increase of pH value, because xanthan gum is an anionic polysaccharide, and the negative charge of the carboxyl group is enhanced in alkaline environment, and the gap between the nanoparticles increases. The charge repulsion increases and the particle size increases accordingly. Under acidic conditions, the particle size becomes small...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Reduction Sensitivity of Xanthan Gum Nanogels:
[0039] Take the light red drug-loaded nano-microgel obtained in Example 1, take 120mL of the drug-loaded nano-gel solution and divide it into 6 parts, put it into a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3500, and place it in 20mL of pH=5, pH=6.5, pH =7.4 and the acetate buffer solution containing 10mM glutathione, placed in a constant temperature oscillator at 37±0.5°C and oscillating, at 12h and 24h respectively take 3mL nano-microgel solution, and use laser light scattering The particle size change of the nano-microgel is tested by the instrument, and the reduction response is observed. After the test, the sample is immediately moved to the original dialysis bag. The observation results found that within 24 hours, the particle size and distribution of the nano-microgels did not change substantially in the PBS buffer solution without glutathione, but in the 10mM glutathione solution, after 12 hours, the particl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com