Preparation and application of novel antithrombotic polymer nano-drug
A nano-drug and anti-thrombotic technology, applied in nano-drug, nano-technology, nano-technology and other directions, can solve the problems of easily causing bleeding complications, interfering with the efficacy of warfarin, obvious side effects, etc., achieving easy operation, improving efficiency, Simple preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
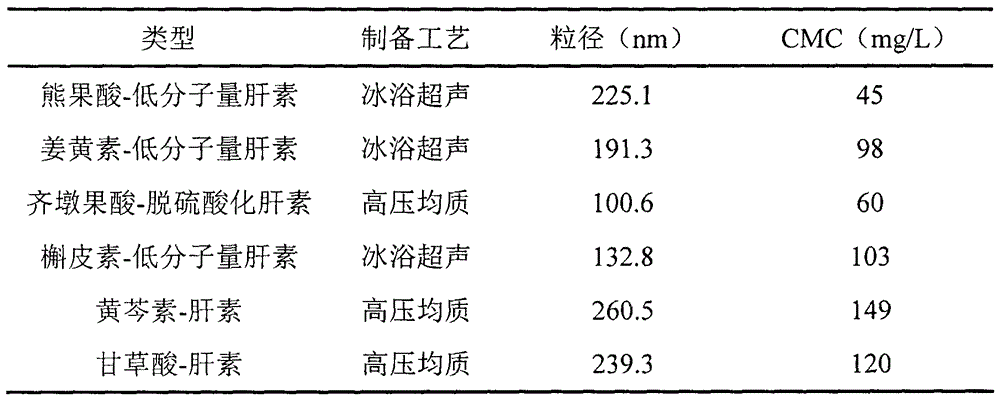
[0053] Example 1: Synthesis of oleanolic acid-desulfated heparin polymer nanomedicine
[0054] Weigh an appropriate amount of oleanolic acid (OA) and place it in an eggplant-shaped bottle, add a mixture of tetrahydrofuran and N,N-dimethylformamide to dissolve completely, the molar concentration of OA is 0.1mmol / mL, ice bath, in an inert gas Under protected conditions, add 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDCI) and 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBT) sequentially, OA, EDCI, HOBT The molar ratios are 1:1.4:1.4 in turn. React in an ice bath for 60 minutes, then slowly add it dropwise to p-phenylenediamine, the molar ratio of OA to p-phenylenediamine is 1:2, control the drop rate at an interval of 10 seconds between each drop, and react at a reaction temperature of 36°C for another 12 hours to saturate Precipitate with salt water, filter, pickle in turn, wash with water, and dry in vacuum to obtain powder OA-NH 2 . Weigh an appropriate amount of desulfated...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2: the synthesis of curcumin-low molecular weight heparin polymer nano drug
[0056] Weigh an appropriate amount of curcumin and low-molecular-weight heparin (the molar ratio of curcumin and low-molecular-weight heparin is 2:1), dissolve them completely with formamide respectively, and add DMAP, EDC and NHS (LMWH, DMAP, EDC, the molar ratio of NHS is 1: 0.2: 3: 3), ice-bath reaction 30min, under the dark condition, slowly add curcumin solution in the LMWH reaction solution again, control dripping speed be every drop interval 5 seconds, Reaction at room temperature for 24h. Add an excess volume of ice acetone to precipitate the product, and filter with suction to obtain the product. The product was reconstituted with ultrapure water, sonicated by the probe for 40 minutes, dialyzed in distilled water for 2 days (MWCO=3500), passed through a 0.8 μm microporous membrane, and freeze-dried to obtain curcumin-low molecular weight heparin polymer nanomedicine.
Embodiment 3
[0057] Embodiment 3: the synthesis of ursolic acid-low molecular weight heparin polymer nano-medicine
[0058] Weigh an appropriate amount of ursolic acid (UA) and place it in an eggplant-shaped bottle, add tetrahydrofuran to dissolve it completely, the molar concentration of UA is 0.05mmol / mL, put it in an ice bath, and under the protection of an inert gas, add dicyclohexylcarbodia Amine (DCC) and hydroxysuccinimide (NHS), the molar ratio of UA, DCC, and NHS is 1:1.2:1.2 in sequence. React in ice bath for 30min, move to room temperature for 24h. The precipitate dicyclohexyl urea (DCU) was removed by vacuum filtration to obtain a filtrate. The filtrate was precipitated with 3 times the amount of n-hexane for 12 h, filtered, and dried in vacuo to obtain succinimide-based UA. Weigh an appropriate amount of succinimide-based UA and dissolve it with N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), slowly add it dropwise to o-phenylenediamine, the molar ratio of UA to o-phenylenediamine is 1:1, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com