A method for improving the corrosion resistance of sintered NdFeB magnets
A NdFeB, corrosion-resistant technology, applied in the manufacture of inductors/transformers/magnets, coatings, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as complex process steps, non-environmental protection, low bonding force between coatings and substrates, and achieve technological progress Simple, improved physical and chemical properties, and improved intrinsic corrosion resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] 1) The sintered NdFeB magnet Nd 9 PR 3 Fe 80 co 2 B 5.5 Cu 0.5 Grinding, polishing, cleaning and drying pretreatment on the surface to be processed;
[0023] 2) Clamp the pretreated sintered NdFeB magnet on the workbench;
[0024] 3) Under vacuum, irradiate the surface of the sintered NdFeB magnet to be processed with continuous laser to melt the grain boundary phase to form a micro-melt pool. The laser power is 500W, the scanning speed is 5mm / s, the spot diameter is 2mm, and the overlap rate is 20%;
[0025] 4) Send 20nm metal Al nanopowder into the grain boundary micro-melting pool through the powder feeding device, so that it can be microalloyed with the grain boundary phase;
[0026] 5) The unalloyed nanopowder is cleaned up to obtain a sintered NdFeB magnet modified by surface grain boundary selective microalloying.
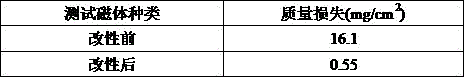
[0027] The corrosion resistance of sintered NdFeB magnets before and after surface modification was tested by autoclave experiment (5-10psig, ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] 1) The sintered NdFeB magnet Nd 13 PR 3 Dy 2 Fe 73 B 8 Al 0.5 Ga 0.5 Grinding, polishing, cleaning and drying pretreatment on the surface to be processed;
[0031] 2) Clamp the pretreated sintered NdFeB magnet on the workbench;
[0032] 3) Under the protection of argon gas, the surface to be processed of the sintered NdFeB magnet is irradiated with pulsed laser until the grain boundary phase is melted to form a micro molten pool, and the laser power density is 1MW / cm 2 , pulse width 100ns, overlap rate 80%;
[0033] 4) Send 100nm compound SiC nanopowder into the grain boundary micro-melting pool through the powder feeding device, so that it can be microalloyed with the grain boundary phase;
[0034] 5) The unalloyed nanopowder is cleaned up to obtain a sintered NdFeB magnet modified by surface grain boundary selective microalloying.
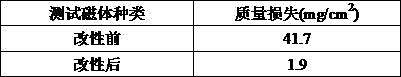
[0035] The corrosion resistance of sintered NdFeB magnets before and after surface modification was tested by autoclave experiment...
Embodiment 3
[0038] 1) The sintered NdFeB magnet Nd 14 Tb 0.1 Fe 79.8 B 6 Zr 0.1 Grinding, polishing, cleaning and drying pretreatment on the surface to be processed;
[0039] 2) Clamp the pretreated sintered NdFeB magnet on the workbench;
[0040] 3) Under the protection of helium, the surface of the sintered NdFeB magnet to be processed is irradiated with continuous laser to melt the grain boundary phase to form a micro-melt pool. The laser power is 100W, the scanning speed is 20mm / s, the spot diameter is 0.5mm, and the overlap rate is 80 %;
[0041] 4) Send the mixed powder of 60nm metal Cu and 100nm metal Co nanopowder with a volume ratio of 2:1 into the grain boundary micro-melting pool through the powder feeding device, so that it can be microalloyed with the grain boundary phase;
[0042] 5) The unalloyed nanopowder is cleaned up to obtain a sintered NdFeB magnet modified by surface grain boundary selective microalloying.
[0043] The corrosion resistance of sintered NdFeB ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com