Solid phase reinforcement reduction-magnetic separation method of vanadium titano-magnetite
A technology for vanadium titanomagnetite and magnetic separation separation, which is applied in the fields of magnetic separation, solid separation, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problem of immature direct reduced iron technology, restricting the development of electric furnace steelmaking, and low iron metallization rate. To achieve the effect of strengthening the direct reduction process, reducing the activation energy of the reaction, and promoting the growth of iron grains
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
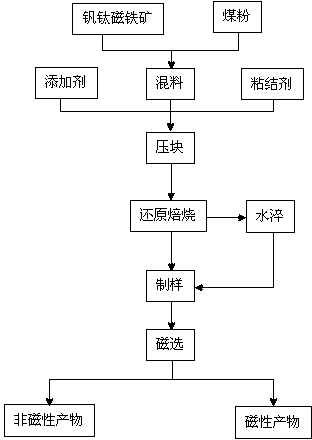
[0022] (1) Mix the vanadium-titanium magnetite and anthracite powder according to the ratio of C / O molar ratio of 1.1:1, mix them in a ball mill, and add the additive Fe which accounts for 7% of the mass of the mixture into the mixed material. 2 O 3 , After mixing, add 0.1% of the binder polyethylene glycol, which accounts for the mass of the mixture, and mold it into a cylindrical sample under a pressure of 40MPa;
[0023] (2) Embed the cylindrical sample in a crucible containing anthracite powder, and reduce it at 1100°C for 120 minutes to obtain reduced iron powder;
[0024] (3) Quench the reduced iron powder to room temperature, and grind the reduced product to 100-300 mesh with a 2M2-100 sealed sample preparation pulverizer to obtain the ground reduced iron powder with a metallization rate of 86.53%;
[0025] (4) The ground reduced iron powder is magnetically separated at a magnetic separation intensity of 200kA / m to obtain an iron powder with a recovery rate of 96.12%. The magne...
Embodiment 2
[0027] (1) Mix the vanadium-titanium magnetite and anthracite powder in a C / O molar ratio of 1.4:1, mix them in a ball mill, and add 3% of the additive Na, which accounts for the mass of the mixture, to the mixed material. 2 CO 3 , After mixing, add 0.2% of the binder polyethylene glycol, which accounts for the mass of the mixture, and mold it into a cylindrical sample under a pressure of 60MPa;
[0028] (2) Embed the cylindrical sample in a crucible containing anthracite powder, and reduce it at 1350°C for 60 minutes to obtain reduced iron powder;
[0029] (3) Naturally cool the reduced iron powder to room temperature, and grind the reduced product to 100-300 mesh with a 2M2-100 sealed sample preparation pulverizer to obtain finely ground reduced iron powder;
[0030] (4) Magnetic separation of the ground reduced iron powder at a magnetic separation intensity of 120kA / m, to obtain iron powder with a recovery rate of 94.82%.
[0031] Among the magnetic products: TFe is 89.50%, MFe is 8...
Embodiment 3
[0033] (1) Mix the vanadium-titanium magnetite and anthracite powder according to the ratio of C / O molar ratio of 1.2:1, mix them in a ball mill, and add 3% of the additive CaF to the mixed material. 2 , After mixing, add 0.15% of the binder polyethylene glycol of the mass of the mixture, and mold it into a cylindrical sample under a pressure of 50MPa;
[0034] (2) Embed the cylindrical sample in a crucible containing anthracite powder, and reduce it at 1300°C for 30 minutes to obtain reduced iron powder;
[0035] (3) Naturally cool the reduced iron powder to room temperature, and grind the reduced product to 100-300 mesh with a 2M2-100 sealed sample preparation pulverizer to obtain finely ground reduced iron powder with a metallization rate of 89.68%;
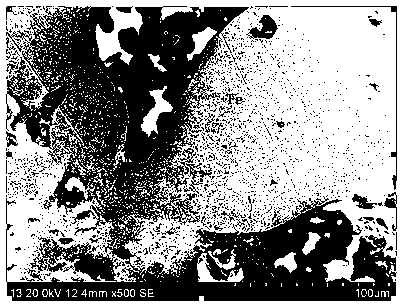
[0036] (4) The ground reduced iron powder is magnetically separated at a magnetic separation intensity of 160kA / m to obtain iron powder with a recovery rate of 94.37%. The ore phase diagram is as follows figure 2 As shown, in the mag...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com