SiC IEMOSFET (Implantation and Epitaxial Metal-Oxide -Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) device with epitaxy channel and manufacturing method of SiC IEMOSFET device
A channel and epitaxy technology, applied in the field of microelectronics, can solve problems such as rough contact interface, high interface state density, reduced electron mobility of inversion layer, and increased device on-resistance, so as to reduce roughness and suppress contact interface Roughness, the effect of reducing the on-resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Step 1. In N + Epitaxial growth of N on SiC substrate samples - Drift layer.
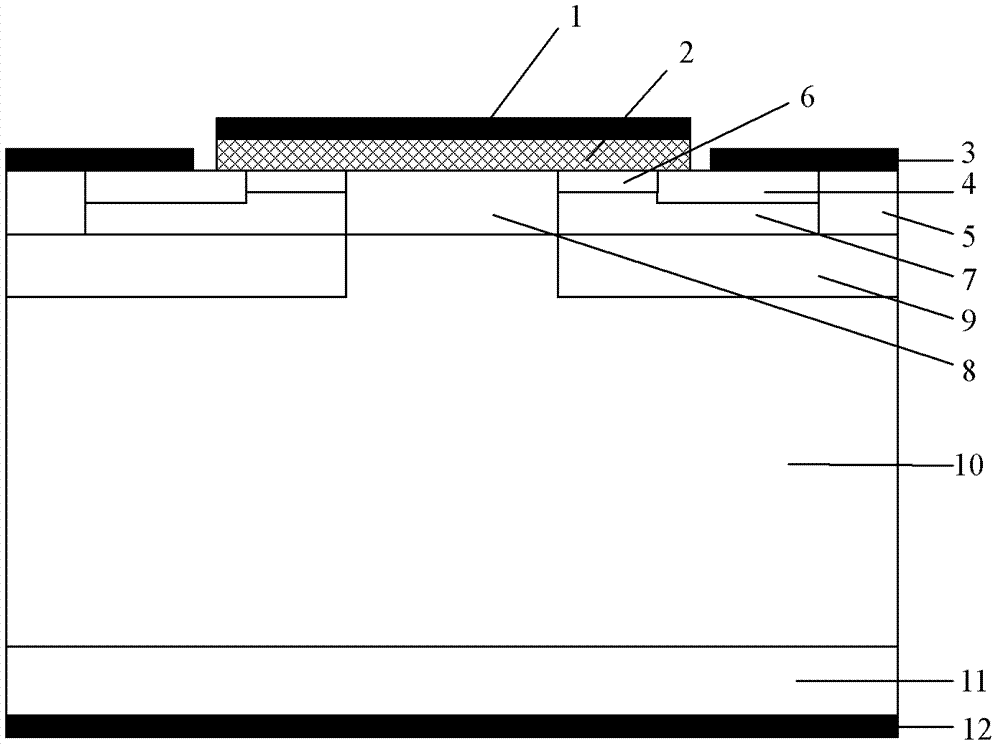
[0034] to N + The silicon carbide substrate sample 11 was cleaned by RCA cleaning standard, and then epitaxially grown on the entire substrate surface with a thickness of 8 μm and a nitrogen ion doping concentration of 1×10 15 cm -3 N - Drift layer 10, such as image 3 a. The process conditions are as follows: the epitaxy temperature is 1570°C, the pressure is 100mbar, the reaction gas is silane and propane, the carrier gas is pure hydrogen, and the impurity source is liquid nitrogen.
[0035] Step 2. Selective implantation of aluminum ions four times to form a P well.
[0036] (2.1) Deposit a layer of Al with a thickness of 1.5 μm on the front side of the silicon carbide sample by low-pressure hot-wall chemical vapor deposition as a barrier layer for the ion implantation of the P well 9, and form the P well implantation region by photolithography and etching;
[0037] (2.2) Four times...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Step 1. In N + Epitaxial growth of N on SiC substrate samples - Drift layer.
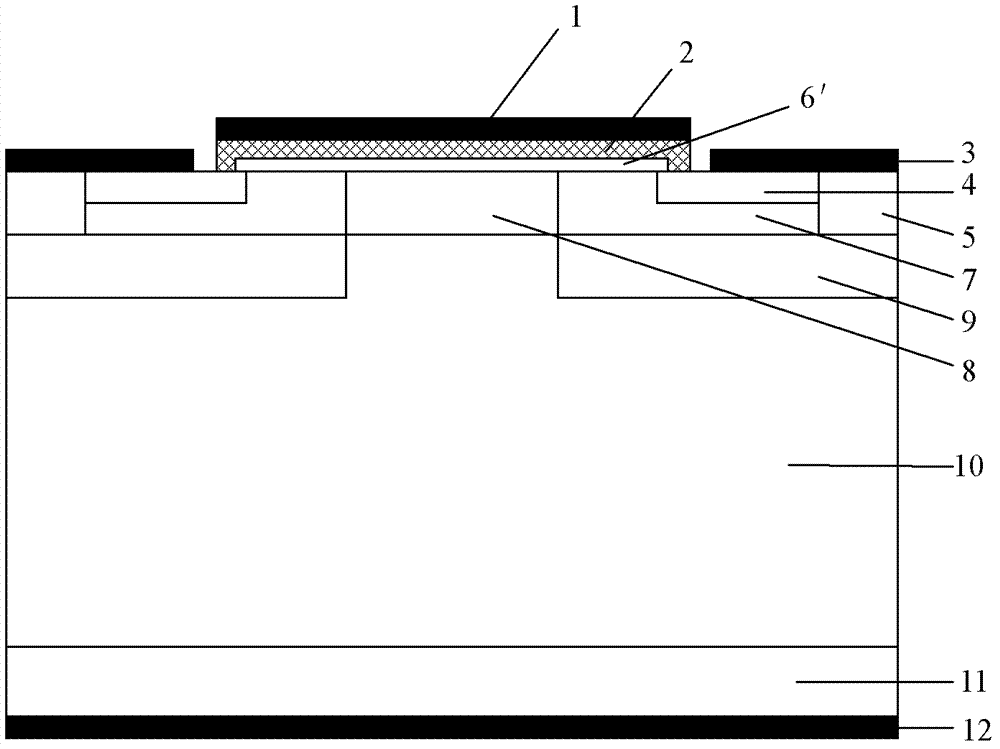
[0070] to N + The silicon carbide substrate 11 is cleaned by RCA cleaning standard, and then the epitaxial growth thickness is 8.5 μm on the entire substrate surface, and the nitrogen ion doping concentration is 1.5×10 15 cm -3 N - Drift layer 10, such as image 3 a. The process conditions are as follows: the epitaxy temperature is 1570°C, the pressure is 100mbar, the reaction gas is silane and propane, the carrier gas is pure hydrogen, and the impurity source is liquid nitrogen.
[0071] The second step. Three times of selective implantation of aluminum ions to form a P well.
[0072] (2.1) Deposit a layer of Al with a thickness of 1.5 μm on the front side of the silicon carbide sample by low-pressure hot-wall chemical vapor deposition as a barrier layer for the ion implantation of the P well 9, and form the P well implantation region by photolithography and etching;
[0073] (2.2) Pe...
Embodiment 3
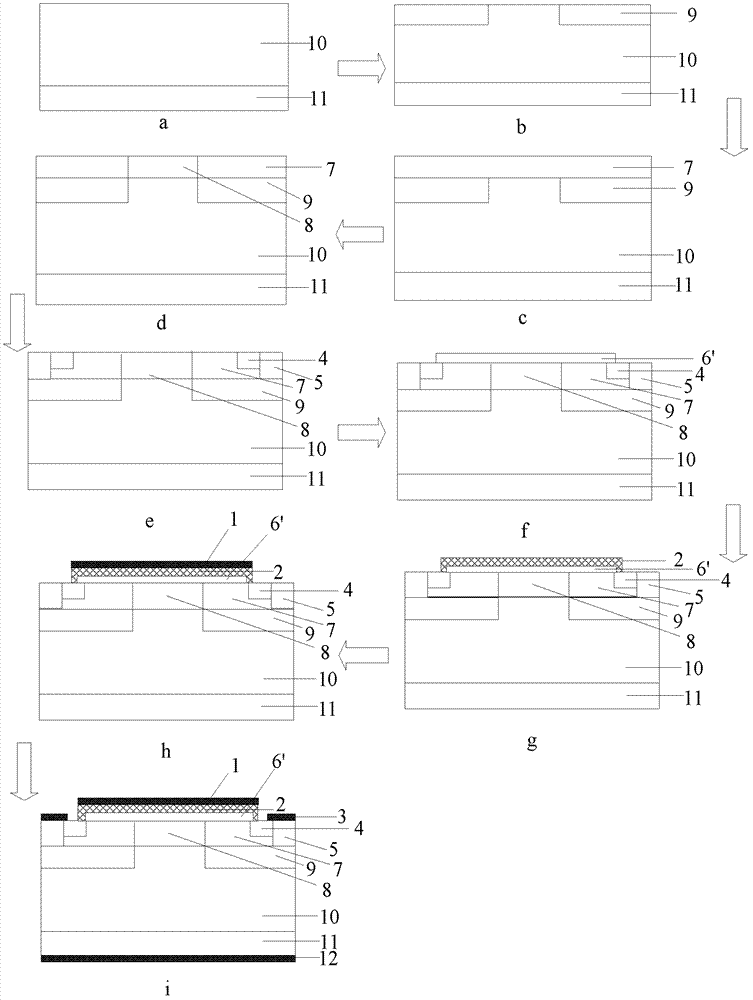
[0105] Step A. For N + The silicon carbide substrate 11 is cleaned by RCA cleaning standard, and then the epitaxial growth thickness is 9 μm on the entire substrate surface, and the nitrogen ion doping concentration is 2×10 15 cm -3 N - Drift layer 10, such as image 3 a, The epitaxial growth conditions are: the epitaxial temperature is 1570°C, the pressure is 100mbar, the reaction gas is silane and propane, the carrier gas is pure hydrogen, and the impurity source is liquid nitrogen.
[0106] Step B. Selective implantation of aluminum ions four times to form a P well.
[0107] (B1) Deposit a layer of Al with a thickness of 1.5 μm on the front side of the silicon carbide sample by low-pressure hot-wall chemical vapor deposition as a barrier layer for the ion implantation of the P well 9, and form the P well implantation region by photolithography and etching;
[0108] (B2) Perform Al ion implantation on the front side of the silicon carbide sample four times at an ambient ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com