Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47results about How to "Reduce viewing angle dependence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
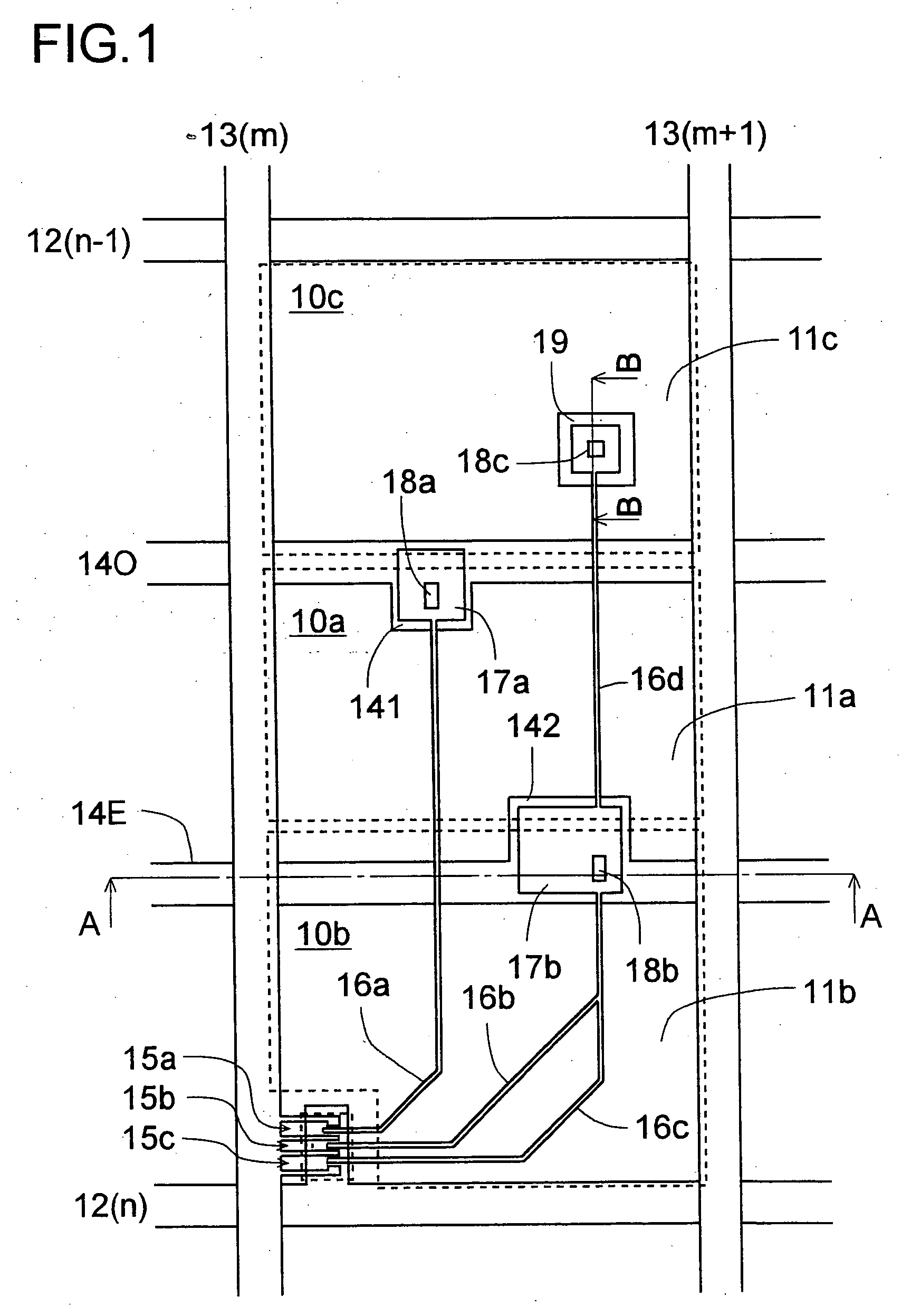
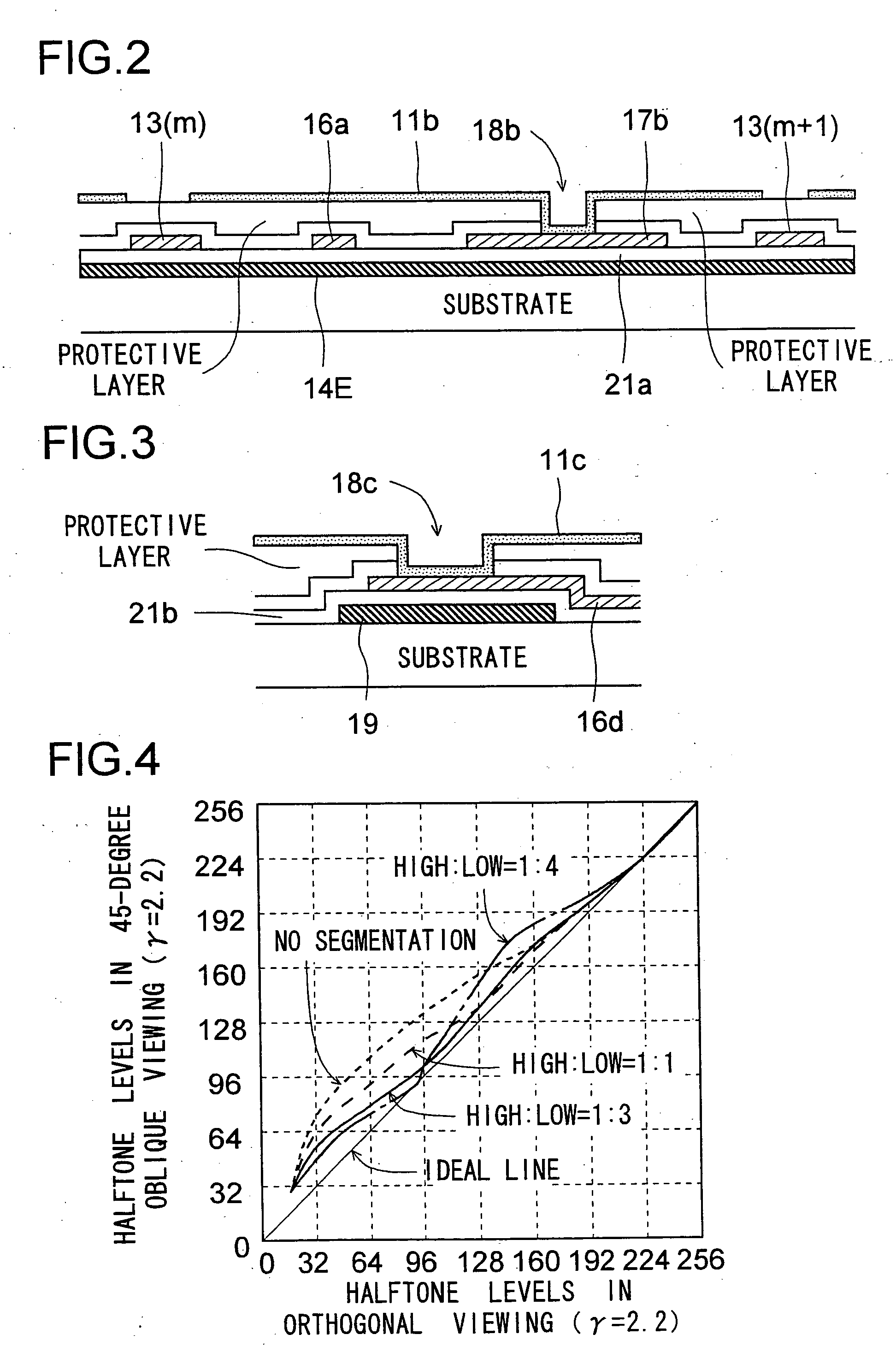
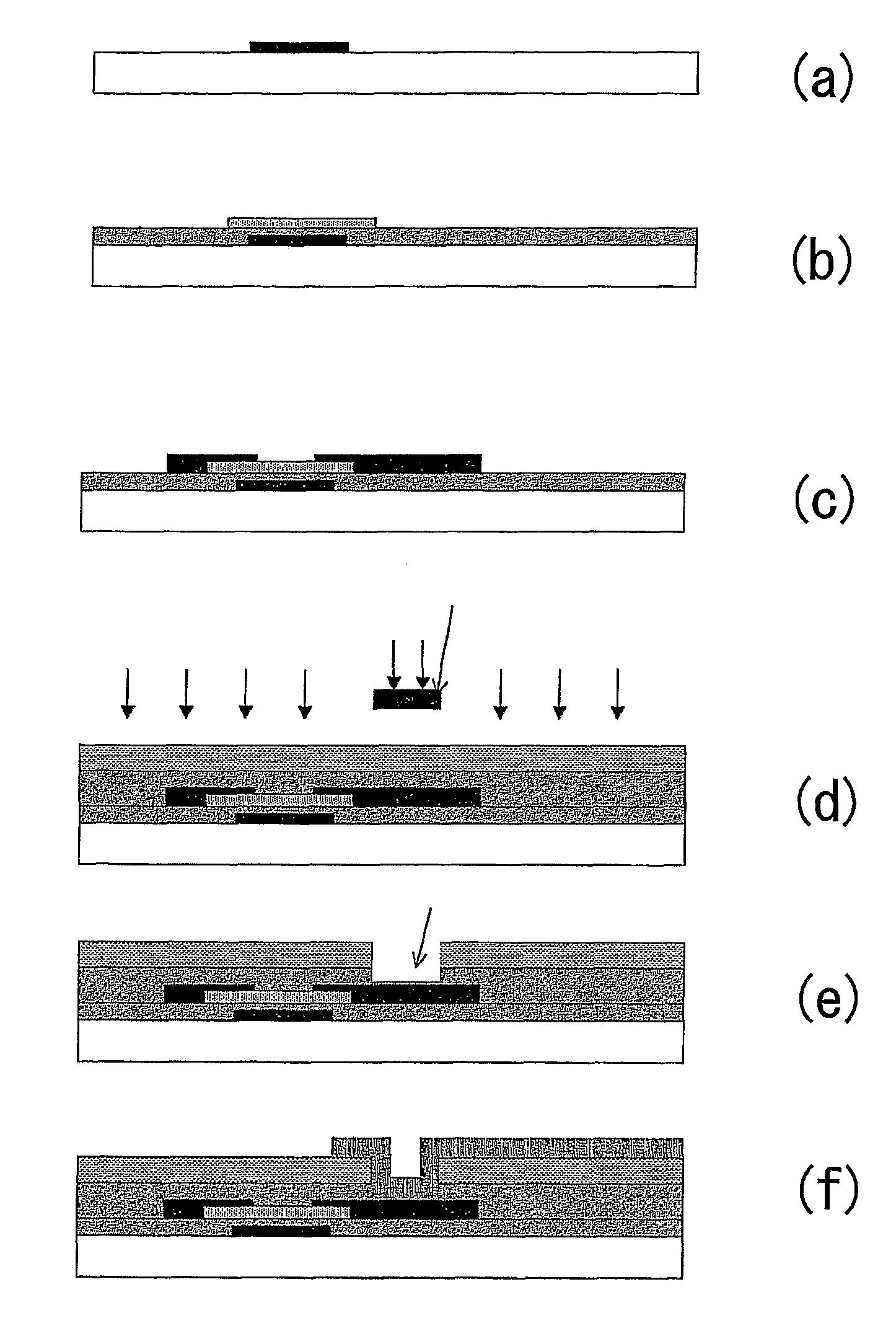
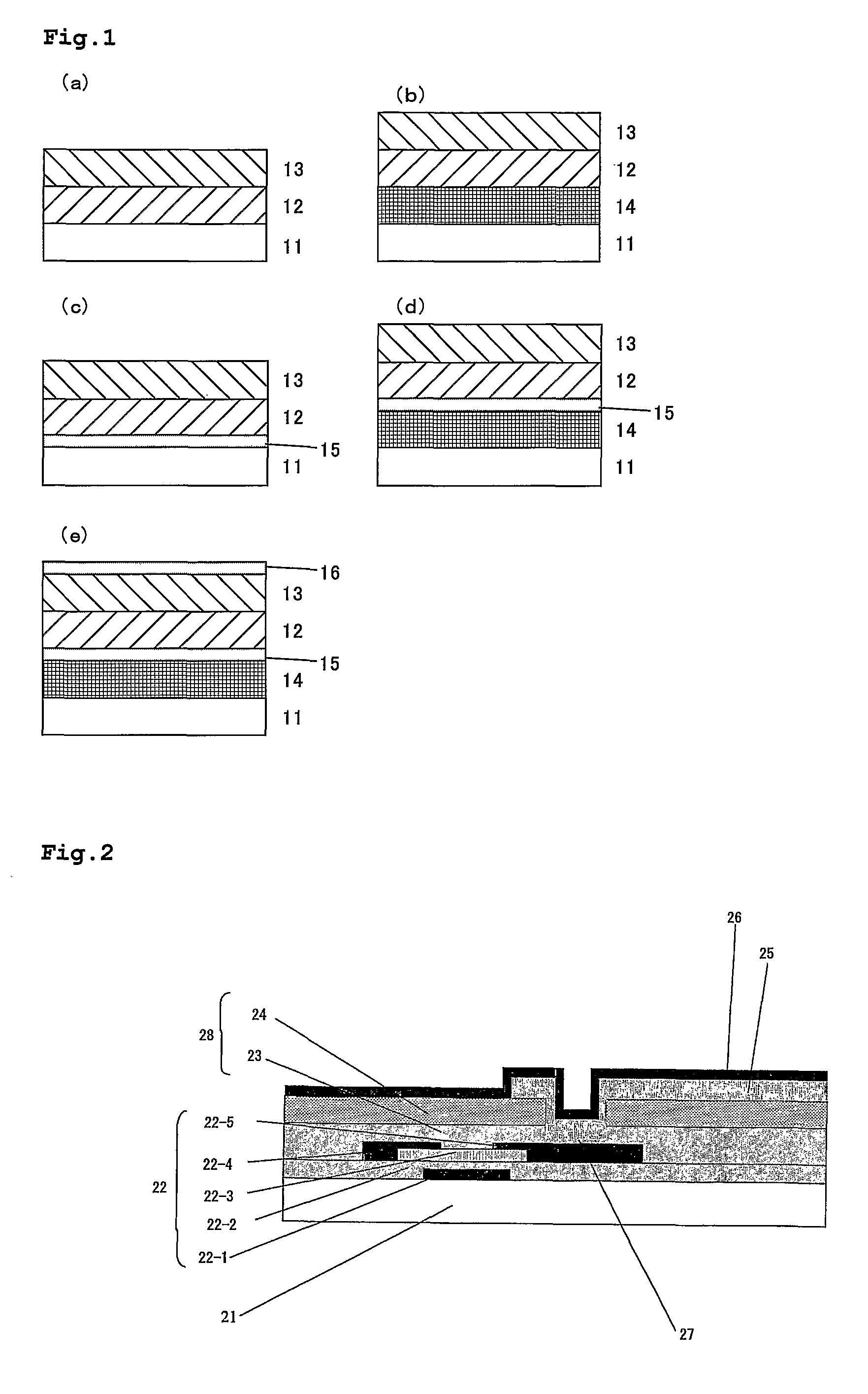
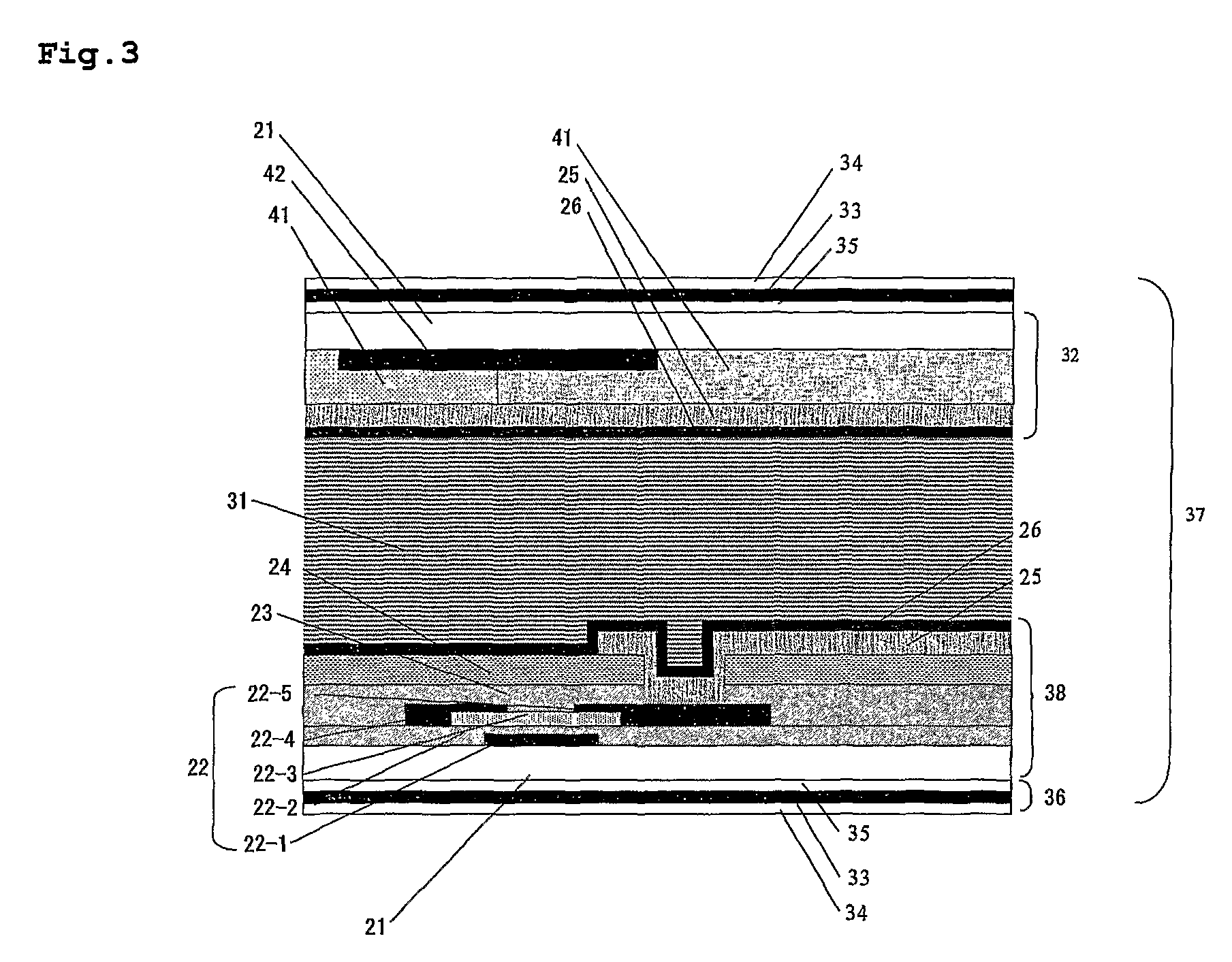
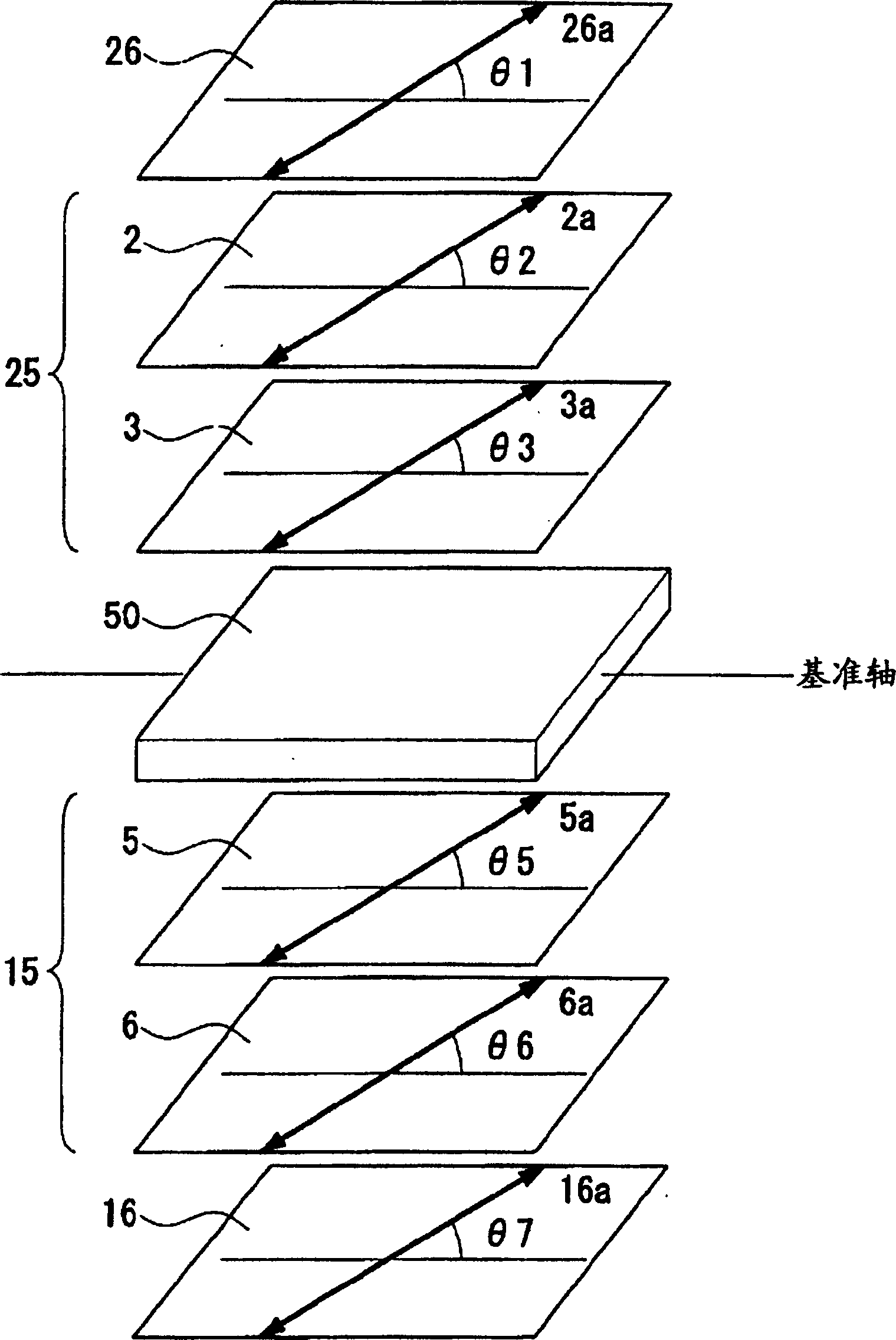
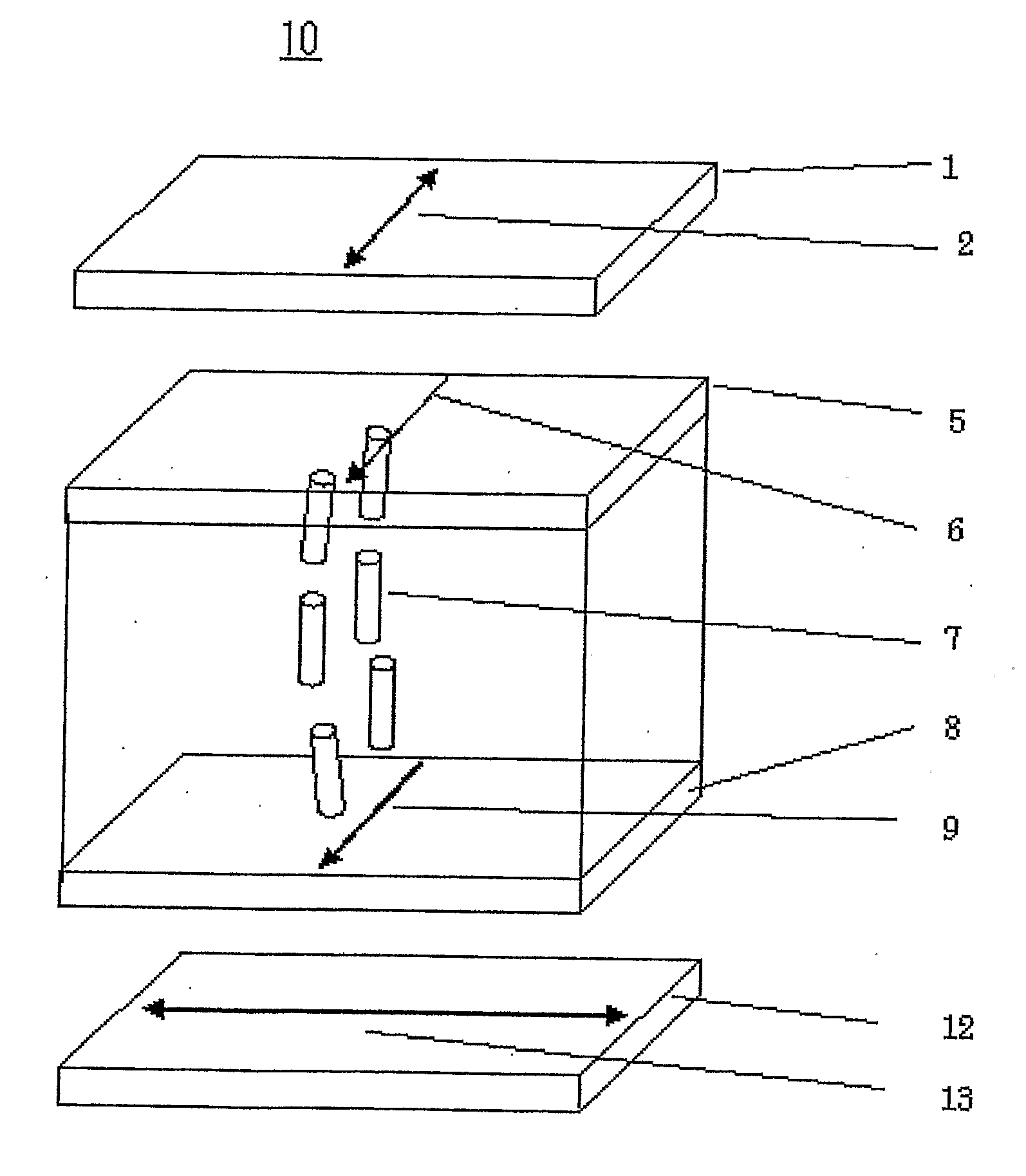
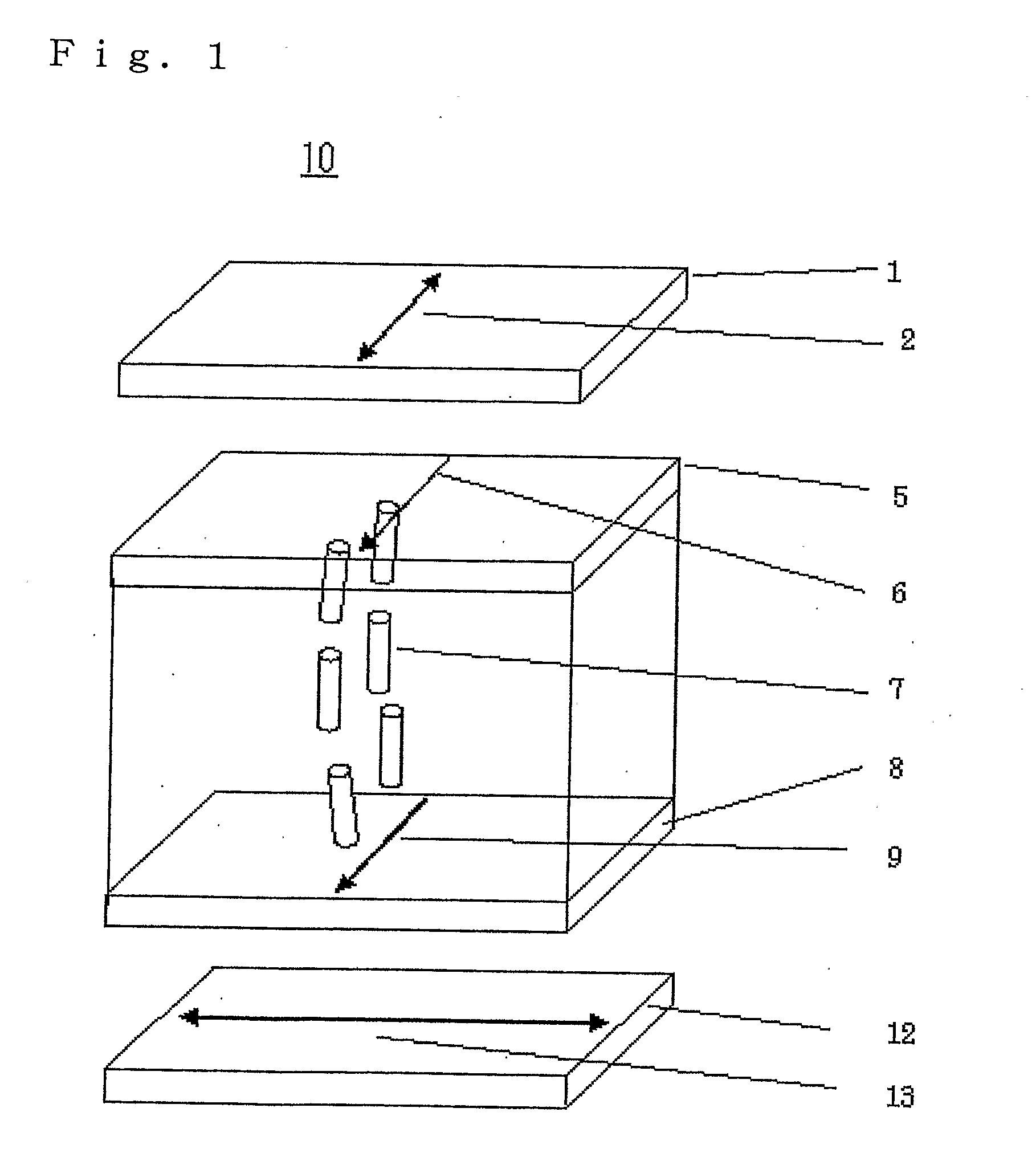
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS8159432B2Reduce dependenceReduce viewing angle dependenceCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayLighting-up time
A liquid crystal display device includes a plurality of pixels each connected to a signal line via a switching element. Each pixel includes first and second sub-pixels having voltage vs. luminance characteristics different from each other with respect to a signal voltage supplied from the signal line. A threshold signal voltage of the first sub-pixel is lower than that of the second sub-pixel. The pixels form color display pixels which are red, green pixel and blue pixels. Where the area ratio of the first sub-pixel in each of the red, green and blue pixels is SR1, SG1 and SB1, and the ratio of the lighting-up time period of the first sub-pixel of each of the red, green and blue pixels in one vertical scanning period is TR1, TG1 and TB1, the relationship of (SR1×TR1)>(SG1×TG1)>(SB1×TB1) holds.
Owner:SHARP KK
Light emitting device
InactiveUS20100164364A1Reduce viewing angle dependenceImproved luminous efficiency per unit areaMaterial nanotechnologyDischarge tube luminescnet screensFluorescenceLight emitting device
A light emitting apparatus (1) including: a supporting substrate (10), a fluorescence medium (20) and an emitting device (30) for covering the fluorescence device (20); the emitting device (30) having two or more emitting surfaces which are not parallel to each other; wherein the light emitting apparatus (1) emits light obtained by mixing light emitted by the emitting device (30) and light emitted by the fluorescence medium (20).
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device
ActiveUS20150263076A1Reduce power consumptionHigh puritySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh colorLight emitting device
Provided is a light-emitting device which can emit monochromatic lights with high color purity due to a microcavity effect and which can provide a white light with a broad spectrum when the monochromatic lights are combined. The light-emitting device has a red-, green-, blue-, and yellow-emissive light-emitting elements each of which has a reflective electrode and a semi-transmissive and semi-reflective electrode. The red-, green-, blue-, and yellow-emissive light-emitting elements have the same structure other than the reflective electrode and a layer in contact with the reflective electrode to selectively emit red, green, blue, and yellow lights, respectively. Red, green, and blue color filters are also provided over the red-, green-, blue-, light-emitting elements, respectively. An EL layer is commonly shared by the red-, green-, blue-, and yellow-emissive light-emitting elements, and the semi-transmissive and semi-reflective electrode covers an edge portion of the EL layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Substantially colorless and optically anisotropic material
InactiveUS6881454B2Slim shapeDisplay thinner and lighterLiquid crystal compositionsPolarising elementsMicelleChemistry
A substantially colorless and optically anisotropic material is obtained from substantially colorless and optically anisotropic micelles. The micelles are oriented in a definite direction. The optically anisotropic material is usable in optical films and polarization elements.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Liquid crystal display panel
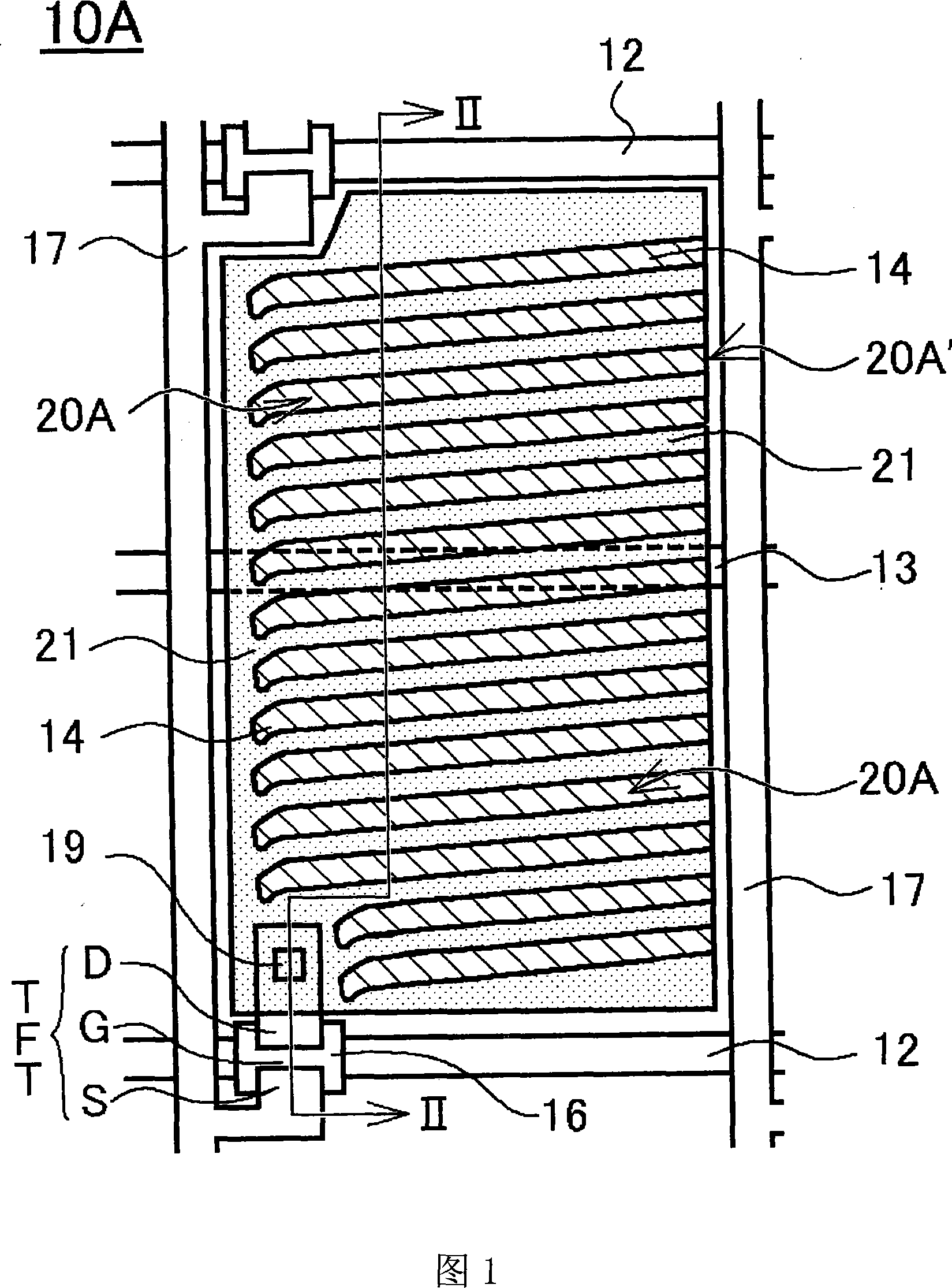
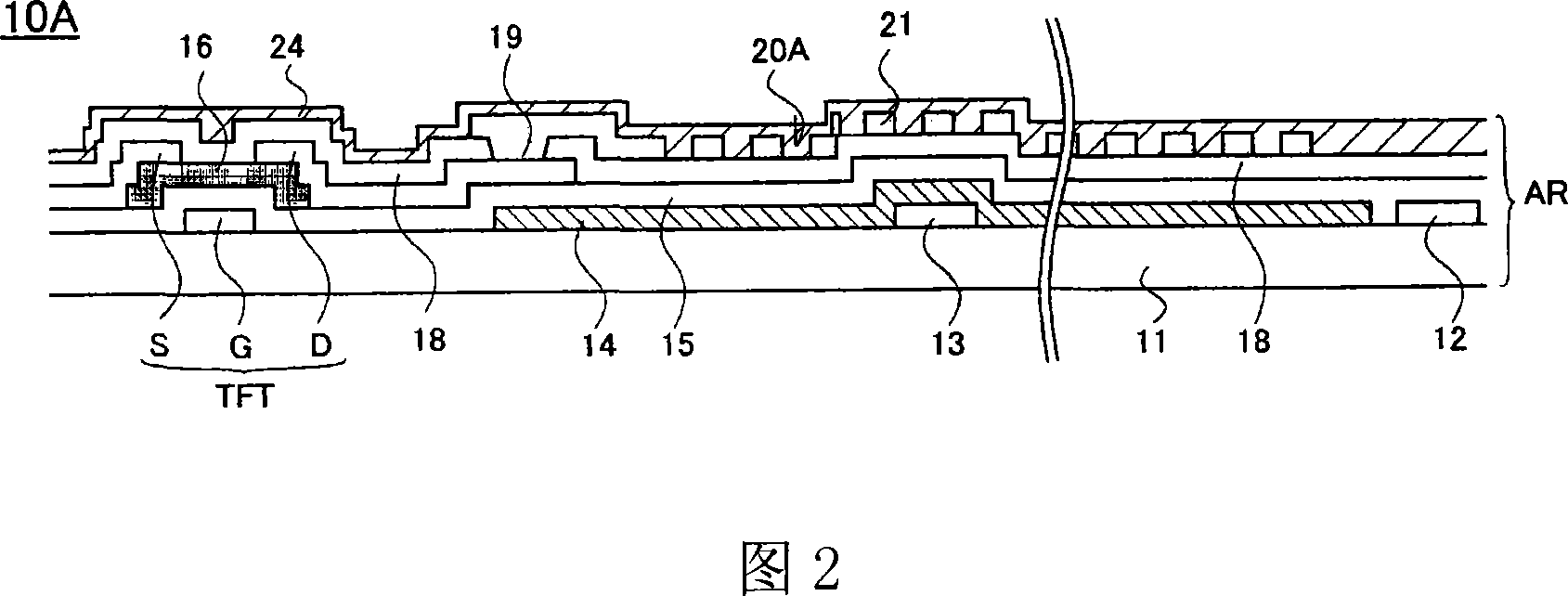
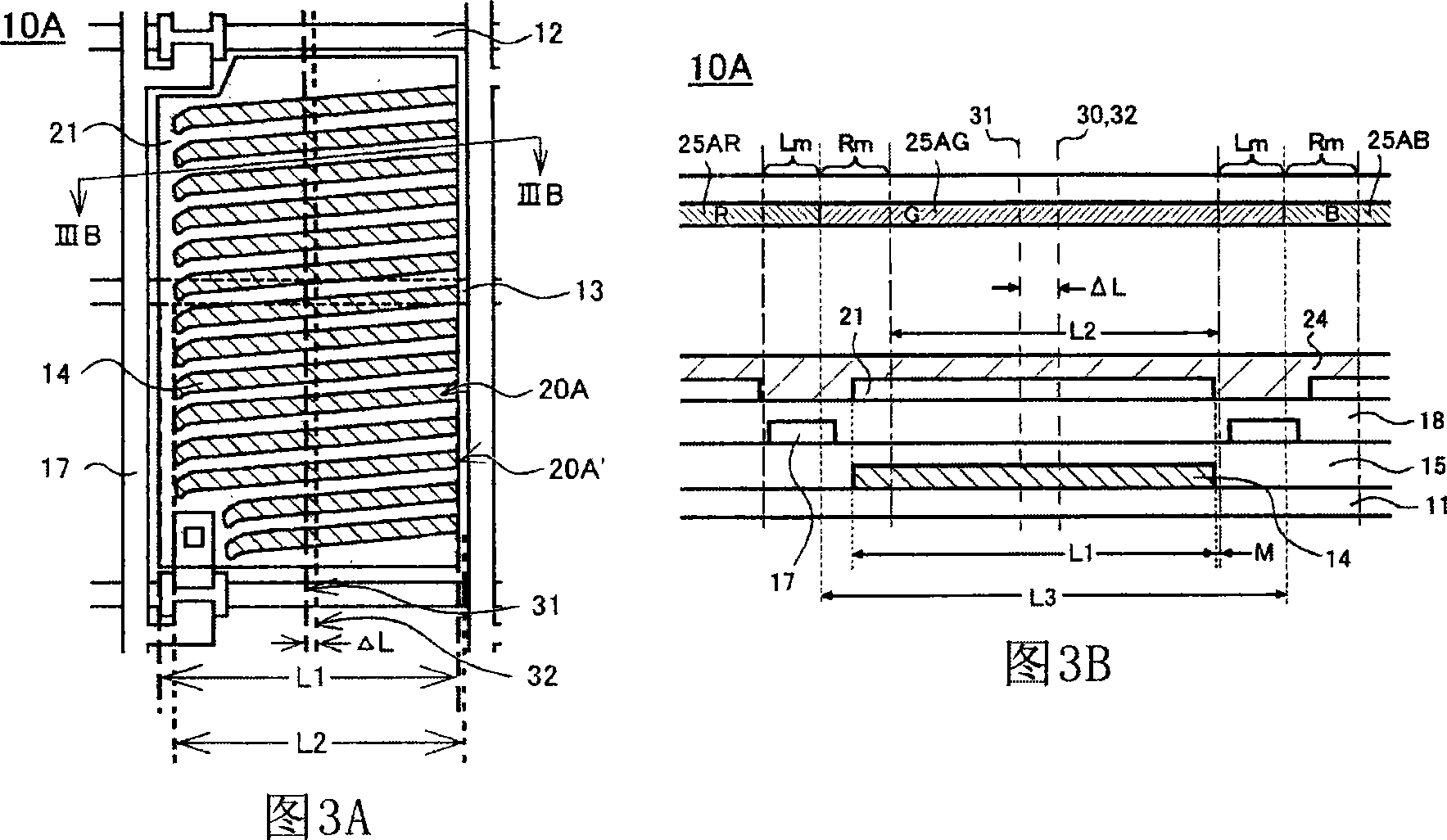
ActiveCN101144951ACorrect transmissionLess color mixingStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayScan line
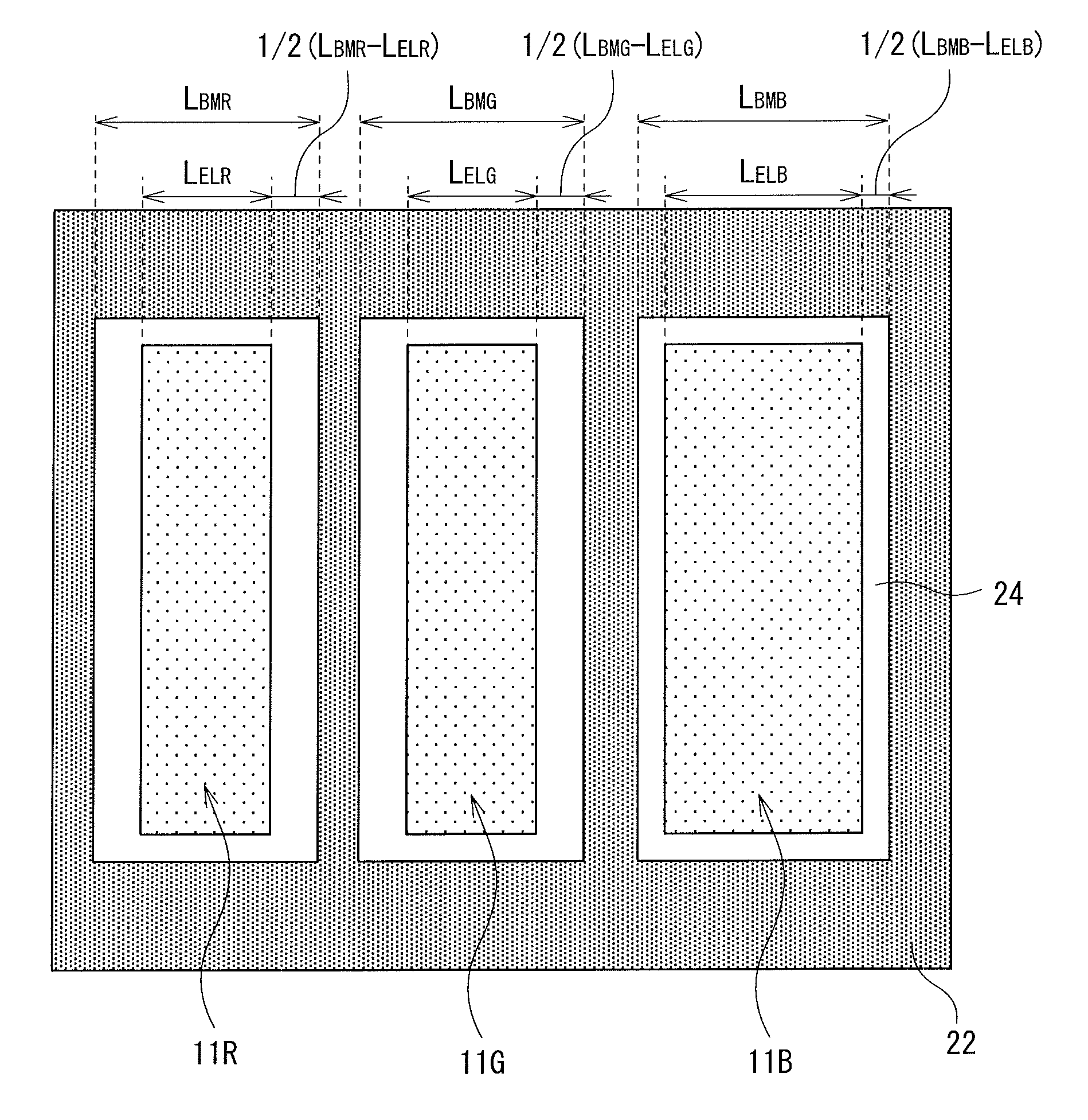
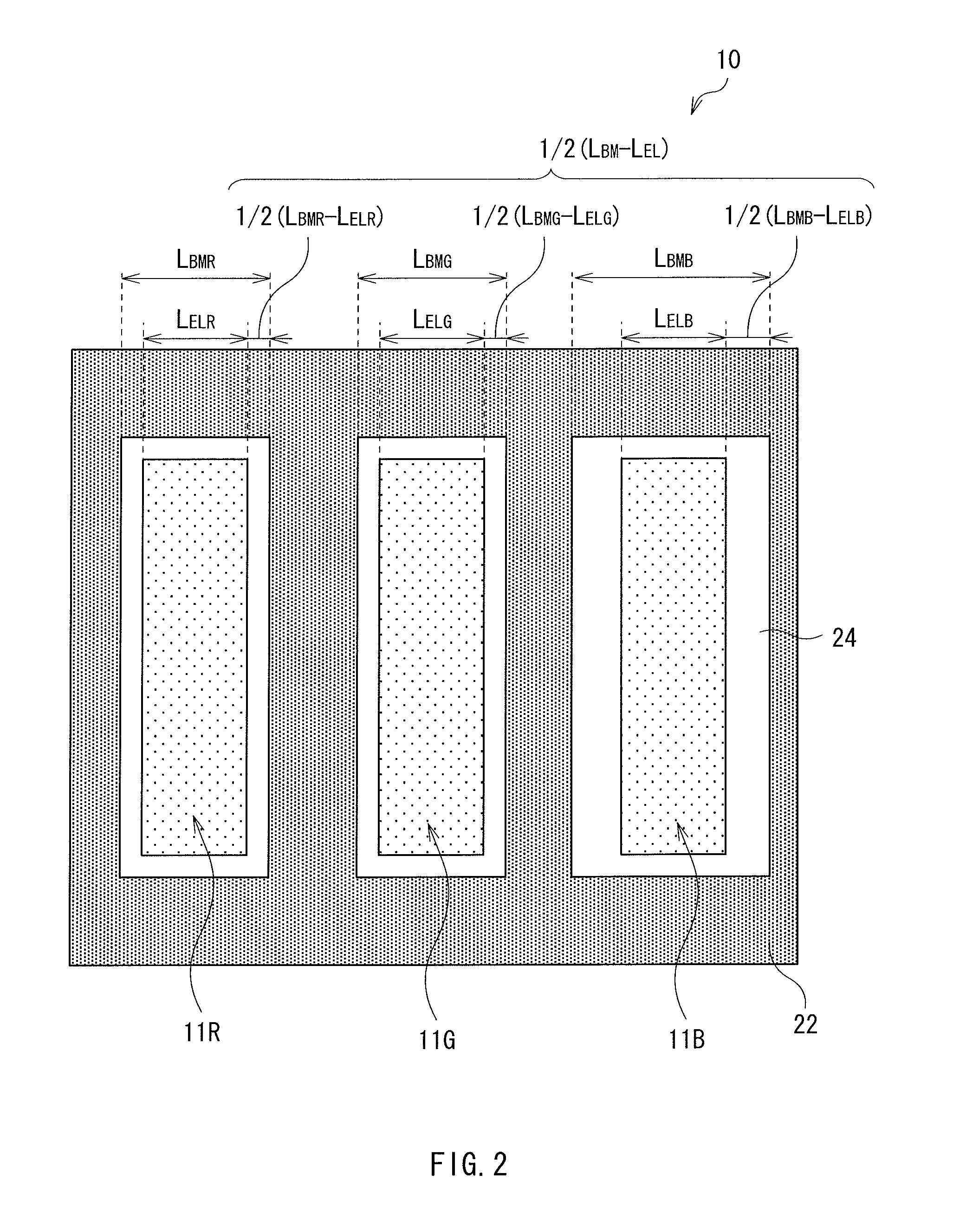
An FFS mode liquid crystal display panel 10 A includes an array substrate having first electrodes 14 each provided in a space delimited by a plurality of scan lines 12 and signal lines 17, second electrodes 21 provided on the first electrodes 14 with an insulator therebetween, and a plurality of slits 20 A provided to each of the second electrodes 21 in parallel with one another in a direction crossing the signal lines 17; and a color filter substrate having a color filter layer. Each of the slits 20 A has an open end 20 A' on one side. The color filter layer has a centerline 30 extending along the signal lines 17 for individual pixels, and the centerline 30 coincides with a display centerline 32 that is shifted toward the open end side of the slits from a centerline 31 of each second electrode 21 as viewed from above. Accordingly, an FFS mode liquid crystal display panel is obtained that causes no color mixture with this arrangement in which the slits each having an open end on one side are formed in each second electrode.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
Top-emitting OLED device and method of manufacturing the same, display device
InactiveUS20180166648A1Improve the display effectReduce viewing angle dependenceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAngle dependenceDisplay device
A top-emitting OLED device includes: a substrate; a first electrode disposed on the substrate; an organic layer disposed on the first electrode; and a second electrode disposed on the organic layer, through which light emitted from the organic layer exits from the OLED device; wherein the first electrode comprises a curved structure recessed towards the substrate. The top-emitting OLED device can reduce the viewing angle dependence of the top-emitting OLED device, so that it can prevent color difference of exiting light, narrowed visual angle of the OLED device and lateral light leakage from occurring.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Liquid crystal dislay
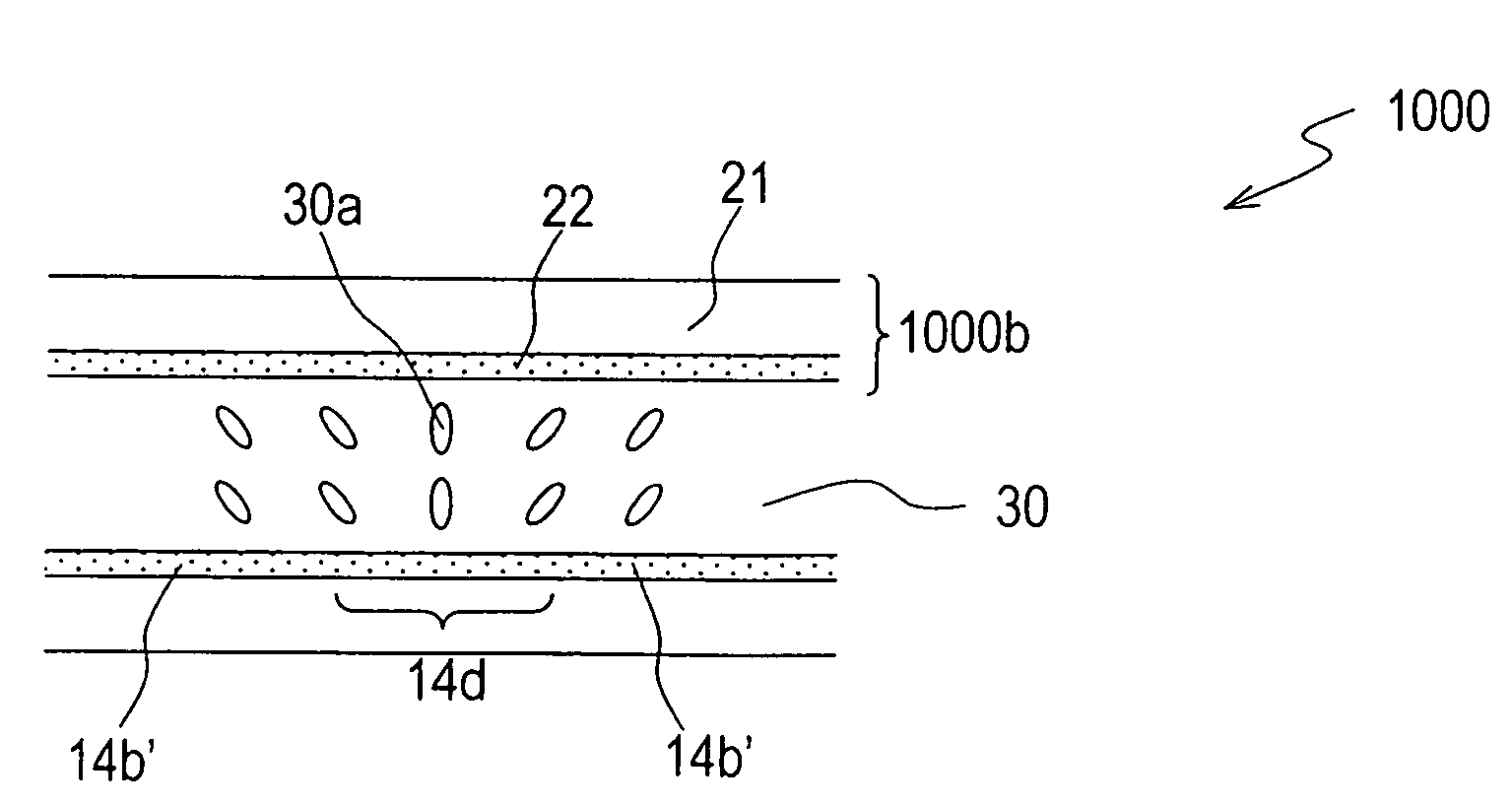
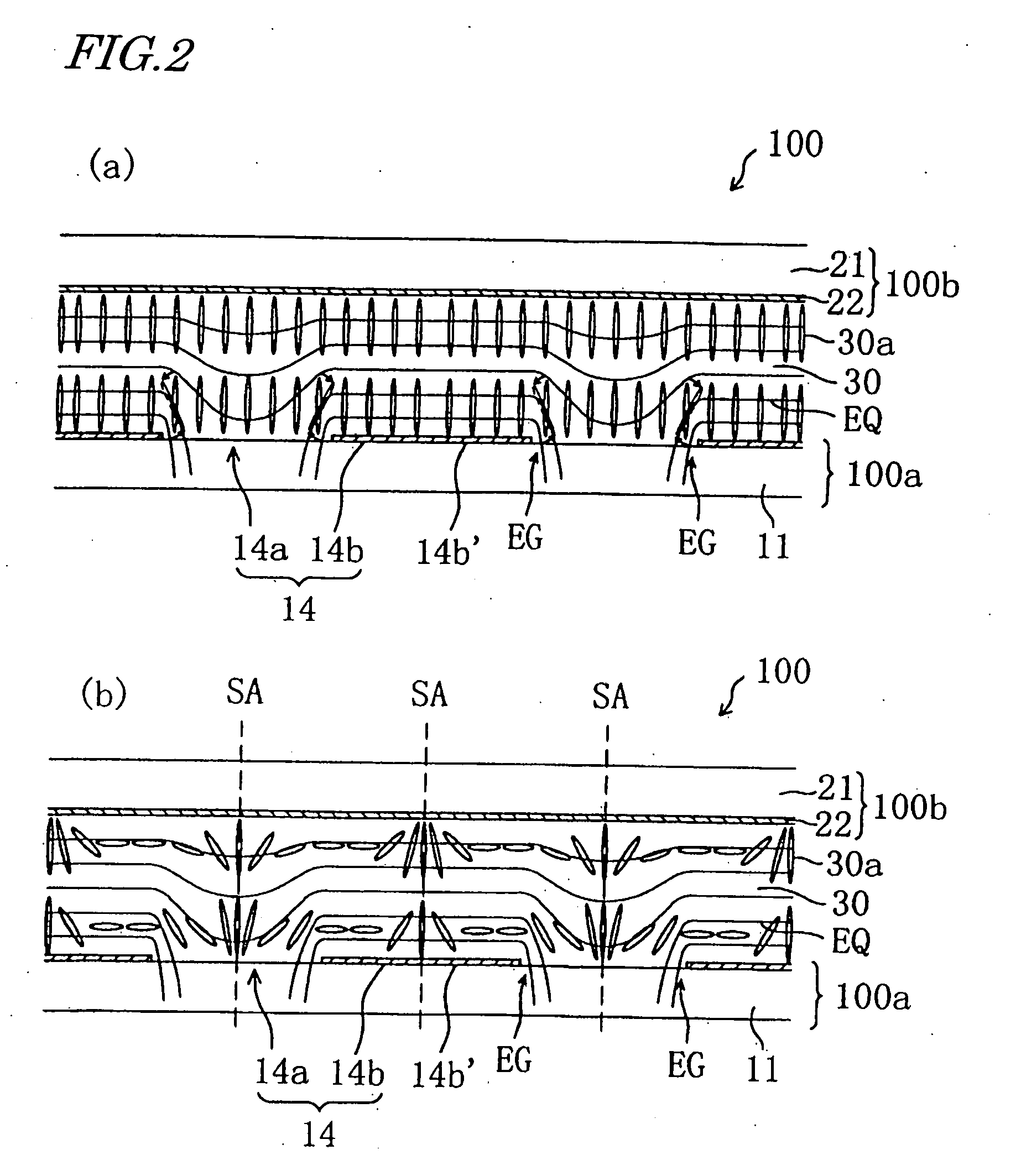
InactiveUS20060119776A1Angle dependence can be alleviatedHigh degree of symmetryNon-linear opticsVertical alignmentEngineering
A liquid crystal display device of the present invention comprises picture element regions each defined by a first electrode on a first substrate on the liquid crystal layer side and a second electrode provided on a second substrate and opposing the first electrode via the liquid crystal layer. In each picture element region, the first electrode includes openings and a solid portion; and the liquid crystal layer is in a vertical alignment with no voltage, and upon voltage application, forms liquid crystal domains each taking a radially-inclined orientation above the openings and the solid portion by an oblique electric field produced in edge portions of the openings. The solid portion of the first electrode includes unit solid portions and connecting portions each for connecting at least three unit solid portions to one another. The second substrate has a first orientation-regulating structure above each connecting portion for exerting an orientation-regulating force for placing liquid crystal molecules in the liquid crystal layer above the connecting portion into the radially-inclined orientation at least with voltage application.
Owner:SHARP KK
Liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20090195488A1Reduce viewing angle dependenceReduce the ratioStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayComputer science
Owner:SHARP KK
Liquid crystal display device
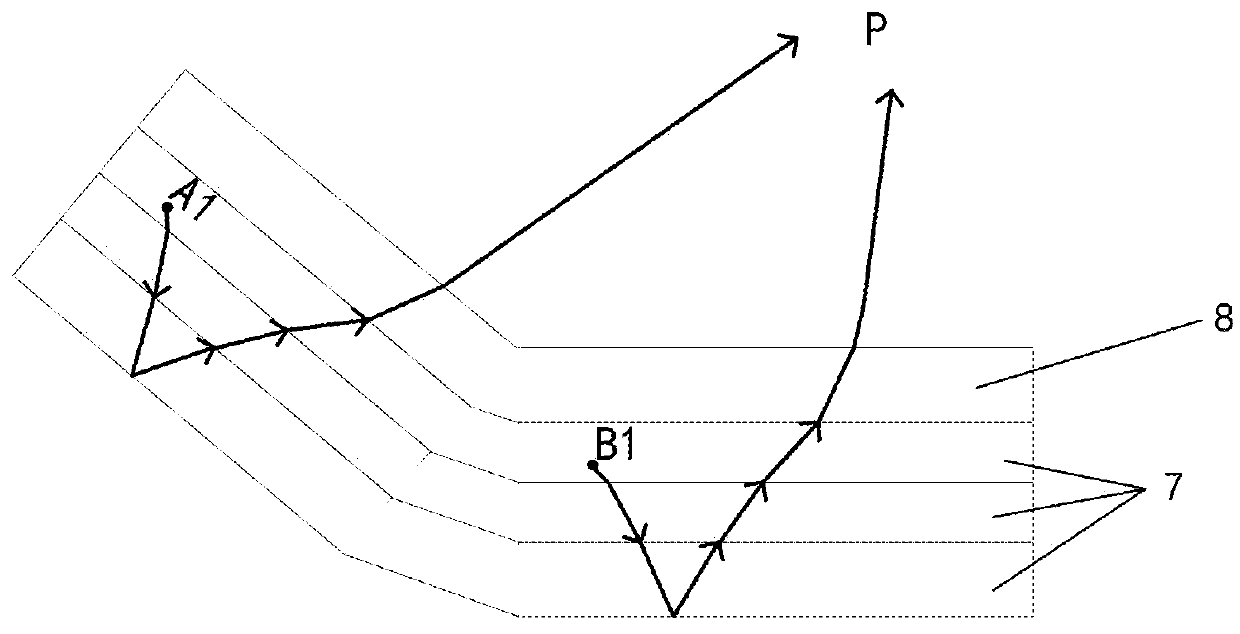
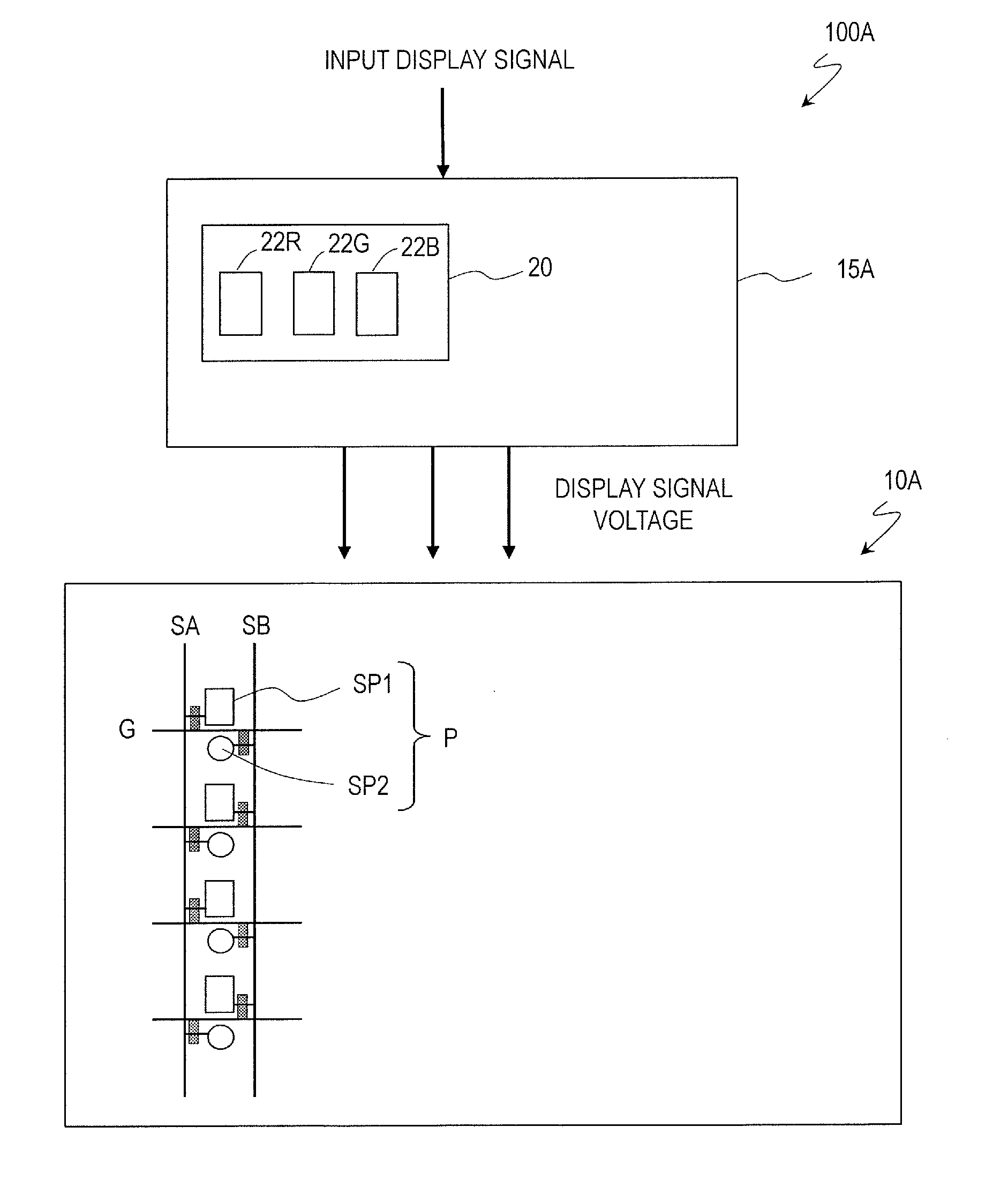
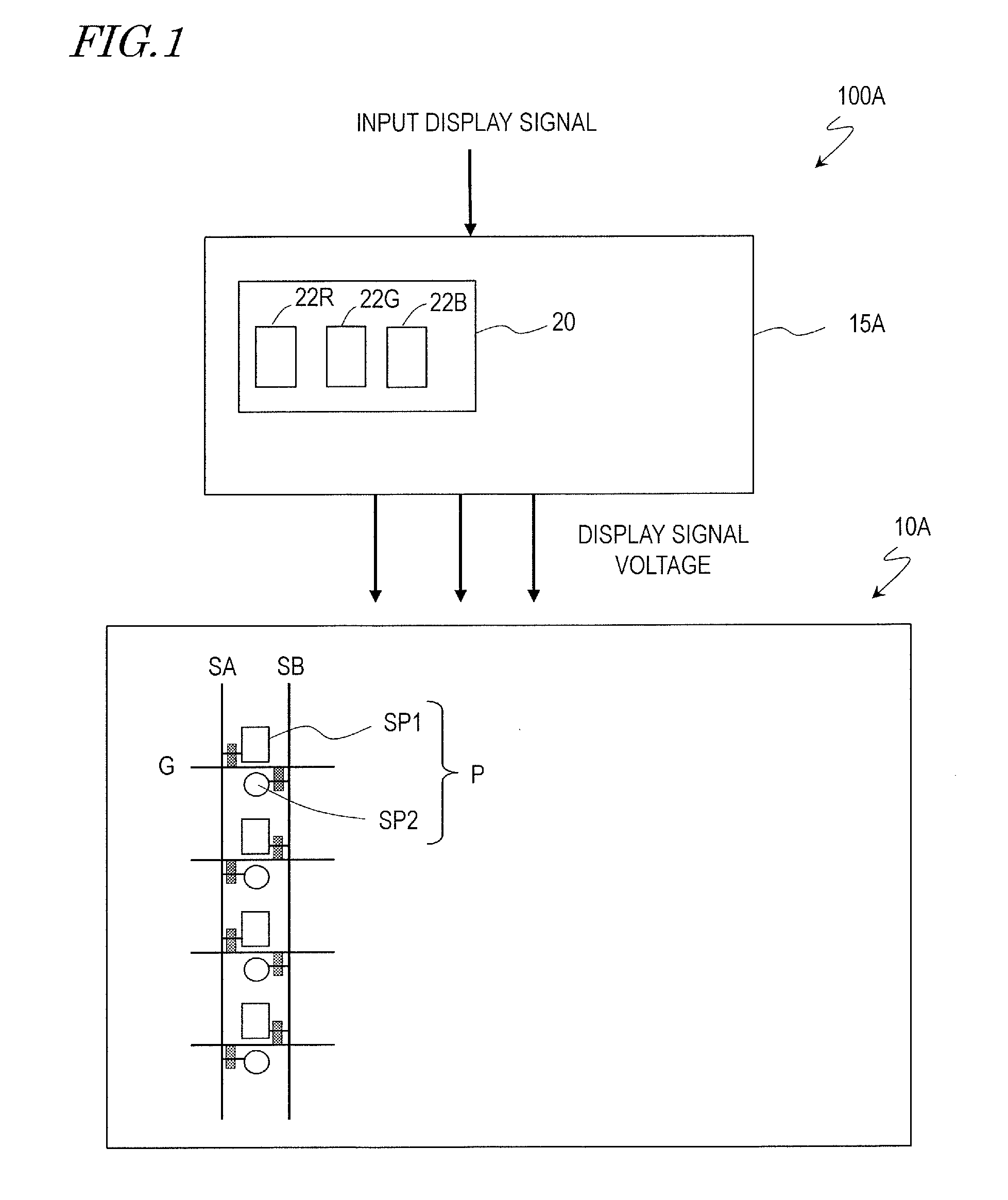
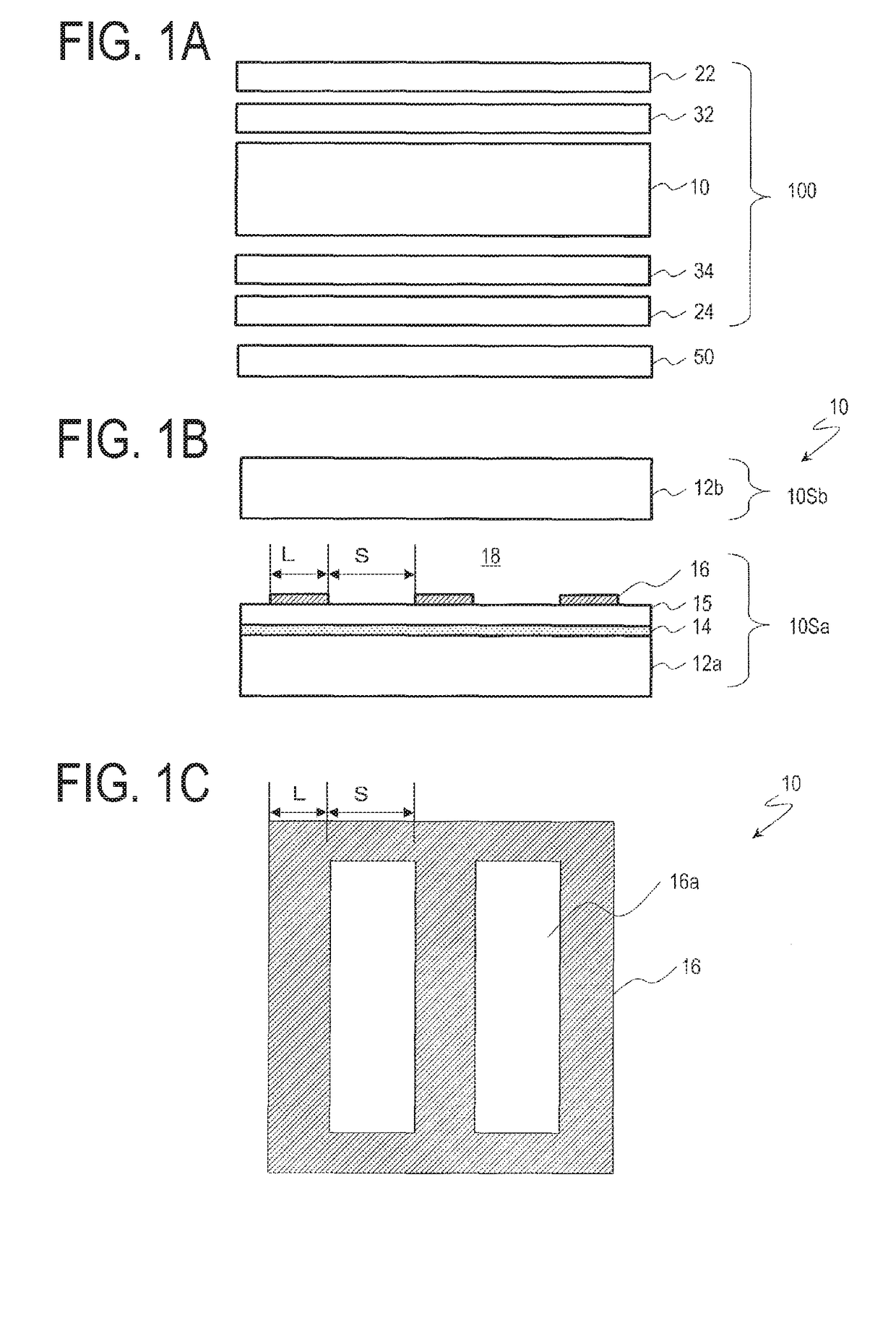
ActiveUS20150221267A1Reduce viewing angle dependenceAngle dependence is reducedCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingElectricityLiquid-crystal display
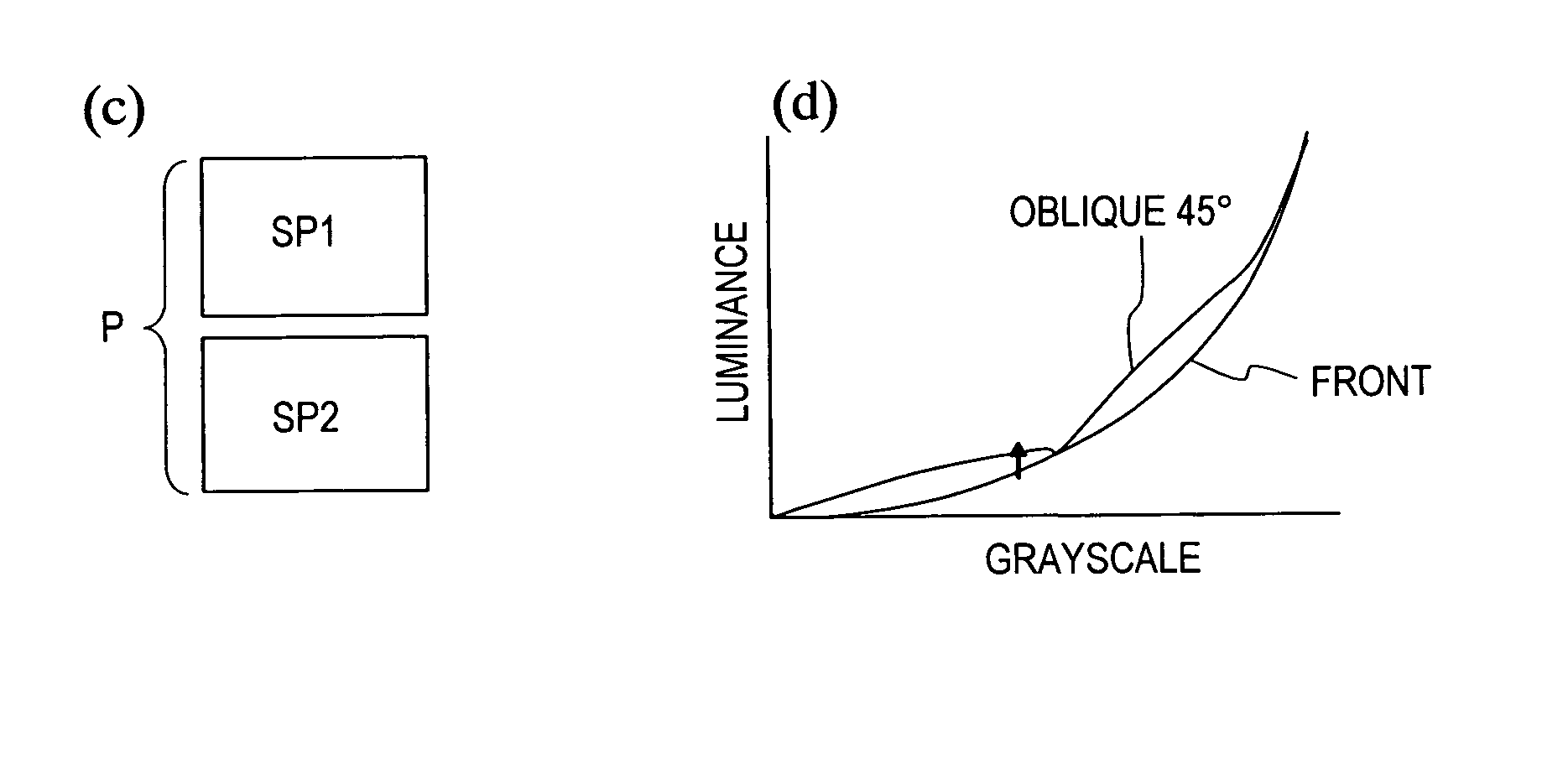
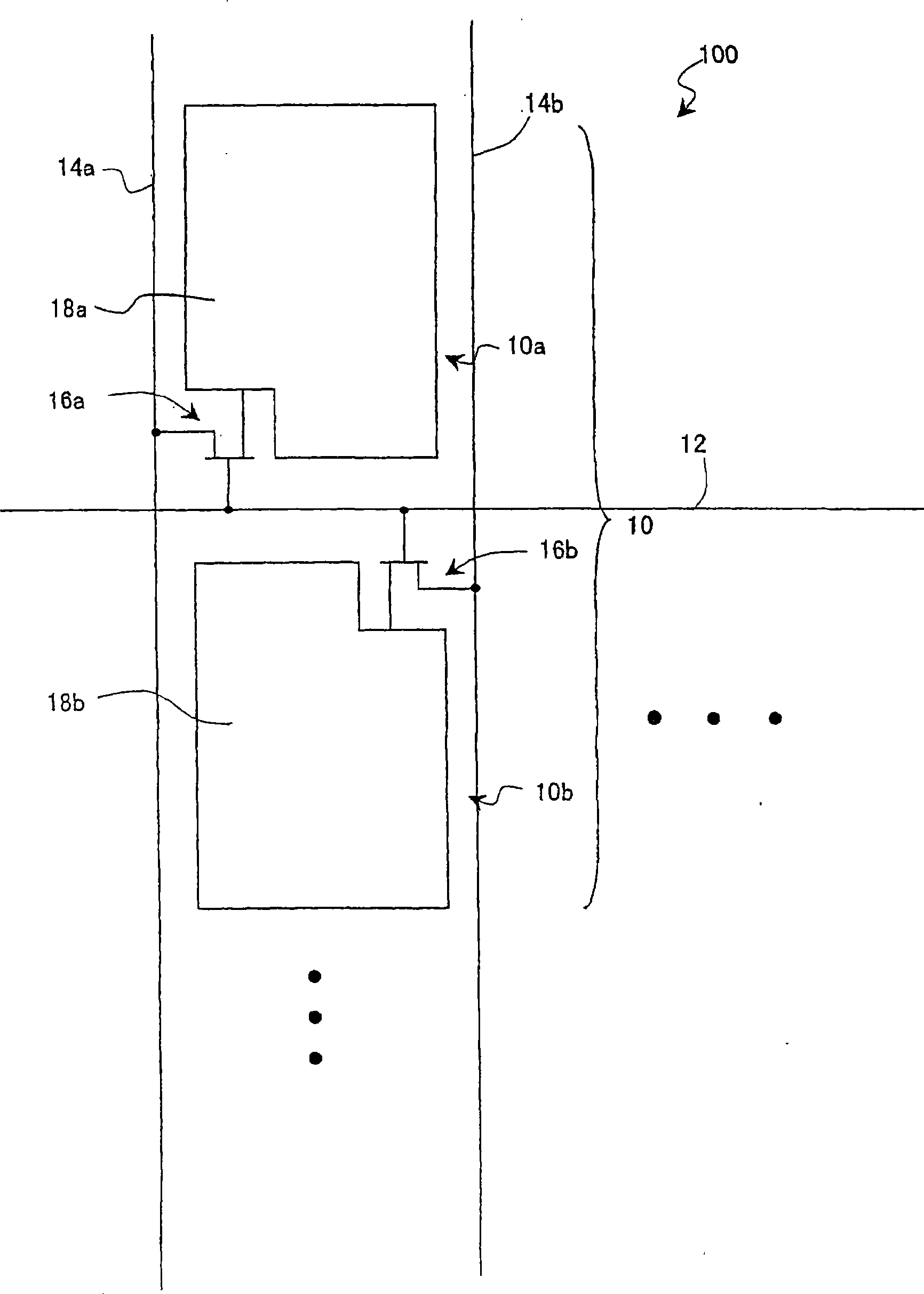
In a liquid crystal display device (100) according to an embodiment of the present invention, a plurality of color display pixels (CP) include three or more pixels (P) which exhibit different colors. The pixels (P) include a first sub-pixel (SP1) electrically connected to a first source bus line (SA) via a first TFT (T1) and a second sub-pixel (SP2) electrically connected to a second source bus line (SB) via a second TFT (T2). The control circuit (15) is configured to generate a first display signal voltage and a second display signal voltage that are to be supplied to the first sub-pixel (SP1) and the second sub-pixel (SP2) of a pixel (P) based on a grayscale level to be exhibited by the pixel (P) and grayscale levels to be exhibited by two or more remaining pixels (P) included in a color display pixel (CP) to which the pixel (P) belongs that are indicated by an input display signal, and output the generated first and second display signal voltages to the first source bus line (SA) and the second source bus line (SB), respectively.
Owner:SHARP KK
Producing process for microfined organic pigment, microfined organic pigment and microfined organic pigment coloring composition
ActiveCN101544847AHigh degree of miniaturizationLower latencyOrganic dyesOptical elementsSolubilityInorganic salts
The invention relates to a producing process for microfined organic pigment, a microfined organic pigment and a microfined organic pigmet coloring composition. the problem to be addressed is to provide a producing method for obtaining microfined organic pigment which can be applied on the coloring film of the liquid crystal television with low lantency, excellent view angle dependency, high transparency, a microfined organic pigment produced thereby, and microfined organic pigment coloring composition using the microfined organic pigment. The invention solves the problem by the producing process of the microfined organic pigment, which is characterized in that an organic pigment, a water-soluble inorganic salt, a water-soluble organic solvent and a resin (A) are mechanically compounded toobtain a compounding composition, then the water-soluble inorganic salt and the water-soluble organic solvent are removed by water, wherein the resin (A) has solubility of over a weight part with respect to 100 weight parts of water-soluble organic solvent under 25 DEG C., and containing an amino group and / or a quaternary ammonium cations.
Owner:TOYO INK SC HOLD CO LTD
Liquid crystal display
ActiveCN101510034AReduce viewing angle dependenceImprove display qualityStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsCapacitanceLiquid-crystal display
A liquid crystal display of the invention includes a plurality of pixels each of which has a liquid crystal layer and a plurality of electrodes for applying a voltage to the liquid crystal layer and which are arranged in a matrix of rows and columns, wherein: each of the plurality of pixels has a first sub-pixel and a second sub-pixel which can apply mutually different voltages to the liquid crystal layer, where the first sub-pixel has a higher brightness than the second sub-pixel in certain gradations; the first sub-pixel and the second sub-pixel each has: a liquid crystal capacitor formed by a counter electrode and a sub-pixel electrode opposing the counter electrode via the liquid crystal layer, and a storage capacitor formed by a storage capacitor electrode connected electrically to the sub-pixel electrode, an insulating layer, and a storage capacitor counter electrode opposing the storage capacitor electrode via the insulating layer; the counter electrode is a single electrode shared by the first sub-pixel and the second sub-pixel, and the storage capacitor counter electrodes of the first sub-pixel and the second sub-pixel are electrically independent of each other; and the storage capacitor counter electrode of the first sub-pixel in any of the plurality of pixels and the storage capacitor counter electrode of the second sub-pixel of a pixel adjacent to any of the pixelsin the column direction are electrically independent of each other.
Owner:SHARP KK
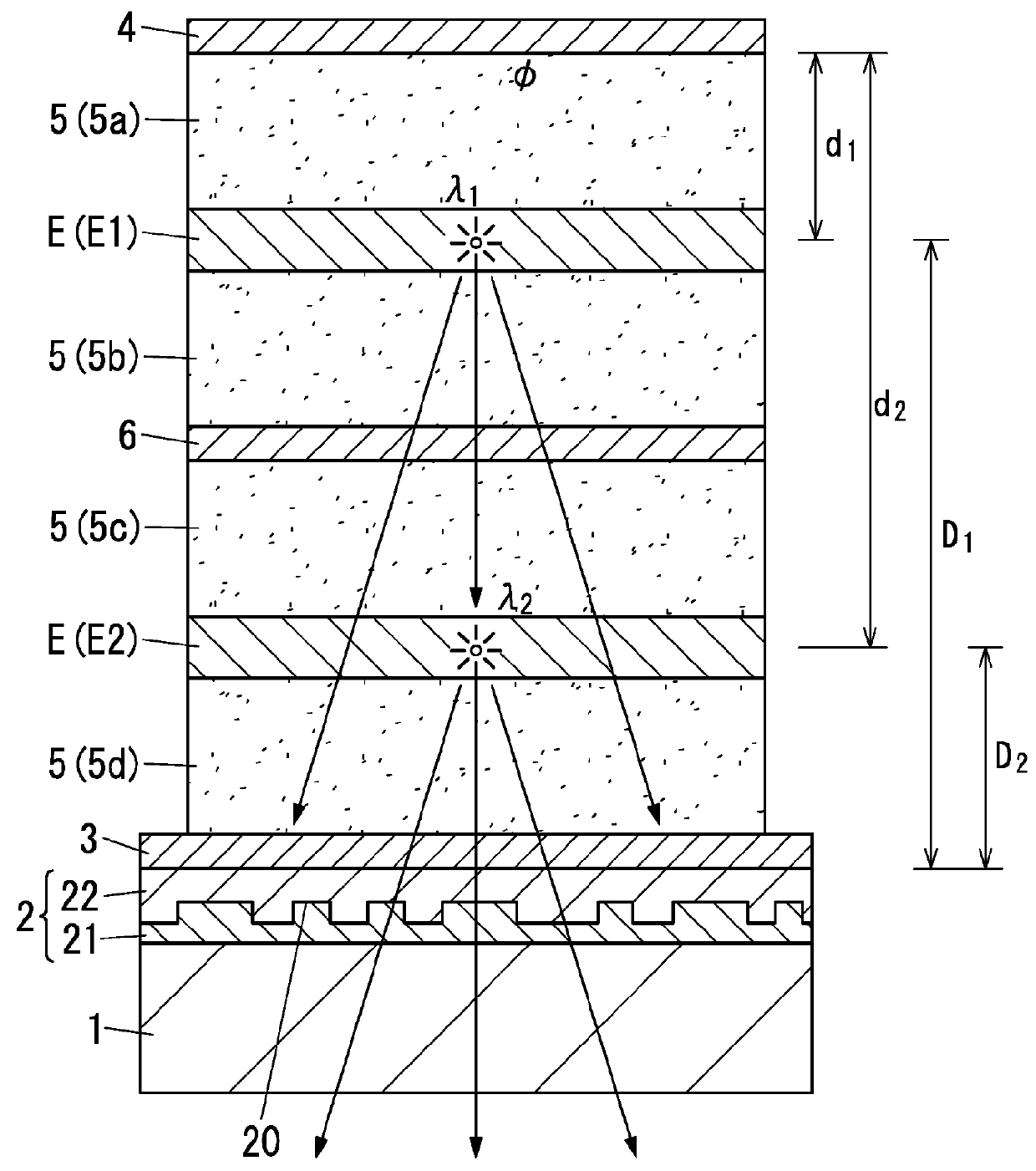
Organic electroluminescence element and lighting device using same
ActiveUS20160035991A1Amount of light can be efficientlyImprove luminous performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight reflectionRefractive index
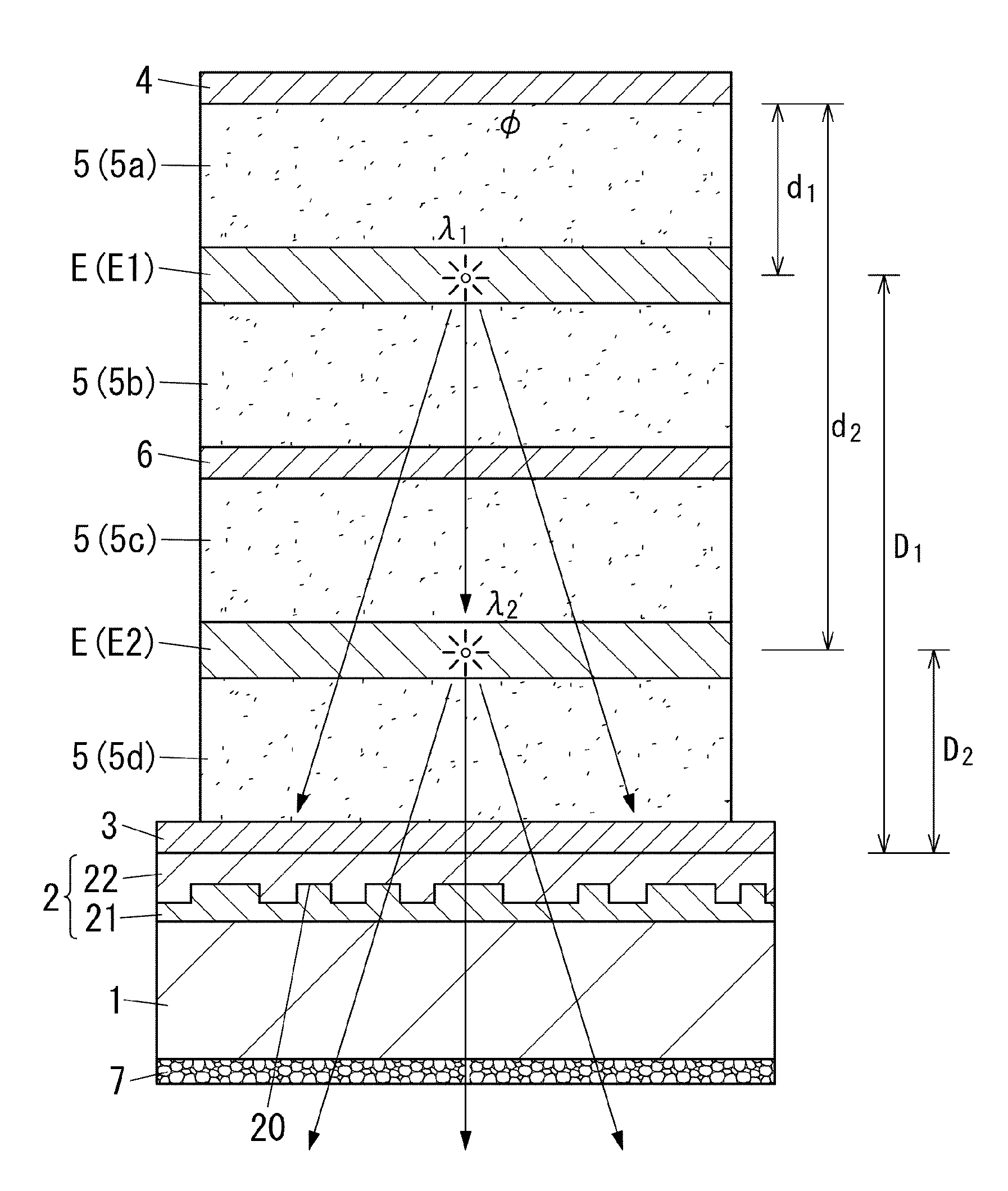
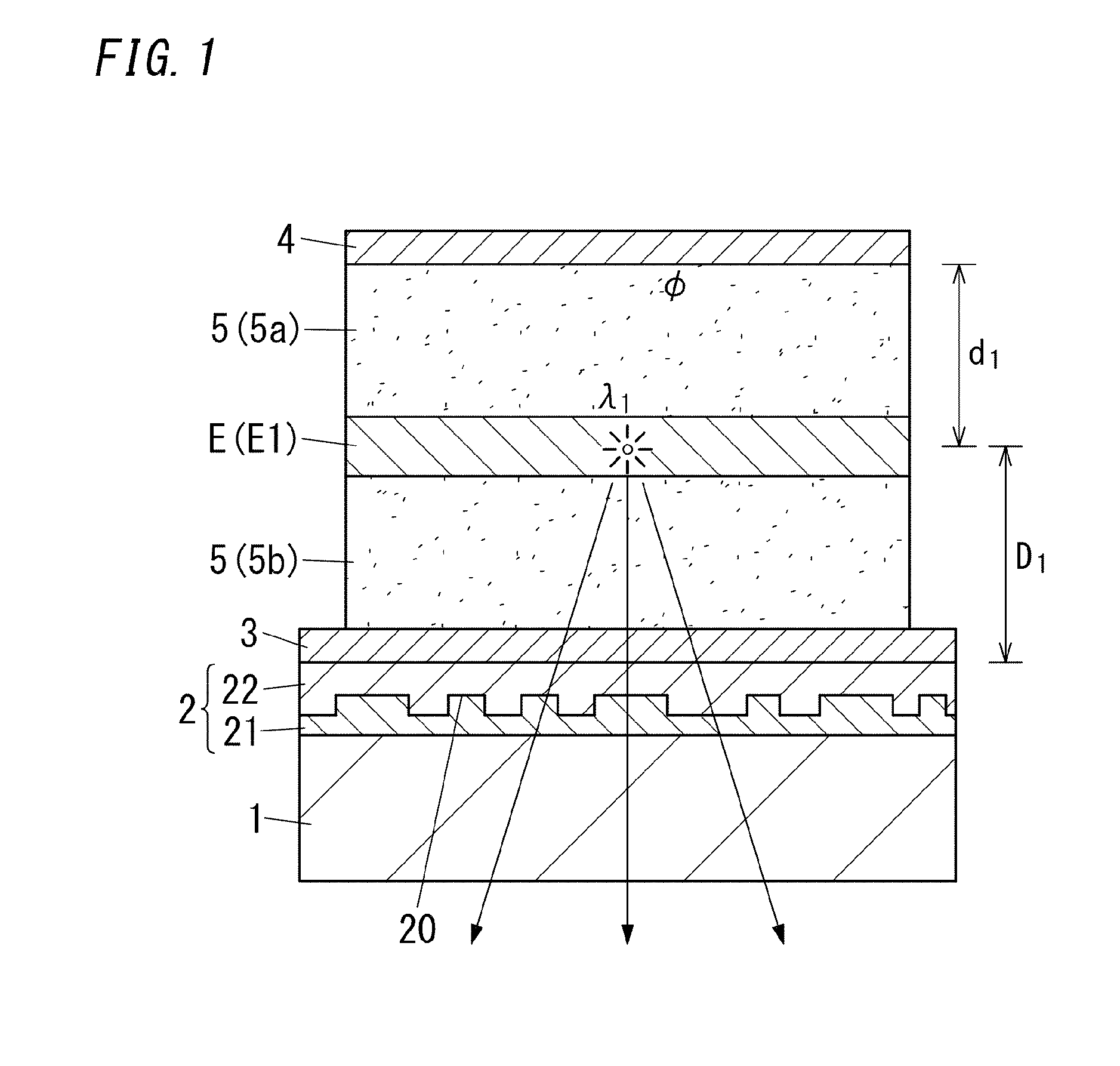
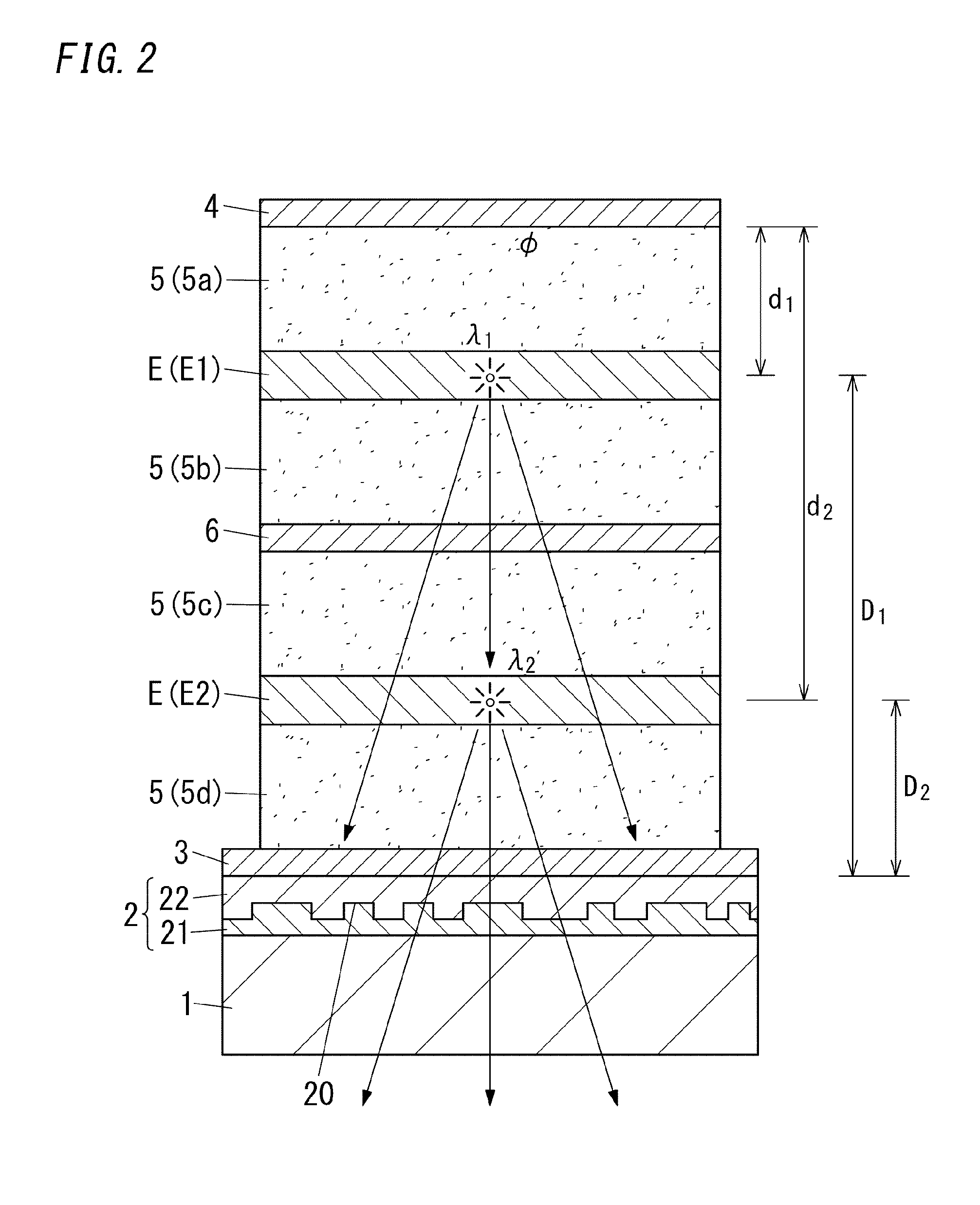
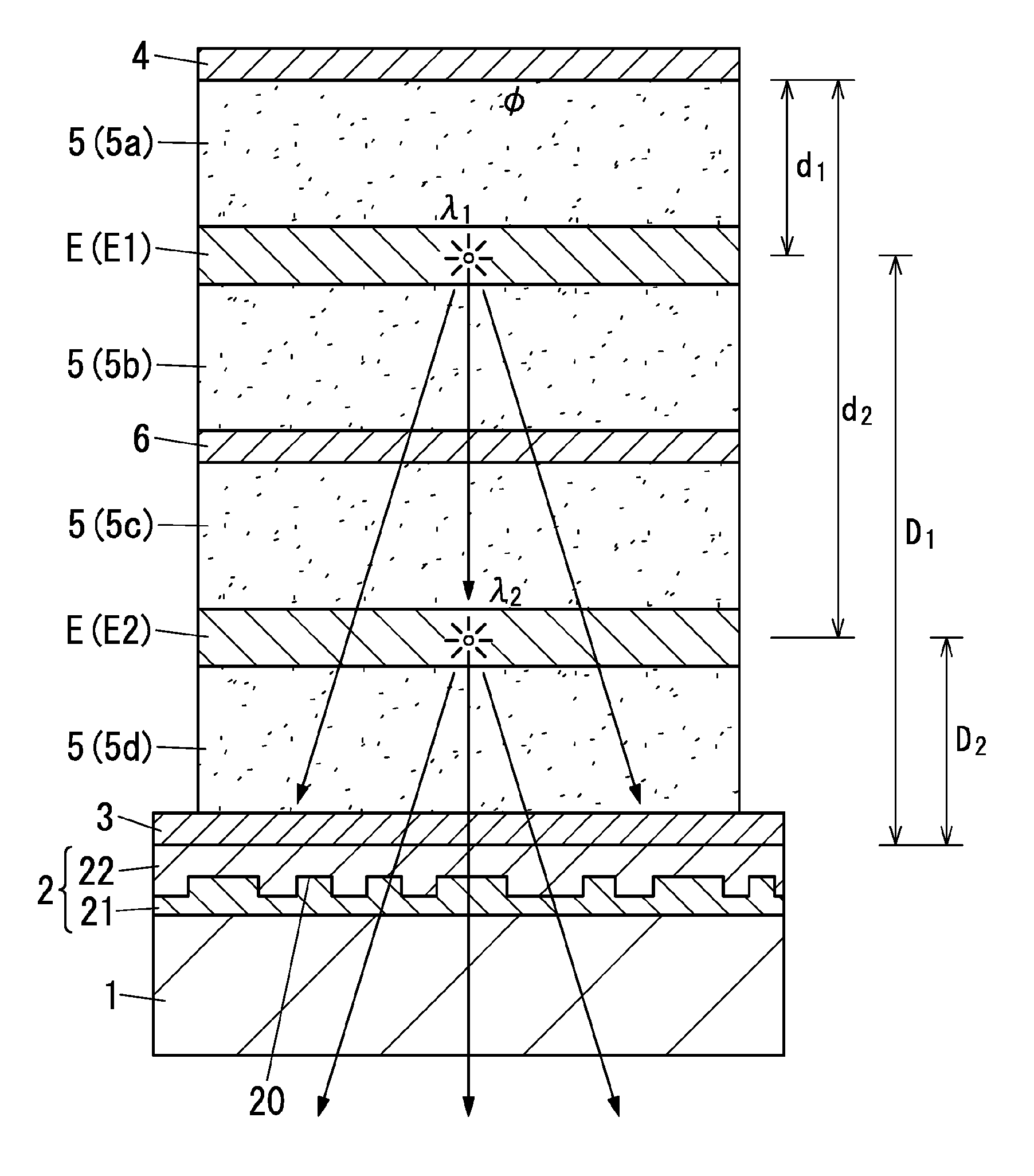
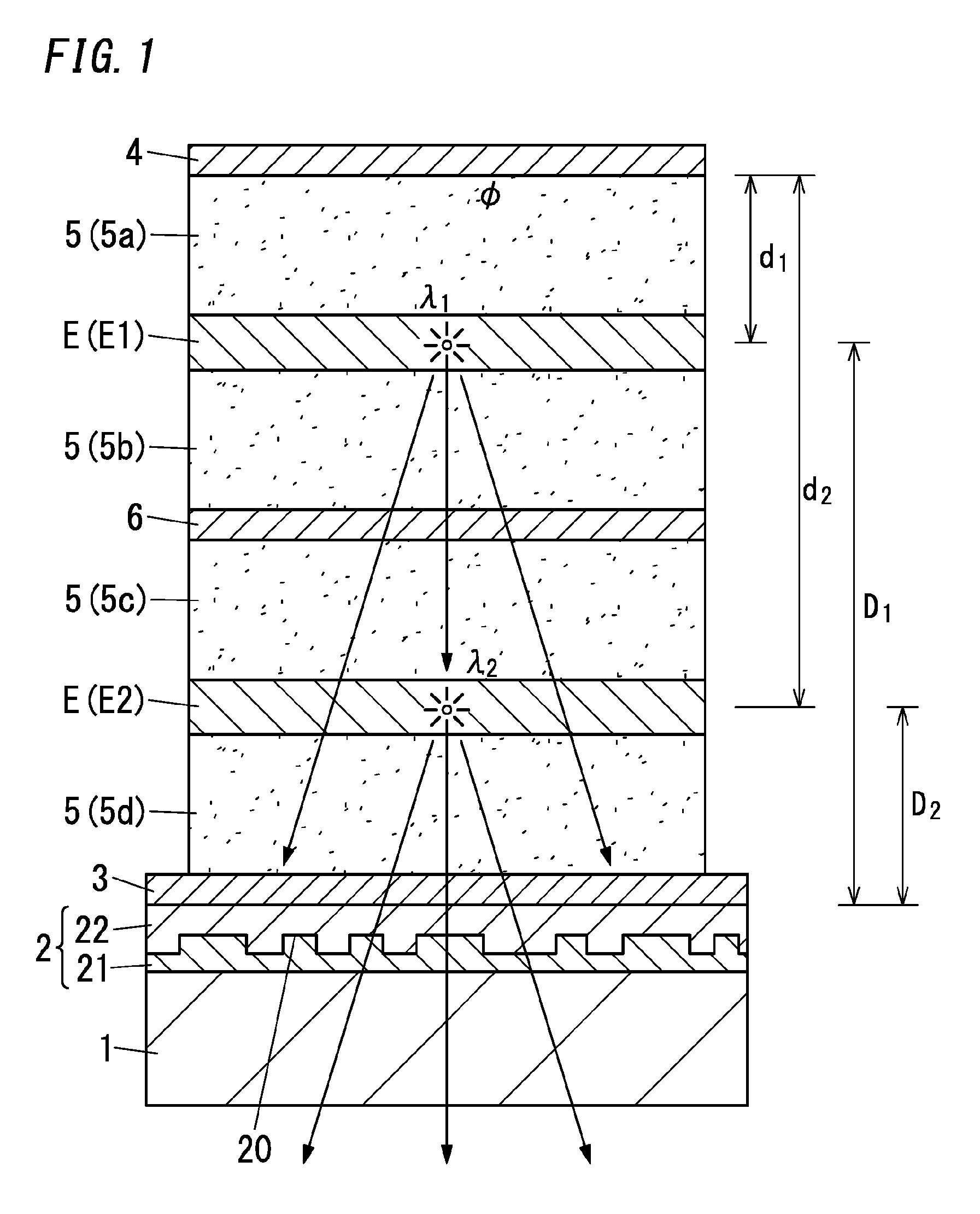
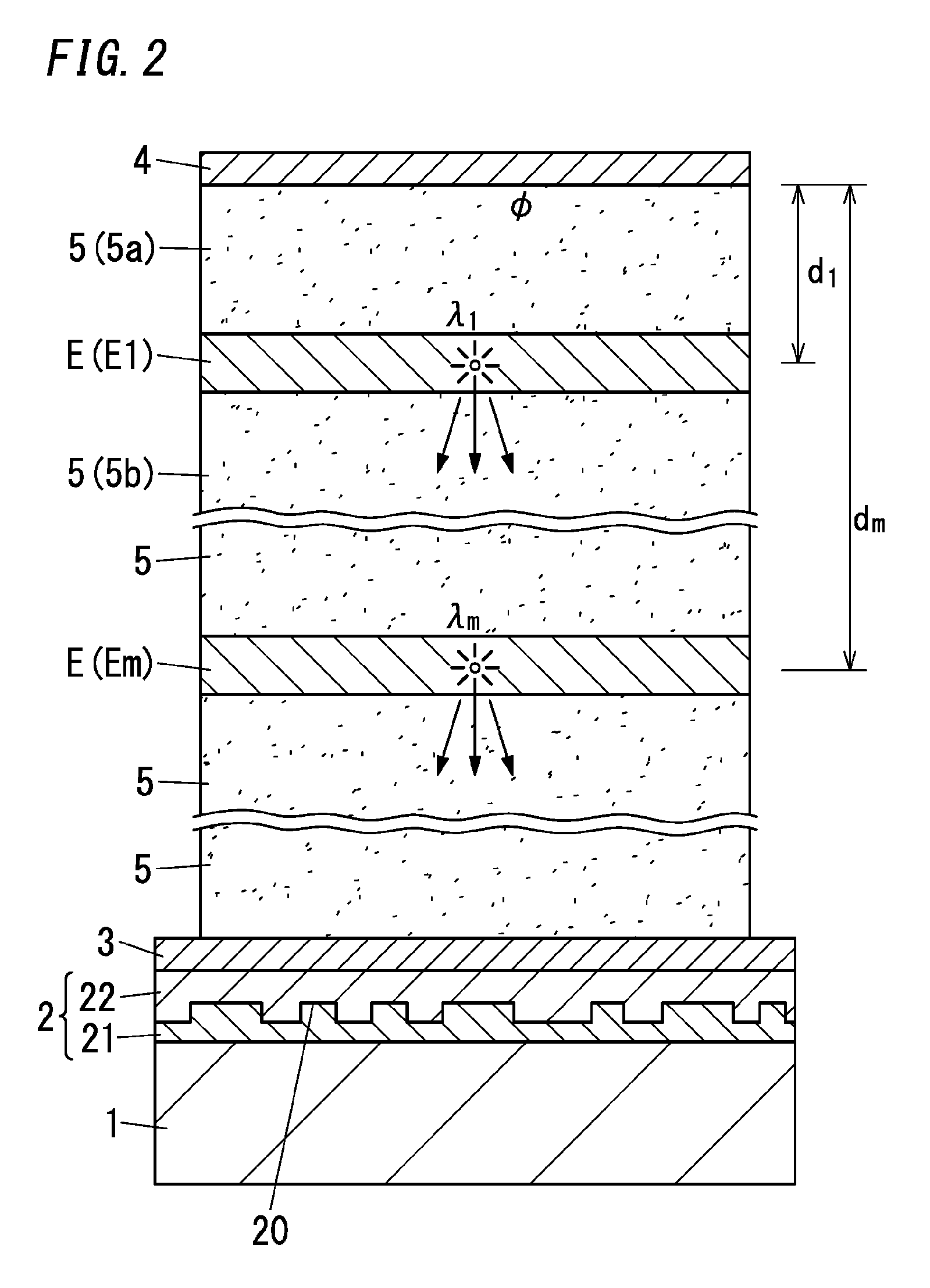
The present disclosure relates to an organic electroluminescence element including: a substrate having a light transmissive property; a light diffusion layer; a light transmissive electrode; a light reflective electrode; and multiple light emitting layers spaced from each other. With regard to the m-th light emitting layer being the m-th closest light emitting layer to the light reflective electrode, relations defined by following expressions (2) and (3) are satisfied. In the following expressions, λm represents the weighted average emission wavelength, Ø(λm) represents the phase shift, nm(λm) represents the average refractive index of a medium filling a space between the light reflective electrode and the m-th light emitting layer, and dm represents the distance from the light reflective electrode to the m-th light emitting layer. 1 is an integer equal to or more than 0.φ(λm)×λm4π+l+0.12λm≤nm(λm)×dm≤φ(λm)×λm4π+l+0.62λm(2)nm(λm)×dm≥0.6λm(3)
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Electro-optical light control element, electro-optical display and control medium
ActiveUS20100188630A1Short response timeEffect response timeLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingAngle dependenceLiquid crystalline
The present invention relates to an electro-optical light-modulation element of the FFS type, and to electro-optical displays and display systems, such as, for example, television screens and computer monitors, which contain elements of this type. The light-modulation elements according to the invention contain a liquid-crystalline modulation medium which has optimised elastic constants and are distinguished, in particular, by high contrast and / or optimised transmission in addition to good contrast, a low viewing-angle dependence, short response times and low addressing voltages. The present invention likewise relates to the liquid-crystalline modulation media used in the electro-optical light-modulation elements.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Liquid crystal display
InactiveCN101365979AIncrease contrastReduce viewing angle dependencePolarising elementsNon-linear opticsPolarizerLength wave
Owner:NIPPON OIL CO LTD
Organic electroluminescence element and lighting device using same
ActiveUS20160020431A1Light-outcoupling efficiency can be improvedReduce viewing angle dependenceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase shiftedRefractive index
The present disclosure relates to an organic electroluminescence element including: a substrate having a light transmissive property; a light diffusion layer; a light transmissive electrode; a light reflective electrode; and a light emitting layer. With regard to the first light emitting layer being the first closest light emitting layer to the light reflective electrode, the relation defined by following expression (2) is satisfied,[FORMULA1]φ(λm)×λm4π+l+0.12λm≤nm(λm)×dm≤φ(λm)×λm4π+l+0.52λm(2)wherein, λm represents the weighted average emission wavelength, Ø(λm) represents the phase shift, nm(λm) represents the average refractive index of a medium filling a space between the light reflective electrode and the first light emitting layer, and dm represents the distance from the light reflective electrode to the first light emitting layer. m is equal to 1.1 is an integer equal to or more than 0.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Transfer material, process for producing a color filter using the same, a color filter and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20090290102A1Easy to produceReduce viewing angle dependenceDecorative surface effectsOptical filtersLiquid-crystal displayPhotosensitive polymer
A transfer material comprising at least one optically anisotropic layer and at least one photosensitive polymer layer on at least one support, wherein said optically anisotropic layer comprises one or more compounds having a reactive group, and said photosensitive polymer layer comprises two or more types of photopolymerization initiators having different photoreaction mechanisms to each other, and a compound having a reactive group which can react with one or more of the reactive groups present in the optically anisotropic layer by the action of the at least one of said photopolymerization initiators. By using the transfer material, a color filter which contributes to reducing viewing angle dependence of color of a liquid crystal display device, and a liquid crystal display device having less corner non-uniformities and less viewing angle dependence of color.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Process for producing a liquid crystal cell substrate having a TFT driver element, a liquid crystal cell substrate, and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20090286340A1Easy to produceReduce viewing angle dependenceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolarising elementsAngle dependencePhotosensitive polymer
A process for easy production of a liquid crystal cell substrate having a TFT driver element which contributes to reducing viewing angle dependence of color of a liquid crystal display device is provided: a process using a transfer material, more preferably, a process which comprises the following steps [1] to [4] in this order: [1] transferring on a TFT substrate a transfer material having a photosensitive polymer layer and an optically anisotropic layer on a temporary support; [2] separating the temporary support from the transfer material on the TFT substrate; [3] subjecting the transfer material to light exposure on the TFT substrate; and [4] removing unnecessary parts of the photosensitive polymer layer and the optically anisotropic layer on the substrate.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Electro-optical light control element, electro-optical display and control medium
ActiveUS8168083B2Reduce viewing angle dependenceHigh color fidelityLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingLiquid crystallineDisplay device
The present invention relates to an electro-optical light-modulation element of the FFS type, and to electro-optical displays and display systems, such as, for example, television screens and computer monitors, which contain elements of this type. The light-modulation elements according to the invention contain a liquid-crystalline modulation medium which has optimised elastic constants and are distinguished, in particular, by high contrast and / or optimised transmission in addition to good contrast, a low viewing-angle dependence, short response times and low addressing voltages. The present invention likewise relates to the liquid-crystalline modulation media used in the electro-optical light-modulation elements.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Light emitting device
InactiveCN101455122AReduce viewing angle dependenceImprove luminous brightnessElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesFluorescenceLight emitting device
A light emitting apparatus (1) including: a supporting substrate (10), a fluorescence medium (20) and an emitting device (30) for covering the fluorescence device (20); the emitting device (30) having two or more emitting surfaces which are not parallel to each other; wherein the light emitting apparatus (1) emits light obtained by mixing light emitted by the emitting device (30) and light emitted by the fluorescence medium (20).
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Process of producing substrate for liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20080259268A1Reduce view angle dependence of colorEasily produceLiquid crystal compositionsNon-linear opticsChemistryAngle dependence
A process of producing a substrate for liquid crystal display device comprising an optically anisotropic layer, which comprises forming the optically anisotropic layer by a process comprising the following [1] to [3]:[1] preparing a substrate having a raw optically anisotropic layer;[2] subjecting the raw optically anisotropic layer to patterned exposures of two or more types having different exposure conditions to each other;[3] subjecting the substrate obtained after the exposure to a heat treatment at 80° C. or higher and 400° C. or lower. By the process, a substrate for liquid crystal display device which contribute to reducing viewing angle dependence of color of a liquid crystal display device can be easily produced.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
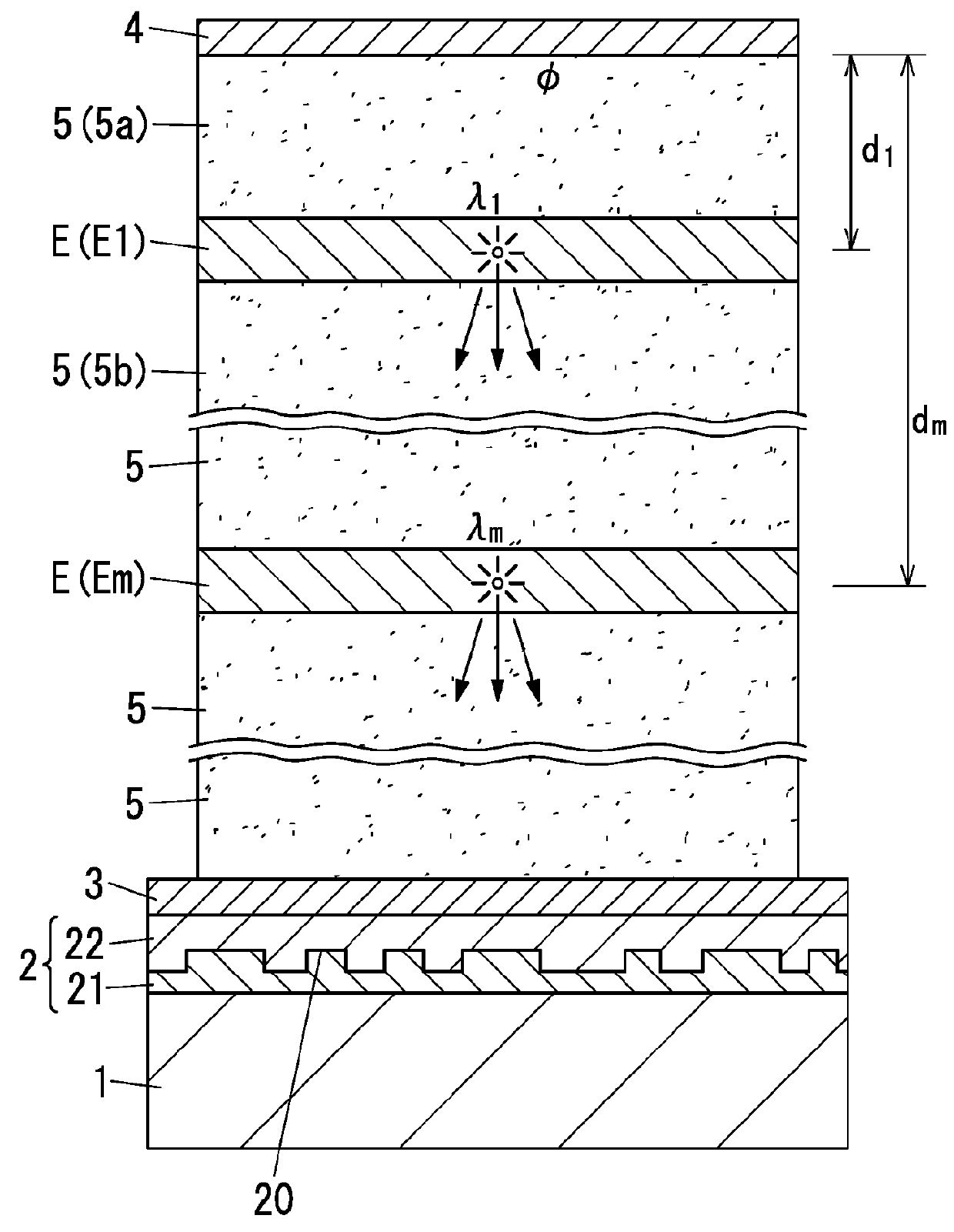
Organic electroluminescence element and lighting device using same
ActiveUS9577206B2Improve luminous performanceAmount of light emerging outside can be increased efficientlySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase shiftedRefractive index
The present disclosure relates to an organic electroluminescence element including: a substrate having a light transmissive property; a light diffusion layer; a light transmissive electrode; a light reflective electrode; and multiple light emitting layers spaced from each other. With regard to the m-th light emitting layer being the m-th closest light emitting layer to the light reflective electrode, relations defined by following expressions (2) and (3) are satisfied. In the following expressions, λm represents the weighted average emission wavelength, Ø(λm) represents the phase shift, nm(λm) represents the average refractive index of a medium filling a space between the light reflective electrode and the m-th light emitting layer, and dm represents the distance from the light reflective electrode to the m-th light emitting layer. l is an integer equal to or more than 0.[FORMULA1]ϕ(λm)×λm4π+l+0.12λm≤nm(λm)×dm≤ϕ(λm)×λm4π+l+0.62λm(2)nm(λm)×dm≥0.6λm(3)
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Process for producing a liquid crystal cell substrate having a TFT driver element, a liquid crystal cell substrate, and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS7879634B2Easy to produceReduce viewing angle dependencePolarising elementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive polymerLight exposure
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Illumination apparatus and display apparatus
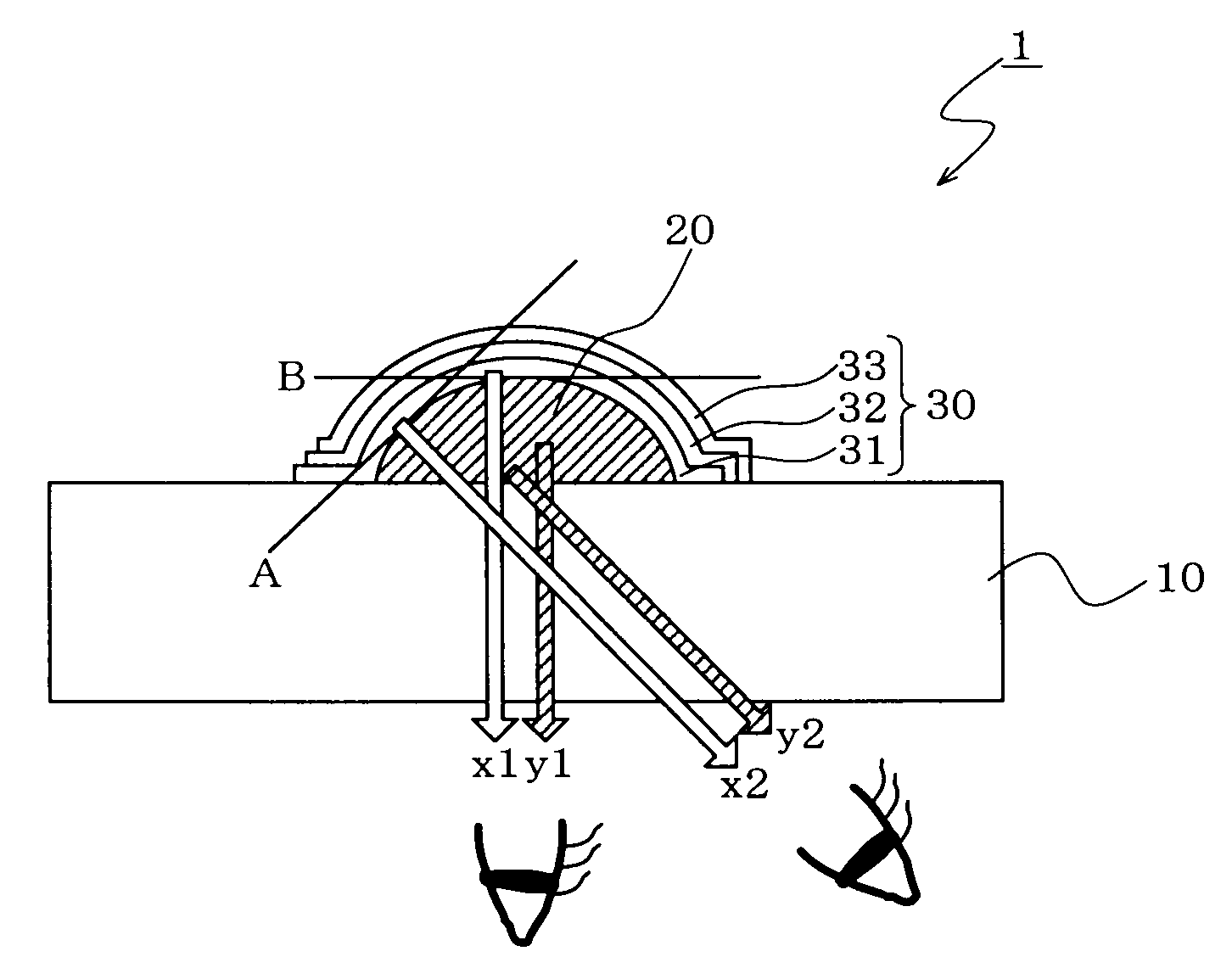
ActiveUS8403512B2Reduce viewing angle dependenceImprove display qualityPoint-like light sourcePortable electric lightingFluorescencePhosphor
[Object] To provide an illumination apparatus capable of reducing a view angle dependency of a chromaticity distribution in a light-emitting surface of a phosphor layer.[Solving Means] A light beam control device (11) that controls emitted light from light-emitting diodes (10) so that a view angle dependency of a chromaticity distribution in a light-emitting surface (22a) of a phosphor layer (22) is suppressed is interposed between the light-emitting diodes (10) and the phosphor layer (22). The light beam control device (11) causes the emitted light from the light-emitting diodes (10) to be bent in a vertical direction or an approximately-vertical direction with respect to the light-emitting surface (22a) of the phosphor layer (22) and thus causes the light to enter the phosphor layer (22). As a result, light that obliquely enters a surface of the phosphor layer (22) is lessened, and the view angle dependency of the chromaticity distribution in the light-emitting surface (22a) of the phosphor layer (22) is reduced.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Light emitting device, illumination apparatus and display apparatus
InactiveCN102683612AReduce viewing angle dependenceEfficient acquisitionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight equipmentLight reflection
Disclosed herein are a light emitting device, an illumination apparatus and a display apparatus, the light emitting device including: an organic layer sandwiched between a first electrode and a second electrode to serve as an organic layer including a light emitting layer for emitting monochromatic light at one location; a first light reflection boundary face provided on a side close to the first electrode to serve as a boundary face for reflecting light emitted from the light emitting layer so as to radiate the reflected light from a side close to the second electrode; and a second light reflection boundary face, a third light reflection boundary face and a fourth light reflection boundary face which are sequentially provided at positions separated away from each other in a direction from the first electrode to the second electrode on the side close to the second electrode.
Owner:SONY CORP
Display device with clearance
ActiveUS9140427B2Light extraction efficiency can be improvedDisruption of luminanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
A display device is provided, in which view-angle dependence of chromaticity of white or an intermediate color may be reduced. The display device includes a pair of opposed substrates, a light blocking layer provided on one of the pair of substrates while having a plurality of openings, and a plurality of self-luminous elements provided on the other of the pair of substrates, each of the self-luminous elements having an emission region facing each of the openings, and having an emission color different from an emission color of another element, at least one self-luminous element being different from other self-luminous elements in clearance in a display plane direction from an end of the emission region to an opening of the light blocking film.
Owner:SONY CORP
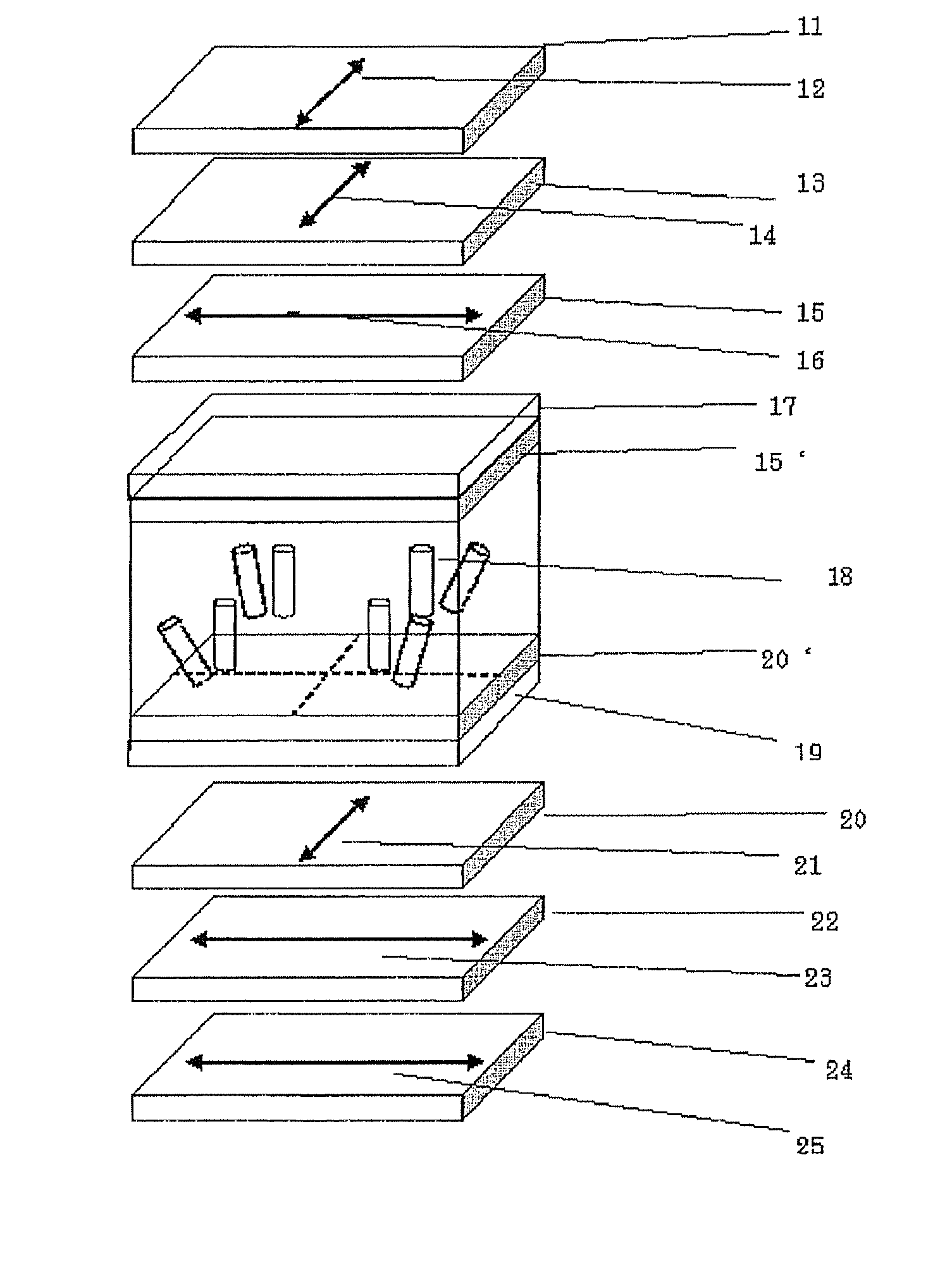
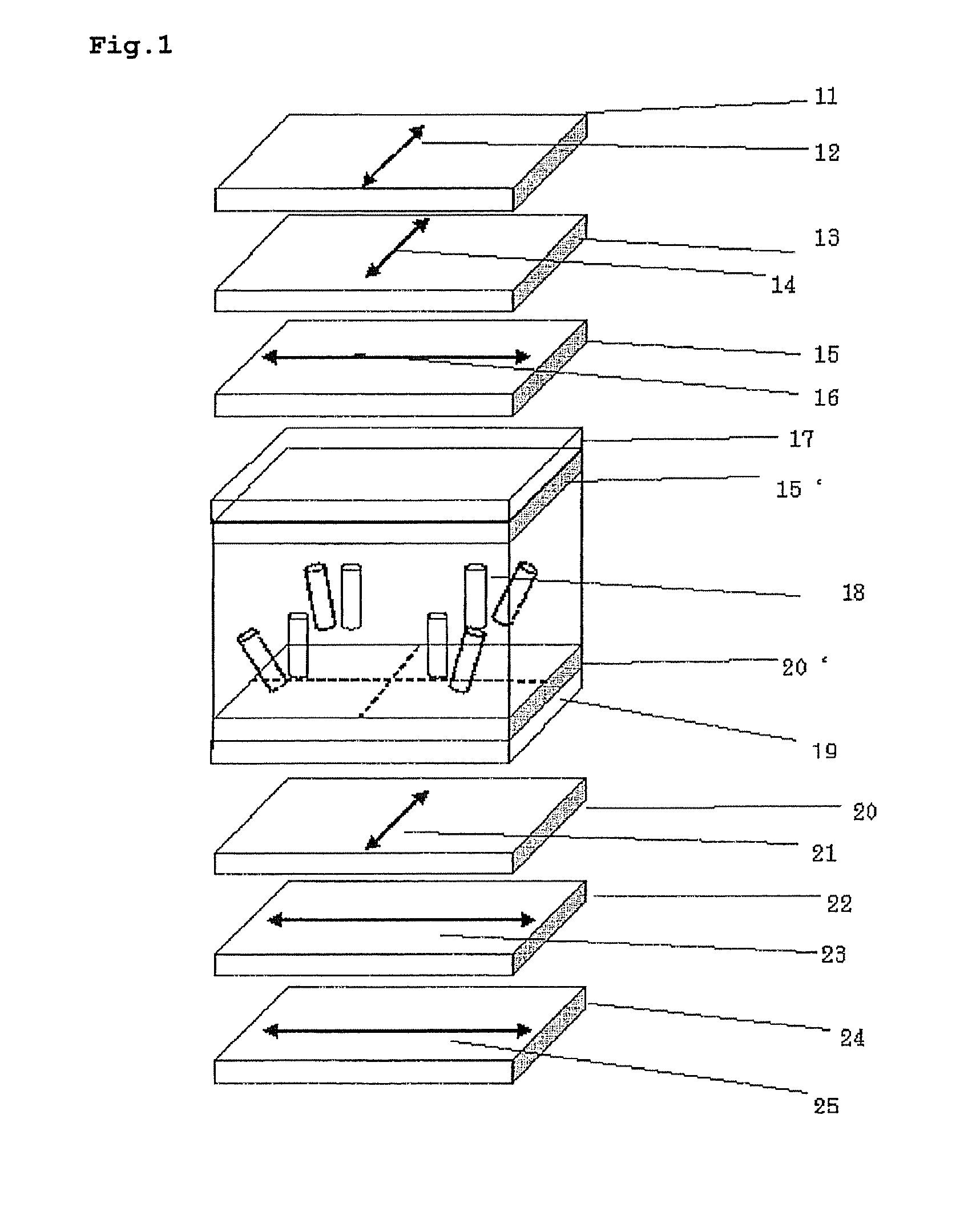
Liquid crystal display device and electronic apparatus
ActiveCN1573426AIncrease display brightnessIncrease contrastPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsPolarizerElliptically polarized light
The invention provides a transflective liquid crystal display device in which display is bright, with high contrast, and with less dependence on the viewing angle in the transmissive display mode. A liquid crystal display device includes a liquid crystal cell, the liquid crystal cell including an upper substrate, a lower substrate, a liquid crystal layer between the upper and lower substrates, and a transflective layer on the inner surface of the lower substrate. The liquid crystal display device further includes a first elliptical polarizer elliptical polarized light from the upper substrate being incident on the liquid crystal layer; and a second elliptical polarizer, elliptical polarized light from the lower substrate being incident on the liquid crystal layer. Only the first elliptical polarizer has a liquid crystal film in which a hybrid alignment is fixed.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Polymer Film, Polarizing Plate Protective Film, Polarizing Plate and Liquid Crystal Display Device
InactiveUS20090066887A1Low viewing angle dependency of hueReduce viewing angle dependencePolarising elementsNon-linear opticsTectorial membraneLiquid-crystal display
A polymer film satisfying the following formulae (1) to (3):20 nm≦Rth(548)<100 nm (1)1.0<Rth(446) / Rth(548)<4.0 (2)0.5<Rth(628) / Rth(548)<1.0 (3)wherein Rth(λ) represents the value of Rth that is measured at a wavelength of λ nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Liquid crystal display panel
ActiveUS20180231844A1High light efficiencyReduce viewing angle dependenceNon-linear opticsOptical elementsIn planeLiquid-crystal display
A liquid crystal display panel (100A) includes a first polarizing plate (22) and a first phase difference plate (32a) disposed on an observer side, and a second polarizing plate (24) and a second phase difference plate (34a) disposed on a back surface side. Δnd of a liquid crystal layer having a homogeneous alignment when no electrical field is applied is 360 nm or greater and 490 nm or less, and an in-plane retardation R1 of the first phase difference plate is 100 nm or greater and 160 nm or less. A thickness direction retardation of at least one of the first and second phase difference plates has a negative value. The slow axes of the first and second phase difference plates are substantially parallel to each other and substantially orthogonal to an azimuthal direction of the liquid crystal director.
Owner:SHARP KK
Liquid crystal cell and liquid crystal display apparatus
InactiveUS20090213302A1High color reproductionReduce changesPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsEngineeringLiquid crystal cell
A novel liquid crystal display apparatus is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a liquid crystal cell comprising a pair of substrates which are provided in mutually opposed manner and which has an electrode in at least either thereof, and a liquid crystal material supported between the pair of substrates; a first polarizing film disposed outside the liquid crystal cell; and at least an in-cell optical compensation film disposed between the pair of substrates, with plural domains per a pixel having a different mean alignment direction each other.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20150331276A1Reduce viewing angle dependenceMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesDielectric anisotropyVertical alignment
Provided is a liquid crystal device including: a liquid crystal panel including a first substrate having a first vertical alignment film, a second substrate having a second vertical alignment film, a liquid crystal layer which is interposed between the first vertical alignment film and the second vertical alignment film and has a negative dielectric anisotropy, a first polarizing plate that is disposed on a light-incident side of the liquid crystal layer, and a second polarizing plate that is disposed on a light-emitting side of the liquid crystal layer; an illuminating device which is disposed on a light-incident side of the liquid crystal panel, and emits light toward the liquid crystal panel; and a light control member which is disposed on a light-emitting side of the liquid crystal panel, and diffuses light that is emitted from the liquid crystal panel in an azimuth angle direction and a polar angle direction viewed from a normal direction of the liquid crystal panel to control an emission direction of the light. The liquid crystal panel includes a plurality of pixels, each being a basic unit of display, and each of the pixels has a plurality of regions in which a director direction or an alignment of liquid crystal molecules at a central portion of the liquid crystal layer in a thickness direction during application of a voltage is different.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com