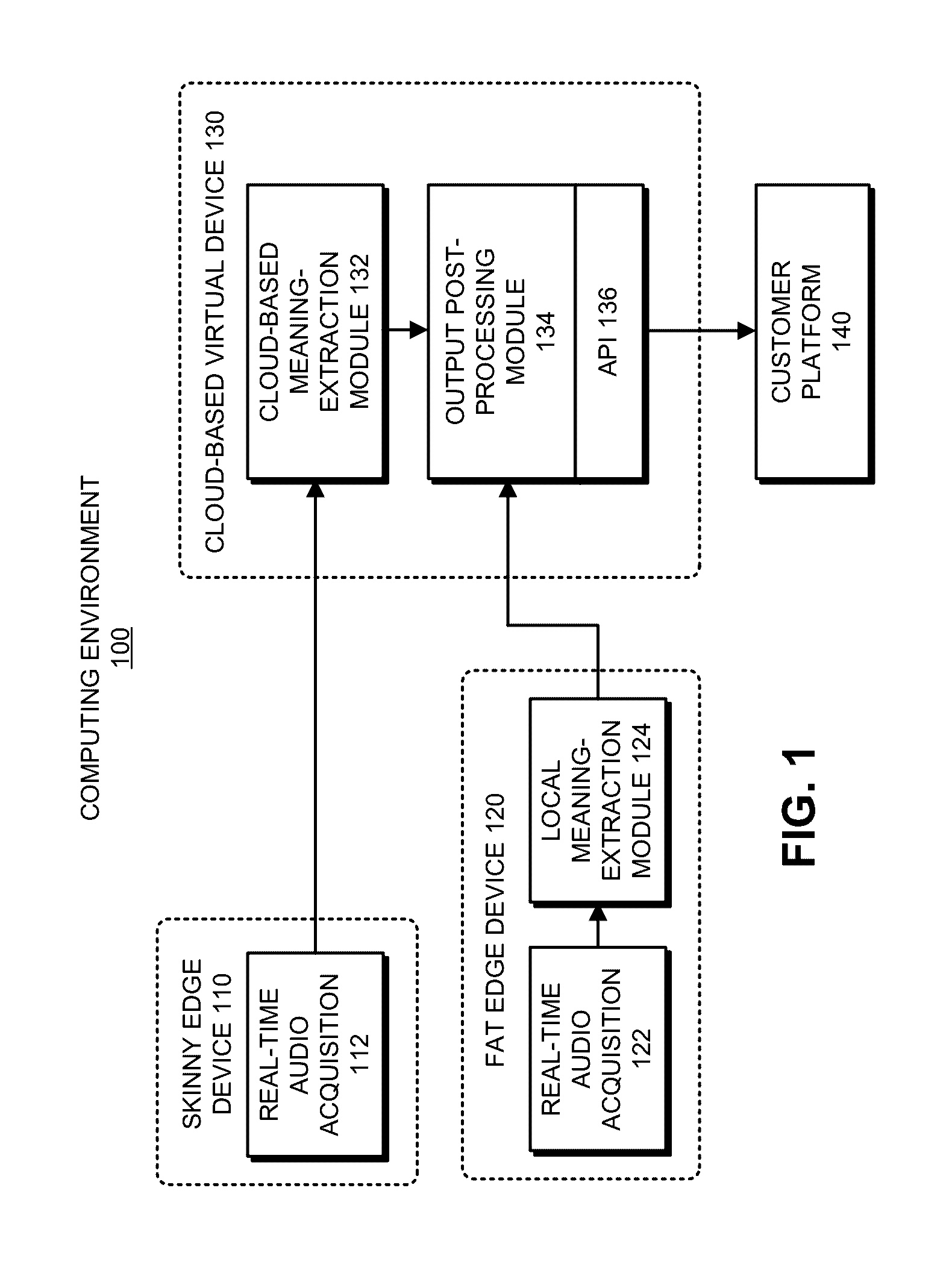
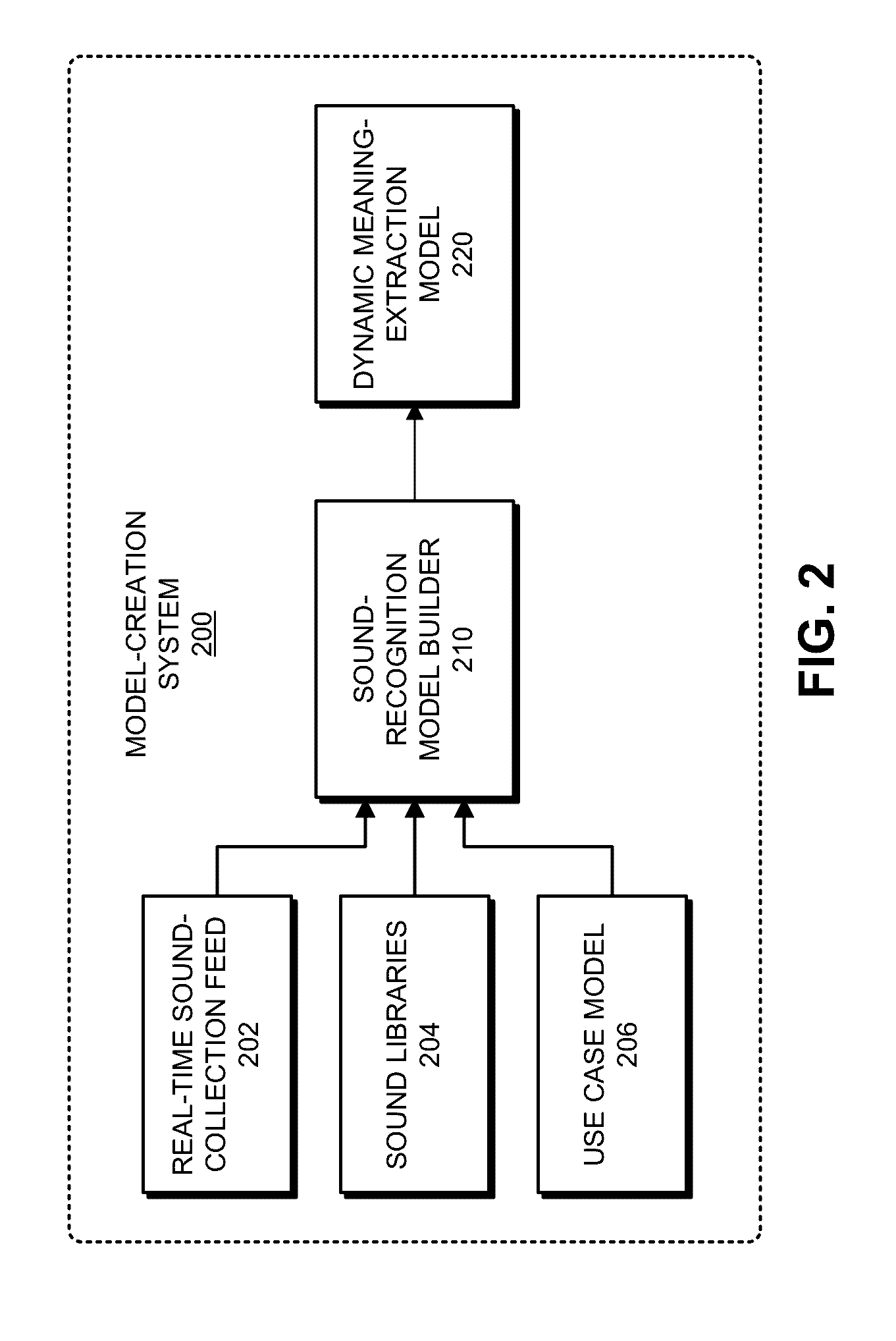
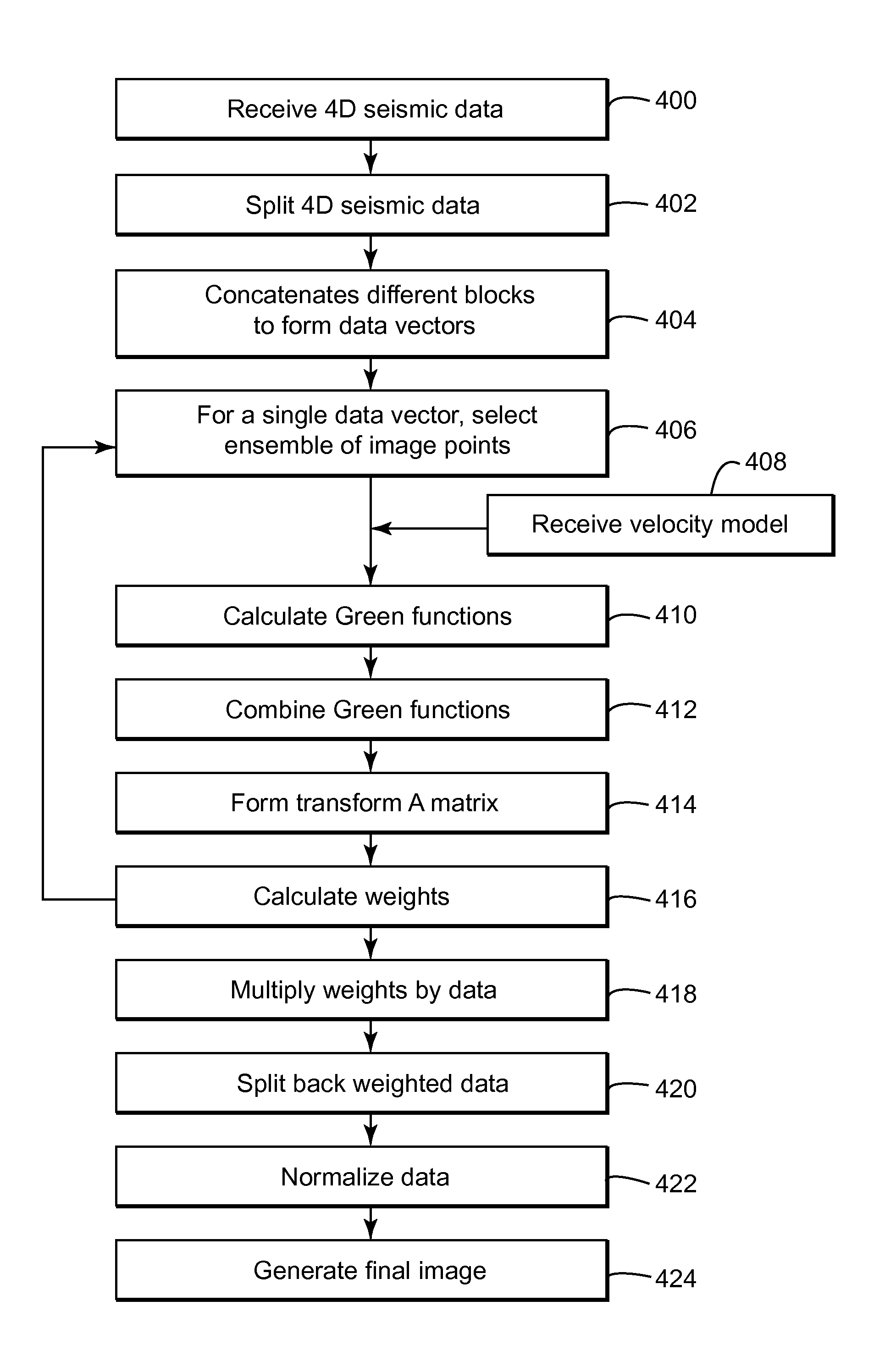
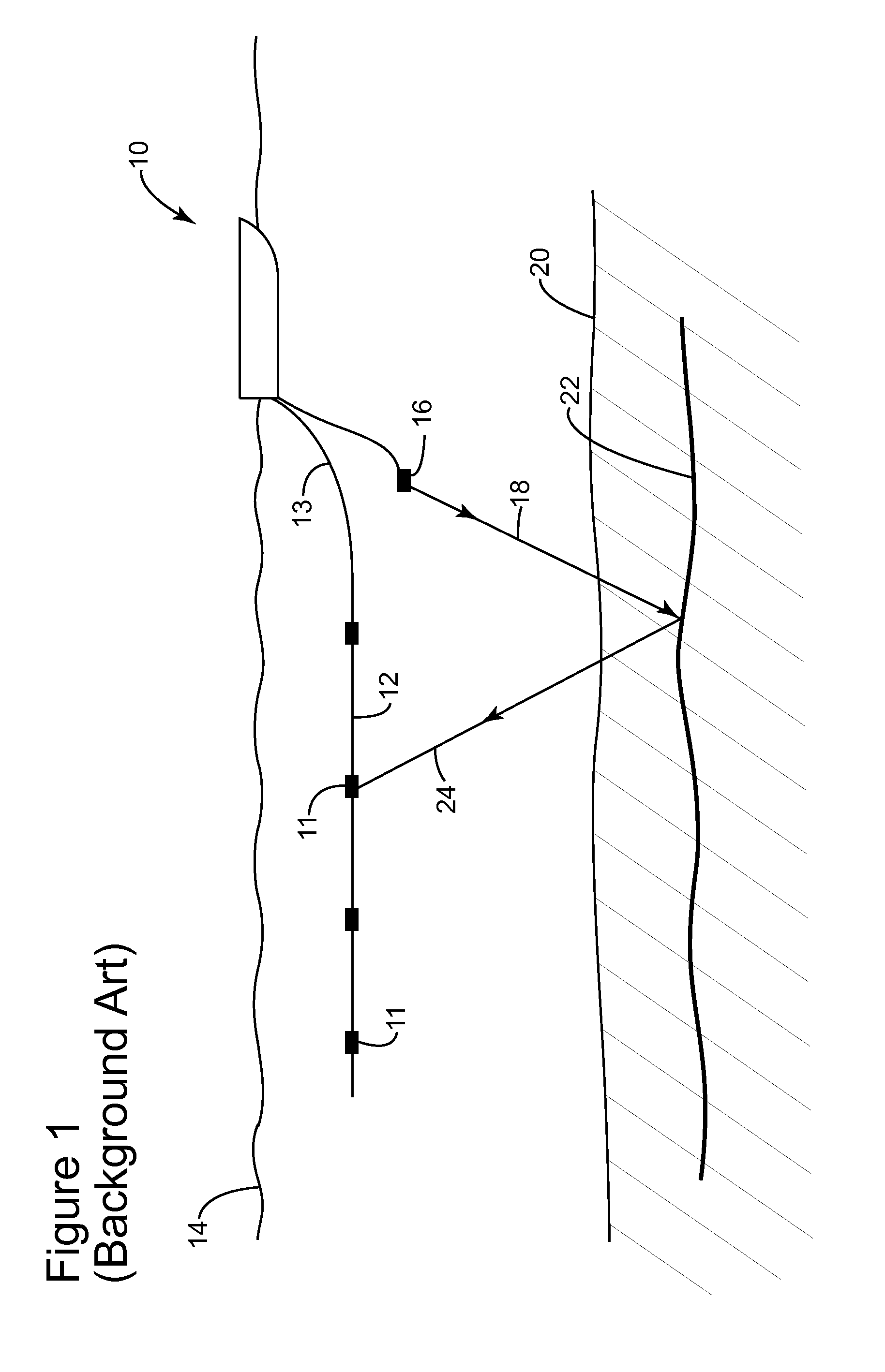
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
52results about How to "Maximizing similarity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and system for providing multimedia content recommendations
InactiveUS20150120722A1Promote assimilationImprove trustDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsApplication softwareClient-side
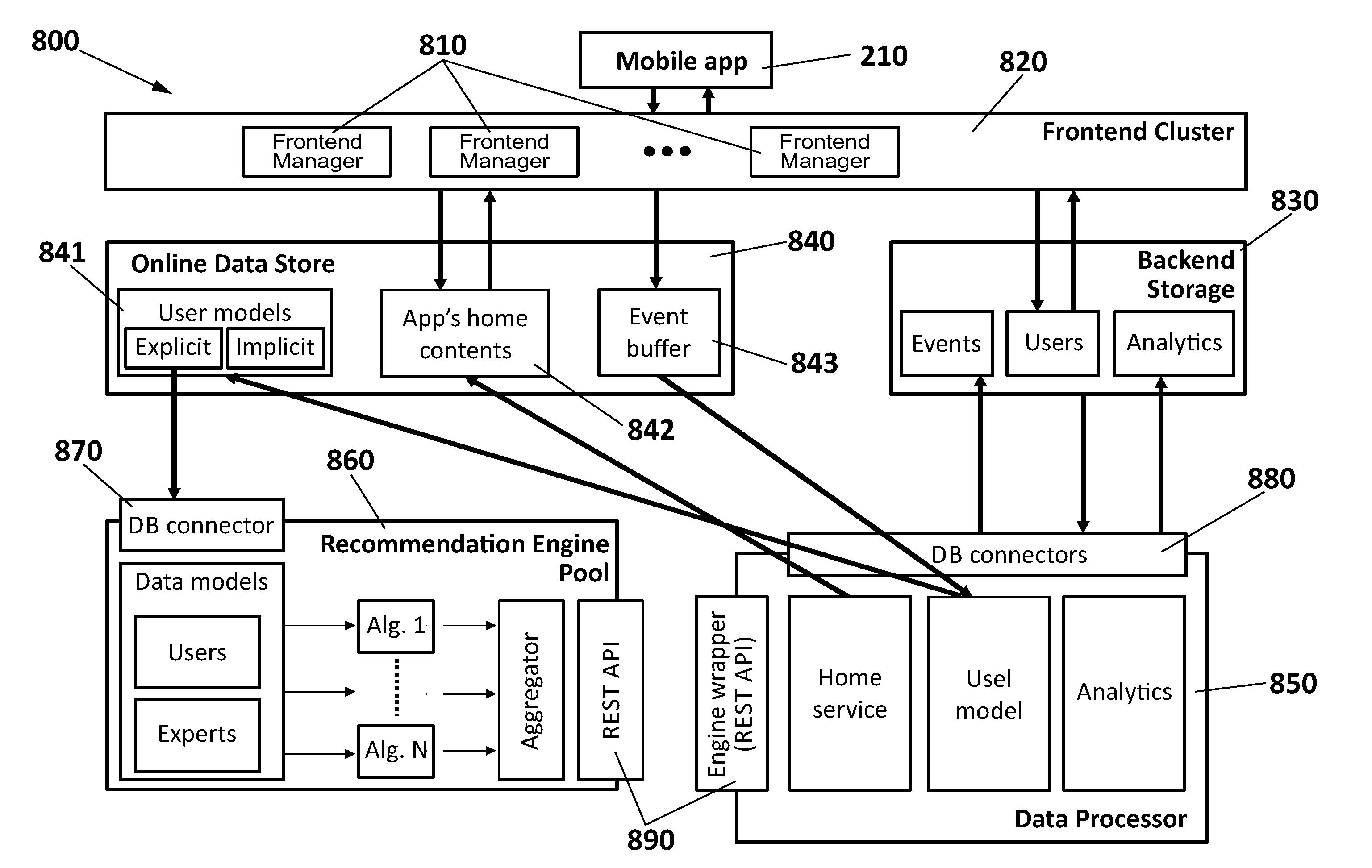
A system for providing content recommendations, including a frontend manager for receiving explicit events from a client application of a user and generating implicit events based upon additional user actions within the client application; a backend storage of data on events and users and an Online Data Store for the explicit events and the implicit events; a Data Processor for creating an explicit user model from the explicit events and an implicit user model from the implicit events; a pool of recommendation engines with one or more recommendation algorithms for receiving the explicit user model and assigning a ranked recommendation list of content items to the user as a result, and further including an aggregator controlled by the Data Processor for aggregating the ranked recommendation lists based on a user-dependent strategy, in order to obtain multiple content recommendation lists of ranked items to be delivered by the frontend server to the client application in a final arrangement, pull from the Online Data Store along with data on the content sources.
Owner:TELEFONICA DIGITAL ESPANA
Apparatus, method, and medium for generating panoramic image
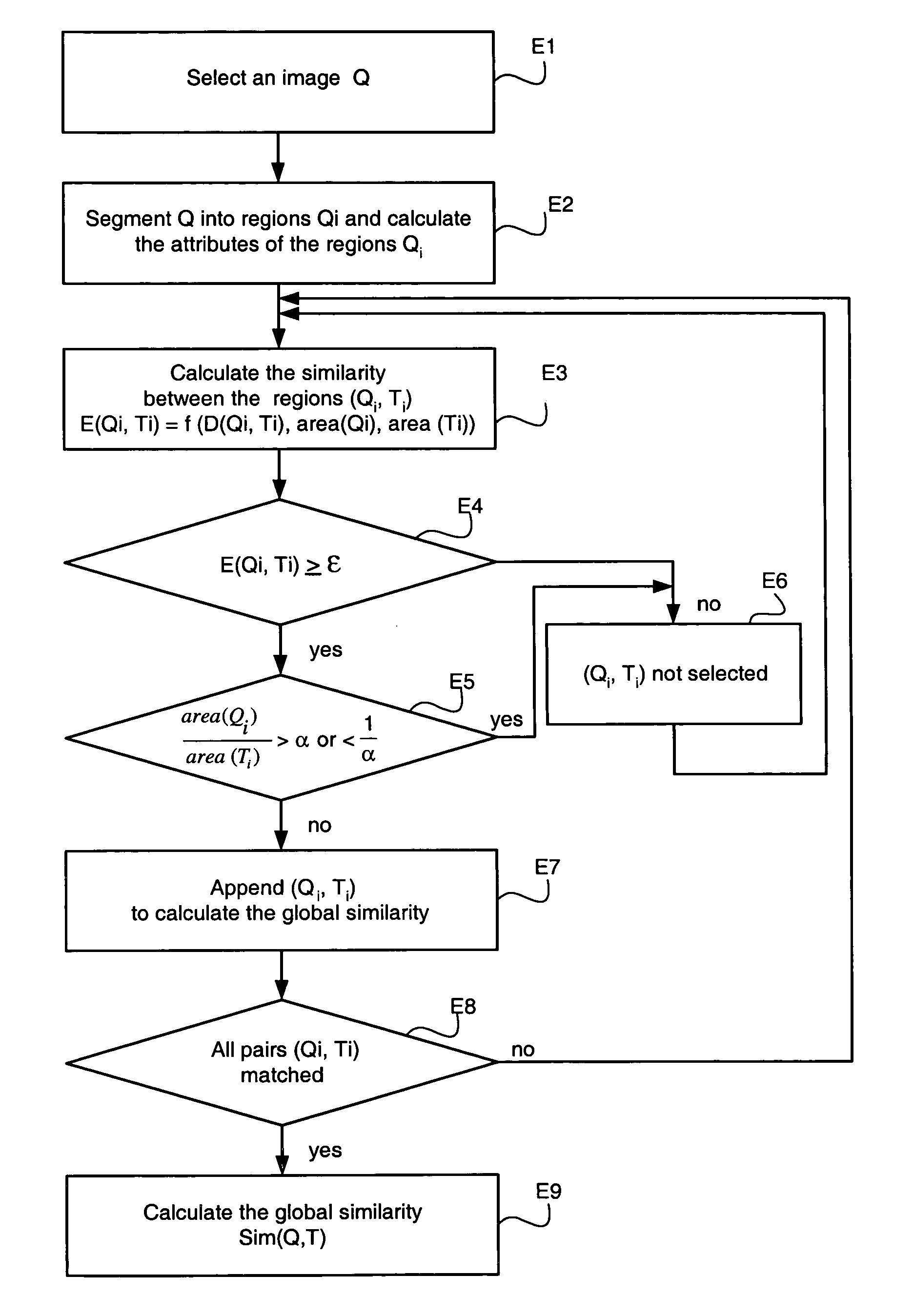
ActiveUS20080074489A1Precise alignmentMaximizing similarityTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationComputer visionPattern recognition
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for 3-d biopsy
ActiveUS20080039723A1Improve efficiencyMaximizing similarityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryCancers locationBiopsy procedure
A system and method (i.e, utility) are disclosed for positioning a needle in three-dimensions based on patient related statistics for extracting tissue during biopsy procedures. Aspects of the utility can be applied independently or serve as an aid to the urologist when regions of interest are hard to discern in an ultrasound image. Regions of interest that correspond to high cancer risk regions (e.g., statistically) are automatically superimposed on an ultrasound image of a patient in real time. Additionally a statistical map based on one or more demographic parameters of a patient and containing cancer probability locations are also automatically mapped on the ultrasound image in real time displaying potential cancer locations. Aspects of the system are also capable of displaying optimal needle placement positions based on statistical priors and will be able to accurately navigate the needle to that position for biopsy extraction and / or treatment.
Owner:EIGEN HEALTH SERVICES LLC
Method and device for measuring visual similarity
InactiveUS20050002568A1Reduce complexityMinimize calculationDigital data information retrievalImage analysisPattern recognitionImage segmentation
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
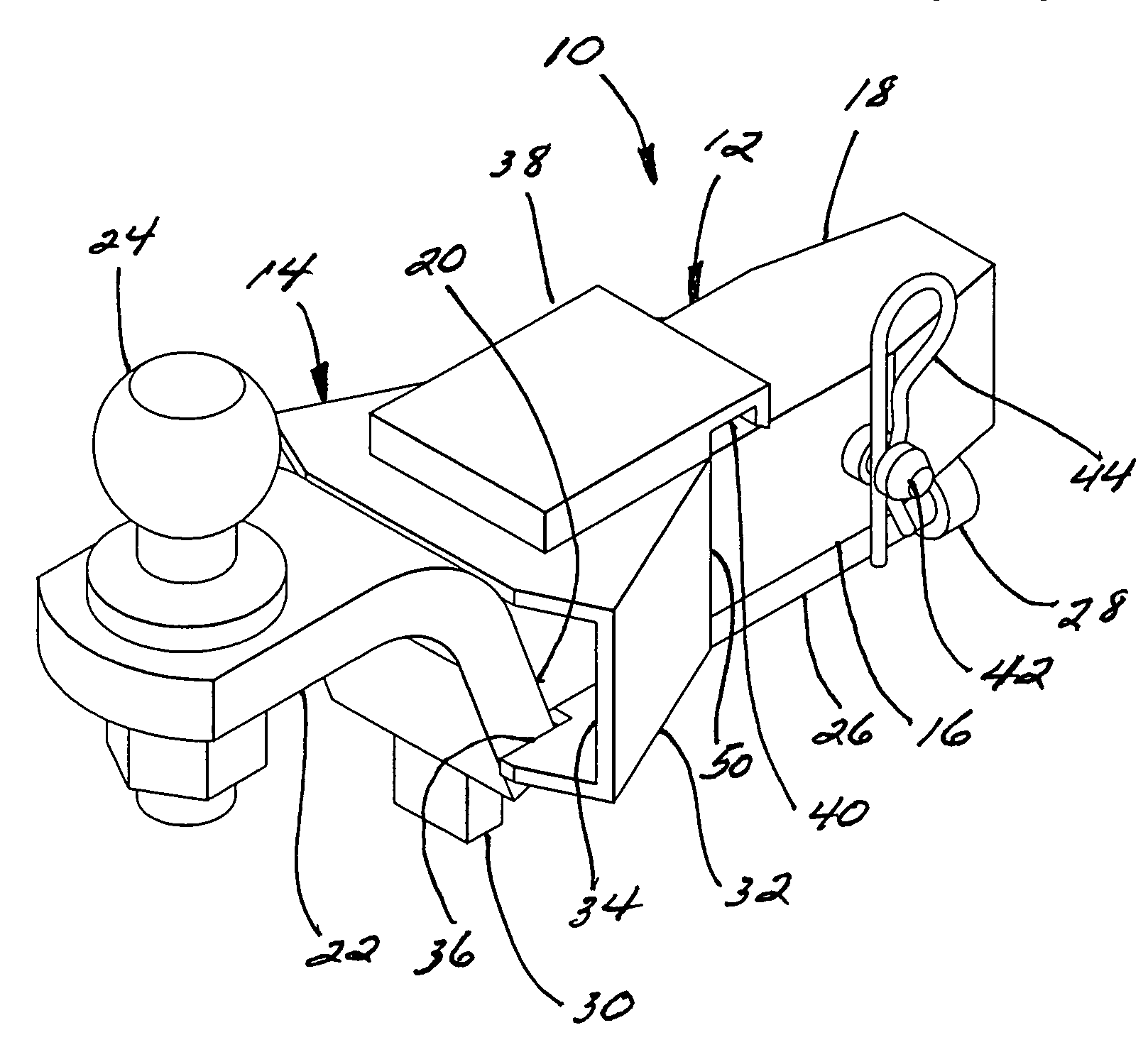
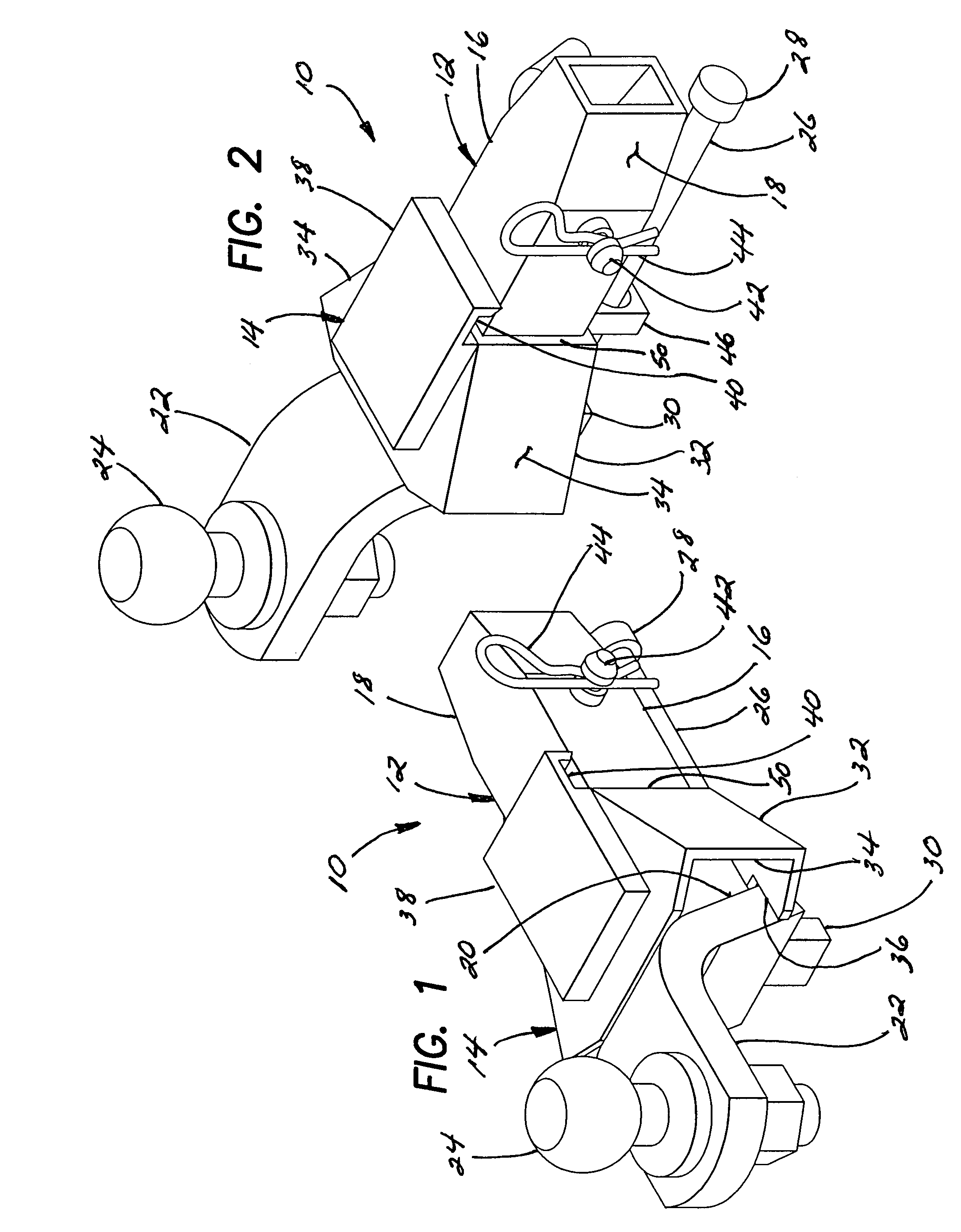
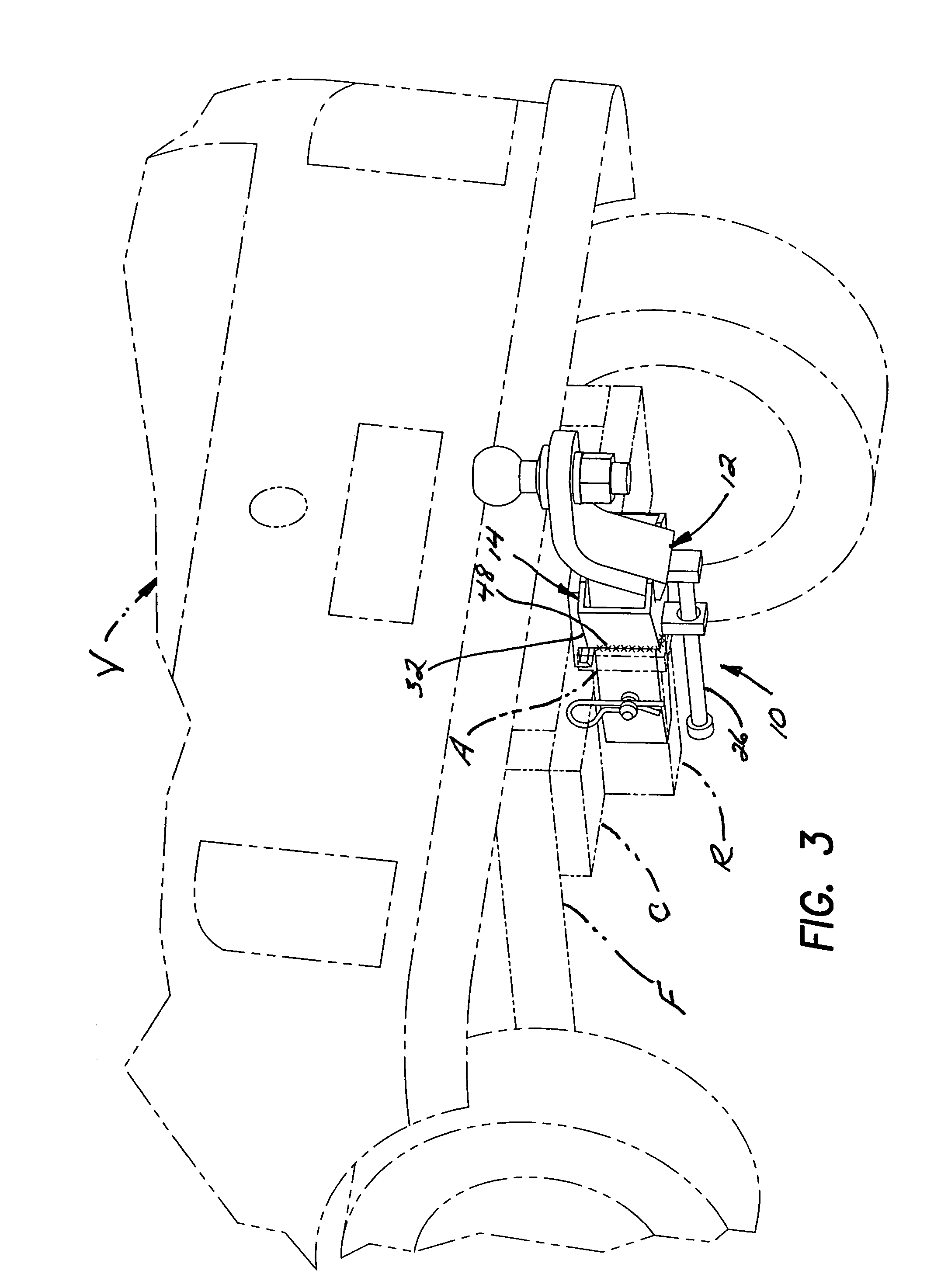
Trailer hitch
A trailer hitch facilitating proper alignment and connection to the hitch coupler of a trailer. The trailer hitch includes a tow bar assembly and a throat having spaced parallel top and floor panels generally equal in spacing to a vertical thickness of the tow bar and rearwardly diverging side panels. The front of the throat is connected or connectable to an elongated tubular extension or receiver and is sized to be slidably carried within the throat assembly. A slide bar is carried between the tow bar and the throat and includes a stop which limits the distance the tow bar may be extended rearwardly from the throat and, when in the fully or a partially extended position, is movable side-to-side to facilitate proper coupling alignment between the hitch ball and a hitch coupling of a trailer.
Owner:PALMER VAN BRADFORD
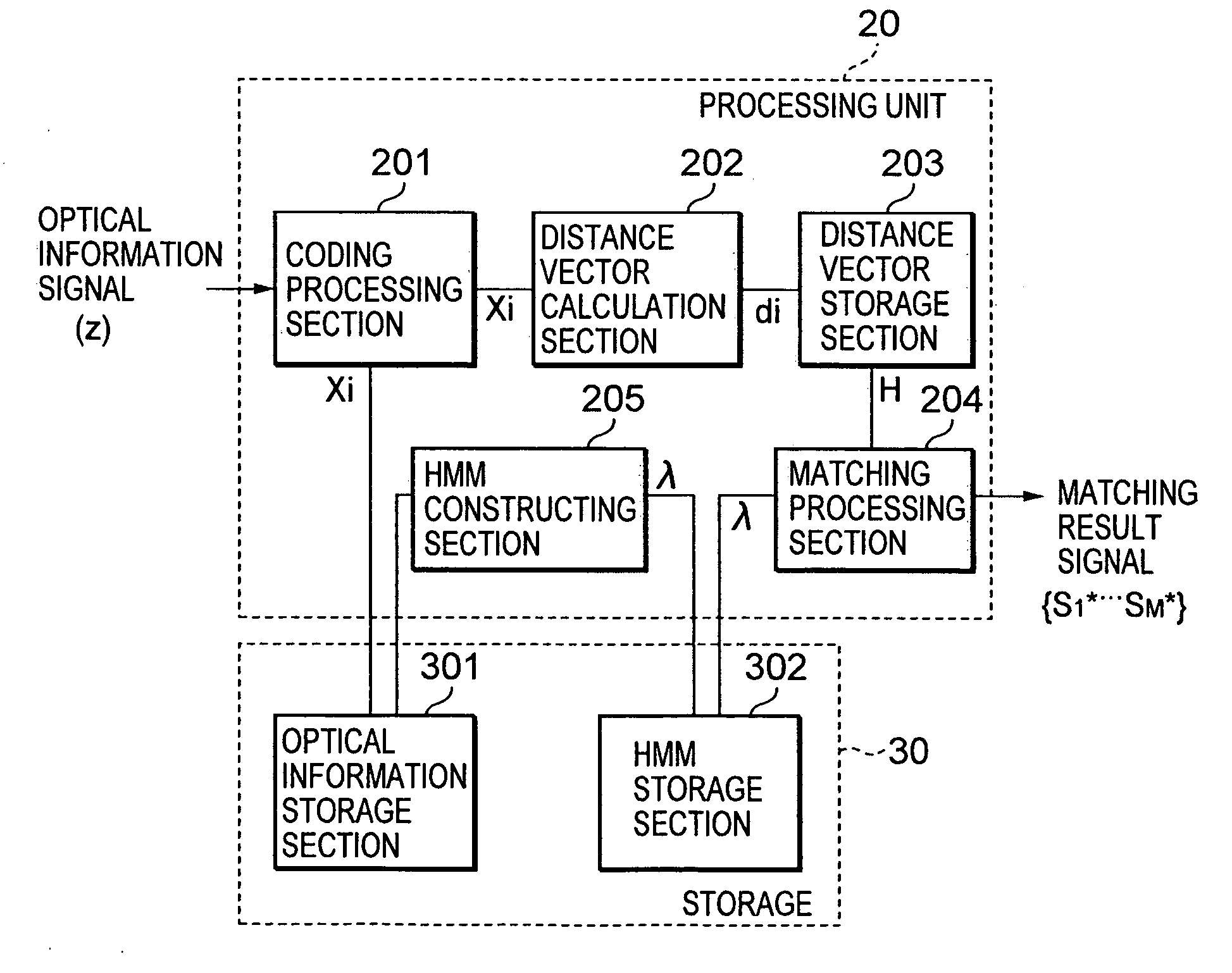
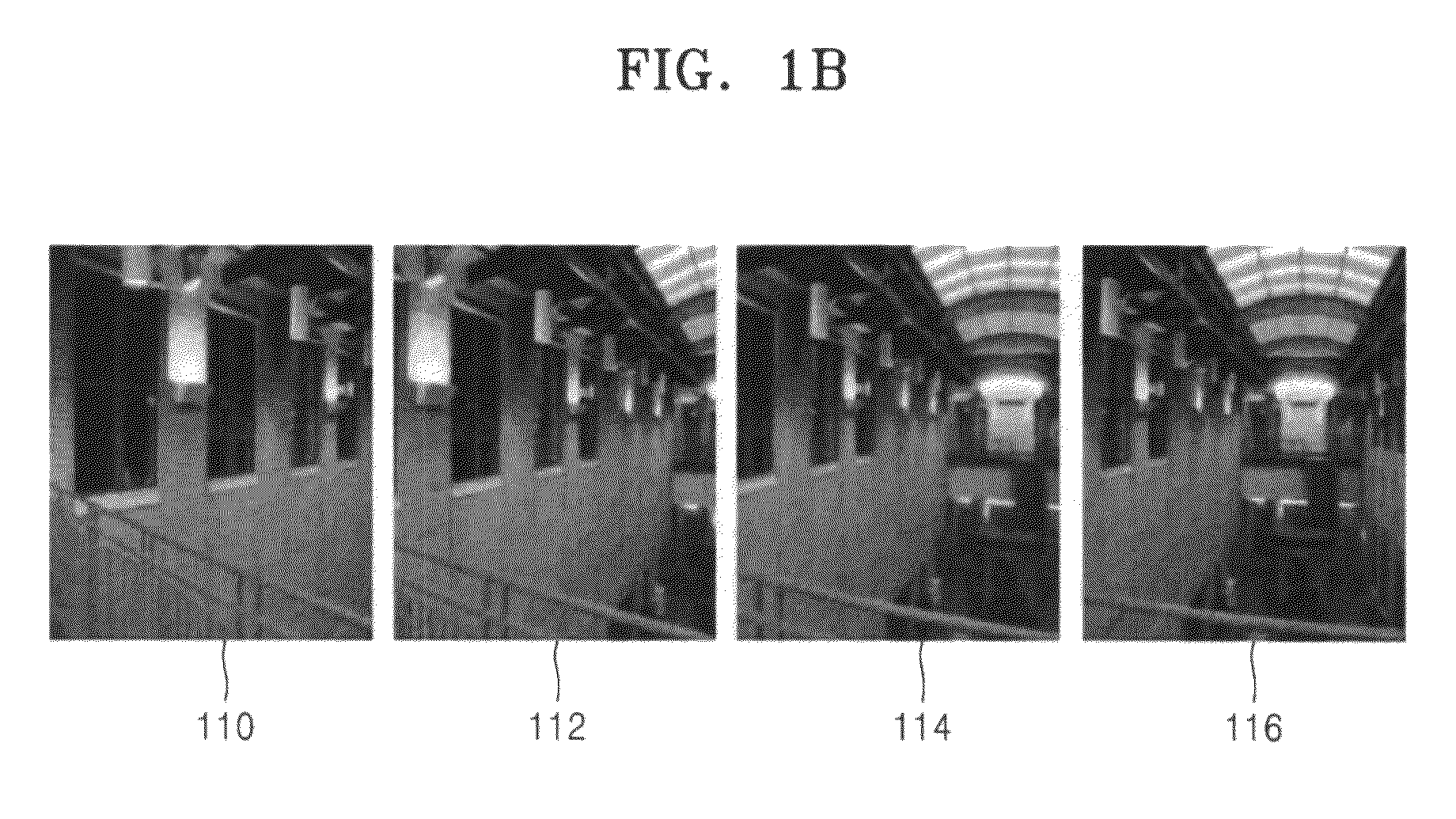
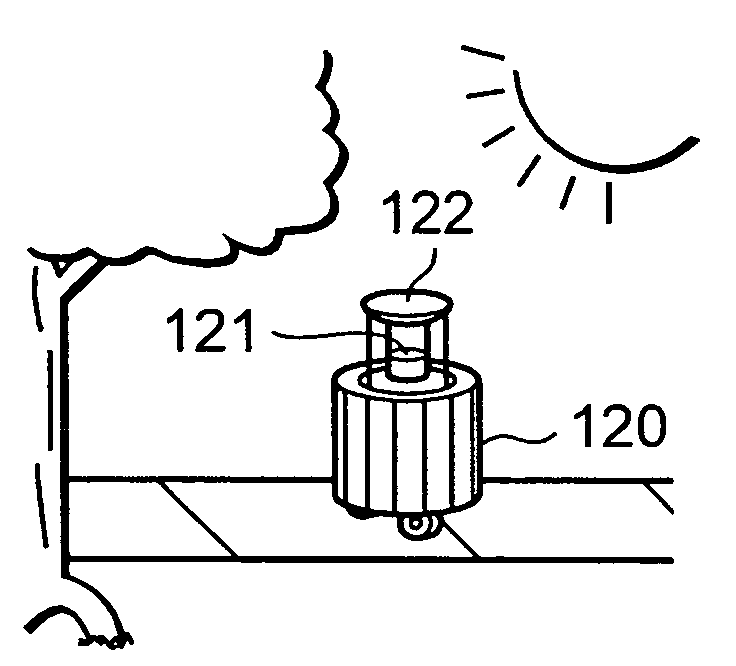
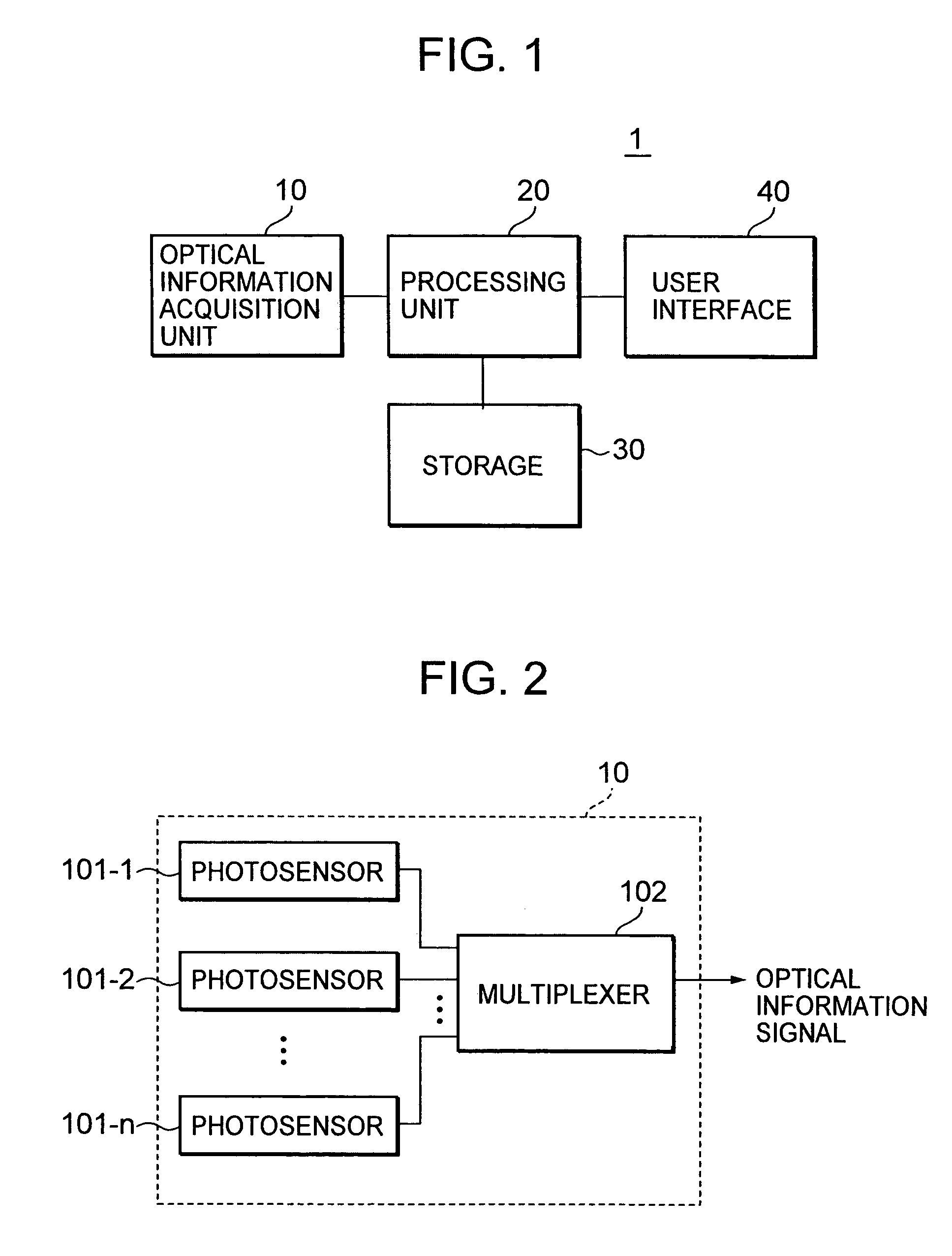
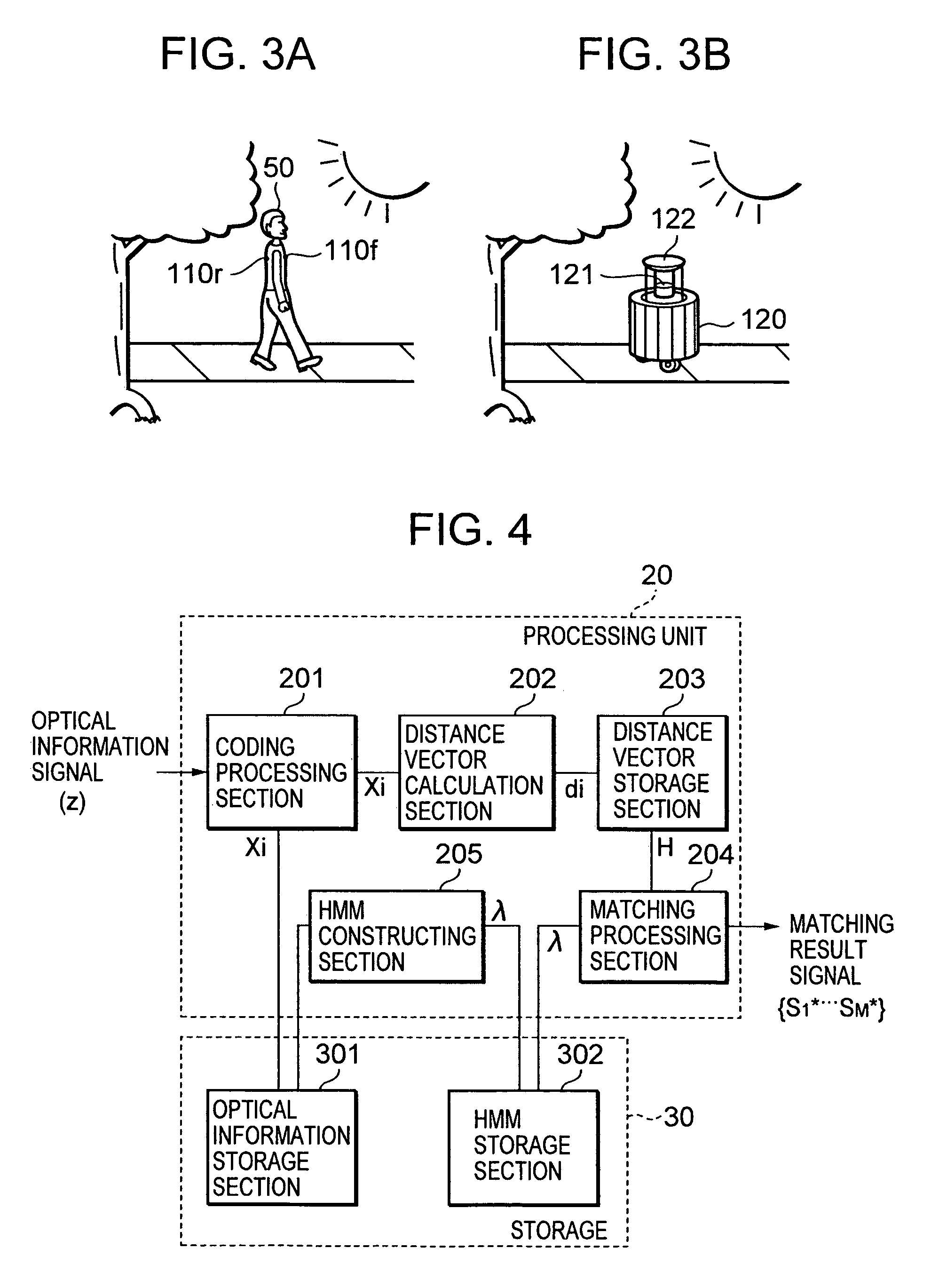
Method and apparatus for situation recognition using optical information
InactiveUS20060088187A1Maximizing similarityMaximize effectivenessImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionProbit modelOperating system
A situation recognition apparatus includes: an optical information acquisition unit configured to acquire optical information; a storage configured to store a plurality of pieces of optical information; a processing unit configured to match a plurality of the pieces of optical information stored in the storage and optical information newly acquired by the optical information acquisition unit; and an output unit configured to output a result of the matching. The storage further stores a probabilistic model that numerically represents transitions between the plurality of pieces of optical information.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
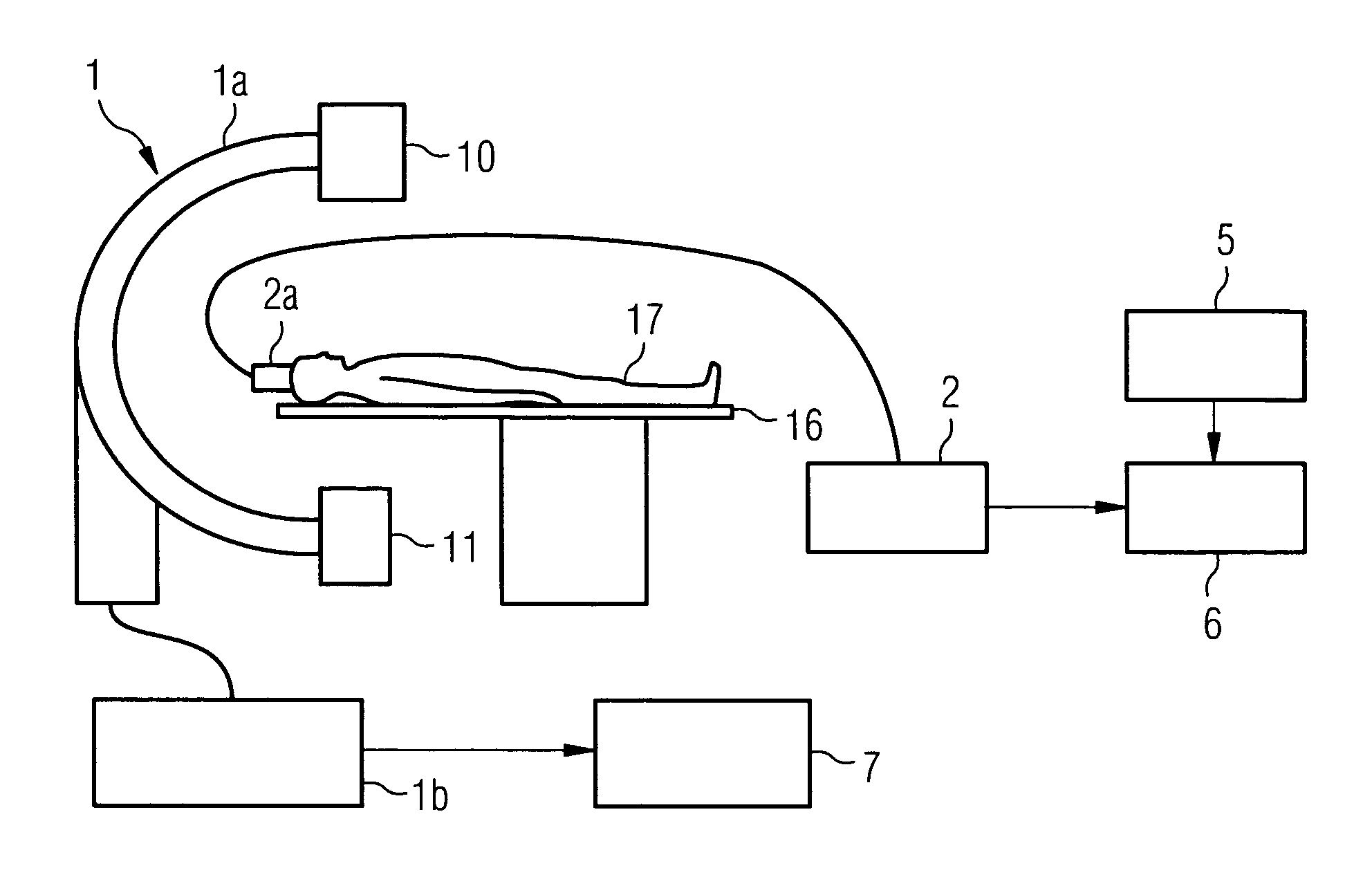
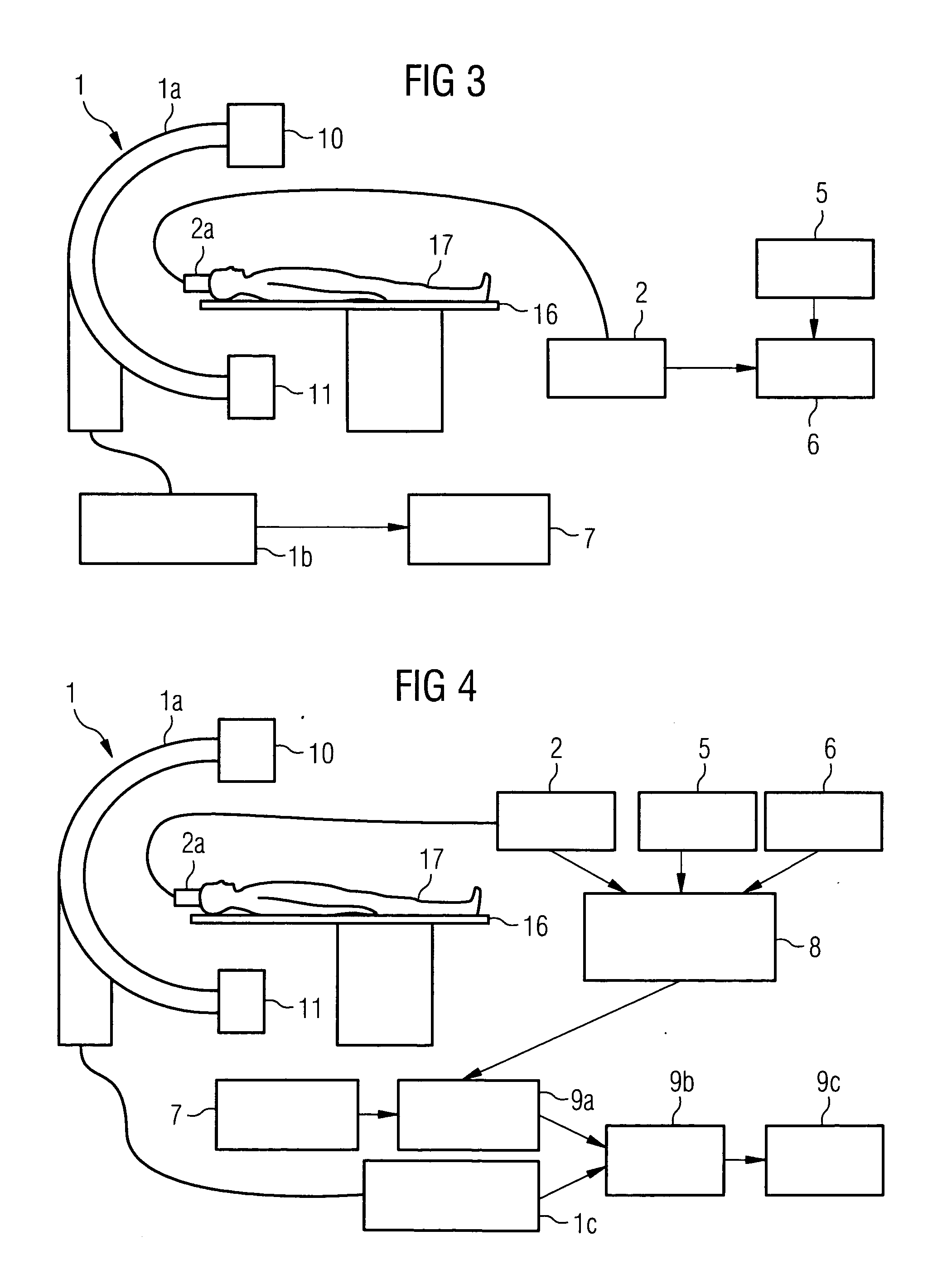
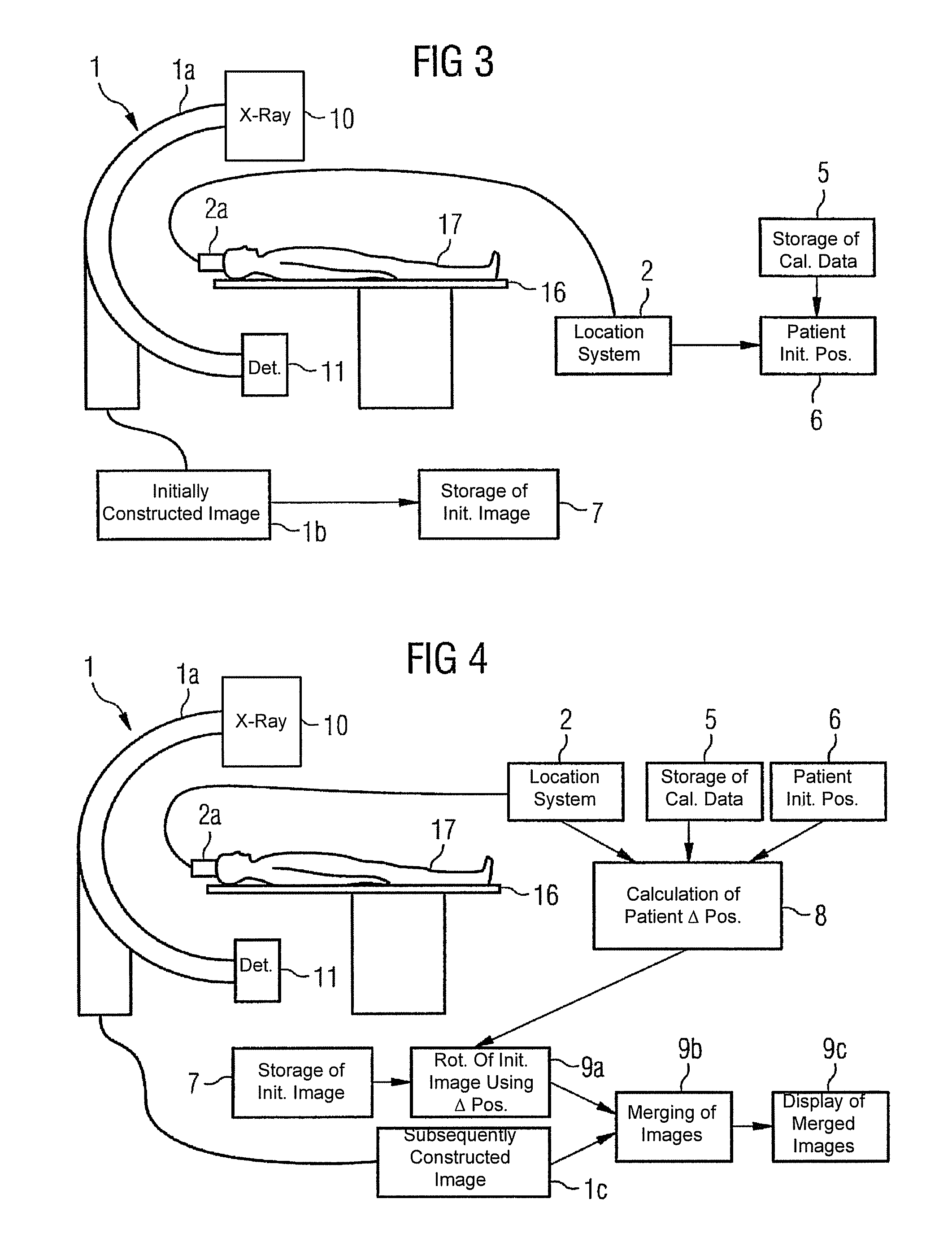
Method for registering and merging medical image data
ActiveUS20050245807A1Accurate guideMaximizing similarityImage enhancementImage analysisData setSuperimposition
The present invention relates to a method for the registration and superimposition of image data when taking serial radiographs in medical imaging, wherein a plurality of image data sets for a region of a patient (17) that is being investigated are constructed at time intervals using an imaging system (1) and are referenced with a first image data set for the region that is being investigated that was constructed previously using said imaging system (1). In the above method, a location system (2) is used during the production of serial radiographs constantly, or at least at a respective proximity in time to the construction of individual data sets, to determine a current spatial position of the region being investigated in a reference system that is firmly connected to the imaging system (1), whereby in the construction of the first image data set, a first spatial position of the region that is being investigated is recorded. In the construction of some or all further image data sets, the respective current spatial position of the region that is being investigated is determined and an image content of each first image data set is geometrically adapted on the basis of the difference between the first and the current spatial position, such that compensation is made for a different spatial position of the region that is being investigated. The geometrically adapted first image data set or an image data set derived therefrom, or an image data set that is positionally connected thereto by registration is then displayed superimposed with the respective further image data set.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Detection Of Protected Subject Matter In Three Dimensional Print Media
ActiveUS20130235037A1Maximizing similarityComputer security arrangements3D modellingVirtualizationPrint media
A contemplated system analyzes files used to create 3D objects by first virtually constructing the 3D object, and then by examining the virtual construct in a variety of different ways to determine if the 3D object has protected content. The system could examine the virtualized object from a variety of different angles, read characters embossed or imprinted upon the 3D object, and could even play virtualized records and other virtualized video / audio tools to determine if the 3D object has protected content. If the system rules that the 3D object has a high probability of having protected content, an alert is sent to an appropriate authority.
Owner:BUILD NETWORKS LLC
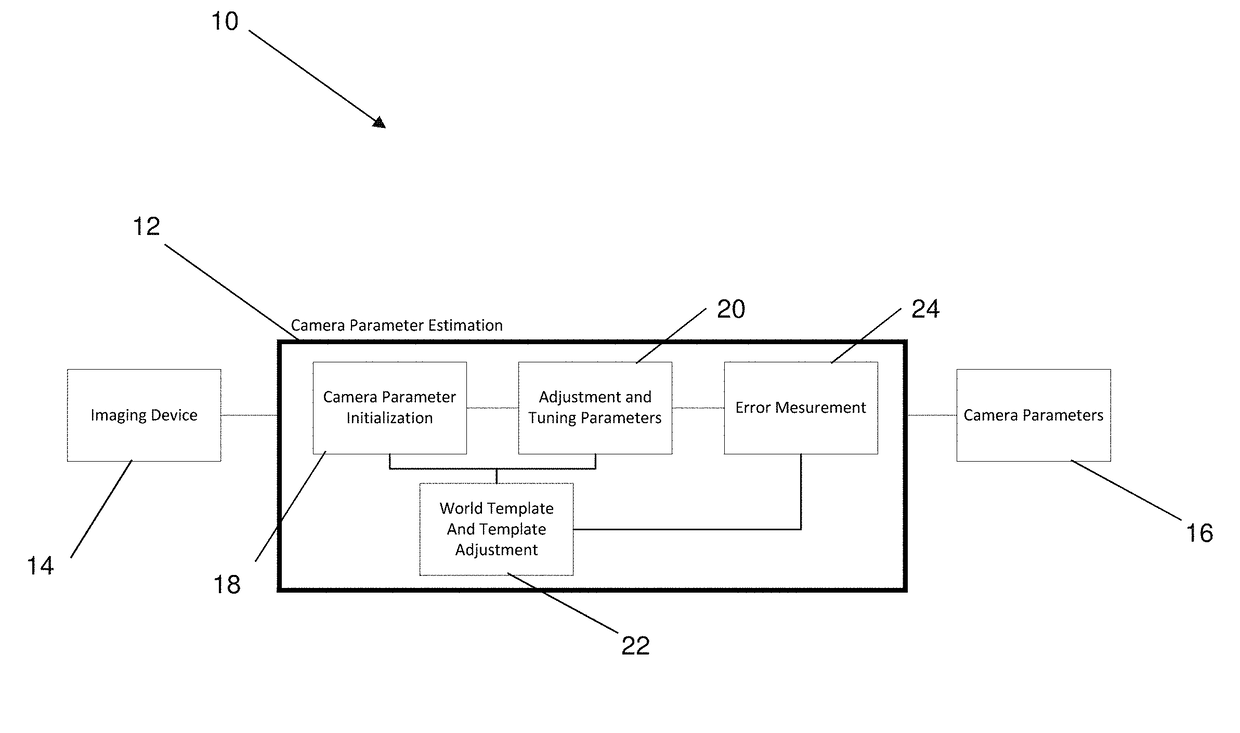
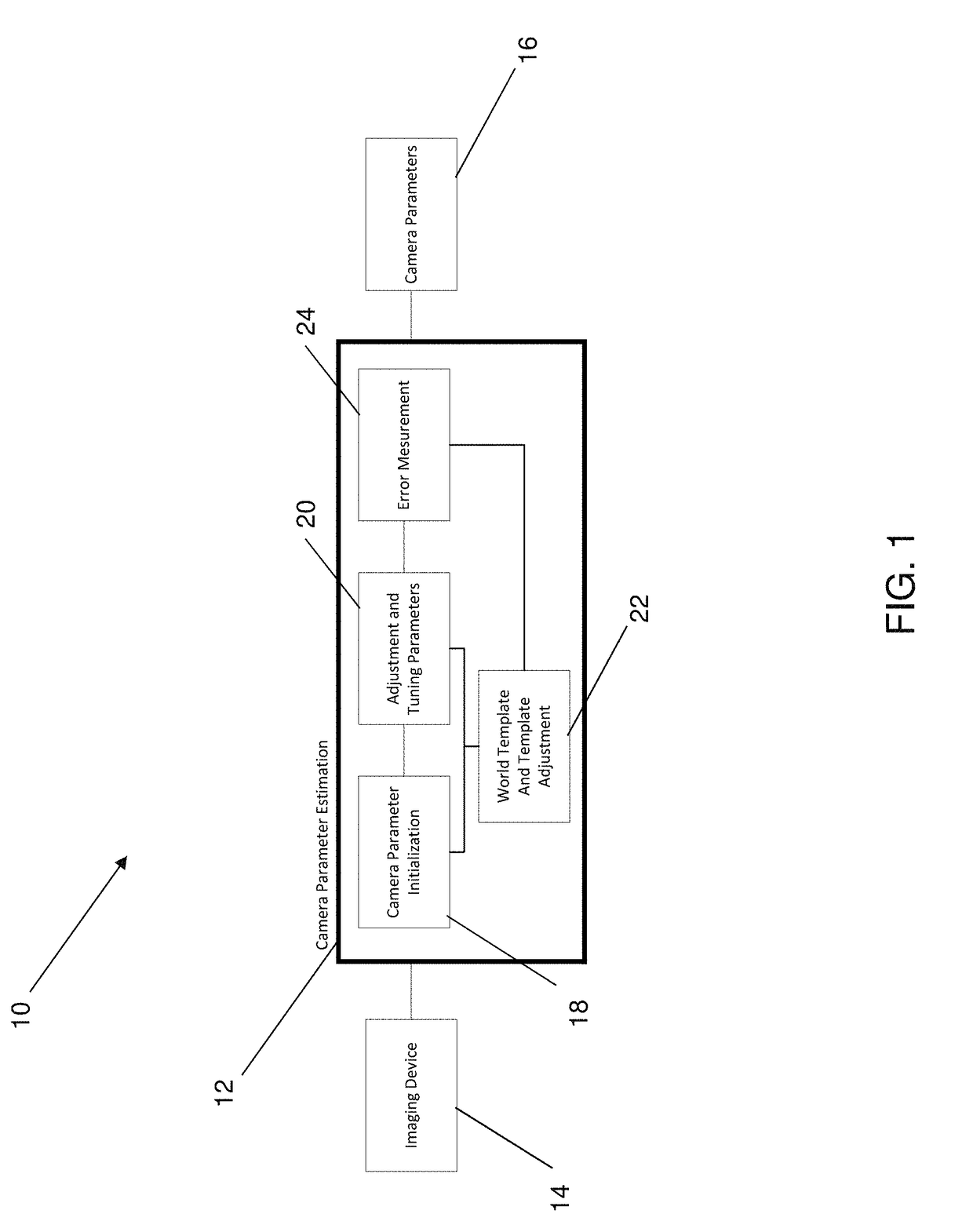
Systems and Methods for Automated Camera Calibration
ActiveUS20180336704A1Maximizing similarityMinimize the differenceImage enhancementImage analysis3d shapesImage frame
A system and method are provided for calibrating and re-calibrating an imaging device. The image device comprises at least one varying intrinsic or extrinsic parameter value based on a view of 3D shapes and a 2D template therefor. The method and system are operable to receive a sequence of images from the imaging device, wherein a planar surface with known geometry is observable from the sequence of images; perform an initial estimation of a set of camera parameters for a given image frame; perform a parameter adjustment operation to minimize a dissimilarity between the template and the sequence of images; perform a parameter adjustment operation to maximize similarities in either the camera's coordinate system or the template's coordinate system; and update an adaptive world template to incorporate an additional stable point from the observed images to the template.
Owner:SPORTLOGIQ
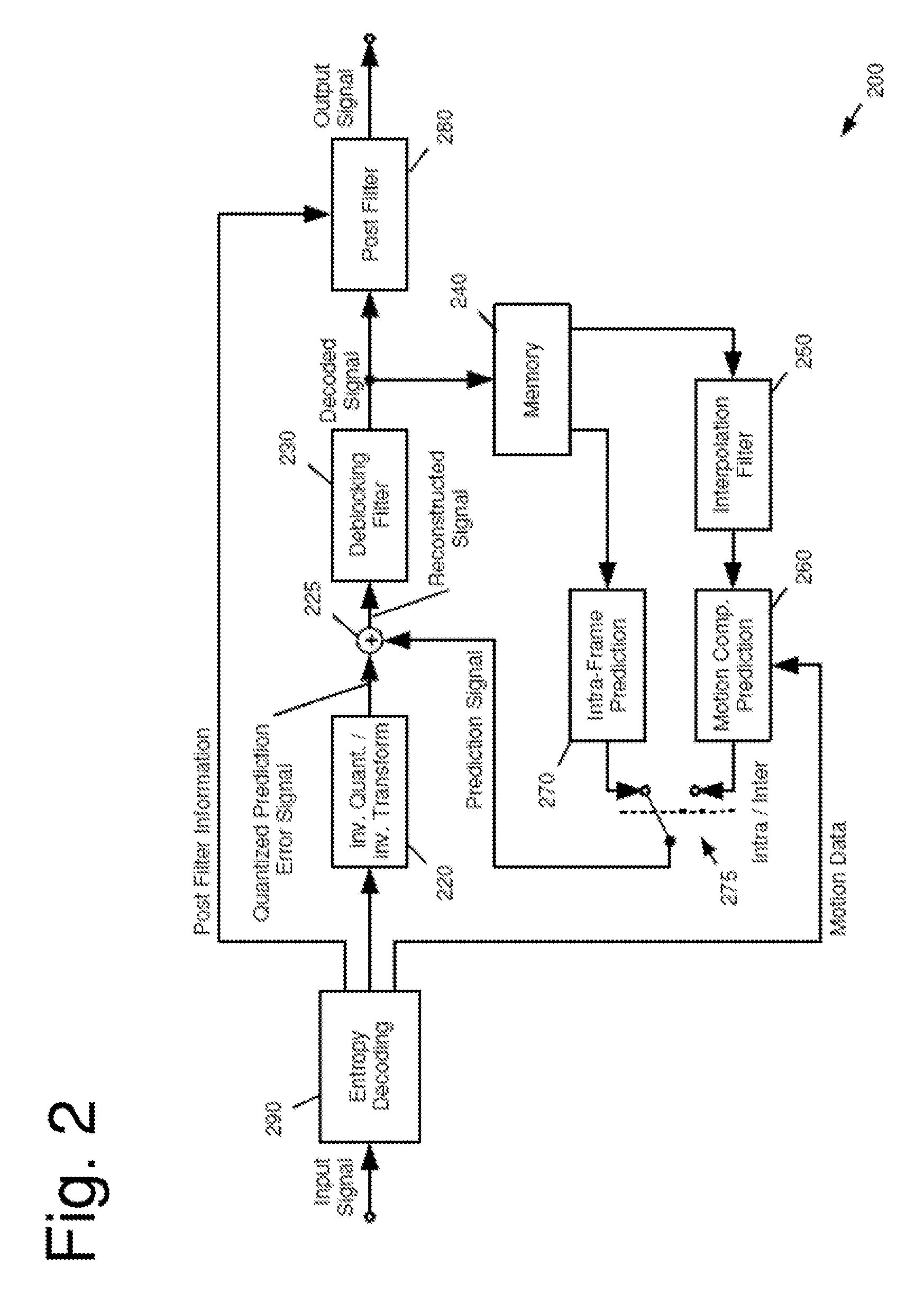
Filter positioning and selection
ActiveUS20130028327A1Maximizing similarityMinimize the differenceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionComputer science
The present invention relates to a method for encoding and decoding an image signal and to corresponding apparatuses therefor. In particular, during the encoding and / or decoding of an image signal filtering with at least two filters is performed. The sequence of the filter application and possibly the filters are selected and the filtering is applied in the selected filtering order and with the selected filters. The determination of the sequence of applying the filters may be performed either separately in the same way at the encoder and at the decoder, or, it may be determined at the encoder and signaled to the decoder.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
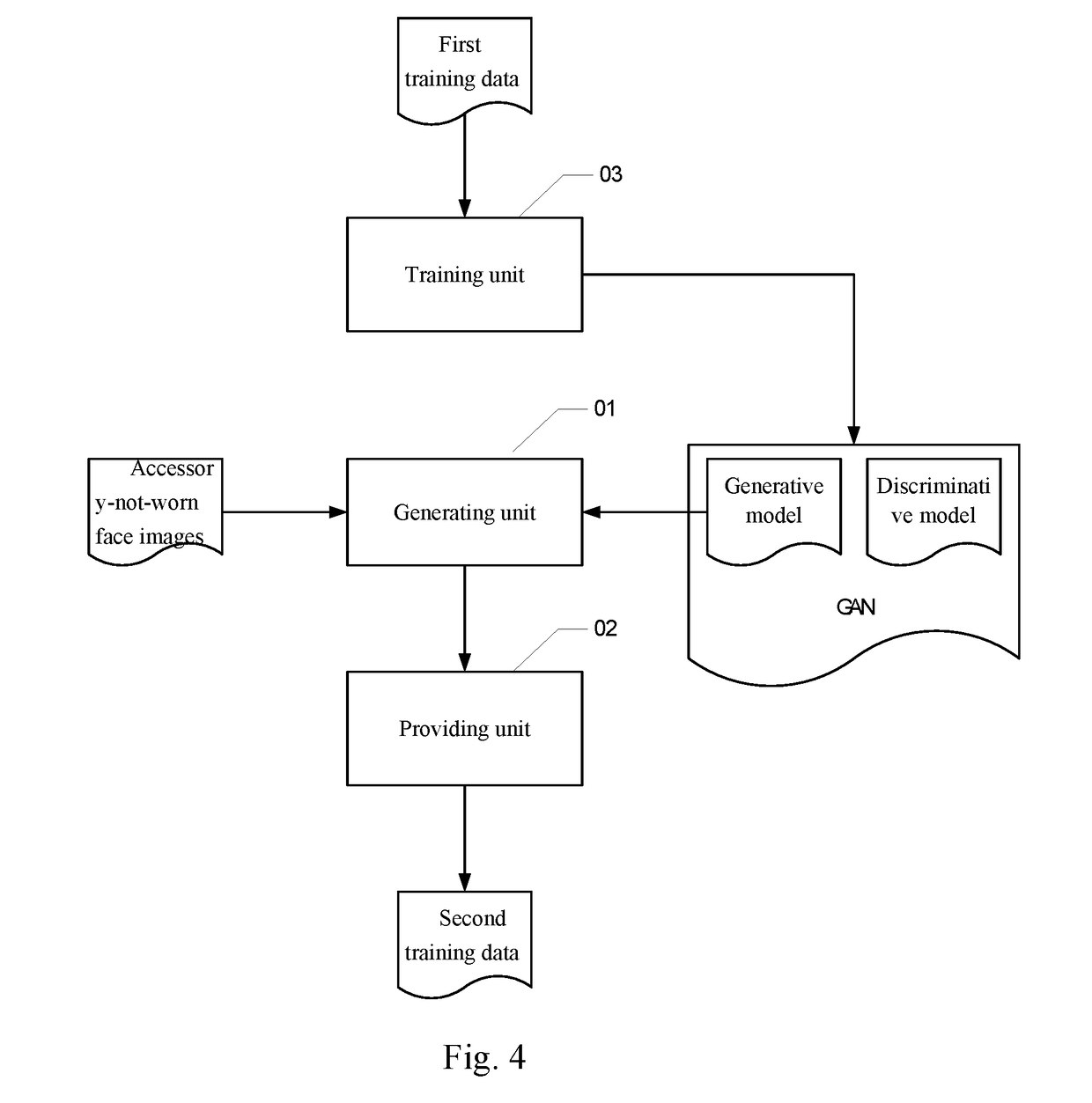
Method and apparatus for generating training data for human face recognition, device and computer storage medium
ActiveUS20190050632A1Increase volumeImprove recognition accuracyMathematical modelsKernel methodsPattern recognitionGenerative adversarial network
The present disclosure provides a method and apparatus for generating training data for human face recognition, a device and a computer storage medium, wherein the method comprises: inputting accessory-not-worn face images into a generative network, to obtain accessory-worn face images; using the accessory-worn face images as second training data for building the human face recognition model; wherein the generative network is a generative network in a generative adversarial network obtained by pre-training with first training data, the first training data including the accessory-not-worn face images and accessory-worn face images corresponding to a same user identifier. In the present disclosure, the accessory-worn face images obtained in a data augmentation manner greatly expand the amount of training data for building the human face recognition model, and thereby improve the recognition accuracy of the accessory-worn face images.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
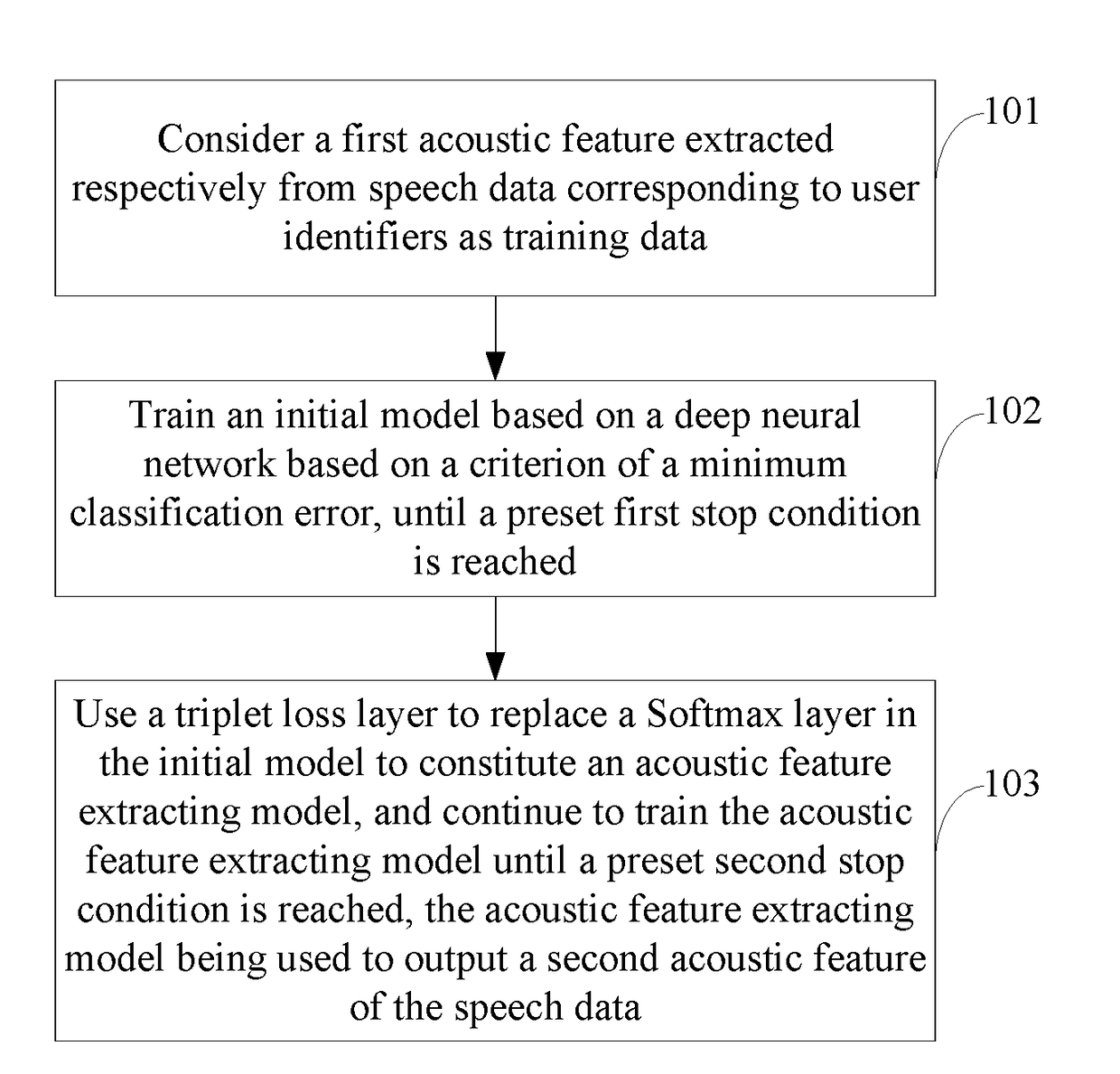
Method and Apparatus of Training Acoustic Feature Extracting Model, Device and Computer Storage Medium
ActiveUS20180336888A1Improve accuracyImprove performanceSpeech recognitionNeural architecturesFeature extractionUser identifier
A method and apparatus of training an acoustic feature extracting model, a device and a computer storage medium. The method comprises: considering a first acoustic feature extracted respectively from speech data corresponding to user identifiers as training data; training an initial model based on a deep neural network based on a criterion of a minimum classification error, until a preset first stop condition is reached; using a triplet loss layer to replace a Softmax layer in the initial model to constitute an acoustic feature extracting model, and continuing to train the acoustic feature extracting model until a preset second stop condition is reached, the acoustic feature extracting model being used to output a second acoustic feature of the speech data; wherein the triplet loss layer is used to maximize similarity between the second acoustic features of the same user, and minimize similarity between the second acoustic features of different users.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Methods and systems for registration of radiological images
ActiveUS20130322723A1Maximizing similarityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImage resolution
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
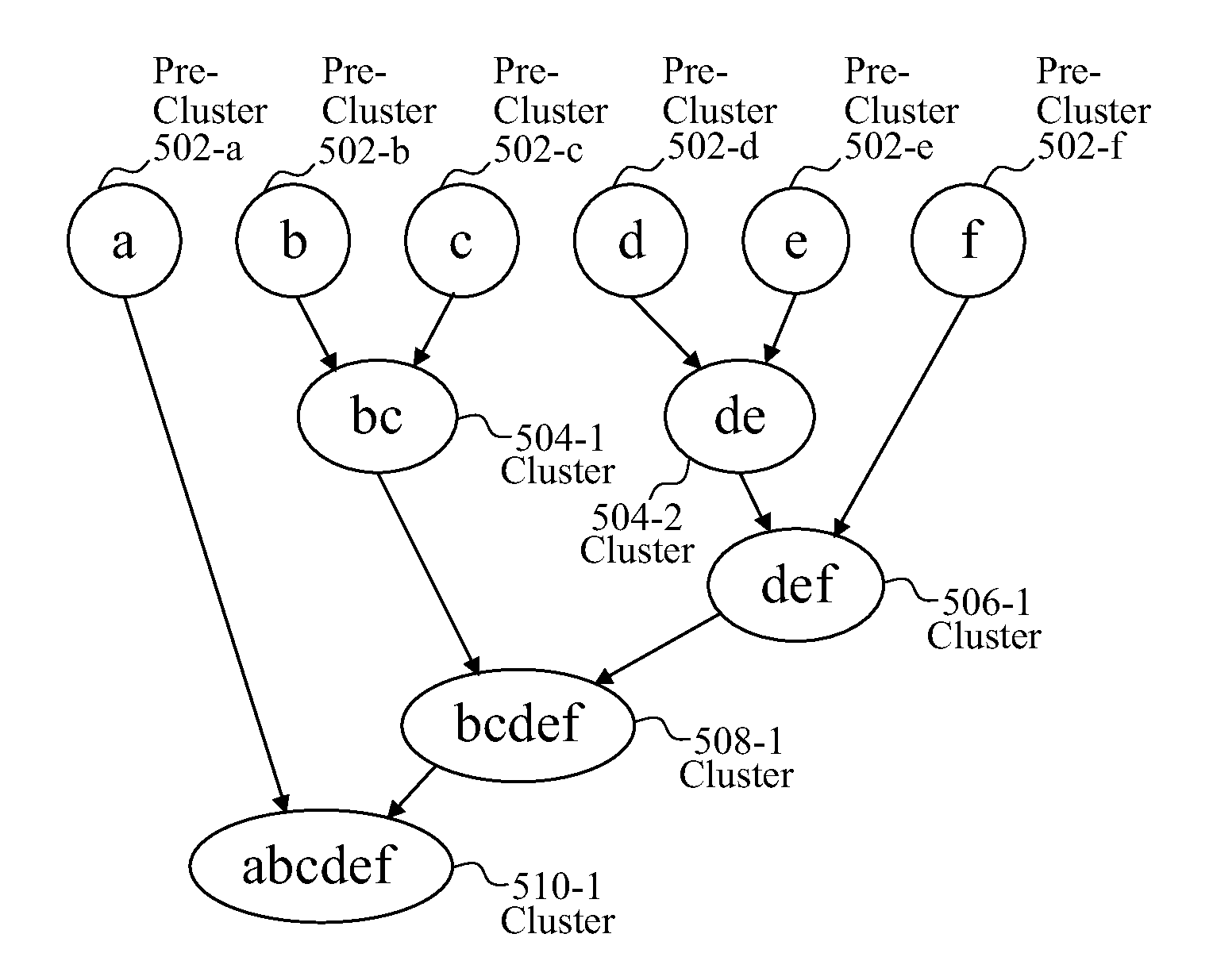
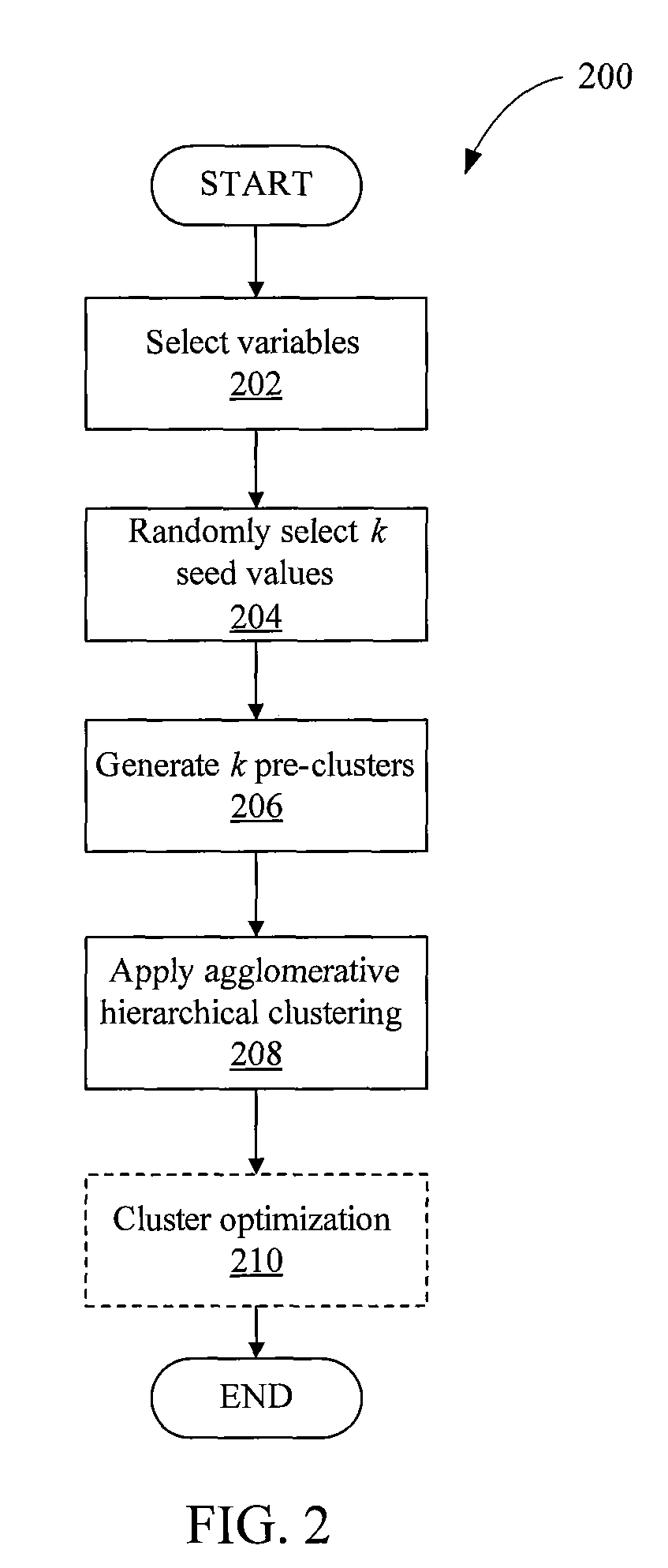
System and method for hybrid hierarchical segmentation
ActiveUS8402027B1Prevent deviationMaximizing similarityDigital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionHierarchical cluster algorithmValue set
A computer-implemented method for clustering a plurality of observations included in a dataset. The method includes selecting a subset of variables from a set of variables, where each variable in the subset is associated with each observation in the dataset; for each of a first number of times, randomly selecting an initial value for each variable in the subset to generate a seed value set that includes an initial value for each variable in the subset; generating a number of pre-clusters equal to the first number based on a similarity between each observation in the dataset and each of the first number of seed value sets; and applying a hierarchical clustering algorithm to the first number of pre-clusters to derive a second number of clusters.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Fault localization using directed test generation
InactiveUS20120054552A1Maximizing similarityImprove efficiencySoftware testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsDirect testStatistical analysis
Disclosed is a novel computer implemented system, on demand service, computer program product and a method for fault-localization techniques that apply statistical analyses to execution data gathered from multiple tests. The present invention determines the fault-localization effectiveness of test suites generated according to several test-generation techniques based on combined concrete and symbolic (concolic) execution. These techniques are evaluated by applying the Ochiai fault-localization technique to generated test suites in order to localize 35 faults in four PHPWeb applications. The results show that the test-generation techniques under consideration produce test suites with similar high fault-localization effectiveness, when given a large time budget.
Owner:IBM CORP
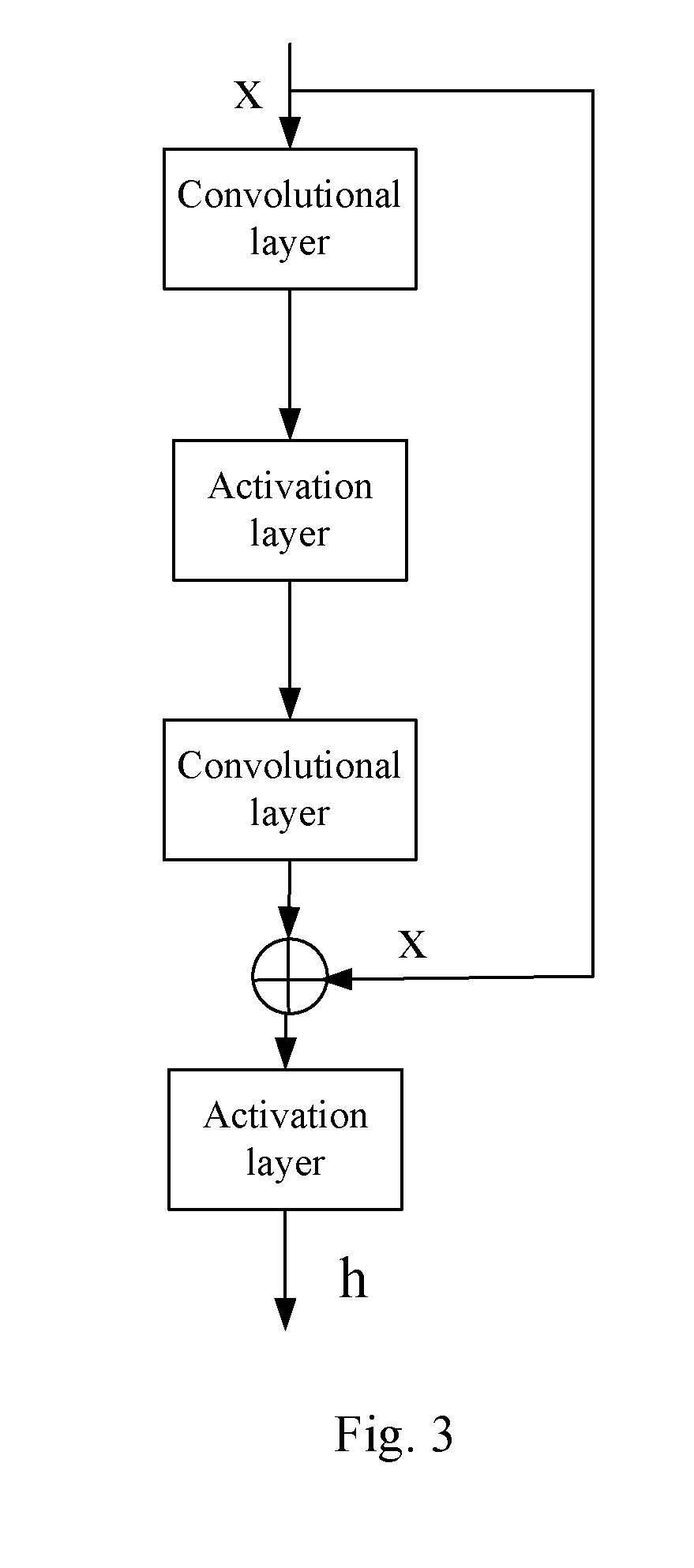
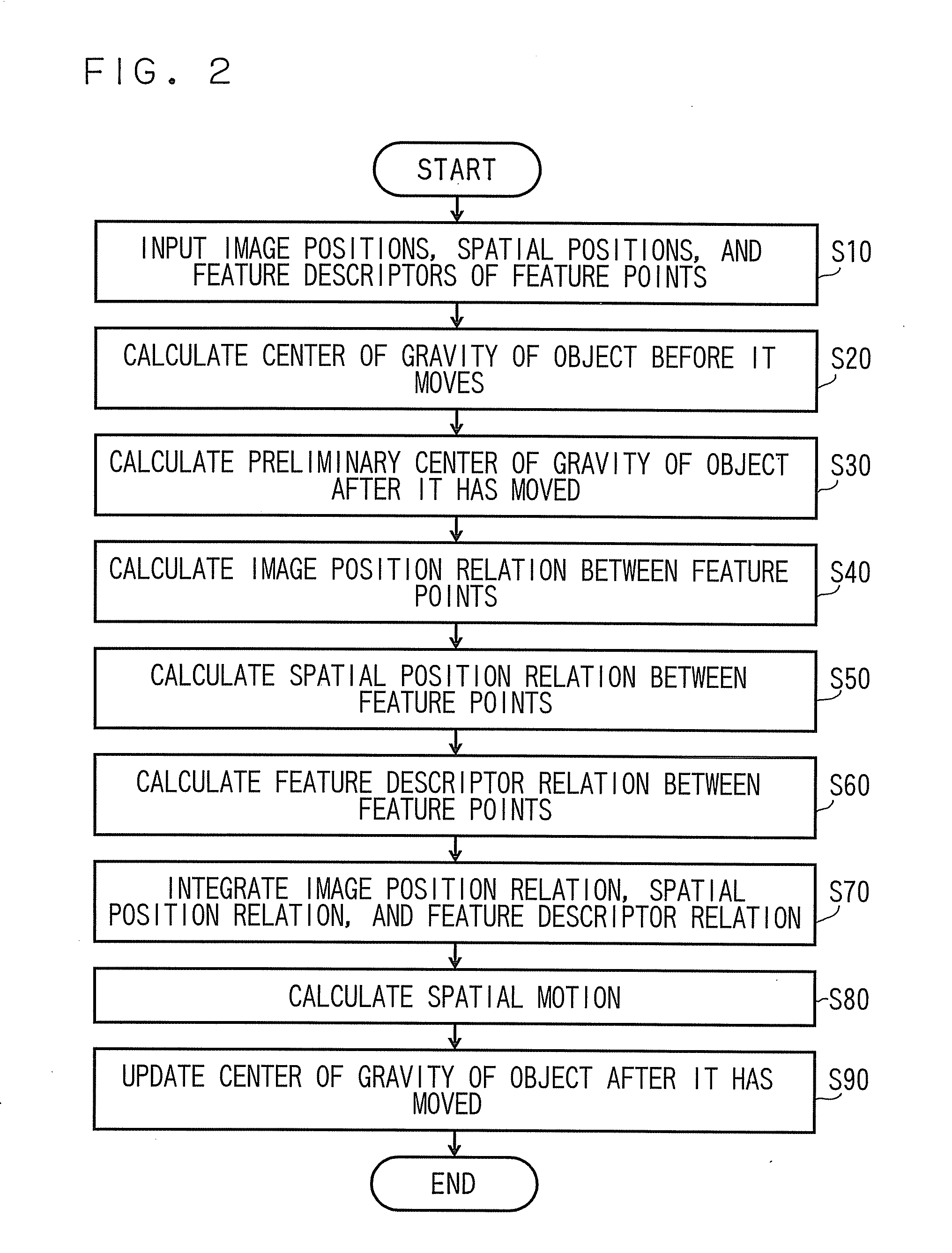
Spatial motion calculation apparatus and method for the same
ActiveUS20090226034A1Maximizing similarityImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A spatial motion calculation apparatus includes an image position relation calculation unit that calculates first similarities based on an image position relation between an inputted groups of feature points 1 and 2, a spatial position relation calculation unit that calculates second similarities based on an spatial position relation between said inputted groups, a feature descriptor relation calculation unit that calculates third similarities based on a feature descriptor relation between said inputted groups, and a spatial motion calculation unit that estimates the spatial motion based on the result that integrates the first to third similarities.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
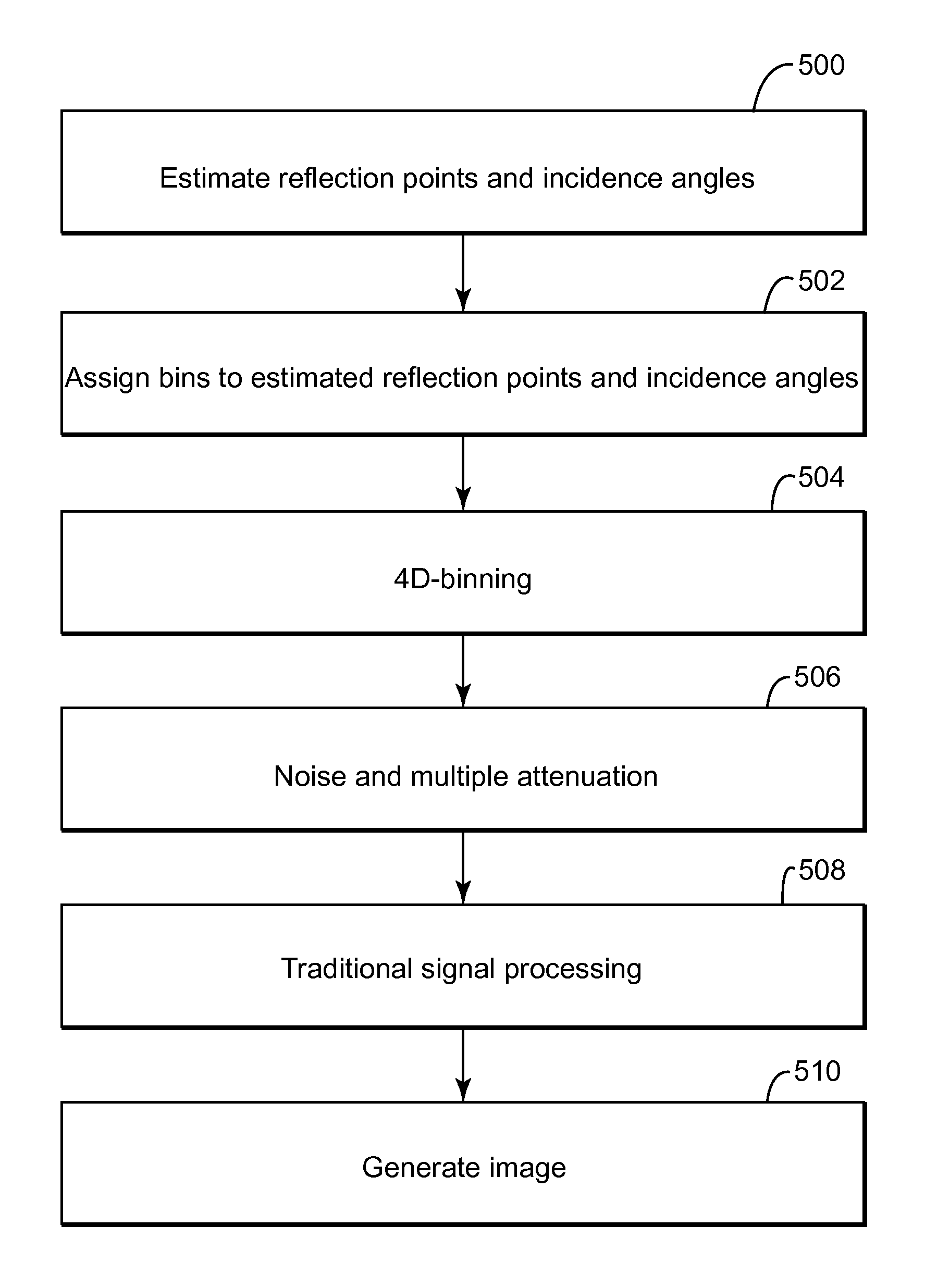
Wavefield modelling and 4d-binning for seismic surveys from different acquisition datums
ActiveUS20140198605A1High similarityMaximizing similaritySeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyRepeatability
A method for maximizing a repeatability between a base seismic survey and a monitor seismic survey of a same surveyed subsurface during a 4-dimensional (4D) project. The method includes receiving first seismic data associated with the base seismic survey; receiving second seismic data associated with the monitor seismic survey, wherein the monitor seismic survey is performed later in time than the base seismic survey; estimating subsurface reflection-points and incidence angles; determining 4D-binning based on the estimated subsurface reflection-points and incidence angles; and maximizing the repeatability between the first seismic data and the second seismic data by using the 4D-binning.
Owner:CGG SERVICES SA
Method and Apparatus of Building Acoustic Feature Extracting Model, and Acoustic Feature Extracting Method and Apparatus
ActiveUS20180336889A1Improve accuracyIncrease flexibilitySpeech recognitionFeature extractionUser identifier
A method and apparatus of building an acoustic feature extracting model, and an acoustic feature extracting method and apparatus. The method of building an acoustic feature extracting model comprises: considering first acoustic features extracted respectively from speech data corresponding to user identifiers as training data; using the training data to train a deep neural network to obtain an acoustic feature extracting model; wherein a target of training the deep neural network is to maximize similarity between the same user's second acoustic features and minimize similarity between different users' second acoustic features. The acoustic feature extracting model according to the present disclosure can self-learn optimal acoustic features that achieves a training target. As compared with a conventional acoustic feature extracting manner with a preset feature type and transformation manner, the acoustic feature extracting manner of the present disclosure achieves better flexibility and higher accuracy.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Data Remapping for Predictive Video Coding
InactiveUS20140192866A1Maximizing similarityReduce coding costsColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionBitstream
Specifically, a method decodes a picture. The picture is encoded and represented by blocks in a bitstream. For each block, a remap flag is obtained from the bit-stream. The block is either a remapped reconstructed block or a non-remapped reconstructed block. Either the non-mapped reconstructed block or an inverse remapped reconstructed block is output according to the remap flag. The remapped reconstructed block maximizes a similarity with the neighboring blocks, as compared to the similarity of the non-mapped reconstructed block and the neighboring blocks, by applying point operations to the remapped reconstructed block.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Employing user input to facilitate inferential sound recognition based on patterns of sound primitives
ActiveUS20160379666A1Mitigates distortionMaximize similarityElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisSystem definitionFeature detection
The disclosed embodiments provide a system that generates sound primitives to facilitate sound recognition. First, the system performs a feature-detection operation on sound samples to detect a set of sound features, wherein each sound feature comprises a measurable characteristic of a window of consecutive sound samples. Next, the system creates feature vectors from coefficients generated by the feature-detection operation, wherein each feature vector comprises a set of coefficients for sound features detected in a window. The system then performs a clustering operation on the feature vectors to produce feature-vector clusters, wherein each feature-vector cluster comprises a set of feature vectors that are proximate to each other in a feature-vector space that contains the feature vectors. After the clustering operation, the system defines a set of sound primitives, wherein each sound primitive is associated with a feature-vector cluster. Finally, the system associates semantic labels with the set of sound primitives.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Image-domain 4d-binning method and system
ActiveUS20140247693A1High similarityMaximizing similaritySeismic signal processingSeismic surveyImage domain
A method for increasing similarity between a base seismic survey and a monitor seismic survey of a same surveyed subsurface during a 4-dimensional (4D) project. The method includes receiving first seismic data associated with the base seismic survey; receiving second seismic data associated with the monitor seismic survey, wherein the monitor seismic survey is performed later in time than the base seismic survey; migrating the first and second seismic data to an image-domain; and calculating, with a processor, a set of decimating weights based on the migrated first and second seismic data in the image-domain, to maximize a similarity between the first seismic data and the second seismic data.
Owner:CGGVERITAS SERVICES
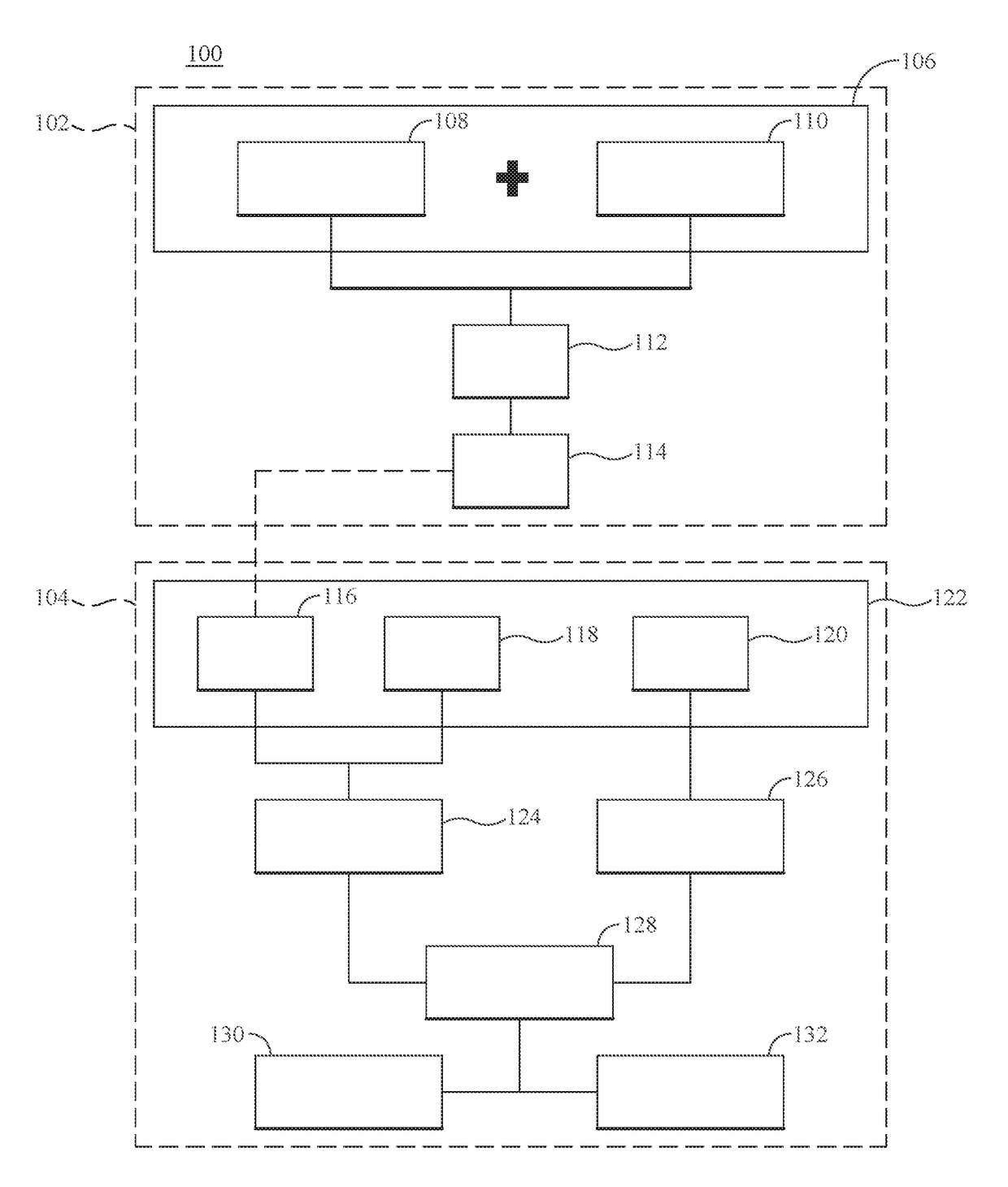
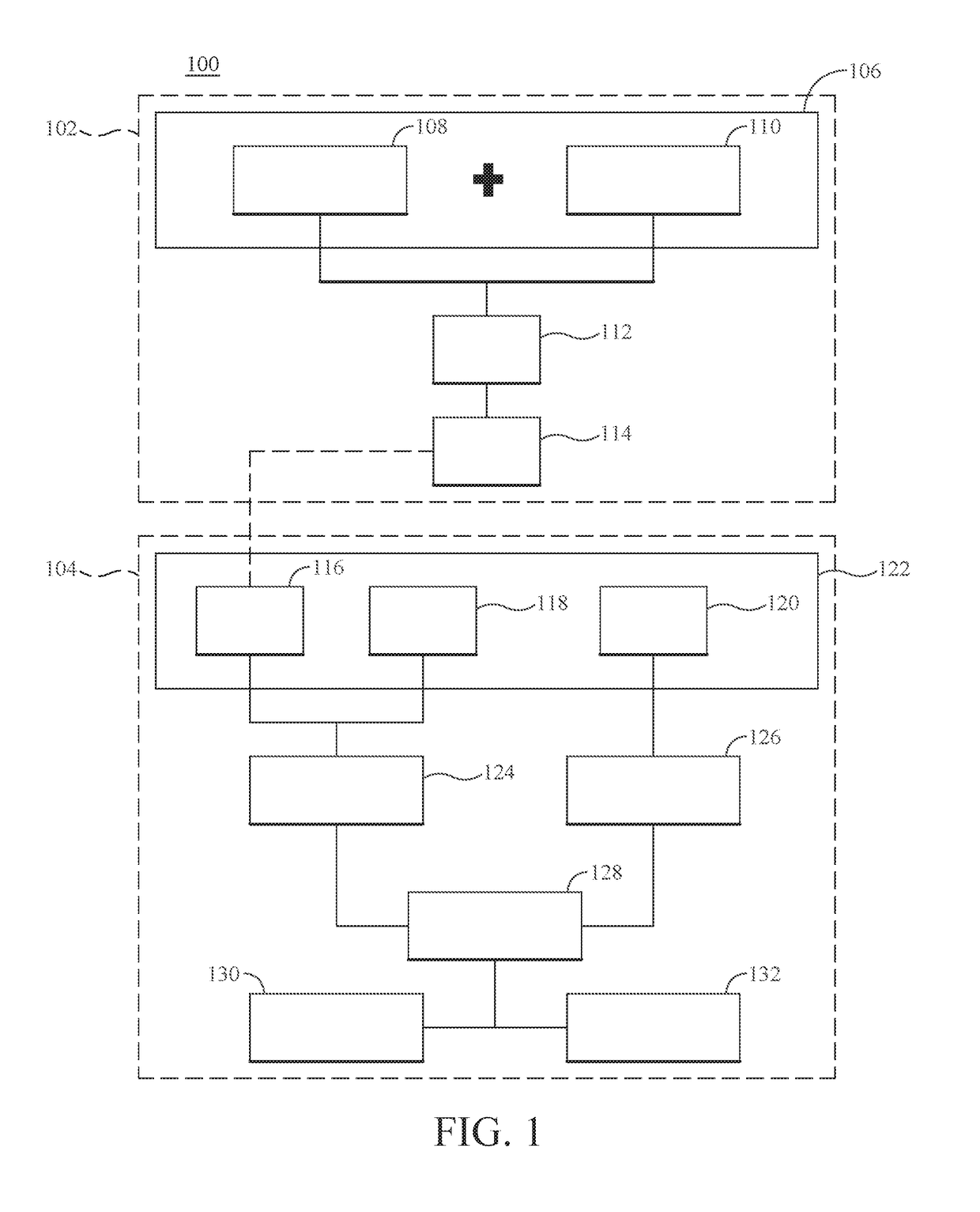
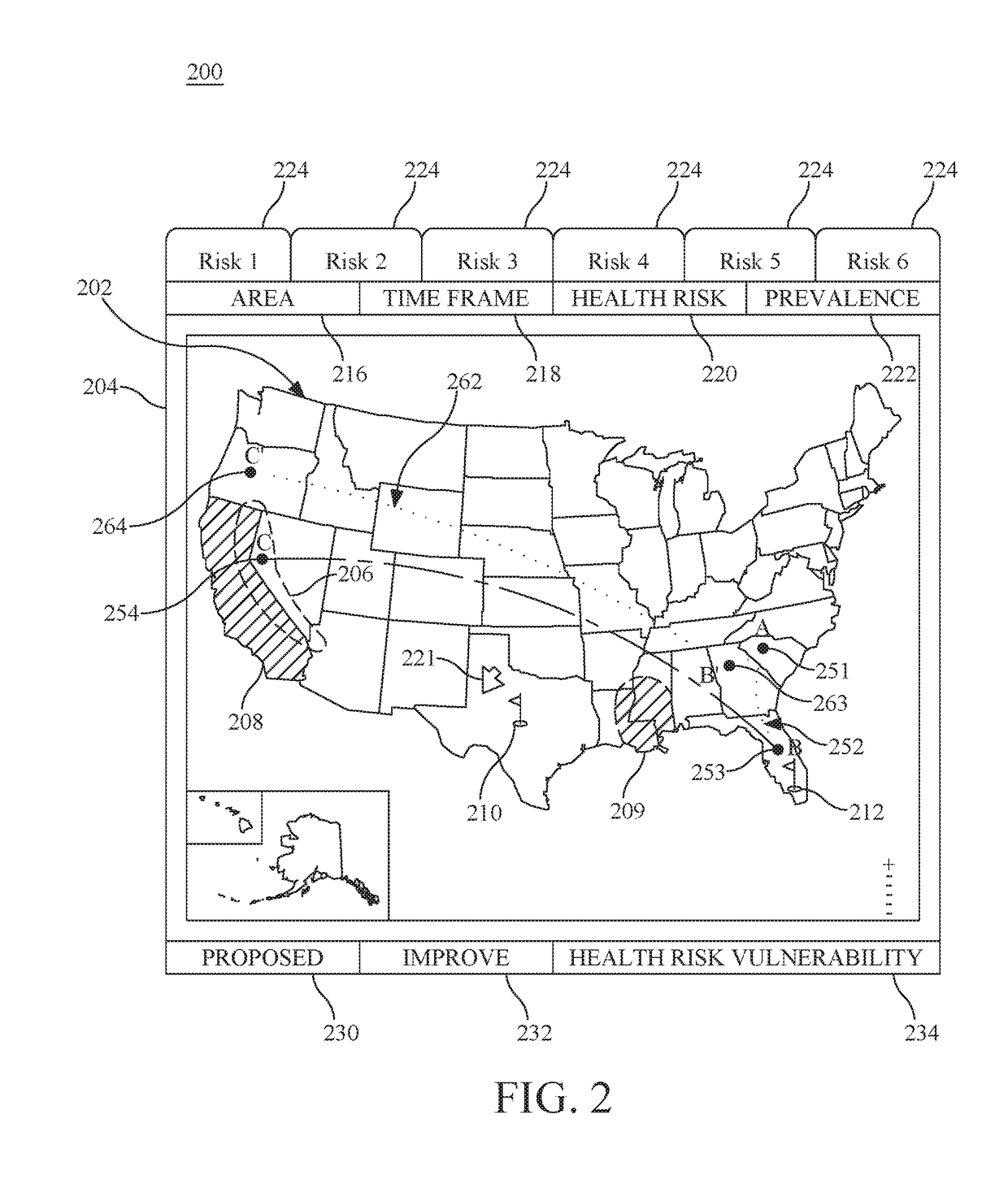
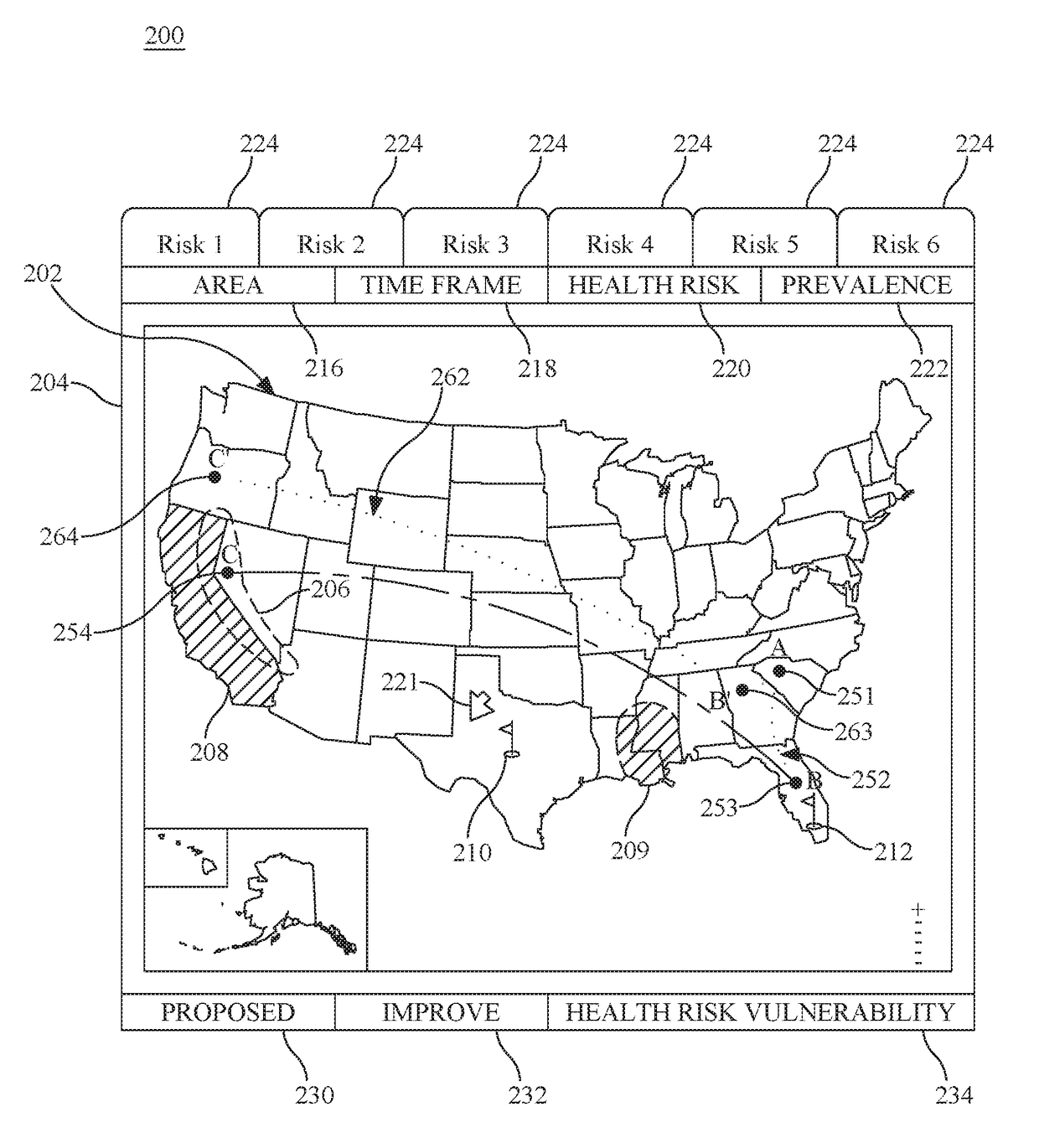
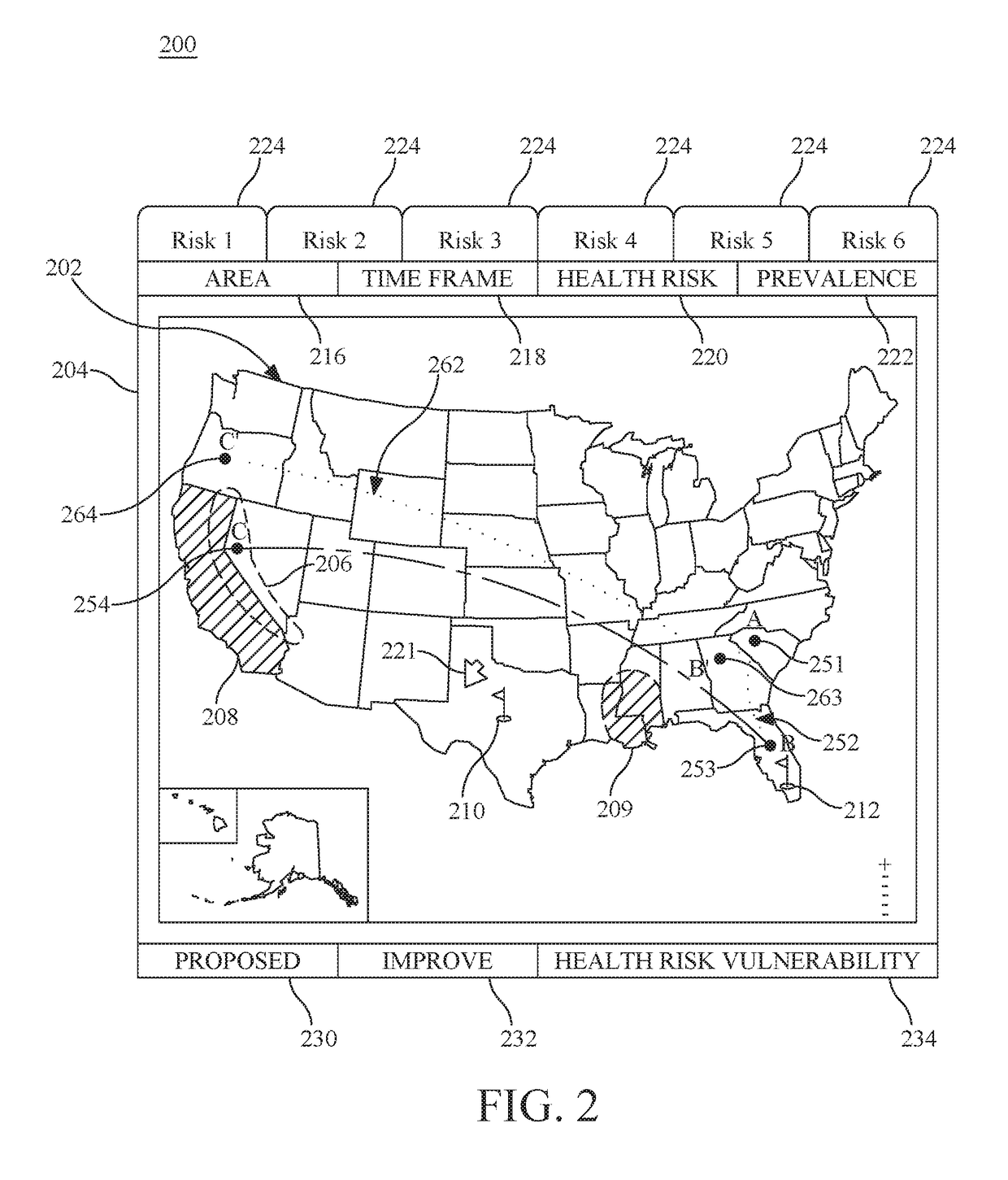
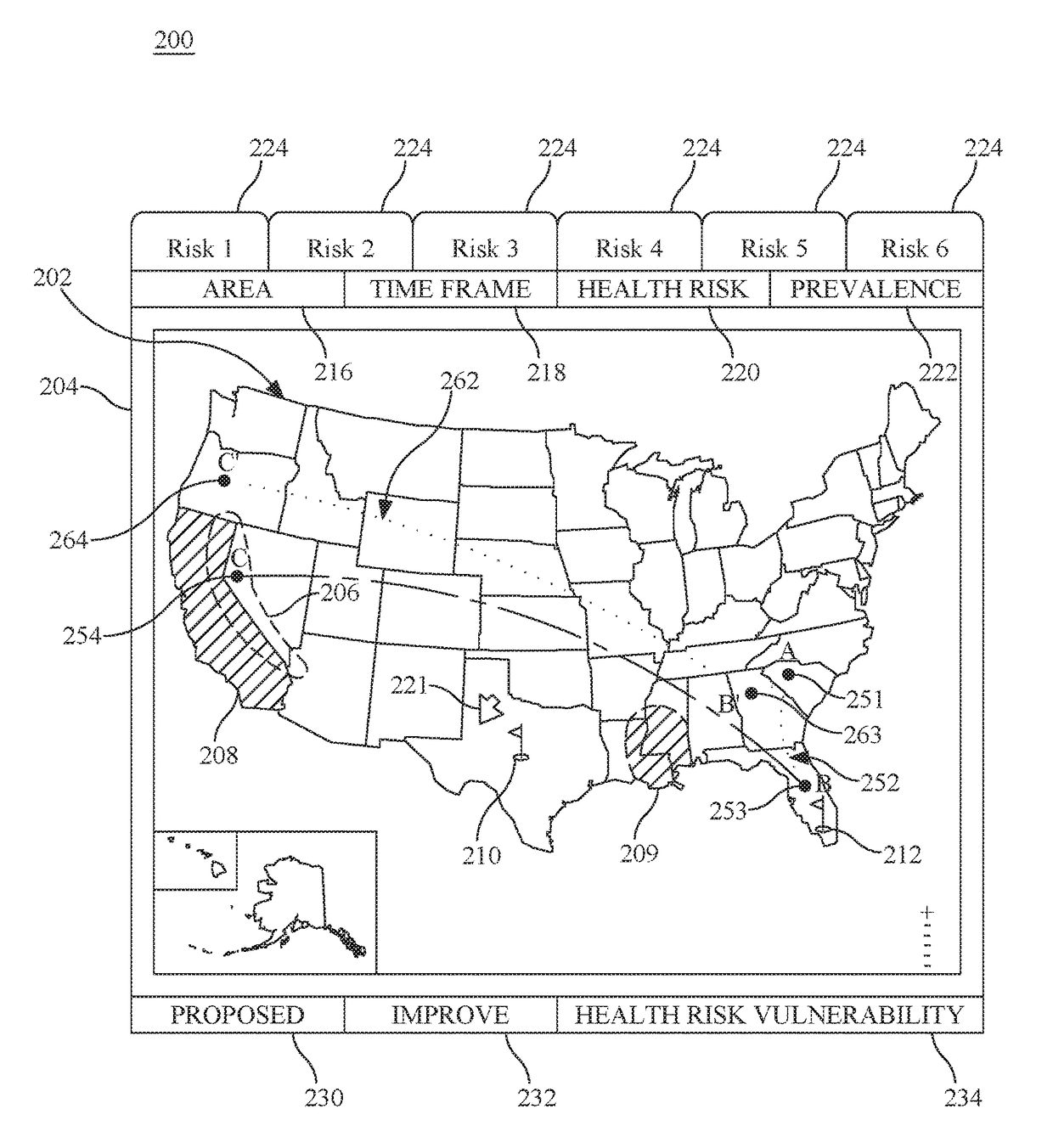
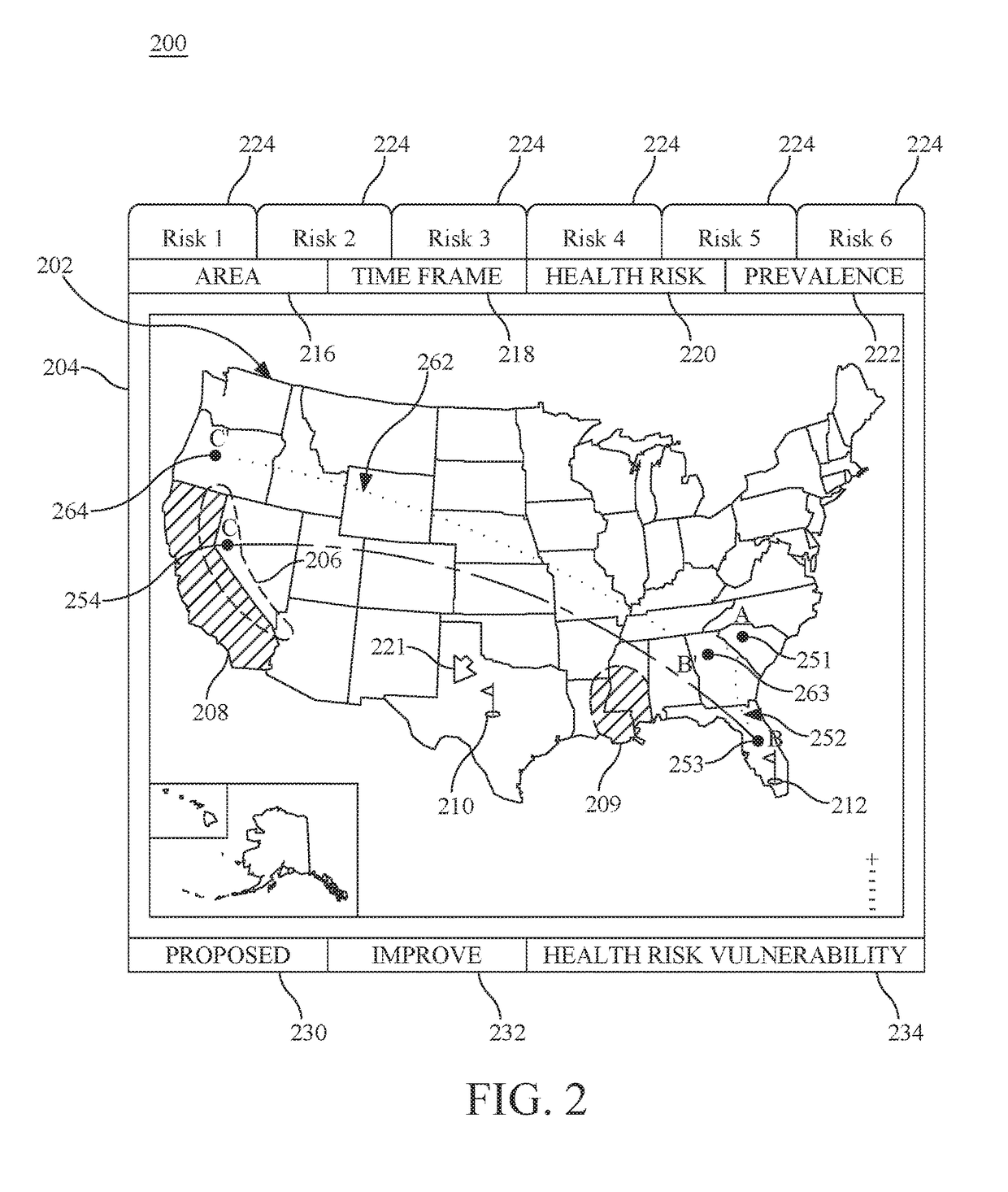
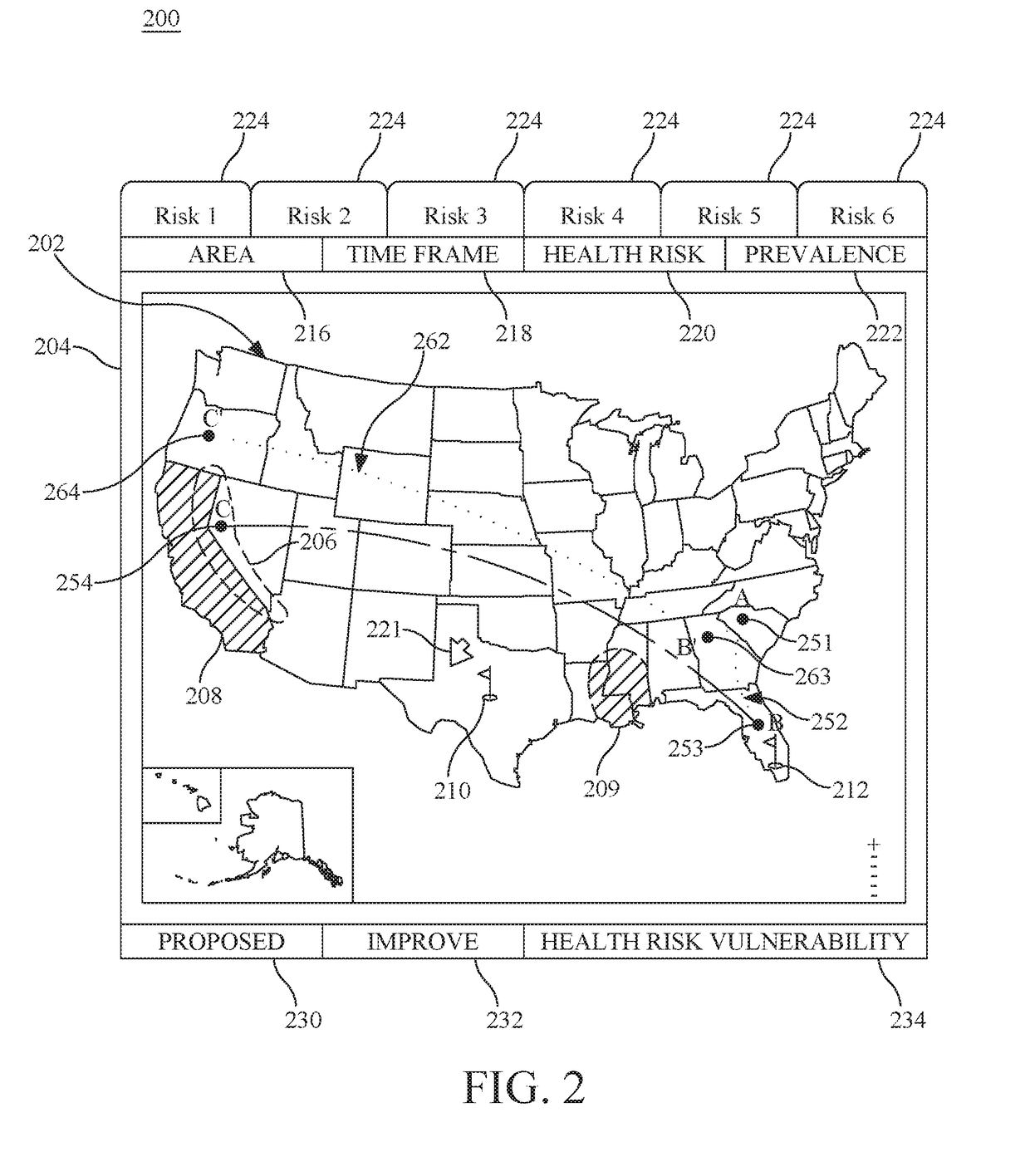
Personal travel health vulnerability navigator
InactiveUS20170351832A1Minimizes vulnerabilityImprove travelMedical simulationData processing applicationsLevel dataRisk vulnerability
Individual health vulnerability is assessed by obtaining health risk prevalence level data containing health risk prevalence levels for one or more health risks over a given geographical area. The health risk prevalence level data to generate for each health risk a prevalence level forecast as a function of time and location. A health risk prevalence level map is generated for the given geographical area illustrating current and future health risk prevalence levels for each health risk at a plurality of locations within the given geographical area. Personal health status data are obtained for a given individual along with a proposed travel itinerary f covering at least a portion of the geographical area over a given time duration. The personal health status data, travel itinerary and map generate a personal health risk vulnerability model containing a quantification of vulnerability to the one or more health risks resulting from the travel itinerary.
Owner:IBM CORP
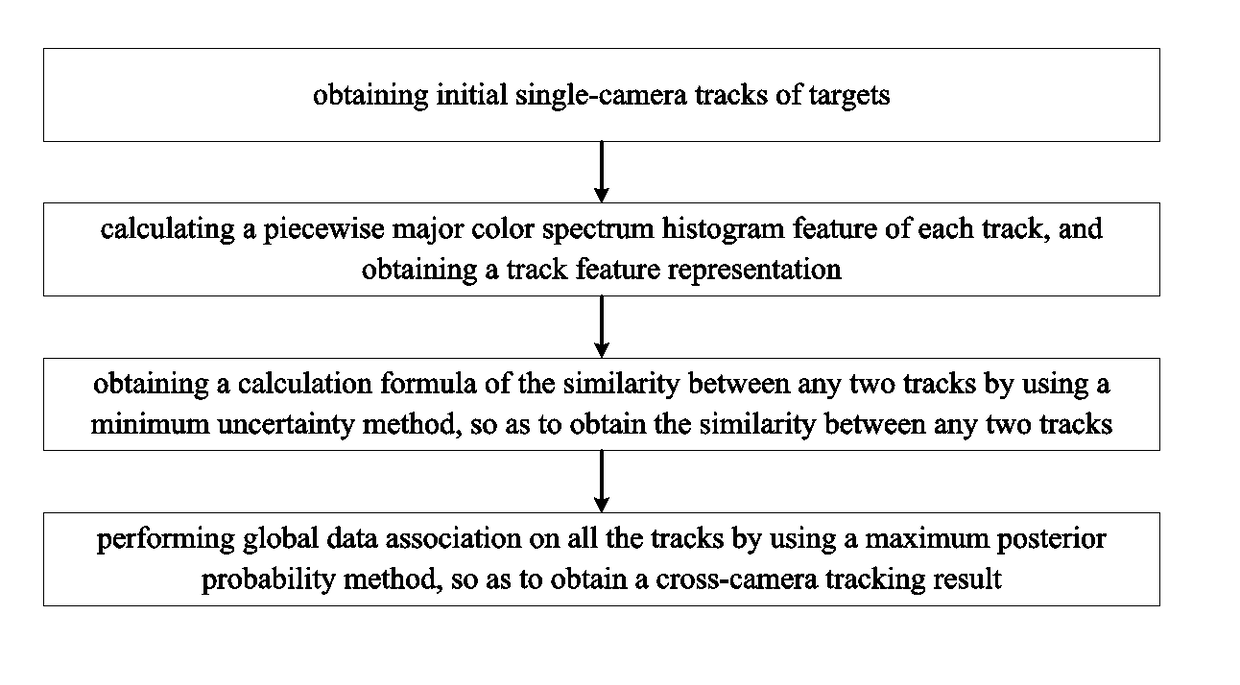
Large-Range-First Cross-Camera Visual Target Re-identification Method
InactiveUS20170116753A1Improve identification accuracyHigh identification accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisRe identificationOrbit
The present invention relates to a large-range-first cross-camera visual target re-identification method. The method comprises: step S1, obtaining initial single-camera tracks of targets; step S2, calculating a piecewise major color spectrum histogram feature of each track, and obtaining a track feature representation; step S3, obtaining a calculation formula of the similarity between any two tracks by using a minimum uncertainty method, so as to obtain the similarity between any two tracks; and step S4, performing global data association on all the tracks by using a maximum posterior probability method, so as to obtain a cross-camera tracking result. The target re-identification method of the present invention achieves high correct identification accuracy.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus, method, and medium for generating panoramic image using a series of images captured in various directions
ActiveUS8768098B2Precise alignmentMaximizing similarityTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationImage captureComputer science
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for situation recognition using optical information
InactiveUS7421092B2Maximizing similarityMaximize effectivenessImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionProbit modelOperating system
A situation recognition apparatus includes: an optical information acquisition unit configured to acquire optical information; a storage configured to store a plurality of pieces of optical information; a processing unit configured to match a plurality of the pieces of optical information stored in the storage and optical information newly acquired by the optical information acquisition unit; and an output unit configured to output a result of the matching. The storage further stores a probabilistic model that numerically represents transitions between the plurality of pieces of optical information.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Method for registering and merging medical image data
ActiveUS8244064B2Maximizing similarityReduce morbidityImage enhancementImage analysisData setSuperimposition
The present invention relates to a method for the registration and superimposition of image data when taking serial radiographs in medical imaging, wherein a plurality of image data sets for a region of a patient (17) that is being investigated are constructed at time intervals using an imaging system (1) and are referenced with a first image data set for the region that is being investigated that was constructed previously using said imaging system (1). In the above method, a location system (2) is used during the production of serial radiographs constantly, or at least at a respective proximity in time to the construction of individual data sets, to determine a current spatial position of the region being investigated in a reference system that is firmly connected to the imaging system (1), whereby in the construction of the first image data set, a first spatial position of the region that is being investigated is recorded. In the construction of some or all further image data sets, the respective current spatial position of the region that is being investigated is determined and an image content of each first image data set is geometrically adapted on the basis of the difference between the first and the current spatial position, such that compensation is made for a different spatial position of the region that is being investigated. The geometrically adapted first image data set or an image data set derived therefrom, or an image data set that is positionally connected thereto by registration is then displayed superimposed with the respective further image data set.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Personal travel health vulnerability navigator
InactiveUS20170351833A1Minimize health vulnerability of individualIncrease the itineraryData processing applicationsHealth-index calculationHealth riskLevel data
Individual health vulnerability is assessed by obtaining health risk prevalence level data containing health risk prevalence levels for one or more health risks over a given geographical area. The health risk prevalence level data to generate for each health risk a prevalence level forecast as a function of time and location. A health risk prevalence level map is generated for the given geographical area illustrating current and future health risk prevalence levels for each health risk at a plurality of locations within the given geographical area. Personal health status data are obtained for a given individual along with a proposed travel itinerary f covering at least a portion of the geographical area over a given time duration. The personal health status data, travel itinerary and map generate a personal health risk vulnerability model containing a quantification of vulnerability to the one or more health risks resulting from the travel itinerary.
Owner:IBM CORP
Personal travel health vulnerability navigator
InactiveUS20170351834A1Minimize health vulnerability of individualIncrease the itineraryMedical simulationData processing applicationsHealth riskLevel data
Individual health vulnerability is assessed by obtaining health risk prevalence level data containing health risk prevalence levels for one or more health risks over a given geographical area. The health risk prevalence level data to generate for each health risk a prevalence level forecast as a function of time and location. A health risk prevalence level map is generated for the given geographical area illustrating current and future health risk prevalence levels for each health risk at a plurality of locations within the given geographical area. Personal health status data are obtained for a given individual along with a proposed travel itinerary f covering at least a portion of the geographical area over a given time duration. The personal health status data, travel itinerary and map generate a personal health risk vulnerability model containing a quantification of vulnerability to the one or more health risks resulting from the travel itinerary.
Owner:IBM CORP
Personal travel health vulnerability navigator
InactiveUS20170351831A1Minimize health vulnerability of individualIncrease the itineraryData processing applicationsHealth-index calculationHealth riskLevel data
Individual health vulnerability is assessed by obtaining health risk prevalence level data containing health risk prevalence levels for one or more health risks over a given geographical area. The health risk prevalence level data to generate for each health risk a prevalence level forecast as a function of time and location. A health risk prevalence level map is generated for the given geographical area illustrating current and future health risk prevalence levels for each health risk at a plurality of locations within the given geographical area. Personal health status data are obtained for a given individual along with a proposed travel itinerary f covering at least a portion of the geographical area over a given time duration. The personal health status data, travel itinerary and map generate a personal health risk vulnerability model containing a quantification of vulnerability to the one or more health risks resulting from the travel itinerary.
Owner:IBM CORP
Wavefield modelling and 4D-binning for seismic surveys from different acquisition datums
ActiveUS9684085B2High similarityMaximizing similaritySeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyRepeatability
A method for maximizing a repeatability between a base seismic survey and a monitor seismic survey of a same surveyed subsurface during a 4-dimensional (4D) project. The method includes receiving first seismic data associated with the base seismic survey; receiving second seismic data associated with the monitor seismic survey, wherein the monitor seismic survey is performed later in time than the base seismic survey; estimating subsurface reflection-points and incidence angles; determining 4D-binning based on the estimated subsurface reflection-points and incidence angles; and maximizing the repeatability between the first seismic data and the second seismic data by using the 4D-binning.
Owner:CGG SERVICES SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com