Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40results about How to "High propensity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
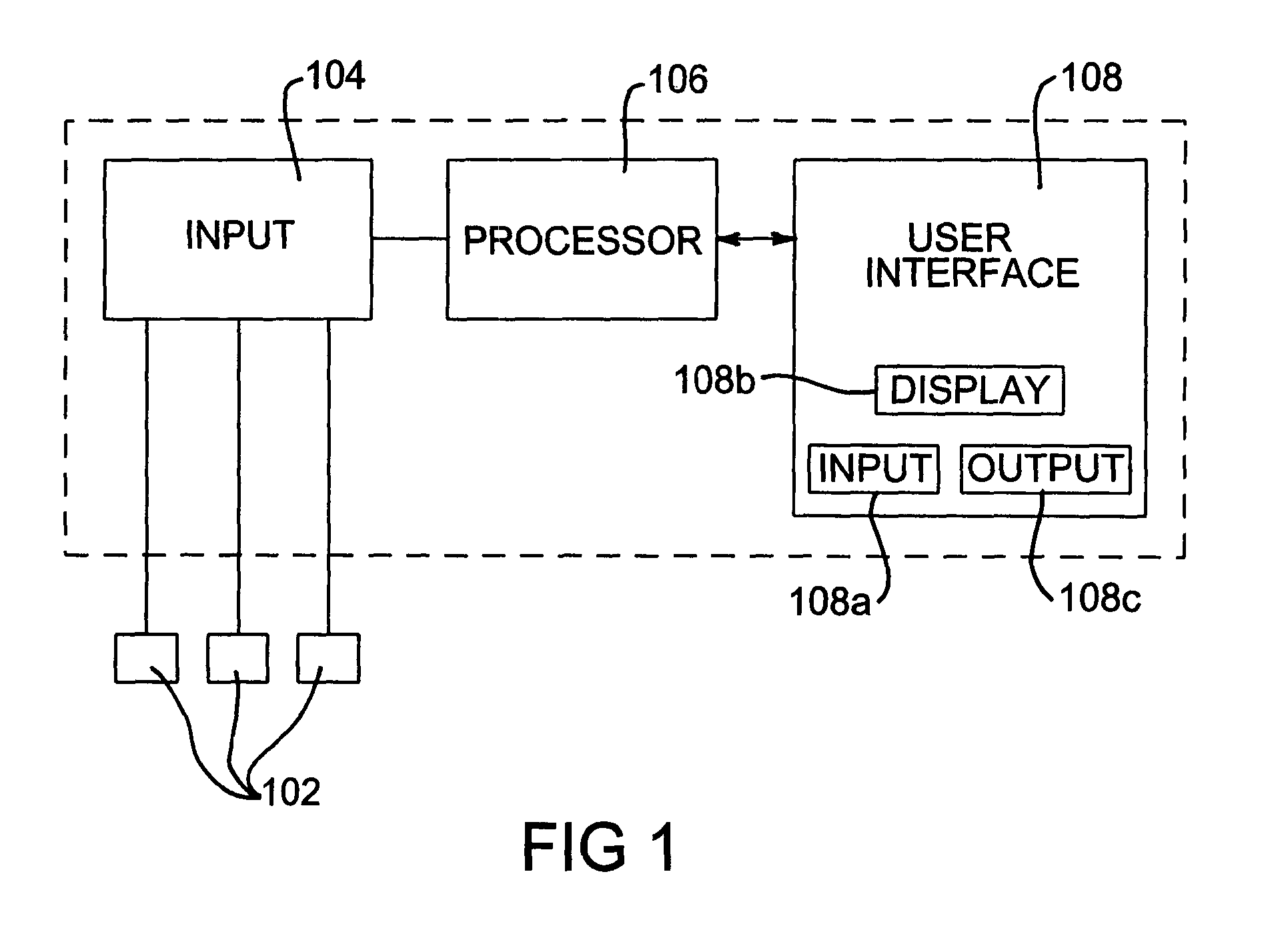
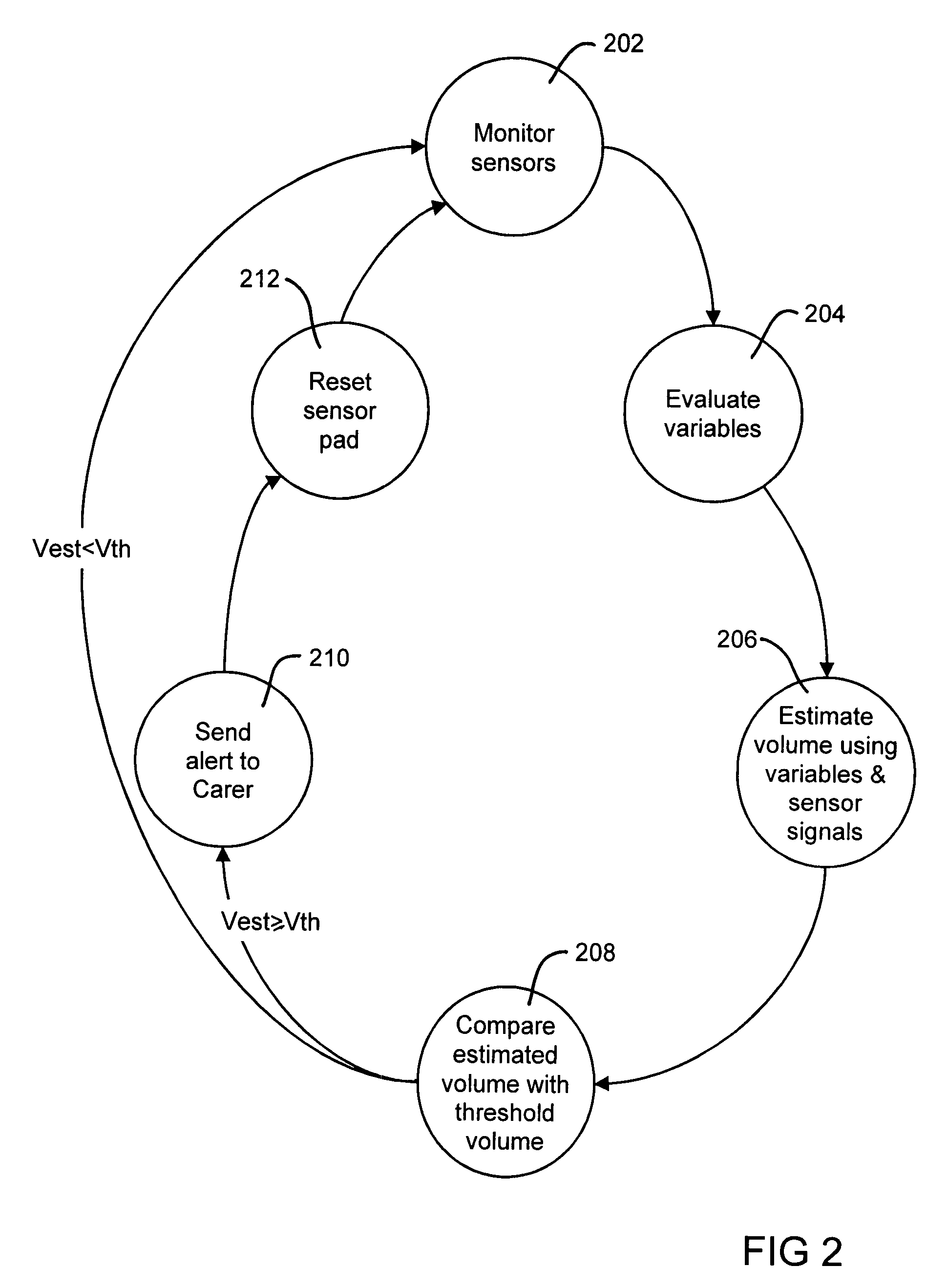
Incontinence management system and diaper
ActiveUS20070270774A1Streamline patient careEasy to reconfigureTime indicationSynchronous motors for clocksObservation dataMathematical model
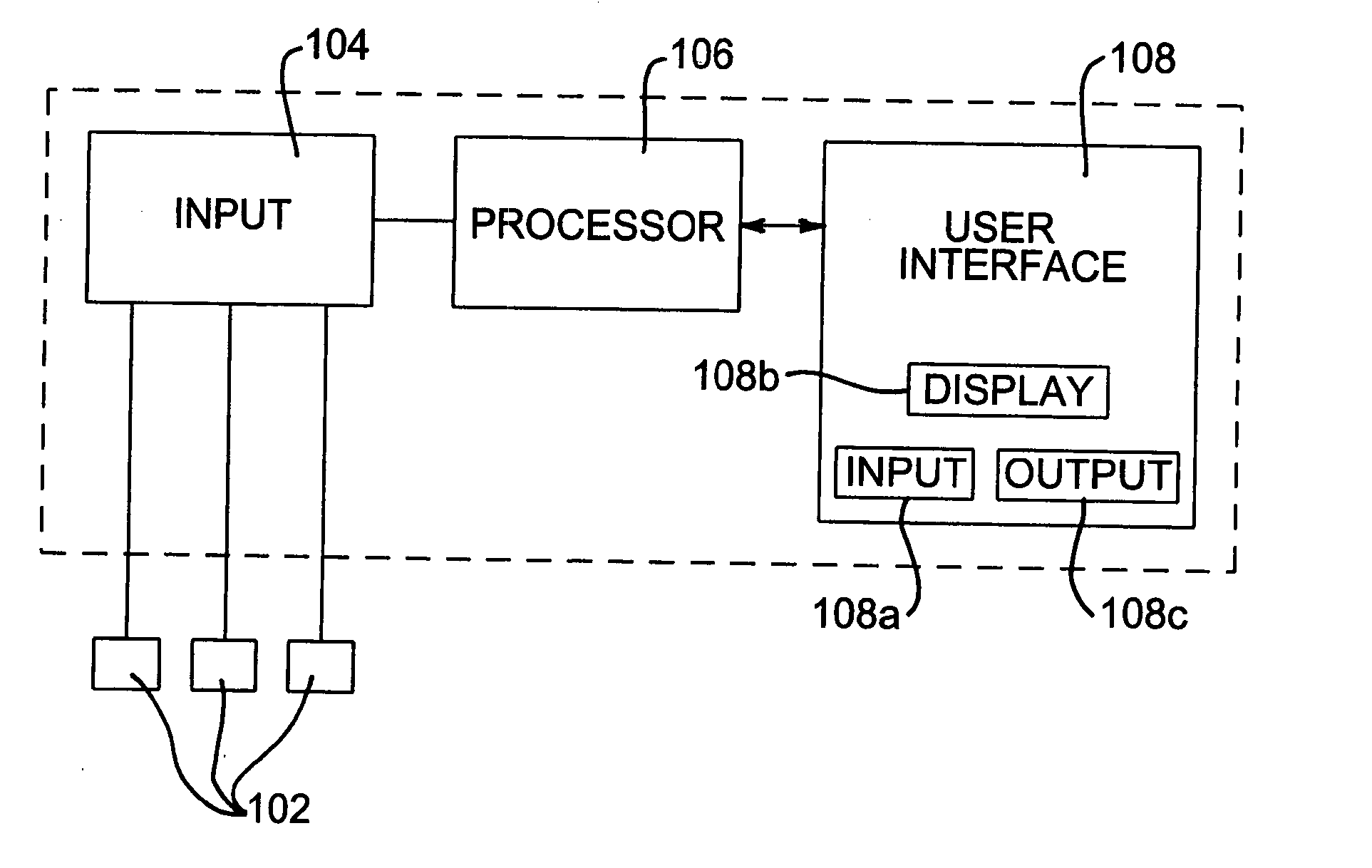
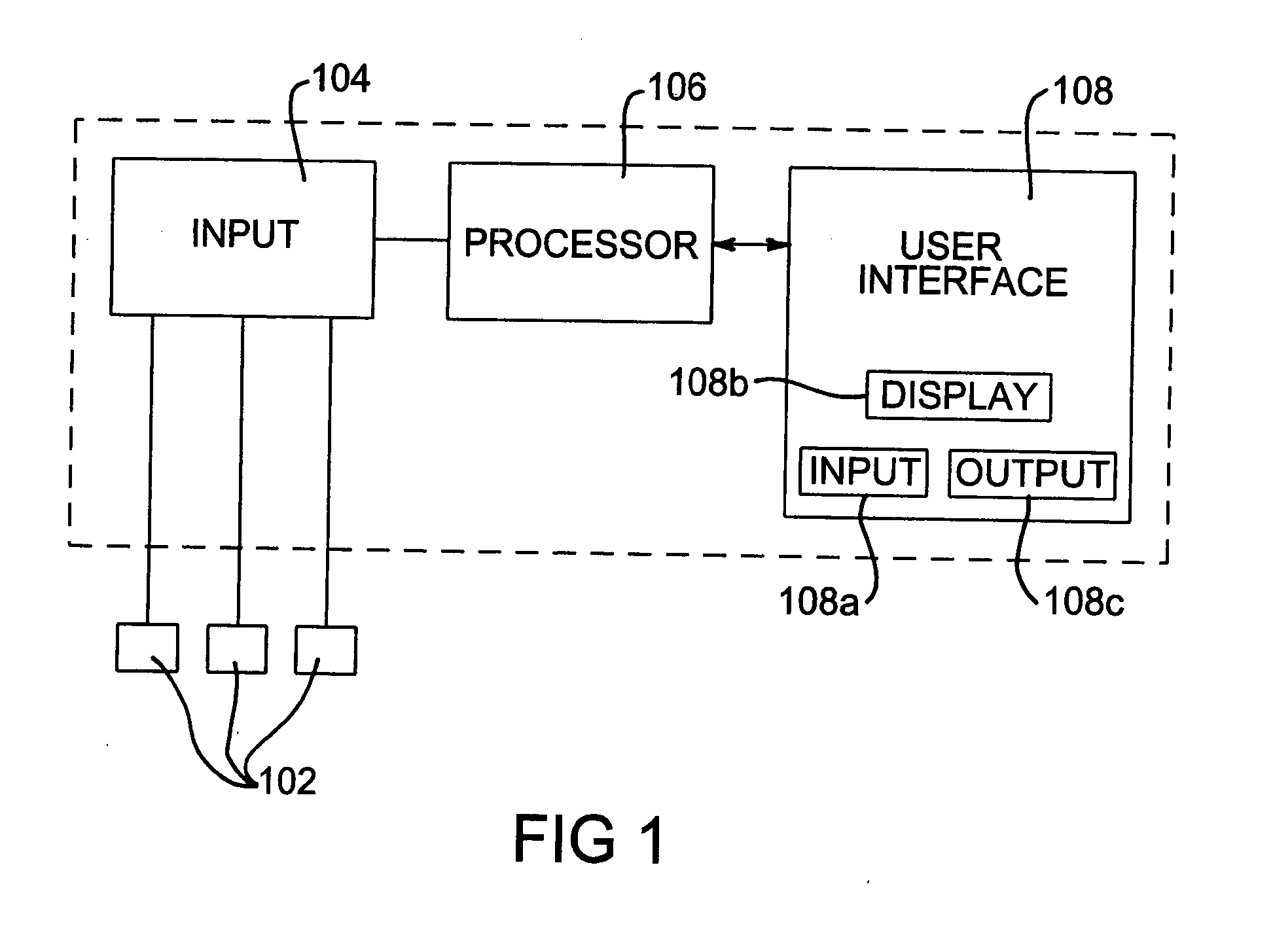
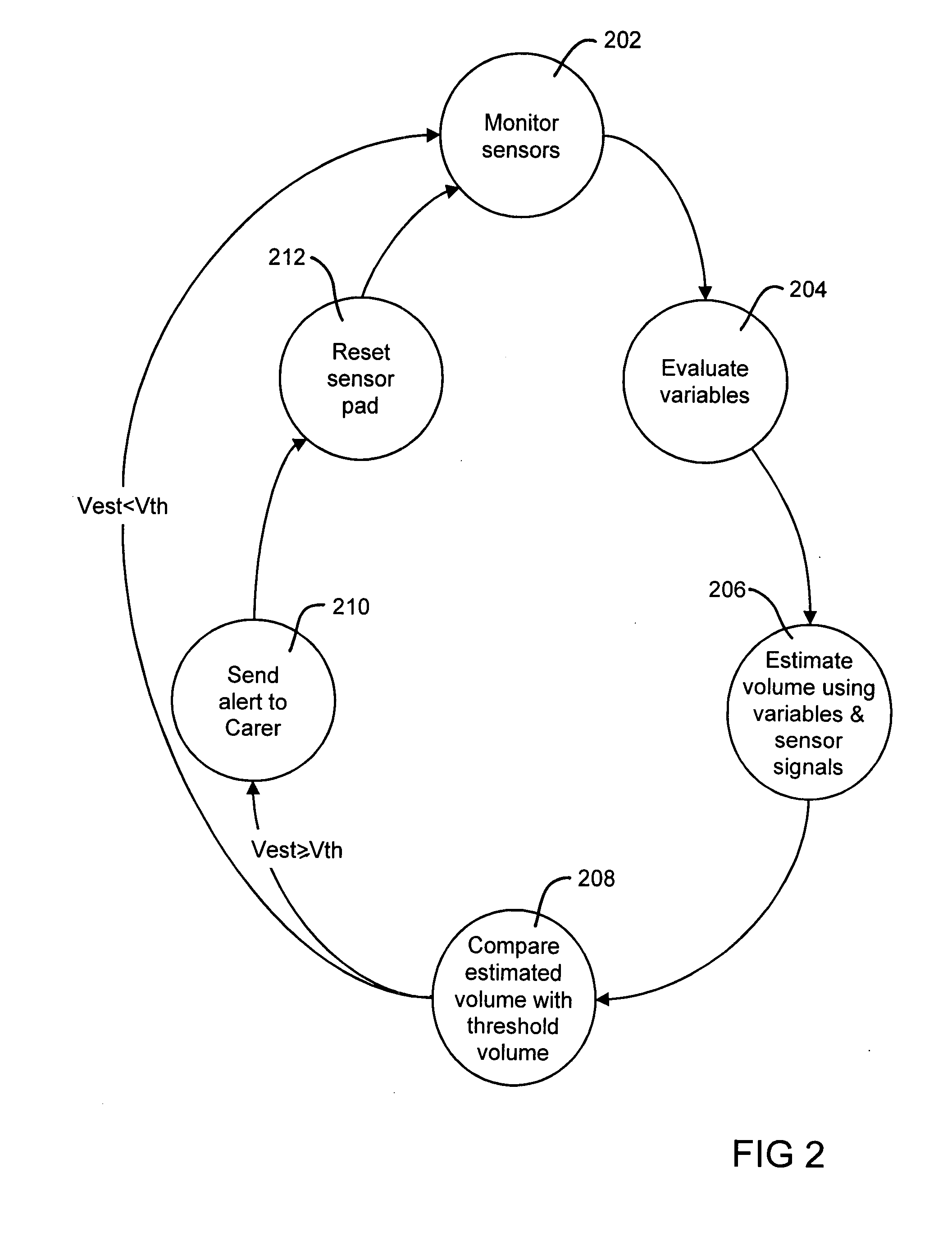
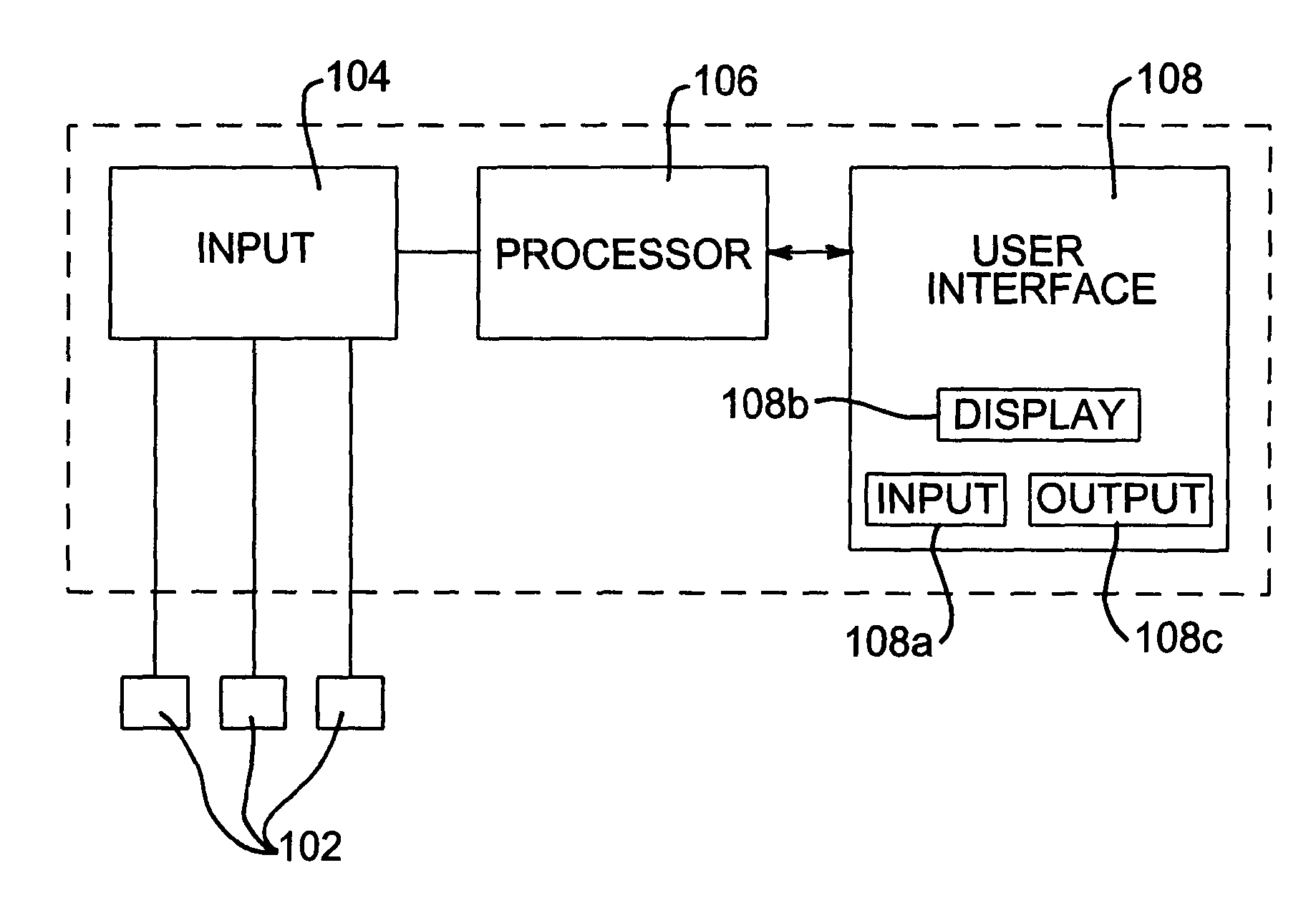
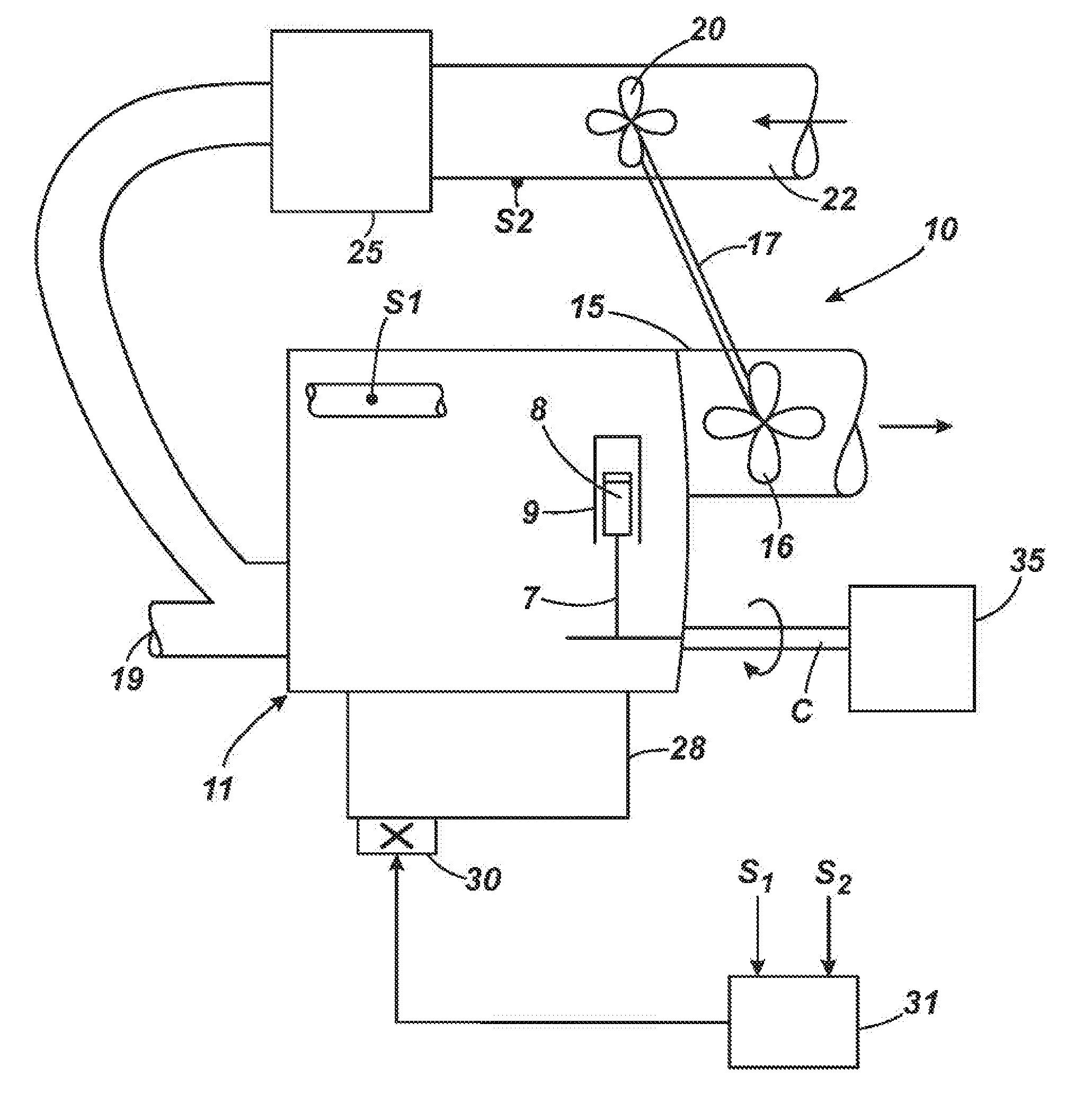
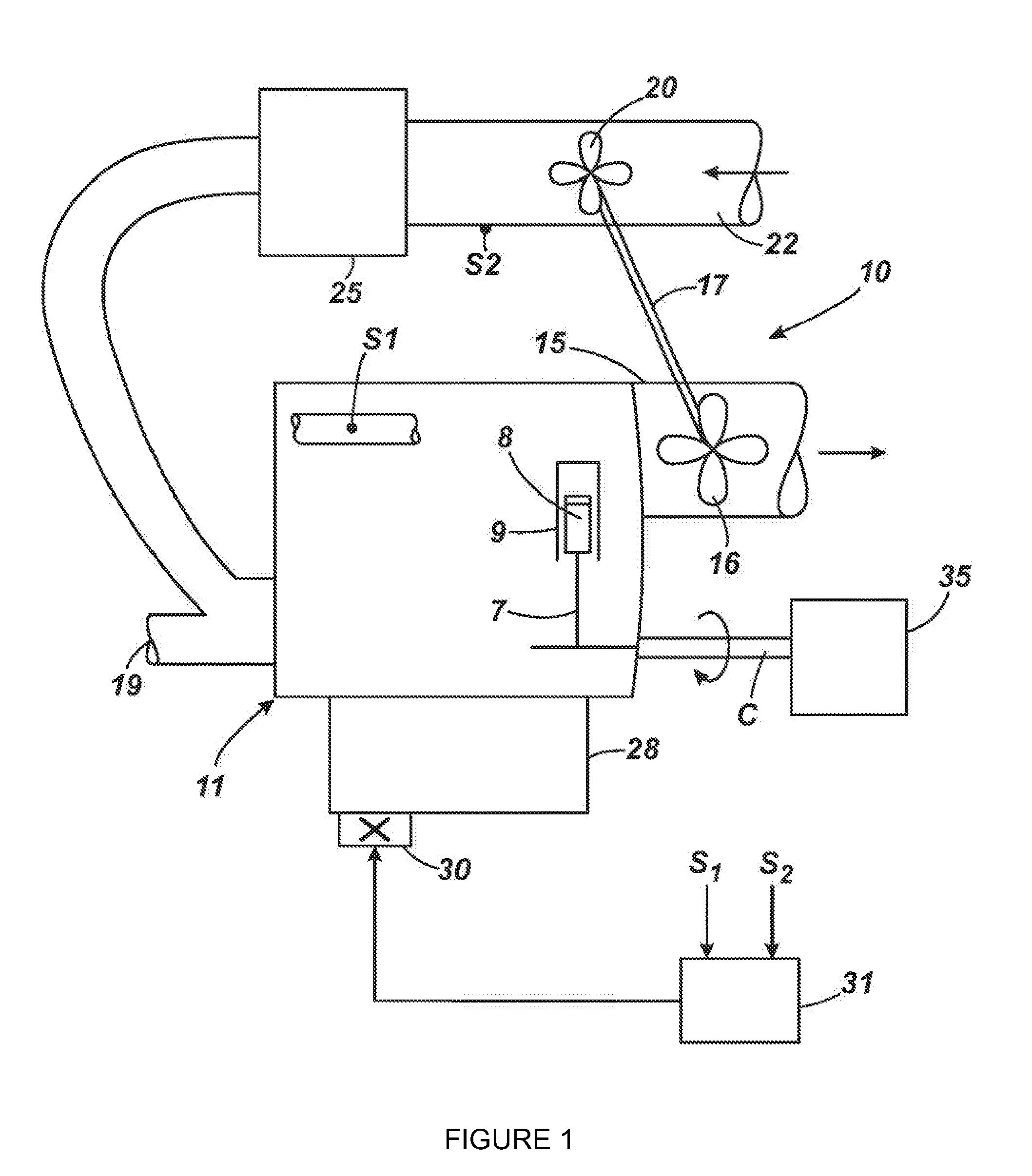
An incontinence management system for monitoring wetness in one or more absorbent articles, includes input for receiving one or more sensor signals indicative of a presence of wetness in an absorbent article, processor for processing the one or more sensor signals and for performing an analysis of the signals to characterise wetness events occurring in an absorbent article and user interface for communicating with a user of the system. A mathematical model is used to characterise wetness events, receiving as inputs variables derived from sensor signals and optionally, patient and demographic data. The mathematical model can be configured and / or re-configured utilising observation data obtained while monitoring a patient for wetness. A diaper for use with such as system is also disclosed.
Owner:FRED BERGMAN HEALTHCARE PTY LTD
Incontinence management system and diaper
ActiveUS7977529B2Improve abilitiesHigh propensityTime indicationSynchronous motors for clocksMathematical modelObservation data
An incontinence management system for monitoring wetness in one or more absorbent articles, includes input for receiving one or more sensor signals indicative of a presence of wetness in an absorbent article, processor for processing the one or more sensor signals and for performing an analysis of the signals to characterise wetness events occurring in an absorbent article and user interface for communicating with a user of the system. A mathematical model is used to characterise wetness events, receiving as inputs variables derived from sensor signals and optionally, patient and demographic data. The mathematical model can be configured and / or re-configured utilising observation data obtained while monitoring a patient for wetness. A diaper for use with such as system is also disclosed.
Owner:FRED BERGMAN HEALTHCARE PTY LTD
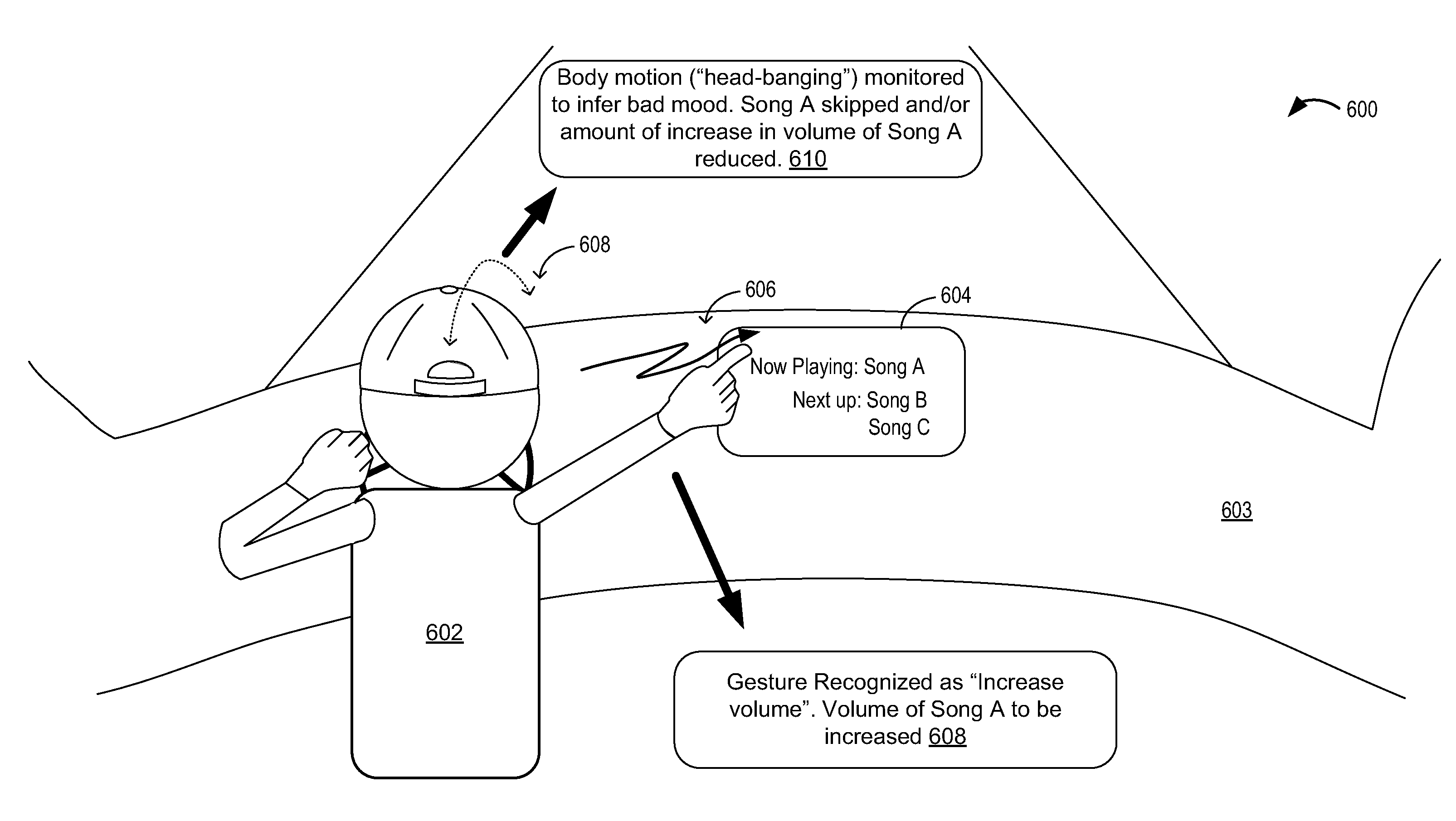
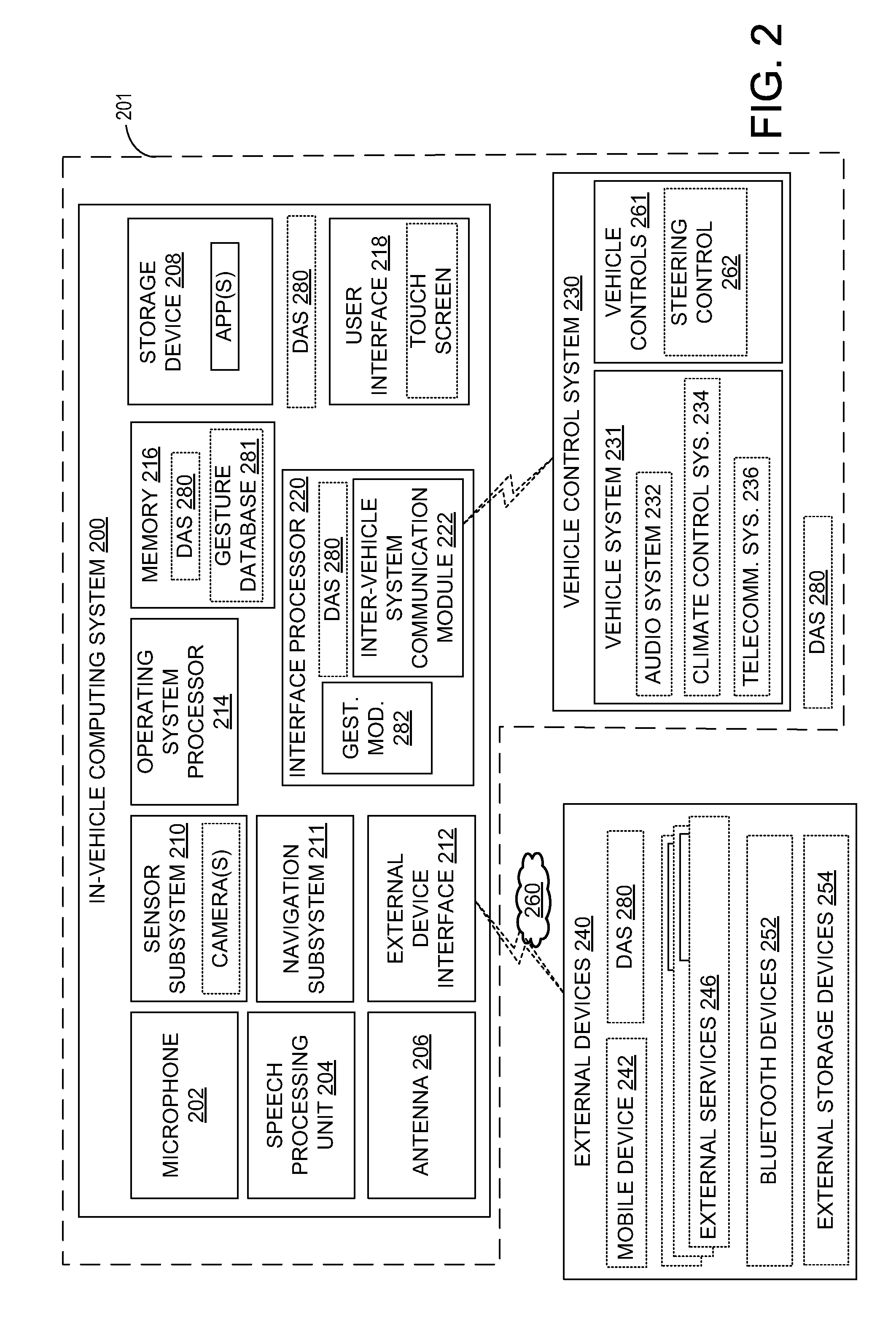
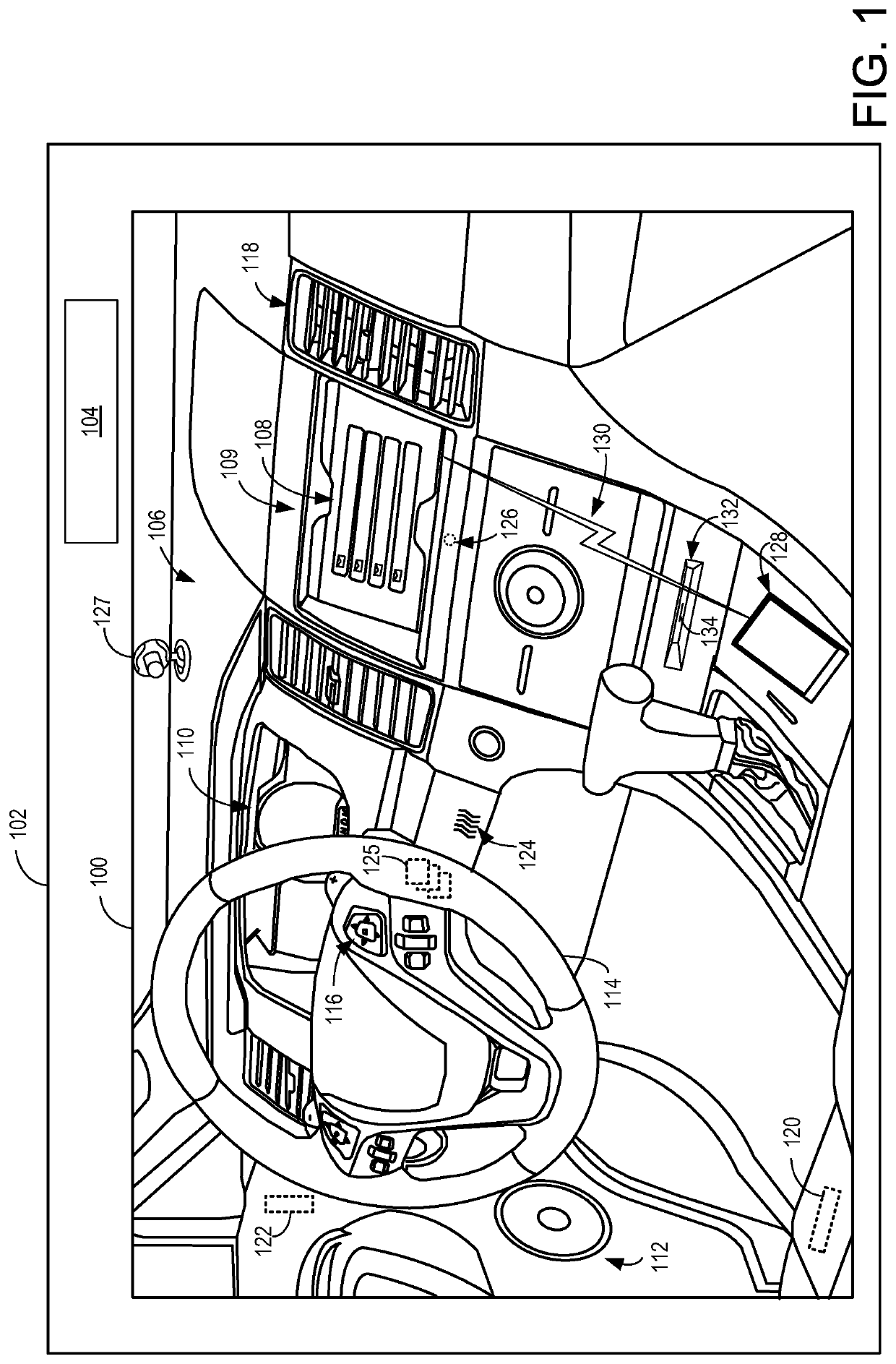
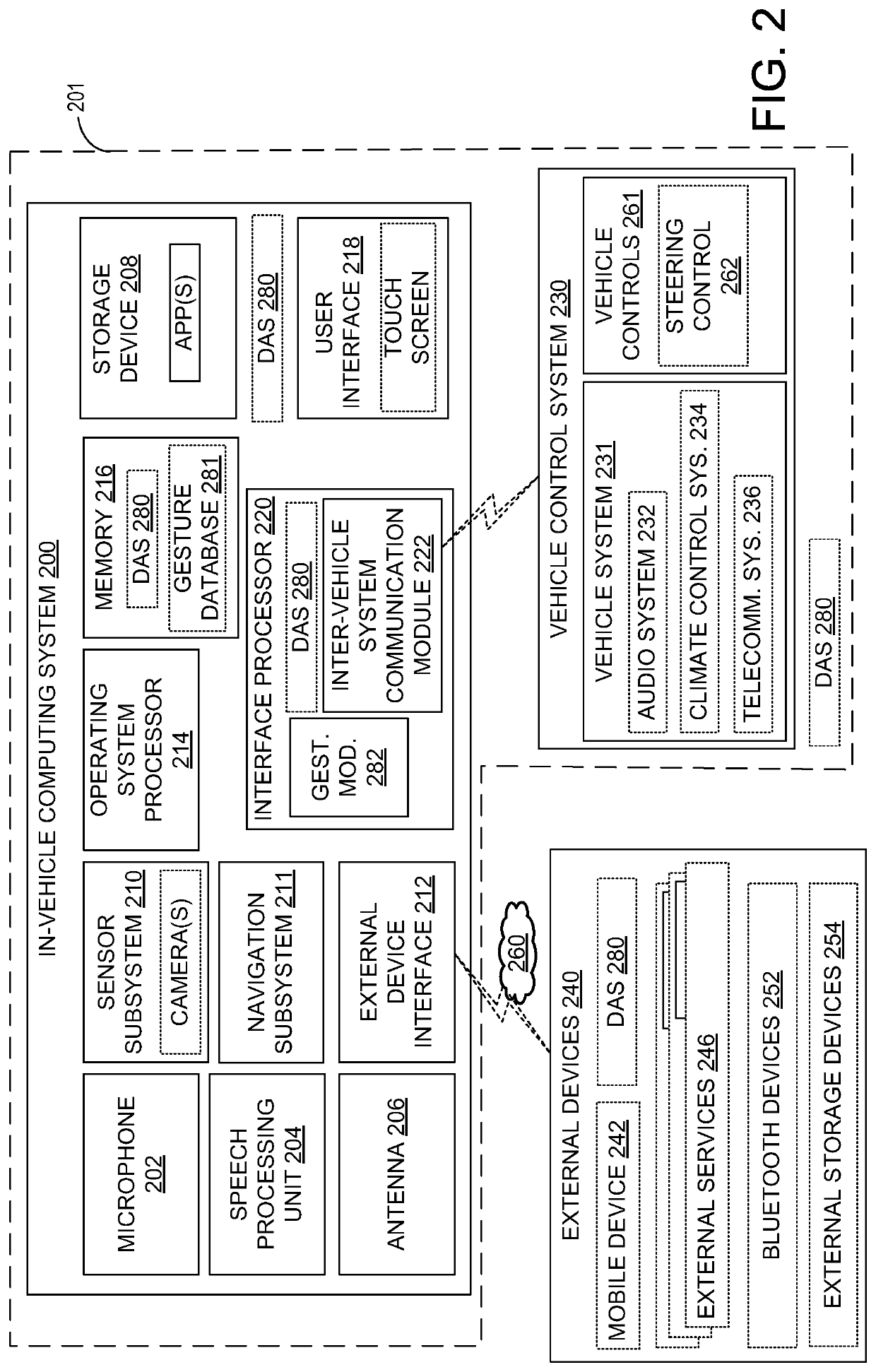
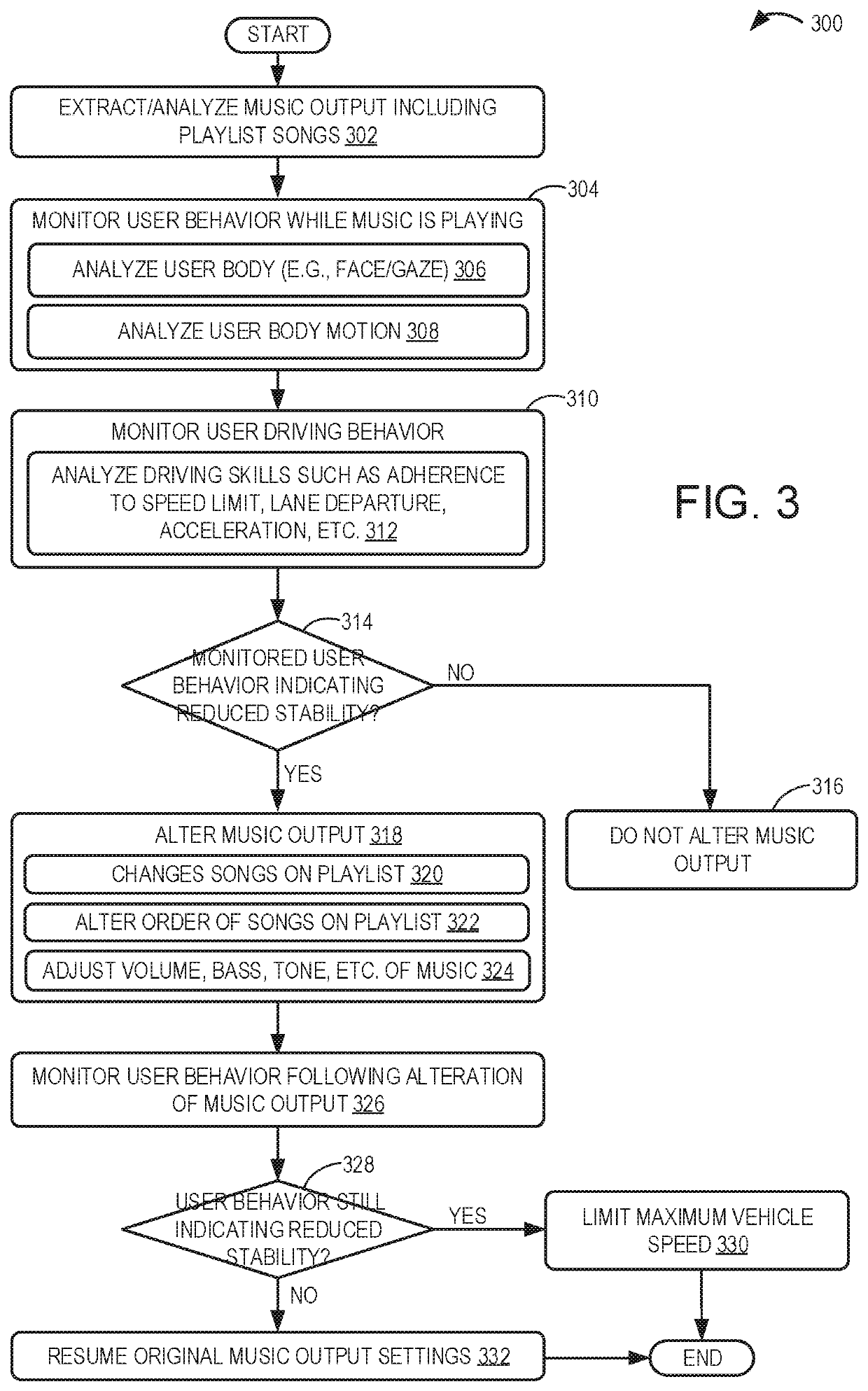
Driver assistance system
ActiveUS20150053066A1Low cognitive stateDestabilizeElectrophonic musical instrumentsDashboard fitting arrangementsDriver/operatorComputer science
Methods are provided for adjusting a music output of a vehicle audio system based on driver movements performed while listening to the music. In one embodiment, a music output of a vehicle infotainment system is adjusted responsive to monitored user behavior inside a vehicle, the monitored user behavior manifesting a user mood. In another embodiment, the music output is adjusted based on each of a user mood and a control gesture, wherein both the user mood and the gesture are identified based on user information gathered from vehicle biometric sensors and cameras while music is playing inside the vehicle.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
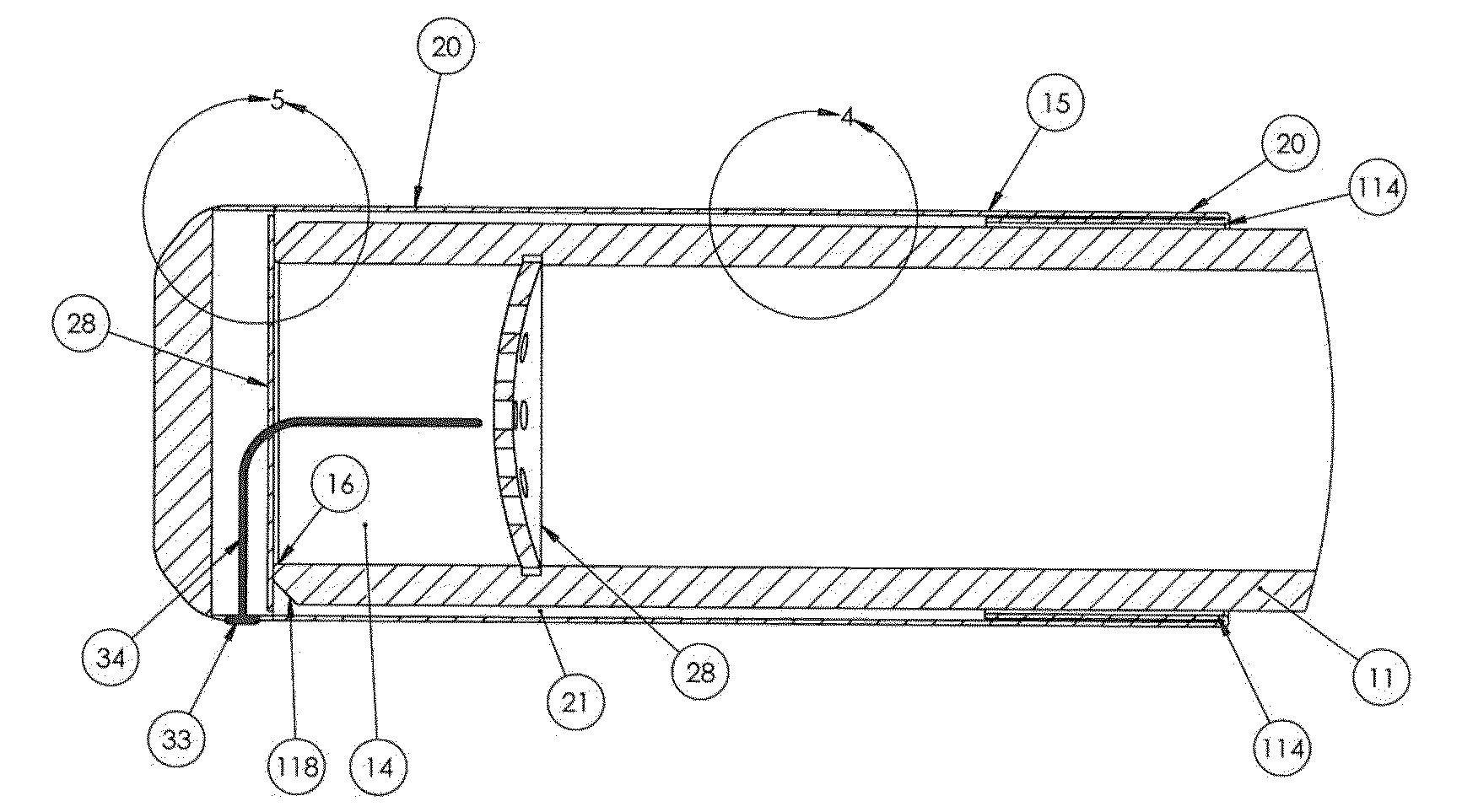
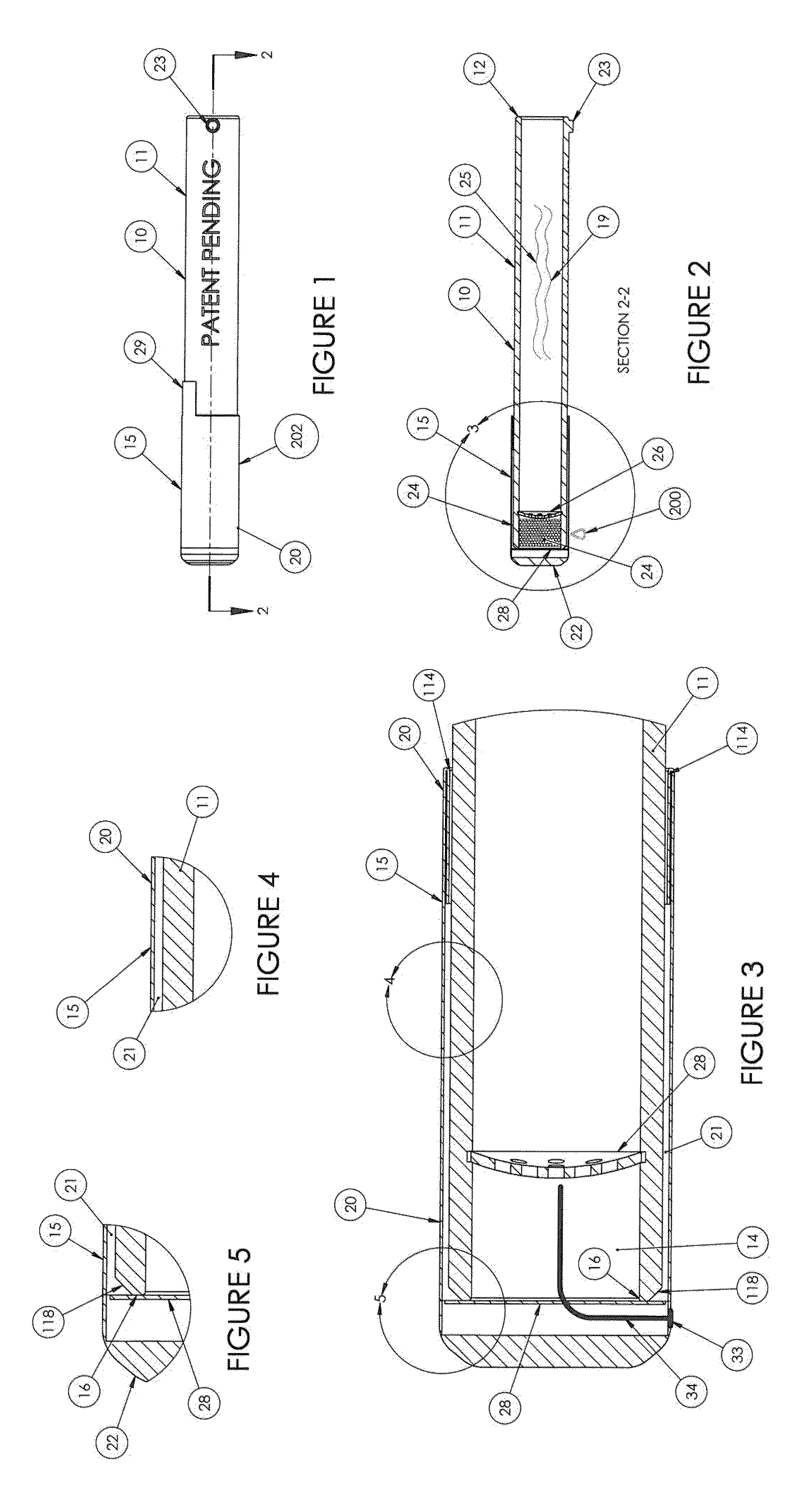
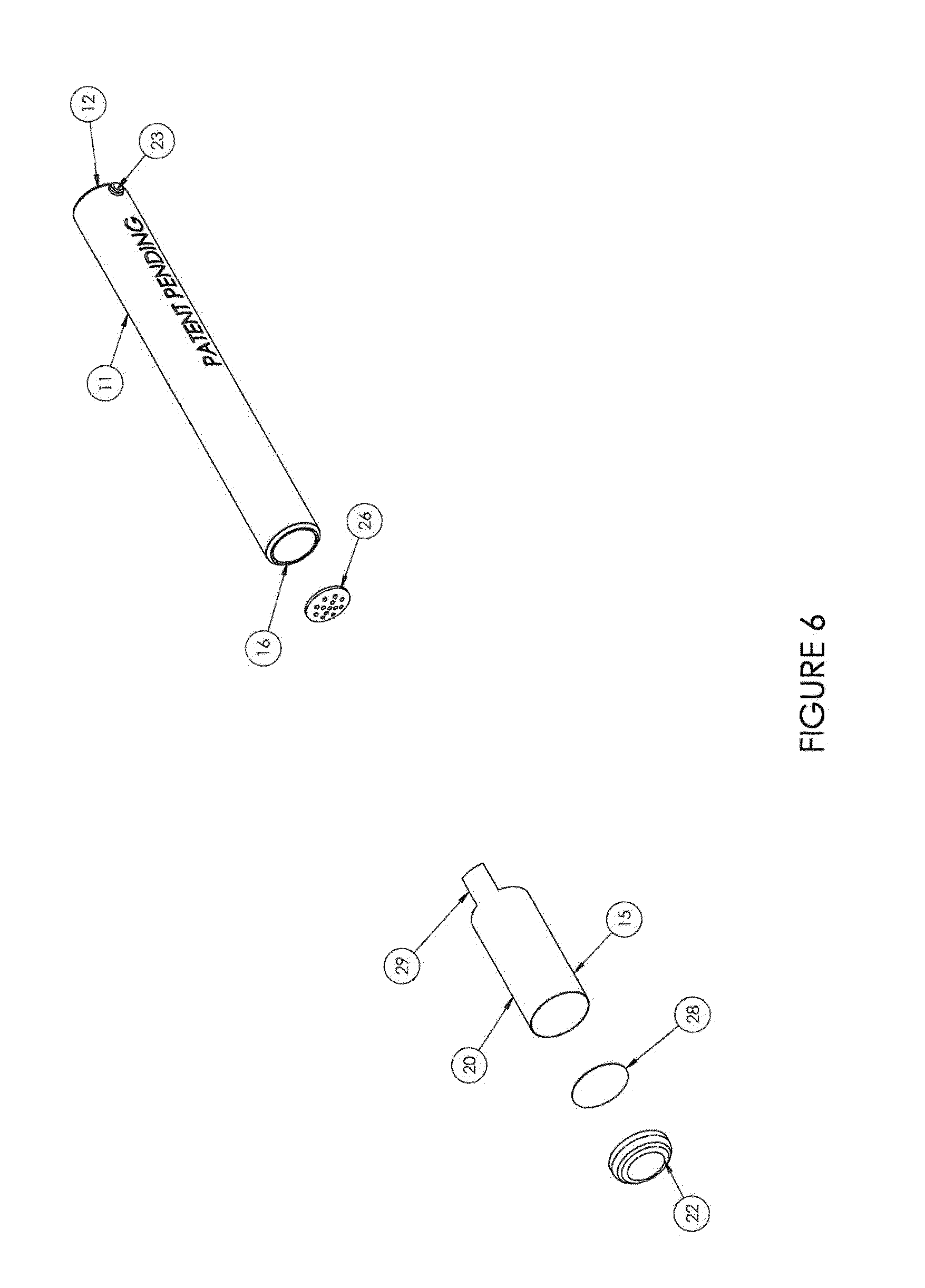
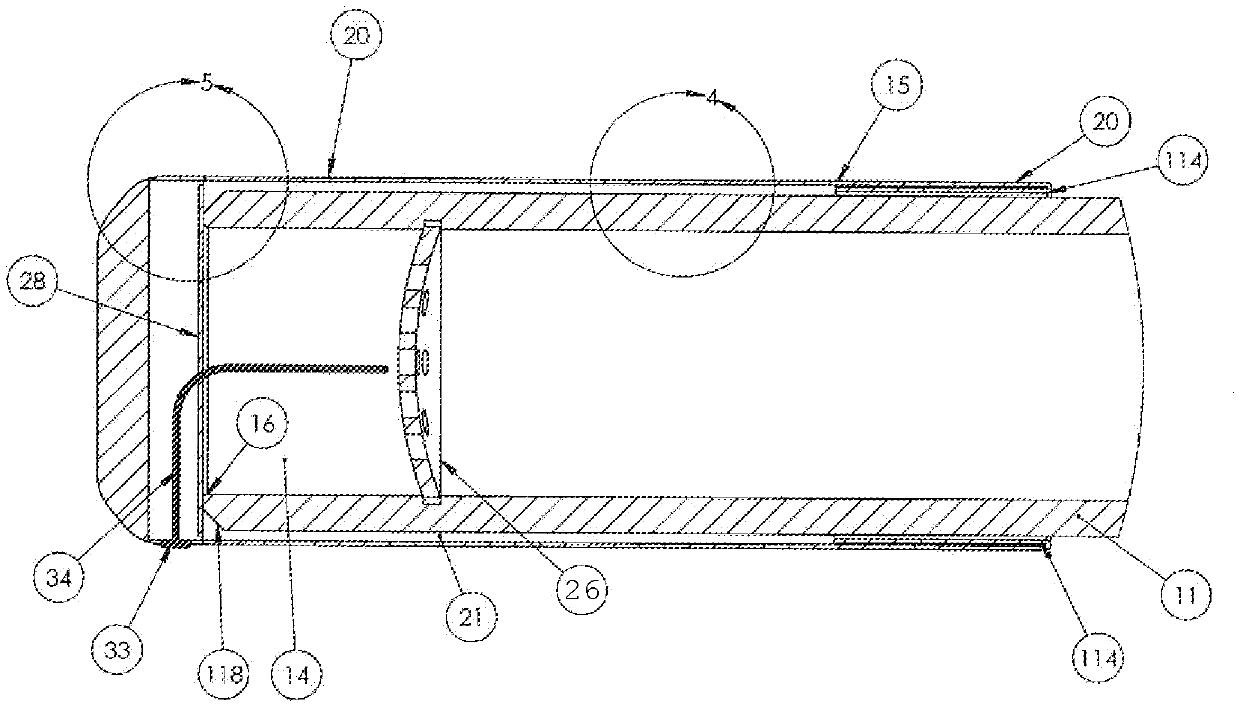
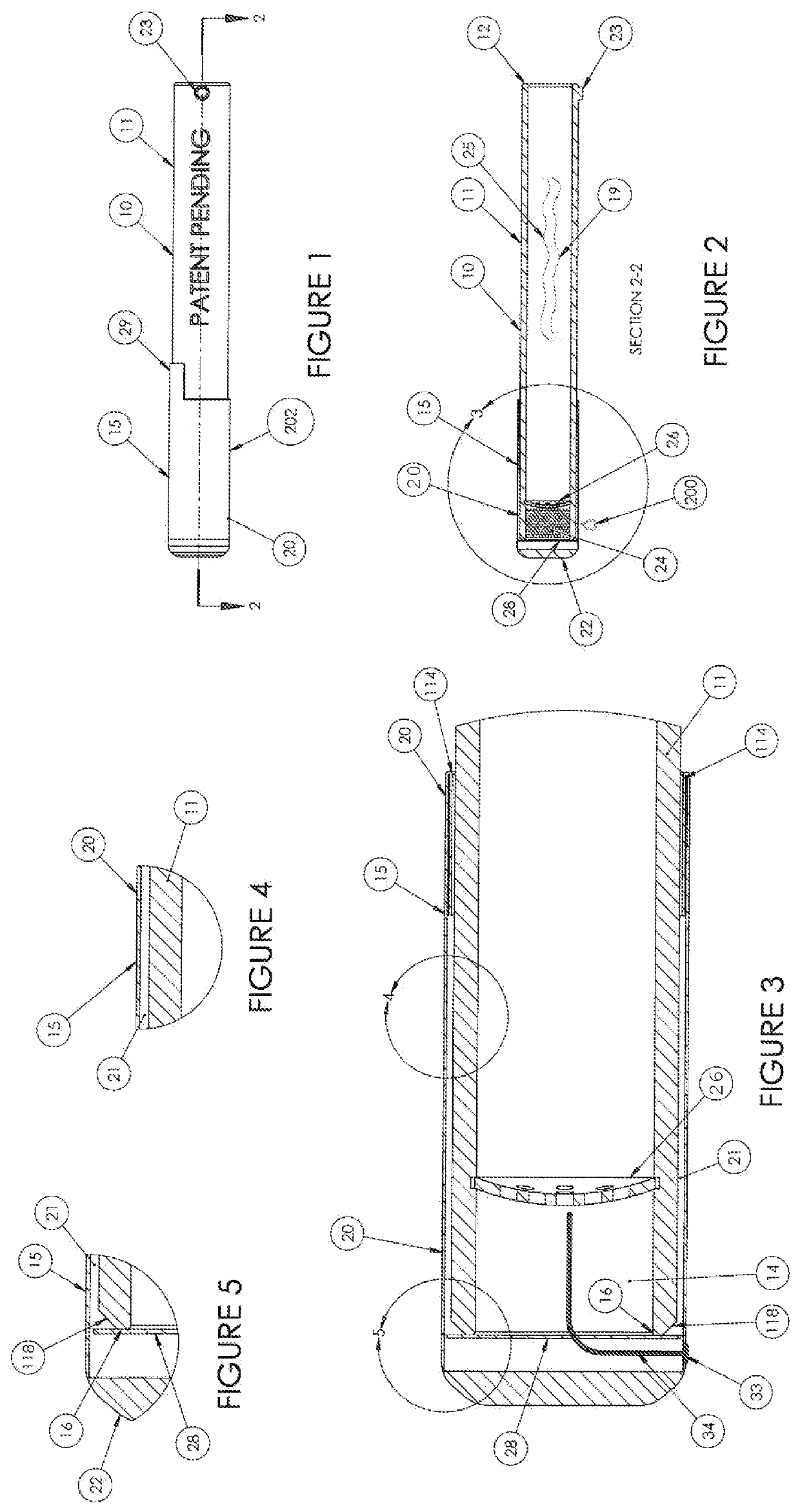
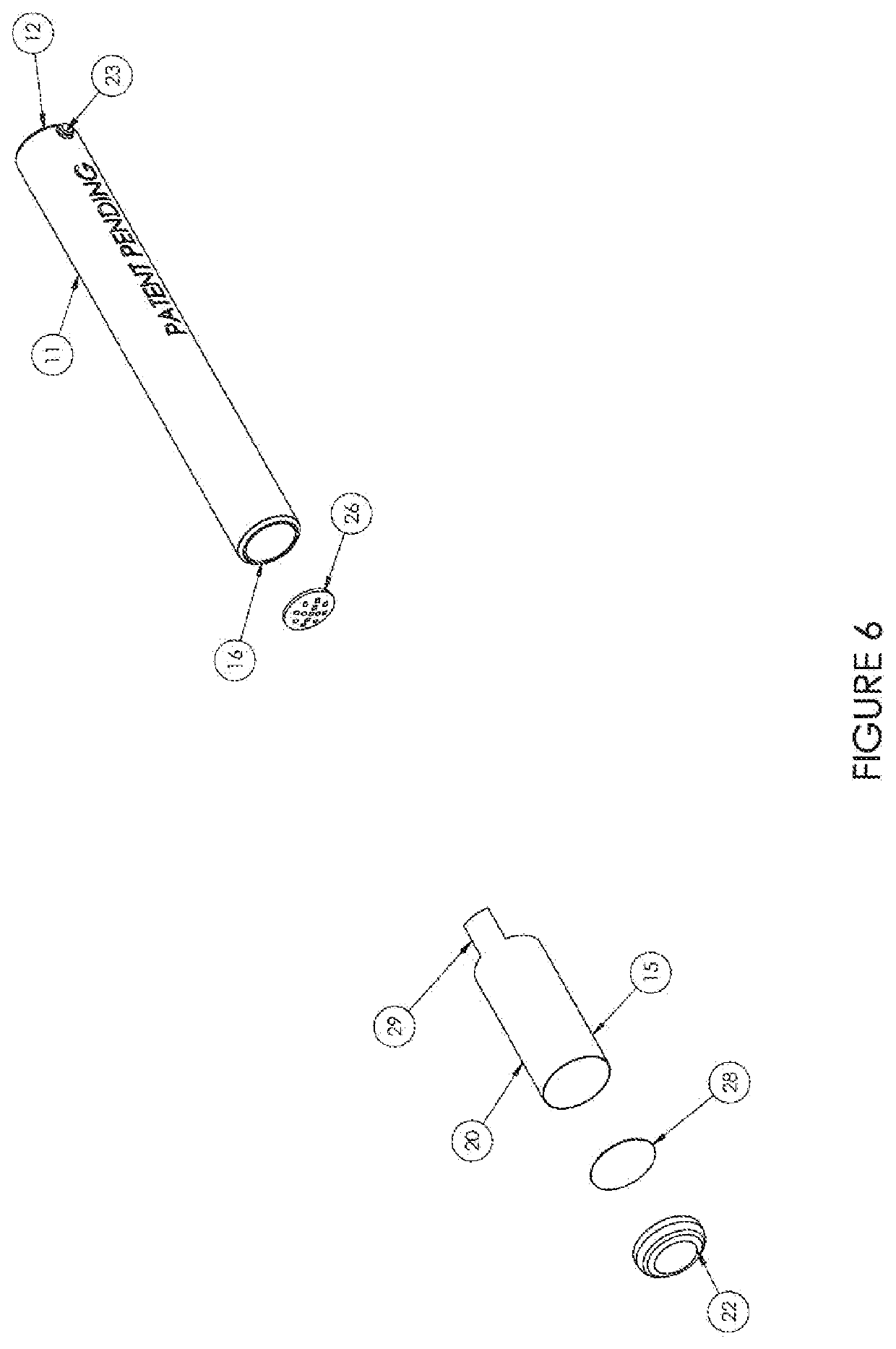
Tubular Volatizing Device
ActiveUS20140186015A1Reduce preparation timeDecreases warm up timeMedical devicesTobacco devicesEngineeringMultiple function
Owner:BREIWA III GEORGE R +2
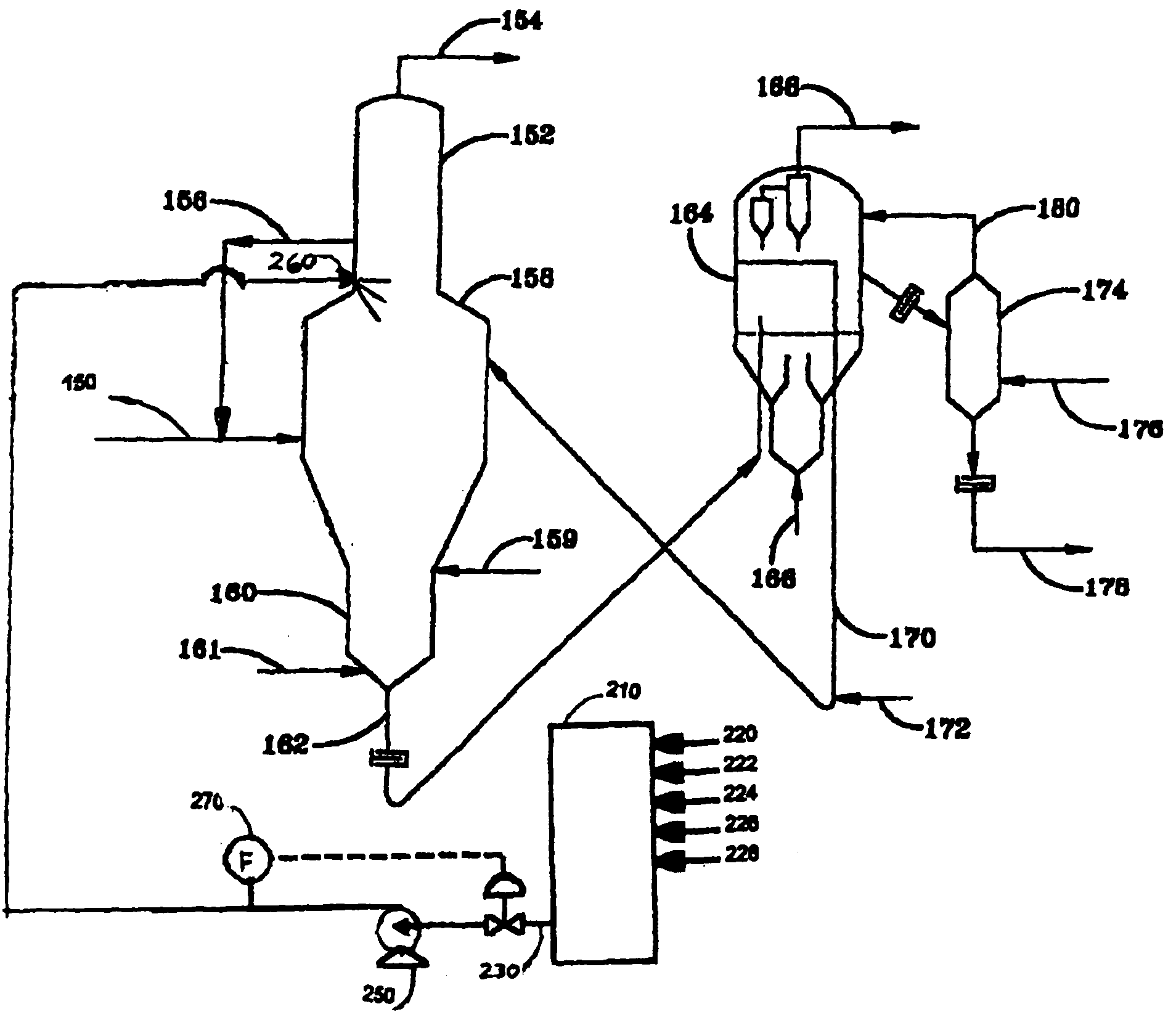
System and Method for Introducing an Additive into a Coking Process to Improve Quality and Yields of Coker Products
InactiveUS20090152165A1Promotes cokingImprove cokingThermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyBoiling pointTar
Gas oil components, coking process recycle, and heavier hydrocarbons are cracked or coked in the coking vessel by injecting an additive into the vapors of traditional coking processes in the coking vessel. The additive contains catalyst(s), seeding agent(s), excess reactant(s), quenching agent(s), carrier(s), or any combination thereof to modify reaction kinetics to preferentially crack or coke these components. The quenching effect of the additive can be effectively used to condense the highest boiling point compounds onto the catalyst(s), thereby focusing the catalyst exposure to these target reactants. With a catalyst to crack these highest boiling point materials, this mechanism can effectively increase the catalyst's selectivity, thereby increasing its efficiency and reducing catalyst requirements and costs. Selective, catalytic conversion of the highest boiling point materials in the coking process product vapors (coker recycle and / or ‘heavy tail’ of the heavy coker gas oil) may be accomplished with an exemplary embodiment of the present invention in varying degrees. Exemplary embodiments of the present invention can also provide methods to control the (1) coke crystalline structure and (2) the quantity and quality of volatile combustible materials (VCMs) in the resulting coke. Pet coke from this process may have unique characteristics with substantial utility.
Owner:ETTER ROGER G
Flocculant Composition For Dewatering Solids Laden Slurries
ActiveUS20110094968A1Minimize any propensityReducing suspended fine solidSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningOther chemical processesChemistryPolymer
Owner:PROFILE PRODS
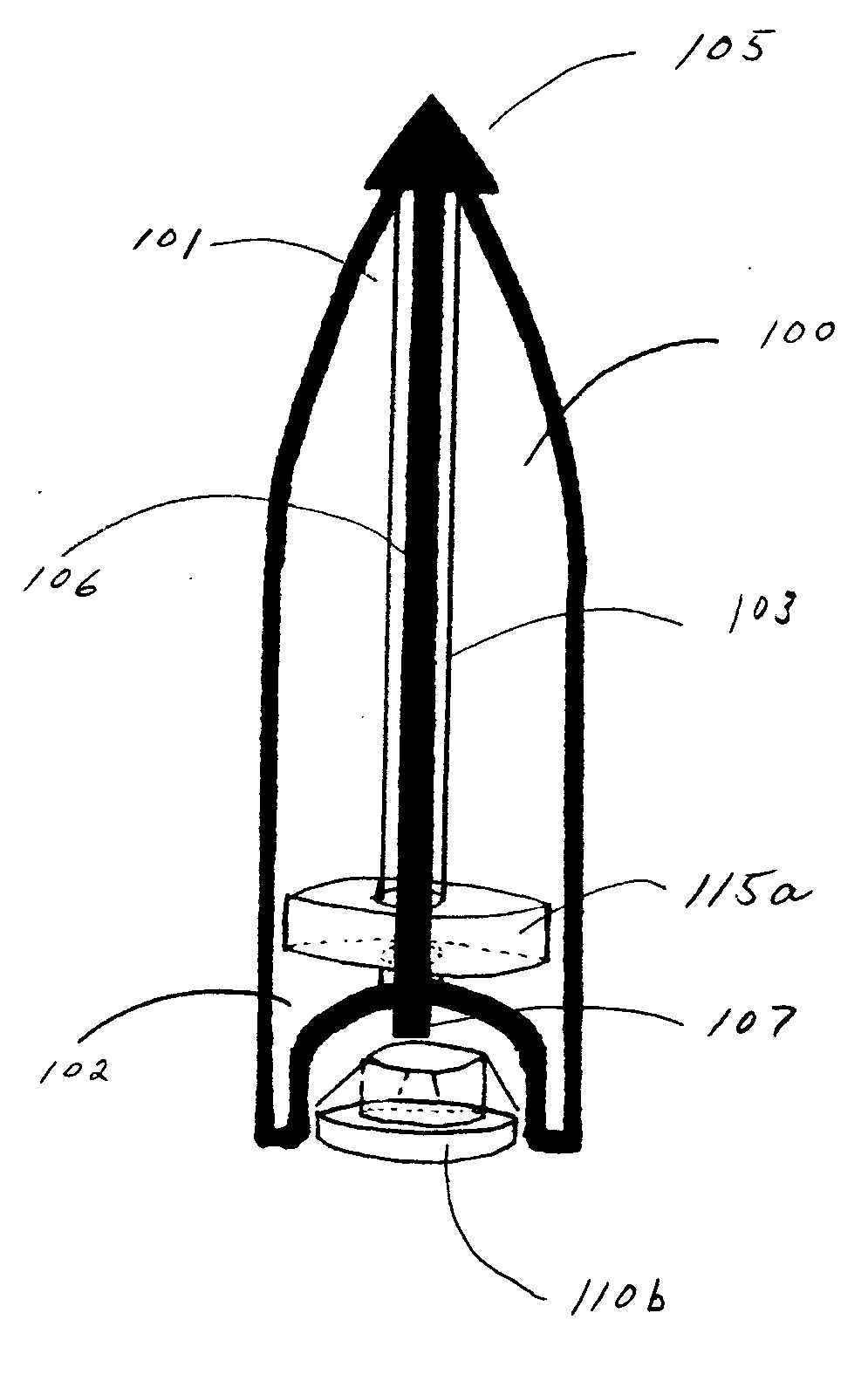
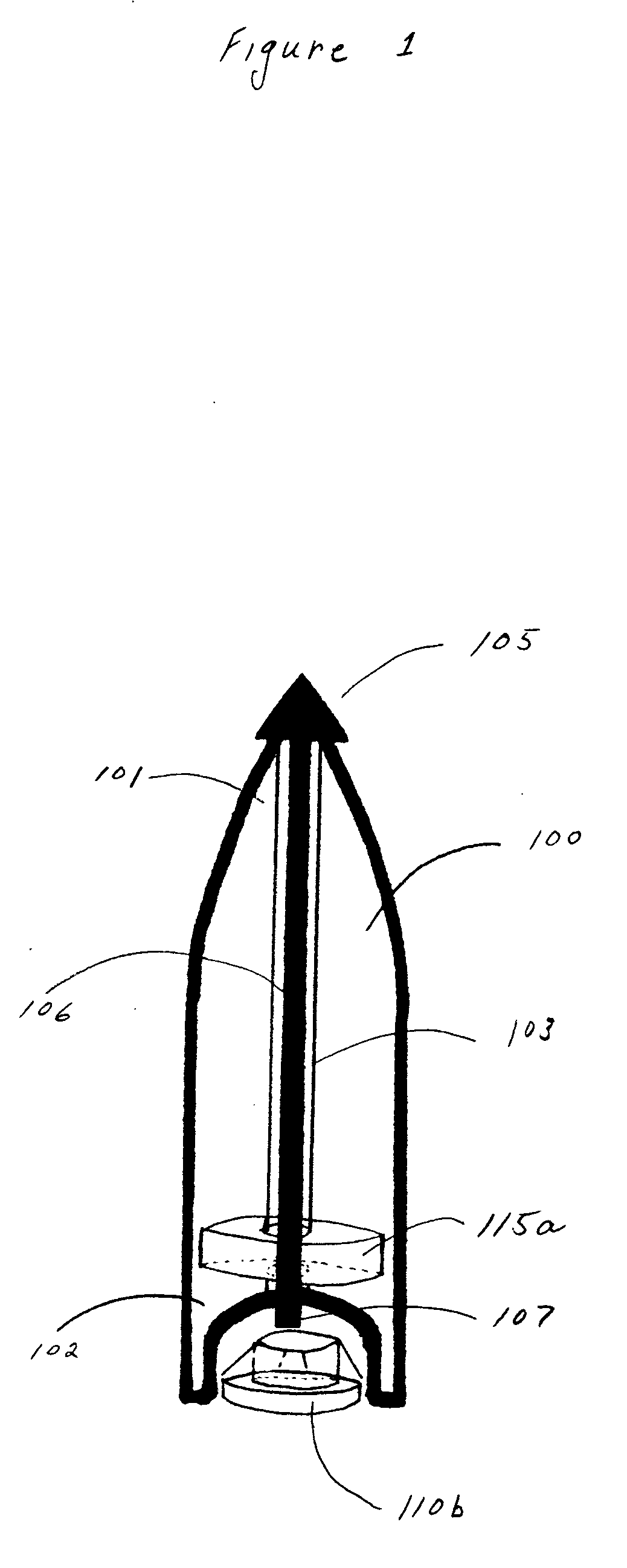
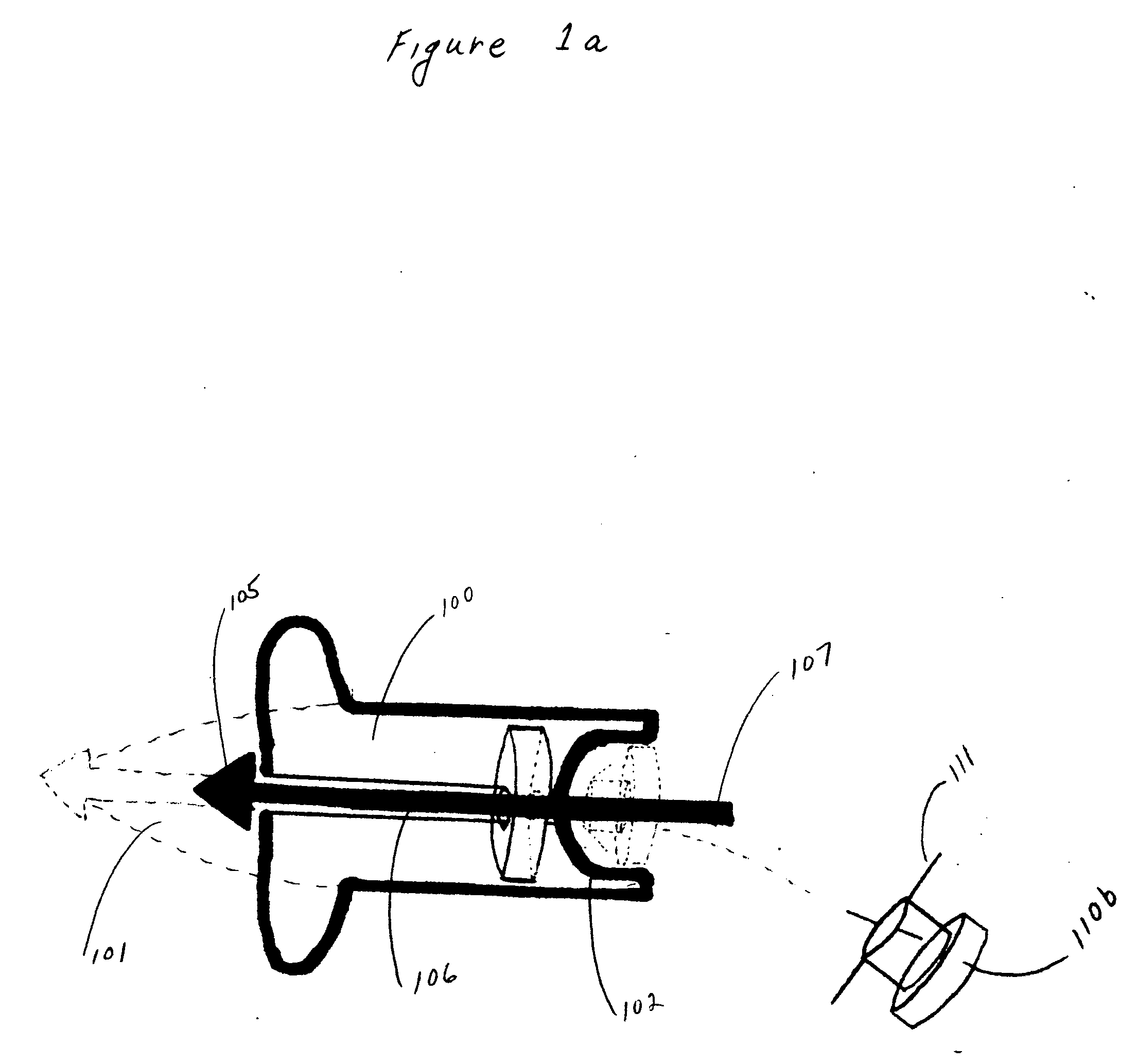
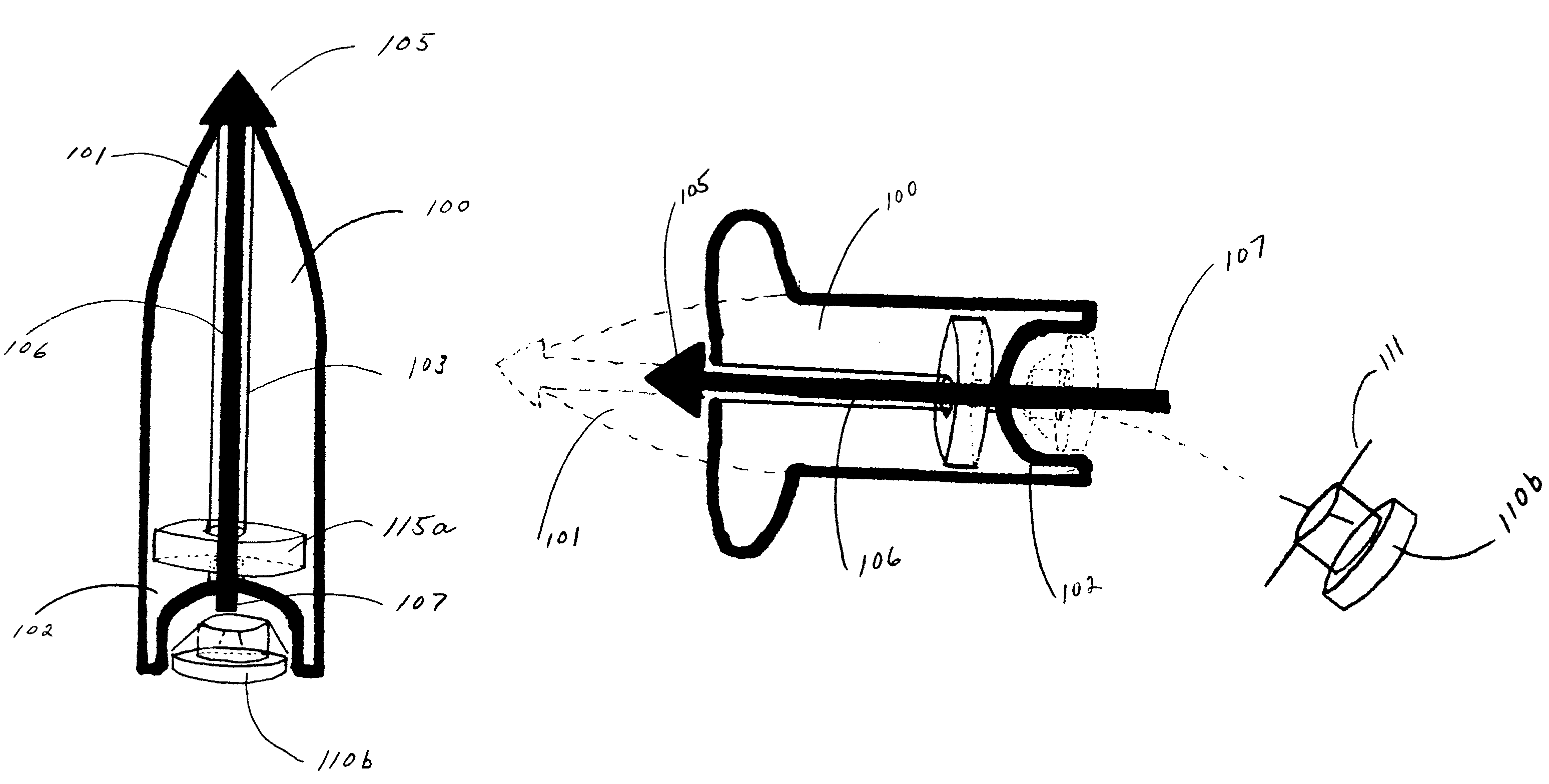
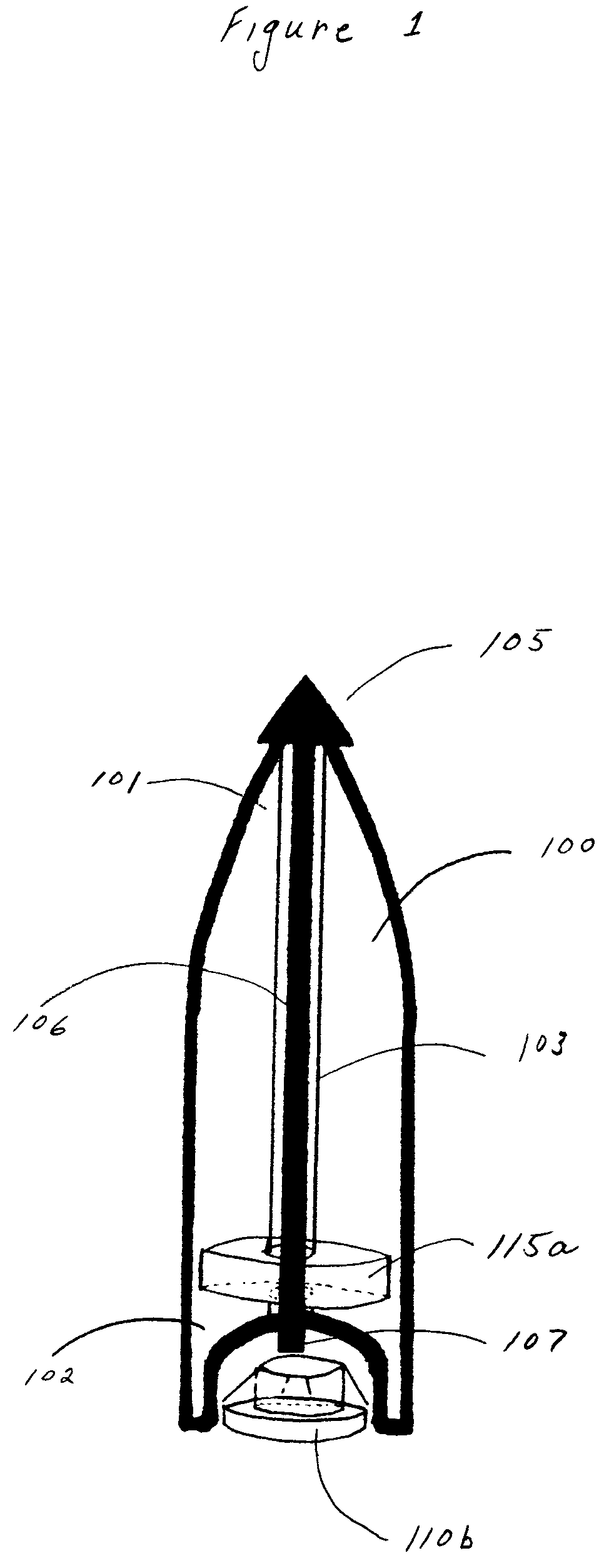
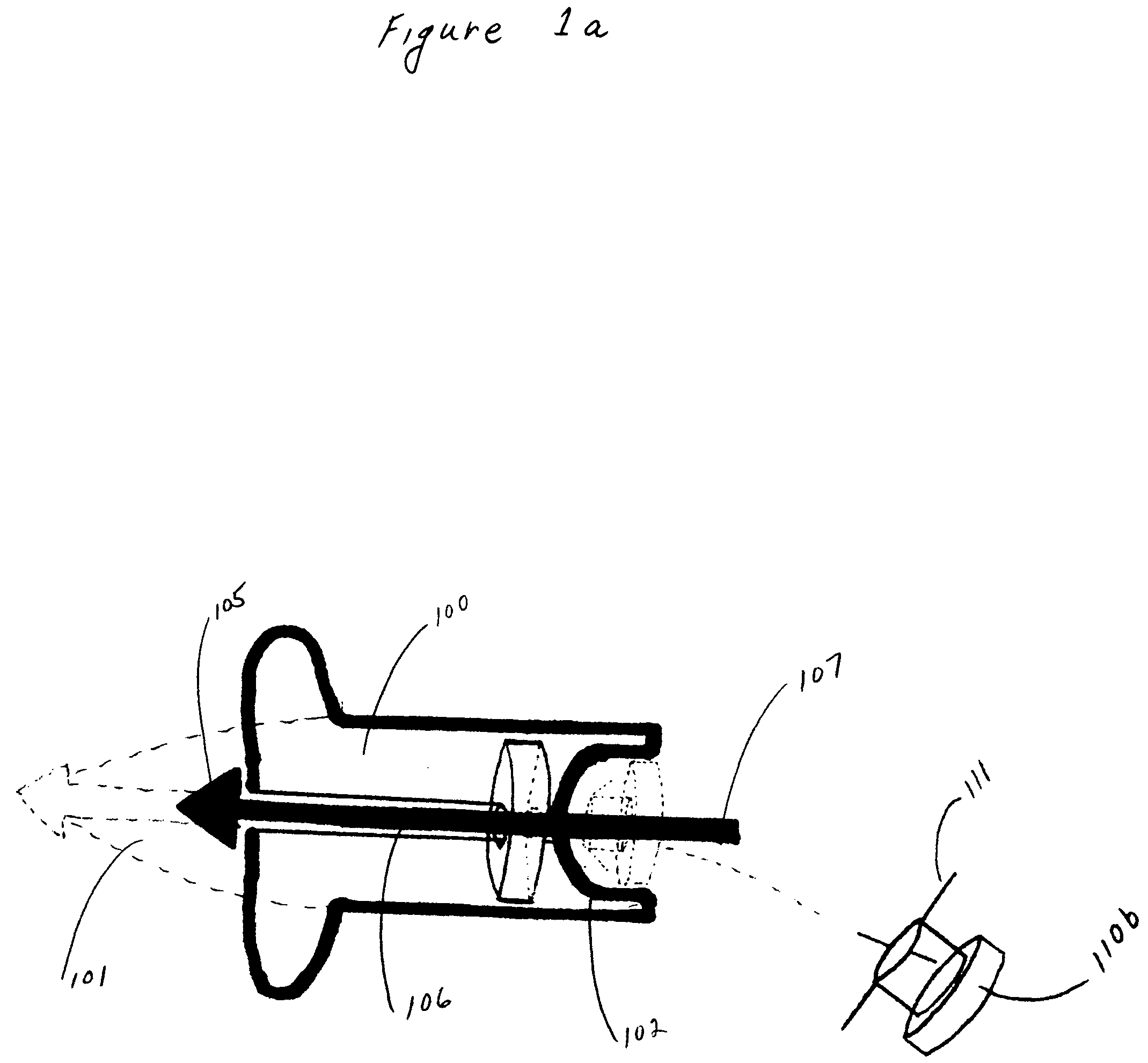
Bullet identification and tracking device
ActiveUS20060213105A1Find quicklyWound quicklyAmmunition projectilesAmmunition testingEngineeringIdentification device
An identification and tracking device (110b) for use in combination with a firearm bullet (100) comprising a means for detaching the device (110b) from the bullet (100) during penetration of the target. In this manner, the tracking device (110b) and / or identification device (110b) will be attached to an object when the bullet (100) penetrates the object.
Owner:CUGLIARI GREGORY ANTHONY
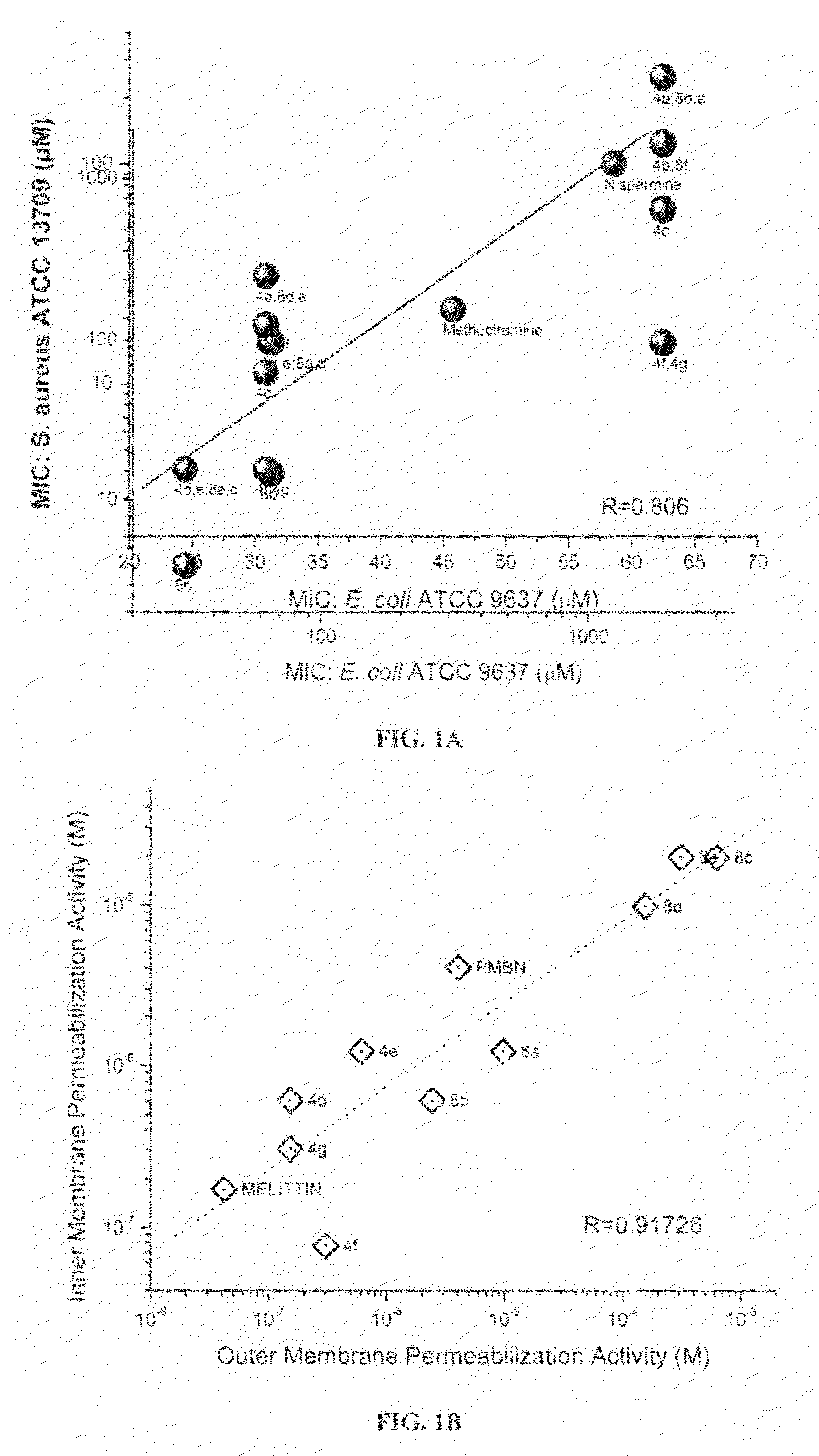
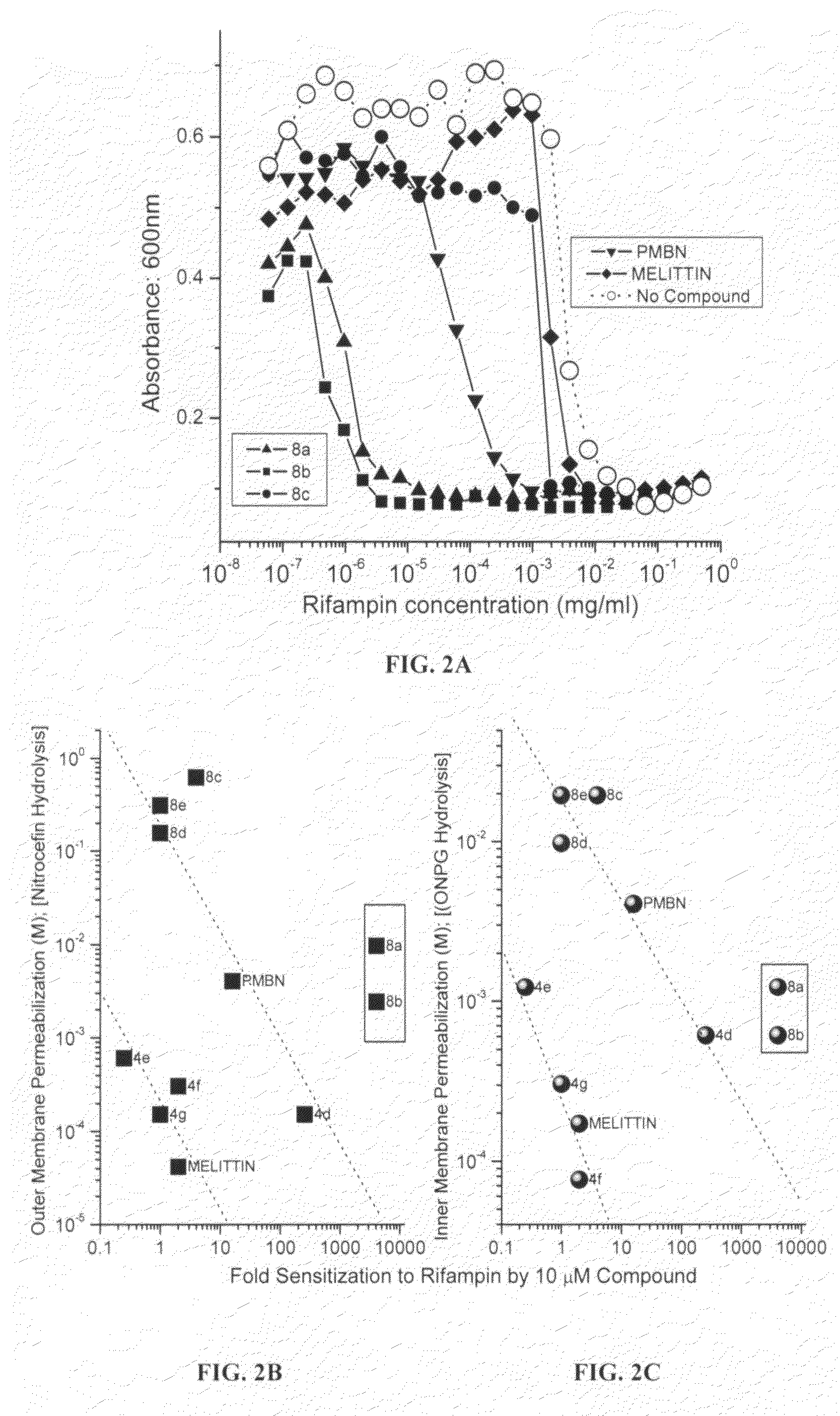
Polyamines and their use as antibacterial and sensitizing agents
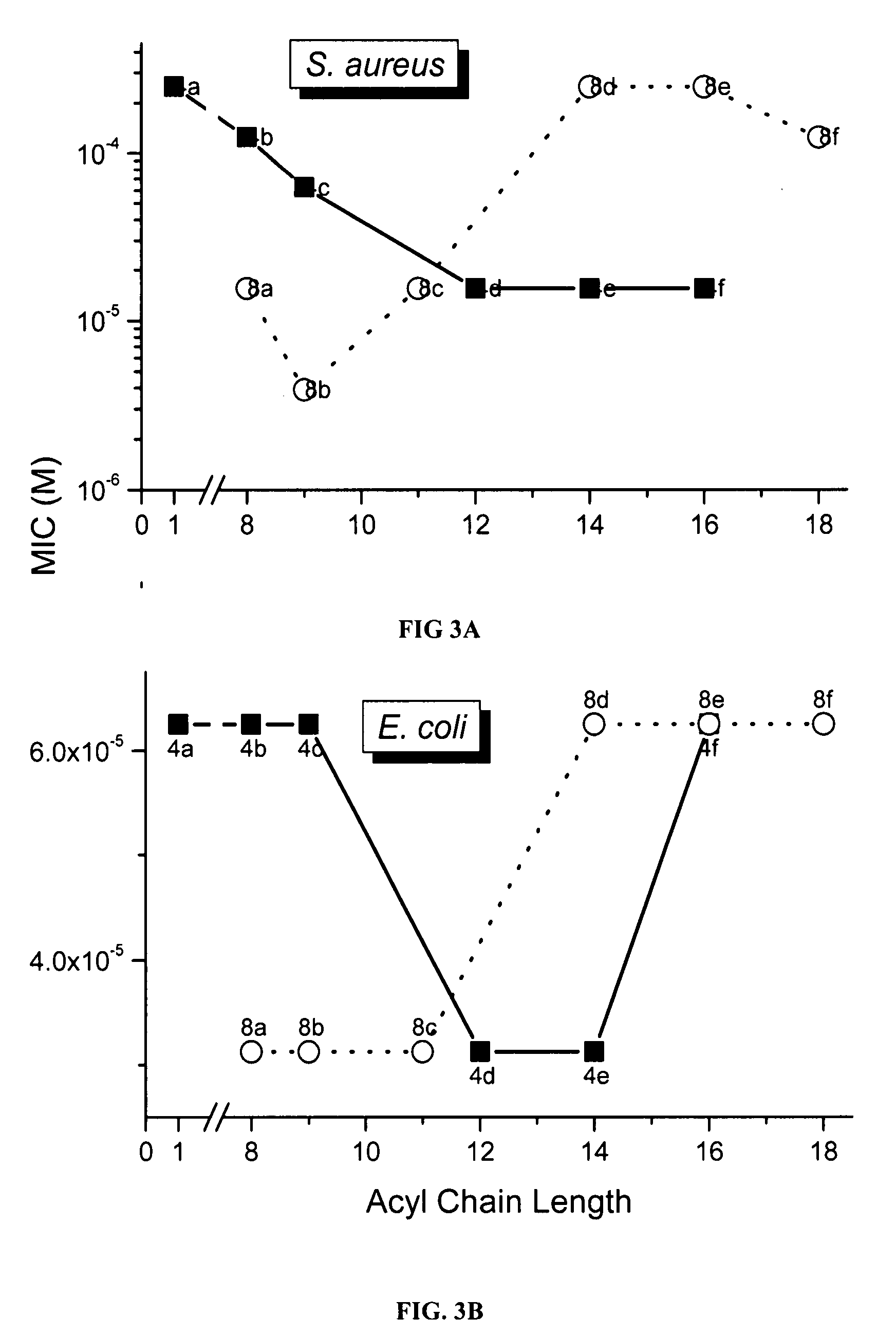
InactiveUS20070197658A1High activityHigh propensityBiocideOrganic chemistryEscherichia coliChain length
Polyamines with varying chain-lengths were evaluated for antimicrobial activity in order to test the hypothesis that these bis-cationic amphipathic compounds may also bind to and permeabilize intact Gram negative bacterial membranes. The compounds were found to possess significant antimicrobial activity and mediated via permeabilization of bacterial membranes. Homologated spermine, bis-acylated with C8 or C9 chains was found to profoundly sensitize E. coli to hydrophobic antibiotics such as rifampicin.
Owner:KANSAS UNIV OF
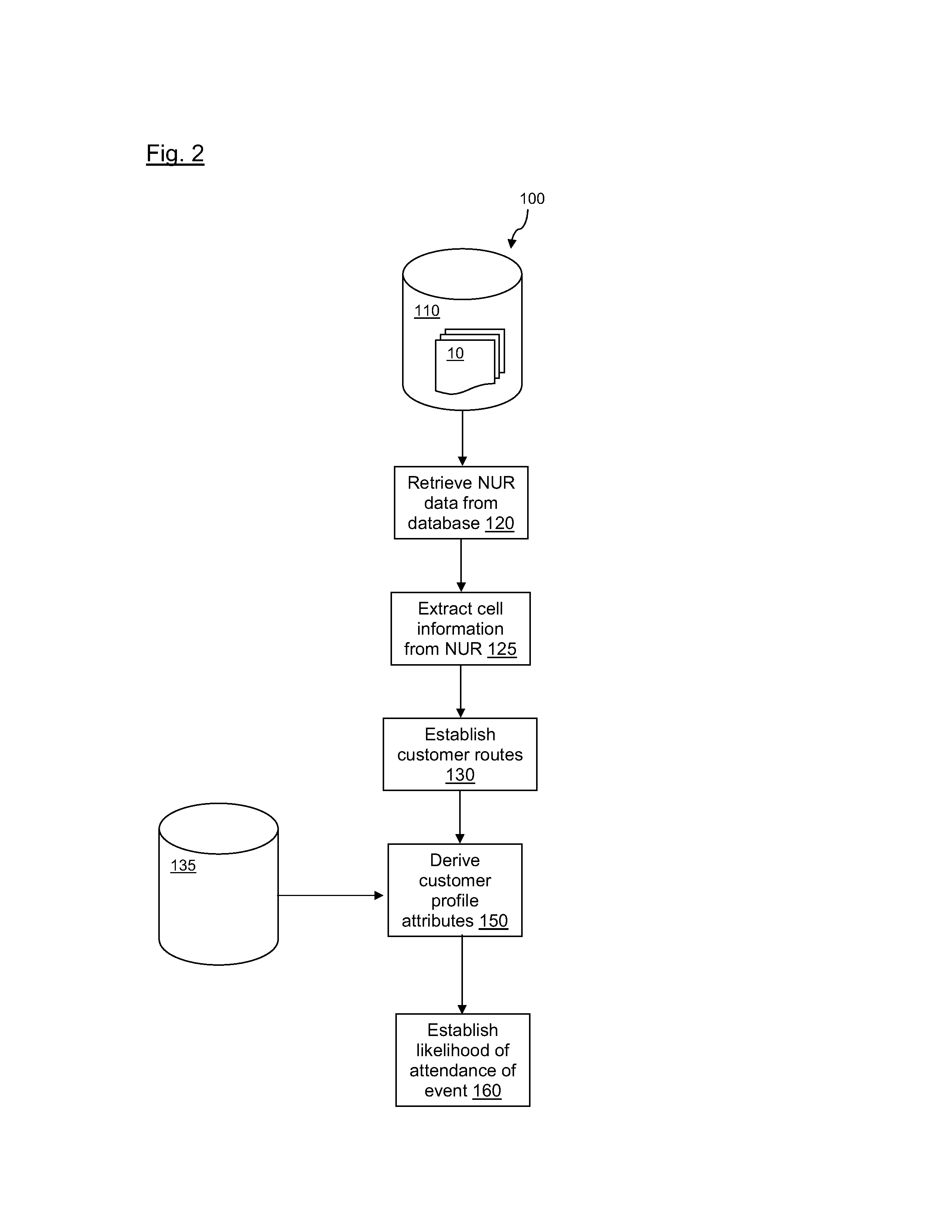
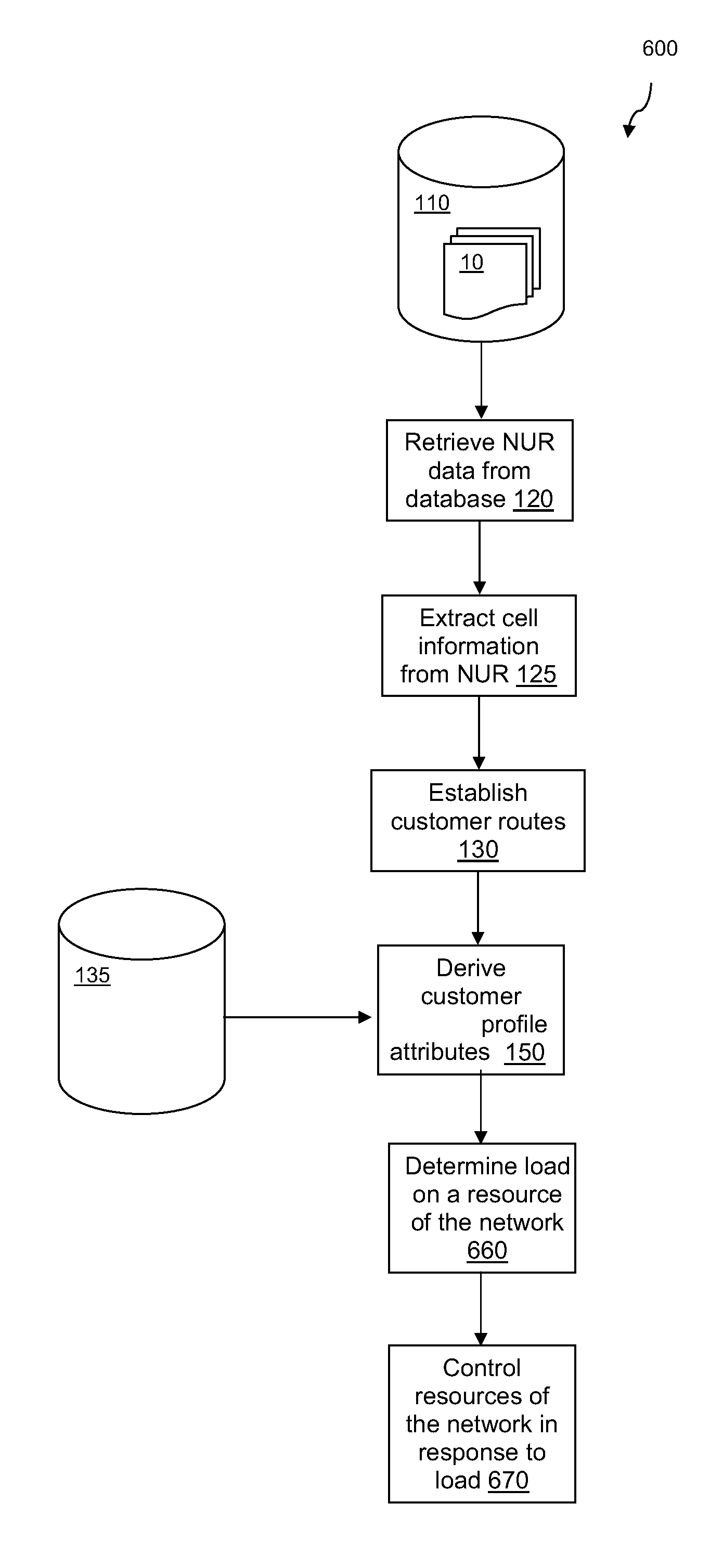
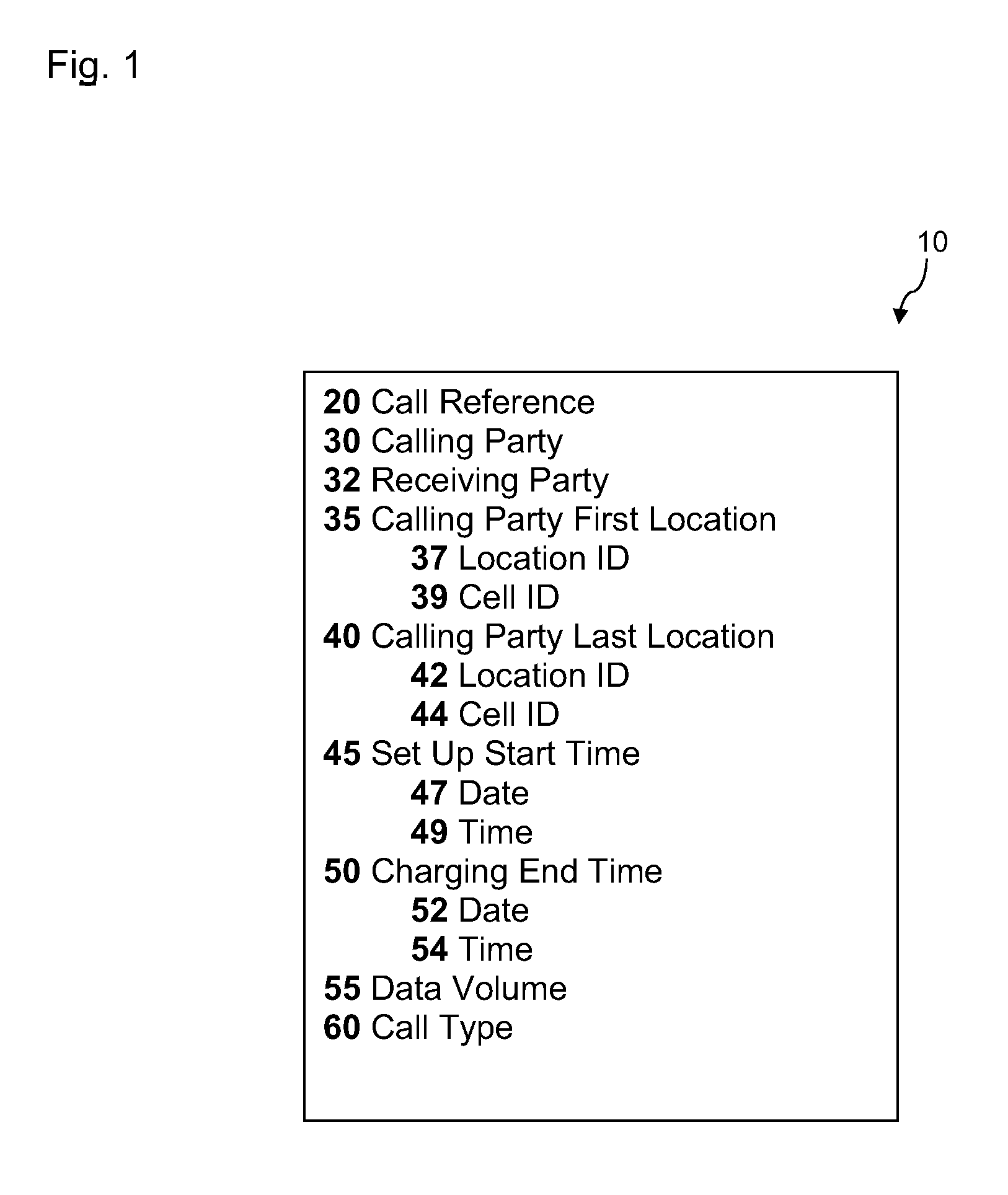
Methods of analysing a cellular network
ActiveUS20130183996A1Precise processPrecise and accurate inferenceNetwork traffic/resource managementLocation information based serviceCarrier signalComputer science
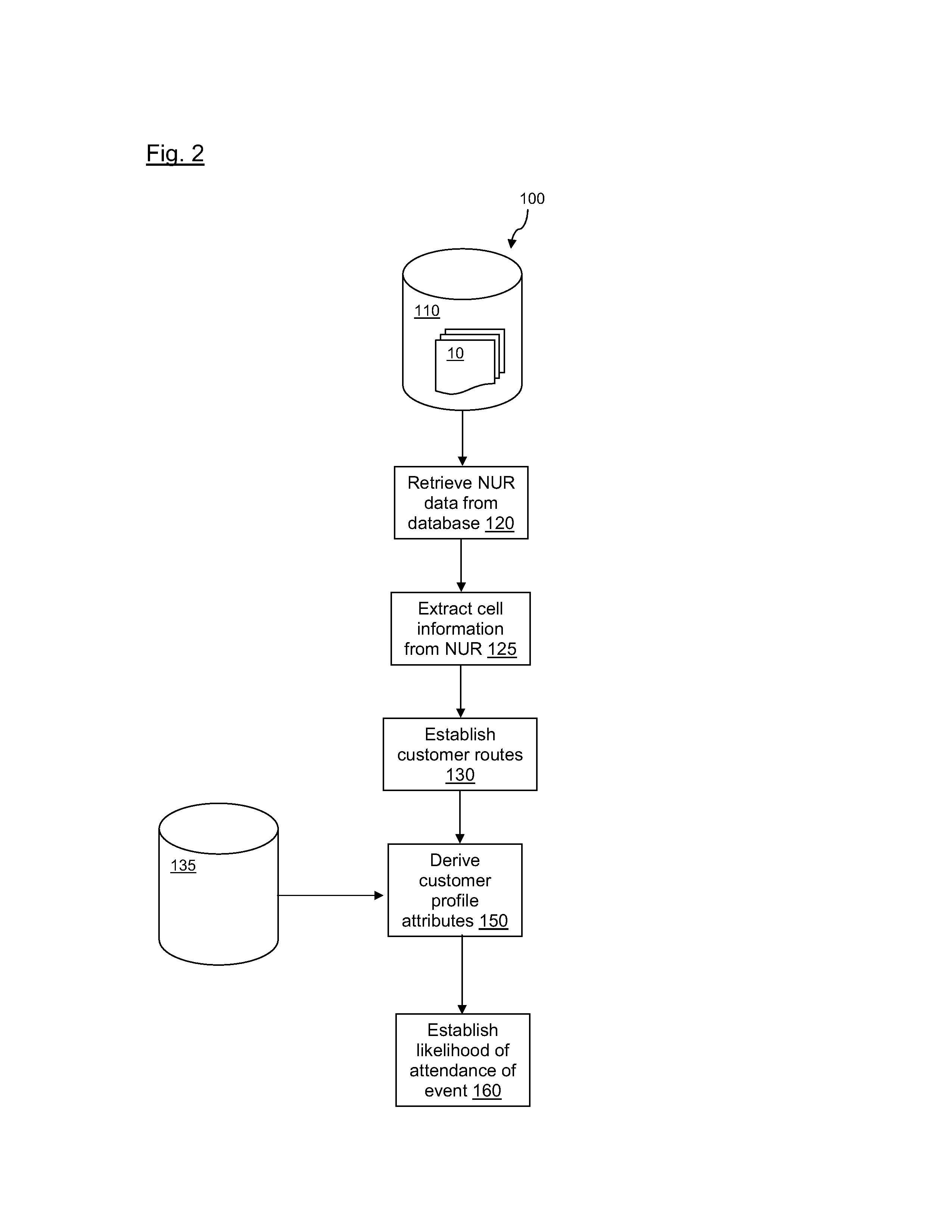
A method of managing a load within a cellular network. The method includes obtaining network usage records from the cellular network; extracting cell information from the network usage records; establishing terminal carrier routes for cellular terminals that have changed location as determined from the extracted cell information; deriving terminal carrier profile attributes for the cellular terminals that have changed location, based on the established terminal carrier routes; determining a load on a resource of the cellular network, based on the established terminal carrier routes and the derived terminal carrier profile attributes; and controlling resources of the cellular network in response to the determined load, so as to manage the load within the cellular network. By combining established terminal carrier routes with derived terminal carrier profile attributes, it is possible to anticipate areas where cellular terminal carriers are likely to be concentrated at specific times during the day and allocate resources accordingly.
Owner:VODAFONE IP LICENSING +1
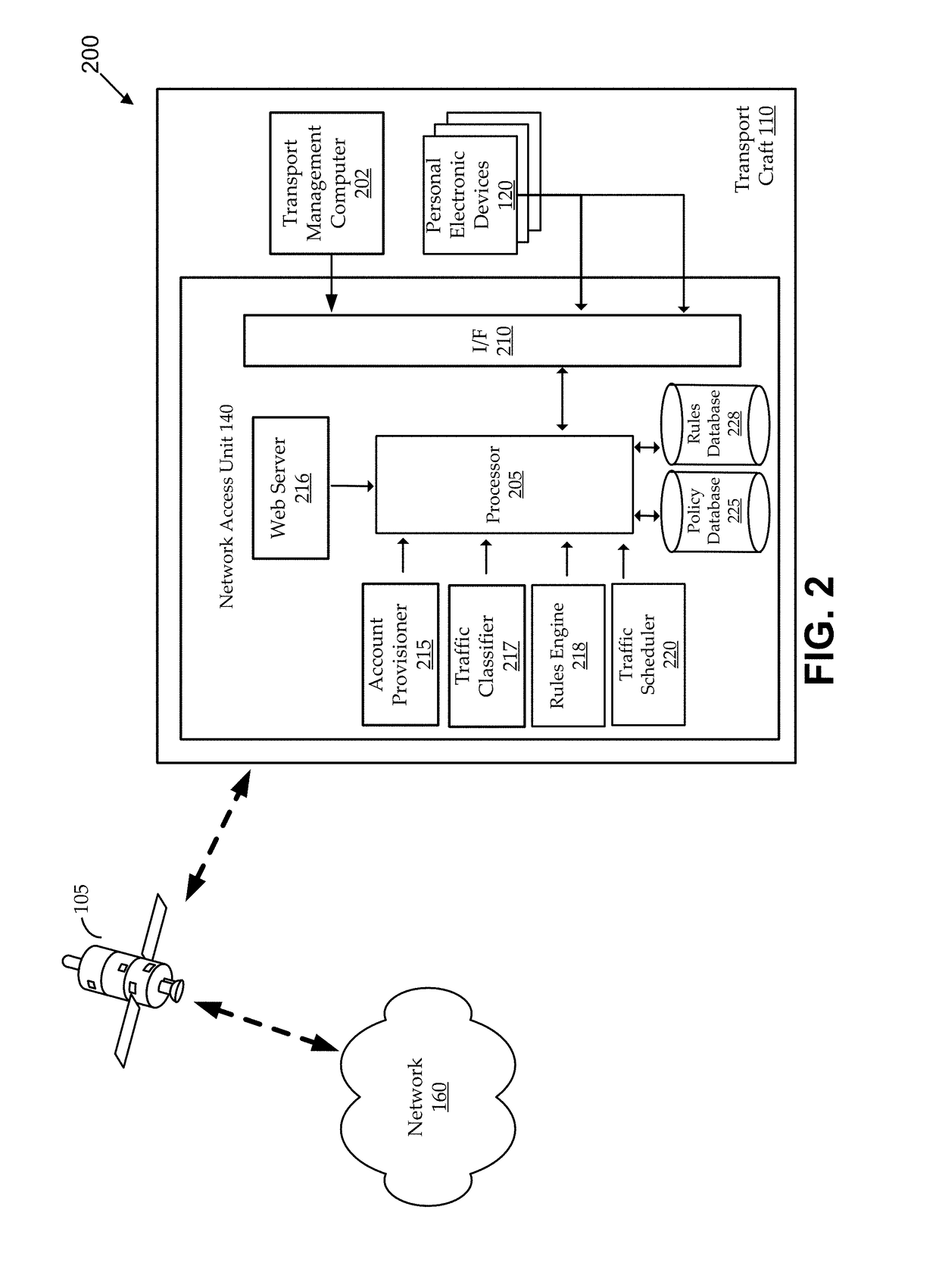
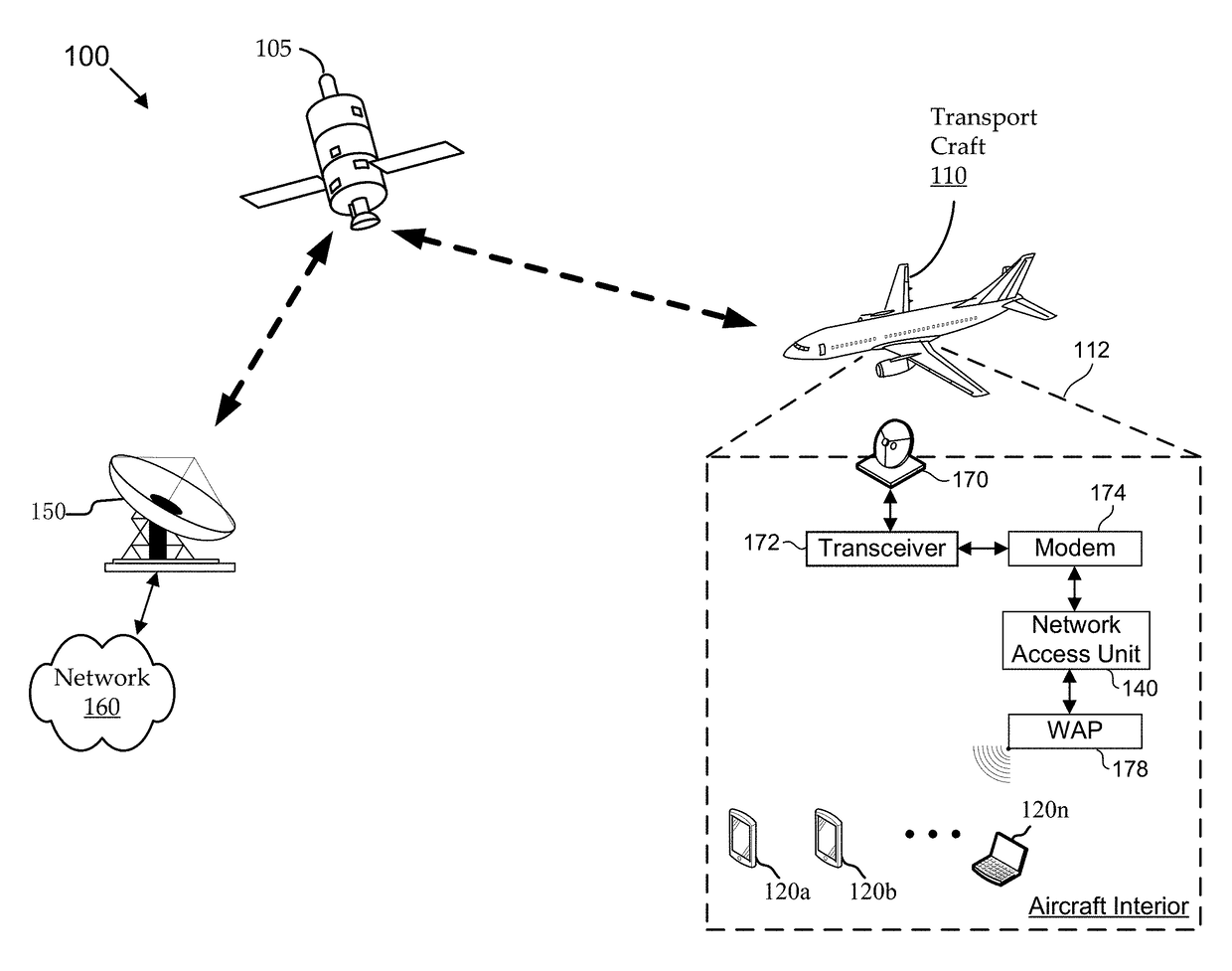
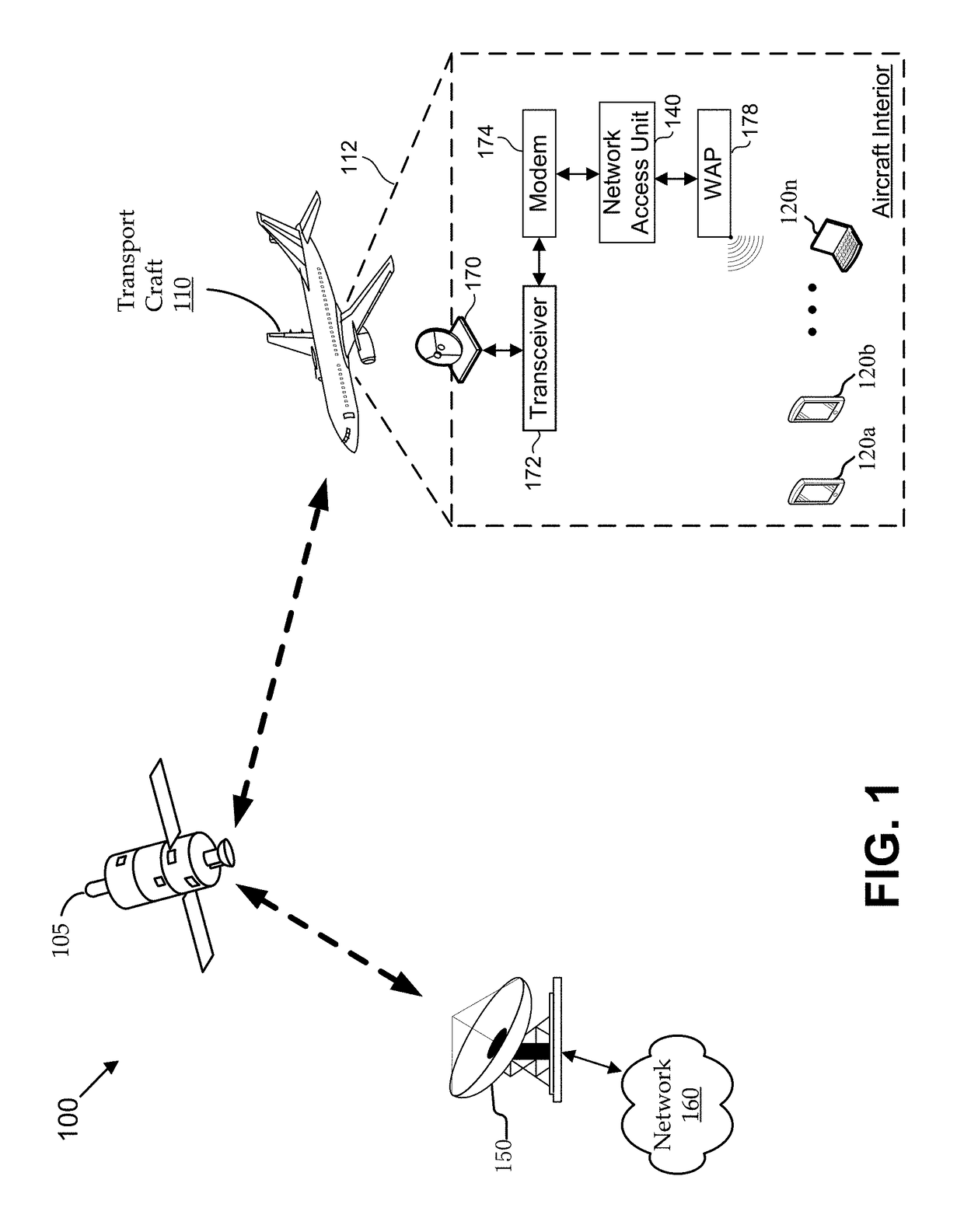
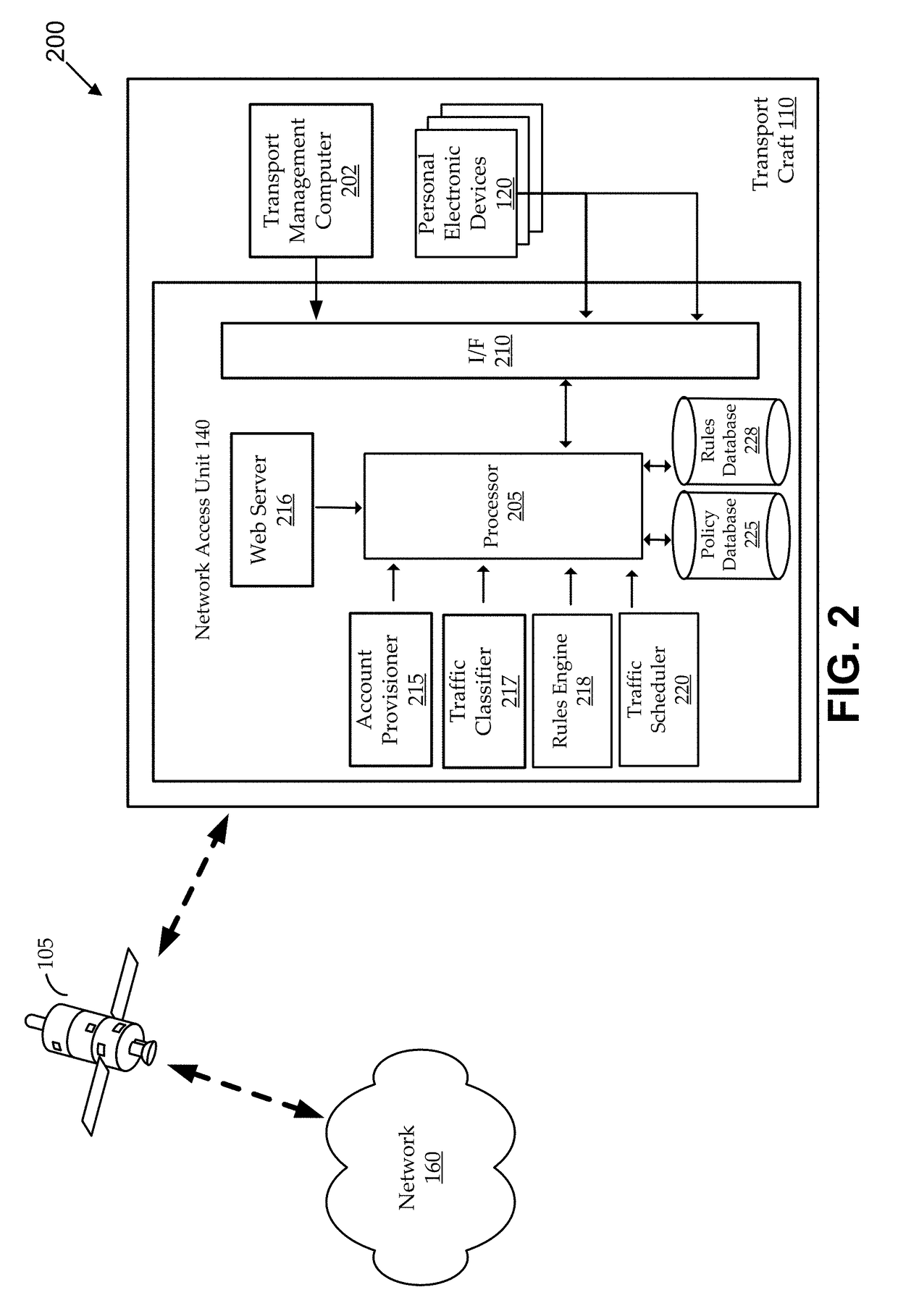
Methods and systems for establishing in-flight network traffic policies for personal electronic devices
ActiveUS20170245298A1High resolutionHigh quality video playbackSubstation equipmentData switching networksTelecommunications linkInternet traffic
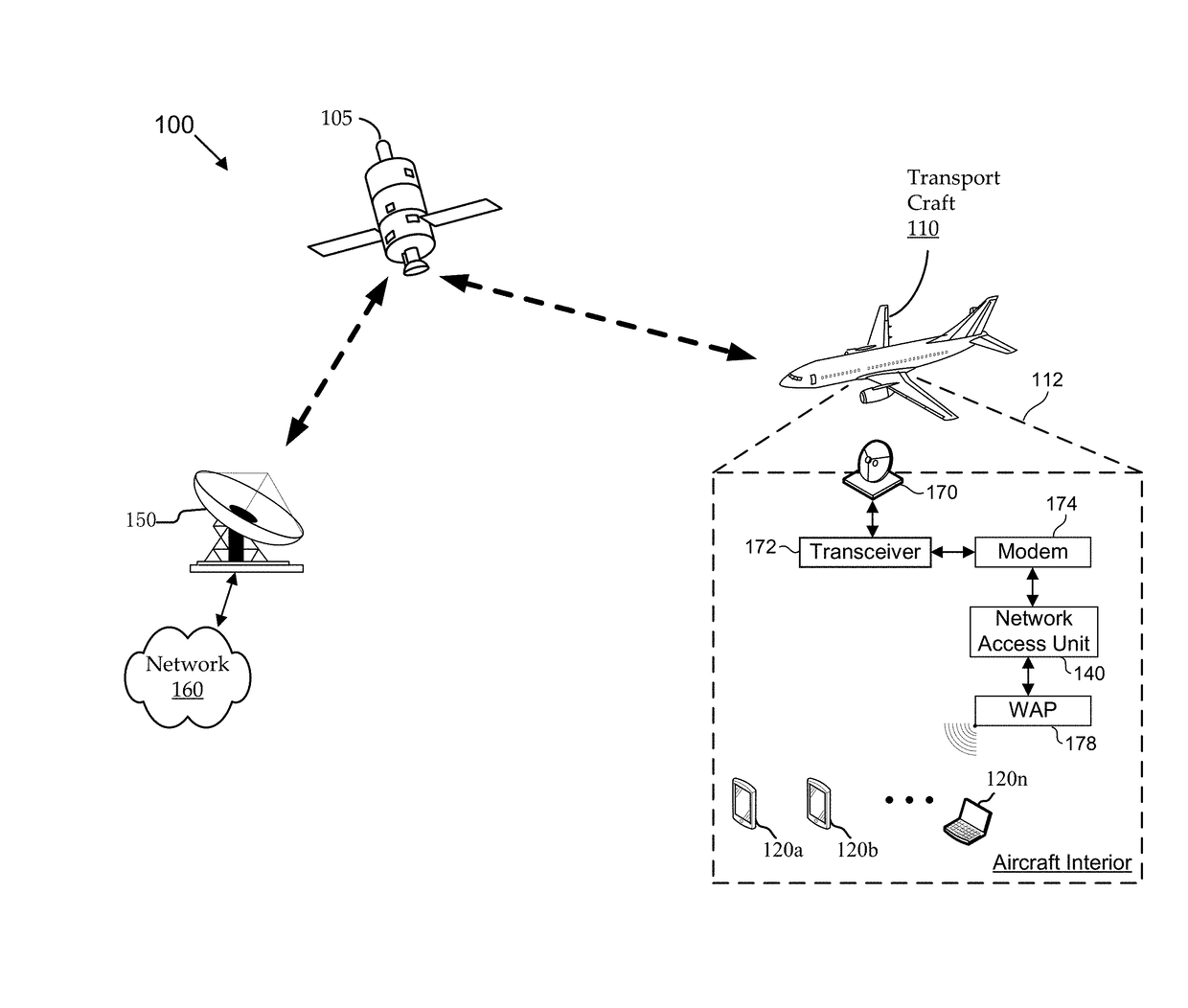
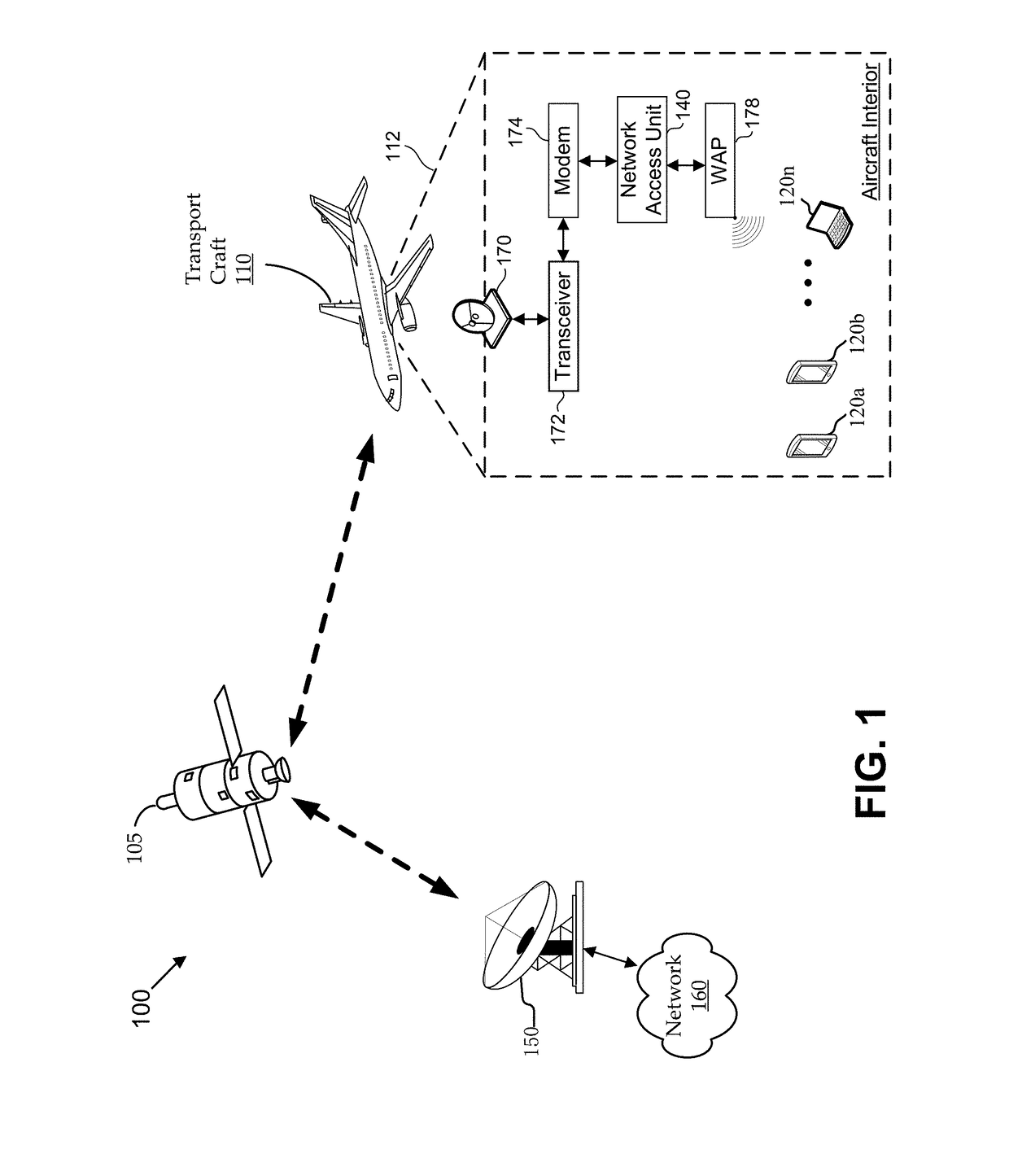
Methods and systems establish a traffic policy for a personal electronic device based on one or more physical characteristics of the device. In some aspects, a database of traffic policies is maintained. The traffic policies are for accessing a network via a wireless communications link. A network access unit receives a request from a personal electronic device to access the network. The request is analyzed to determine a physical characteristic of the device. A traffic policy is established from the database for the a personal electronic device based, at least in part, on the determined physical characteristic of the device. Transmission of network traffic for the device is then scheduled based at least in part, on the established traffic policy.
Owner:VIASAT INC
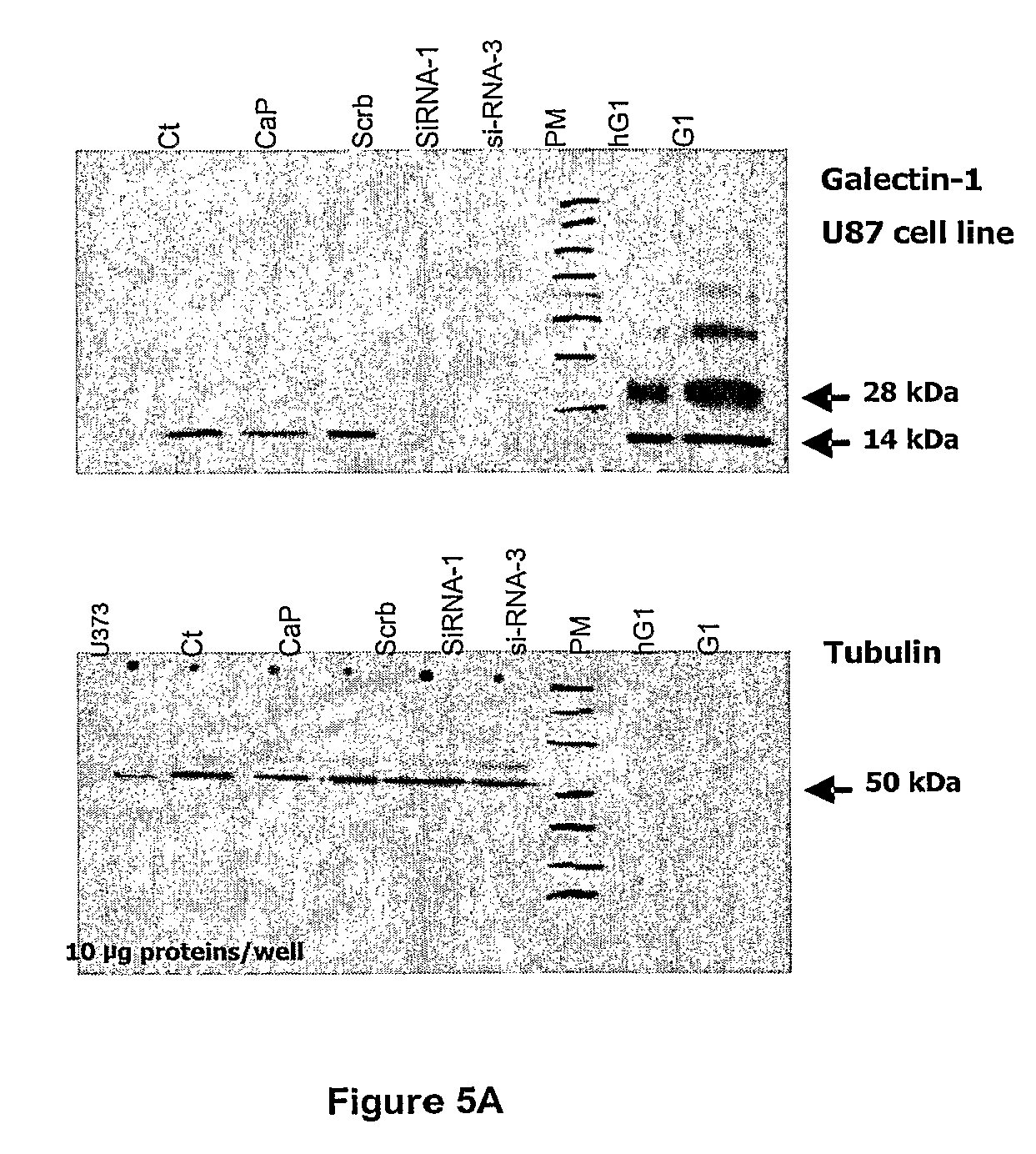
Use of a galectin-1-targeted rnai-based approach for the treatment of cancer
ActiveUS20100120891A1Reduce migrationEnhance efficacyOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesFhit geneHead and neck cancer
The present invention relates to an RNAi molecule suitable for reducing the expression of galectin-1 containing any of the sequences of SEQ ID NOs: 1-33, and preferably the sequences of SEQ ID NO: 2, 3, or 4, and to the use thereof as a medicament, or for the manufacture of a medicament for treating and / or for delaying the progression of cancer, preferably glioma, pancreatic cancer, head and neck cancer, melanoma, non-small-cell lung cancer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The present invention also relates to compositions and methods for treating and for delaying the progression of cancer, preferably glioma, pancreatic cancer, head and neck cancer, melanoma, non-small-cell lung cancer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, for reducing the migration of tumor cells, preferably cells of glioma, pancreatic cancer, head and neck cancer, melanoma, non-small-cell lung cancer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and / or for enhancing the efficacy of cancer therapies for the treatment of cancer, preferably glioma, pancreatic cancer, head and neck cancer, melanoma, non-small-cell lung cancer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, selected from the group comprising chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and / or gene therapy.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES +1
Use of a galectin-1-targeted RNAi-based approach for the treatment of cancer
InactiveUS7964575B2Dramatic efficacyReduce expressionSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsMelanomaRadical radiotherapy
The present invention relates to an RNAi molecule suitable for reducing the expression of galectin-1 containing any of the sequences of SEQ ID NOs: 1-33, and preferably the sequences of SEQ ID NO: 2, 3, or 4, and to the use thereof as a medicament, or for the manufacture of a medicament for treating and / or for delaying the progression of cancer, preferably glioma, pancreatic cancer, head and neck cancer, melanoma, non-small-cell lung cancer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The present invention also relates to compositions and methods for treating and for delaying the progression of cancer, preferably glioma, pancreatic cancer, head and neck cancer, melanoma, non-small-cell lung cancer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, for reducing the migration of tumor cells, preferably cells of glioma, pancreatic cancer, head and neck cancer, melanoma, non-small-cell lung cancer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and / or for enhancing the efficacy of cancer therapies for the treatment of cancer, preferably glioma, pancreatic cancer, head and neck cancer, melanoma, non-small-cell lung cancer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, selected from the group comprising chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and / or gene therapy.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES +1
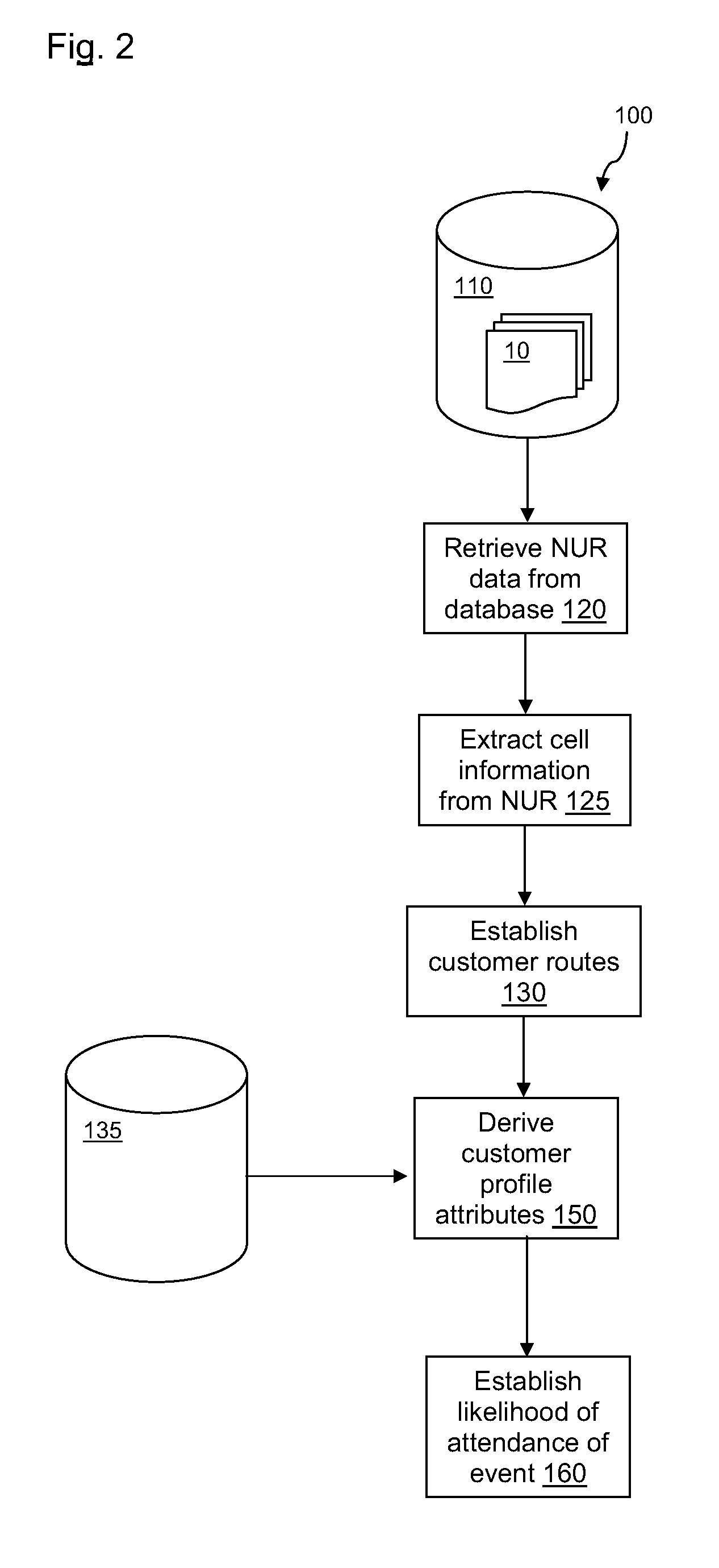
Methods of analysing a cellular network
InactiveUS20130183928A1Precise processPrecise and accurate inferenceNetwork traffic/resource managementDetection of traffic movementCarrier signalCarrier profile
There is provided a method of establishing a likelihood of one or more cellular terminal carriers travelling to a predetermined location, using cellular network data. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining network usage records from a cellular network; extracting cell information from the network usage records; establishing terminal carrier routes for cellular terminals that have changed location as determined from the extracted cell information; deriving terminal carrier profile attributes for the terminal carriers that have changed location, based on the established terminal carrier routes; and establishing the likelihood of one or more cellular terminal carriers travelling to the predetermined location, based on the established terminal carrier routes and the derived terminal carrier profile attributes. By combining a terminal carrier route with one or more terminal carrier profile attributes, a more precise and accurate inference of the likelihood of the cellular terminal carrier travelling to a predetermined location, or attending an event, may be obtained.
Owner:VODAFONE IP LICENSING
Bullet identification and tracking device
ActiveUS7621062B2Minimize the numberHigh propensityAmmunition projectilesAmmunition testingIdentification deviceEngineering
An identification and tracking device (110b) for use in combination with a firearm bullet (100) comprising a means for detaching the device (110b) from the bullet (100) during penetration of the target. In this manner, the tracking device (110b) and / or identification device (110b) will be attached to an object when the bullet (100) penetrates the object.
Owner:CUGLIARI GREGORY ANTHONY
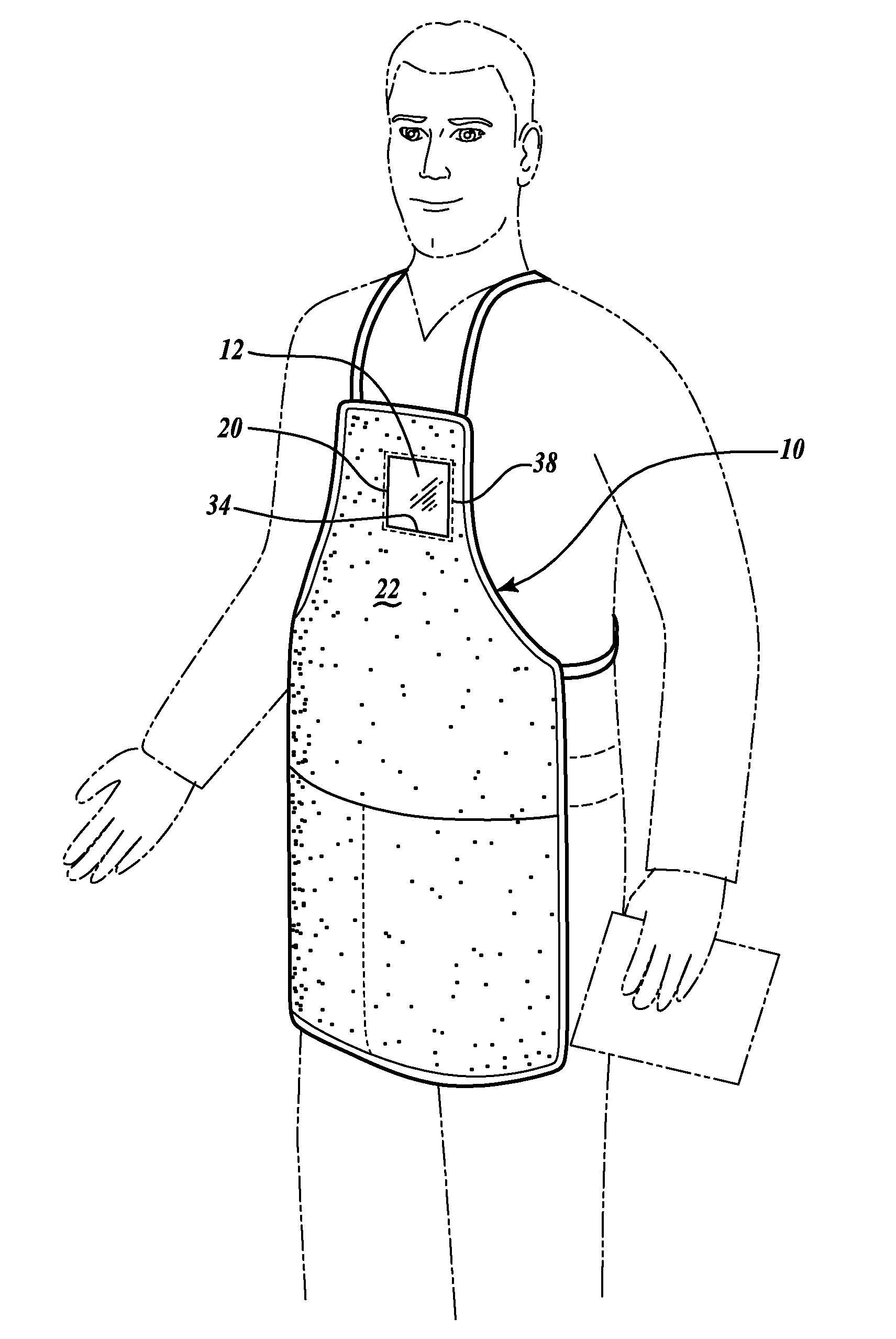
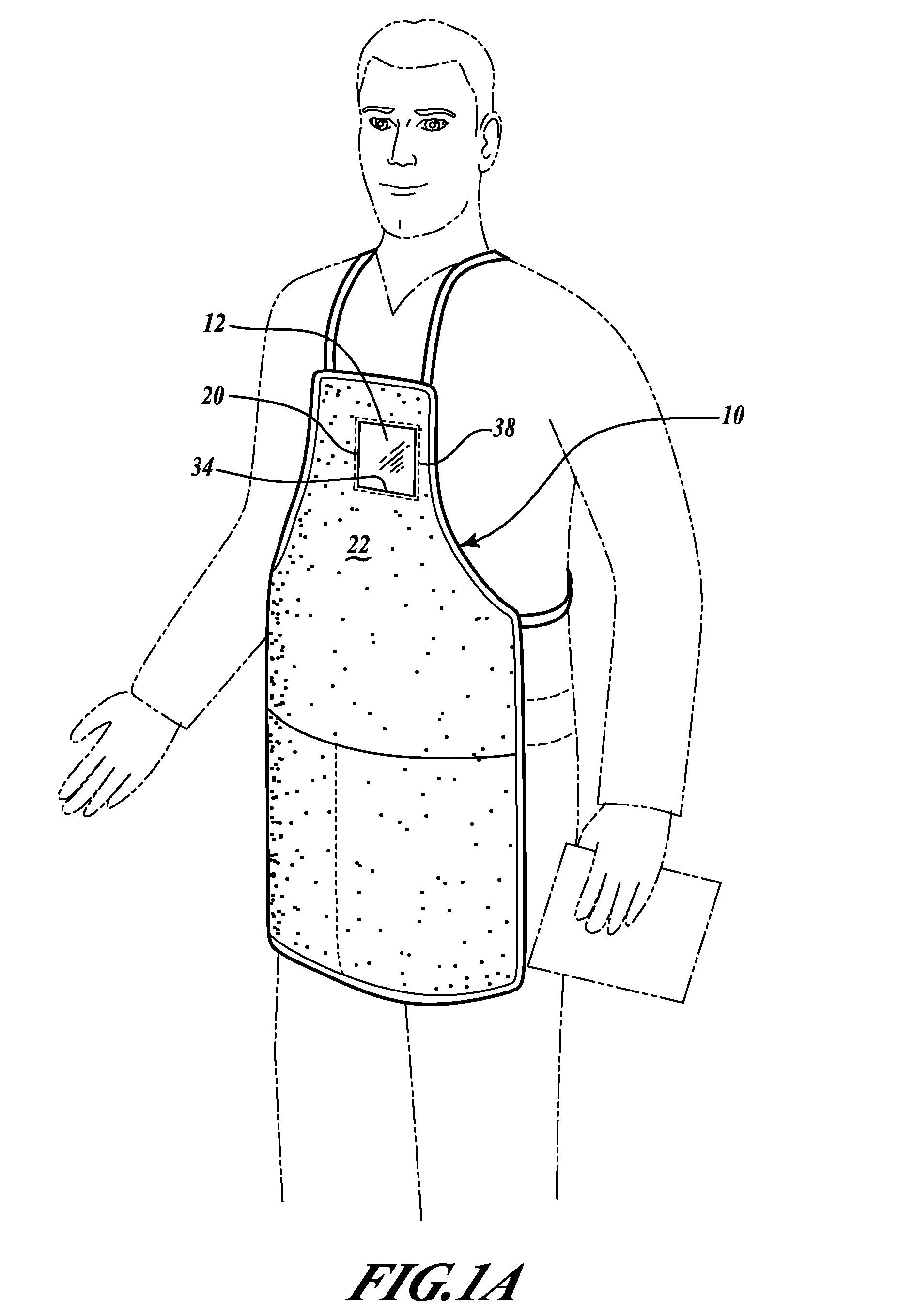
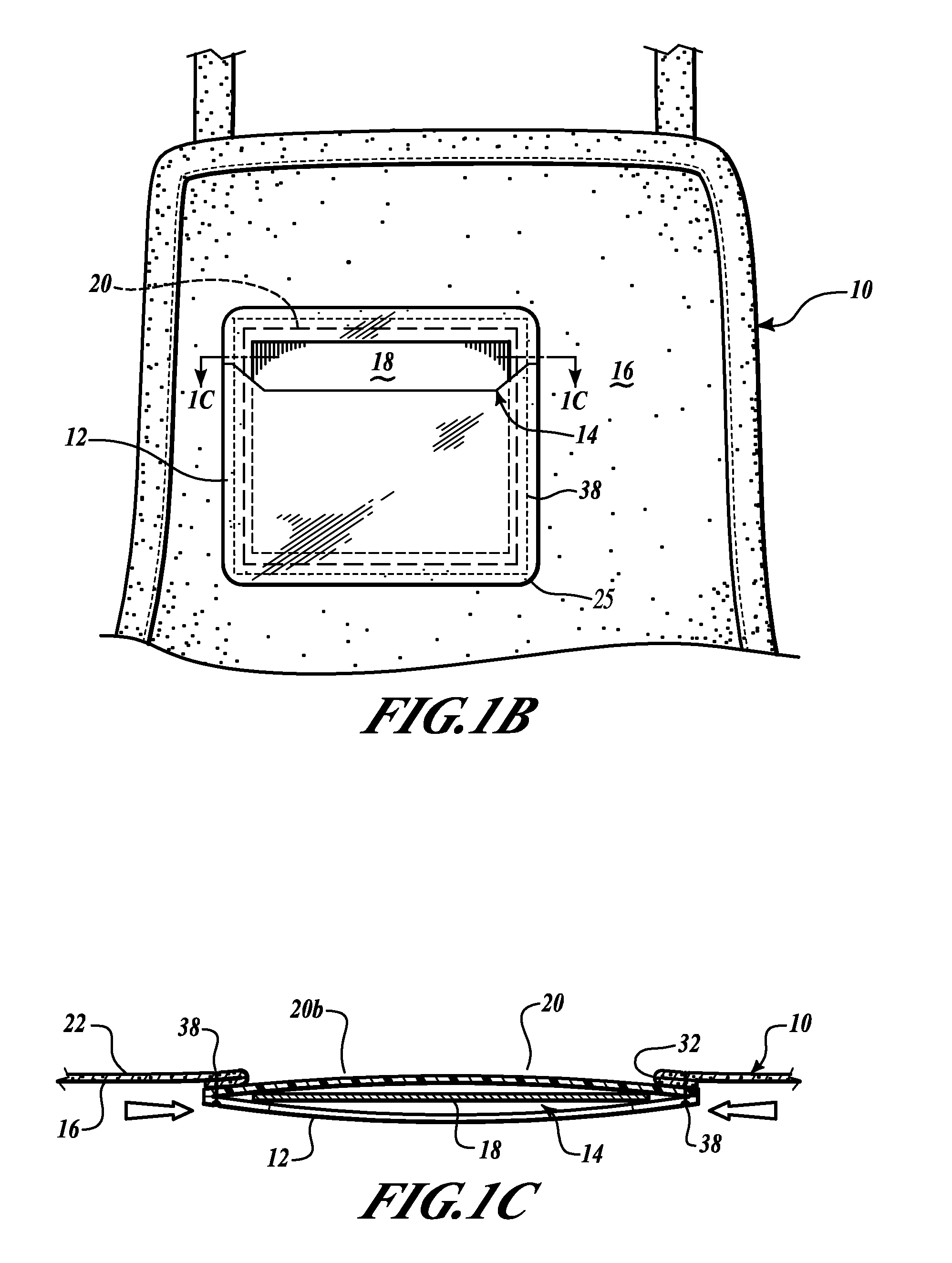
Garment badge holder
A garment generally includes a badge that can accessible from an interior of the garment and visible from an exterior of the garment. The garment includes a flap portion formed from a portion of the garment. The flap portion is folded over to form an edge that defines at least a portion of a hole formed in the garment. The garment also includes a generally transparent badge holder having a pocket operable to receive the badge. A fastener attaches the badge holder to the interior of the garment. The badge holder is attached to an interior surface of the garment so that the hole in the garment is disposed on a surface of the badge holder that is opposite the pocket.
Owner:PASSMAN ENTERPRISES
Large animal model of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in an immunocompromised host
InactiveUS6444872B1High propensityEfficient designCompounds screening/testingMicrobiological testing/measurementClinical settingsImmune compromised
A model of systemic mold / Aspergillus infection in a profoundly immunocompromised host has been established in the beagle dog. The beagle was rendered immunosuppressed using a combination of total body irradiation and daily steroids, which provided a window of time where the mold could be successfully inoculated through a bronchoscope. This created a localized infection in one lung lobe, which subsequently spread diffusely throughout the lung parenchyma, and uniformly resulted in the animal's death. The invention contemplates the further study of the pathophysiology of opportunistic mold infections in vivo and also provides examples for the development of new antifungal agents and more effective combinations of agents. Finally, the invention contemplates the development of technology for the early detection of systemic mold infections. The inventors envision, that the use of the model should help save patients from clinical trials of antifungal drugs that may be effective in vitro without living up to the expectations in a clinical setting.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
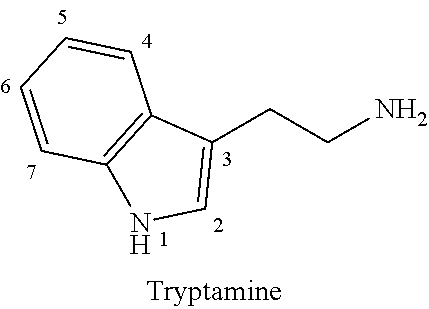
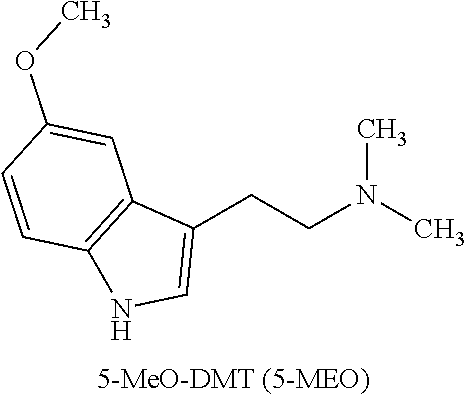
5-methoxy-n,n-dimethyltryptamine (5-meo-dmt) for treating depression
PendingUS20220071958A1DurableImprove compliancePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDosing regimenCompulsive disorders
Provided are compositions for use in treating a patient suffering from a mental disorder in particular major depressive disorder, persistent depressive disorder, anxiety disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, body dysmorphic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, eating disorder and psychoactive substance abuse. Further provided are dosing regimens for treating these disorders.
Owner:GH RES IRELAND LTD
Methods and systems for establishing in-flight network traffic policies for personal electronic devices
ActiveUS10051652B2Modest loadSolve low usageDigital computer detailsSubstation equipmentTraffic capacityComputer network
Owner:VIASAT INC
Methods of analyzing a cellular network
ActiveUS9357553B2Precise and accurate inferenceHigh propensityNetwork traffic/resource managementLocation information based serviceCarrier signalComputer terminal
A method of managing a load within a cellular network. The method includes obtaining network usage records from the cellular network; extracting cell information from the network usage records; establishing terminal carrier routes for cellular terminals that have changed location as determined from the extracted cell information; deriving terminal carrier profile attributes for the cellular terminals that have changed location, based on the established terminal carrier routes; determining a load on a resource of the cellular network, based on the established terminal carrier routes and the derived terminal carrier profile attributes; and controlling resources of the cellular network in response to the determined load, so as to manage the load within the cellular network. By combining established terminal carrier routes with derived terminal carrier profile attributes, it is possible to anticipate areas where cellular terminal carriers are likely to be concentrated at specific times during the day and allocate resources accordingly.
Owner:VODAFONE IP LICENSING +1
Driver assistance system
ActiveUS10878787B2Low cognitive stateHigh propensityElectrophonic musical instrumentsDashboard fitting arrangementsDriver/operatorEngineering
Methods are provided for adjusting a music output of a vehicle audio system based on driver movements performed while listening to the music. In one embodiment, a music output of a vehicle infotainment system is adjusted responsive to monitored user behavior inside a vehicle, the monitored user behavior manifesting a user mood. In another embodiment, the music output is adjusted based on each of a user mood and a control gesture, wherein both the user mood and the gesture are identified based on user information gathered from vehicle biometric sensors and cameras while music is playing inside the vehicle.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
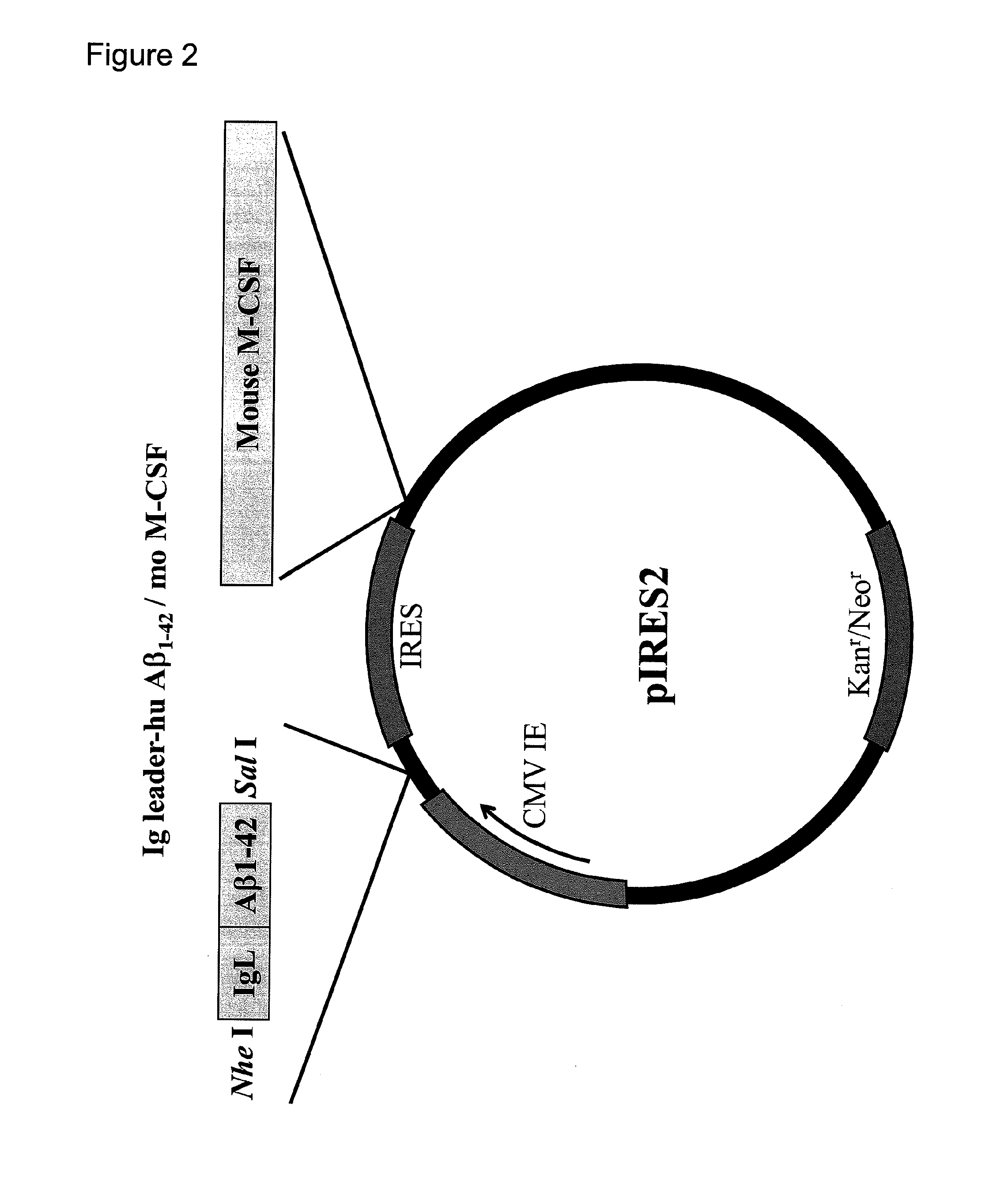
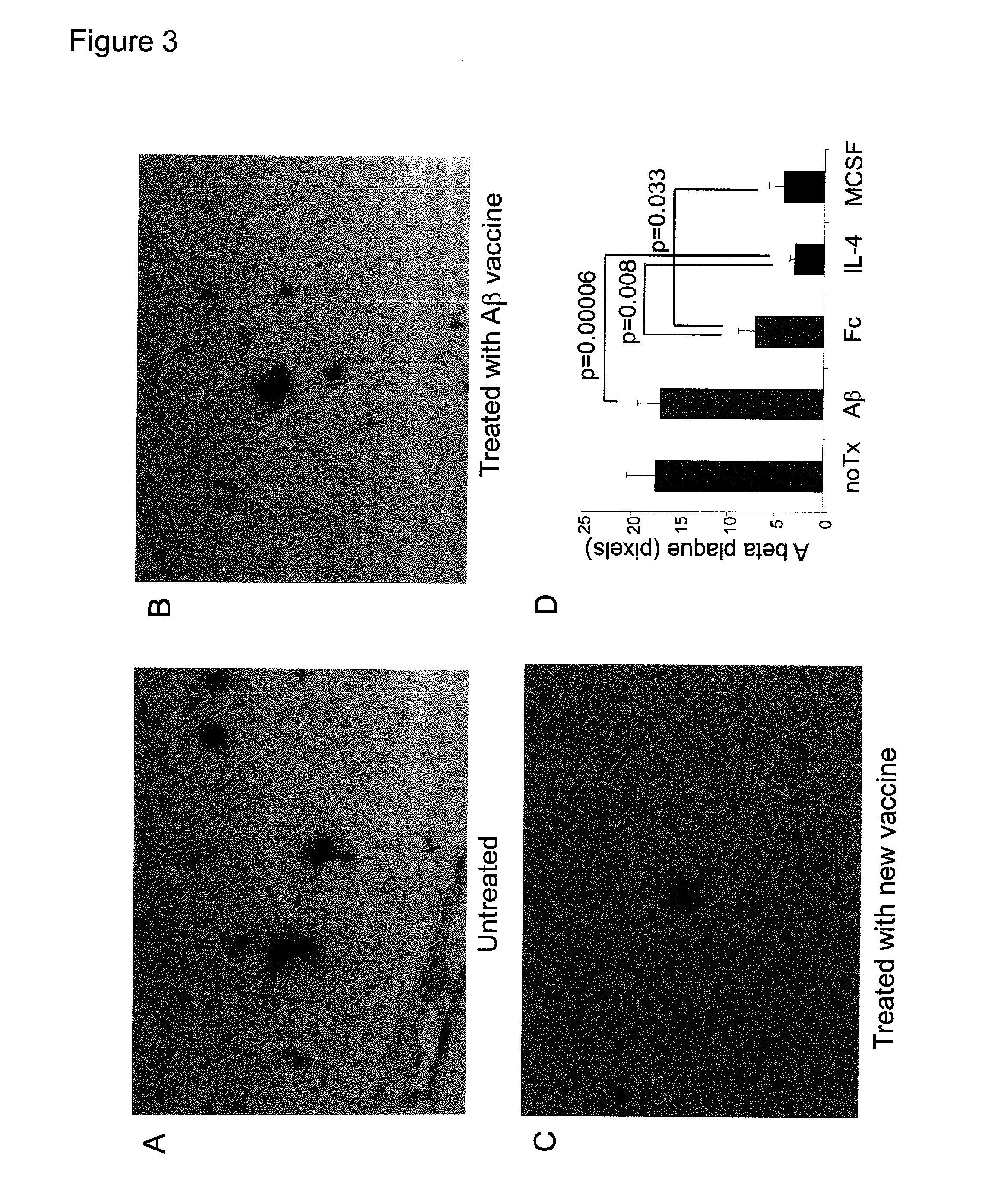
DNA vaccine for alzheimer's disease
InactiveUS20120014987A1High effectHigh amyloid aggregation propensityNervous disorderAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDna encodingCancer research
Owner:TOKYO METROPOLITAN INST OF MEDICAL SCI
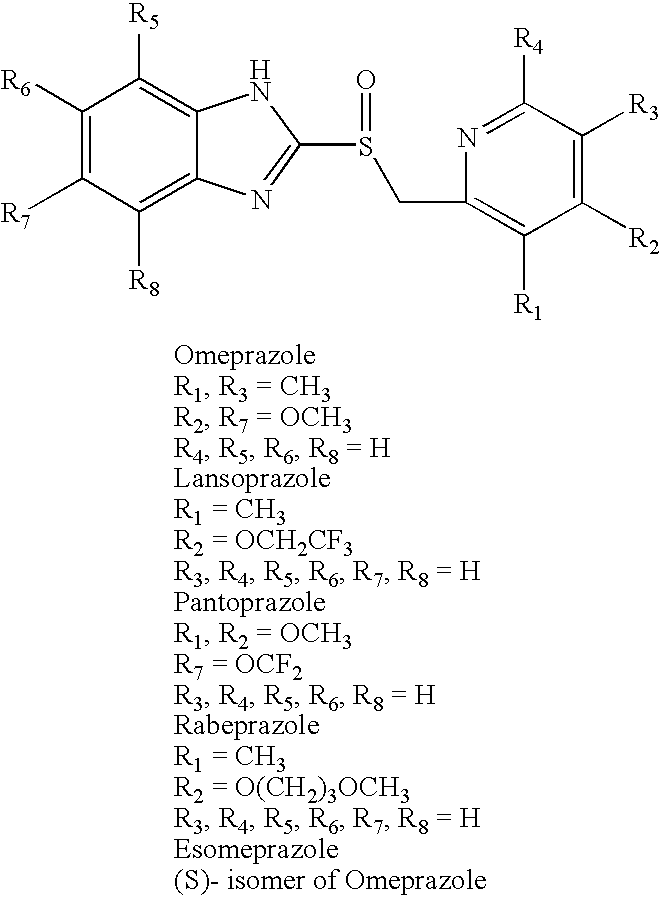
Pharmaceutical Compositions Comprising Amorphous Benzimidazole Compounds
InactiveUS20080146615A1Improve responseHigh propensityBiocideOrganic chemistryPolymer chemistryBenzimidazole
Owner:DR REDDYS LAB LTD +1
Thermo-acoustic nuclear power distribution measurement assembly
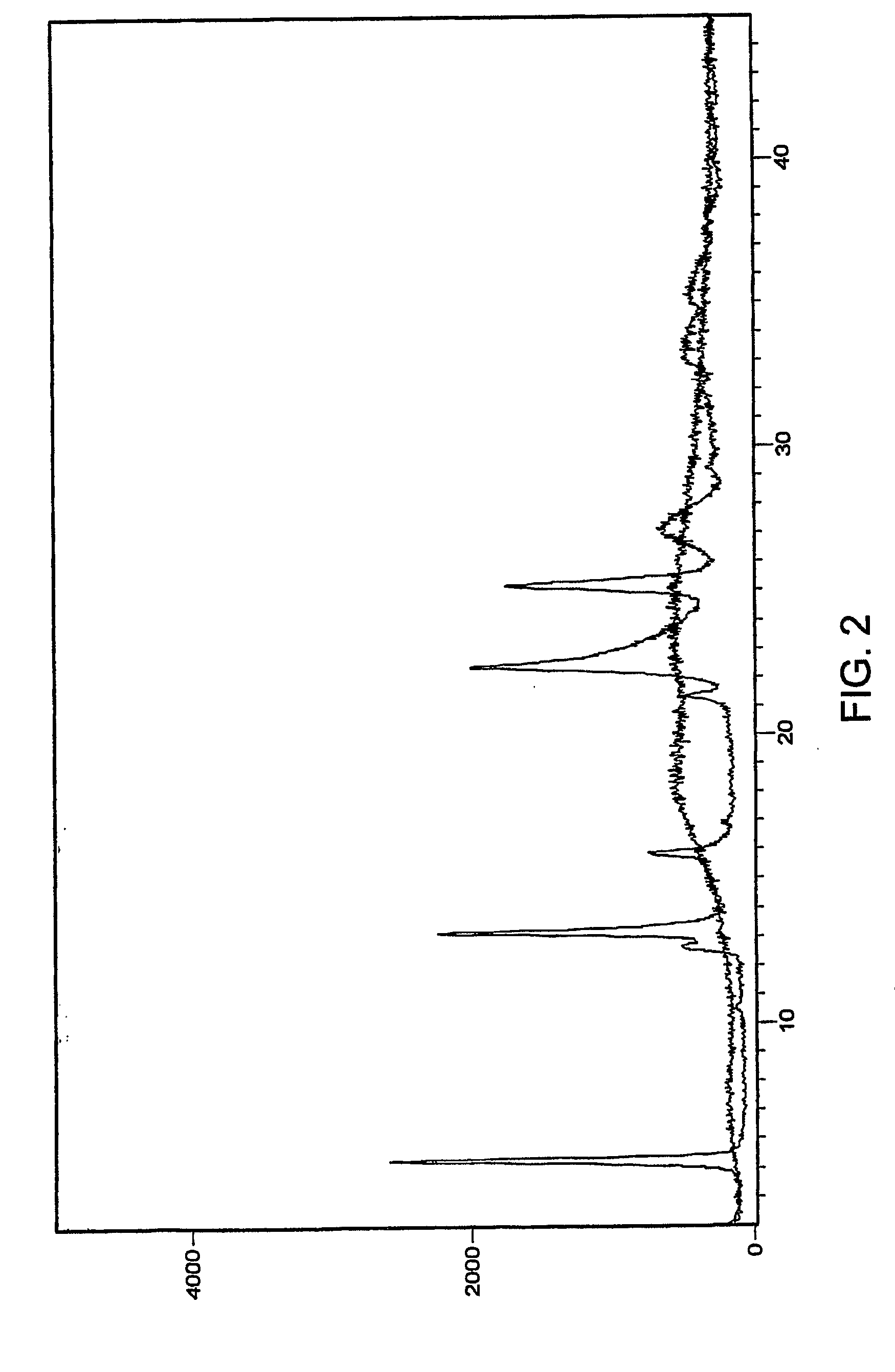
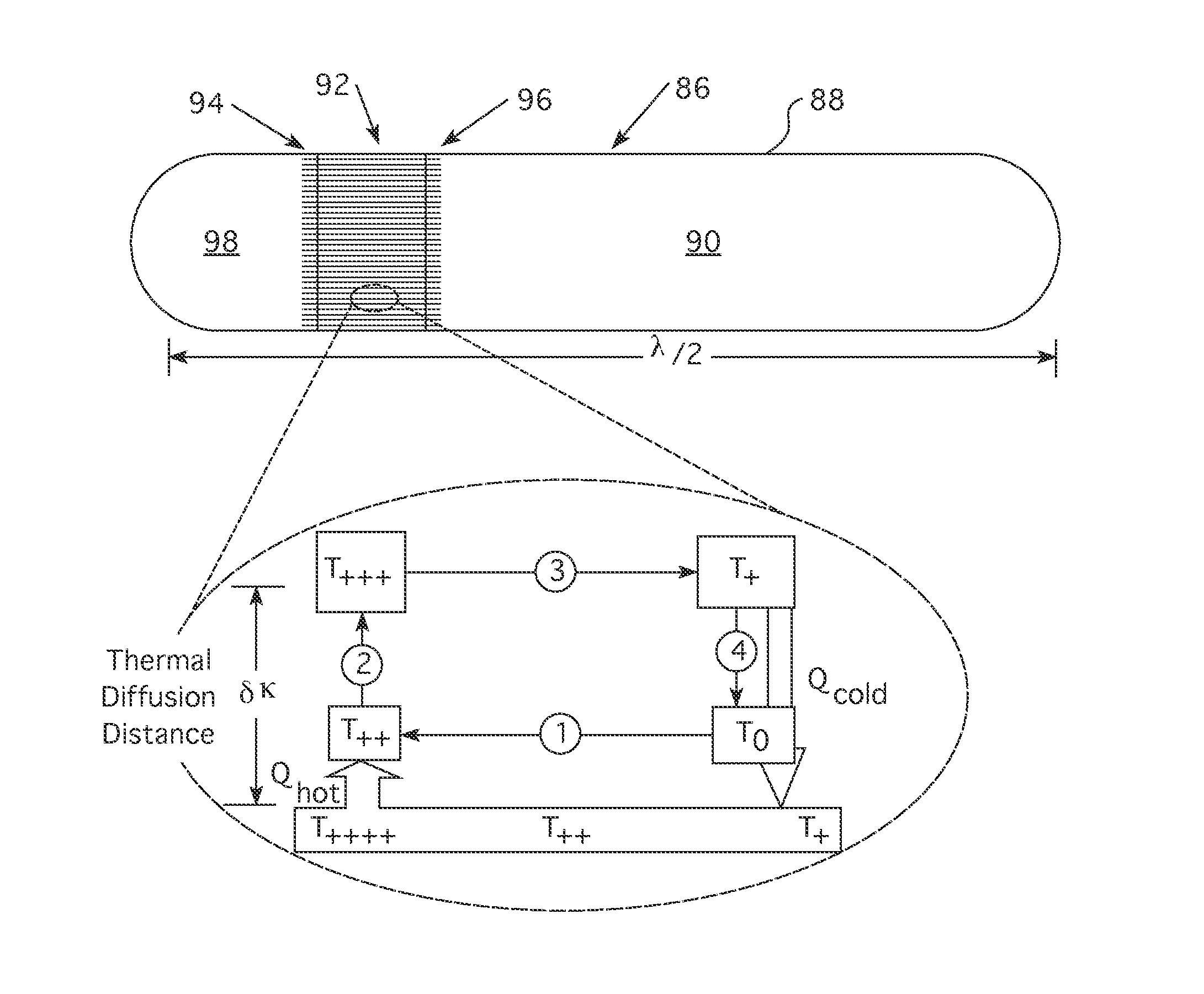
ActiveUS20140362965A1High propensityMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNuclear energy generationCold sideResonant cavity
A nuclear power distribution measurement assembly that is sized to fit within an instrumentation thimble of a nuclear fuel assembly, that employs a spaced tandem arrangement of thermo-acoustic engines, each of which has a heat source side that is insulated from the reactor coolant traversing the nuclear core in which the fuel assembly is to be placed and a cold side housing a resonator chamber with enhanced thermal conductance to the coolant. The resonator chamber of each of the thermo-acoustic engines is of a different length to generate a different frequency whose amplitude is proportional to the neutron activity at the axial and radial position of the thermo-acoustic engine. The frequency identifies the measurement assembly's position. Acoustic telemetry is employed to monitor the acoustic waves generated by the individual thermo-acoustic engines to provide a remote reading of the axial and radial power distribution of a reactor core.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Flocculant composition for dewatering solids laden slurries
ActiveUS20160024291A1Reducing suspended fine solidHigh propensitySludge treatmentOther chemical processesCellulose compoundsMaterials science
Owner:PROFILE PRODS LLC
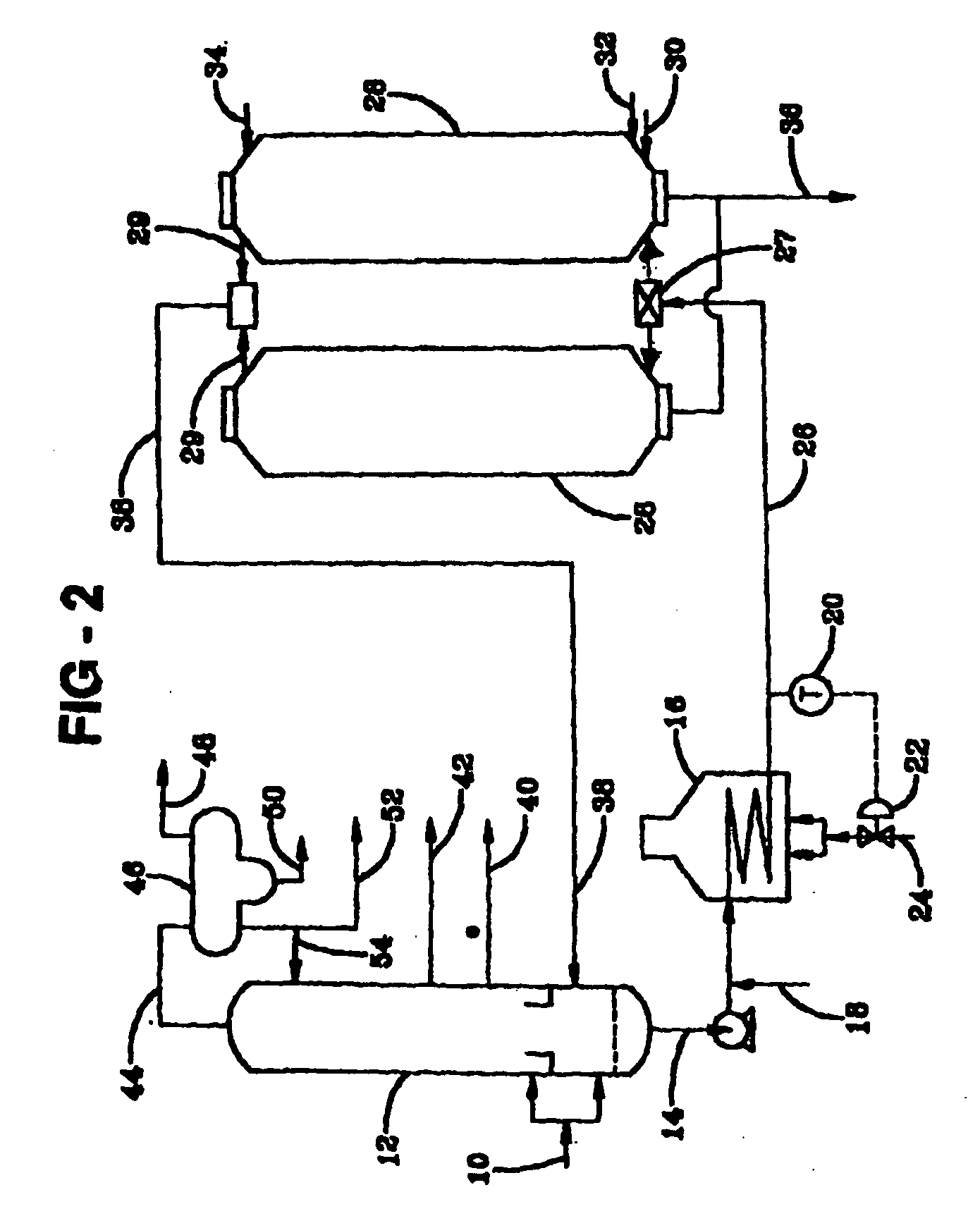
Method of operating a compression ignition engine
ActiveUS20100242913A1Facilitates start-upHigh propensityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesPistonOperating temperature
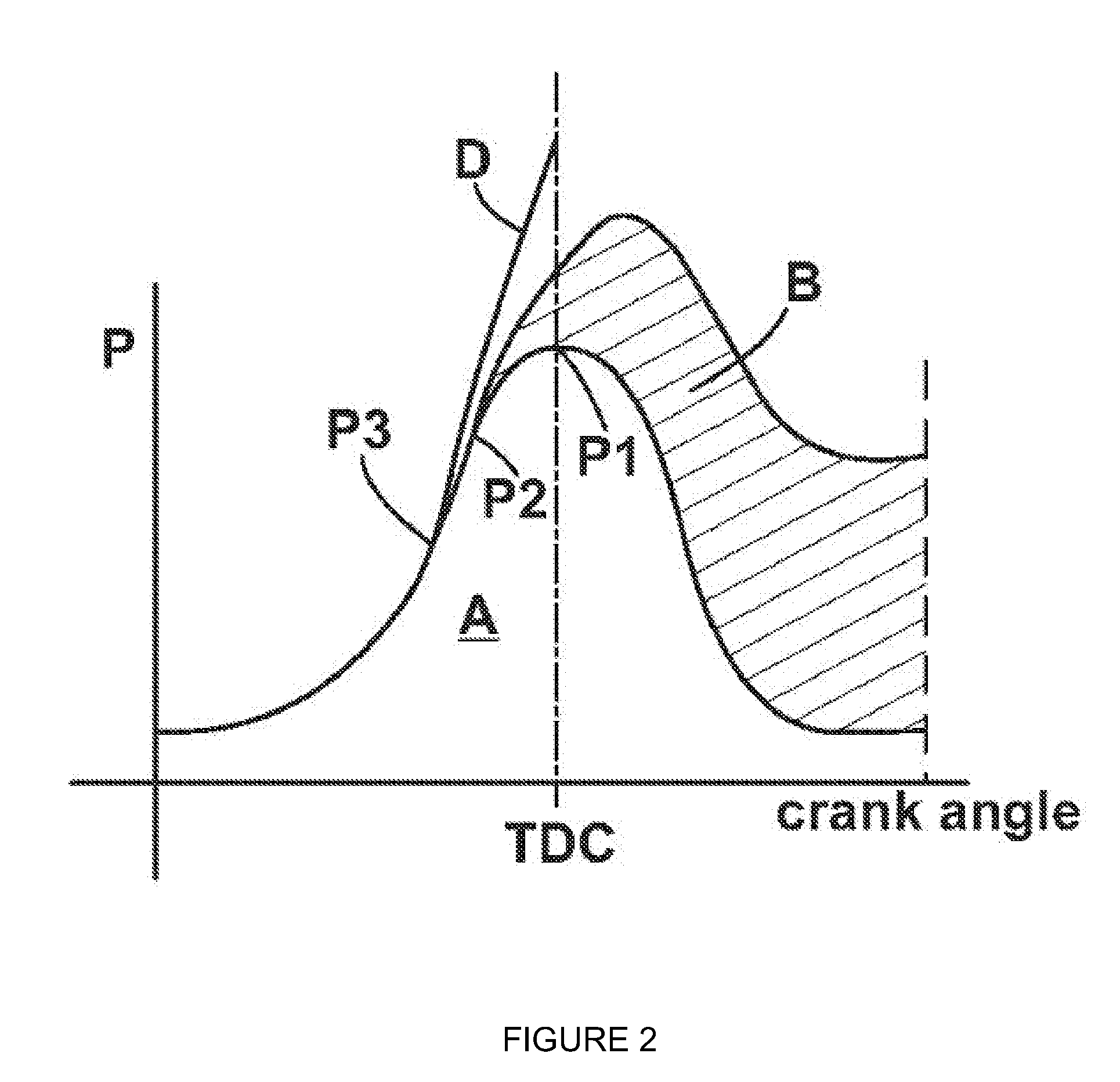
A method of operating a compression ignition engine, which includes at least one combustion chamber containing a piston, and a mechanically operated fuel injection pump apparatus. The method includes sensing the engine operating temperature with a first sensor, and providing input to a controller. The controller operates the fuel injection pump apparatus to deliver fuel to each of the combustion chambers according to a first timing regime when the engine operating temperature is above a threshold temperature, and according to a second, advanced timing, regime when the engine operating temperature is below the threshold temperature. The method further includes sensing the pressure in the combustion chambers with a second sensor. When the controller is operating the fuel injection pump apparatus according to the second timing regime and the combustion chamber pressure exceeds a desired pressure, the method includes changing operation from the second timing regime to the first timing regime.
Owner:J C BAMFORD EXCAVATORS LTD
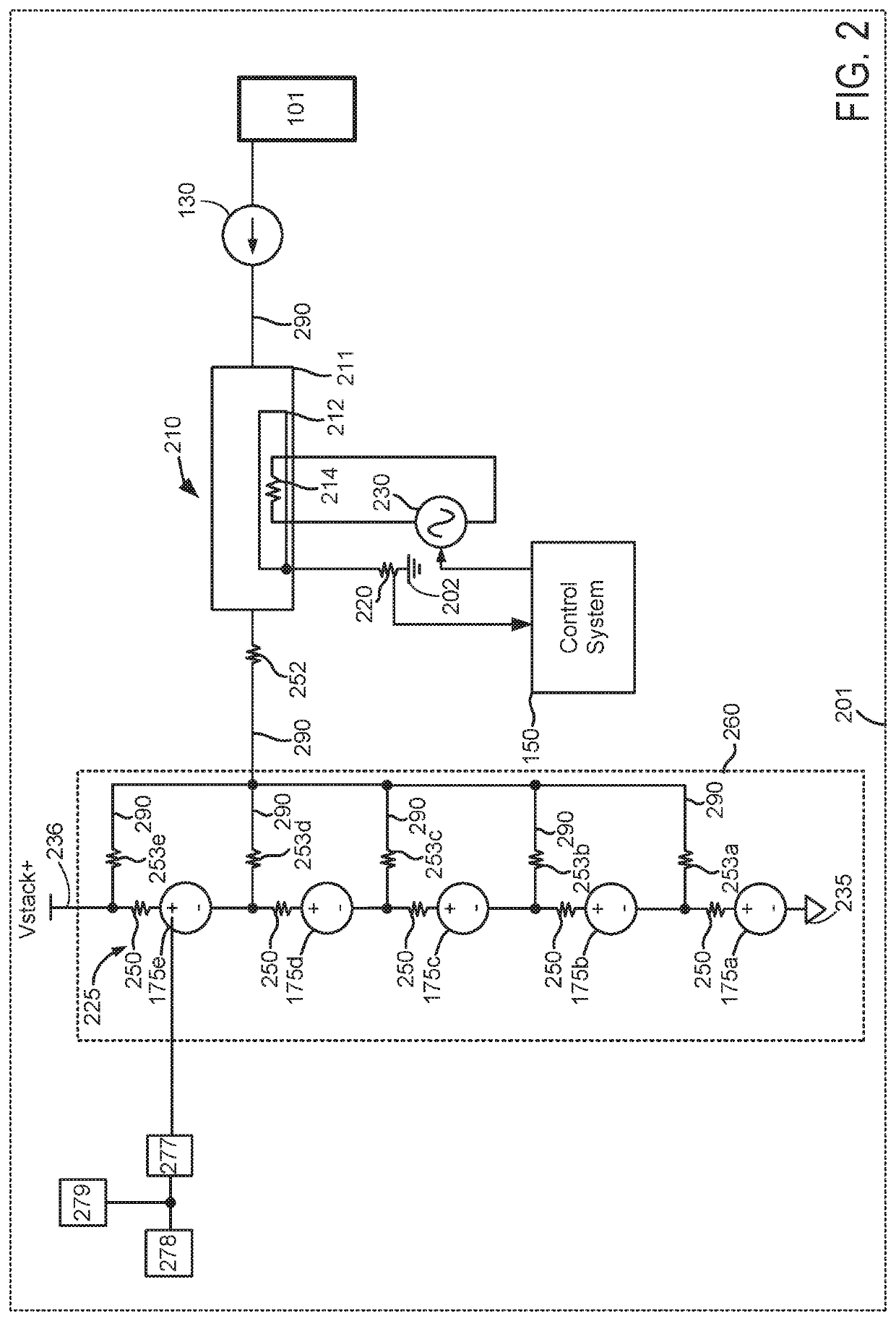
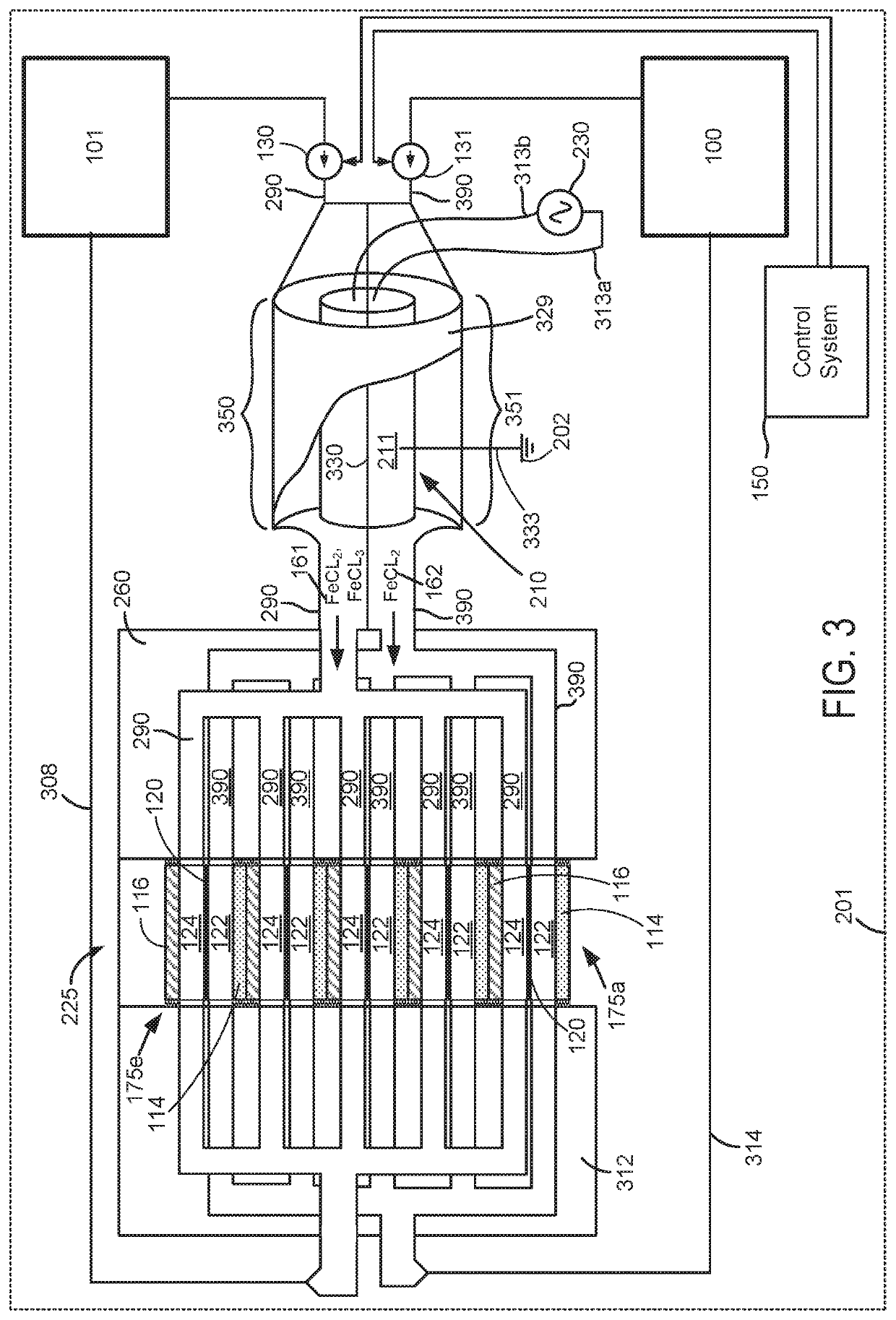
Power delivery system and method
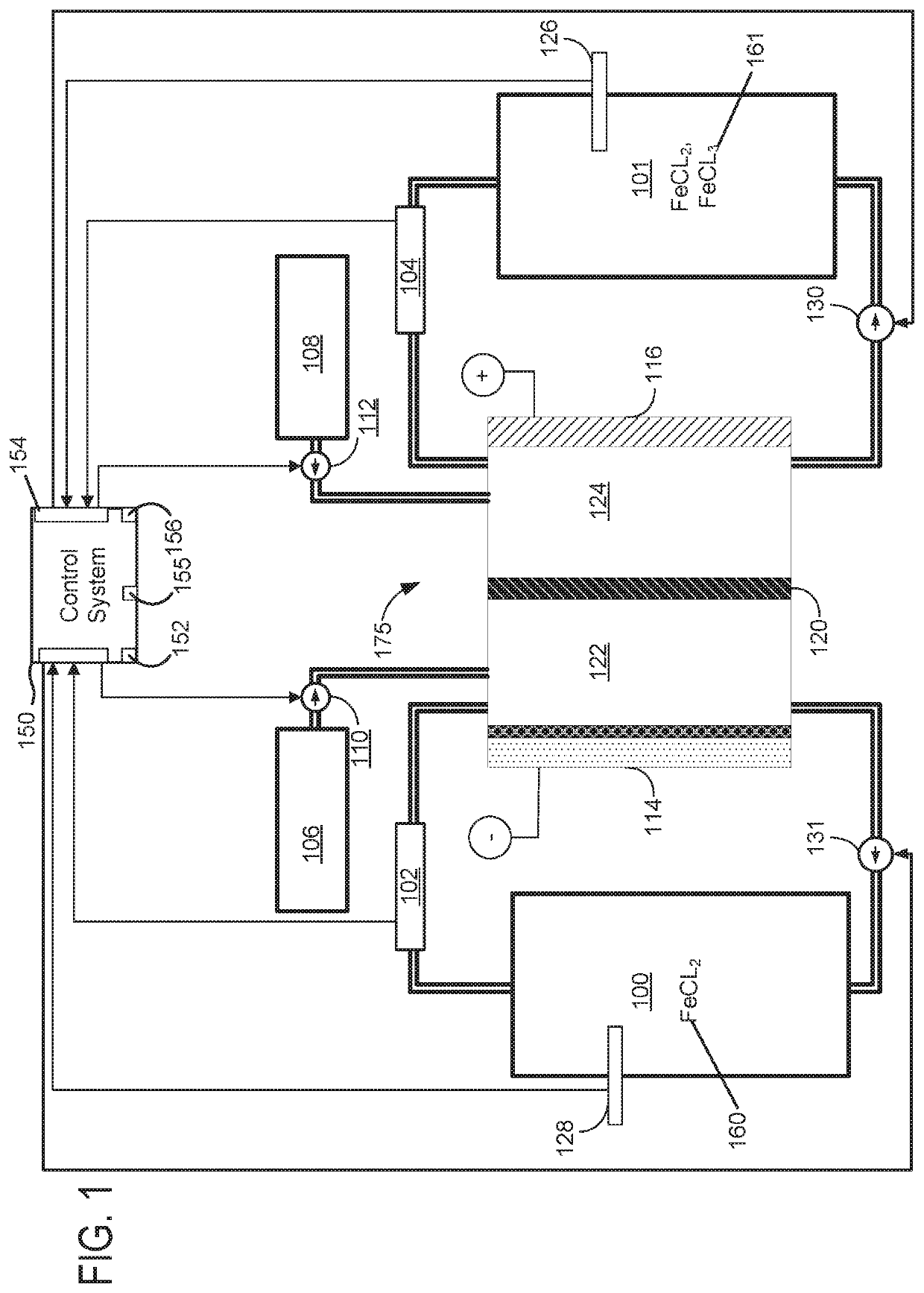
ActiveUS10930949B2Raise the potentialImprove output performanceReactant parameters controlElectrolyte stream managementElectricity deliveryControl theory
Owner:ESS TECHNOLOGY
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising amorphous benzimidazole compounds
InactiveUS20090324728A1Improve responseHigh propensityBiocidePowder deliveryPolymer chemistryBenzimidazole
Owner:DR REDDYS LAB LTD +1
Garment badge holder
A garment generally includes a badge that can accessible from an interior of the garment and visible from an exterior of the garment. The garment includes a flap portion formed from a portion of the garment. The flap portion is folded over to form an edge that defines at least a portion of a hole formed in the garment. The garment also includes a generally transparent badge holder having a pocket operable to receive the badge. A fastener attaches the badge holder to the interior of the garment. The badge holder is attached to an interior surface of the garment so that the hole in the garment is disposed on a surface of the badge holder that is opposite the pocket.
Owner:PASSMAN ENTERPRISES
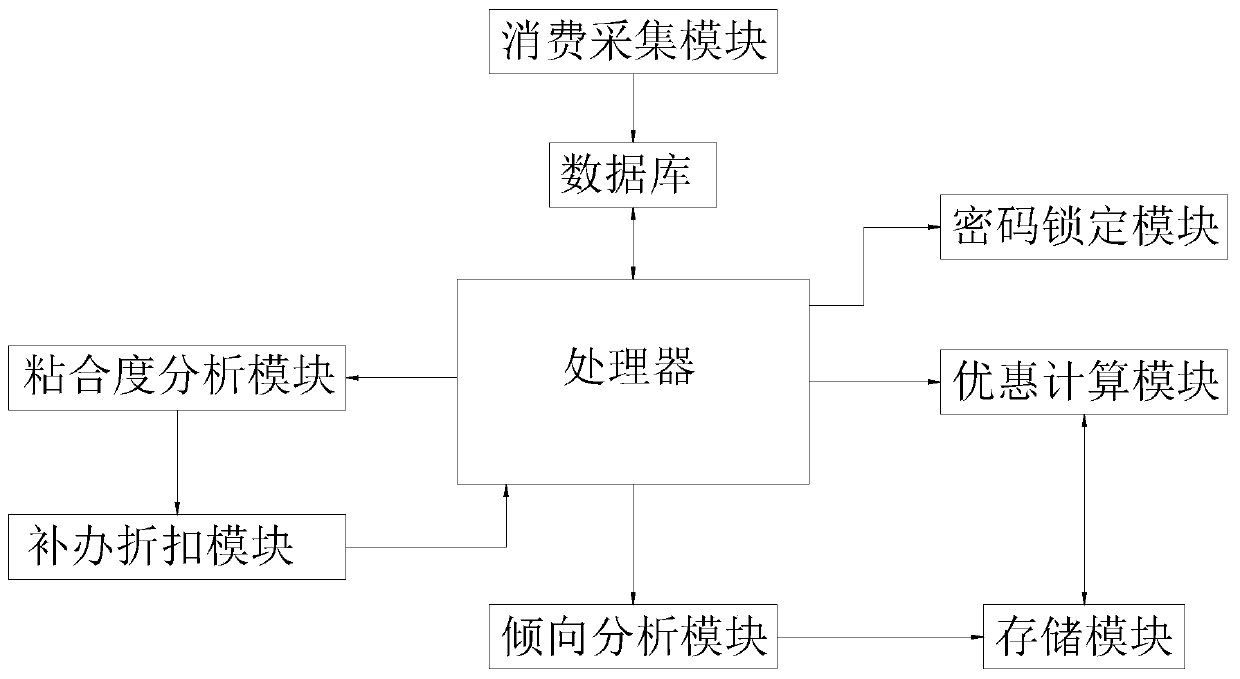
All-purpose card consumption tendency analysis and processing system
InactiveCN109801114AHigh propensityImprove adhesionPayment architectureMarketingContinuous usePassword
The invention discloses an all-purpose card consumption tendency analysis and processing system. The method is used for solving the problems of how to calculate the consumption tendency of an all-purpose card user, formulate corresponding discounts according to the tendency and how to calculate the adhesion degree of the all-purpose card user so as to reasonably reduce, avoid and reapply the costof the all-purpose card. The system comprises a consumption collection module, a database, a processor, a tendency analysis module, a storage module, a discount calculation module, an adhesion analysis module, a reissue discount module and a password locking module. According to the one-card consumption tendency analysis and processing system, a tendency value Qi is obtained by using a formula; the formula is used for obtaining the tendency value Qi according to the formula; the maximum tendency value Qmax is obtained in the tendency value Qi of the one-card consumer; a discount value Yi is acquired by using a formula shown in the specification, wherein the formula shown in the specification is shown in the specification to acquire a discount value Yi; the adhesion analysis module is usedfor analyzing the adhesion of the all-purpose card consumer to the all-purpose card; The adhesion Ni is obtained through a formula and the longer the consumption time of continuous use of the one-cardis, the larger the adhesion is.
Owner:合肥浮点信息科技有限公司
Tubular volatizing device
PendingUS20210008242A1Reduce preparationShorten the timeElectric heatingMedical devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:DYNAVAP LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com