Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54results about How to "Great customization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
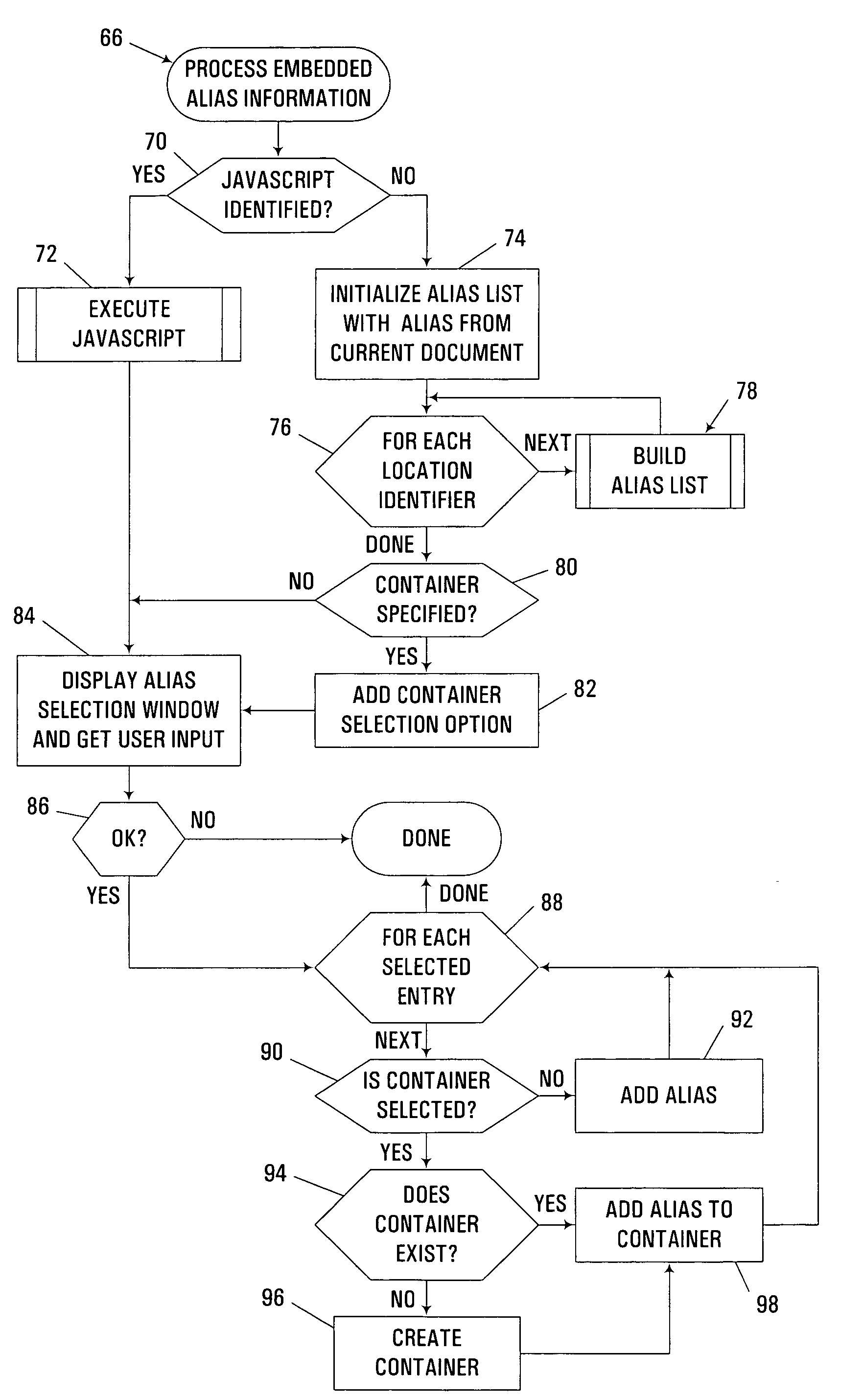
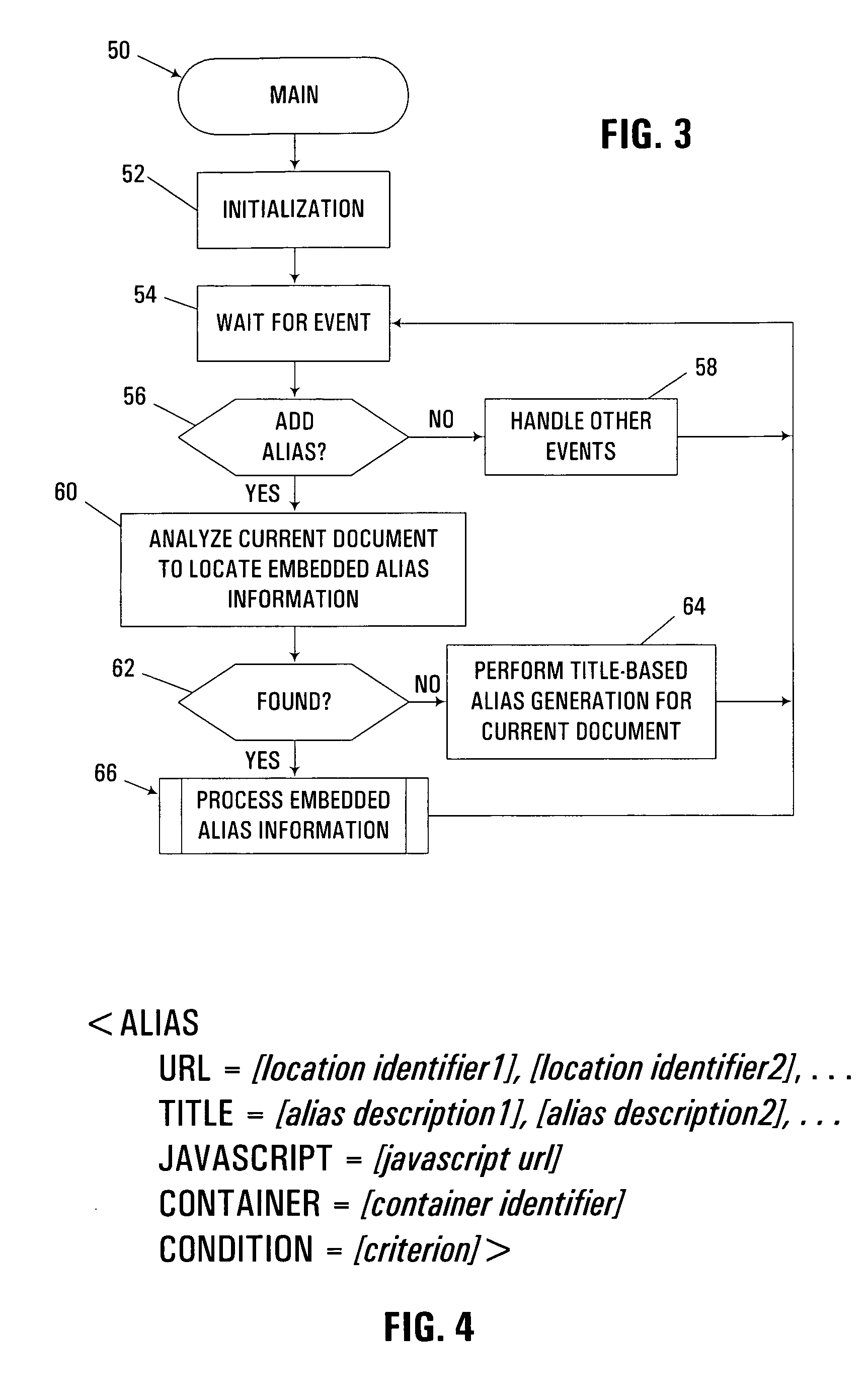
Automated generation of aliases based on embedded alias information
InactiveUS7284232B1Increase flexibilityGreat relevancyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalPosition dependentDocumentation
An apparatus, program product and method incorporate embedded alias information into a document for use in automatically generating aliases (e.g., bookmarks, favorites, shortcuts, etc.) in a computer environment. The embedded alias information may incorporate both an identification of a predetermined storage location and an alias description to be associated therewith, such that, during generation of an alias, both the location and the description for the alias are obtained from the embedded alias information. The embedded alias information may also incorporate a condition associated with a predetermined storage location, in addition to or in lieu of an identification of the actual predetermined storage location, such that, during generation of an alias, the condition may be tested so that the alias will be generated only upon the condition being met. The embedded alias information may also incorporate an executable program to further customize or enhance the generation of aliases.
Owner:IBM CORP
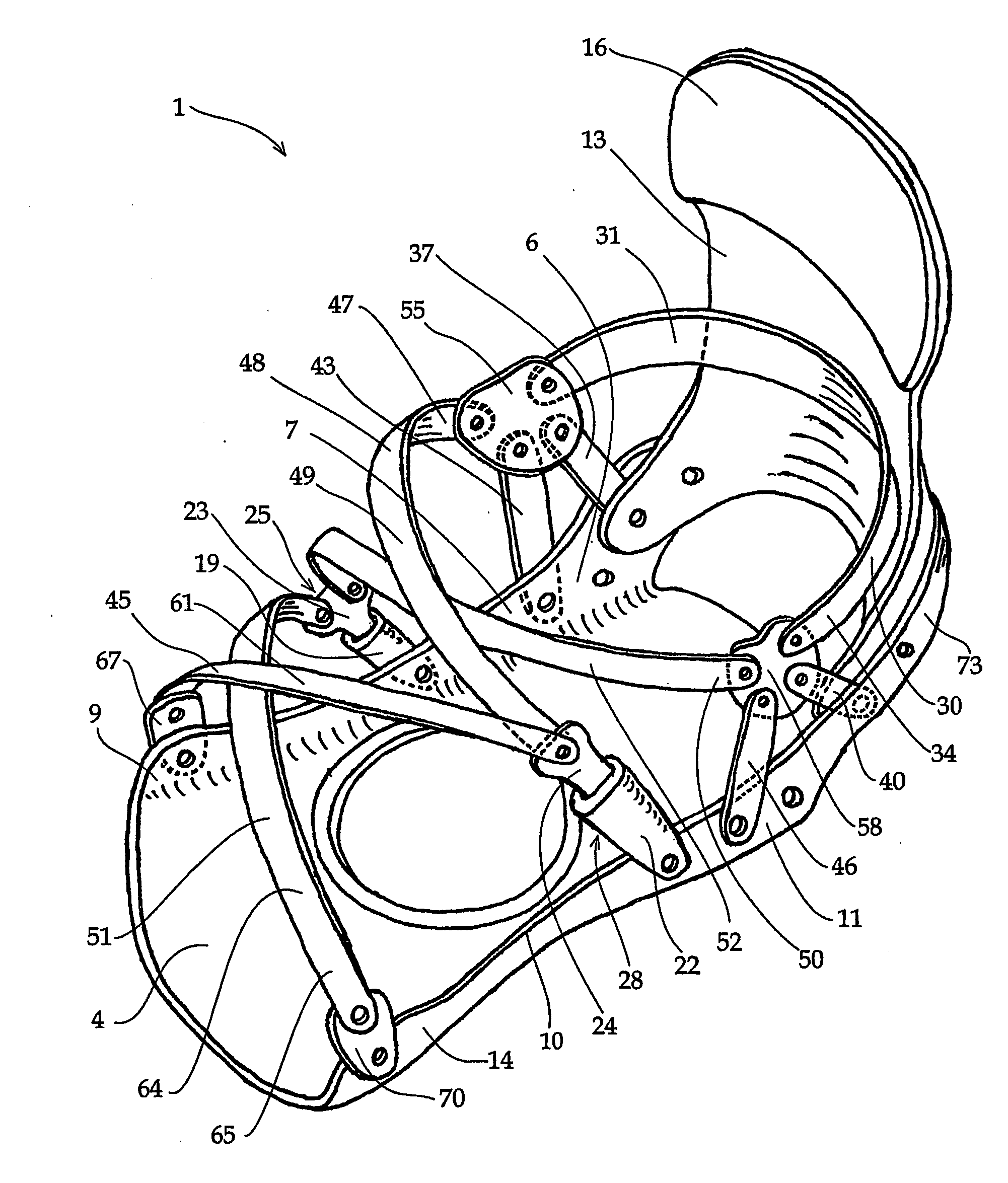
Interface system for retaining a foot or a boot on a sports article
InactiveUS20070063459A1More natural and responsive interfaceImprove the level ofCarriage/perambulator accessoriesSnowboard bindingsEngineeringAnkle
An interface system (1) comprising one or more linkage member(s) (30, 48, 49, 51, 52, 61) that have the purpose of retaining an individual's foot / ankle (either bare or covered) on a sports article. The system (1) comprises a rigid base structure (4) a having lateral edge (7) and medial edge (10), and heel loop portion (73); one or more pliable linkage members (30, 48, 49, 51, 52, 61) that wrap around the user's foot / ankle or boot and are tensionably adjustable and disconnectable.
Owner:KAVARSKY RAYMOND R
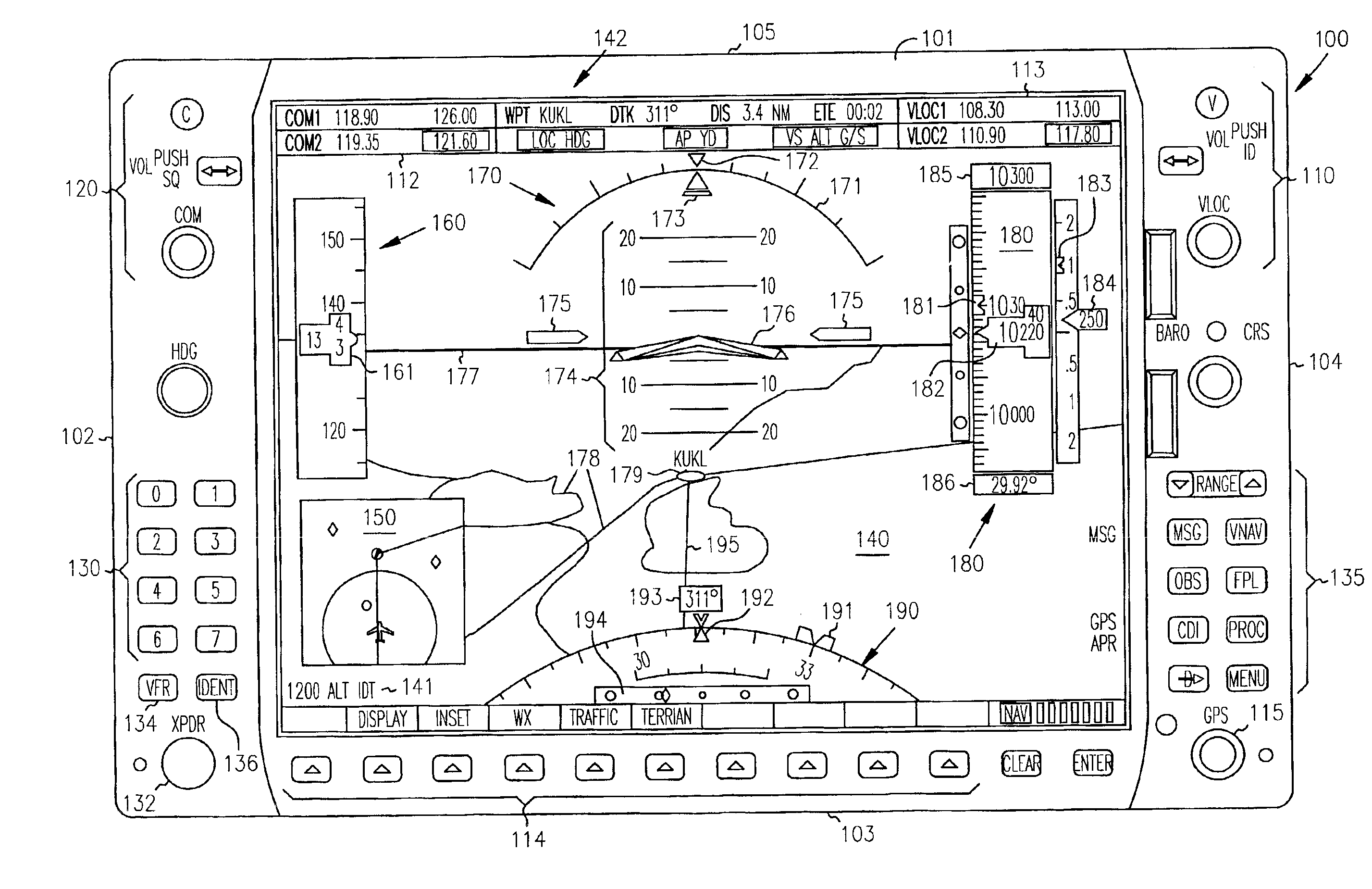
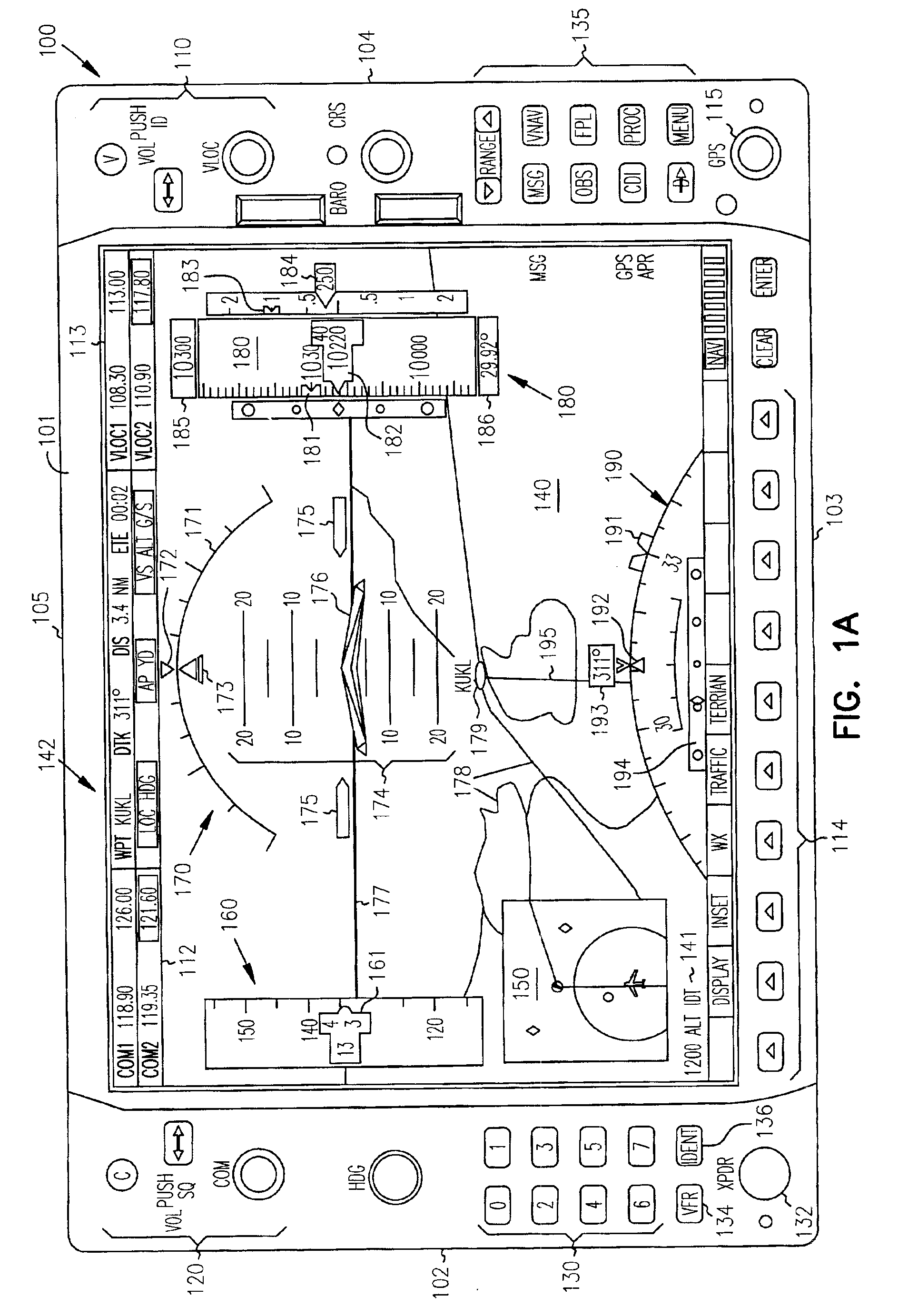
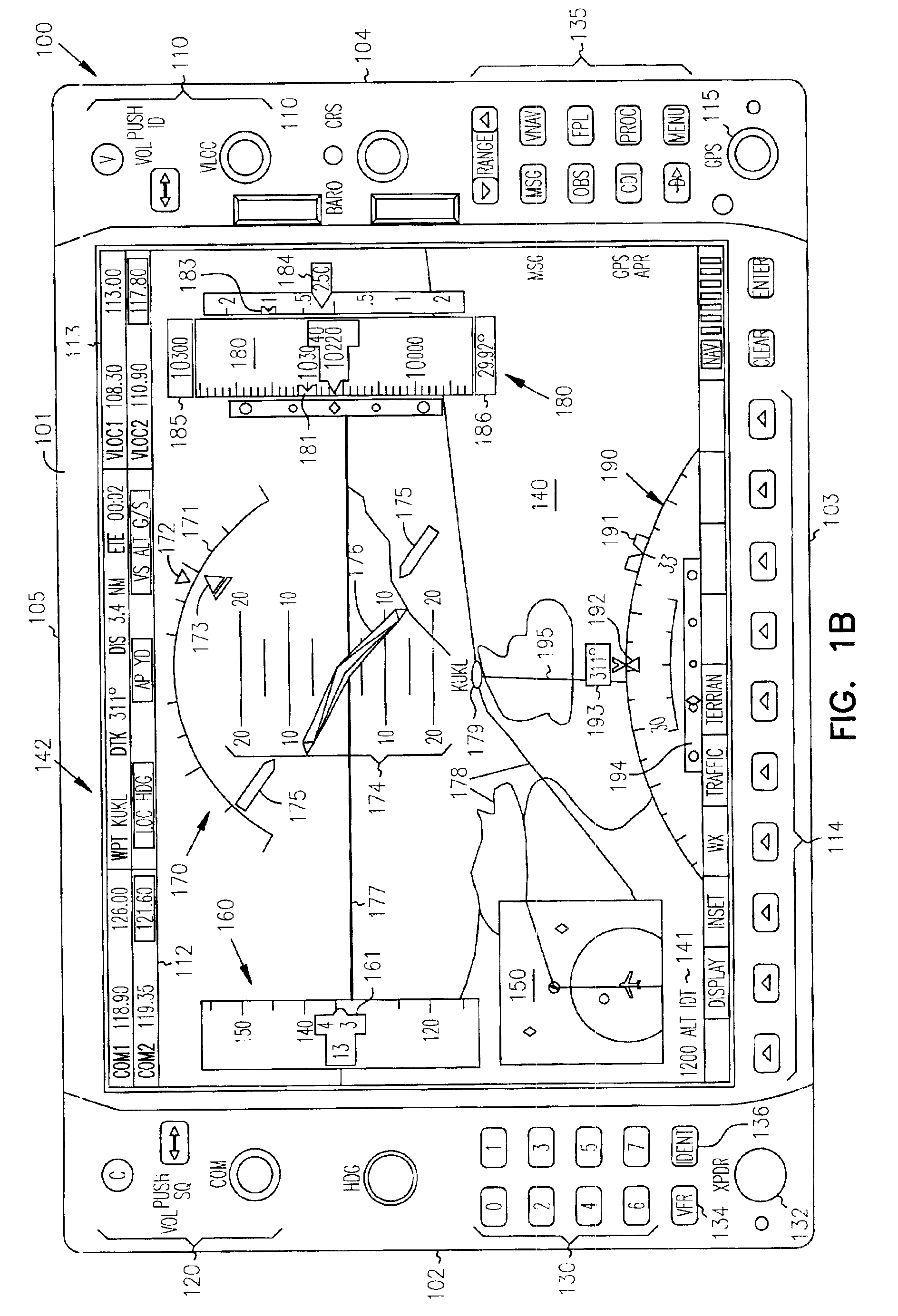
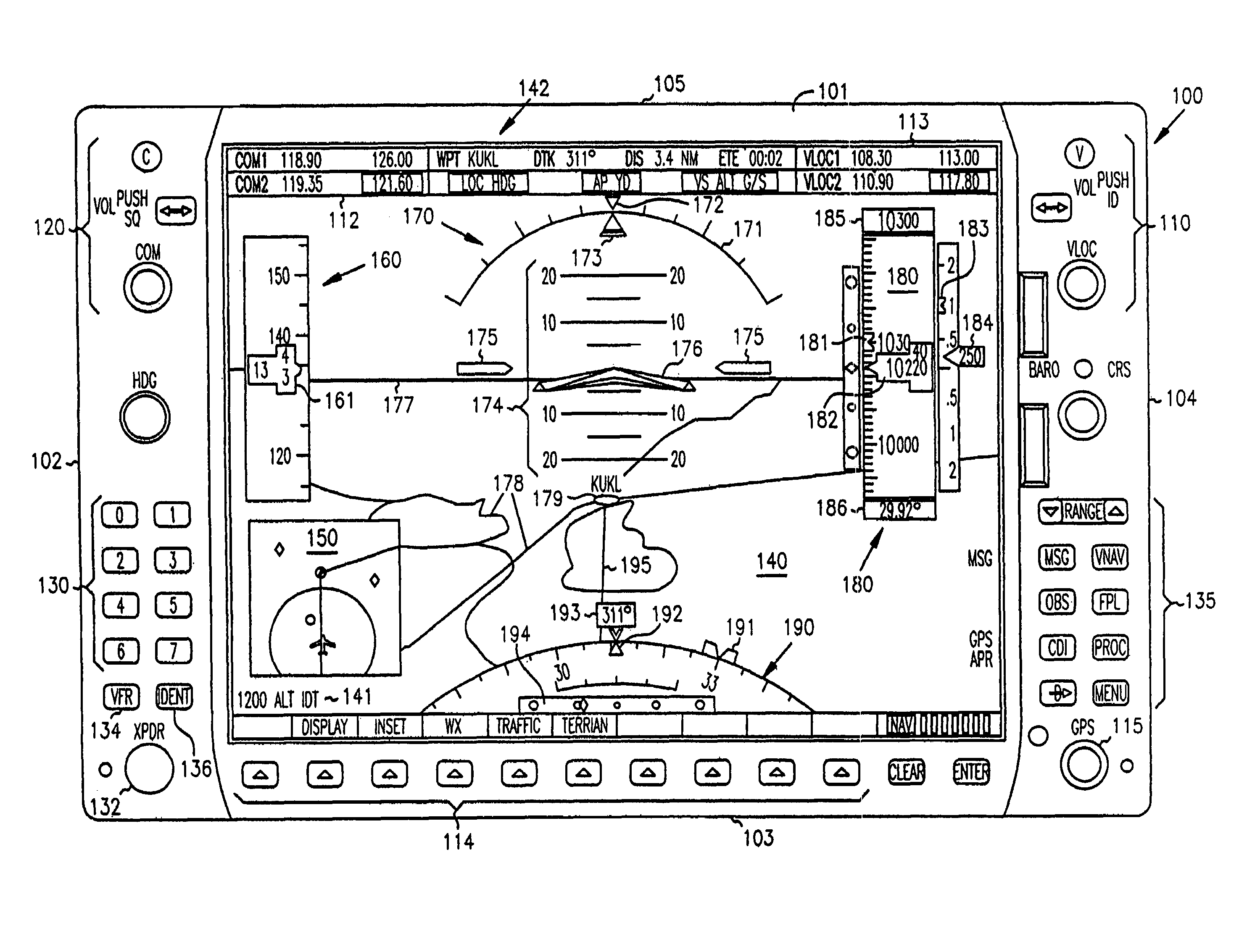
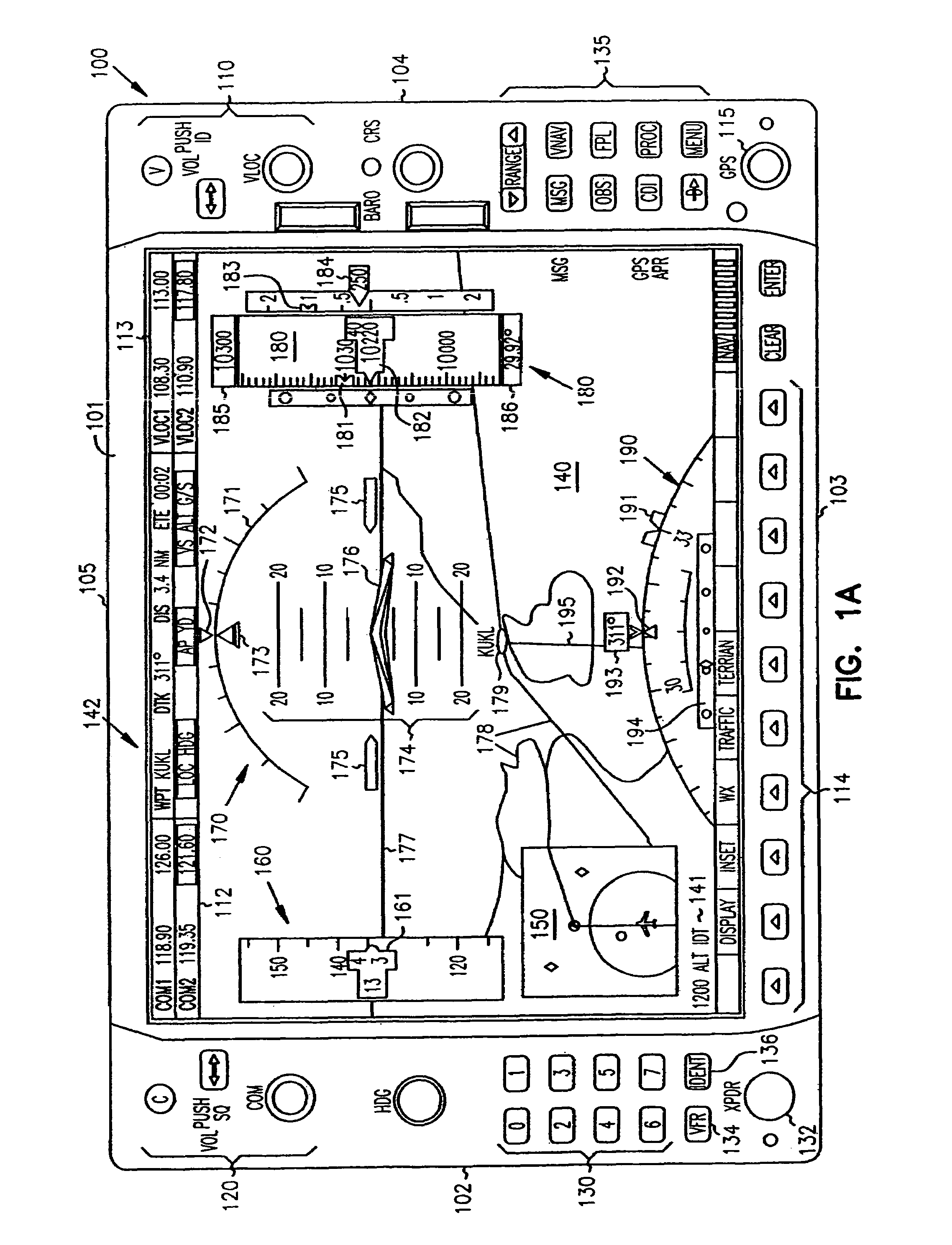
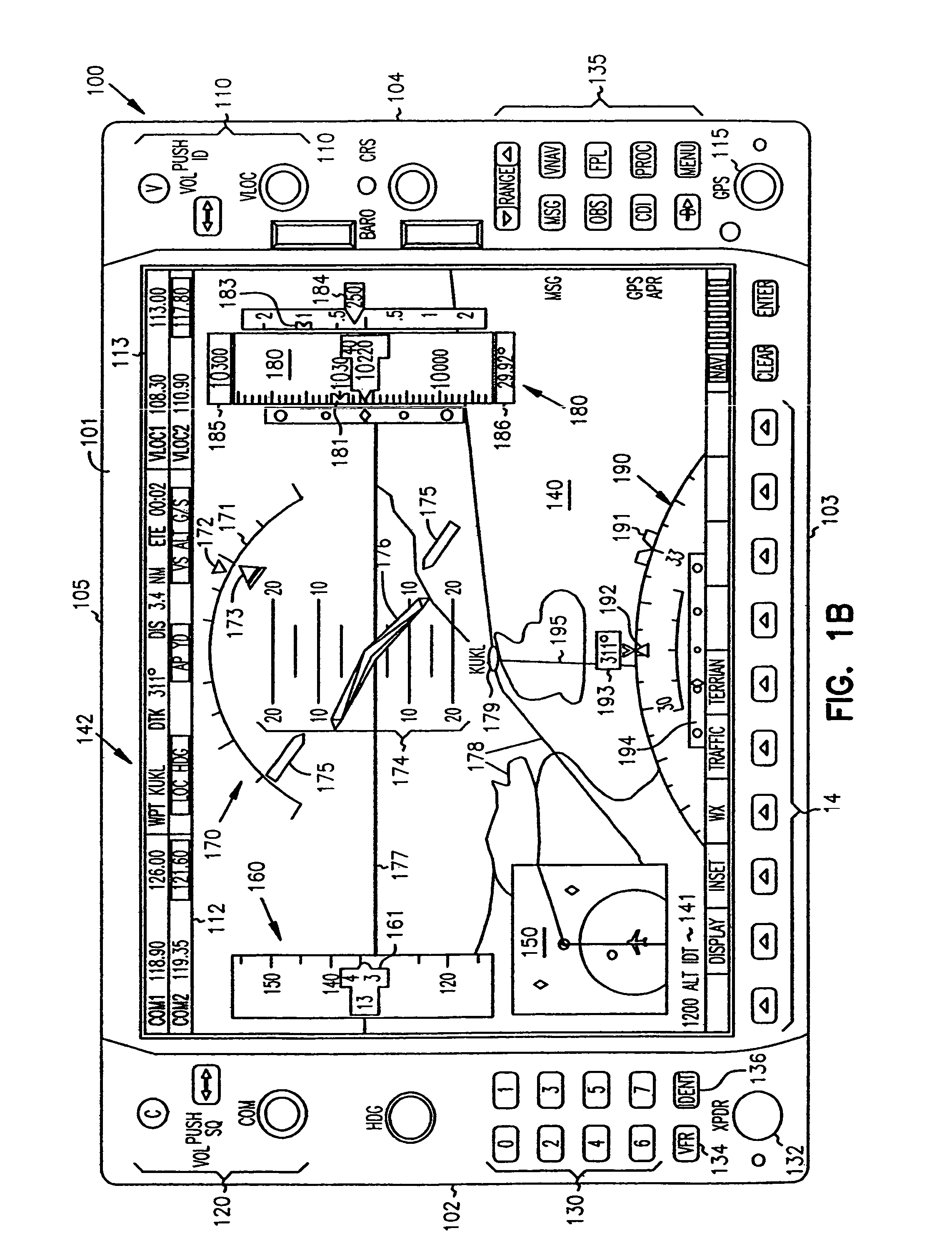
Cockpit instrument panel systems and methods with variable perspective flight display
InactiveUS6867711B1Great customizationEffective presentationAircraft displaysNavigation instrumentsMulti-function displayComputer science
Systems and methods are provided for integrated control, access, and customizable presentation of navigation related, flight information data on a multifunction display (MFD) within a cockpit. The MFD includes a bezel having controls located thereon which are adapted for controlling display formats, communication devices, navigational devices, and equipment sensors. A display is located adjacent to the bezel. The display is adapted to include at least one display region having navigation related data. At least one of the controls is operable to variably select a display format for the at least one display region.
Owner:GARMIN INT
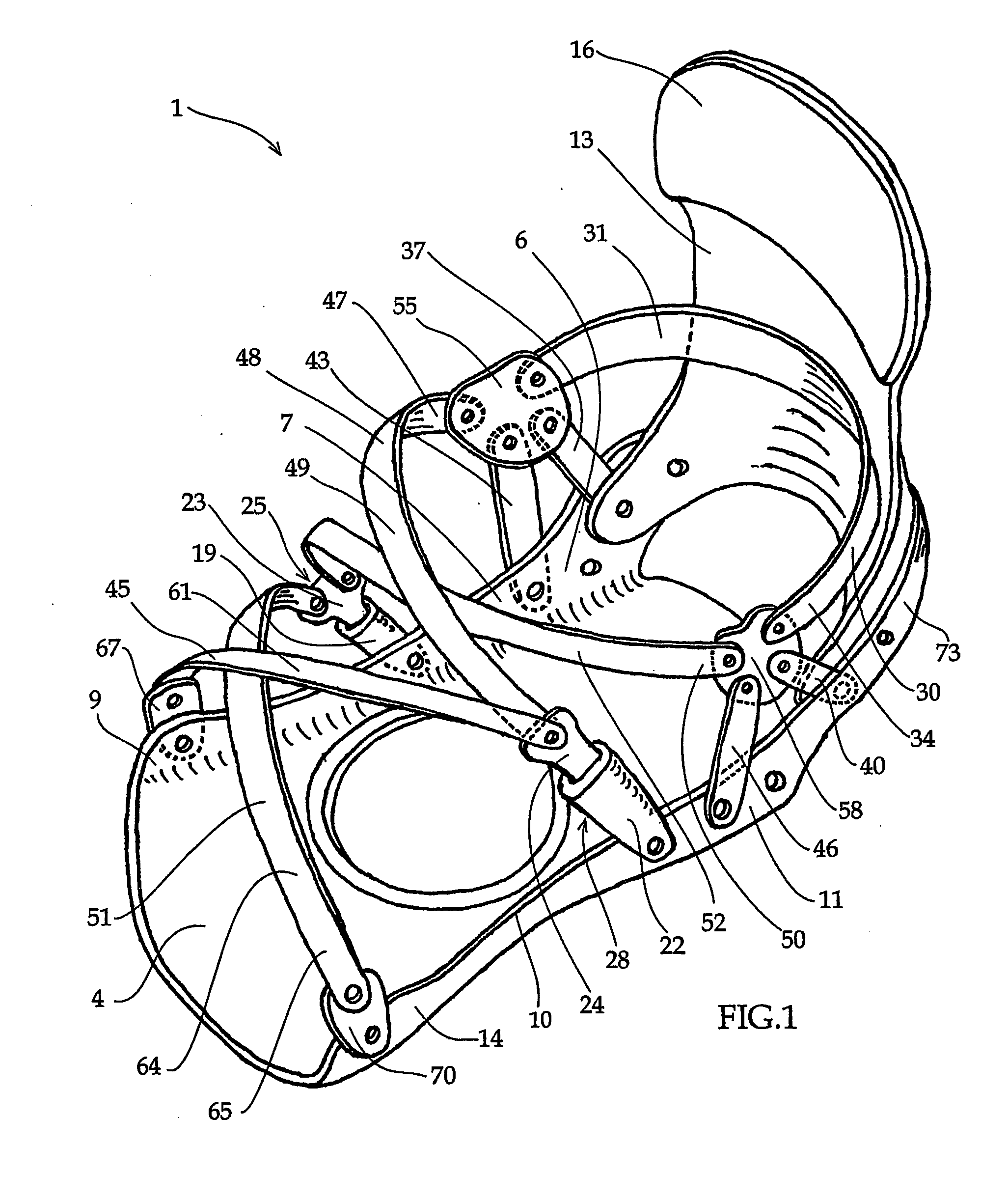
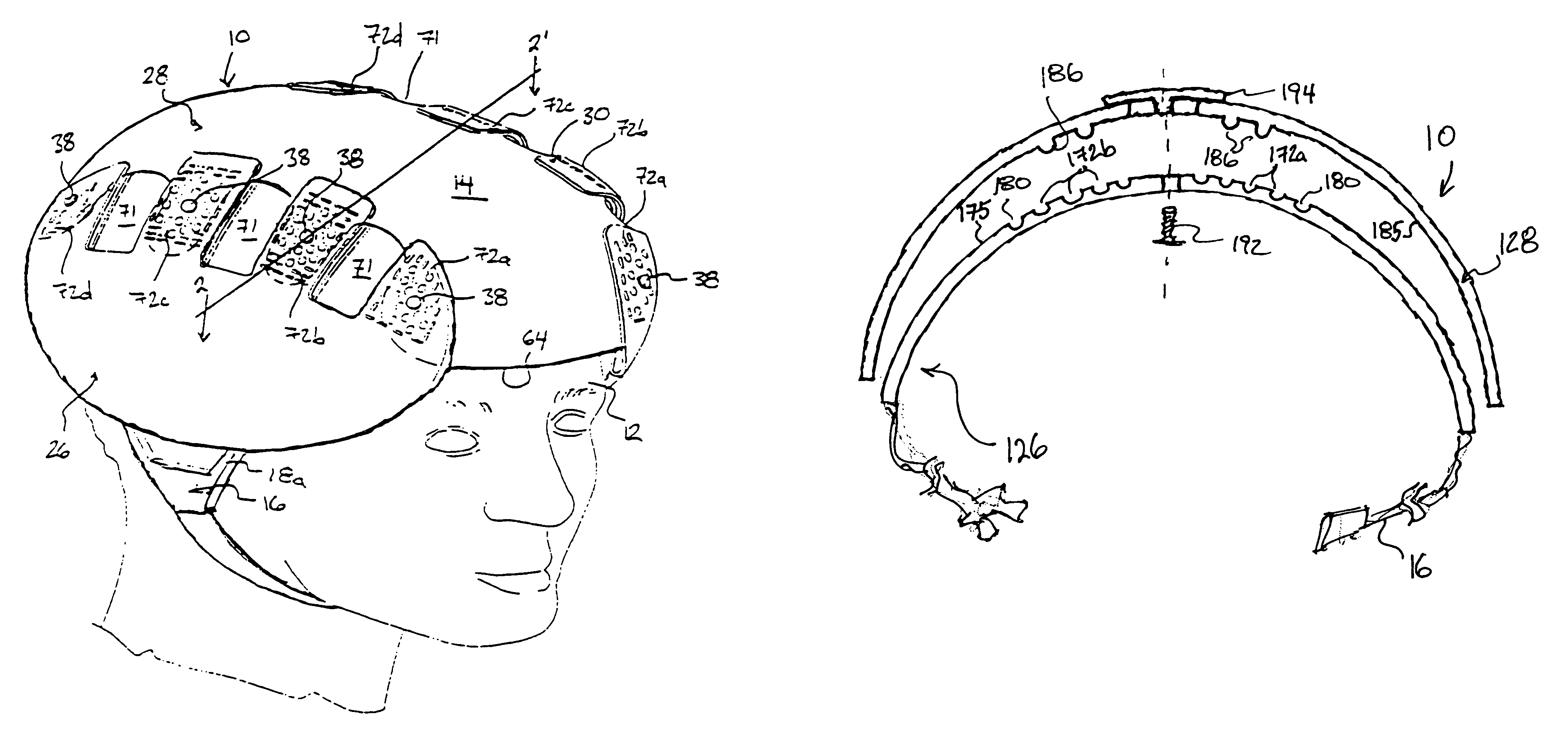
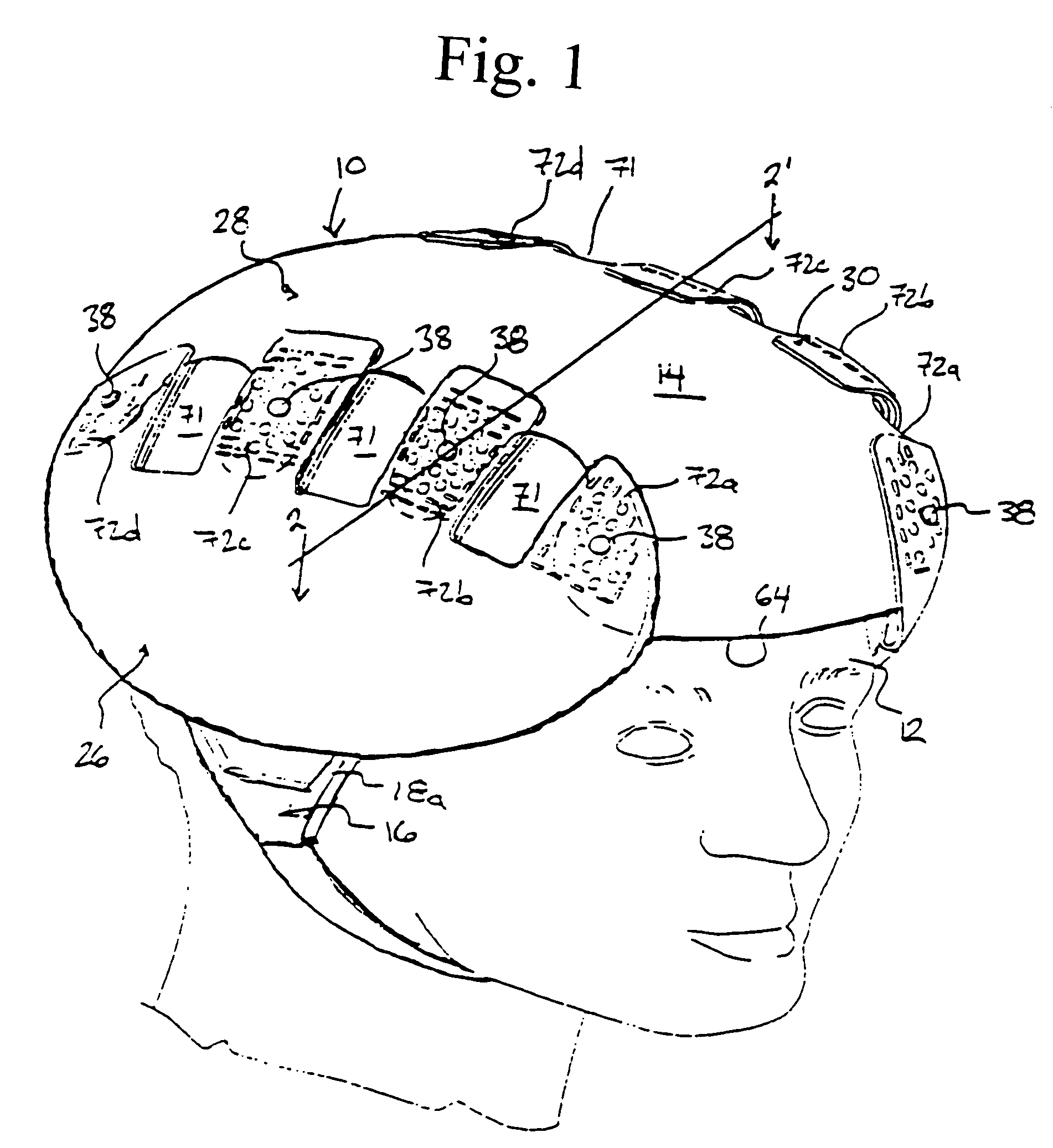
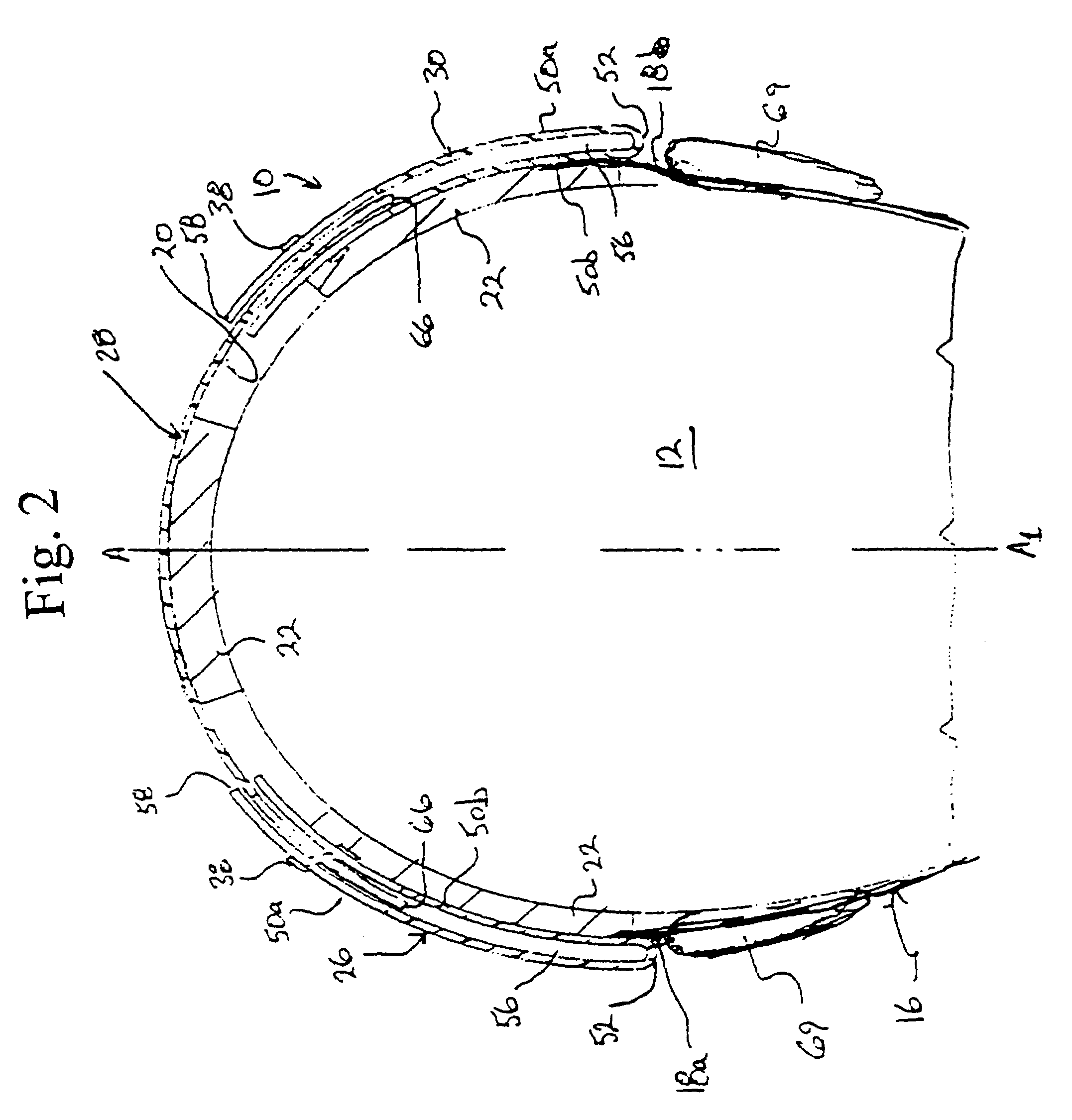
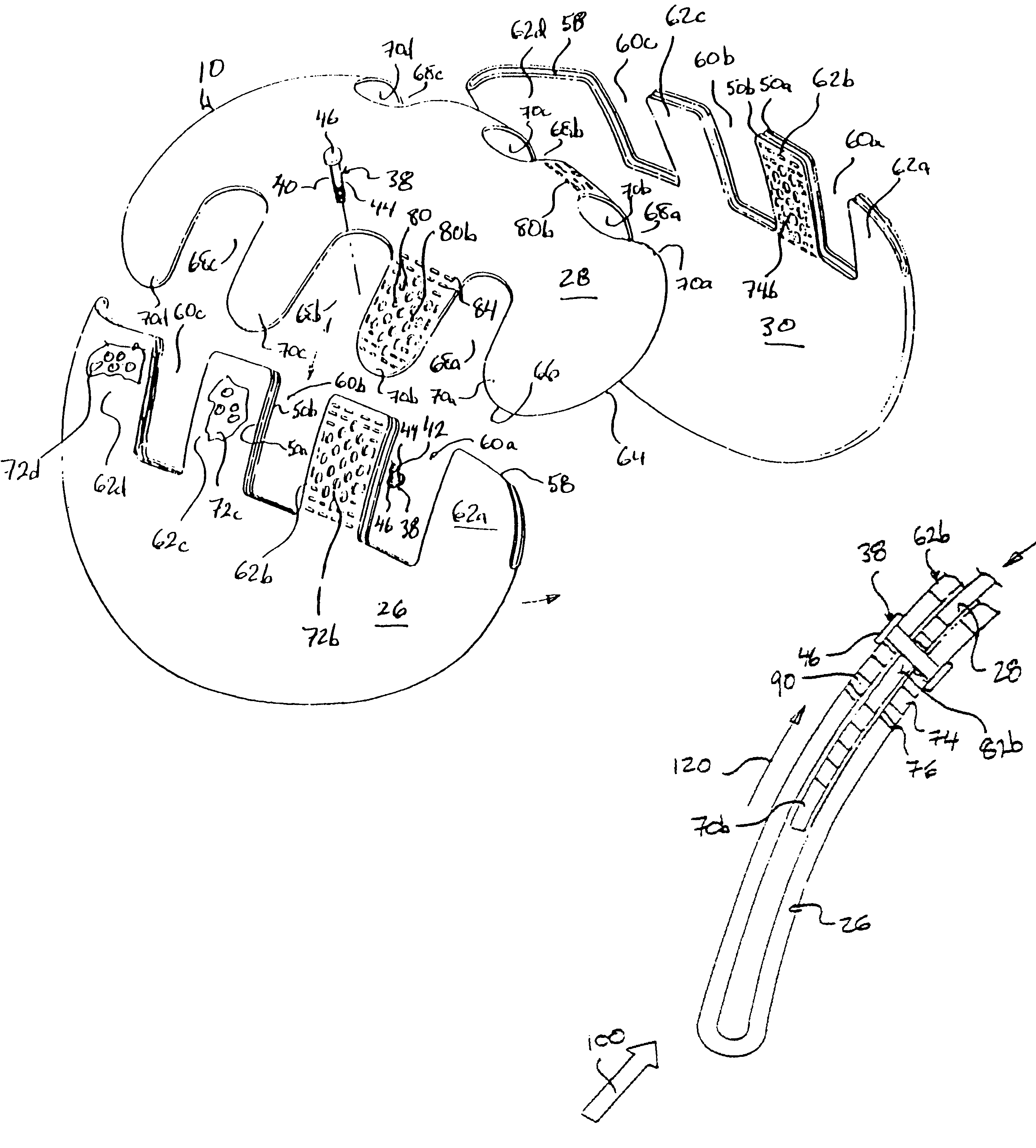
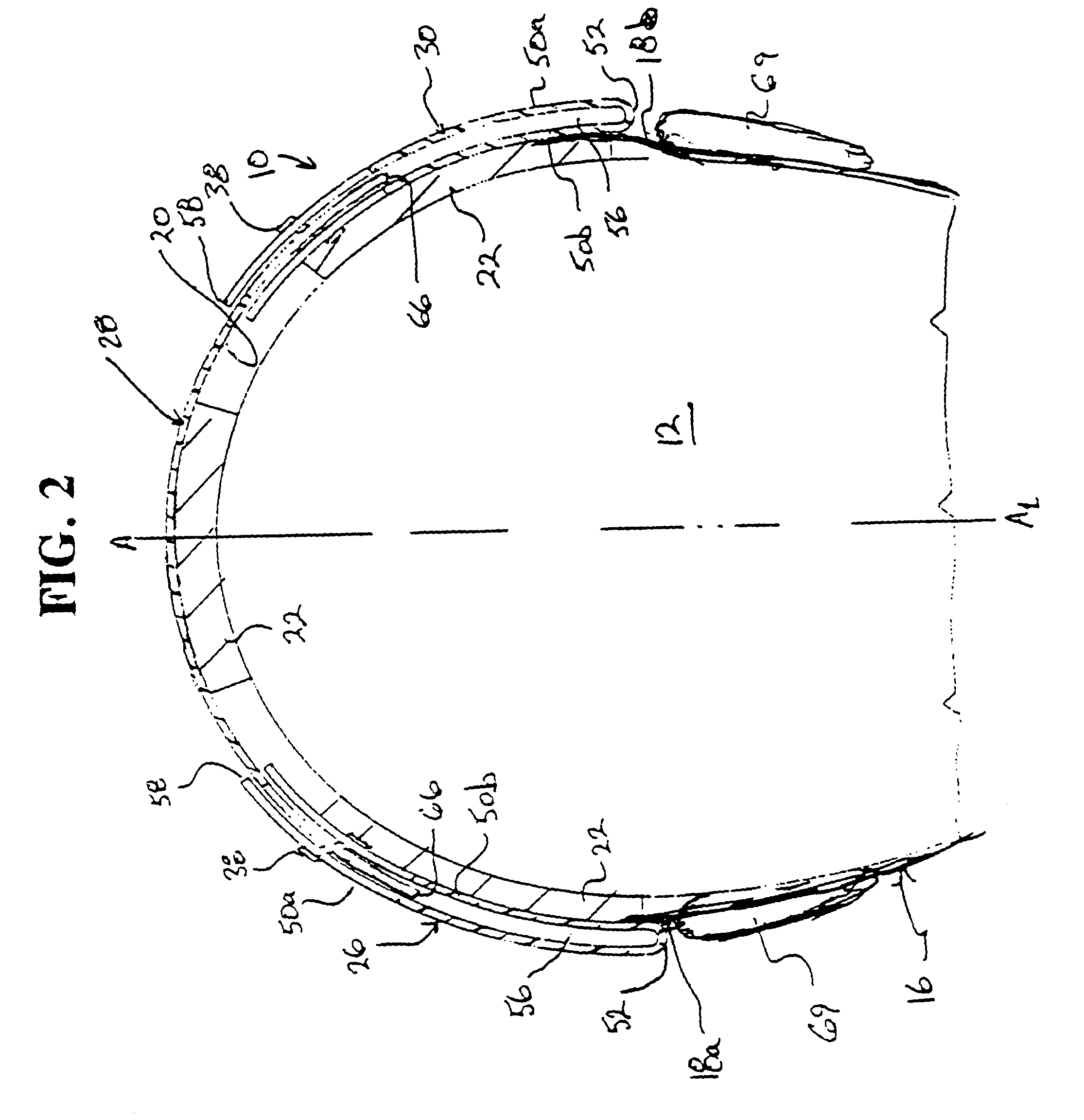
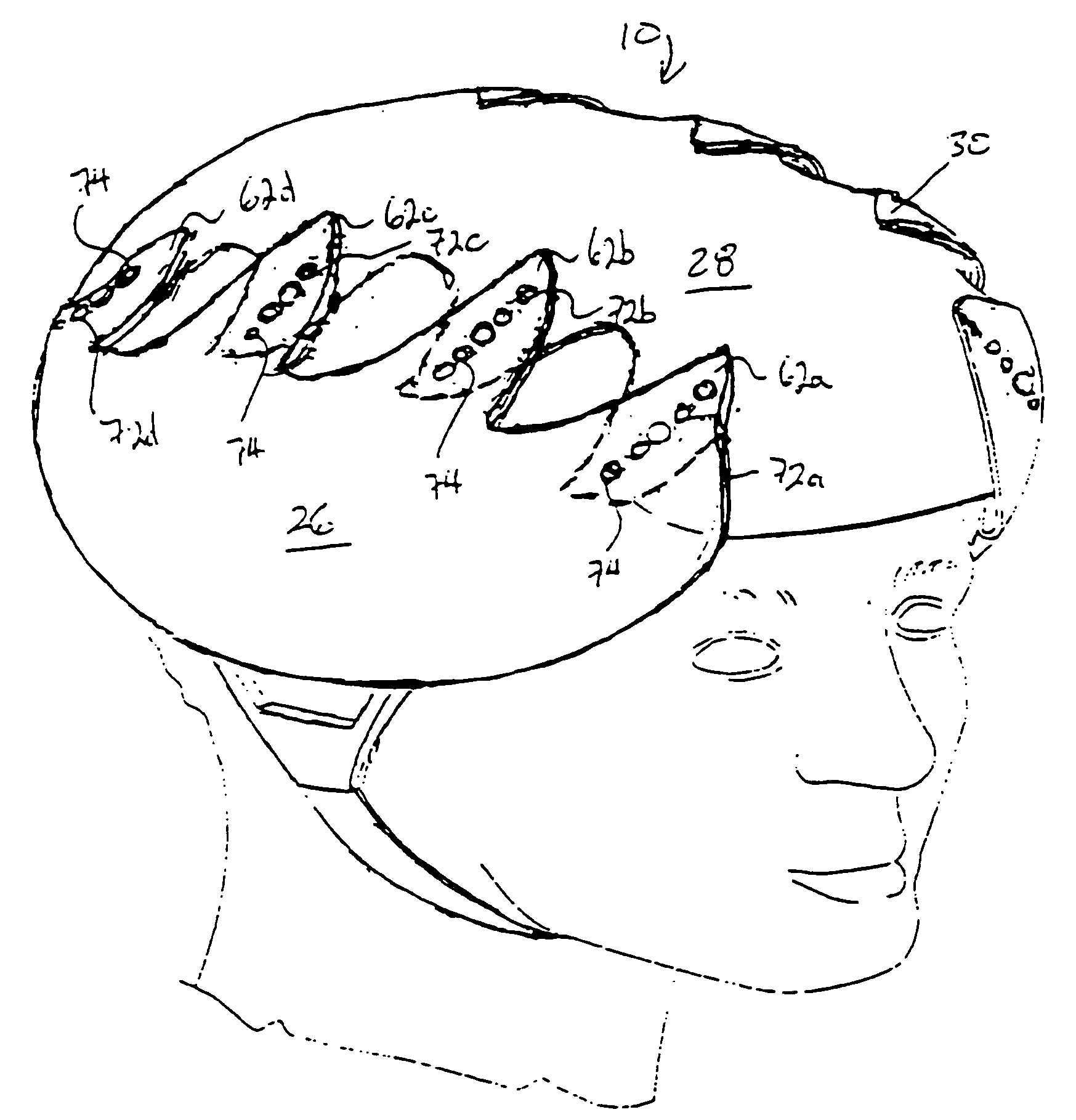
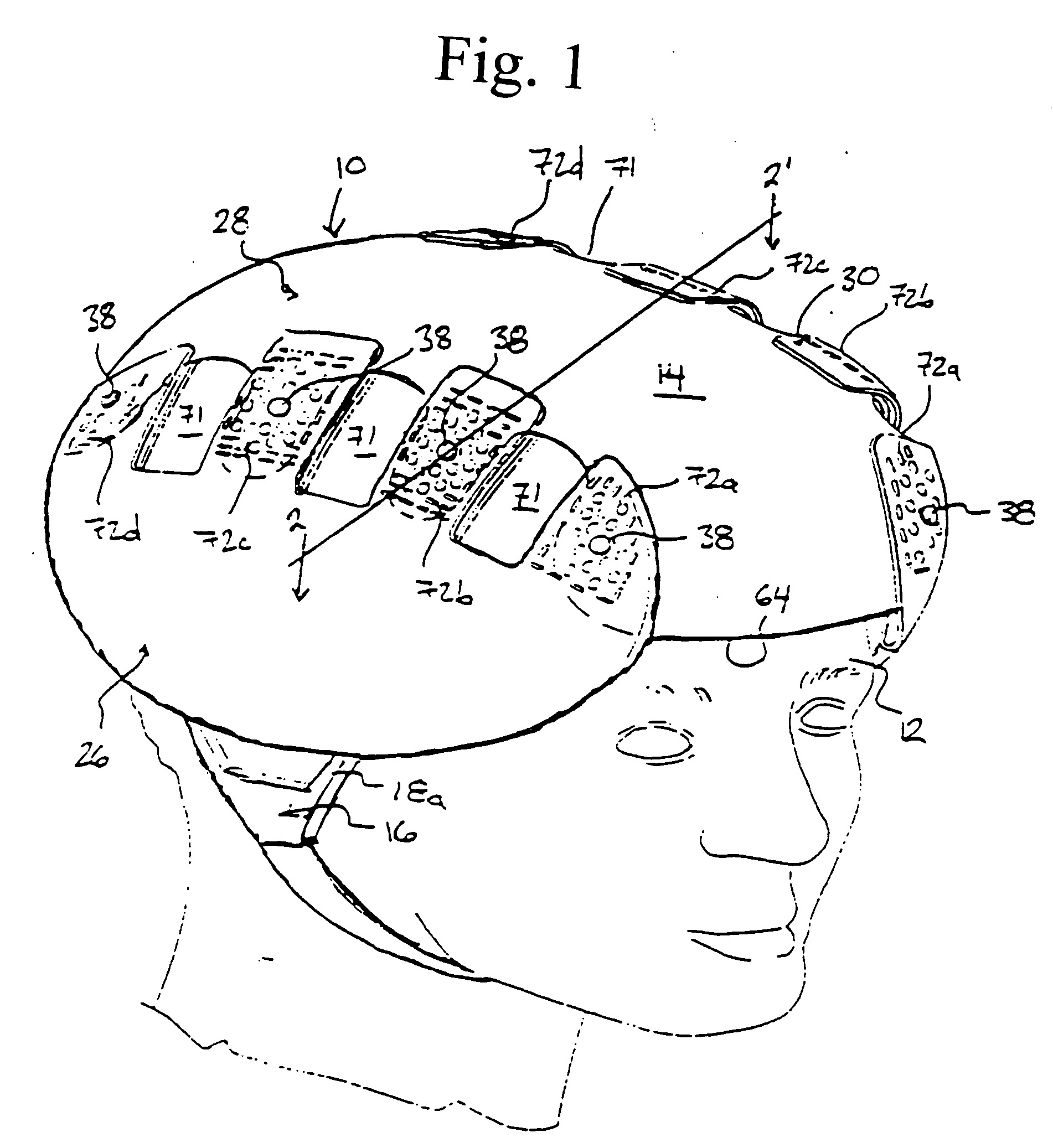
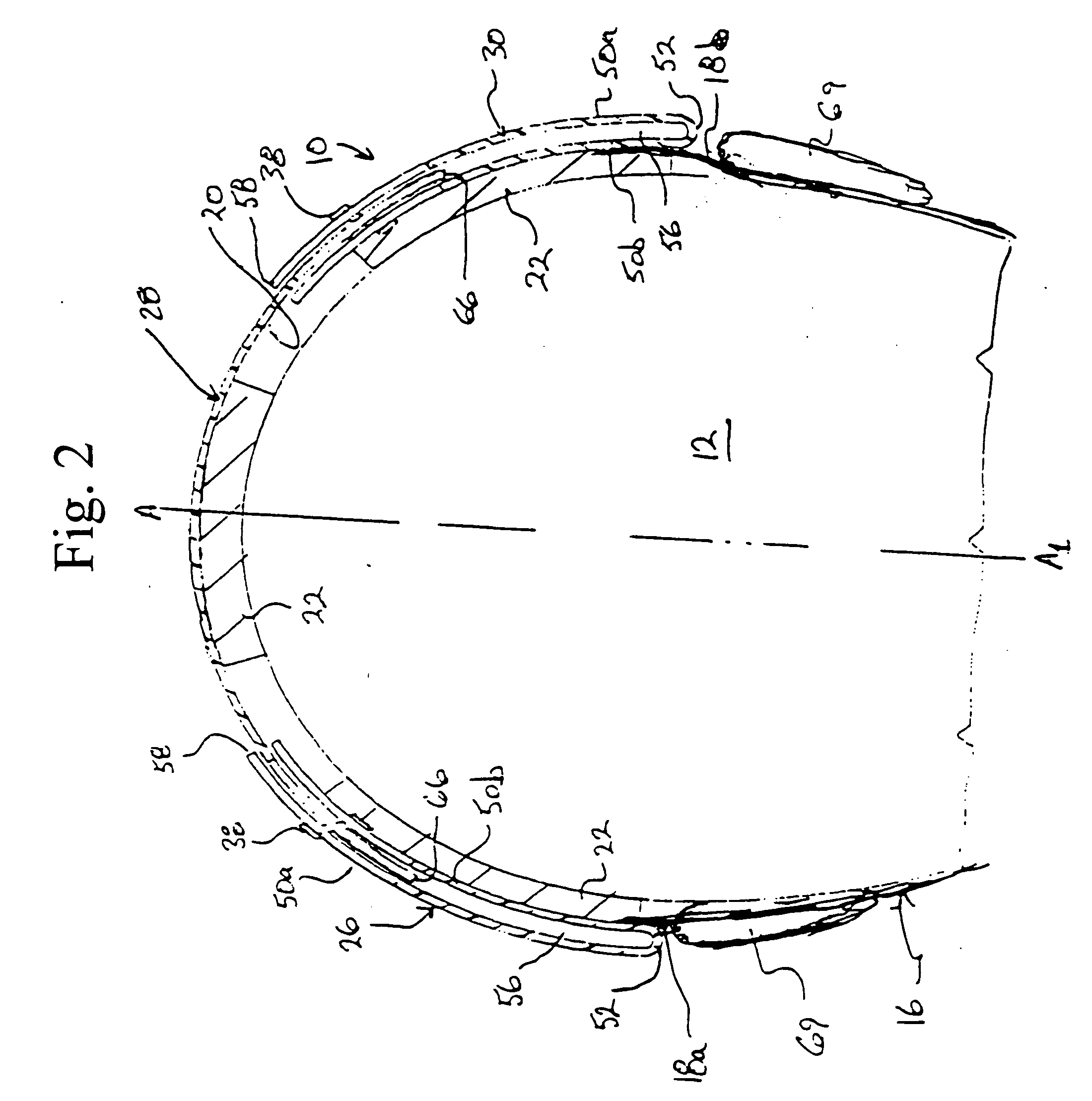
Protective head covering having impact absorbing crumple zone
InactiveUS6996856B2Closer in weight and sizeMinimizing resultant disproportionHatsSport apparatusMostly TrueEngineering
A helmet construction for protecting a user's head, and the brain within the cranium from impact forces, includes a shell contoured to the shape of the user's head, with cushioning along at least part of the shell interior and a chinstrap. The shell consists of three (or more) discrete panels that are physically and firmly coupled together providing rigid protection under most circumstances, but upon impact the panels move relative to one another, but not relative to the user's head, thereby permitting impact forces to be dissipated and / or redirected away from the cranium and brain within. Upon impact to the helmet, there are sequential stages of movement of the panels relative to each other, these movements initially being recoverable, but with sufficient vector forces the helmet undergoes structural changes in a pre-determined fashion, so that the recoverable and permanent movements cumulatively provide a protective ‘crumple zone’ or ‘shear zone’. The first two stages of protection arise from the design of the fasteners that have the ability to invaginate and collapse within themselves, and their design having a 45 degree angle, which will allow movement of a region of connected panels to translate along the fastener shaft. Both of these movements will be recoverable and provide a ‘functional crumple zone’. The final stage of protection arises from the braking function of the pins, as they are forced from one aperture through to the next, the direction and extent of which is determined by the impact force and direction. This final level of panel movement and protection is not recoverable and thus provides a ‘structural crumple zone’. Finally the fastener size and thickness, together with the thickness of webbing and distance between apertures, functions to provide varying degrees of resistance to impact forces, thus making the helmet design suitable for activities with different levels of impact speed and risk potential.
Owner:PUCHALSKI TECHN
Protective head covering having impact absorbing crumple or shear zone
A helmet construction for protecting a user's head, and the brain within the cranium from impact forces, includes a shell contoured to the shape of the user's head, with cushioning along at least part of the shell interior and a chinstrap. The shell consists of three (or more) discrete panels that are physically and firmly coupled together providing rigid protection under most circumstances, but upon impact the panels move relative to one another, but not relative to the user's head, thereby permitting impact forces to be dissipated and / or redirected away from the cranium and brain within. Upon impact to the helmet, there are sequential stages of movement of the panels relative to each other, these movements initially being recoverable, but with sufficient vector forces the helmet undergoes structural changes in a pre-determined fashion, so that the recoverable and permanent movements cumulatively provide a protective ‘crumple zone’ or ‘shear zone’. The first two stages of protection arise from the design of the fasteners that have the ability to invaginate and collapse within themselves, and their design having a 45 degree angle, which will allow movement of a region of connected panels to translate along the fastener shaft. Both of these movements will be recoverable and provide a ‘functional crumple zone’. The final stage of protection arises from the braking function of the pins, as they are forced from one aperture through to the next, the direction and extent of which is determined by the impact force and direction. This final level of panel movement and protection is not recoverable and thus provides a ‘structural crumple zone’. Finally the fastener size and thickness, together with the thickness of webbing and distance between apertures, functions to provide varying degrees of resistance to impact forces, thus making the helmet design suitable for activities with different levels of impact speed and risk potential.
Owner:PUCHALSKI TECHN
Protective head covering having impact absorbing crumple zone
InactiveUS20050257312A1Closer in weight and sizeMinimizing resultant disproportionHatsSport apparatusMostly TrueEngineering
A helmet construction for protecting a user's head, and the brain within the cranium from impact forces, includes a shell contoured to the shape of the user's head, with cushioning along at least part of the shell interior and a chinstrap. The shell consists of three (or more) discrete panels that are physically and firmly coupled together providing rigid protection under most circumstances, but upon impact the panels move relative to one another, but not relative to the user's head, thereby permitting impact forces to be dissipated and / or redirected away from the cranium and brain within. Upon impact to the helmet, there are sequential stages of movement of the panels relative to each other, these movements initially being recoverable, but with sufficient vector forces the helmet undergoes structural changes in a pre-determined fashion, so that the recoverable and permanent movements cumulatively provide a protective ‘crumple zone’ or ‘shear zone’. The first two stages of protection arise from the design of the fasteners that have the ability to invaginate and collapse within themselves, and their design having a 45 degree angle, which will allow movement of a region of connected panels to translate along the fastener shaft. Both of these movements will be recoverable and provide a ‘functional crumple zone’. The final stage of protection arises from the braking function of the pins, as they are forced from one aperture through to the next, the direction and extent of which is determined by the impact force and direction. This final level of panel movement and protection is not recoverable and thus provides a ‘structural crumple zone’. Finally the fastener size and thickness, together with the thickness of webbing and distance between apertures, functions to provide varying degrees of resistance to impact forces, thus making the helmet design suitable for activities with different levels of impact speed and risk potential.
Owner:PUCHALSKI TECHN
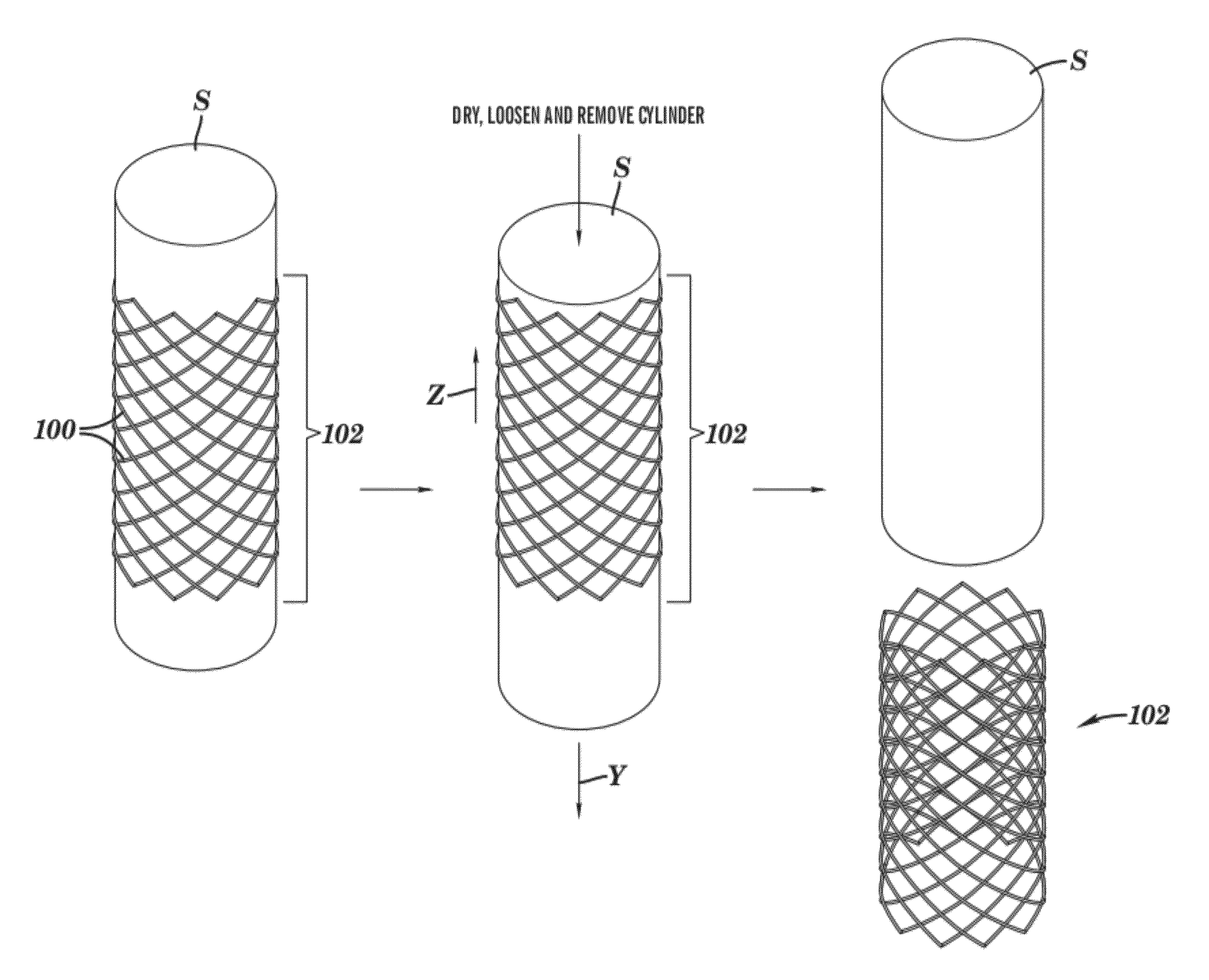
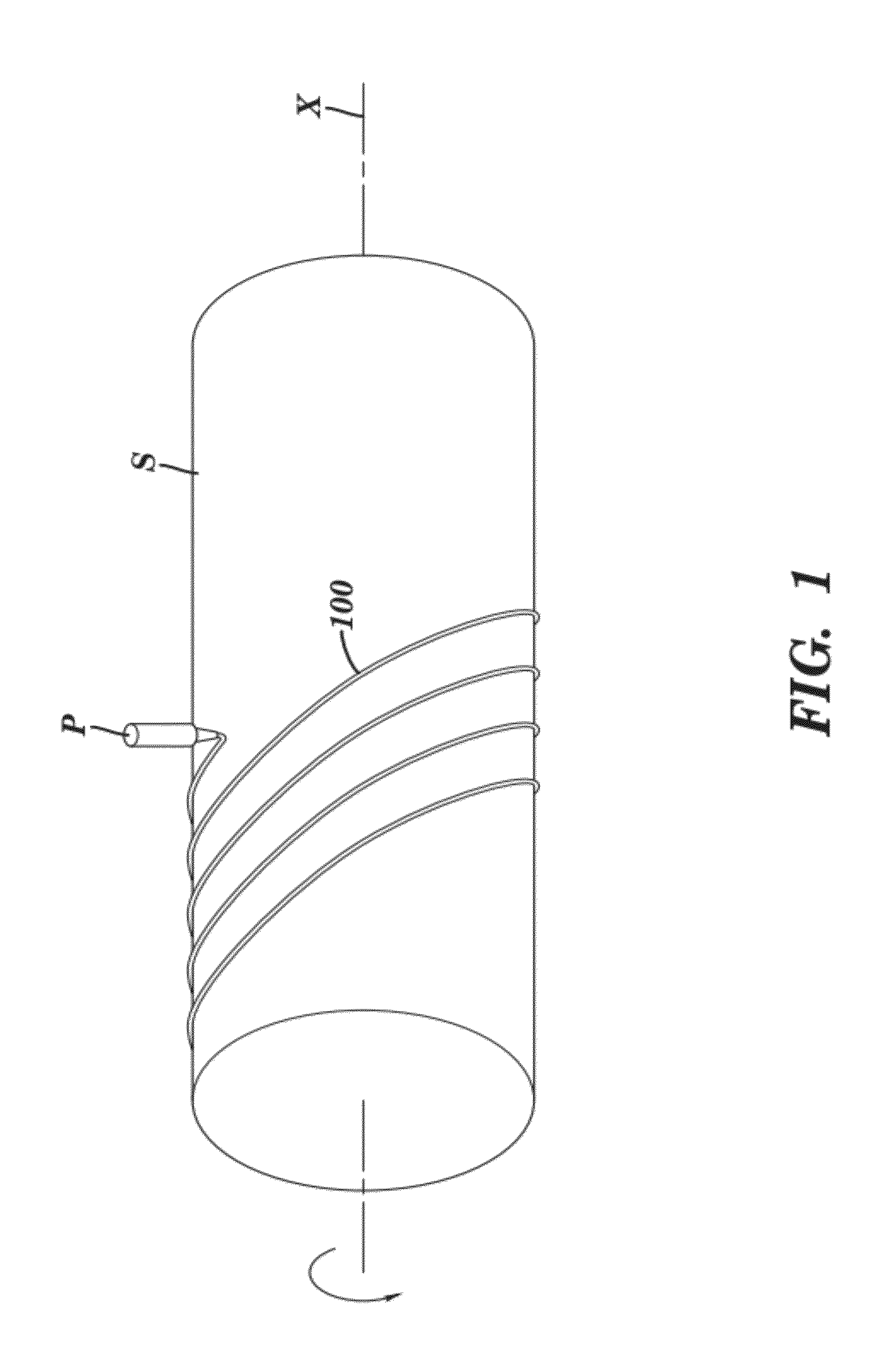
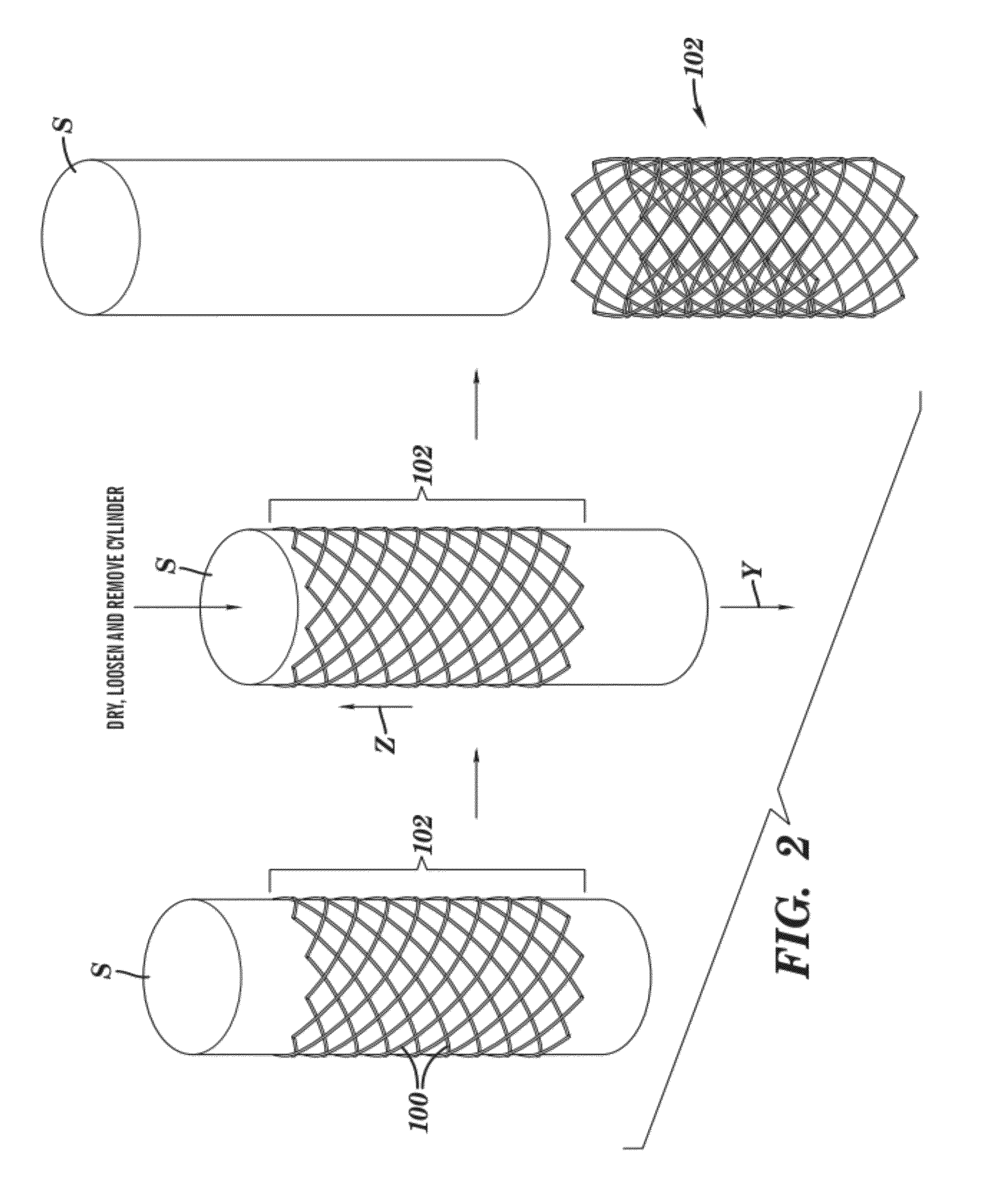
Stents and methods of making stents
InactiveUS20120150275A1Reduce manufacturing costReduce material wasteStentsPretreated surfacesBiomedical engineeringStent
The present invention relates to a stent having a longitudinally-extending passage defined by a plurality of seamless strut elements with spacing between them. Each of these strut elements are in the form of lines defining the passage. The strut elements have a thickness in the range of 30 microns to 150 microns and are formed as at least one written layer. Also disclosed are methods of making the stent.
Owner:MICROPEN TECH CORP
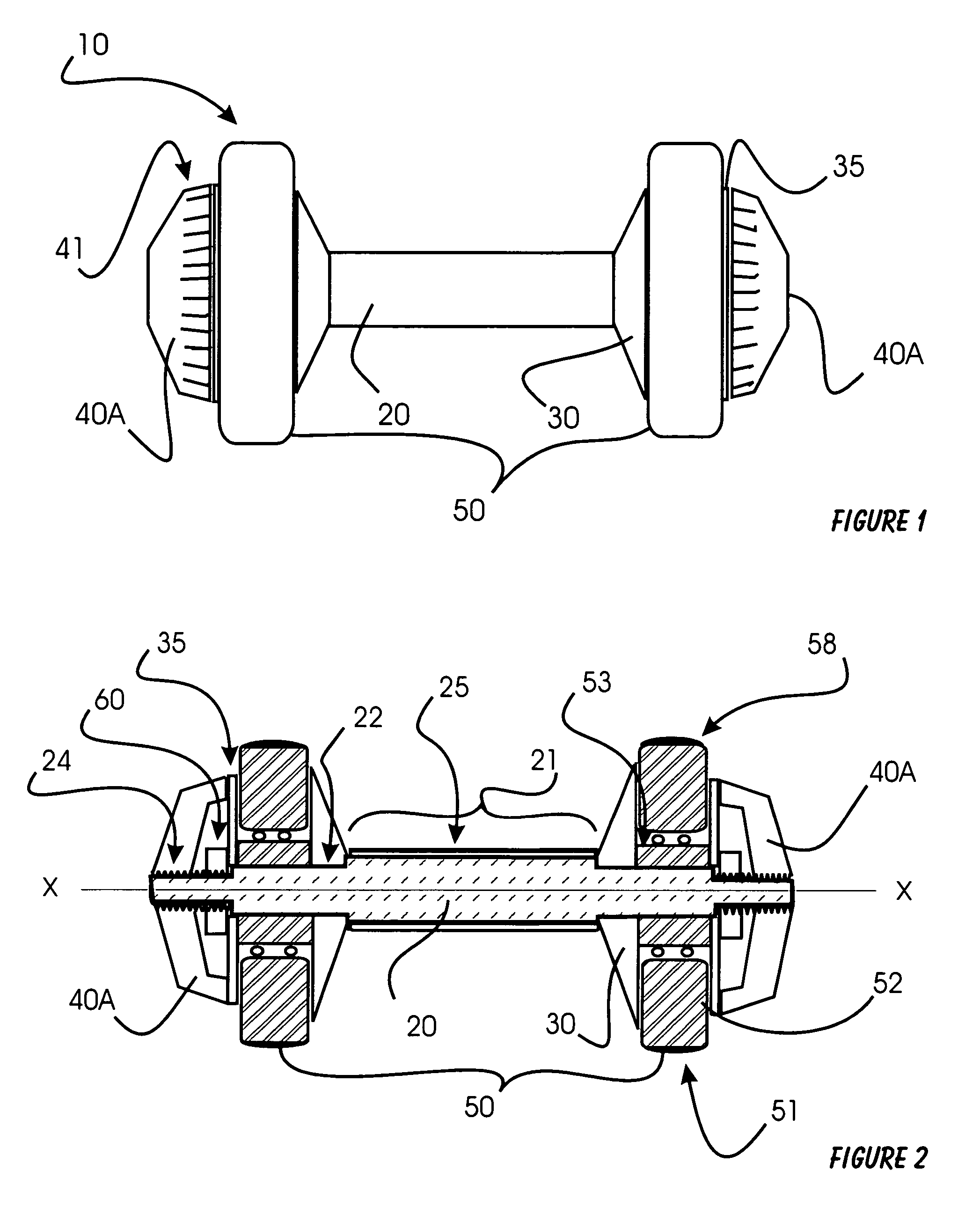
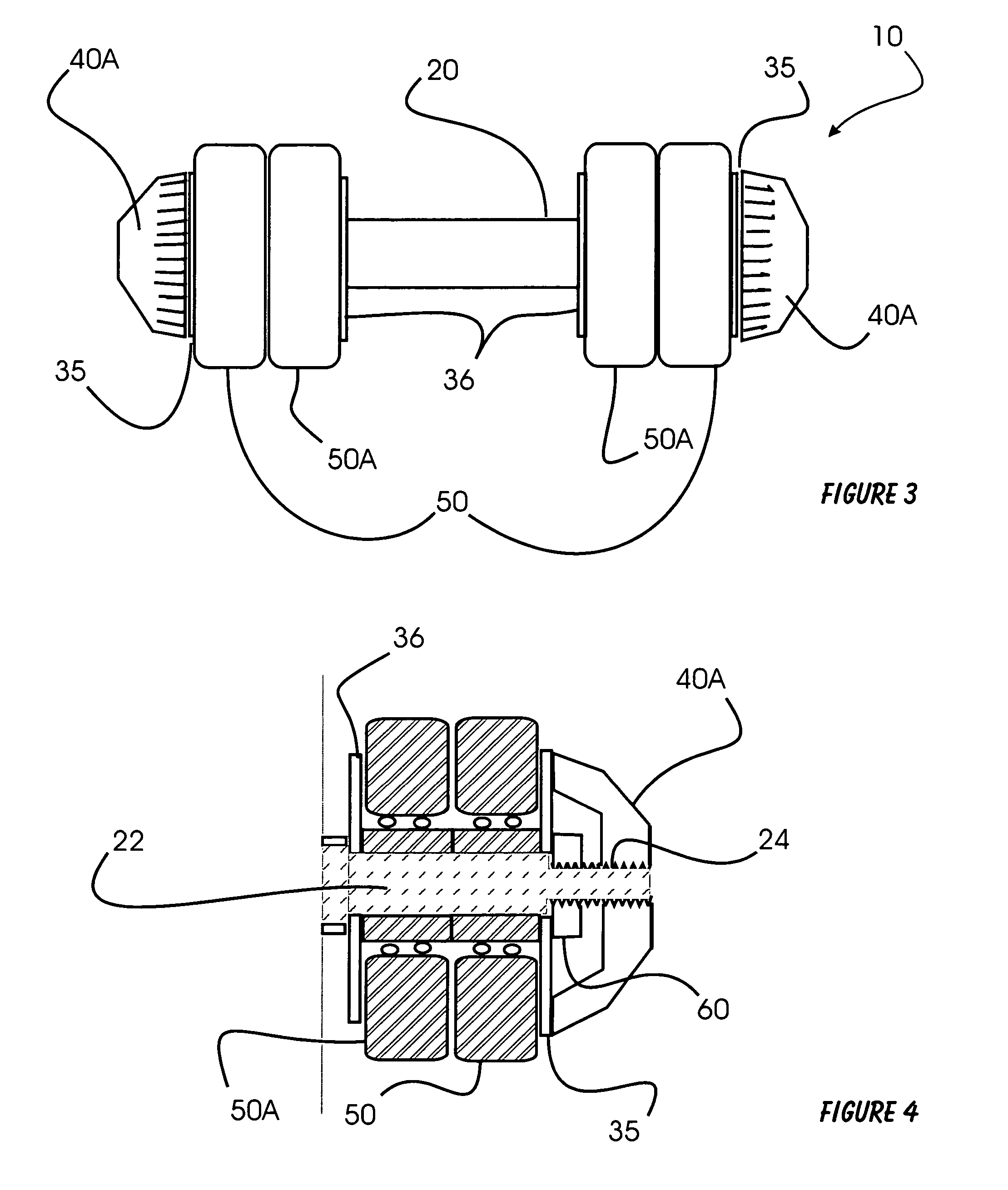
Roll-able dumbbells
InactiveUS7011610B2Simple and valueLarge massDumb-bellsMovement coordination devicesDumbbellSurface layer
Roll-able dumbbells are disclosed. An improved roll-able dumbbell utilizing gravitation and roll-resistance is presented having a handle and a plurality of circular weights attached to its ends. Regular dumbbells are generally held in hands and lifted up and down. The improved roll-able hand weights, in addition to providing benefits of a regular dumbbell, can be held and rolled against a variety of horizontal, slanted or vertical surfaces in a multitude of body positions. Each entire circular weight, its outer segments and / or the surface layer can rotate independently in respect to the handle. In addition, rotational resistance can be influenced by the user by tightening / loosening the end caps or other means. The total weight of the improved roll-able hand weights can also be adjusted by the user, who can select proper number and combination of individual components.
Owner:WAWRZYNIAK GREG
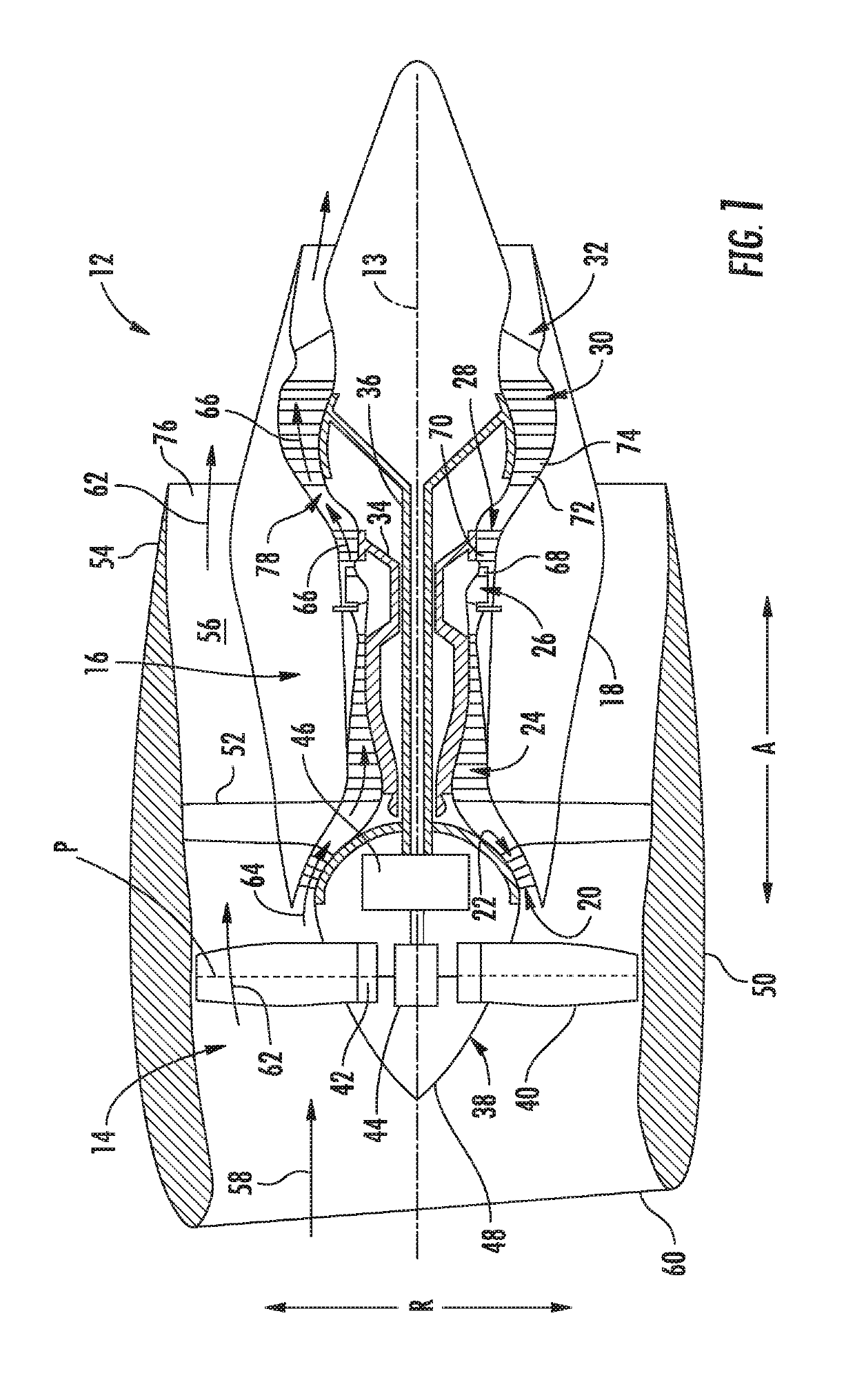
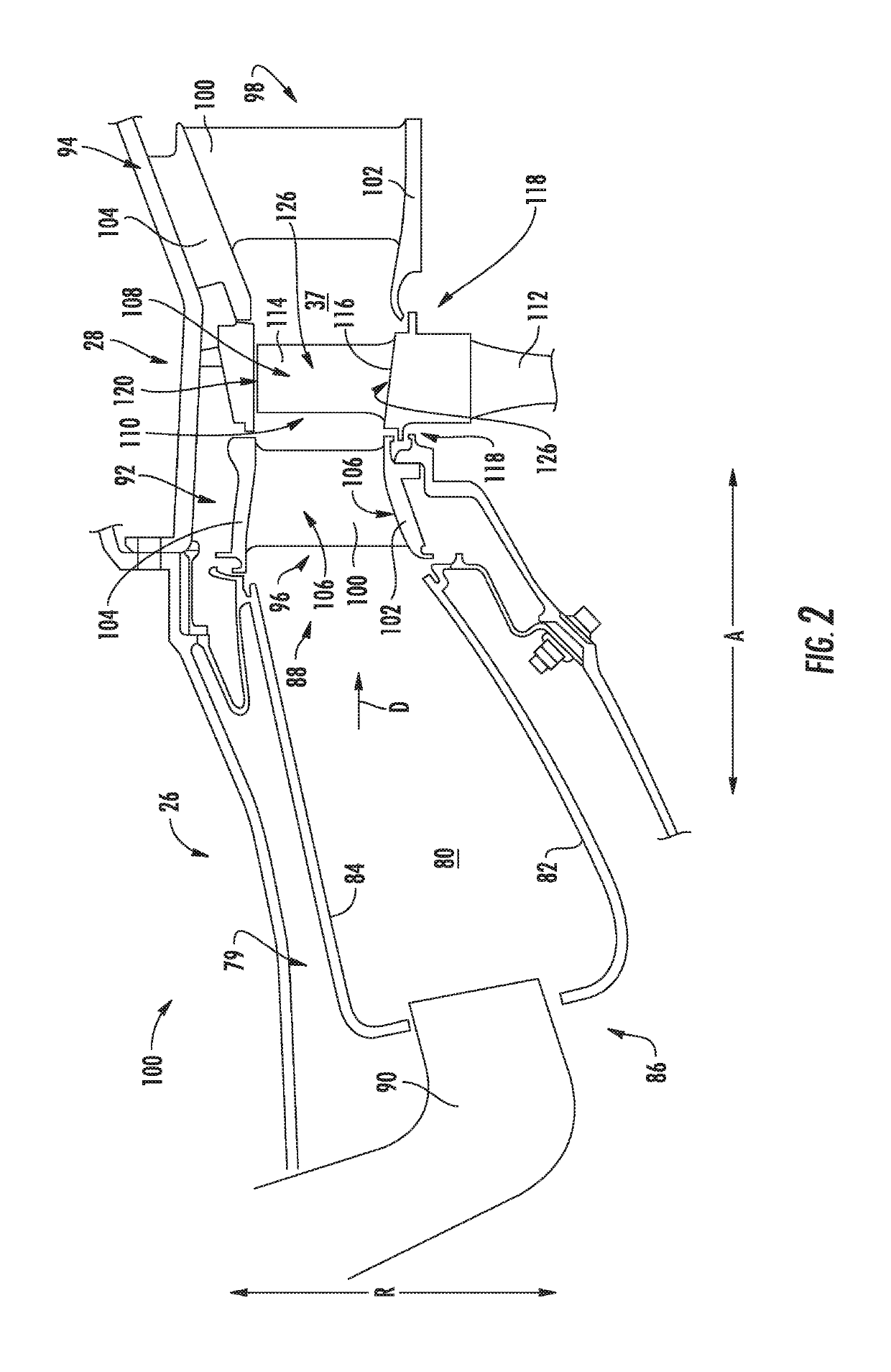
Riblets For A Flowpath Surface Of A Turbomachine
ActiveUS20170234134A1Great customizationEngine manufacturePump componentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Device for attaching a hair enhancer to a person's hair and hair enhancement apparatus incorporating same
A device usable for attaching a hair enhancer to a person's hair and a hair enhancement apparatus incorporating such a device include a strip of flexible material, at least one hair clip attached to a first side of the strip of material, and an adhesive layer attached to a second side of the strip of material. The adhesive layer facilitates attachment of the device to a hair enhancer, such as a hair extension. The strip of material may be sized and shaped to accommodate one hair clip or a plurality of hair clips (e.g., a row of hair clips). The attachment device may also include a backing paper affixed to a side of the adhesive layer which is to be attached to the hair enhancer. In such a case, the backing paper may be removable by a user to enable the adhesive layer to be attached to the hair enhancer.
Owner:KENNA LISA
Massaging device having controller to remove dead points during operation
InactiveUS7429251B2Enhanced and pleasant massaging effectGood effectChiropractic devicesRoller massageReciprocating motionMassage
A massaging device gives different massaging patterns to different parts of a user's body for enhanced and pleasant massaging effect. The device includes an applicator applying a massage force to the user, and at least two driving units for driving the applicator to make different reciprocating movements respectively in different directions from each other. The least two driving units is controlled to reciprocate the applicator for providing the massaging force in different massaging patterns. A sensor is provided to acknowledge the position of the applicator. A massage pattern selector is provided to select one of the massaging patterns depending upon the position of the applicator.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
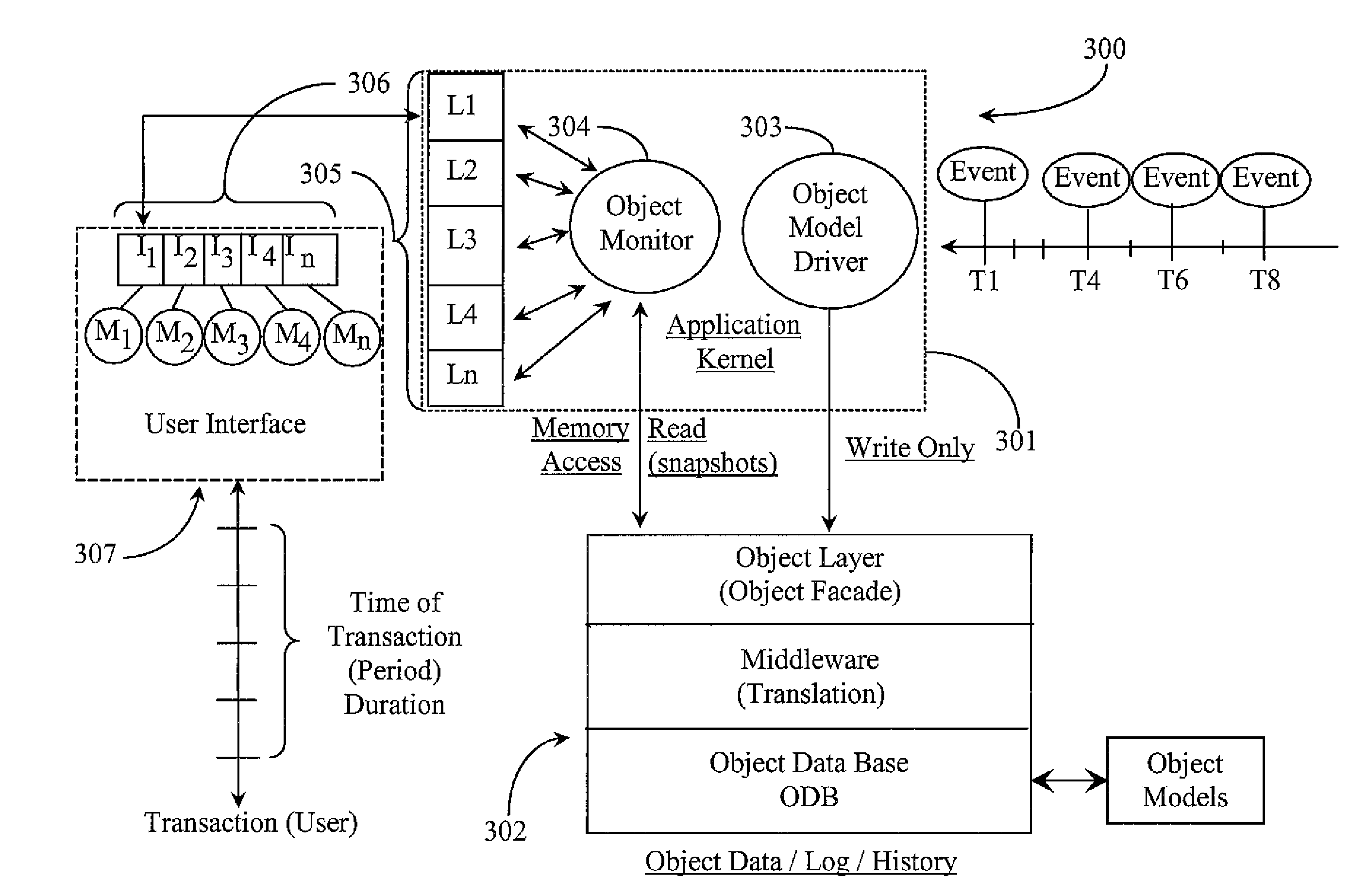
Method for Improving Temporal Consistency and Snapshot Recency in a Monitored Real-Time Software-Reporting-Application Architecture
InactiveUS20080320496A1Great customizationFinanceMultiprogramming arrangementsTemporal consistencyDatabase application
An object-oriented software application is provided for receiving updates that change state of an object model and reporting those updates to requesting users. The application includes a database application for storing data; an object model driver for writing updates into the database; a notification system for notifying about the updates; and, a plurality of external monitors for reading the updates. In a preferred embodiment the object model produces multiple temporal snapshots of itself in co-currency with received events, each snapshot containing associated update information from an associated event and whereupon at the time of occurrence of each snapshot coinciding with an event the notification system notifies the appropriate external monitor or monitors, which in turn access the appropriate snapshot, performs calculations thereupon if required and renders the information accessible to the users.
Owner:GENESYS TELECOMMUNICATIONS LABORATORIES INC
Cockpit instrument panel systems and methods with variable perspective flight display
InactiveUS7626515B1Great customizationEffective presentationAircraft displaysNavigation instrumentsMulti-function displayComputer science
Systems and methods are provided for integrated control, access, and customizable presentation of navigation related, flight information data on a multifunction display (MFD) within a cockpit. The MFD includes a bezel having controls located thereon which are adapted for controlling display formats, communication devices, navigational devices, and equipment sensors. A display is located adjacent to the bezel. The display is adapted to include at least one display region having navigation related data. At least one of the controls is operable to variably select a display format for the at least one display region.
Owner:GARMIN INT
Occupancy sensor and associated methods
ActiveUS20120287245A1Readily stored in memoryGreat customizationImage enhancementImage analysisMicrocontrollerRule engine
A device to detect occupancy of an environment includes a sensor to capture video frames from a location in the environment. The device may compare rules with data using a rules engine. The microcontroller may include a processor and memory to produce results indicative of a condition of the environment. The device may also include an interface through which the data is accessible. The device may generate results respective to the location in the environment. The microcontroller may be in communication with a network. The video frames may be concatenated to create an overview to display the video frames substantially seamlessly respective to the location in which the sensor is positioned. The overview may be viewable using the interface and the results of the analysis performed by the rules engine may be accessible using the interface.
Owner:LIGHTING SCI GROUP
Intelligent security light and associated methods
ActiveUS20120287271A1Readily stored in memoryProvide goodImage enhancementImage analysisMicrocontrollerElectricity
A lighting device capable of detecting a condition in an environment includes a sensor to capture a video frame from a location in the environment. The lighting device may include a microcontroller, a processor and memory. The sensor may be electrically connected to the microcontroller, and the video frame may be transmitted to the microcontroller as data. The lighting device may also include a light source electrically connected to and controlled by the microcontroller and a rules engine stored in the memory. The processor may compare the data to rules contained in the rules engine to produce an output. The lighting device may further include an interface through which the output is accessible. After an analysis is conducted, an output may be generated responsive to detection of an anomaly.
Owner:LIGHTING SCI GROUP
Modular fishing pole with interchangeable components
Multi-component fishing poles and methods of their construction and assembly are disclosed herein. The components of the fishing pole may include a handle component, a reel seat component, and a main rod component. The components may be replacably coupled to one another as desired by a user. The coupling may be performed by threaded regions attached to each of the components and designed to mate with one another. The components of the fishing pole may be aligned with alignment brakes used to limit the rotation of one component onto another as the components are replacably coupled. The reel seat component, as well as one or more of the other components, may include a performance enhancing gripping surface.
Owner:HUANG BEN
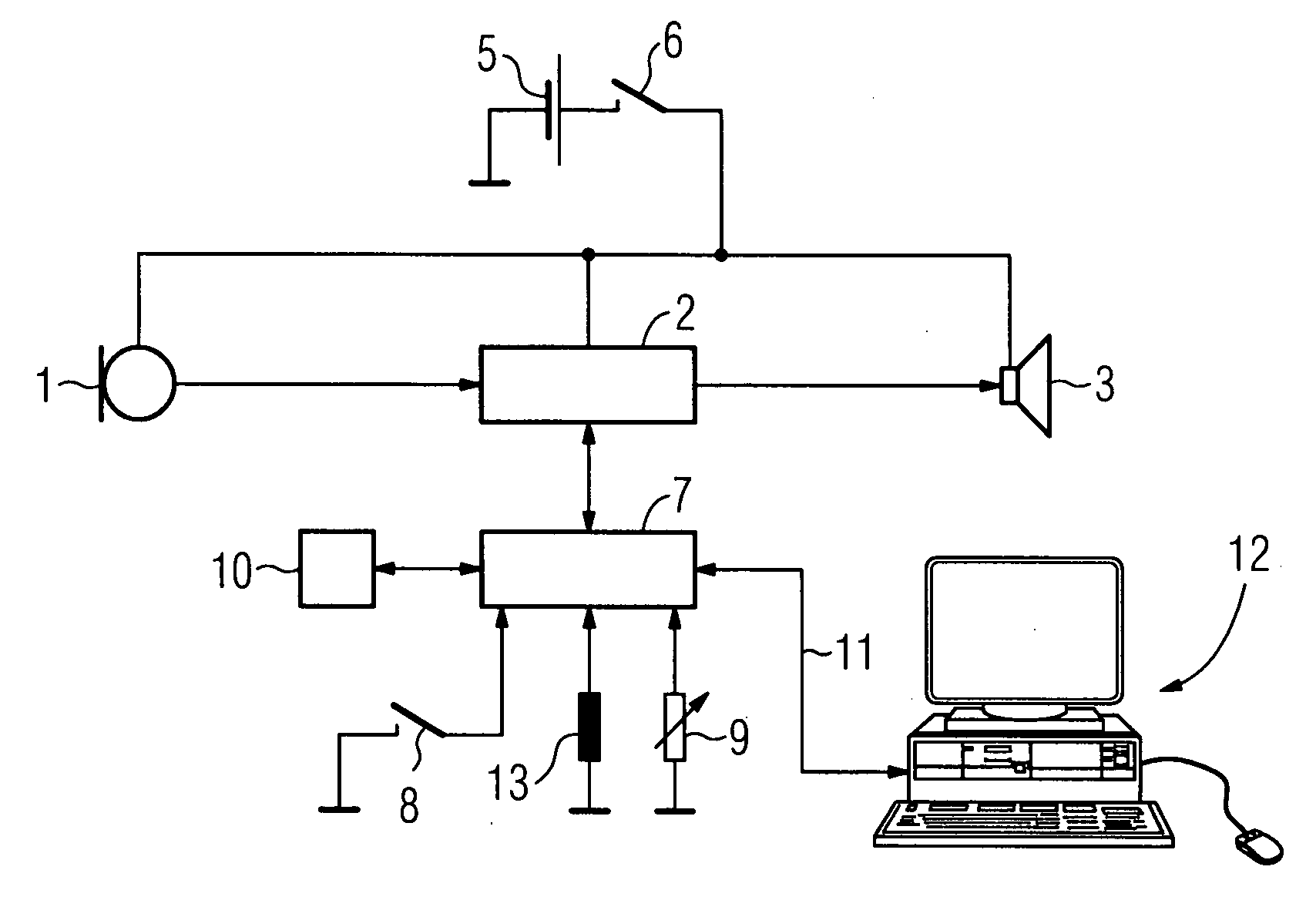
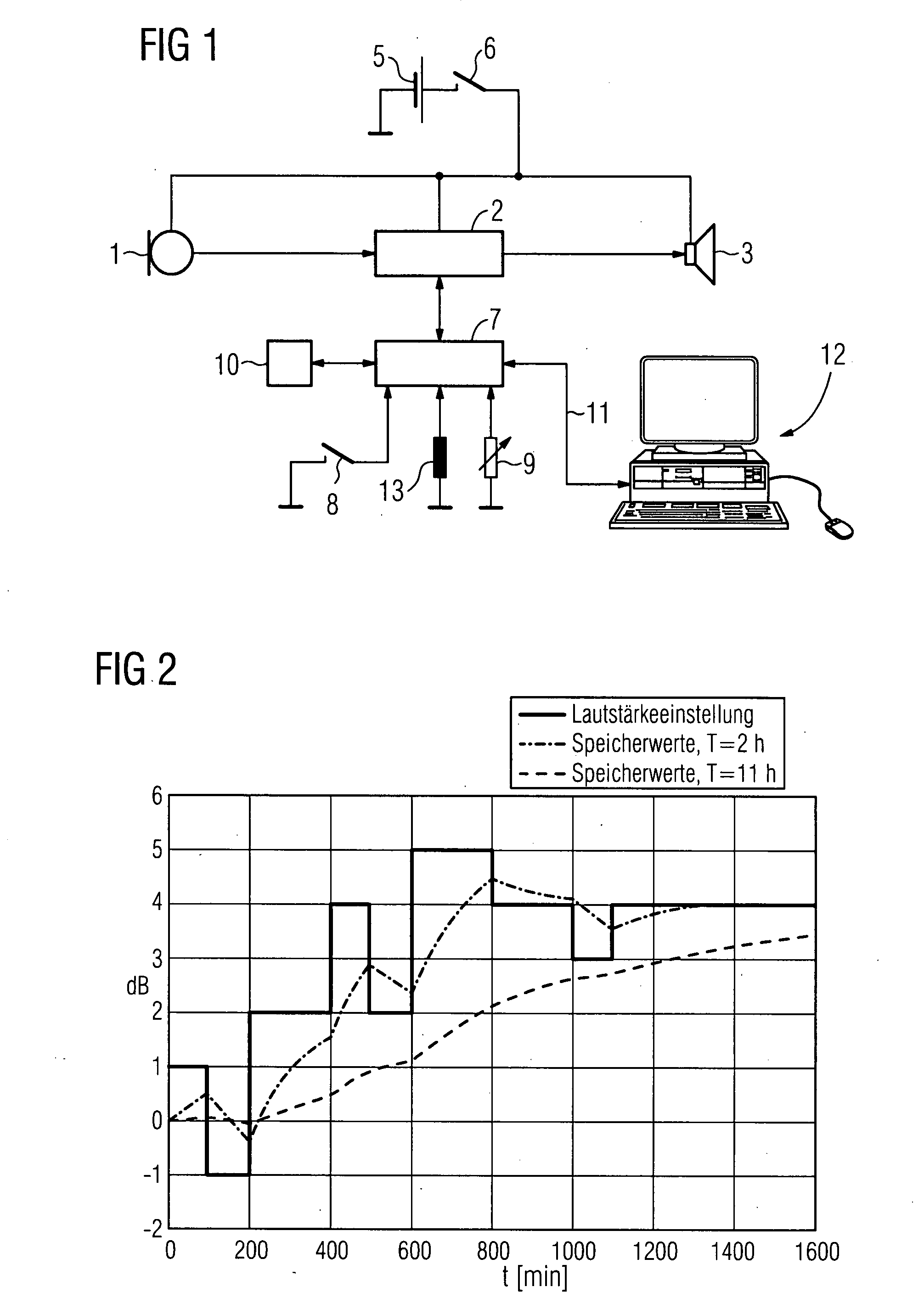
Hearing aid with adaptive start values for apparatus
Fine customization of a hearing aid to the individual hearing environments and habits of a user are to be simplified and improved. To this end, when the hearing aid is turned on or when the hearing aid is switched to a particular operating mode, neither the value most recently valid for the parameter prior to turning off or switching to a different operating mode nor the parameter value transferred to the hearing aid at the beginning of programming is set. Rather, from the changes to the value of the parameter taking place during operation of the hearing aid a new start value is ascertained and stored, which value is then set automatically after turning on or switching mode.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Evaluating content on social media networks
UndeterminedUS10891539B1Rapid customizationQuick modificationCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesUser inputSocial media network
A system and method may be used to evaluate content on one or more social media networks. A deep learning model may be stored. A communication may be received, that has been or is to be communicated on a social network. The deep learning model may be applied to the communication to obtain an automated evaluation of the communication. User input may be received, and may include a user evaluation of the communication. The user evaluation may be applied to train the deep learning model. The steps of receiving the communication, applying the deep learning model to obtain the automated evaluation, receiving the user evaluation, and applying the user evaluation to train the model, may be iterated to enhance the accuracy of the automated evaluations.
Owner:STA GRP INC
Customized content integration in mobile device application
ActiveUS20180137505A1Great customizationTargeted optimizationAdvertisementsNatural language data processingApplication serverGraphical user interface
Described herein is a system in which content presented in a graphic user interface (GUI) of a mobile application may be customized based on user information. In some embodiments, a mobile application server providing backend support for the mobile application executed on a mobile device may provide notification templates populated with account-specific data to the mobile device. In some embodiments, the notification templates may be populated by an authorization server based on account-specific information. In some embodiments, the notification templates may be populated by the mobile application server based on account-specific information provided to it by an authorization server.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
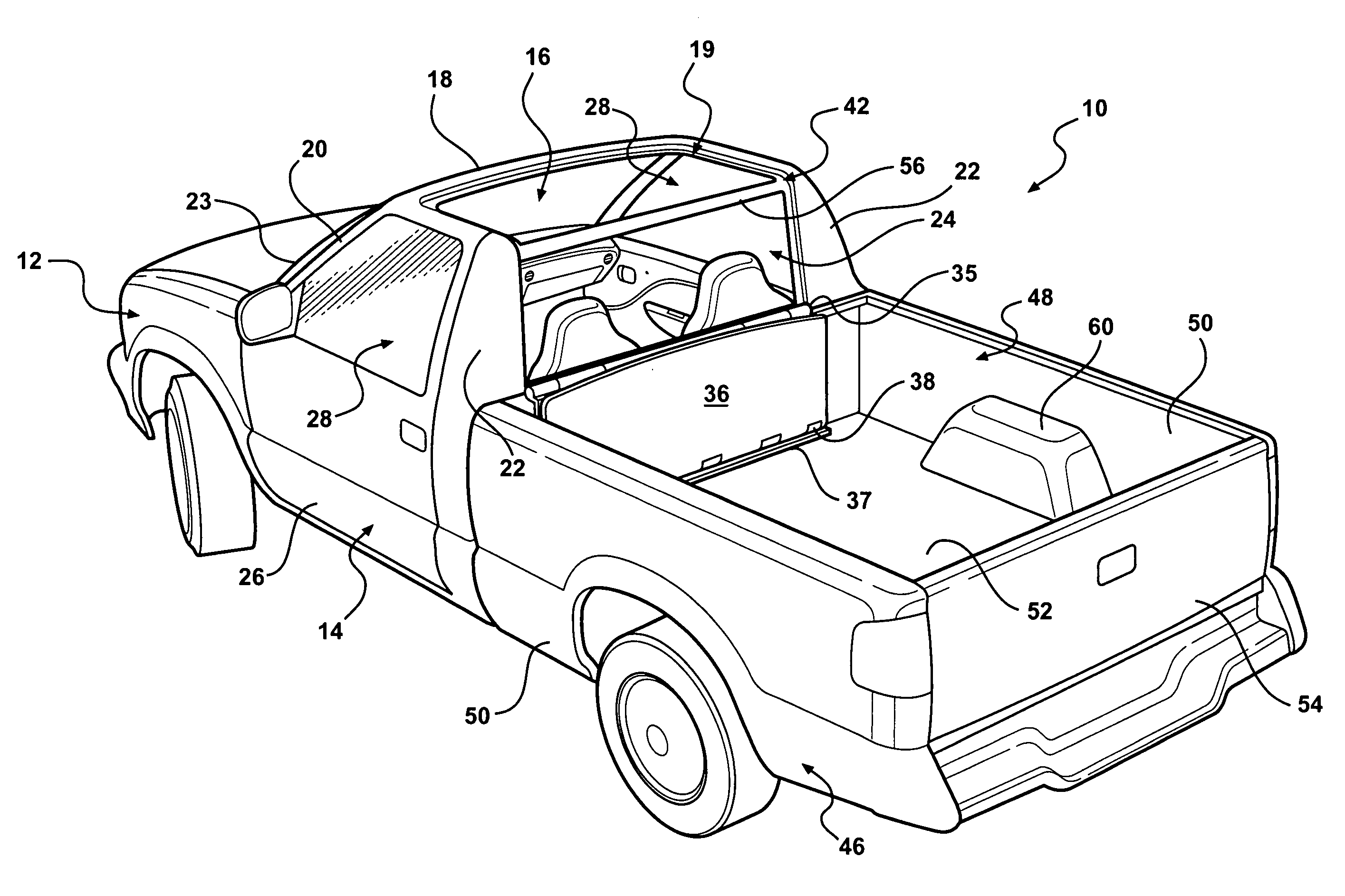
Open-air pickup truck
A vehicle body has a first body portion forming an enclosed passenger compartment that includes a roof having a panel opening and a rear window opening. A rear window is fixed in a frame that is hingedly attached to the first body portion. A rigid roof panel is hingedly attached to the frame, forming a roof assembly that is movable between a storage position and a closed position. The roof assembly closes the panel opening and the rear window opening in the closed position. A second body portion forms a storage compartment external to the passenger compartment and is open adjacent the rear window opening. The roof assembly is movable to the storage position in the storage compartment, exposing the passenger compartment to outside air through the panel opening and the rear window opening.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
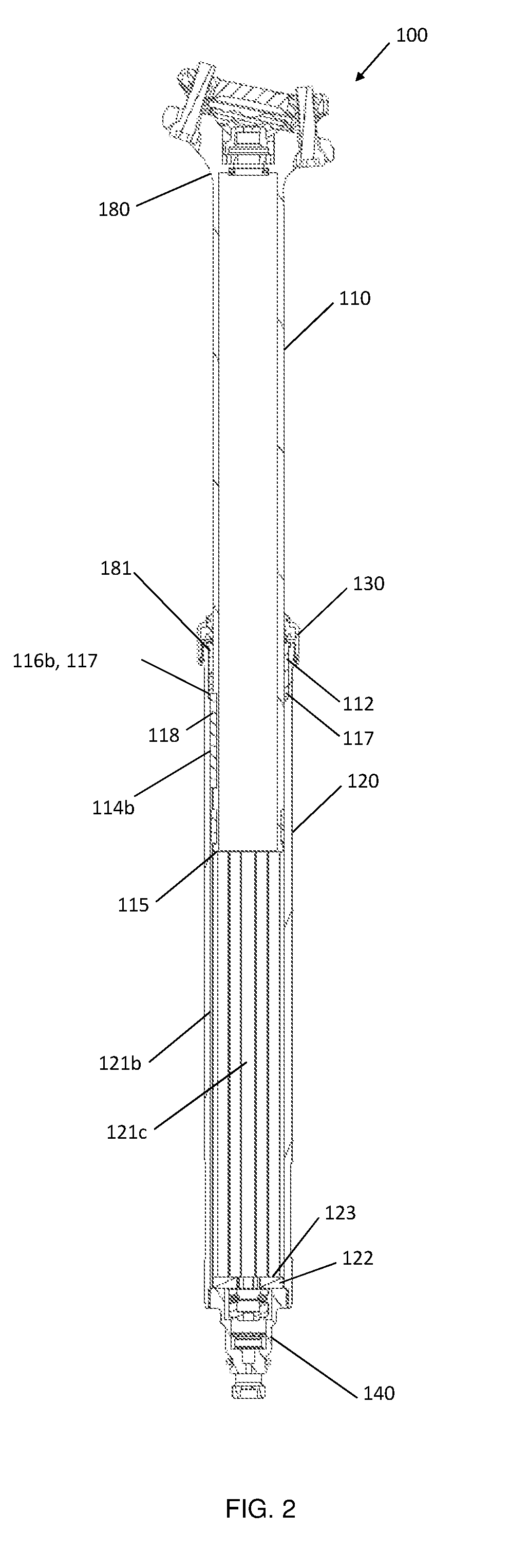
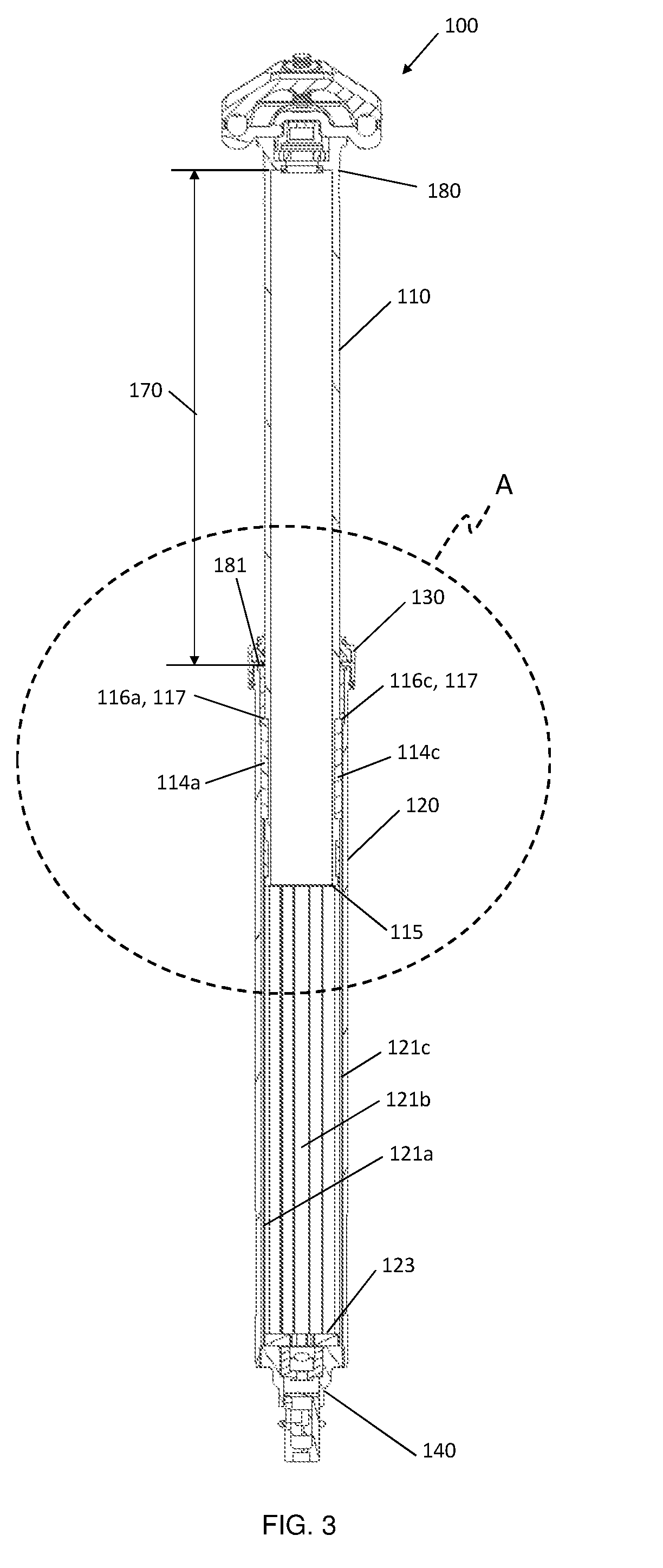
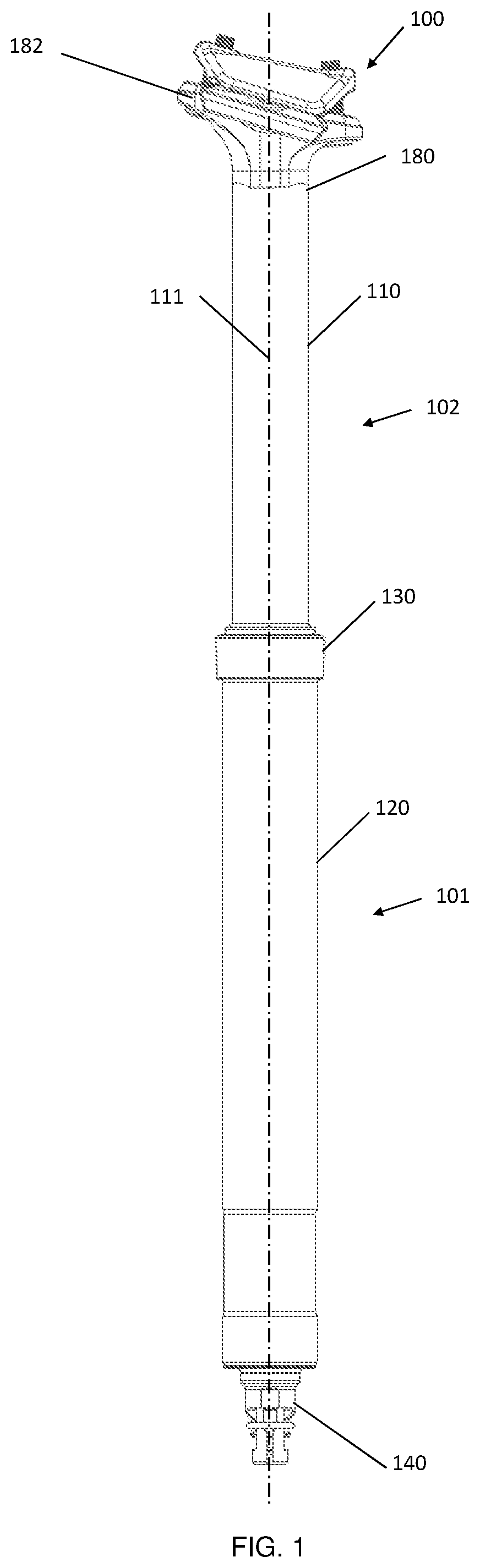
Bicycle Seat Post Travel Adjustment Assembly
ActiveUS20190308681A1Lower a bicycle seatReducing maximum available dropCycle saddlesEngineeringGuide tube
There is described a bicycle seat post assembly in which the travel distance of the seat post can be adjusted. The seat post assembly includes an outer tube that is configured to telescopically receive an inner tube. The inner tube is axially slidable relative to the outer tube between a retracted position and an extension position, the extension position being determined by an extension assembly in which a slider engages an upper retainer surface, thereby setting the upper limit of axial extension of the inner tube. The extension of the inner tube can be limited to an intermediary extension position that lies between the retracted and extension positions by an insertable extension stopper that is positionable under the upper retainer surface.
Owner:D3 INNOVATION INC
Fiduciary screener test and benefit plan selection process
A process for enrolling individual participants in compensation and employee benefit plans using performance scores from a psychometric testing instrument to determine whether individual participants understand the risks of their plan choices. As an individual's score increases on the test, a larger array of plan choices become available allowing greater opportunity for plan customization. This screening process benefits the individual plan participant by limiting plan choices where risks are not properly understood. Additionally, the use of the test as a screener to curtail unsuitable plan choices affords plan sponsors a mechanism to demonstrate that they have properly exercised their fiduciary duty.
Owner:MAHONEY DENNIS F
Bicycle seat post travel adjustment assembly
ActiveUS10974781B2Lower a bicycle seatReducing maximum available dropCycle saddlesClassical mechanicsStructural engineering
There is described a bicycle seat post assembly in which the travel distance of the seat post can be adjusted. The seat post assembly includes an outer tube that is configured to telescopically receive an inner tube. The inner tube is axially slidable relative to the outer tube between a retracted position and an extension position, the extension position being determined by an extension assembly in which a slider engages an upper retainer surface, thereby setting the upper limit of axial extension of the inner tube. The extension of the inner tube can be limited to an intermediary extension position that lies between the retracted and extension positions by an insertable extension stopper that is positionable under the upper retainer surface.
Owner:D3 INNOVATION INC
Riblets for a flowpath surface of a turbomachine
InactiveUS10450867B2Great customizationEngine manufacturePump componentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
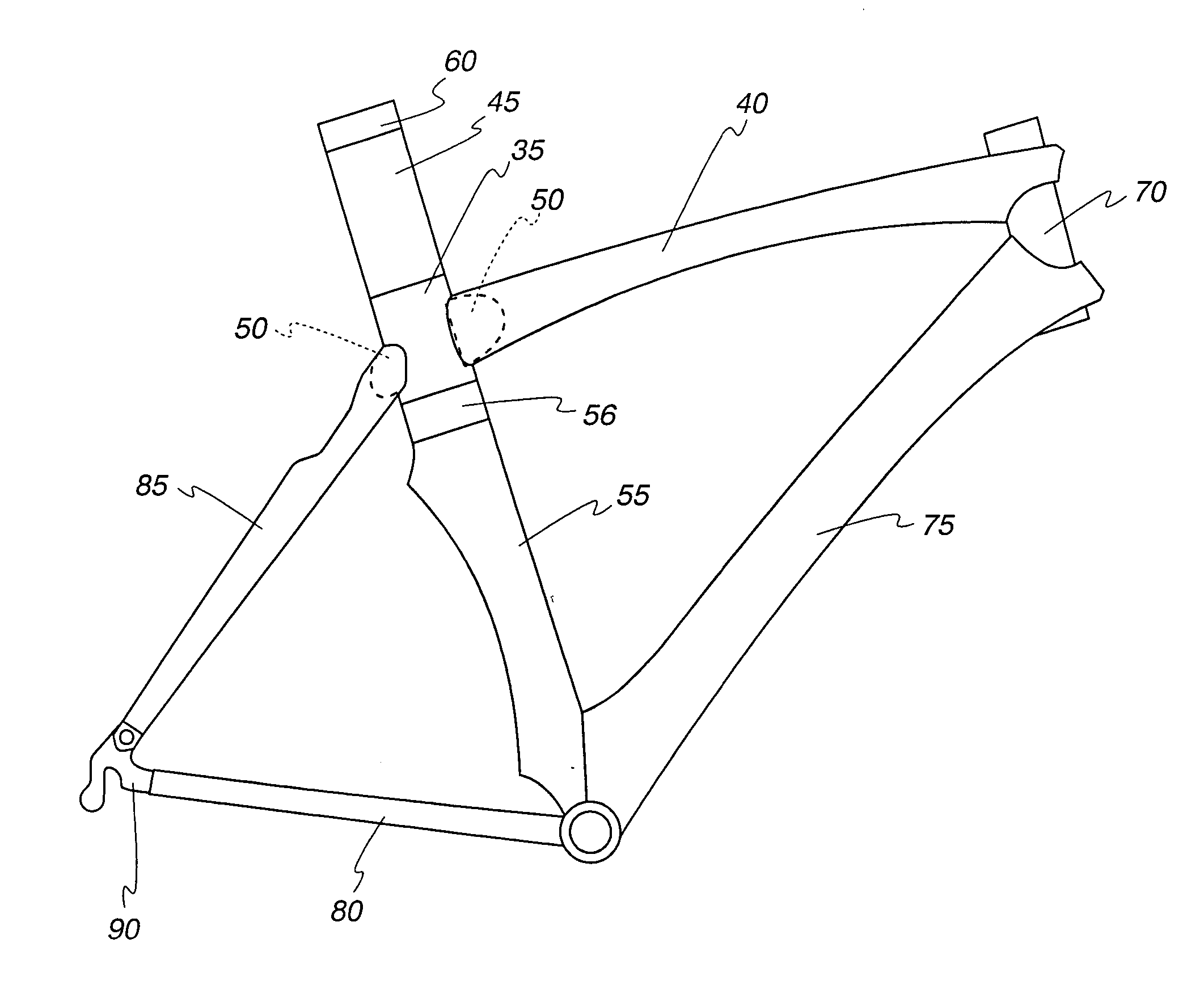
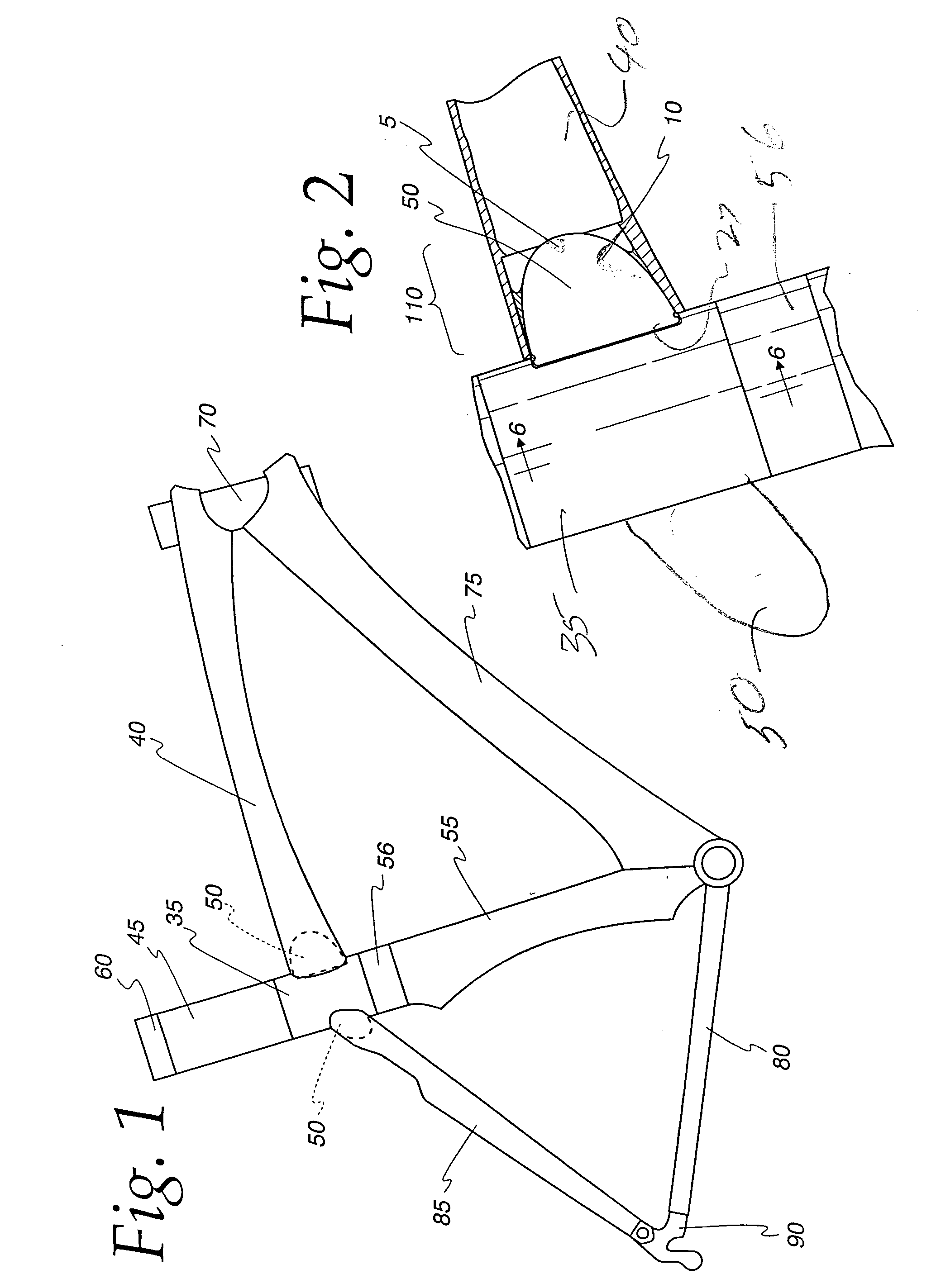
Customizable carbon frames for bicycle or other vehicles
InactiveUS20070289136A1Enhance frame 's ride qualityEfficient use ofVehicle seatsPassenger cyclesEpoxyVehicle frame
A method of manufacturing a lightweight vehicle frame, and the end product fame, are disclosed. A first tube, which can be a cured hollow reinforced resin composite tube, is connected to a second part by a tab. The tab is tapered and is affixed to the first tube. The tab is bonded to the second part by an epoxy. The taper of the tab allows the angle at which the parts are connected to be controlled through a wide range.
Owner:SEVEN CYCLES
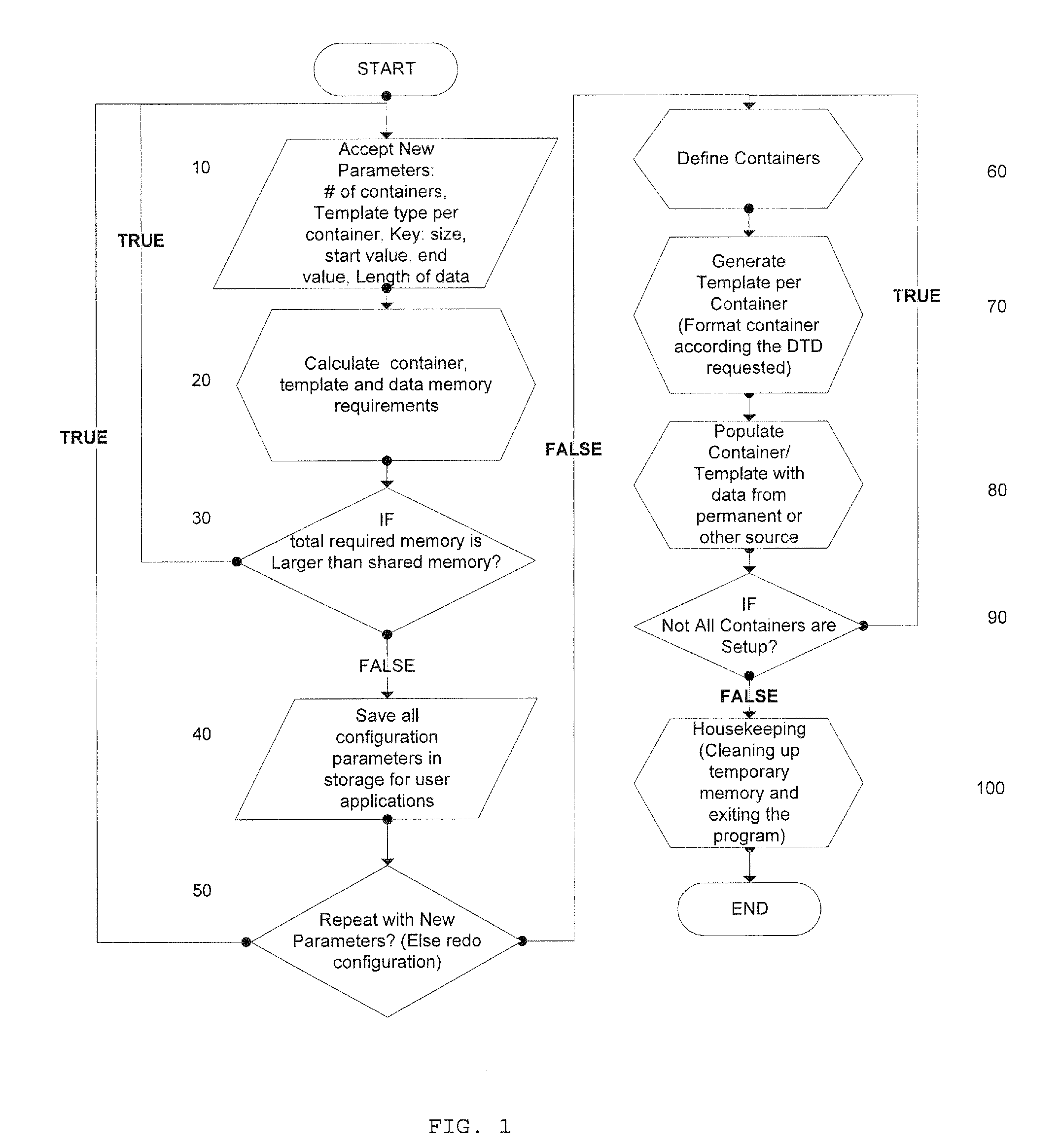
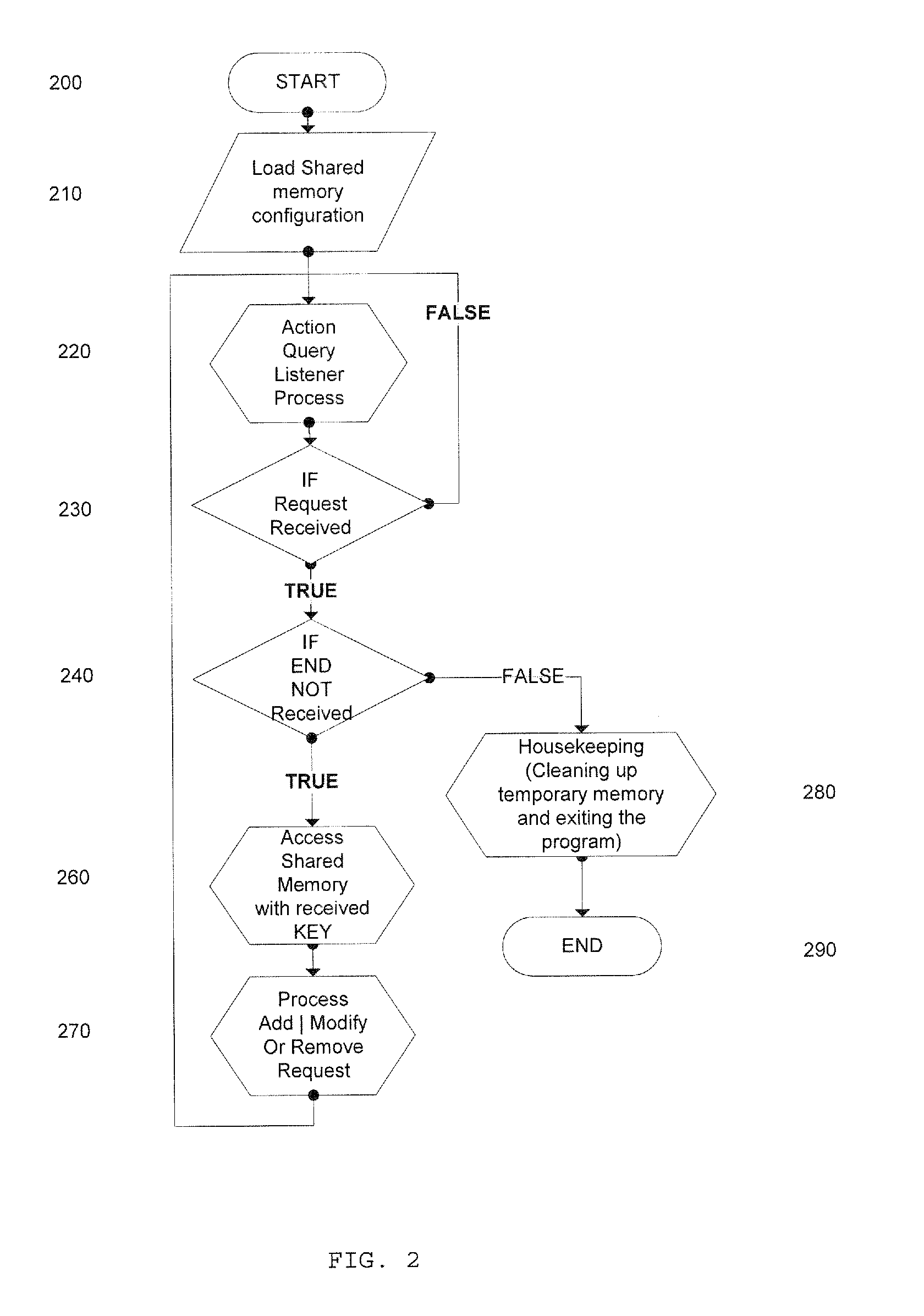
In-memory data optimization system
InactiveUS20100191764A1Easy accessExtension of timeDigital data processing detailsTransmissionDatabase applicationResponse process
The present invention is directed to database applications in which the identification of entries is structured in a custom way using templates. The means for identification is used as a vehicle for submitted queries to and obtaining responses from the database such that the query and response process is significantly faster than applications presently in use.
Owner:OBIE TECH LLC
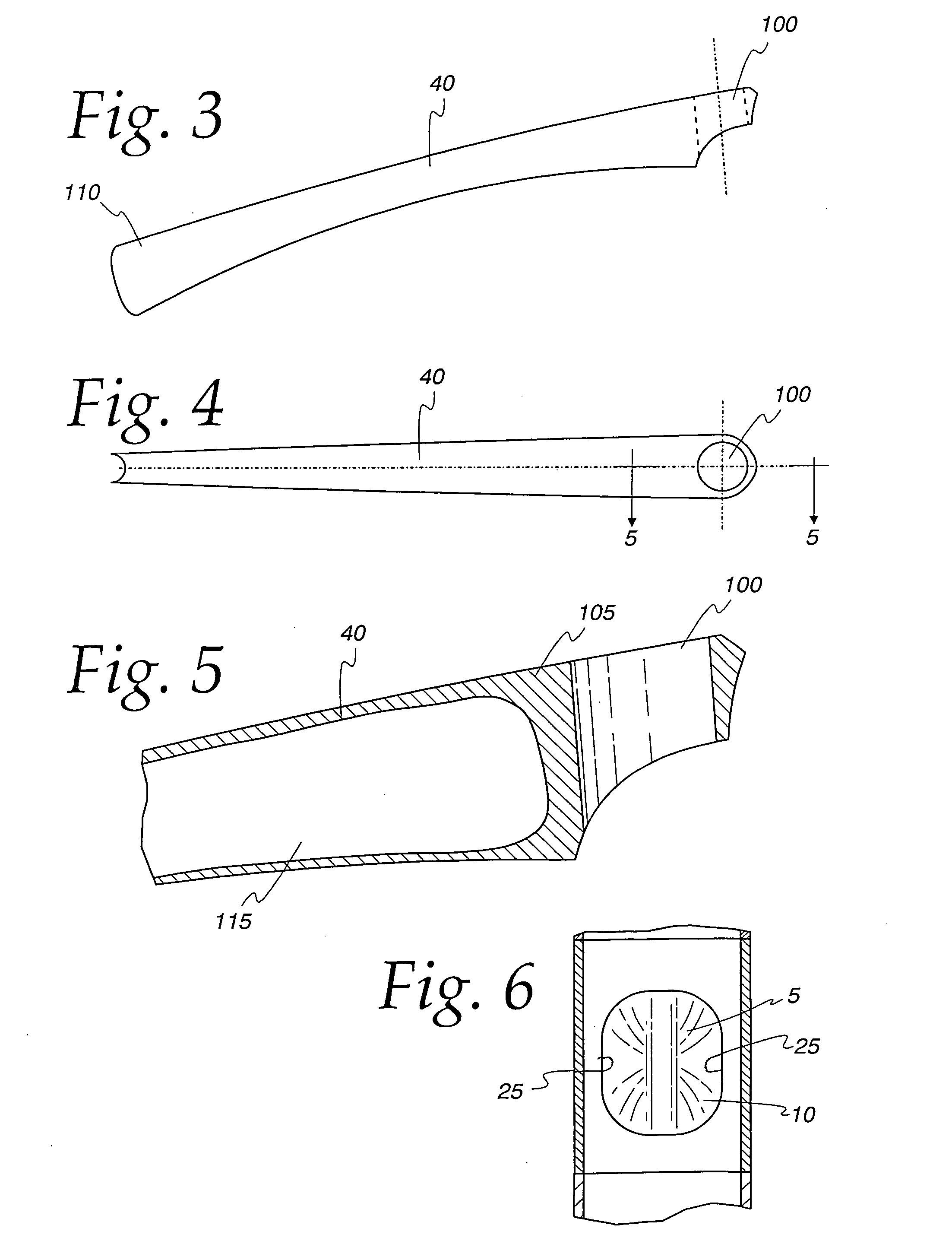
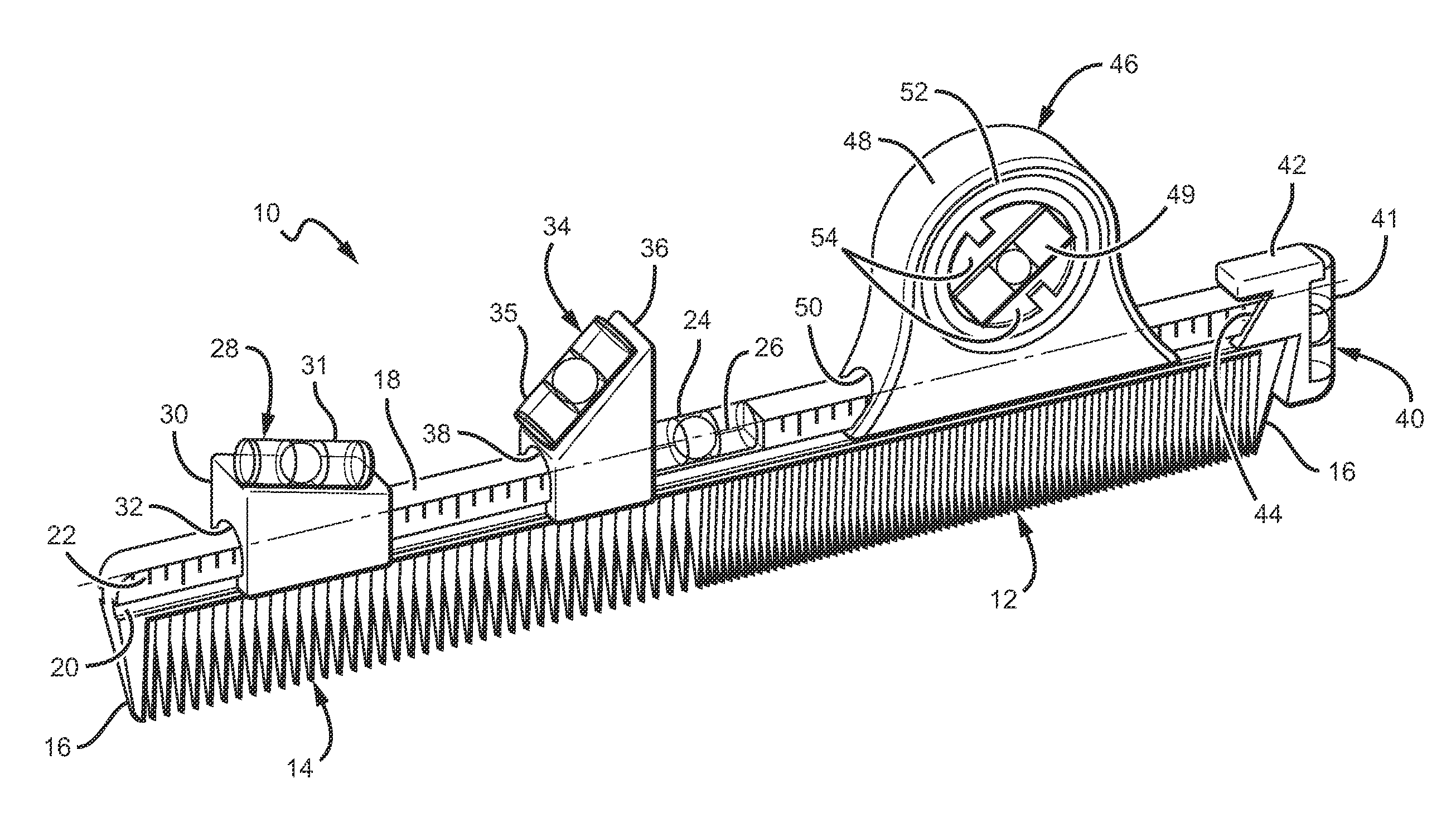
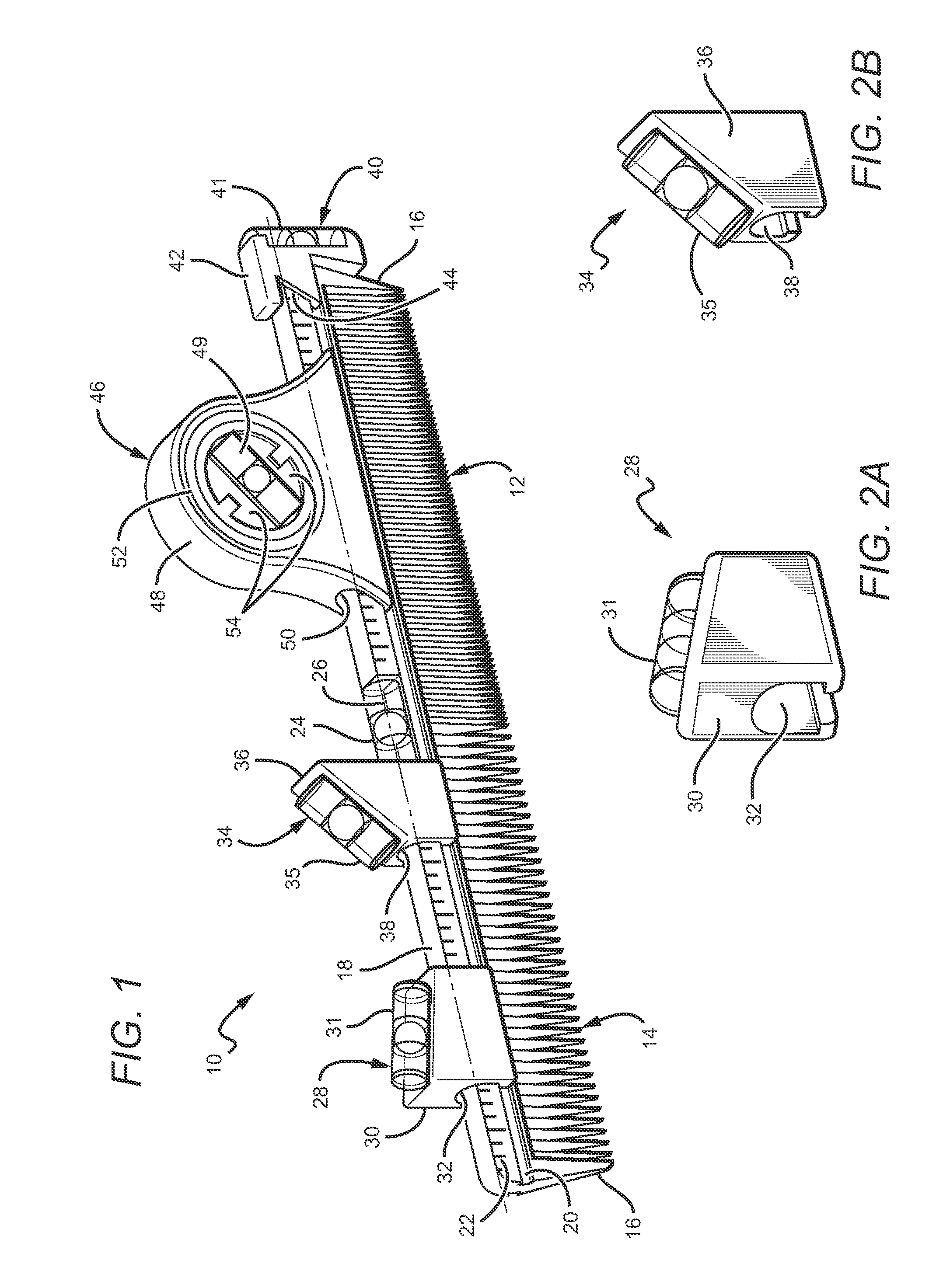
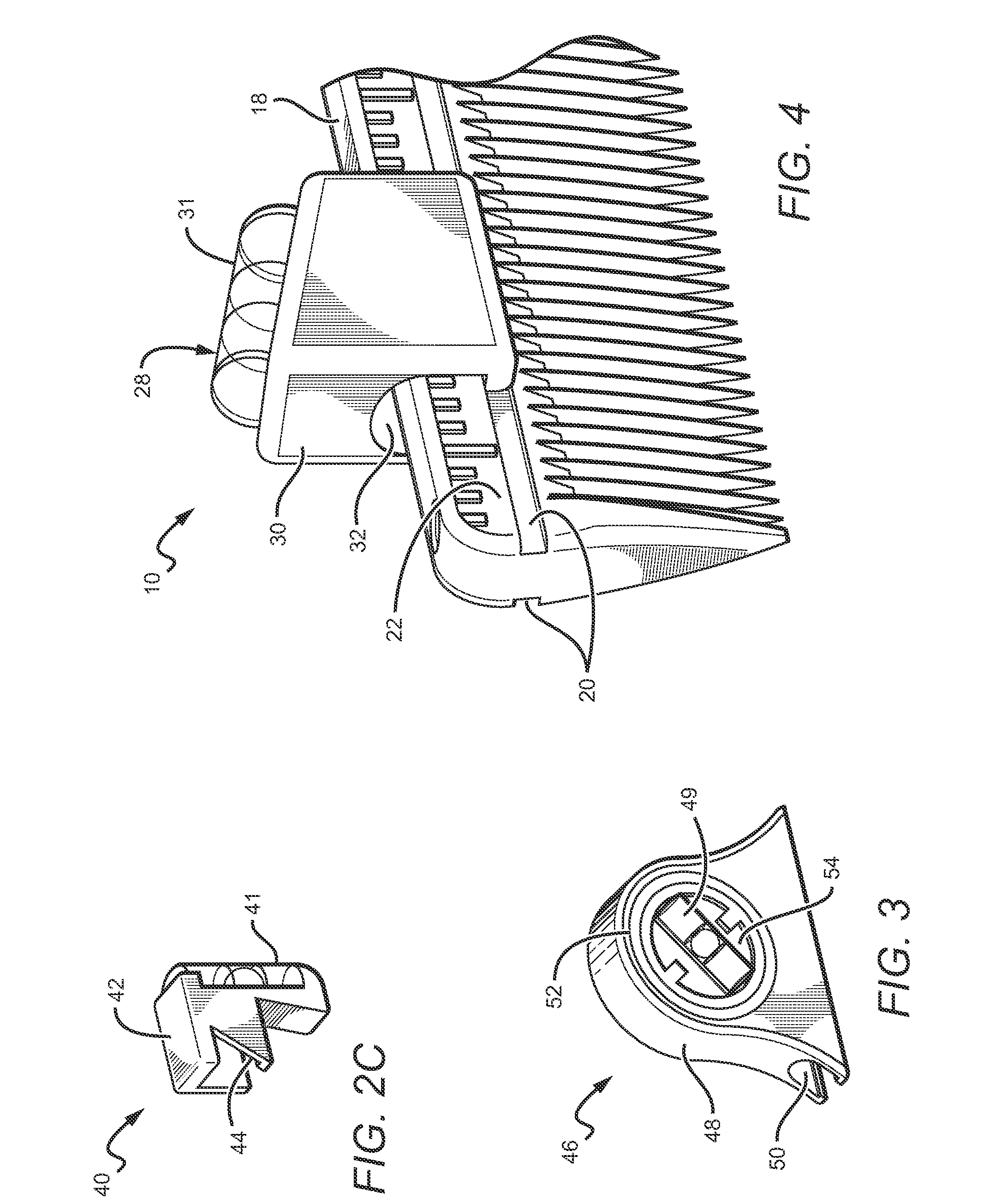
Flexible level system for a comb
Owner:HSE PARTNERS
Bicycle seat post travel adjustment assembly
ActiveUS20200070913A1Lower a bicycle seatGreat customizationCycle saddlesCycle framesClassical mechanicsEngineering
There is described a bicycle seat post assembly in which the travel distance of the seat post can be adjusted. The seat post assembly includes an outer tube that is configured to telescopically receive an inner tube. The inner tube is axially slidable relative to the outer tube between a retracted position and an extended position, the extended position being determined by an extension assembly in which an inner contact member engages an outer contact member, thereby setting the upper limit of axial extension of the inner tube. The extension of the inner tube can be limited to an intermediate position that lies between the retracted and extended positions by an insertable shim that is positionable between the inner and outer contact members.
Owner:D3 INNOVATION INC
Method for making leg model and orthopedic brace
Owner:ENGELMAN IAN
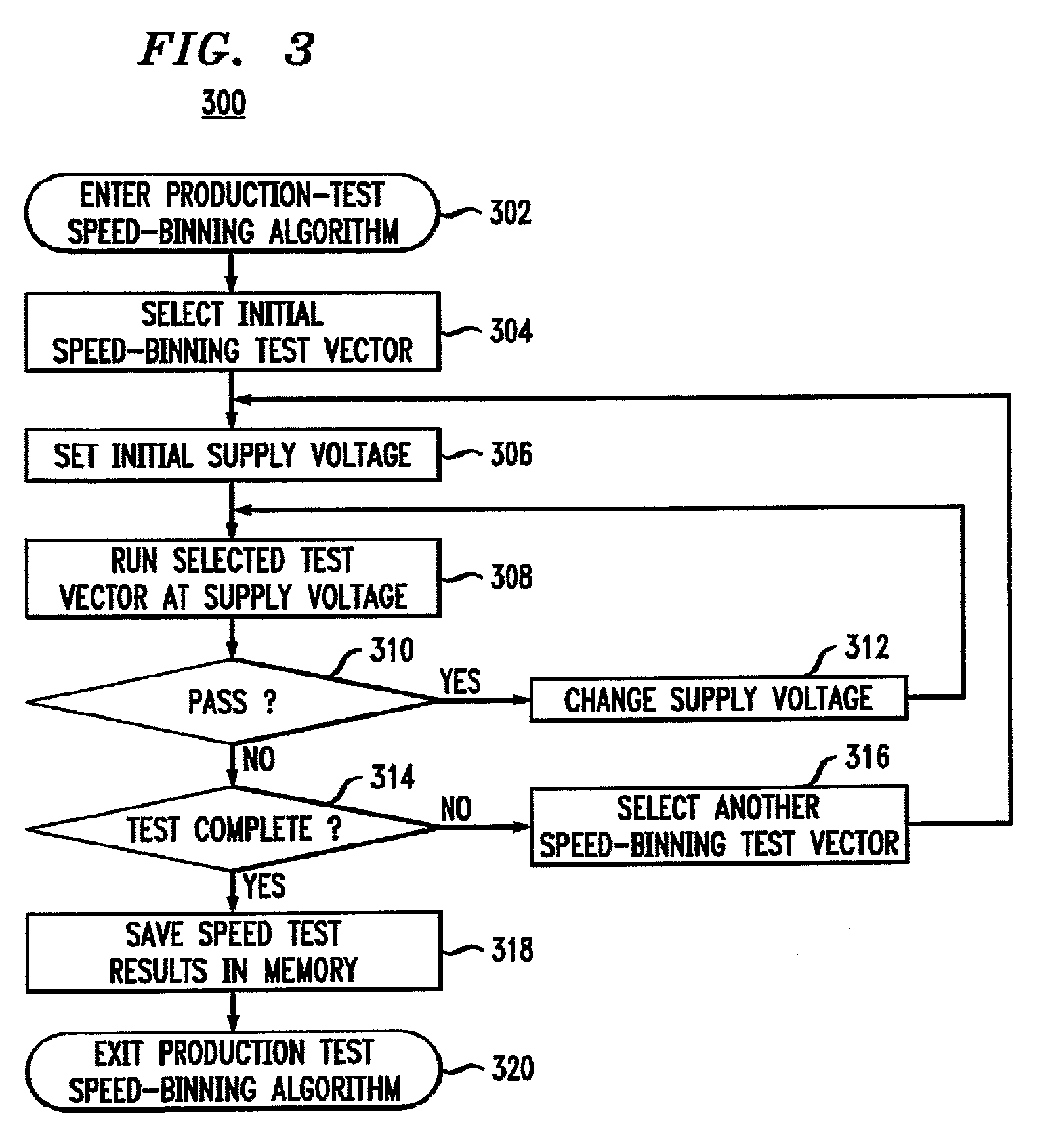
Speed binning for dynamic and adaptive power control
ActiveUS8234511B2Great customizationOptimize (Mechanical power/torque controlLevel controlPower controllerEngineering
A representative digital circuit of the invention has an on-chip, non-volatile memory, to which chip-specific speed-binning data that characterize performance of the digital circuit are written during production testing. During normal operation, the power controller that controls power-supply signals applied to the digital circuit reads the speed-binning data from the on-chip memory for use as input parameters for dynamic supply-voltage scaling, dynamic clock scaling, and / or adaptive power control that optimize (e.g., minimize) power consumption in the digital circuit. Advantageously over the prior art, the accuracy and efficiency of dynamic and / or adaptive power control arc improved because the chip-specific speed-binning data enable the power controller to better customize the power-management algorithm for the given digital circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com