Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
135results about How to "Avoid excessive friction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
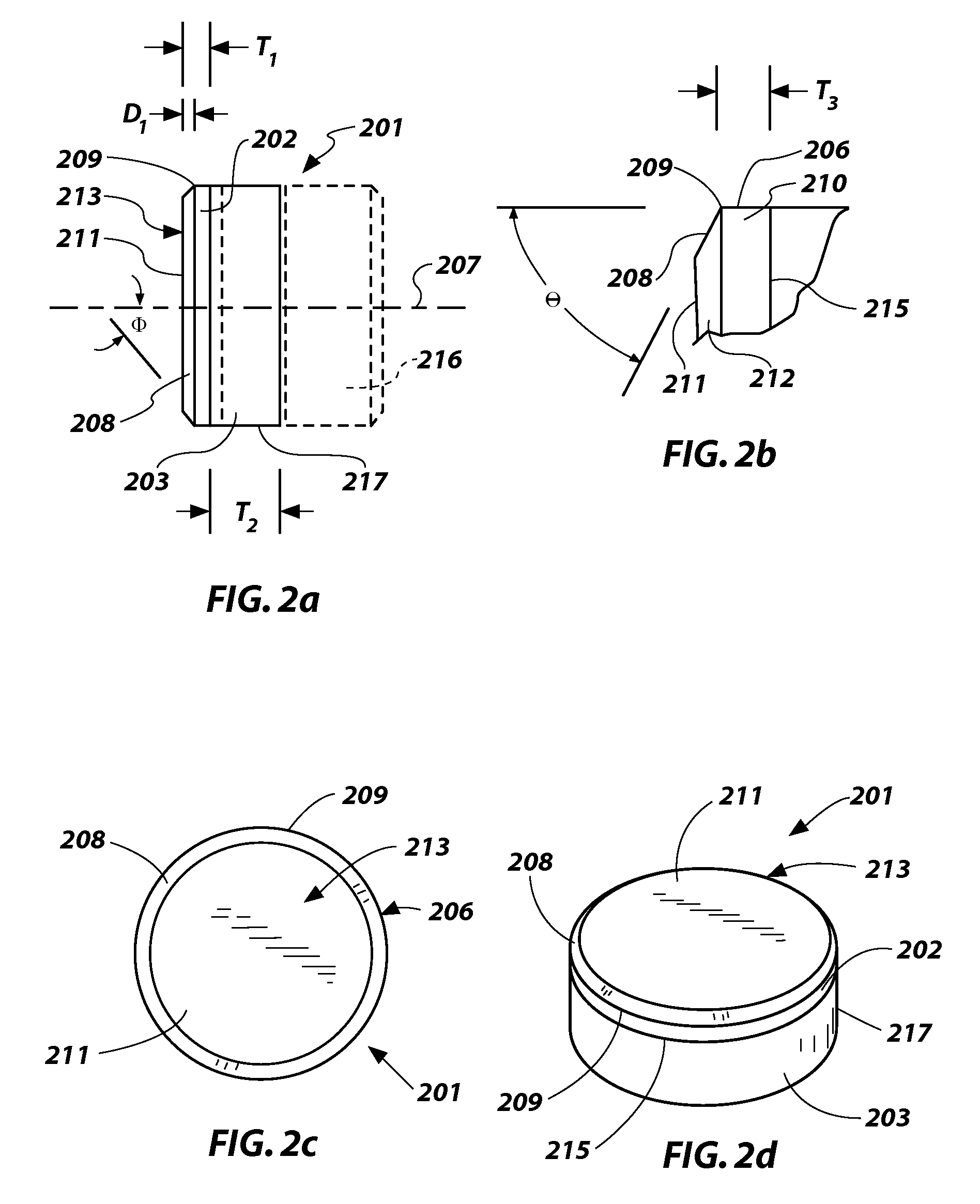
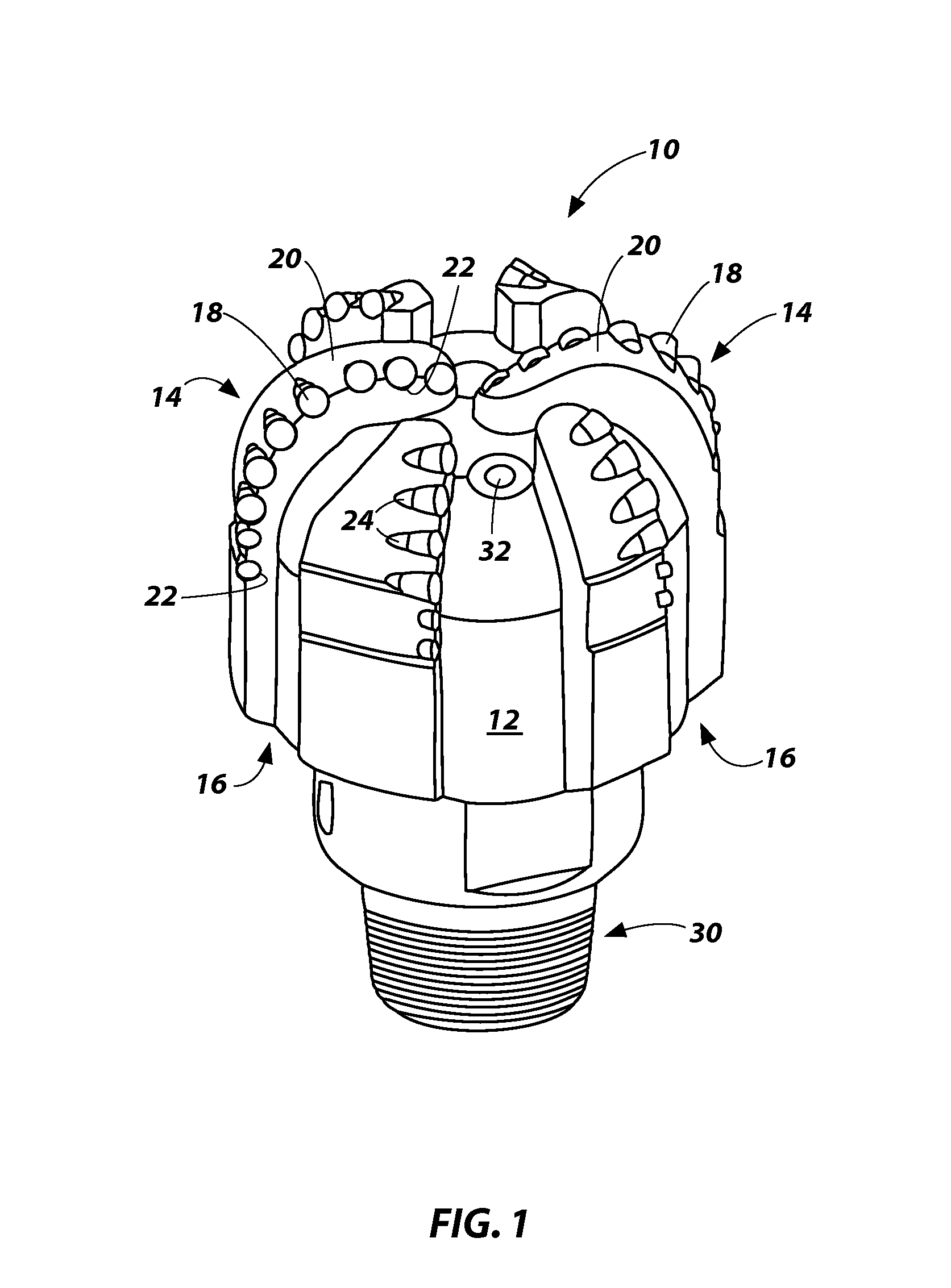
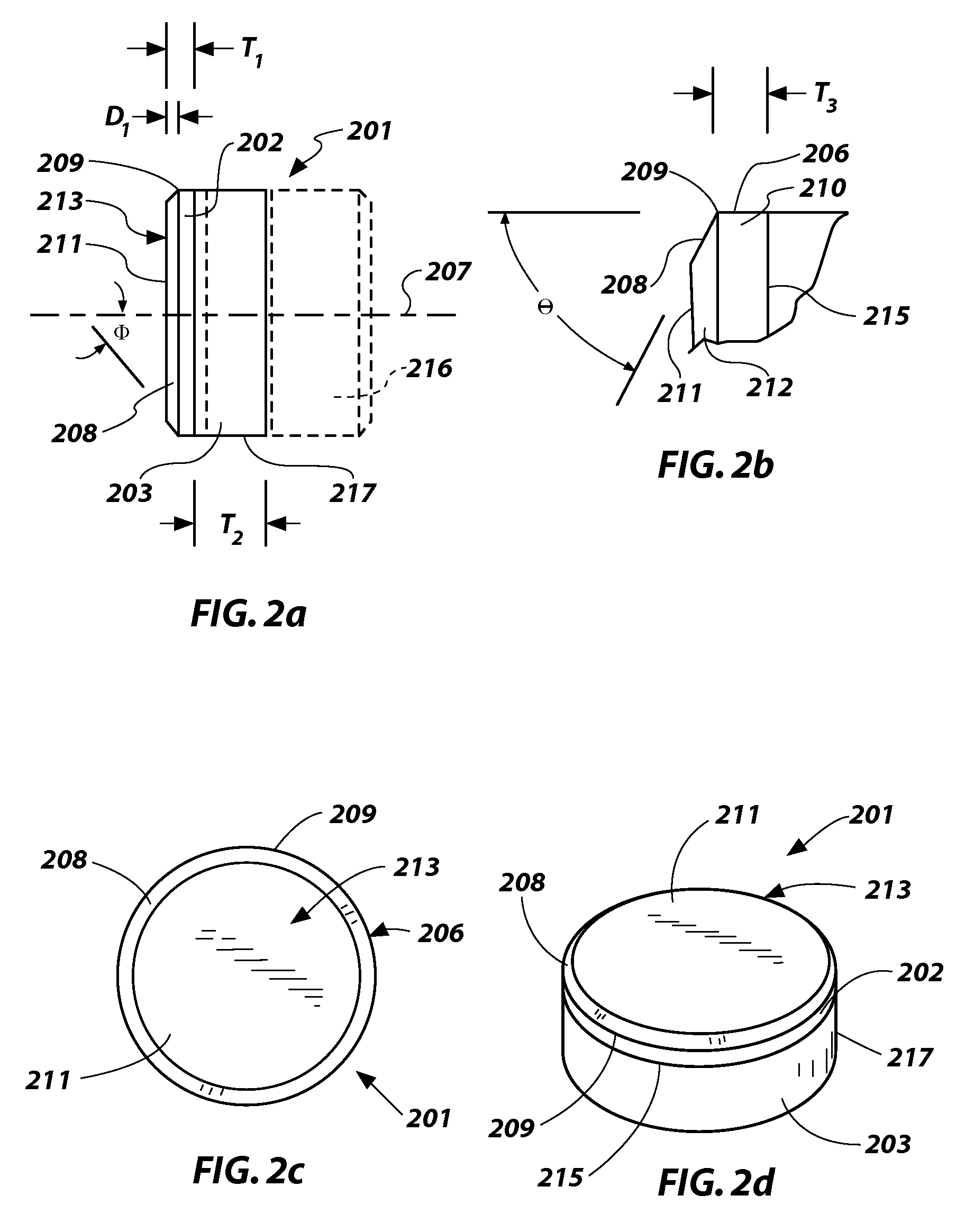
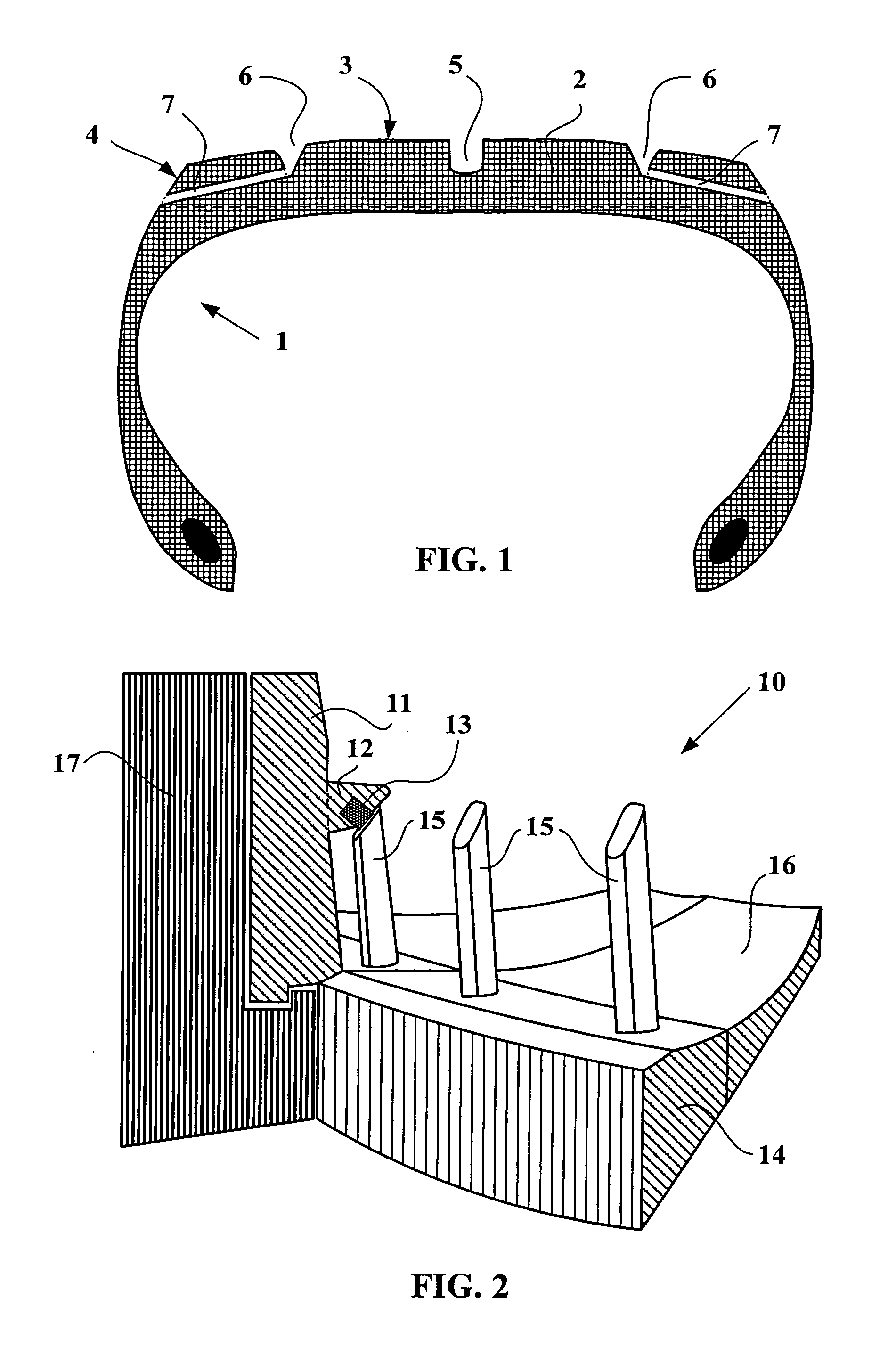
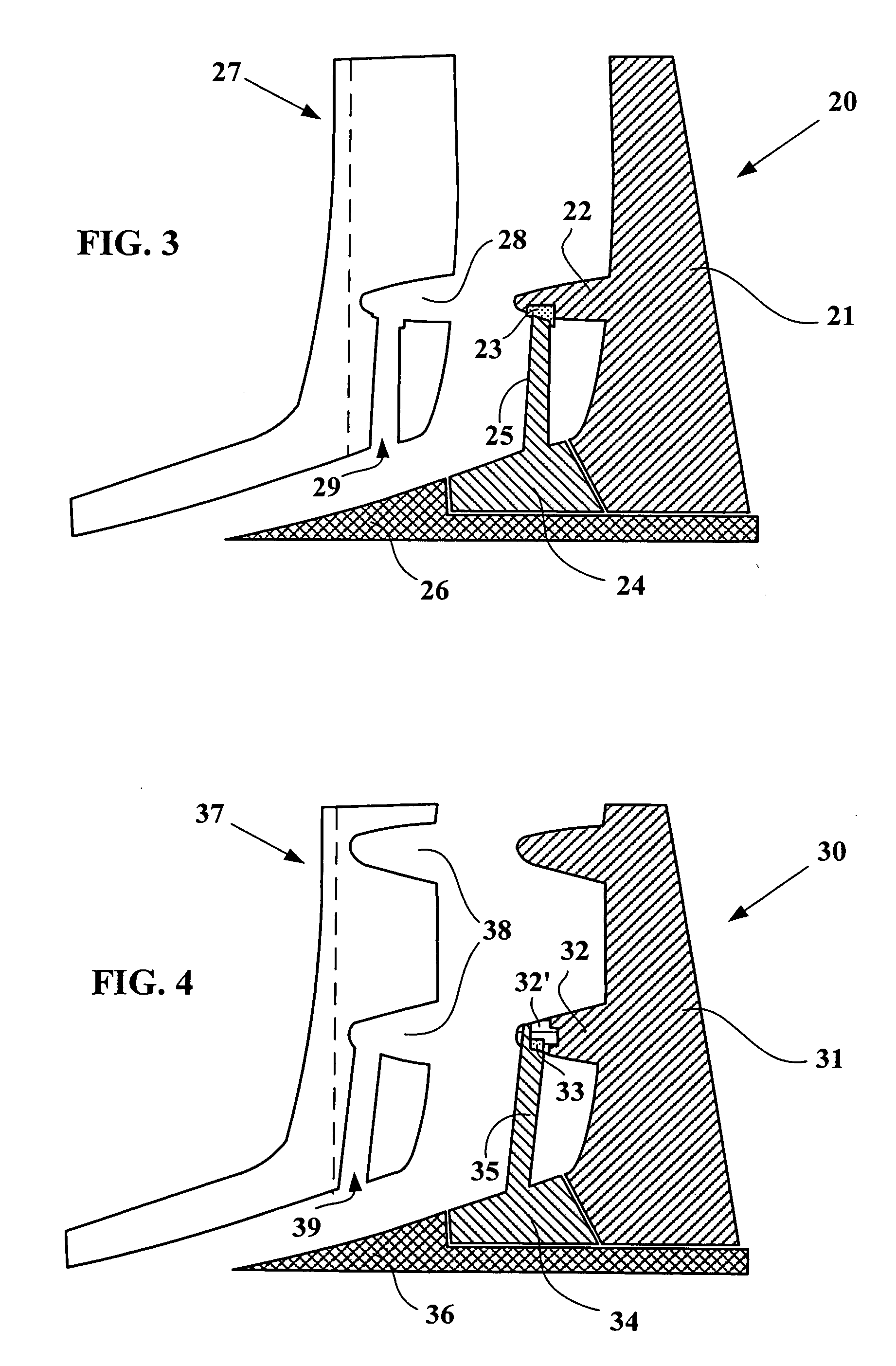
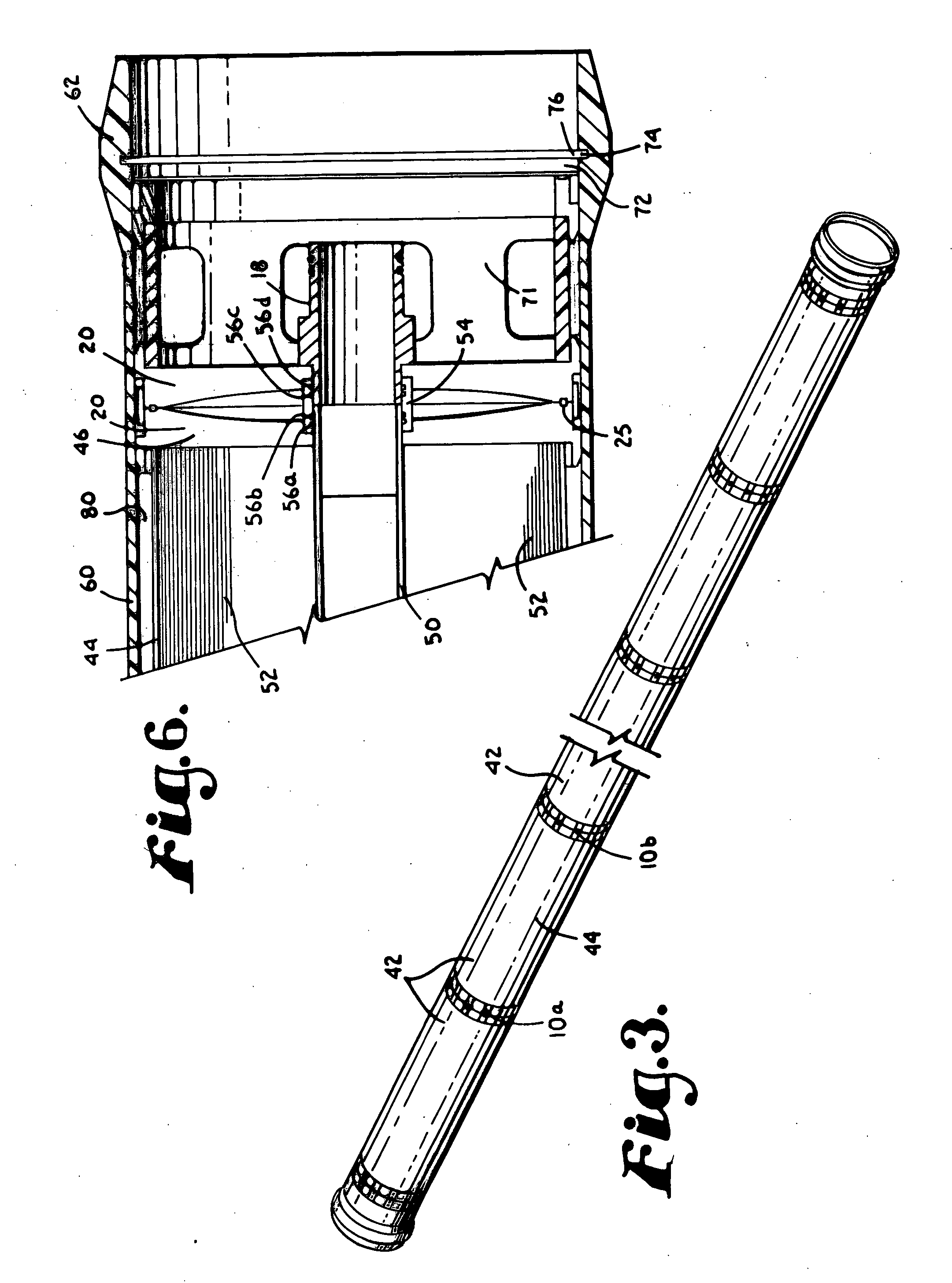
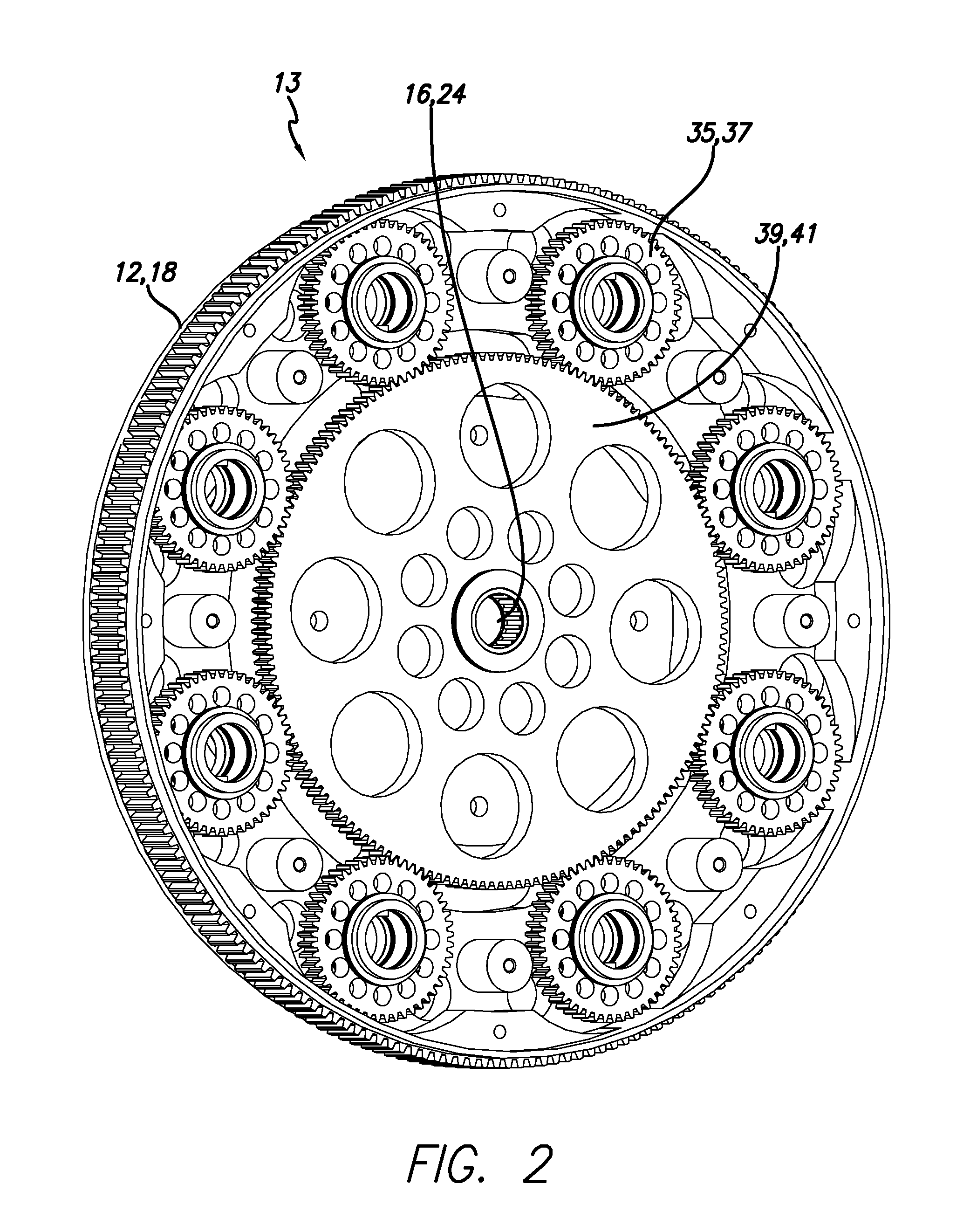
Superabrasive cutting elements with enhanced durability and increased wear life, and drilling apparatus so equipped
A cutting element for use in drilling subterranean formations. The cutting element includes a superabrasive table mounted to a supporting substrate. The superabrasive table includes a two-dimensional cutting face having a cutting edge along at least a portion of its periphery, and a surface comprising a chamfer extending forwardly and inwardly from proximate a peripheral cutting edge at a first acute angle of orientation of greater than about 45° with respect to the longitudinal axis of the cutting element, and to no greater than a selected depth. The chamfer may be arcuate or planar, and of a dimension sufficient to ensure that a wear flat generated during use of the cutting element remains outside the inner boundary of the chamfer within the chamfer envelope, and small enough to maintain aggressive cutting characteristics for the cutter. Drill bits and drilling tools bearing the cutting elements are also disclosed.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Hydrophilic coating and substrates coated therewith having enhanced durability and lubricity
InactiveUS20020013549A1Improve adhesionExcellent wear resistance and lubricitySurgeryCellulosic plastic layered productsHydrophilic coatingOrganic acid
A substrate, such as a catheter or a guide wire, or a portion of the substrate is provided with a lubricous, hydrophilic abrasion-resistant coating by: (a) coating the substrate with a first aqueous coating composition having an aqueous dispersion or emulsion of a polymer having organic acid functional groups and a polyfunctional crosslinking agent having functional groups capable of reacting with organic acid groups, and drying the coating to obtain a substantially water-insoluble coating layer having excess polyfunctional including functional groups being reactive with organic acid groups remaining; and (b) contacting the dried water-insoluble coating layer with a second aqueous coating composition having an aqueous solution or dispersion of a hydrophilic polymer having organic acid functional groups, a polymer having organic acid functional groups and a polyfunctional crosslinking agent having functional groups capable of reacting with organic acid groups, and drying the combined coating to form an intermediate coating, whereby the polymer and the hydrophilic polymer of the second composition become bonded to the polymer of the first coating composition through the excess crosslinking agent; and (c) contacting the dried intermediate coating with a third aqueous coating composition having an aqueous solution or dispersion of a hydrophilic polymer having organic acid functional groups, and drying the combined coatings, the hydrophilic polymer of the third coating composition thereby becoming bonded to the polymers of the second coating composition through the excess crosslinking agent. The dryings can be carried out at ambient (room) temperature.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
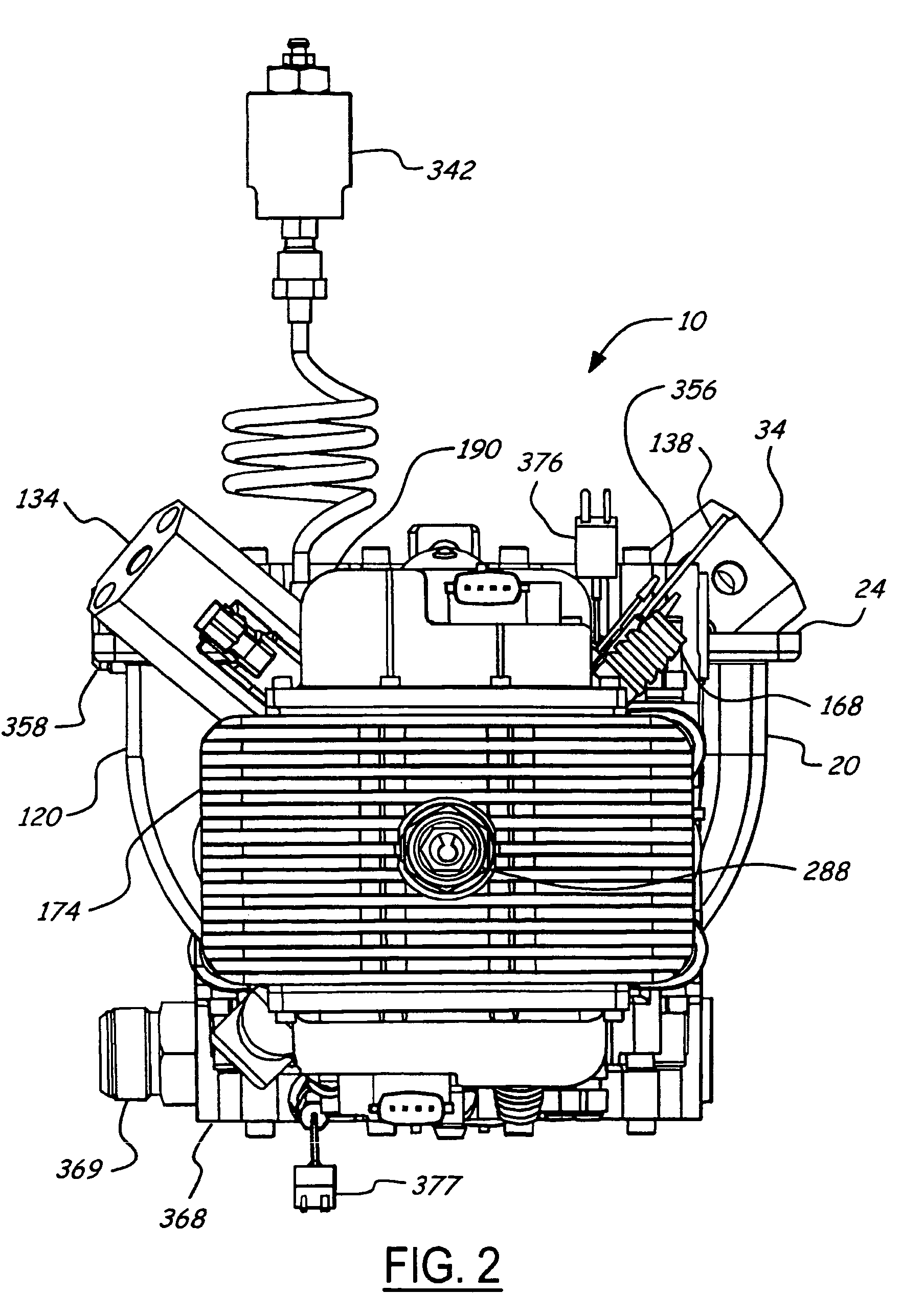
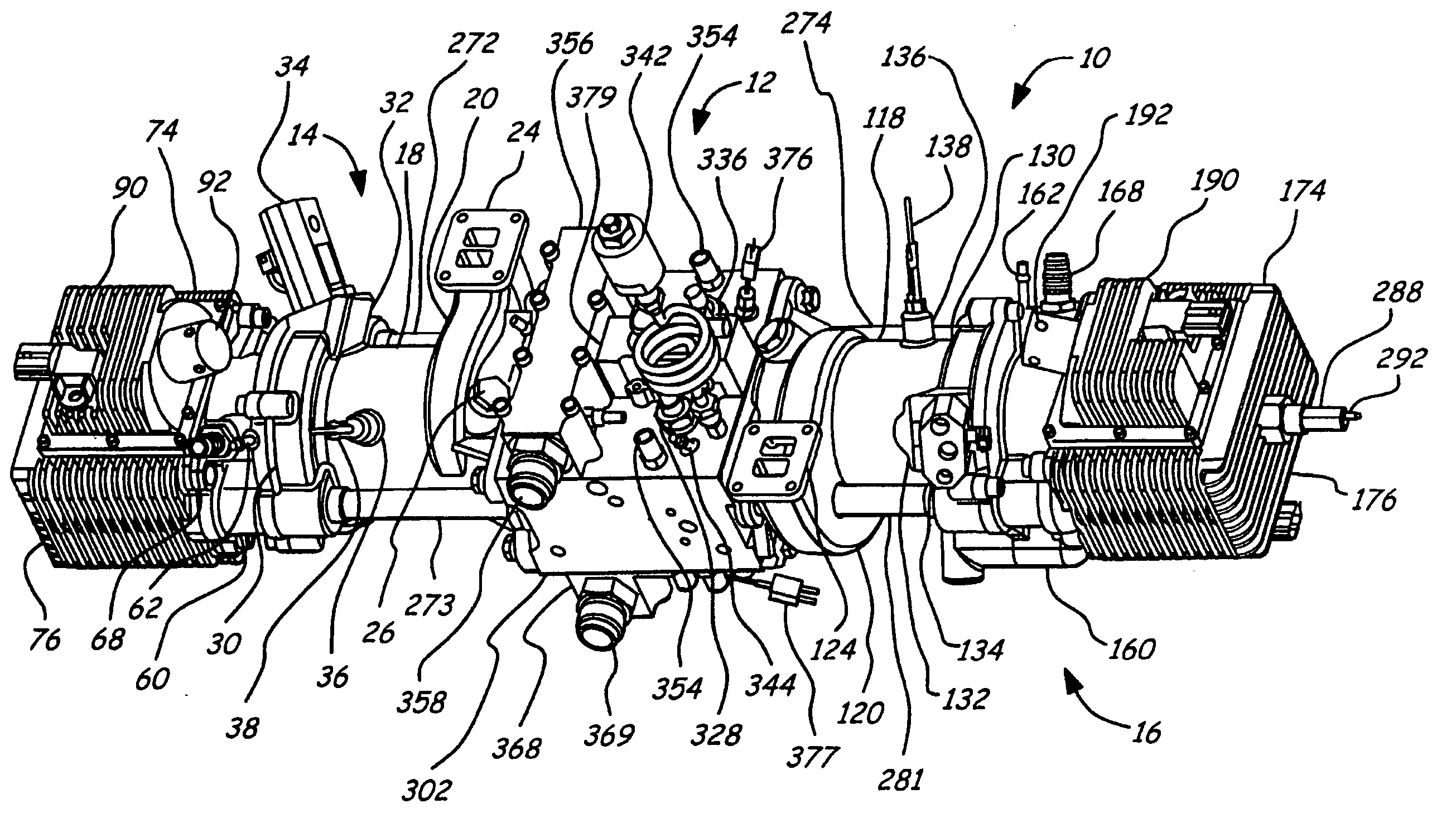
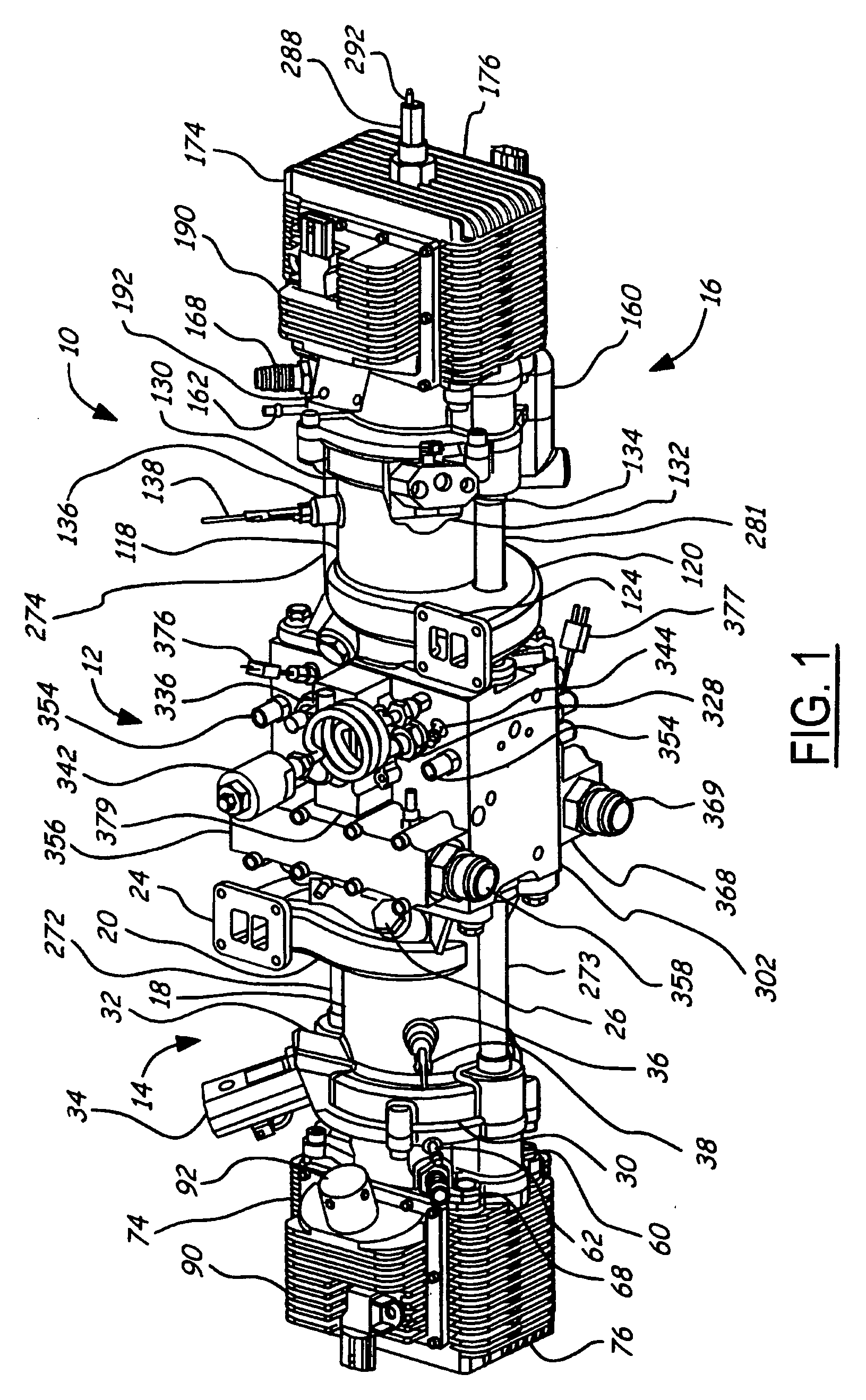
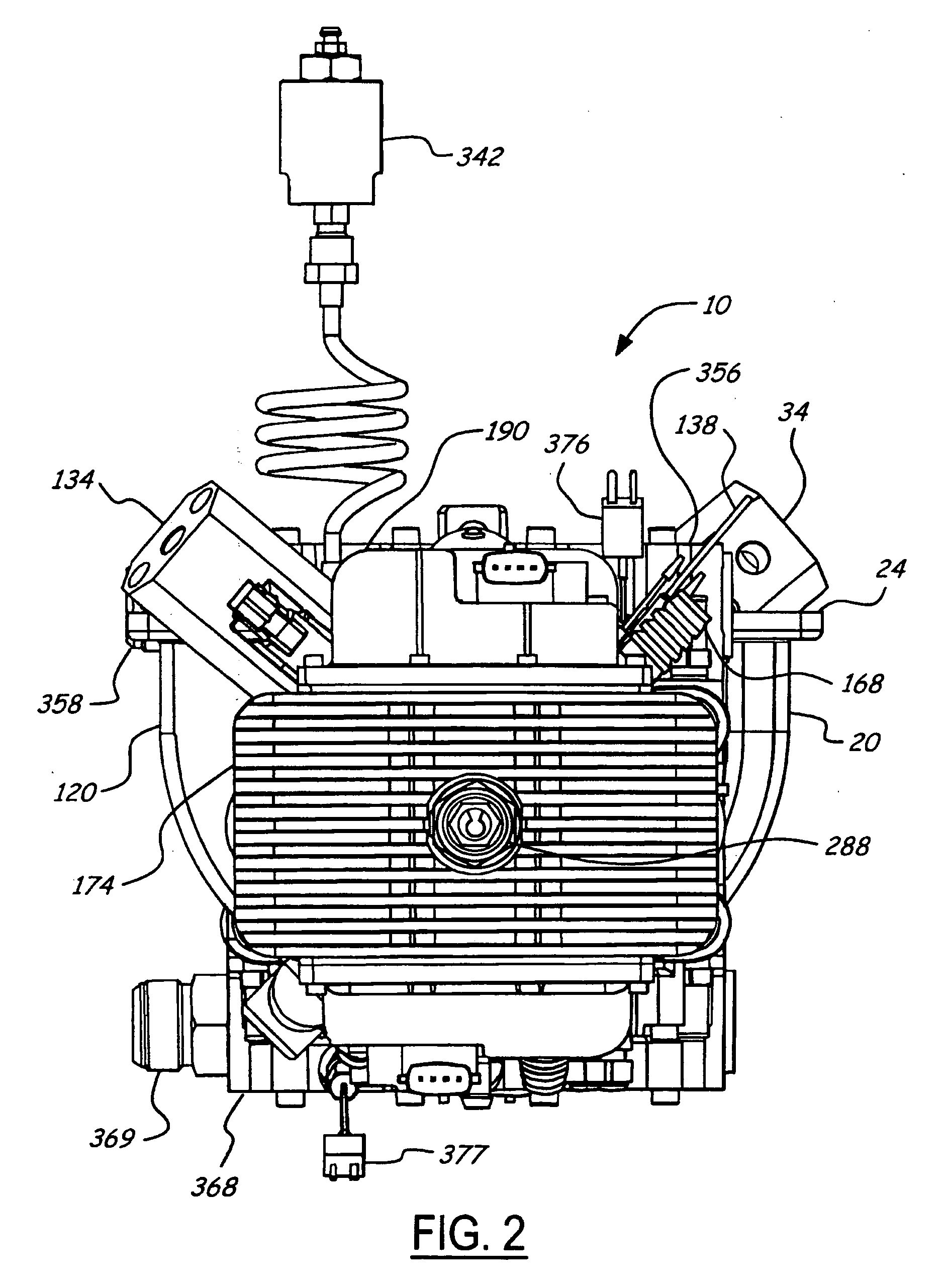
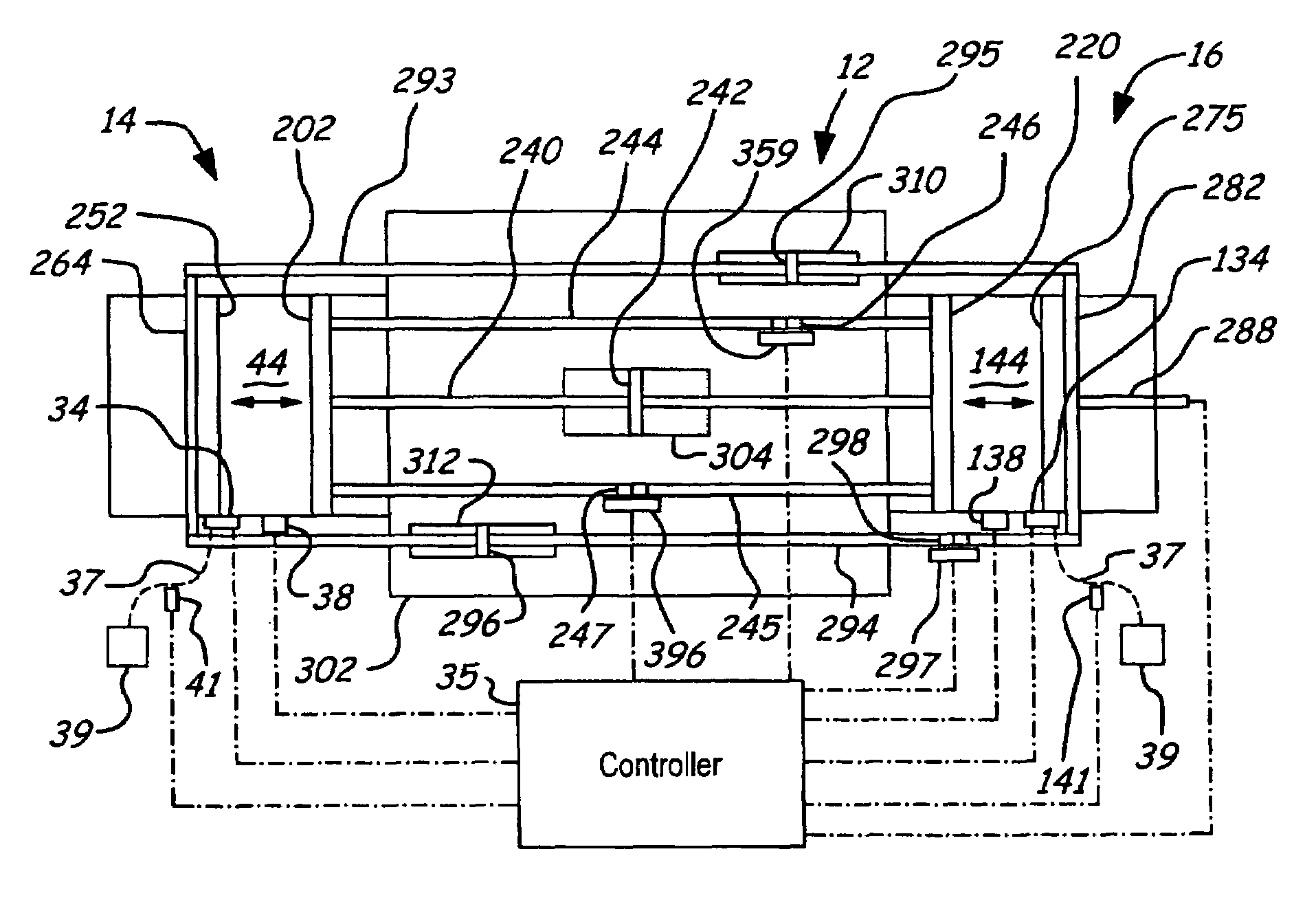
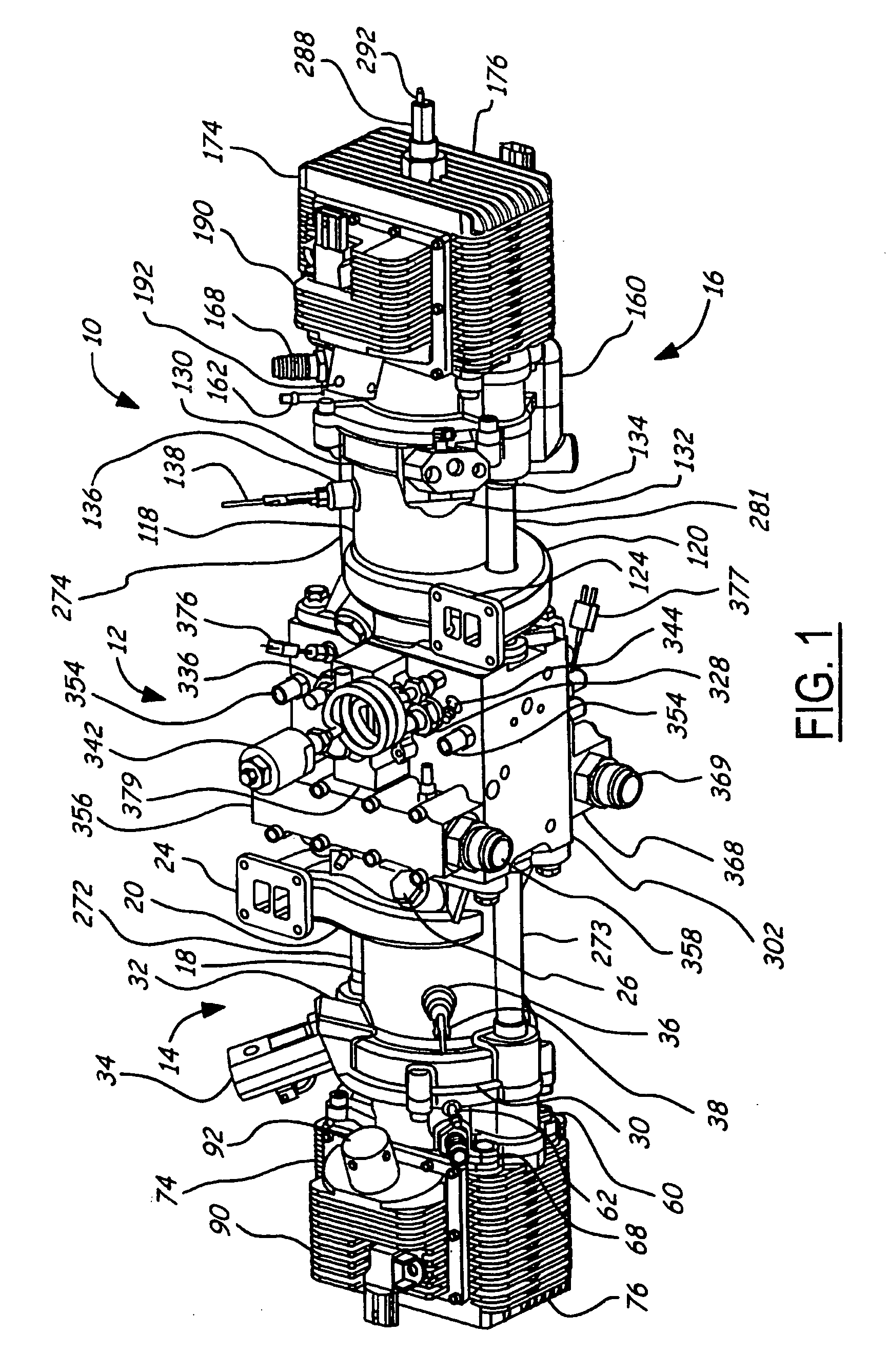
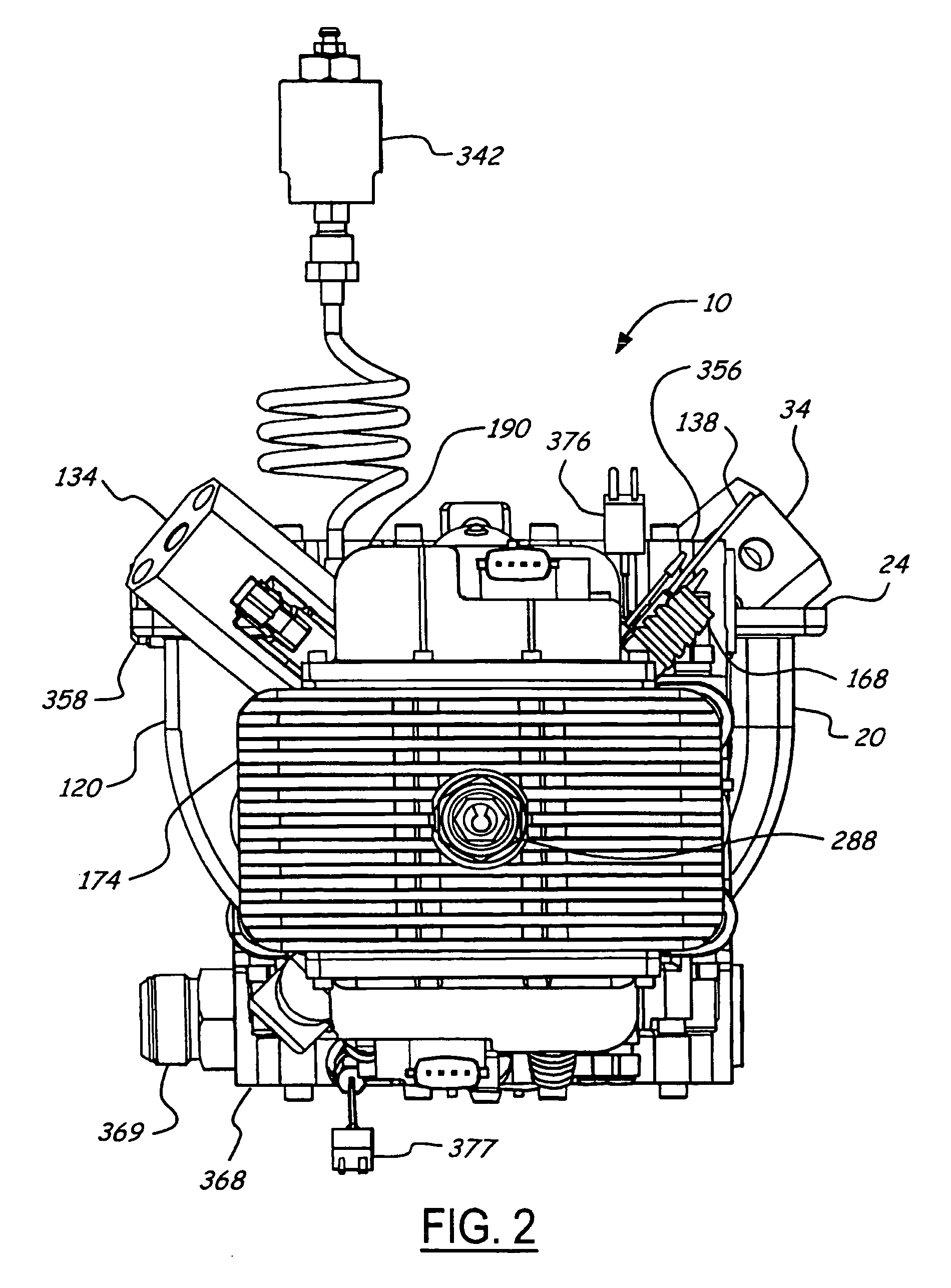
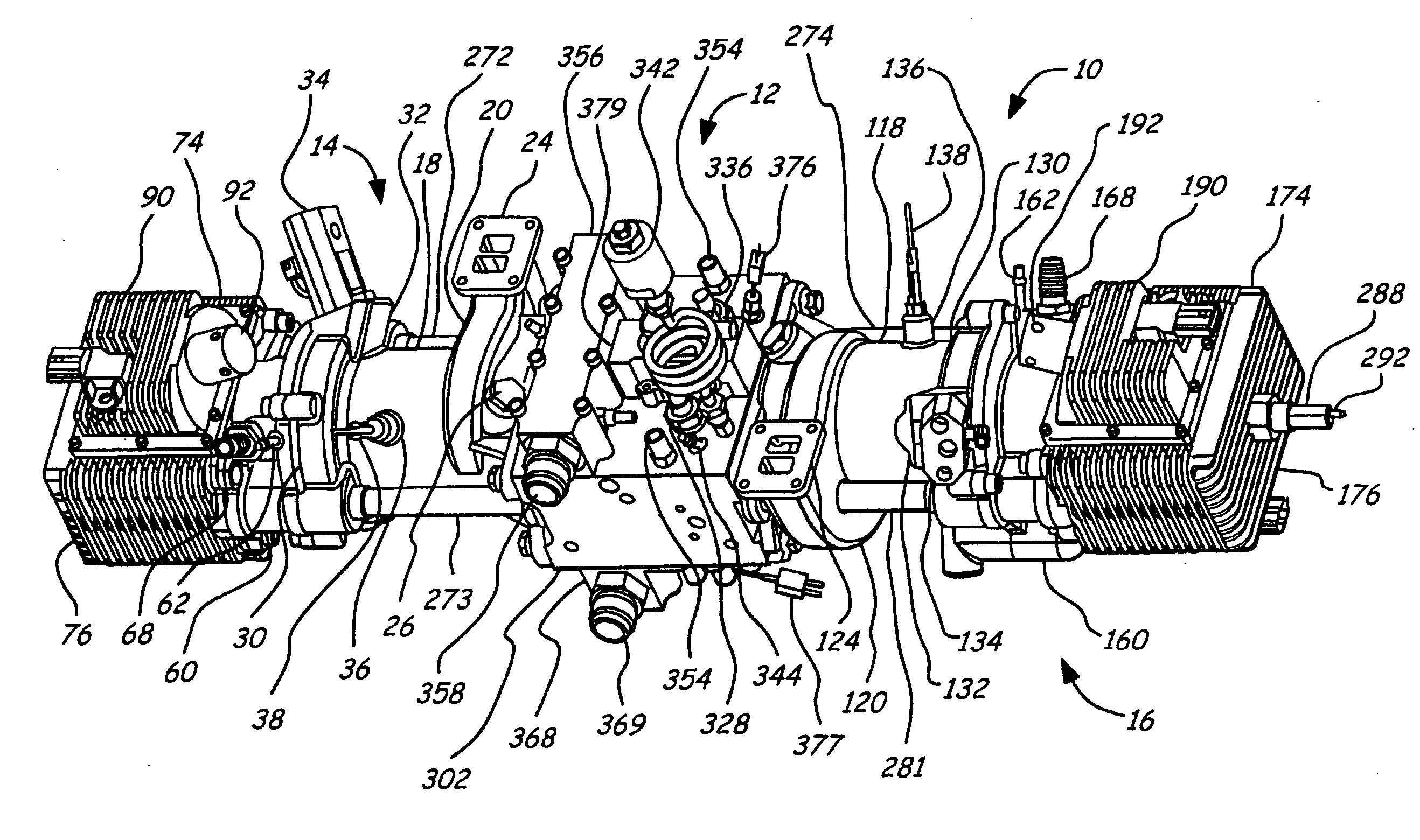
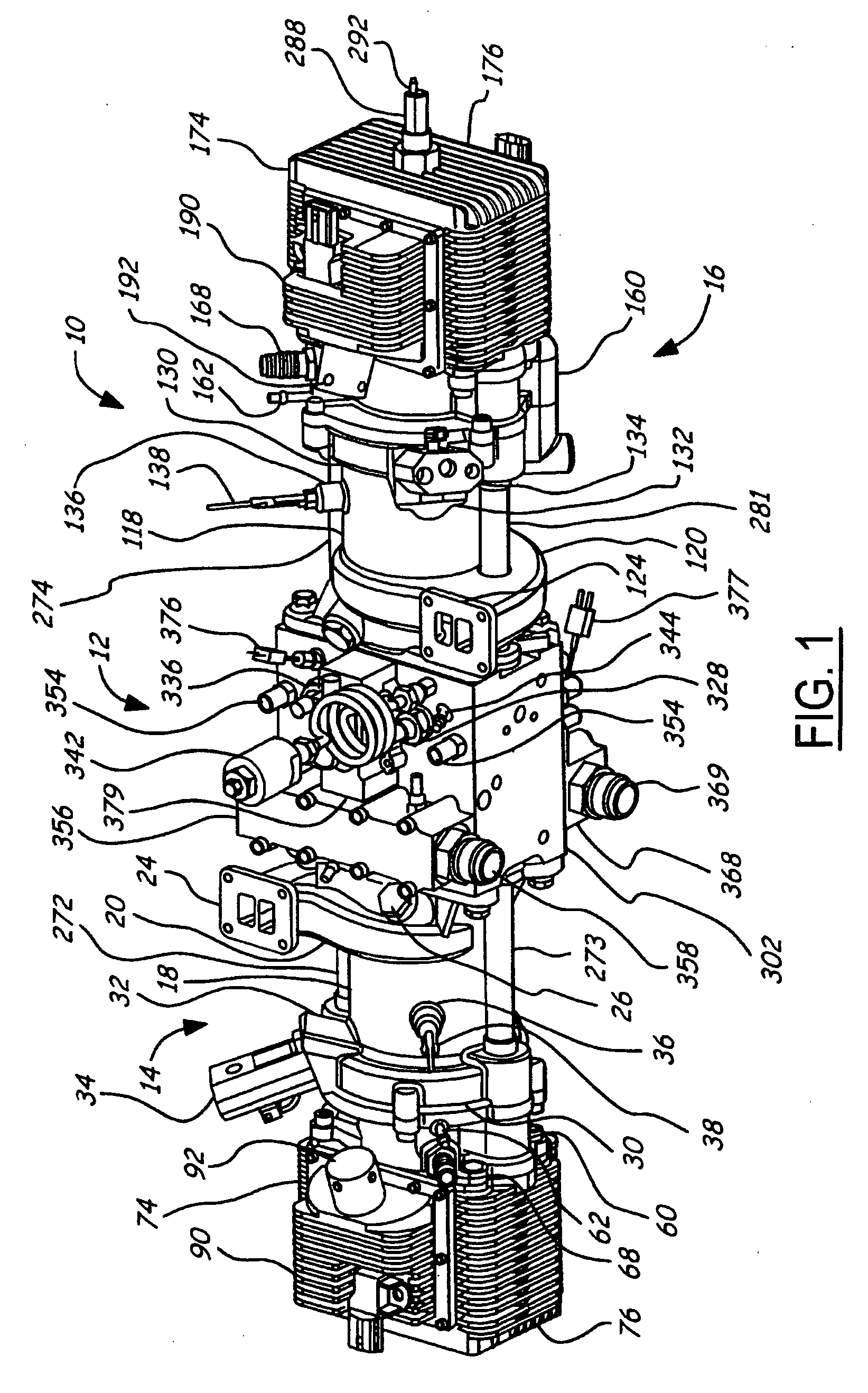
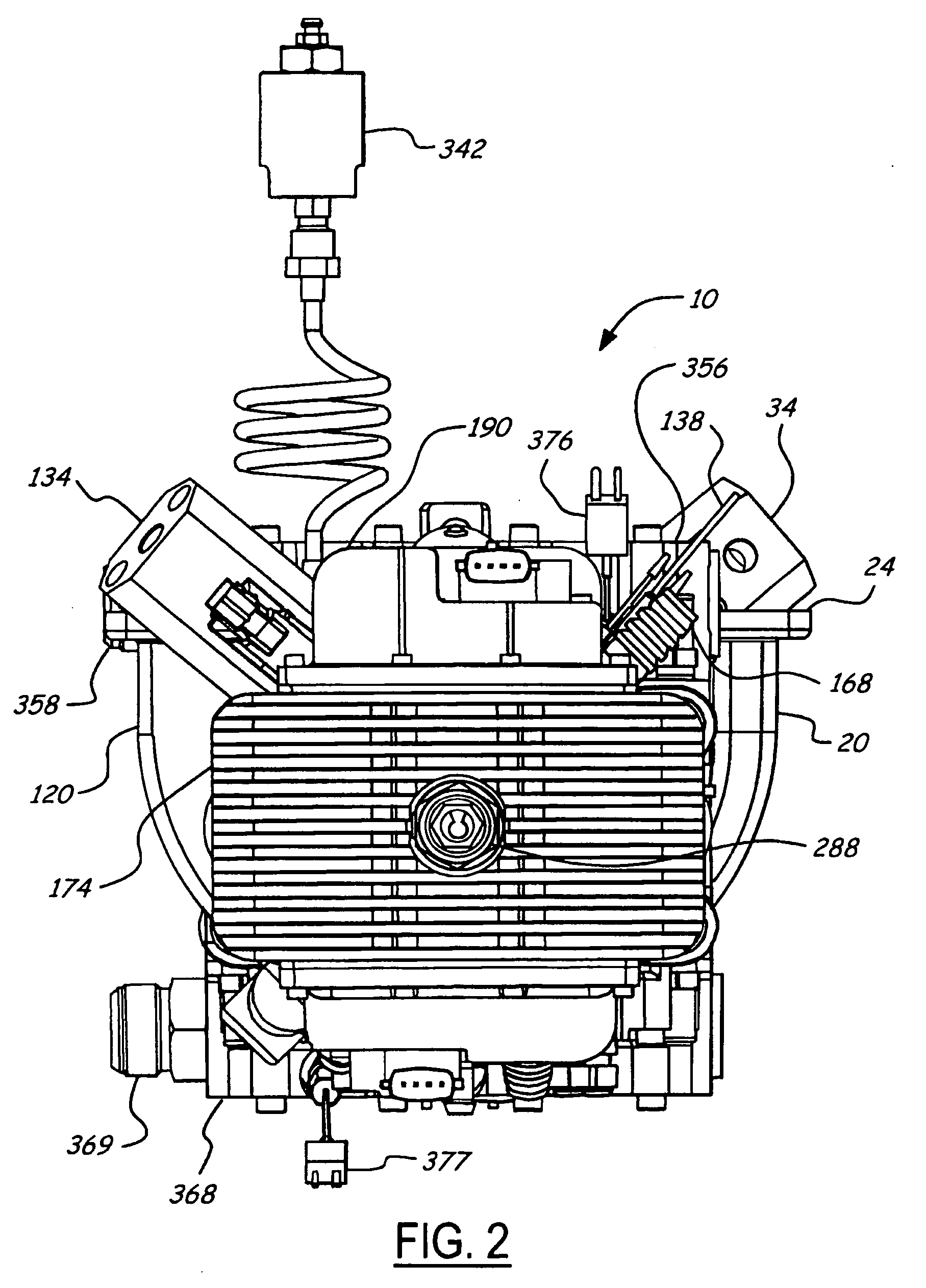
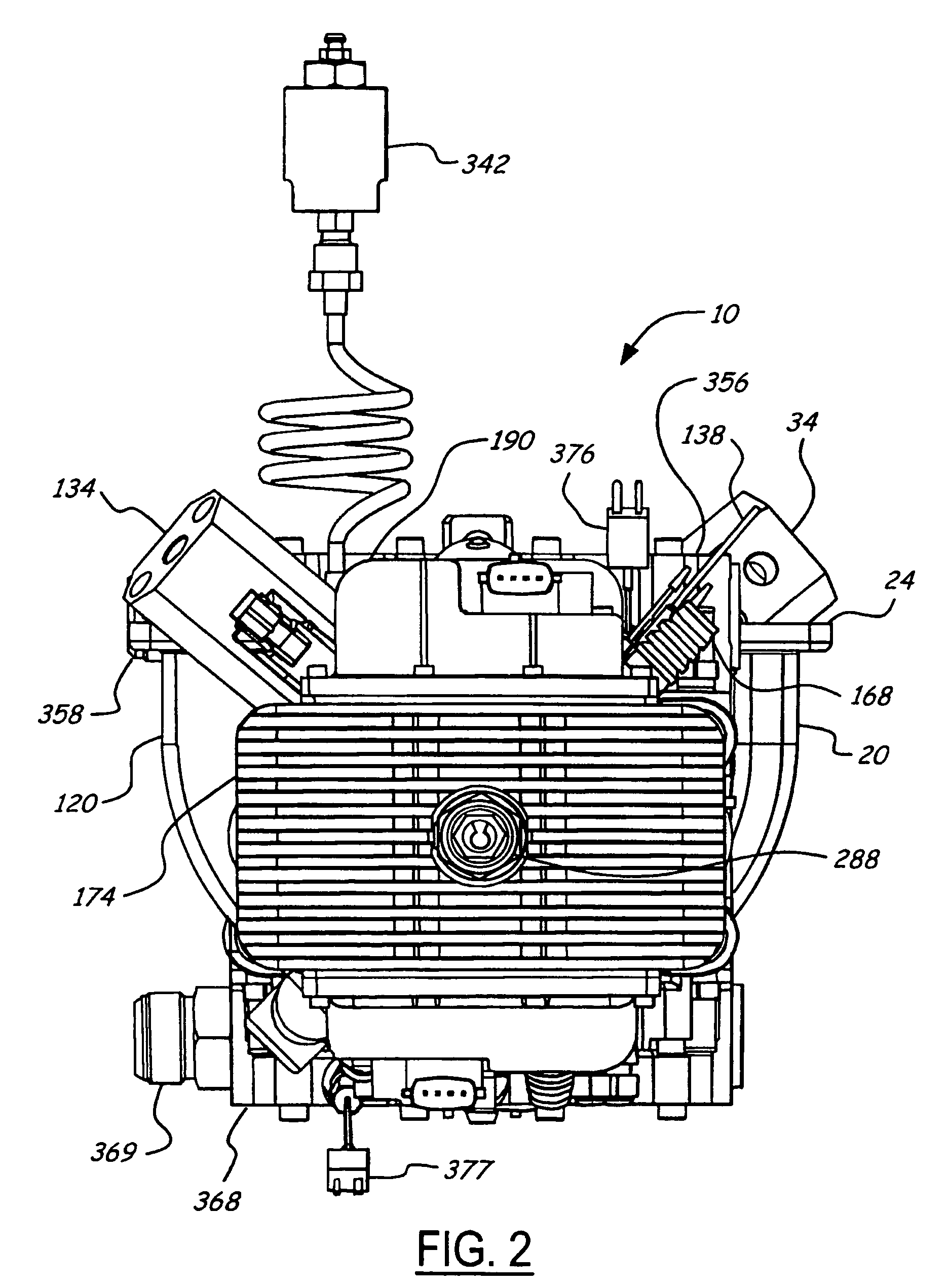
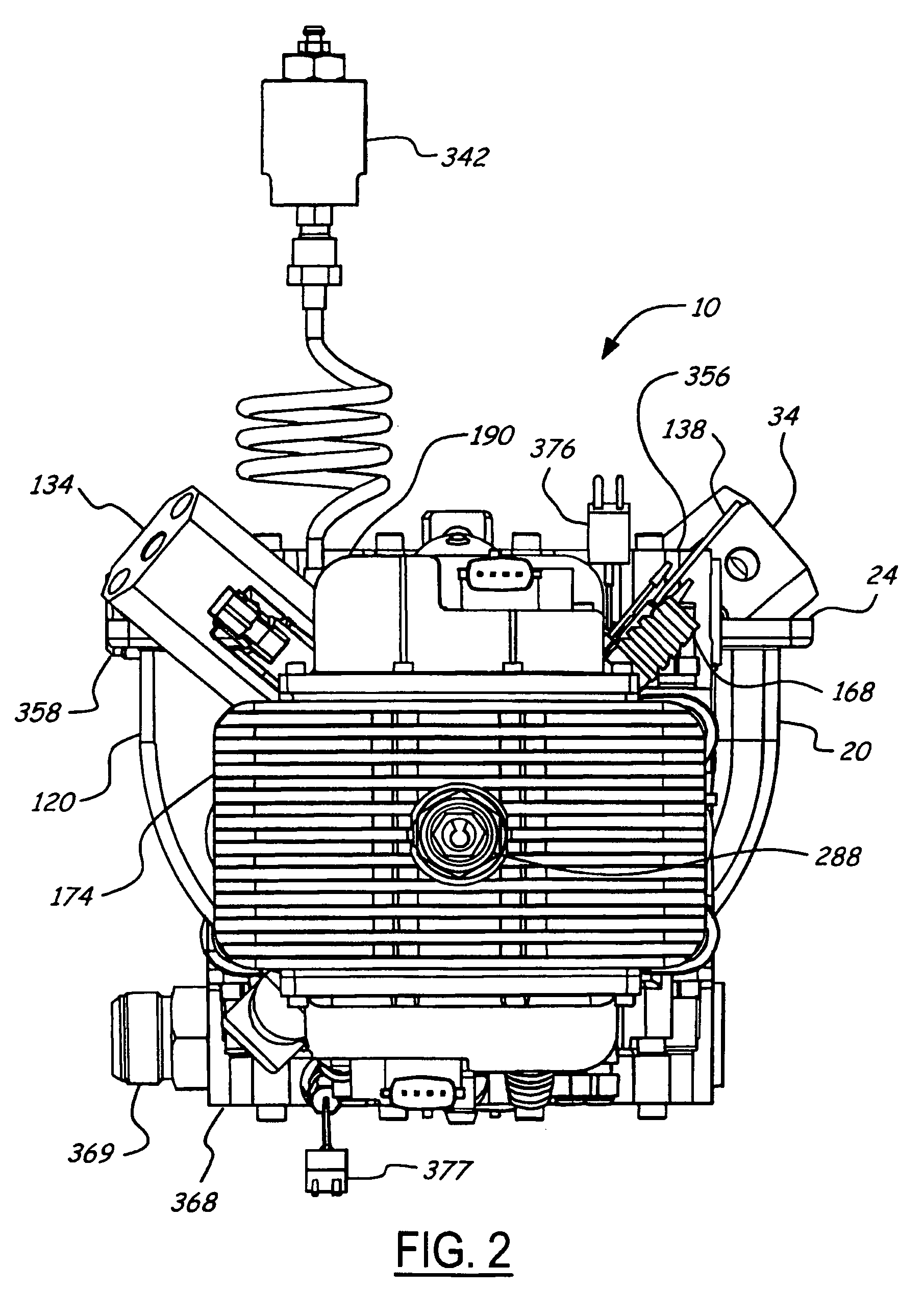
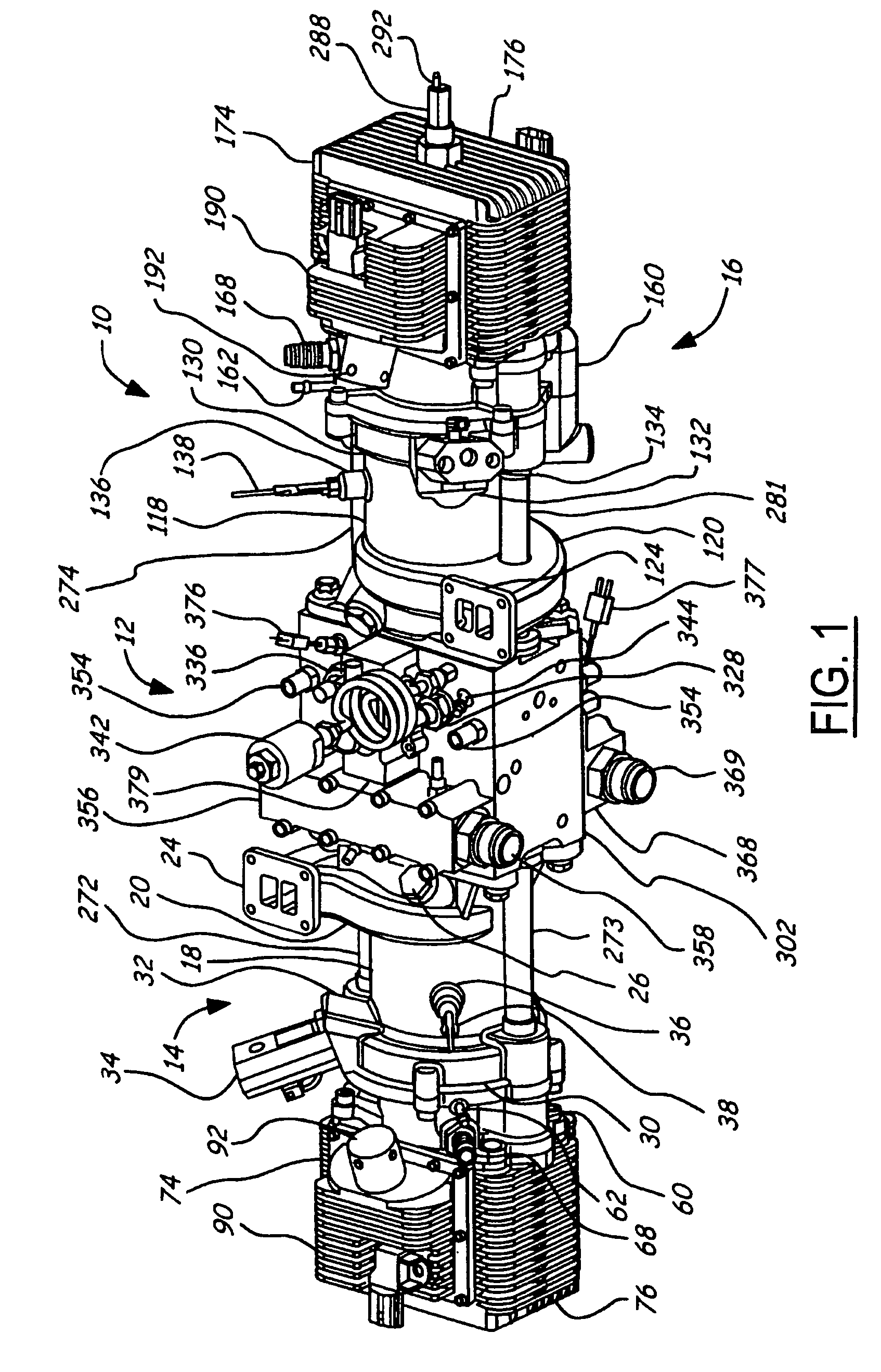
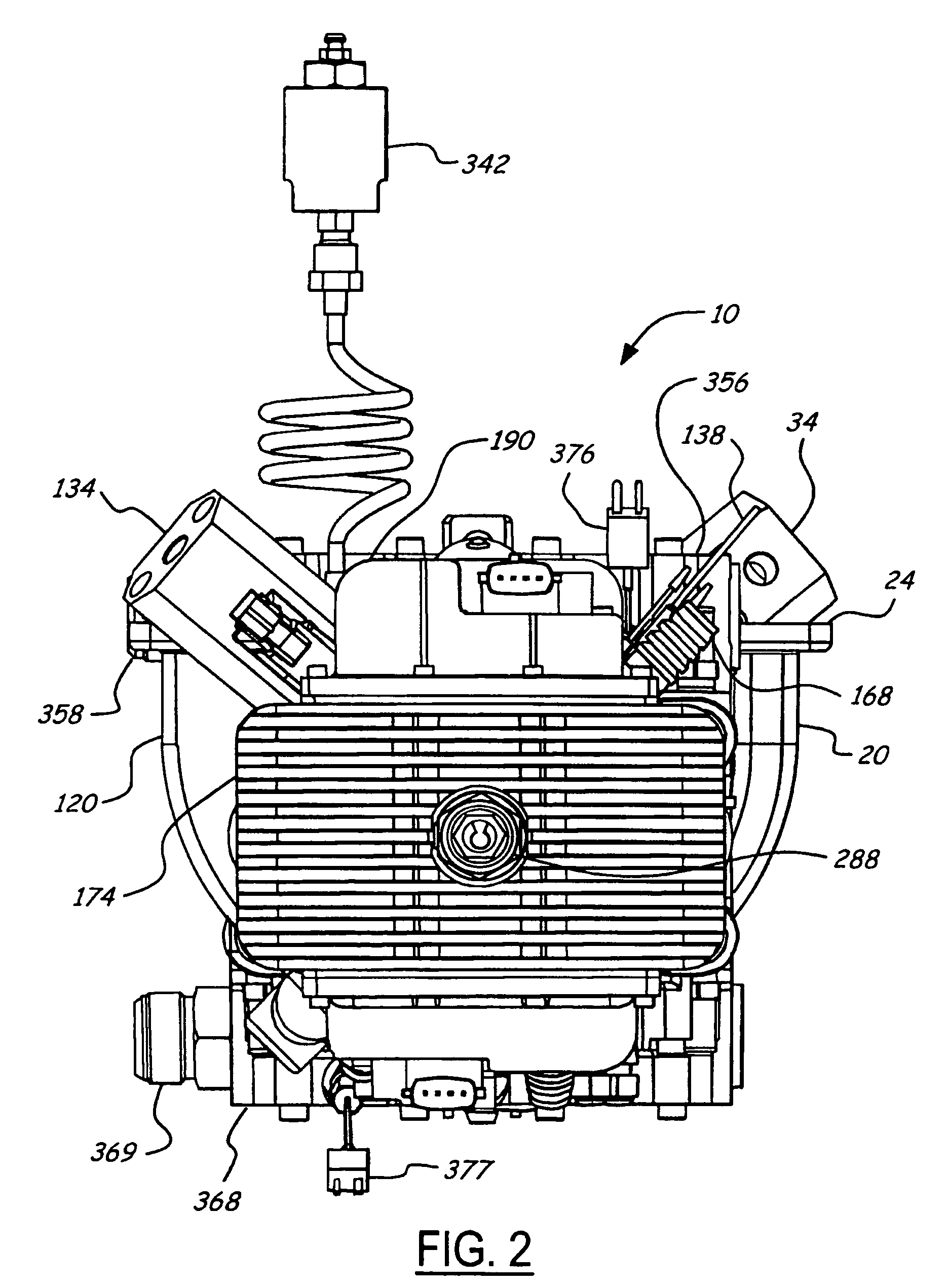
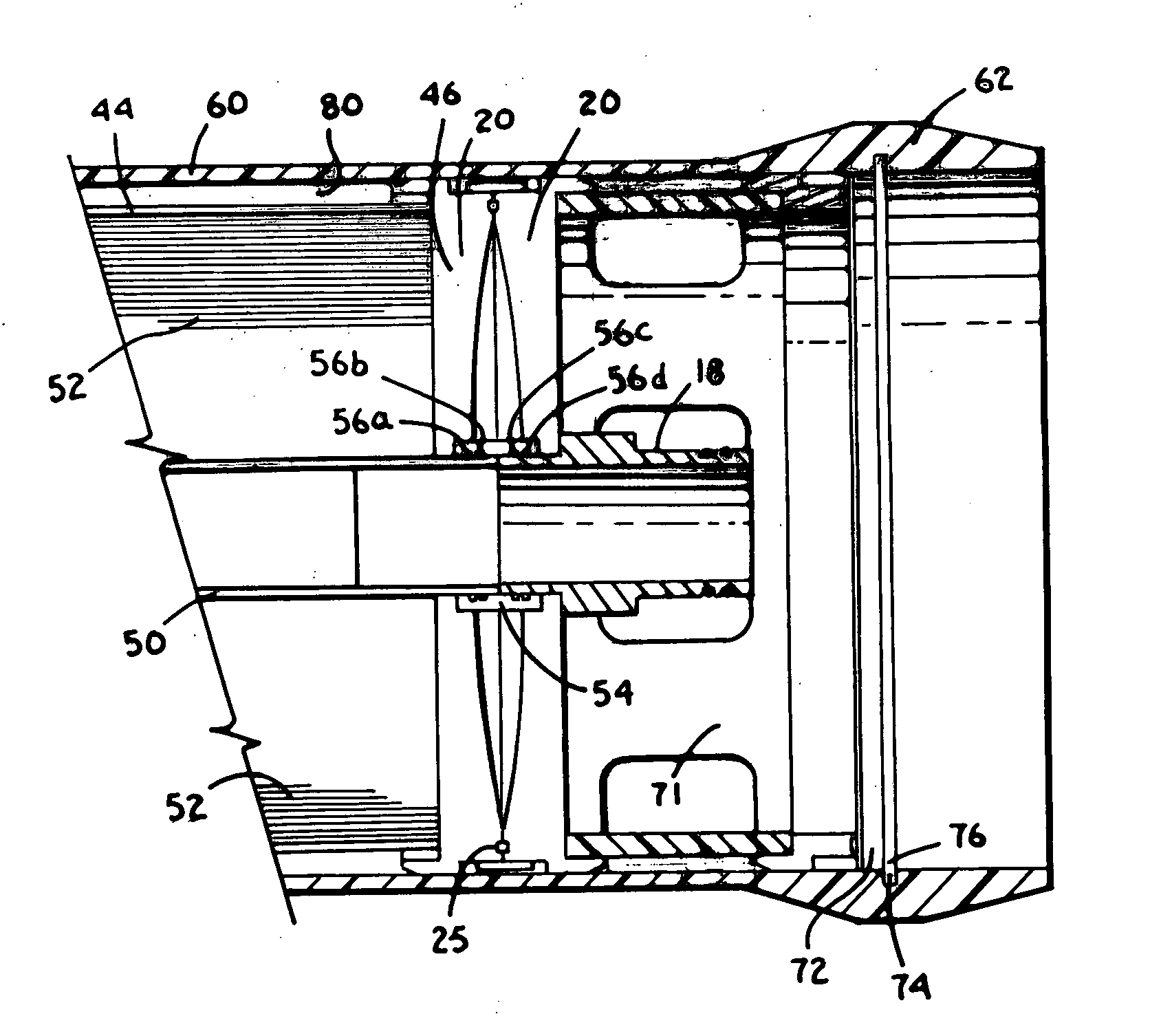
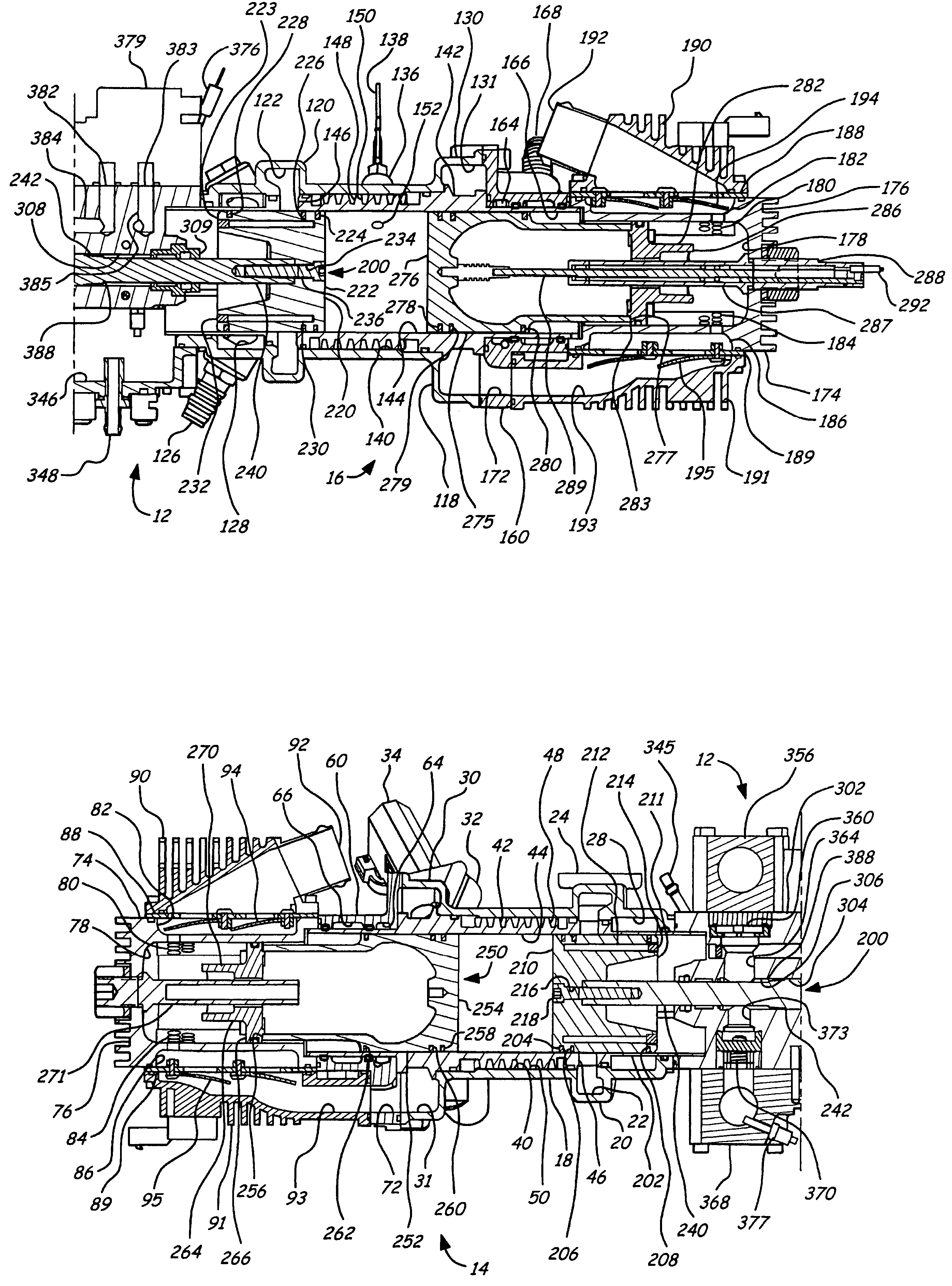
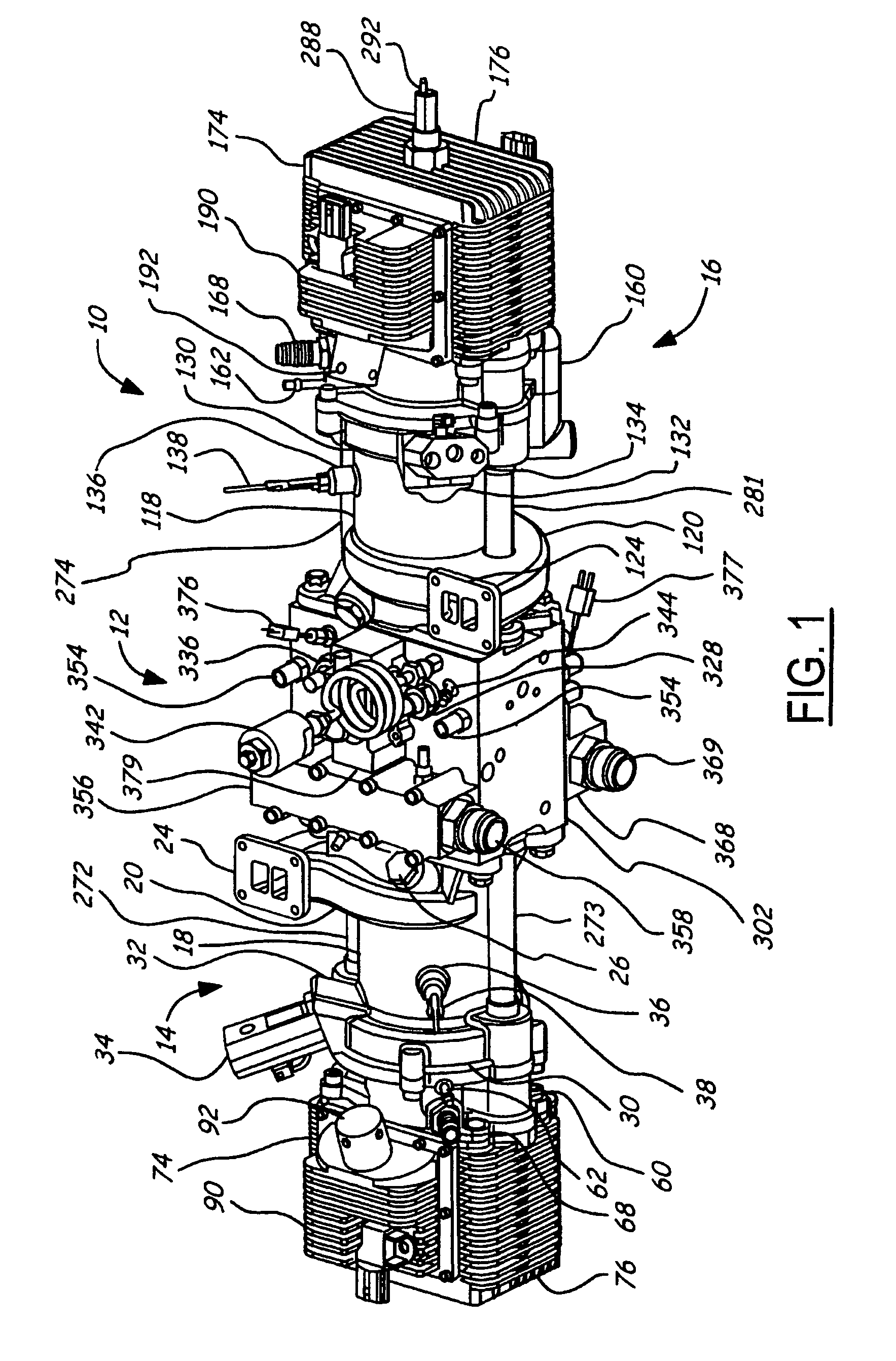
Air charging system for an opposed piston opposed cylinder free piston engine
InactiveUS6957632B1Avoid less frictionEfficient chargingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesFree-piston enginePump chamber
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. Each outer piston cooperates with an integrated scavenge pump in order to compress the charge air, thus significantly increasing the air charge density into the engine cylinders for each stroke of the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Exhaust gas recirculation for a free piston engine
InactiveUS6925971B1Easy to changeConducive effective homogeneous chargeNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust gas recirculationFree-piston engineExhaust valve
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. Alternatively, the piston assemblies may drive a linear alternator. The exhaust ports for each engine cylinder are sized and located to retain the desired amount of internal EGR in each cylinder without the need for exhaust valves. As an alternative, an external EGR system may supplement the internal EGR in order to obtain the desired EGR at the desired temperature.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
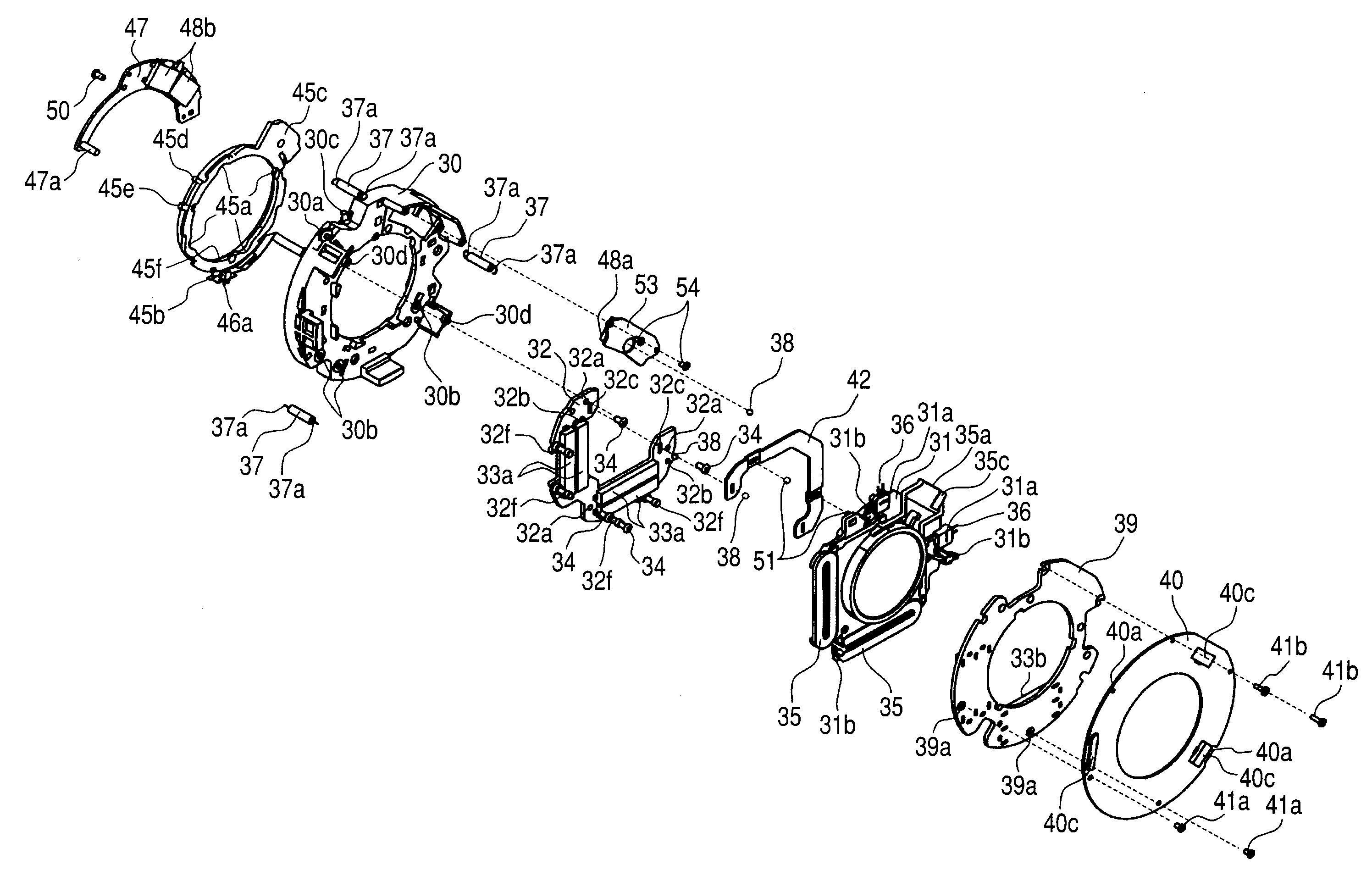
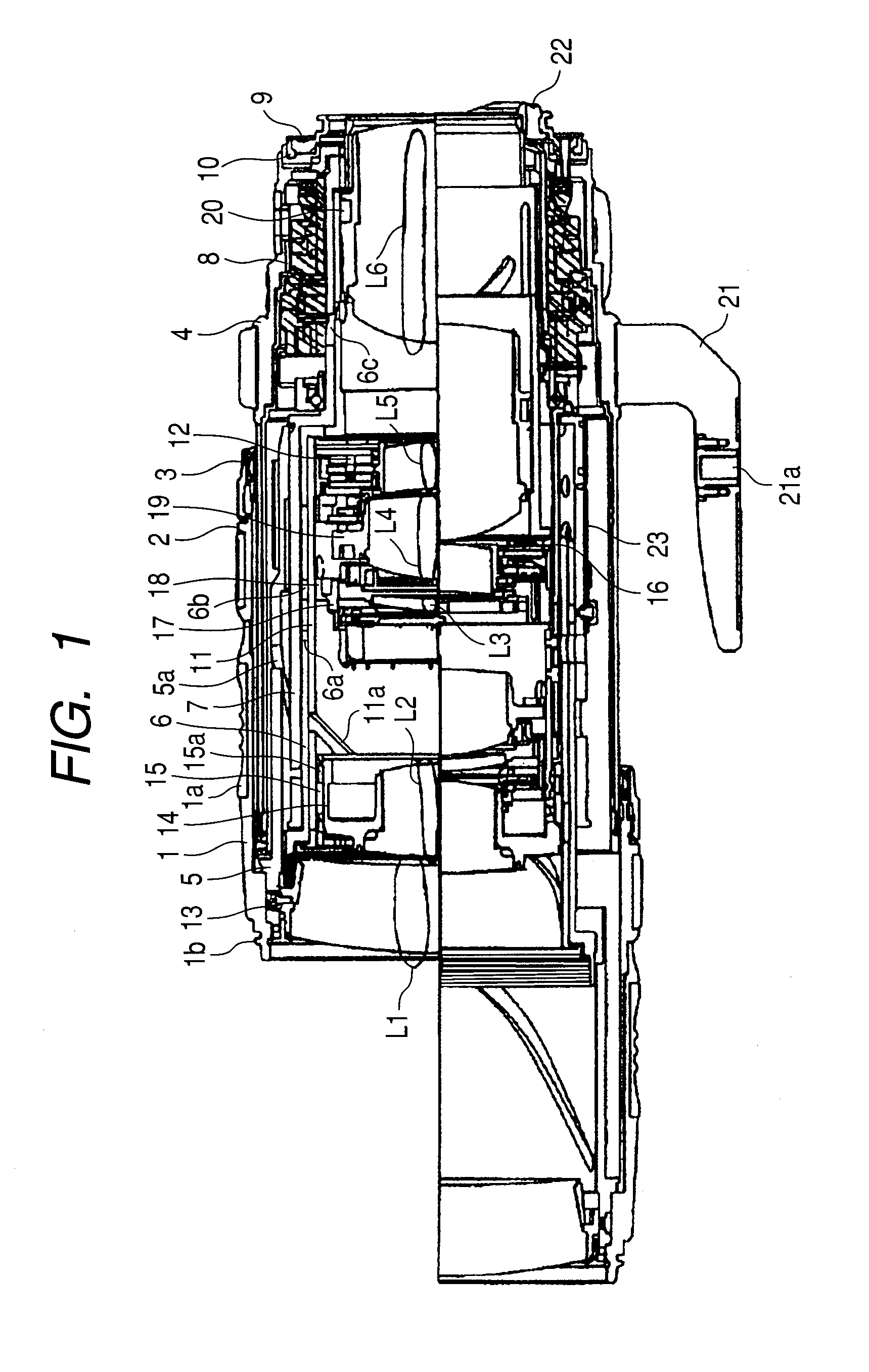
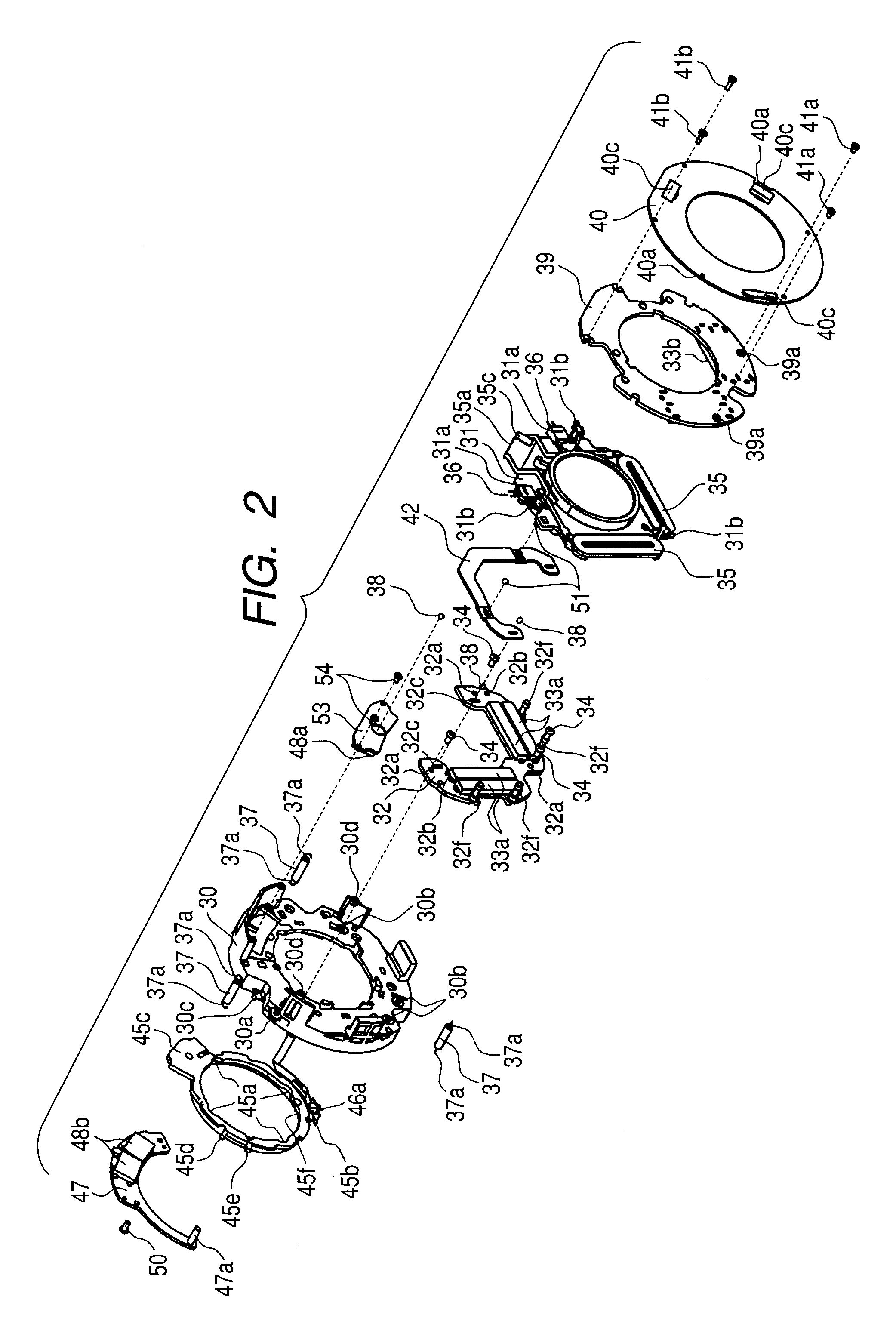
Optical apparatus including an image stabilizing apparatus
ActiveUS20110013283A1Precise positioningHigh positioning accuracyCamera body detailsOptical elementsOptical axisEngineering
An image stabilizer includes: an optical system movable in a plane perpendicular to an optical axis (“orthogonal plane”) and correcting image blur; a movable member holding the optical system and movable relative to a fixed member in an orthogonal plane; a guide guiding the movable member while preventing from rotating in an orthogonal plane; three first balls rollably interposed between the fixed and guide members; two second balls rollably interposed between the guide and movable members; one third ball rollably interposed between the fixed and movable members; a biasing unit biasing the movable member toward the fixed member; and a drive unit driving the movable member relative to the fixed member in two directions perpendicular to the optical axis, wherein in an orthogonal plane, two of the first balls are rollable only in first direction; the second balls are rollable only in second direction different from the first direction.
Owner:CANON KK
Hydrophilic coating and substrates coated therewith having enhanced durability and lubricity
InactiveUS6558798B2Improve adhesionExcellent wear resistance and lubricityDecorative surface effectsSurgeryOrganic acidHydrophilic coating
A substrate, such as a catheter or a guide wire, or a portion of the substrate is provided with a lubricous, hydrophilic abrasion-resistant coating by: (a) coating the substrate with a first aqueous coating composition having an aqueous dispersion or emulsion of a polymer having organic acid functional groups and a polyfunctional crosslinking agent having functional groups capable of reacting with organic acid groups, and drying the coating to obtain a substantially water-insoluble coating layer having excess polyfunctional including functional groups being reactive with organic acid groups remaining; and (b) contacting the dried water-insoluble coating layer with a second aqueous coating composition having an aqueous solution or dispersion of a hydrophilic polymer having organic acid functional groups, a polymer having organic acid functional groups and a polyfunctional crosslinking agent having functional groups capable of reacting with organic acid groups, and drying the combined coating to form an intermediate coating, whereby the polymer and the hydrophilic polymer of the second composition become bonded to the polymer of the first coating composition through the excess crosslinking agent; and (c) contacting the dried intermediate coating with a third aqueous coating composition having an aqueous solution or dispersion of a hydrophilic polymer having organic acid functional groups, and drying the combined coatings, the hydrophilic polymer of the third coating composition thereby becoming bonded to the polymers of the second coating composition through the excess crosslinking agent. The dryings can be carried out at ambient (room) temperature.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
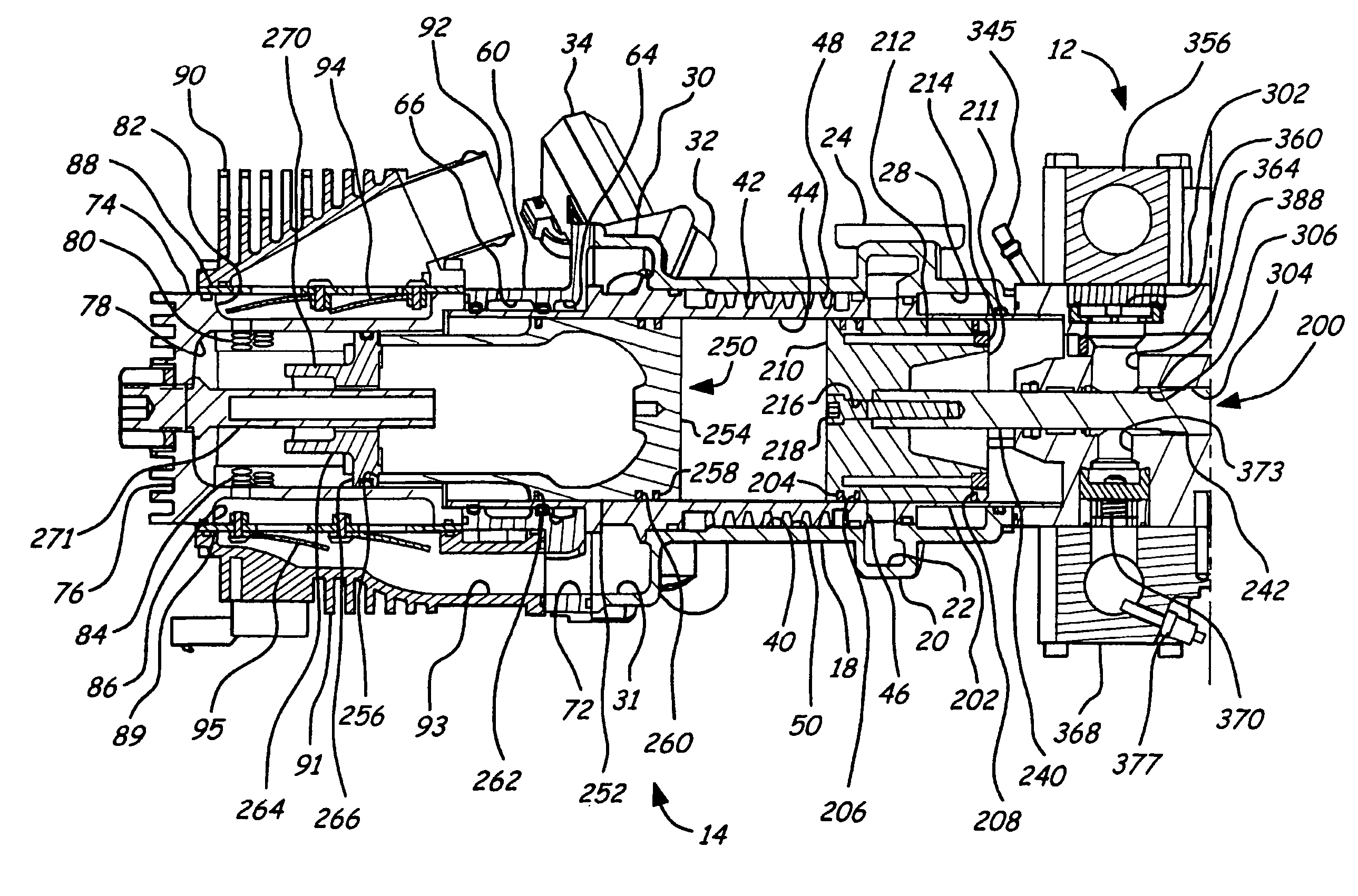
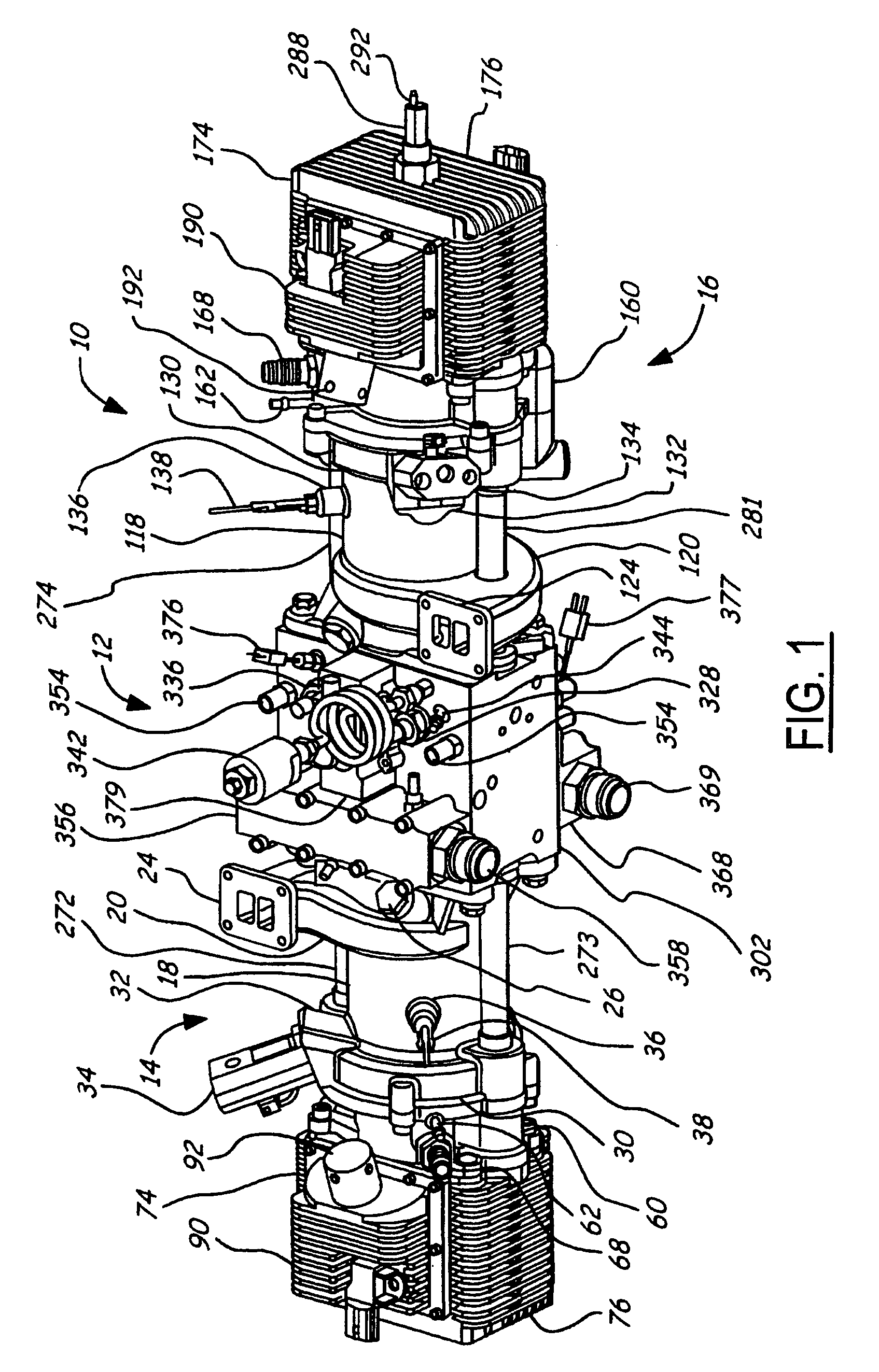
Position sensing for a free piston engine
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. Also connected between the pistons are a position sensor and a calibration position sensor that are employed to determine the position and velocity of the inner piston assembly. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. Also engaging the outer piston assembly are a position sensor and a calibration position sensor that are employed to determine the position and velocity of the outer piston assembly. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
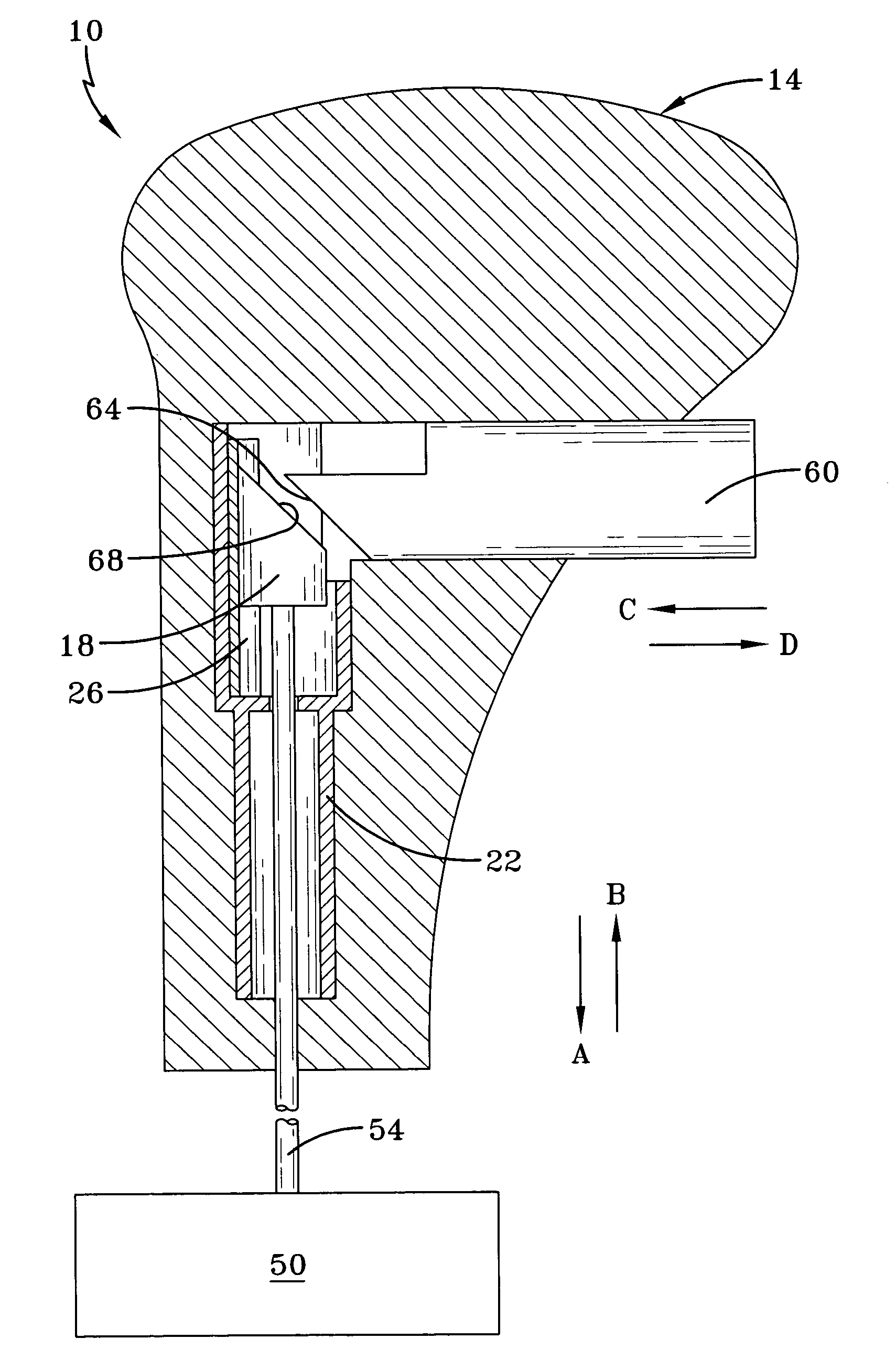
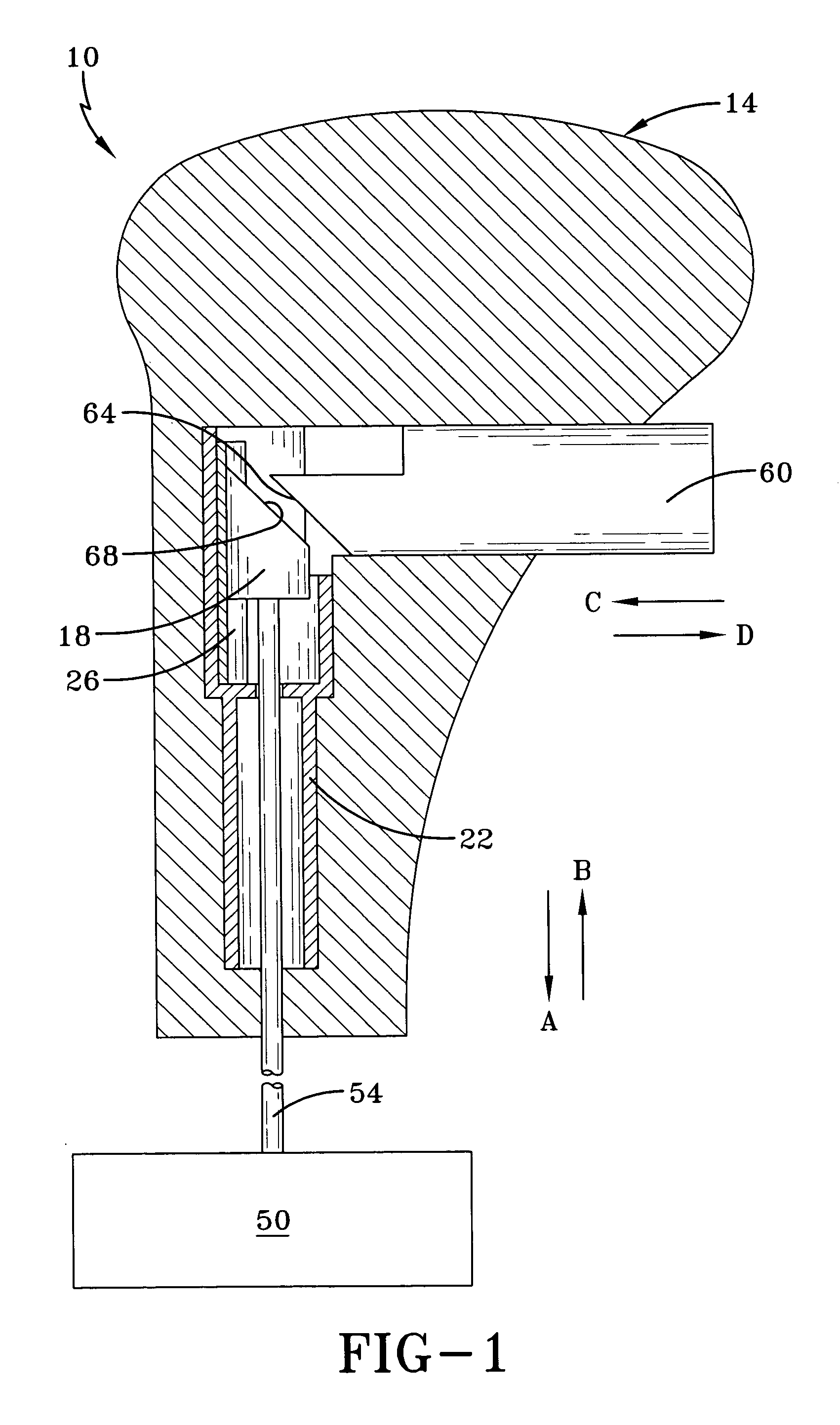
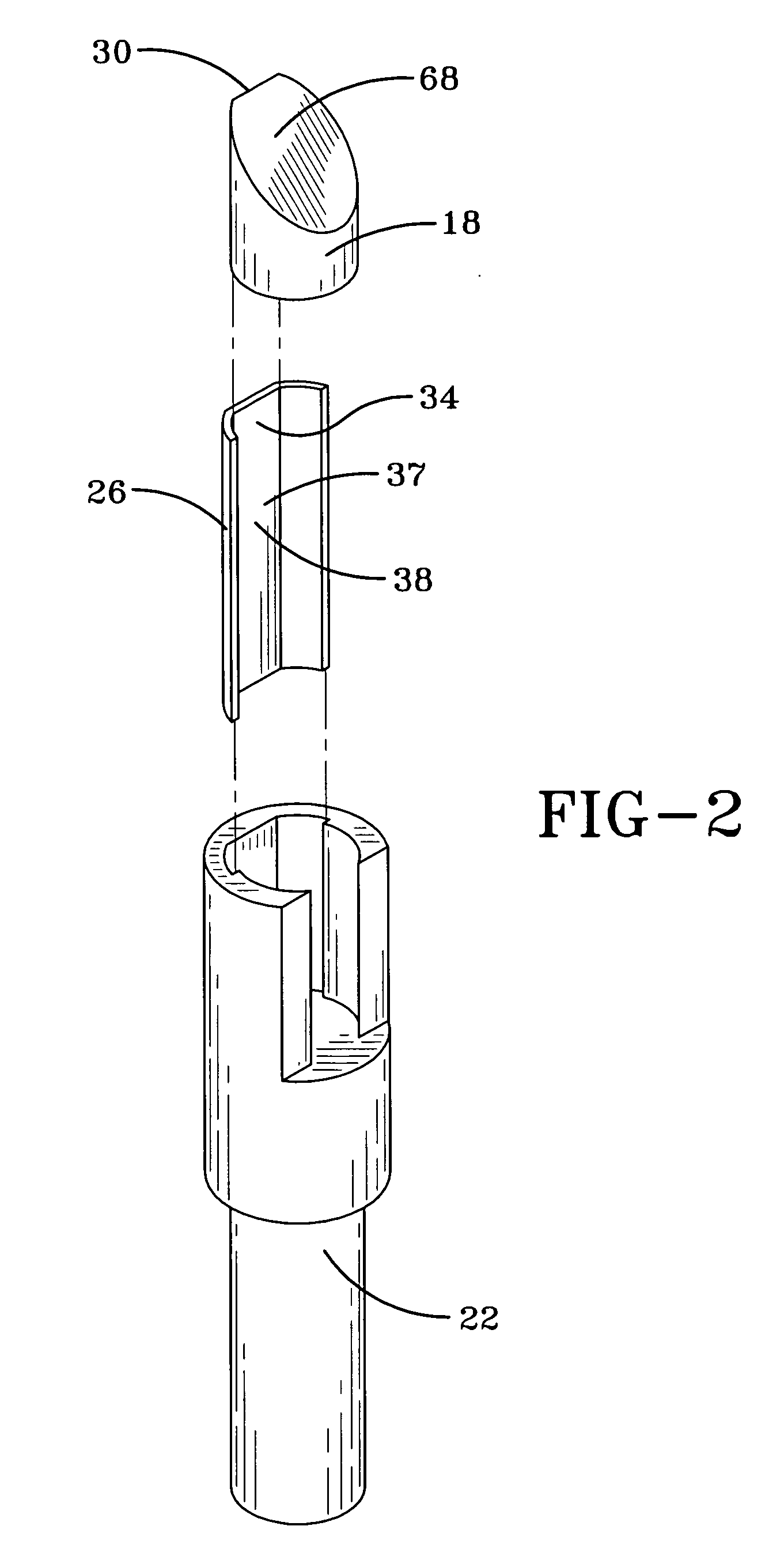
Automatic closing door hinge, automatic closing door mechanism, and hinge of automatic closing door mechanism
An automatic closing door hinge, an automatic closing door mechanism, and a hinge of the automatic closing door mechanism, for smoothly opening a door or closing, with damping, a door. For example, an automatic door closing mechanism has a hinge having a pair of wing plates one of which has a cylinder in a circular cylindrical form received therein a piston, the other wing plate fixing an upper portion of an operation rod engaged with the piston, the piston being to be advanced and retracted through the operation rod associatively with a rotation of the other wing plate. The automatic closing door mechanism comprises a cam formed on the piston. An engaging part provided in the operation rod and movable in the cam. The cam and the engaging part engaging between the piston and the operation rod. A sphere arranged in a recess formed in an outer surface of the piston. A recess groove formed lengthwise in the cylinder. The sphere rolls along the recess groove, to allow the piston to slide within the cylinder. Impact upon door closing is to be damped by an action of air cushioning within the cylinder due to a return movement of the piston.
Owner:SAWA MASAKO +1
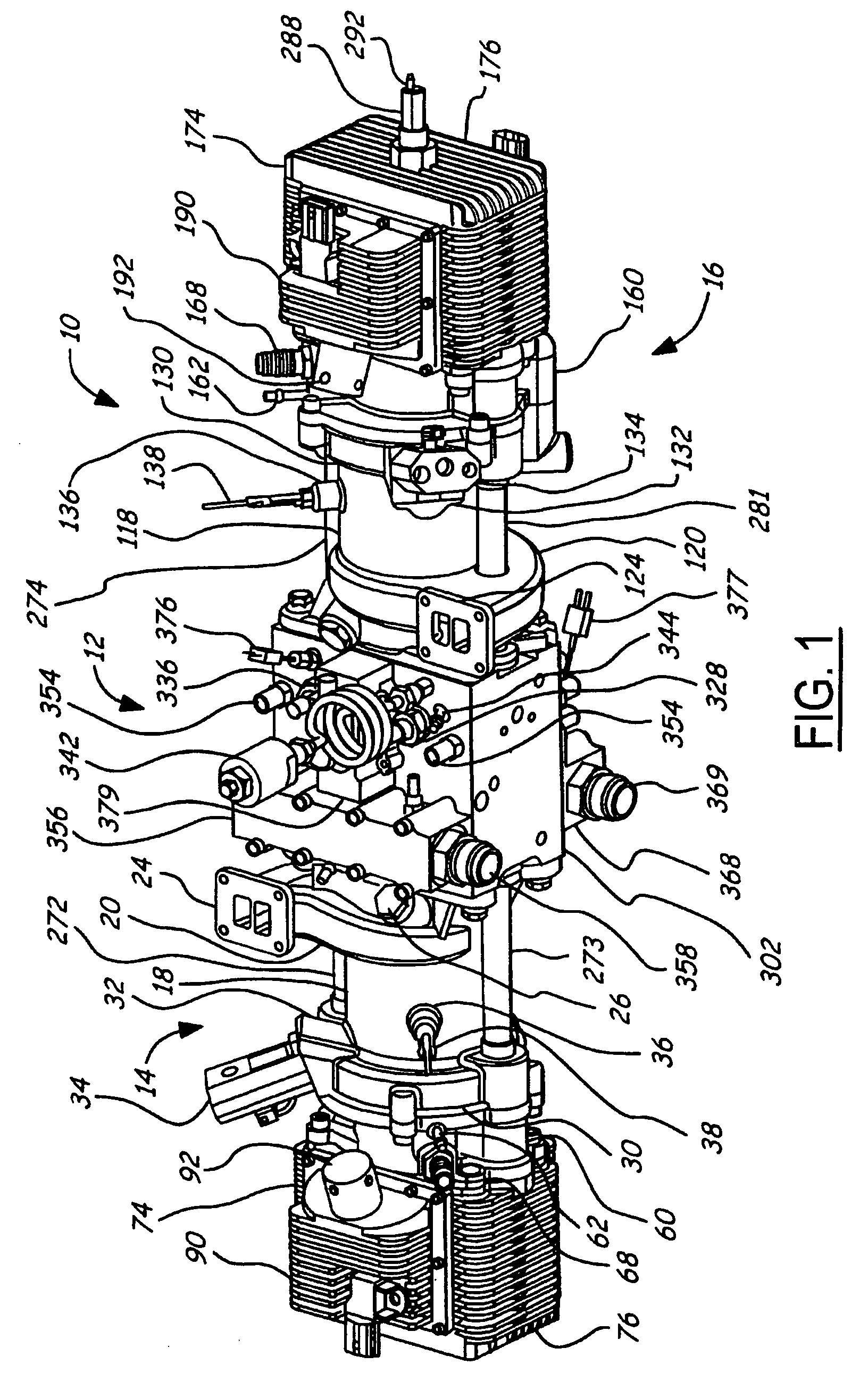
Piston guides for a free piston engine
InactiveUS20050284426A1Easy to changeConducive effective homogeneous chargeFree piston enginesFree-piston enginePump chamber
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. Alternatively, the piston assemblies may drive a linear alternator. Piston guide posts are fixed and guide the outer pistons as they reciprocate within the engine cylinders.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Piston guides for a free piston engine
InactiveUS7032548B2More balancedEfficient chargingFree piston enginesFree-piston engineReciprocating motion
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. Alternatively, the piston assemblies may drive a linear alternator. Piston guide posts are fixed and guide the outer pistons as they reciprocate within the engine cylinders.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Tire tread mold
Owner:MICHELIN RECH & TECH SA
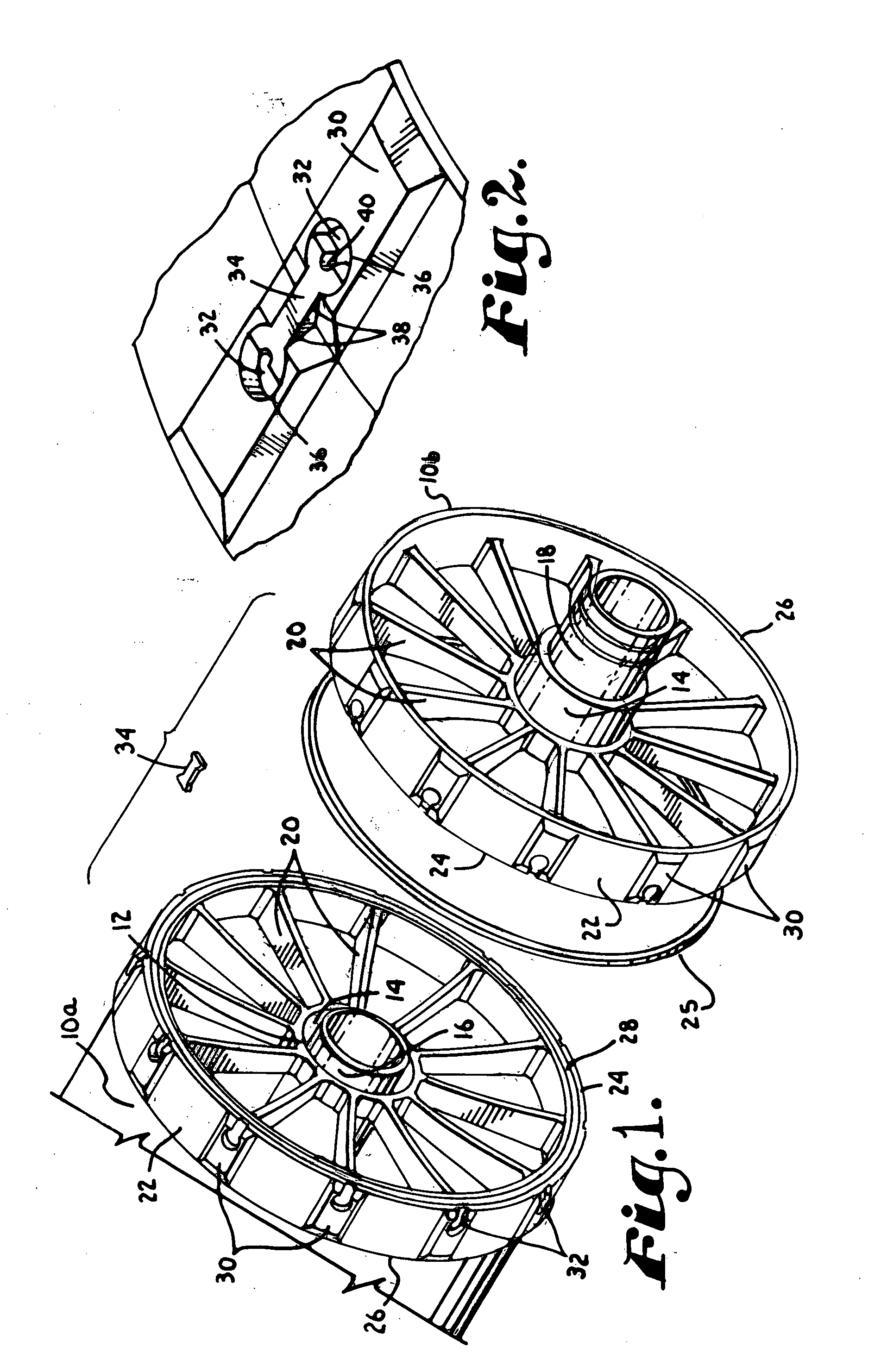
Filtration element and method of constructing a filtration assembly
InactiveUS20050035047A1Easily and securely couplingMinimized contact areaSemi-permeable membranesGeneral water supply conservationEngineeringSpoke
A coupler for a spiral membrane filtration element having a spiral membrane enclosed within a rigid outerwrap includes a center support, a plurality of spokes extending outwardly from the center support, a circular rim coupled with the spokes, with the face of the rim being perpendicular to the axis of the overwrap. The rim includes a channel on its face for receiving a compressible seal, and a plurality of receptacles around its outer surface for joining two face-to-face adjacent couplers when a pair of aligned keepers is place in each receptacle. Exemplary embodiments of the coupler and filtration elements and filtration assemblies are provided, as well as an associated method.
Owner:KOCH MEMBRANE SYST
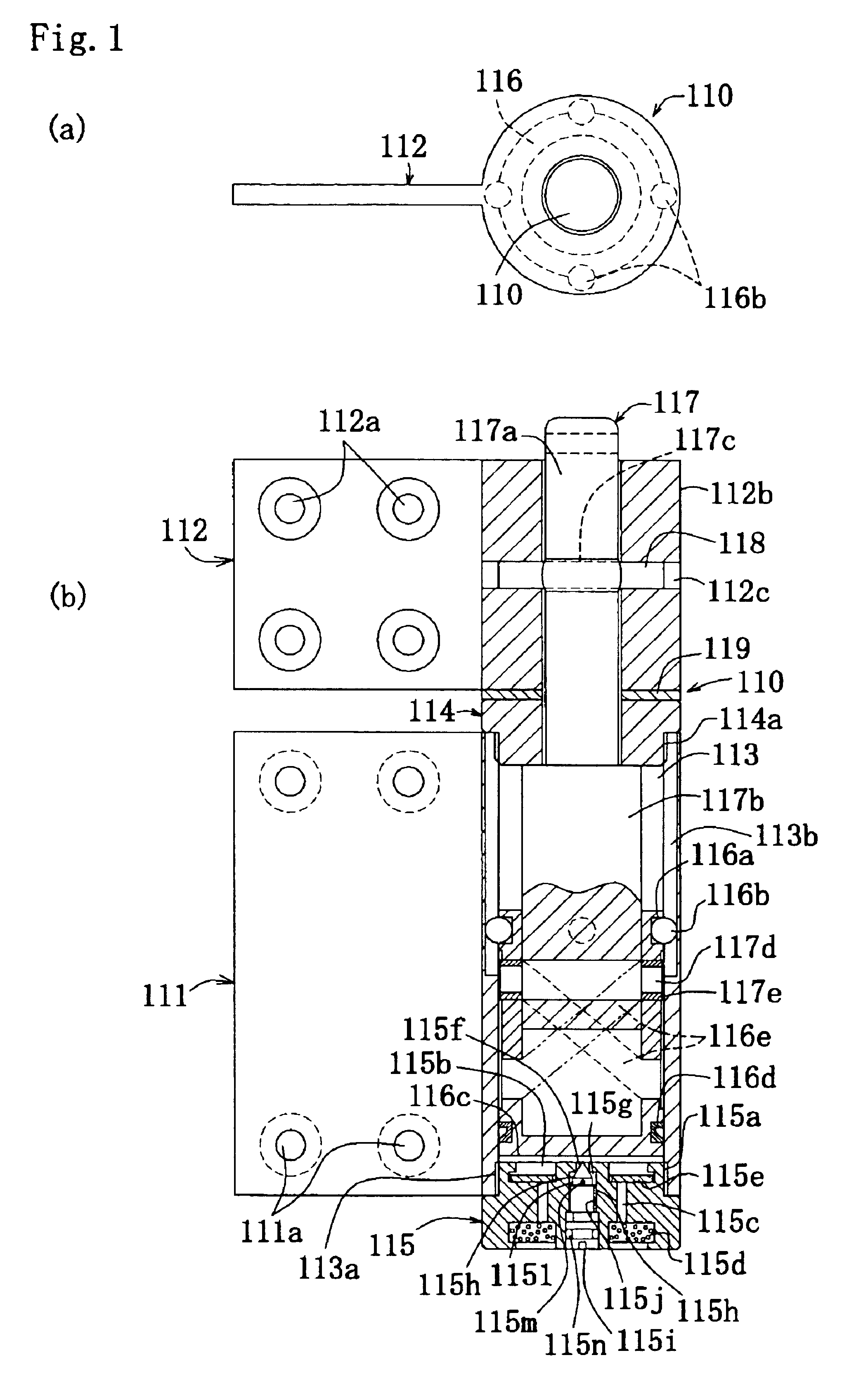
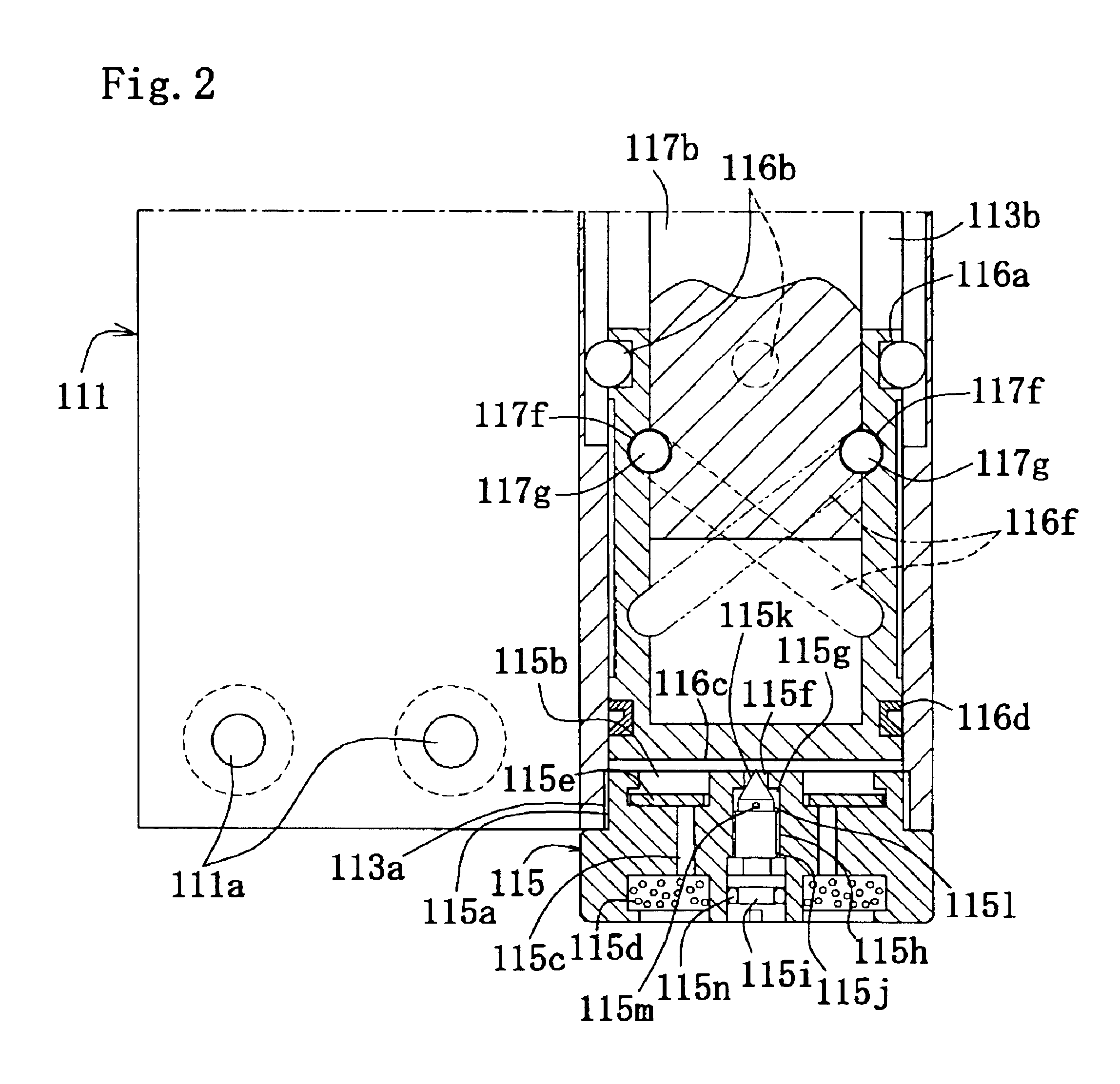
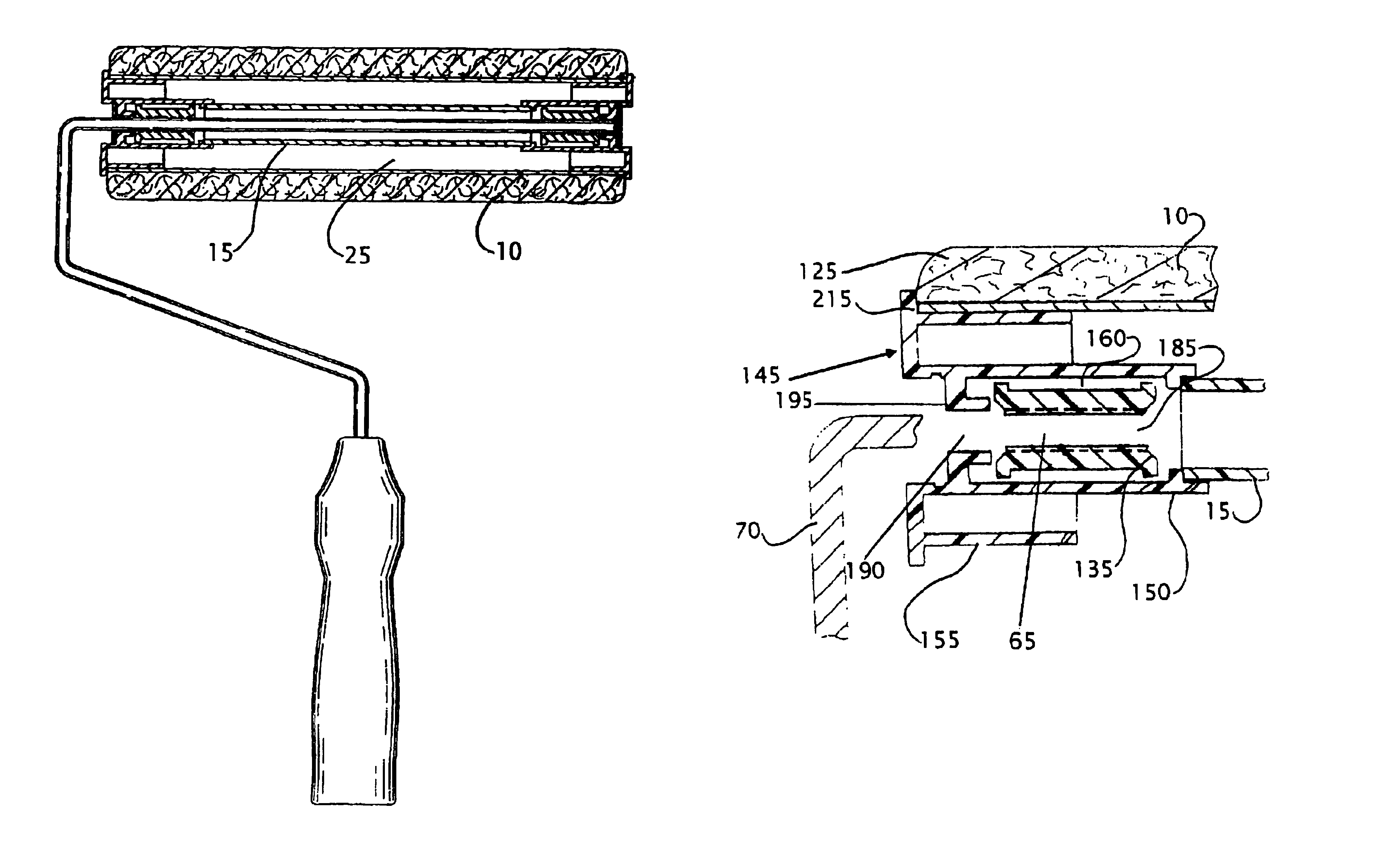
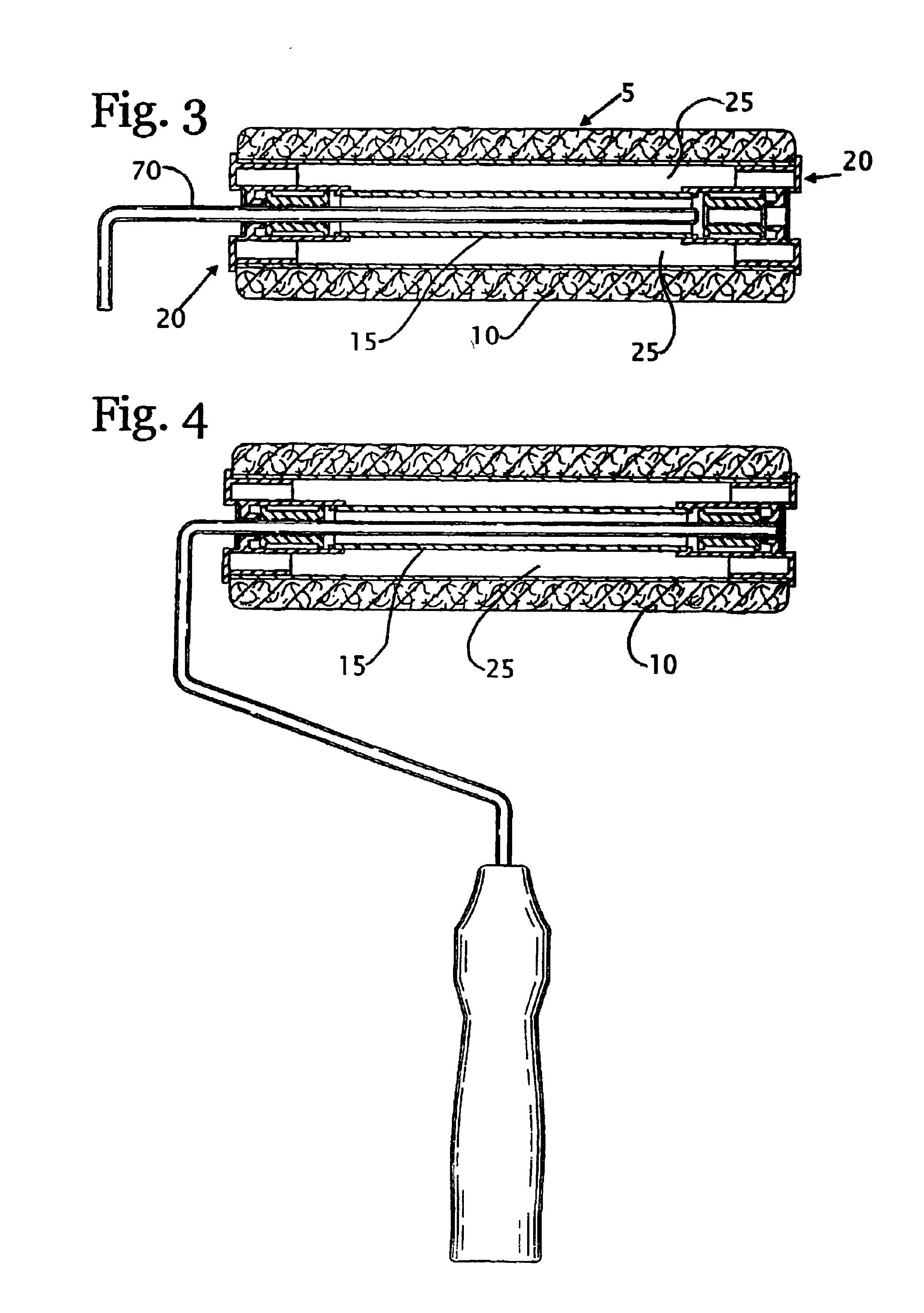
Developing roller, developing roller production method, process cartridge, and electrophotographic apparatus
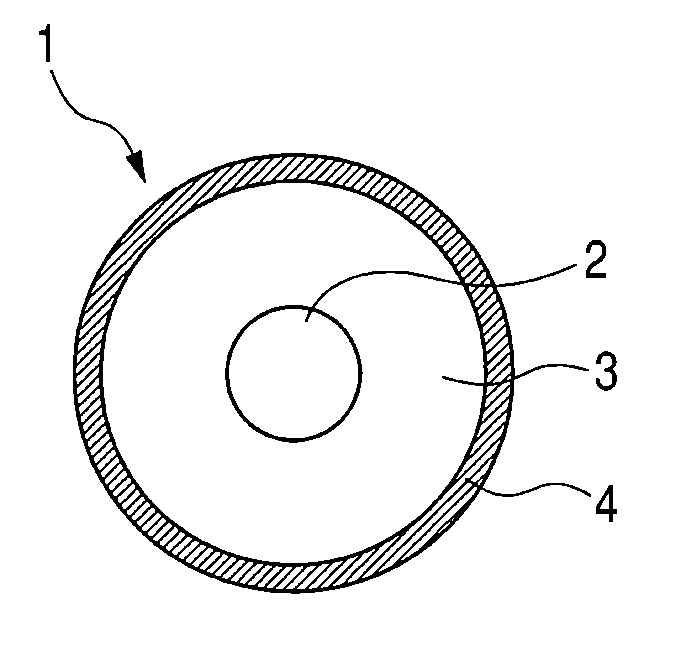
ActiveUS20100080611A1High quality imagingAvoid excessive frictionLiquid surface applicatorsShaft and bearingsSurface layerLatent image
A developing roller is provided which supplies a toner to a photosensitive member to develop an electrostatic latent image formed on the photosensitive member. The developing roller has a surface layer which includes carbon black and a polyurethane resin. The polyurethane resin has a specific structure. The surface layer has a specific ester group concentration and a specific urethane group concentration.
Owner:CANON KK
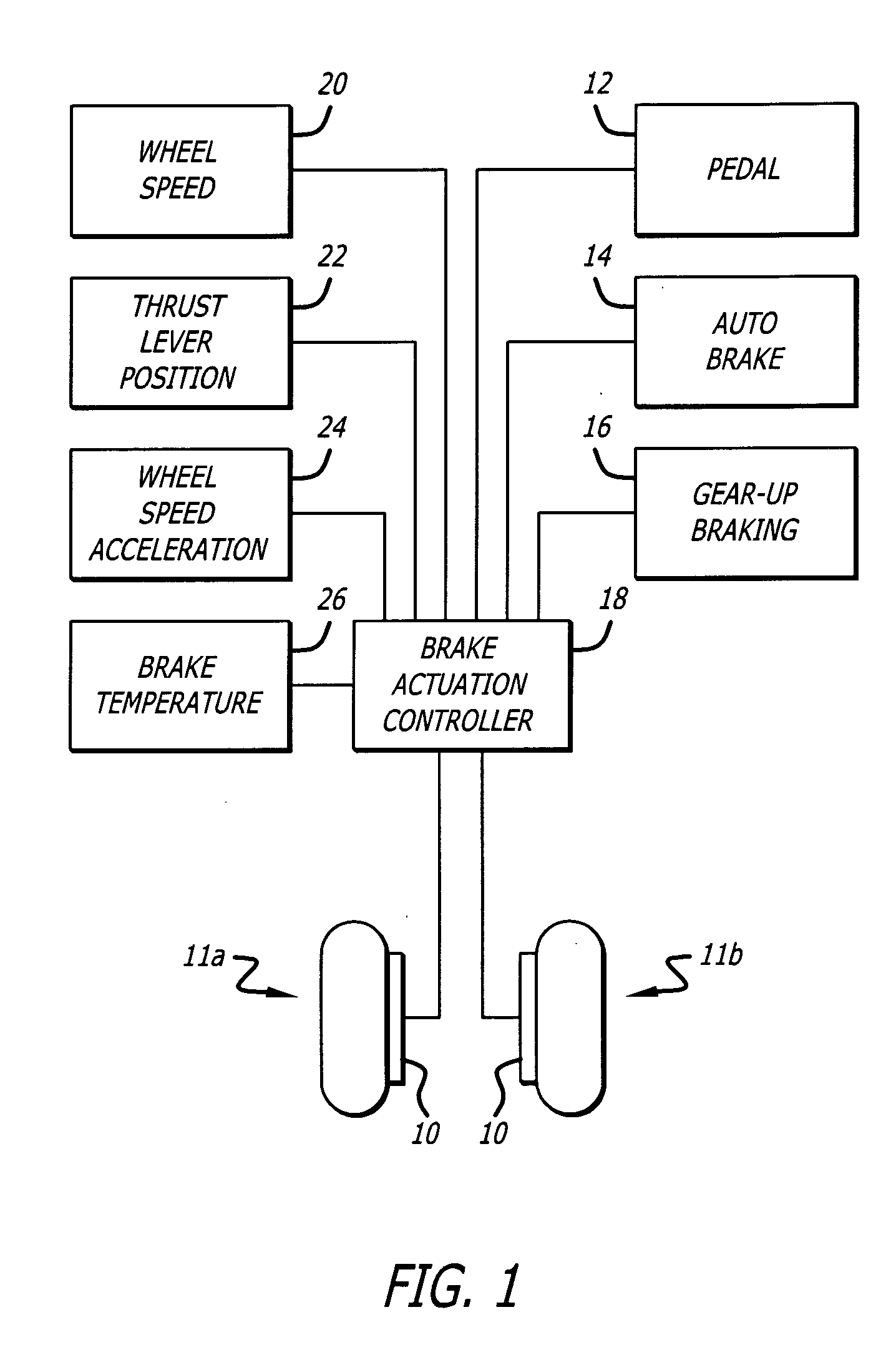
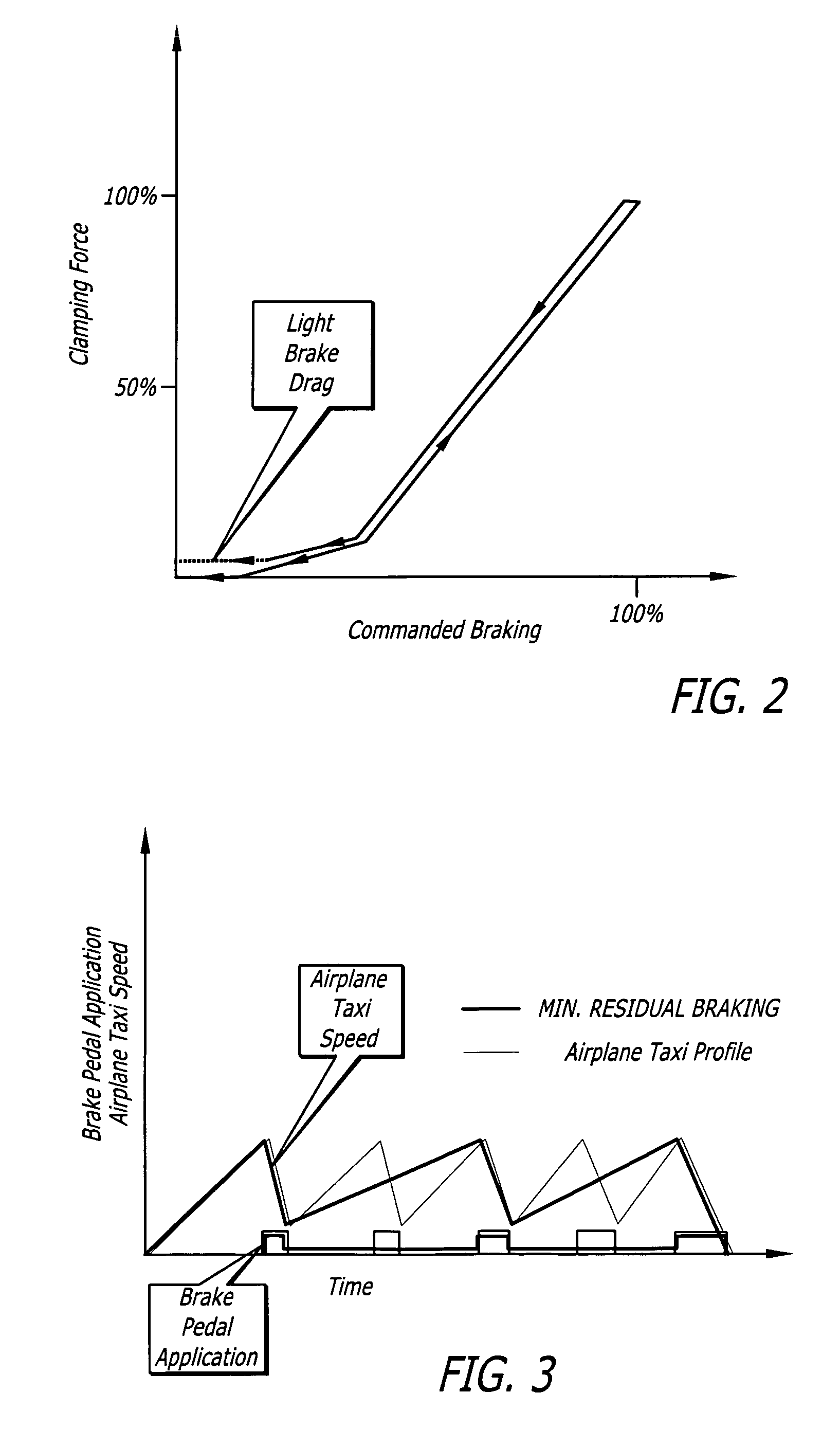
Method to reduce carbon brake wear through residual brake force
ActiveUS20060186736A1Reduced brake wearAvoid excessive frictionAutomatic braking sequenceBraking action transmissionAirplaneBrake force
The method for reducing aircraft carbon brake wear involves monitoring the commanded initiation of braking, and setting a residual brake clamping force to a predetermined minimum residual brake clamping force, which is maintained following the commanded initiation of braking to prevent release of braking during taxiing of the aircraft. The minimum residual brake clamping force is applied despite a commanded release of braking until at least one predetermined control logic condition occurs.
Owner:HYDRO AIRE AEROSPACE CORP
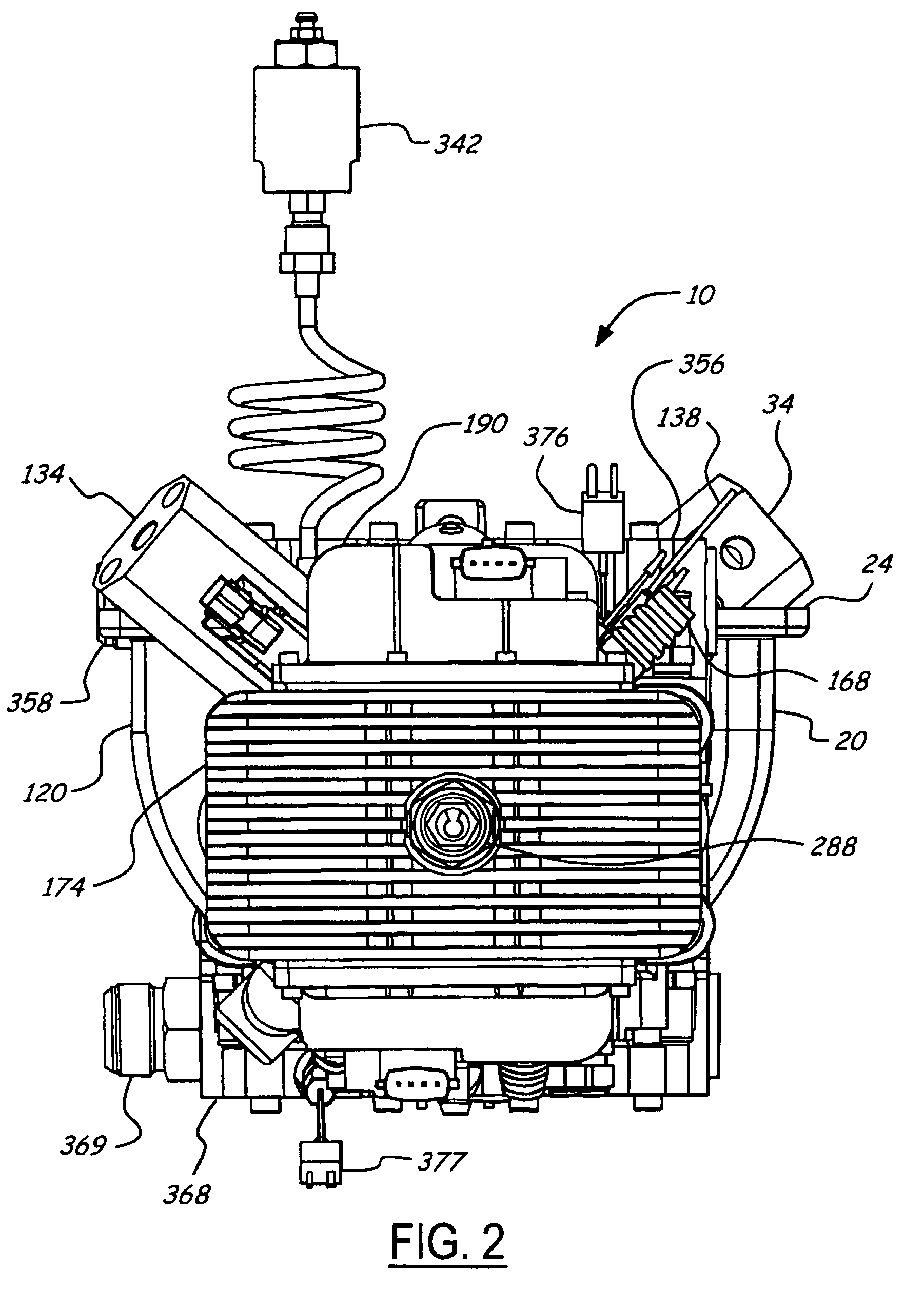
Hydraulic synchronizing coupler for a free piston engine
InactiveUS20060042575A1Easy to changeConducive effective homogeneous chargeFree piston enginesFree-piston enginePump chamber
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. A hydraulic coupler in communication with the pumping chambers will synchronize the motion of the inner and outer piston assemblies to assure that the pistons in the opposed cylinders are operating in opposition to one another.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Sodium cooled pistons for a free piston engine
InactiveUS6904876B1Easy to changeConducive effective homogeneous chargeAir coolingPistonsFree-piston enginePump chamber
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. Alternatively, the piston assemblies may drive a linear alternator. At least one of the pistons includes one or more generally axially extending bores partially filled with a sodium compound. As the piston reciprocates, the sodium moves back and forth in each cooling bore, thereby better distributing heat in the piston.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
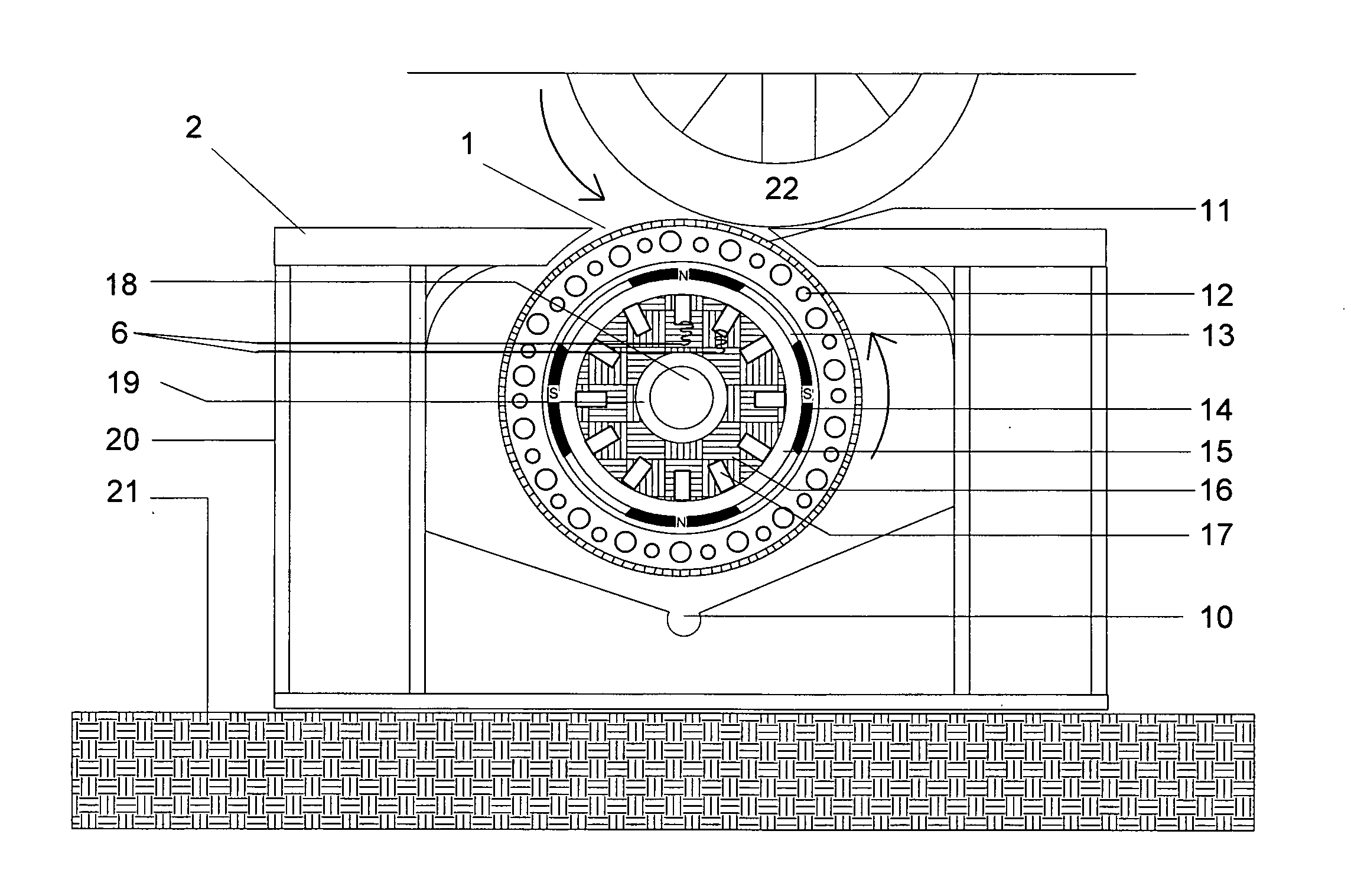
Locking mechanism for a wind turbine
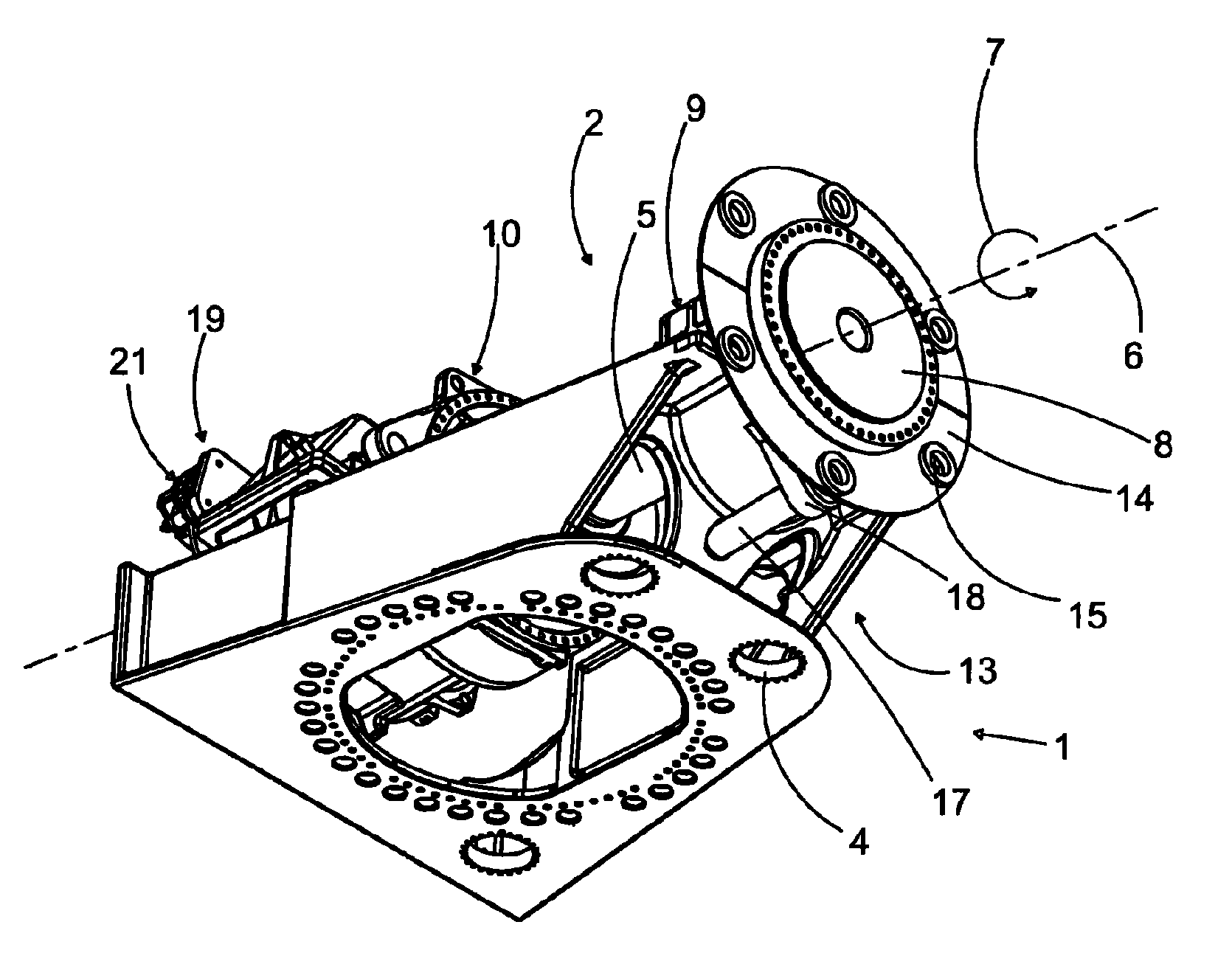
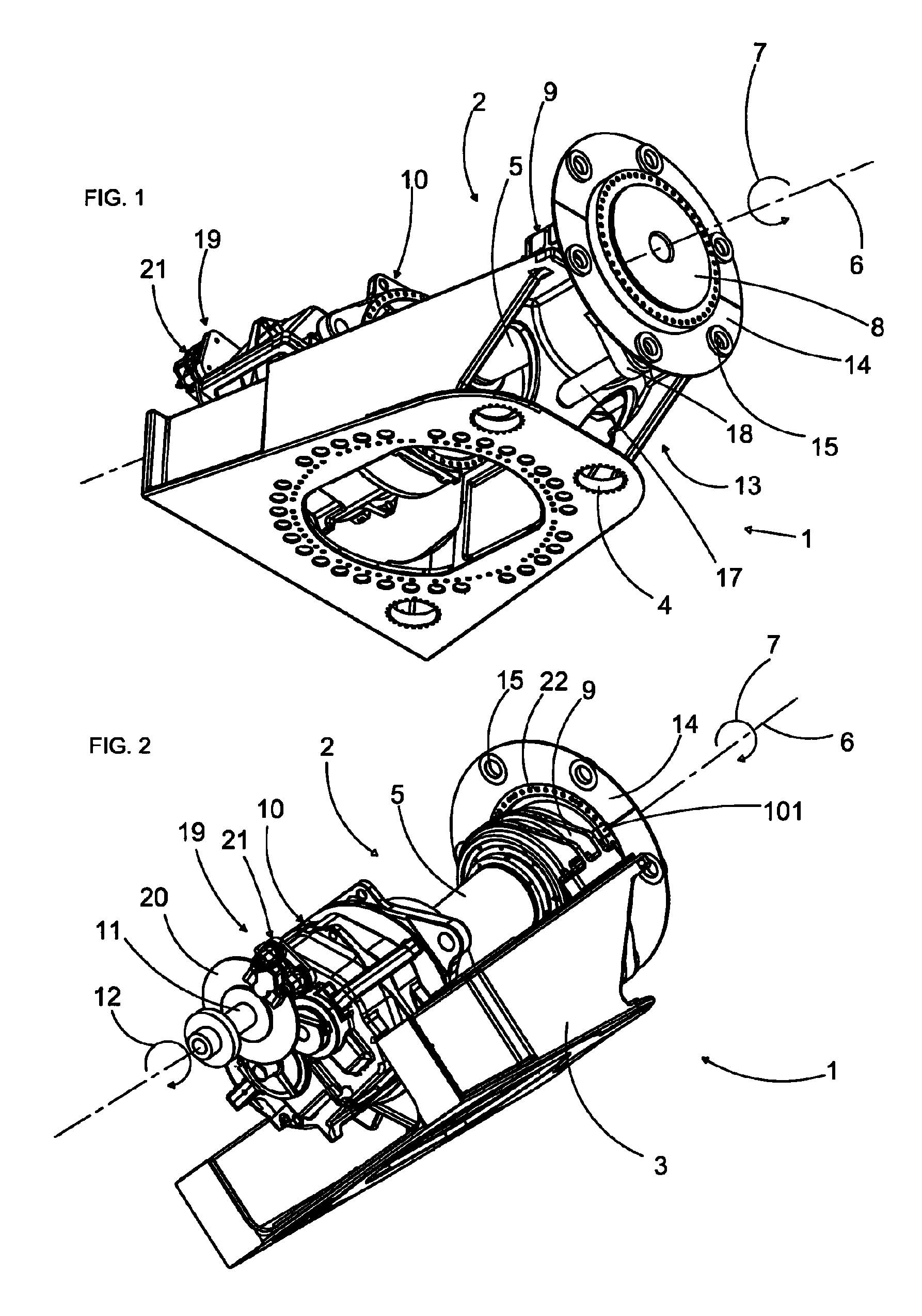
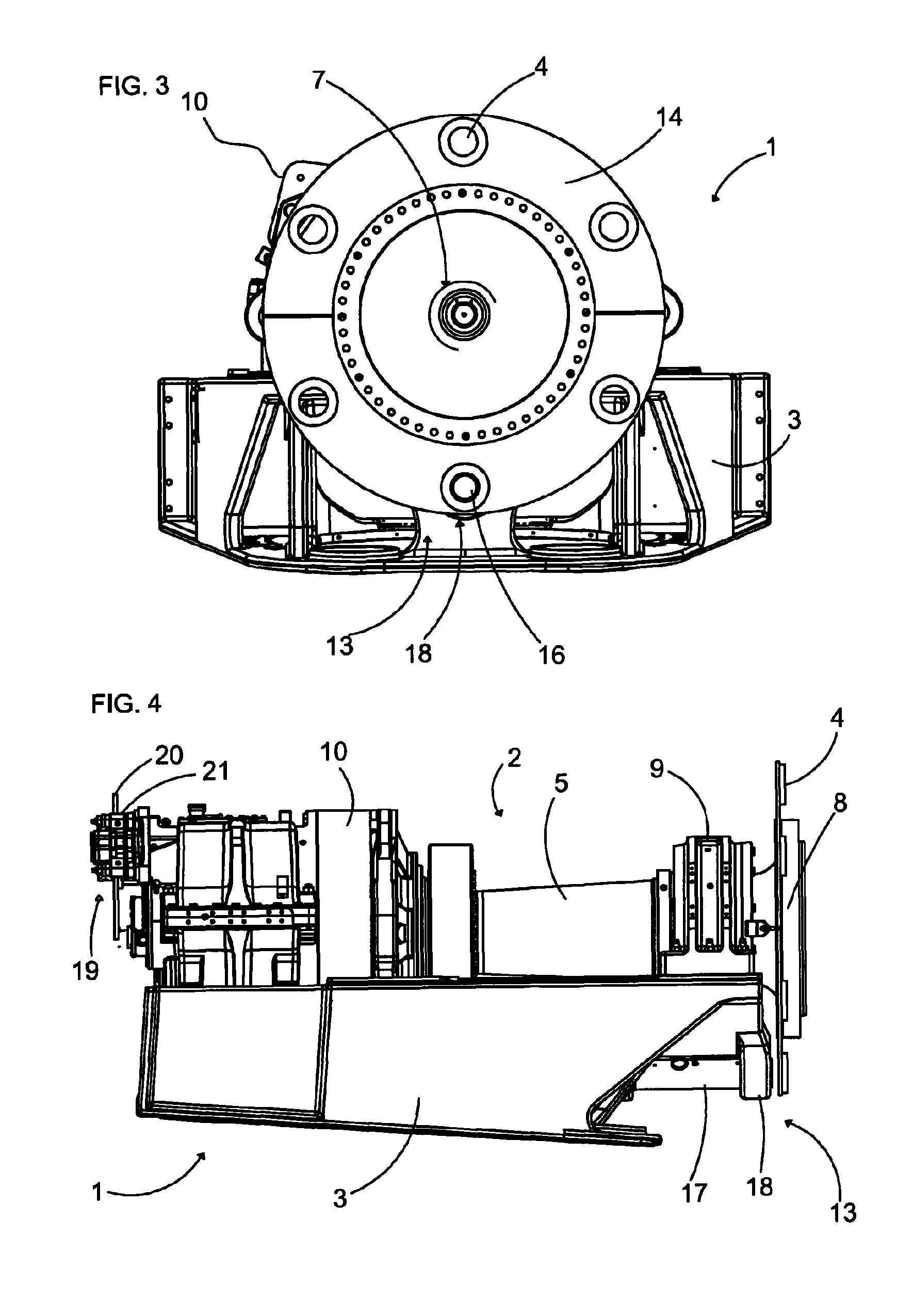
InactiveUS8334608B2Reduced actuation forceImprove performanceWind motor controlEngine fuctionsClassical mechanicsMachine
A locking mechanism for a wind turbine decelerates and / or locks a rotor or a rotor shaft of the wind turbine. For maintenance work, the rotor or the rotor shaft is lockable to a machine support of the wind turbine in a form-fit manner by utilizing the locking mechanism. A rotational position of the rotor shaft is automatically detected in a DESIRED position. Moreover, the locking mechanism is configured to be automatically engaged when the DESIRED position has been reached. The locking mechanism additionally has at least one deceleration device for affecting the drive train and / or allowing the rotational speed of the rotor and the rotor shaft to be reduced.
Owner:AE ROTOR HLDG BV
Hydraulic synchronizing coupler for a free piston engine
A free piston engine has a pair of opposed cylinders on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each in a respective one of the cylinders, with a push rod connected therebetween. The push rod forms a fluid plunger. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each in a respective one of the cylinders, with a pull rod connected therebetween. The pull rod forms a fluid plunger. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output. A hydraulic coupler synchronizes the inner and outer piston assemblies.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Superabrasive cutting elements with enhanced durability and increased wear life, and drilling apparatus so equipped
ActiveUS7814998B2Less formationAggressivity is maintainedDrill bitsConstructionsAcute angleEngineering
A cutting element for use in drilling subterranean formations. The cutting element includes a superabrasive table mounted to a supporting substrate. The superabrasive table includes a two-dimensional cutting face having a cutting edge along at least a portion of its periphery, and a surface comprising a chamfer extending forwardly and inwardly from proximate a peripheral cutting edge at a first acute angle of orientation of greater than about 45° with respect to the longitudinal axis of the cutting element, and to no greater than a selected depth. The chamfer may be arcuate or planar, and of a dimension sufficient to ensure that a wear flat generated during use of the cutting element remains outside the inner boundary of the chamfer within the chamfer envelope, and small enough to maintain aggressive cutting characteristics for the cutter. Drill bits and drilling tools bearing the cutting elements are also disclosed.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Tire tread mold
A mold for molding a tread of rubber mix, this tread comprising a running surface delimited axially by lateral faces, this mold comprising (i) a central part for molding the running surface, movable between an open configuration allowing filling of the mold and a closed configuration allowing molding, the central part comprising at least one rib for molding a groove in the running surface; (ii) two lateral parts for molding the lateral faces, at least one of the lateral parts being axially movable relative to the central part; et (iii) at least one pin for molding a channel inside the tread, this pin being anchored in one of the lateral parts; and in which, when the mold is closed, a contact surface is formed between the pin and the rib, and the pin and / or the rib comprise a buffer made of a deformable material, deformation of which makes it possible to fill in the clearance between the pin and the rib at the contact surface when the mold is closed.
Owner:MICHELIN RECH & TECH SA
Filtration element and method of constructing a filtration assembly
InactiveUS20060070940A1Easily and securely couplingMinimized contact areaSemi-permeable membranesGeneral water supply conservationFiltrationEngineering
A coupler for a spiral membrane filtration element having a spiral membrane enclosed within a rigid outerwrap includes a center support, a plurality of spokes extending outwardly from the center support, a circular rim coupled with the spokes, with the face of the rim being perpendicular to the axis of the overwrap. The rim includes a channel on its face for receiving a compressible seal, and a plurality of receptacles around its outer surface for joining two face-to-face adjacent couplers when a pair of aligned keepers is place in each receptacle. Exemplary embodiments of the coupler and filtration elements and filtration assemblies are provided, as well as an associated method.
Owner:KOCH MEMBRANE SYST
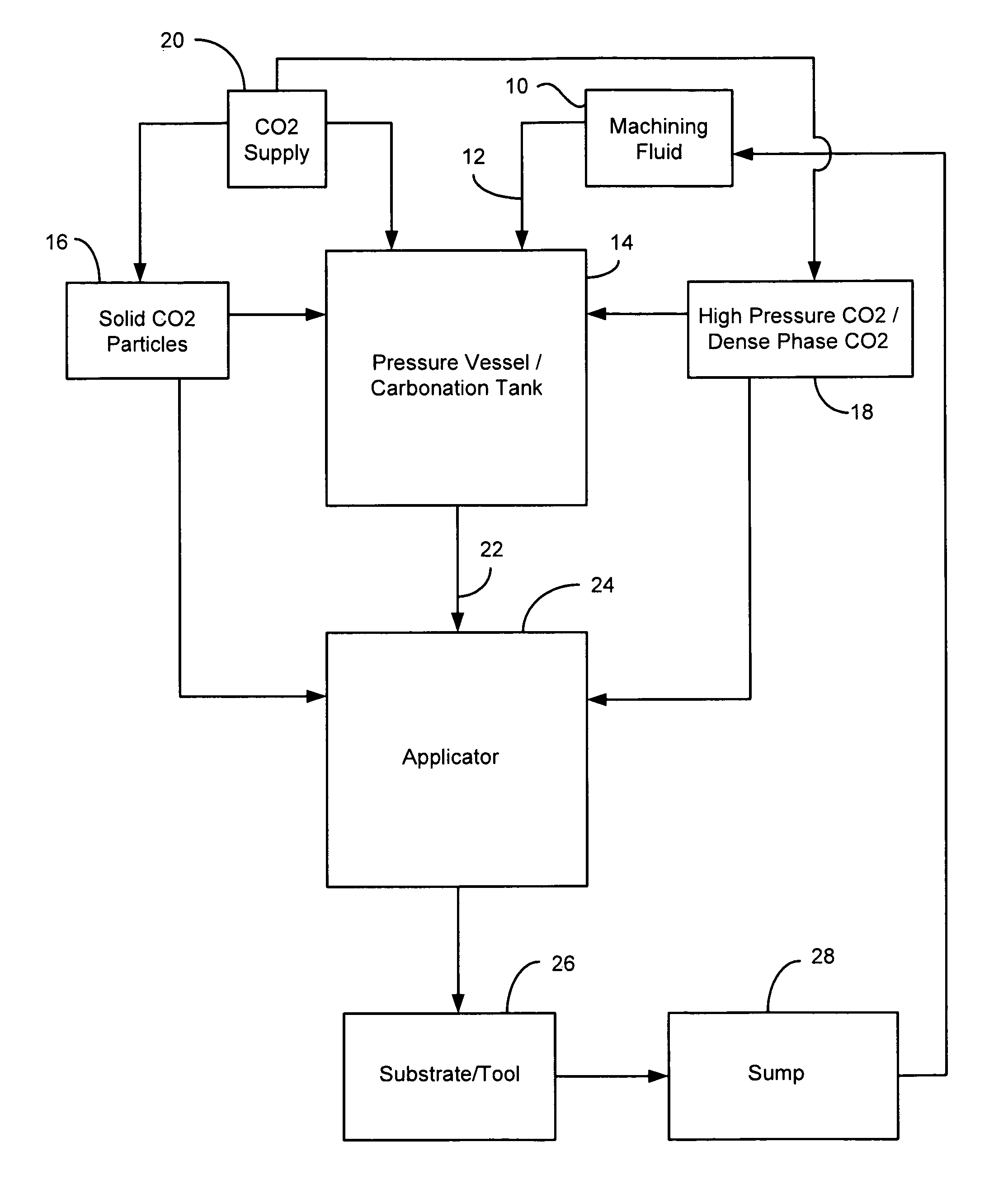
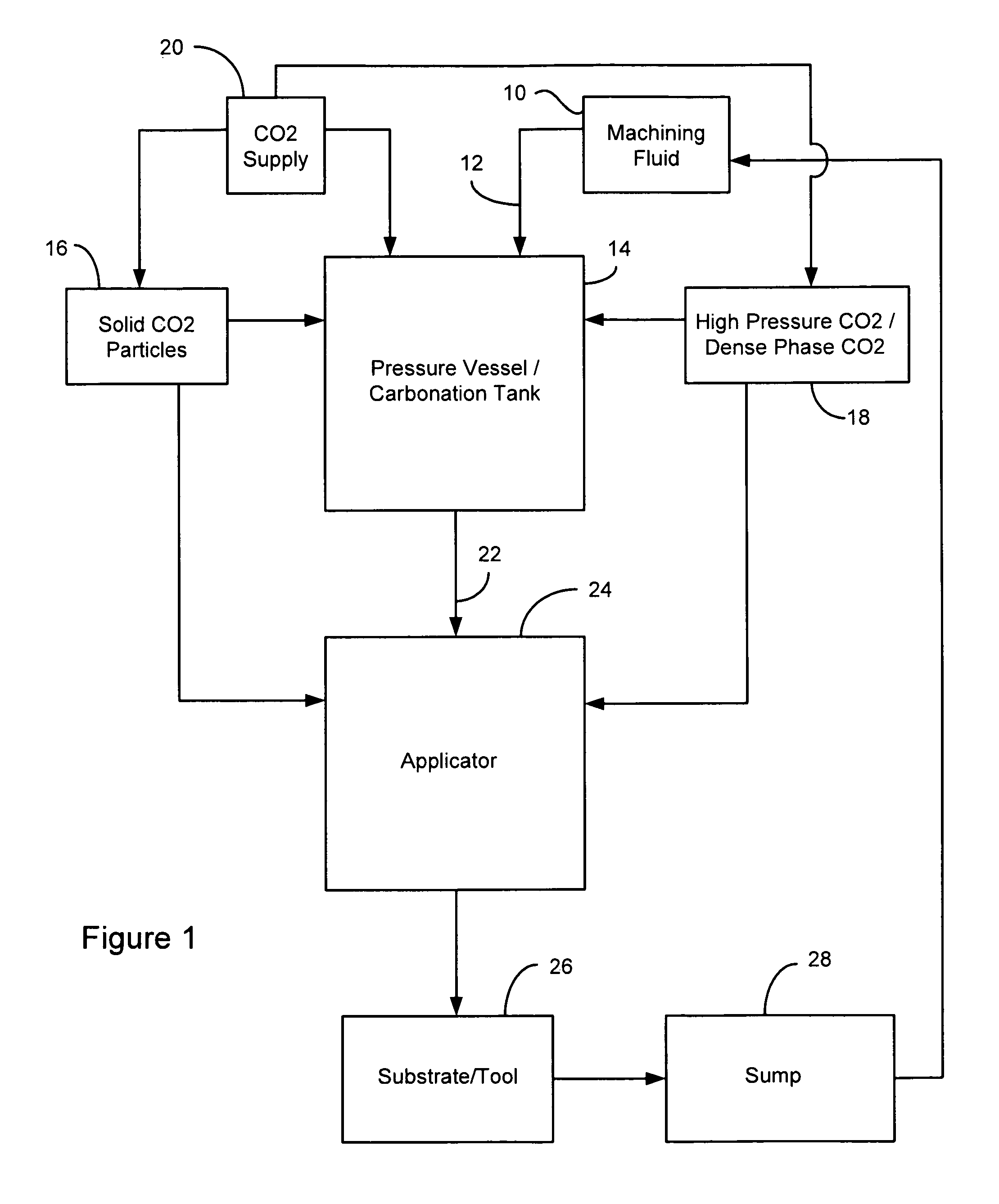
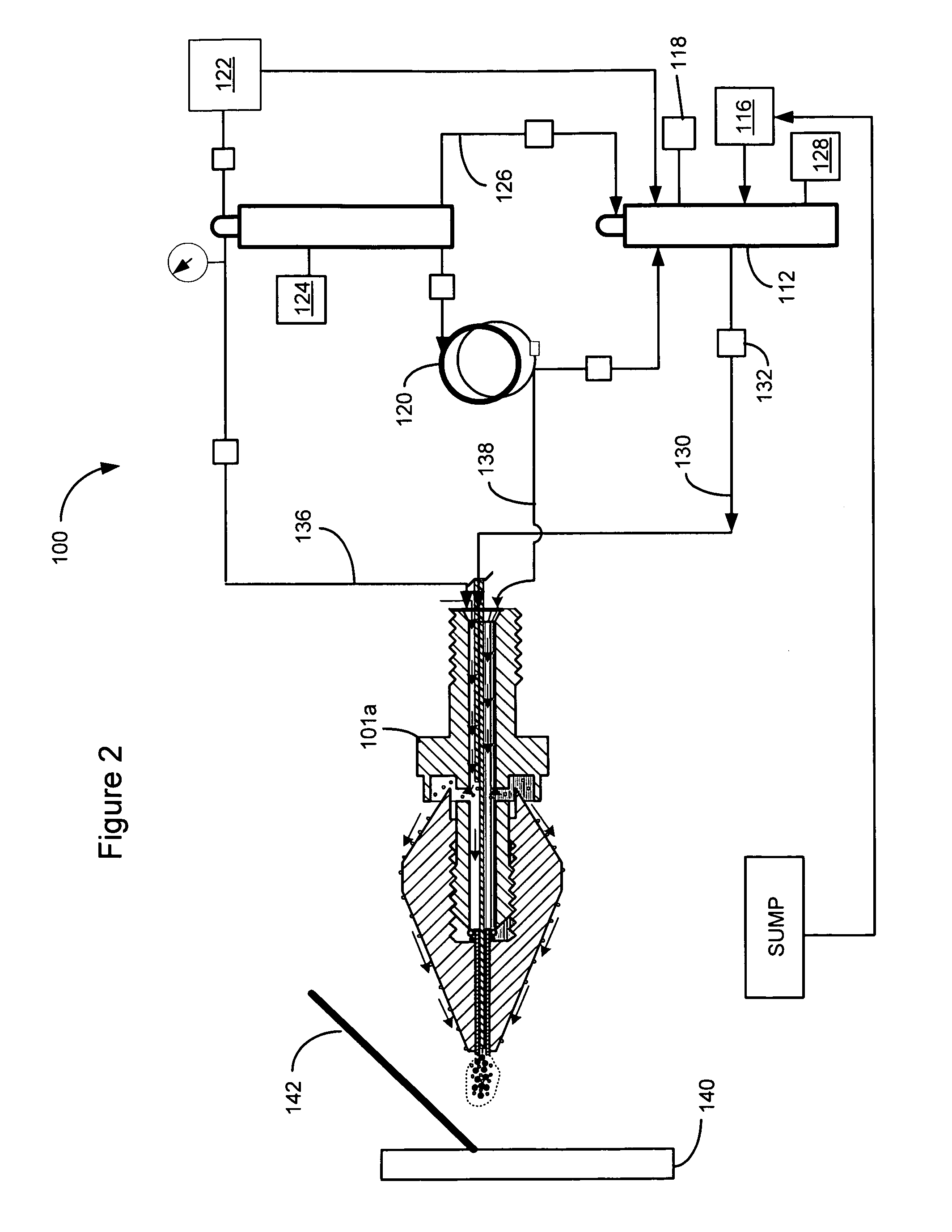
Method of forming and using carbonated machining fluid
ActiveUS8048830B1Optimization propertiesBeneficial change in flow and penetration and heat transfer qualityAdditivesMaintainance and safety accessoriesEngineeringMachining process
A method of forming and delivering a carbonated machining fluid to be used in a machining process, the machining process including a tool contacting a substrate, comprises supplying a pressure vessel with a non-carbonated machining fluid and non-supercritical carbon dioxide. The machining fluid and carbon dioxide are allowed to admix such that at least a portion of the carbon dioxide dissolves into the machining fluid to form the carbonated machining fluid. The carbonated machining fluid is then delivered under pressure from the vessel to an applicator and applied to the tool or the substrate to impart cooling and lubricating effects.
Owner:COOL CLEAN TECH
Electric power generation from moving vehicles
InactiveUS20110298222A1Improve security featuresMinimizing amountMachines/enginesMechanical energy handlingMobile vehiclePower grid
Owner:BAILEY MATTHEW R +2
Fuel injection for a free piston engine
InactiveUS6959672B1Easy to changeConducive effective homogeneous chargeInternal combustion piston enginesLow pressure fuel injectionFree-piston engineCombustion
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. Alternatively, the piston assemblies may drive a linear alternator. Each fuel injector is located so that it injects directly into its cylinder near the intake ports, while also being covered during combustion events in order to avoid exposing the fuel injector to the harsh environment of combustion.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
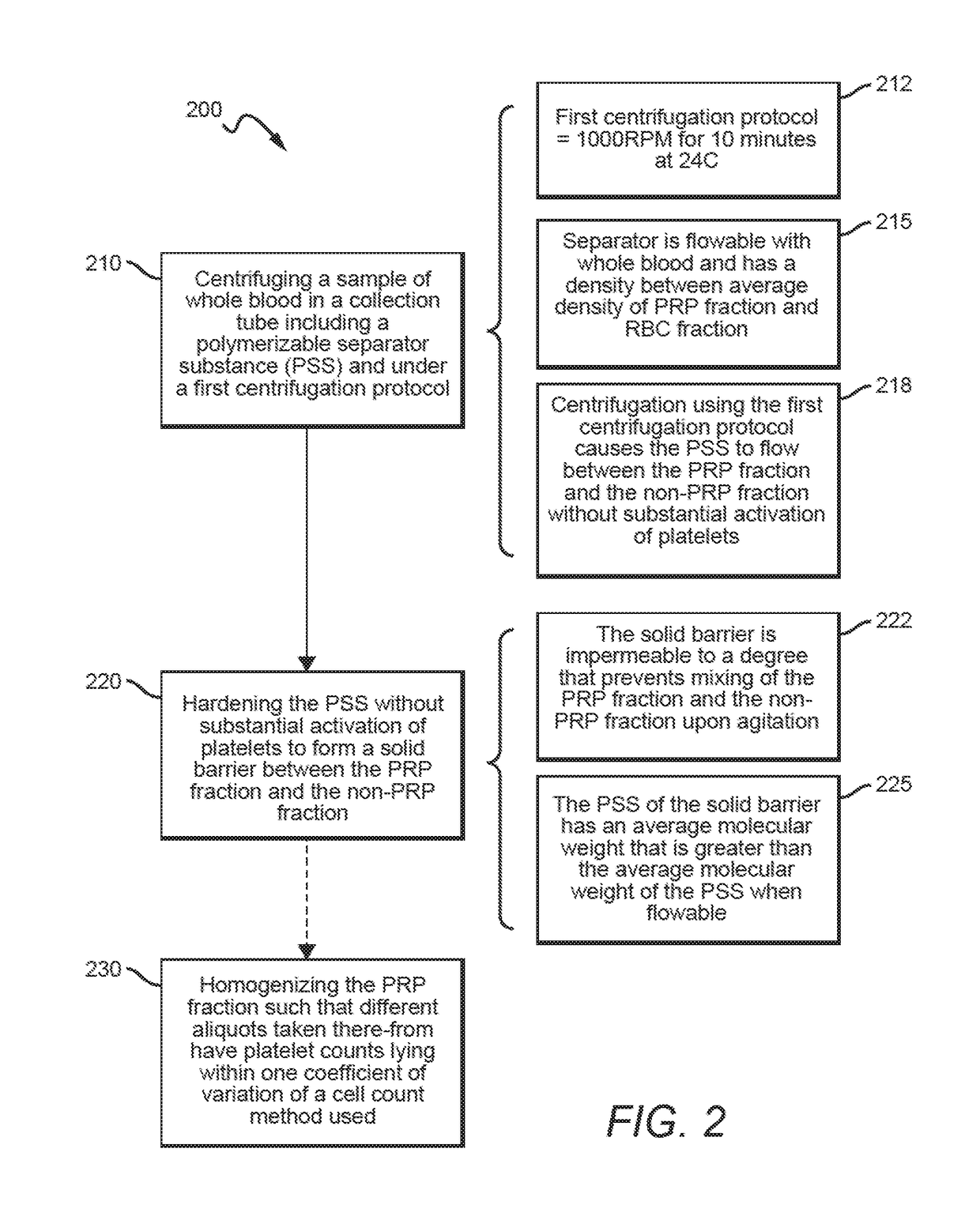
Platelet rich plasma and bone marrow aspirate cell separation and removal methods and devices
ActiveUS20180296748A1Without compromising sterilityPrevent leakageOther blood circulation devicesPharmaceutical containersMedicineCentrifugation
Compositions and methods for separating a sample of whole blood or bone marrow aspirate into a fraction rich in at least one of platelets and pluripotent cells are provided. A sample of whole blood can be centrifuged in a collection tube comprising a separator substance formulated to settle between the PRP fraction and the at least one other fraction. Preferably, centrifugation is completed without substantial activation of platelets. Optionally, the separator substance could be hardened to form a solid barrier that allows removal of all or substantially all of the platelets in the PRP fraction without remixing of the PRP fraction with the at least one other fraction. Transfer devices and methods are also provided in which a sterile sample can be transferred from a separation / preparation container (e.g., vacutainer) to a consumer or other container (e.g., dropper) while maintaining sterility of the sample.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Automatic shift knob actuator
InactiveUS20050061102A1Less frictional resistanceCoefficient of frictionControlling membersPortable liftingActuatorControl theory
A stick shift handle assembly has a stick shift handle and an actuator for releasing the stick shift handle for movement between a plurality of gear positions. The actuator has a housing. A sleeve is disposed between the actuator and the housing. The sleeve has a first co-efficient of friction lower than a second co-efficient of friction of the housing.
Owner:KEY SAFETY SYST
Roller cage assembly
InactiveUS6928689B2Easy to cleanSmooth rotationLiquid surface applicatorsArtistic surface treatmentRidgeLiquid transfer
A roller cage assembly for use with a support rod is described. The roller cage assembly has a roller sleeve, a pair of end hub members, and a tube for use with a support rod. Each end hub member has an inner hub, an outer hub, a cavity, and a keeper. Each cavity receives and allows rotational movement of a corresponding keeper. Each cavity has a slightly reduced outer aperture defined by an annular tab to facilitate rotational movement of the keeper. Each keeper has a passage for receiving the support rod, an expandable gap for securing the support rod, and slip ridges to facilitate rotational movement of the keeper. Each keeper also typically has a joined slit membrane for maintaining a substantially constant degree of tension on the support rod. The tube is connected between the inner hub of each end hub member, and the roller sleeve is connected between the outer hub of each end hub member. The roller sleeve, each end hub member, and the tube form an integral unit and are arranged to define a sealed inner cavity, whereby liquid transfer into the inner cavity is substantially prevented.
Owner:DOVE MICHAEL J
Media Control Valve
ActiveUS20130105717A1Eliminate the problemQuicker and efficient and reliable valve actionCheck valvesSlide valveMedia controlsEngineering
A media control valve includes a body, a plunger assembly of multiple components housed in the body with a plunger control valve cap assembly secured to the body for housing a control knob. The body and the plunger assembly include resilient seals between adjacent multiple components of the body and the plunger assembly, respectively, to permit relative movement therebetween. A diaphragm physically isolates and seals the chambers above and below. All of the plunger seals and bushings held within the sleeve. Replacement seals and bushings can be replaced and inspected with relative ease due to the accessibility at both ends of the sleeve. Component parts are assembled using resilient seals to facilitate assembly and repair.
Owner:NGUYEN PHUONG TAYLOR
Orbital, non-reciprocating, internal combustion engine
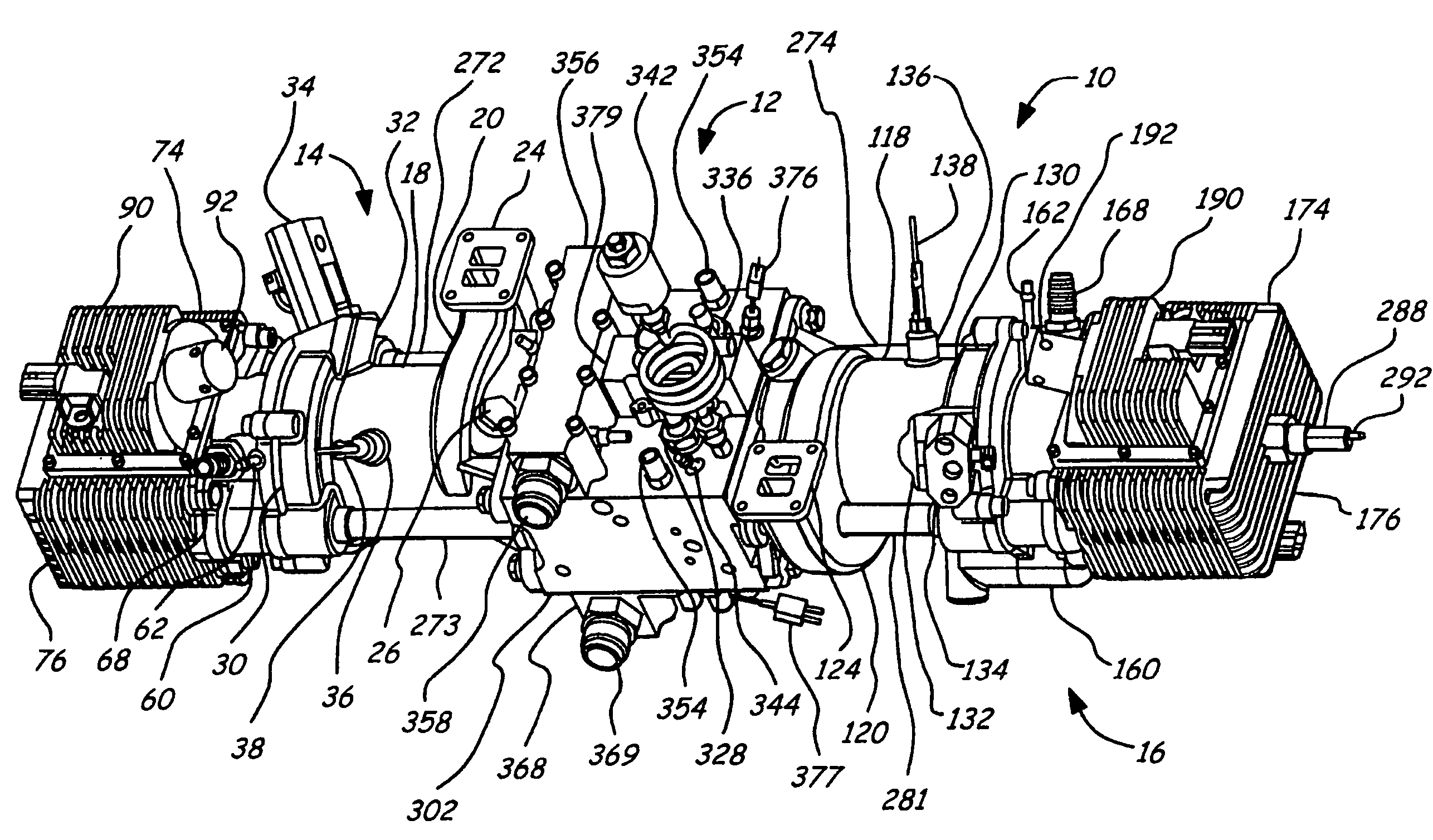
ActiveUS8161924B1Reduce coolingLow in smog producing emissionInternal combustion piston enginesEngines with rotating cylindersPistonInternal combustion engine
A combustible fluid operated orbital engine has plural sets of cooperating cylinder and piston members with respective parallel axes of rotation, respective cylinder and piston carrier wheels with respective axes of rotation parallel to the members' axes of rotation carrying said members circularly and orbitally and at all times in opposed relation on a common longitudinal axis along intersecting counter paths. Respective gearing structures supported by the cylinder and piston carrier wheels rotate the members counter to their circular motion direction to maintain their opposed relation for their periodic interfittment when their respective paths intersect. A combustible fluid supply is provided to the cylinder member for combustion coincident with the periodic interfittment in engine operating relation. The common longitudinal axes of the cylinder / piston sets are at all times parallel with each other.
Owner:LOCKSHAW JAMES +1
Piston lubrication for a free piston engine
InactiveUS6971341B1Easy to changeEasy to operateLubrication of auxillariesLubricant conduit arrangementsFree-piston enginePump chamber
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com