Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73results about "Simultaneous traffic control systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
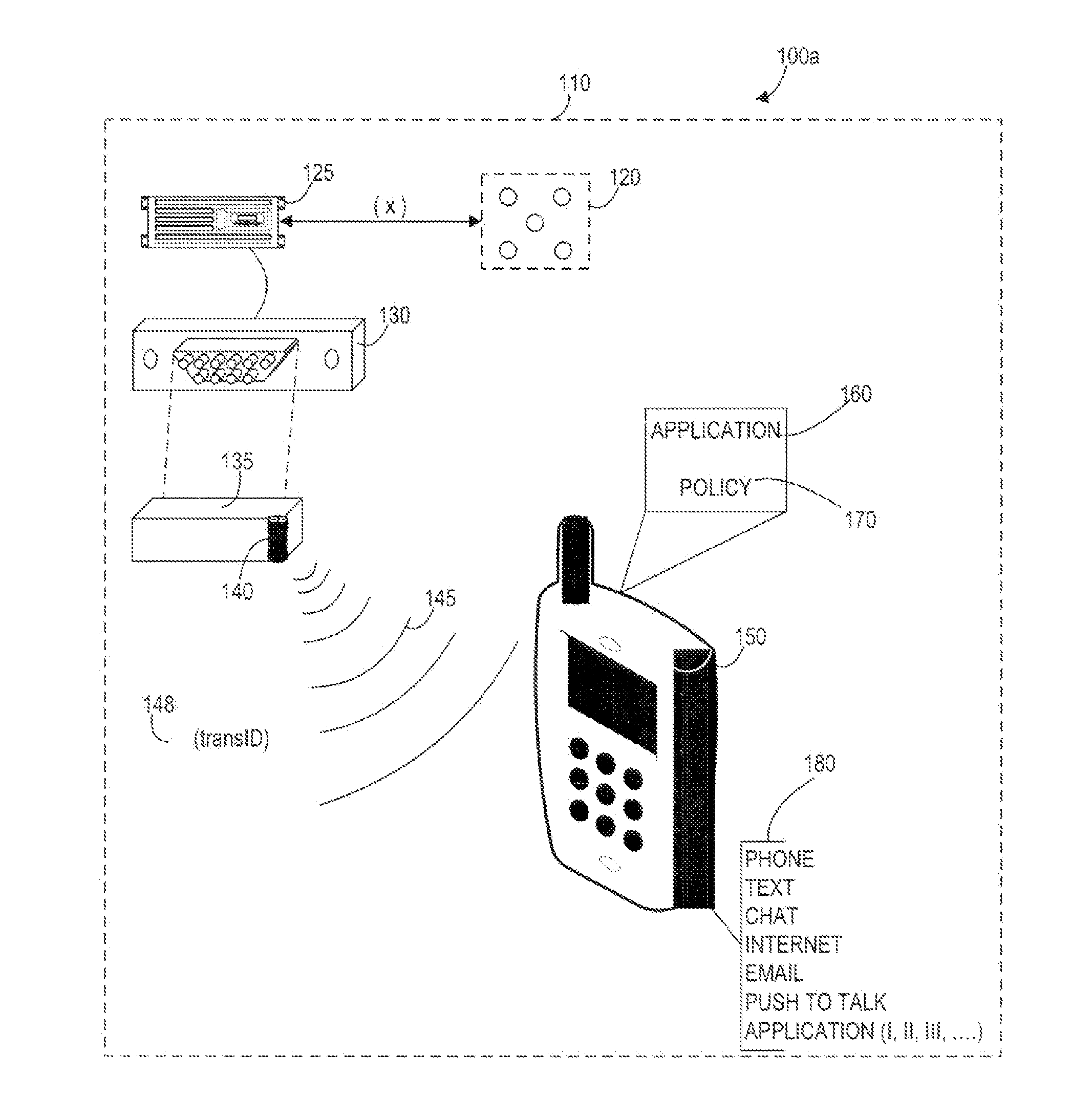
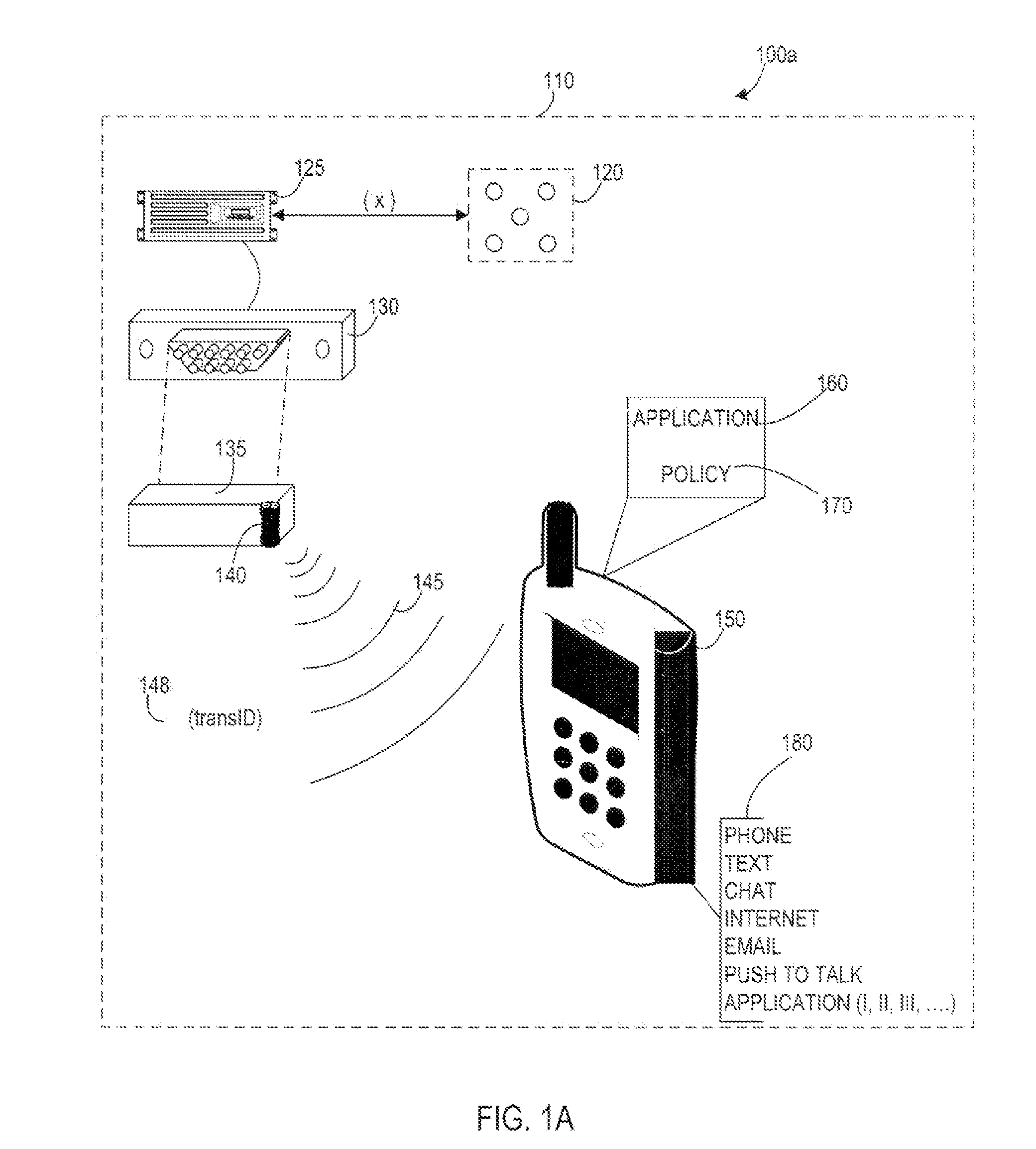
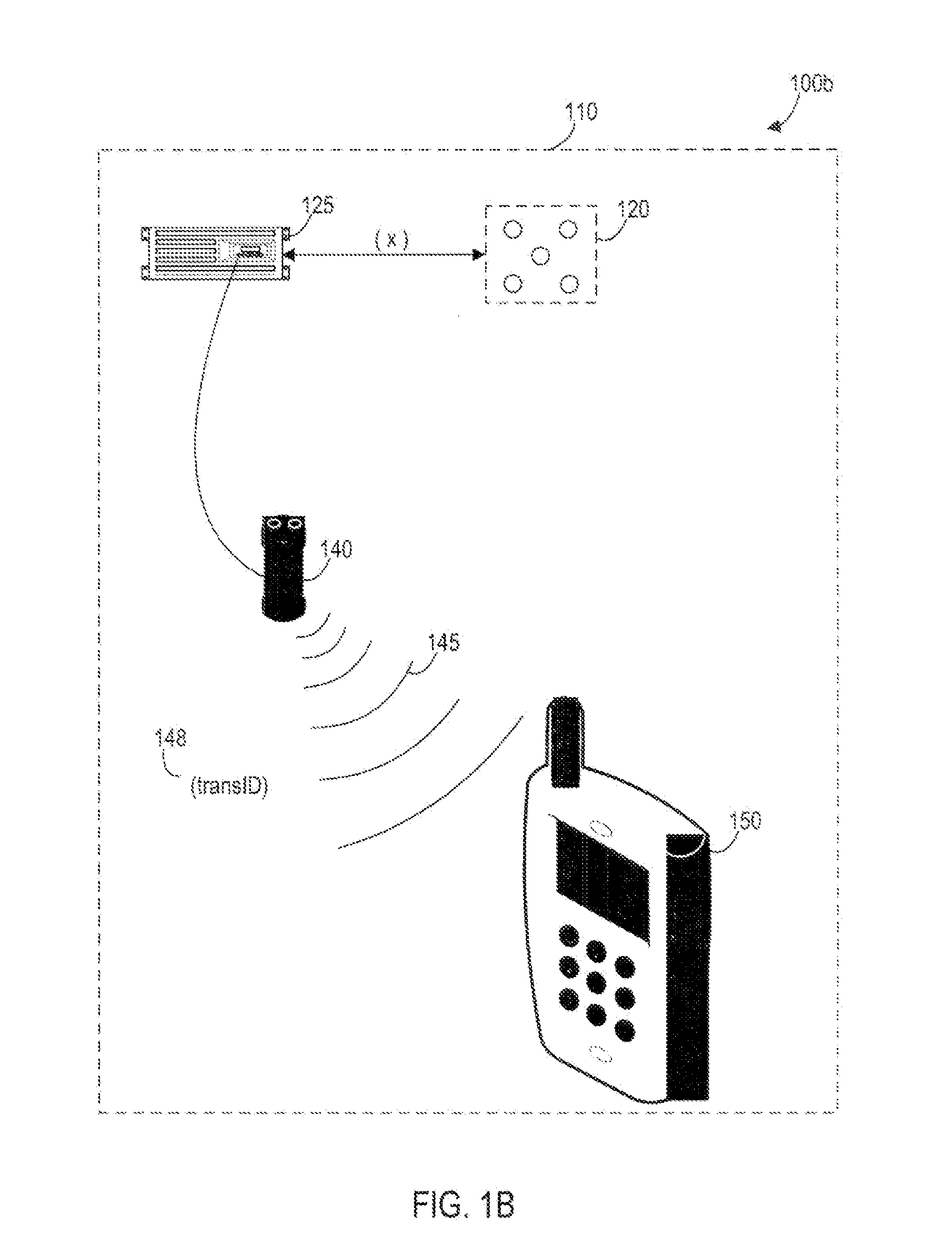
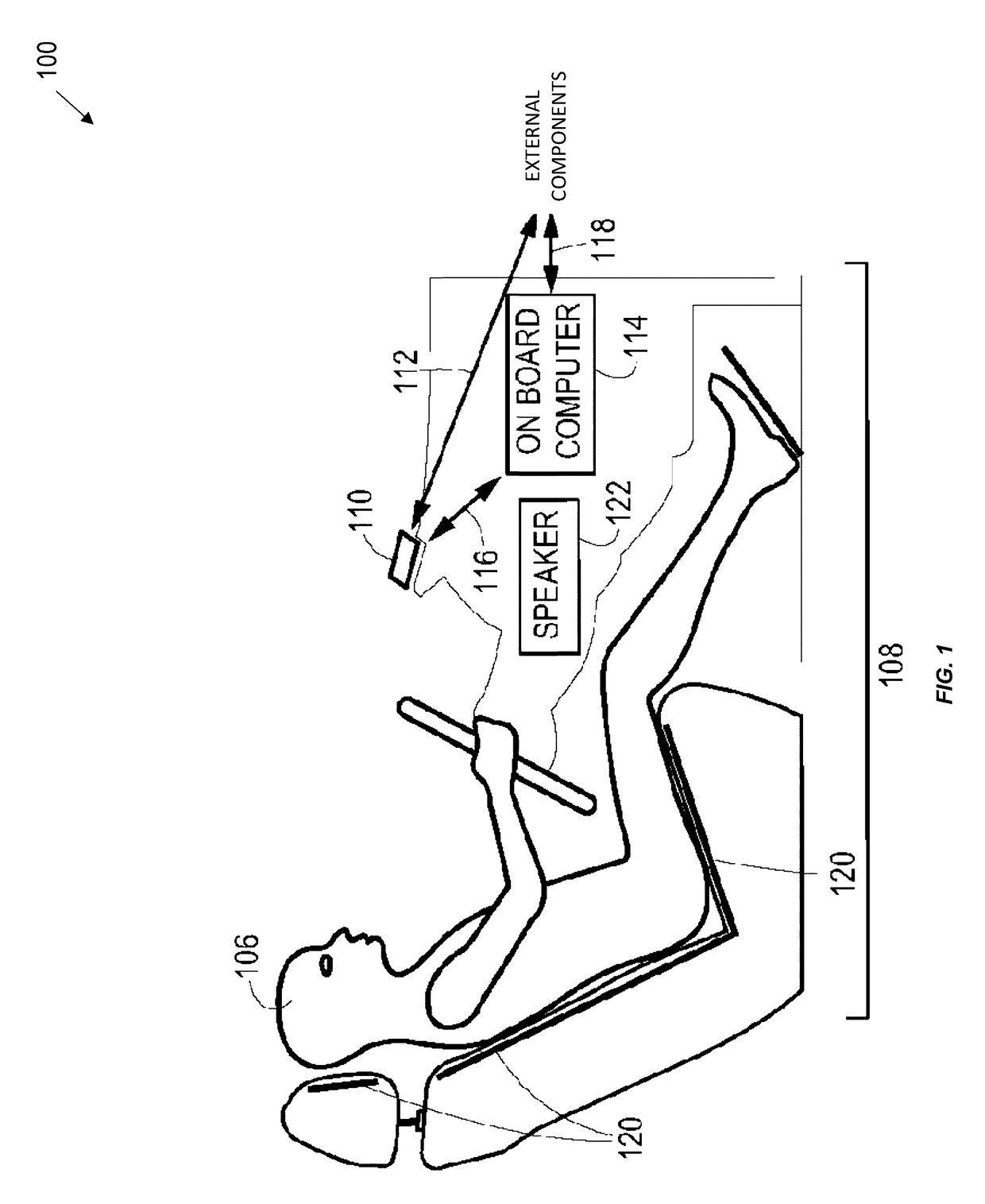
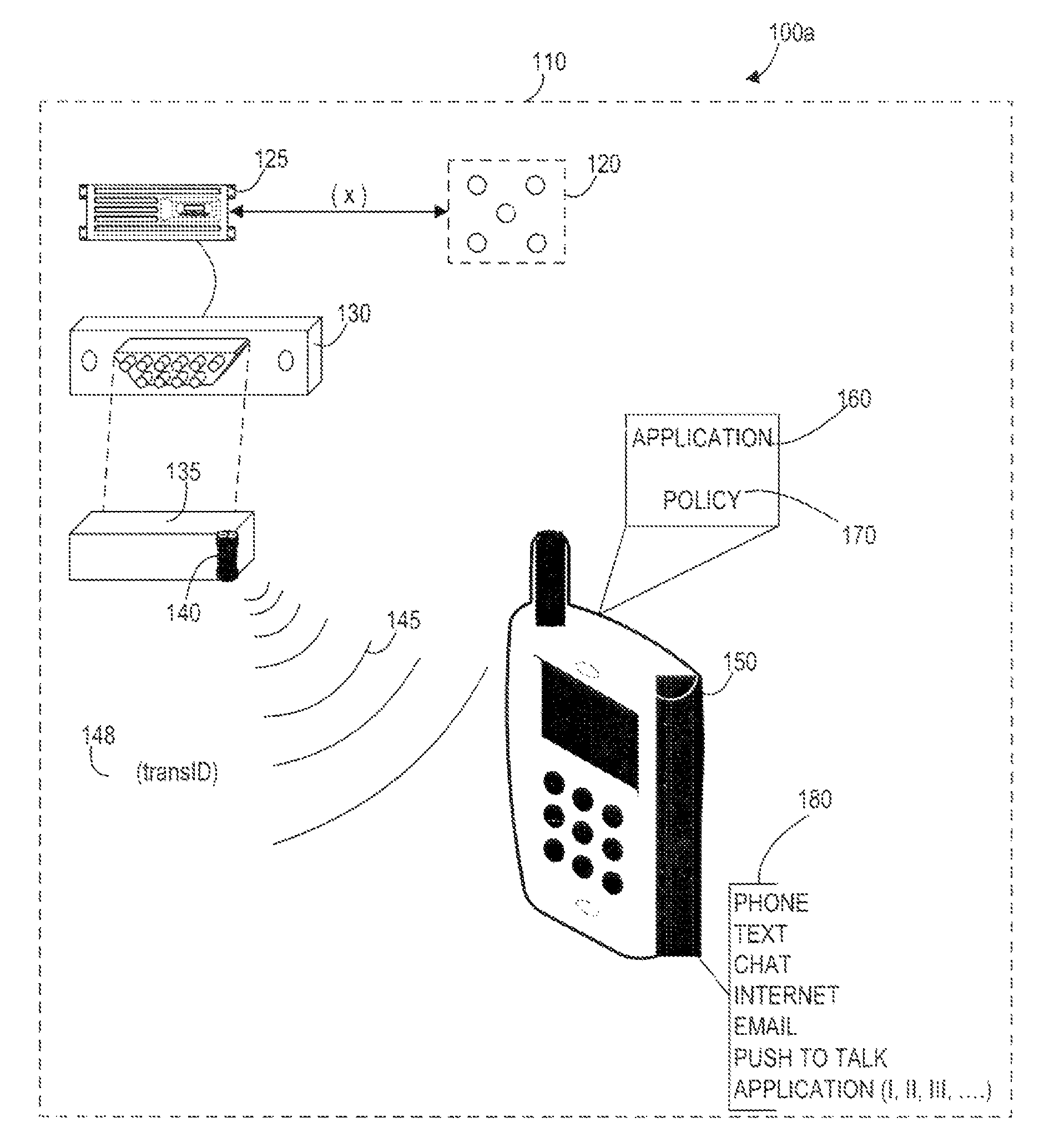
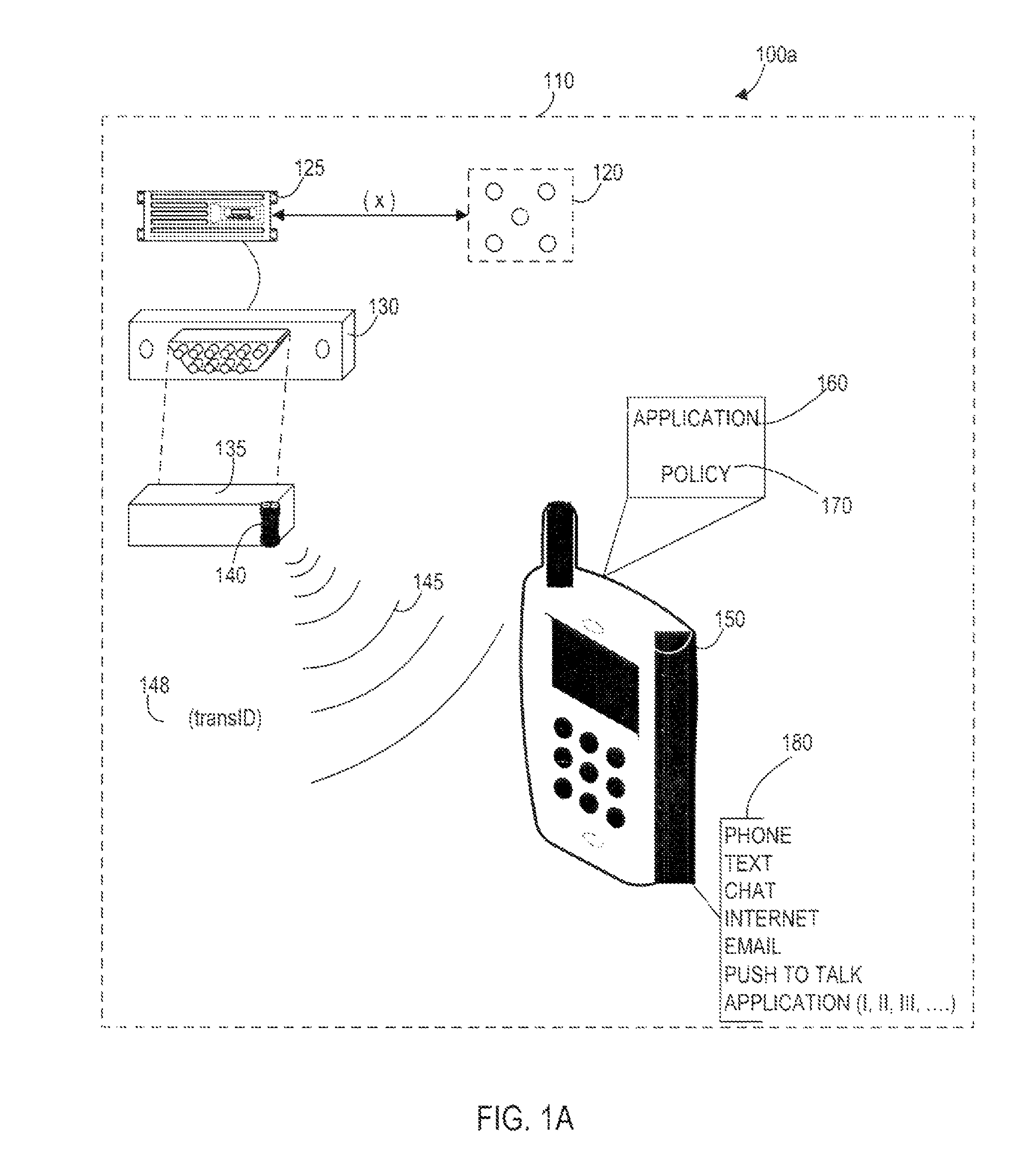
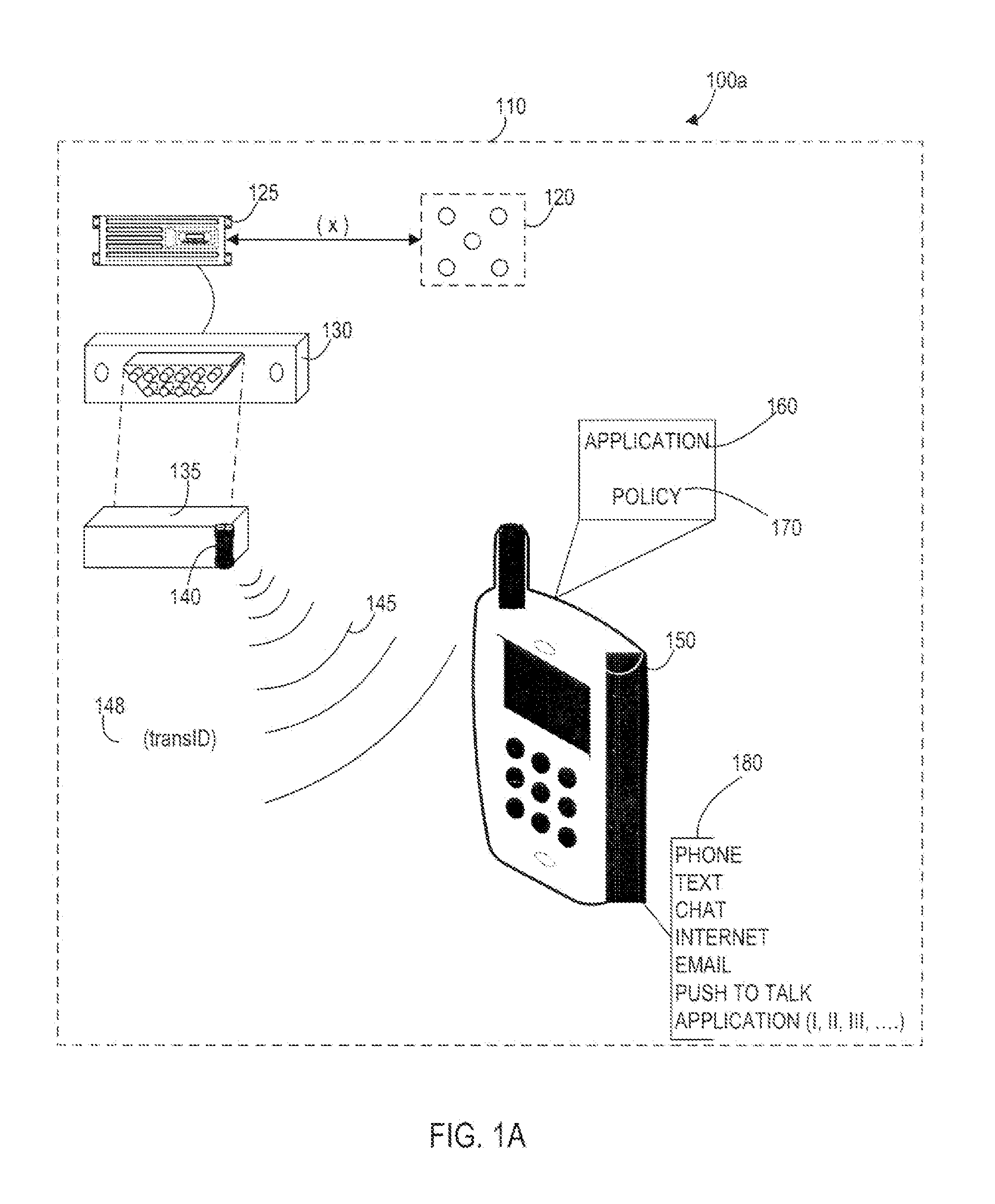
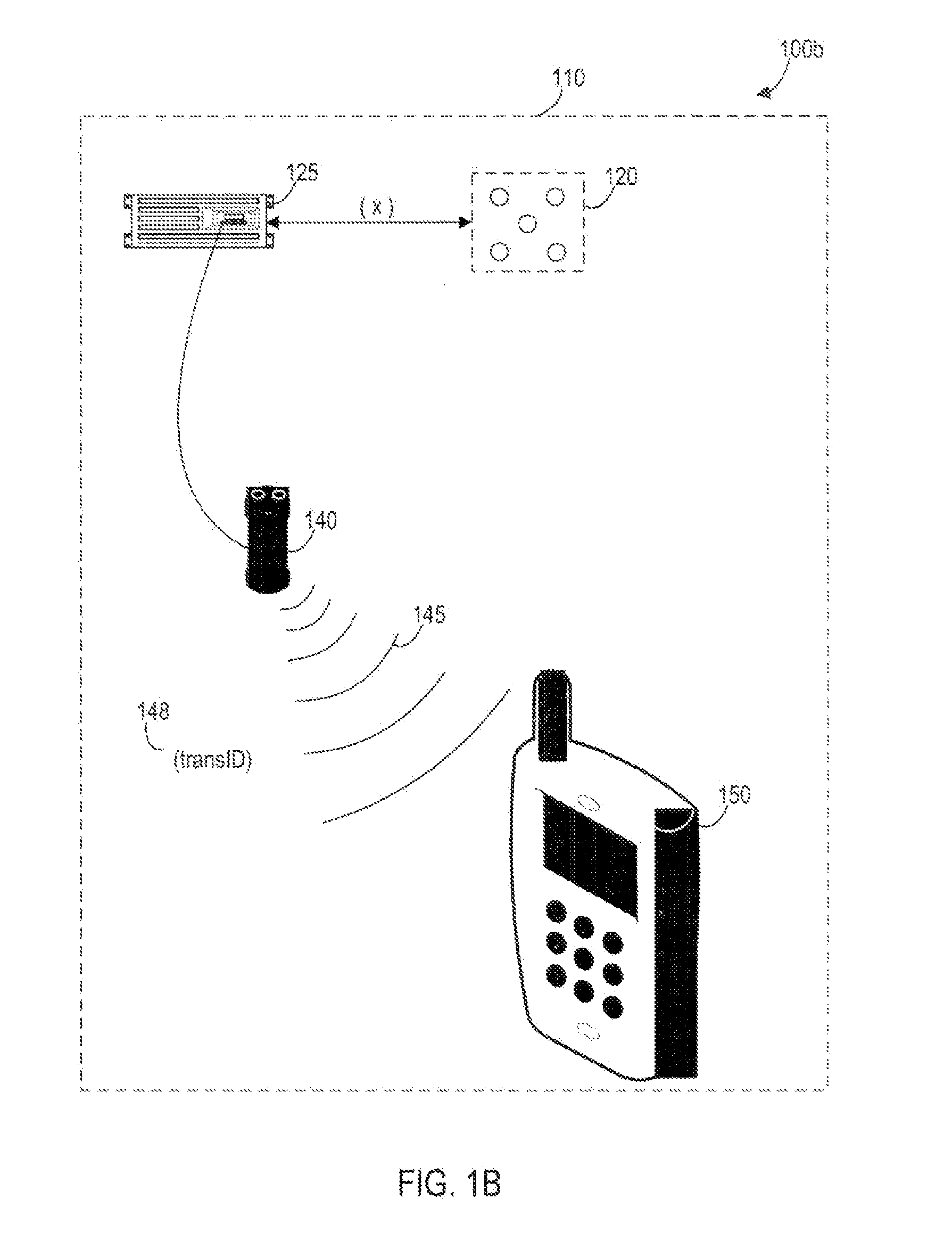
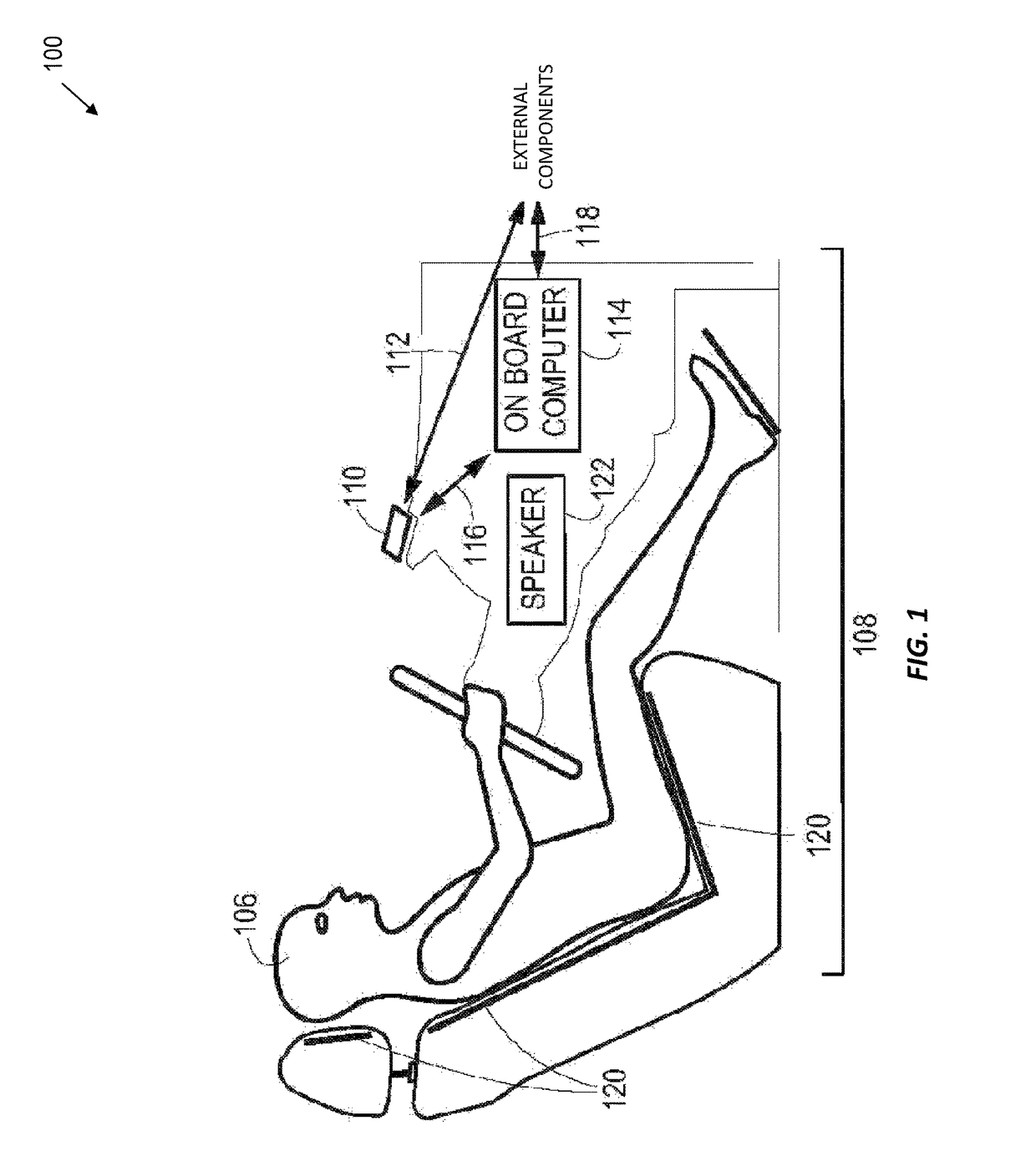
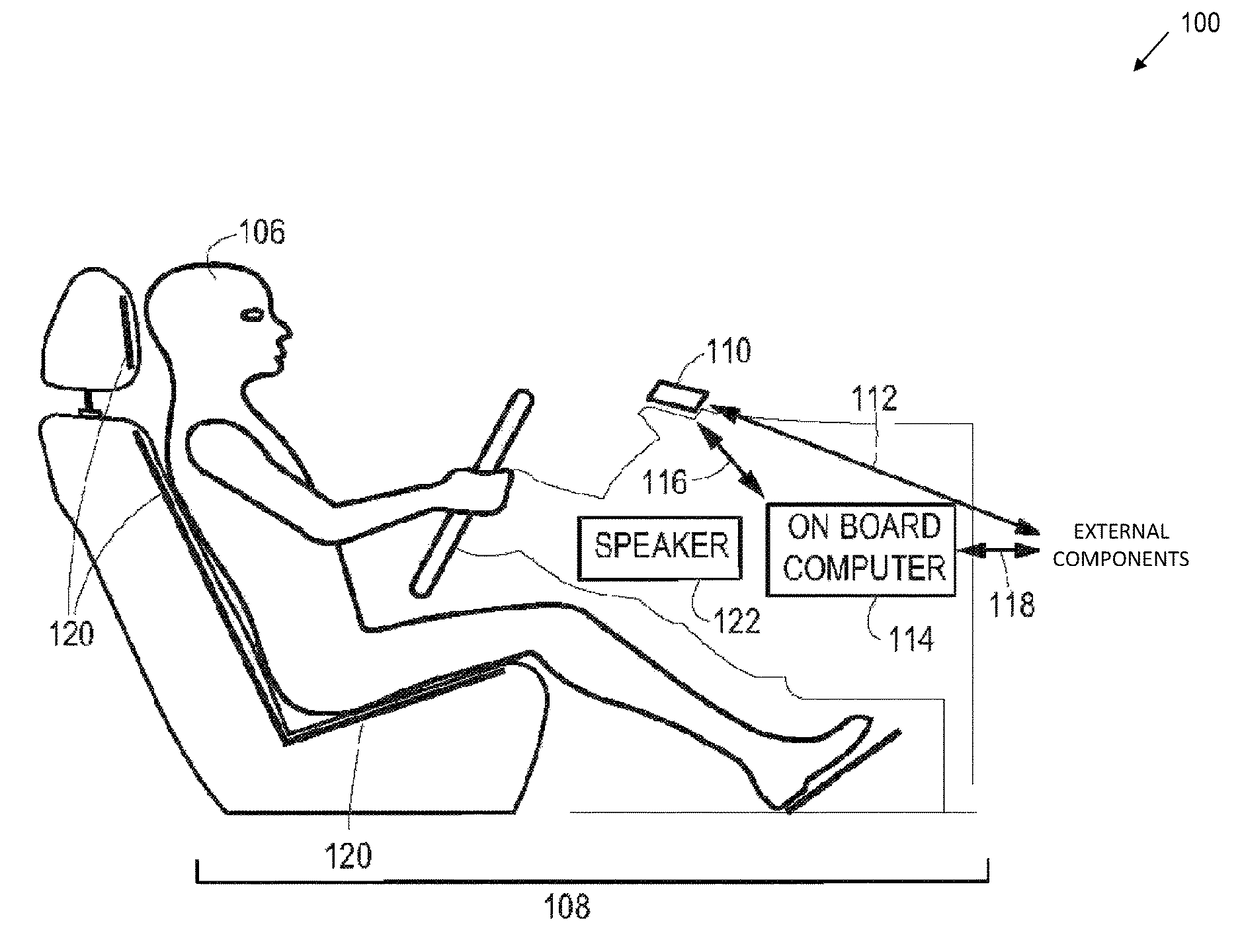
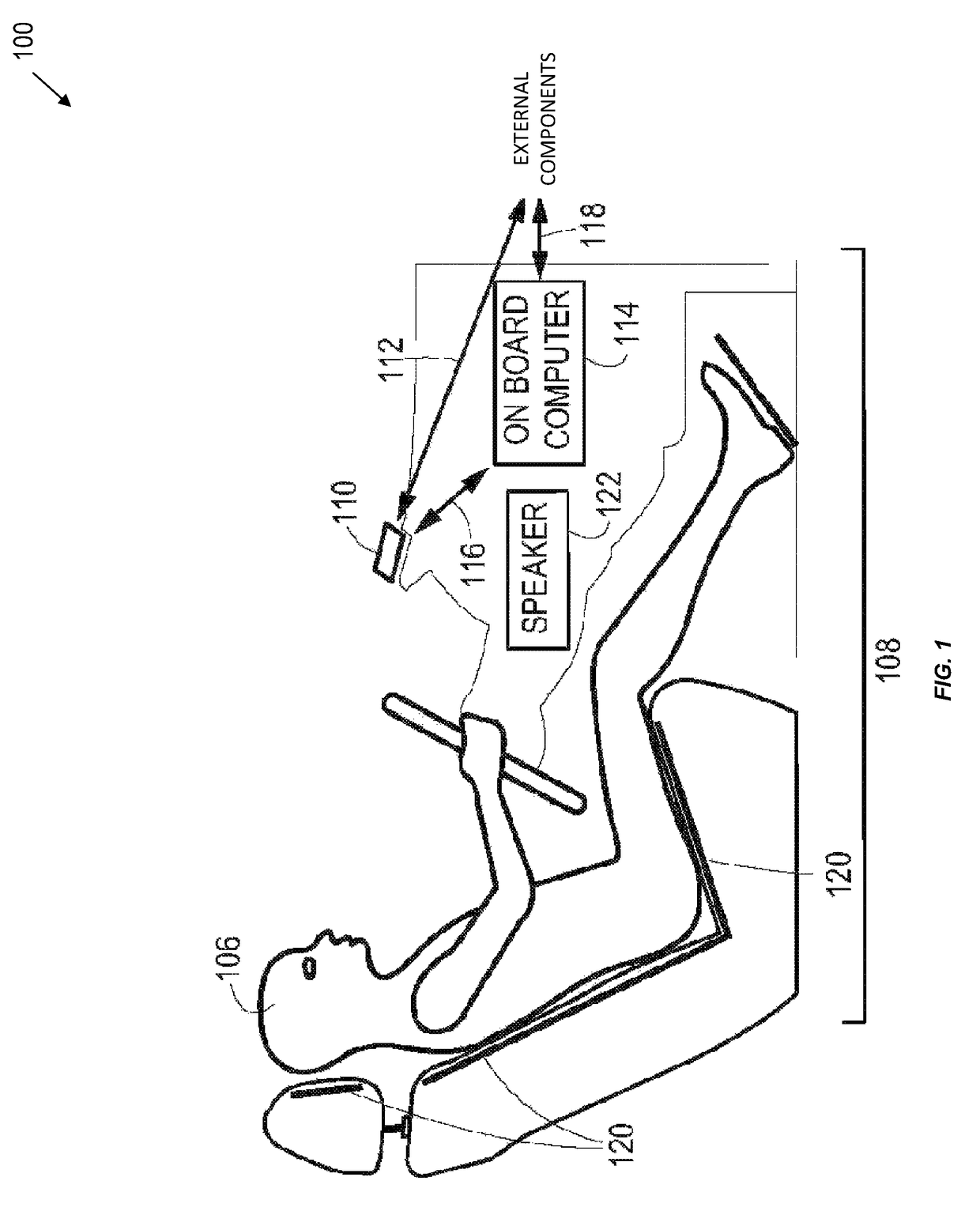
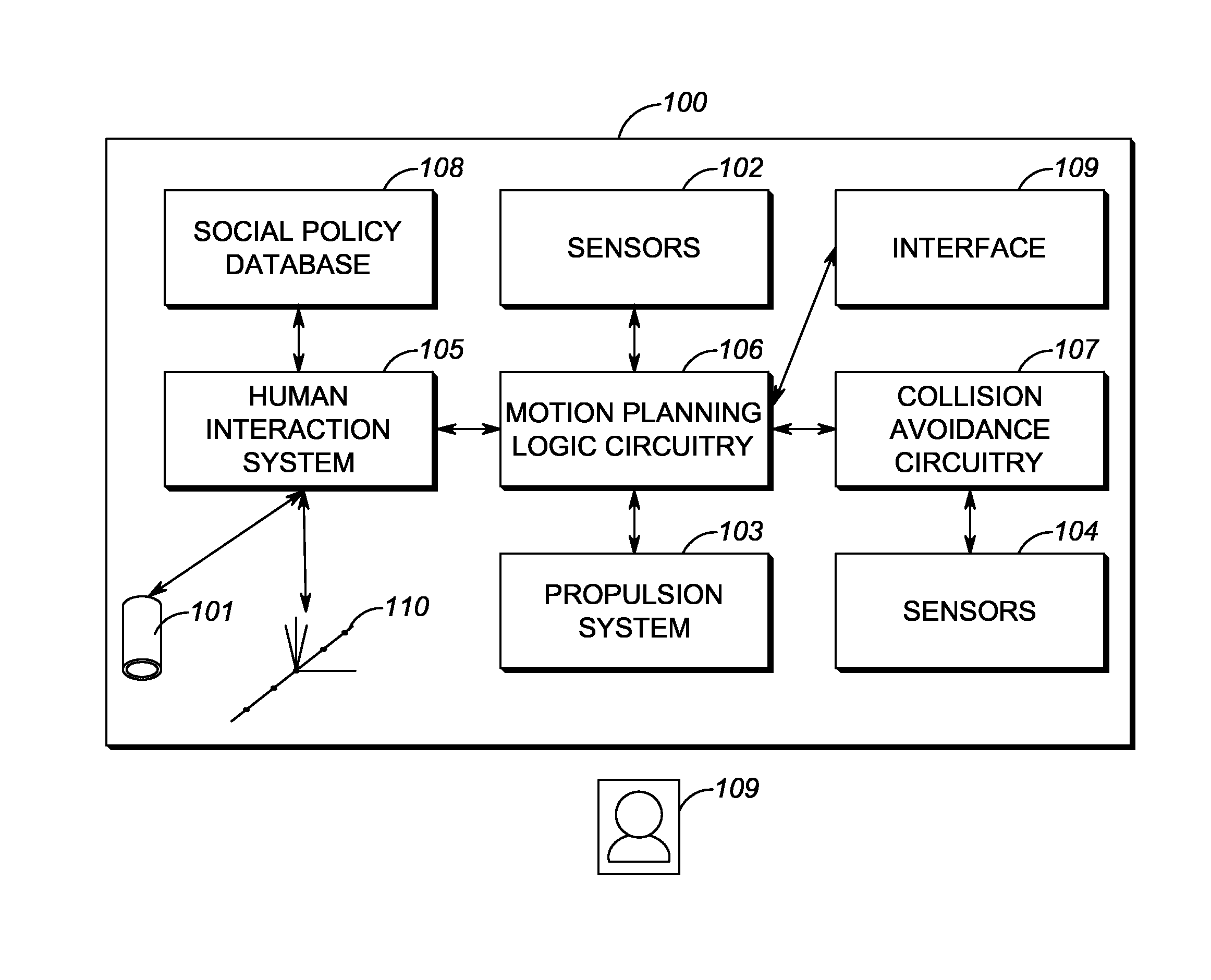
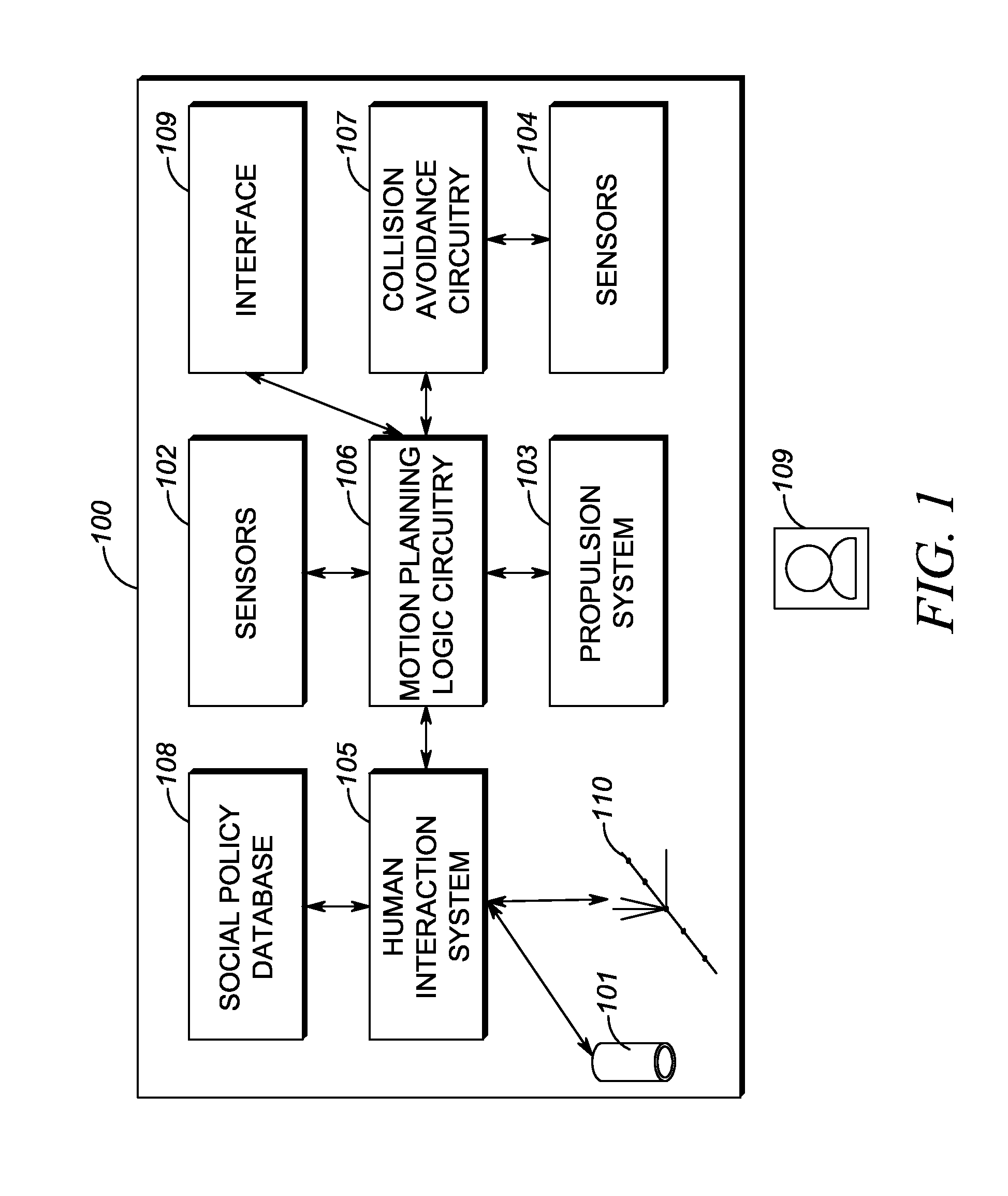
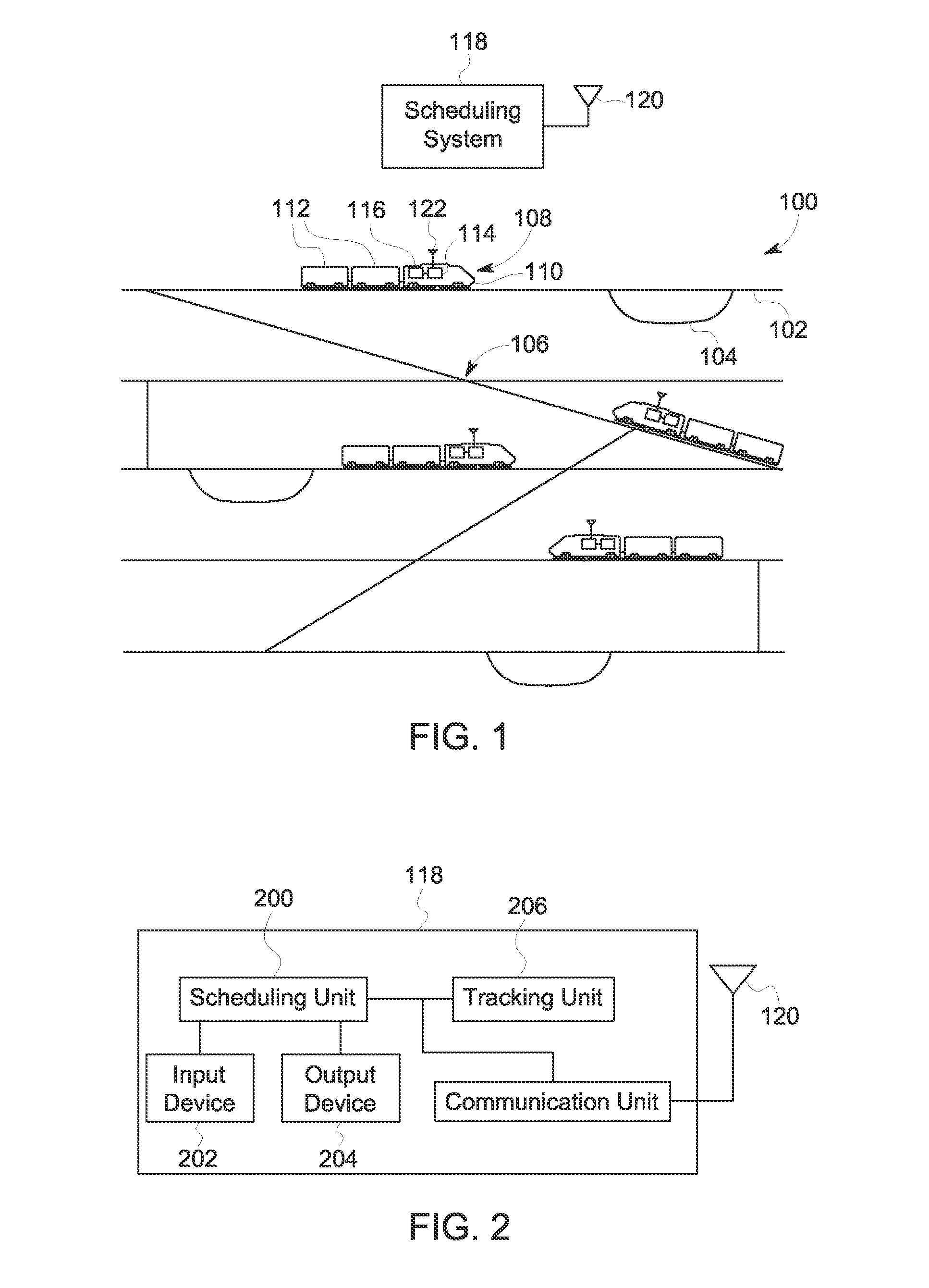
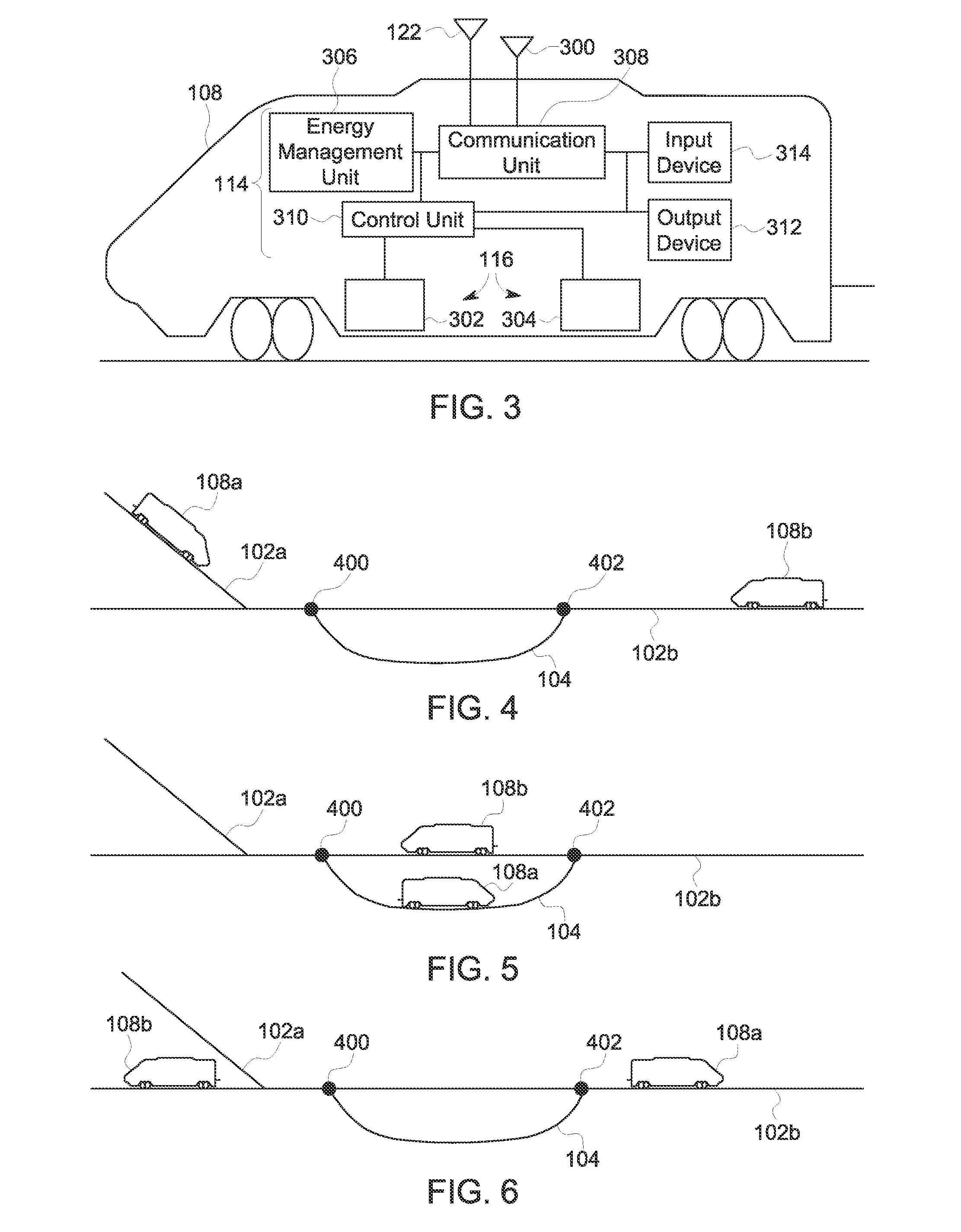
Systems, Methods, And Devices For Policy-Based Control and Monitoring of Use of Mobile Devices By Vehicle Operators
ActiveUS20110009107A1Reduce the cost of insuranceSpecial service provision for substationRoad vehicles traffic controlMobile vehicleOn board
Systems, methods, and devices for controlling and limiting use of functions, such as calling, texting, chatting, emailing, Internet surfing, and similar applications, on a mobile device when the mobile device is in a moving vehicle, includes use of an on-board computer installed within the vehicle, a transmitter in electronic communication with the on-board computer that periodically transmits speed data of the vehicle to a receiver installed on the mobile device, wherein the mobile device includes suitable software and a rules-based policy that define and control when and which functions of the mobile device are disabled or interrupted by the software when the vehicle is in motion above a minimum threshold speed. Policies are set by default but may be customized for particular individuals, devices, or circumstances. Policies may also be customized for particular groups or subgroups of employees or contractors for company or legal compliance to reduce distracted driving.
Owner:WESTERN ALLIANCE BANK
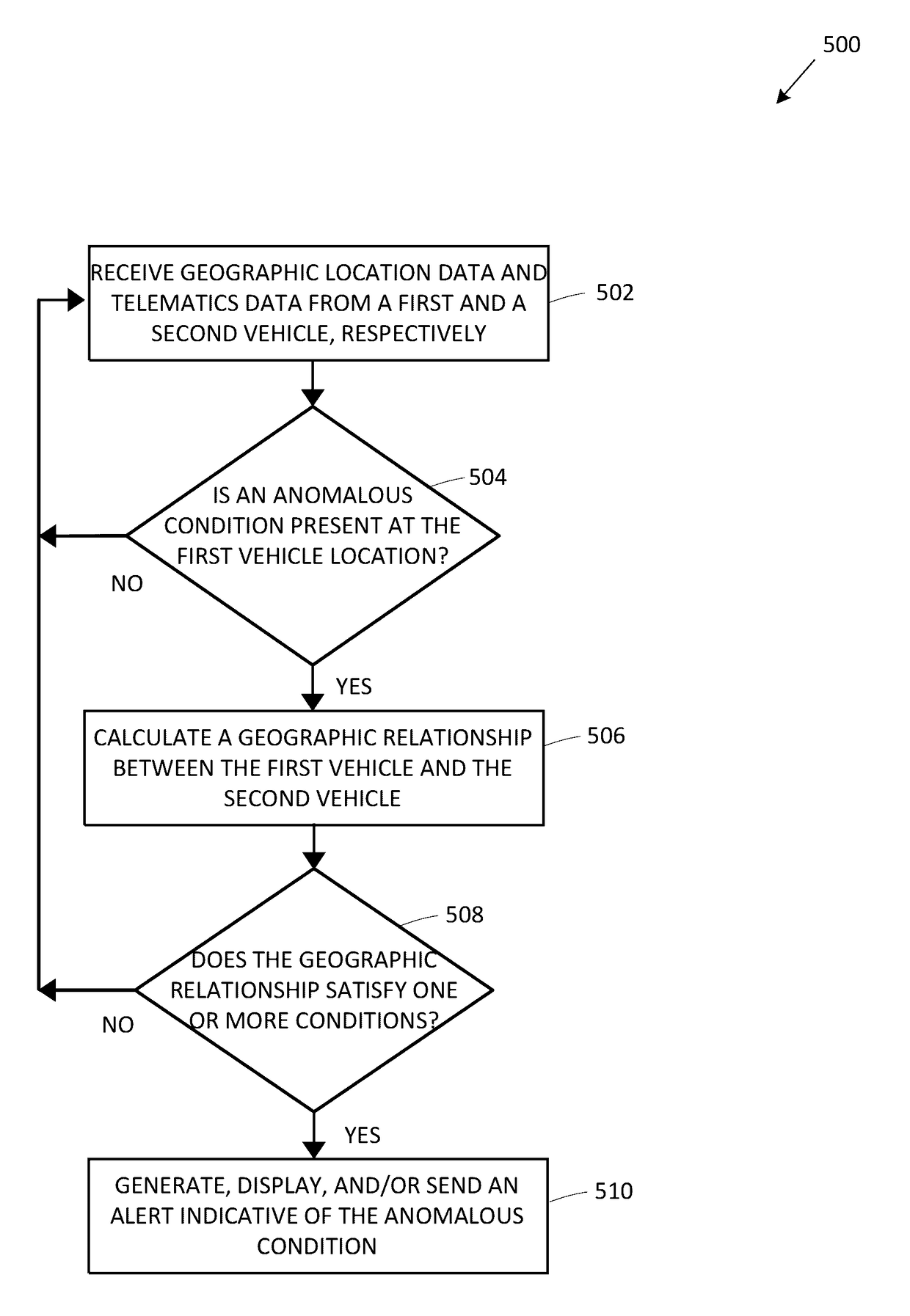
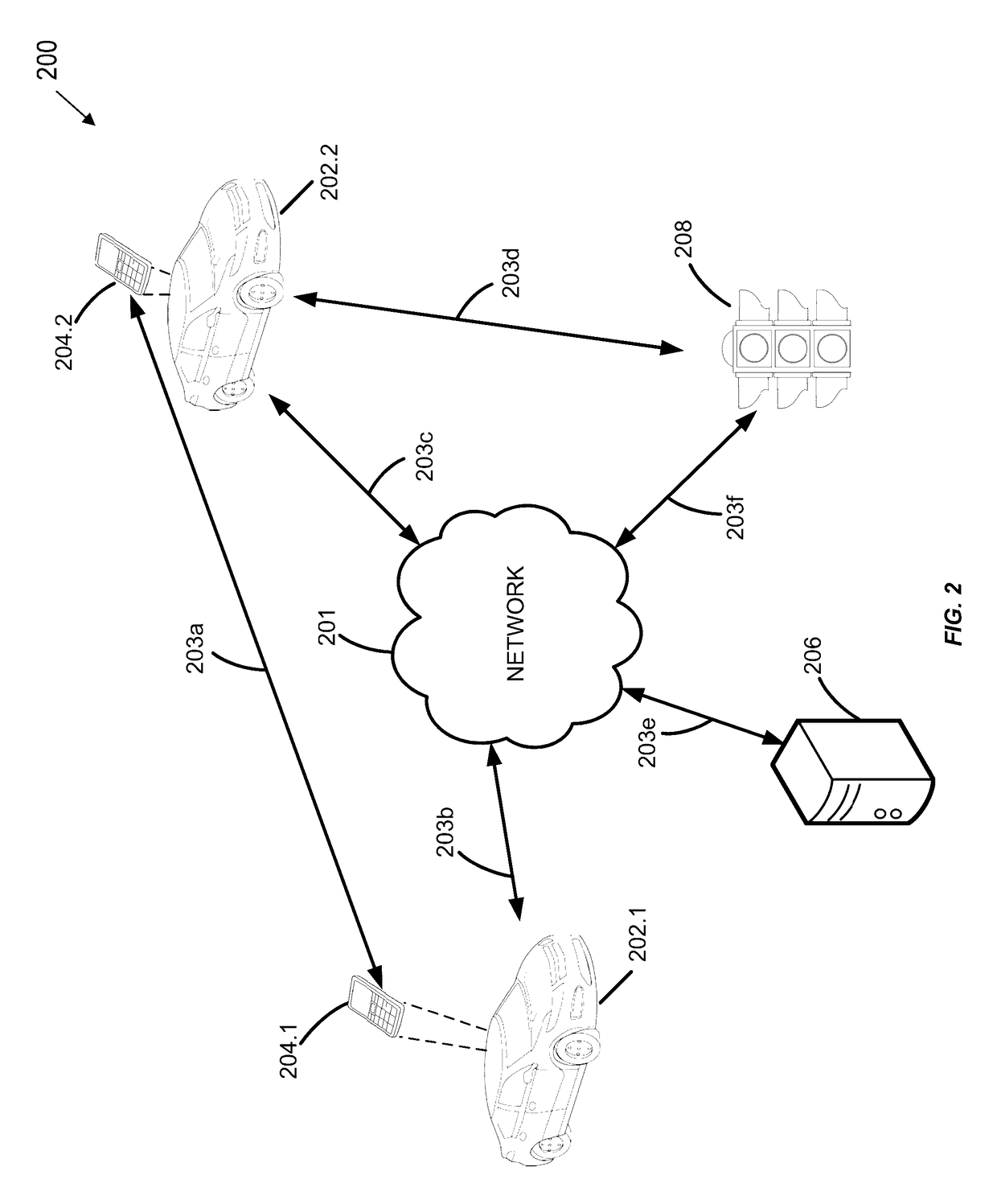
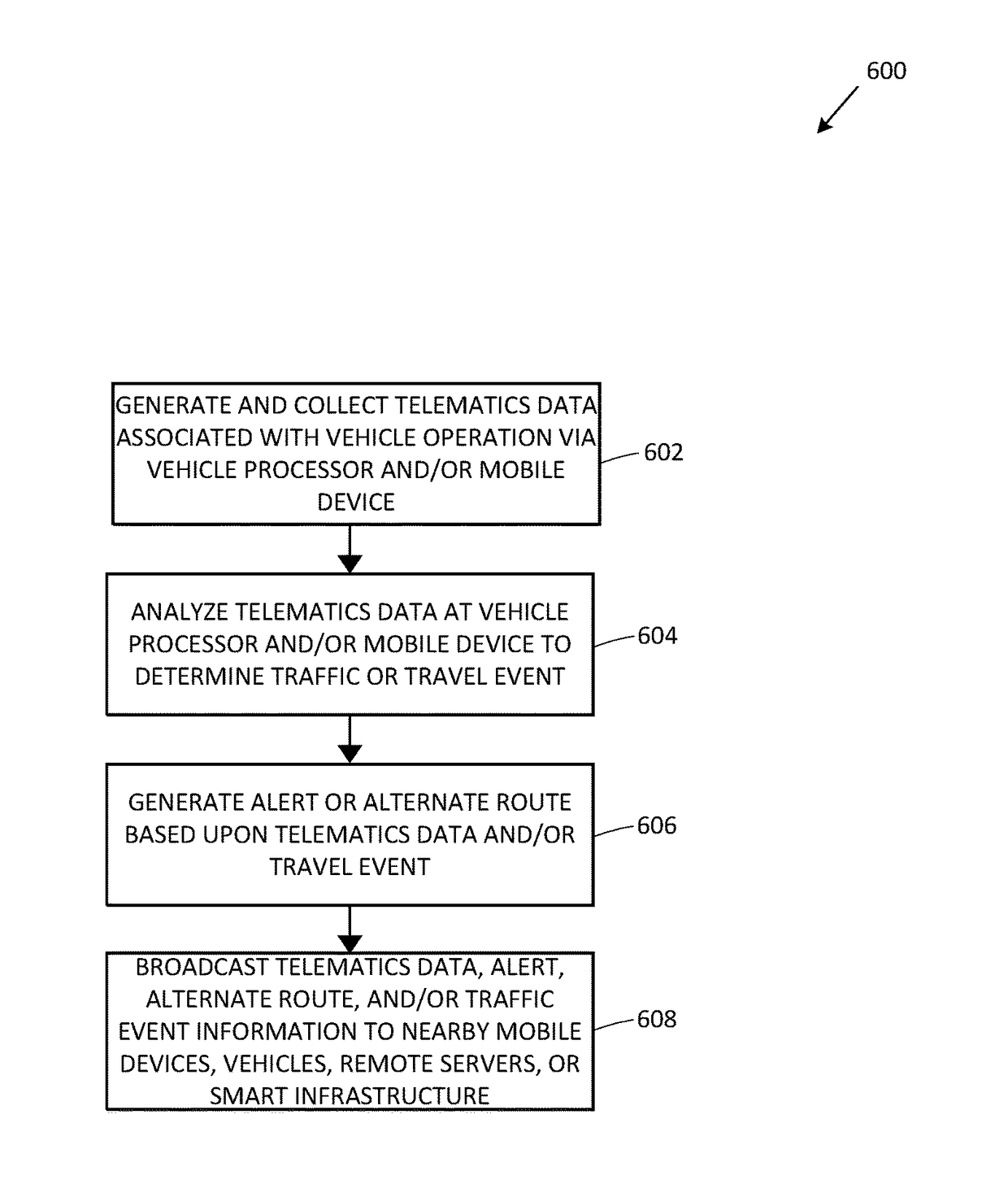
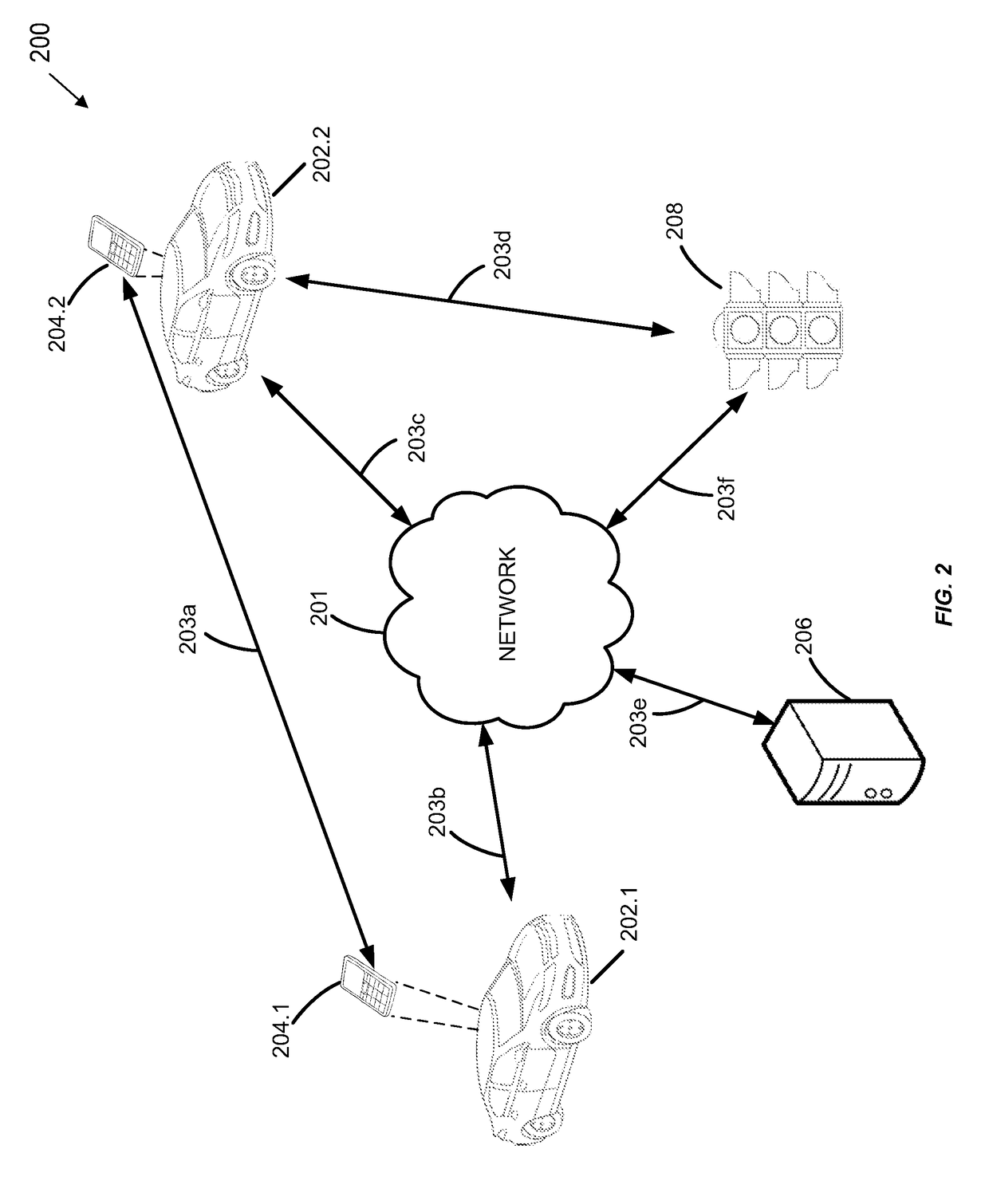
Alert notifications utilizing broadcasted telematics data
ActiveUS9679487B1Easy to driveReduce riskInstruments for road network navigationRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesGeolocationEngineering
Geographic location data and telematics data may be collected in real-time by a mobile device within a vehicle, or the vehicle itself. The telematics data may indicate vehicle direction, speed, motion, etc., as well as traffic hazards in the surrounding environment. A remote server may receive the location and telematics data from two vehicles. If an anomalous or hazardous condition exists in the vicinity of the first vehicle, a geographic relationship with the second vehicle is determined, and if within a predetermined distance, an alert or alternate route for the second vehicle is determined and transmitted to the second vehicle. As a result, a negative impact or risk of collision caused by the anomalous condition on the second vehicle is alleviated. The amount of the insured's usage of the telematics data-based risk mitigation or prevision functionality may be used to calculate or adjust insurance premiums, rates, or discounts.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Systems, methods, and devices for policy-based control and monitoring of use of mobile devices by vehicle operators
ActiveUS8527013B2Reduce the cost of insuranceSpecial service provision for substationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionMobile vehicleOn board
Owner:WESTERN ALLIANCE BANK
Control and communication system and method
InactiveUS20050090978A1Satisfies requirementEnhanced informationInstruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsCommunications systemLibrary science
The invention relates to a control and communication system and method for objects, the system comprising an object space-information database in an object centre of the object, the database storing an object plan for the object, wherein the control of the object is adjusted to the object plan, a regional control centre having a regional space-information database storing a regional plan, and a main control centre having a central space-information database storing a central plan. The central plan approved by the regional control centres is prepared by the main control centre, the regional plans are updated at the regional control centres on the basis of the central plan, and the object plans are updated at the object centres on the basis of the regional plans.
Owner:RDS X FEJLESZTESI & TANACSADO
Accident monitoring using remotely operated or autonomous aerial vehicles
A system to monitor vehicle accidents using a network of aerial based monitoring systems, terrestrial based monitoring systems and in-vehicle monitoring systems is described. Aerial vehicles used for this surveillance include manned and unmanned aircraft, satellites and lighter than air craft. Aerial vehicles can also be deployed from vehicles. The deployment is triggered by sensors registering a pattern in the data that is indicative of an accident that has happened or an accident about to happen.
Owner:SCOPE TECH HLDG
Systems, Methods, and Devices for Policy-Based Control and Monitoring of Use of Mobile Devices by Vehicle Operators
ActiveUS20130316737A1Reduce the cost of insuranceSpecial service provision for substationRoad vehicles traffic controlMobile vehicleOn board
Systems, methods, and devices for controlling and limiting use of functions, such as calling, texting, chatting, emailing, Internet surfing, and similar applications, on a mobile device when the mobile device is in a moving vehicle, includes use of an on-board computer installed within the vehicle, a transmitter in electronic communication with the on-board computer that periodically transmits speed data of the vehicle to a receiver installed on the mobile device, wherein the mobile device includes suitable software and a rules-based policy that define and control when and which functions of the mobile device are disabled or interrupted by the software when the vehicle is in motion above a minimum threshold speed. Policies are set by default but may be customized for particular individuals, devices, or circumstances. Policies may also be customized for particular groups or subgroups of employees or contractors for company or legal compliance to reduce distracted driving.
Owner:WESTERN ALLIANCE BANK
Broadcasting telematics data to nearby mobile devices, vehicles, and infrastructure
ActiveUS9832241B1Travel efficientlyReduce negative impactInstruments for road network navigationArrangements for variable traffic instructionsTraffic conditionsBroadcasting
A computer-implemented method of generating and broadcasting telematics and / or image data is provided. Telematics and / or image data may be collected, with customer permission, in real-time by a mobile device (or a Telematics App running thereon) traveling within an originating vehicle. The telematics data may include acceleration, braking, speed, heading, and location data associated with the originating vehicle. The mobile device may generate an updated telematics data broadcast including up-to-date telematics data at least every few seconds; and then broadcast the updated telematics data broadcast at least every few seconds via wireless communication to another computing device to facilitate alerting another vehicle or driver of an abnormal traffic condition or event that the originating vehicle is experiencing. An amount that an insured uses or otherwise employs the telematics data-based risk mitigation or prevention functionality may be used with usage-based insurance, or to calculate or adjust insurance premiums or discounts.
Owner:STATE FARM MUTUAL AUTOMOBILE INSURANCE
Autonomous driving method and apparatus
ActiveUS20180061253A1Well formedAutonomous decision making processRoad vehicles traffic controlEngineeringAutopilot
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
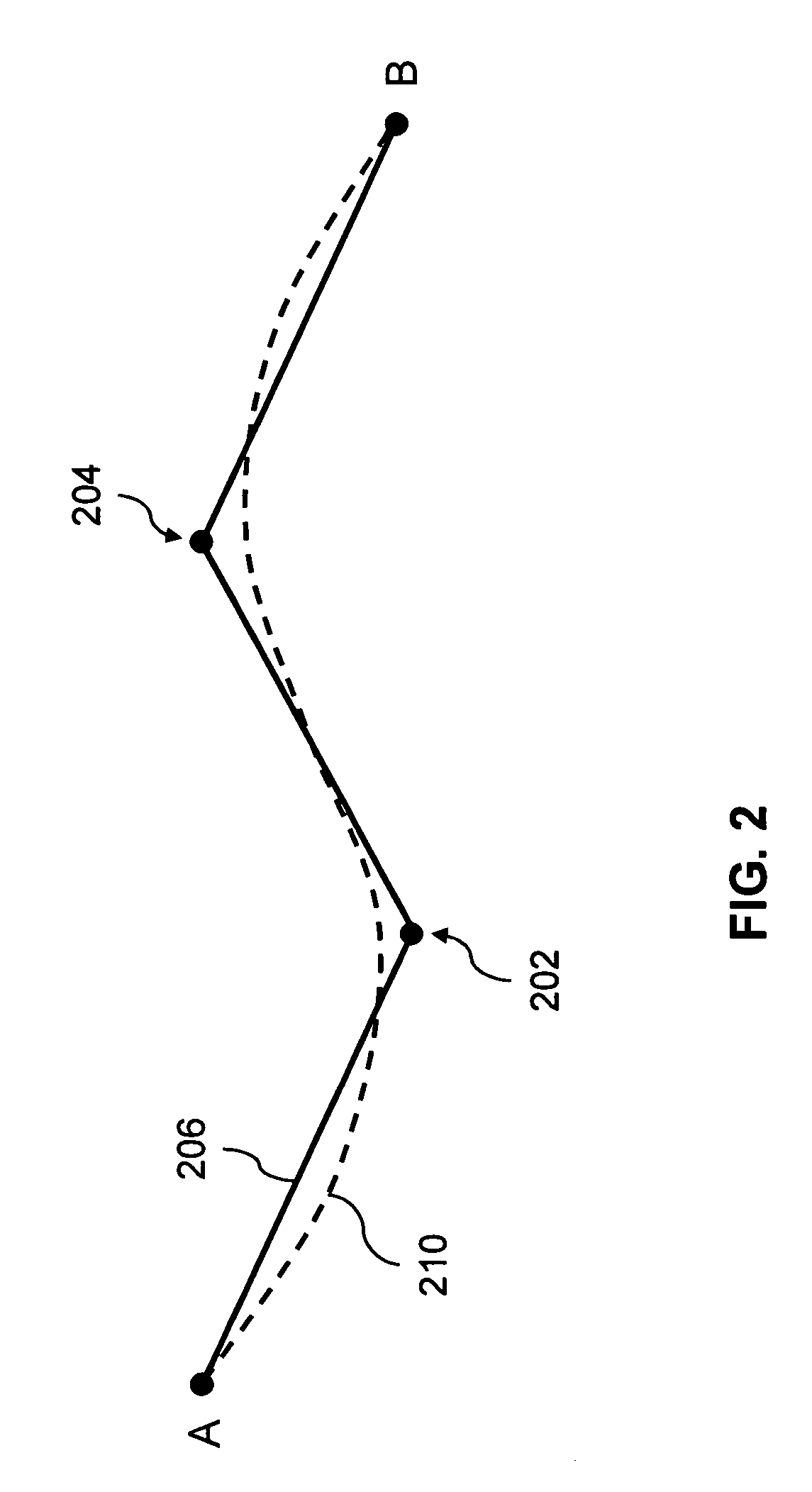
Systems and methods for coordination of entities and/or communicating location information
ActiveUS7894948B2Reduces and eliminates potentialEffective de-conflictionAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficLongitudeInformation system
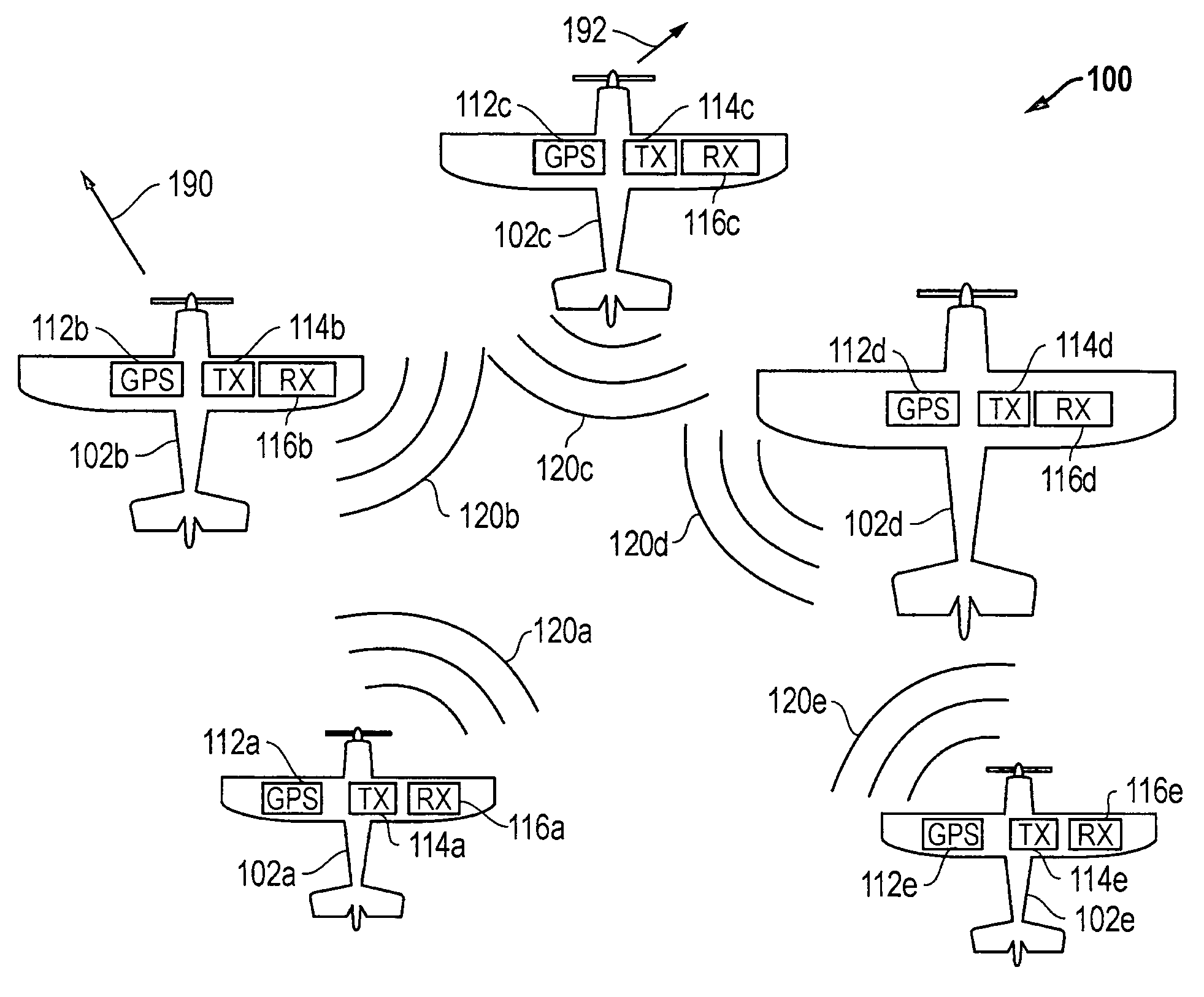
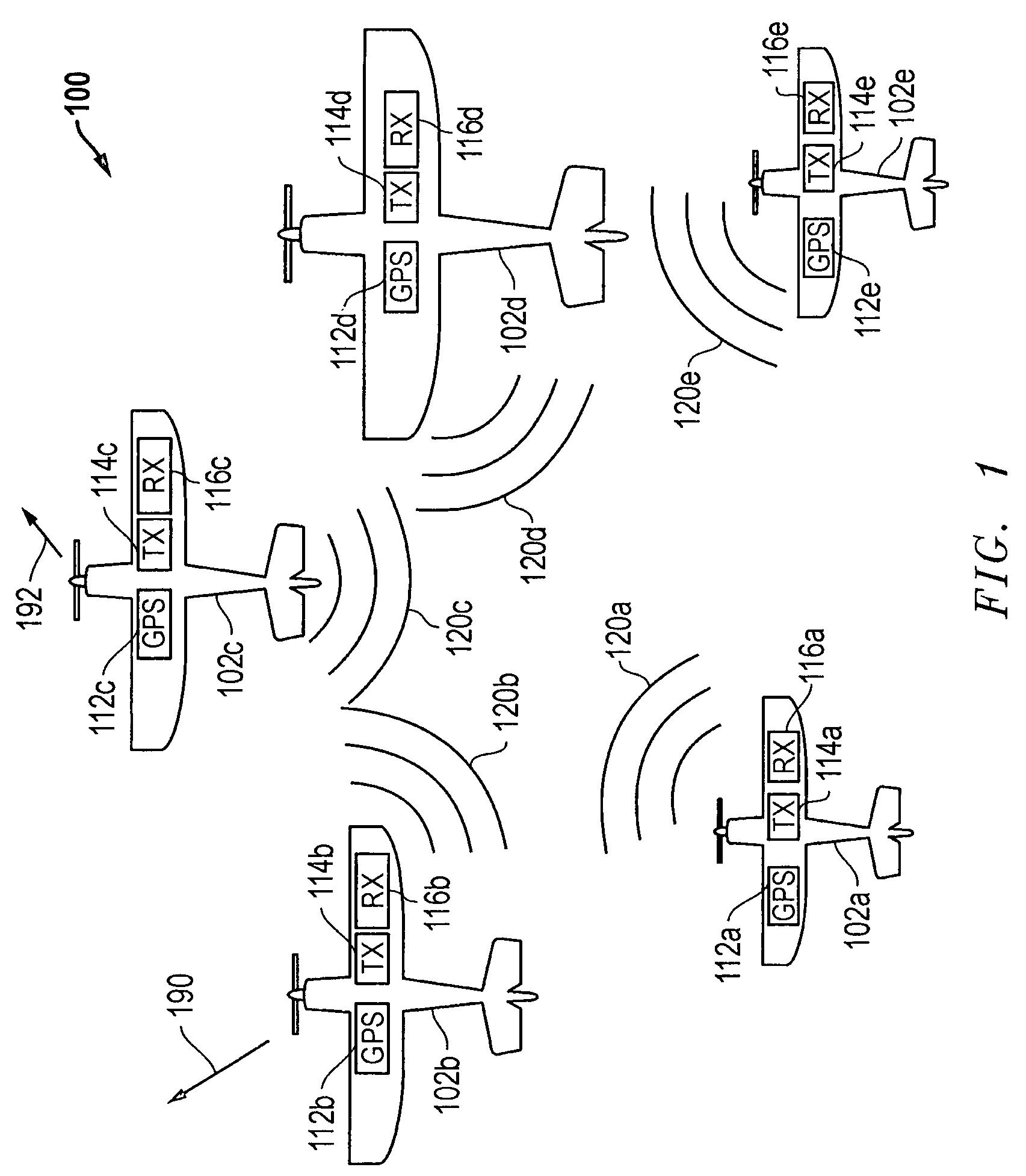
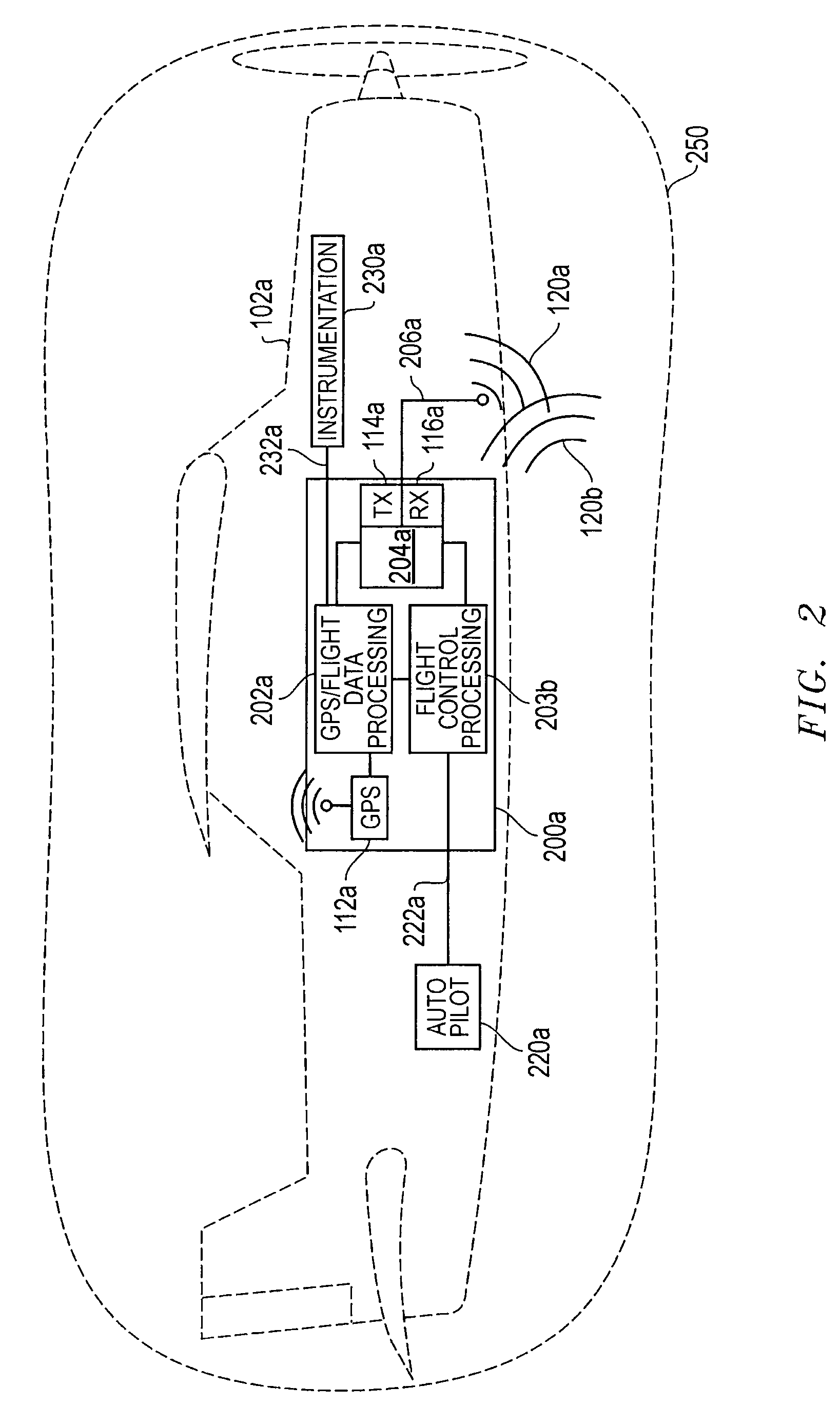
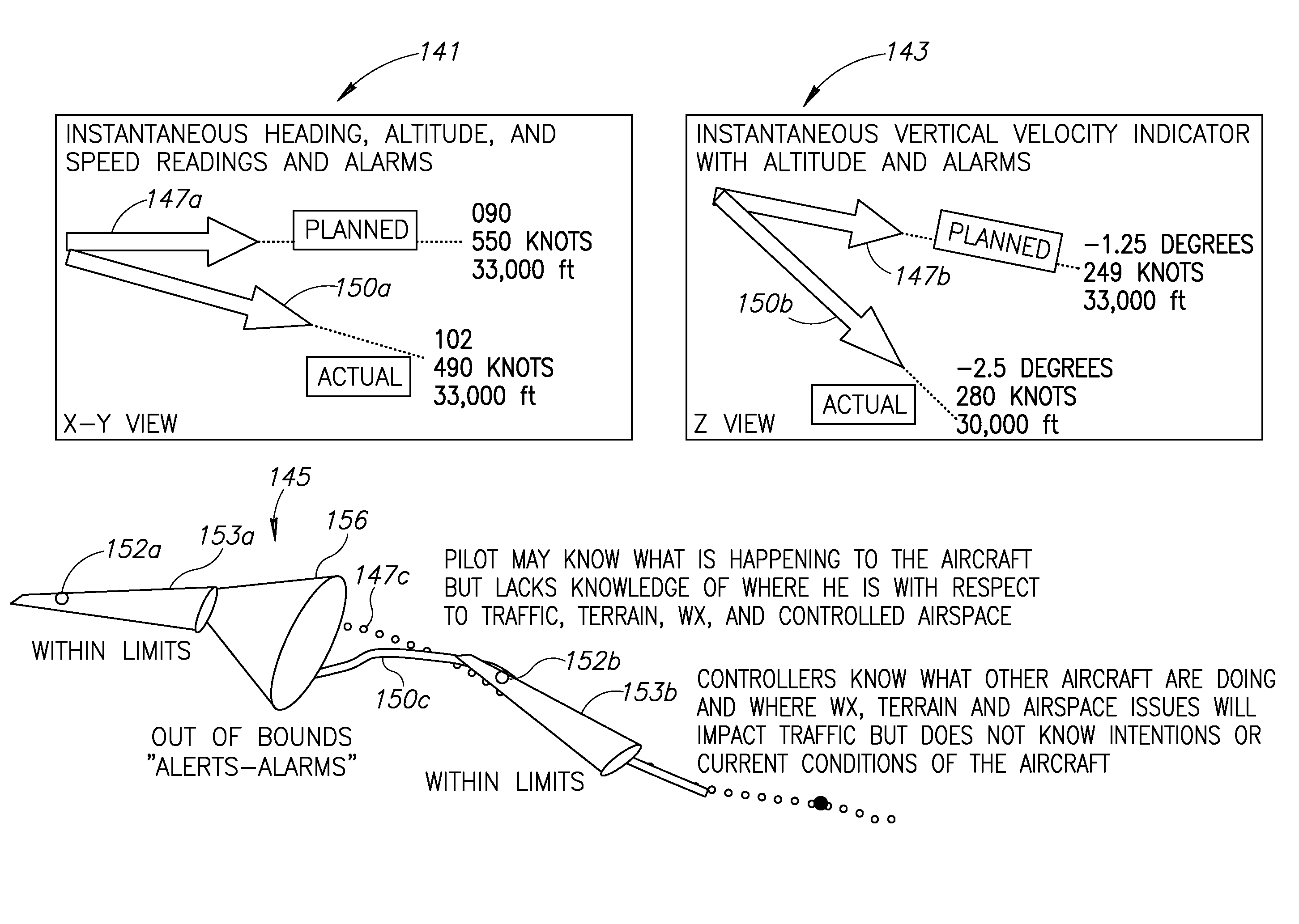
Systems and methods that may be employed to communicate location information between two or more aerial vehicles or other types of vehicles or other entities, and / or that may be used to facilitate coordinated operations of two or more such entities. In one example, an aerial vehicle may be kept aware of one or more location (e.g., longitude, latitude, etc.) and / or flight characteristics (e.g., altitude, directional heading, airspeed, attitude, etc.) of one or more other adjacent aerial vehicles, and each such aerial vehicle may use that location information to adjust its flight path to maintain a safe sphere of empty airspace around itself.
Owner:L3HARRIS TECH INTEGRATED SYST LP
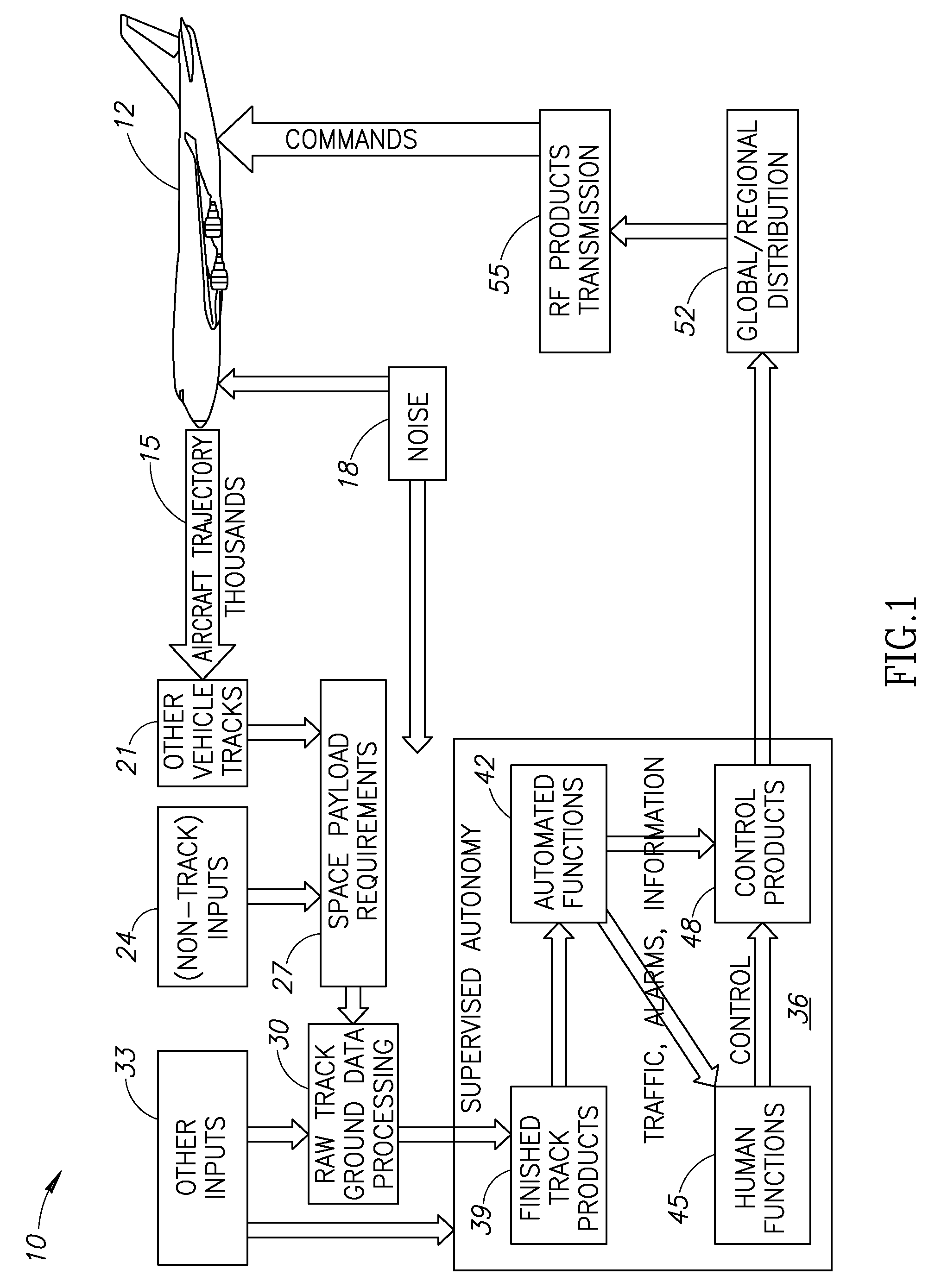
Tracking, relay, and control information flow analysis process for information-based systems
InactiveUS7212917B2Facilitate prioritizationAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficFlight vehicleSpatial model
Methods and apparatus for controlling movement of aircraft through a defined air space are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method includes generating a model of the defined air space. The model is configured to indicate a safe subset of the defined air space for movement. Receiving a trajectory datum from an aircraft facilitates placing the aircraft at an aircraft position in the generated model of the defined air space according to the trajectory datum. A route is generated for the aircraft through the defined air space according to the aircraft position and the safe subset. Control commands are transmitted to the aircraft; the control commands are configured to control the aircraft according to the route.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
System and method for stochastic aircraft flight-path modeling
Stochastic models of aircraft flight paths and a method for deriving such models from recorded air traffic data. Each stochastic model involves identifying the flight plan for one or more aircraft; identifying important parameters from each flight plan, such as aircraft type, cruise altitude, and airspeed; optionally identifying flight plan amendments for each flight; representing each route of flight as a series of navigational fixes; representing at least one aircraft flight parameter probabilistically; modeling realistic differences in at least one dimension between each planned route of flight and the flight path as it might actually be flown; and communicating the modeled deviations or simulated flight paths to the user. At least one aircraft flight parameter is represented as a random variable with a particular statistical distribution, such as a normal (Gaussian), Laplacian, or logistic distribution; or with a more complex algorithm containing one or more random elements. The modeled flight parameters may be any of lateral position, longitudinal position, climb altitude, descent altitude, climb airspeed, descent airspeed, cruise airspeed, cruise altitude transition, or response time to a flight plan amendment.
Owner:MITRE SPORTS INT LTD
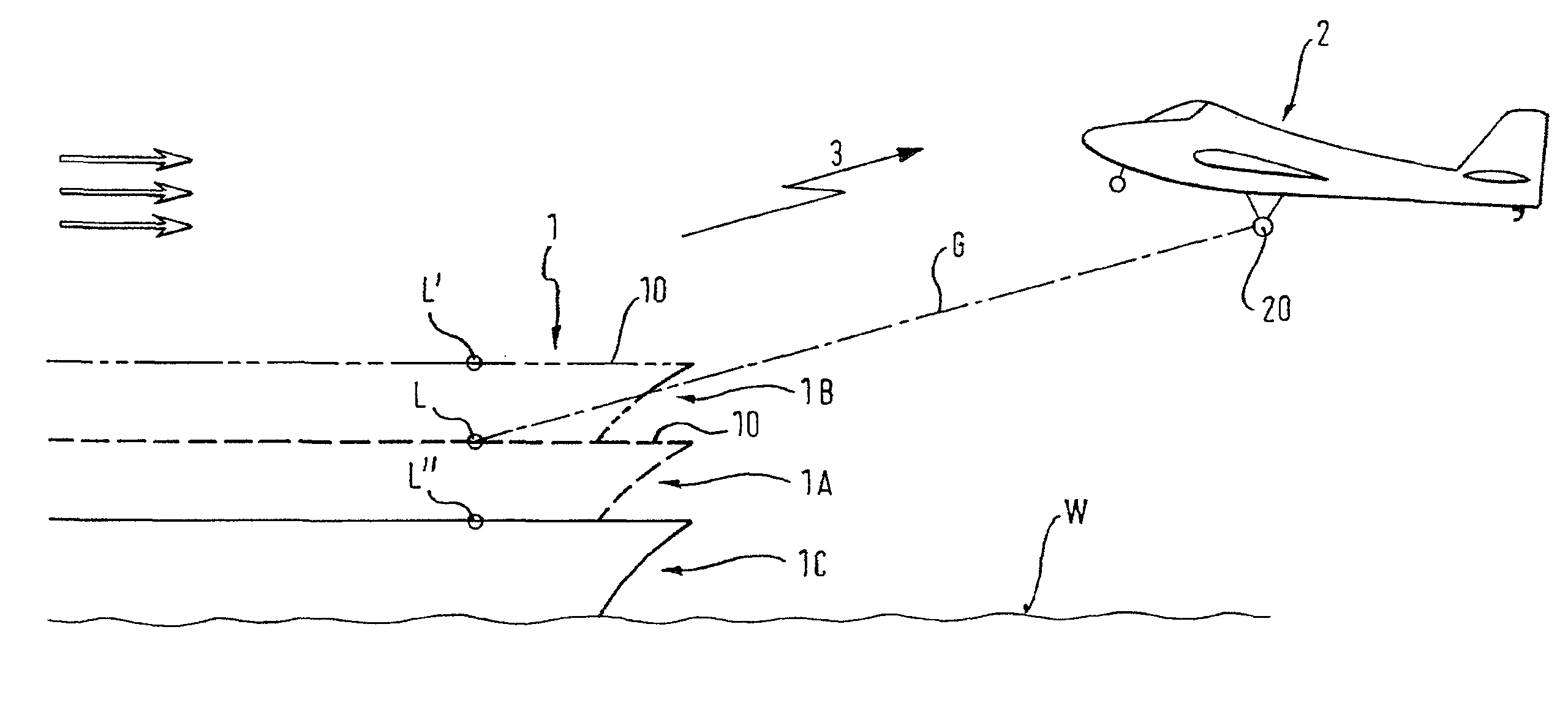
Procedure for Automatically Landing an Aircraft
ActiveUS20110066307A1Simple methodFacilitates holdingAnalogue computers for vehiclesVehicle position/course/altitude controlJet aeroplaneMarine navigation
A procedure and system are provided for automatically landing an aircraft, particularly an unmanned aircraft on a moving, particularly floating landing platform, for example, on an aircraft carrier, the aircraft being equipped with an automatic navigation device and an automatic landing control device. The procedure includes detecting the position of an intended landing spot, detecting motion data of the landing platform, determining at least one imminent point in time at which the landing spot takes up a reference position, transmitting the point in time and the reference position of the landing spot to the landing control device of the aircraft, and controlling the aircraft such that it reaches the landing spot at the point in time.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
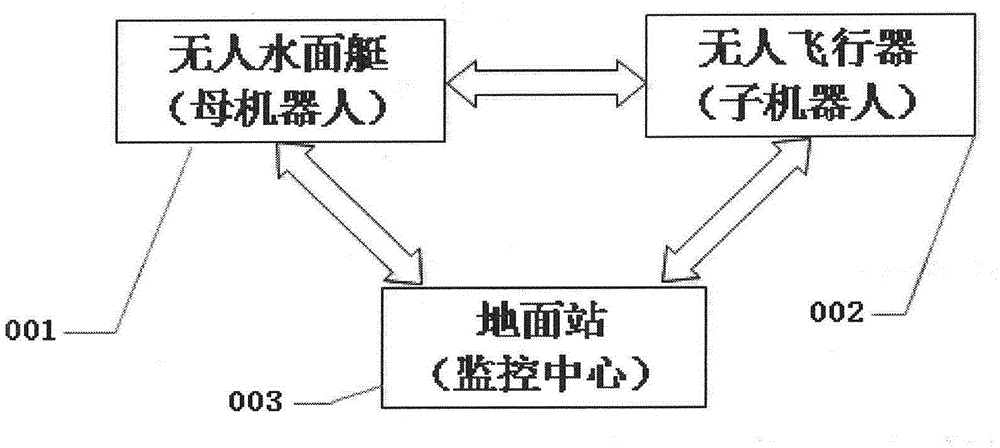
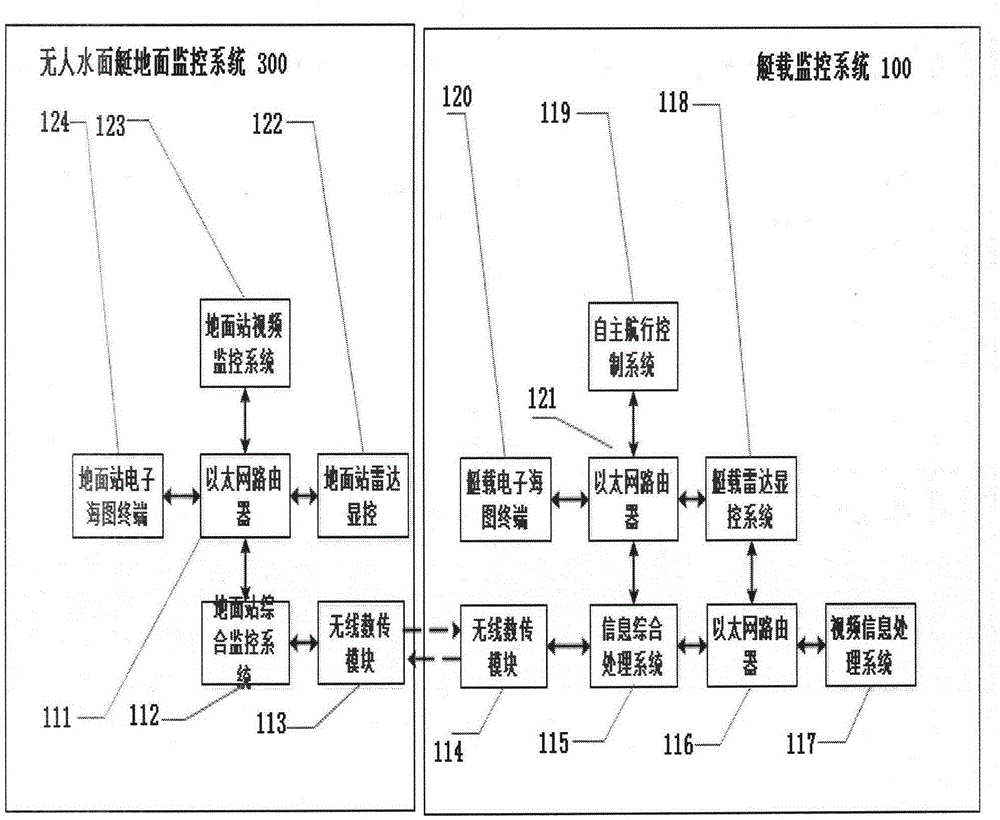
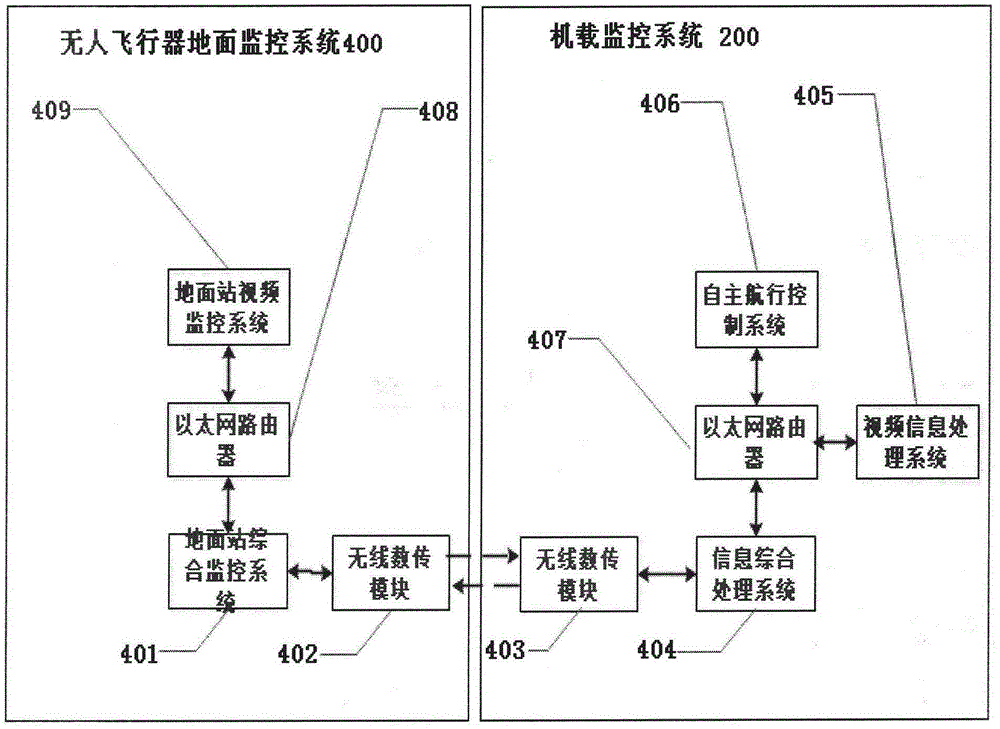
Child-mother type robot cooperation system of combination of unmanned surface vessel and unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN105303899AImprove battery lifeExtended flight radiusSimultaneous traffic control systemsRobotic systemsMarine engineering
The invention discloses a child-mother type robot cooperation system of combination of an unmanned surface vessel and an unmanned aerial vehicle. The child-mother type robot cooperation system comprises the unmanned surface vessel, the unmanned aerial vehicle and a ground station. The unmanned surface vessel comprises a vessel-mounted monitoring system. The unmanned aerial vehicle comprises an airborne monitoring system. The child-mother type robot system is formed by the unmanned surface vessel and the unmanned aerial vehicle. Besides, an unmanned aerial vehicle ground station monitoring system and an unmanned surface vessel ground station monitoring system are respectively arranged in a ground station monitoring system, and cooperative work between the unmanned surface vessel and the unmanned aerial vehicle is realized by information interaction between the two systems on the ground station. In cooperation of the unmanned surface vessel and the unmanned aerial vehicle, endurance of the unmanned aerial vehicle can be enhanced by the unmanned surface vessel, and the flight radius of the unmanned aerial vehicle can be extended; and more comprehensive observation perspectives and observation information can be provided for the unmanned surface vessel by the unmanned aerial vehicle.
Owner:范云生
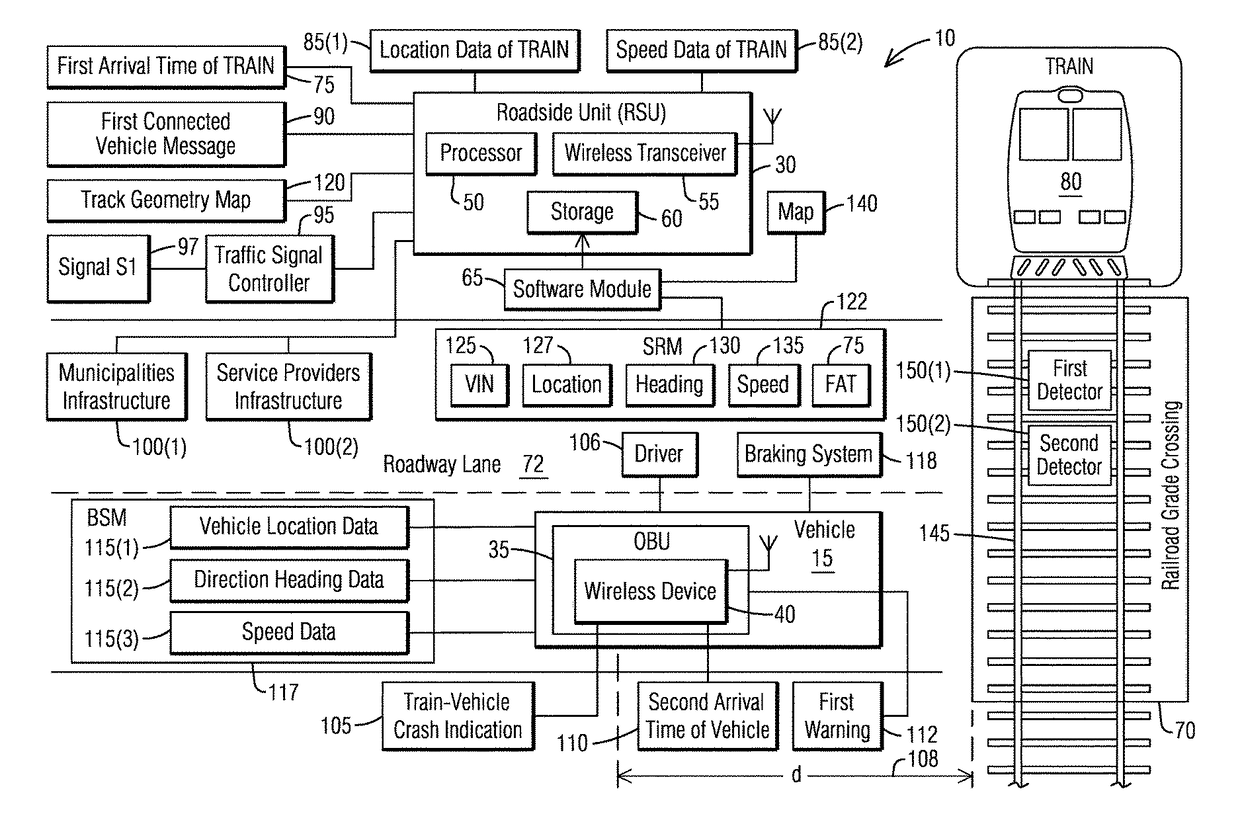
Connected vehicle traffic safety system and a method of predicting and avoiding crashes at railroad grade crossings
ActiveUS20180018888A1Anti-collision systemsSignalling indicators on vehicleCollision detectionEngineering
A connected vehicle train-vehicle collision detection system comprises a roadside unit (RSU) located at a railroad grade crossing near a roadway lane for avoiding TRAIN crashes with Onboard Unit (OBU)-equipped vehicles by issuing advance warnings for a potential vehicle-train crash. The roadside unit (RSU) is configured to act as a proxy Onboard Unit (OBU) for a non-OBU-equipped TRAIN and transmit a train location to a first Onboard Unit (OBU)-equipped vehicle having an Onboard Unit (OBU). The Onboard Unit (OBU) of the first OBU-equipped vehicle is configured to calculate a train-vehicle crash based on the train location of the TRAIN relative to the railroad grade crossing and a vehicle location of the first OBU-equipped vehicle relative to the railroad grade crossing.
Owner:SIEMENS MOBILITY INC
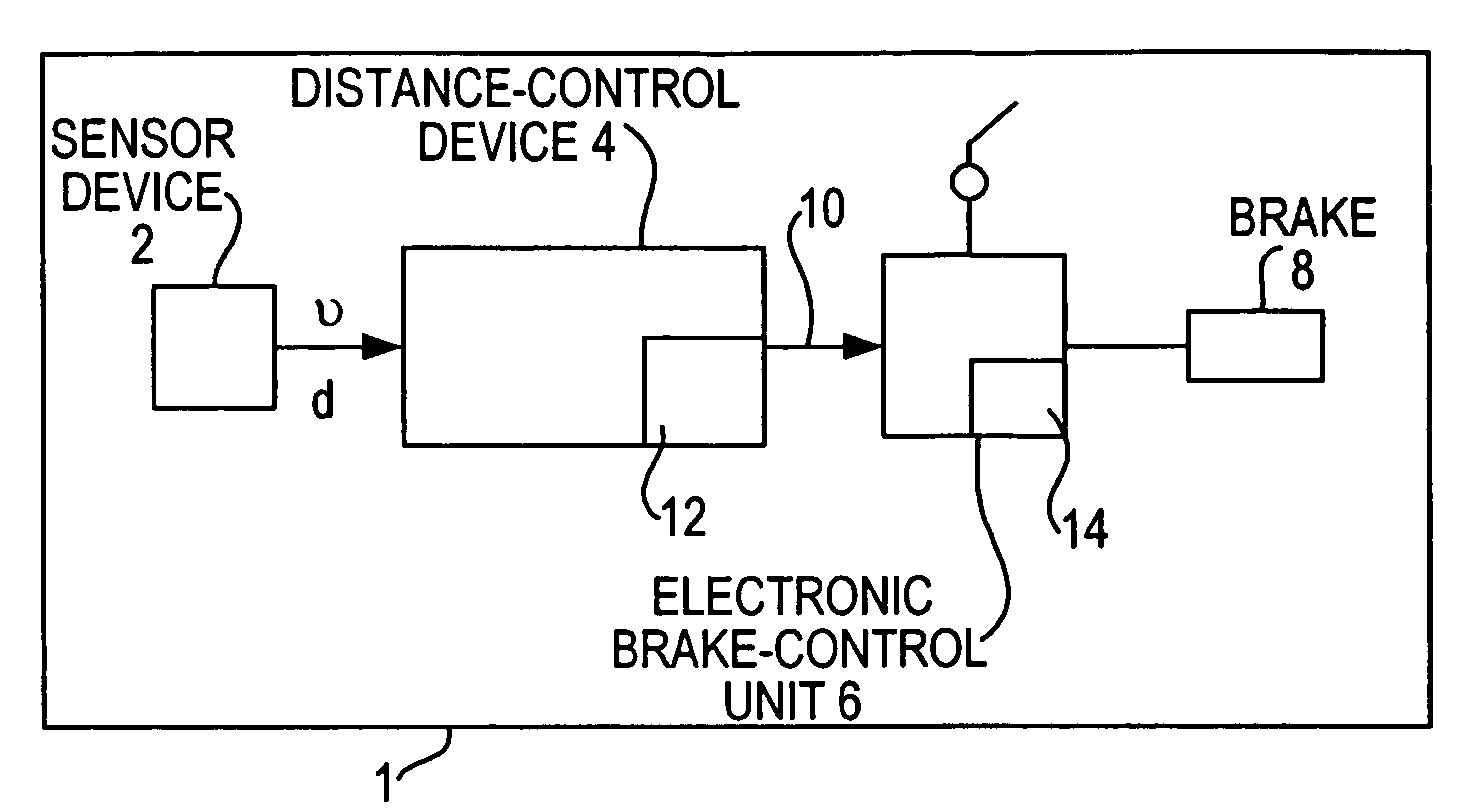
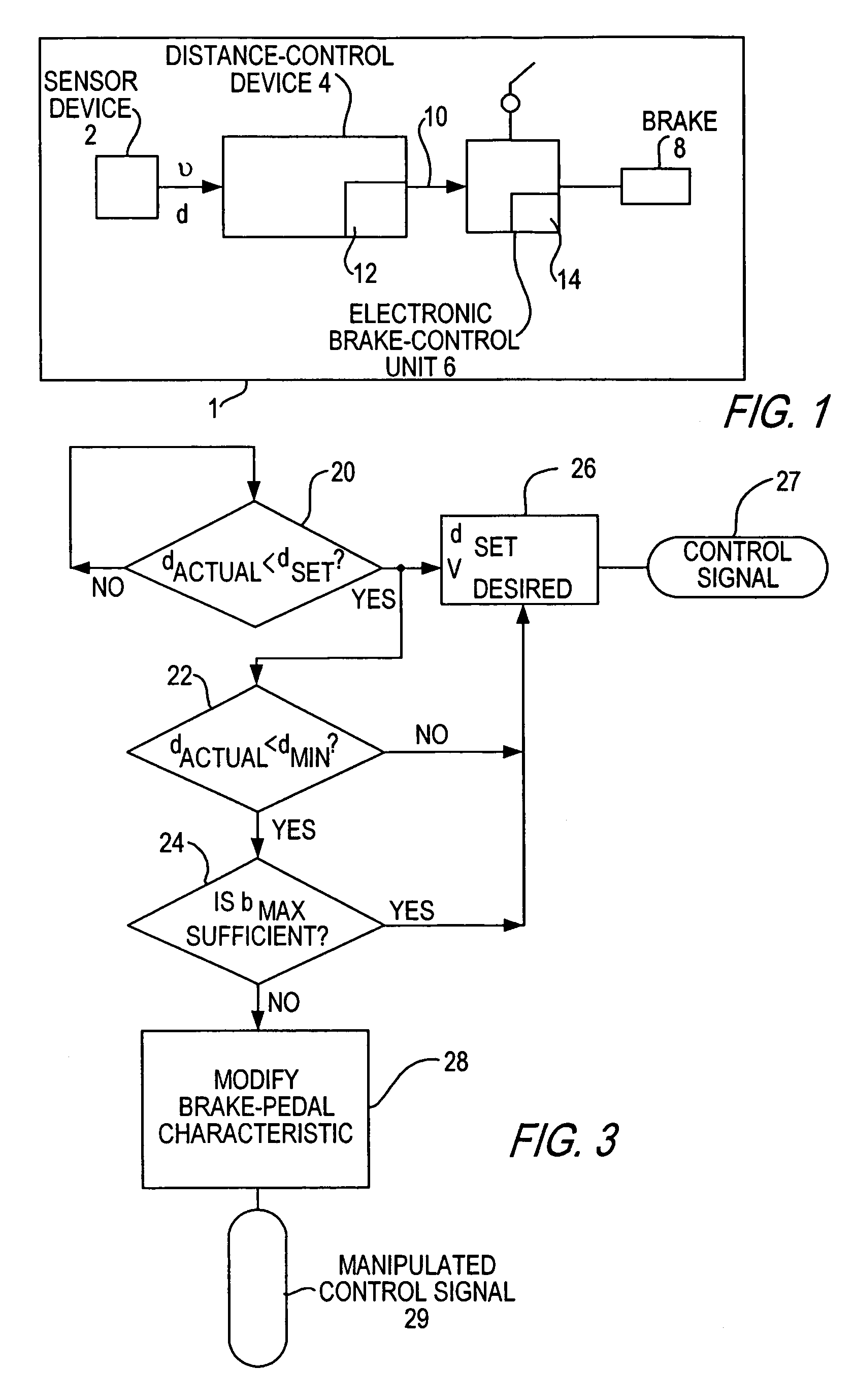
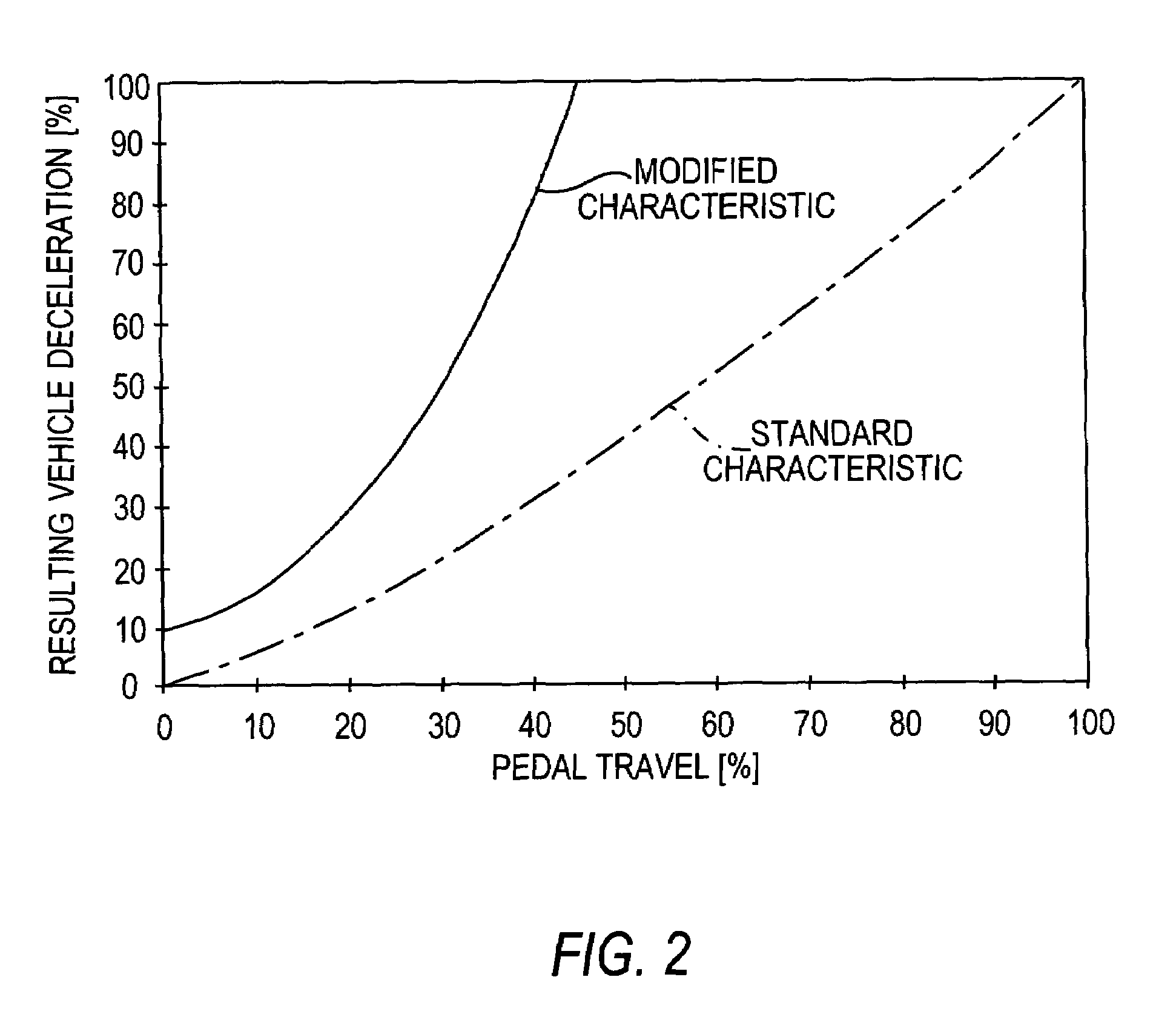
Automatic distance control method and system for motor vehicles
ActiveUS7103464B2Avoid disadvantagesIncreased orVehicle fittingsAnalogue computers for trafficMobile vehicleAutomatic control
A method and system for automatic control of the distance between a vehicle to be controlled and a lead vehicle. The vehicle to be controlled is equipped with a distance-control device having a distance sensor and a brake device with a brake pedal. The distance-control device controls the speed of the controlled vehicle by delivering a brake-actuating signal to the brake device in such a way that the distance between the vehicles does not become shorter than a predefined distance, the distance-control device also generating a warning signal to the driver if the distance becomes shorter than the predefined distance. The distance-control device changes the brake pedal characteristic in such a way that the brake pedal travel required for injection of increased brake pressure is minimized if a criterion that indicates a danger of collision is present.
Owner:WABCO EURO BVBA SPRL
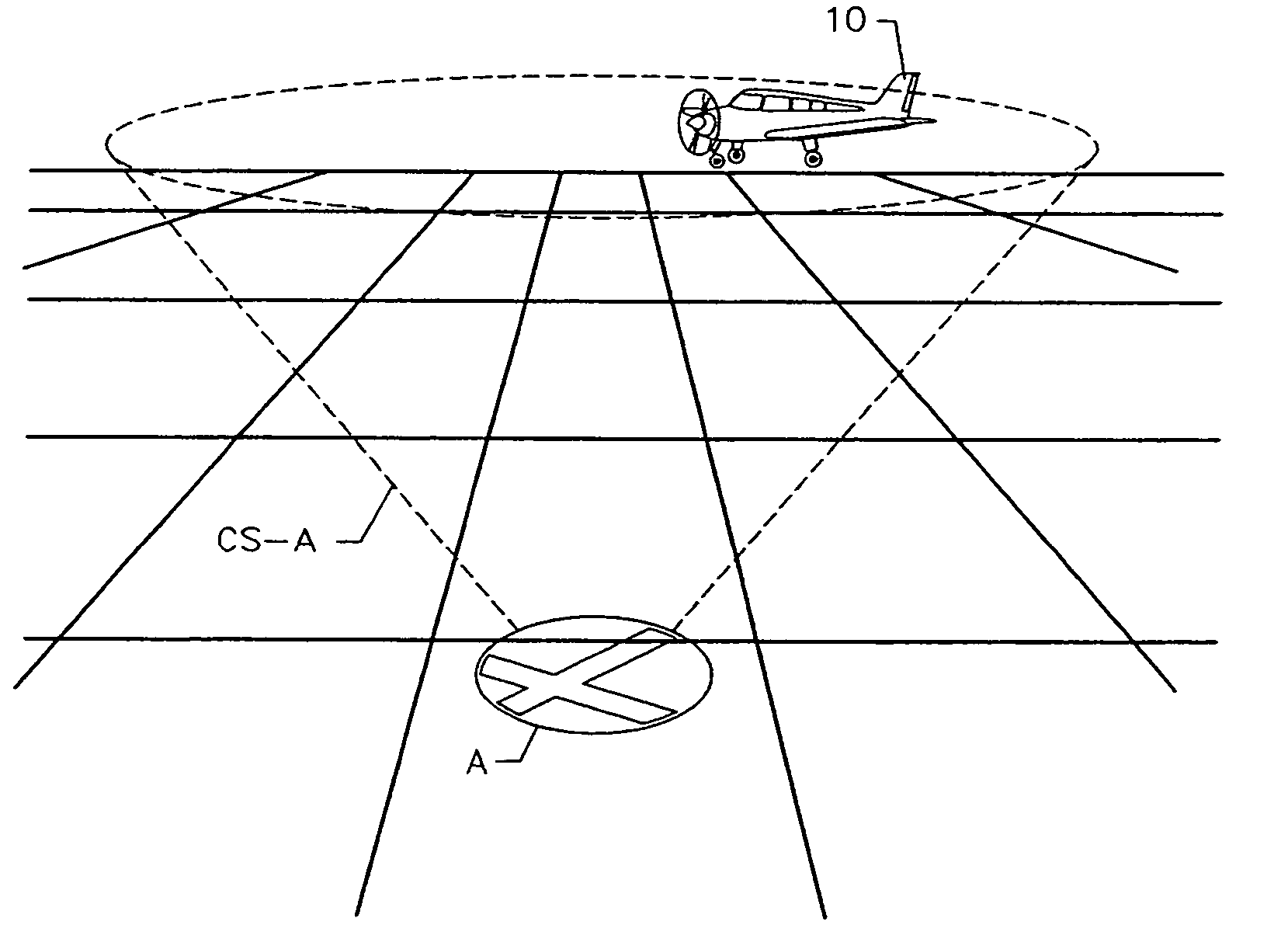
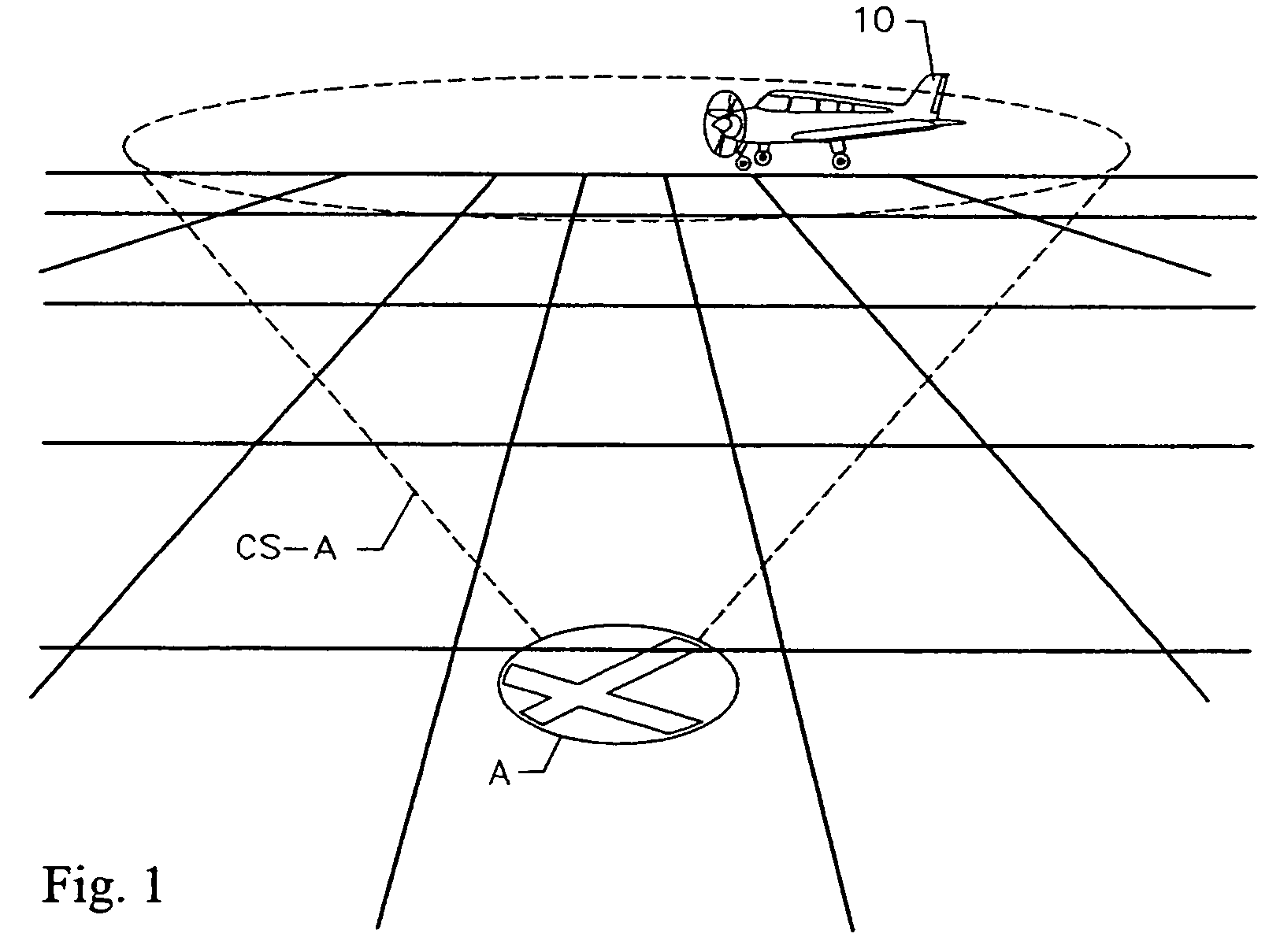
Flight management system and method for providing navigational reference to emergency landing locations
InactiveUS7167782B2Maximize safetyAltitude differential decreasesAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficAviationNavigational system
An aviation navigational system and method for predicting glide range for an aircraft for specific airports and other potential emergency landing locations in proximity to the aircraft. Information is presented to the pilot by complementing a conventional moving map display with symbols centered on each landing location. GPS altitude, airport elevation, and the aircraft's glide ratio are factored into an equation to determine glide range for each airport within proximity to the aircraft. A circular symbol representing the glide range boundary is displayed around each airport. Each circular symbol represents a sectional view of an imaginary inverted cone, having the apex thereof centered on a given landing location. The size and shape of the cone is based on the gliding performance of the aircraft and the altitude differential between the aircraft and the target landing location. As the altitude differential increases the radius of the circle increases. Conversely as the altitude differential decreases, the radius of the circle decreases. As long as the aircraft is anywhere within any one of the three-dimensional inverted cones displayed, as represented by one or more circles on a two dimensional display, it can safely glide to the landing location. This display concept is selectively referred to herein as “cones of safety.”
Owner:CONTROL VISION CORP
Modular hovercar, hovercar system and hovercar sharing method
ActiveCN107627945AEasy transferArrive quicklyLaunching/towing gearRoad vehicles traffic controlModularityAirplane
A modular hovercar comprises a car body and a plane body, wherein the car body comprises a chassis, a first seat cabin and a parking platform; the parking platform is used for parking the plane body;the plane body comprises a second seat cabin and a flight mechanism; the plane body can perpendicularly land on the parking platform and is connected with the car body by a lock catch; and the plane body can take off vertically from the parking platform. The invention further discloses a hovercar system and a hovercar sharing method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GEELY HOLDING (GROUP) CO LTD
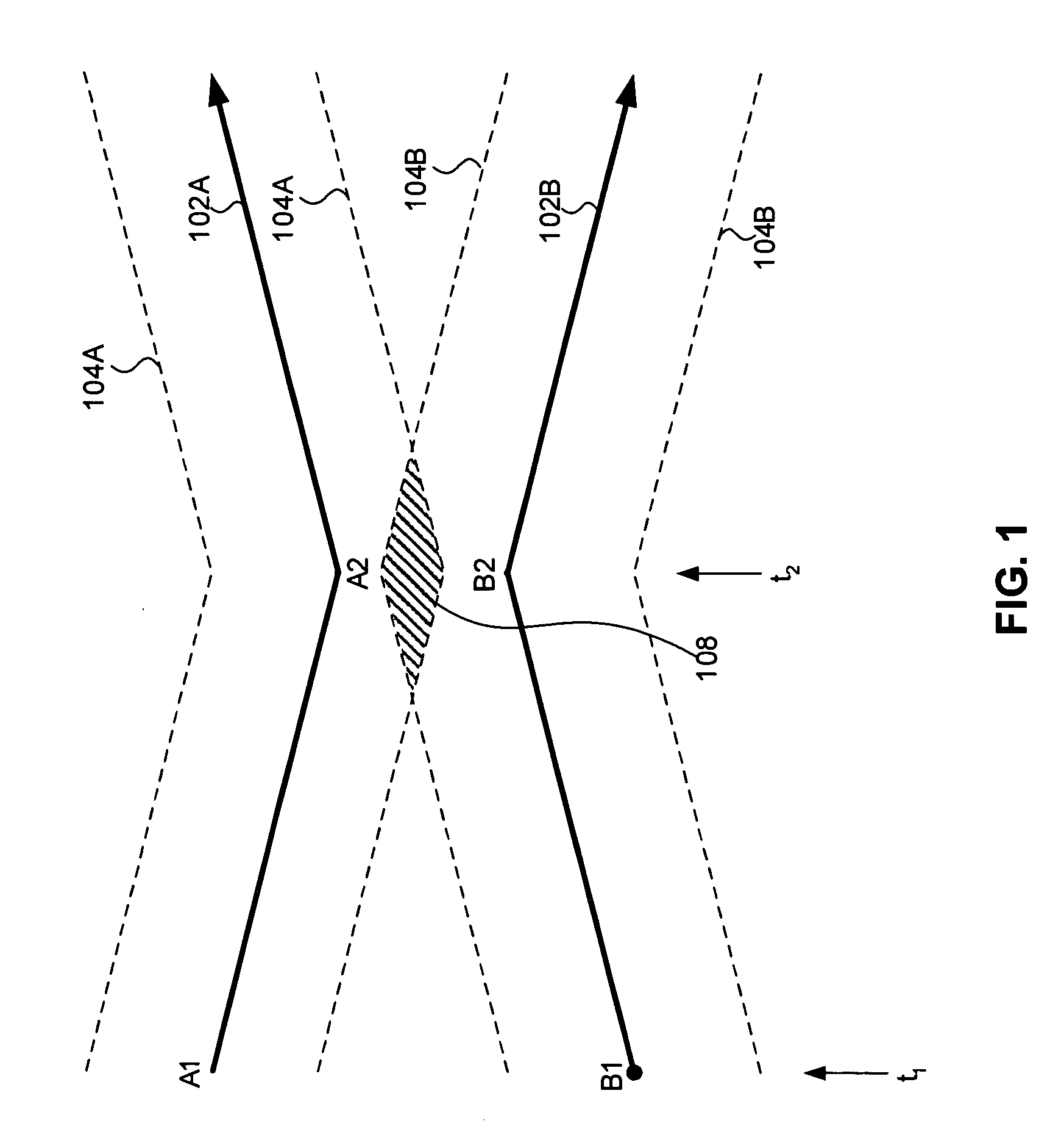
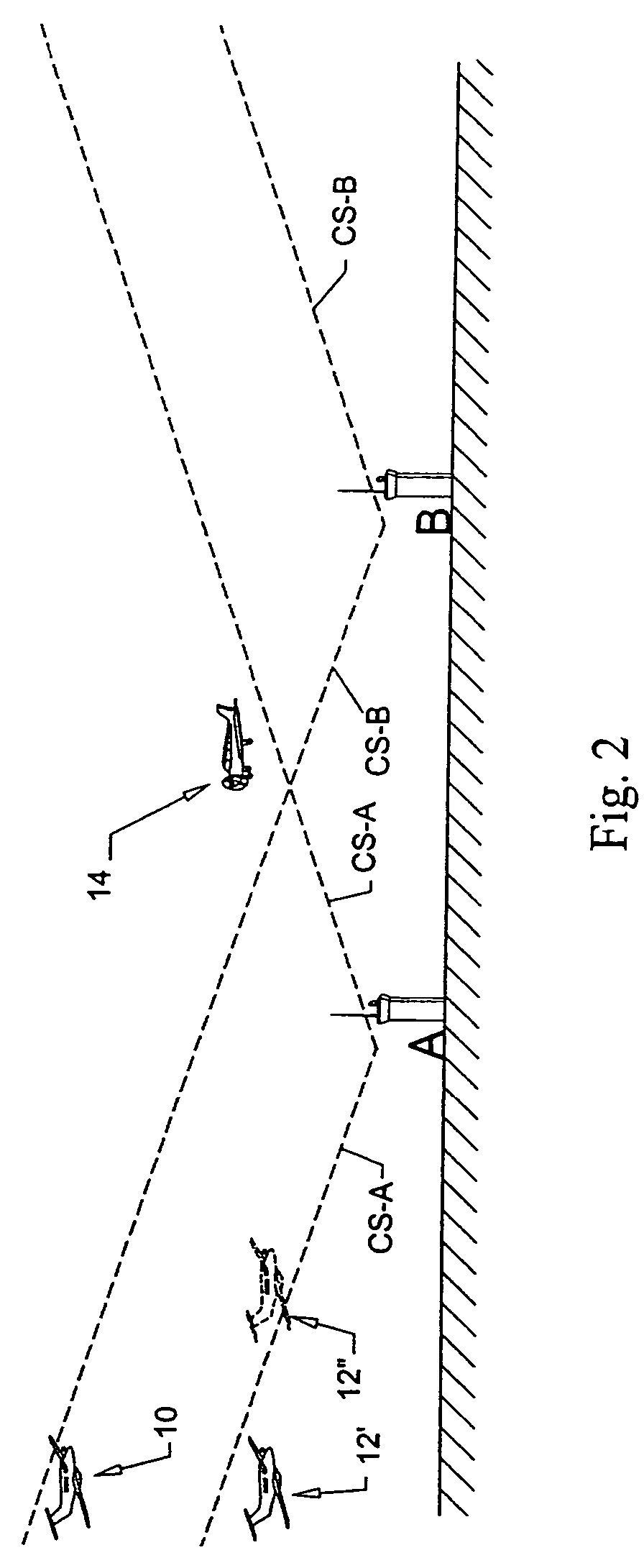
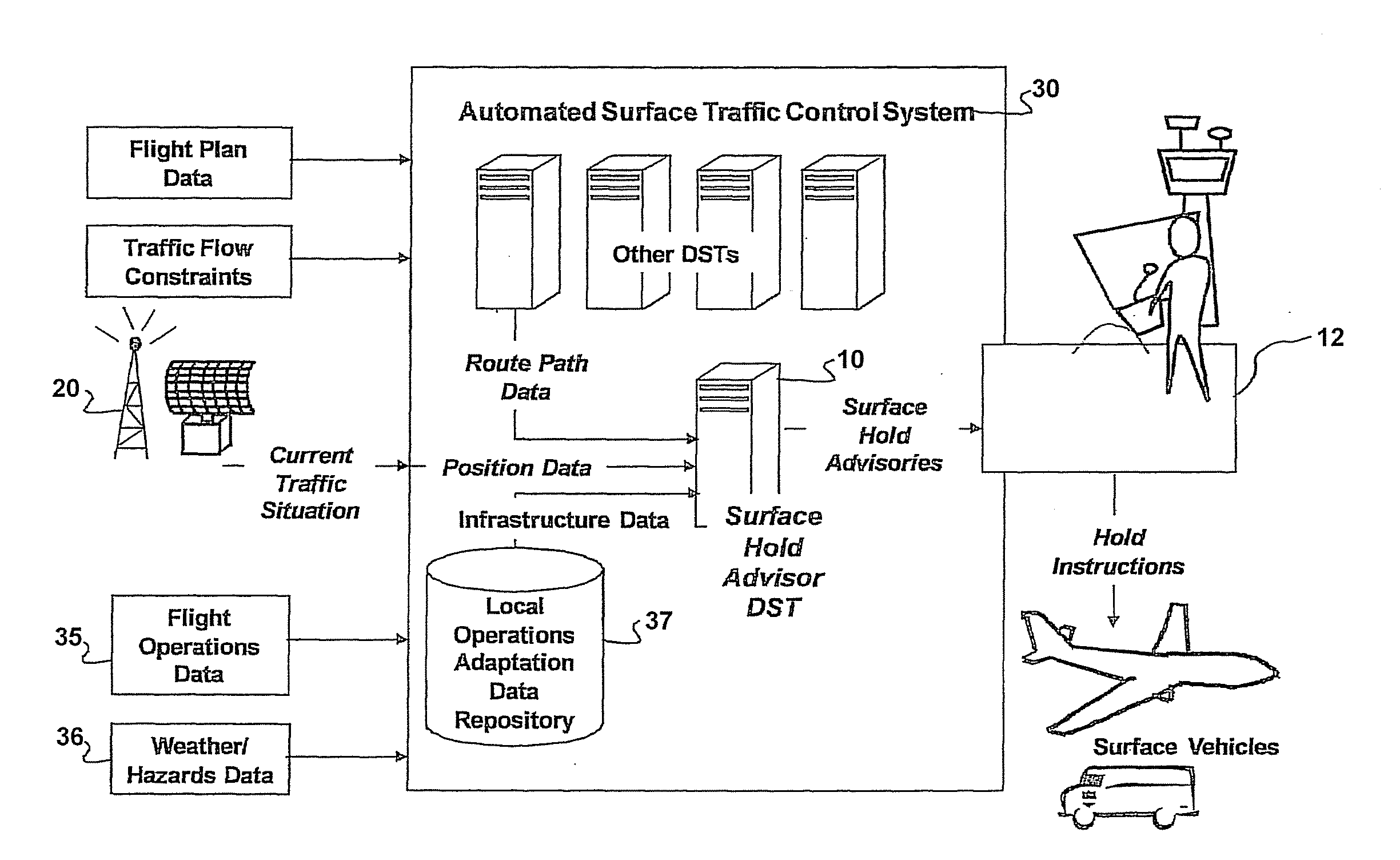
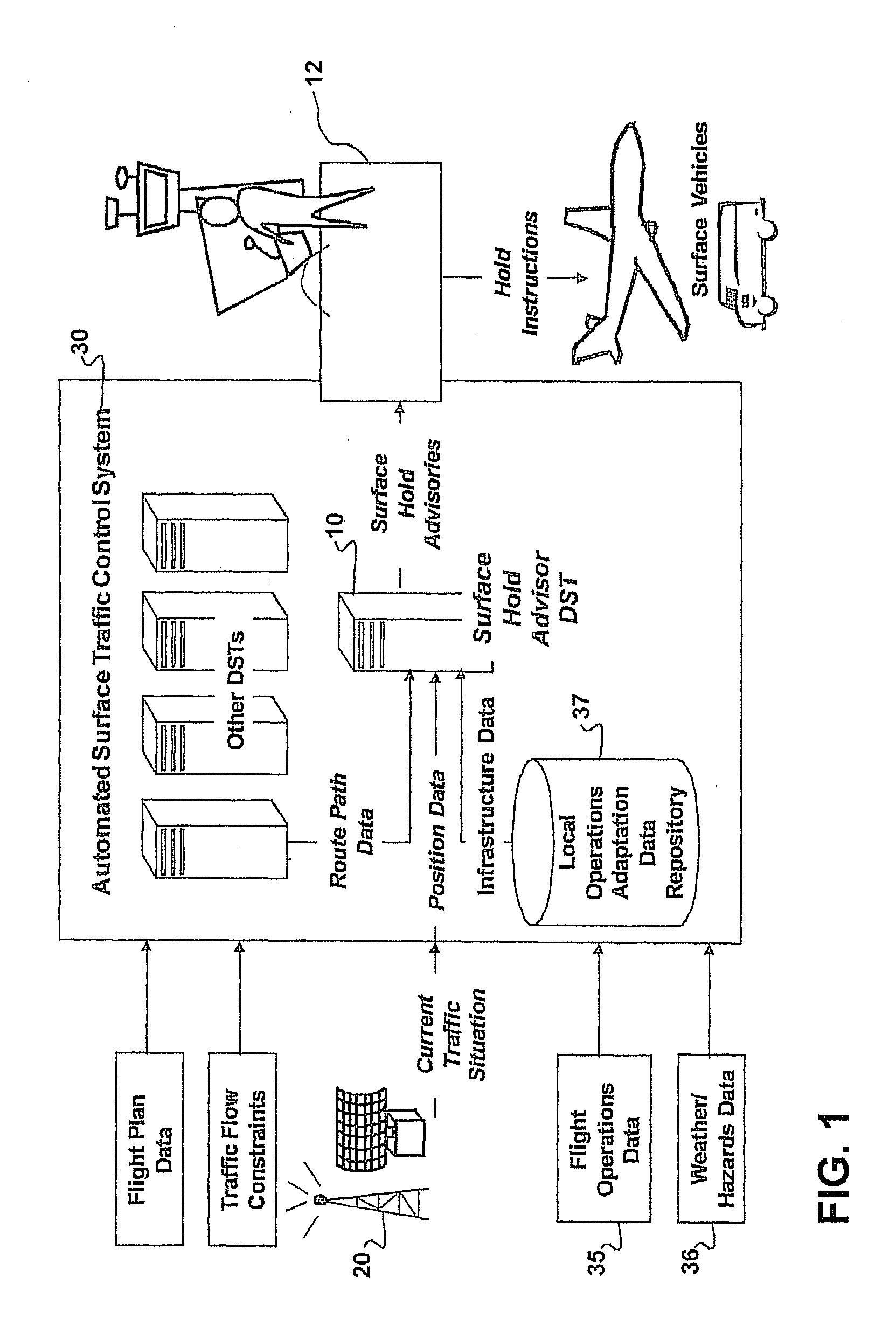
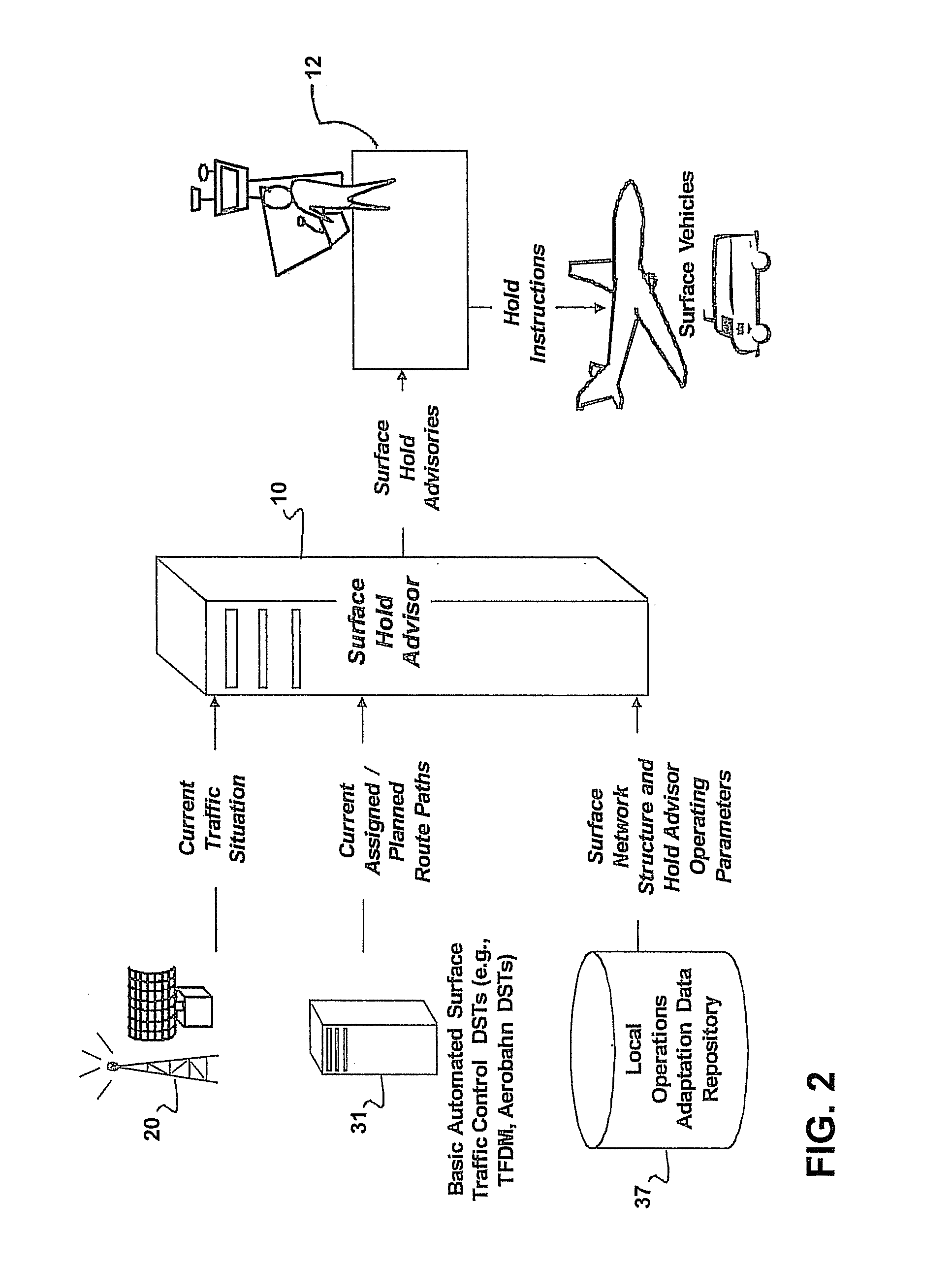
Surface hold advisor using critical sections
ActiveUS20110282565A1Avoid confictAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficRoad traffic controlTraffic network
The Surface Hold Advisor Using Critical Sections is a system and method for providing hold advisories to surface controllers to prevent gridlock and resolve crossing and merging conflicts among vehicles traversing a vertex-edge graph representing a surface traffic network on an airport surface. The Advisor performs pair-wise comparisons of current position and projected path of each vehicle with other surface vehicles to detect conflicts, determine critical sections, and provide hold advisories to traffic controllers recommending vehicles stop at entry points to protected zones around identified critical sections. A critical section defines a segment of the vertex-edge graph where vehicles are in crossing or merging or opposite direction gridlock contention. The Advisor detects critical sections without reference to scheduled, projected or required times along assigned vehicle paths, and generates hold advisories to prevent conflicts without requiring network path direction-of-movement rules and without requiring rerouting, rescheduling or other network optimization solutions.
Owner:ARCHITECTURE TECH
Determining corrective actions based upon broadcast of telematics data originating from another vehicle
ActiveUS9836963B1Instruments for road network navigationRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMobile vehicleSimulation
Owner:STATE FARM MUTAL AUTOMOBILE INSURANCE COMPANY
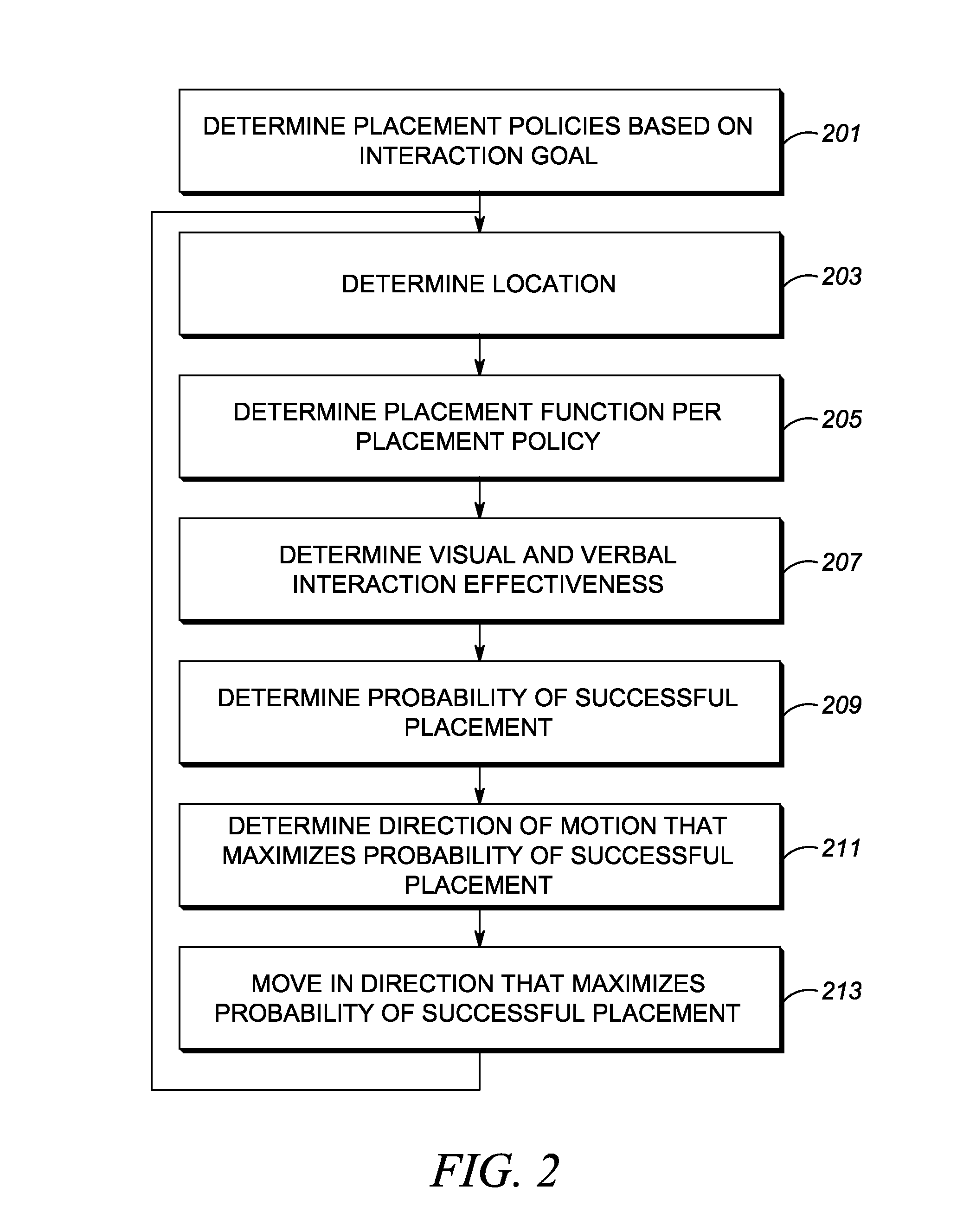
Method and apparatus for positioning an unmanned vehicle in proximity to a person or an object based jointly on placement policies and probability of successful placement
InactiveUS20150057917A1Maximize their success probabilityMaximize probabilityAutonomous decision making processComplex mathematical operationsObject basedComputer science
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Transportation network scheduling system and method
InactiveUS20130144467A1Weaken energyEmission reductionAnalogue computers for vehiclesData processing applicationsTraffic networkArrival time
A method includes forming a first schedule for a first vehicle to travel in a transportation network. The first schedule includes a first arrival time of the first vehicle at a scheduled location. The method also includes receiving a first trip plan for the first vehicle from an energy management system. The first trip plan is based on the first schedule and designates at least one of tractive efforts or braking efforts to be provided by the first vehicle to reduce at least one of an amount of energy consumed by the first vehicle or an amount of emissions generated by the first vehicle when the first vehicle travels through the transportation network to the scheduled location. The method further includes determining whether to modify the first schedule to avoid interfering with movement of one or more other vehicles by examining the trip plan for the first vehicle.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
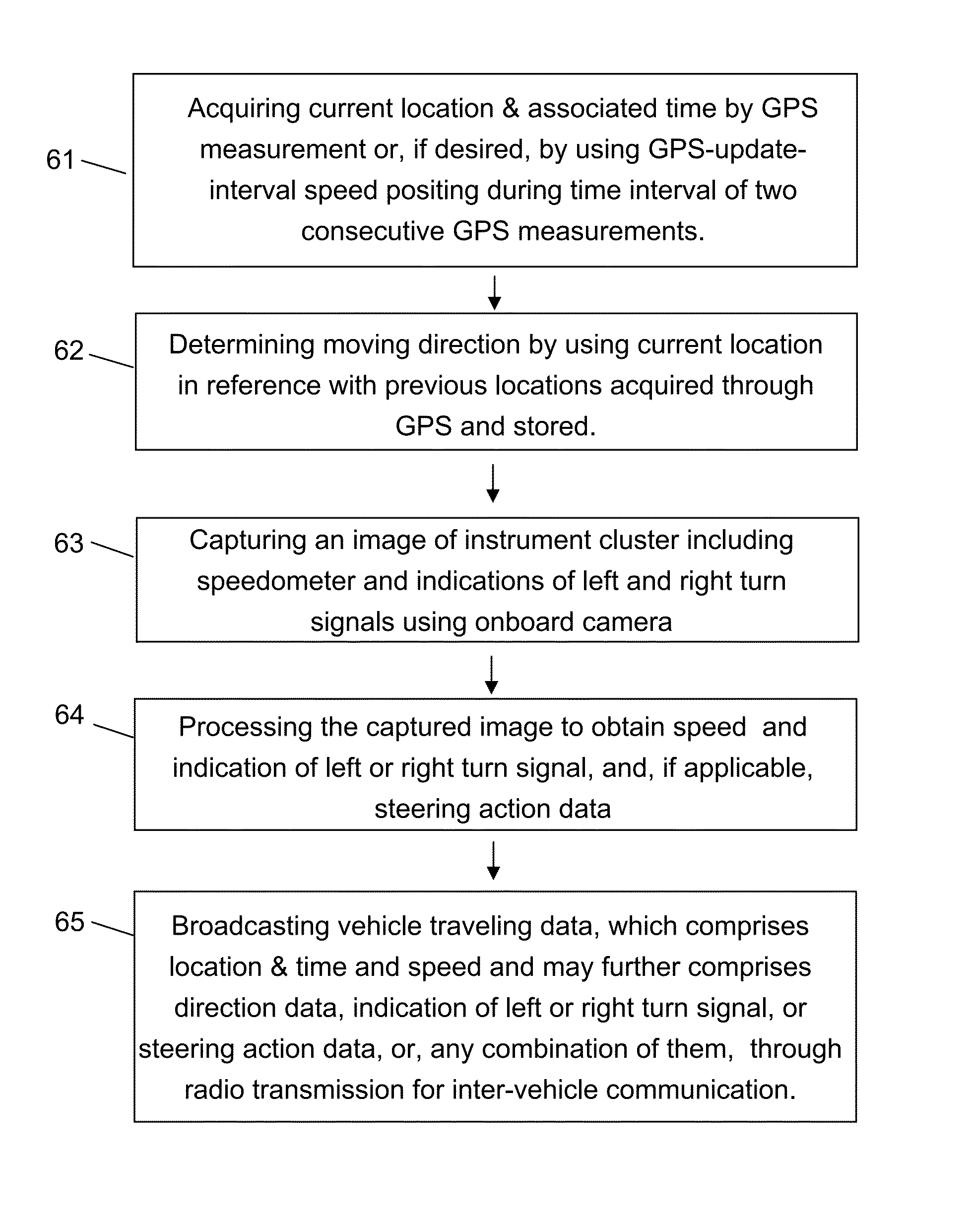
Methods for road safety enhancement using mobile communication device
InactiveUS8791835B2Improve accuracySufficiently accurateRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDetection of traffic movementSimulationBroadcasting
Methods for road safety enhancement use mobile communication device (MCD) onboard vehicle to share traveling data through inter-vehicle communication broadcasting, perform road hazard warning, enhance road navigation, and provide autonomous road assistance. The methods have a variety of vehicle status data, such as moving data, steering data, or indicator data, obtained through GPS or image capturing and recognition of instrument cluster of vehicle. The image capturing and recognition allows to get speed data from indication of speedometer, indication of left or right turn signal, steering action data corresponding to steering wheel rotation, and light-on indication of system status indicators. To facilitate that, the MCD may be placed in front of steering wheel, and, if applicable, also in coupling with movement of steering wheel. The MCD may perform relative positioning map-matching lane correlation and GPS-update-interval speed positioning to improve data quality regarding vehicle moving status.
Owner:ZHANG WEI
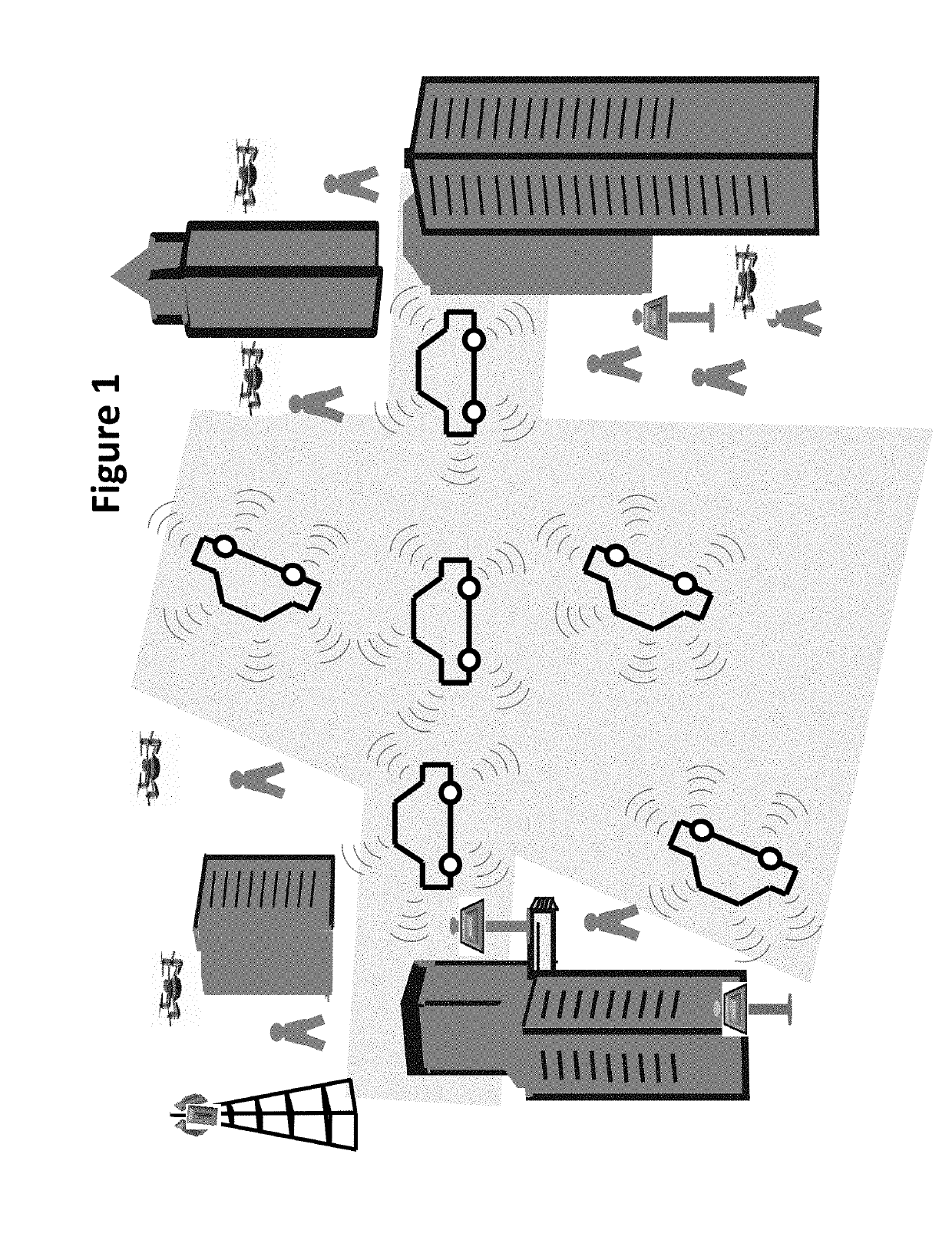
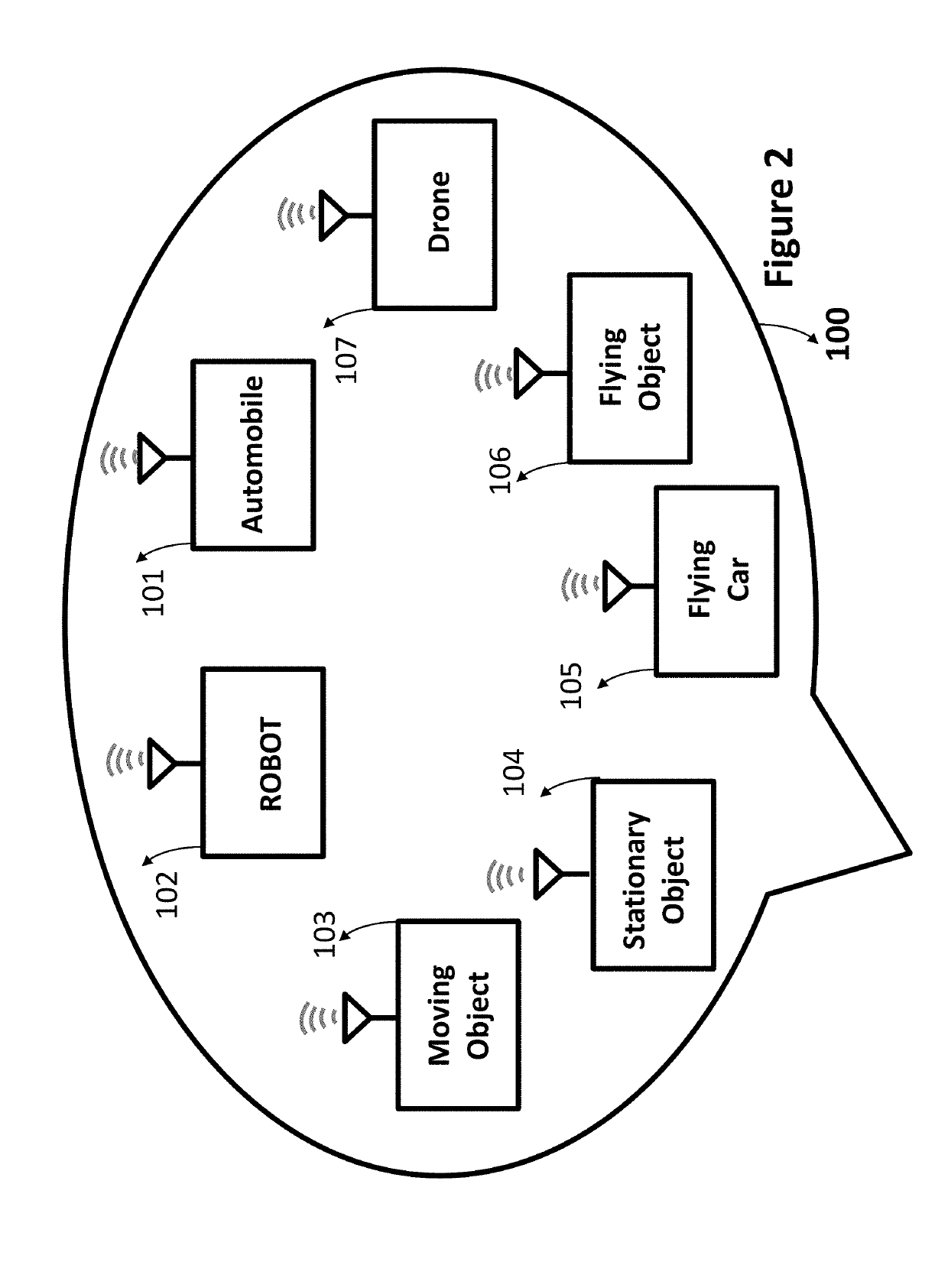
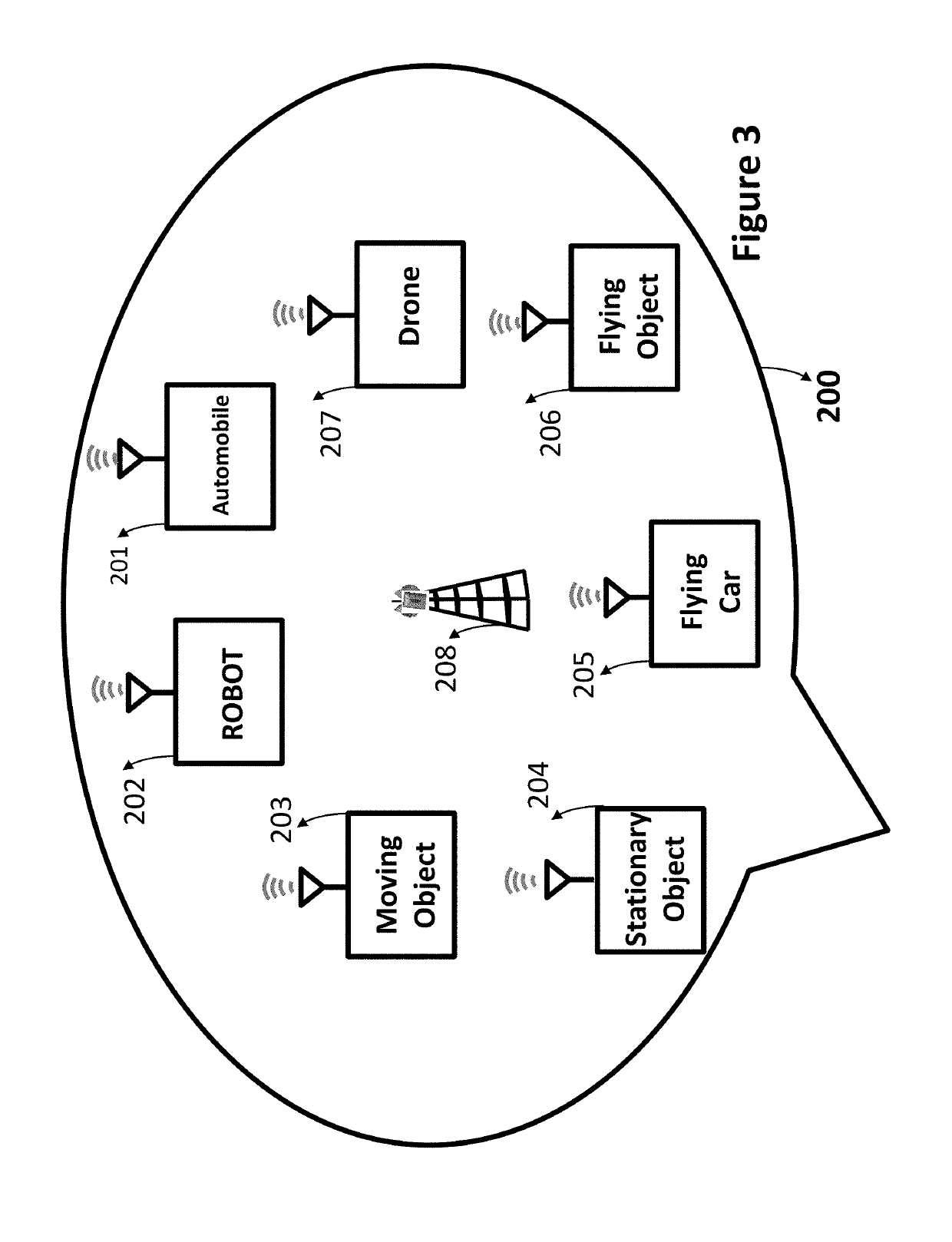
Moving vehicles in a smart environment
ActiveUS20190311625A1Improve accuracyReduce complexityDetection of traffic movementParticular environment based servicesIntelligent environmentMobile vehicle
Smart environments represent the next evolutionary development step in transportation systems. Like any functioning organism, the smart environment relies first and foremost on sensory data from the real world. Sensory data comes from multiple sensors of different modalities in distributed locations. Sensors used by various moving, flying and stationary objects exchange information through broadcasting or indirectly through public or private networks. The information helps various moving vehicles and stationary objects coexist and operate freely without any interruption, interference, and collision.
Owner:ANVARI KIOMARS
Implementing A Restricted-Operation Region For Unmanned Vehicles
ActiveCN106023657ABeacon systems using radio wavesParticular environment based servicesTransmitterReal-time computing
Embodiments are directed to a system for implementing a restricted-operation region. The system includes an instruction development module configured to be utilized in the development of a set of instructions that implement an operation policy of the restricted-operation region. The set of instructions is configured to, when interpreted, implement the operation policy by controlling at least one function of a vehicle that attempts to operate within the restricted-operation region. The system further includes a first transmitter configured to transmit the set of instructions to the vehicle, wherein a processor of the vehicle is configured to interpret the set of instructions based at least in part on a determination that the vehicle is attempting to operate within the restricted-operation region.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Unmanned aerial vehicles and related methods and systems
ActiveUS20190051169A1Unmanned aerial vehiclesRoad vehicles traffic controlDisplay deviceUnmanned air vehicle
Unmanned aerial vehicles and related methods and systems are disclosed. An example unmanned aerial vehicle, comprising: a body and a propulsion source to propel the unmanned aerial vehicle during flight; and a display carried by the unmanned aerial vehicle to display a message to coordinate traffic, the display actuatable between a deployed position to enable the message to be conveyed and a stowed position in which aerodynamics of the unmanned aerial vehicle are enhanced.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System and method for identifying manoeuvres for a vehicle in conflict situations
InactiveCN101427288AMarine craft traffic controlSimultaneous traffic control systemsSimulationArtificial intelligence
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Autonomous Team Formation and Task Negotiation Among Unmanned Vehicles
ActiveUS20180101171A1Autonomous decision making processParticular environment based servicesCommunications systemReceipt
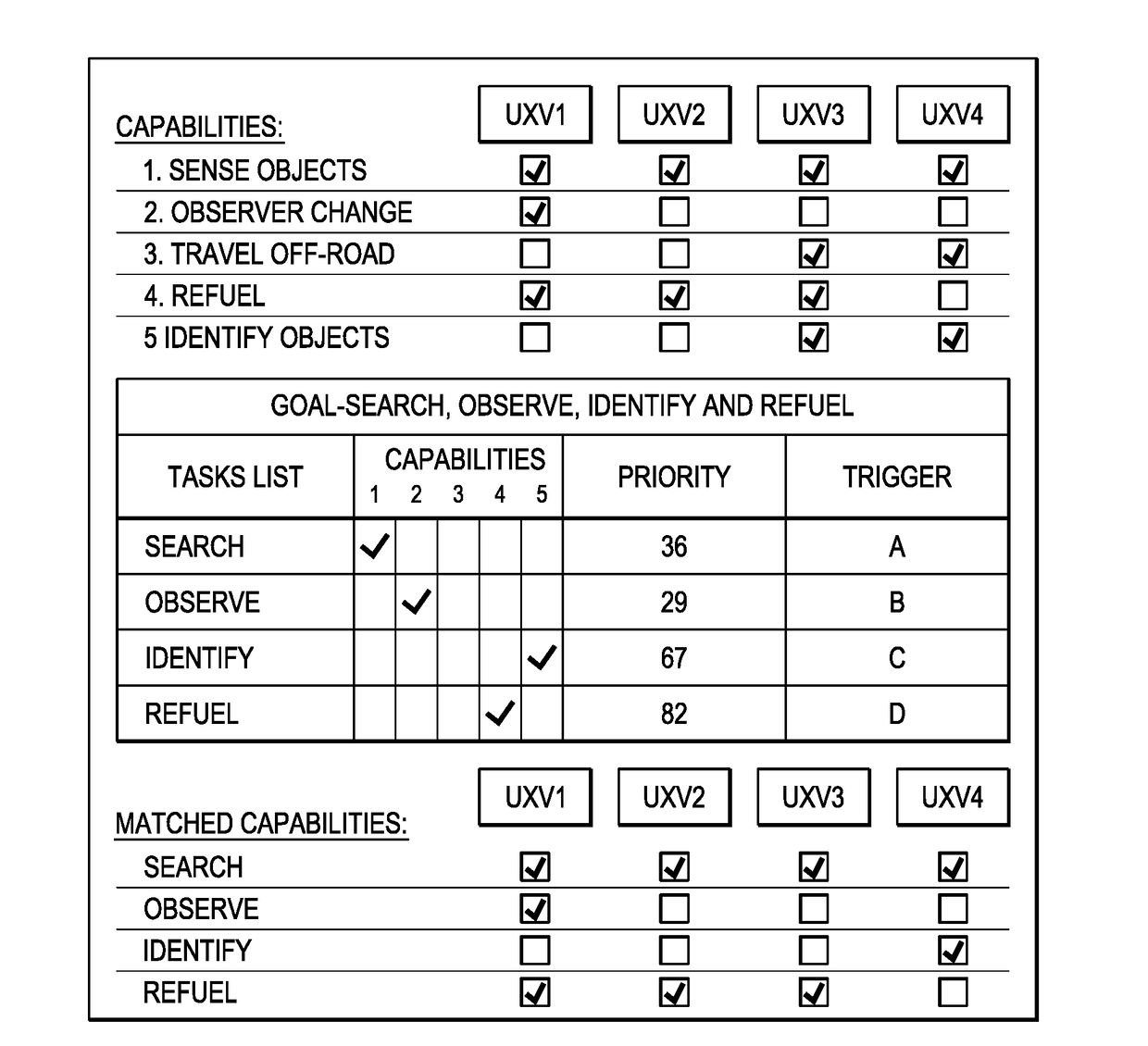
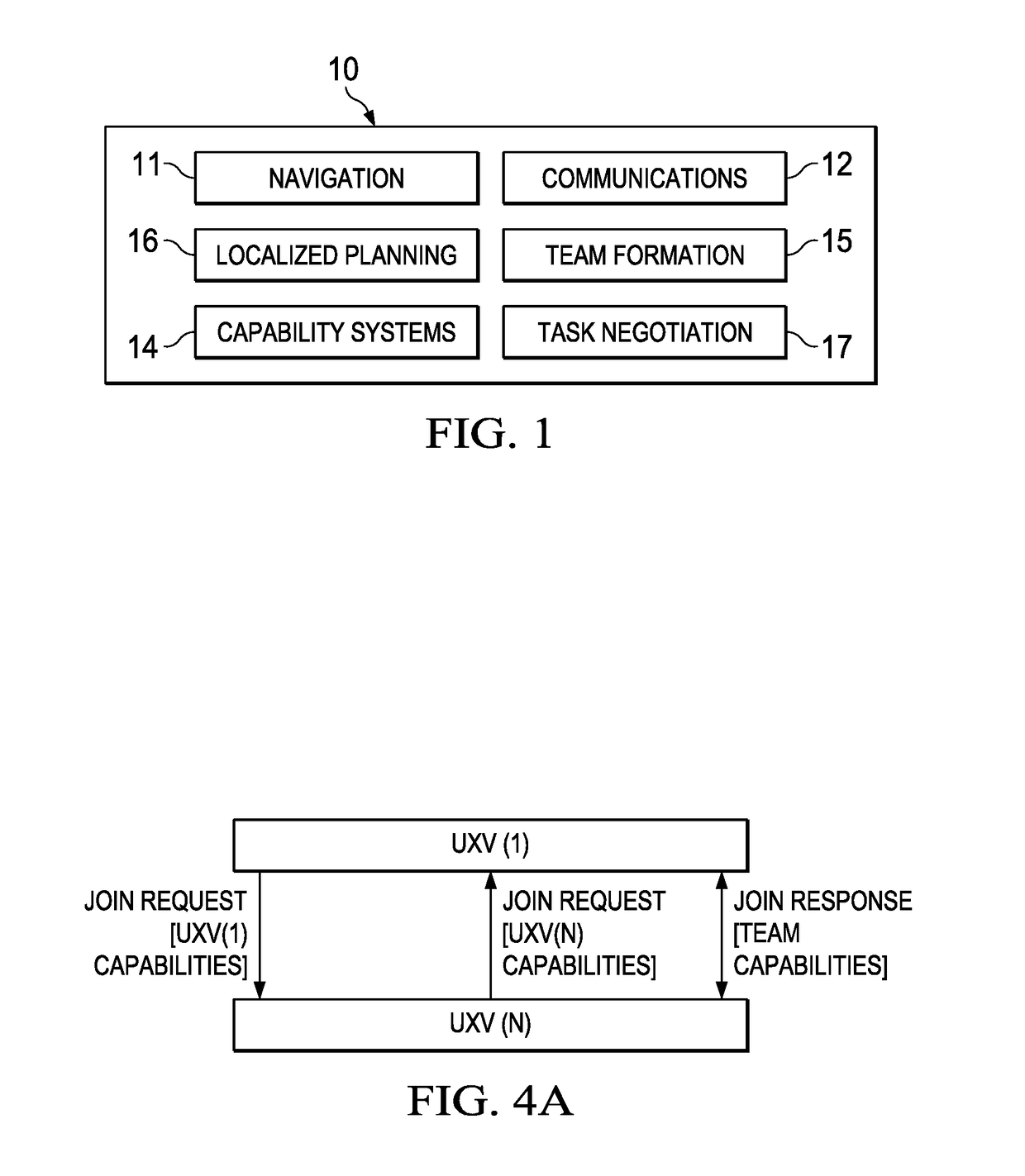
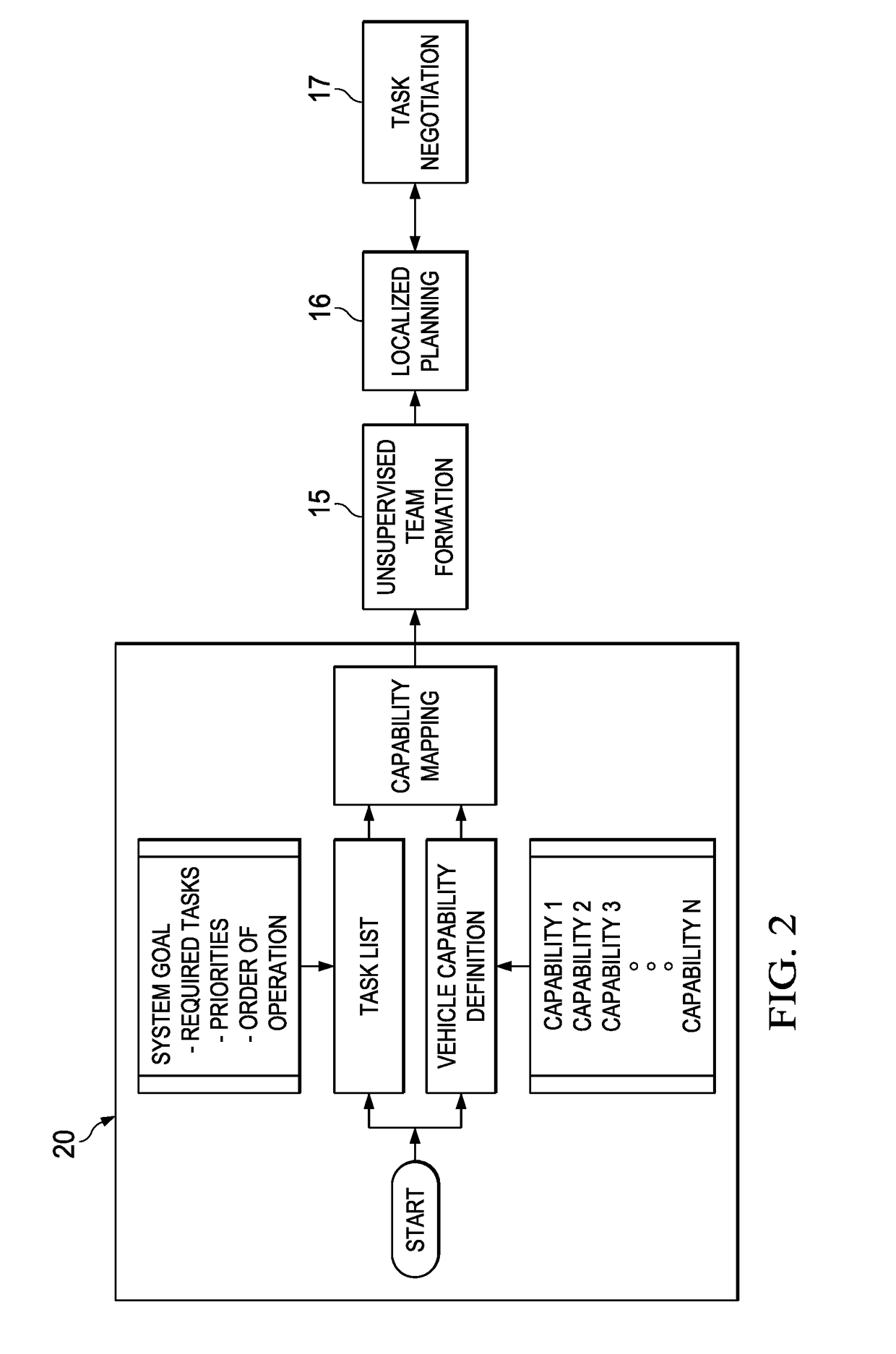
A system of autonomous vehicles for forming a team of autonomous vehicles to perform a designated set of tasks. Each vehicle stores data representing its own capabilities that match the tasks, data representing needed capabilities for the team to perform the tasks, and data representing the capabilities of all current team members. Each of the vehicles is equipped with a communications system operable to send and receive join request messages and join response messages. All join request message contain the capabilities of the sending vehicle. All join response messages contain current team capabilities data. Upon receipt of a join request message, a vehicle compares needed capabilities data to the received capabilities data, and if there are matched capabilities, it updates the team capabilities data and transmits a join response message. Upon receipt of a join response message, if the message indicates the sending vehicle has joined the team, the receiving vehicle updates the team capabilities list.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Procedure to minimize the risk of mid-air collision for personal air vehicles
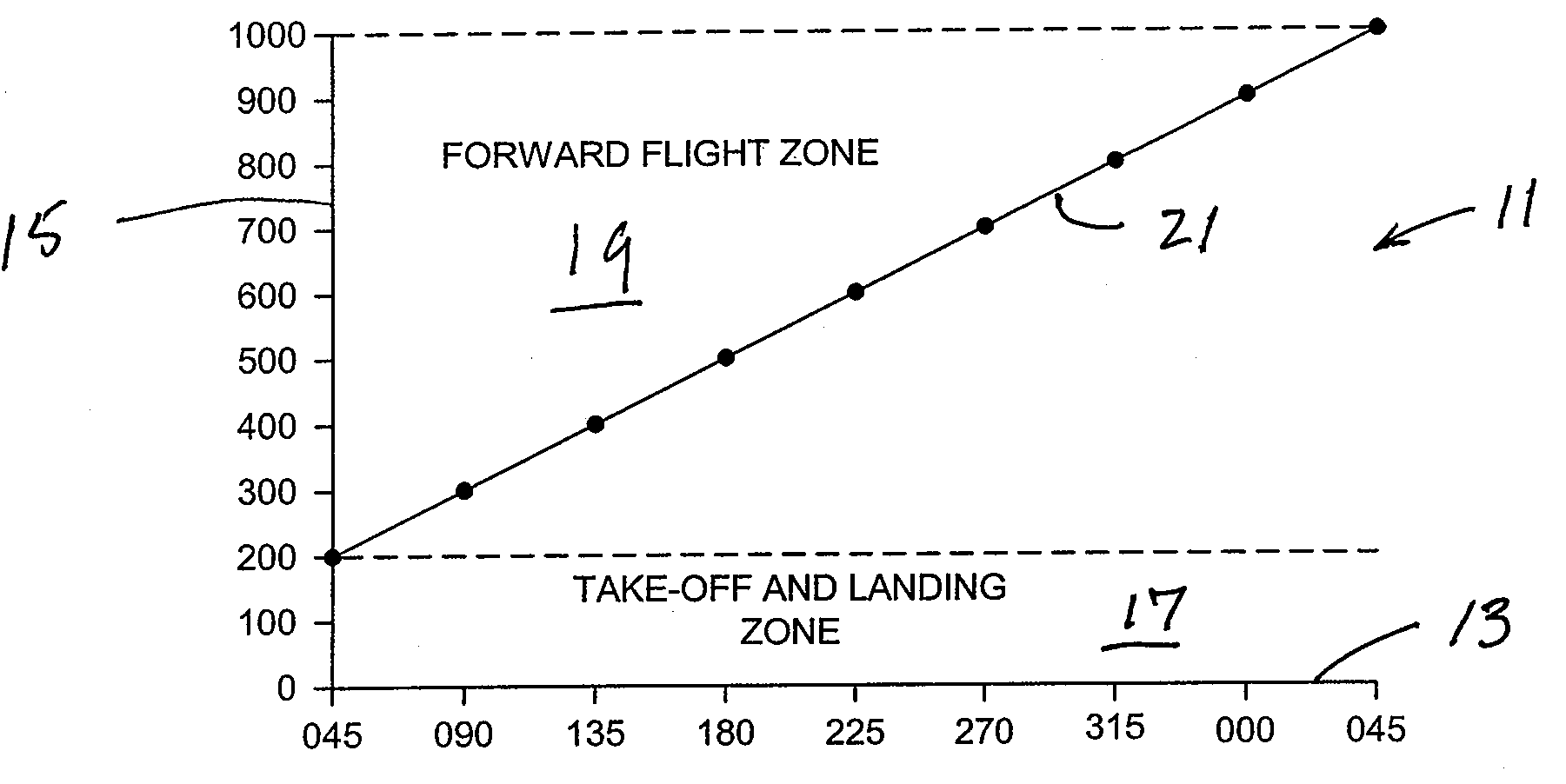
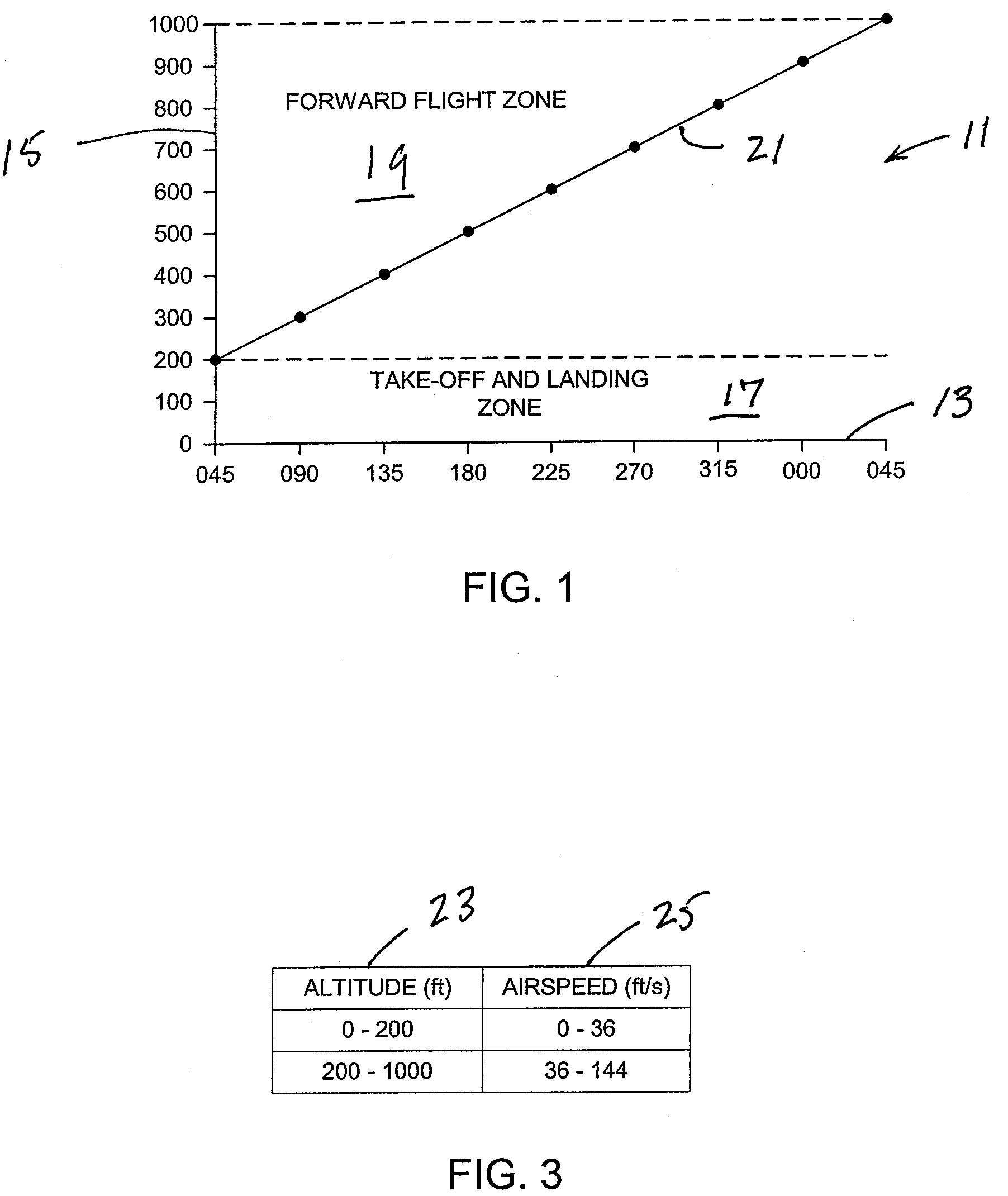
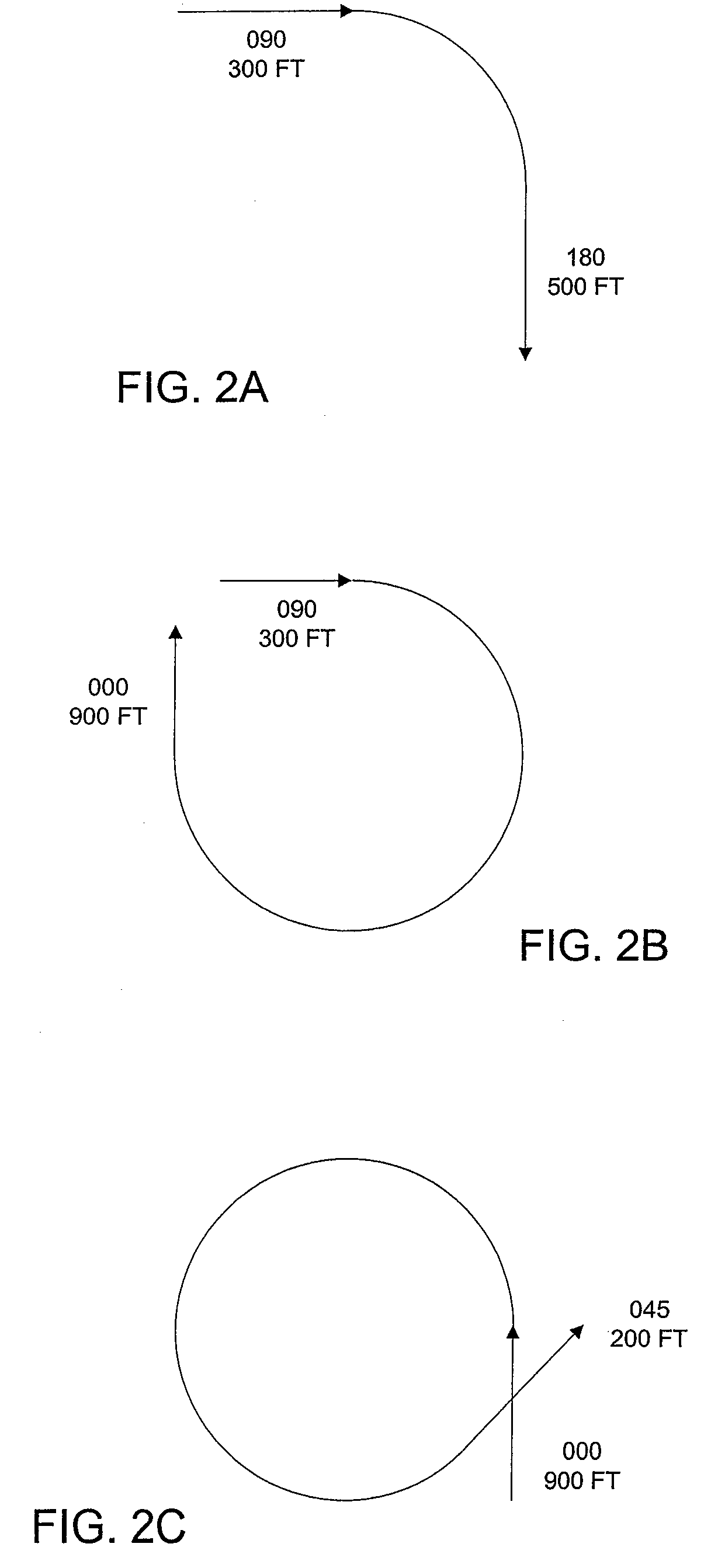
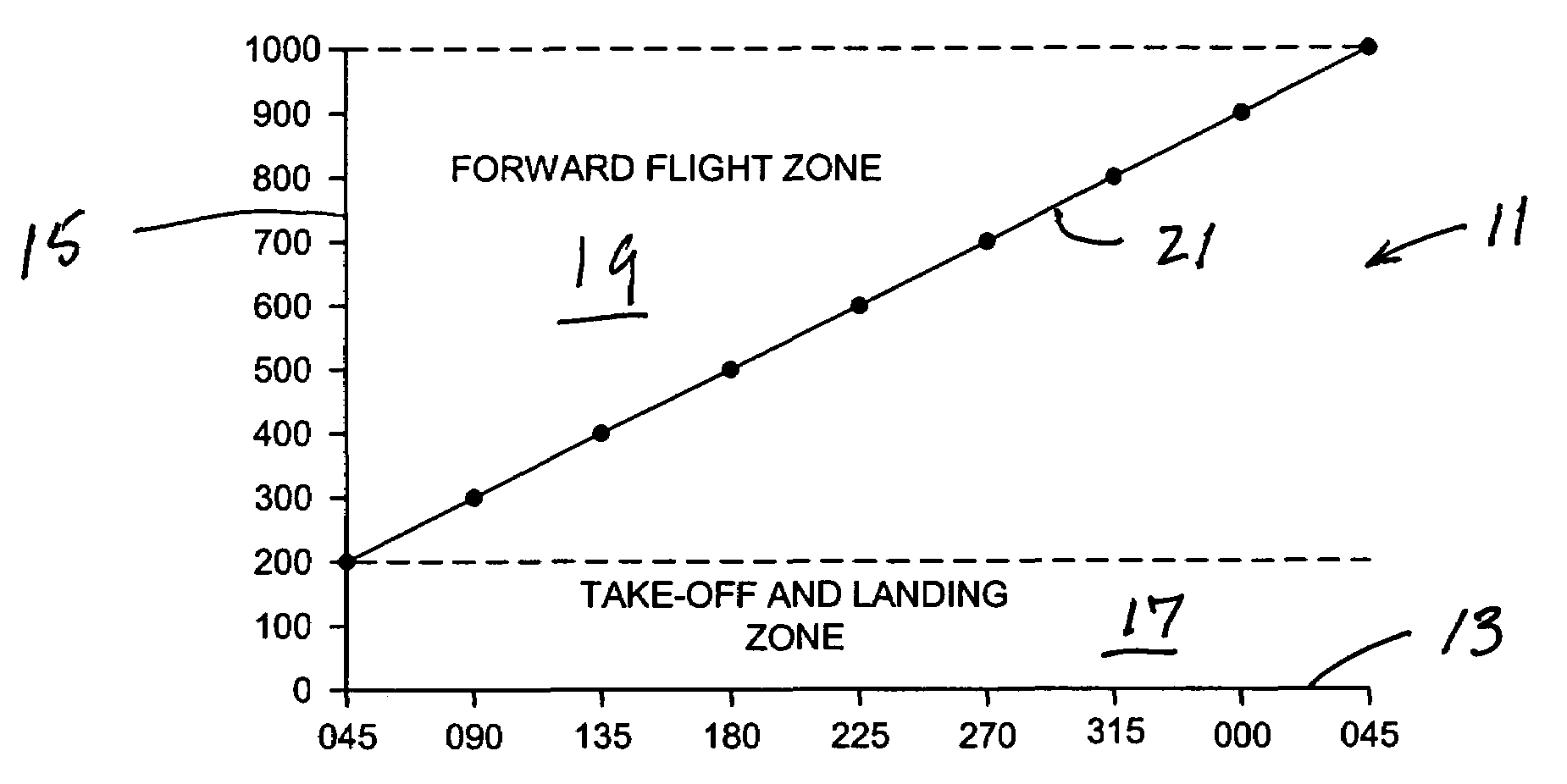
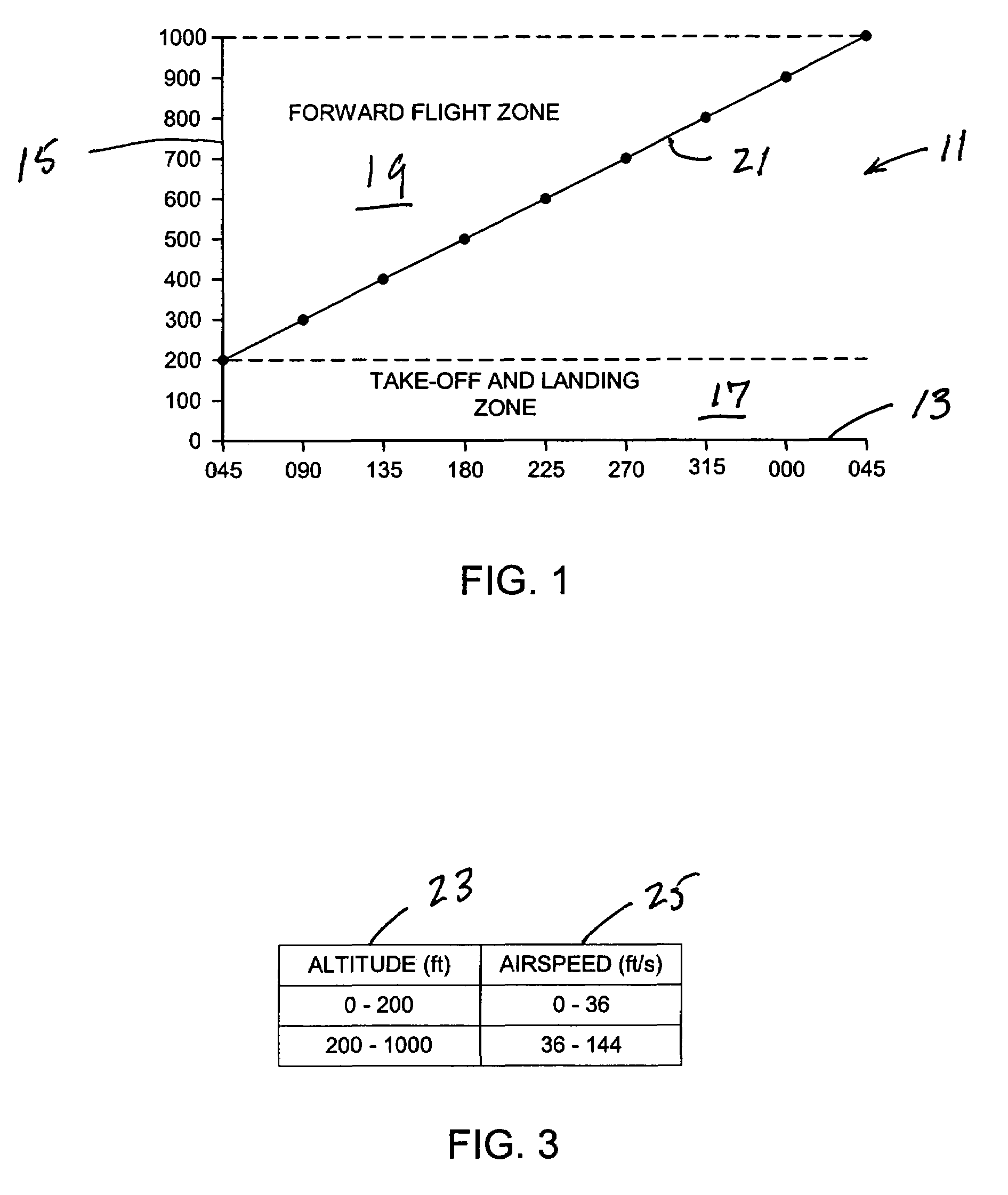
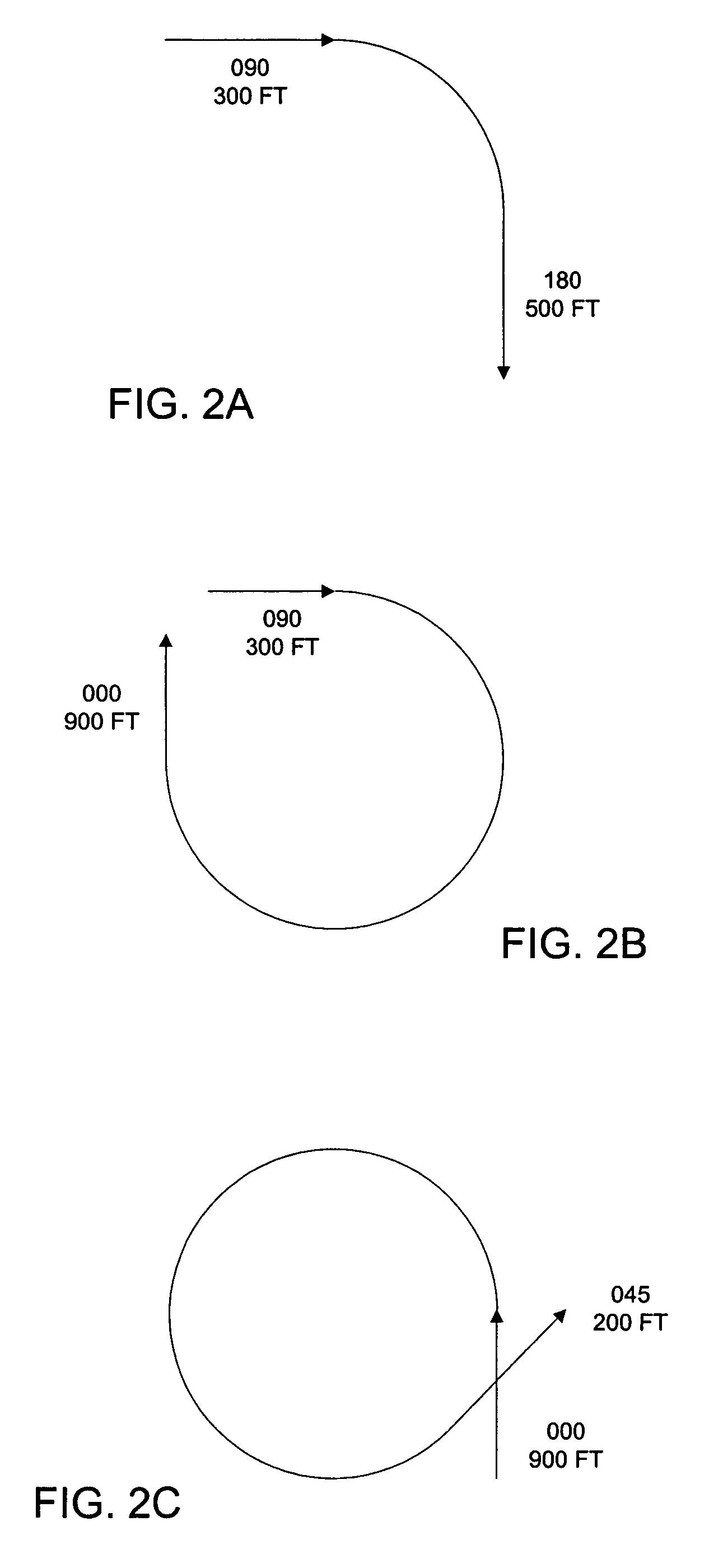
ActiveUS7676304B2Reduce riskAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficFlight vehicleLanding zone
A method of and a system for controlling personal air vehicle (PAV) traffic provides a take-off-and-landing zone, and a forward flight zone. The take-off-and-landing zone may be from the ground up to a first altitude. The forward flight zone may be from the first altitude up to a second altitude. A maximum airspeed is provided in the take-off-and-landing zone. Minimum and maximum airspeeds are provided in the forward flight zone. In the forward flight zone there is a single heading for each altitude. Any change in heading must be accompanied by a change in altitude.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Procedure to minimize the risk of air collision for personal mid-air vehicles
ActiveUS7389163B1Reduce riskReduced risk of collisionAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficFlight vehicleLanding zone
A method of and a system for controlling personal air vehicle (PAV) traffic provides a take-off-and-landing zone, and a forward flight zone. The take-off-and-landing zone may be from the ground up to a first altitude. The forward flight zone may be from the first altitude up to a second altitude. A maximum airspeed is provided in the take-off-and-landing zone. Minimum and maximum airspeeds are provided in the forward flight zone. In the forward flight zone there is a single heading for each altitude. Any change in heading must be accompanied by a change in altitude.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Transportation scheduling system and method
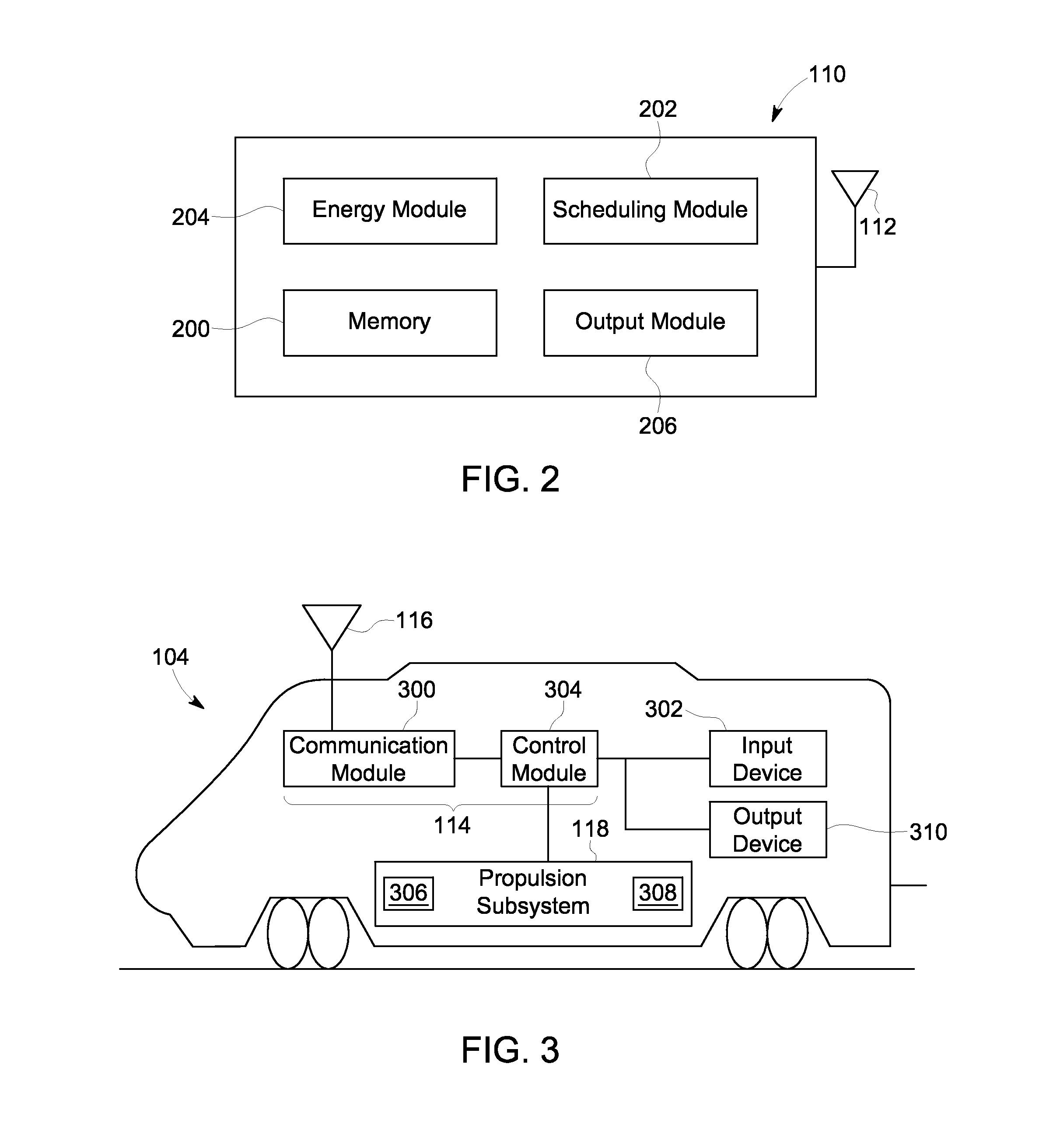
InactiveUS20130131968A1Less energyAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficEngineeringTransportation scheduling
A system includes an energy module and a scheduling module. The energy module is configured to determine a first consumption parameter representative of a first amount of energy that is projected to be expended by a first vehicle during an upcoming movement event involving the first vehicle. The energy module is configured to determine the first consumption parameter as the first vehicle moves along a route toward a destination location and prior to the first vehicle taking part in the upcoming movement event. The scheduling module is configured to receive the first consumption parameter from the energy module and to at least one of create or modify a first schedule for the first vehicle to move along the route based on the first consumption parameter.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com