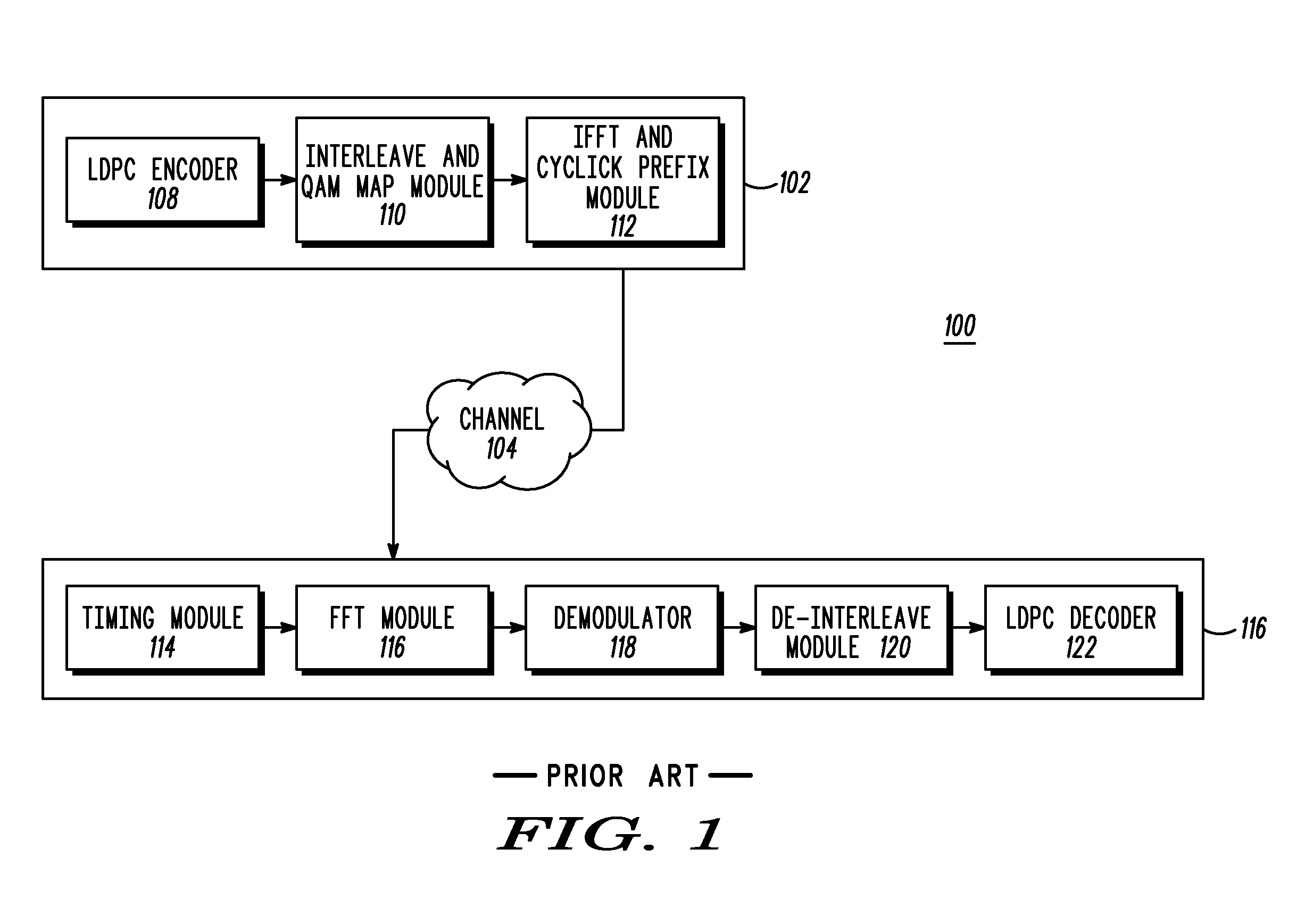
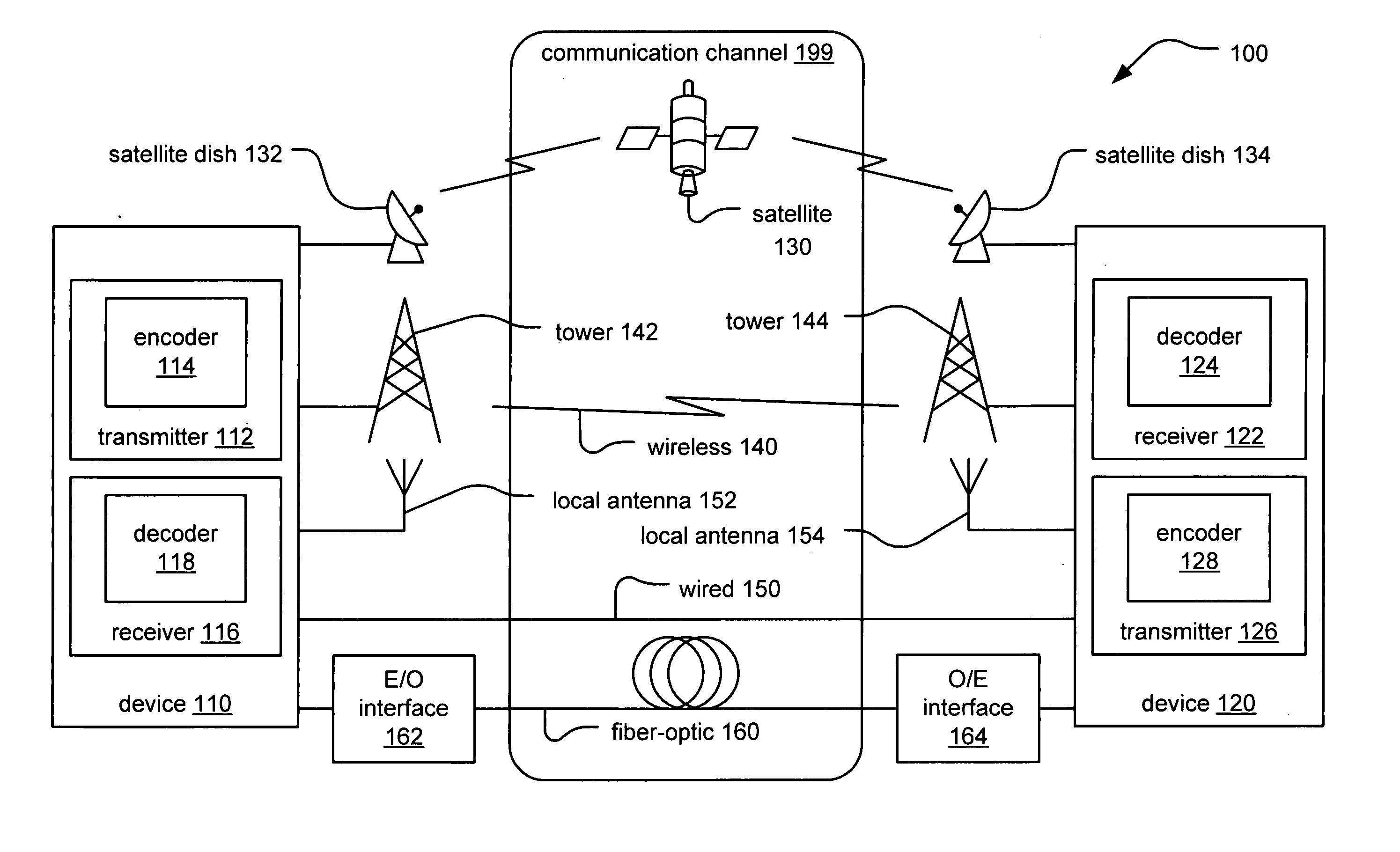
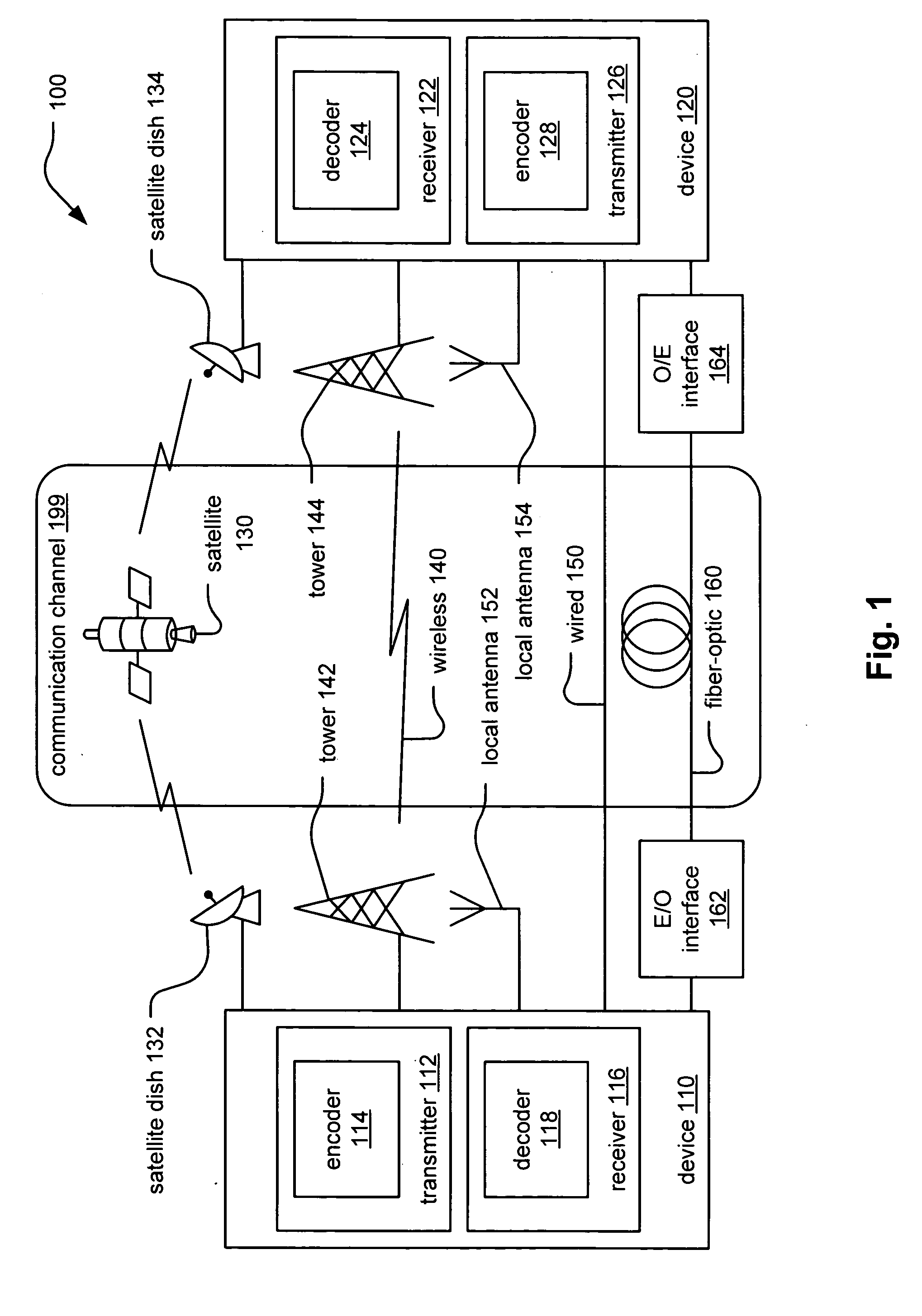
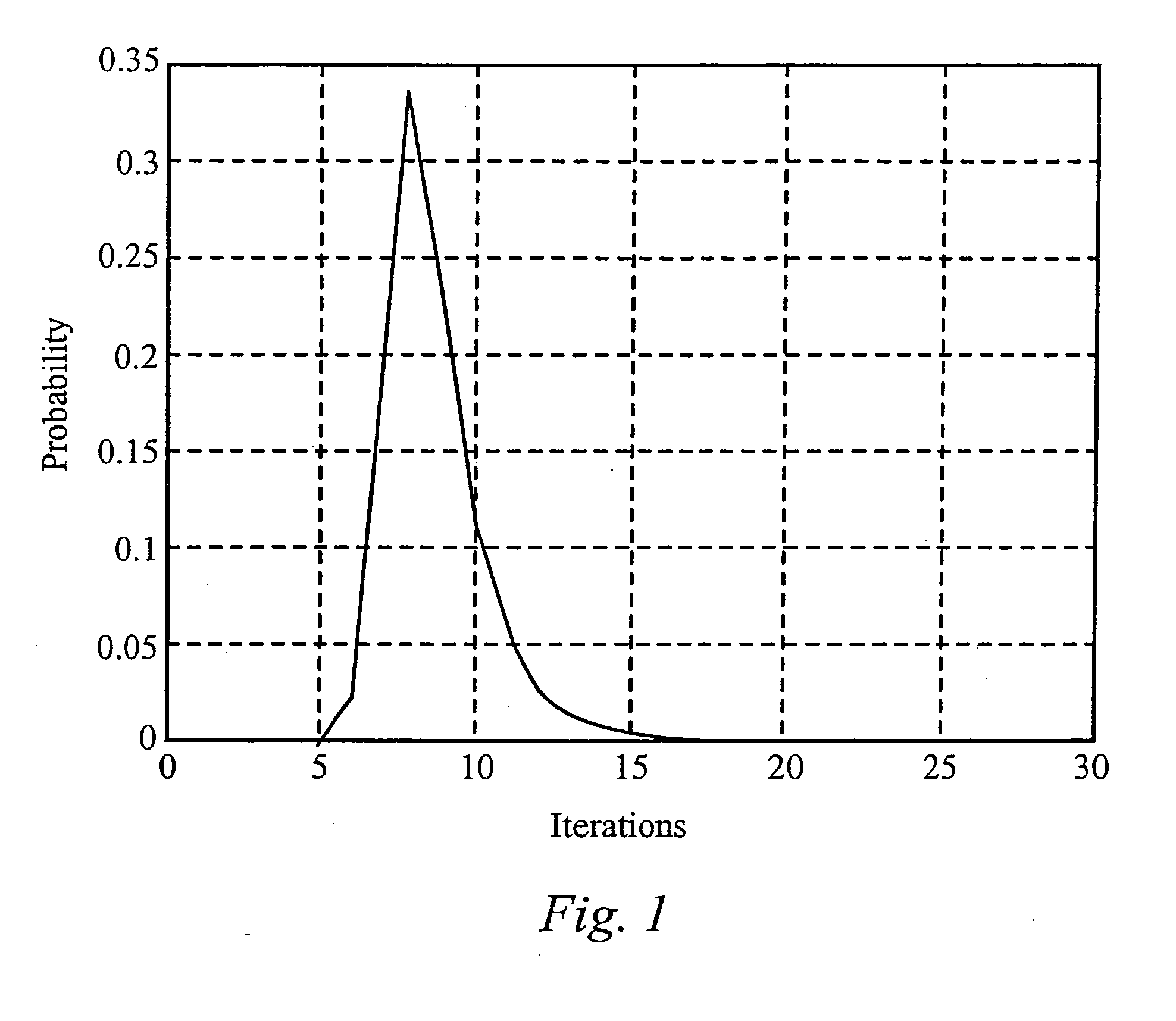
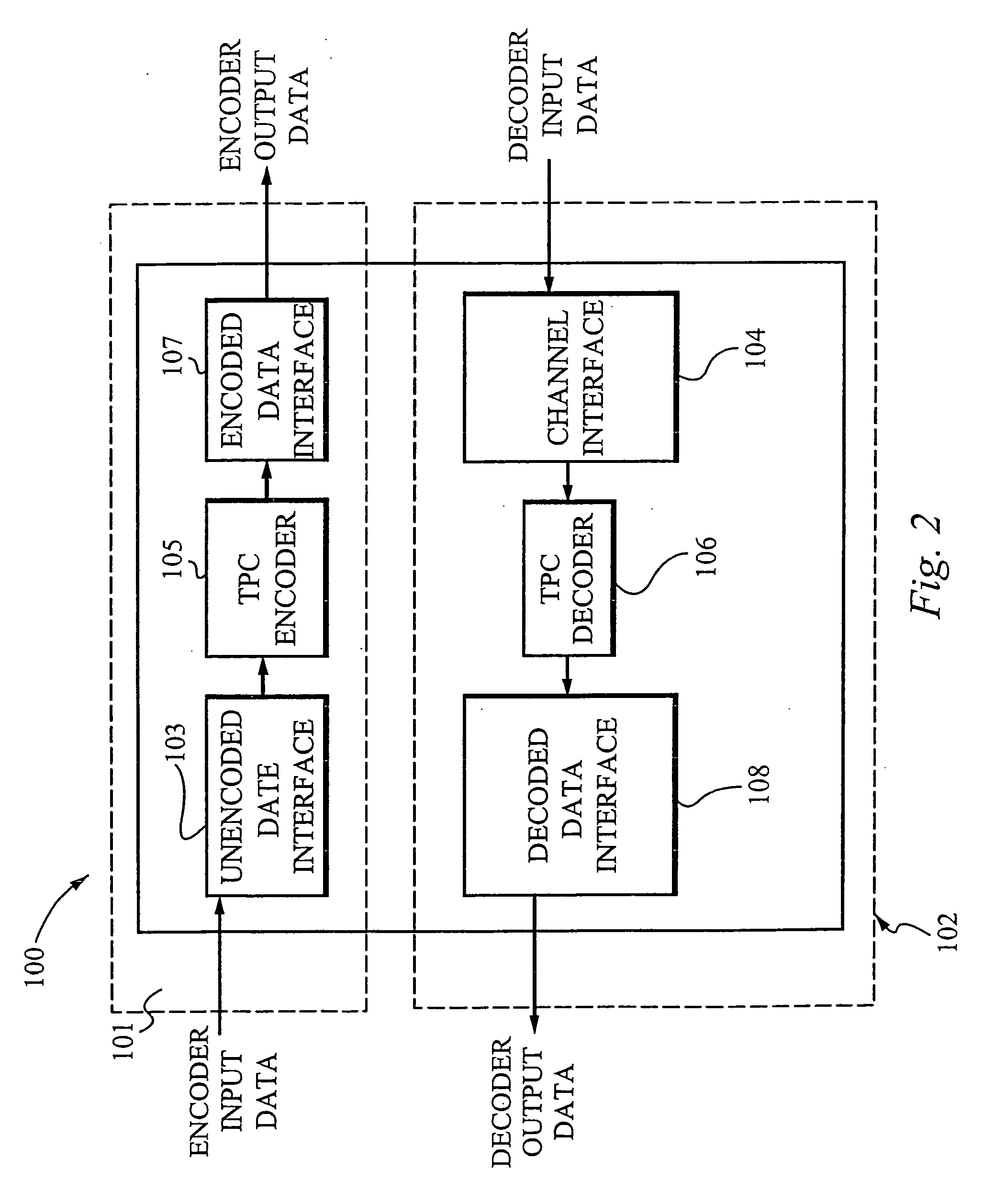
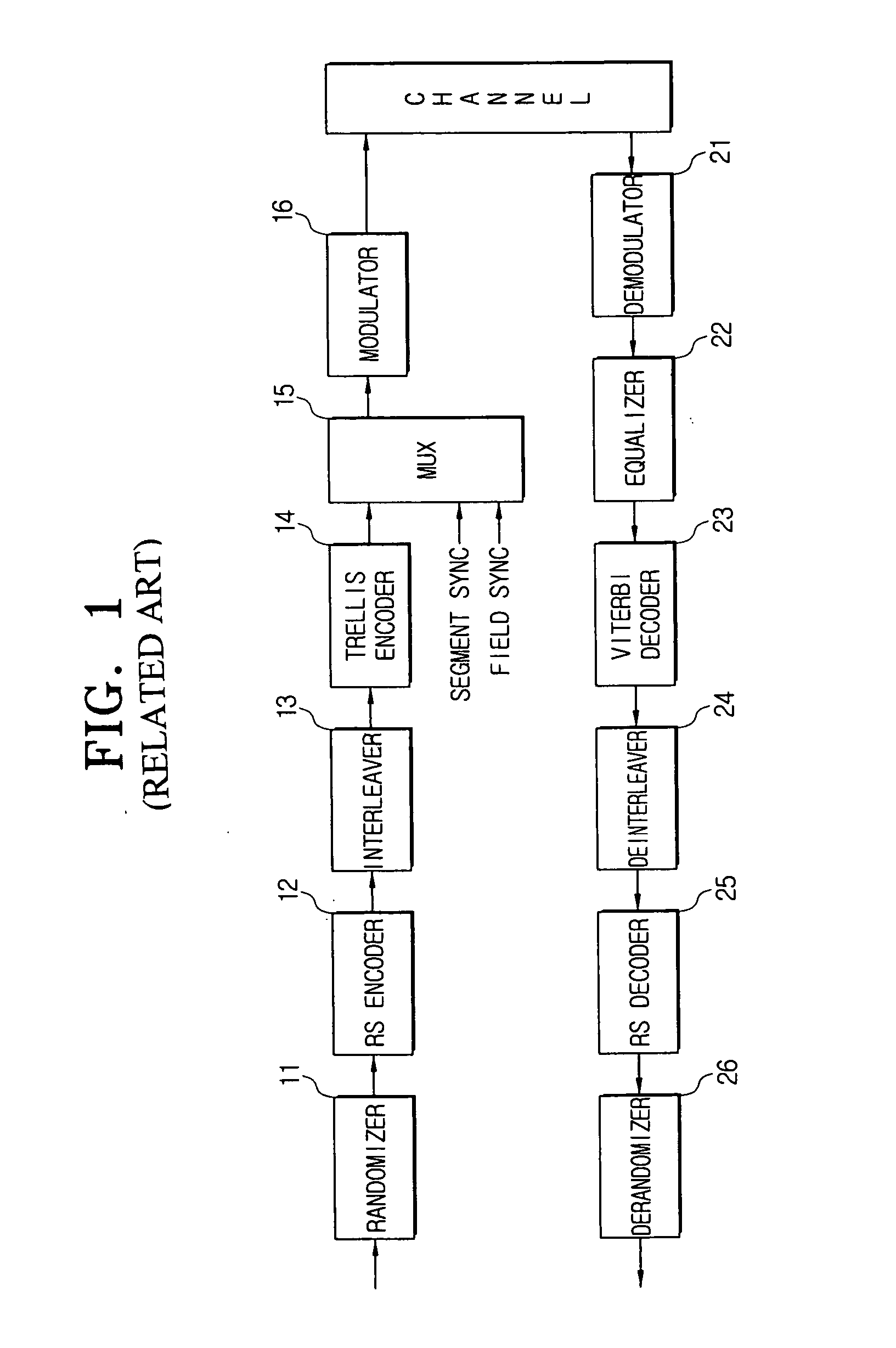
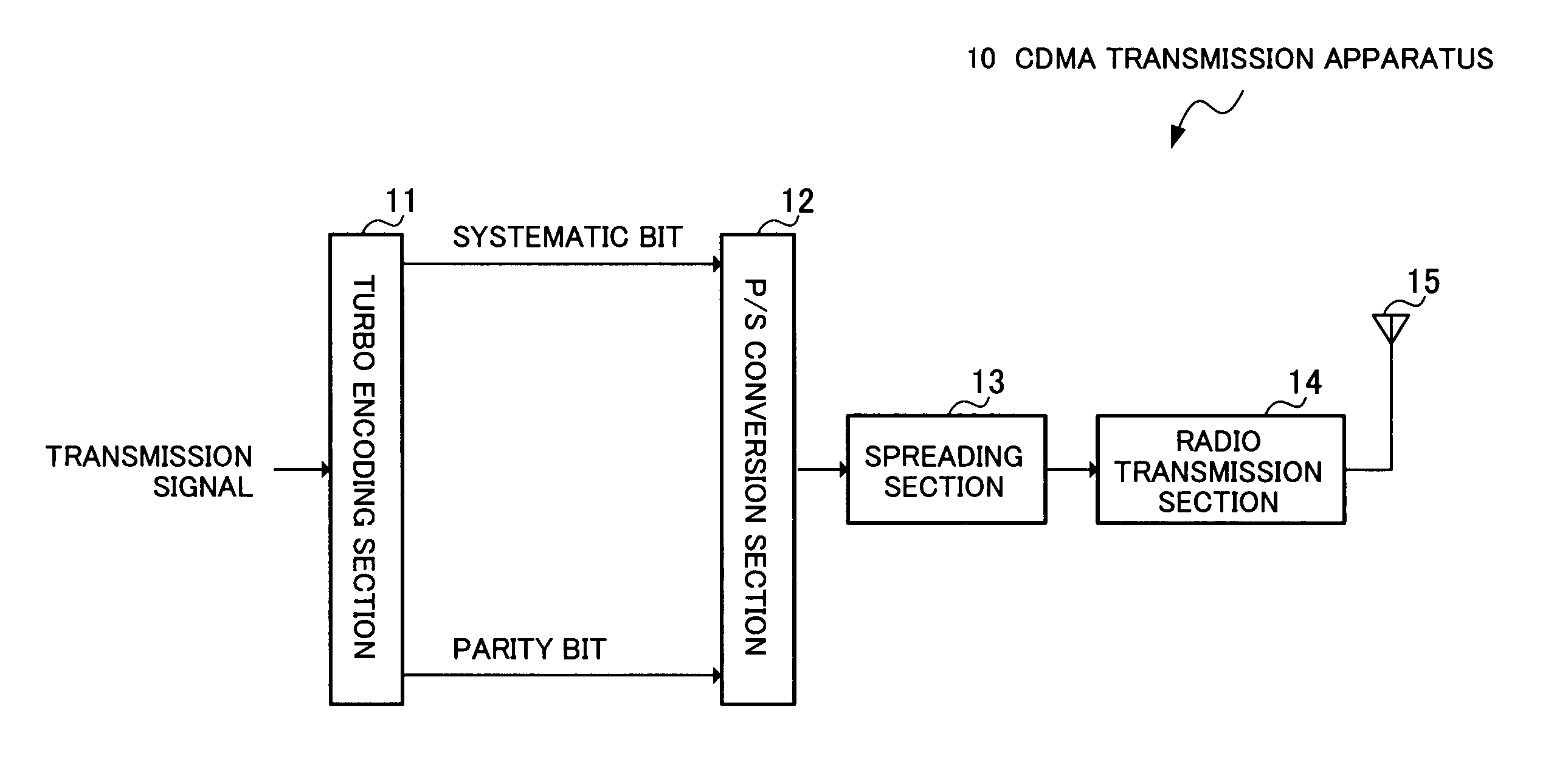
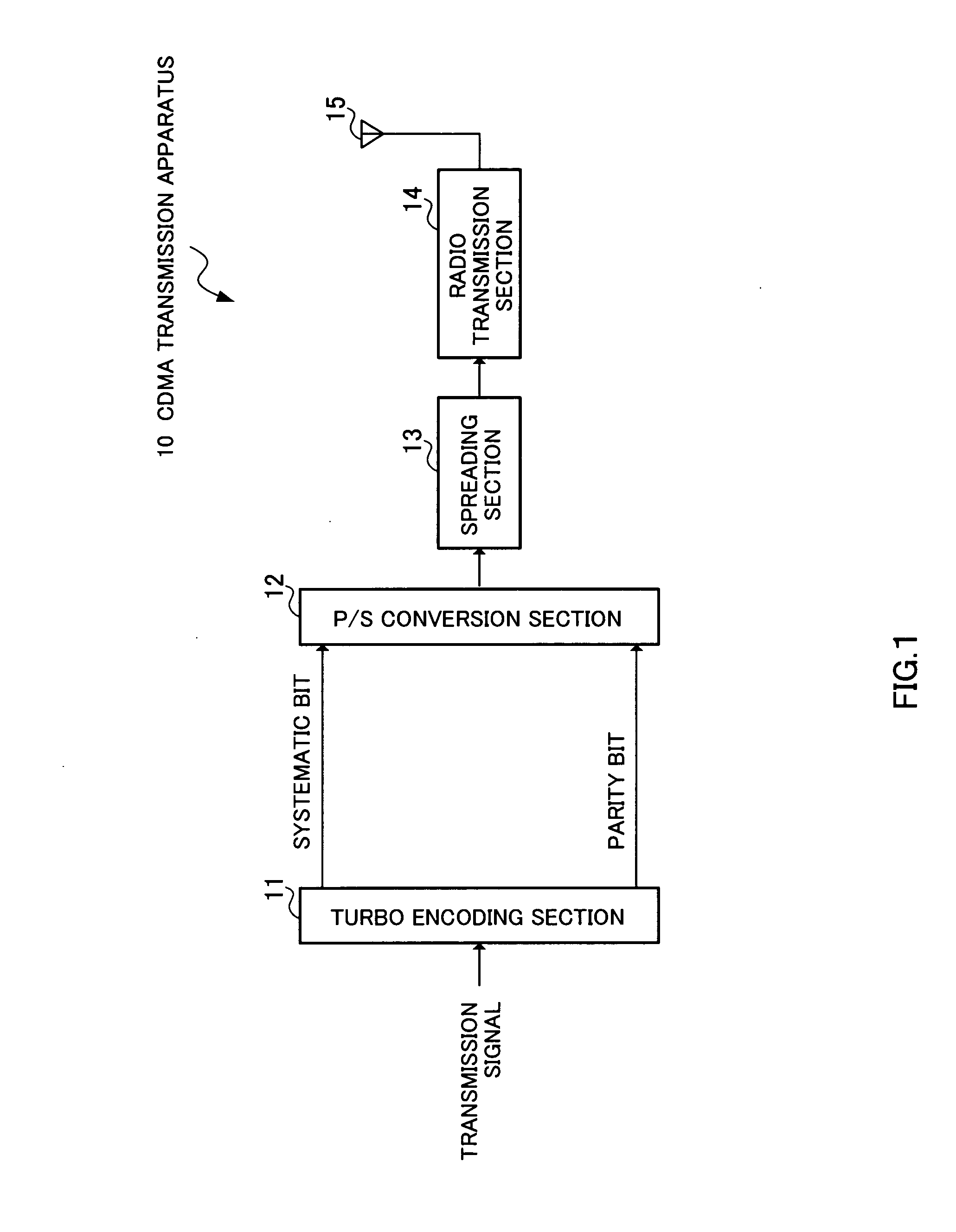
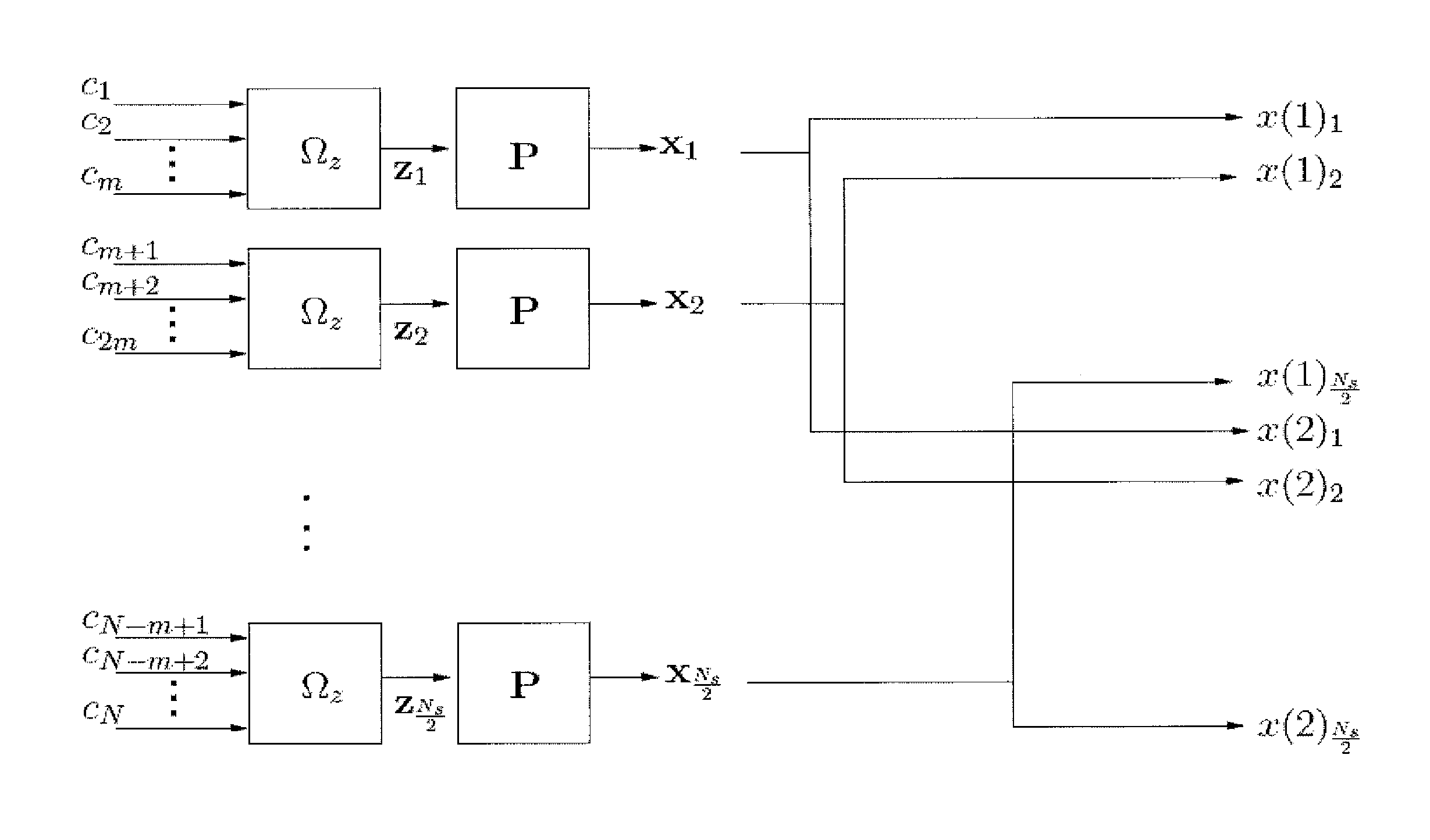
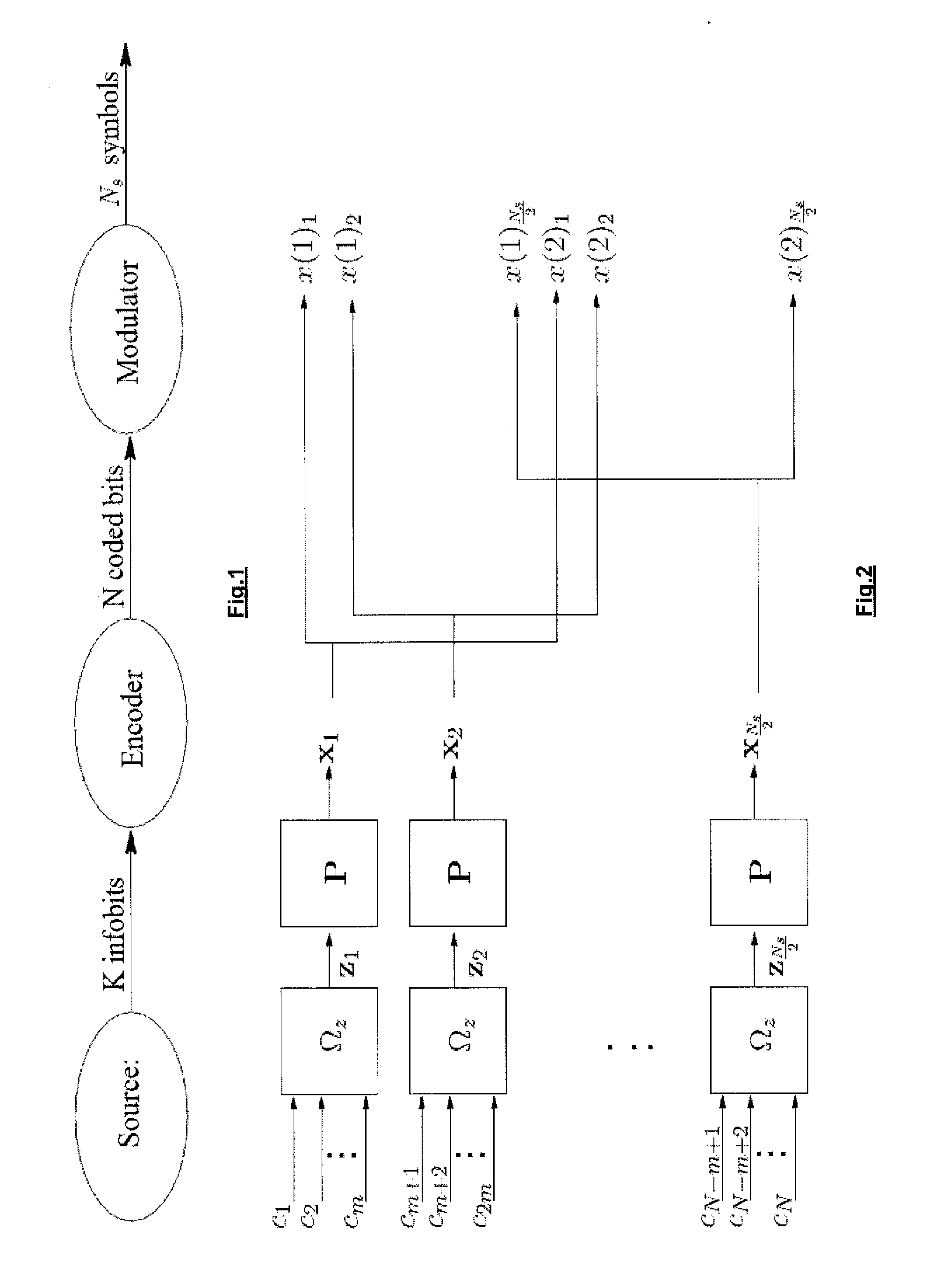
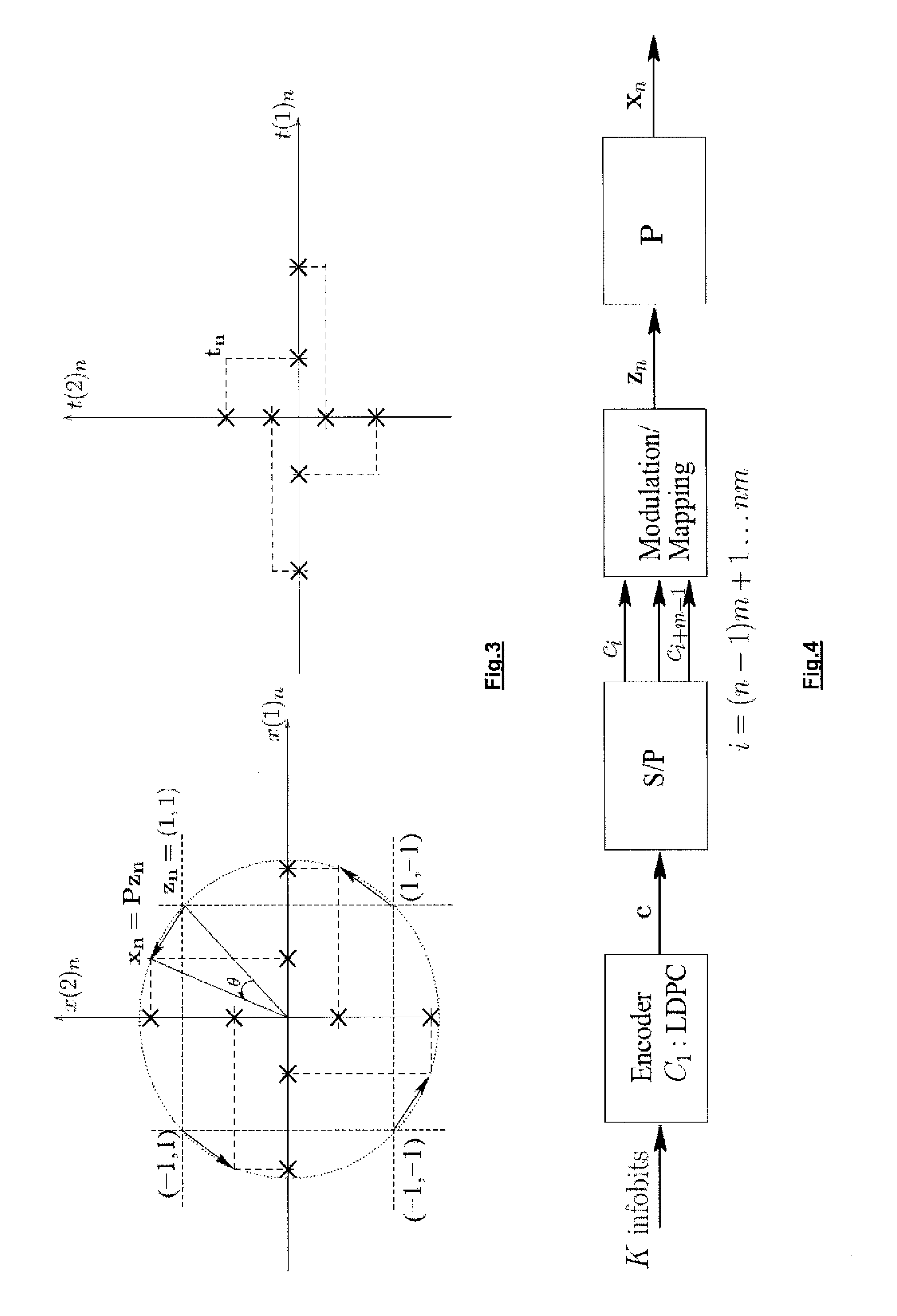
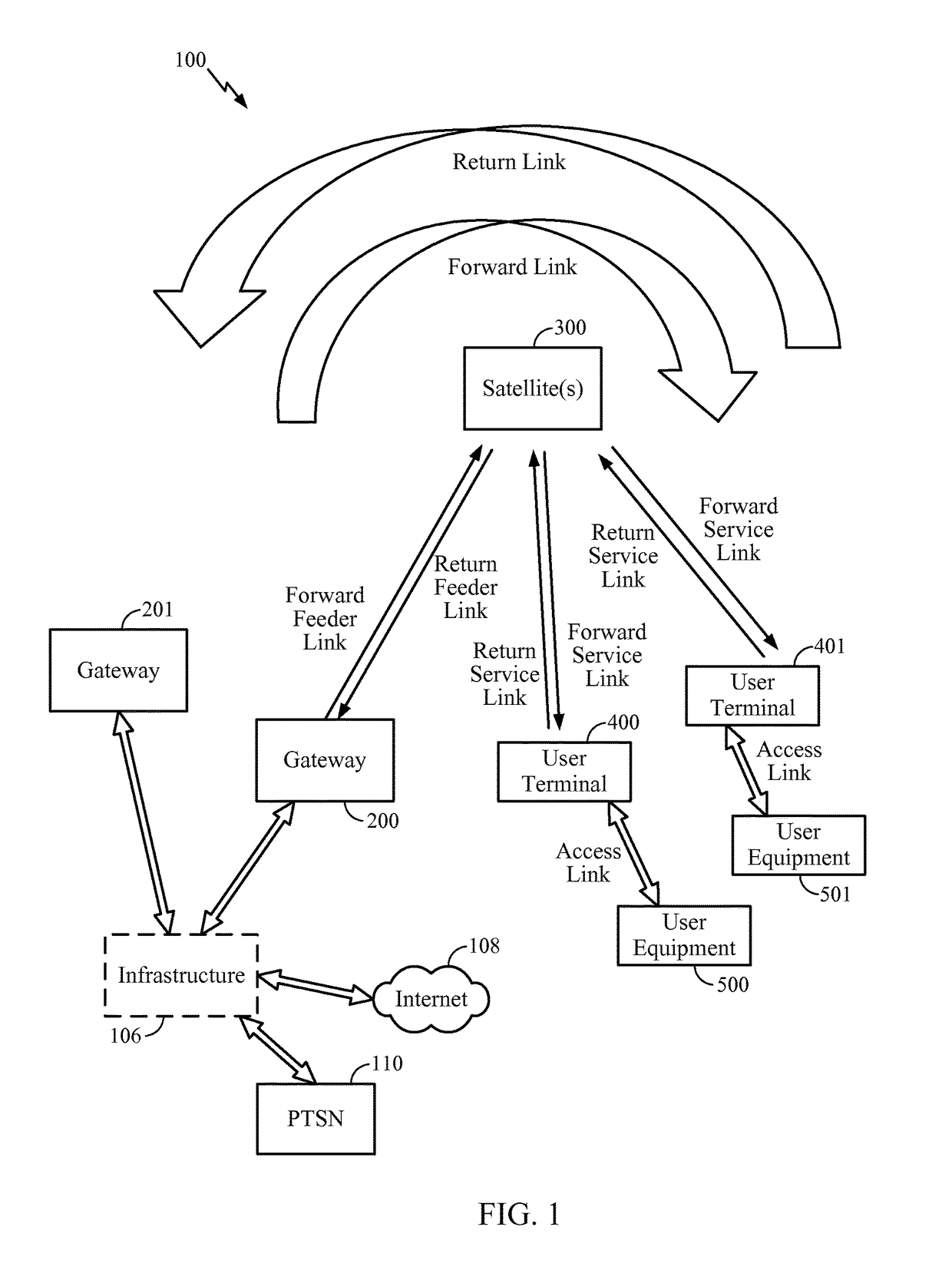
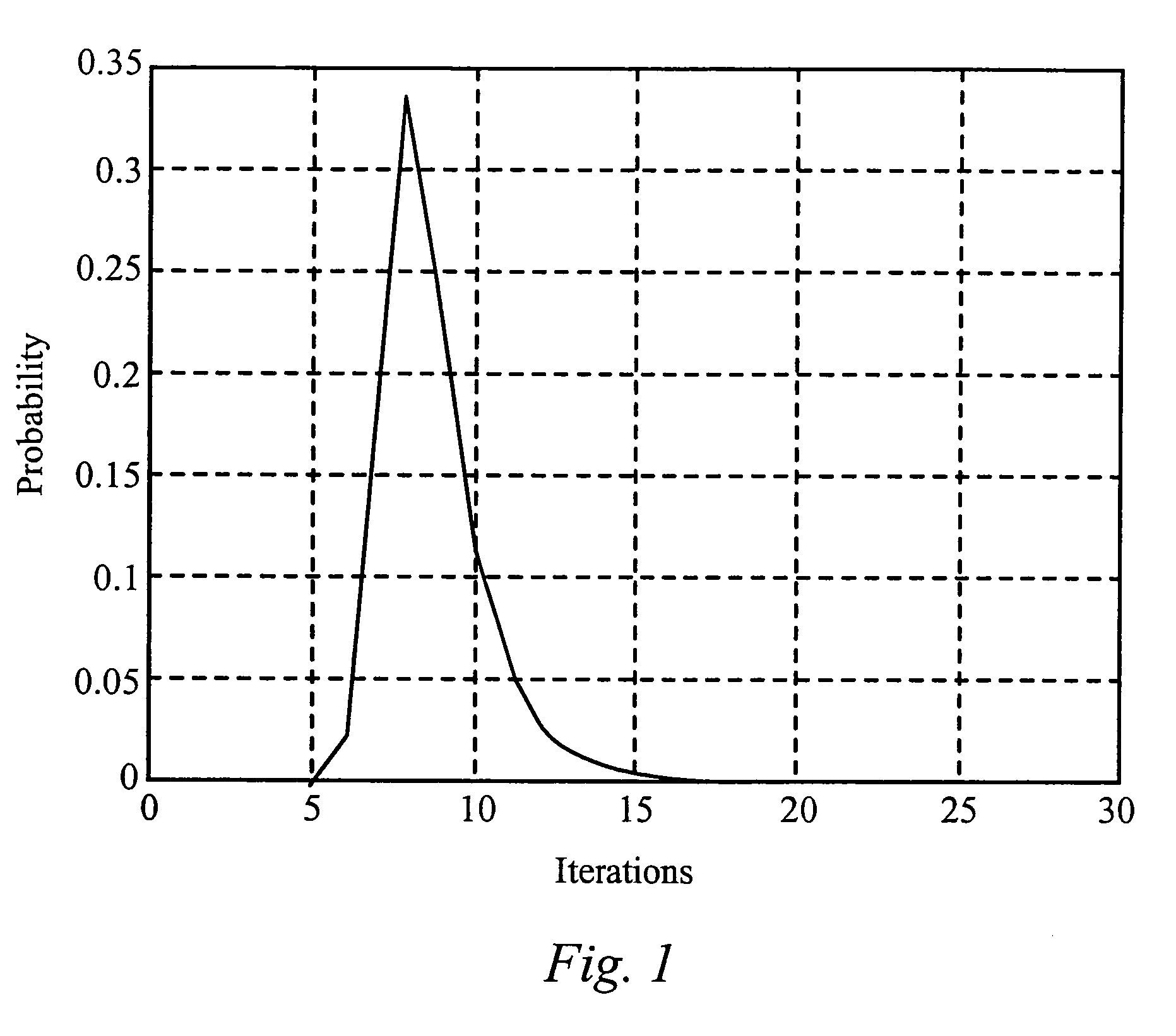
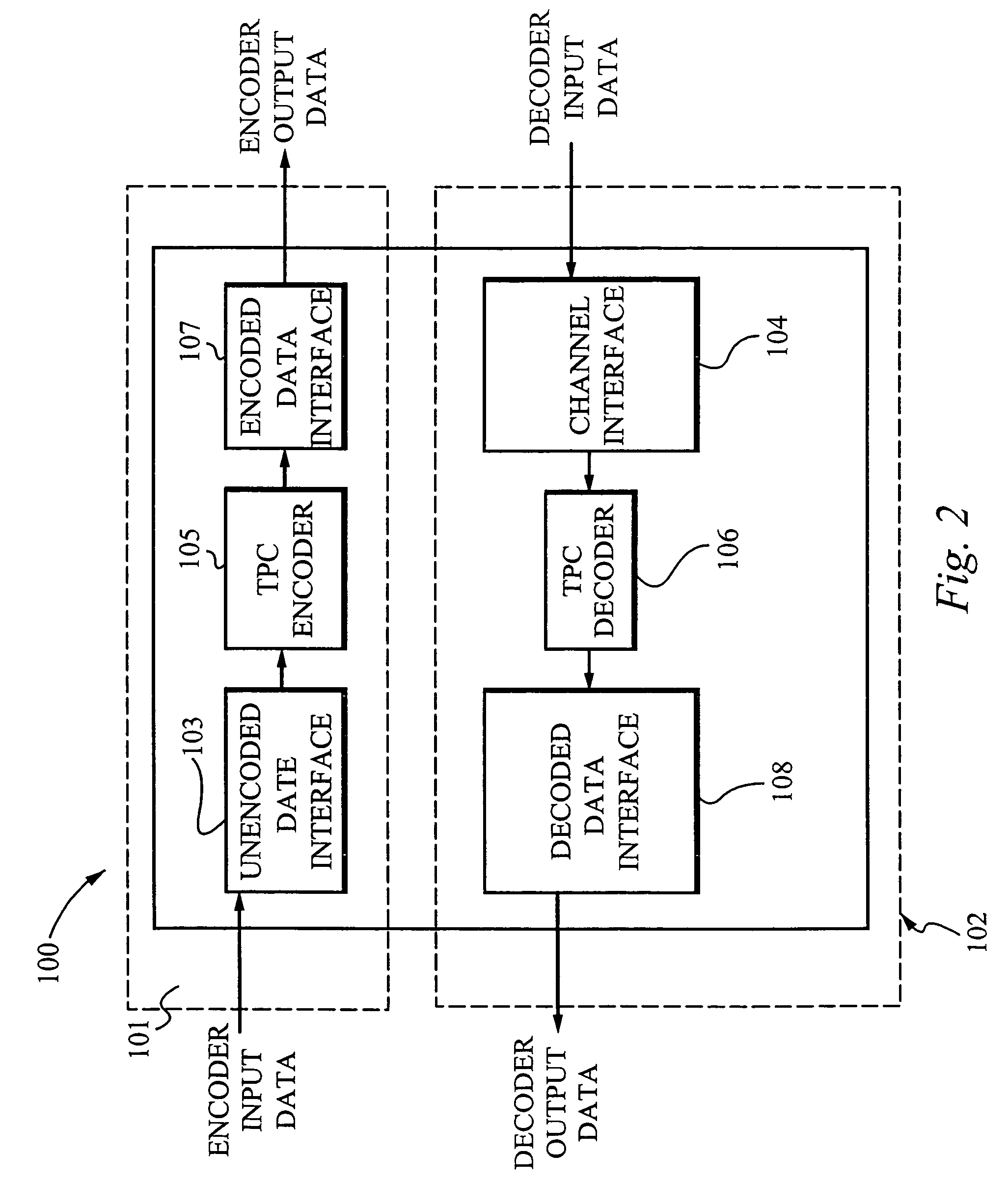
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
154results about "Error correction/detection using turbo codes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
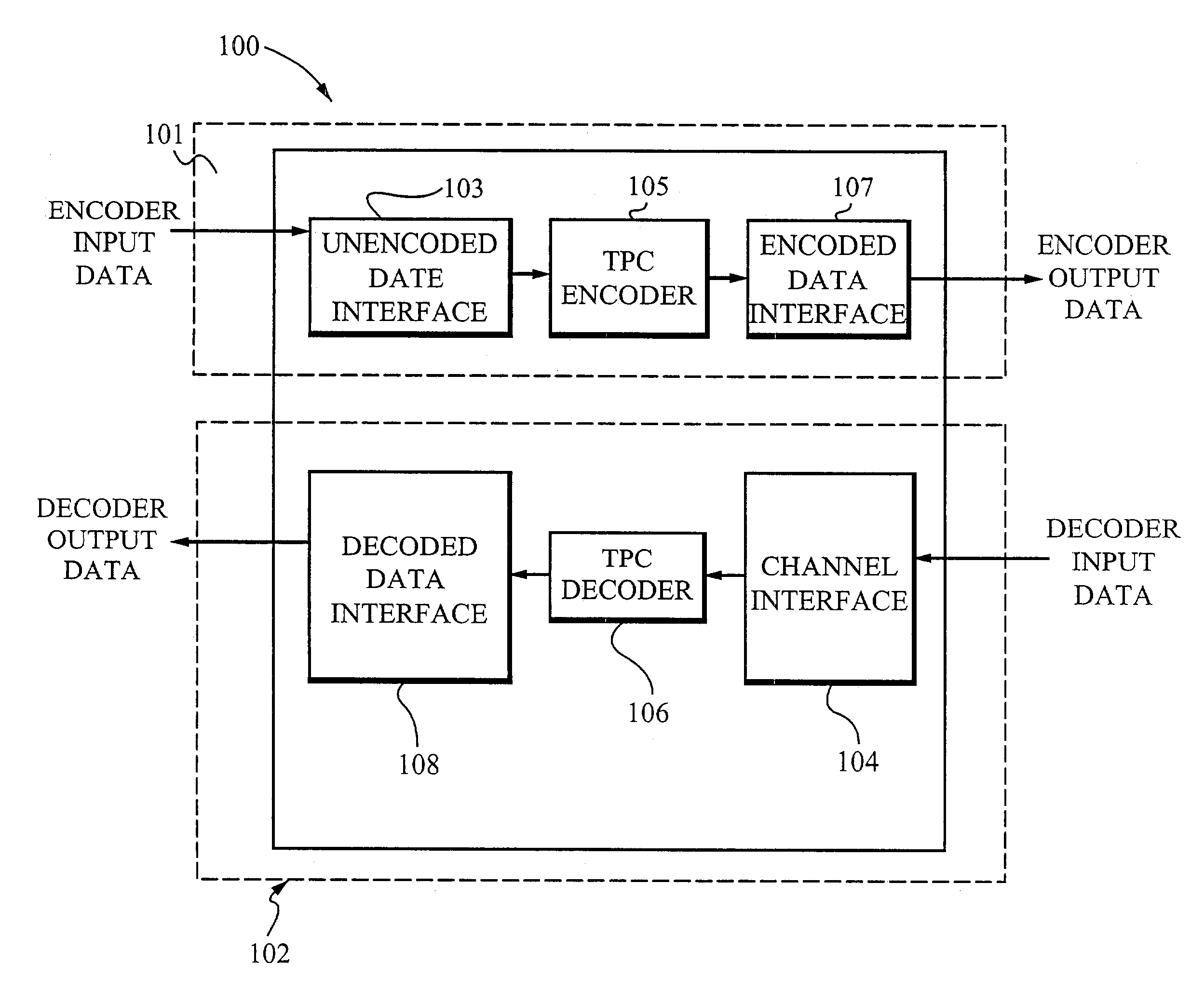
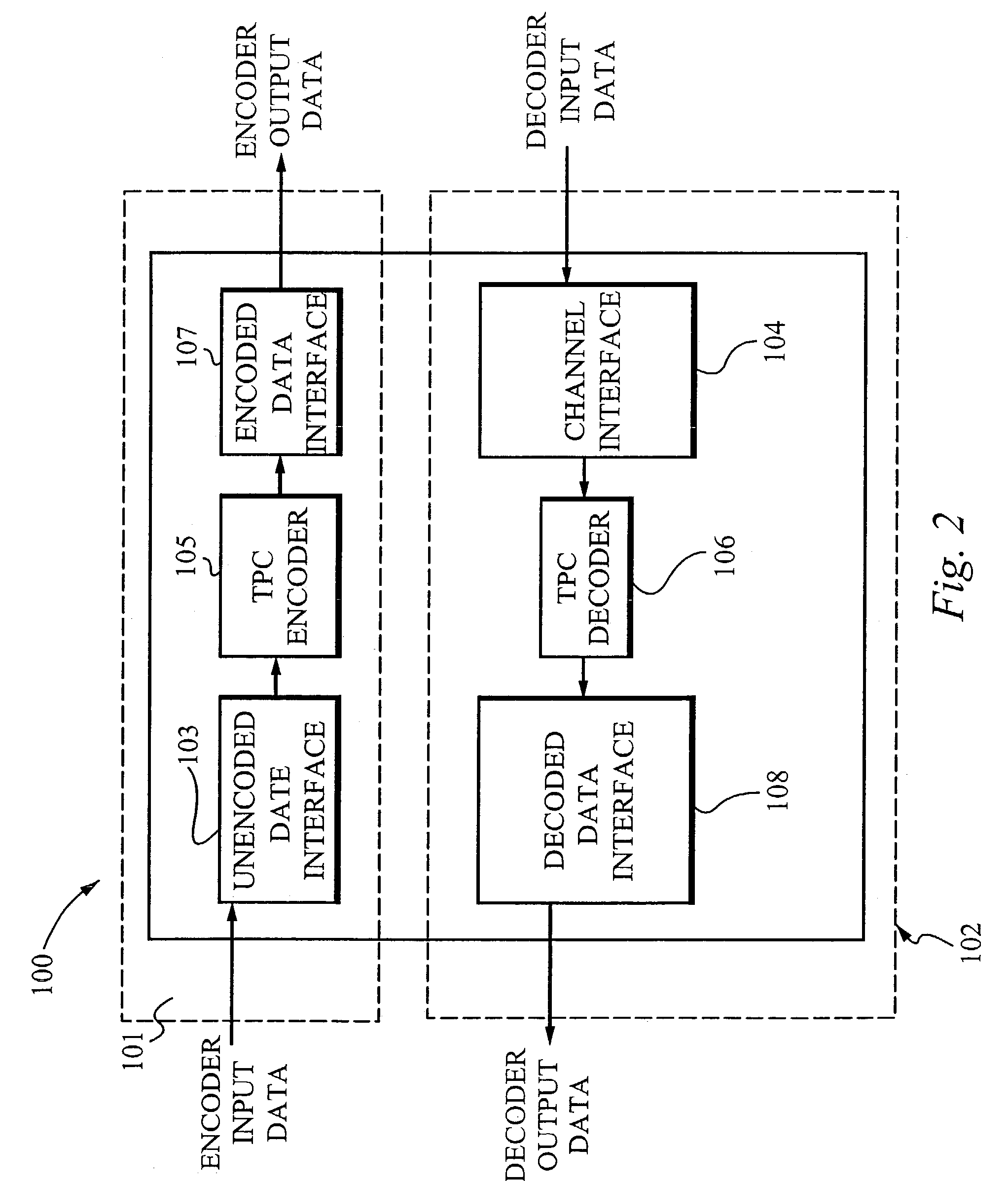
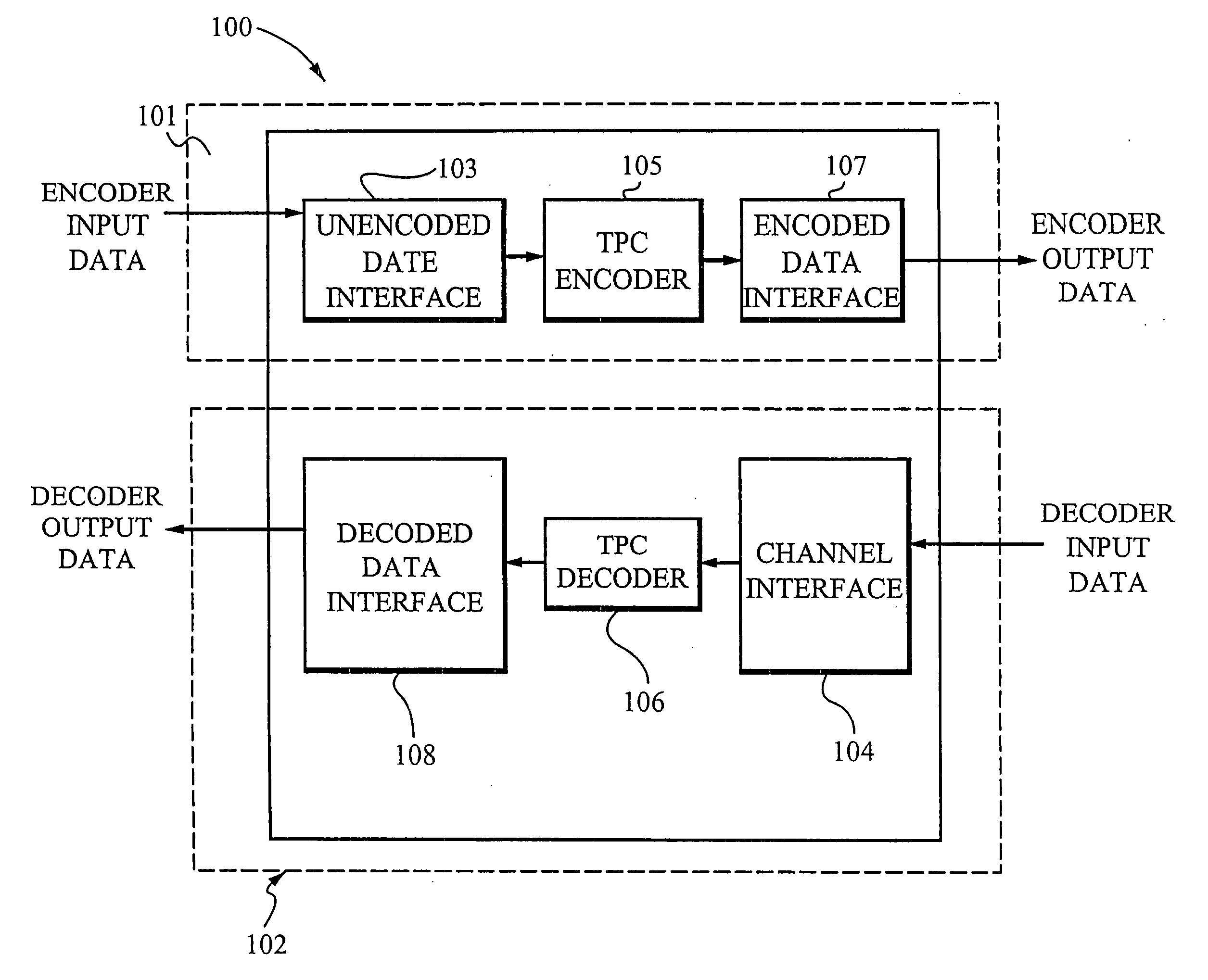
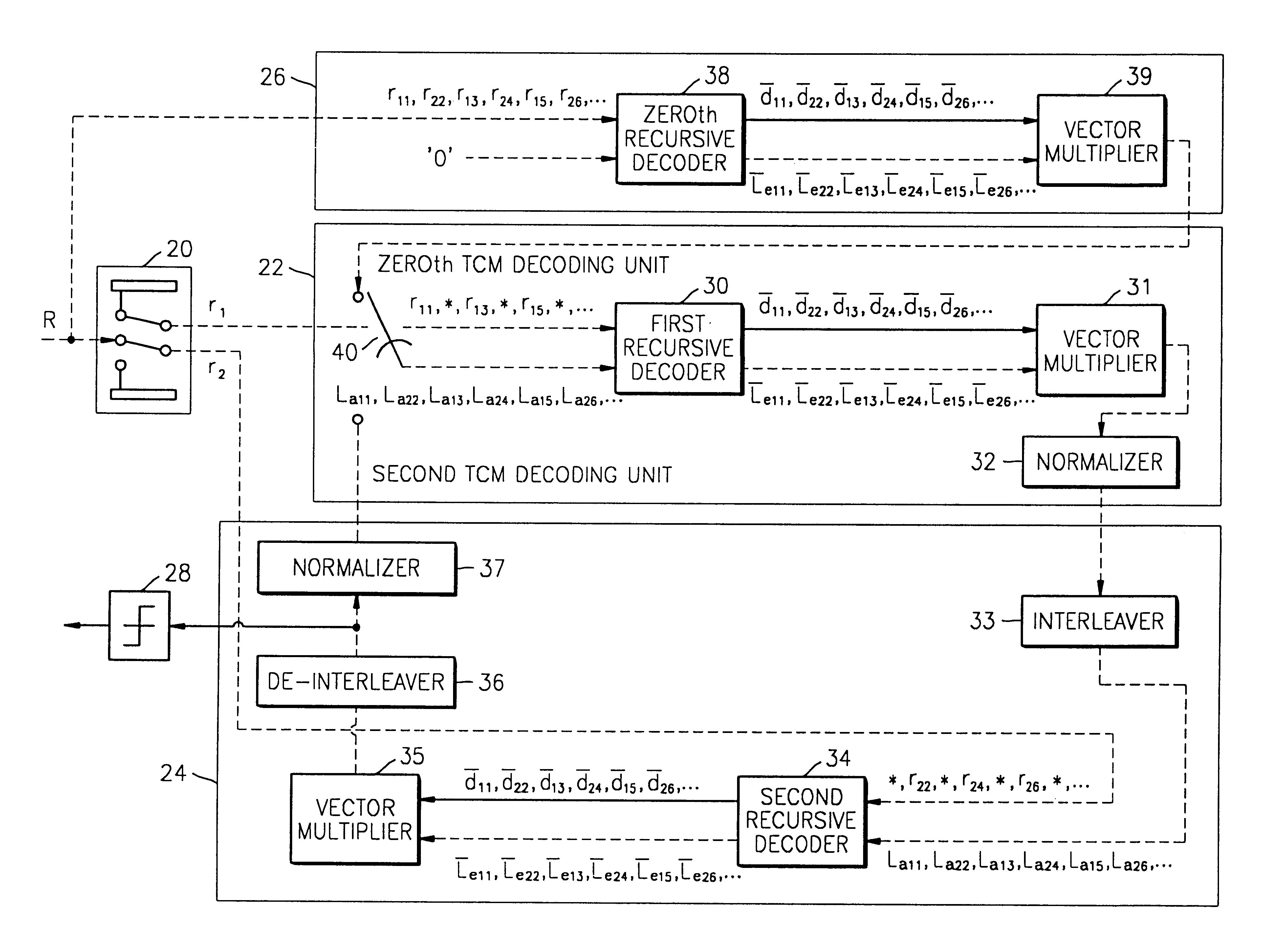
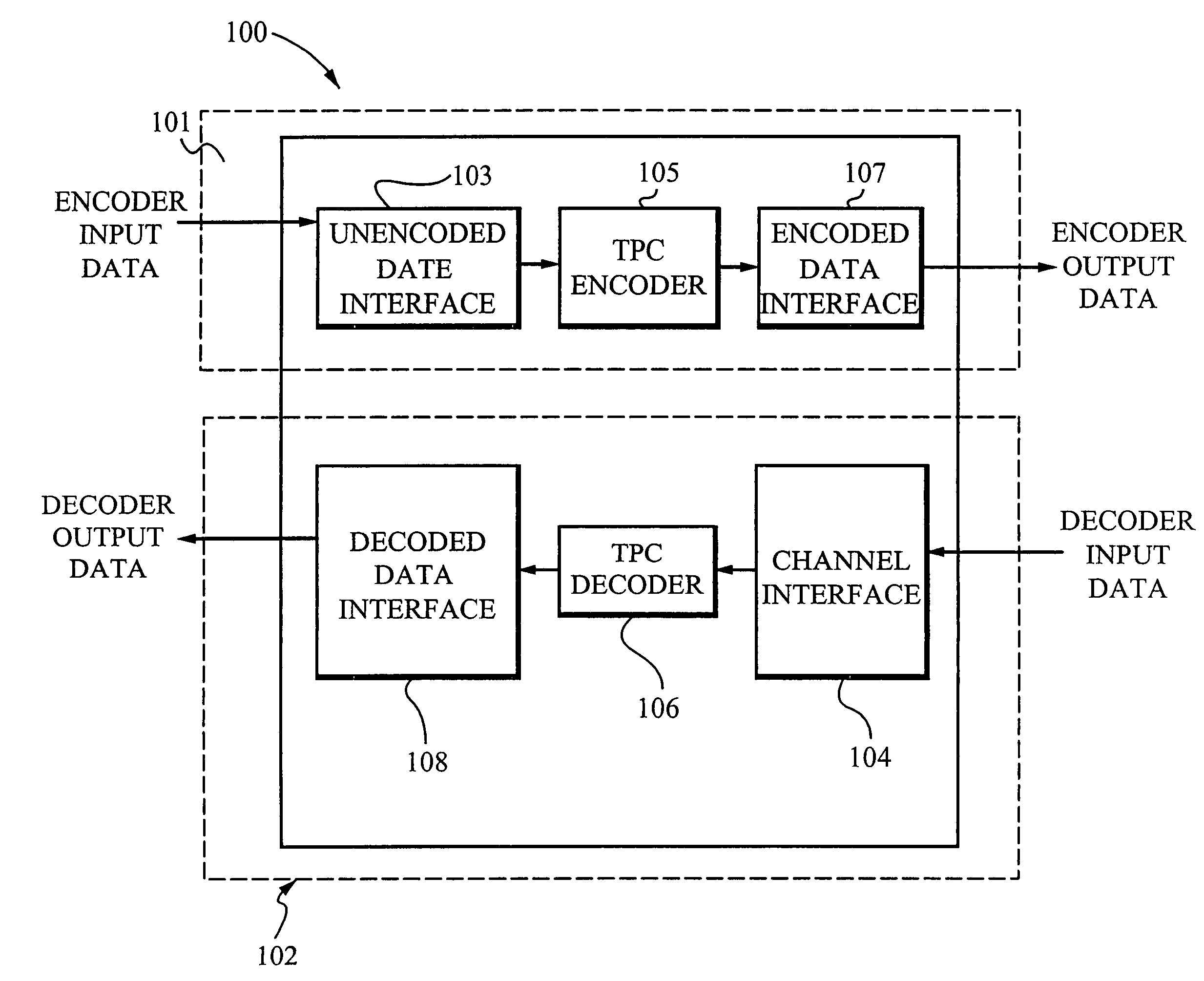
Enhanced turbo product code decoder system utilizing a codeword organization method
InactiveUS7039846B2Error preventionOther decoding techniquesMemory addressTheoretical computer science
A method and apparatus for decoding a linear block encoded string of information bits comprising: converting the string into a plurality of codewords. Performing hard and soft decisions on each codeword to generate a hard and soft decision vector. Computing the syndrome and finding the location of the two minimum values by Galois Field Arithmetic. Designating these values LOW1 and LOW2 and xoring with a Nc1, thus generating Nc2. Swapping Nc1 with Nc2 and determining the lowest soft decision value, Min1 and a next lowest value, Min2. The two bit locations creating Min1 are designated as MinA and MinB. MinA being replaced with Min2 minus the value MinA. MinB being replaced with Min2 minus the value at MinB. Generating an output codeword by subtracting Min1 from all other bit locations values and 2's complementing all soft values with 0 in their location. Creating the new soft value vector. Some embodiments include a system and method that organizes an encoded codeword. The encoded codeword has several codeword bits. The method receives the encoded codeword, assigns multiple codeword bits to at least one memory address in a plurality of memory addresses, and iteratively decodes the received codeword by utilizing the plurality of memory addresses in a predetermined order. The predetermined order is based on a dimension of the received codeword.
Owner:COMTECH TELECOMM CORP
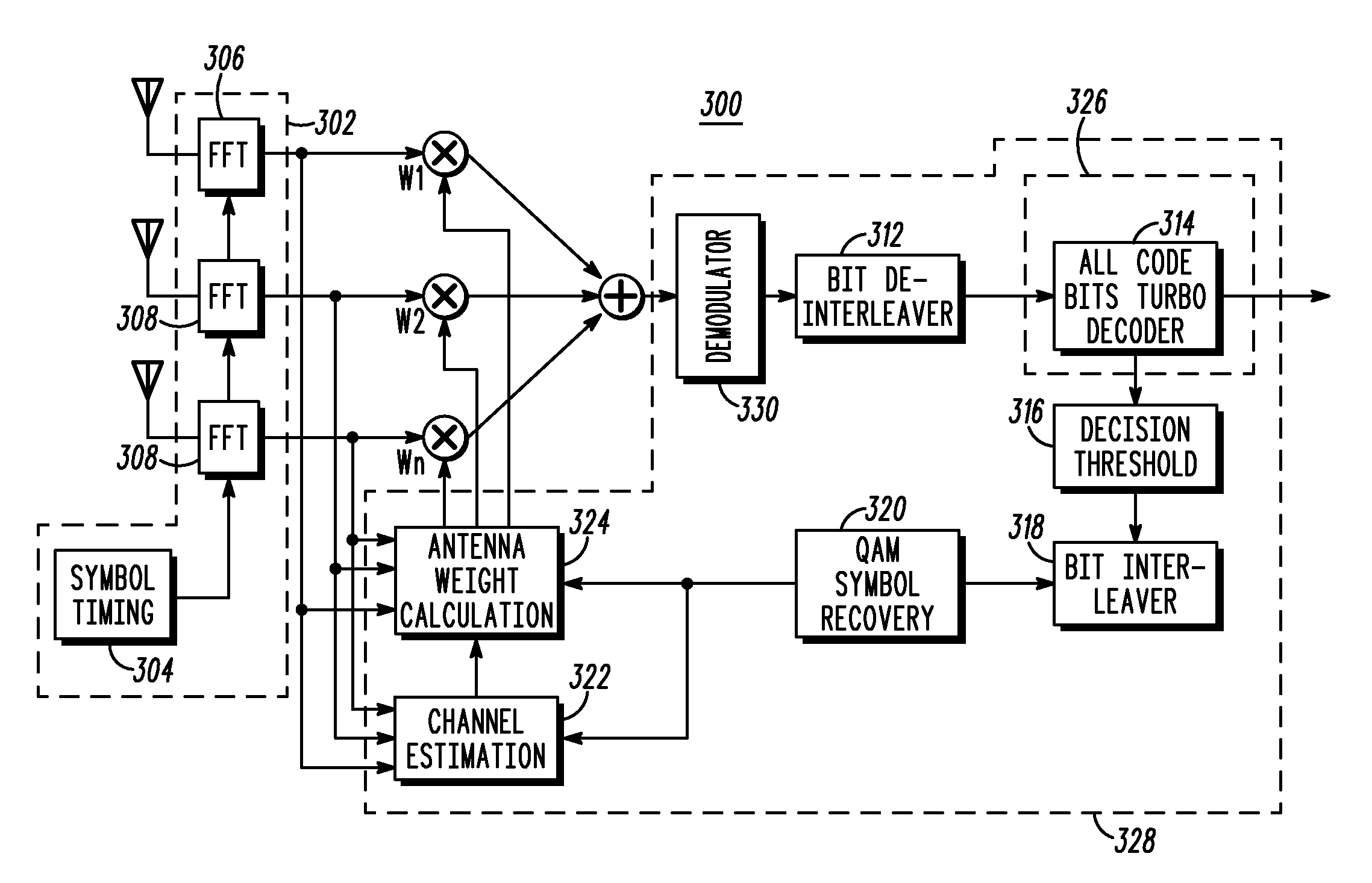
Turbo Interference Suppression in Communication Systems
ActiveUS20080109701A1Reduce chanceError propagation is limitedData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionComputer hardwareCommunications system
Disclosed is a method and communication device for suppressing interference. The method comprises performing, with a turbo decoder (314), at least one turbo decoding attempt (1106) on a received signal (1104). The turbo decoding attempt generates at least one whole word code bit therefrom (1108). The whole word code bit (1108) corresponds to a group of bits comprising a transmitted symbol. The method determines if the whole word code bit (1108) has a confidence level exceeding a given threshold (1110). If the whole word code bit (1108) does have a confidence level exceeding the given threshold, the whole code word bit is selected for use in data symbol recovery (1114).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
IPHD (iterative parallel hybrid decoding) of various MLC (multi-level code) signals
InactiveUS20050166132A1Error detection/correctionError correction/detection using LDPC codesLow densityComputer science
IPHD (Iterative Parallel Hybrid Decoding) of various MLC (Multi-Level Code) signals. Various embodiments are provided by which IPHD may be performed on MLC LDPC (Multi-Level Code Low Density Parity Check) coded modulation signals mapped using a plurality of mappings. This IPHD may also be performed on MLC LDPC coded modulation signals mapped using only a singe mapping as well. In addition, various embodiments are provided by which IPHD may be performed on ML TC (Multi-Level Turbo Code) signals. These principles of IPHD, shown with respect to various embodiments IPHD of MLC LDPC coded modulation signals as well as the IPHD of ML TC signals, may be extended to performing IPHD of other signal types as well. Generally speaking, based on the degree of the MLC signal, a corresponding number of parallel paths operate in cooperation to decode the various levels of the MLC signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
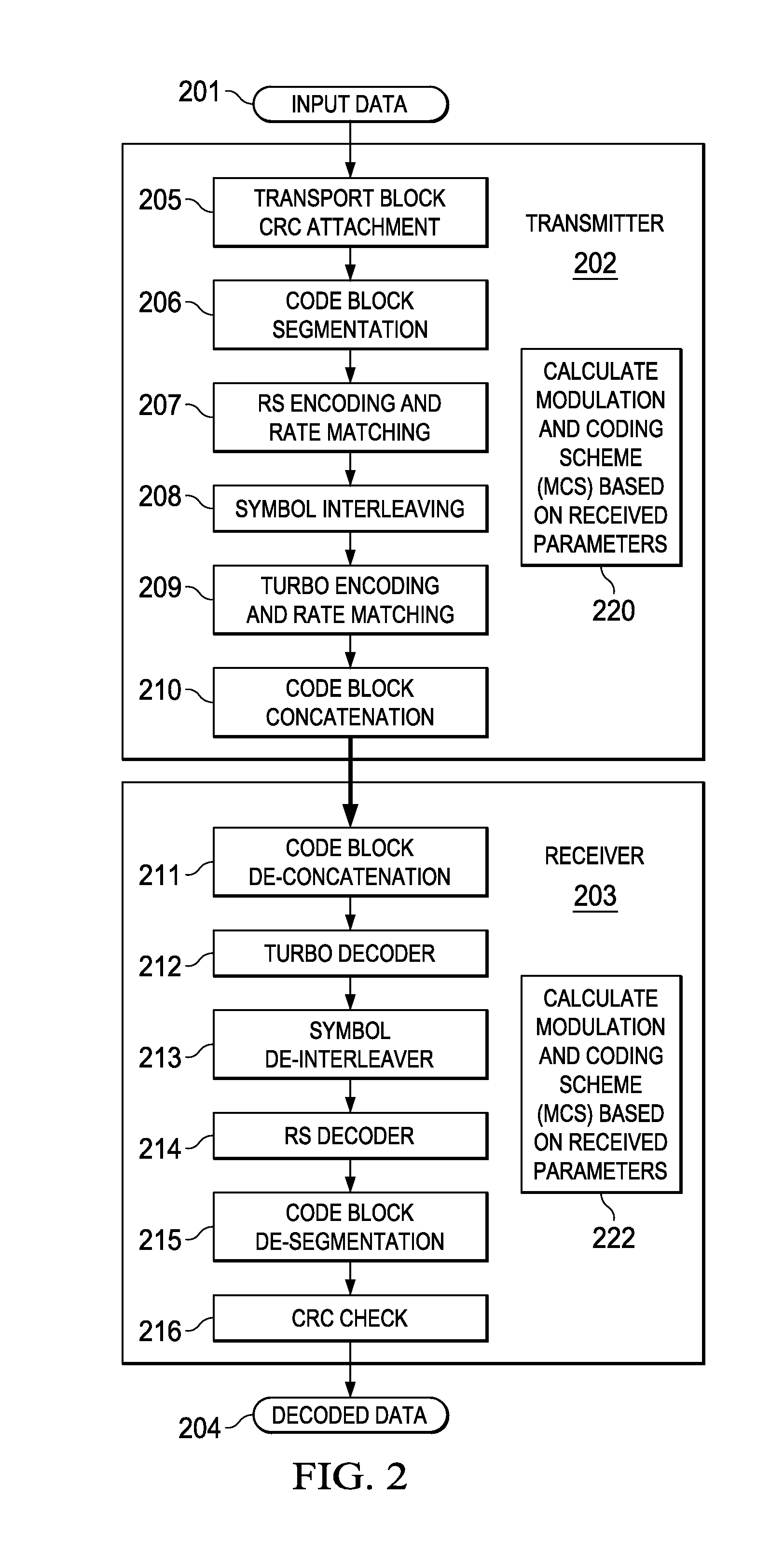
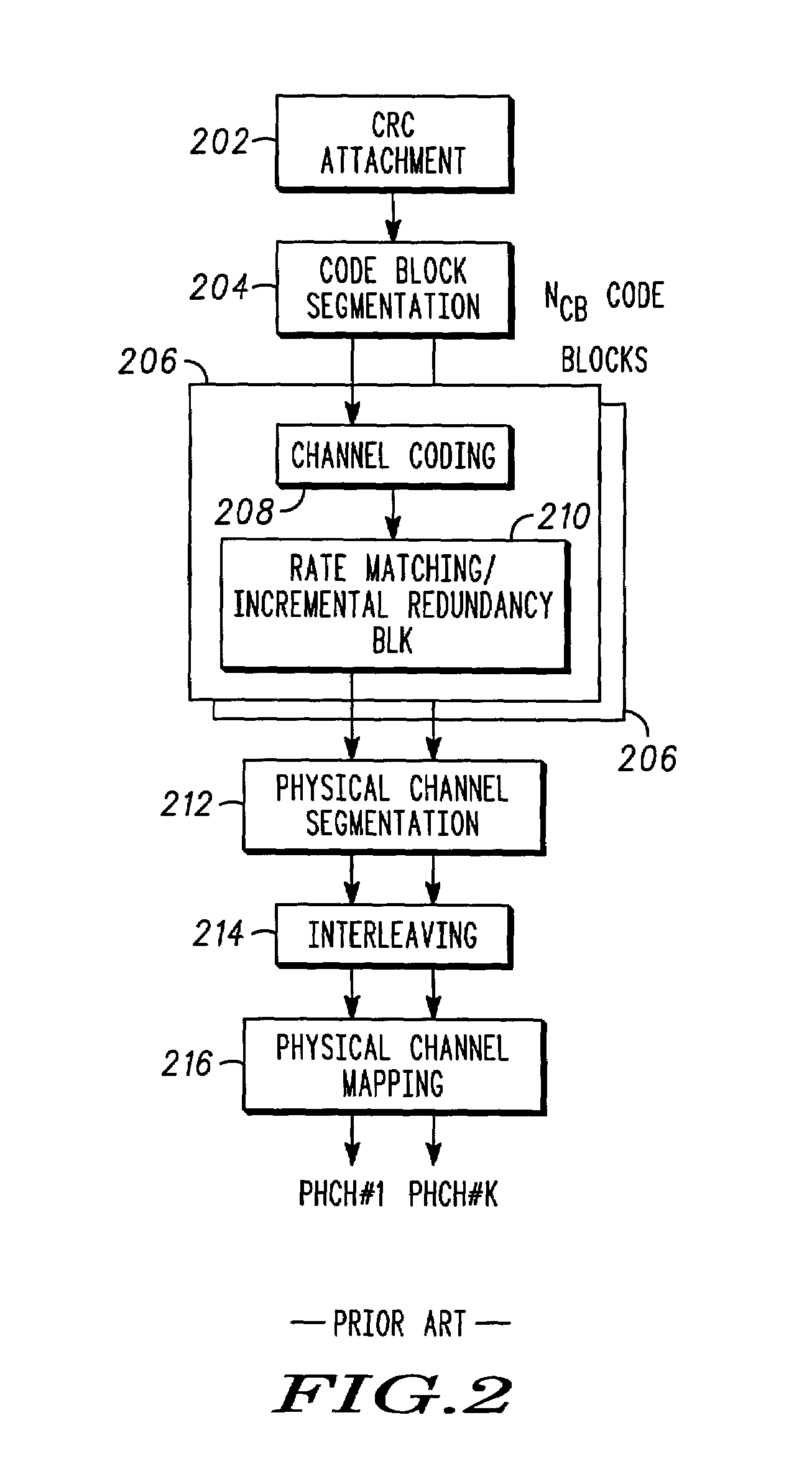
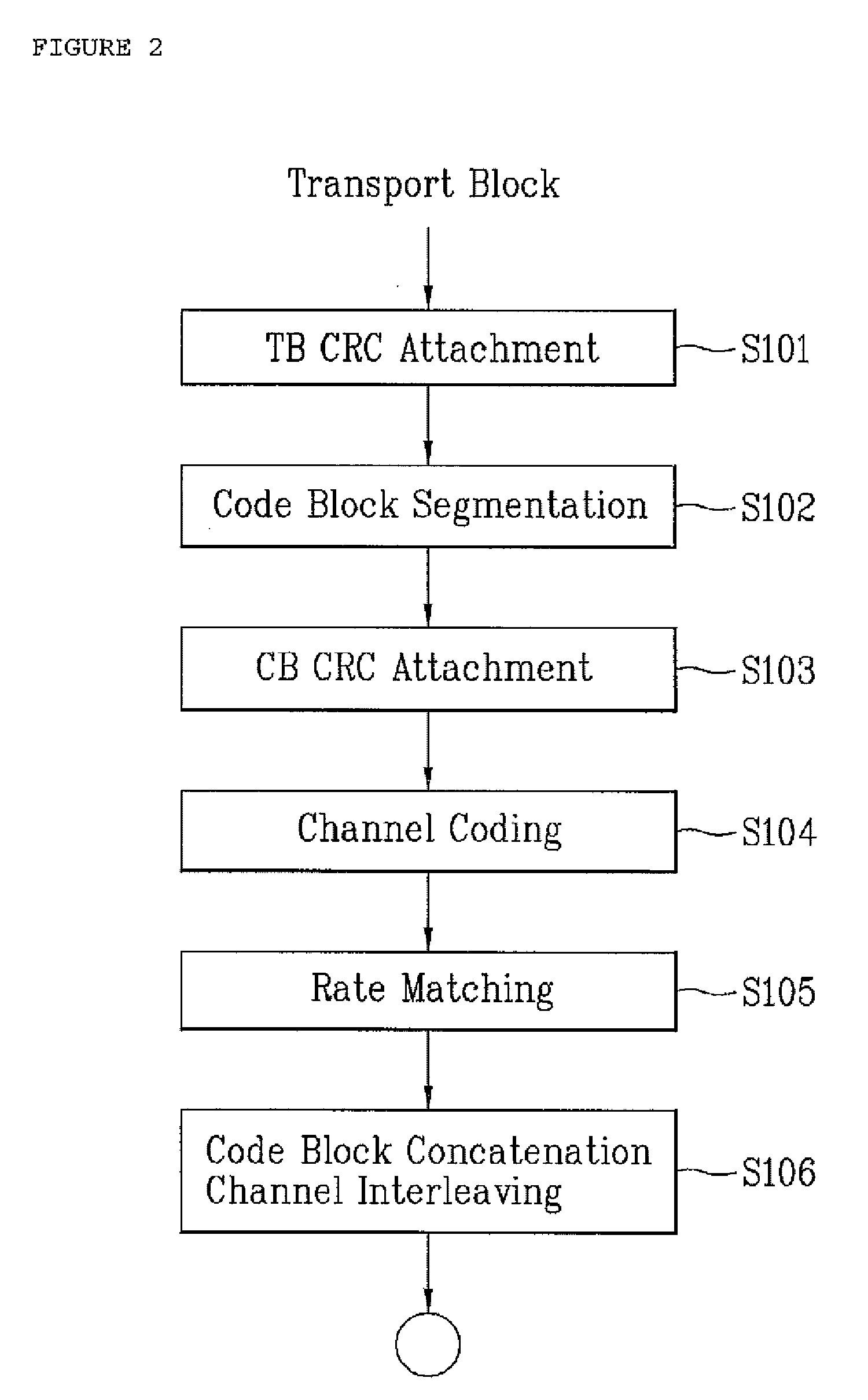
Code Block Segmentation and Configuration for Concatenated Turbo and RS Coding
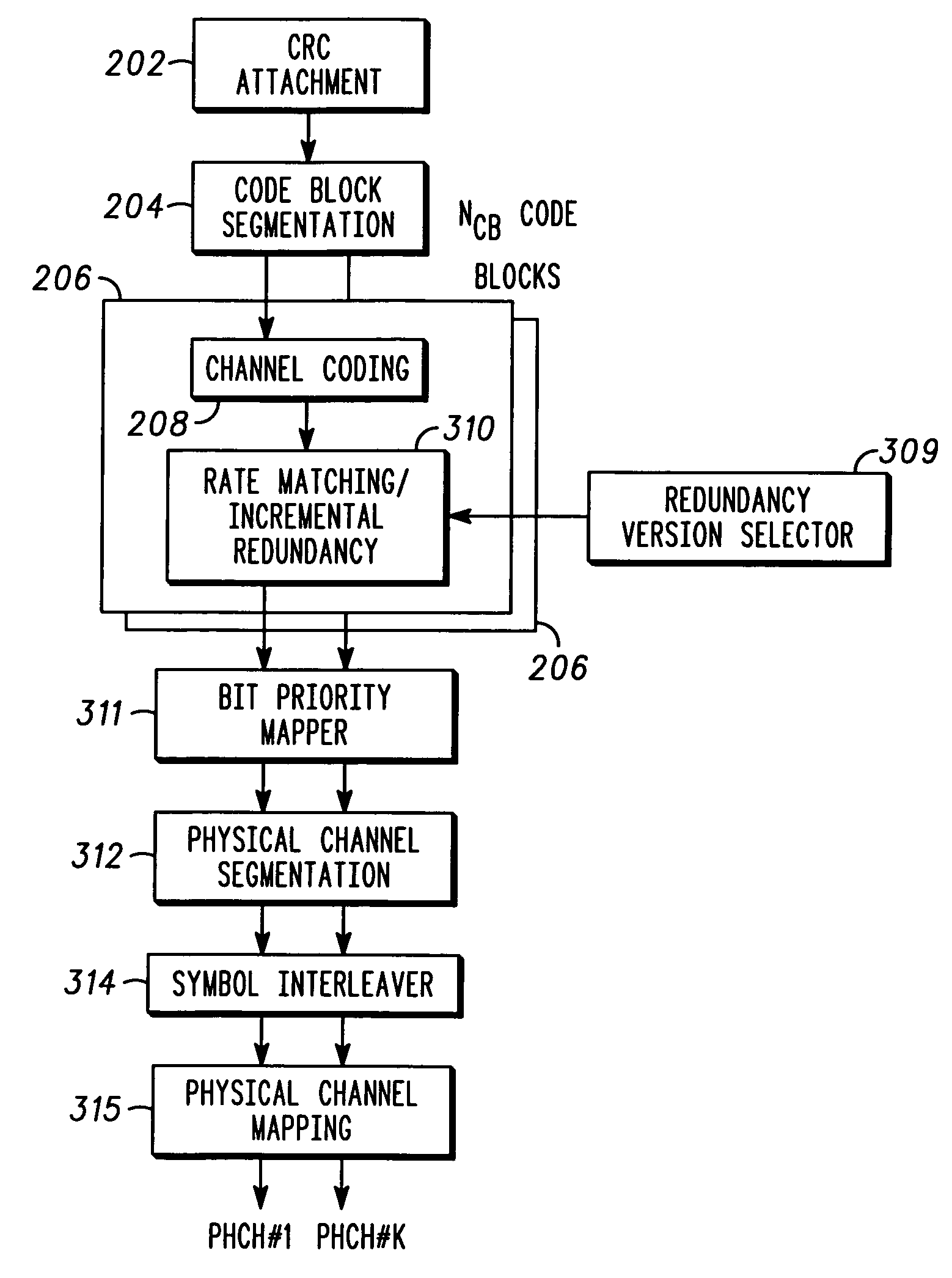
A method for performing code block segmentation for wireless transmission using concatenated forward error correction encoding includes receiving a transport block of data for transmission having a transport block size, along with one or more parameters that define a target code rate. A number N of inner code blocks needed to transmit the transport block is determined. A number M—outer code blocks may be calculated based on the number of inner code blocks and on encoding parameters for the outer code blocks. The transport block may then be segmented and encoded according to the calculated encoding parameters.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
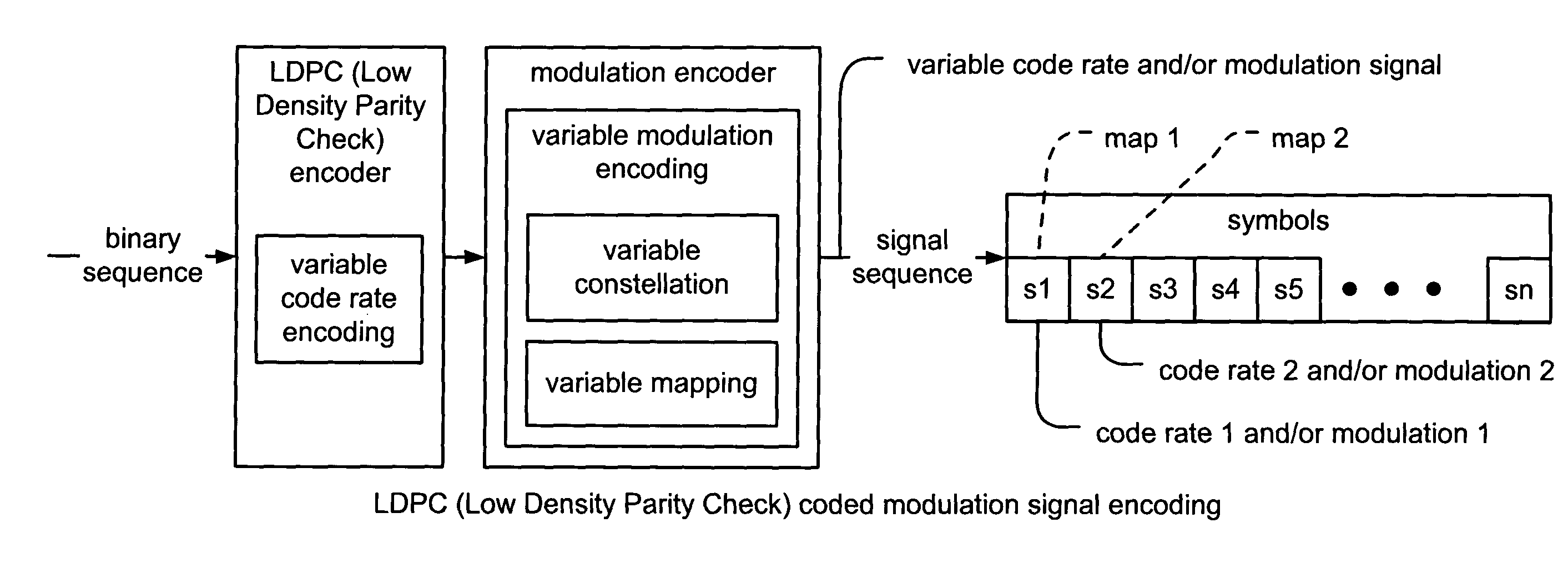
Variable modulation with LDPC (low density parity check) coding
InactiveUS7139964B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelOther decoding techniquesTheoretical computer scienceLow-density parity-check code
Variable modulation within combined LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) coding and modulation coding systems. A novel approach is presented for variable modulation encoding of LDPC coded symbols. In addition, LDPC encoding, that generates an LDPC variable code rate signal, may also be performed as well. The encoding can generate an LDPC variable code rate and / or modulation signal whose code rate and / or modulation may vary as frequently as on a symbol by symbol basis. Some embodiments employ a common constellation shape for all of the symbols of the signal sequence, yet individual symbols may be mapped according different mappings of the commonly shaped constellation; such an embodiment may be viewed as generating a LDPC variable mapped signal. In general, any one or more of the code rate, constellation shape, or mapping of the individual symbols of a signal sequence may vary as frequently as on a symbol by symbol basis.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Digital radio communications method using multi-level modulation scheme and transmitter and receiver
InactiveUS20090161786A1Sufficient effectHigh error rateError correction/detection using trellis codingCode conversionComputer hardwareCommunications system
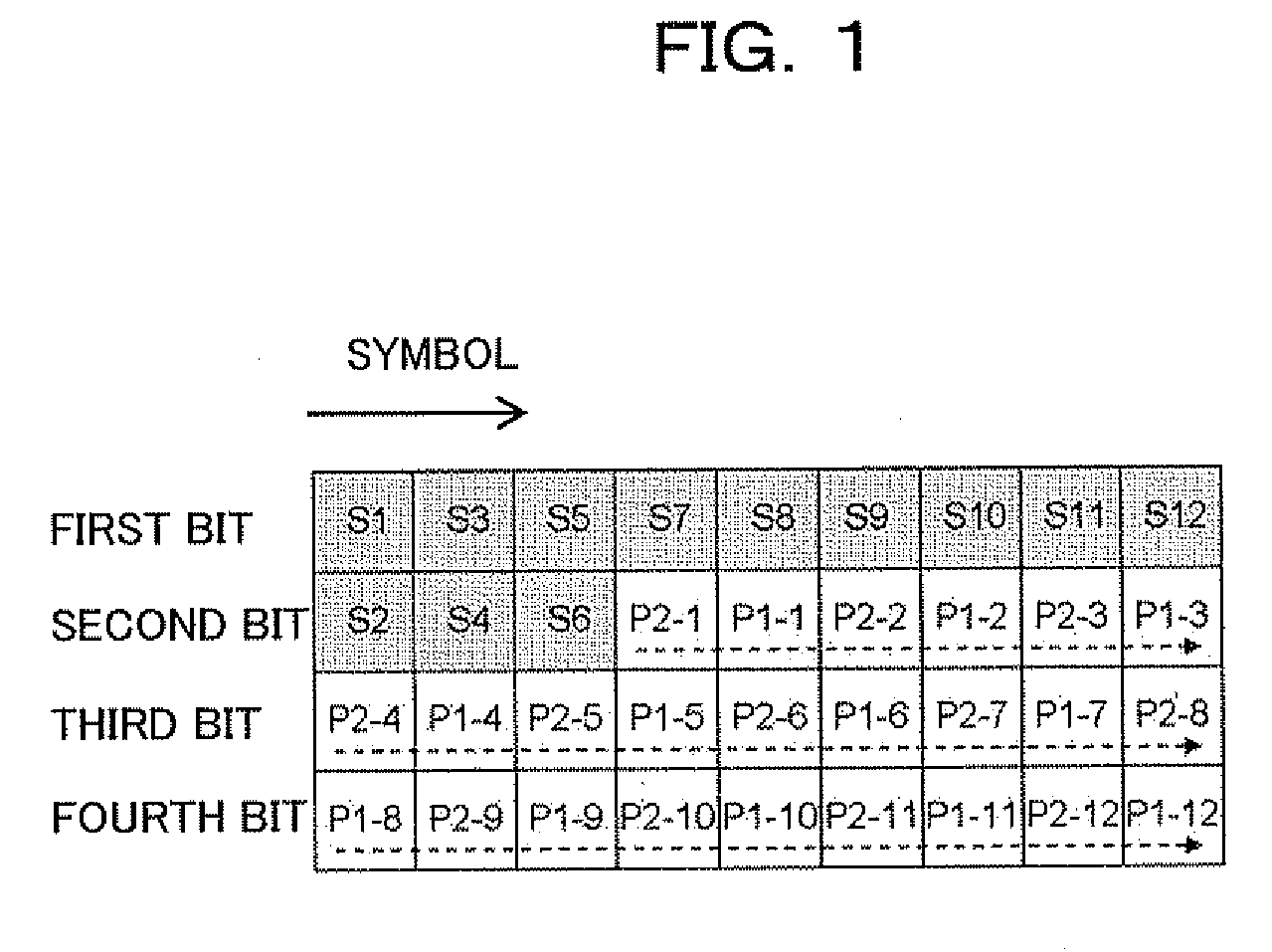
A transmitter for use in digital radio communications systems includes: a bit corrector controls bit arrangement in such a manner that a code having high significance, out of multiple codes obtained by coding, is allocated with high priority to a bit having a tendency that the likelihood enlarges at the time of symbol decision on a receiver; a multi-level modulator allocates the code to the multiple bits in accordance with a predetermined symbol arrangement; and a symbol arrangement controller controls the symbol arrangement from equal distance arrangement to another arrangement in accordance with a ratio of the codes different in significance. To control symbol arrangement increases the effect of bit correction and improves an error rate on the receiver.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
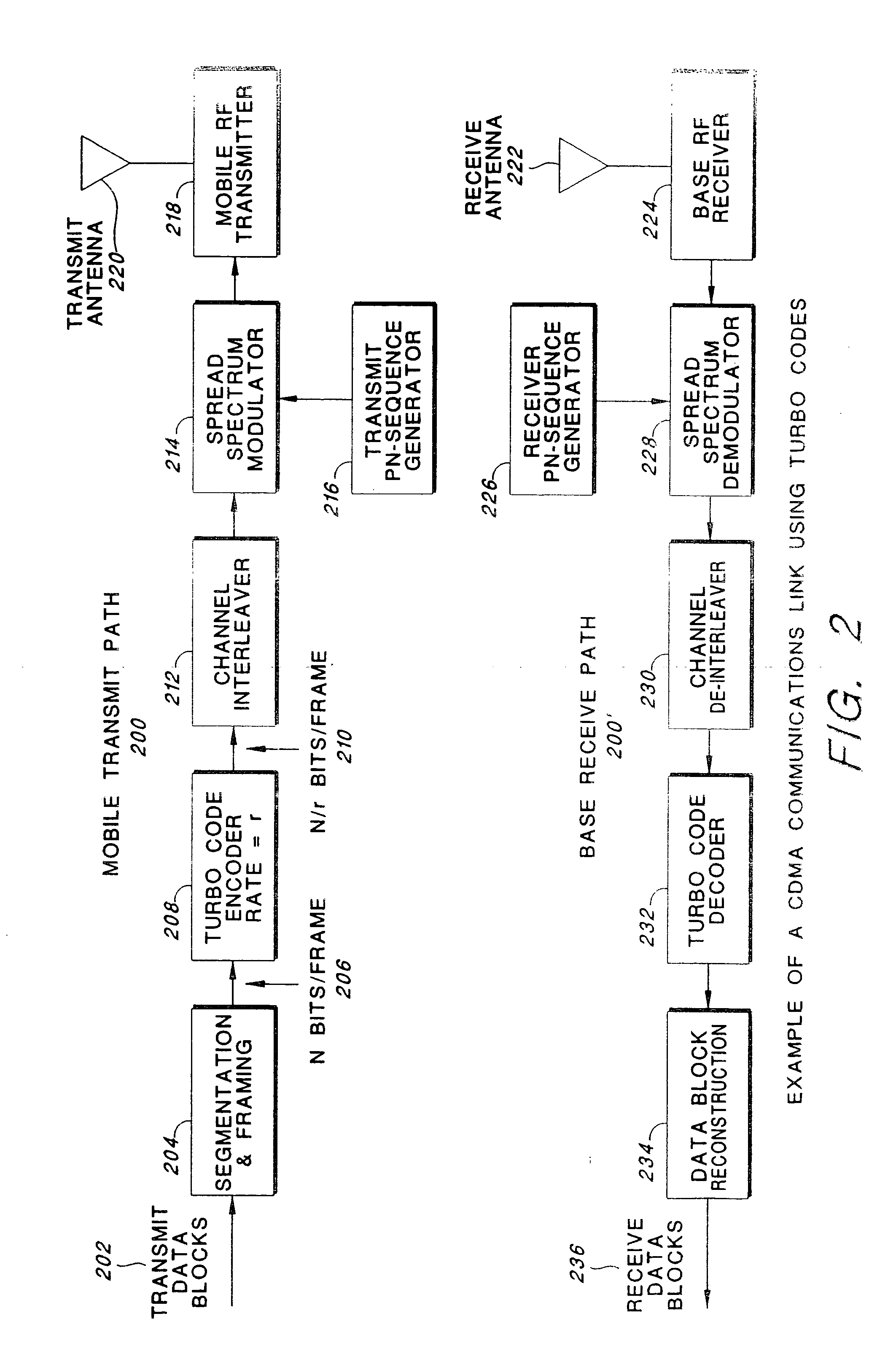
Turbo code based incremental redundancy
InactiveUS7000173B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using convolutional codesData streamComputer science
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
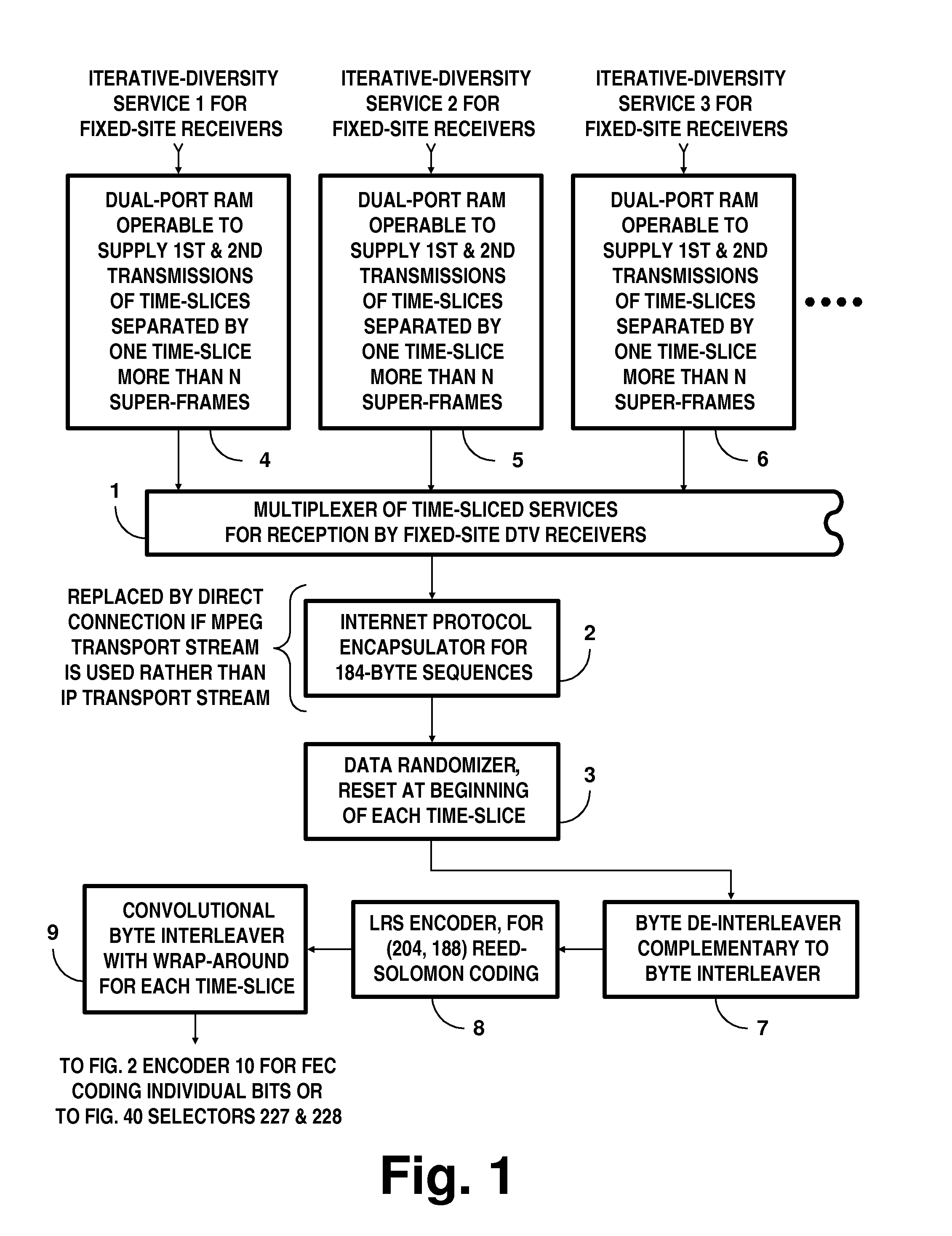
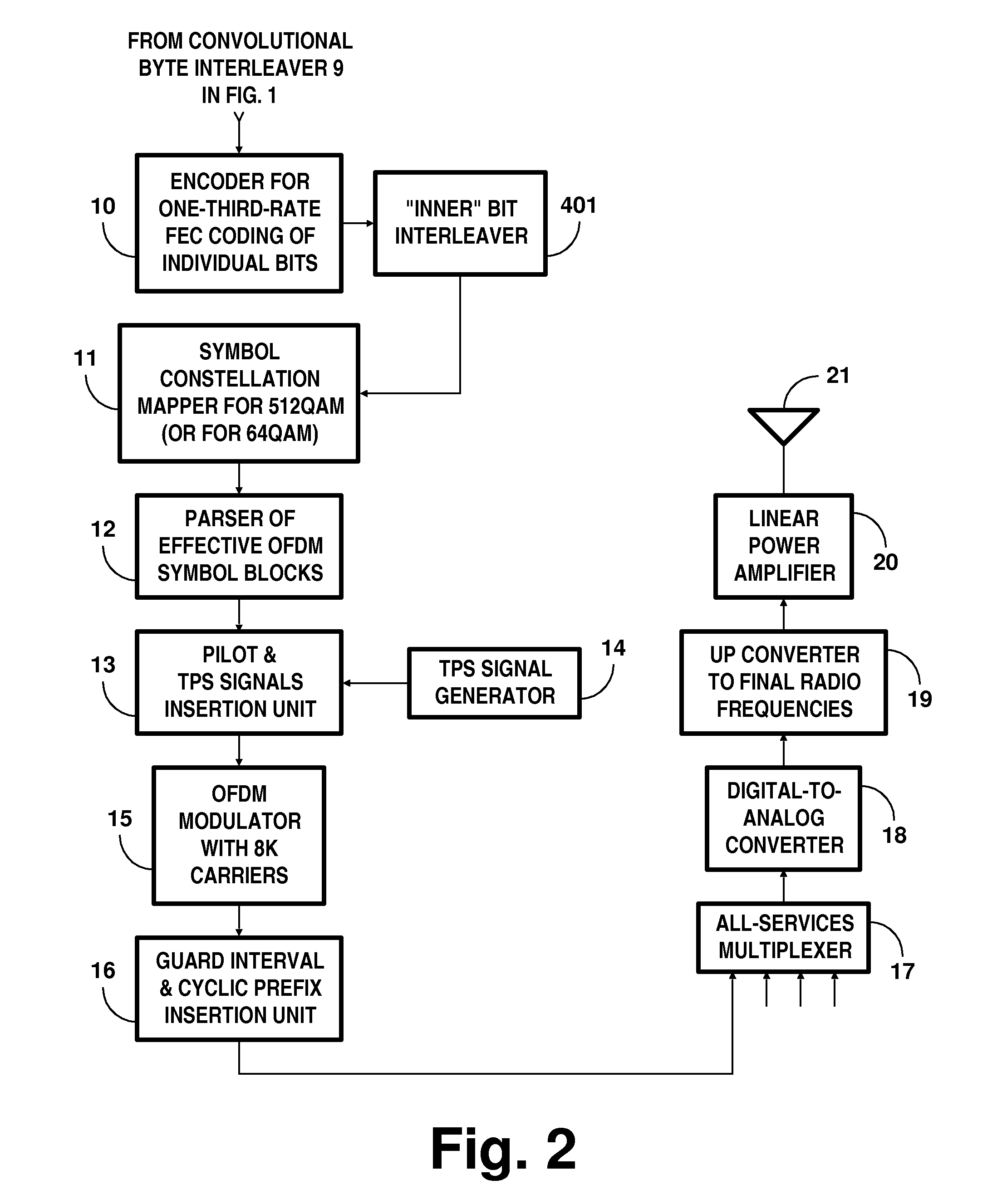
Digital television systems employing concatenated convolutional coded data
InactiveUS20100100793A1ConfidenceAvoid problemsCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresConvolutional codeDiversity scheme
In iterative-diversity (ID) transmission systems for signals with concatenated convolutional coding (CCC), paired iterative diversity signals each have ½ the code rate of the 8VSB DTV signals prescribed by the 1995 ATSC Digital Television Broadcast Standard. Known serial concatenated convolutional coding (SCCC) or novel parallel concatenated convolutional coding (PCCC) is used in such system. Pairs of CCC signals code data bits and ones' complemented data bits respectively, using similar coding algorithms. Receivers for this transmission system use respective turbo decoders for turbo decoding the earlier-transmitted and later-transmitted CCC signals. Turbo decoding of the earlier-transmitted portions of iterative diversity signals is delayed to be contemporaneous with turbo decoding of the later-transmitted portions of iterative diversity signals. This facilitates the turbo decoders exchanging information concerning confidence levels of data bits during the turbo decoding procedures.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Communication device and communication method
InactiveUS7260768B1Code conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresComputer hardwareTurbo encoder
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method for determining transport block size and signal transmission method using the same
ActiveUS20090199066A1Efficiently signaledQuantity minimizationTransmission systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementCoding blockComputer science
A method for determining a transport block size and a signal transmission method using the same are disclosed. When the signal transmission method constructs a transport block size combination by predetermining the transport block size, it prevents the insertion of any dummy bits in consideration of the limitation of an input bit length of an encoder during an encoding step. If a CRC is attached to the transport block and the transport block is segmented into a plurality of code blocks, the signal transmission method can establish a length of the transport block in consideration of a length of the CRC attached to each code block.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
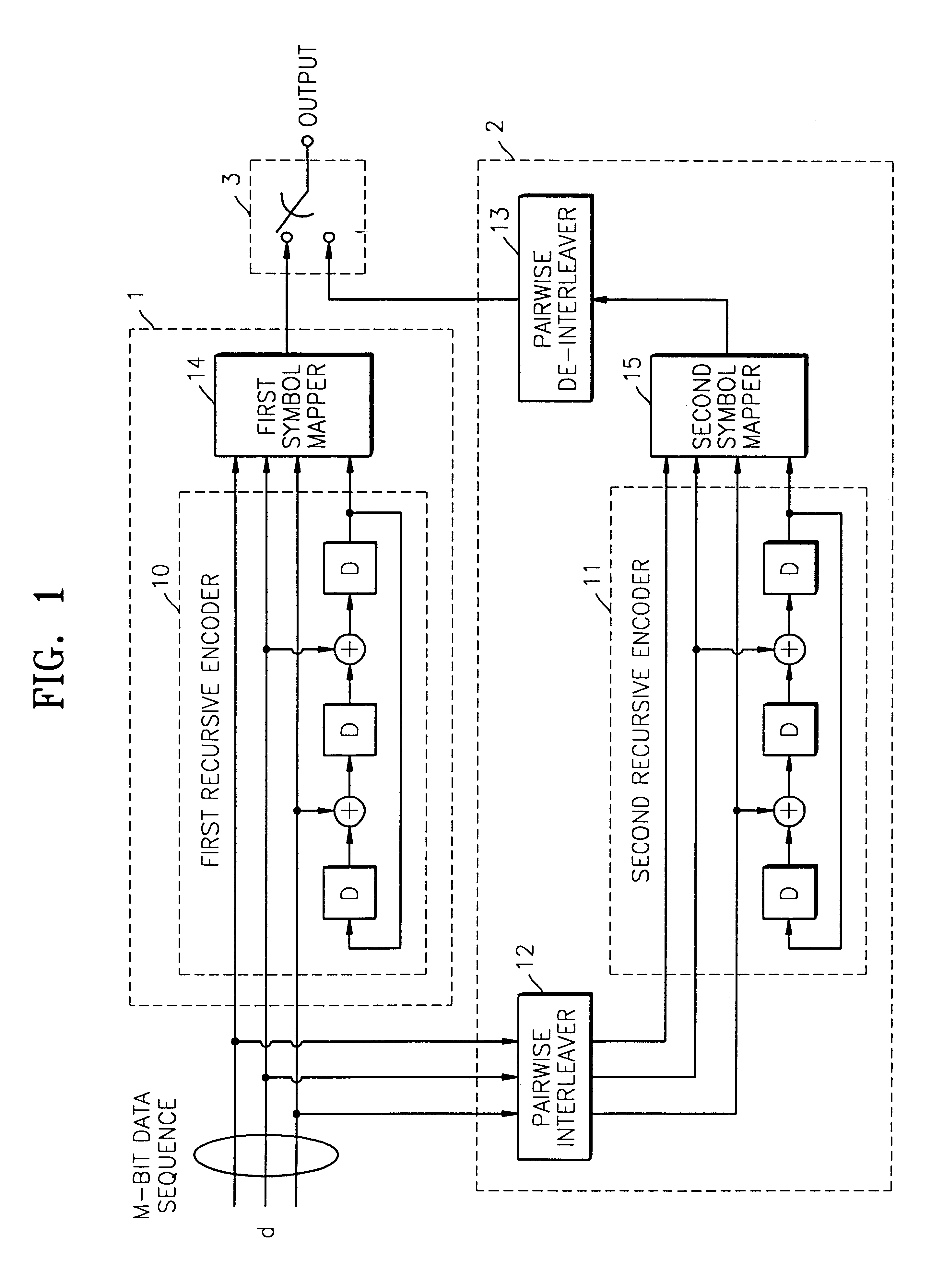
Encoding device for performing serial concatenated coding
InactiveUS7246296B2Improve performanceError correction/detection using convolutional codesCode conversionComputer scienceInfinite impulse response
The present invention is particularly applied to serial concatenated coding and serial concatenated trellis coded modulation. In second encoding 107, which is inner coding, a sequence that is not encoded or that is encoded so as to produce a finite impulse response and a sequence that is encoded so as to produce an infinite impulse response are output. In interleaving 106 before the second encoding 107, the sequences are permuted so as not to be mixed with each other.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC +1
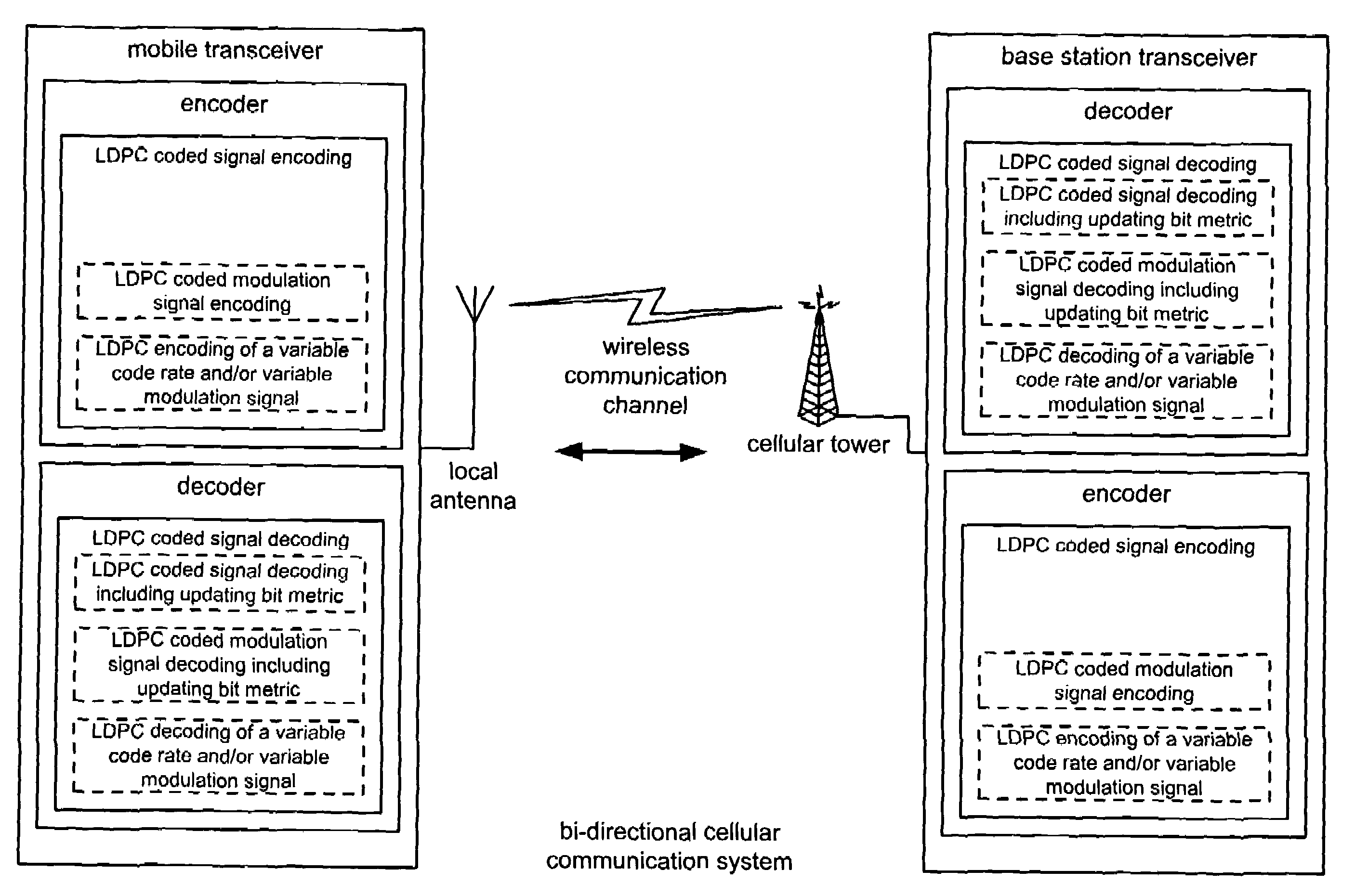
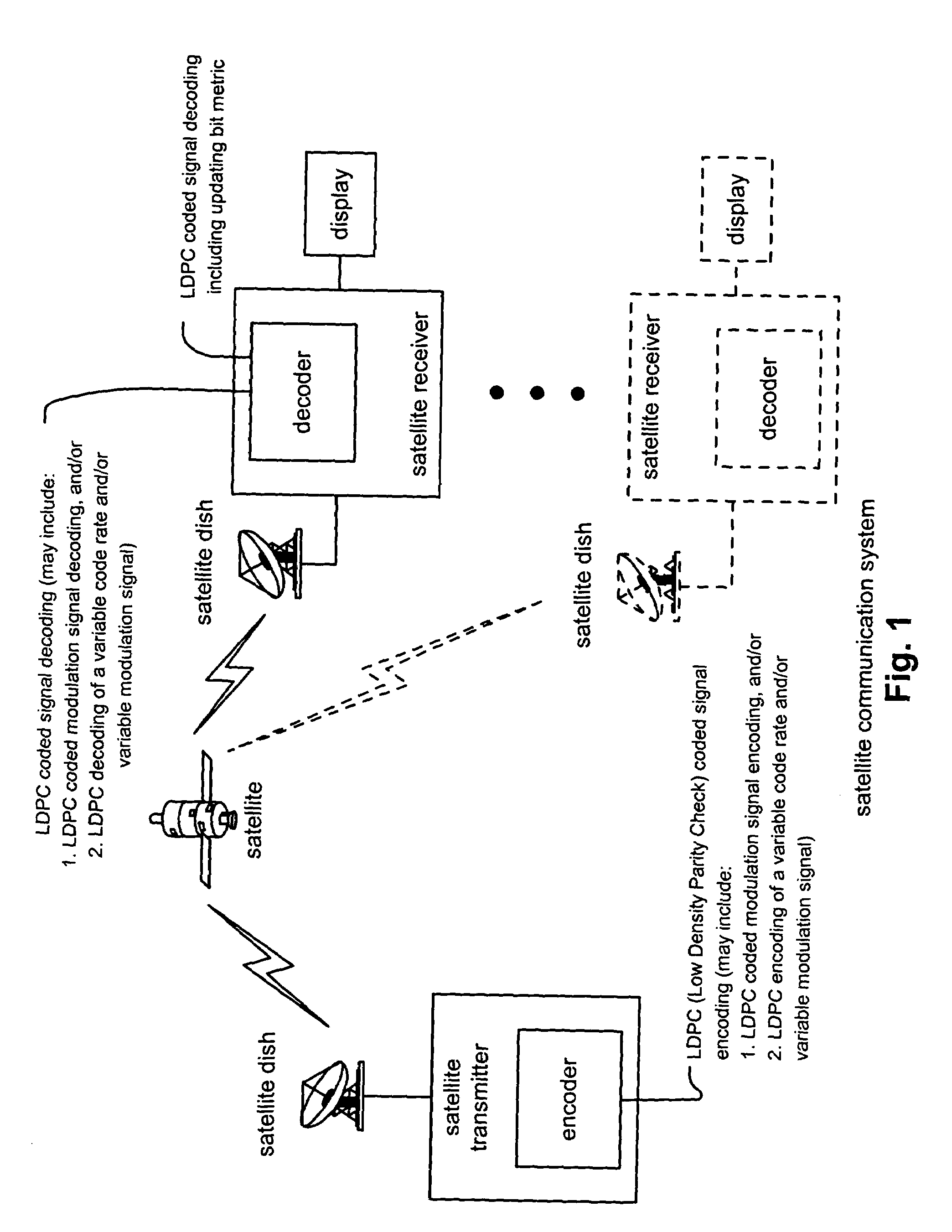
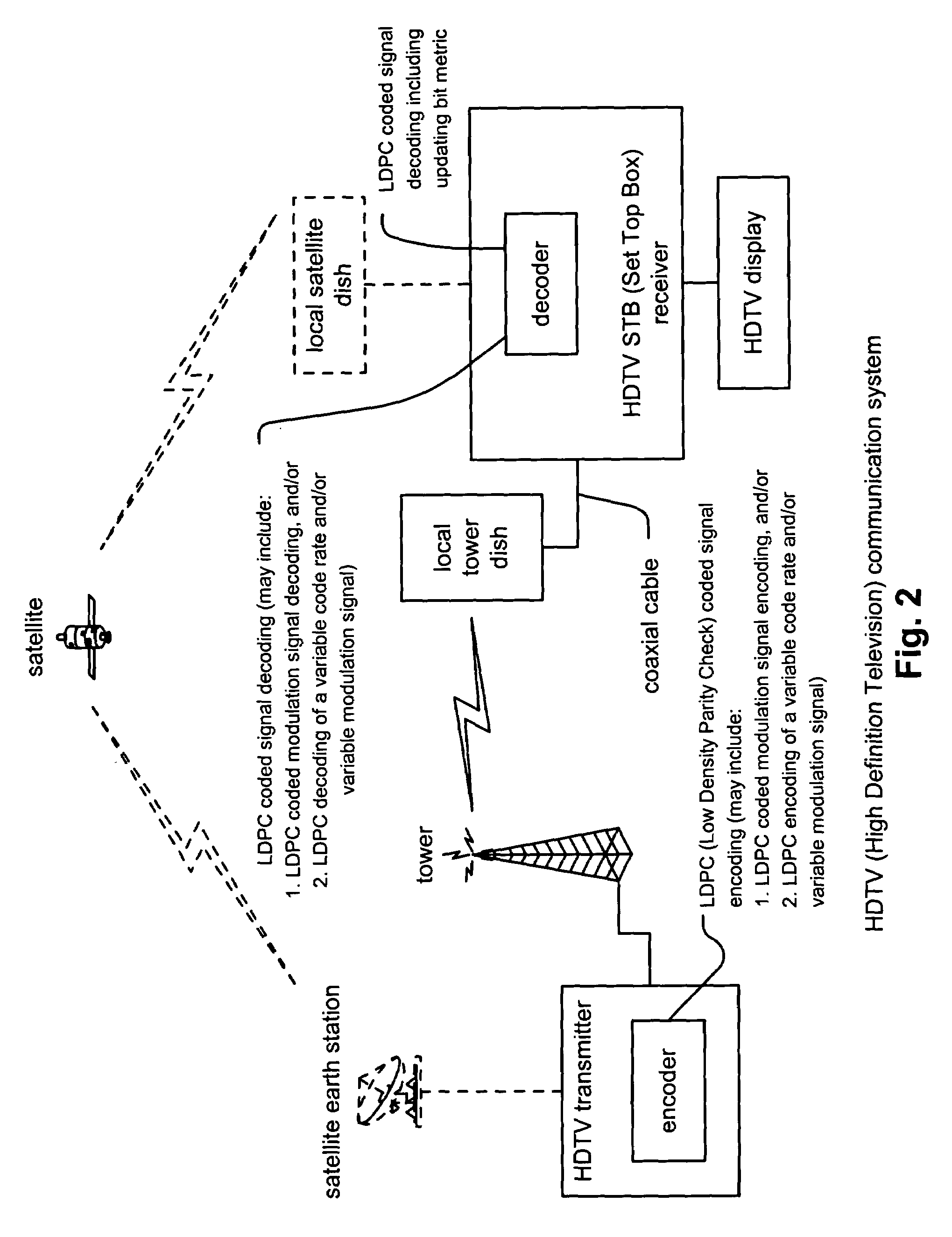
Iterative metric updating when decoding LDPC (low density parity check) coded signals and LDPC coded modulation signals
InactiveUS7216283B2Other decoding techniquesError correction/detection using LDPC codesLow-density parity-check codeLow density
Iterative metric updating when decoding LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) coded signals and LDPC coded modulation signals. A novel approach is presented for updating the bit metrics employed when performing iterative decoding of LDPC coded signals. This bit metric updating is also applicable to decoding of signals that have been generated using combined LDPC coding and modulation encoding to generate LDPC coded modulation signals. In addition, the bit metric updating is also extendible to decoding of LDPC variable code rate and / or variable modulation signals whose code rate and / or modulation may vary as frequently as on a symbol by symbol basis. By ensuring that the bit metrics are updated during the various iterations of the iterative decoding processing, a higher performance can be achieved than when the bit metrics remain as fixed values during the iterative decoding processing.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System for digital television broadcasting using modified 2/3 trellis coding
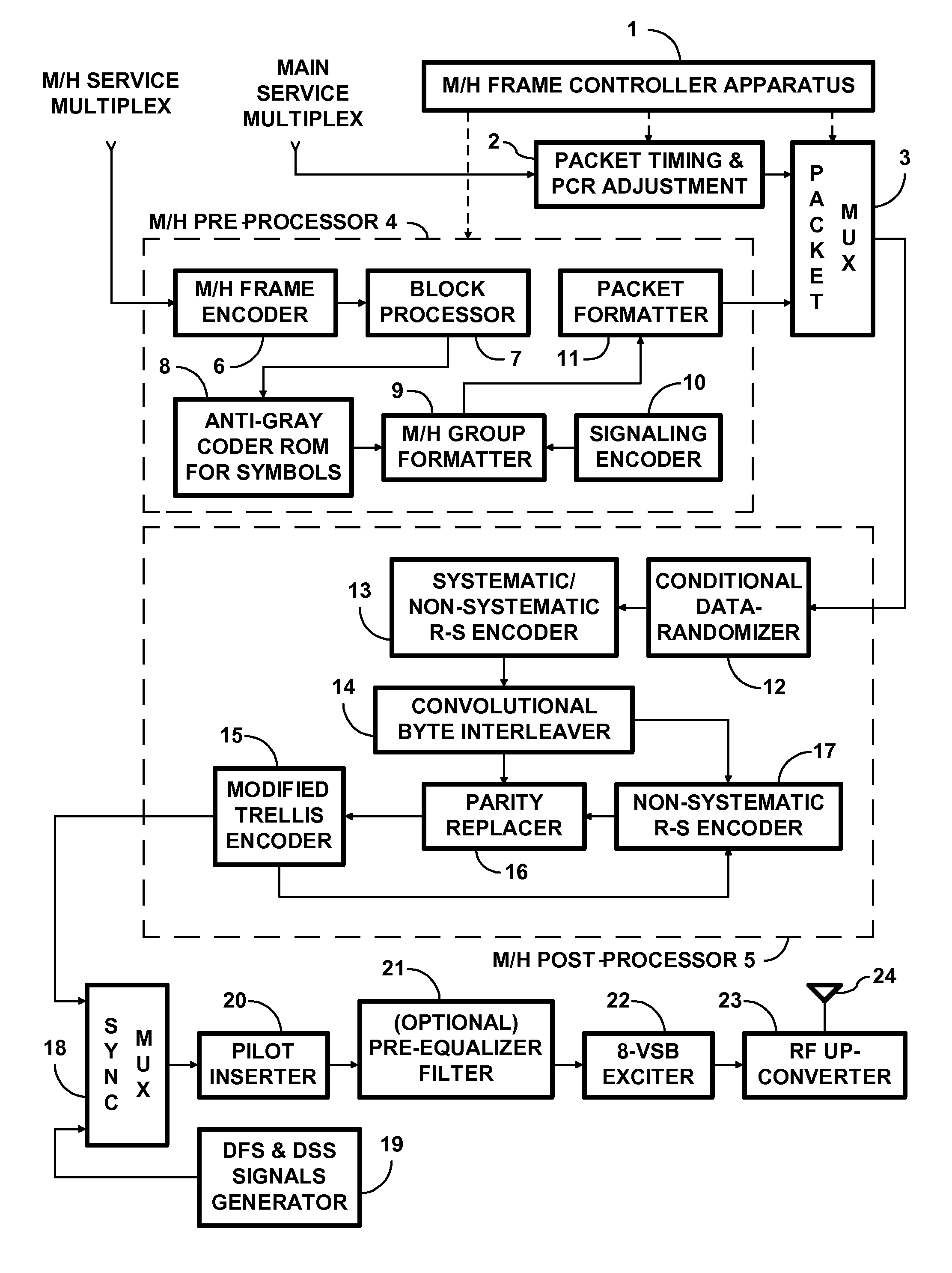
ActiveUS20090323823A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesSymbol interleavingComputer science
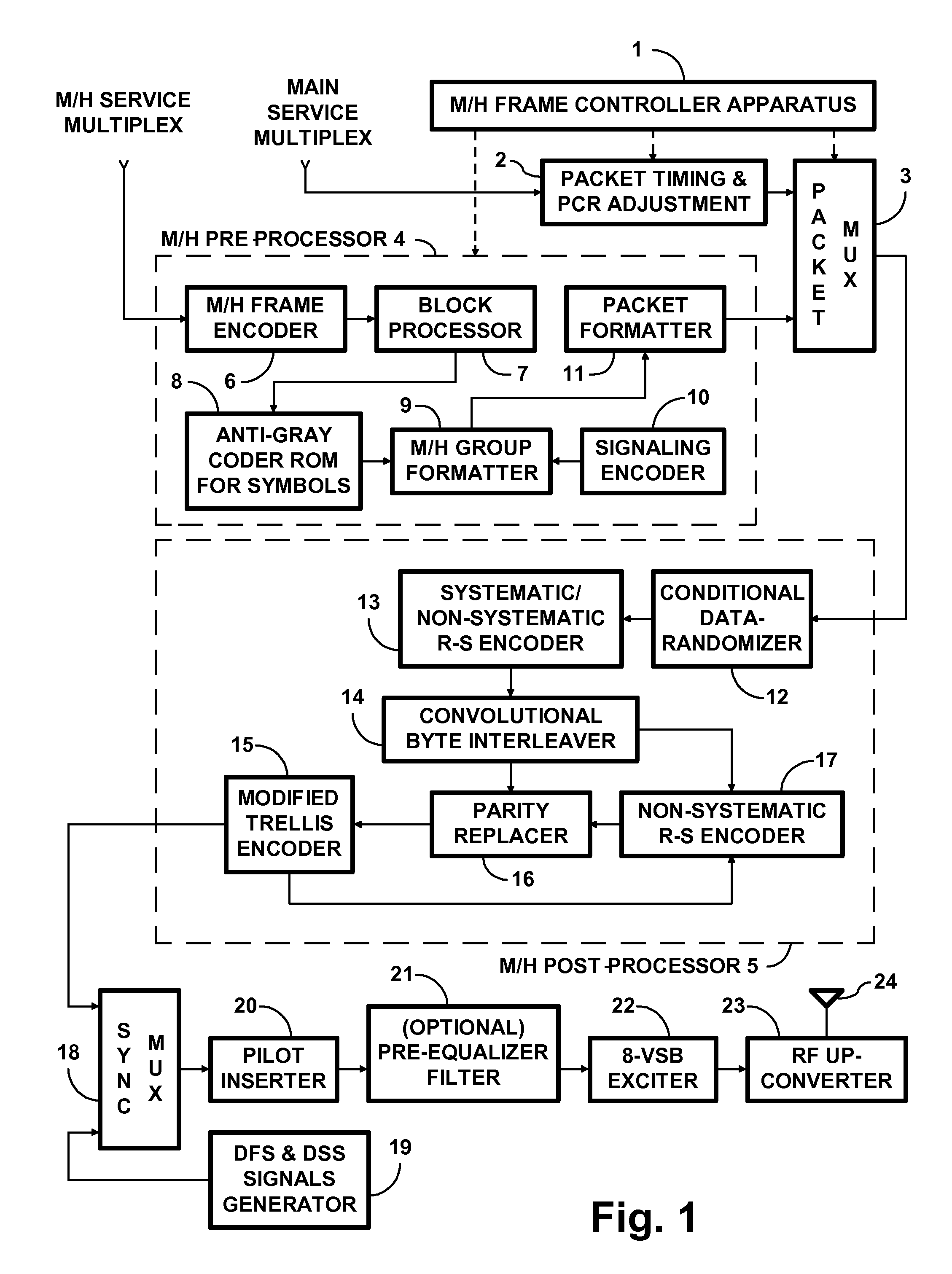
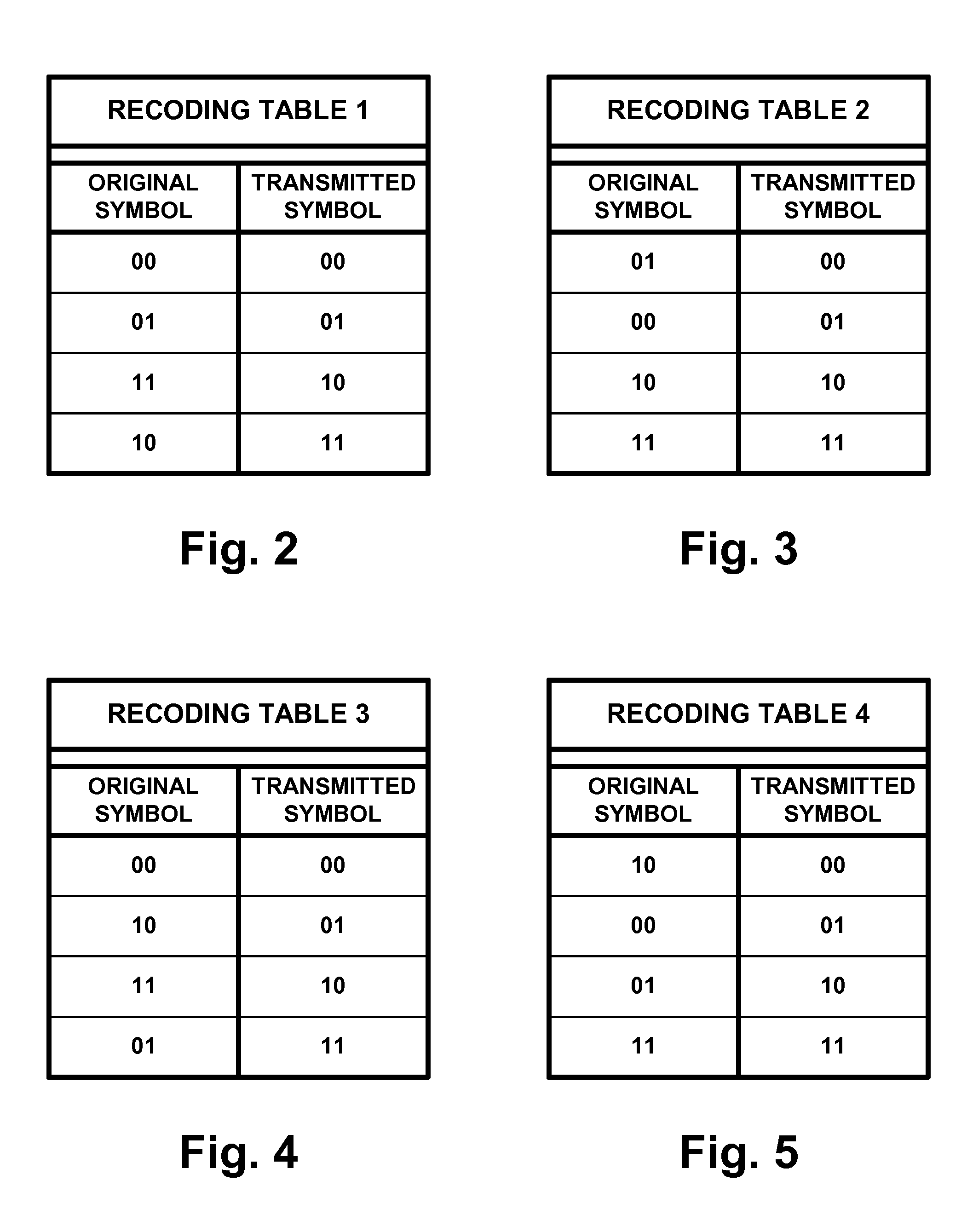
The outer convolutional coding of the signals used to transmit mobile-handheld (M / H) service data within digital-television (DTV) signals is subjected to anti-Gray coding, either before or after its interleaving, but before its inner convolutional coding. In a receiver for such M / H-service data, portions of the trellis decoded DTV signal containing soft decisions concerning symbol-interleaved convolutionally coded M / H-service data are recoded for a Gray-code mapping of symbols to modulation levels. This is done either before or after symbol de-interleaving, but before decoding the outer convolutional coding. Soft decisions concerning extrinsic information to be fed back to the ⅔ trellis decoder to close a turbo decoding loop are derived from soft decisions as to the M / H-service data, which derivation includes re-coding for a binary-code mapping of symbols to modulation levels. Each re-coding procedure can be performed using ROM, but preferably is performed using simple digital logic.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
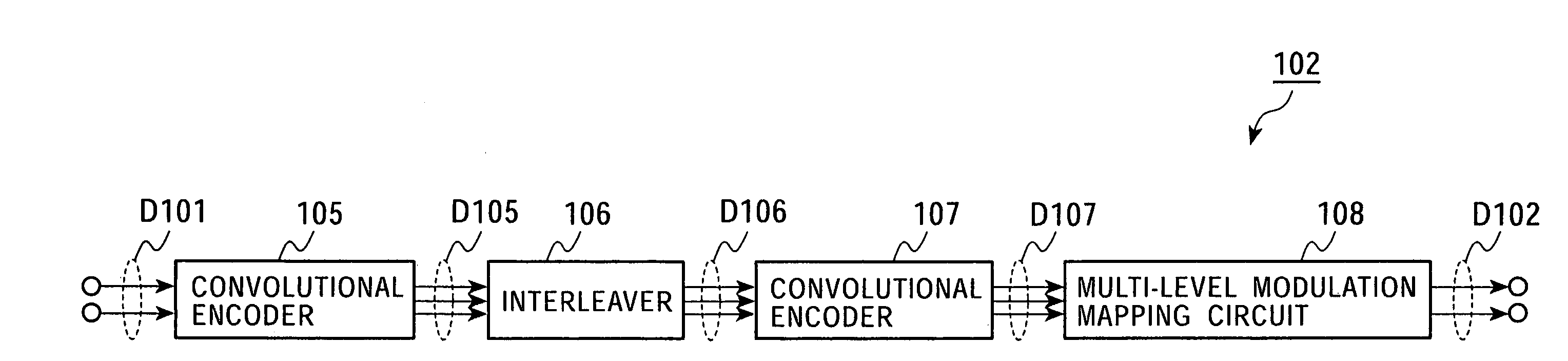
Encoding device and method and decoding device and method
InactiveUS6765507B2Improve performanceImprove accuracyError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesData transmissionComputer science
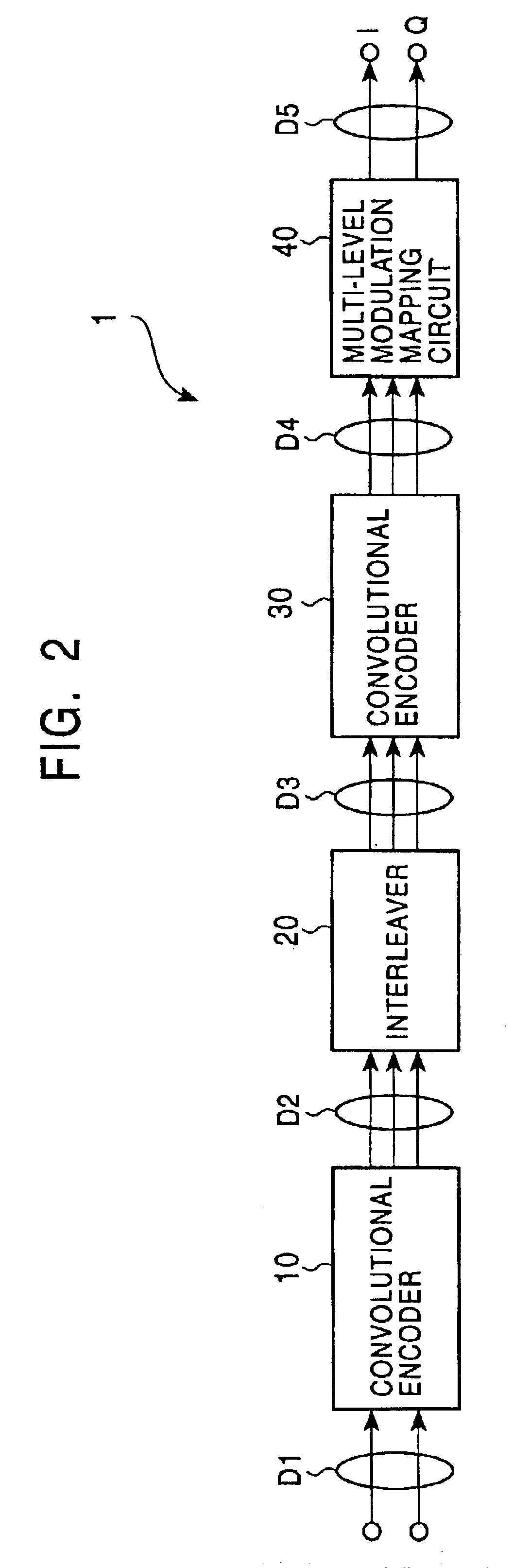
An encoding device in a data transmission / reception system includes a first convolutional encoder that encodes an outer code, an interleaver that permutes input data, a second convolutional encoder that encodes an inner code, and a muti-level modulation mapping circuit that performs signal-point mapping based on eight-phase shift keying. When the encoding device uses the second convolutional encoder having two or more memories, the first convolutional encoder uses, as the outer code, a code with a minimum output distance greater than the maximum input distance at which the minimum-distance inner code is generated.
Owner:SONY CORP
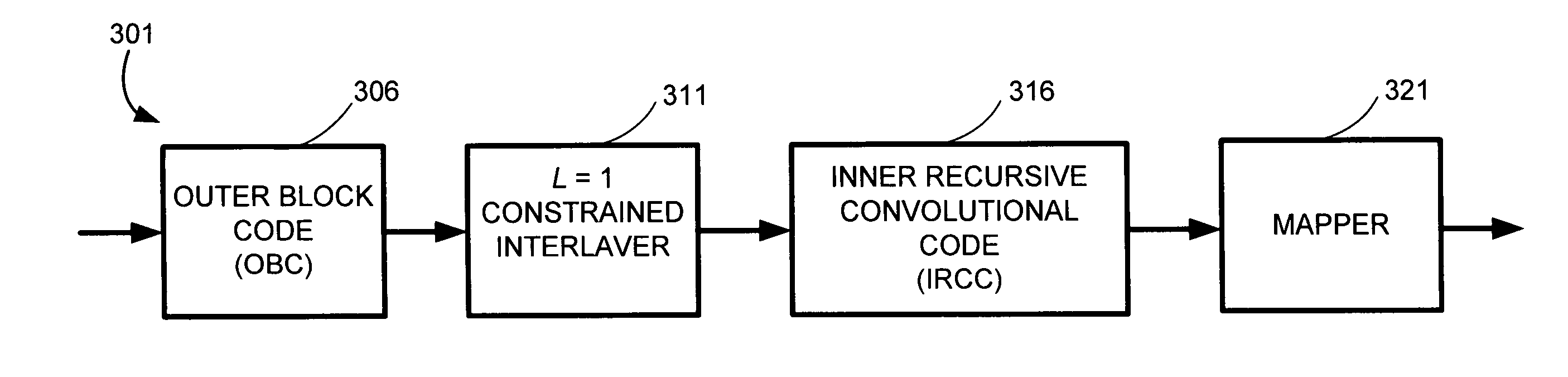
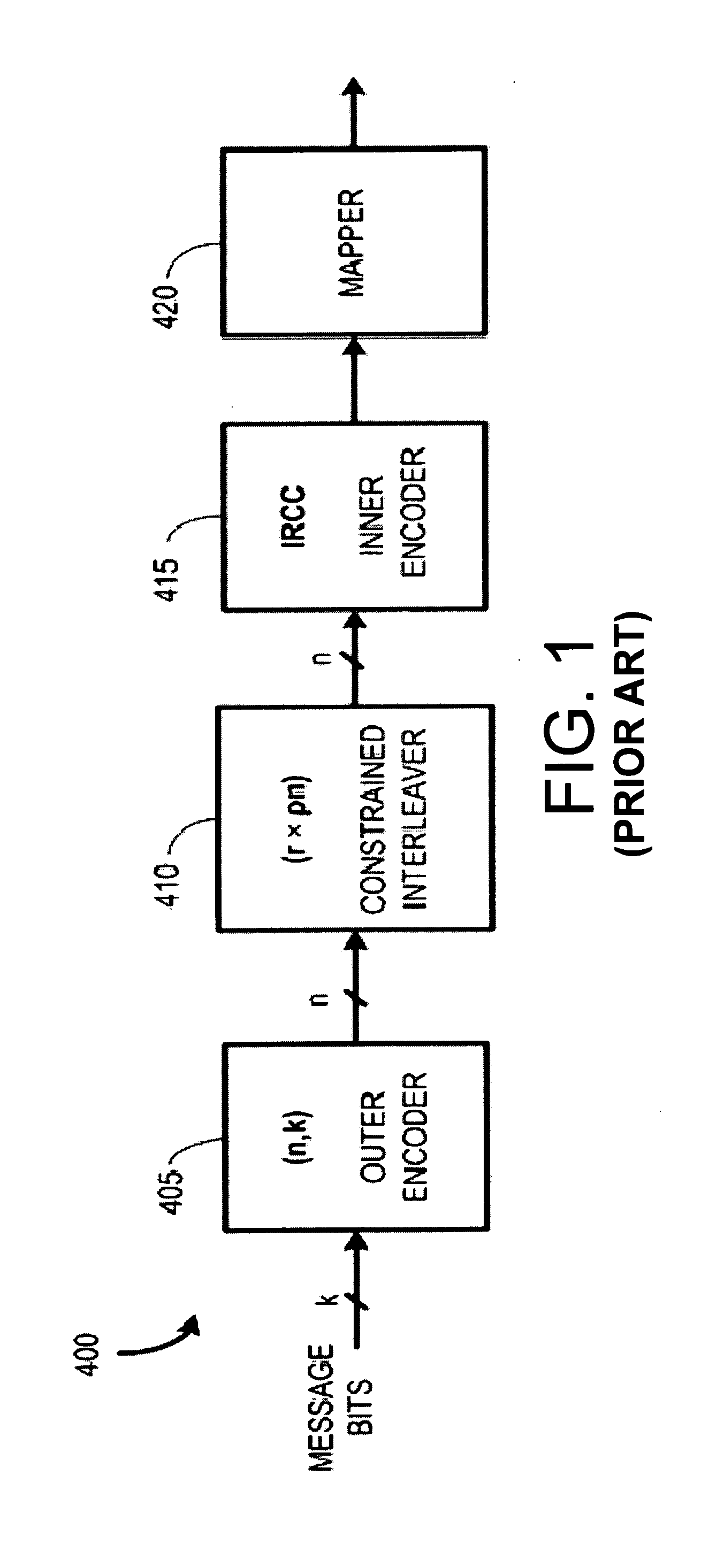
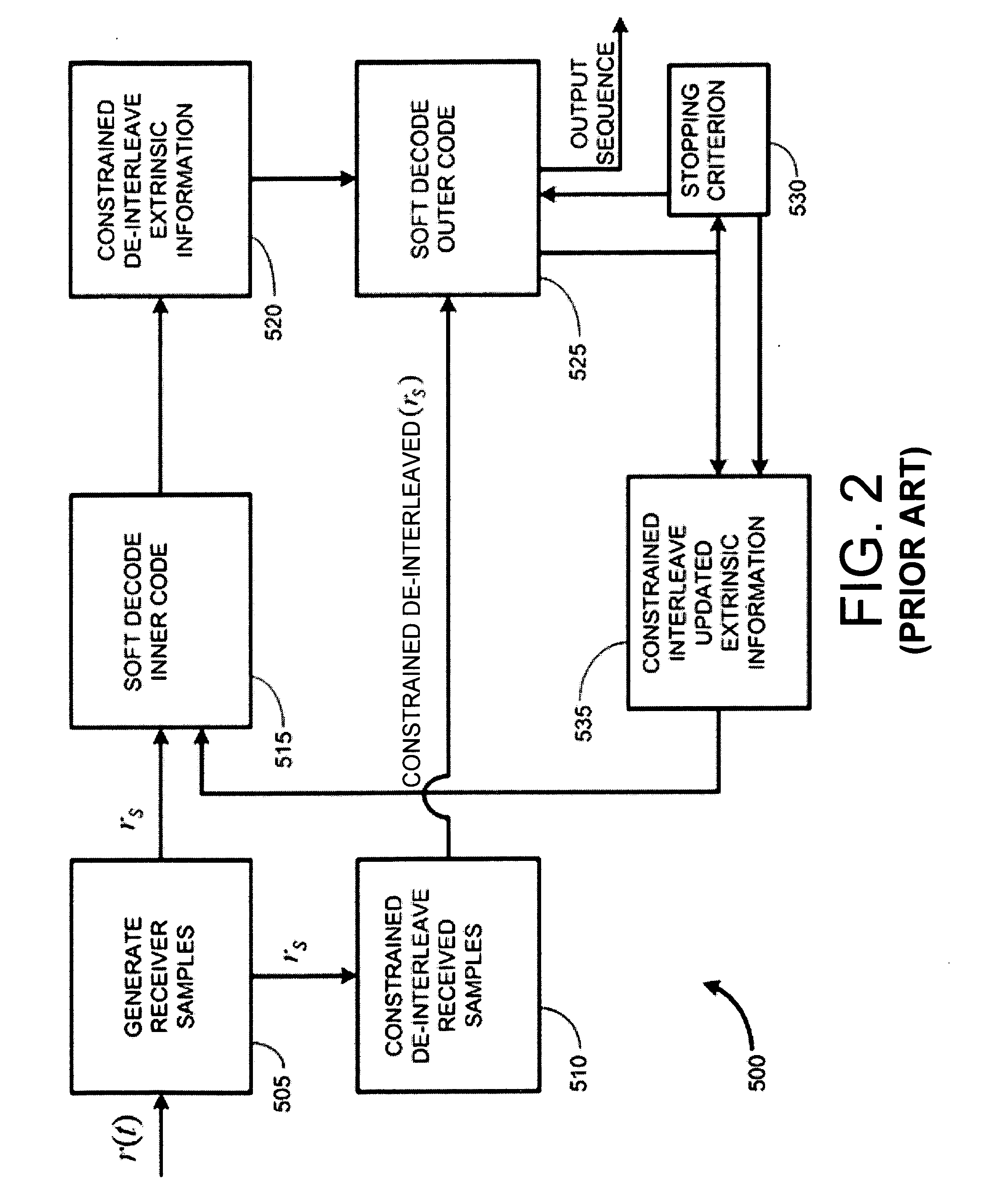
Constrained interleaving for 5G wireless and optical transport networks
InactiveUS20160352362A1Reduce weightInterleaver gain can be improvedError correction/detection using convolutional codesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCommunications systemAlgorithm
The present invention provides a design framework that is used to develop new types of constrained turbo block convolutional (CTBC) codes that have higher performance than was previously attainable. The design framework is applied to design both random and deterministic constrained interleavers. Vectorizable deterministic constrained interleavers are developed and used to design parallel architectures for real time SISO decoding of CTBC codes. A new signal mapping technique called constrained interleaved coded modulation (CICM) is also developed. CICM is then used to develop rate matching, spatial modulation, and MIMO modulation subsystems to be used with CTBC codes and other types of codes. By way of example, embodiments are primarily provided for improved 5G LTE and optical transport network (OTN) communication systems.
Owner:FONSEKA JOHN P +1
Enhanced turbo product code decoder system
InactiveUS20060212781A1Error preventionOther decoding techniquesTheoretical computer scienceGalois field arithmetic
Owner:COMTECH TELECOMM CORP
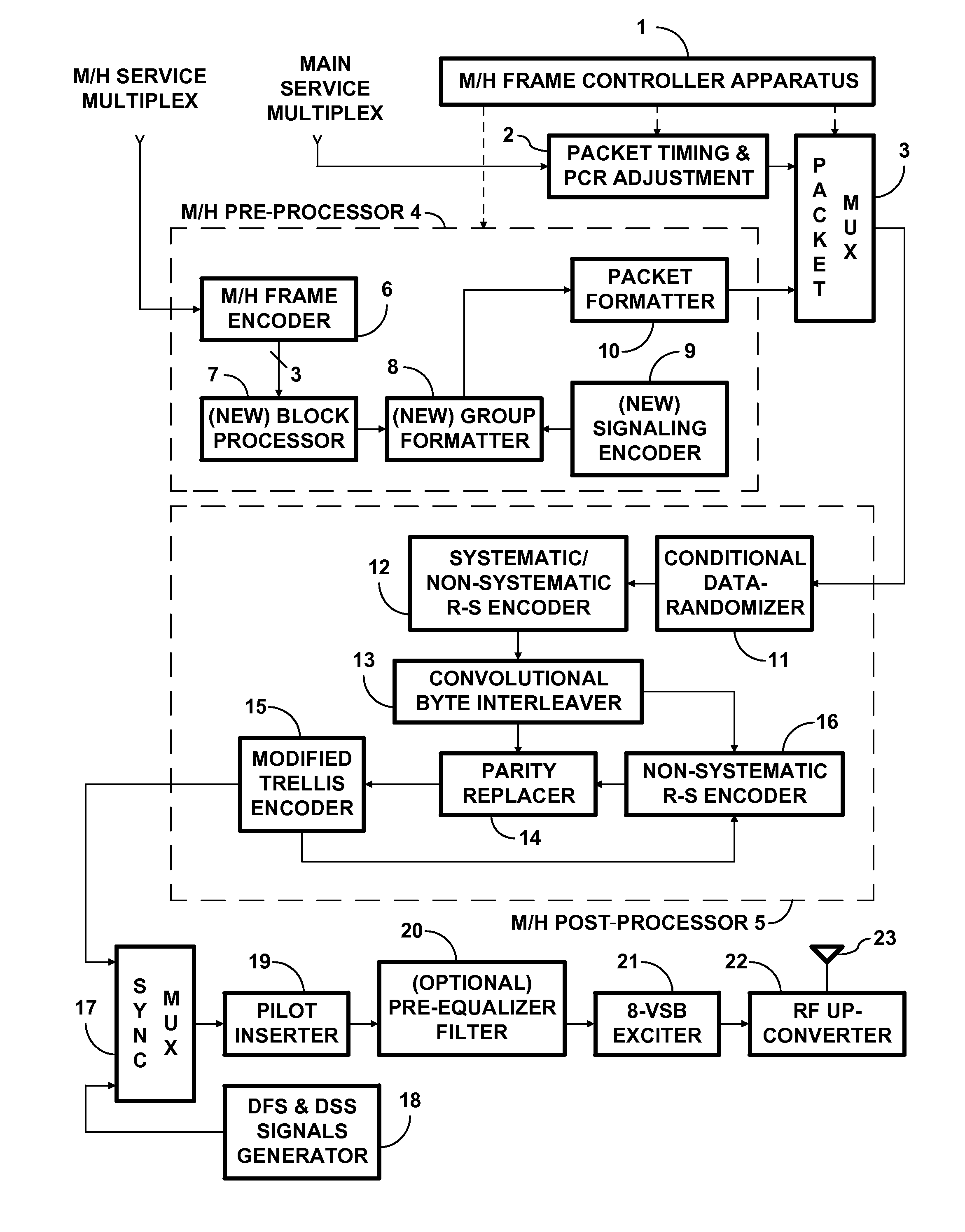
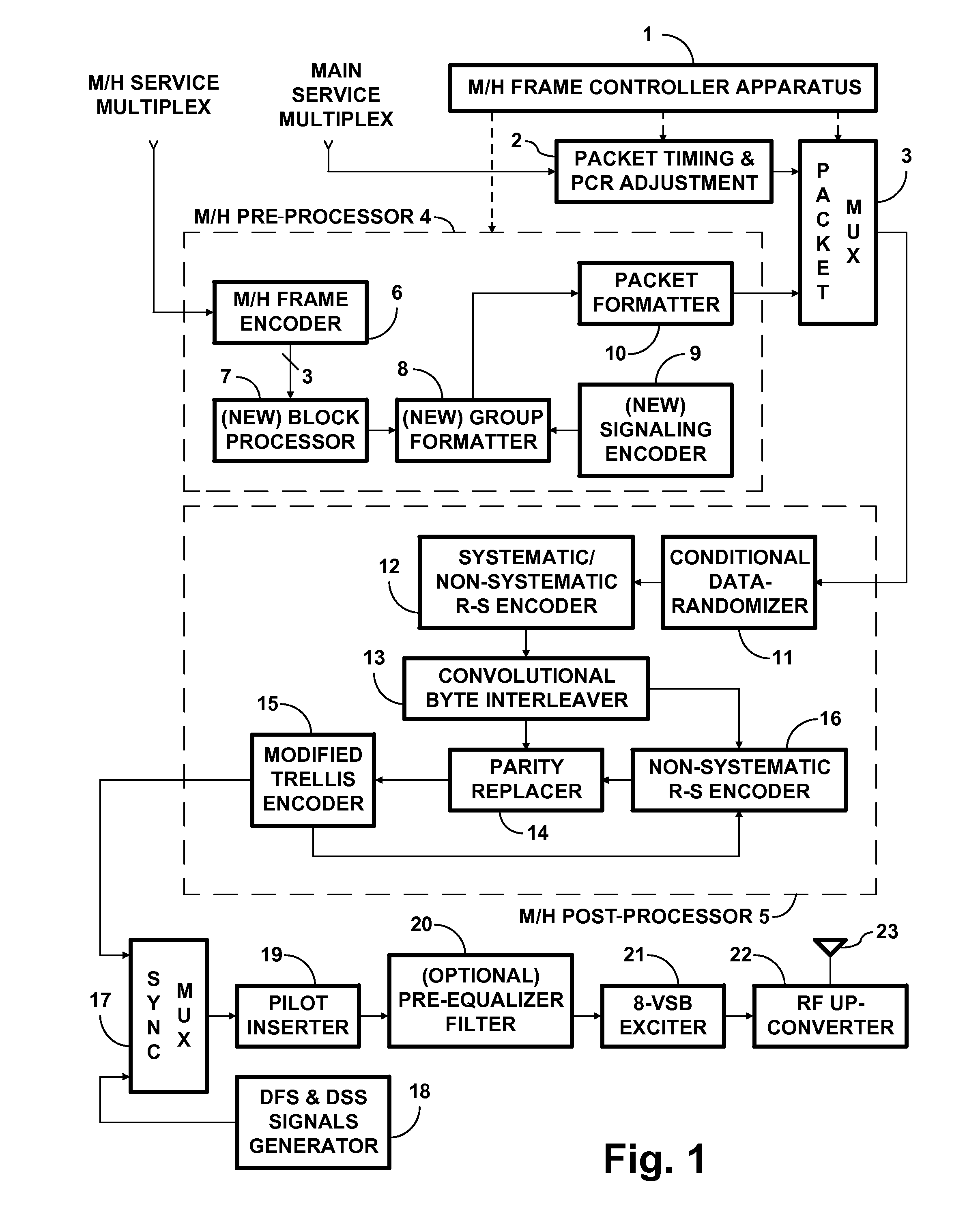
Digital broadcasting transmission and reception systems and methods thereof
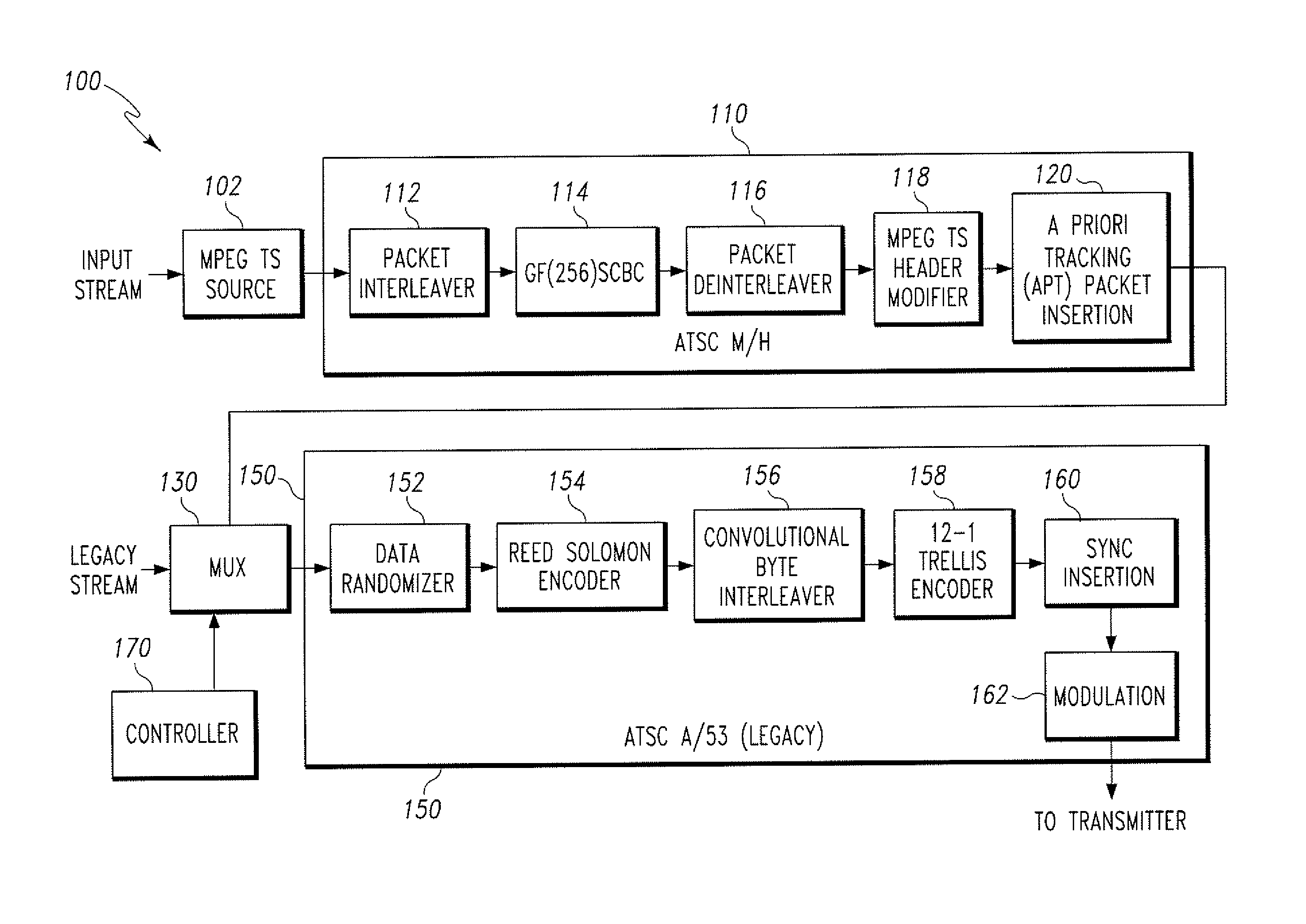
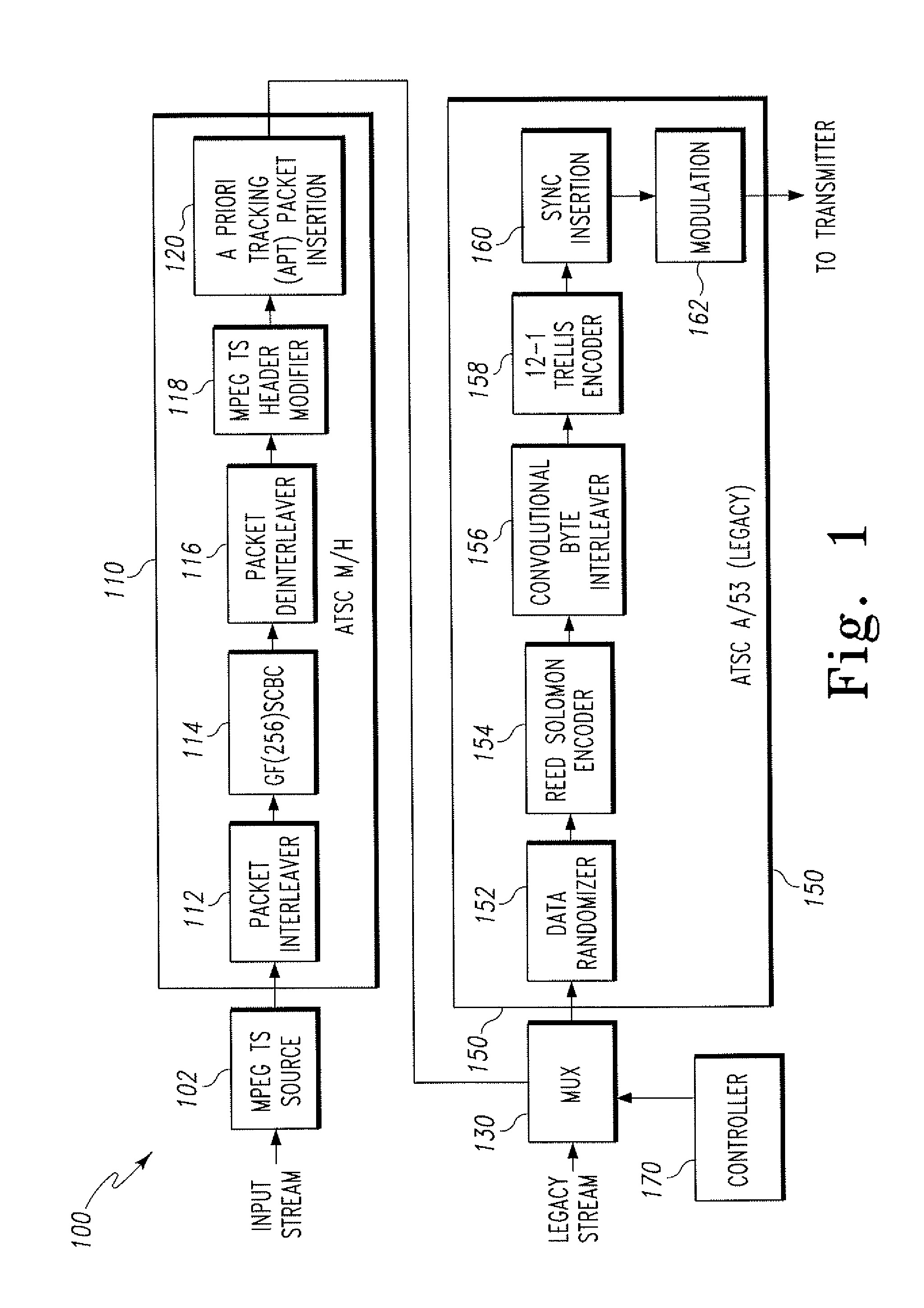
InactiveUS20070091885A1Improve reception performanceImprove performanceError correction/detection using concatenated codesError correction/detection using trellis codingMultiplexingDigital broadcasting
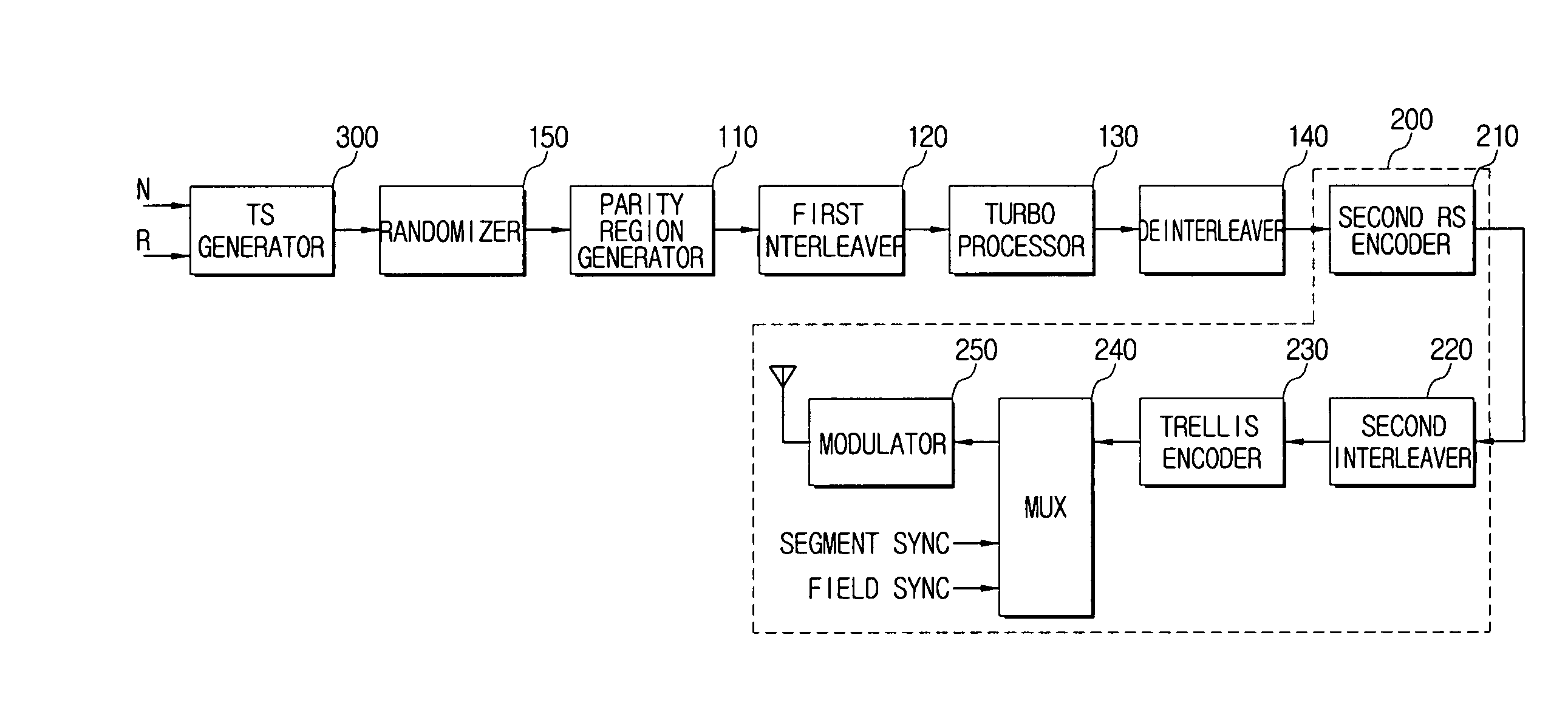
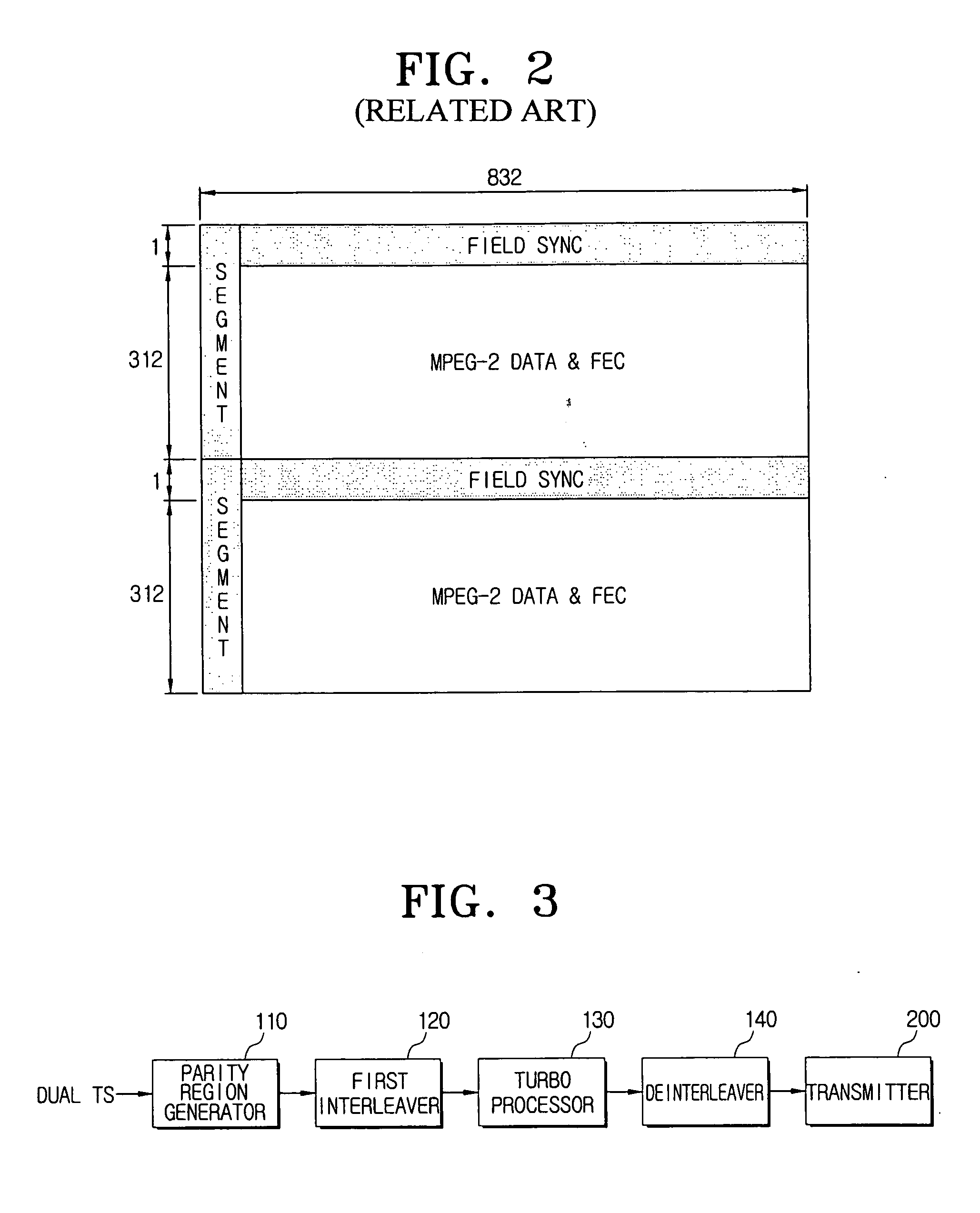
A method for processing a dual transport stream (TS) which is multiplexed from a normal stream and a turbo stream is provided for a digital broadcasting transmission / reception system. The digital broadcasting signal processing method includes encoding a dual transport stream (TS) which is multiplexed from a normal steam and a turbo stream; interleaving the encoded dual transport stream (TS); turbo-processing by detecting the turbo stream from the interleaved dual transport stream (TS), encoding the detected turbo stream, stuffing the encoded turbo stream into the dual transport stream (TS), and compensating a parity corresponding to the encoded turbo stream; and trellis-encoding the turbo-processed dual transport stream (TS). Accordingly, the digital broadcasting reception performance can be improved in diverse environments.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Constrained interleaving for 5G wireless and optical transport networks
InactiveUS20160352361A1Increase data rateIncrease performance rateError correction/detection using convolutional codesCode conversionCommunications systemAlgorithm
The present invention provides a design framework that is used to develop new types of constrained turbo block convolutional (CTBC) codes that have higher performance than was previously attainable. The design framework is applied to design both random and deterministic constrained interleavers. Vectorizable deterministic constrained interleavers are developed and used to design parallel architectures for real time SISO decoding of CTBC codes. A new signal mapping technique called constrained interleaved coded modulation (CICM) is also developed. CICM is then used to develop rate matching, spatial modulation, and MIMO modulation subsystems to be used with CTBC codes and other types of codes. By way of example, embodiments are primarily provided for improved 5G LTE and optical transport network (OTN) communication systems.
Owner:FONSEKA JOHN P +1
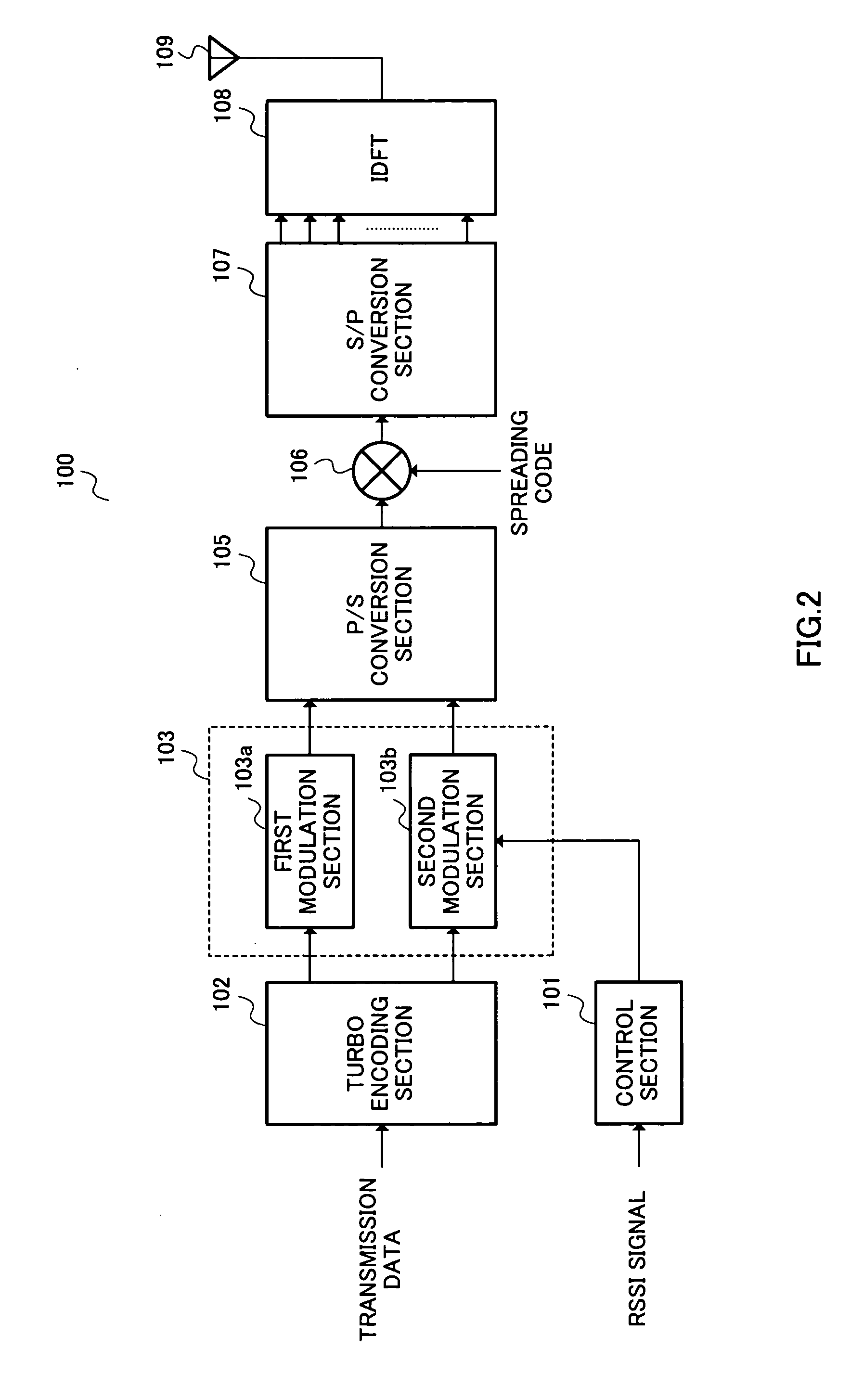
Transmitting device and transmitting method
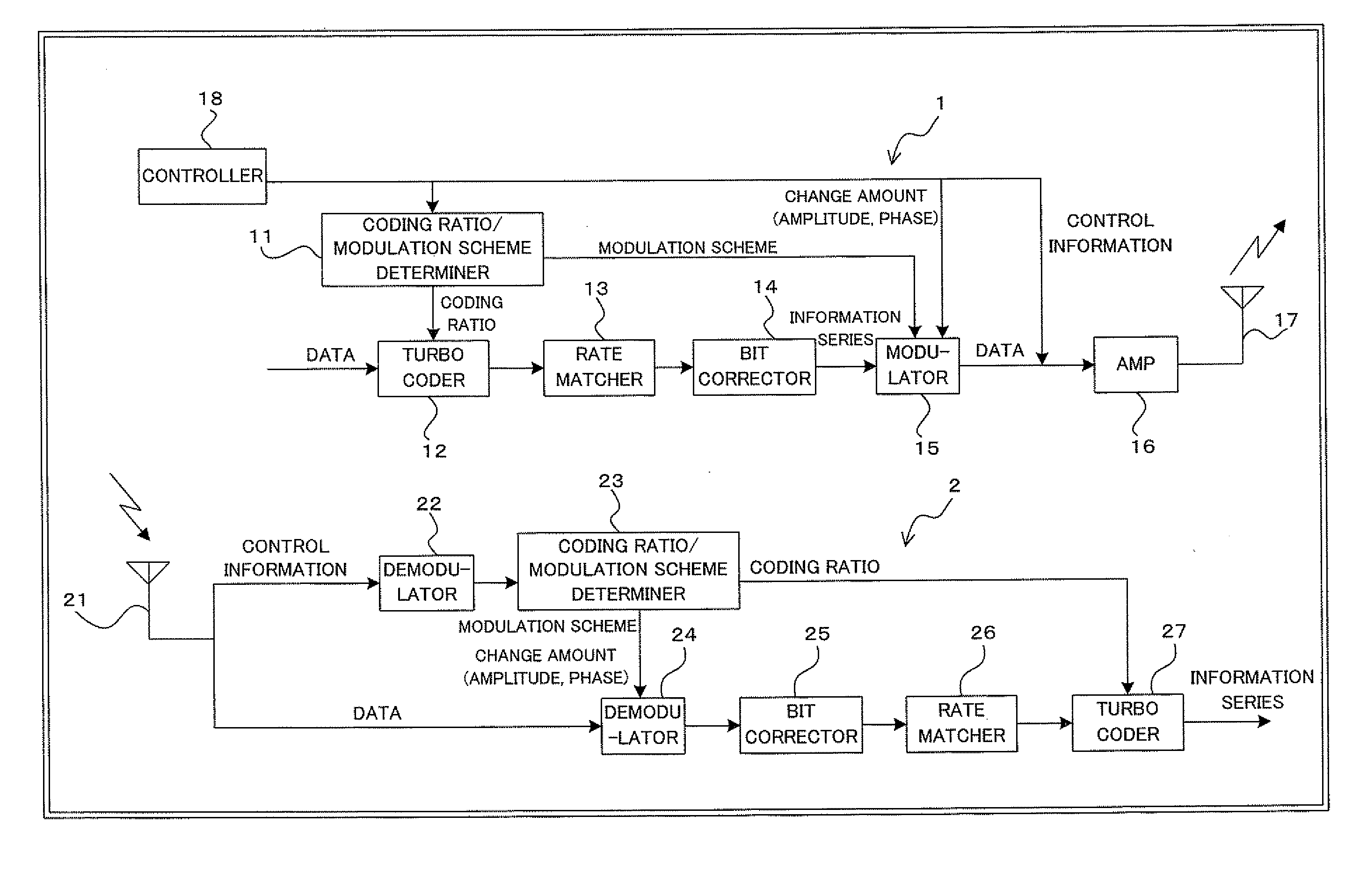
InactiveUS20050229073A1Error characteristicError efficiencyError prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using trellis codingControl signalComputer science
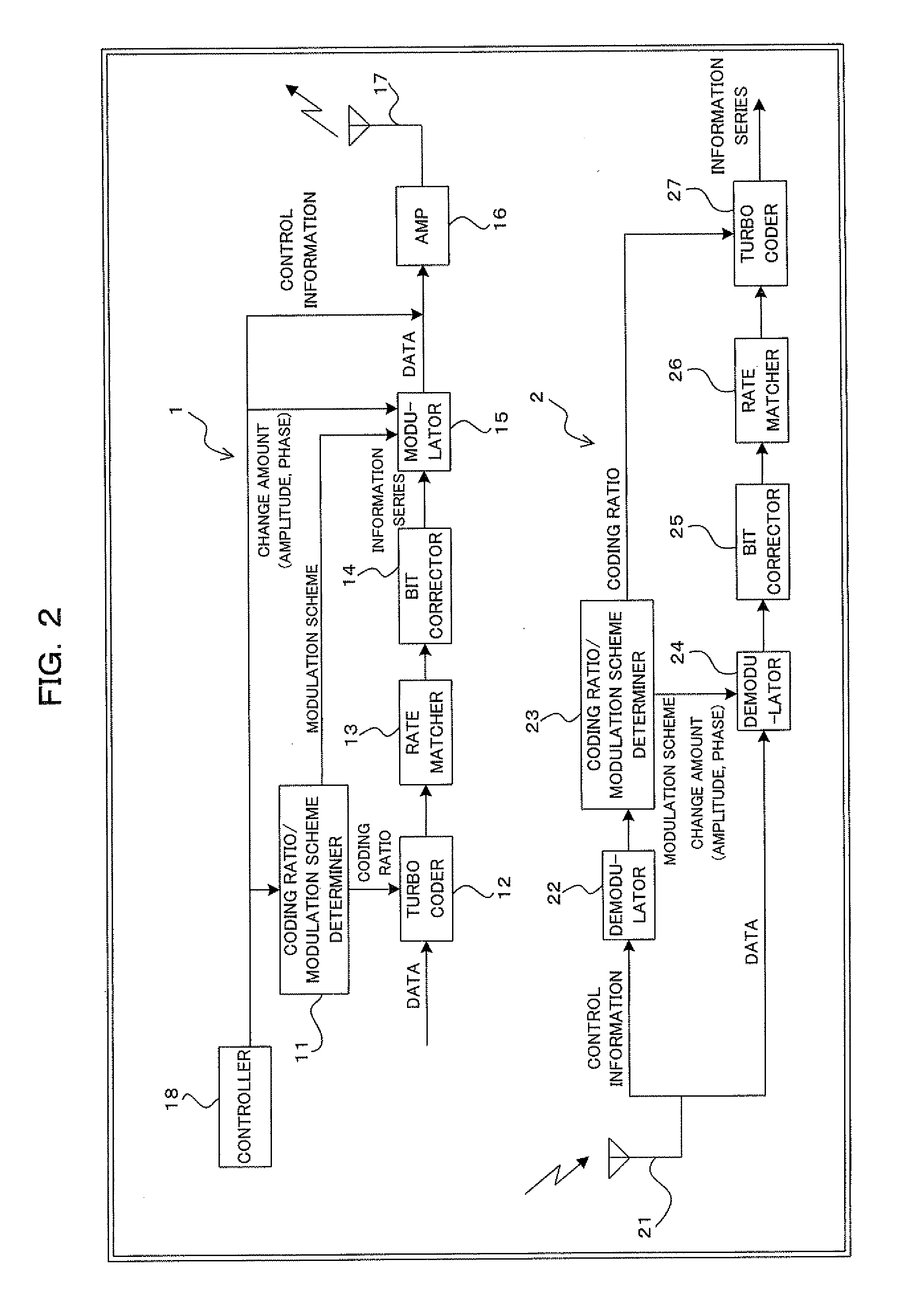
A turbo encoding section 102 turbo-encodes transmission data, outputs systematic bit data to a first modulation section 103a and outputs parity bit data to a second modulation section 104. The first modulation section 103a always QPSK-modulates systematic bit data. The second modulation section 103b adaptively modulates parity bit data. The control section 101 outputs a control signal for carrying out 16 QAM modulation to the second modulation section 103b when the RSSI value is equal to or higher than a threshold and outputs a control signal for carrying out QPSK modulation to the second modulation section 103b when the RSSI signal value is less than the threshold. In this way, it is possible to further make the error rate characteristic compatible with the transmission efficiency.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Method and device for coded modulation
InactiveUS20130215996A1Modulation type identificationError correction/detection using LDPC codesFrequency spectrumSpectral efficiency
A method for optimising a coded modulation scheme with a given spectral efficiency for communication over a fading channel represented / identified by B fading gains, wherein B is an integer number expressing the ratio between a code word duration and the duration over which the fading remains constant. The fading gains belong to a B-dimensional space of fading gains.
Owner:UNIV GENT
Method and apparatus for spectral efficient data transmission in satellite systems
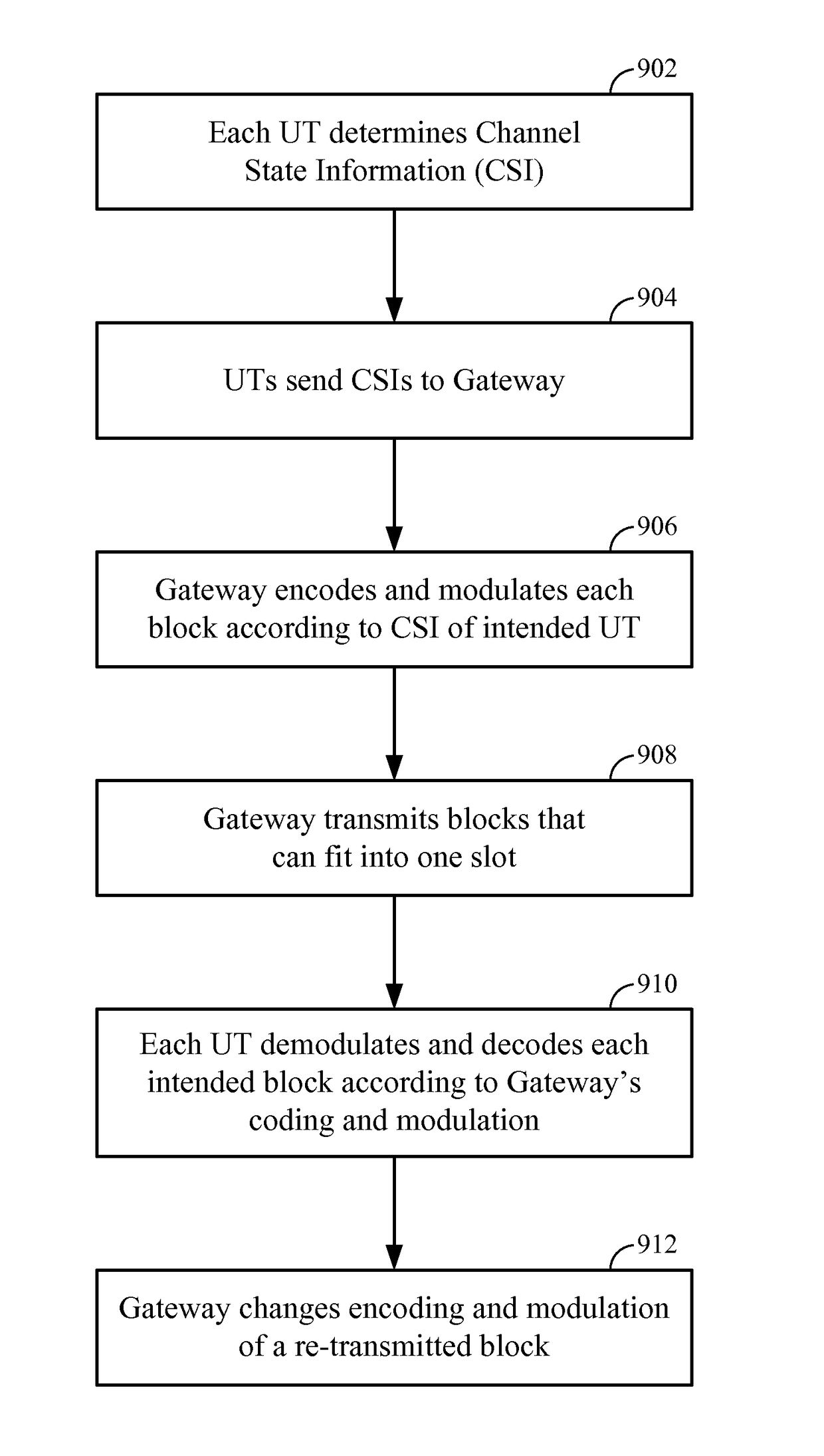
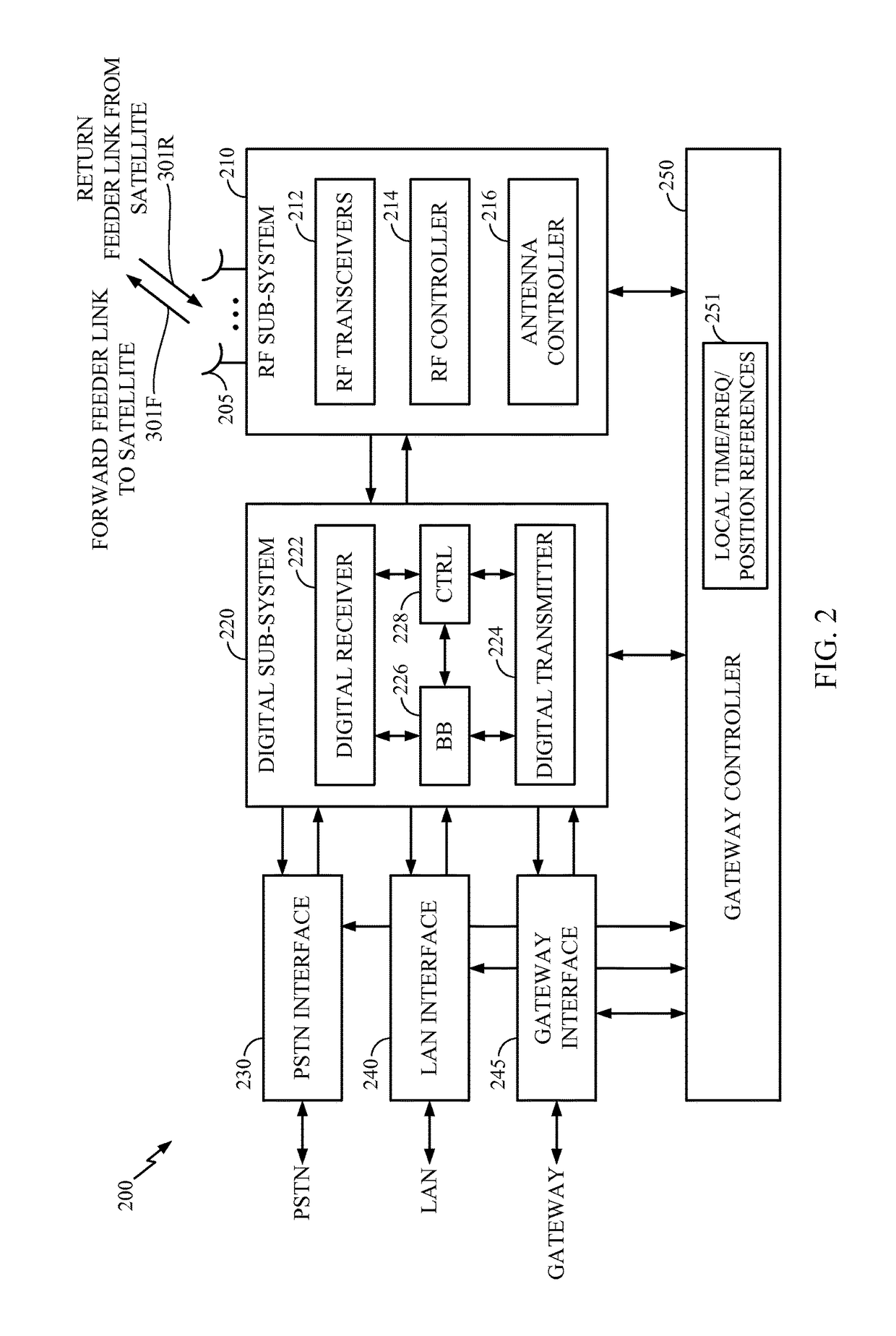
ActiveUS9893800B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelSignal allocationFrequency spectrumData transmission
A communication satellite system provides for spectral efficient data transmissions by a gateway to multiple user terminals by way of a satellite. The gateway transmits multiple blocks in a single slot, each block intended for one of the user terminals, where each block is encoded and modulated according to a scheme that may be different for each intended user terminal. Upon re-transmission of a block if that block is lost or received in error, the block may be encoded and modulated according to another scheme that is less spectrally efficient than in the first transmission of the block.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Apparatus and method for decoding signals
ActiveUS20110026601A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionTheoretical computer scienceBroadcast transmission
New capabilities will allow conventional broadcast transmission to be available to mobile devices. A method of decoding a bitstream is described including receiving a demodulated bitstream, the demodulated bitstream encoded using a byte-code encoding process, arranging a portion of the demodulated bitstream into a subset of bits, reordering the subset of bits, and decoding the subset of bits based on a property of the subset of bits and the encoding process. An apparatus includes means for decoding a bitstream based on a property of the subset of bits and the encoding process.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
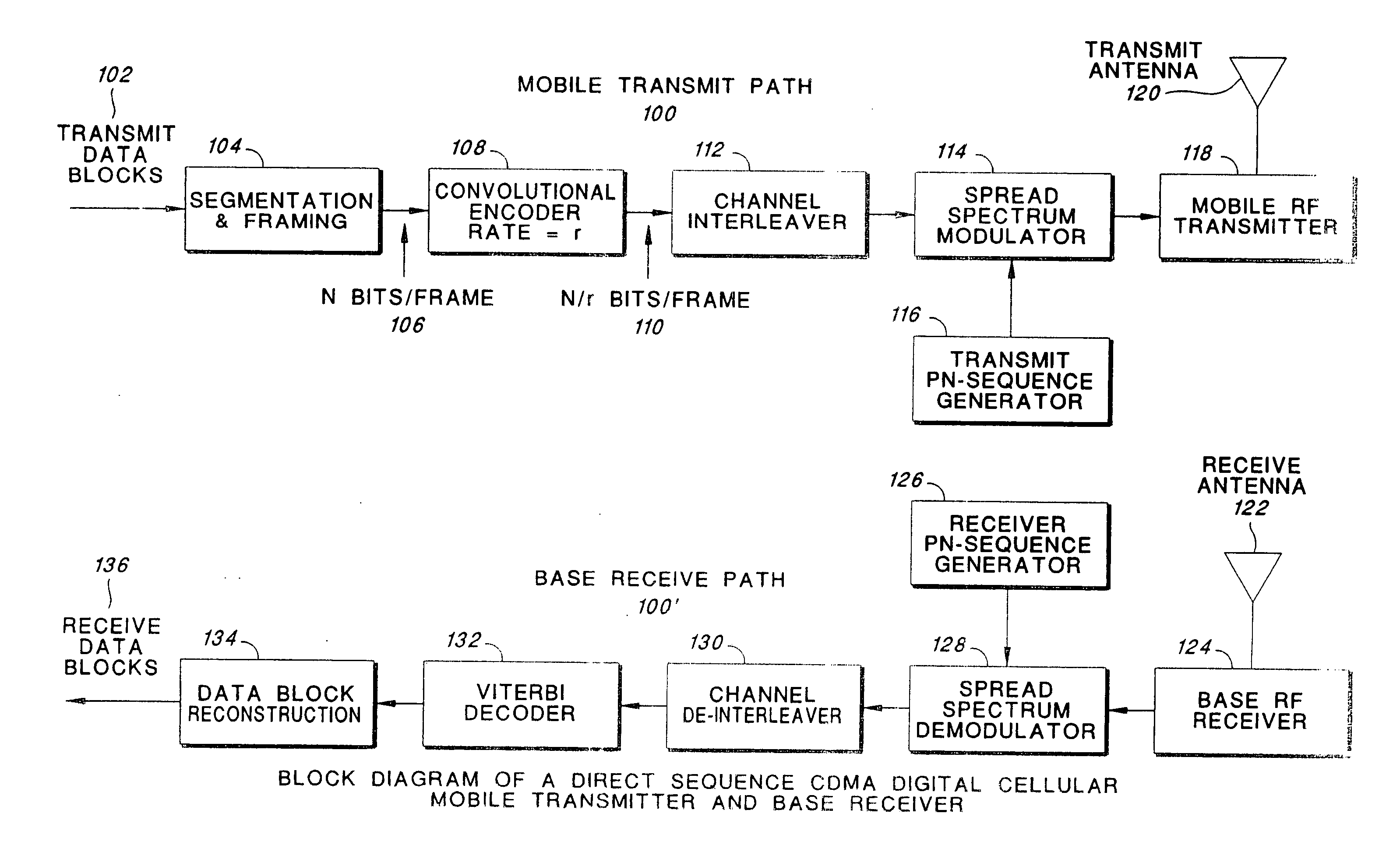
Bandwidth-efficient concatenated trellis-coded modulation decoder and decoding method thereof
InactiveUS6816556B2Reduce bit rateEnergy efficient ICTData representation error detection/correctionCommunications systemHigh bandwidth
A bandwidth-efficient concatenated trellis-coded modulation (TCM) decoder which is realized by combining turbo codes having an advantage of coping effectively with a fading channel with TCM having an advantage of bandwidth efficiency, and a decoding method thereof are provided. A conventional TCM method has high bandwidth efficiency suitable for transmitting information at high speed. However, it is very sensitive to InterSymbol interference (ISI) so it is usually applied to a wire communication system rather than to a wireless communication system. A turbo code method is an error correction encoding method showing steadiness in a channel having severe ISI and having an excellent error correction ability, but has drawbacks of low data transmission rate and low bandwidth efficiency due to a low code rate. Bandwidth-efficient concatenated TCM is provided for enhancing the steadiness against ISI and-improving power and bandwidth efficiency by applying the turbo code method to a TCM having a code rate of m / (m+1) to compensate for the drawbacks of the conventional TCM and turbo codes. A newly provided decoding method in bandwidth-efficient concatenated TCM uses a SOVA algorithm, thereby reducing decoder complexity and path memory. In addition, bandwidth-efficient concatenated TCM encoder and decoder are provided such to have parallel transition, thereby reducing the complexity of the bandwidth-efficient concatenated TCM decoder. Therefore, the Bandwidth-efficient concatenated TCM is applied to a high speed wireless communication system and can increase bandwidth efficiency and coding gain.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
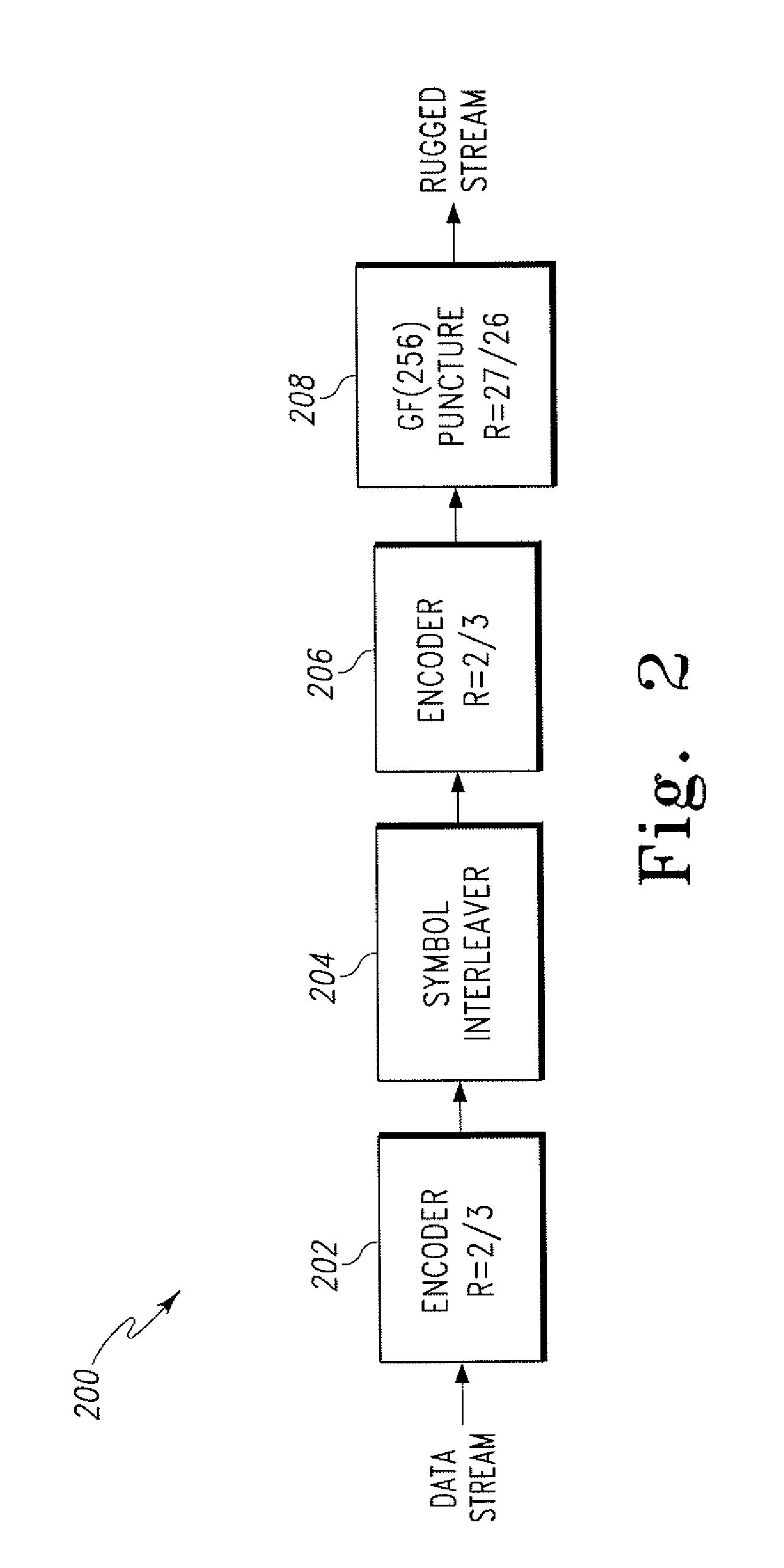
Sets of rate-compatible universal turbo codes nearly optimized over various rates and interleaver sizes
InactiveUS20050172202A1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionHigh rateTurbo encoder
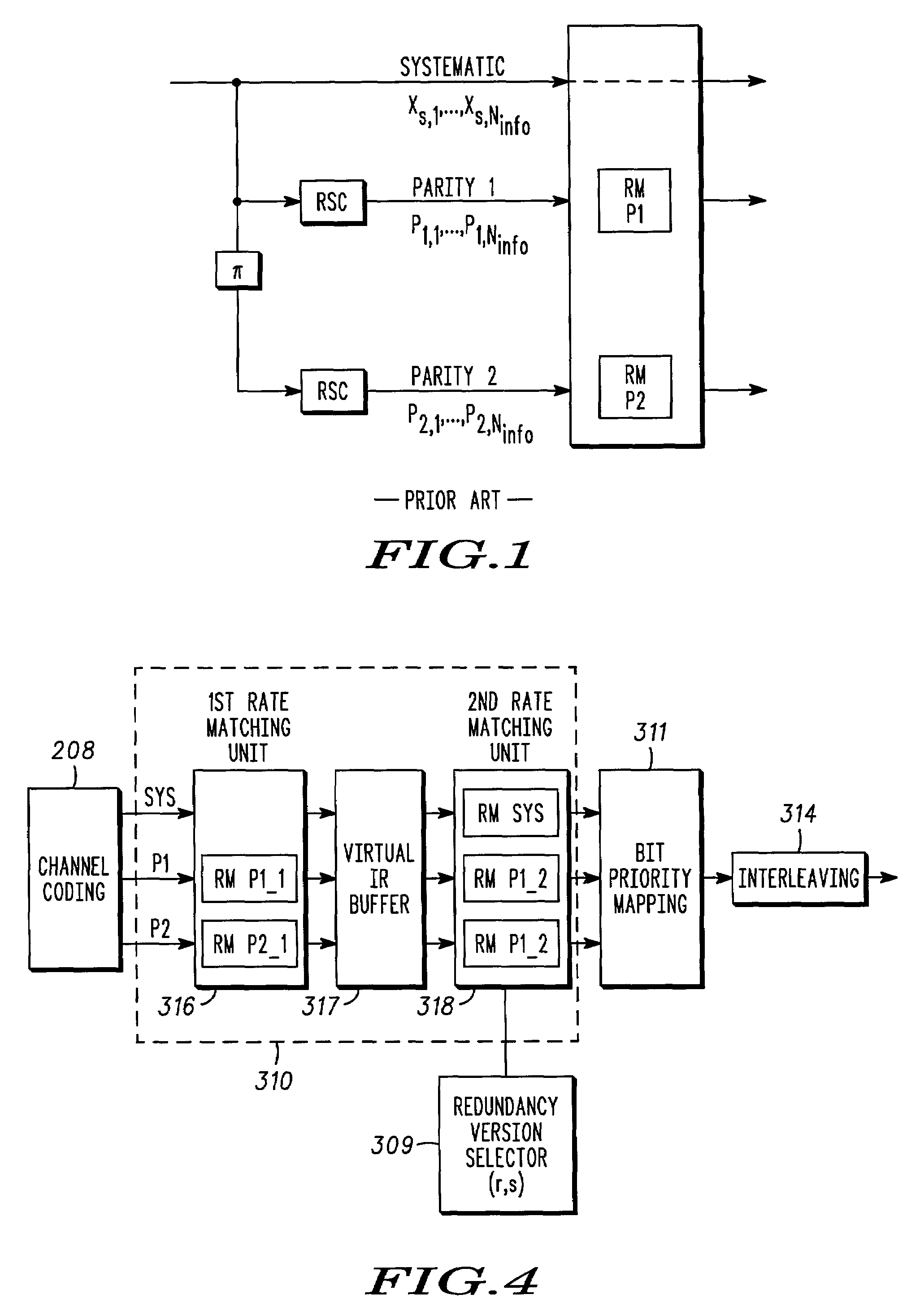
A method and apparatus for Turbo encoding uses a set of rate-compatible Turbo Codes optimized at high code rates and derived from a universal constituent code. The Turbo Codes have rate-compatible puncturing patterns. The method comprises: encoding a signal at a first and second encoder using a best rate 1 / 2 constituent code universal with higher code rates, the first encoder and the second encoder each producing a respective plurality of parity bits for each information bit; puncturing the respective plurality of parity bits at each encoder with a higher rate best puncturing patterns; and puncturing the respective plurality of parity bits at each encoder with a lower rate best puncturing pattern. In a variation, the best rate 1 / 2 constituent code represents a concatenation of polynomials 1+D2+D3 (octal 13) and 1+D+D3 (octal 15), D a data bit. A Turbo Encoder is provided which has hardware to implement the method.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
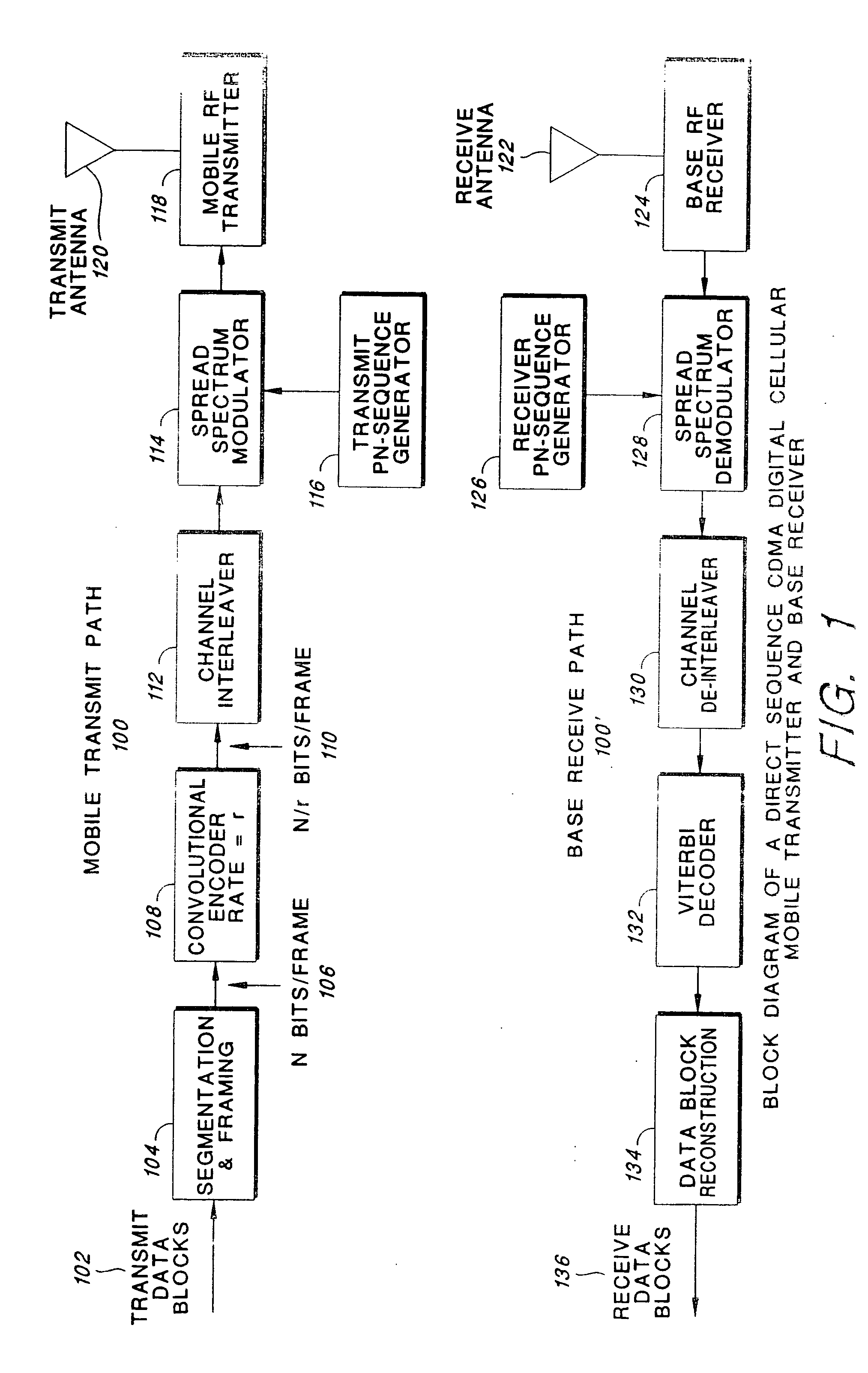
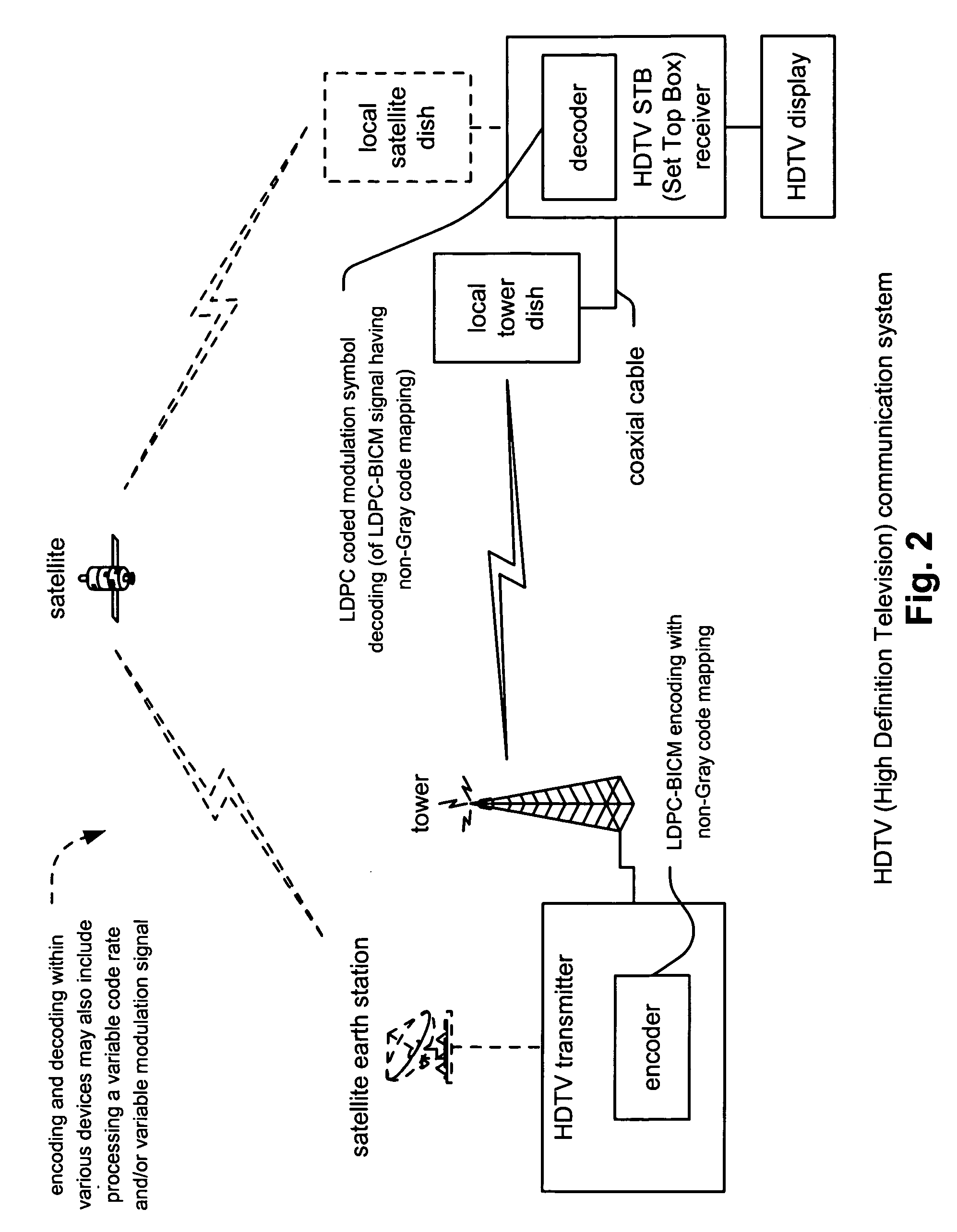
LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) coded modulation symbol decoding using non-Gray code maps for improved performance
InactiveUS7322005B2Reduce complexityError prevention/detection by using return channelOther decoding techniquesSymbol decodingTheoretical computer science
LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) coded modulation symbol decoding using non-Gray code maps for improved performance. Symbol decoding is supported by appropriately modifying an LDPC tripartite graph to eliminate the bit nodes thereby generating an LDPC bipartite graph (such that symbol nodes are appropriately mapped directly to check nodes thereby obviating the bit nodes). The edges that communicatively couple the symbol nodes to the check nodes are labeled appropriately to support symbol decoding of the LDPC coded modulation signal. In addition, the LDPC coded modulation symbol decoding can be employed to decode a signal that has been encoded using LDPC-BICM (Low Density Parity Check-Bit Interleaved Coded Modulation) encoding with non-Gray code mapping. By using the non-Gray code mapping, a performance improvement over such a system using only Gray code mapping may be achieved.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Enhanced turbo product code decoder system
InactiveUS7085987B2Error preventionOther decoding techniquesTheoretical computer scienceGalois field arithmetic
Owner:COMTECH TELECOMM CORP
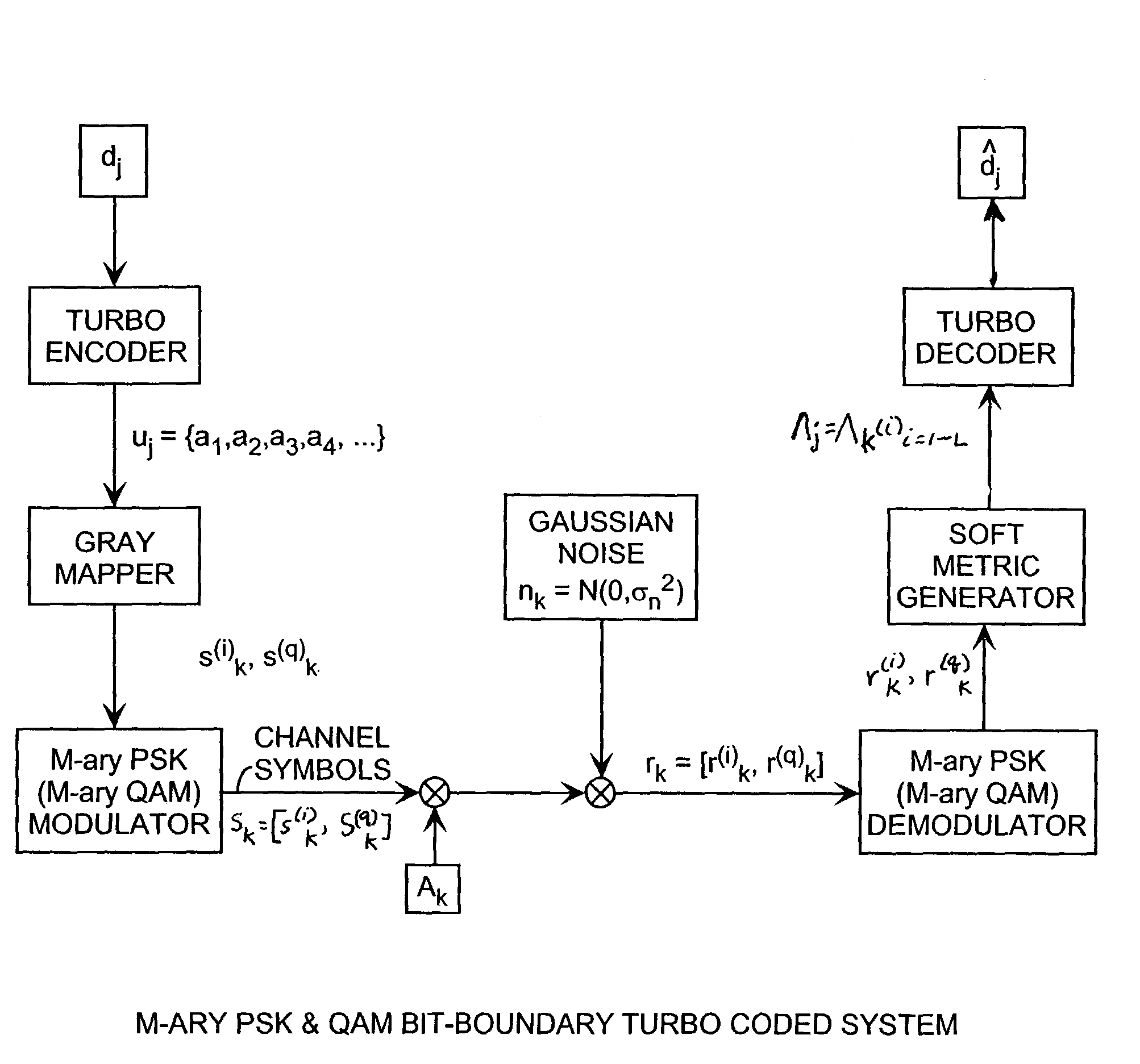
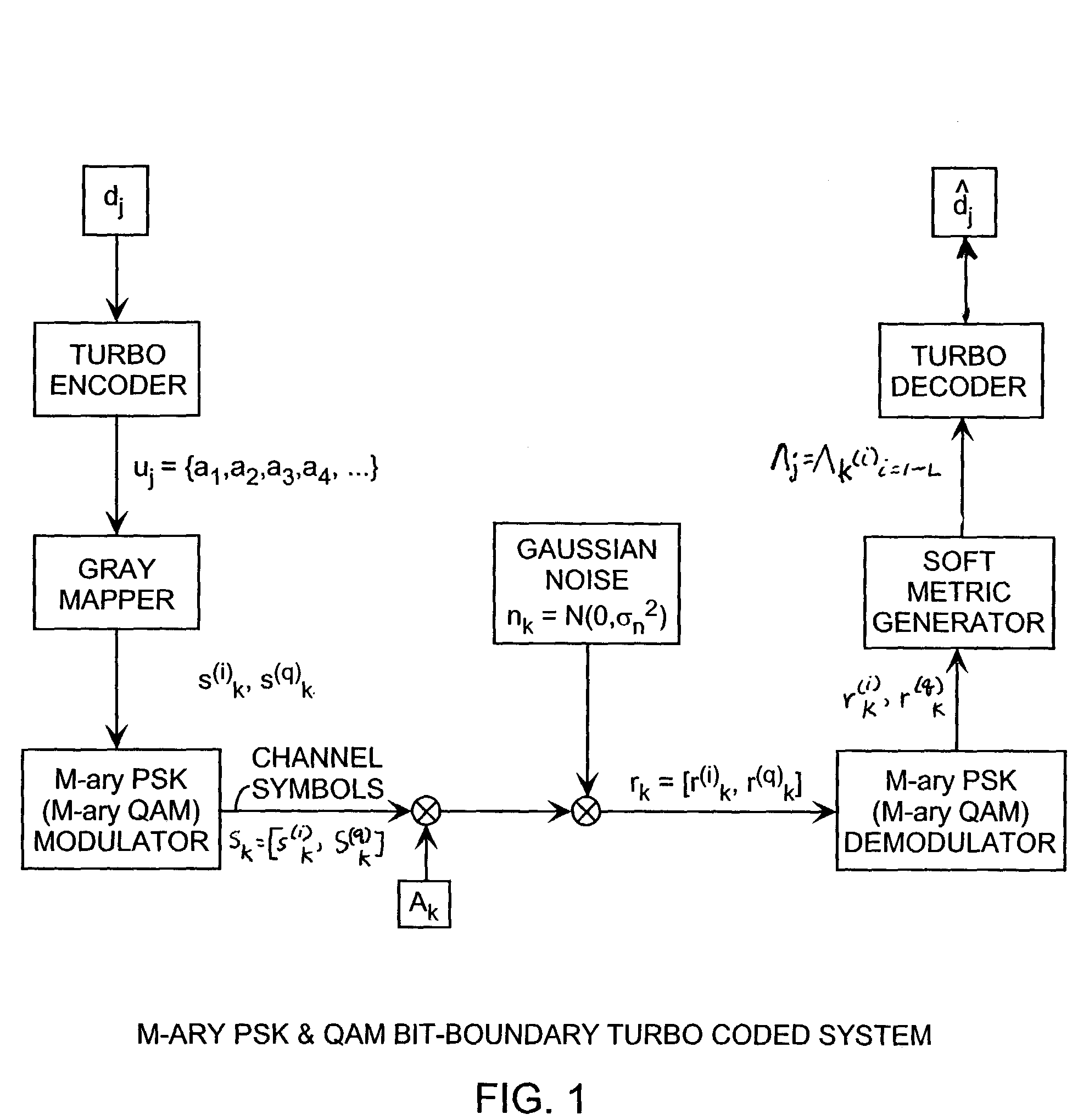
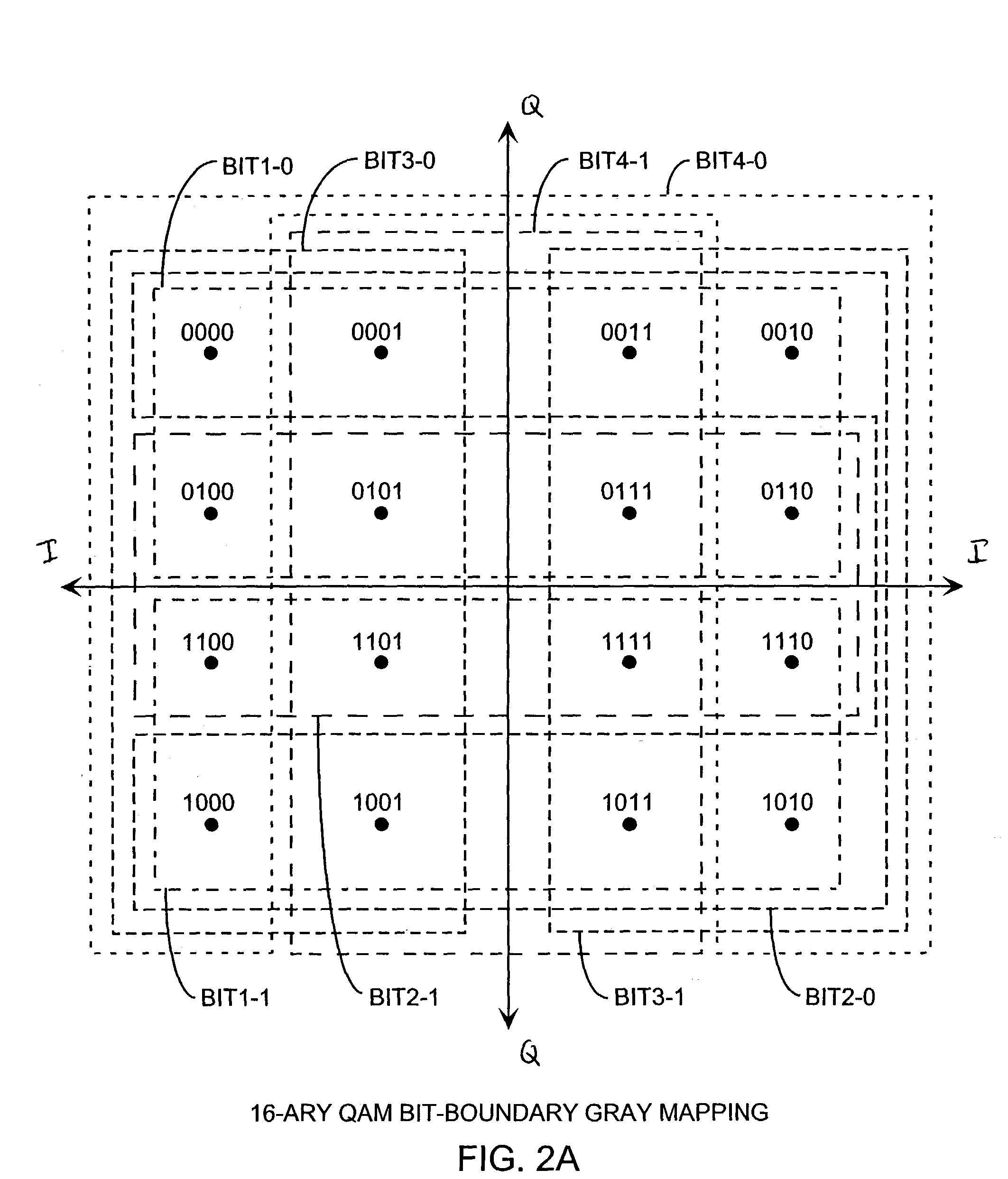
M-Ary quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) bit-boundary turbo coded system
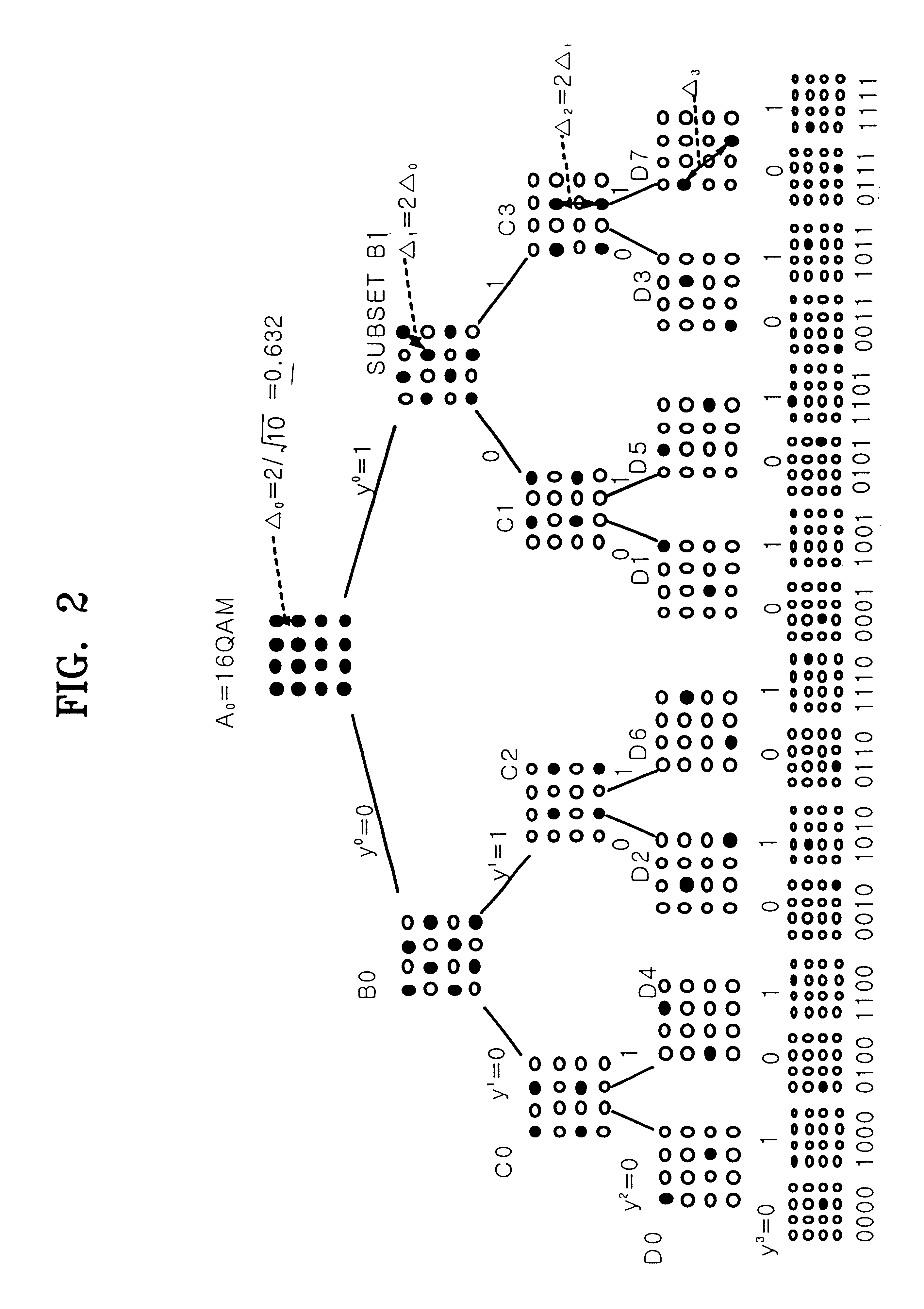
ActiveUS7142610B1Effective bandwidthImprove performanceData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionAlgorithmShortest distance
A turbo coded communication system includes a gray scale mapper in a transmitter for generating a symbol constellation of modulated signals points that can be separated by boundary lines in the constellation space into bitwise groups of zero bits and one bits where the shortest distance from a boundary line to received value in the constellation space indicates the bitwise soft metrics that is computed using a set of bitwise soft metric equations are a function of the minimum distance using closed form algebraic equations in turbo decoding receiver. In the case of quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM), the bit boundary lines are predetermined by a minimum distance in the constellation space for a specified M-ary modulation, so that, the soft metric equations are only a function of the received signal value for providing efficient computation of the bitwise soft metric.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
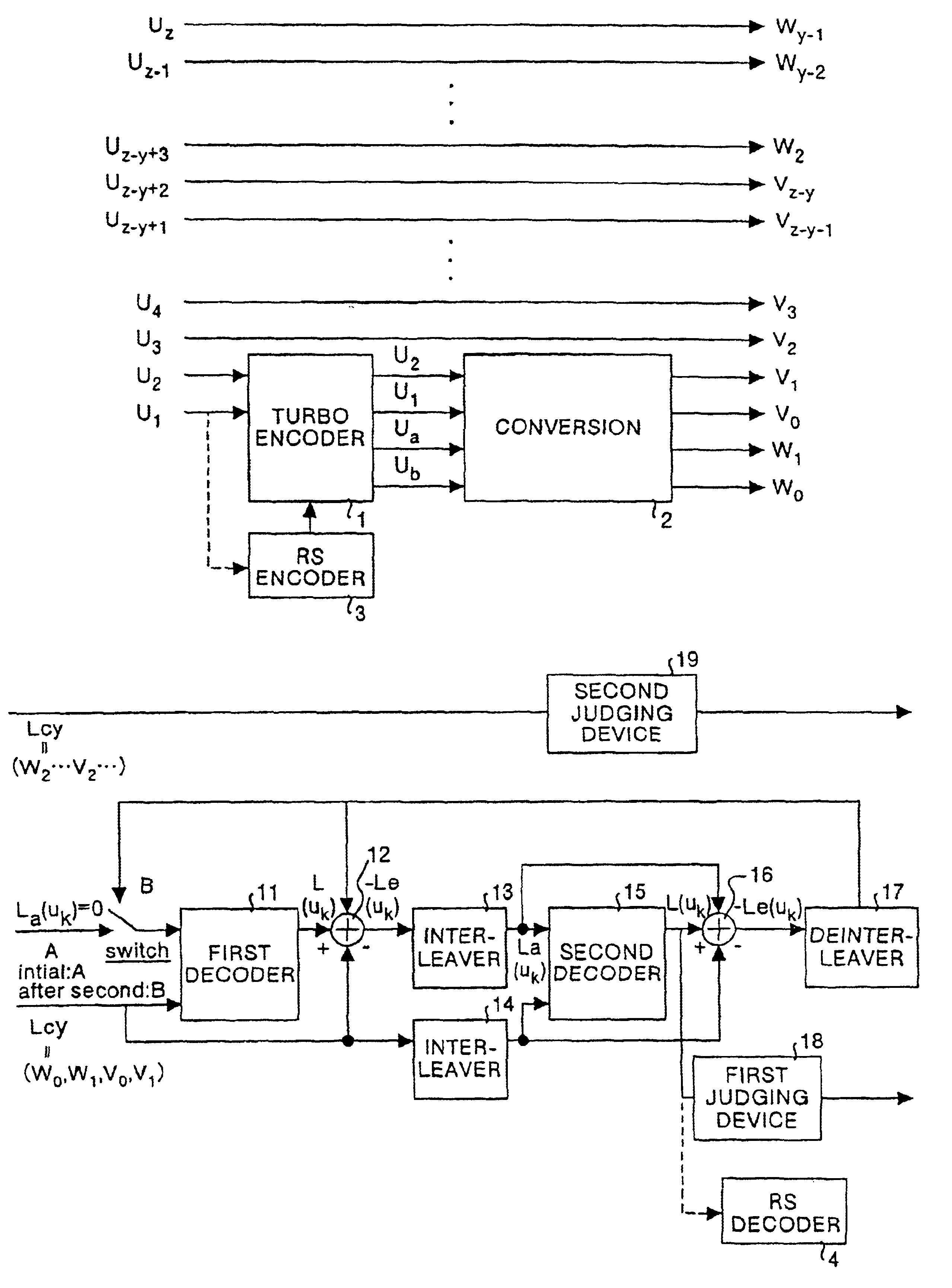
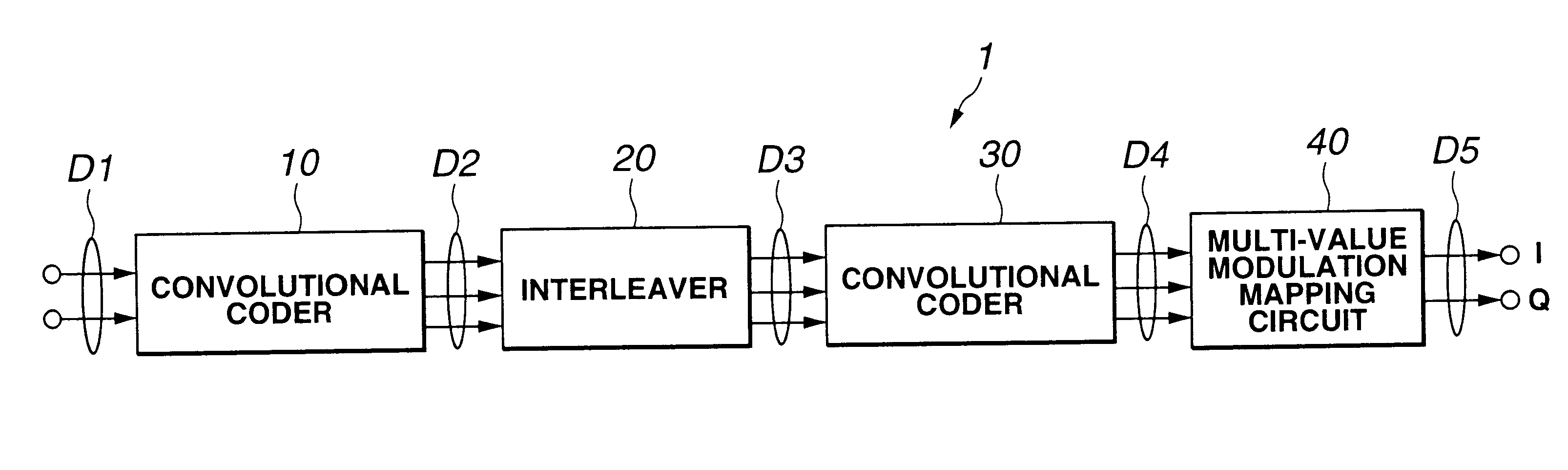
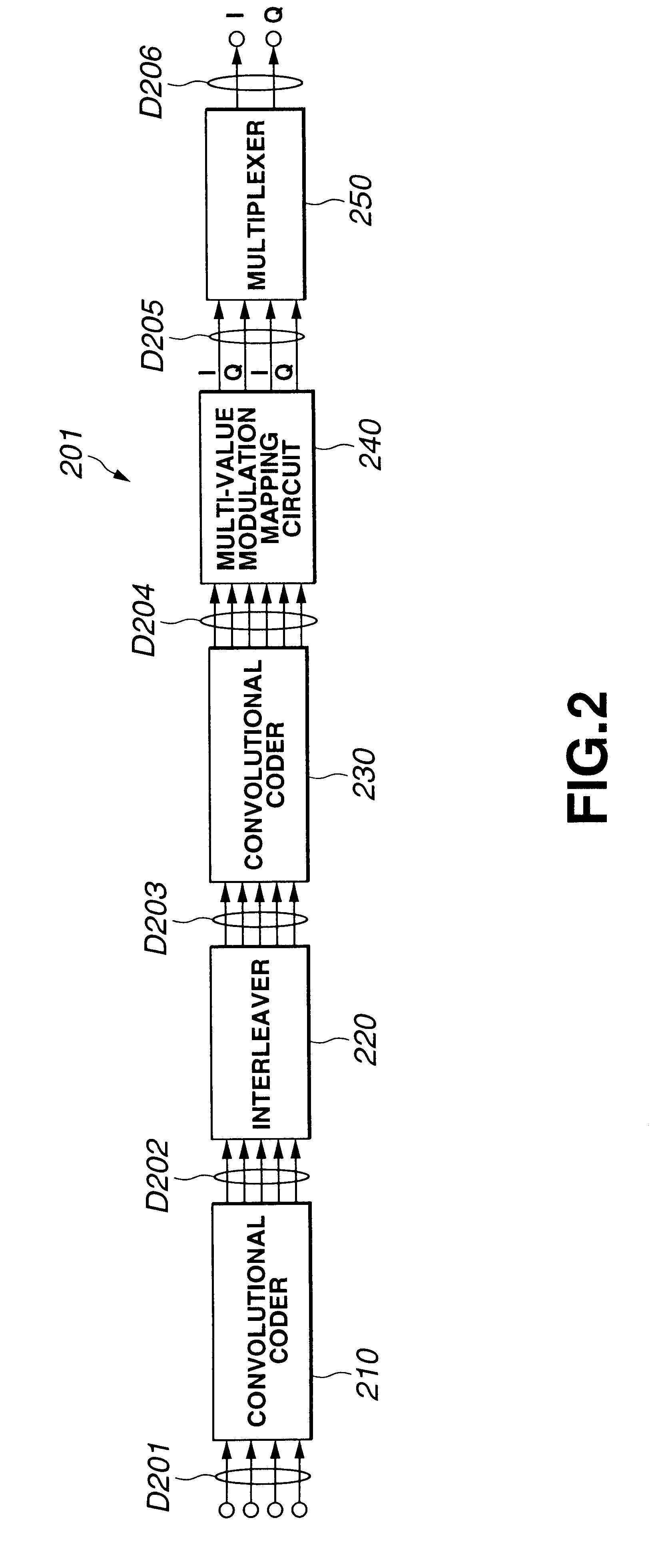
Coding apparatus, coding method and recording medium having coded program recorded therein, and decoding apparatus, decoding method and recording medium having decoded program recorded therein
InactiveUS6901548B2Improve performanceData representation error detection/correctionError preventionComputer hardwareHamming distance
To carry out error correction coding and decoding according to a serially concatenated coded modulation system with a small circuit scale and high performance. A coding apparatus 1 is designed so that an interleaver 20 interleaves order of bits so that all weights are coded by a convolutional coder 30 with respect to data comprising a series of 3 bits supplied from a convolutional coder 10; the convolutional coder 30 makes as small as possible the total value of the hamming distance of input bit between passes to be the minimum Euclidean distance with respect to data of 3 bits supplied from the interleaver 20; and a multi-value modulation mapping circuit 40 causes the hamming distance of input bits in the convolutional coder 30 as the distance between signal point on the I / Q plane is smaller to subject data of 3 bits supplied from the convolutional coder 30 to mapping.
Owner:SONY CORP
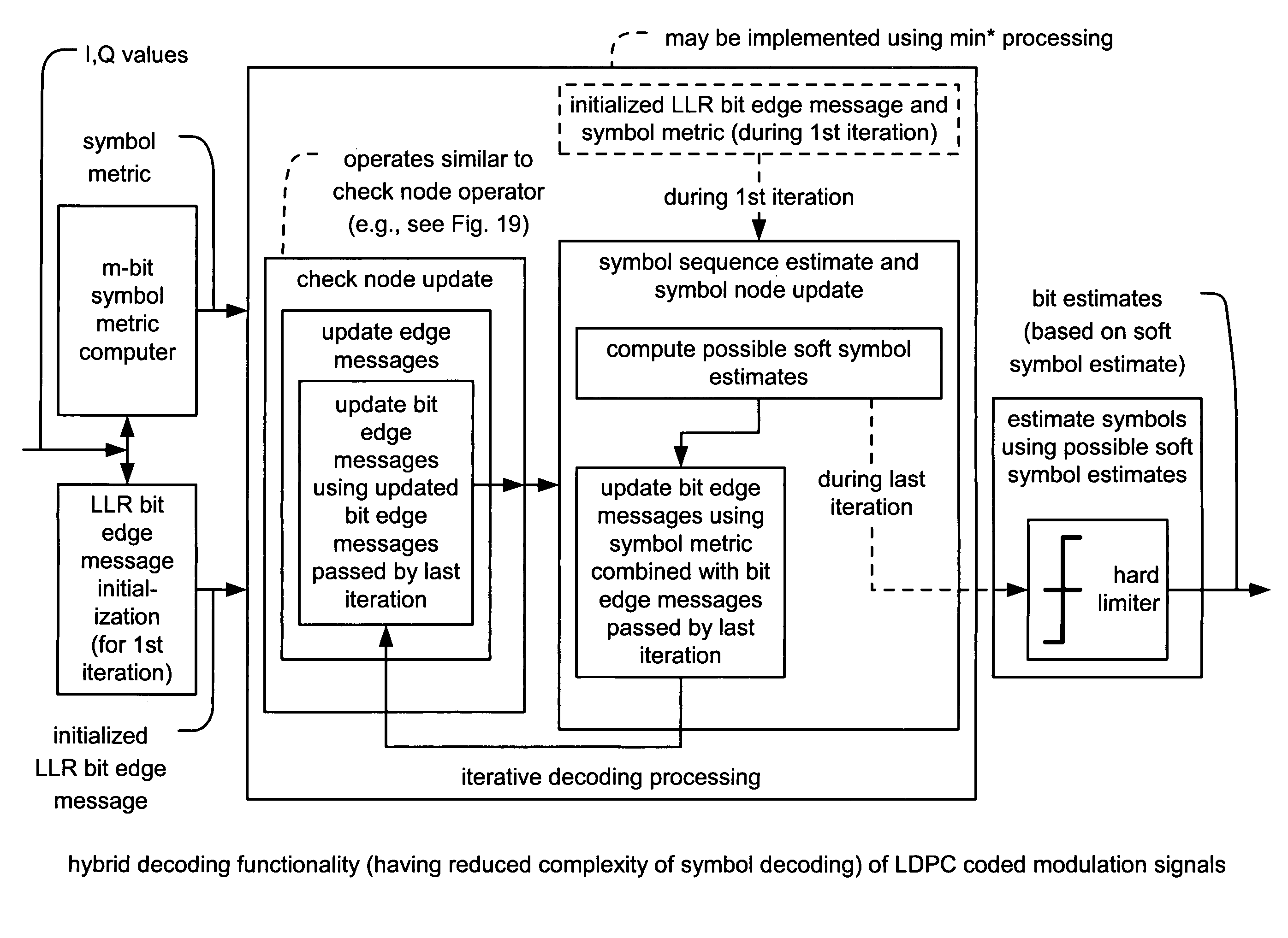
LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) coded modulation hybrid decoding using non-Gray code maps for improved performance
InactiveUS7383493B2Improve performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelOther decoding techniquesTheoretical computer scienceLow density
LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) coded modulation hybrid decoding using non-Gray code maps for improved performance. Check node updating and symbol node updating are successively and alternatively performed on bit edge messages for a predetermined number of decoding iterations or until sufficient degree of precision is achieved. The symbol node updating of the bit edge messages uses symbol metrics corresponding to the symbol being decoded and the bit edge messages most recently updated by check node updating. The check node updating of the bit edge messages uses the bit edge messages most recently updated by symbol node updating. The symbol node updating computes possible soft symbol estimates. LDPC coded modulation hybrid decoding can decode an LDPC-BICM (Low Density Parity Check-Bit Interleaved Coded Modulation) signal having a symbol mapped using non-Gray code mapping. By using the non-Gray code mapping, a performance improvement is achieved over an only Gray code mapping system.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
COFDM broadcast systems employing turbo coding
InactiveUS20140119458A1Maximizing overall confidence levelImprove trustModulated-carrier systemsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDTV receiverCarrier signal
Turbo-coded data are transmitted using quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) of COFDM carrier waves in digital television (DTV) broadcast systems. The QAM symbol constellations map the parity bits of the turbo coded data so as to be de-mapped with higher confidence levels than the data bits, facilitating turbo decoding. A preferred DTV receiver delays the first transmissions of time-slices of a service selected for iterative-diversity reception to concur with second transmissions of those time-slices. The complex coordinates of QAM constellations in the delayed first transmission and the second transmission of the same time-slice are combined by a maximal-ratio QAM combiner after COFDM demodulation, but before de-mapping QAM constellations and turbo decoding. In a less-preferred DTV receiver, QAM constellations in the delayed first transmission of each time-slice and in the second transmission of the same time-slice are de-mapped separately. A maximal-ratio code combiner then combines de-mapping results before turbo decoding.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
Popular searches
Single error correction Error correction/detection using turbo codes Error correction/detection using interleaving techniques Error detection only Redundant data error correction Baseband systems Error correction/detection using multiple codes Multi-frequency code systems Signal channels Local circuits
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com