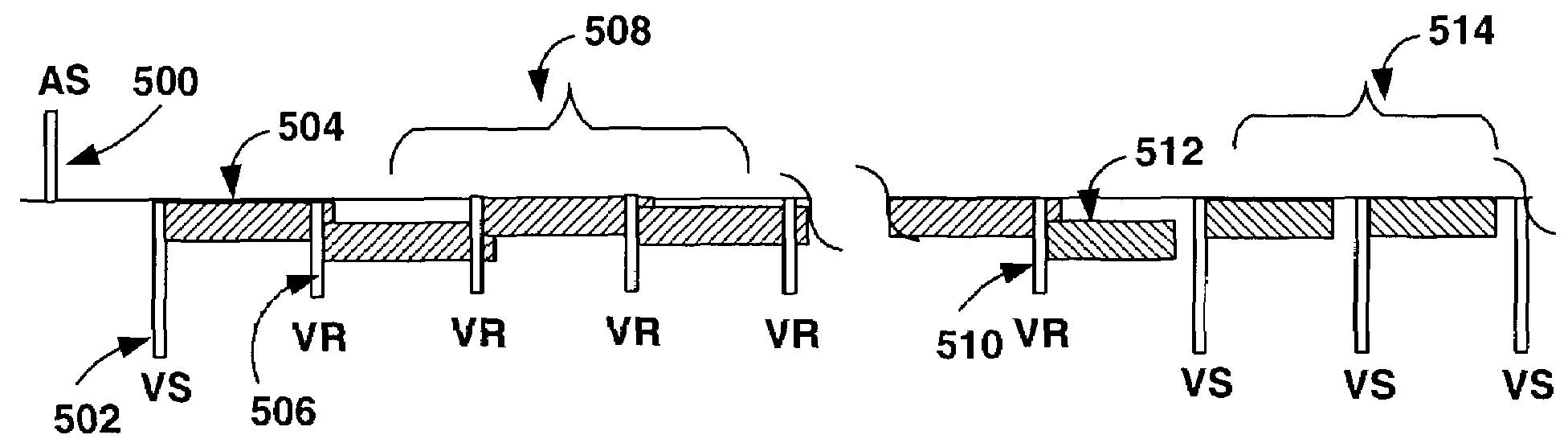
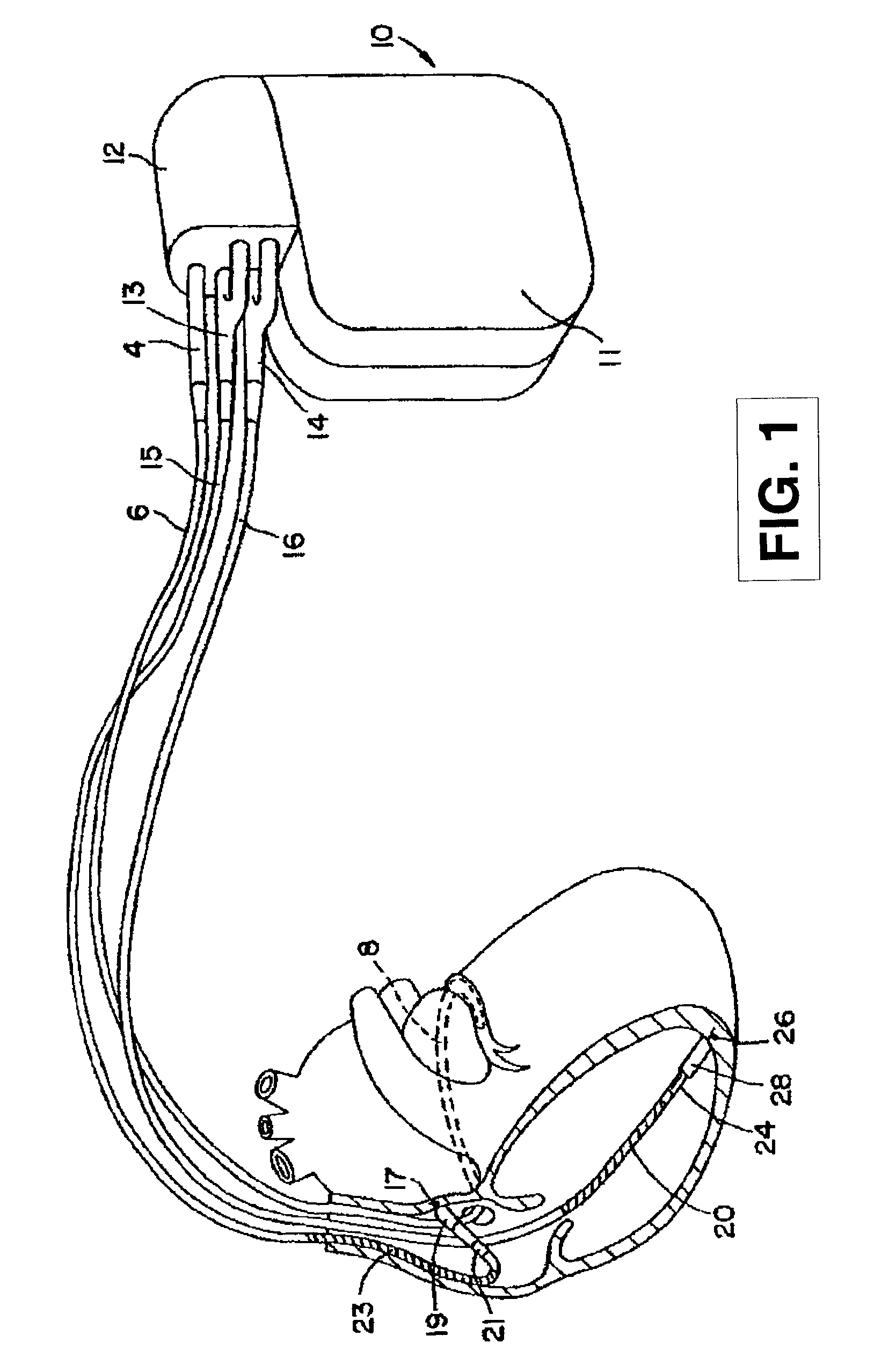
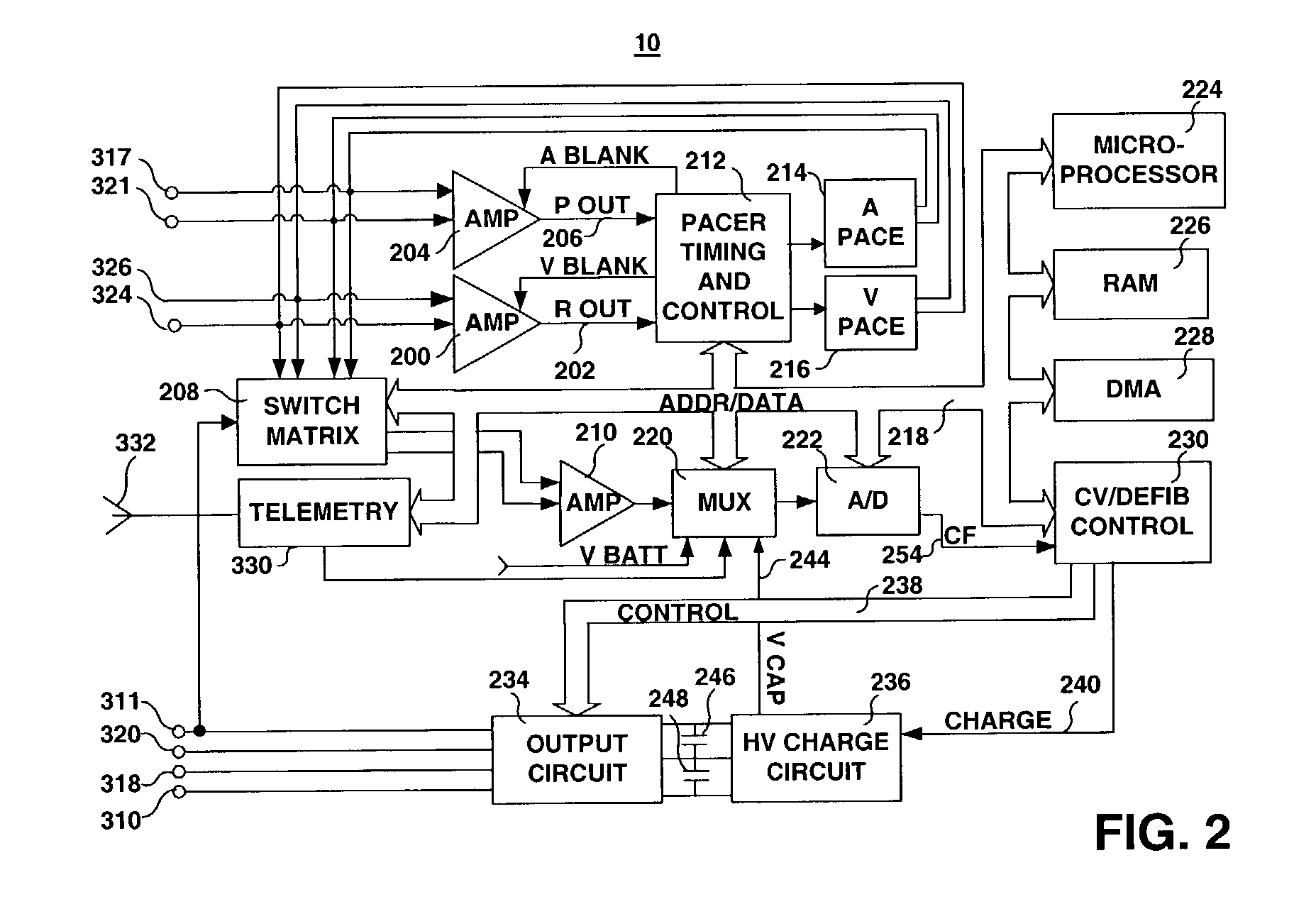
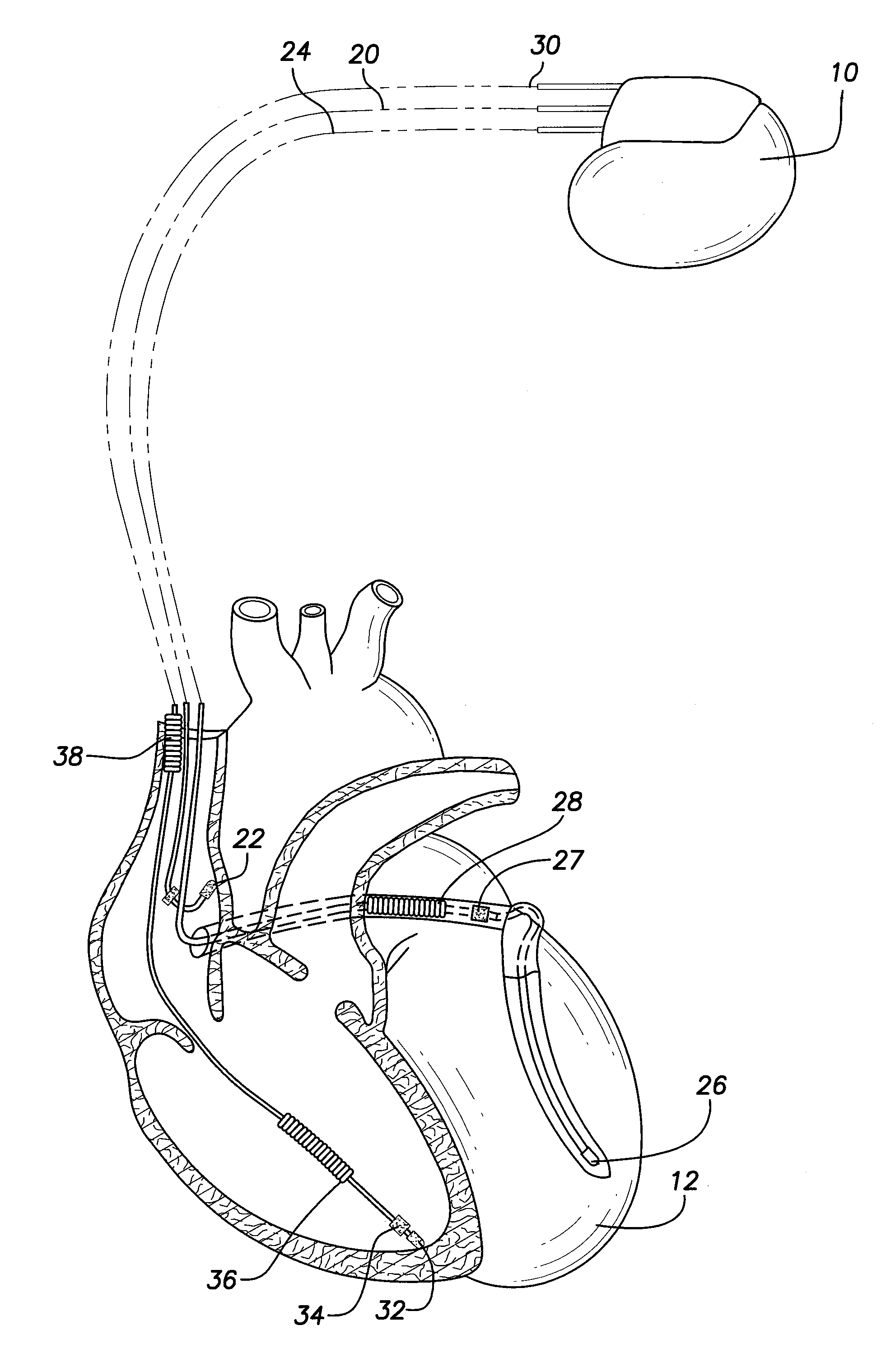
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "VENTRICULAR RHYTHMS" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ventricular arrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms that originate in the bottom chambers of the heart called the ventricles.
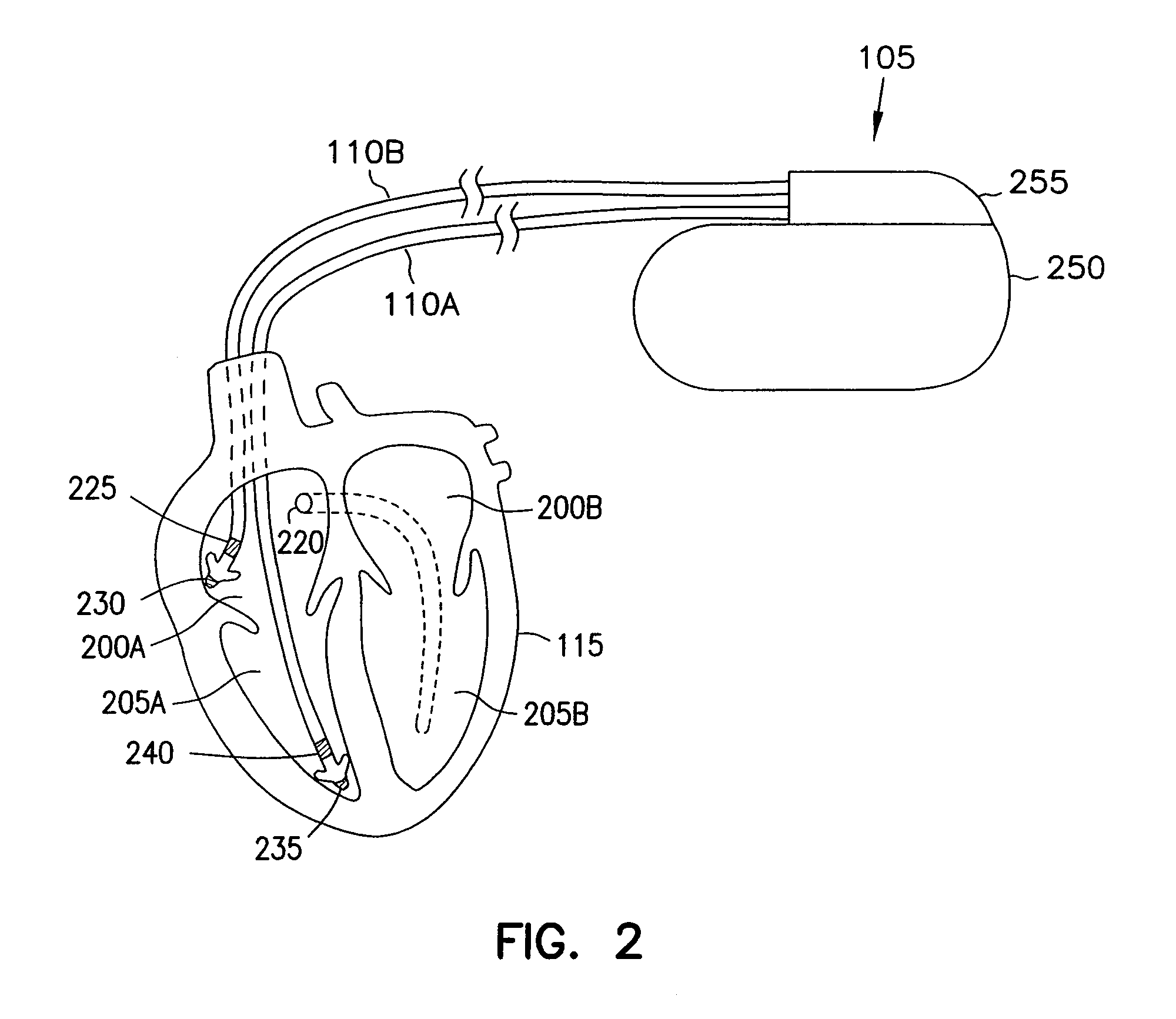
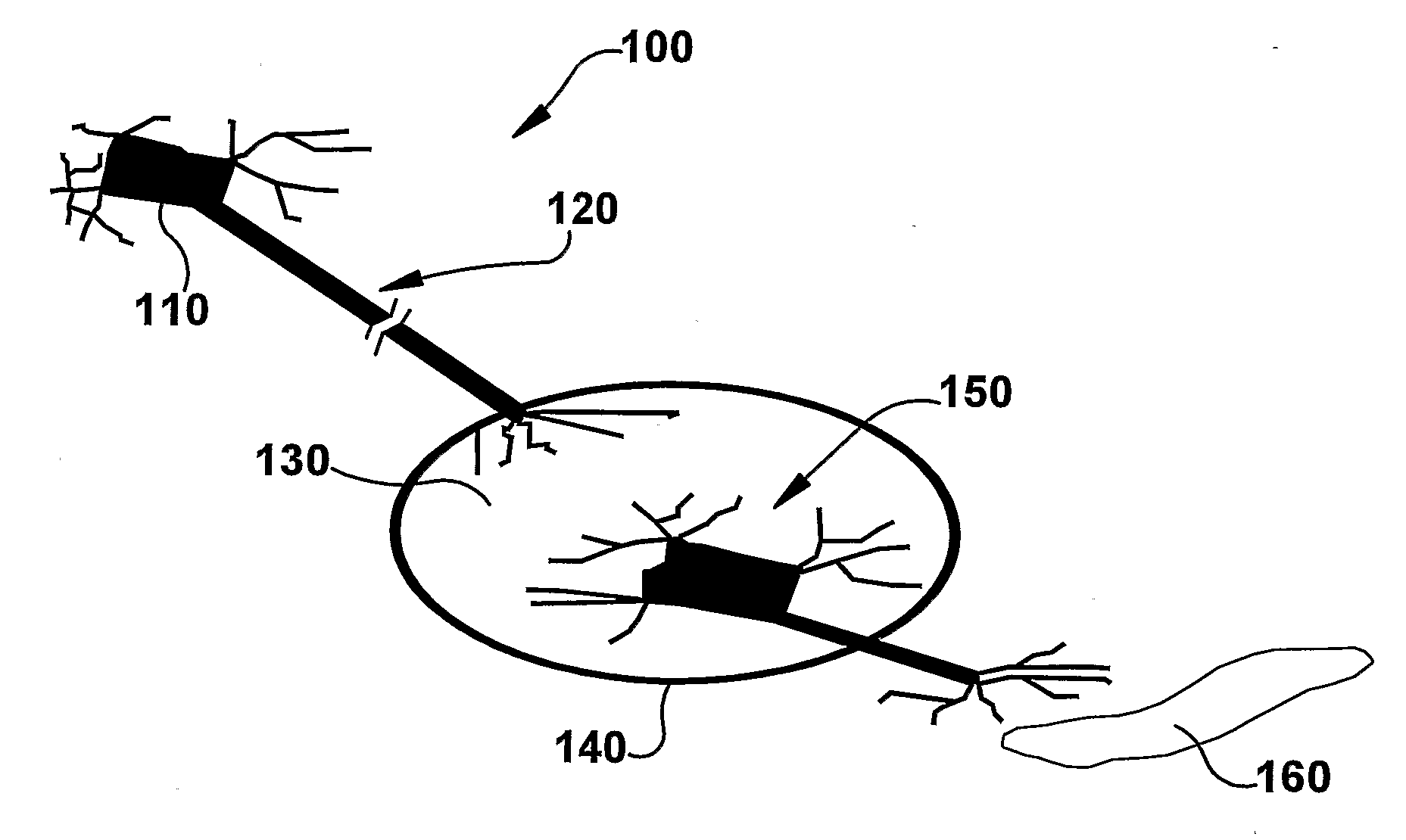
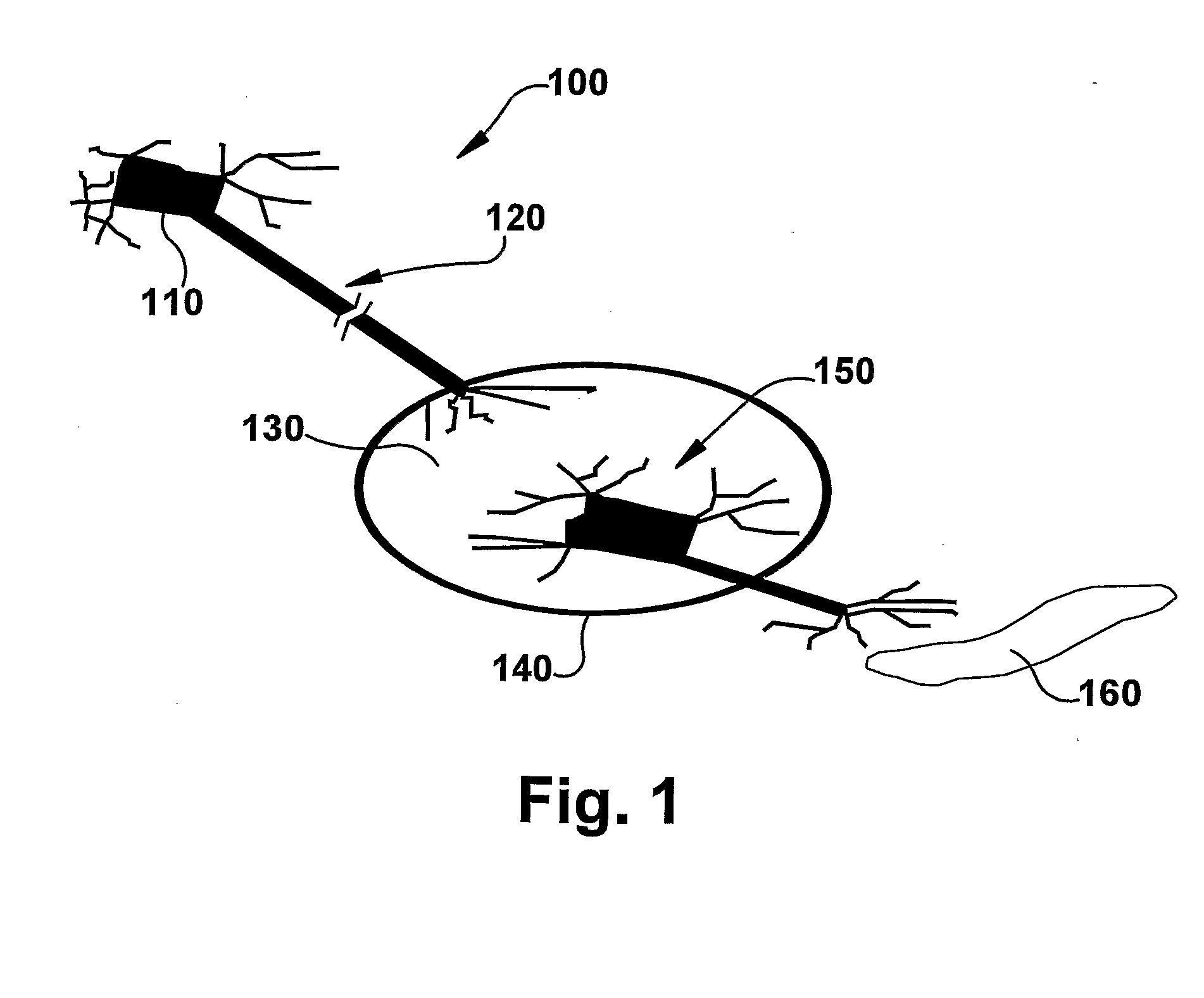
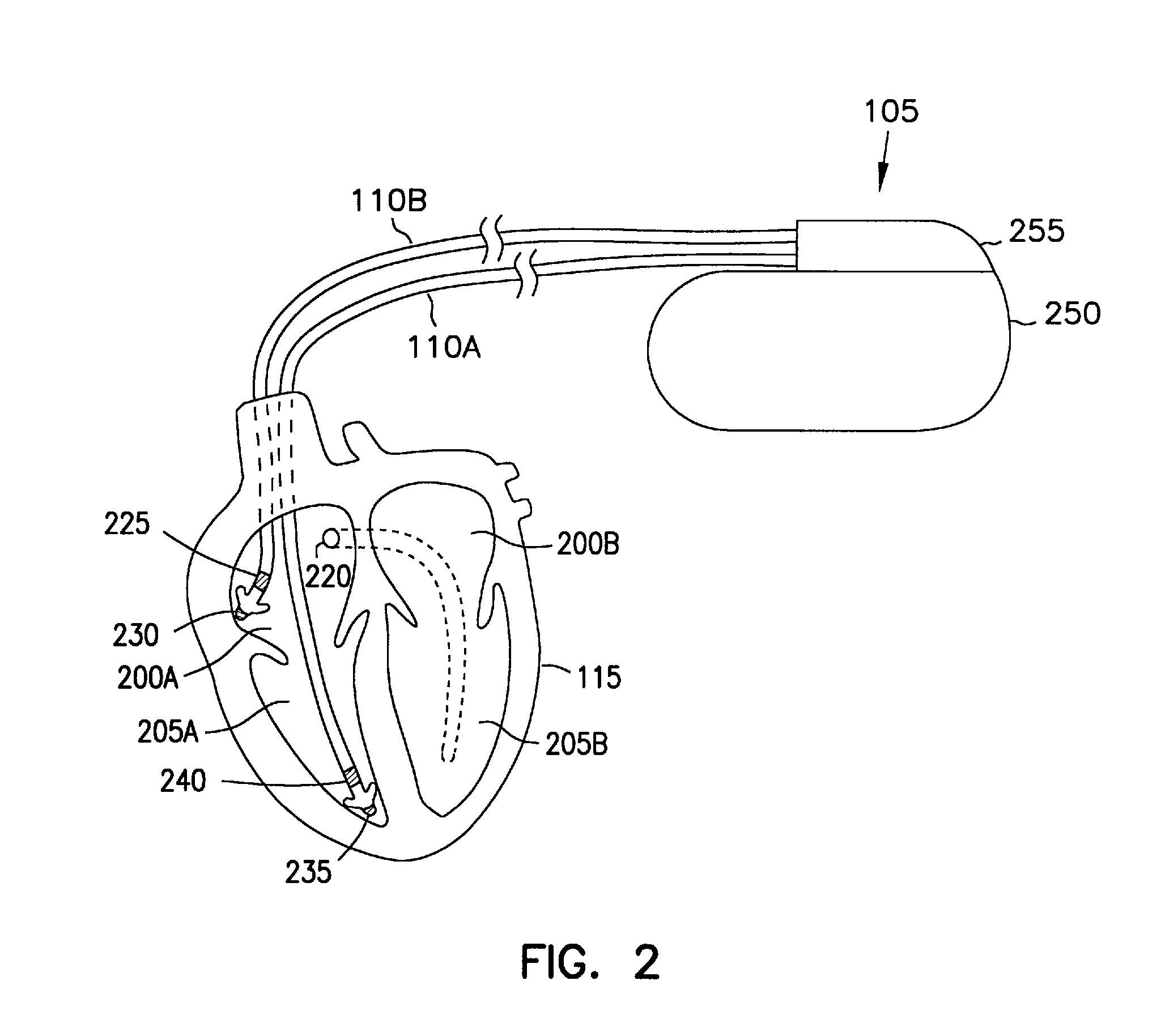
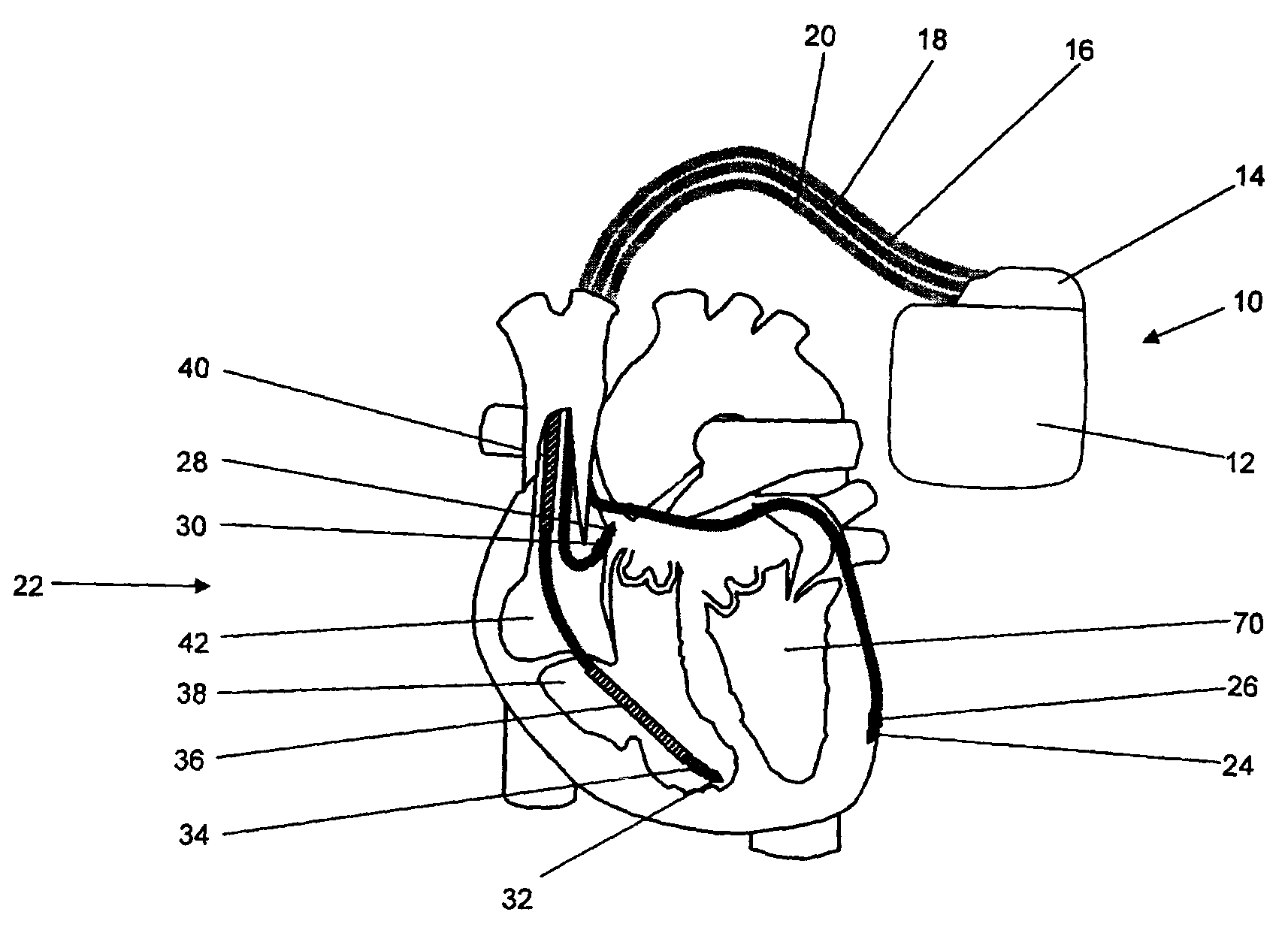
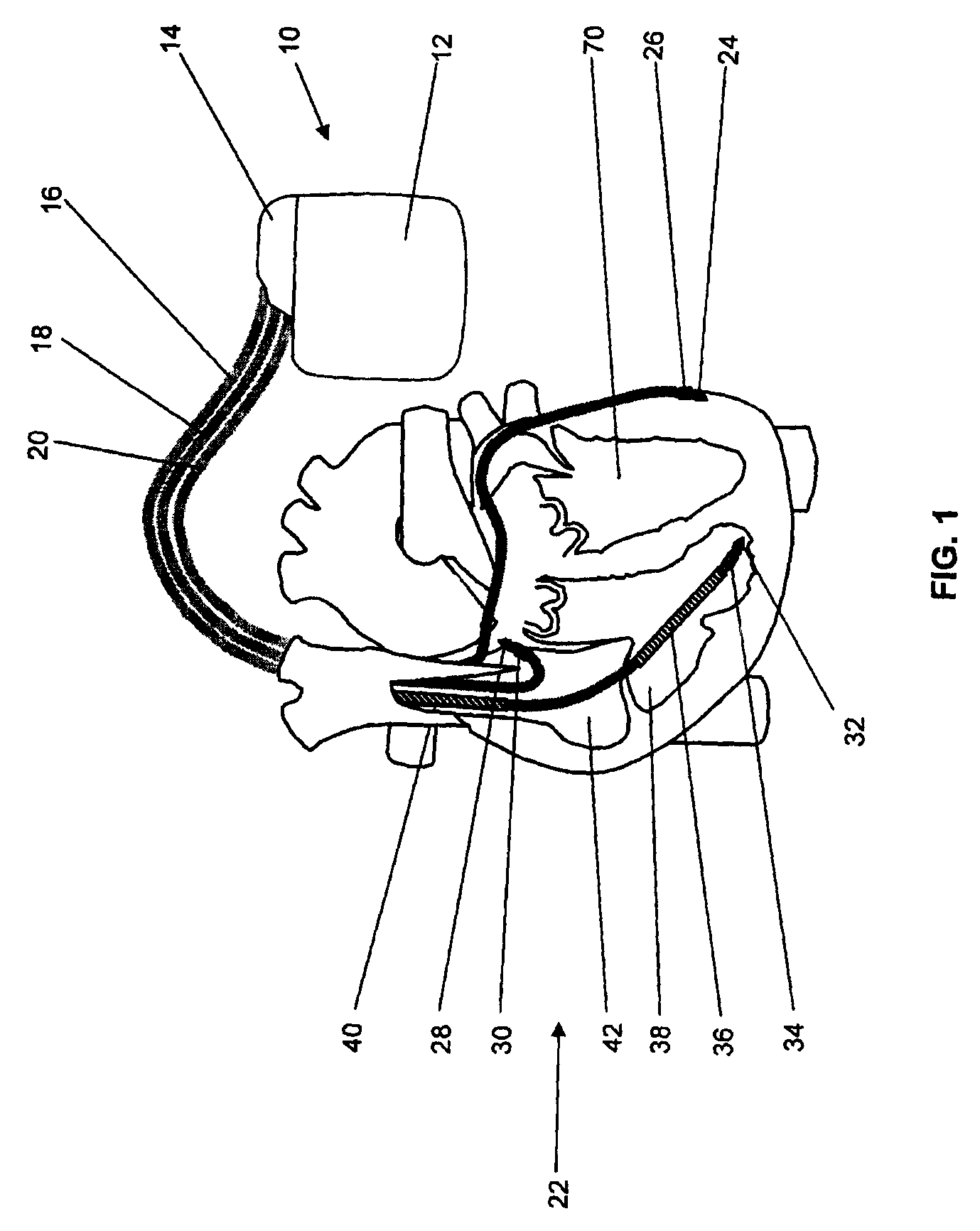
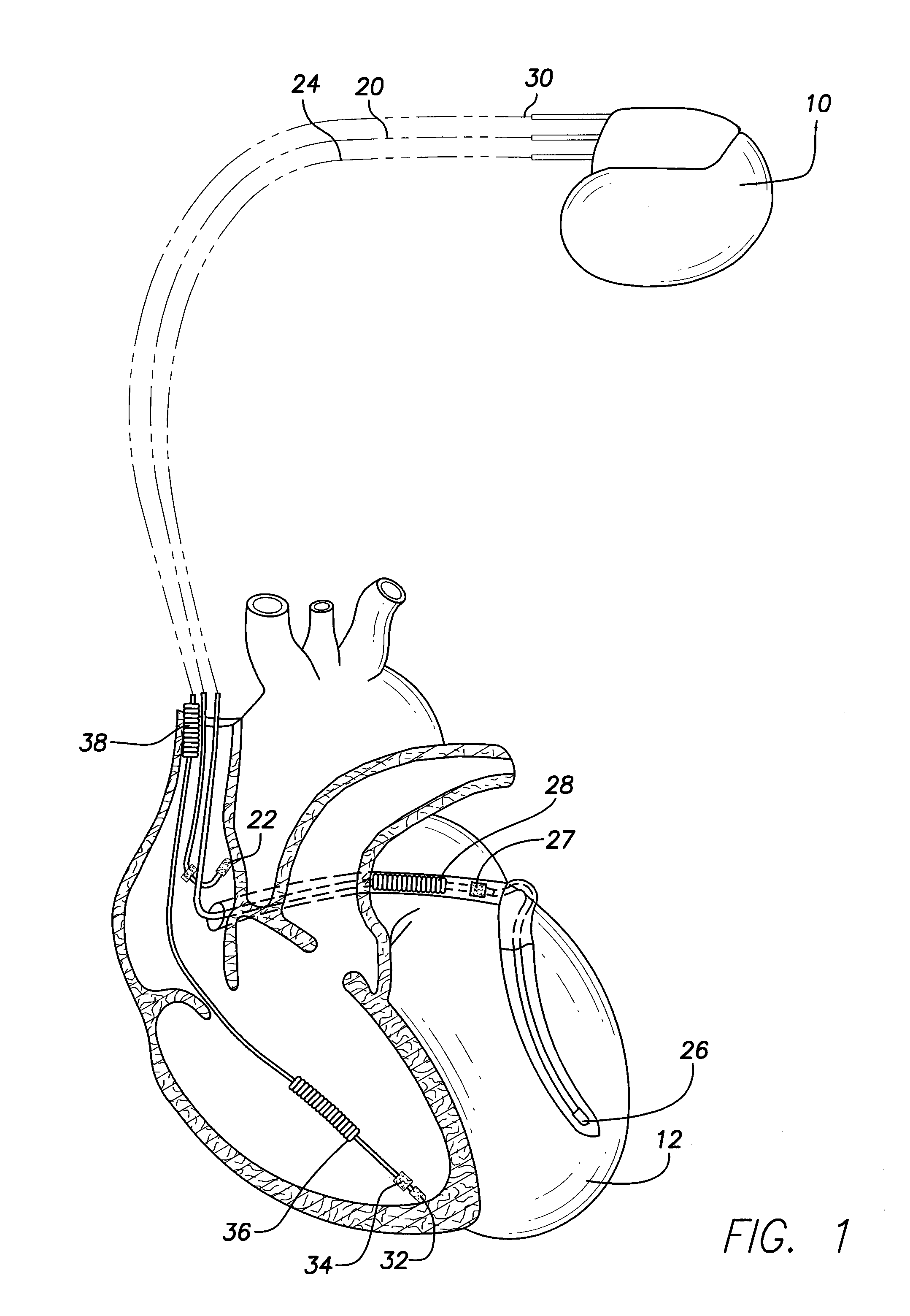
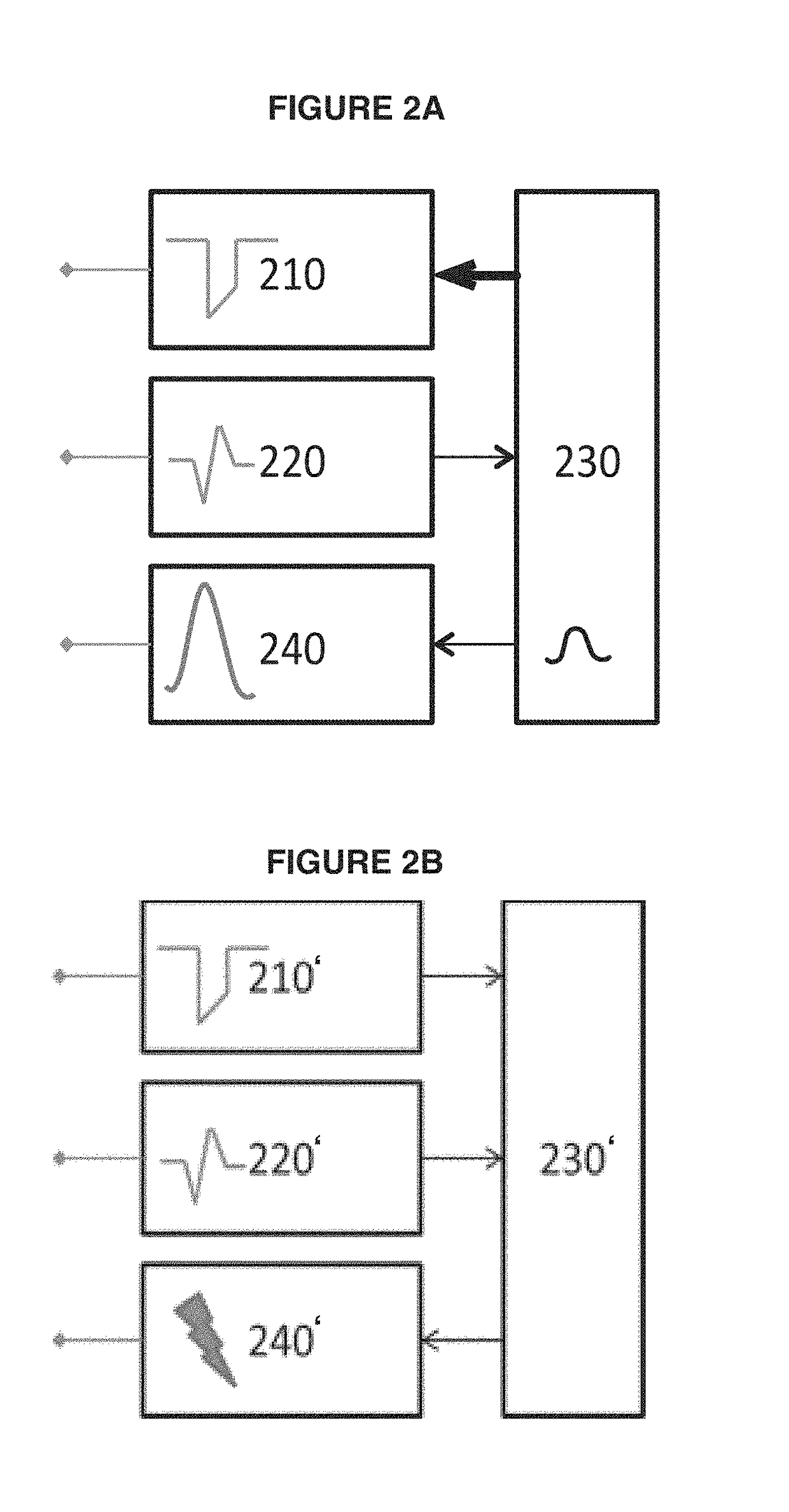
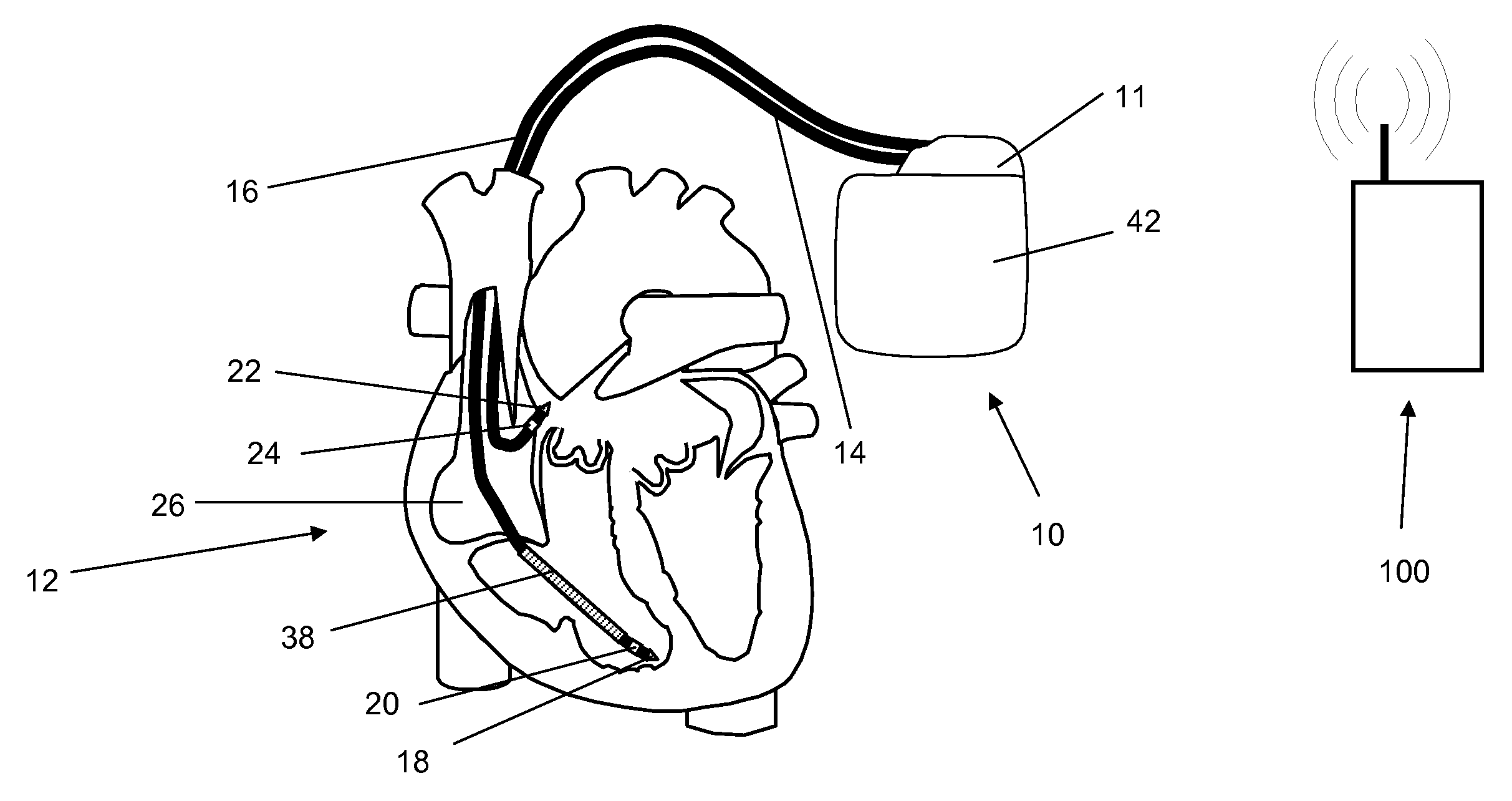
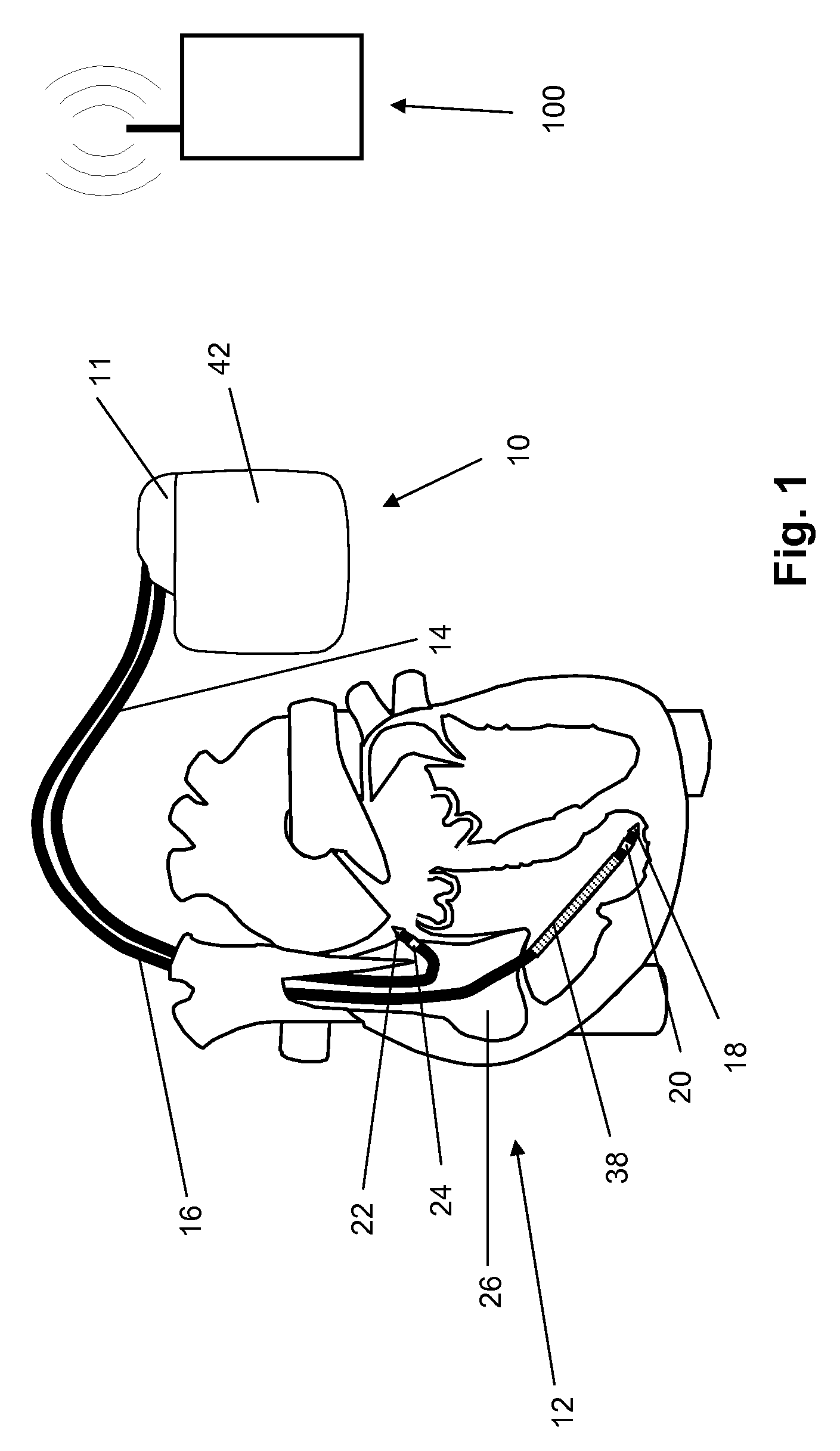
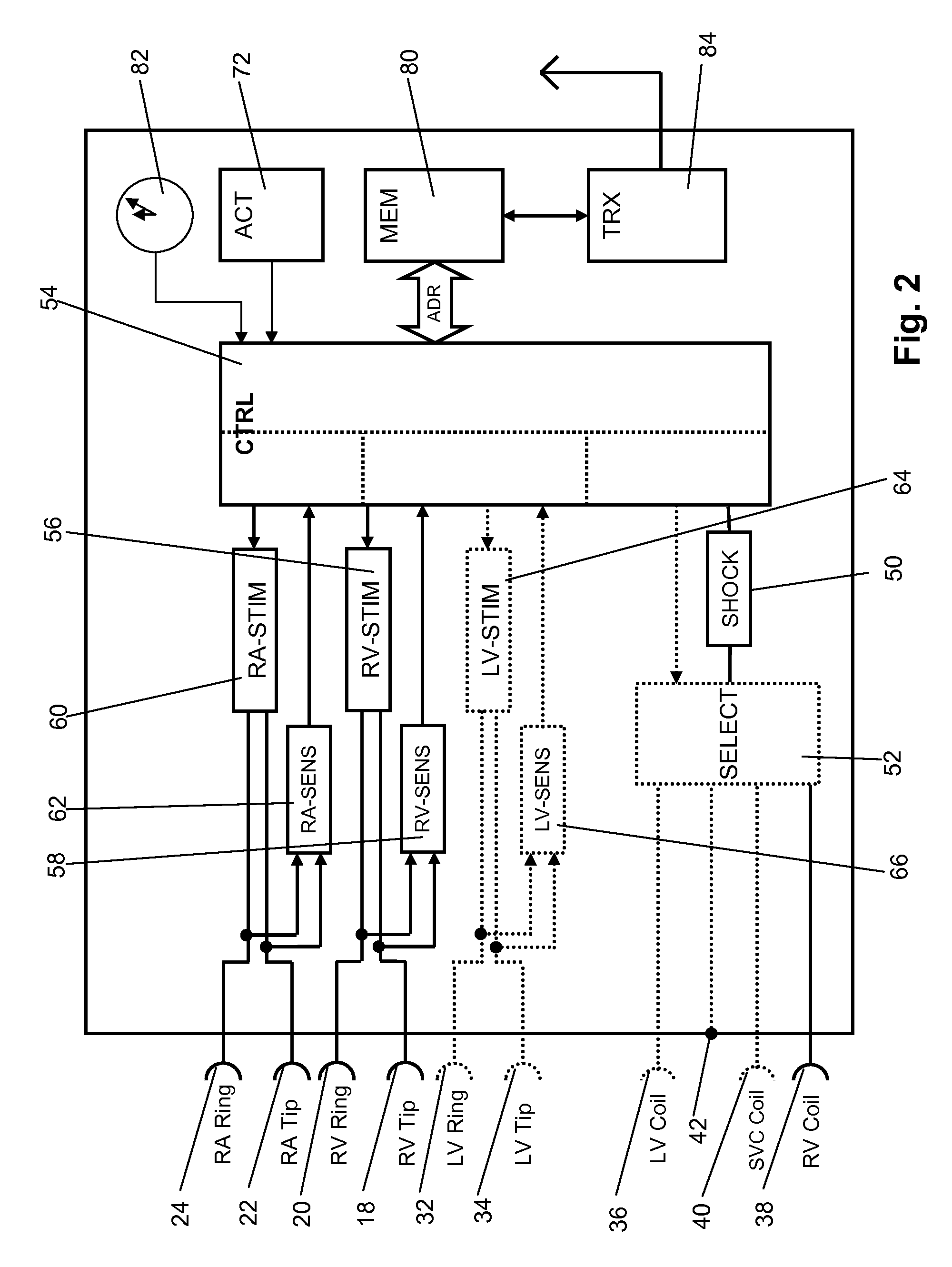
System and method for achieving regular slow ventricular rhythm in response to atrial fibrillation
InactiveUS20070083242A1Decrease ventricular rateEasy to adjustElectrotherapyVentricular rateAtrial cavity
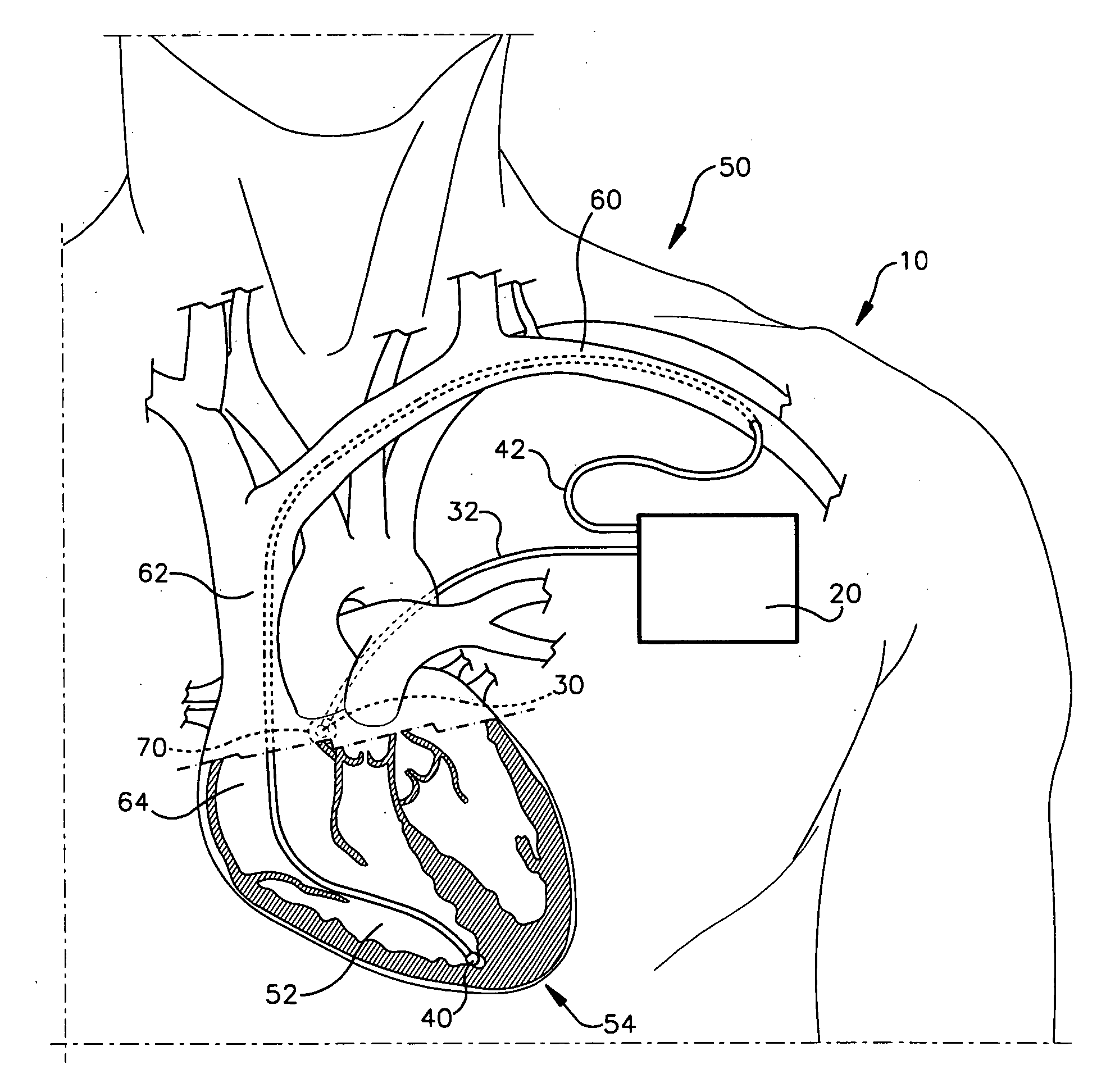
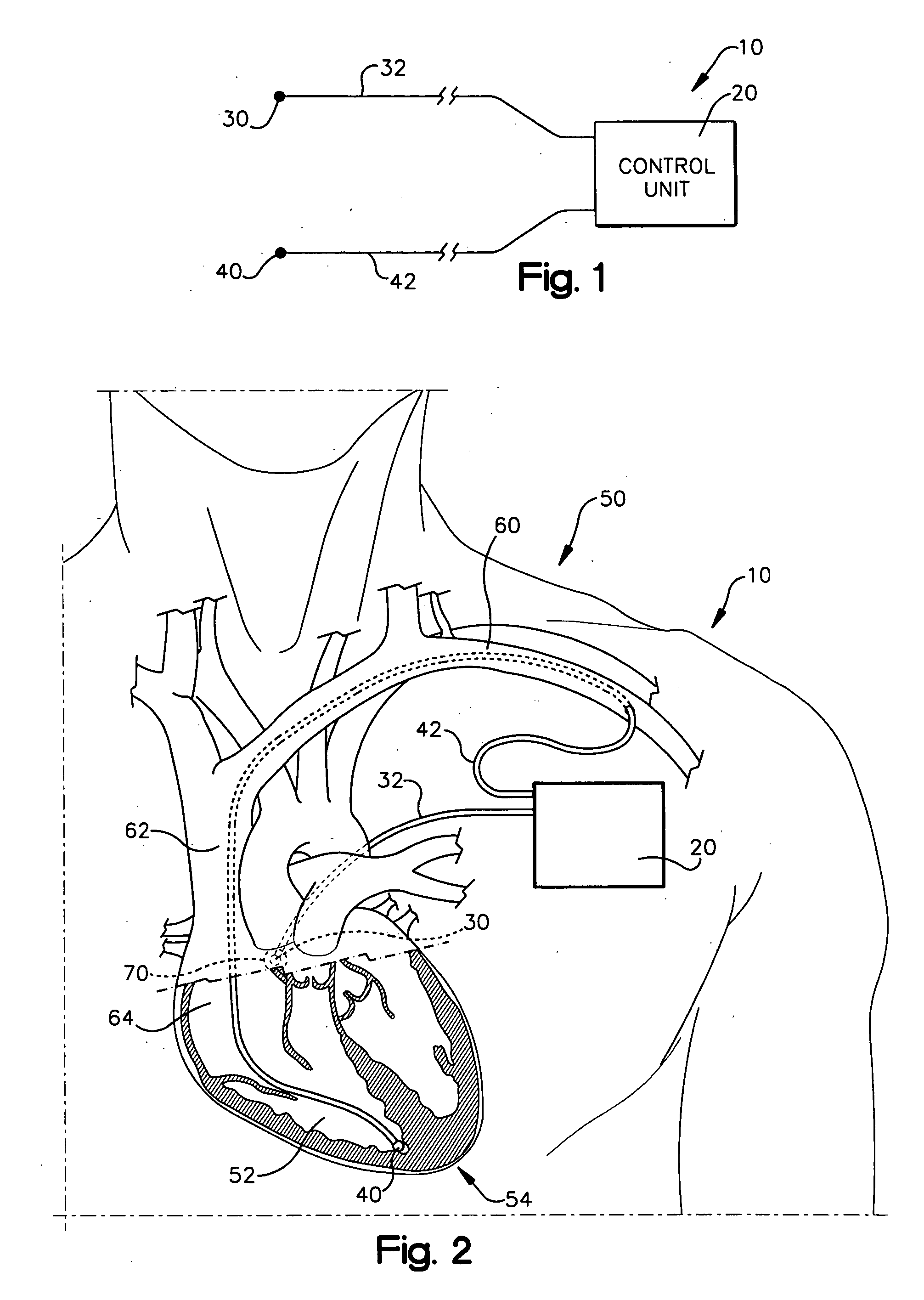
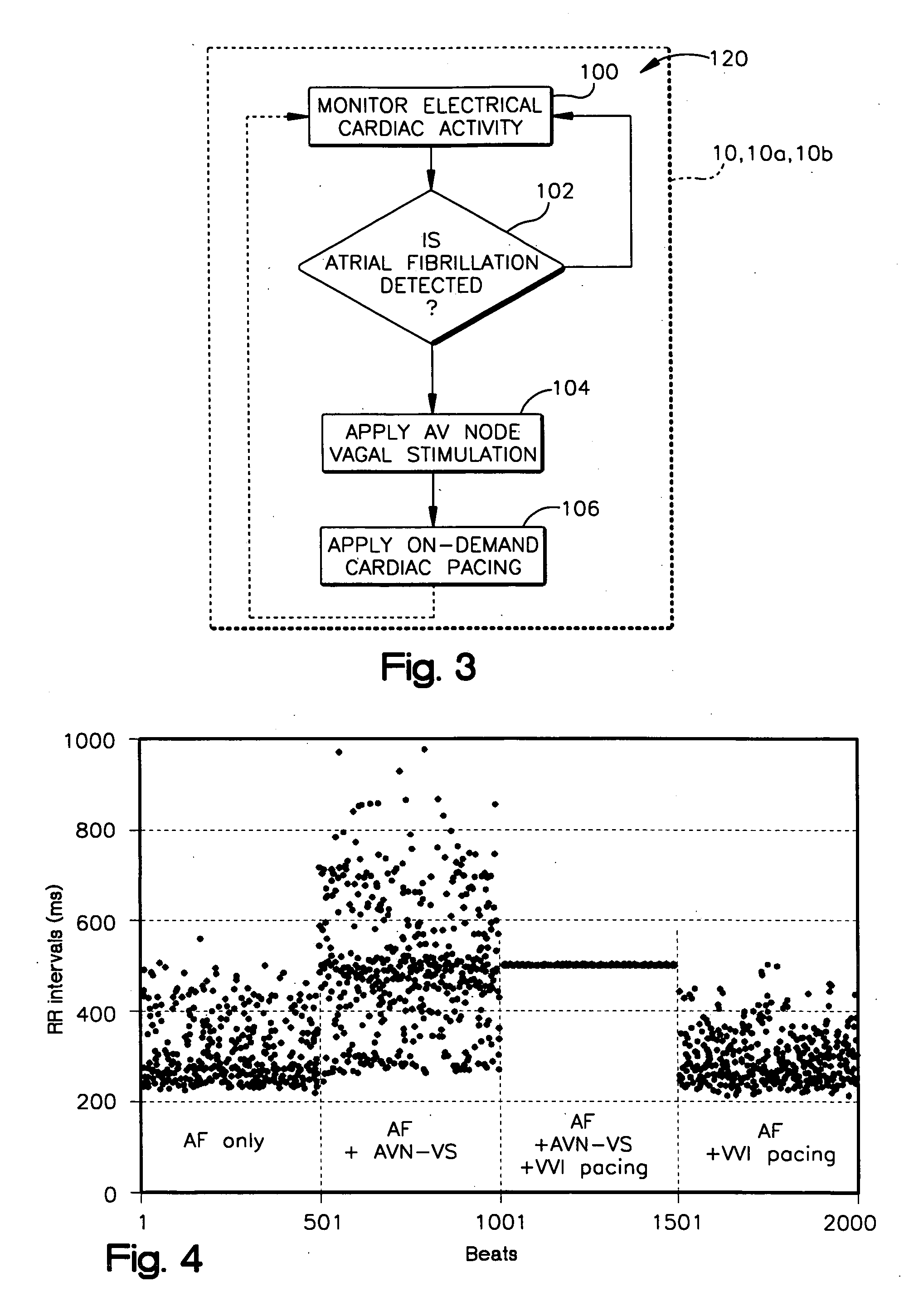
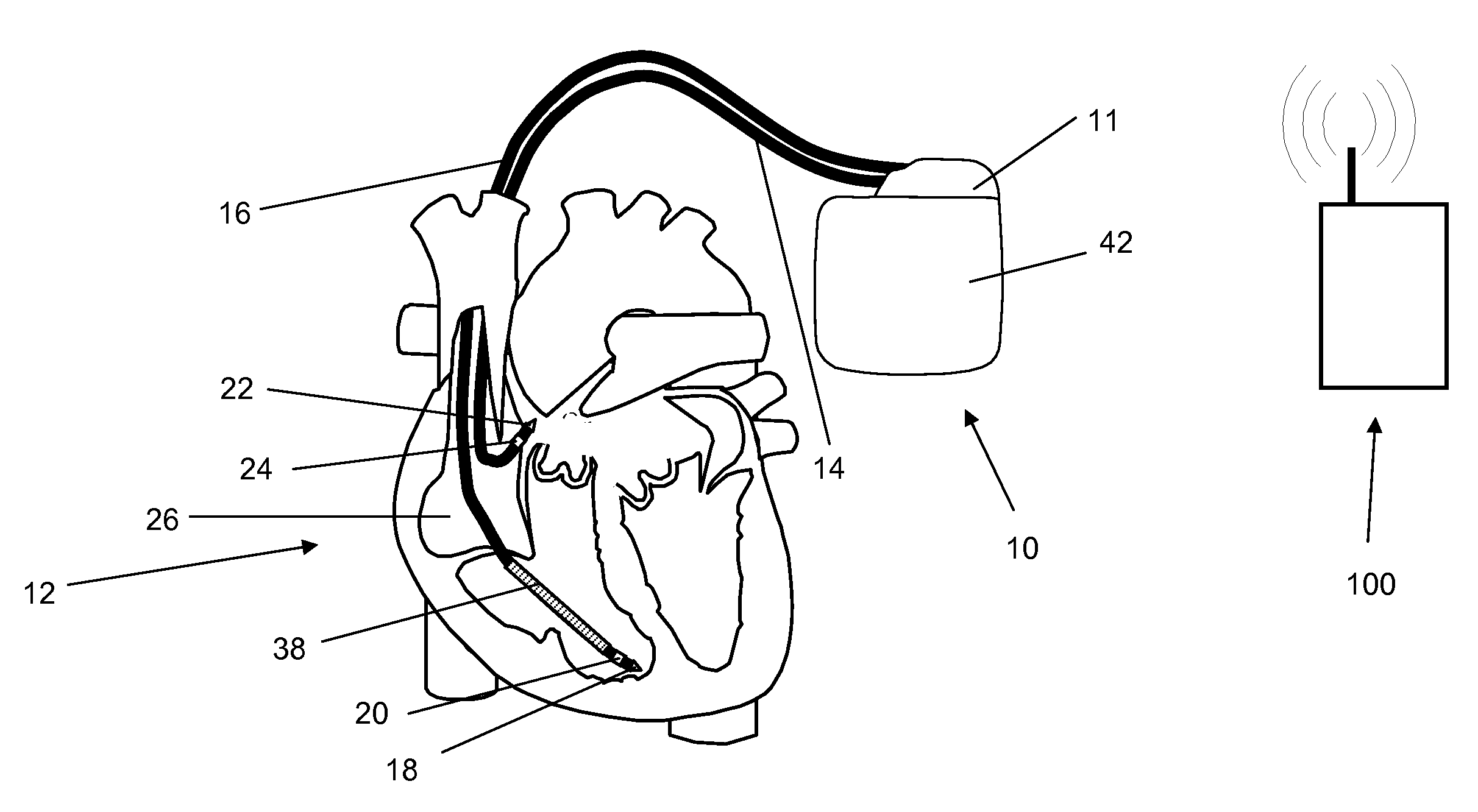
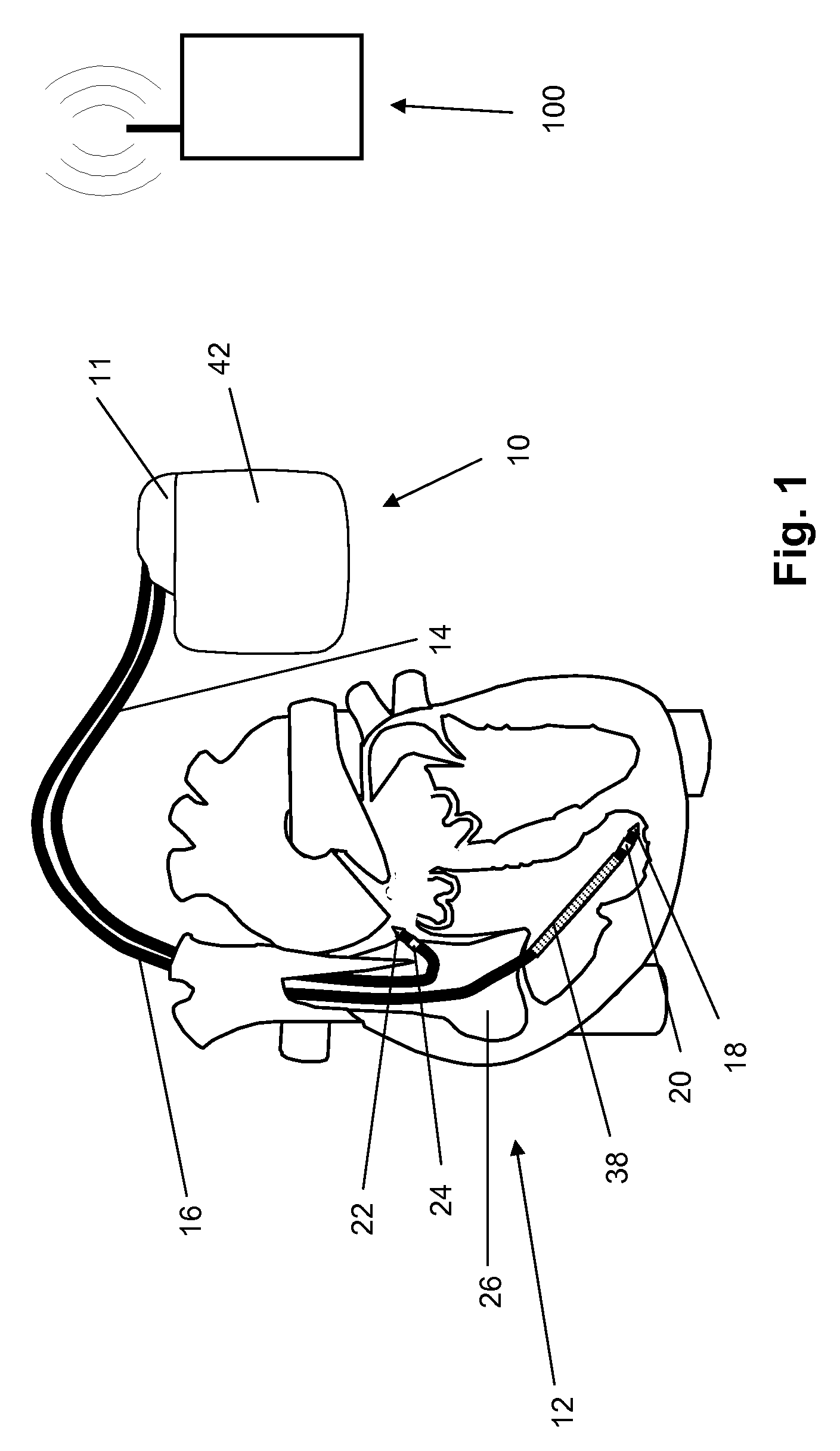
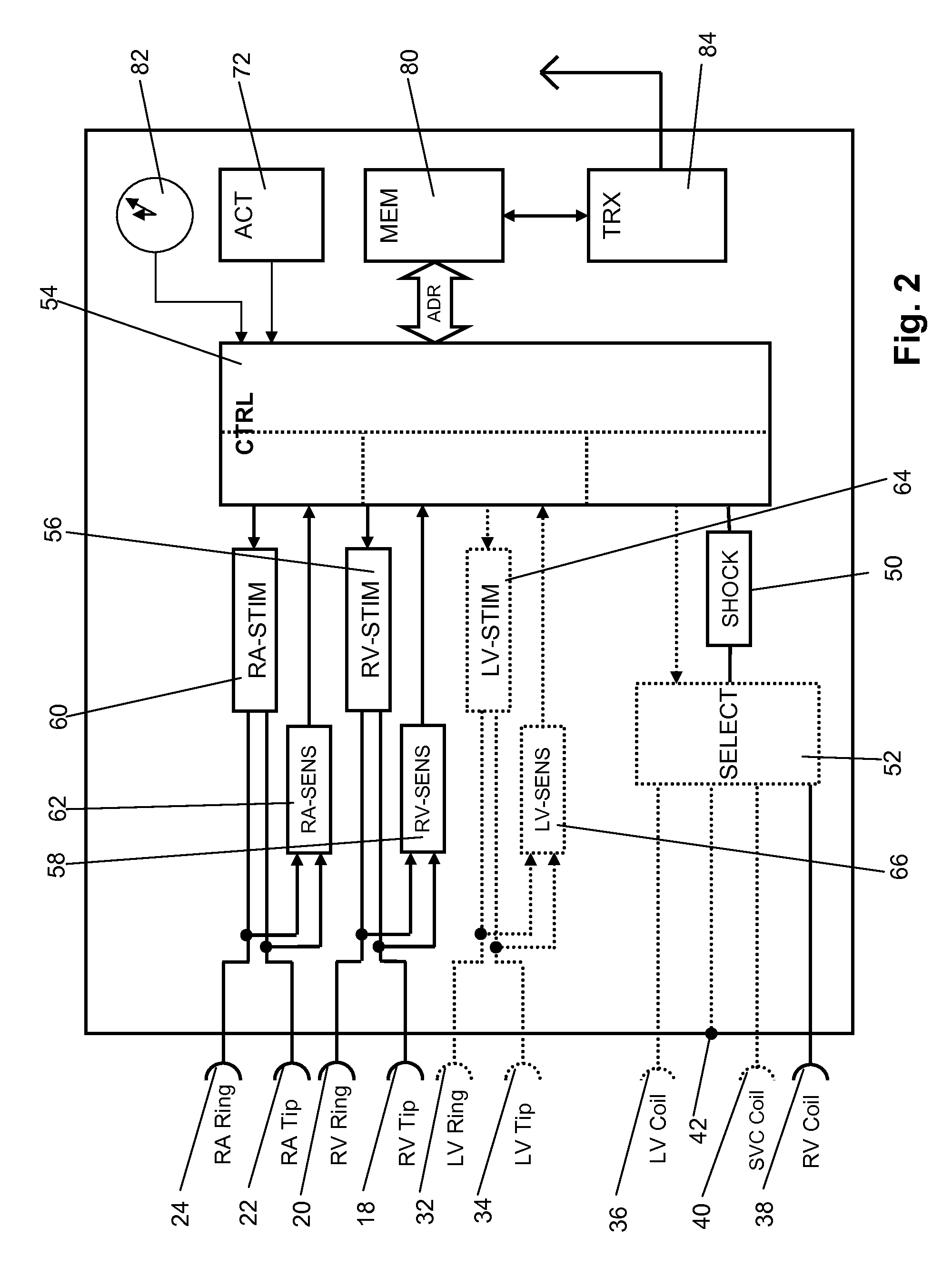
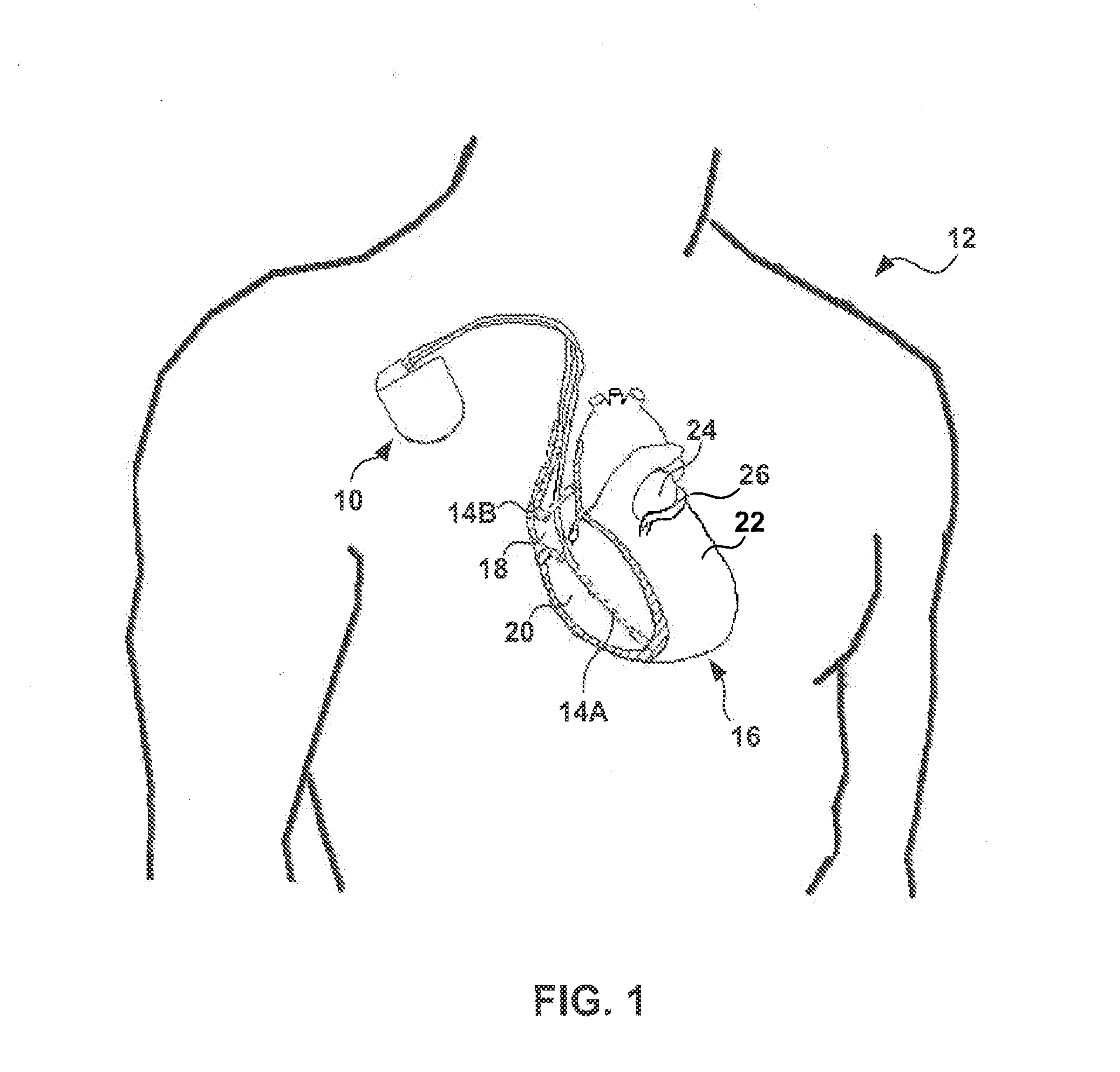
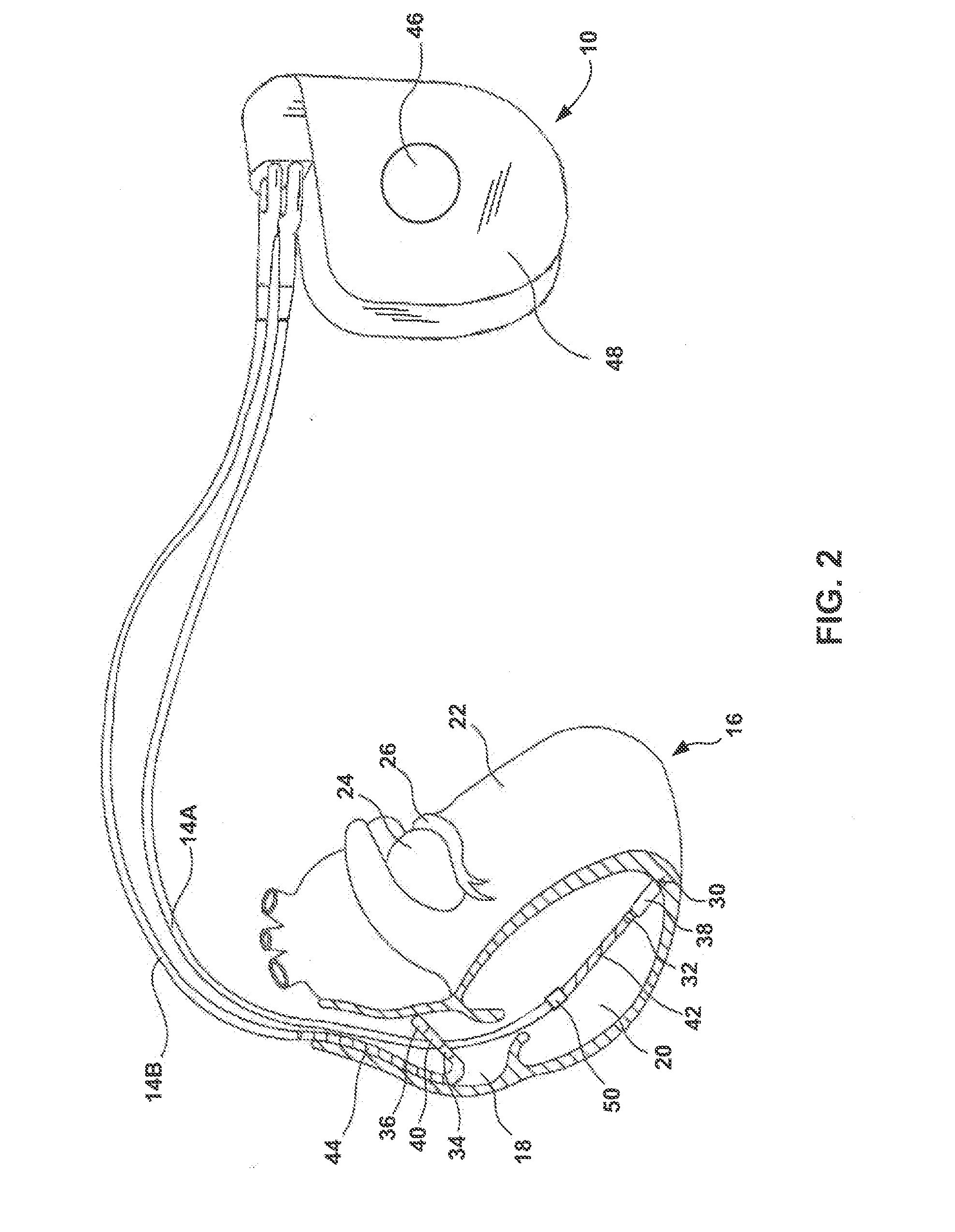
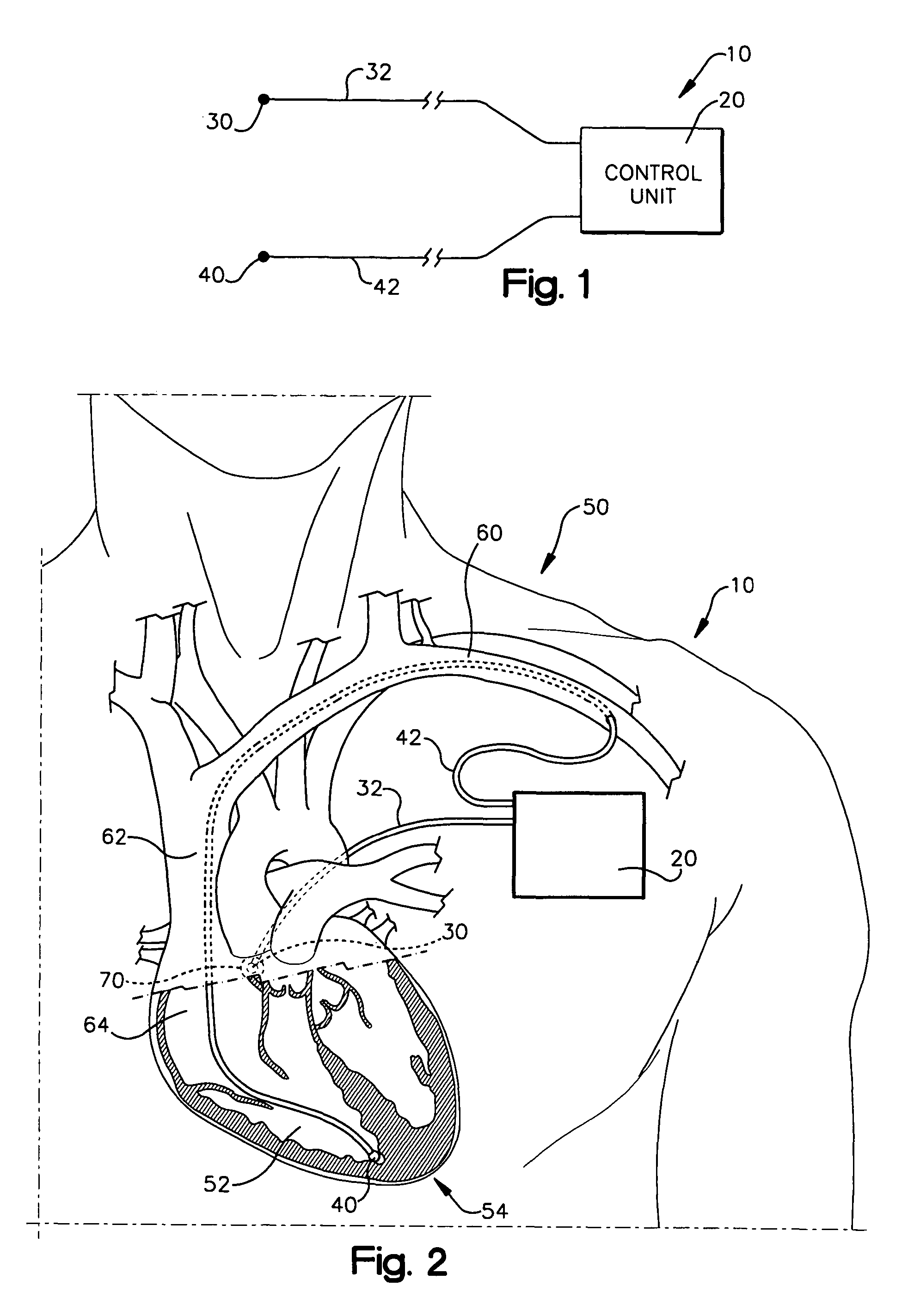
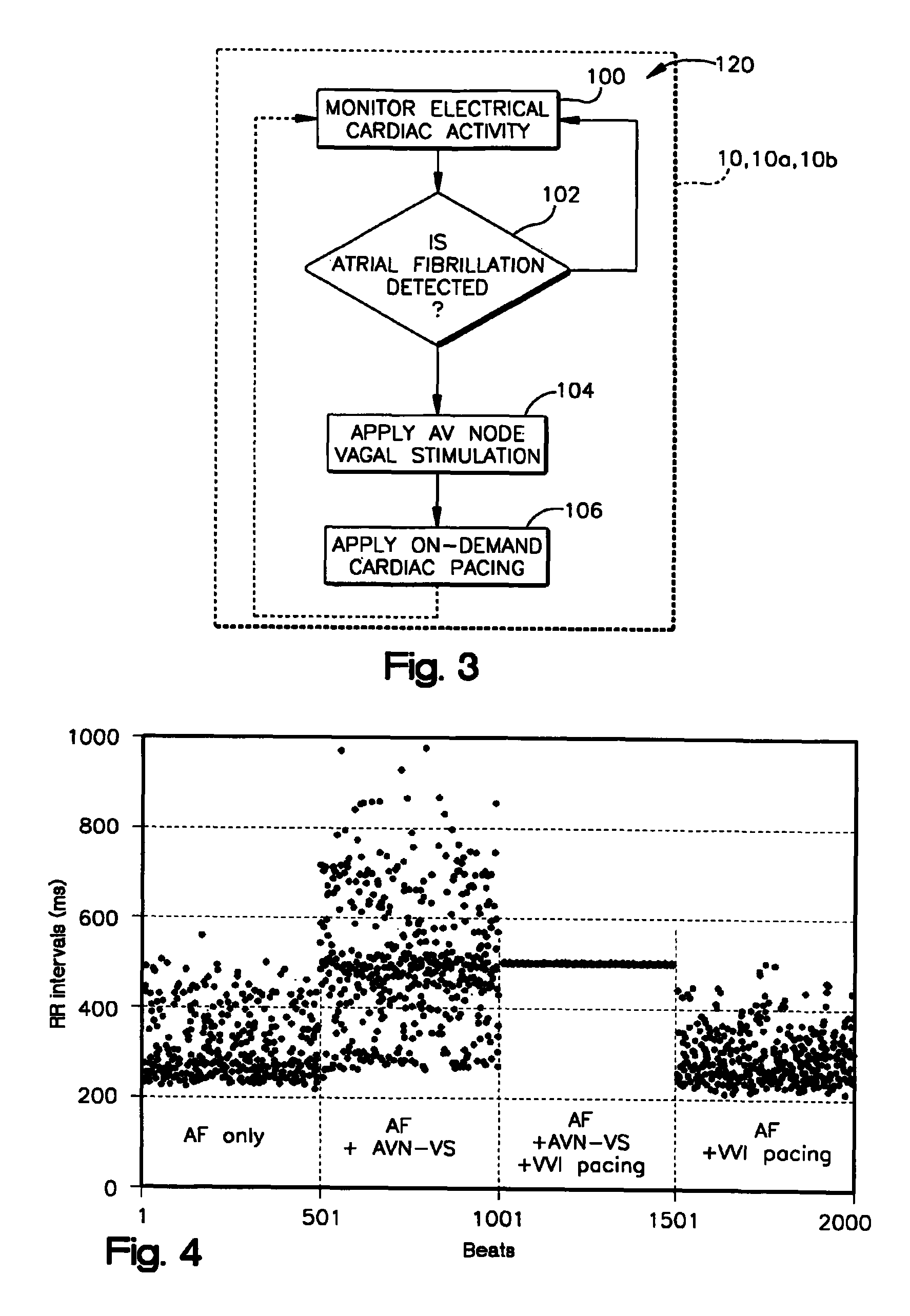
A system (10) for achieving a desired cardiac rate and cardiac rhythm in response to atrial fibrillation in a heart includes an atrial fibrillation (AF) detector (40) for detecting AF. The system also includes an atrioventricular node vagal stimulator (AVN-VS) (30) for stimulating vagal nerves associated with an atrioventricular (AV) node of the heart. The system further includes an on-demand pace maker (40) for providing ventricular pacing stimulation to the heart. A control unit (20) is operatively connected with the AF detection device, the AVN-VS device, and the on-demand pacing device. The control unit is responsive to AF detection by the AF detector to cause the AVN-VS to stimulate the vagal nerves to help reduce the ventricular rate of the heart. The control unit is further responsive to AF detection by the AF detector to cause the on-demand pace maker to help regulate the ventricular rate of the heart.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
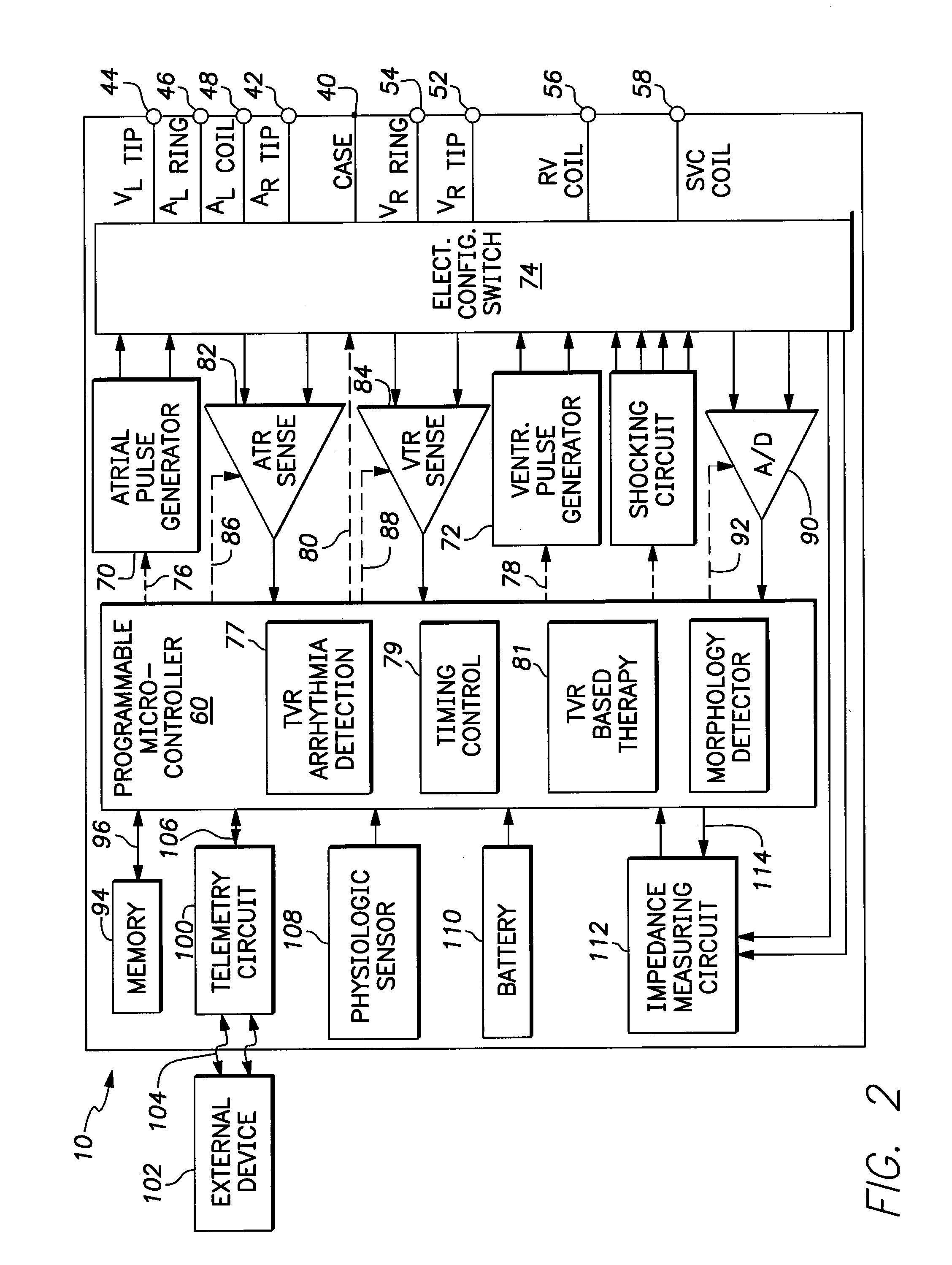
Method and apparatus for treating irregular ventricular contractions such as during atrial arrhythmia
InactiveUS7062325B1Avoids unnecessary pacingAvoid rapid changesHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsPacing intervalVentricular contraction
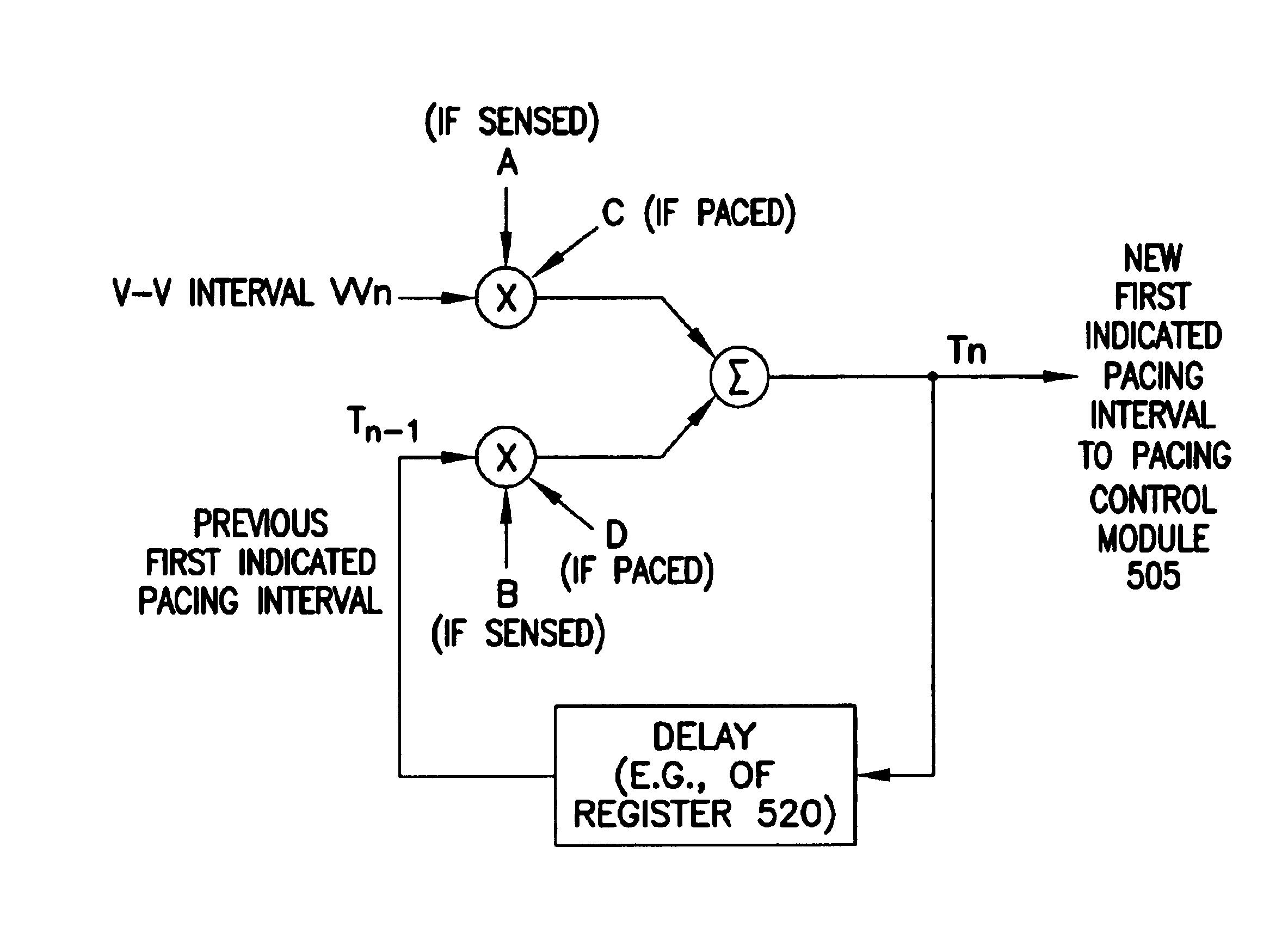
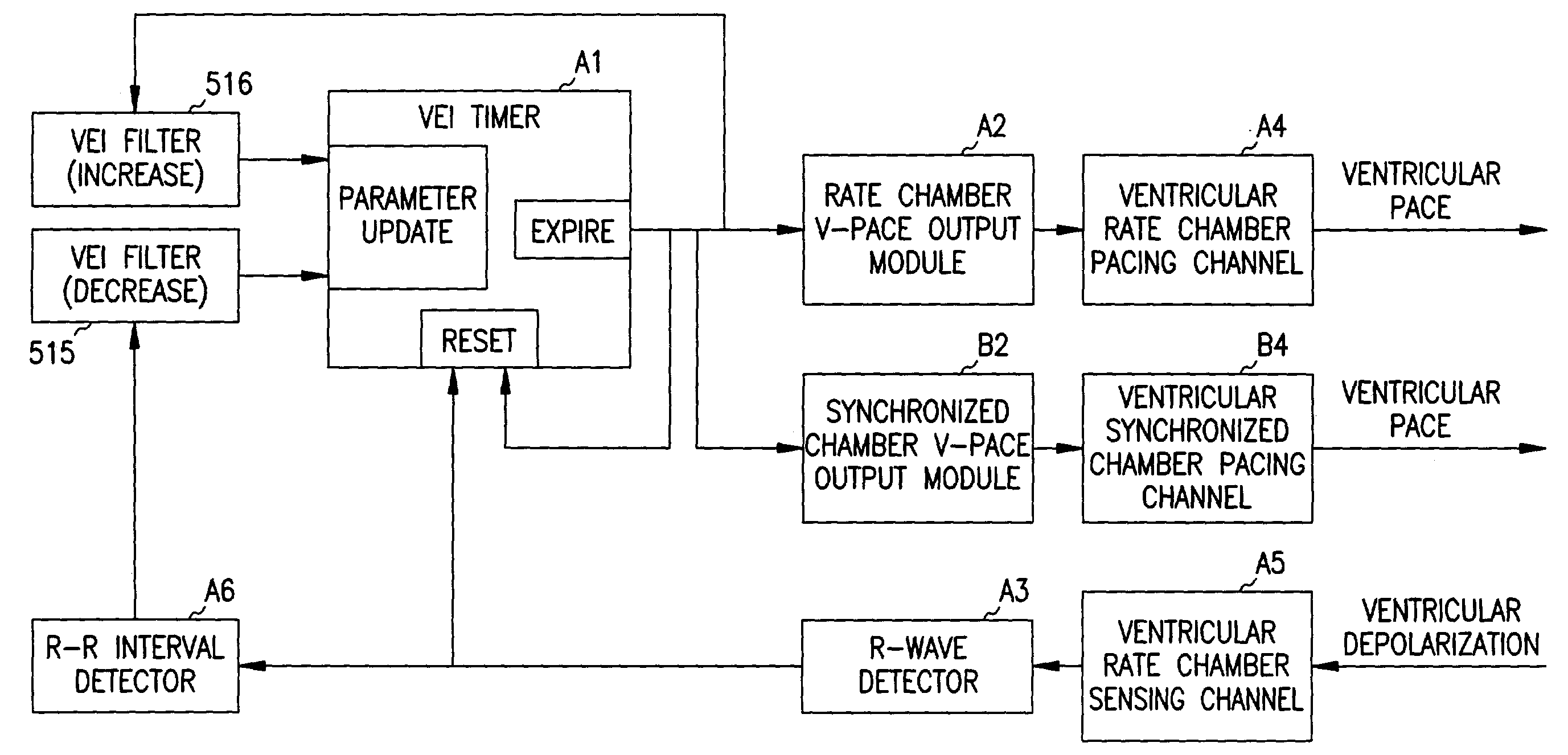
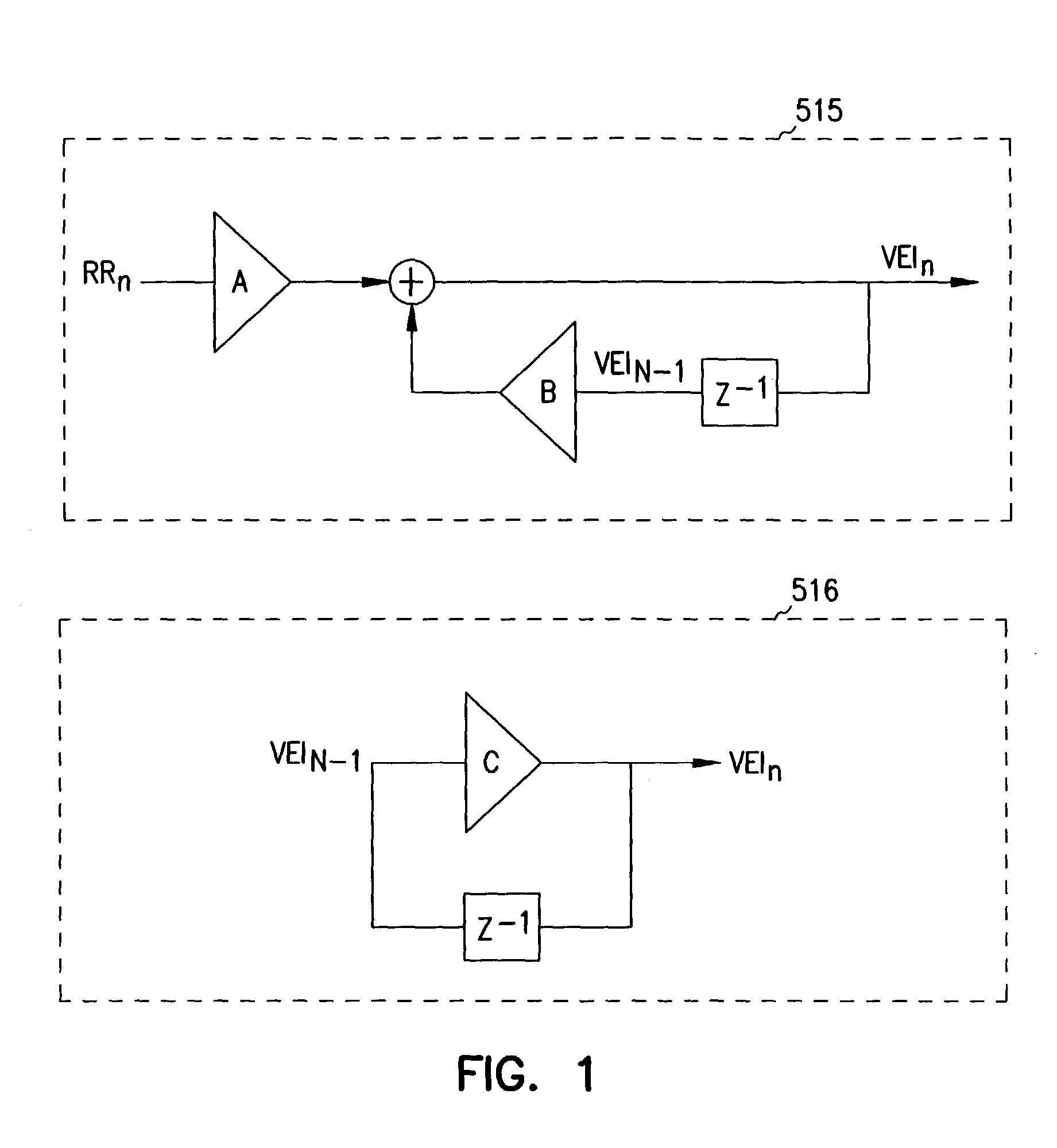
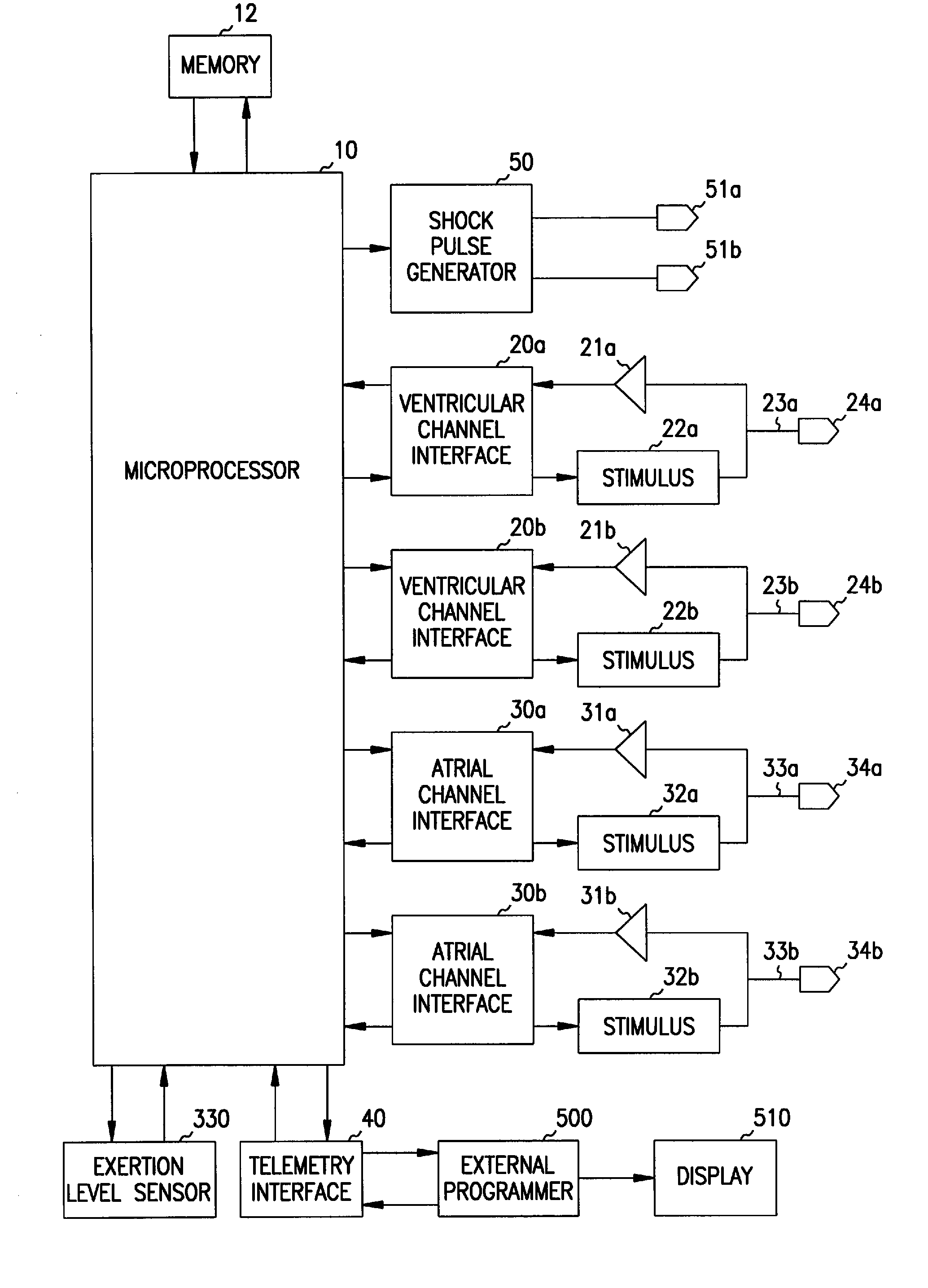
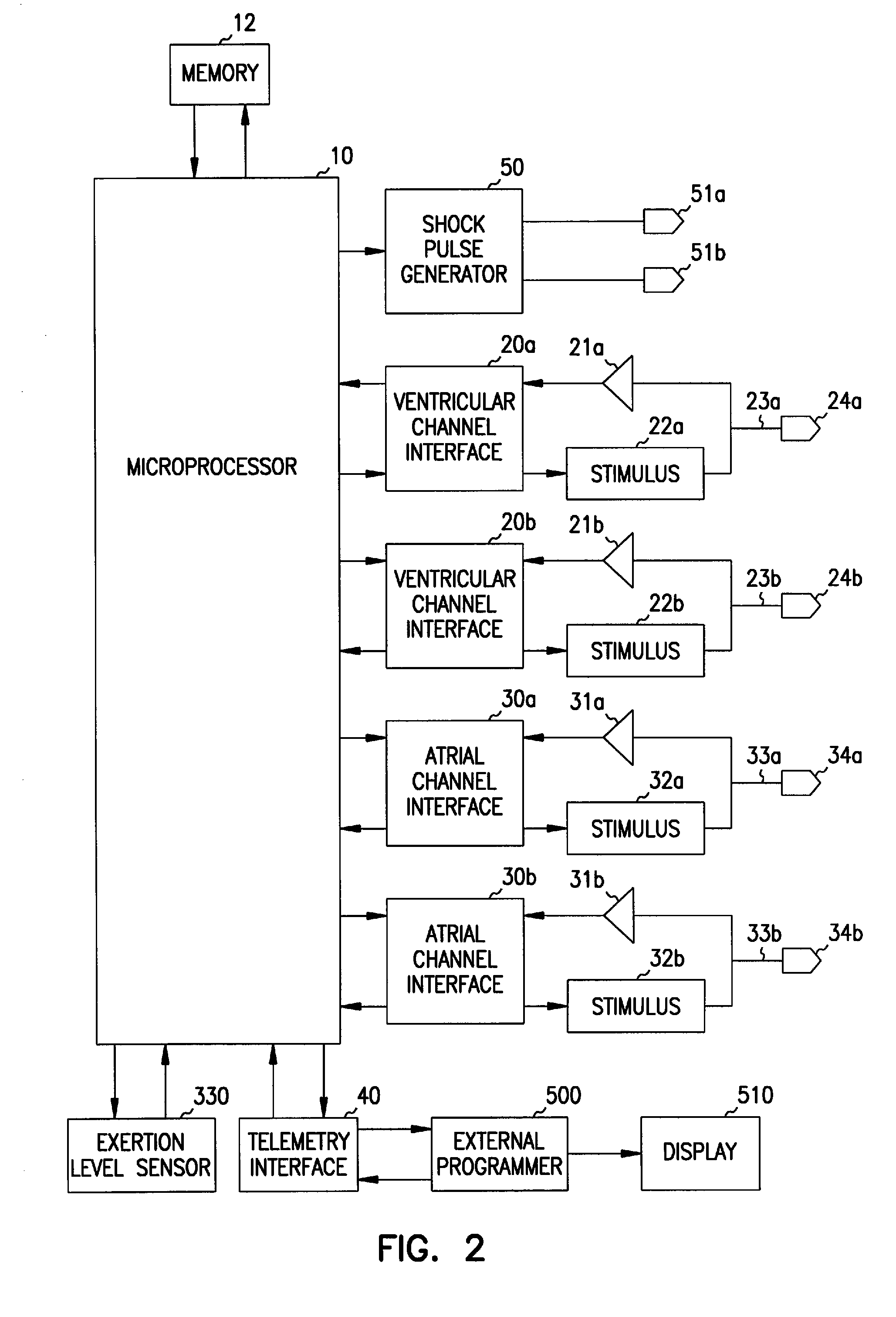
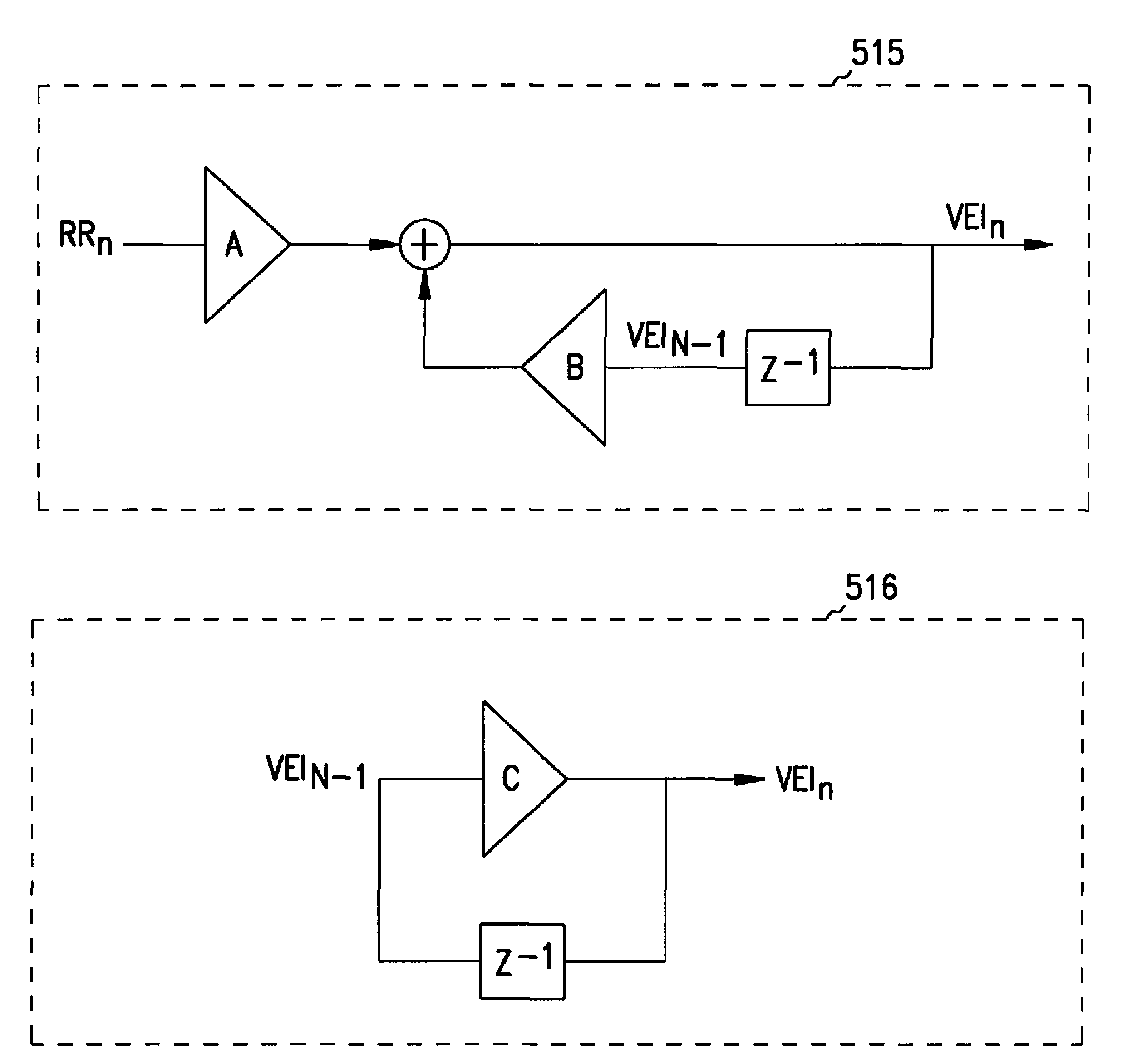
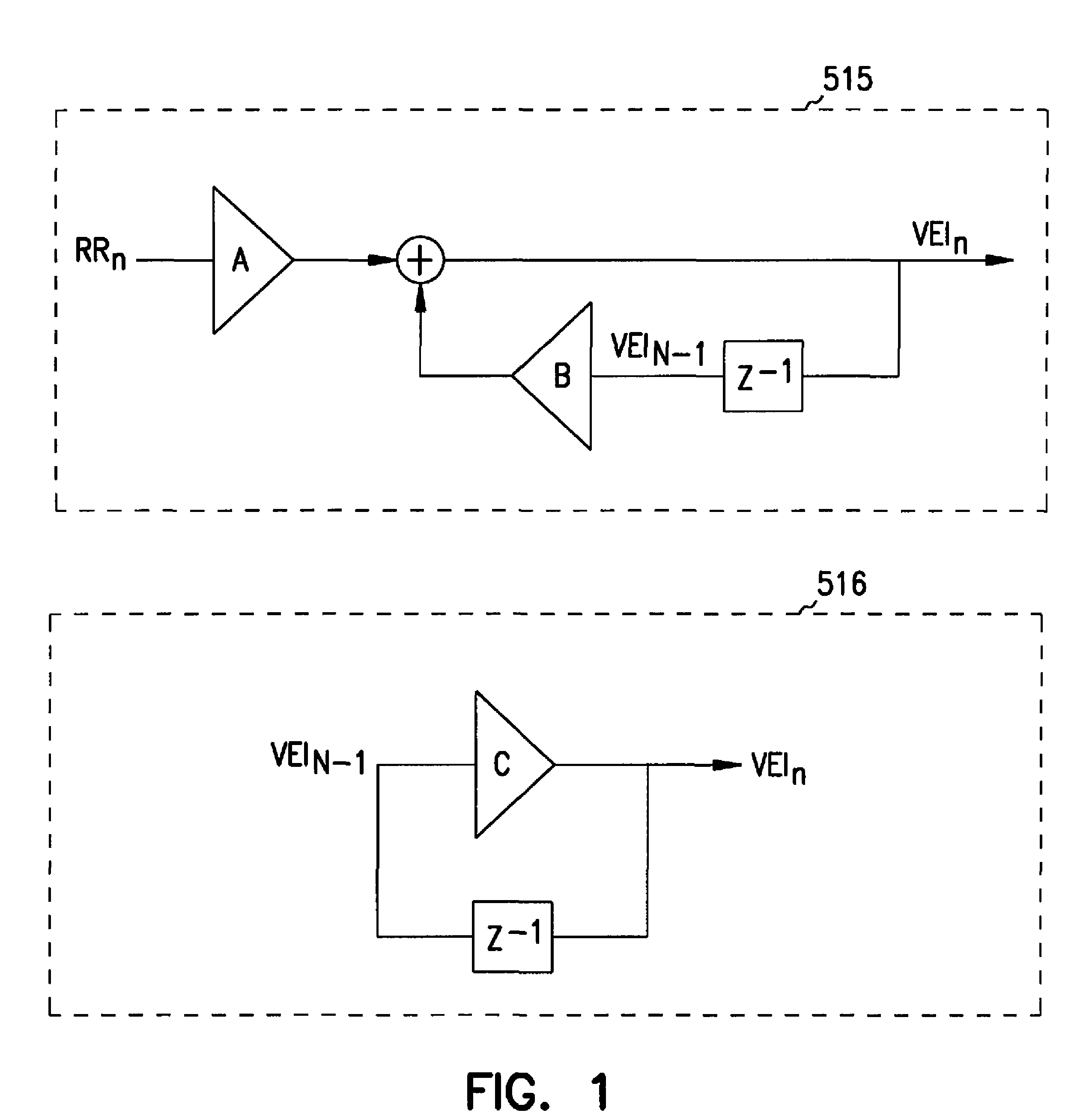
A cardiac rhythm management system is capable of treating irregular ventricular heart contractions, such as during atrial tachyarrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. A first indicated pacing interval is computed based at least partially on a most recent V—V interval duration between ventricular beats and a previous value of the first indicated pacing interval. Pacing therapy is provided based on either the first indicated pacing interval or also based on a second indicated pacing interval, such as a sensor-indicated pacing interval. A weighted averager such as an infinite impulse response (IIR) filter adjusts the first indicated pacing interval for sensed beats and differently adjusts the first indicated pacing interval for paced beats. The system regularizes ventricular rhythms by pacing the ventricle, but inhibits pacing when the ventricular rhythms are stable.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System and method for classifying tachycardia arrhythmias having 1:1 atrial-to-ventricular rhythms
An implantable cardioverter / defibrillator includes a tachycardia detection system that detects one-to-one (1:1) tachycardia, which is a tachycardia with a one-to-one relationship between atrial and ventricular contractions. When the 1:1 tachycardia is detected, the system discriminates ventricular tachycardia (VT) from supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) based on analysis of a cardiac time interval. Examples of the cardiac time interval include an atrioventricular interval (AVI) and a ventriculoatrial interval (VAI). A template time interval is created during a known normal sinus rhythm. The system measures a tachycardia time interval after detecting the 1:1 tachycardia, and indicates a VT detection if the tachycardia time interval differs from the template time interval by at least a predetermined percentage of the template time interval.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
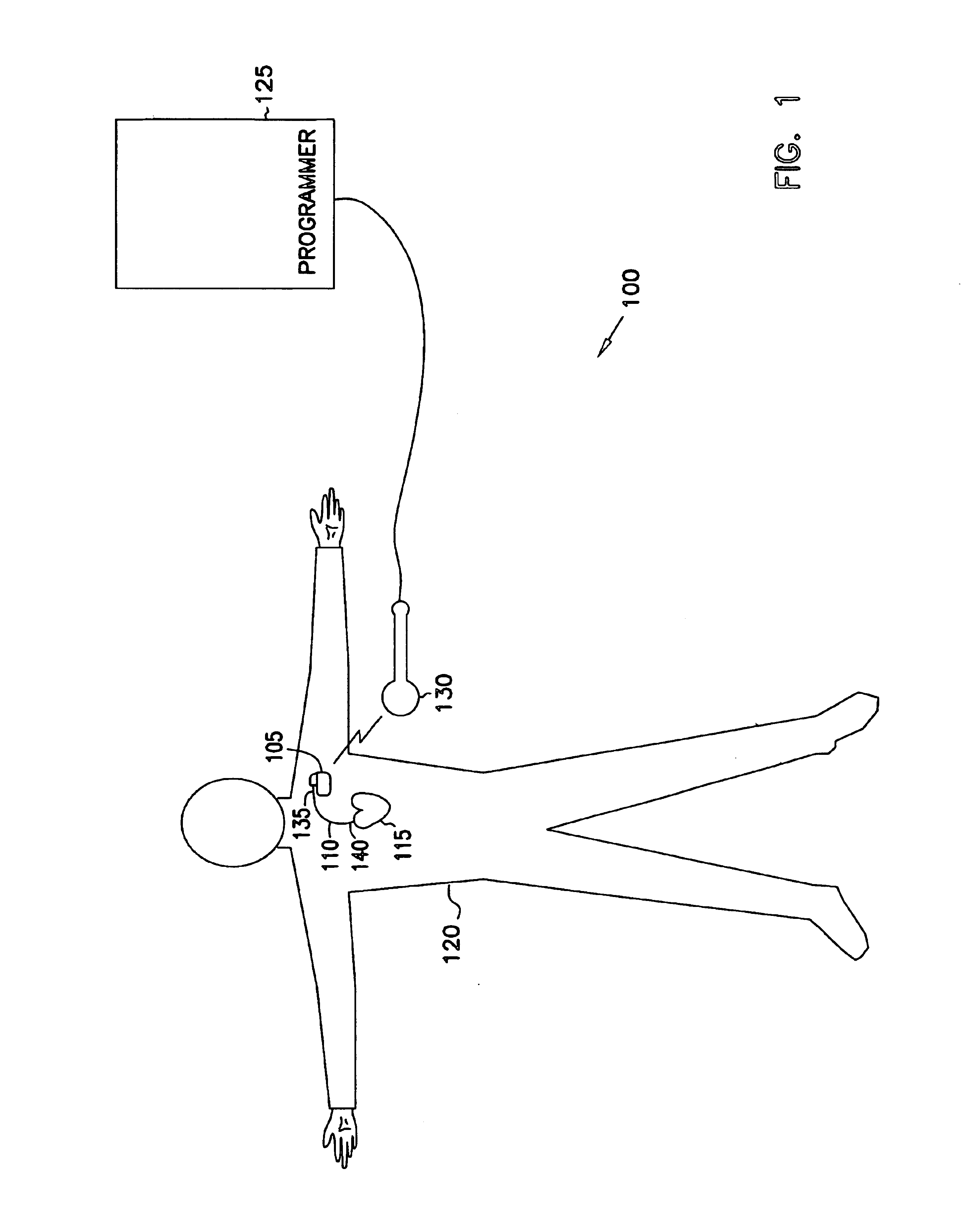
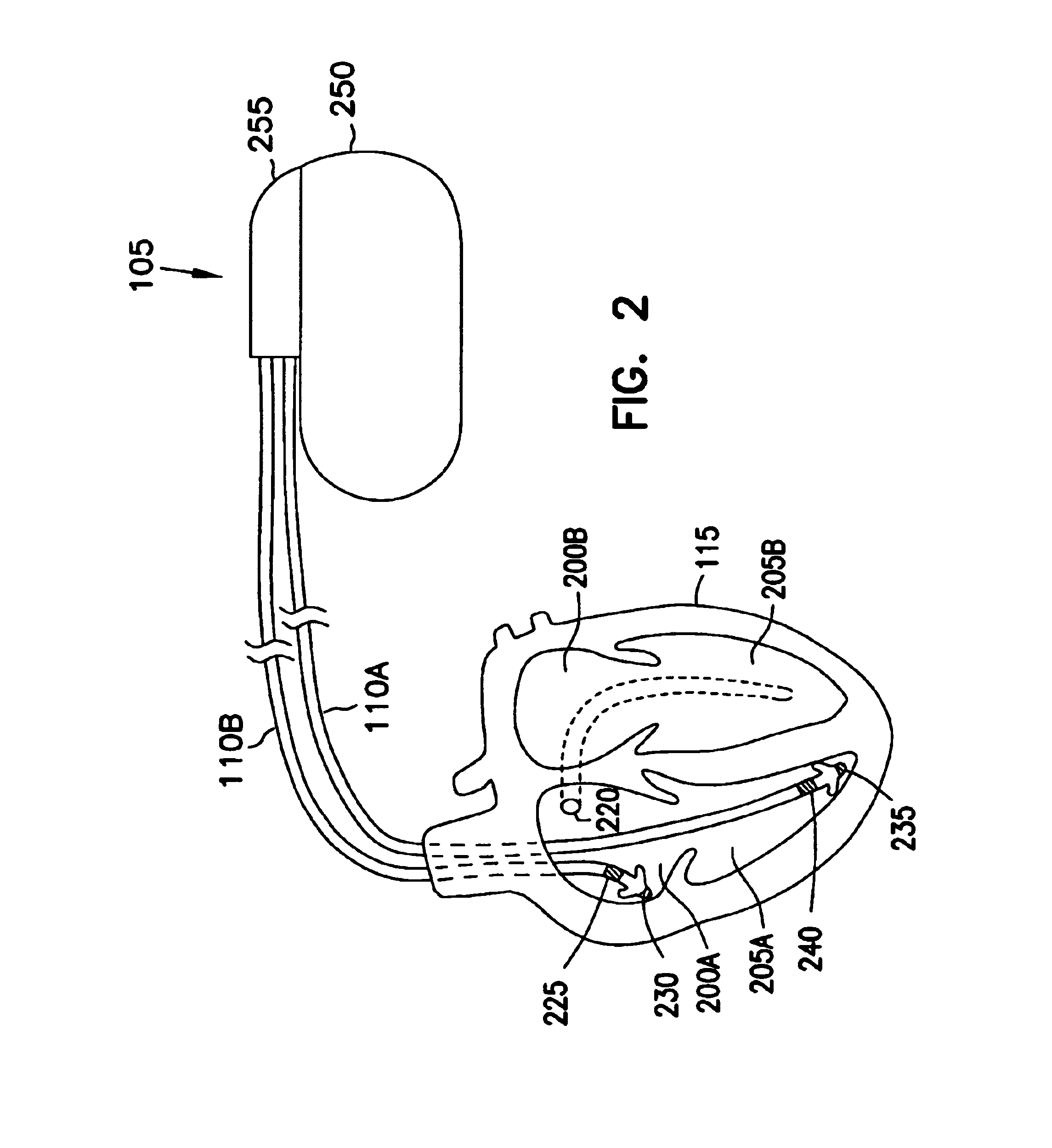
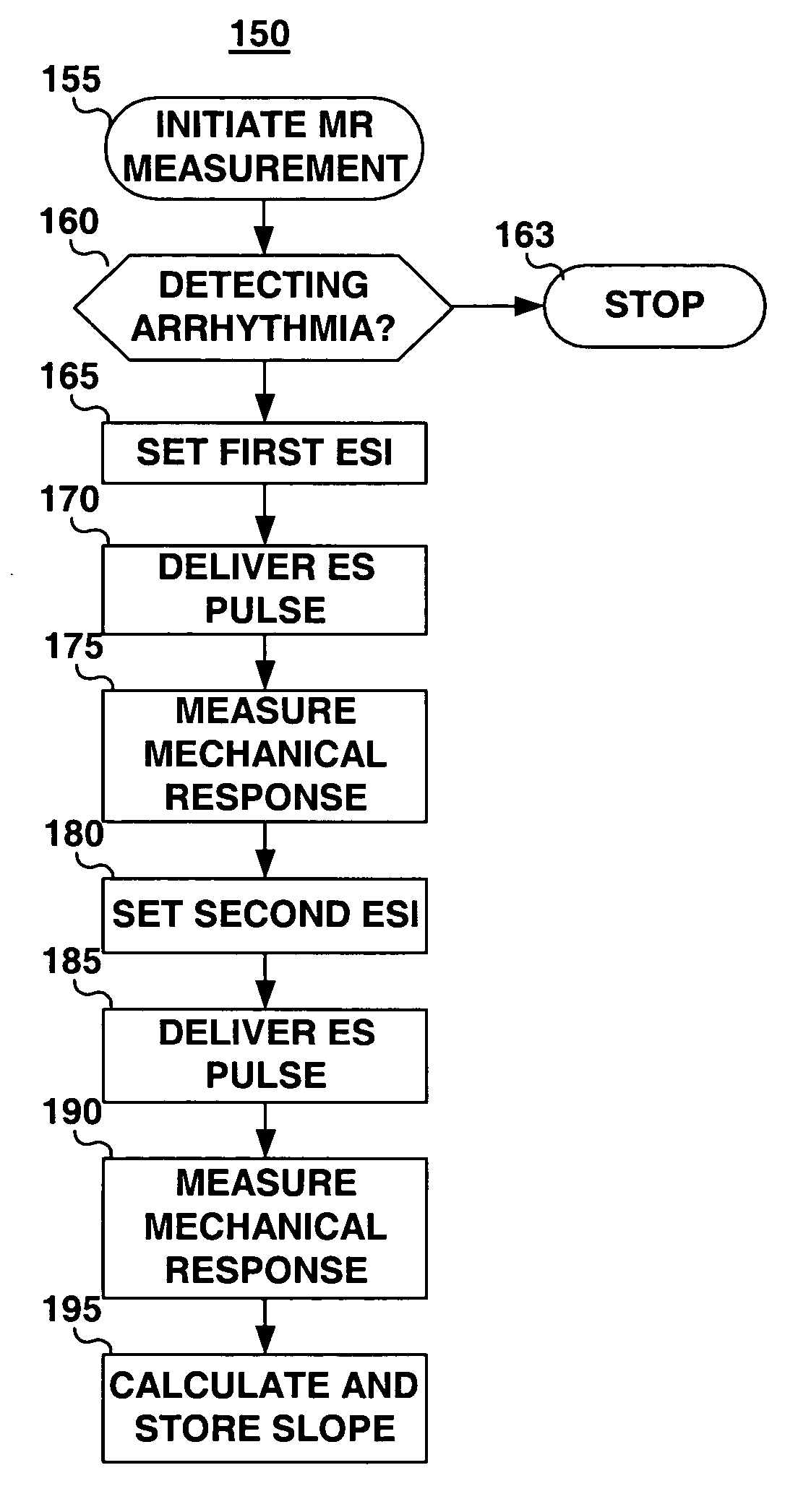
Use of mechanical restitution to predict hemodynamic response to a rapid ventricular rhythm
An implantable cardiac stimulation device and associated method for predicting the hemodynamic response to a rapid heart rhythm. The system includes an implantable cardiac stimulation device and associated sensors of electrical and mechanical heart function. The associated method includes measuring a mechanical restitution (MR) parameter or surrogate thereof, performing a comparative analysis of the MR parameter, and predicting an unstable or stable hemodynamic response to a rapid heart rate based on the comparative analysis. If an unstable hemodynamic response to a rapid rhythm is predicted, a more aggressive menu of arrhythmia therapies may be programmed to treat tachycardia. If a stable hemodynamic response is predicted, a less aggressive menu of therapies may be programmed to treat tachycardia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and method for ventricular rate regularization
InactiveUS7142915B2Less variabilityIncrease cardiac outputHeart stimulatorsVentricular rateBradycardia
A method and system for operating a cardiac rhythm management device which employs pacing therapy to regularize the ventricular rhythm. Such ventricular rate regularization may be employed with conventional bradycardia pacing, ventricular resynchronization therapy, or anti-tachyarrhythmia therapy.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Discrimination of atrial fibrillations for an active implantable medical device, in particular a defibrillator/cardiovertor
InactiveUS6889080B2Minimize the possibilityReduce riskHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsPR intervalRR interval
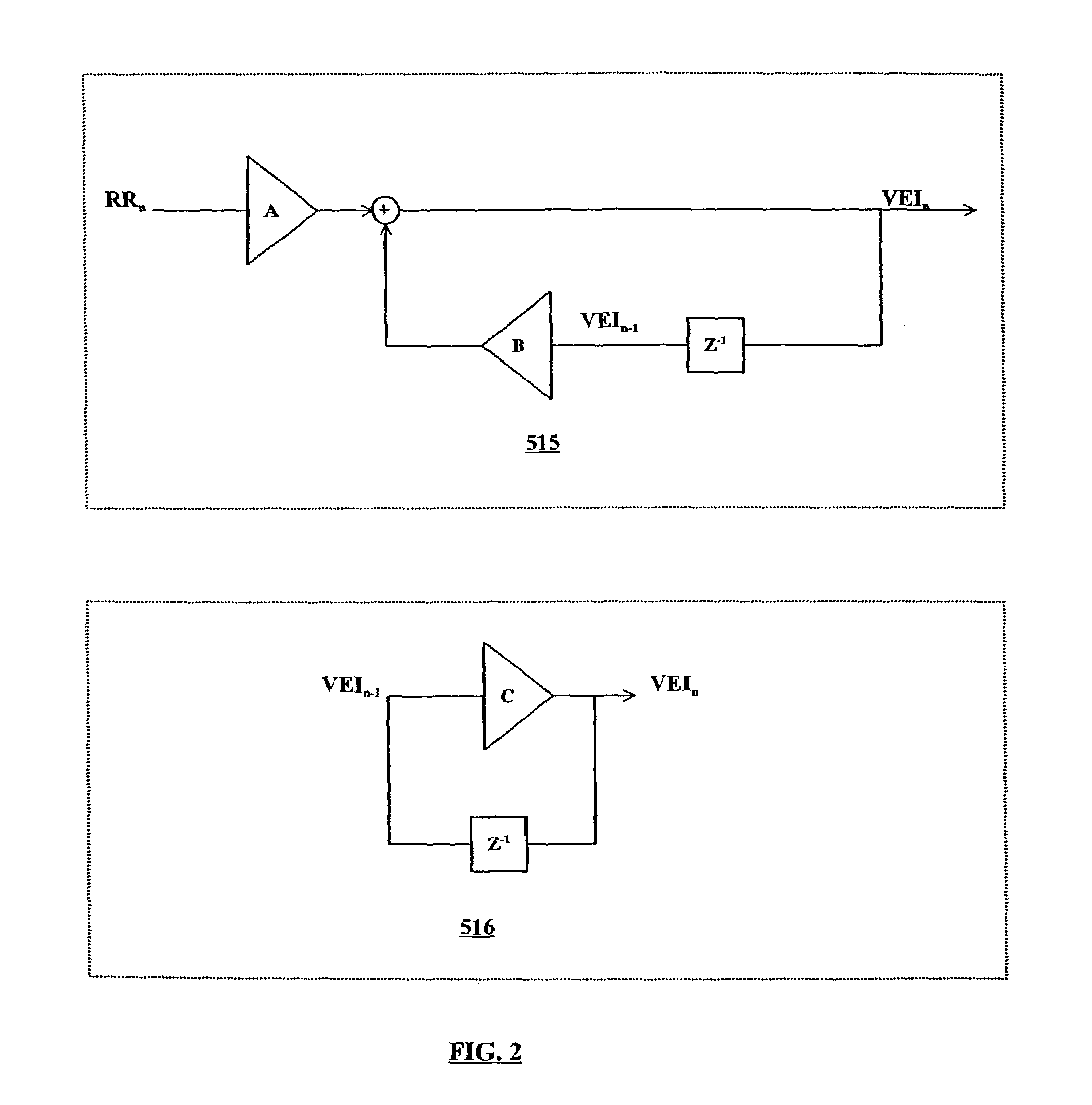
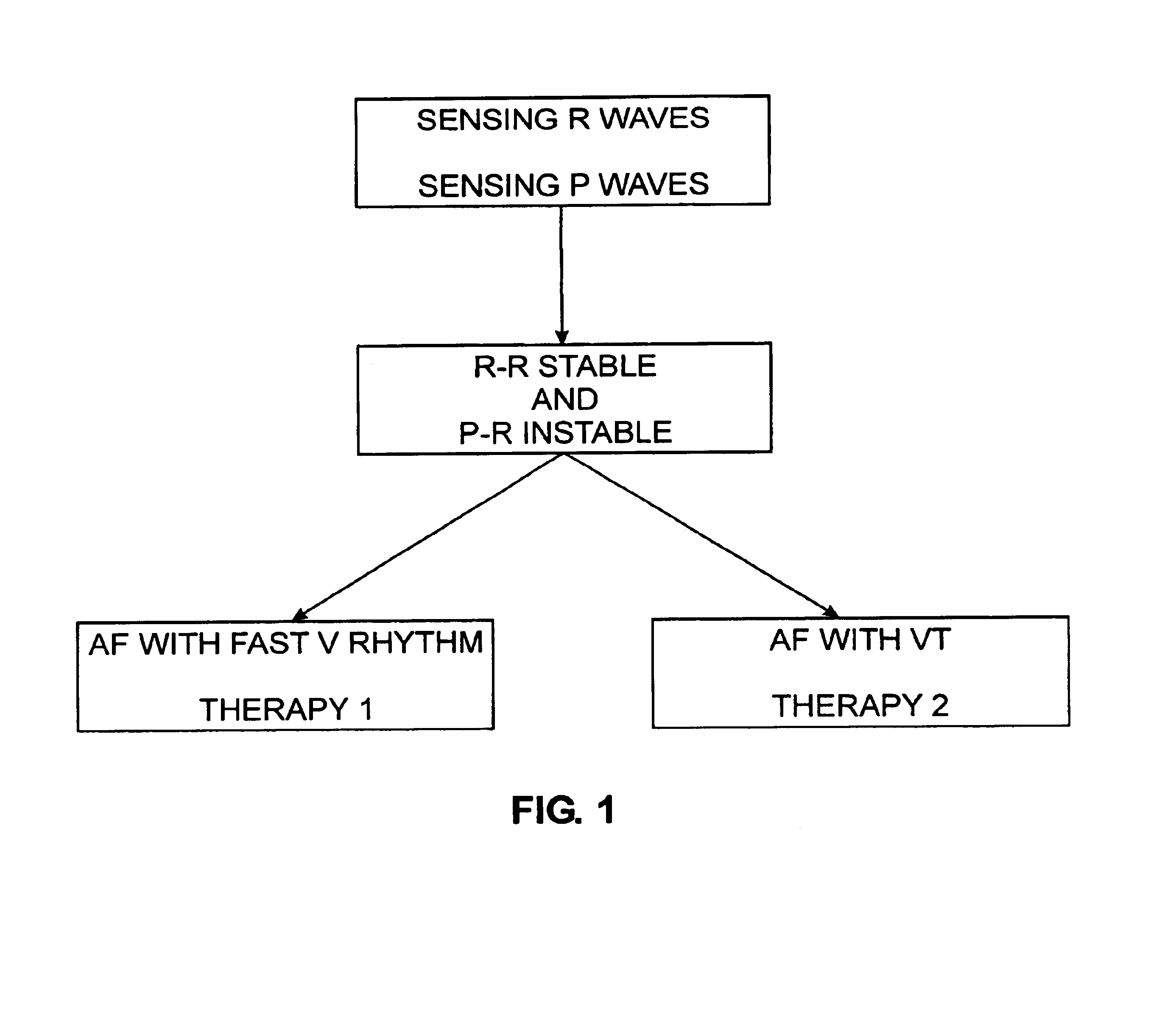
An active implantable medical device, in particular a defibrillator / cardioverter, with a sophisticated discrimination of atrial fibrillations. This device is able to deliver therapy for defibrillation, cardioversion, and / or ventricular and / or atrial antitachycardiac pacing stimulation; sense the ventricular and atrial activity; identify a suspicion of and confirm the presence of episodes of tachycardia in the activity thus sensed; analyze the stability of detected RR intervals and the stability of the associated PR intervals; and, in the event of a detection of stable RR intervals and unstable PR intervals, discriminate between atrial fibrillation with fast ventricular rhythm and atrial fibrillation with ventricular tachycardia, and to control delivery of a differentiated therapy according to one case or the other. A bi-tachycardia discrimination also can be made.
Owner:SORIN CRM
Method and apparatus for treating irregular ventricular contractions such as during atrial arrhythmia
InactiveUS20090076563A1Avoids unnecessary pacingAvoid rapid changesHeart stimulatorsPacing intervalVentricular contraction
A cardiac rhythm management system is capable of treating irregular ventricular heart contractions, such as during atrial tachyarrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. A first indicated pacing interval is computed based at least partially on a most recent V-V interval duration between ventricular beats and a previous value of the first indicated pacing interval. Pacing therapy is provided based on either the first indicated pacing interval or also based on a second indicated pacing interval, such as a sensor-indicated pacing interval. A weighted averager such as an infinite impulse response (IIR) filter adjusts the first indicated pacing interval for sensed beats and differently adjusts the first indicated pacing interval for paced beats. The system regularizes ventricular rhythms by pacing the ventricle, but inhibits pacing when the ventricular rhythms are stable.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Apparatus and method for ventricular rate regularization
InactiveUS7181278B2Less variabilityIncrease cardiac outputHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular rateCardiac pacemaker electrode
A cardiac rhythm management device which employs pacing therapy to regularize the ventricular rhythm. Such ventricular rate regularization may be employed within bradycardia pacemakers, ventricular resynchronization devices, or implantable cardioverter / defibrillators.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System and Method for Achieving Regular Slow Ventricular Rhythm in Response to Atrial Fibrillation
InactiveUS20080300640A1Decrease ventricular rateEasy to adjustHeart stimulatorsVentricular rateAtrioventricular node
A system (10) for achieving a desired cardiac rate and cardiac rhythm in response to atrial fibrillation in a heart includes an atrial fibrillation (AF) detector (40) for detecting AF. The system also includes an atrioventricular node vagal stimulator (AVN-VS) (30) for stimulating vagal nerves associated with an atrioventricular (AV) node of the heart. The system further includes an on-demand pace maker (40) for providing ventricular pacing stimulation to the heart. A control unit (20) is operatively connected with the AF detection device, the AVN-VS device, and the on-demand pacing device. The control unit is responsive to AF detection by the AF detector to cause the AVN-VS to stimulate the vagal nerves to help reduce the ventricular rate of the heart. The control unit is further responsive to AF detection by the AF detector to cause the on-demand pace maker to help regulate the ventricular rate of the heart.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
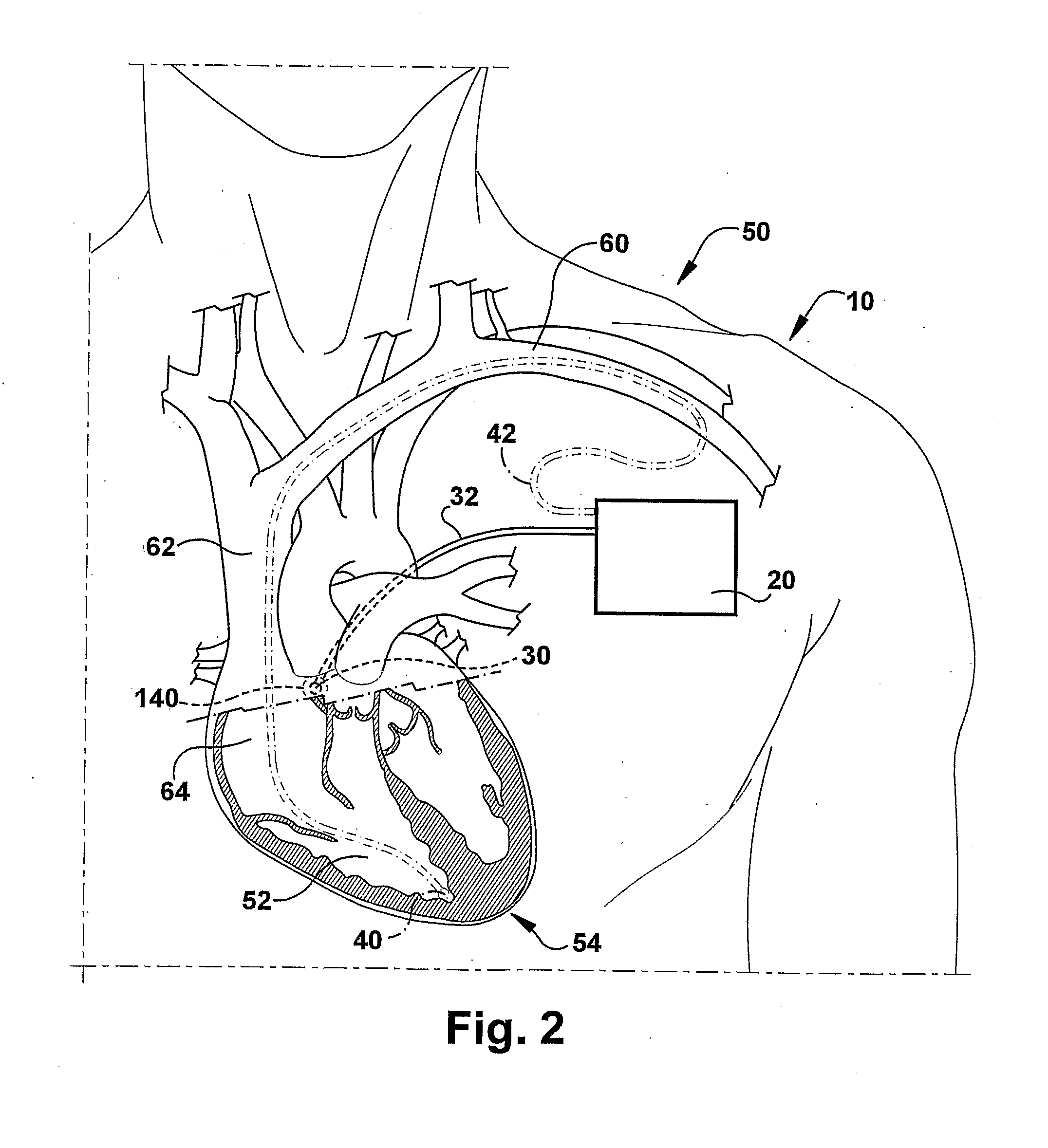
Implantable medical device and method for lv coronary sinus lead implant site optimization
InactiveUS20080249585A1Ease of evaluationTransvascular endocardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsCoronary sinusHemodynamics
A device is connected to electrode leads which performs intracardiac impedance measurements, conducts a transient pacing protocol, analyses the impedance measurements, and generates an LV lead position quality factor. The transient pacing protocol includes a repeated change (“transitions”) between ventricular intrinsic rhythm and biventricular paced rhythm and may also include a variation of the atrioventricular delay (AVD) and / or the interventricular delay (VVD). The quality factor expresses the degree to which hemodynamic properties have improved due to BiV stimulation for the current LV lead position compared to intrinsic ventricular rhythm.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Method and apparatus for treating irregular ventricular contractions such as during atrial arrhythmia
InactiveUS20070016258A1Avoids unnecessary pacingAvoid rapid changesElectrotherapyAtrial cavityPacing interval
A cardiac rhythm management system is capable of treating irregular ventricular heart contractions, such as during atrial tachyarrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. A first indicated pacing interval is computed based at least partially on a most recent V-V interval duration between ventricular beats and a previous value of the first indicated pacing interval. Pacing therapy is provided based on either the first indicated pacing interval or also based on a second indicated pacing interval, such as a sensor-indicated pacing interval. A weighted averager such as an infinite impulse response (IIR) filter adjusts the first indicated pacing interval for sensed beats and differently adjusts the first indicated pacing interval for paced beats. The system regularizes ventricular rhythms by pacing the ventricle, but inhibits pacing when the ventricular rhythms are stable.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Apparatus and method for ventricular rate regularization
InactiveUS20070135853A1Less variabilityHigh outputHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular rateCardiac pacemaker electrode
A cardiac rhythm management device which employs pacing therapy to regularize the ventricular rhythm. Such ventricular rate regularization may be employed within bradycardia pacemakers, ventricular resynchronization devices, or implantable cardioverter / defibrillators.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
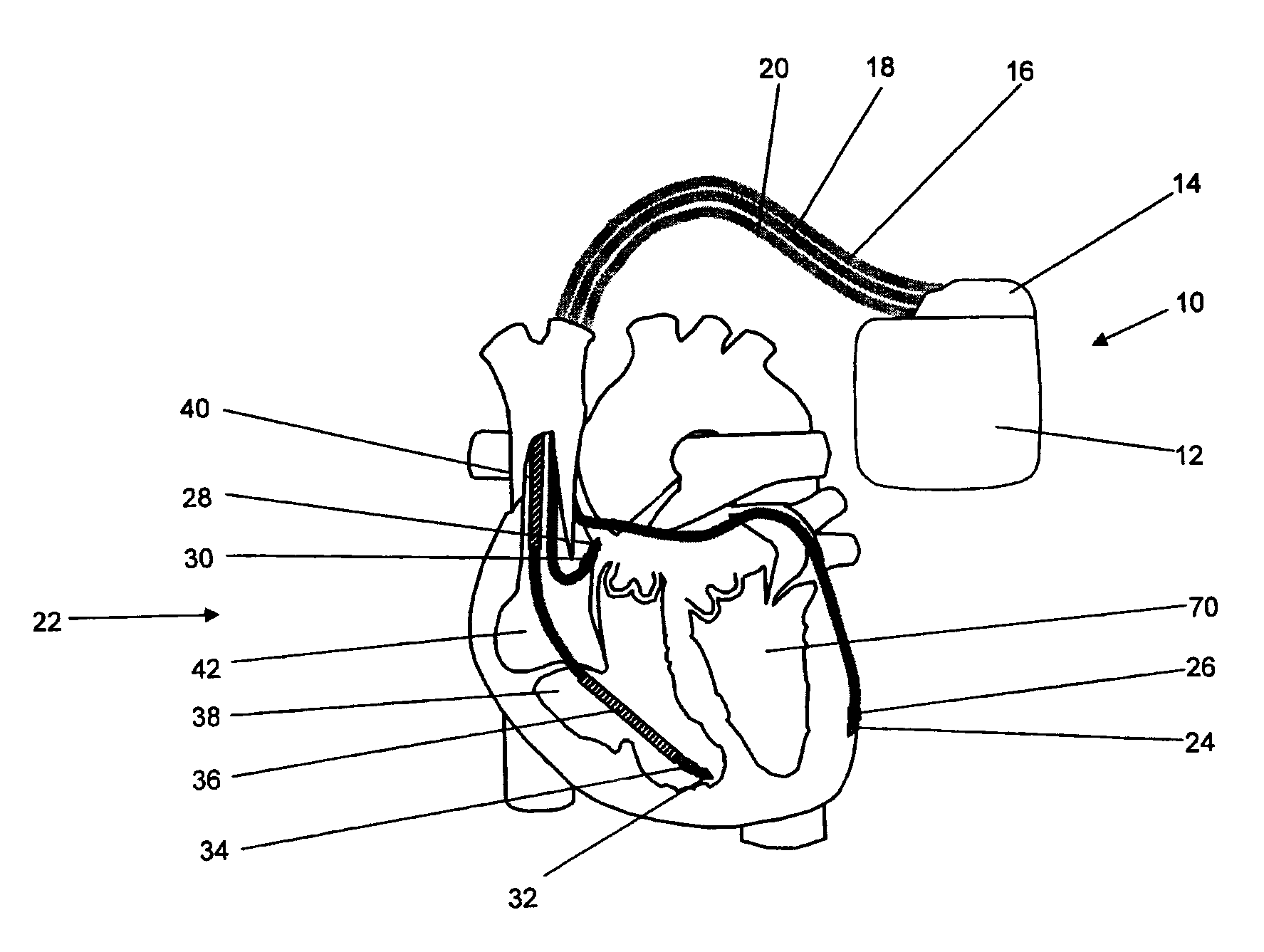
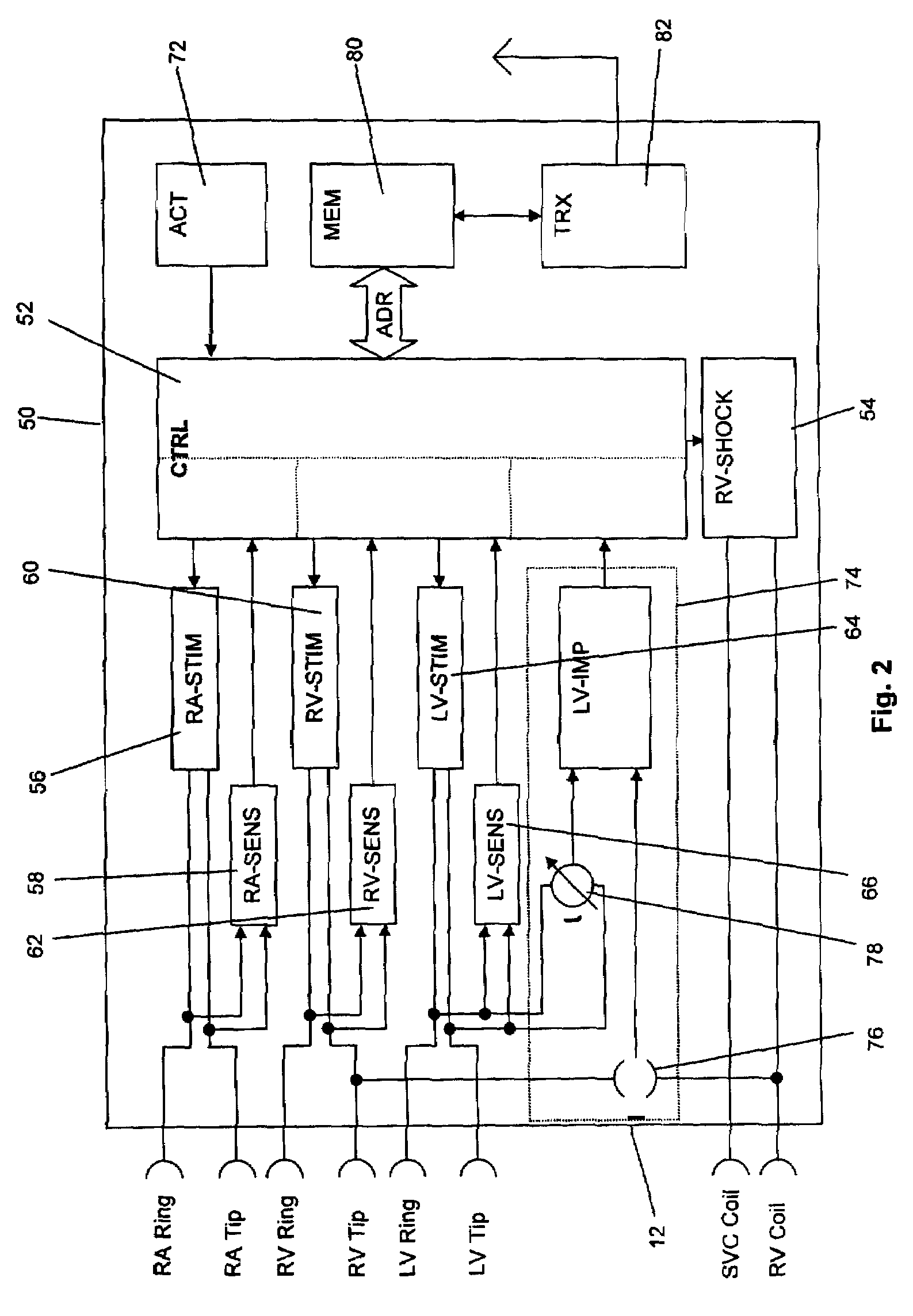
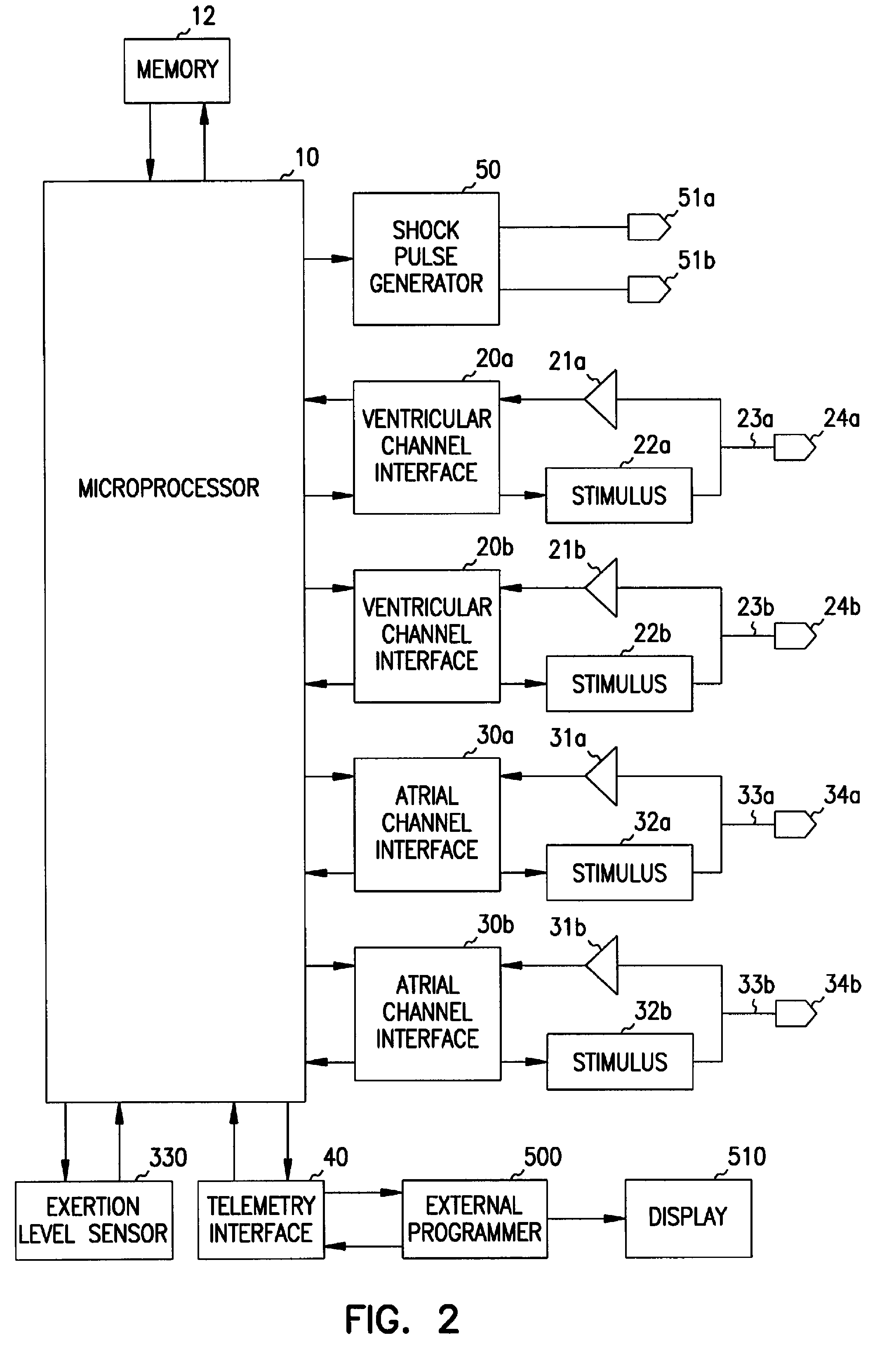
Antitachycardiac heart stimulator
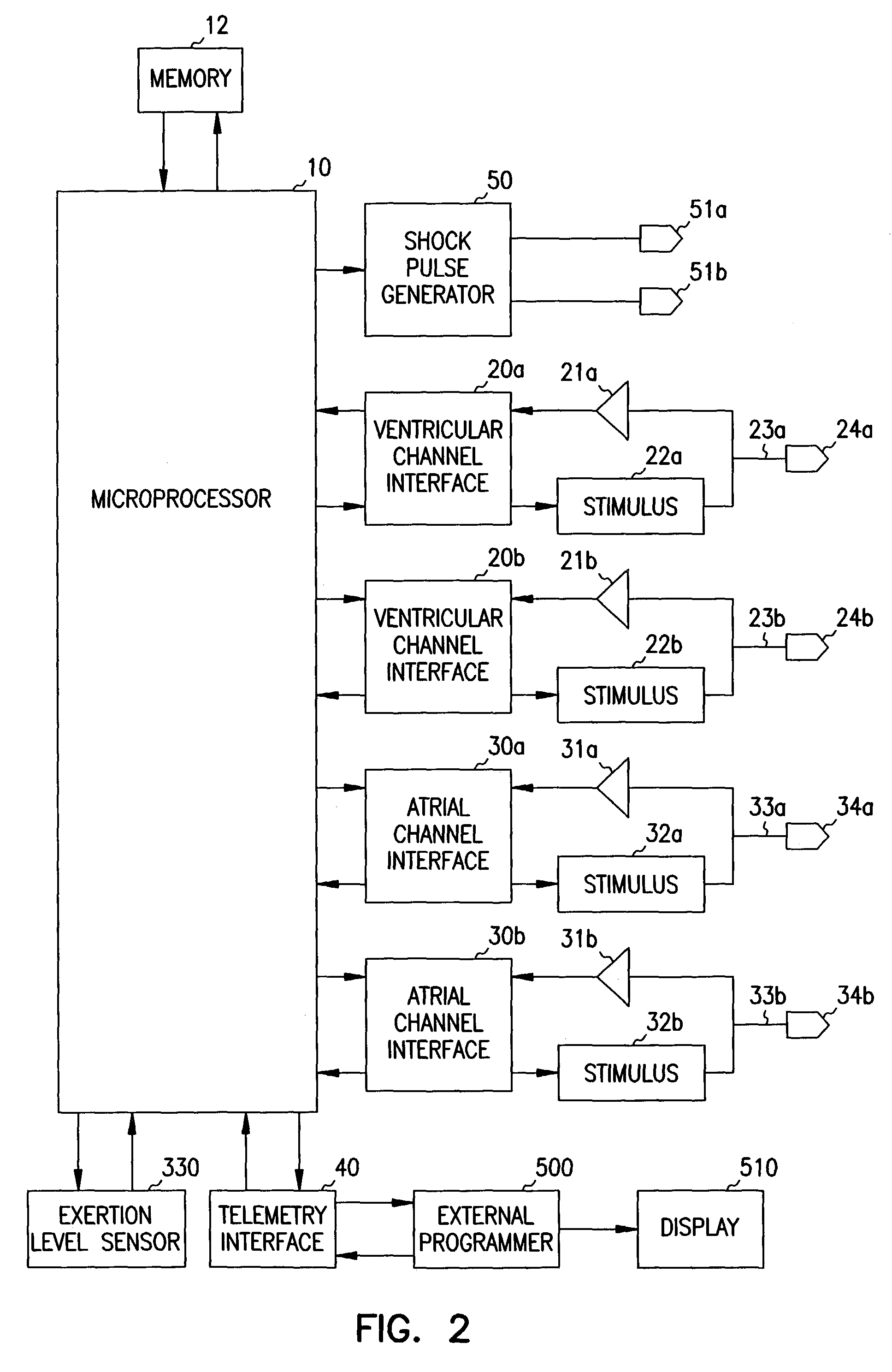
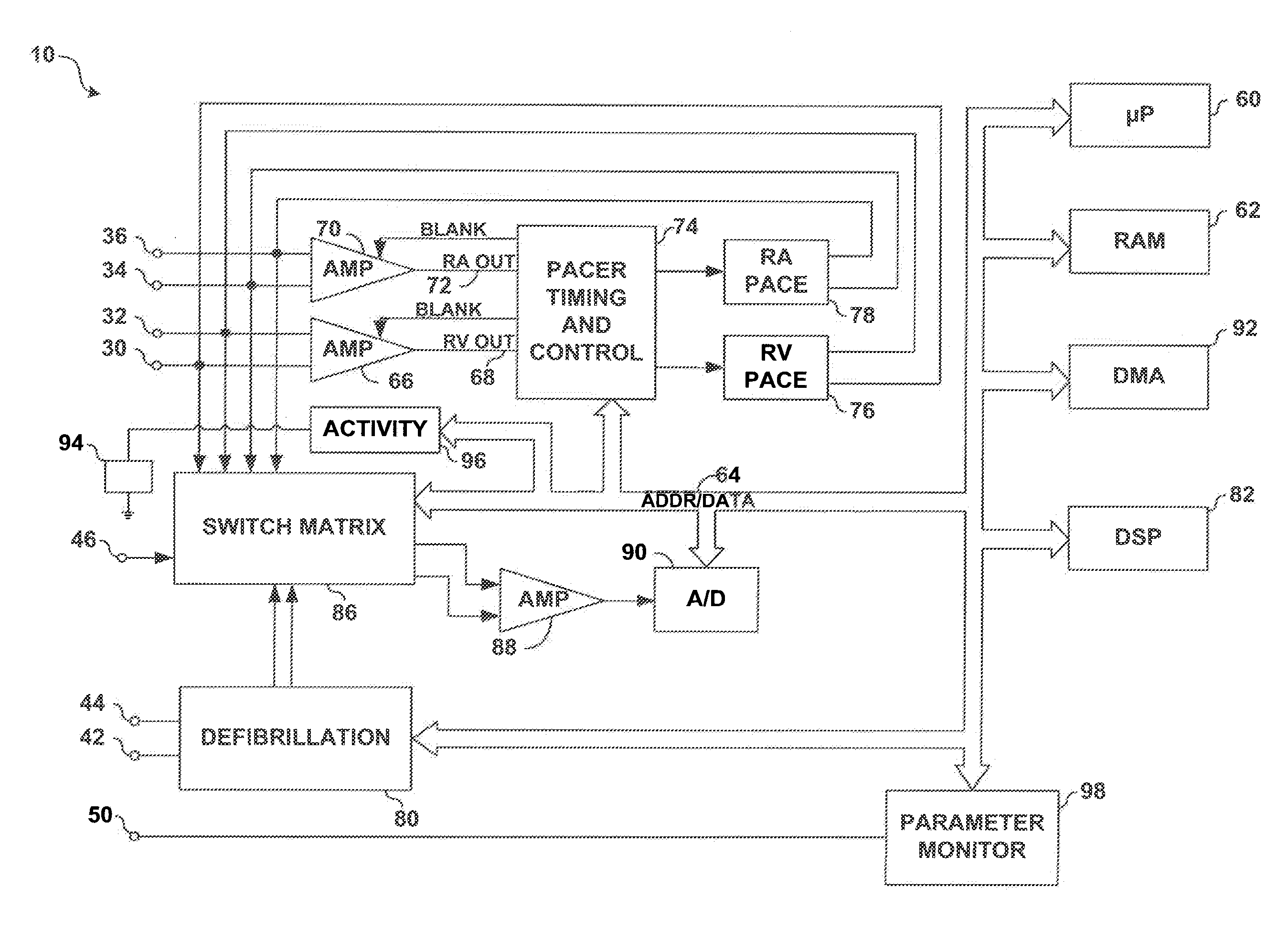
An implantable cardiac stimulator includes a cardioversion / defibrillation unit connected to at least one electrode pair for generation and delivery of cardioversion or defibrillation shocks; an atrial sensing unit detecting atrial contraction, and outputting an atrial sensing signal indicating a atrial event when an atrial contraction is detected; a ventricular sensing unit detecting ventricular contraction, and outputting a ventricular sensing signal when a ventricular contraction is detected; a tachycardia detection unit connected to the atrial and ventricular sensing units and detecting a tachycardia, and classifying it as a ventricular tachycardia (VT) or as a supraventricular tachycardia (SVT); and a treatment control unit designed to trigger at least one atrial cardioversion shock when a ventricular rhythm detected by the ventricular sensing unit is faster than a programmed frequency limit, and the tachycardia detection unit classifies an SVT as an atrial fibrillation (AFib).
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Reducing inappropriate delivery of therapy for suspected non-lethal arrhythmias
ActiveUS20110172727A1Reducing inappropriate delivery of therapyAvoid delayElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsMedical deviceMedical treatment
An implantable medical device (IMD) identifies suspected non-lethal ventricular arrhythmia, and takes one or more actions in response to the identification to avoid or delay delivery of a defibrillation or cardioversion shock. The IMD employs number of intervals to detect (NID) thresholds for detection of ventricular arrhythmias. When a NID threshold is met, the IMD determines whether the ventricular rhythm is a suspected non-lethal rhythm despite satisfying a NID threshold. In some embodiments, the IMD increases the NID threshold, i.e., extends the time for detection, in response to identifying a rhythm as a suspected non-lethal rhythm, and monitors subsequent ventricular beats to determine if the increased NID threshold is met before detecting a ventricular arrhythmia and delivering therapy. The IMD can determine whether a rhythm is a suspected non-lethal arrhythmia by, for example, comparing the median ventricular cycle length (VCL) to the median atrial cycle length (ACL).
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method for achieving regular slow ventricular rhythm in response to atrial fibrillation
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
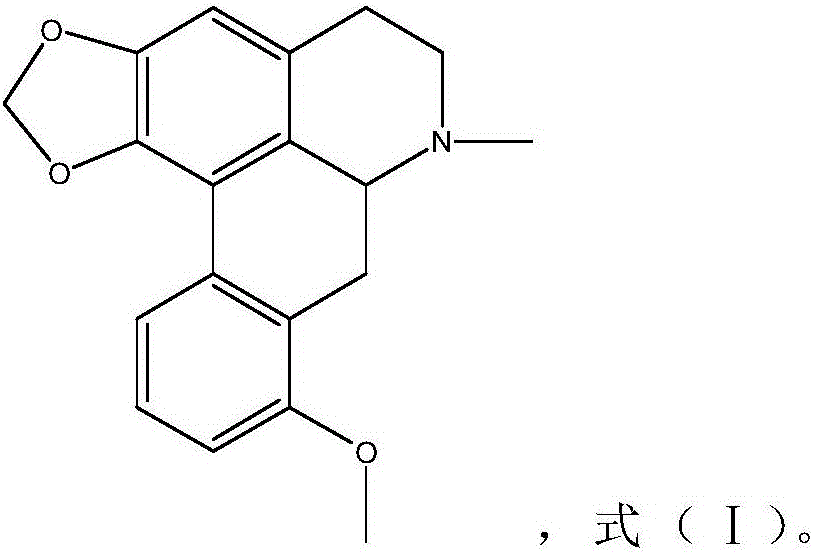
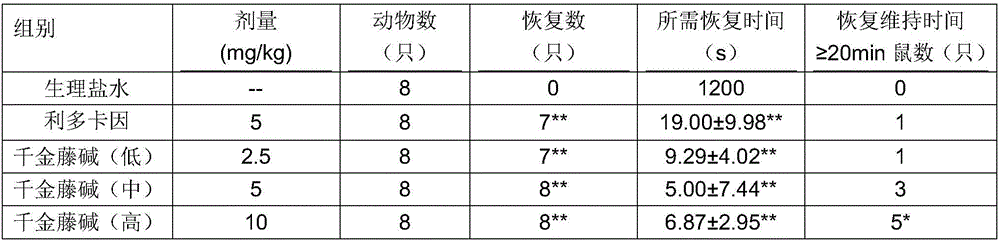
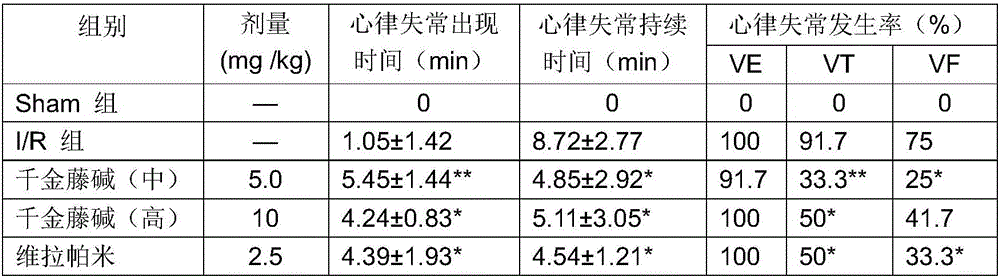
Stephanine and its pharmaceutically acceptable salt and application of solvate for preparing antiarrhythmic medicine
InactiveCN106466317AHas antiarrhythmic effectNo adverse reactionOrganic active ingredientsDispersion deliveryAntiarrhythmic effectStructural formula
The invention relates to stephanine and its pharmaceutically acceptable salt and an application of a solvate for preparing an antiarrhythmic medicine, which belongs to the technical field of medicine. A structural formula of stephanine is shown as a formula (I); the researches on chloroform-induced mice arrhythmia show that stephanine can resist chloroform-induced ventricular fibrillation, preliminary determination is confirmed that the stephanine has antiarrhythmic effect; then barium chloride-induced rat ventricular rhythm test, aconitine intravenous injection-induced rat cardiac rhythm test and rat myocardial ischemia and ischemia reperfusion arrhythmia test are carried out, so that stephanine has good antiarrhythmic effect, and provides a good base for preparing various antiarrhythmic medicines next time.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Implantable medical device and method for LV coronary sinus lead implant site optimization
InactiveUS7844335B2Ease of evaluationTransvascular endocardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsCoronary sinusMedical device
A device is connected to electrode leads which performs intracardiac impedance measurements, conducts a transient pacing protocol, analyses the impedance measurements, and generates an LV lead position quality factor. The transient pacing protocol includes a repeated change (“transitions”) between ventricular intrinsic rhythm and biventricular paced rhythm and may also include a variation of the atrioventricular delay (AVD) and / or the interventricular delay (VVD). The quality factor expresses the degree to which hemodynamic properties have improved due to BiV stimulation for the current LV lead position compared to intrinsic ventricular rhythm.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Active implantable medical device of the defibrillator/cardiovertor type with sophisticated management of ventricular tachycardias
An active implantable medical device of the multisite defibrillator / cardioverter type having a sophisticated management of ventricular tachycardias. This device delivers a one of a defibrillation and / or cardioversion and / or ventricular antitachycardia pacing (“ATP”) stimulation therapy mode, as desired and known in the art. The device senses the cardiac activity and detects in the sensed activity a disorder of the ventricular rhythm that is distinct from a ventricular fibrillation condition. The device also includes delivery of biventricular stimulation, connected to at least two ventricular sites, right and left, which is triggered on the detection of the aforesaid disorder of the ventricular rhythm prior to delivering the conventional ATP or shock therapy mode.
Owner:SORIN CRM
Automatic adjusting R-wave synchronization algorithm for atrial cardioversion and defibrillation
An implantable medical device system and method are provided for synchronizing atrial cardioversion shocks to the ventricular rhythm using an adjustable atrial cardioversion / defibrillation ventricular refractory period. Upon determining a need for an atrial shock therapy, the method determines if the ventricular rate meets synchronization criteria based on an upper ventricular refractory period limit. If synchronization criteria are not met, the refractory period is automatically adjusted in stepwise decrements until the synchronization criteria are met, or until a lower refractory period limit is exceeded. If synchronization criteria are met, an atrial shock is synchronized to the next ventricular depolarization occurring outside the current refractory period. If the lower refractory period limit is exceeded, the atrial therapy is aborted.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
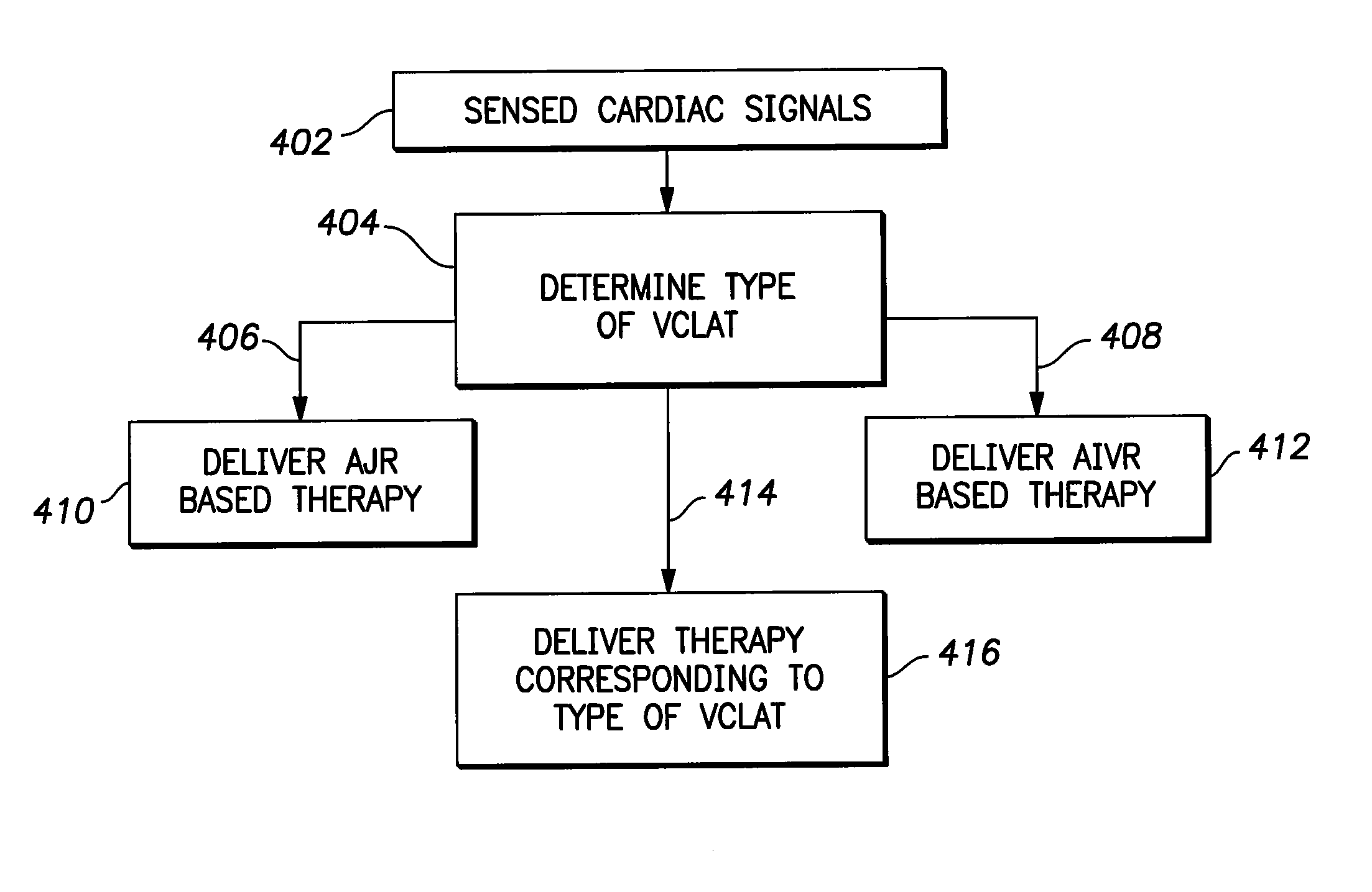
Method and system for detecting and treating junctional rhythms
ActiveUS20110230927A1Reduce patient symptomImprove the quality of lifeElectrocardiographyCatheterVENTRICULAR RHYTHMSPaced Rhythm
An implantable medical device is provided for detecting transportless ventricular rhythm of a heart lacking atrial transport and comprises a housing, sensors configured to be located proximate to a heart, a sensing module to sense cardiac signals representative of a rhythm originating from the heart and a rhythm detection module. The rhythm detection module determines a change in AV association and identifies a potential ventricular complex with loss of atrial transport (VCLAT) based on the change in AV association.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Implantable cardiac system having an r-spike amplifier
ActiveUS20180020940A1Increase amplitudeIncreases R-wave to T-wave signal to noise ratioElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsImplantable rodSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
An implantable cardiac system that includes an implantable cardiac pacemaker or leadless pacemaker (iLP) and a second device such as a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (S-ICD). The pacemaker includes an R-spike amplifier that amplifies stimulated ventricle excitations or R-waves to increase R-wave to T-wave signal to noise ratio and to improve indirect detection of ventricular rhythm classification by the S-ICD. The S-ICD includes an electrode line for defibrillation, a sensing unit and a stimulation detection unit. The S-ICD records a subcutaneous electrocardiogram between shock electrode poles and provides potentially life-saving therapy based thereon. The system significantly increases the specificity and sensitivity of an S-ICD in combination with an implanted cardiac pacemaker or iLP having an R-spike amplifier.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Cardiac pace making system
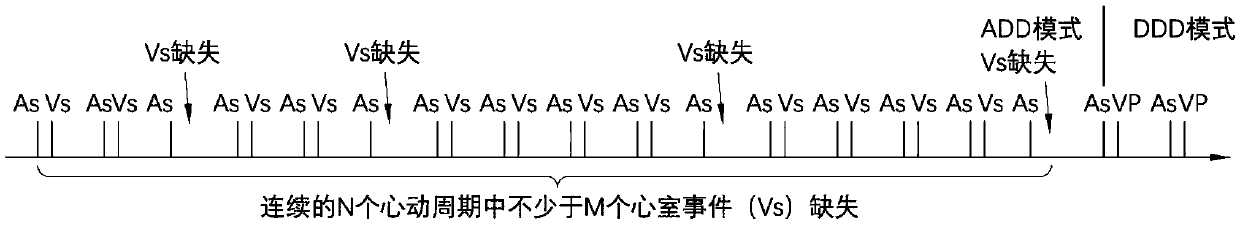
ActiveCN109589499AAccurate judgmentHeart stimulatorsAtrioventricular conductionCardiac pacemaker electrode
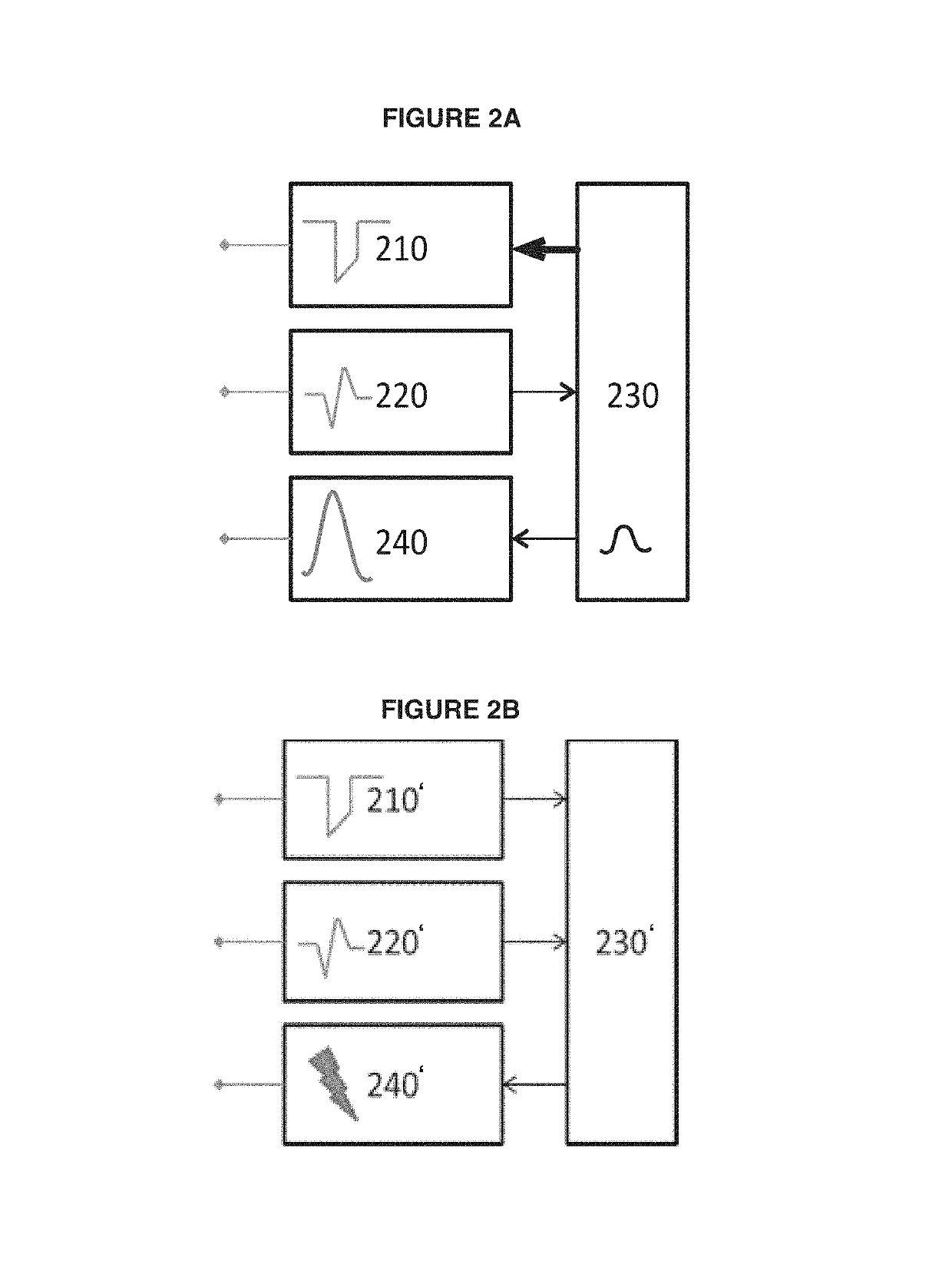
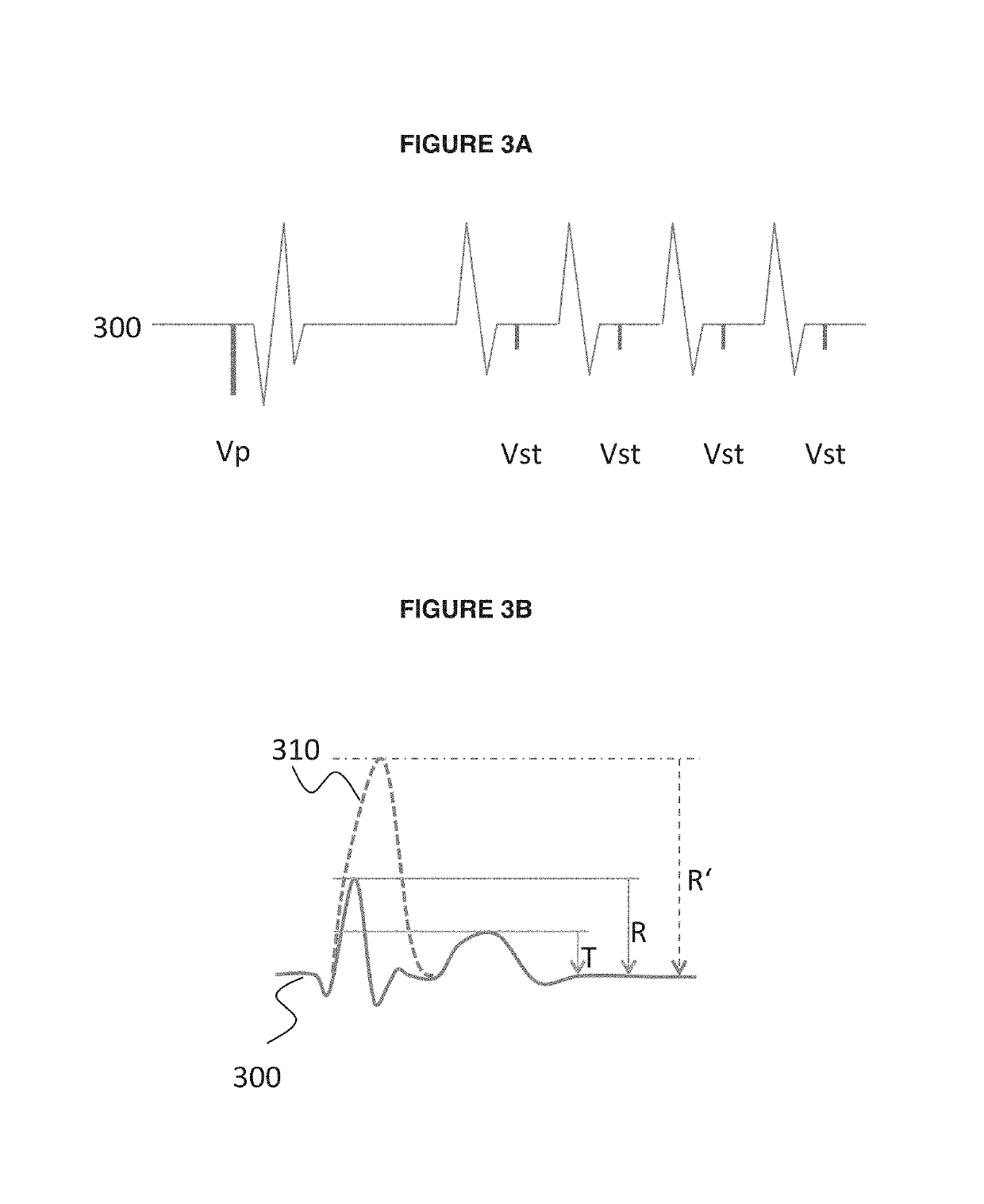
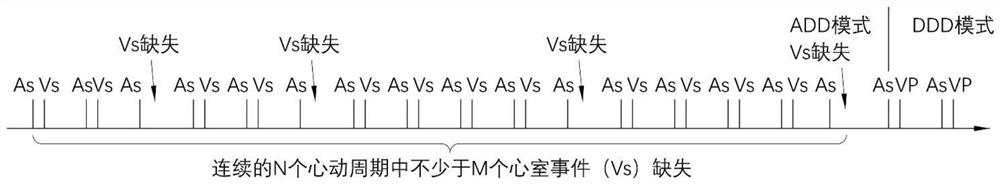
The invention provides a cardiac pace making system which comprises a perception module, a pace making module and a control module. Under a normal atrioventricular conduction condition, the control module controls the cardiac pace making system to work in a first mode and detect whether atrioventricular block occurs; various atrioventricular block events can be judged accurately by sensing and comparing PR (punctum remotum) intervals and ventricular event missing; when the atrioventricular block occurs, the control module controls the cardiac pace making system to work in a second mode; and acardiac pacemaker can timely work in an appropriate mode and provide an appropriate AV (atrioventricular) time sequence and a ventricular rhythm.
Owner:MICROPORT SORIN CRMSHANGHAICO LTD
Bromocarbanine compound and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN106380472BLow acute toxicityAntagonize ventricular fibrillationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAntiarrhythmic effectAcute toxicity testing
The invention relates to a brominated crebanine compound and preparation method and an application thereof, which belongs to the technical field of medicine. The invention firstly discloses the synthesis of 3-brominated crebanine and 10, 11-brominated crebanine, through research on effect of chloroform for inducing mice arrhythmia, the research shows that the 3-brominated crebanine and 10, 11-brominated crebanine can antagonize the chloroform-induced ventricular fibrillation, so that the 3-brominated crebanine and 10, 11-brominated crebanine have anti-arrhythmia effect through preliminary determination; the barium chloride-induced rat ventricular rhythm tests confirm that the 3-brominated crebanine and 10, 11-brominated crebanine have good anti-arrhythmia effect, acute toxicity of two brominated crebanine compounds is lower than that of crebanine, LD50 is 65.15+ / -1.132 mg / kg of 3-brominated crebanine and 59.62+ / -2.610 mg / kg of 10,11-brominated crebanine respectively, and a good base can be established for further deep researches.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
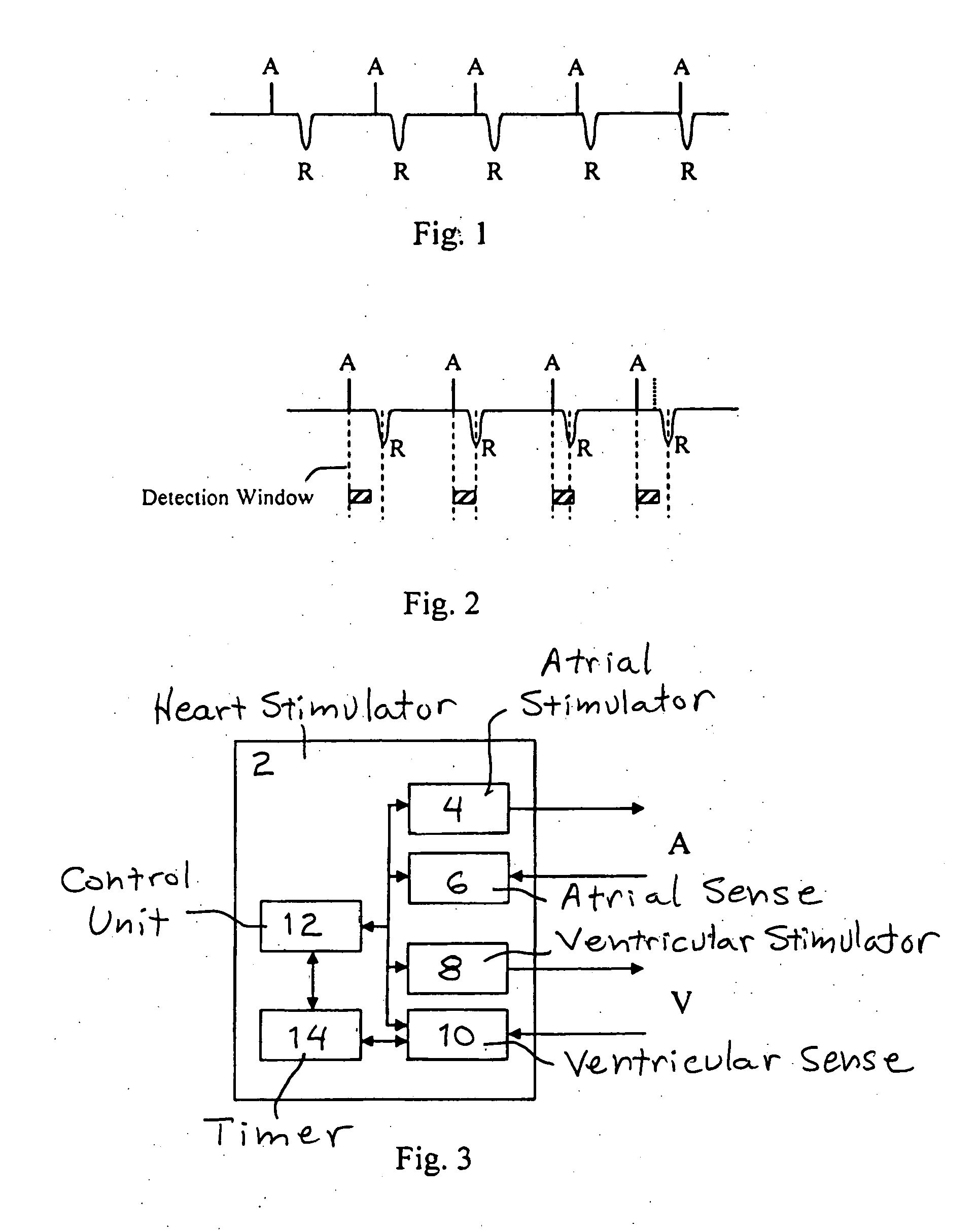
Implantable Heart Stimulator for Enabling Normal Atrio-Ventricular Stimulation Sequence in the Presence of Av-Nodal Interference
InactiveUS20080234775A1Increase atrial stimulation rateLess-optimal hemodynamicsHeart stimulatorsNODALAtrial cavity
A heart stimulator for enhancing cardiac performance of a patient suffering from ventricular rhythms that tend to overdrive the patient's atrial rhythm, has sensing circuitry that detects atrial events and ventricular events, and an atrial stimulator that generates and supplies stimulation pulses to the atrium. A timer generates a detection window having a predetermined duration for the ventricular sensing, the detection window starting upon detection of an intrinsic or stimulated atrial event. If an R-wave is sensed from the ventricle during the detection window, a control unit determines that a focus, that pre-depolarizes the ventricles, exists, and the control unit operates the atrial stimulator to increase the atrial stimulation rate for a predetermined number of consecutive heart cycles.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Apparatus and method for ventricular rate regularization
InactiveUS8249703B2Less variabilityHigh outputHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular rateCardiac pacemaker electrode
A cardiac rhythm management device which employs pacing therapy to regularize the ventricular rhythm. Such ventricular rate regularization may be employed within bradycardia pacemakers, ventricular resynchronization devices, or implantable cardioverter / defibrillators.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and system for detecting and treating junctional rhythms
ActiveUS8694082B2Improve the quality of lifeRelieve symptomsElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyProximateJunctional rhythm
An implantable medical device is provided for detecting transportless ventricular rhythm of a heart lacking atrial transport and comprises a housing, sensors configured to be located proximate to a heart, a sensing module to sense cardiac signals representative of a rhythm originating from the heart and a rhythm detection module. The rhythm detection module determines a change in AV association and identifies a potential ventricular complex with loss of atrial transport (VCLAT) based on the change in AV association.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Implantable cardiac system having an R-spike amplifier
ActiveUS10285614B2Increase amplitudeImprove R-spike detectionElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsAudio power amplifierCardiac pacemaker electrode
An implantable cardiac system that includes an implantable cardiac pacemaker or leadless pacemaker (iLP) and a second device such as a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (S-ICD). The pacemaker includes an R-spike amplifier that amplifies stimulated ventricle excitations or R-waves to increase R-wave to T-wave signal to noise ratio and to improve indirect detection of ventricular rhythm classification by the S-ICD. The S-ICD includes an electrode line for defibrillation, a sensing unit and a stimulation detection unit. The S-ICD records a subcutaneous electrocardiogram between shock electrode poles and provides potentially life-saving therapy based thereon. The system significantly increases the specificity and sensitivity of an S-ICD in combination with an implanted cardiac pacemaker or iLP having an R-spike amplifier.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
cardiac pacing system
The present invention provides a cardiac pace making system. The cardiac pace making system comprises a sensing module, a pace making module, and a control module. Under a normal atria ventricular conduction condition, the control module controls the cardiac pace making system to work in a first mode and detect whether an atria ventricular block has occurred; various atria ventricular block events are determined accurately by sensing and comparing PR intervals and missed ventricular events; when an atria ventricular block occurs, the control module controls the cardiac pace making system to work in a second mode, so that a cardiac pacemaker may work in a timely manner and in an appropriate mode and provide an appropriate AV time sequence and ventricular rhythm.
Owner:MICROPORT SORIN CRM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Distinguishing device and equipment for malignant ventricular arrhythmia
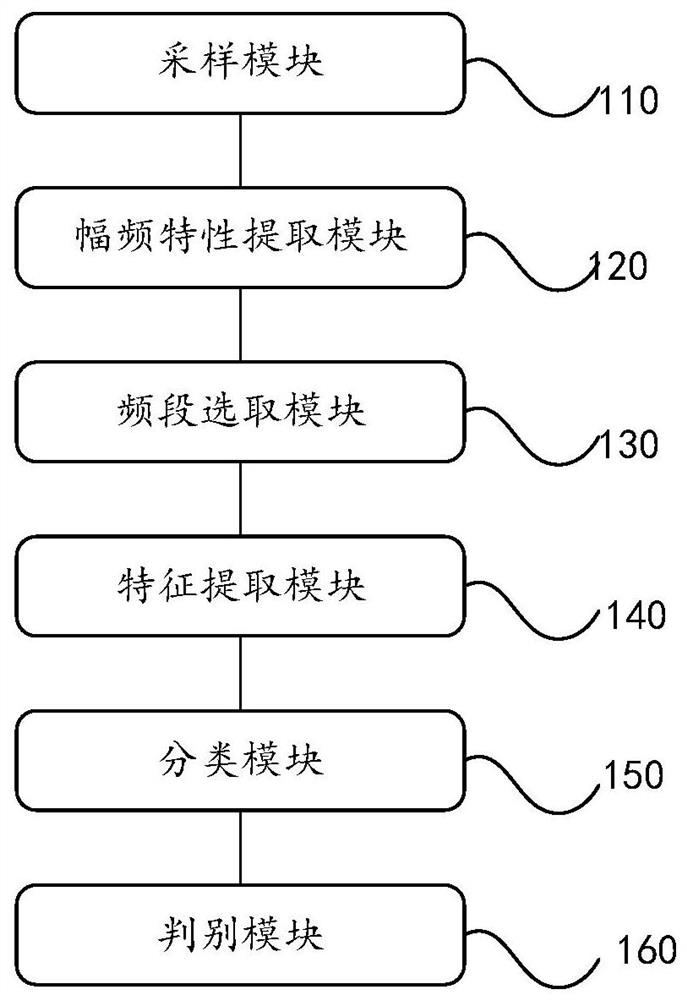
ActiveCN108615026BSmall amount of calculationShorten the timeCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalPhysical therapy
The invention discloses a device for discriminating malignant ventricular arrhythmia. After the sampling module discretely samples the continuous ECG signal; the amplitude-frequency characteristic extraction module extracts the amplitude-frequency characteristic of the signal and obtains a matrix; then the frequency band selection module Select the vector of the preset frequency band from the matrix to obtain a new matrix; then the feature extraction module will select the column vector of the preset number with the largest variance from the new matrix as the feature vector of the signal; the classification module will then The feature vector is input into a pre-trained classifier to obtain a classification result; finally, the discrimination module judges whether the electrocardiographic signal is a malignant ventricular rhythm according to the classification result. It can be seen that the device can select a preset number of vectors with the largest variance from the vectors of the preset frequency band as feature vectors, which effectively reduces the amount of calculation of the classifier and saves the time spent on discrimination. The present invention also provides a device for judging malignant ventricular rhythm, the function of which is corresponding to that of the above-mentioned device.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Antitachycardiac heart stimulator
ActiveUS8244353B2Heart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringSustained ventricular tachycardiaVentricular contraction
An implantable cardiac stimulator includes a cardioversion / defibrillation unit connected to at least one electrode pair for generation and delivery of cardioversion or defibrillation shocks; an atrial sensing unit detecting atrial contraction, and outputting an atrial sensing signal indicating a atrial event when an atrial contraction is detected; a ventricular sensing unit detecting ventricular contraction, and outputting a ventricular sensing signal when a ventricular contraction is detected; a tachycardia detection unit connected to the atrial and ventricular sensing units and detecting a tachycardia, and classifying it as a ventricular tachycardia (VT) or as a supraventricular tachycardia (SVT); and a treatment control unit designed to trigger at least one atrial cardioversion shock when a ventricular rhythm detected by the ventricular sensing unit is faster than a programmed frequency limit, and the tachycardia detection unit classifies an SVT as an atrial fibrillation (AFib).
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com