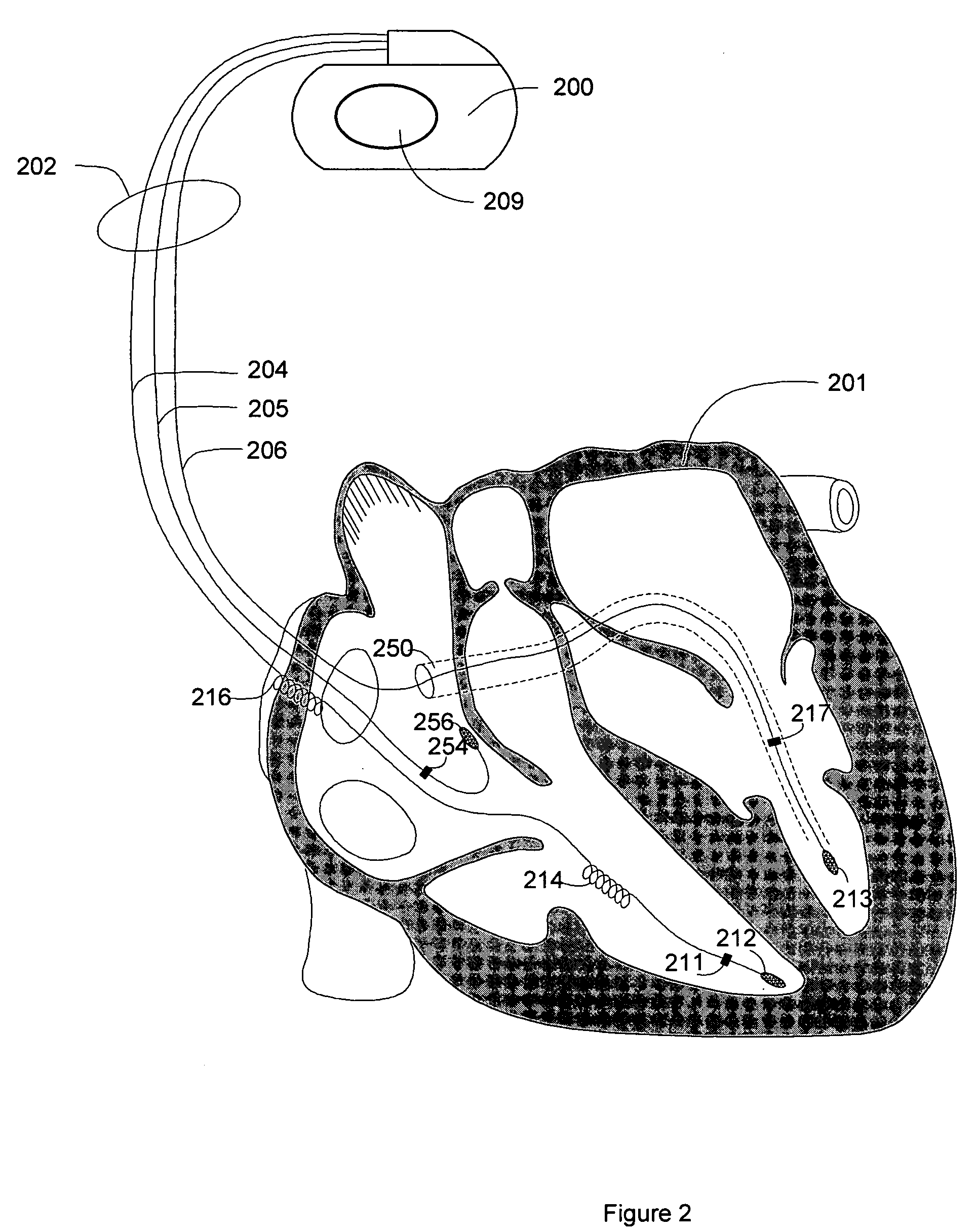
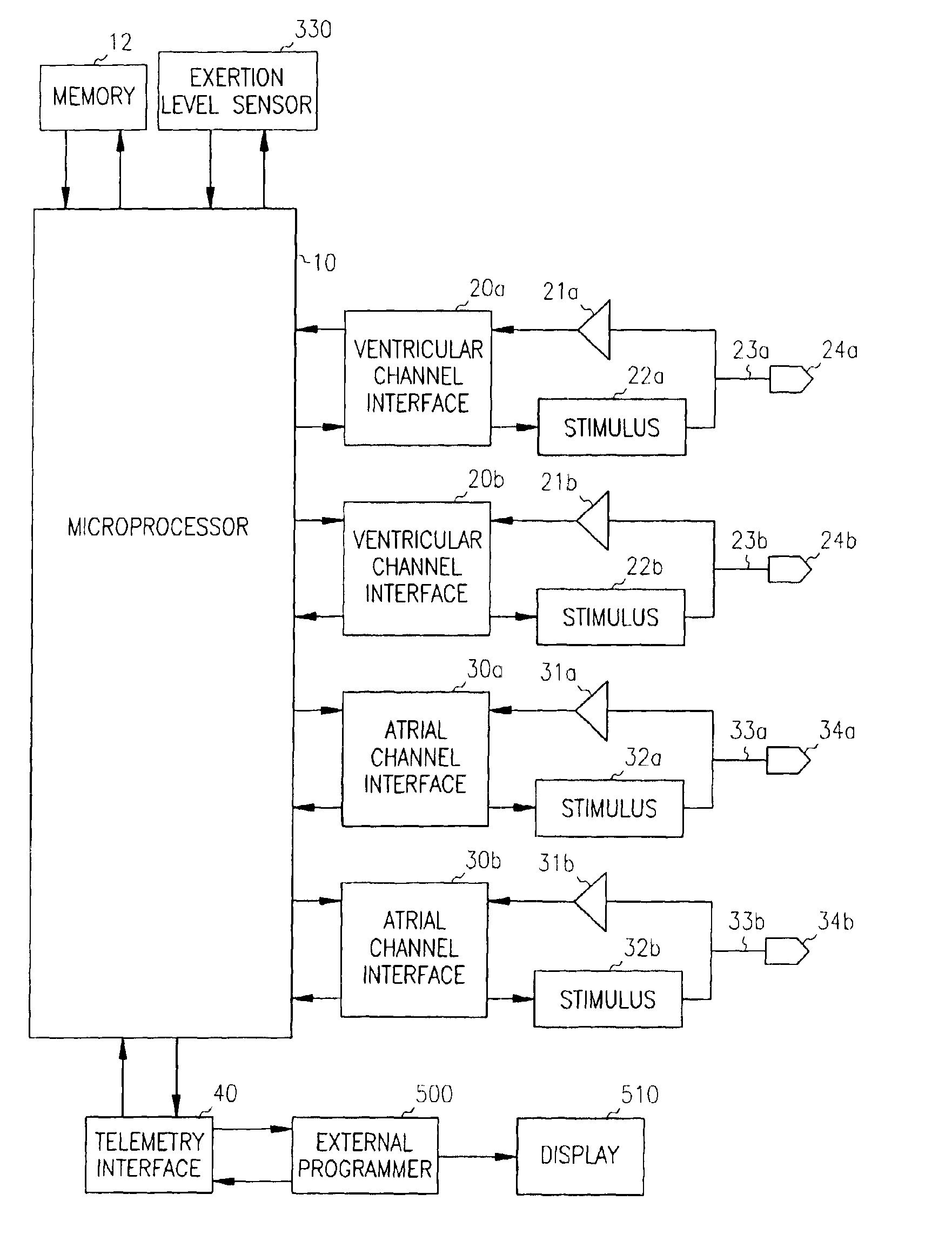
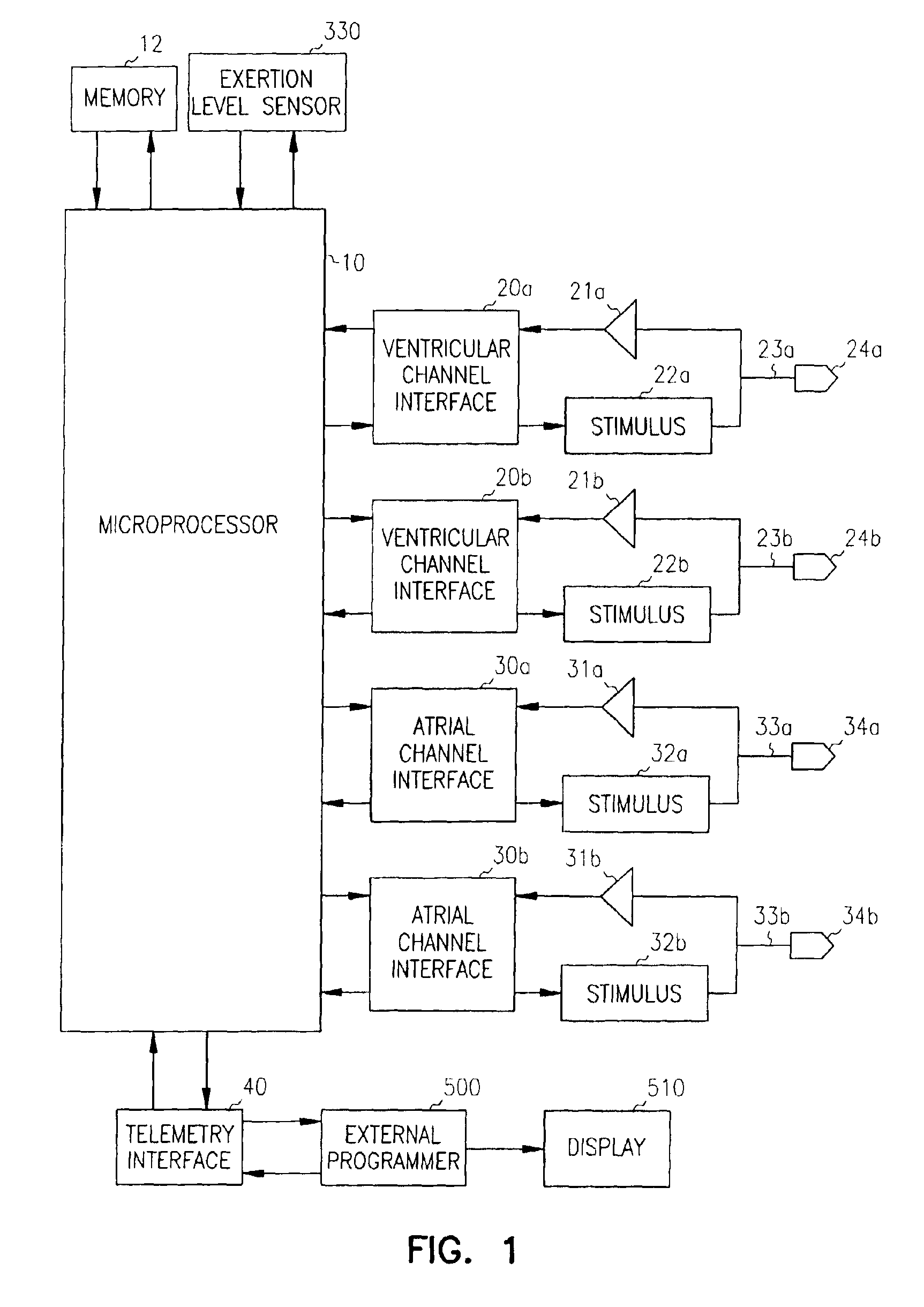
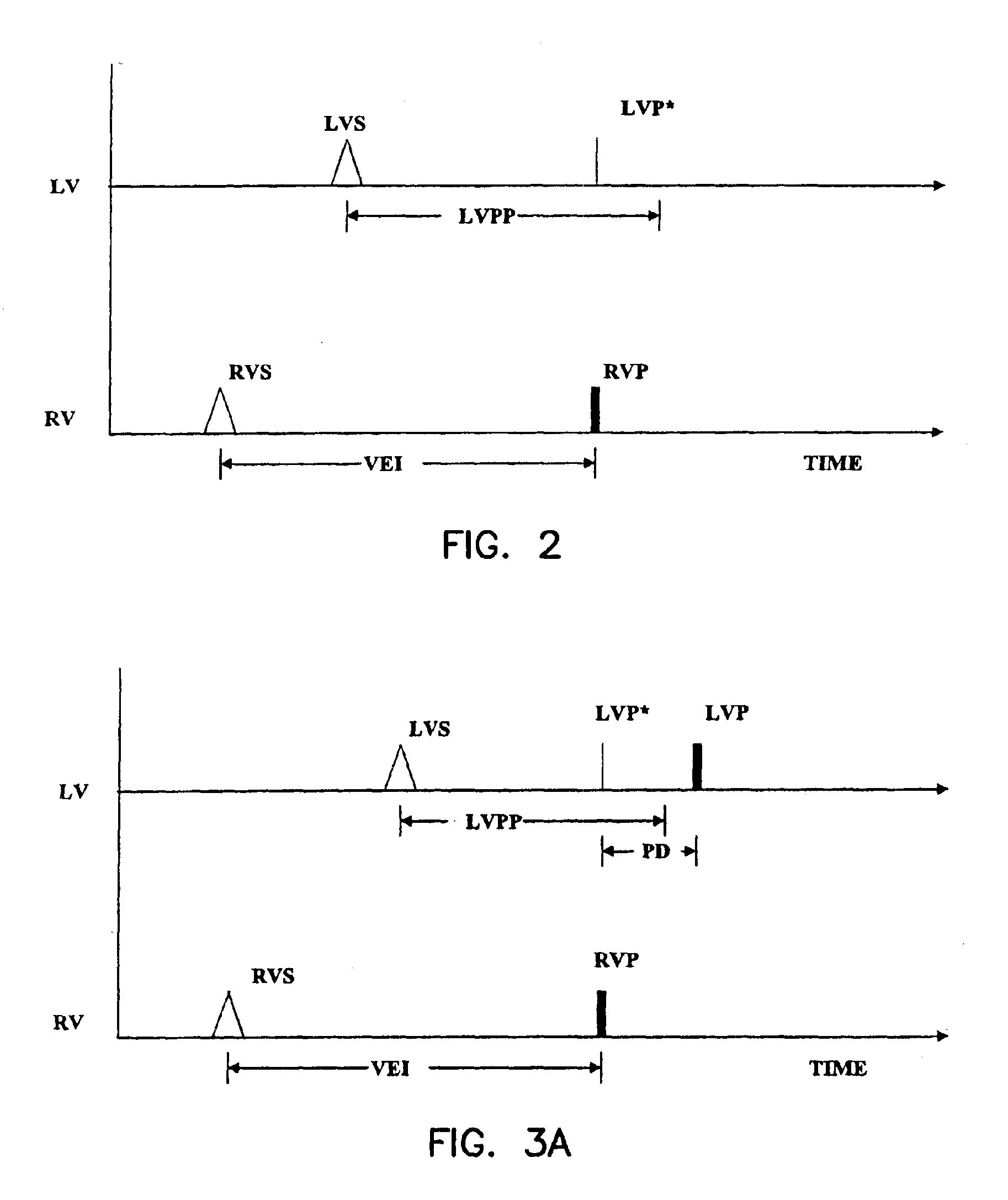
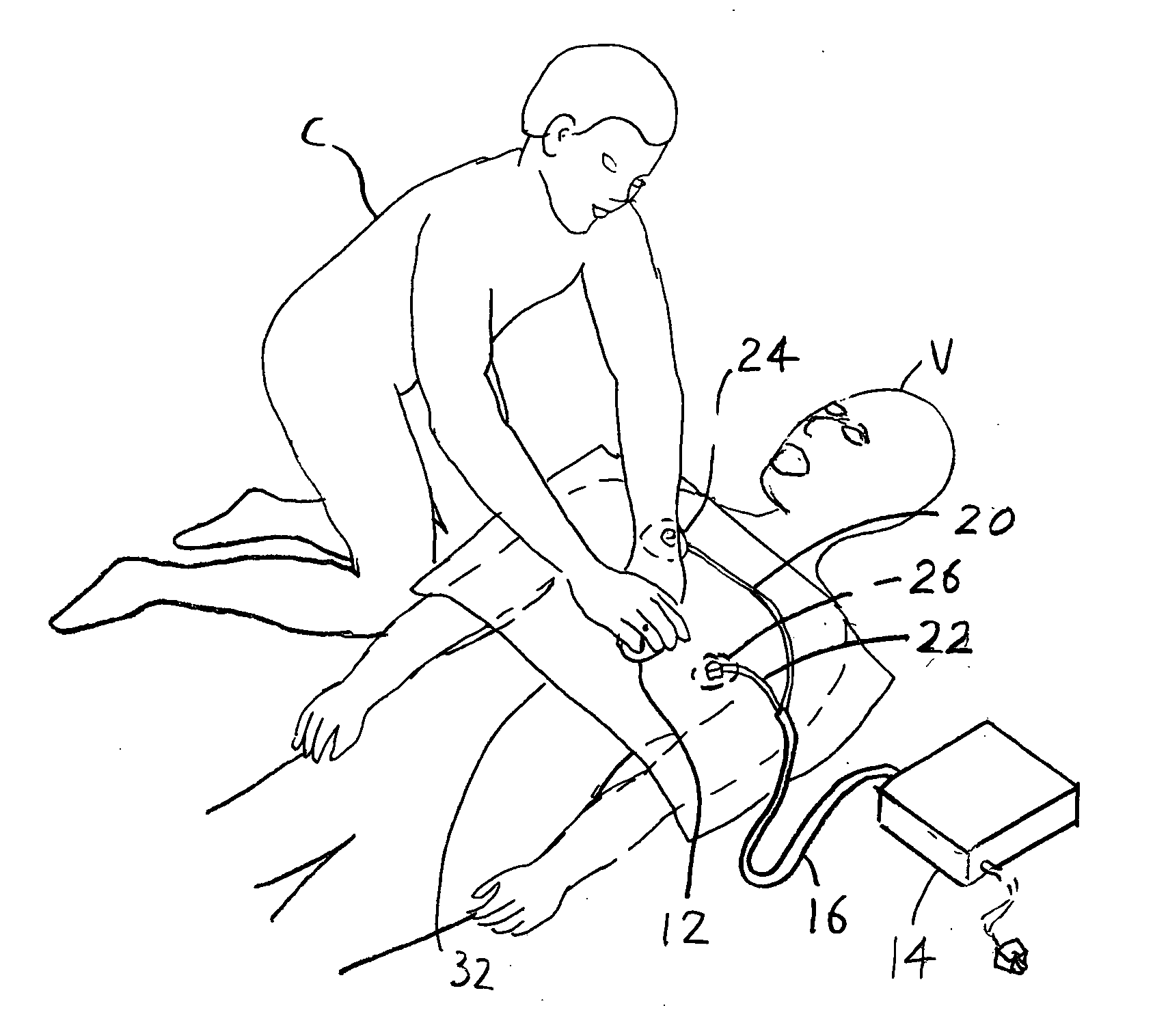
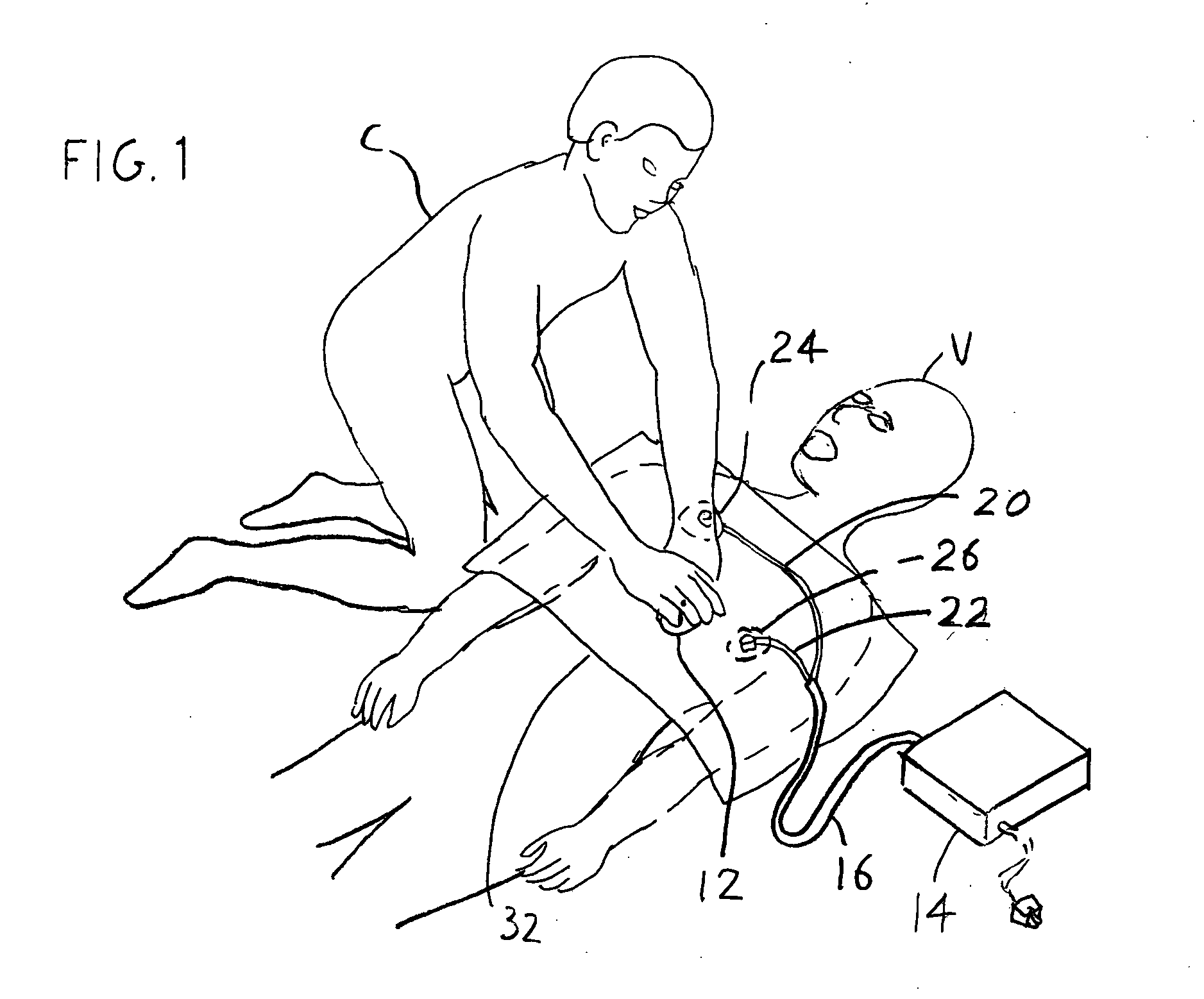
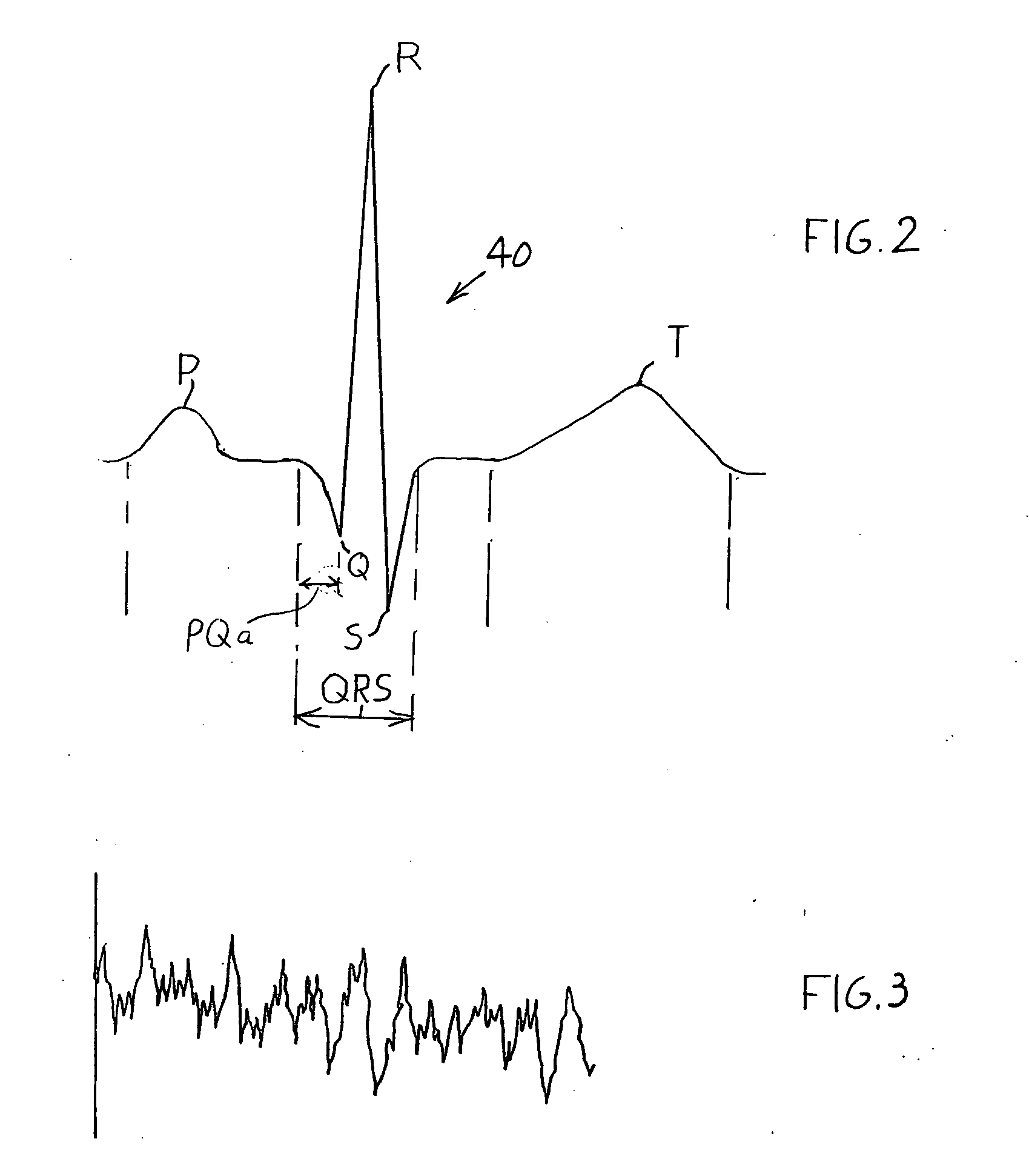
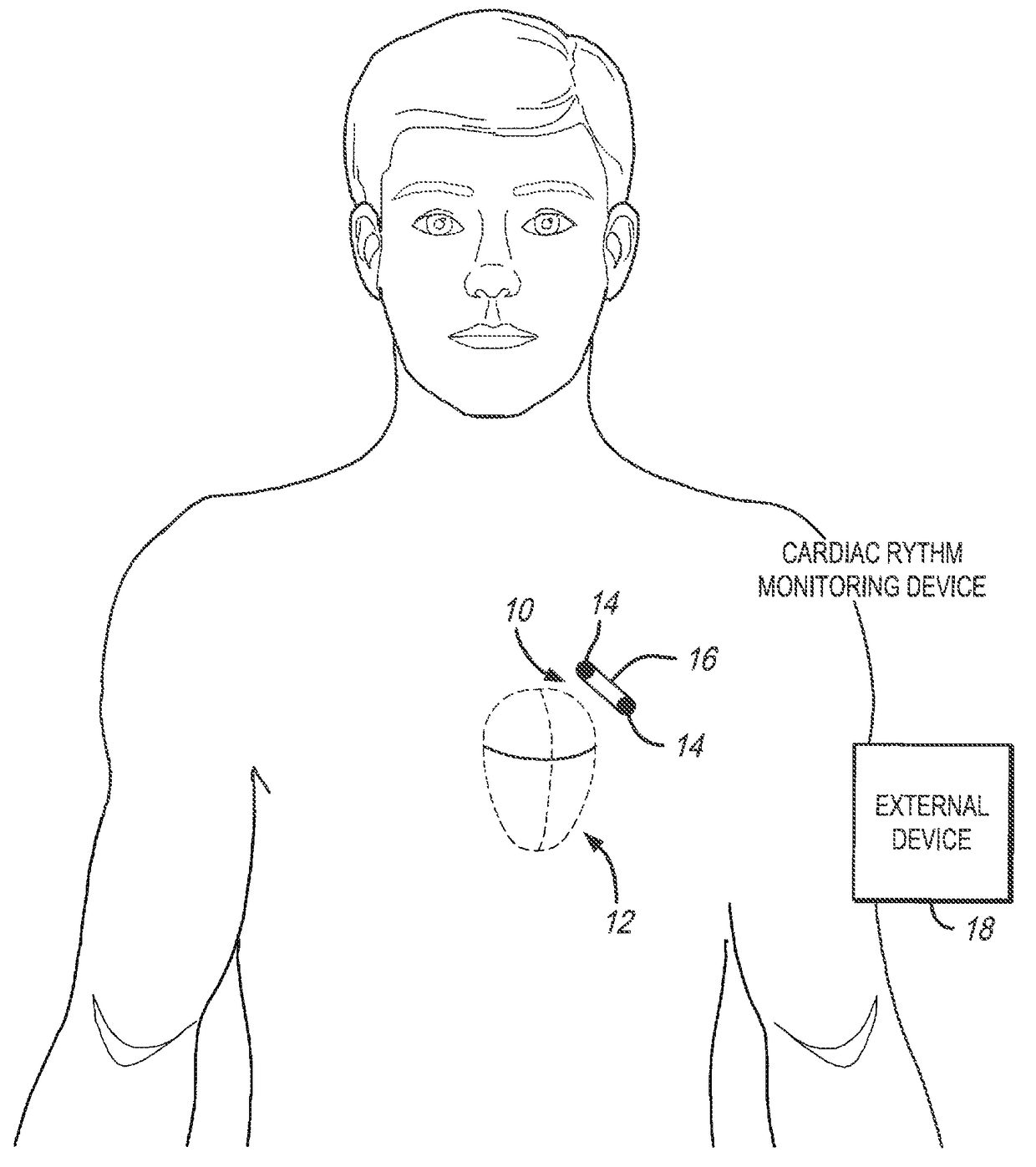
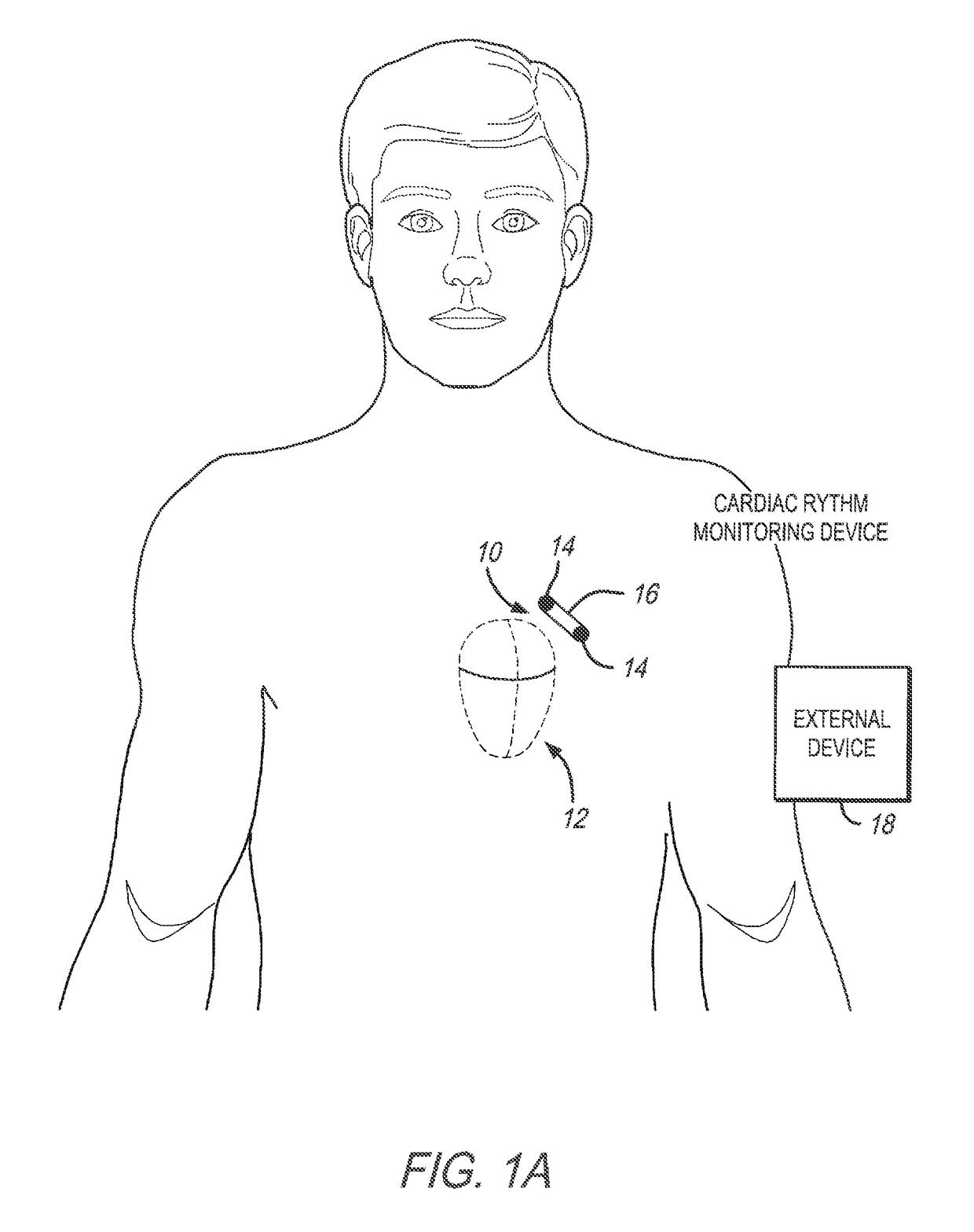
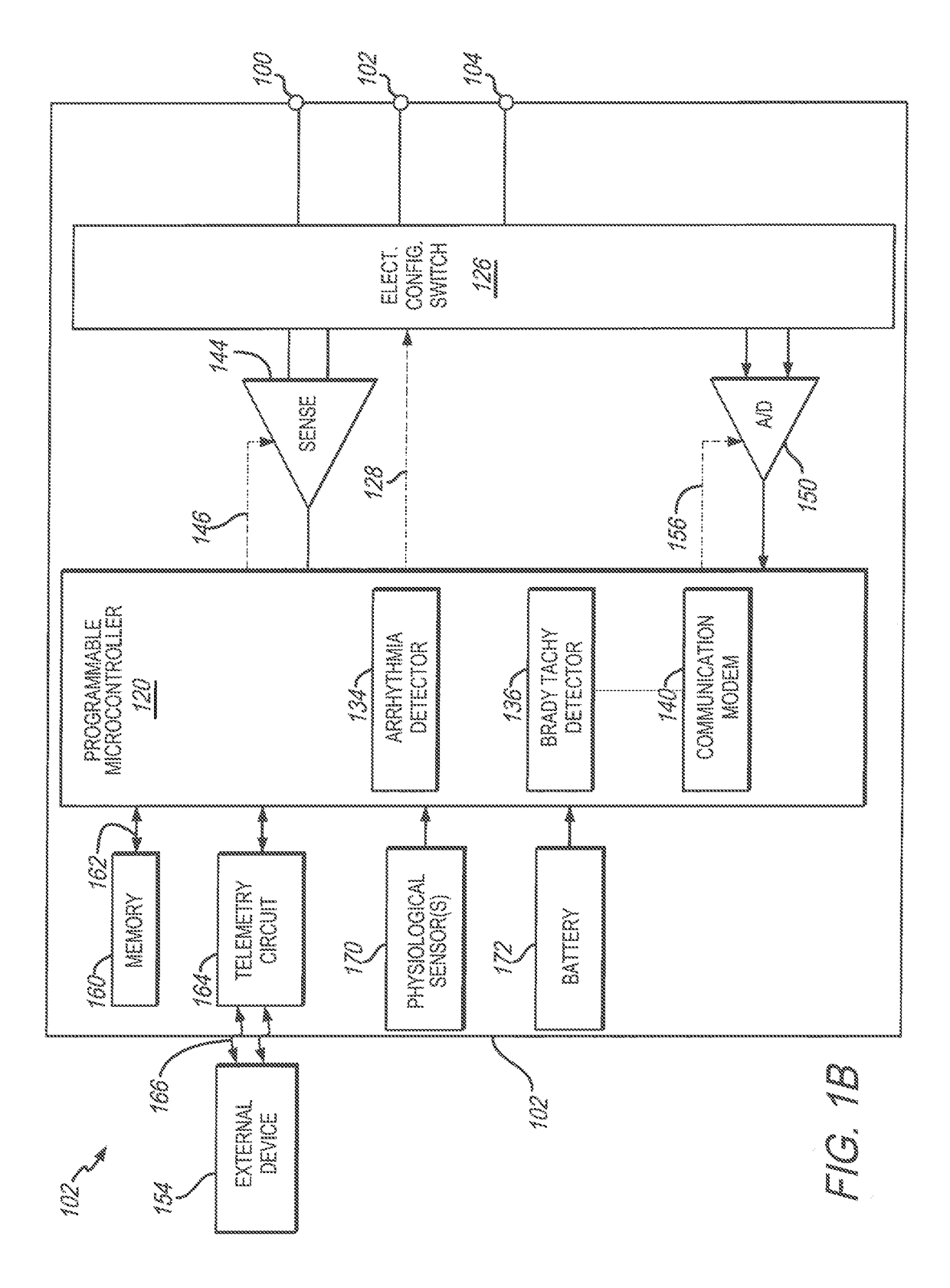
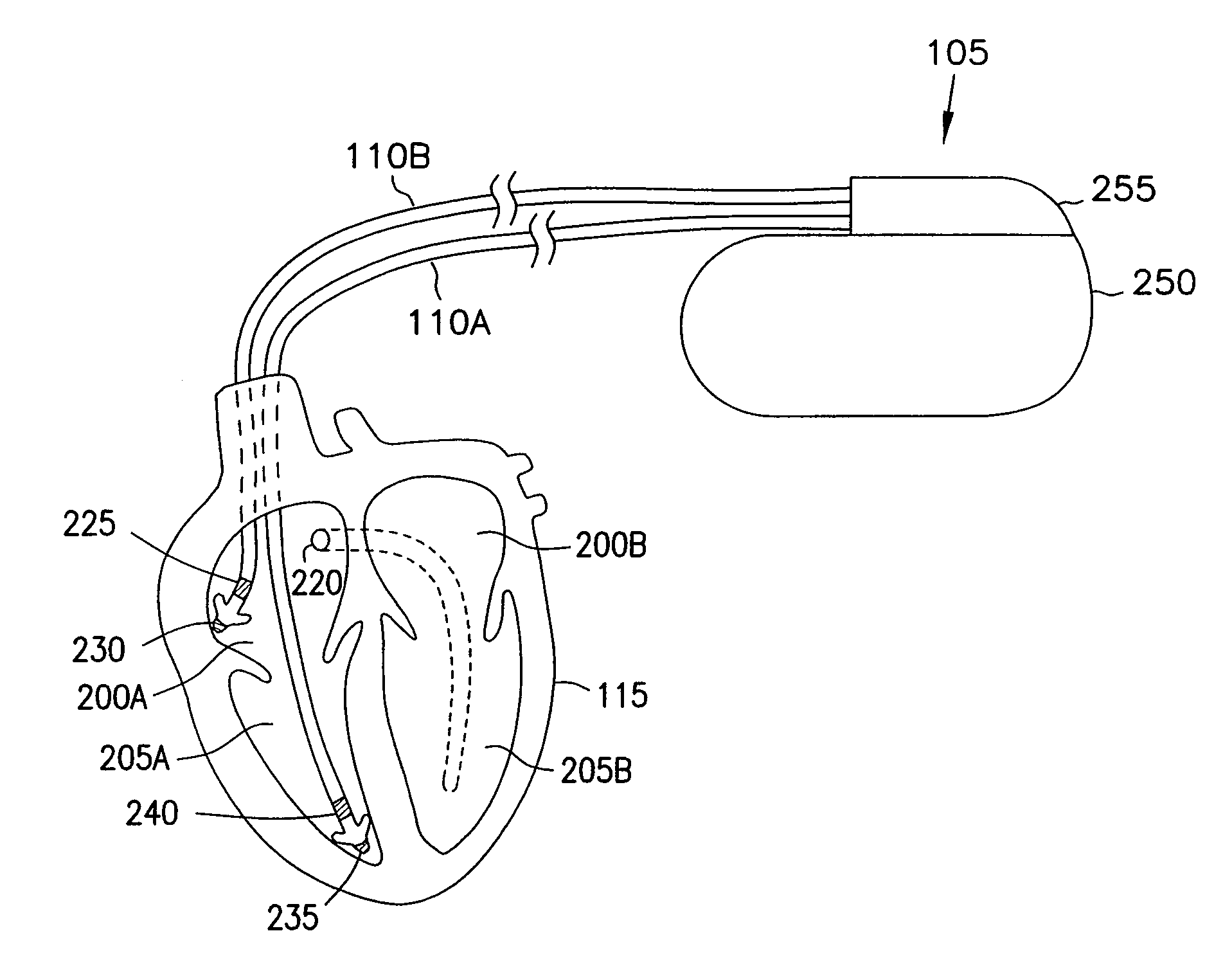
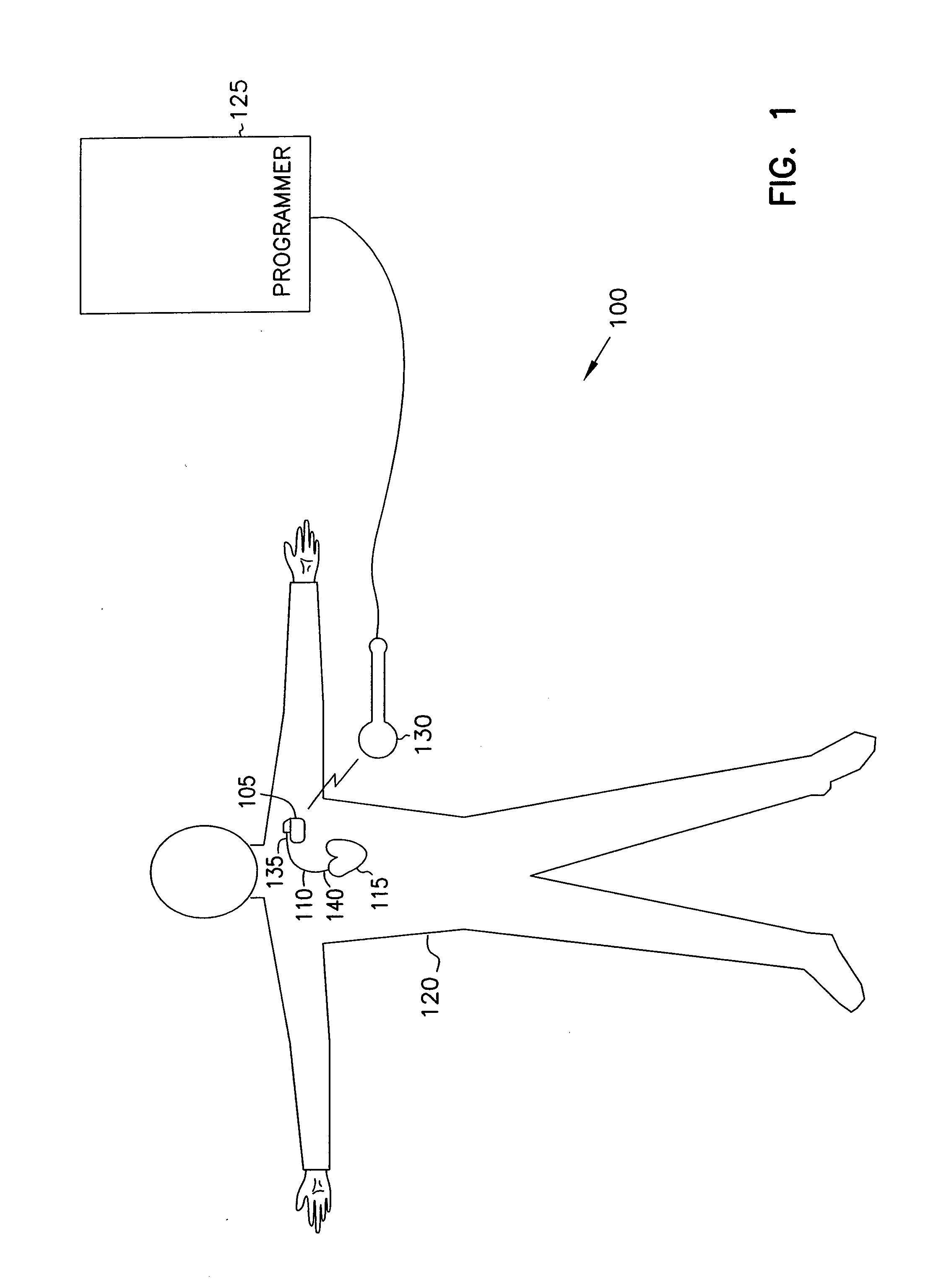
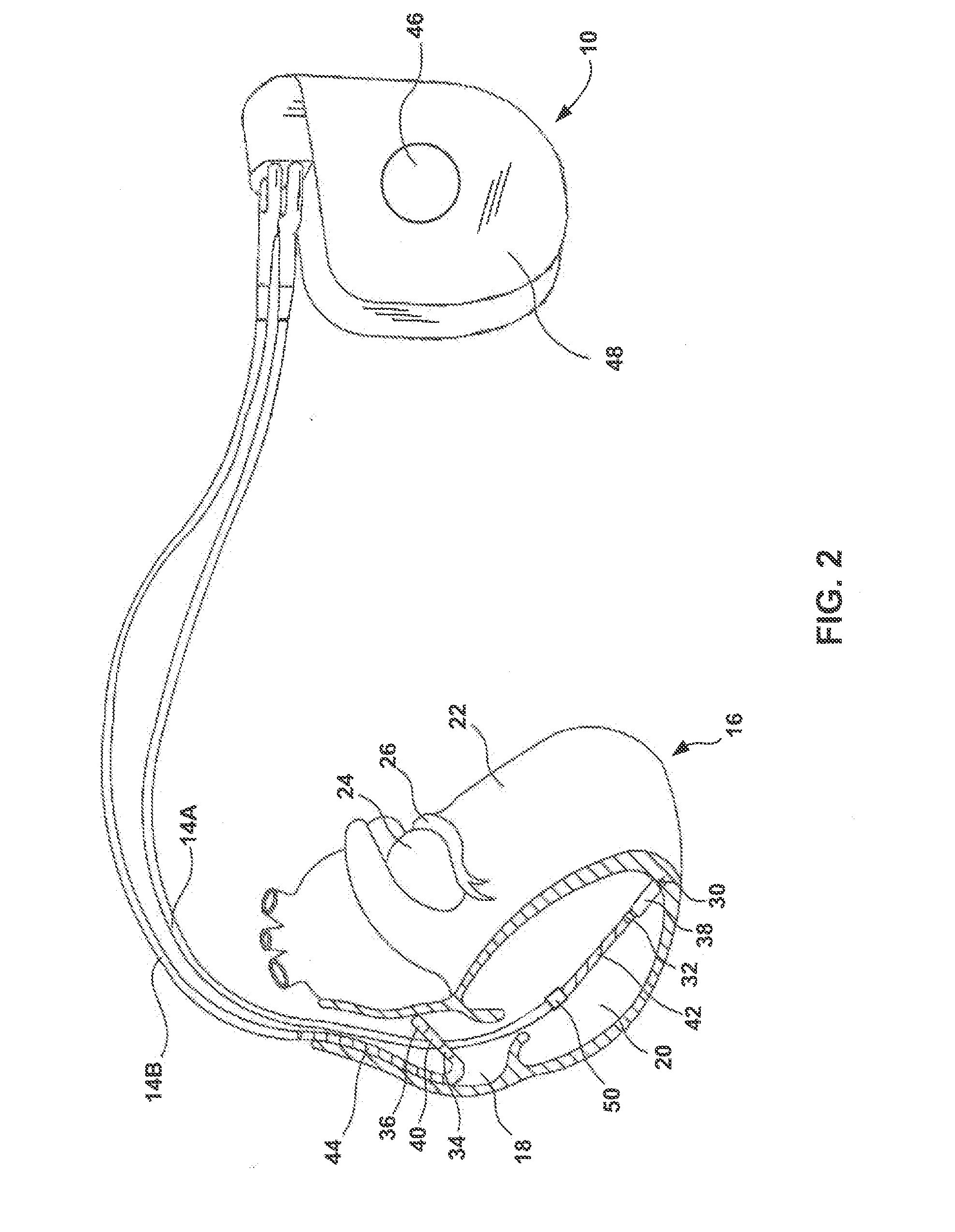
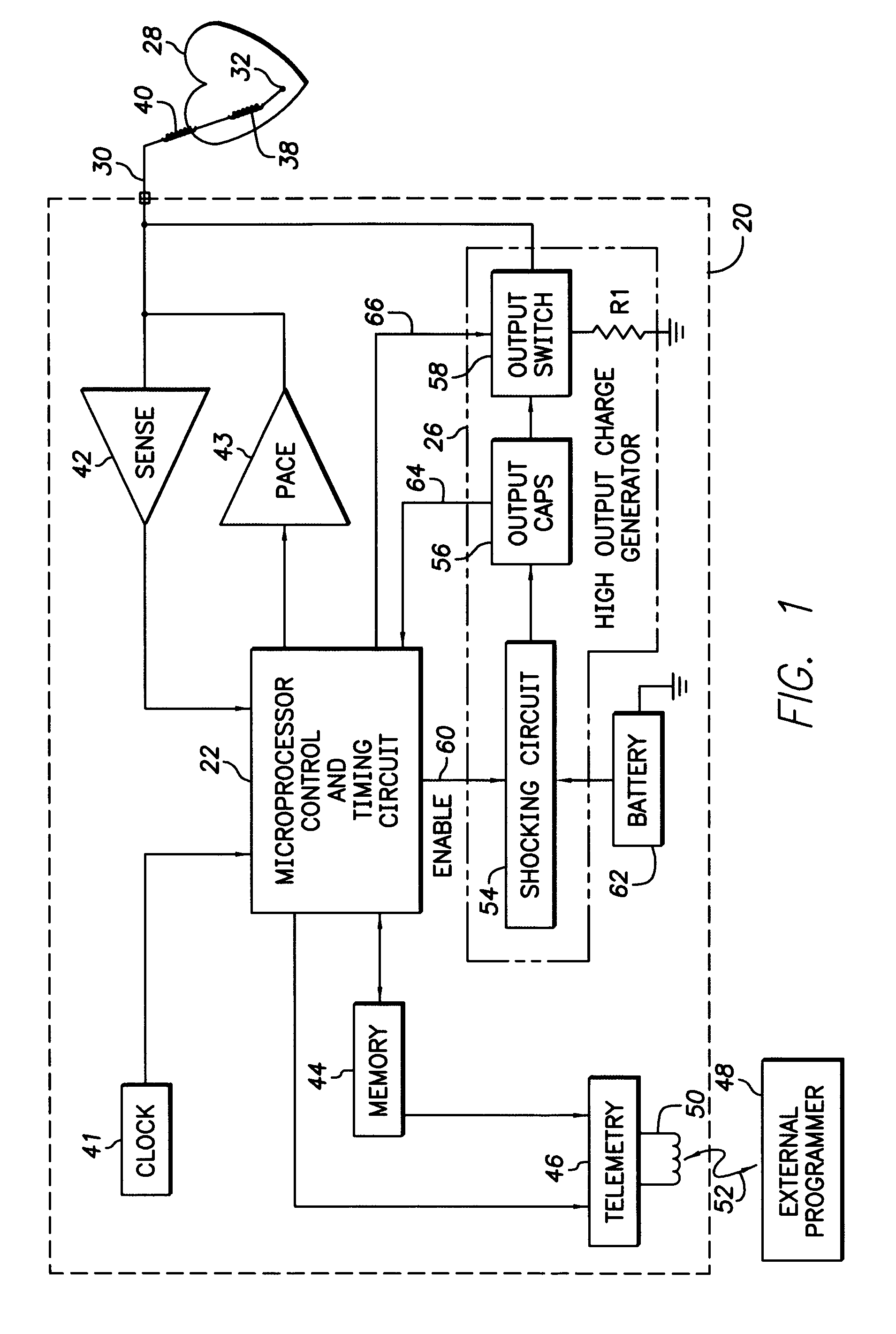
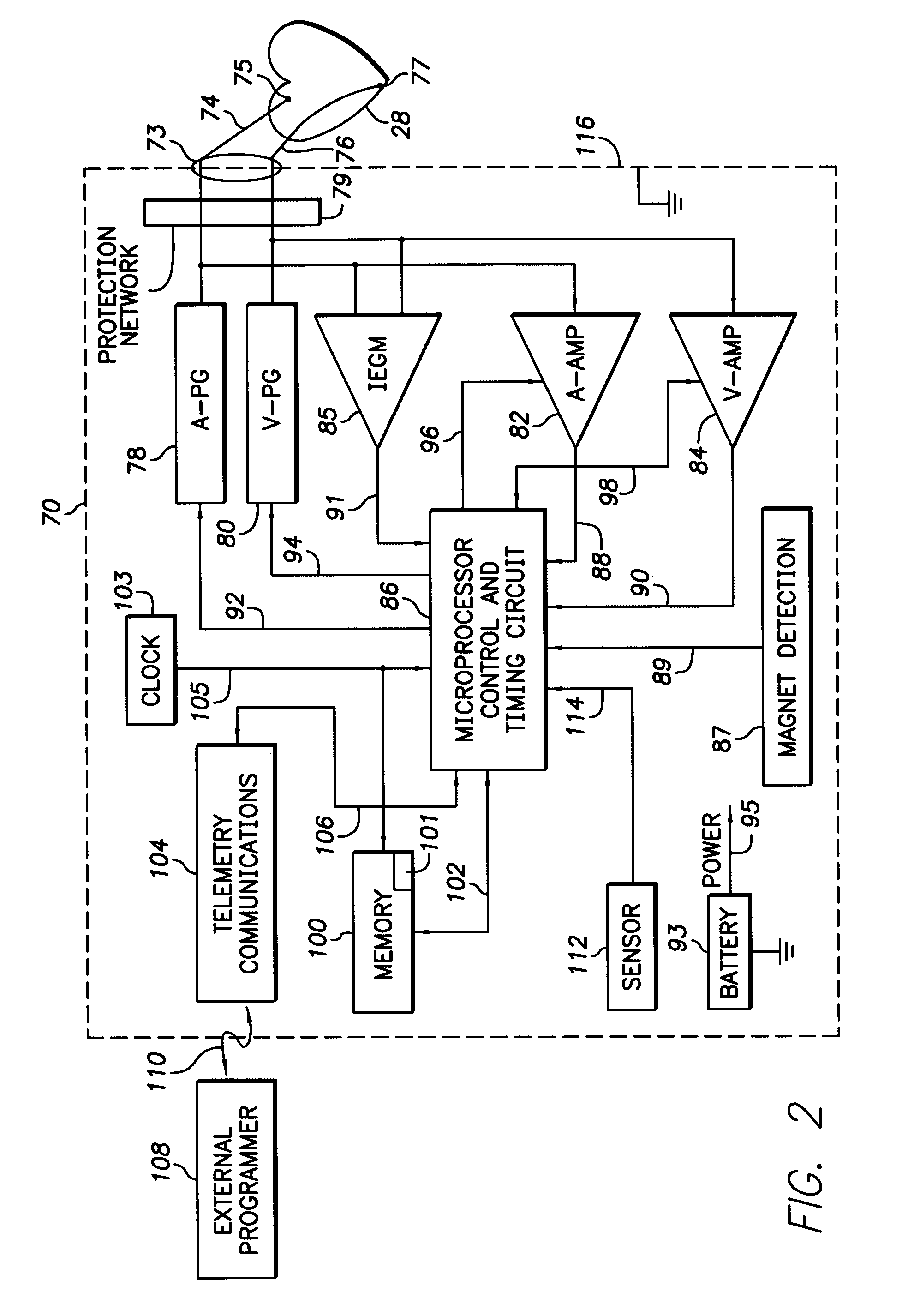
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Paced Rhythm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An electrocardiographic finding in which the cardiac rhythm is controlled by an electrical impulse from an artificial cardiac pacemaker. (CDISC)
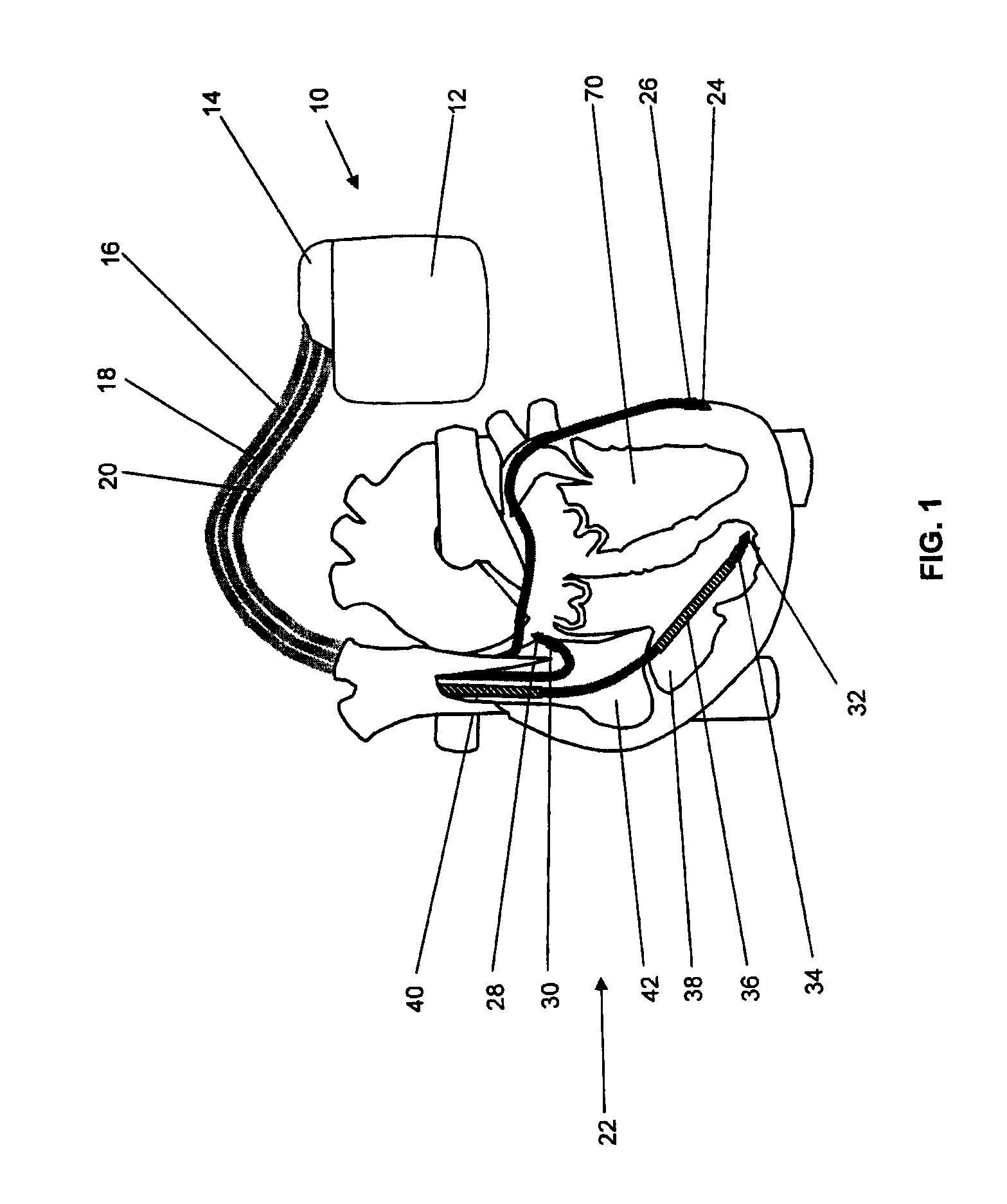
Cardiac rhythm management system promoting atrial pacing
InactiveUS6353759B1Promoting atrial pacingReduce the possibilityHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular dysrhythmiaInfinite impulse response
A cardiac rhythm management system includes an atrial pacing preference (APP) filter for promoting atrial pacing. The APP filter includes an infinite impulse response (IIR) or other filter that controls the timing of delivery of atrial pacing pulses. The atrial pacing pulses are delivered at an APP-indicated pacing rate that is typically at a small amount above the intrinsic atrial heart rate. For sensed beats, the APP indicated rate is increased until it becomes slightly faster than the intrinsic atrial heart rate. The APP-indicated pacing rate is then gradually decreased to search for the underlying intrinsic atrial heart rate. Then, after a sensed atrial beat, the APP filter again increases the pacing rate until it becomes faster than the intrinsic atrial rate by a small amount. As a result, most atrial heart beats are paced, rather than sensed. This decreases the likelihood of the occurrence of an atrial tachyarrhythima, such as atrial fibrillation. The decreased likelihood of atrial tachyarrhythmia, in turn, decreases the likelihood of inducing a ventricular arrhythmia, either as a result of the atrial tachyarrhythmia, or as the result of delivering a defibrillation shock to treat the atrial tachyarrhythmia.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
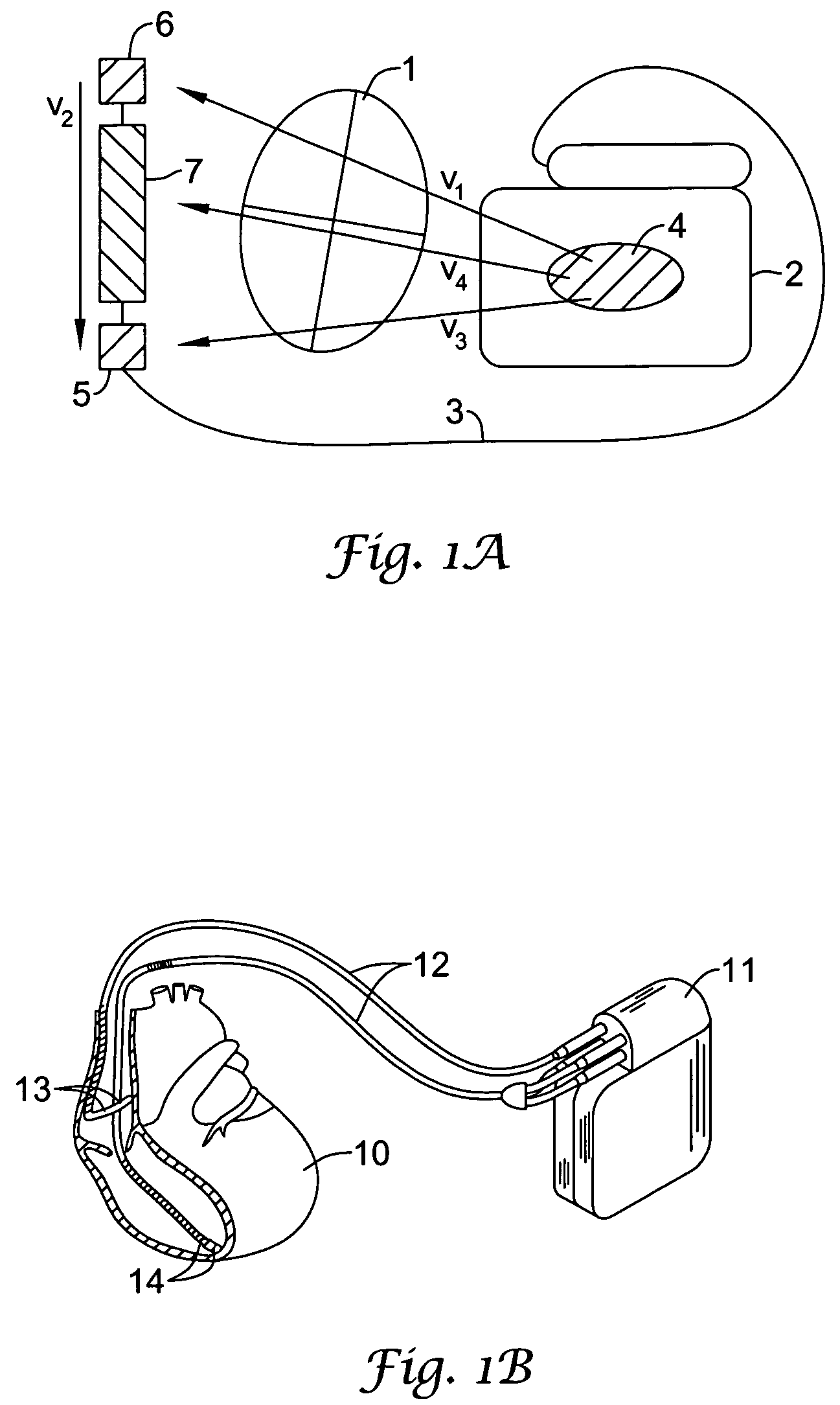
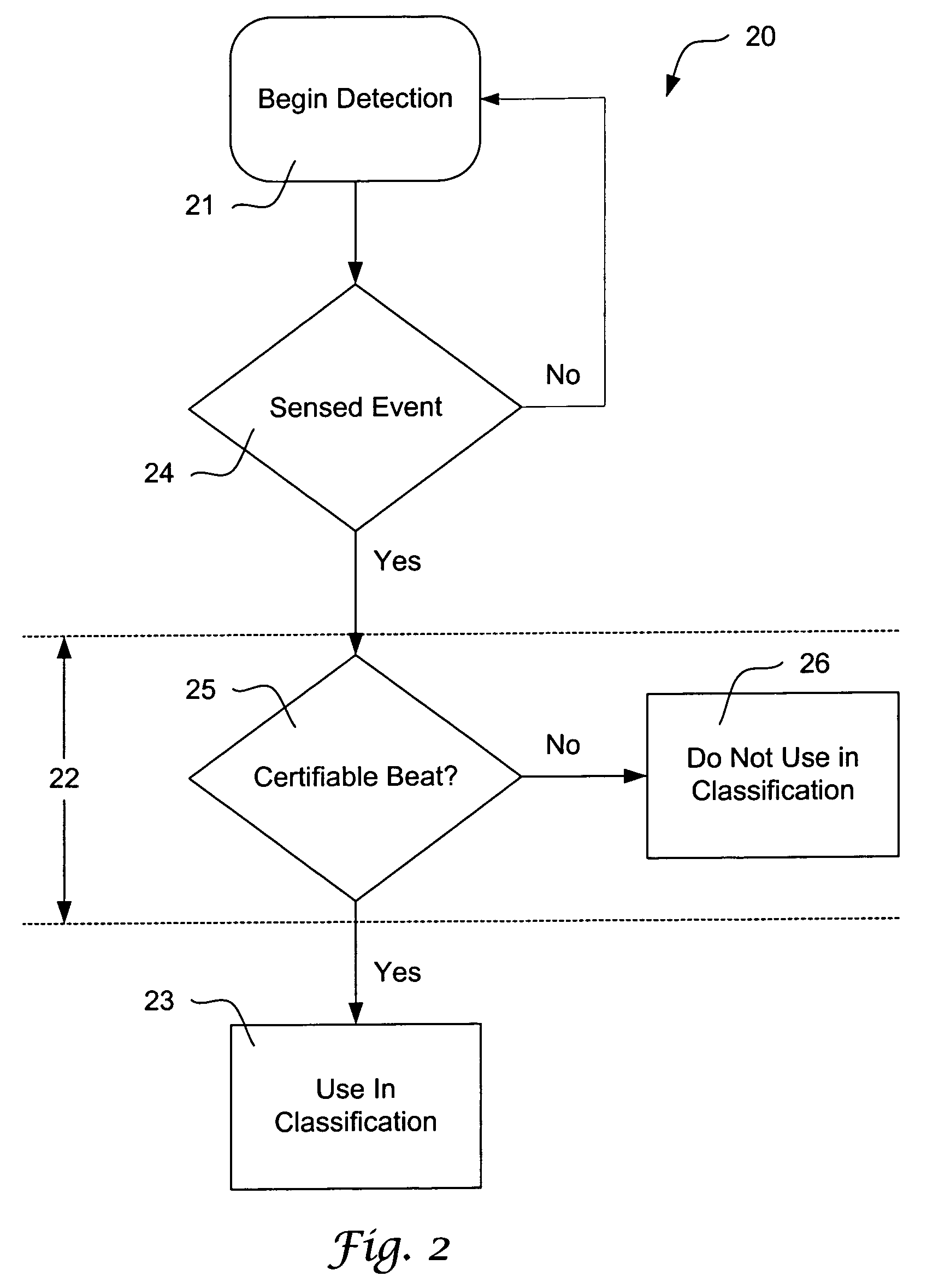
Method and devices for performing cardiac waveform appraisal
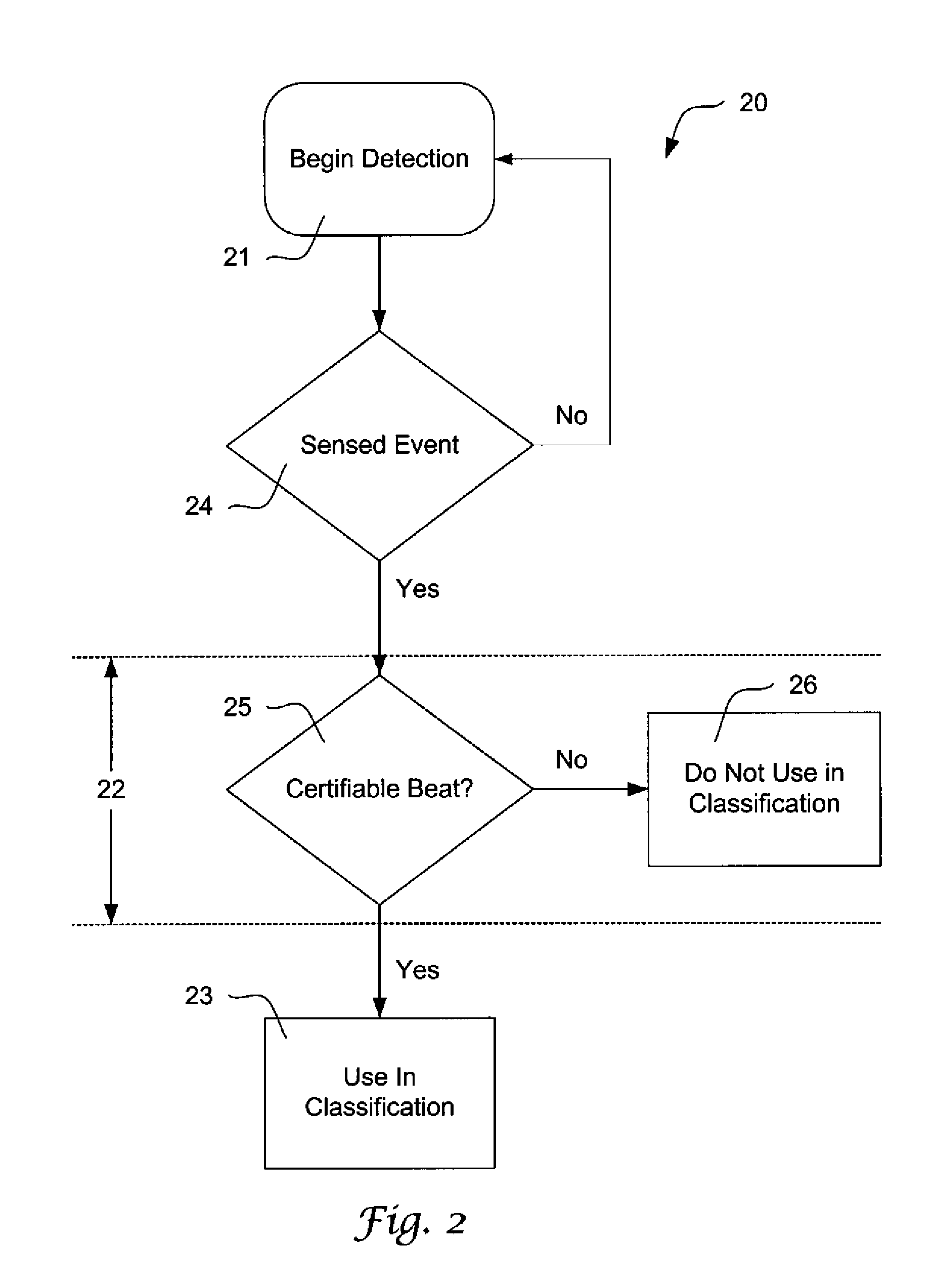
The present invention is directed toward a sensing architecture for use in cardiac rhythm management devices. The sensing architecture of the present invention provides a method and means for certifying detected events by the cardiac rhythm management device. Moreover, by exploiting the enhanced capability to accurately identifying only those sensed events that are desirable, and preventing the use of events marked as suspect, the sensing architecture of the present invention can better discriminate between rhythms appropriate for device therapy and those that are not.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
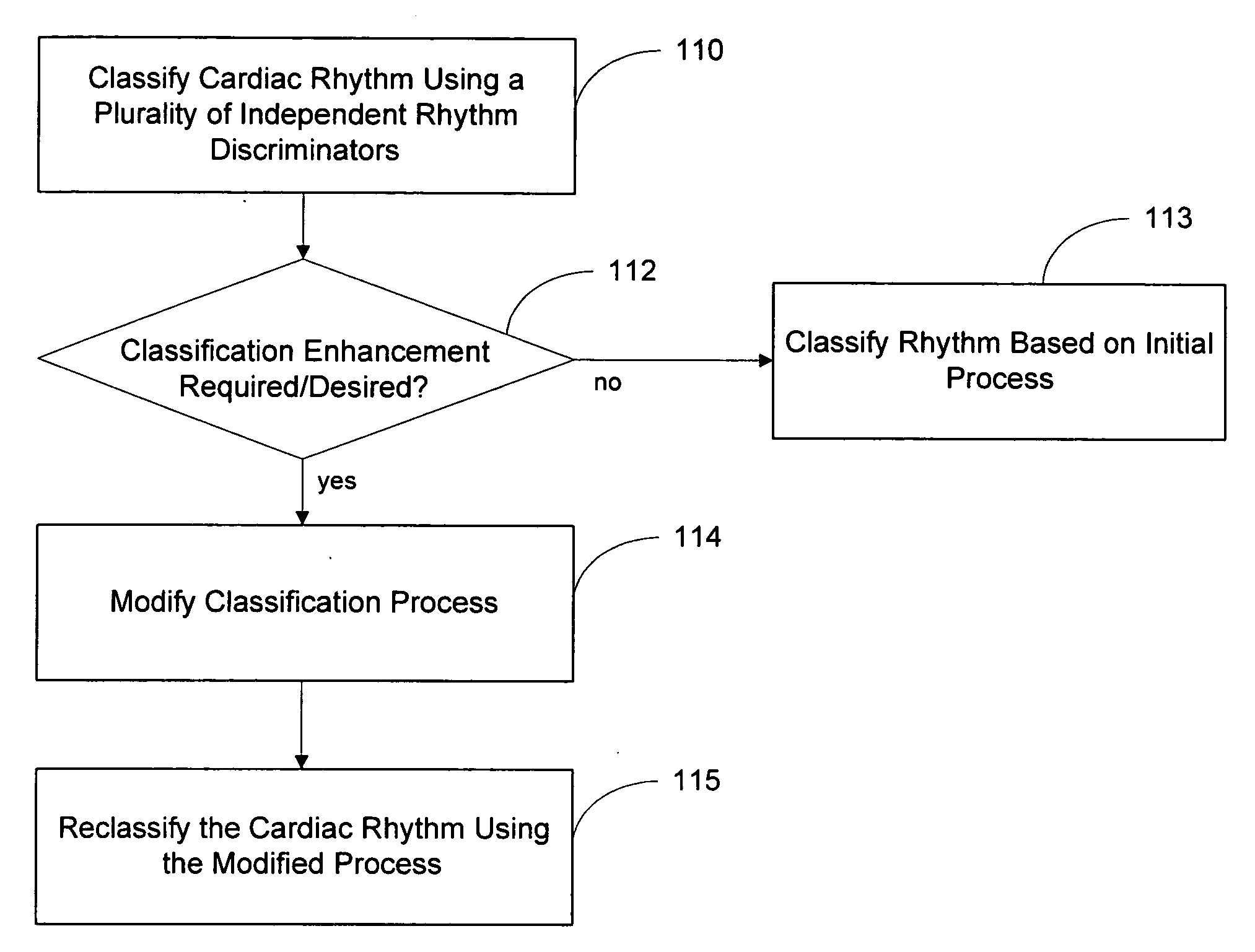
Blending cardiac rhythm detection processes
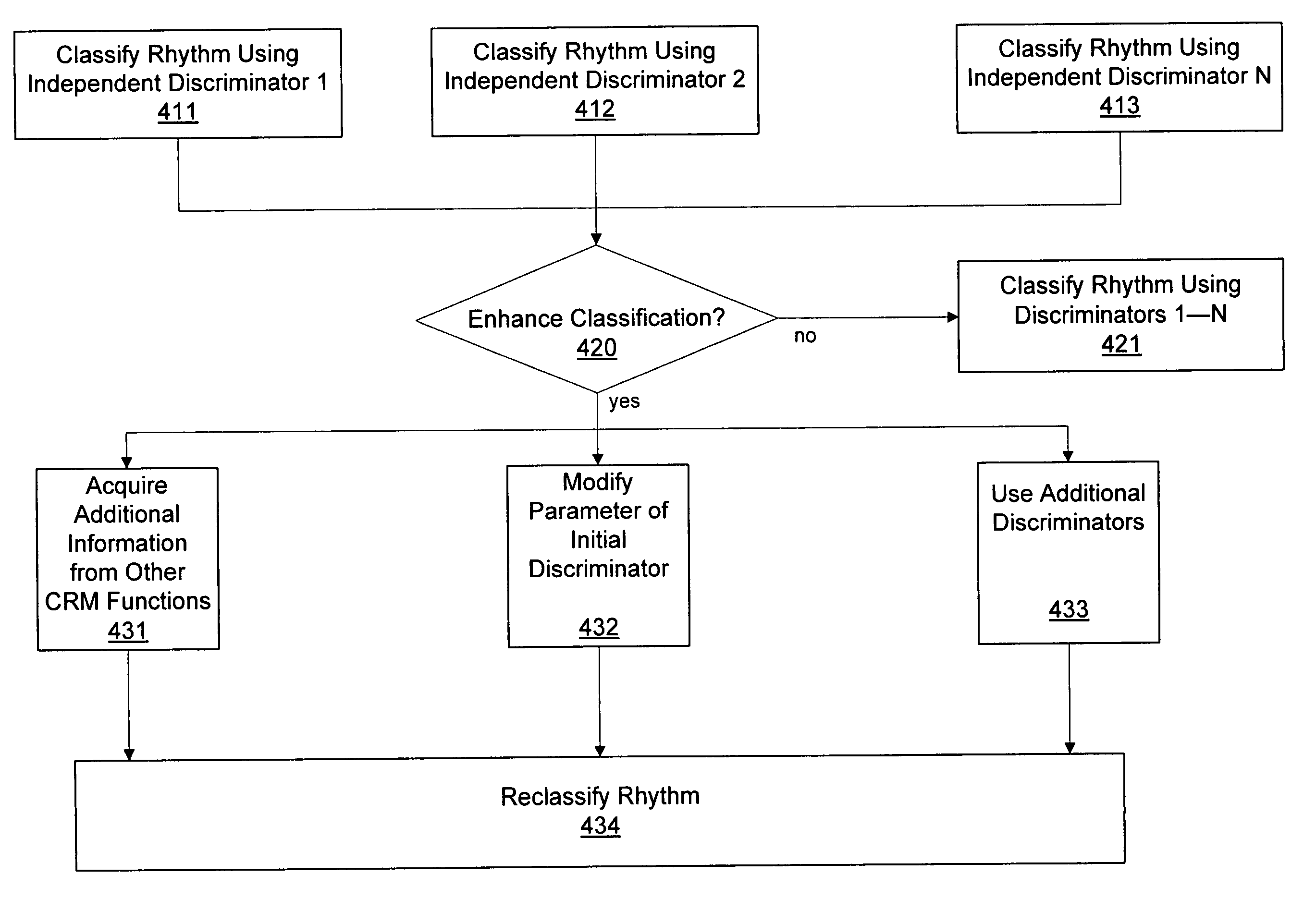
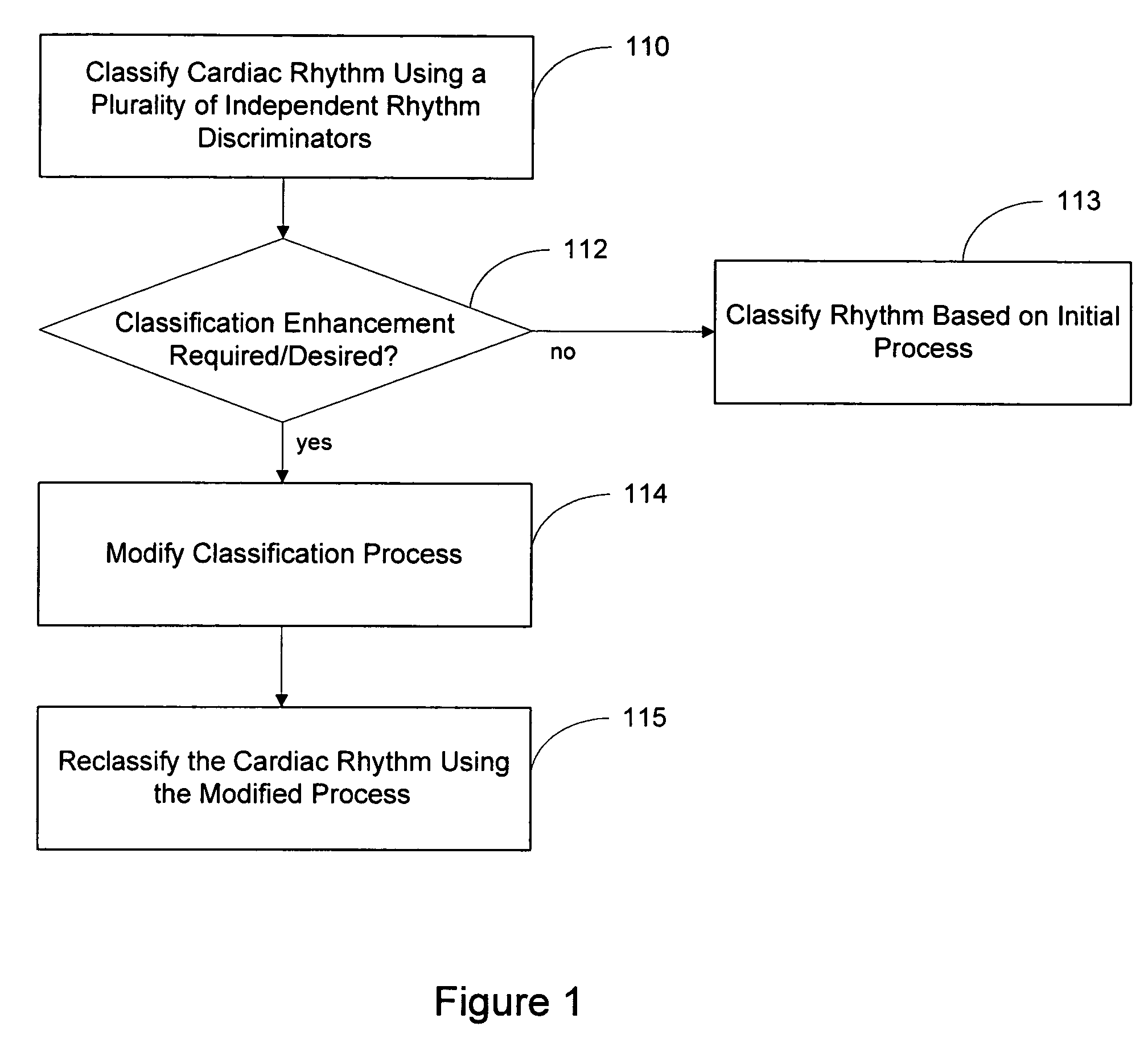
ActiveUS20060217621A1Easy to classifyRhythm classificationElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyProcess systemsDiscriminator
Systems and methods are described for classifying a cardiac rhythm. A cardiac rhythm is classified using a classification process that includes a plurality of cardiac rhythm discriminators. Each rhythm discriminator provides an independent classification of the cardiac rhythm. The classification process is modified if the modification is likely to produce enhanced classification results. The rhythm is reclassified using the modified classification process.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and apparatus for maintaining synchronized pacing
A device and method for cardiac rhythm management in which a cardiac site is paced in accordance with a pacing mode that employs sense signals from a different cardiac site. A protective period triggered by the sensing of intrinsic activity at the paced site is used to delay pacing by a protective delay interval without otherwise disturbing the pacing algorithm.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and apparatus for treating irregular ventricular contractions such as during atrial arrhythmia
InactiveUS7062325B1Avoids unnecessary pacingAvoid rapid changesHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsPacing intervalVentricular contraction
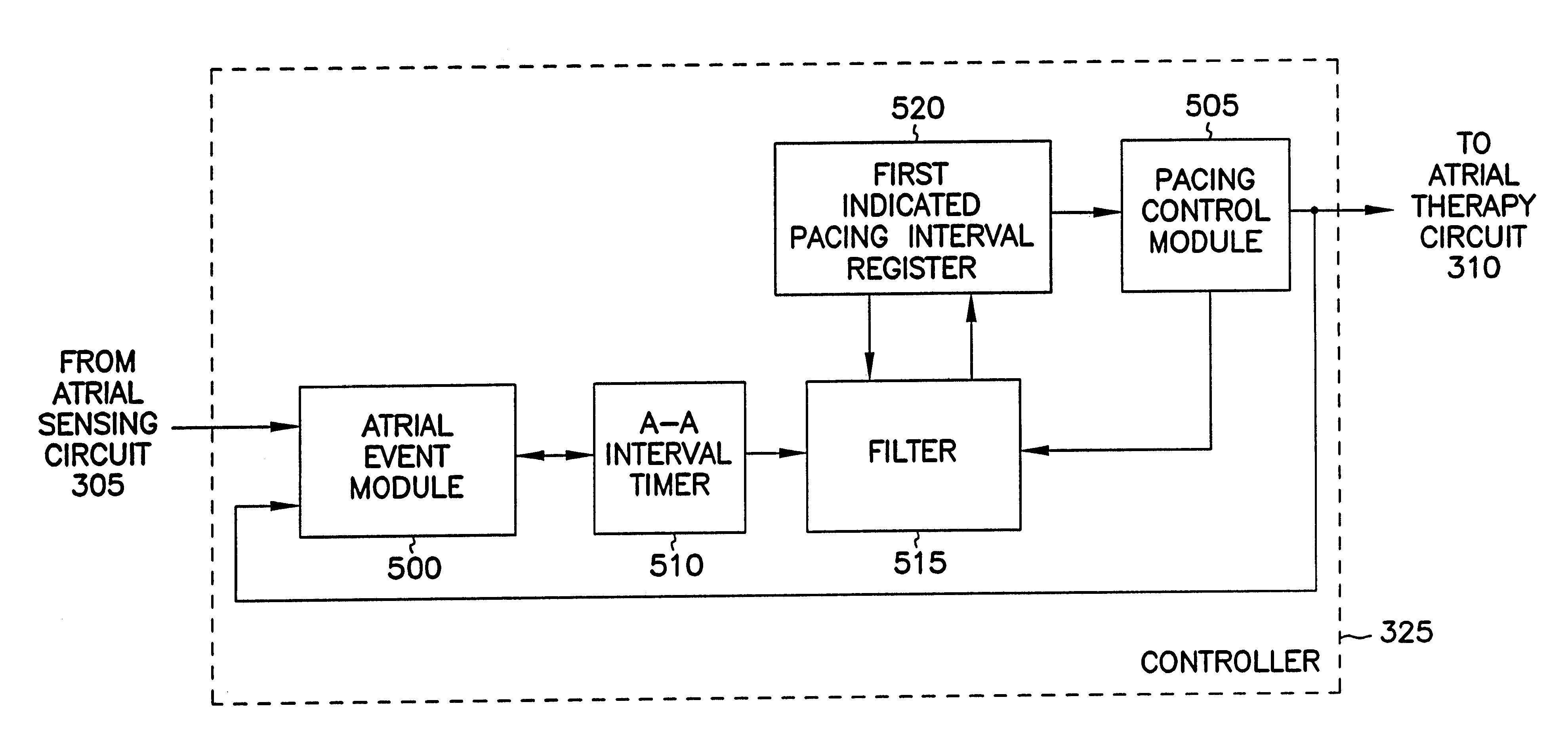
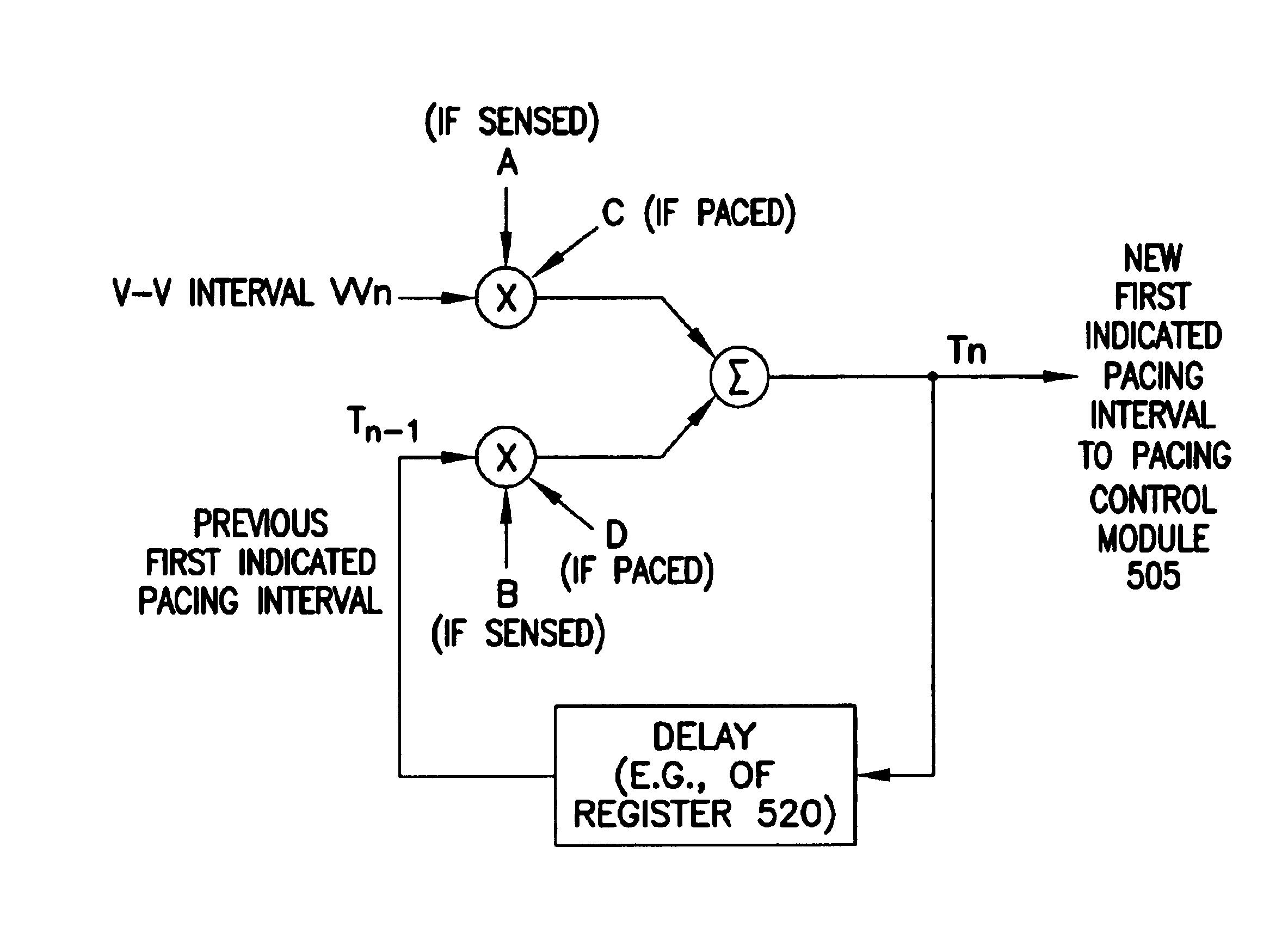
A cardiac rhythm management system is capable of treating irregular ventricular heart contractions, such as during atrial tachyarrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. A first indicated pacing interval is computed based at least partially on a most recent V—V interval duration between ventricular beats and a previous value of the first indicated pacing interval. Pacing therapy is provided based on either the first indicated pacing interval or also based on a second indicated pacing interval, such as a sensor-indicated pacing interval. A weighted averager such as an infinite impulse response (IIR) filter adjusts the first indicated pacing interval for sensed beats and differently adjusts the first indicated pacing interval for paced beats. The system regularizes ventricular rhythms by pacing the ventricle, but inhibits pacing when the ventricular rhythms are stable.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and system to discriminate rhythm patterns in cardiac activity
Methods and systems are provided for discriminating rhythm patterns in cardiac activity. The method and system obtain cardiac activity data for multiple cardiac beats over a predetermined period of time. Multi-beat segments within the cardiac activity data exhibit different rhythm patterns of interest including fast and slow rhythm patterns. The method and system calculate a cardiac beats timing relation representative of intervals between the cardiac beats within a measurement window, wherein the measurement window is configured to overlap the corresponding multi-beat segment. The method and system designate the cardiac beats timing relation to have one of the rhythm patterns of interest based on a rate threshold, identifies when successive multi-beat segments exhibit rhythm patterns that transition between the fast and slow irregular rhythm patterns and records the irregular rhythm pattern transition in connection with the cardiac activity data.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
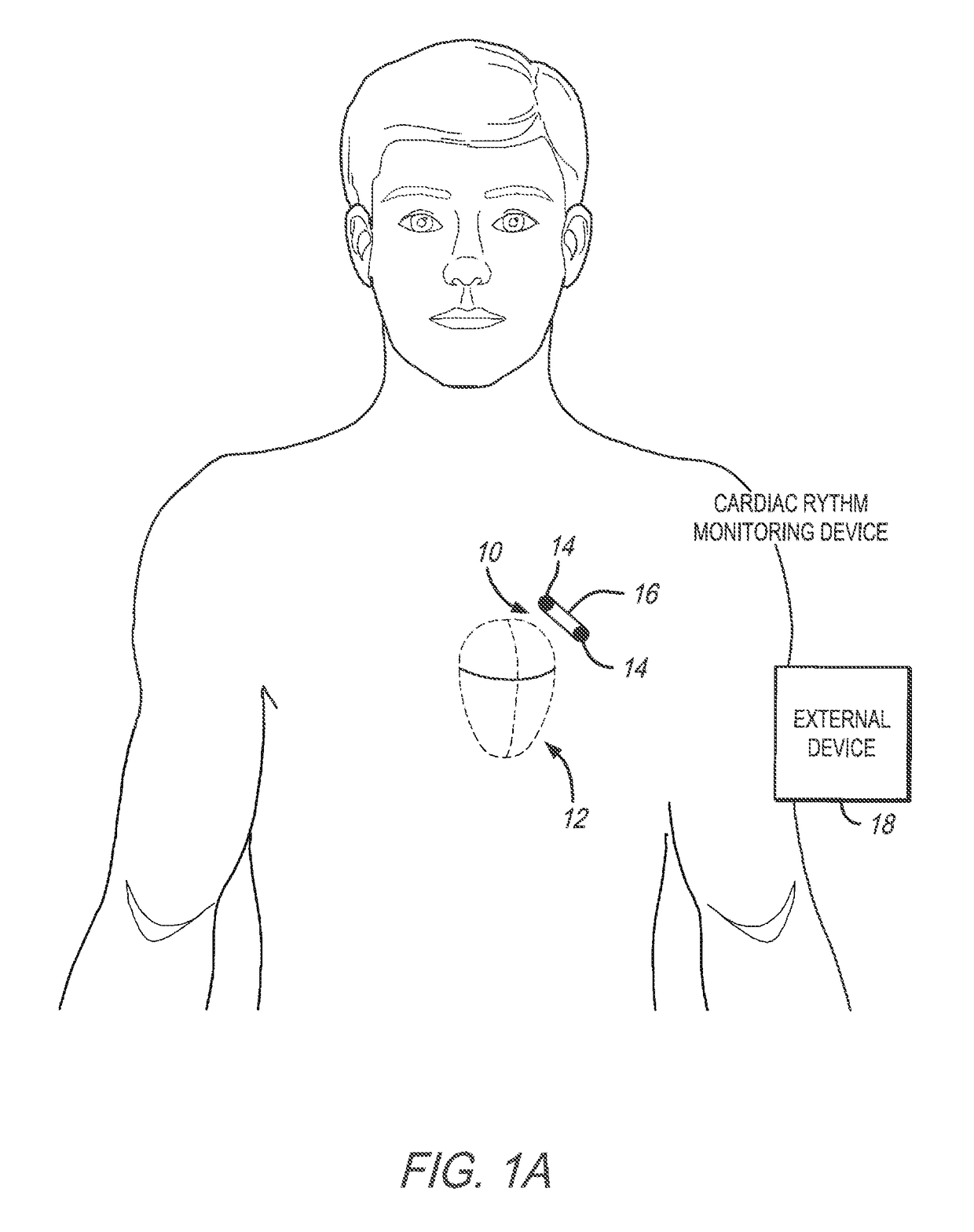
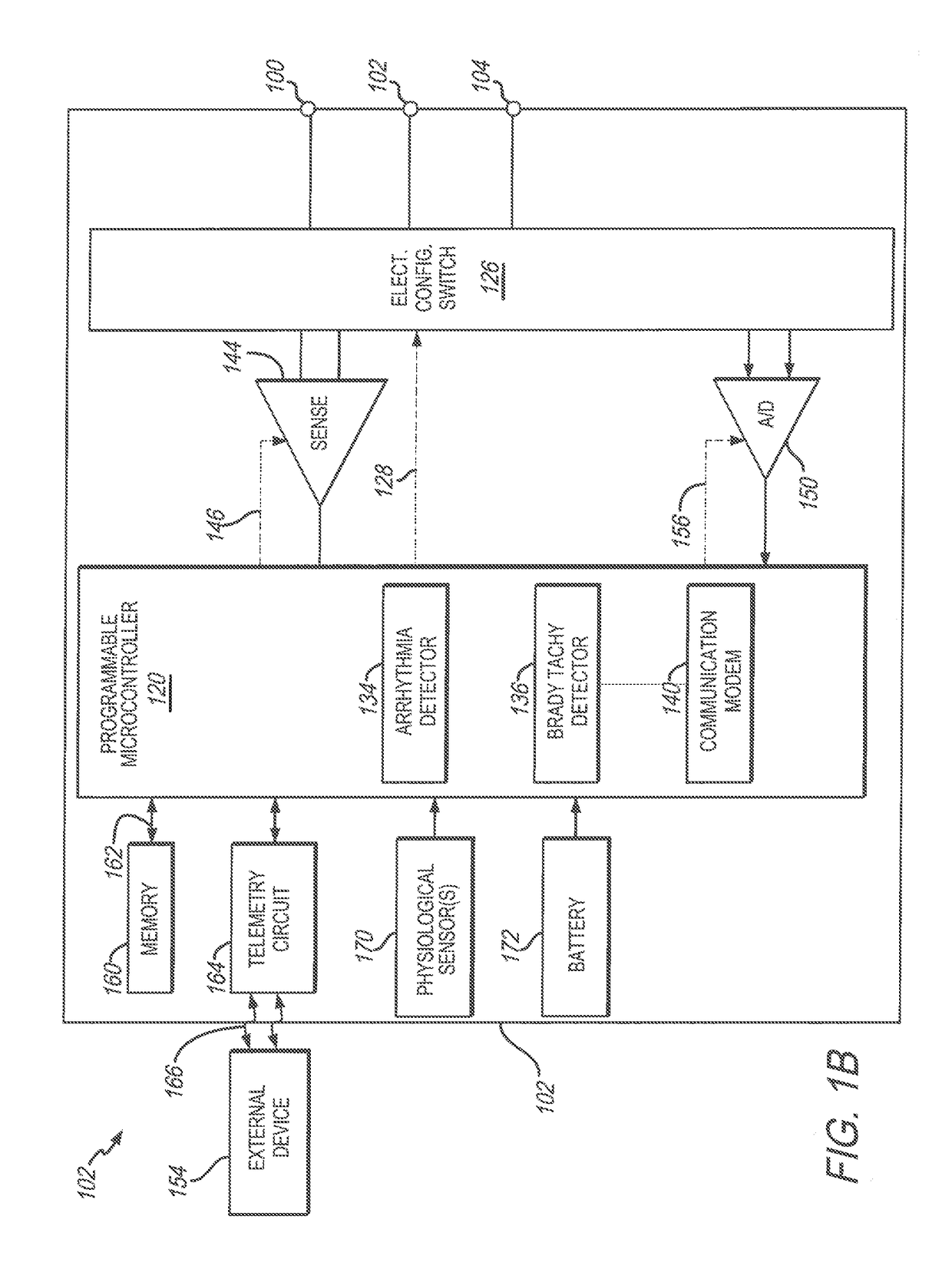
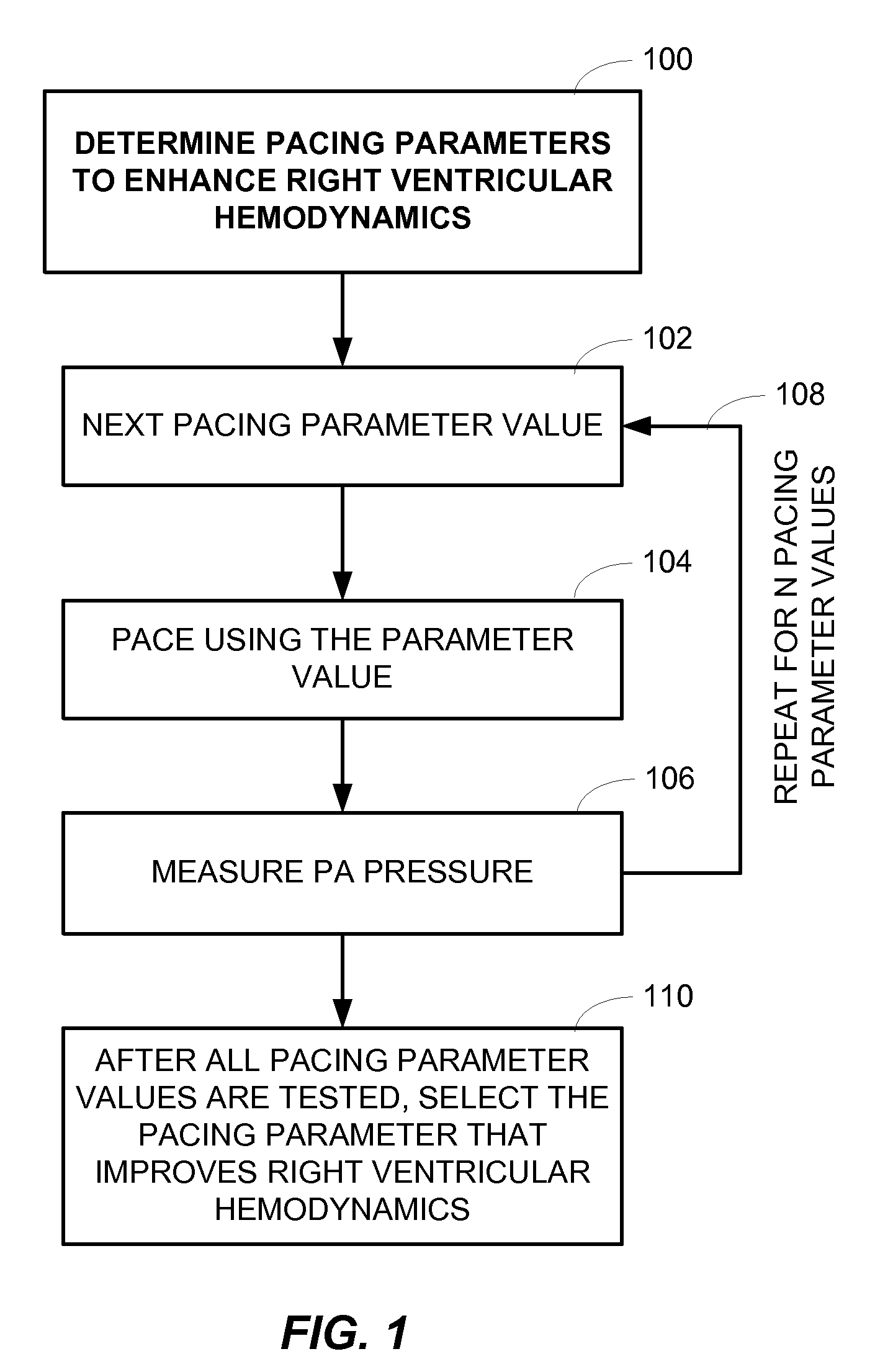
Monitoring Right Ventricular Hemodynamic Function During Pacing Optimization
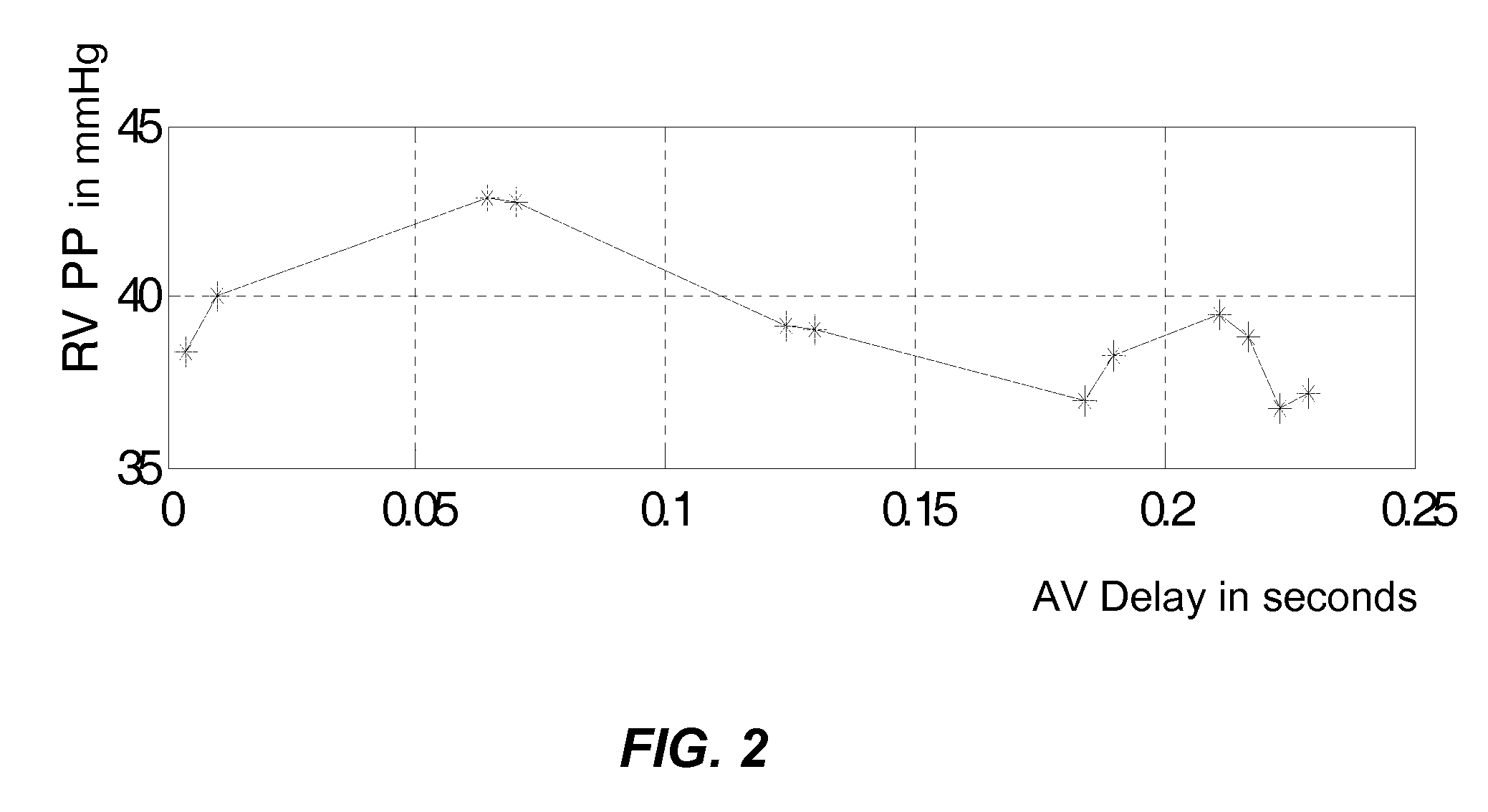
Method and systems related to monitoring right ventricular function during pacing by a cardiac rhythm management device are described. One or more pacing parameters are selected to provide cardiac resynchronization therapy. For example, the one or more pacing parameters may be selected to provide an optimal or improved therapy. The heart is paced using the selected pacing parameters. While pacing with the selected parameters, pressure is sensed via a pressure sensor disposed the pulmonary artery. The sensed pressure is analyzed to determine right ventricular function achieved during the pacing using the selected pacing parameters. A signal, such as an alert signal or control signal, is generated based on the right ventricular function achieved during the pacing.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Enhanced rhythm identification in compression corrupted ECG
InactiveUS7567837B2ElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular tachycardiaVentricular fibrillation
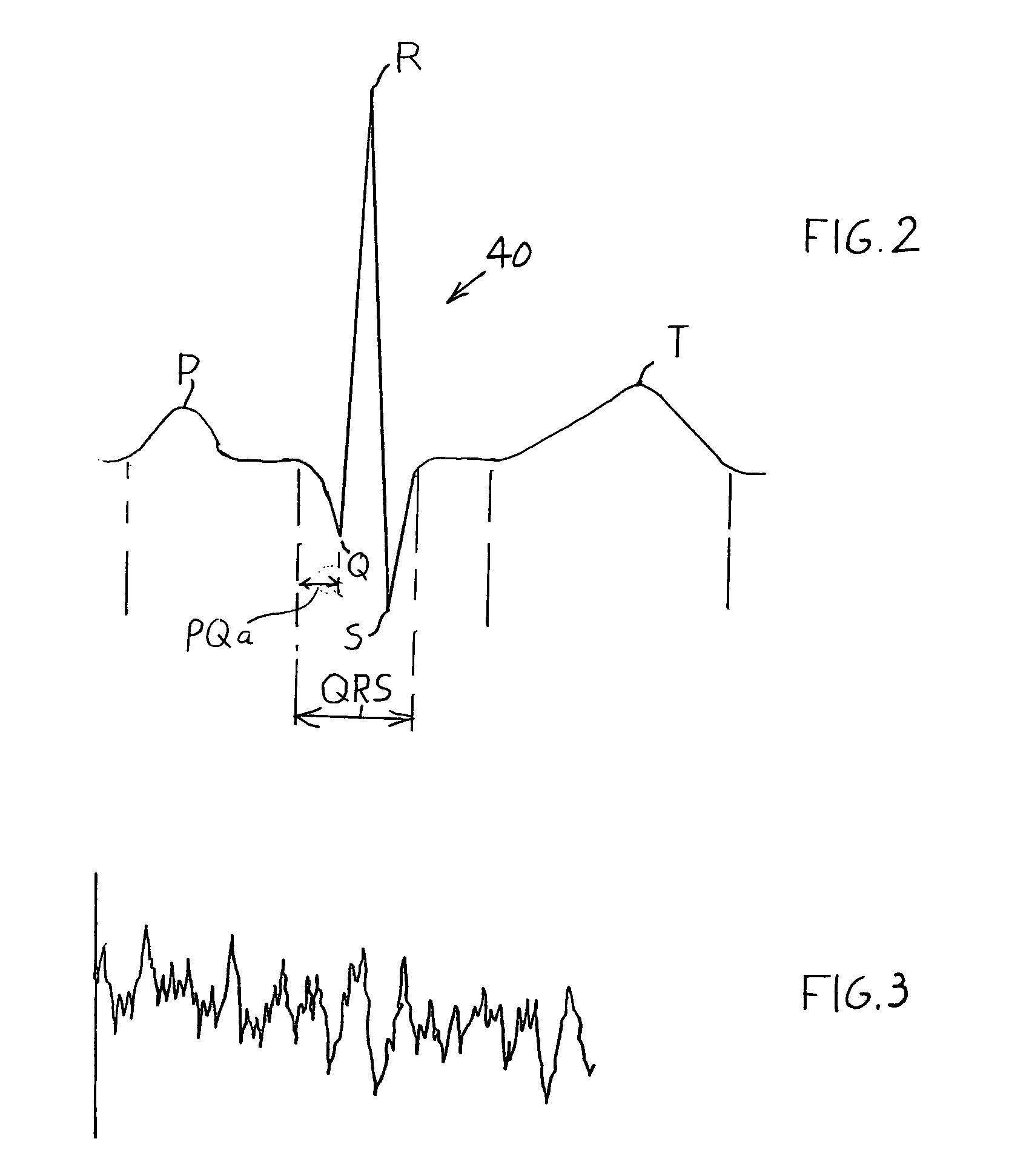
A method is provided for analyzing the condition of a patient to determine whether or not a defibrillation shock should be applied, without stopping CPR (primarily chest compressions). While chest compressions continue to be applied to the victim, the system differentiates between (1) a perfusing rhythm that has the capability of leading to a beating heart without a shock and (2) ventricular fibrillation (VF) which sometimes occurs in the presence of ventricular tachycardia (VT), in which there is no capability for leading to a beating heart without a shock. Defibrillation shocks should be applied only when needed and that is in the presence of VF and sometimes in the presence of VT. Electrocardiographic (ECG or EKG) signals obtained from electrodes applied to the patient's chest are analyzed so that the presence of a QRS signal characteristic of a rhythm which has the potential of supporting a beating heart, or the absence of a QRS signal which indicates ventricular fibrillation, may be detected in the presence of artifacts resulting from chest compressions.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Method and apparatus for discriminating ventricular and supraventricular tachyarrhythmias
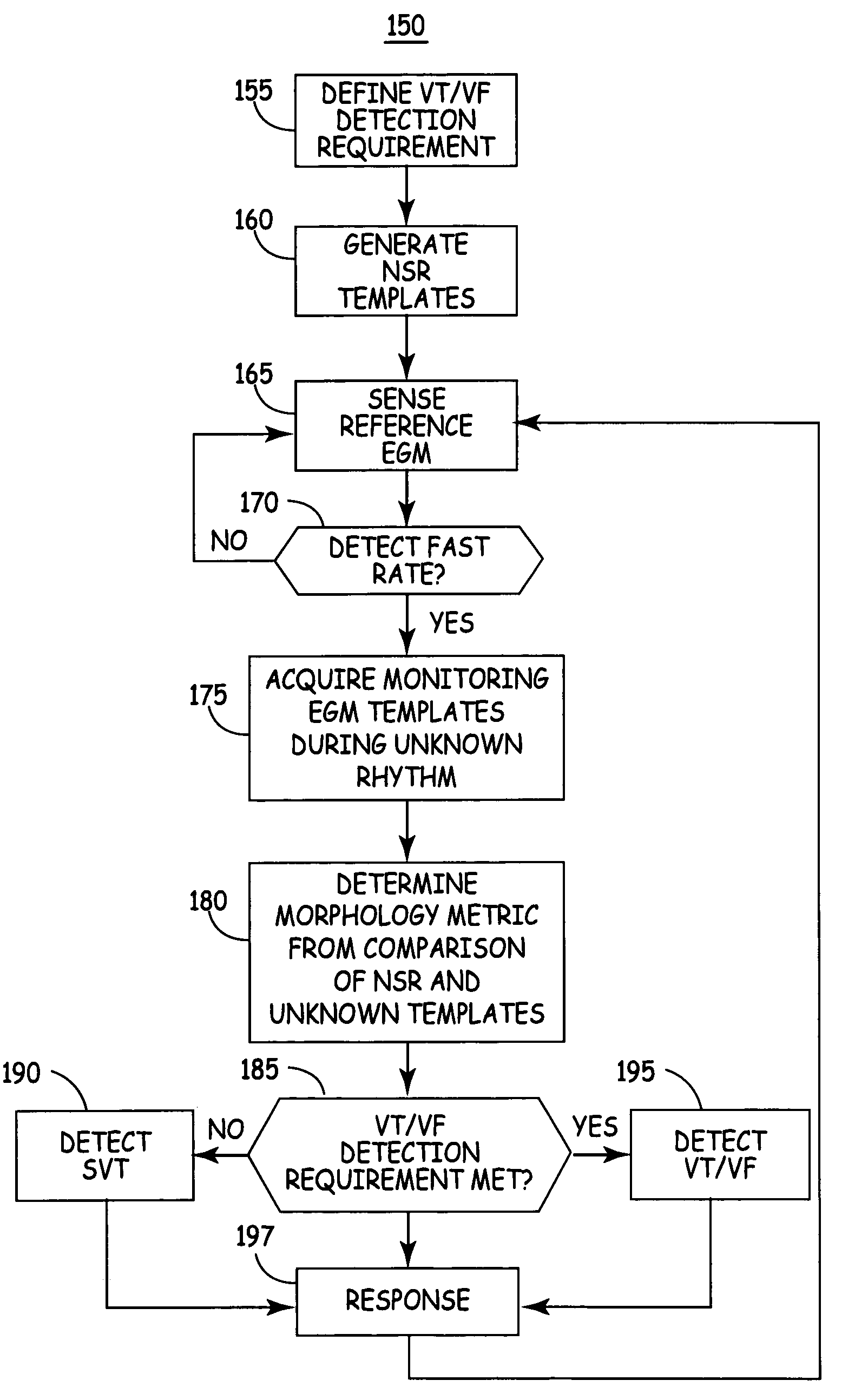
A system and method are provided for discriminating supra-ventricular tachycardia (SVT) from ventricular tachycardia (VT). A monitoring EGM signal is acquired during a sensing window timed according to the time of R-wave detection on a reference EGM signal. A normal sinus rhythm (NSR) template is generated using the monitoring EGM signal during the time-referenced sensing window. During an unknown rhythm, the monitoring EGM signal sensed during the time-referenced sensing window is compared to the NSR template for use in computing a morphology metric. The morphology metric is compared to a VT / VF detection threshold for discriminating SVT from VT / VF.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Wavelet based feature extraction and dimension reduction for the classification of human cardiac electrogram depolarization waveforms
ActiveUS7751873B2Improving implant accuracyImprove accuracyElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisRhythmTime scale decomposition
A depolarization waveform classifier based on the Modified lifting line wavelet Transform is described. Overcomes problems in existing rate-based event classifiers. A task for pacemaker / defibrillators is the accurate identification of rhythm categories so correct electrotherapy can be administered. Because some rhythms cause rapid dangerous drop in cardiac output, it's desirable to categorize depolarization waveforms on a beat-to-beat basis to accomplish rhythm classification as rapidly as possible. Although rate based methods of event categorization have served well in implanted devices, these methods suffer in sensitivity and specificity when atrial / ventricular rates are similar. Human experts differentiate rhythms by morphological features of strip chart electrocardiograms. The wavelet transform approximates human expert analysis function because it correlates distinct morphological features at multiple scales. The accuracy of implanted rhythm determination can then be improved by using human-appreciable time domain features enhanced by time scale decomposition of depolarization waveforms.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Wearable cardiac defibrillator system diagnosing differently depending on motion
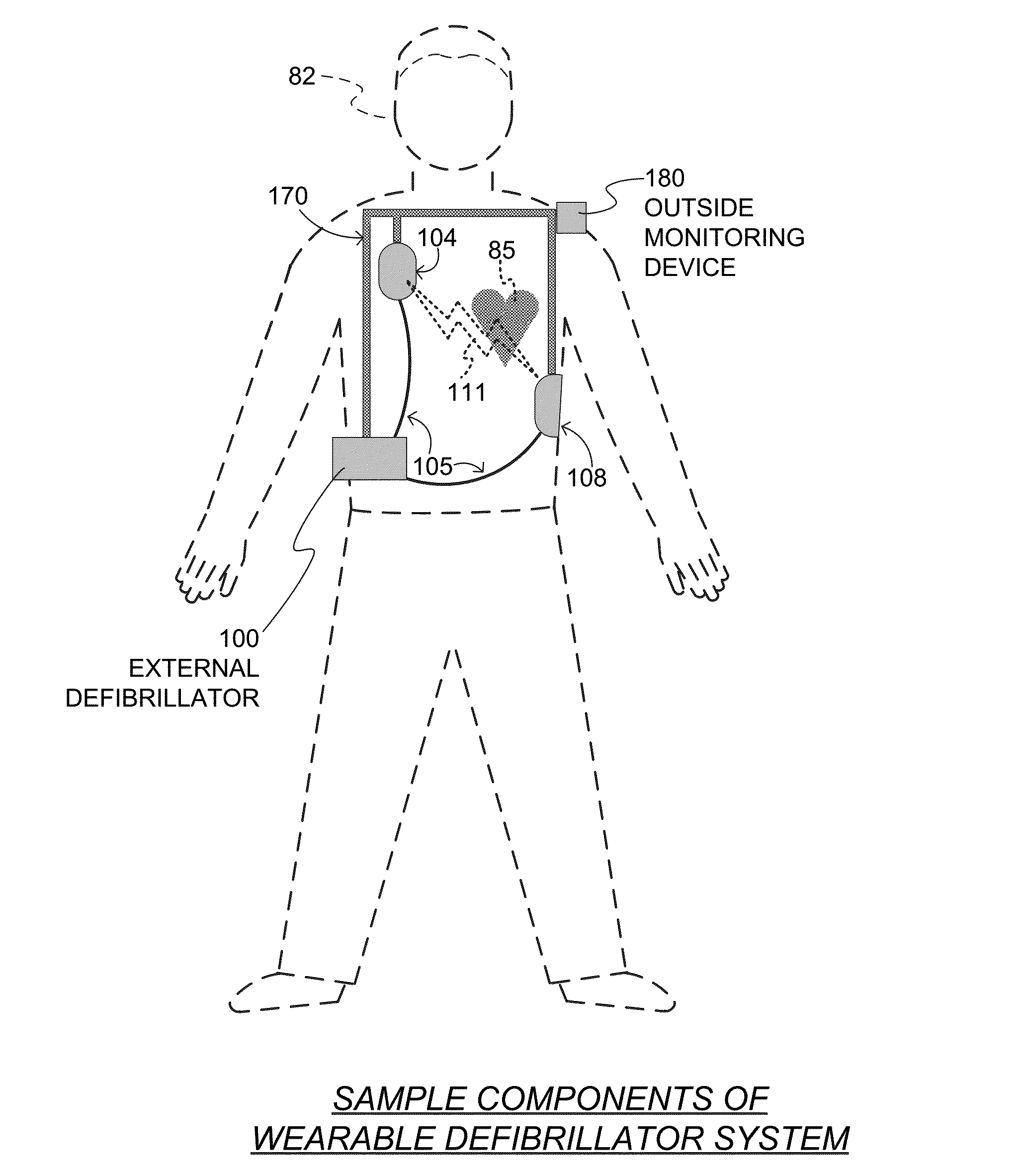
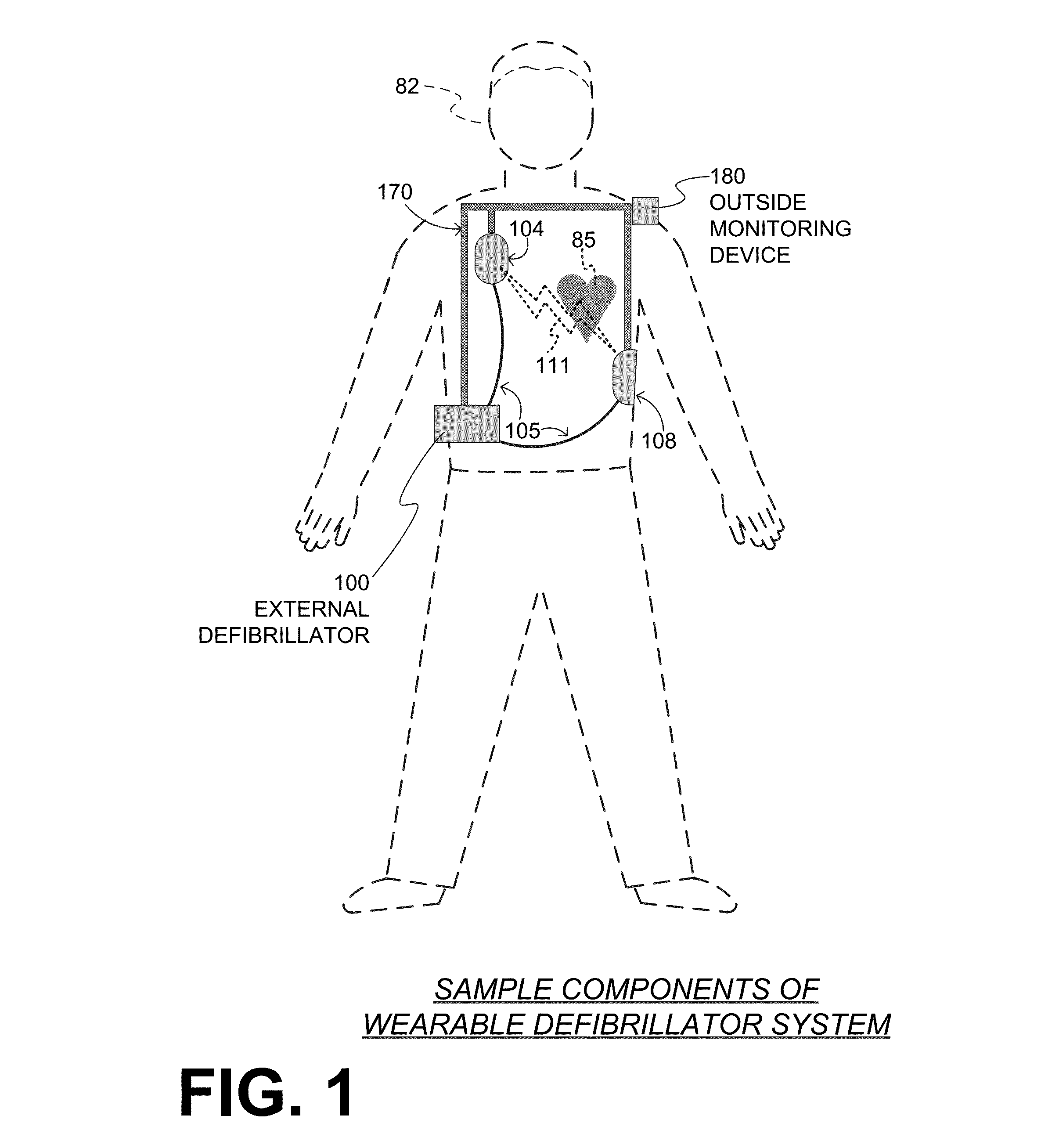
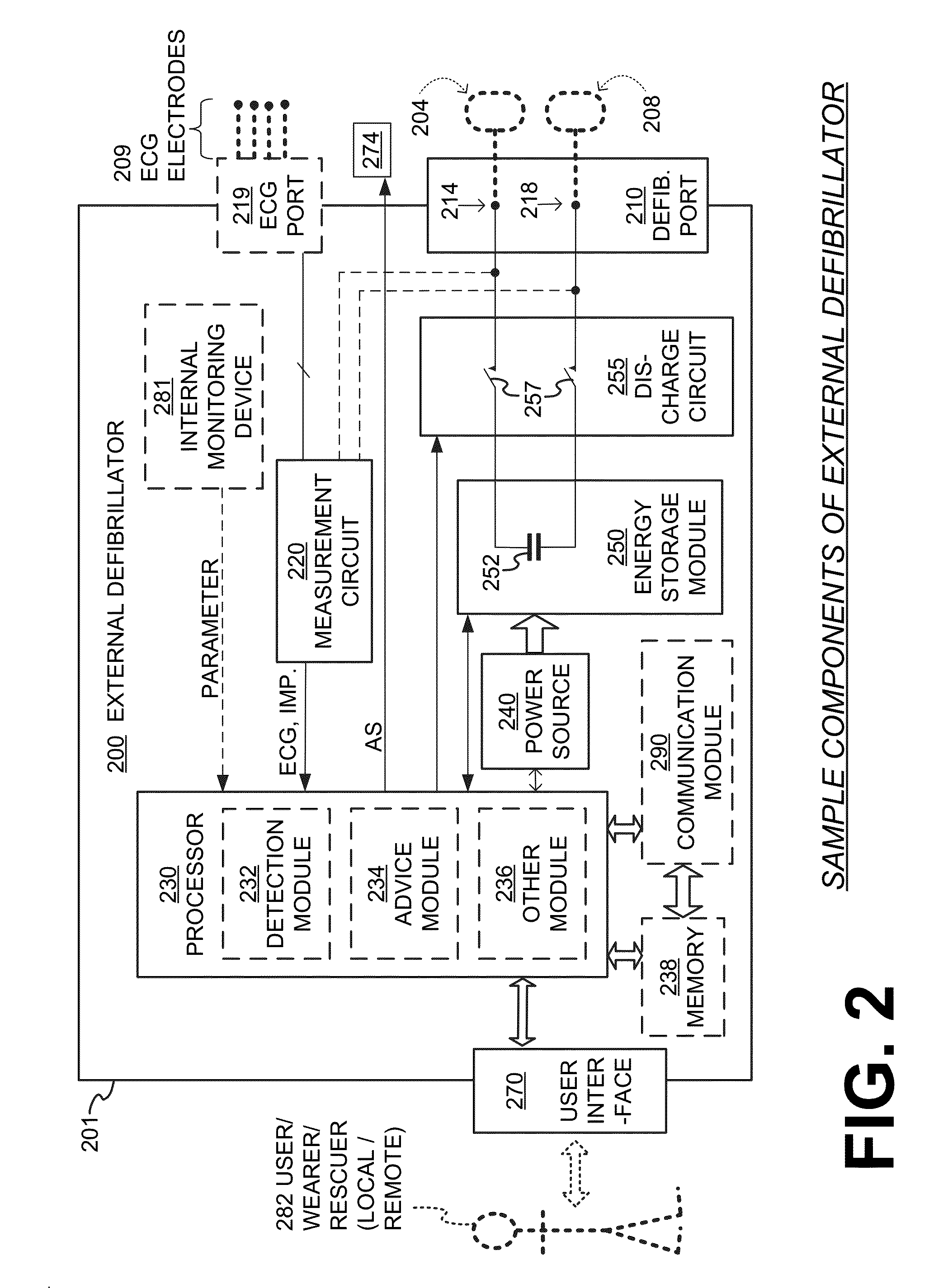
PendingUS20160074667A1Accurate measurementHeart defibrillatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringMotion detectorWearable eeg
Embodiments of a WCD system include a measurement circuit that can render a physiological input from the patient. Such WCD systems may also receive a motion detection input that reveals whether a motion event has been detected by a motion detector. In some embodiments, a value becomes assigned to a motion level parameter in response to any motion event detected or not, and the rhythm analysis can be based on the physiological input and on the assigned value. In some embodiments, a rhythm analysis of the physiological input may be performed in different manners, depending on whether or not a motion event has been detected. In some embodiments, a different shock / no shock criterion may be applied to the rhythm analysis, depending on whether or not a motion event has been detected. The patient may receive an electrical shock according to a shock / no shock determination.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
Method and devices for performing cardiac waveform appraisal
Implementations of various technologies described herein are directed toward a sensing architecture for use in cardiac rhythm management devices. The sensing architecture may provide a method and means for certifying detected events by the cardiac rhythm management device. Moreover, by exploiting the enhanced capability to accurately identifying only those sensed events that are desirable, and preventing the use of events marked as suspect, the sensing architecture can better discriminate between rhythms appropriate for device therapy and those that are not.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Enhanced rhythm identification in compression corrupted ECG
InactiveUS20060149157A1ElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular tachycardiaVentricular fibrillation
A method is provided for analyzing the condition of a patient to determine whether or not a defibrillation shock should be applied, without stopping CPR (primarily chest compressions). While chest compressions continue to be applied to the victim, the system differentiates between (1) a perfusing rhythm that has the capability of leading to a beating heart without a shock and (2) ventricular fibrillation (VF) which sometimes occurs in the presence of ventricular tachycardia (VT), in which there is no capability for leading to a beating heart without a shock. Defibrillation shocks should be applied only when needed and that is in the presence of VF and sometimes in the presence of VT. Electrocardiographic (ECG or EKG) signals obtained from electrodes applied to the patient's chest are analyzed so that the presence of a QRS signal characteristic of a rhythm which has the potential of supporting a beating heart, or the absence of a QRS signal which indicates ventricular fibrillation, may be detected in the presence of artifacts resulting from chest compressions.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Method and system to discriminate rhythm patterns in cardiac activity
Methods and systems are provided for discriminating rhythm patterns in cardiac activity. The method and system obtain cardiac activity data for multiple cardiac beats over a predetermined period of time. Multi-beat segments within the cardiac activity data exhibit different rhythm patterns of interest including fast and slow rhythm patterns. The method and system calculate a cardiac beats timing relation representative of intervals between the cardiac beats within a measurement window, wherein the measurement window is configured to overlap the corresponding multi-beat segment. The method and system designate the cardiac beats timing relation to have one of the rhythm patterns of interest based on a rate threshold, identifies when successive multi-beat segments exhibit rhythm patterns that transition between the fast and slow irregular rhythm patterns and records the irregular rhythm pattern transition in connection with the cardiac activity data.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method and apparatus for treating irregular ventricular contractions such as during atrial arrhythmia
InactiveUS20090076563A1Avoids unnecessary pacingAvoid rapid changesHeart stimulatorsPacing intervalVentricular contraction
A cardiac rhythm management system is capable of treating irregular ventricular heart contractions, such as during atrial tachyarrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. A first indicated pacing interval is computed based at least partially on a most recent V-V interval duration between ventricular beats and a previous value of the first indicated pacing interval. Pacing therapy is provided based on either the first indicated pacing interval or also based on a second indicated pacing interval, such as a sensor-indicated pacing interval. A weighted averager such as an infinite impulse response (IIR) filter adjusts the first indicated pacing interval for sensed beats and differently adjusts the first indicated pacing interval for paced beats. The system regularizes ventricular rhythms by pacing the ventricle, but inhibits pacing when the ventricular rhythms are stable.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
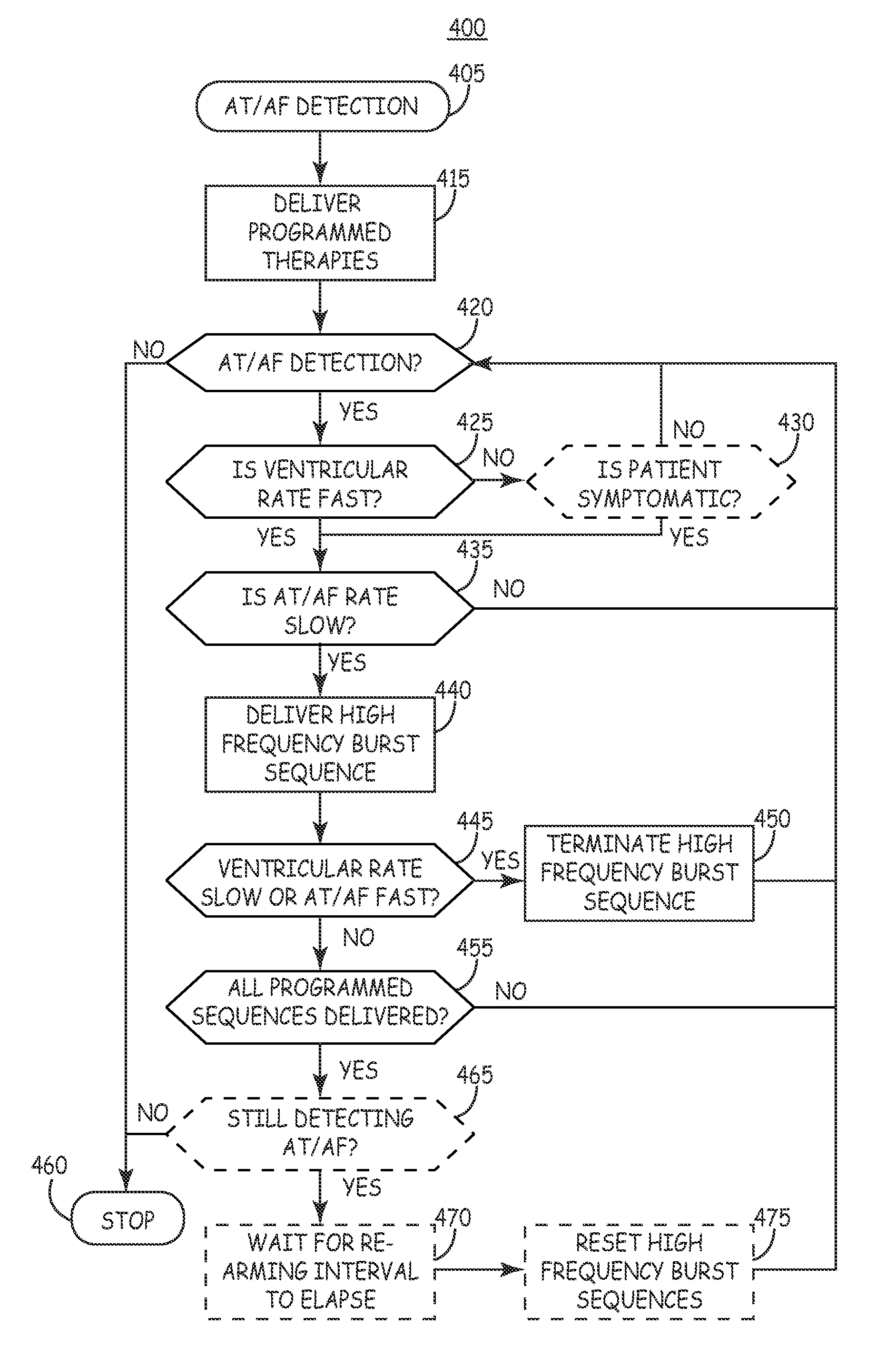
High frequency atrial burst pacing for improved ventricular rate control during atrial arrhythmias
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
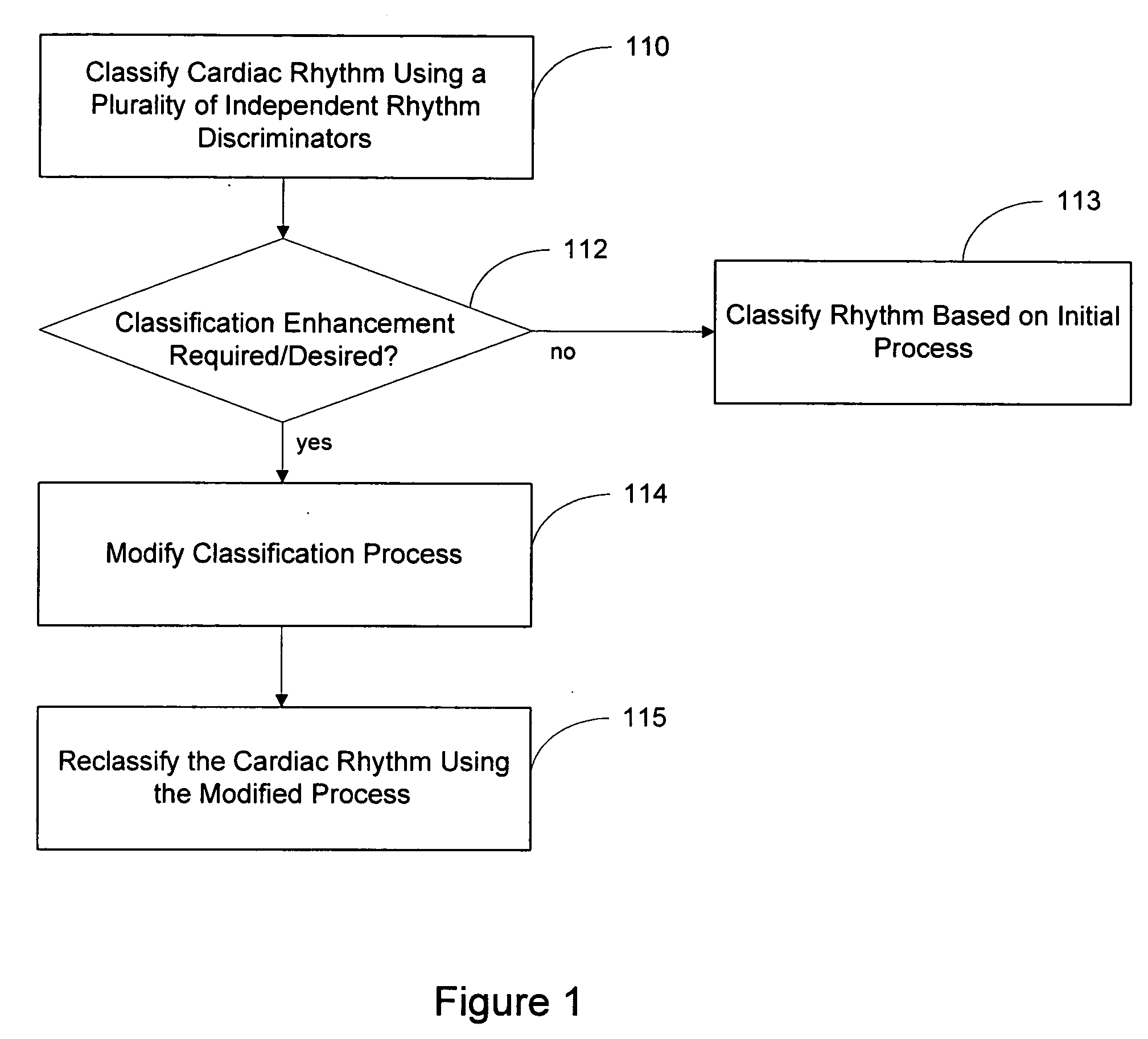
Blending cardiac rhythm detection processes
Systems and methods are described for classifying a cardiac rhythm. A cardiac rhythm is classified using a classification process that includes a plurality of cardiac rhythm discriminators. Each rhythm discriminator provides an independent classification of the cardiac rhythm. The classification process is modified if the modification is likely to produce enhanced classification results. The rhythm is reclassified using the modified classification process.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
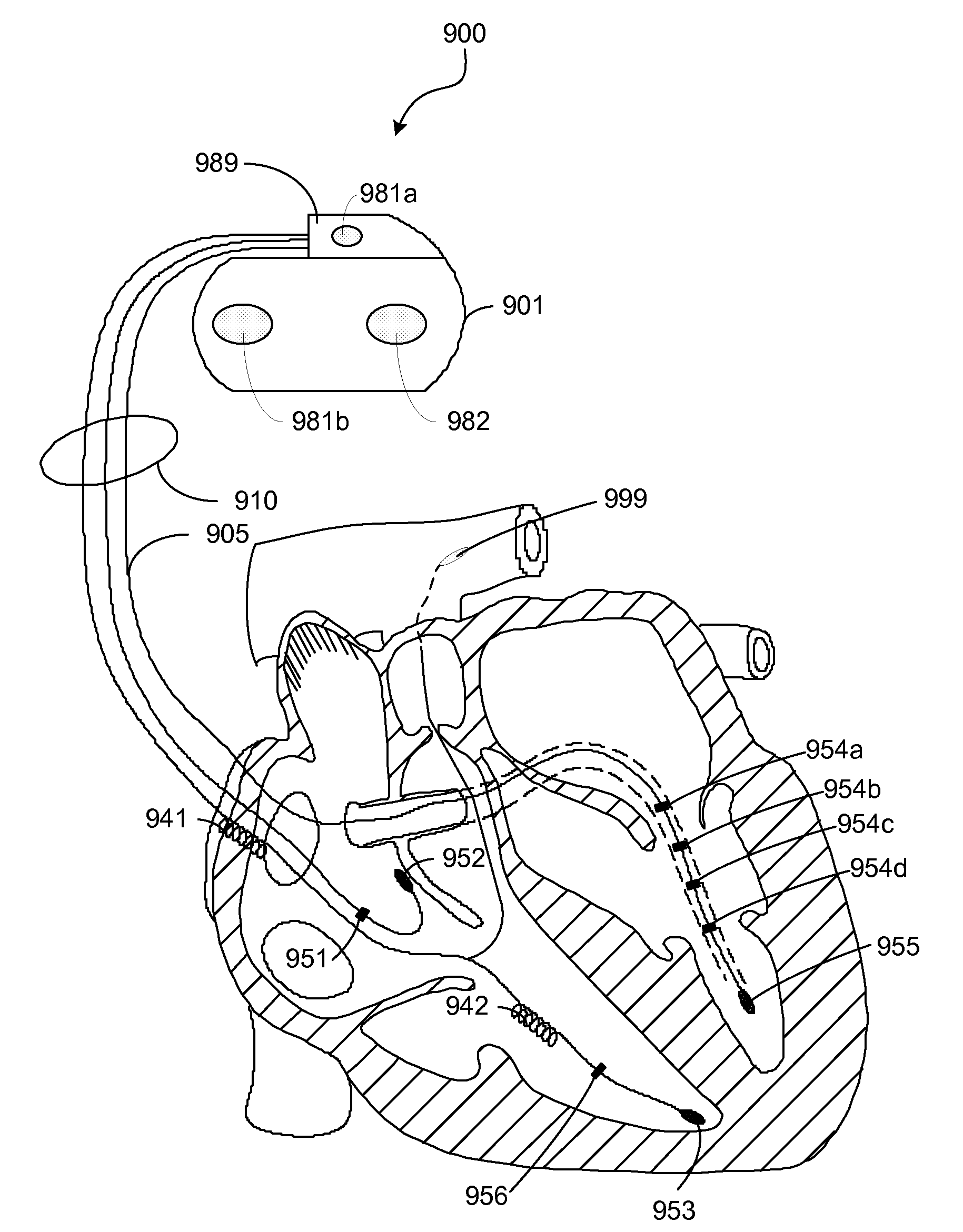
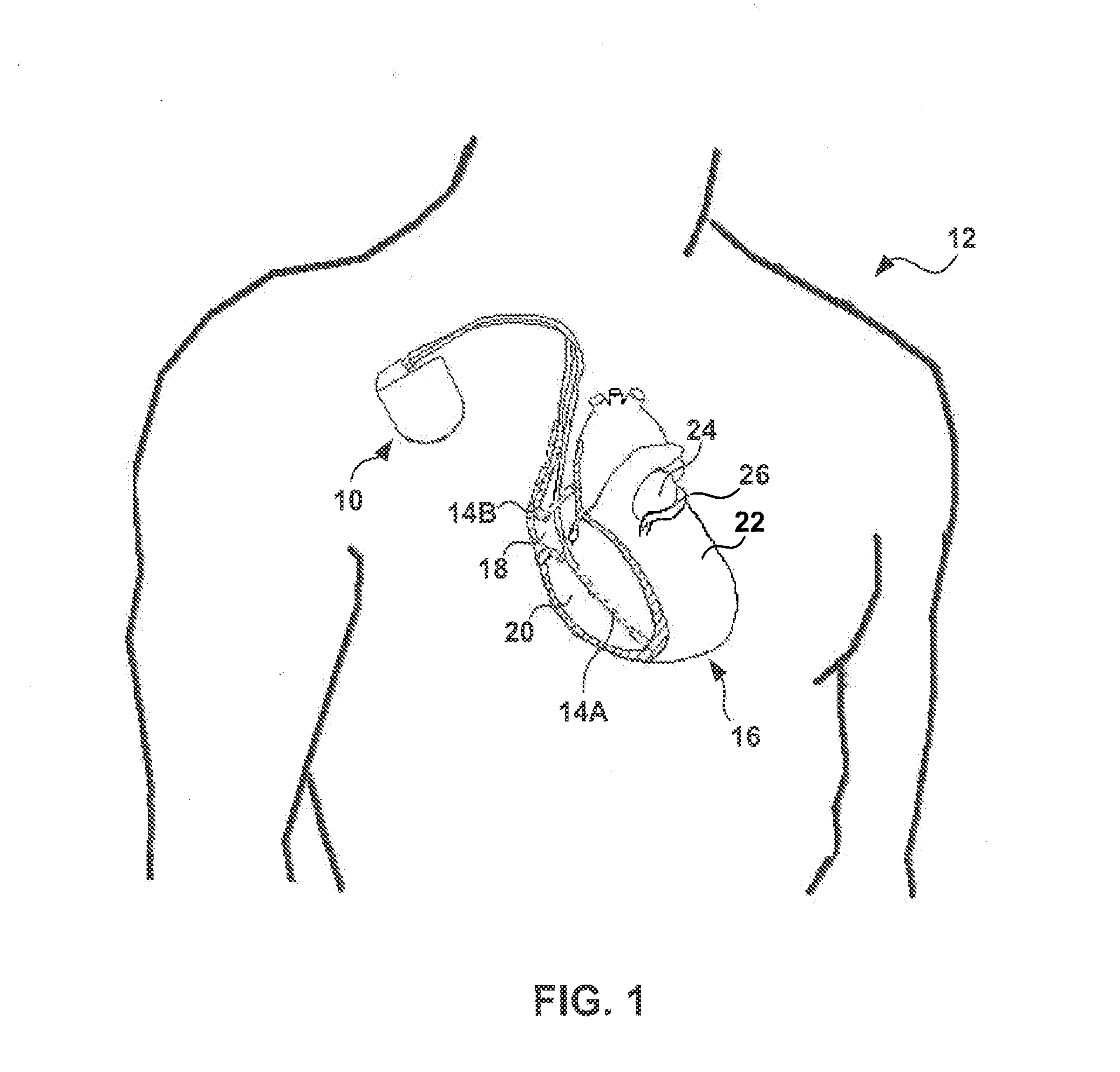
Implantable medical device and method for lv coronary sinus lead implant site optimization
InactiveUS20080249585A1Ease of evaluationTransvascular endocardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsCoronary sinusHemodynamics
A device is connected to electrode leads which performs intracardiac impedance measurements, conducts a transient pacing protocol, analyses the impedance measurements, and generates an LV lead position quality factor. The transient pacing protocol includes a repeated change (“transitions”) between ventricular intrinsic rhythm and biventricular paced rhythm and may also include a variation of the atrioventricular delay (AVD) and / or the interventricular delay (VVD). The quality factor expresses the degree to which hemodynamic properties have improved due to BiV stimulation for the current LV lead position compared to intrinsic ventricular rhythm.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
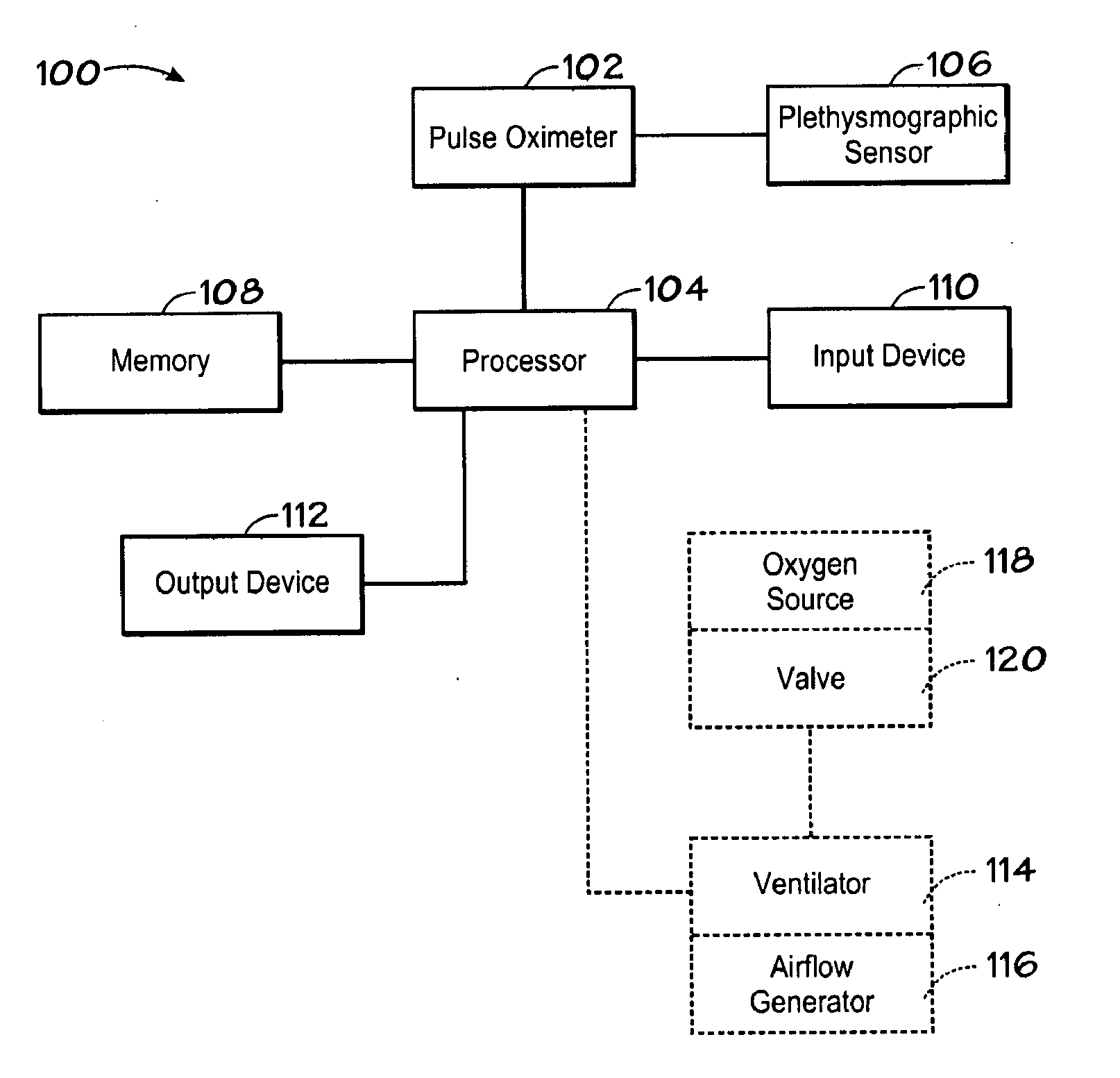
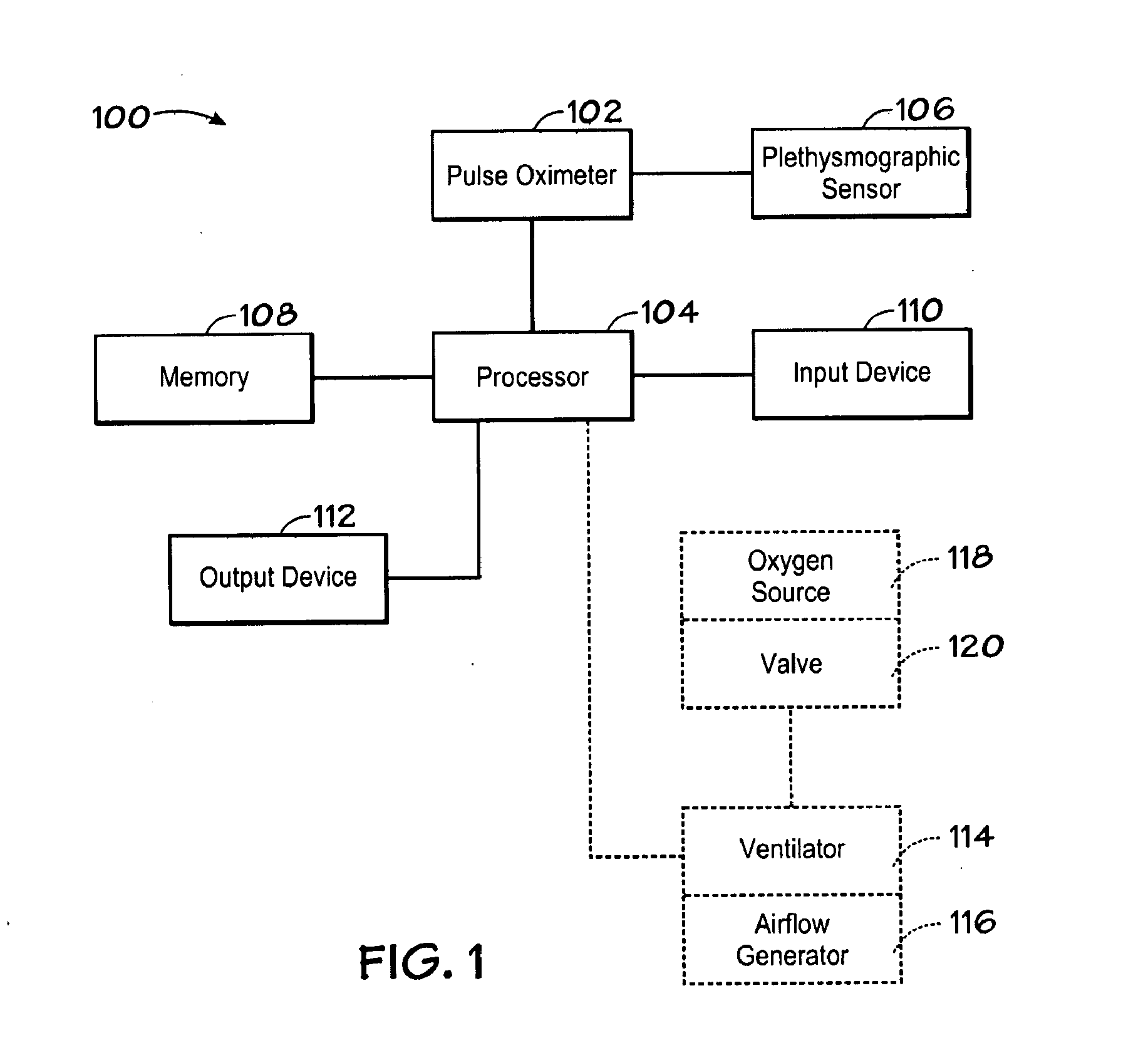
Alarm Processor for Detection of Adverse Hemodynamic Effects of Cardiac Arrhythmia
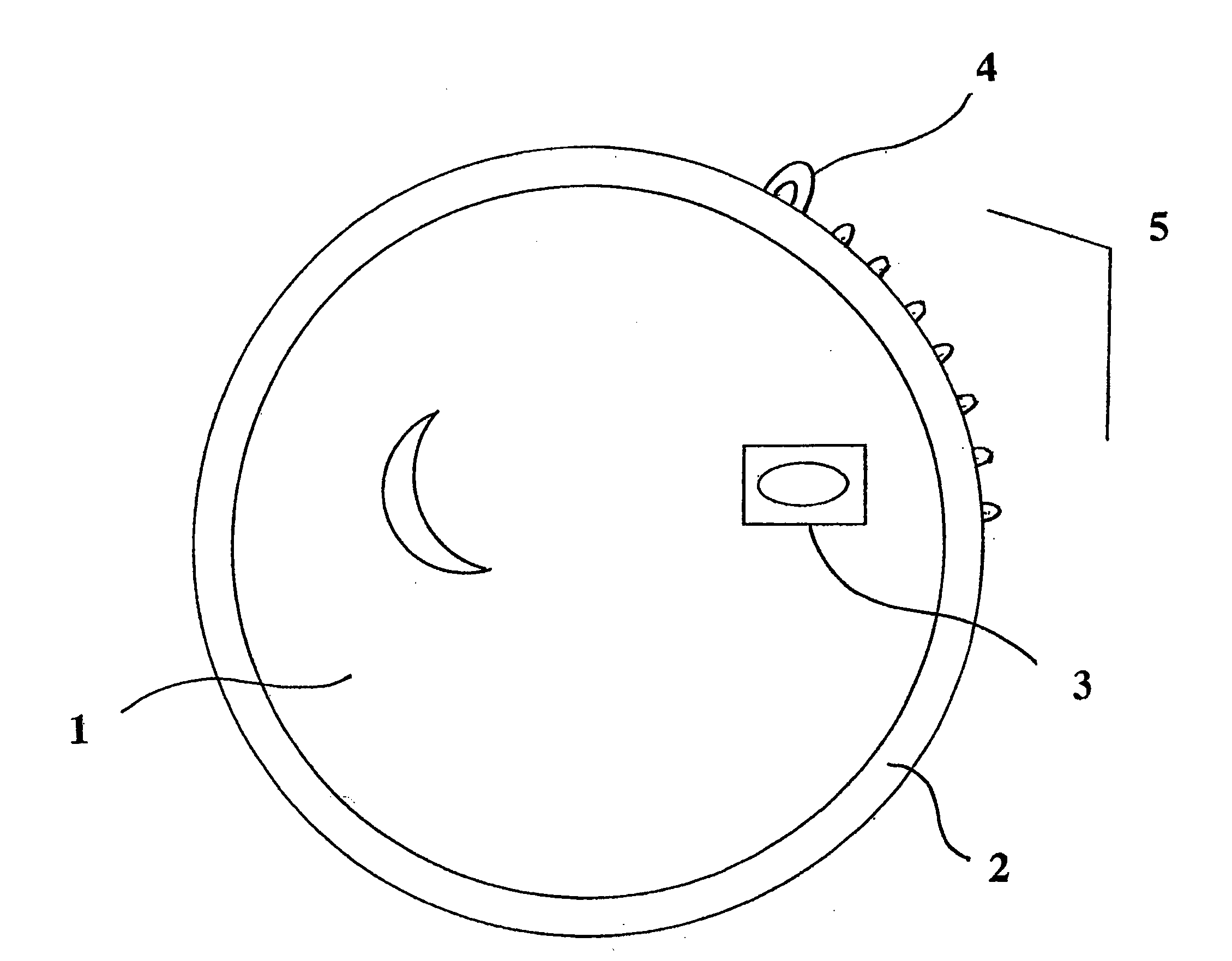
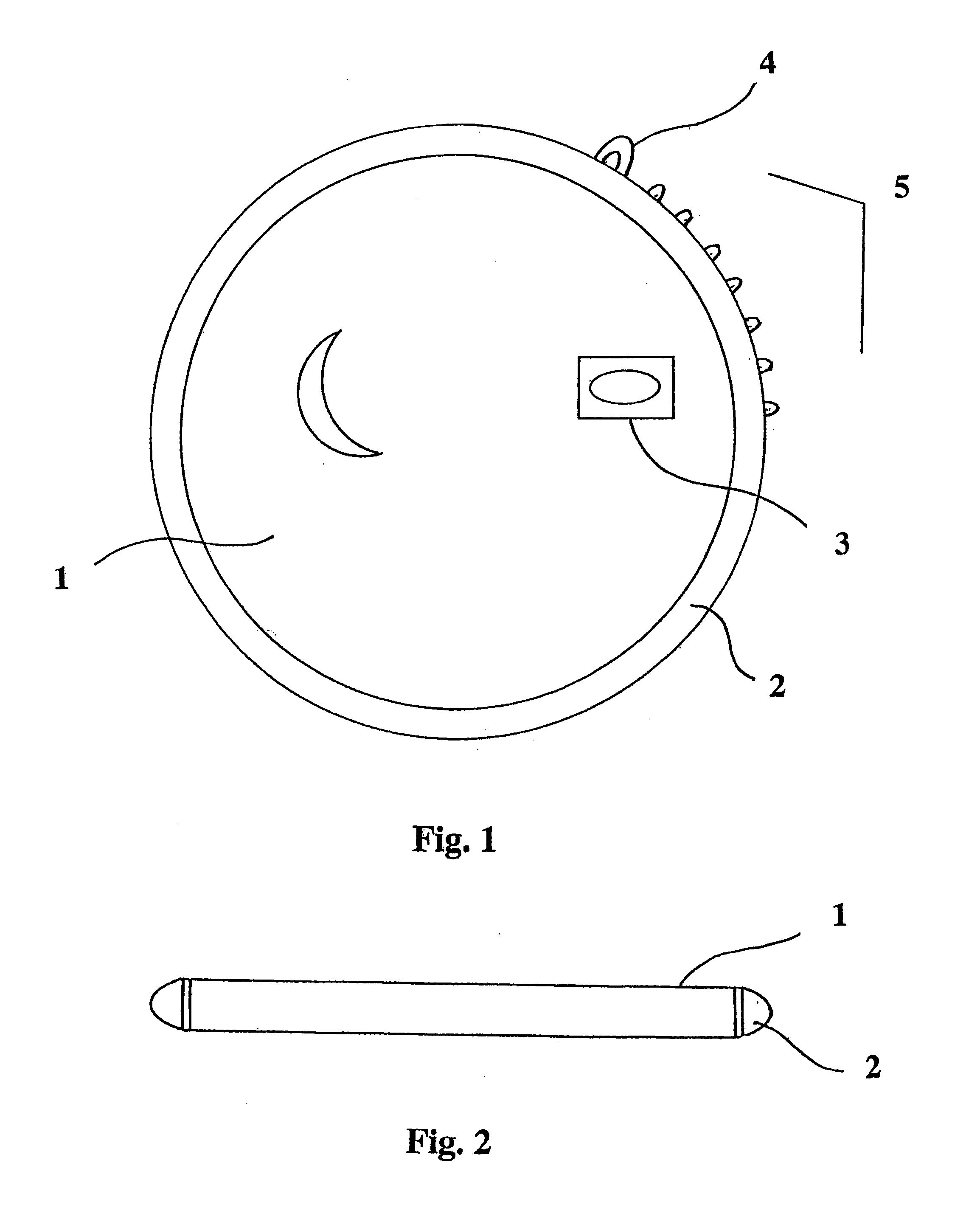
The disclosed embodiments relate to an apparatus and method for providing a warning. In one example, an apparatus includes a sensor, which is configured to be coupled to a body of a patient and to output a photoplethysmograph signal, which is indicative of pulse waveforms in the body. The apparatus also includes a processor, which is coupled to process the photoplethysmograph signal so as to identify sequential pulse waveforms in the signal, the processor detecting a cardiac arrhythmia based on identifying a shape feature of the pulse waveform occurring simultaneously with a change in rate or rhythm of the pulse waveforms or an electrocardiographic waveform, and to output a warning responsive to the simultaneous occurrence.
Owner:LYNN LAWRENCE A
Vibrational delta and theta brain wave induction apparatus and method for the stimulation of sleep
InactiveUS20100168503A1Improve efficiencyIncrease influenceMedical devicesSleep inducing/ending devicesPower flowTransducer
An apparatus and method for generating sleep-inducing stimuli, including a programmable controller operable for generating a sleep-inducing rhythm; and a transducer unit containing at least one transducer connected to the controller for receiving the sleep-inducing rhythm and generating and applying the sleep-inducing stimuli to a user in accordance with the rhythm. The stimuli may be in the form of vibration, warmth, light, sound, and / or electrical current. The stimuli are adapted to induce alpha, theta, and / or delta brain waves to induce sleep.
Owner:SUNNEN GERARD V
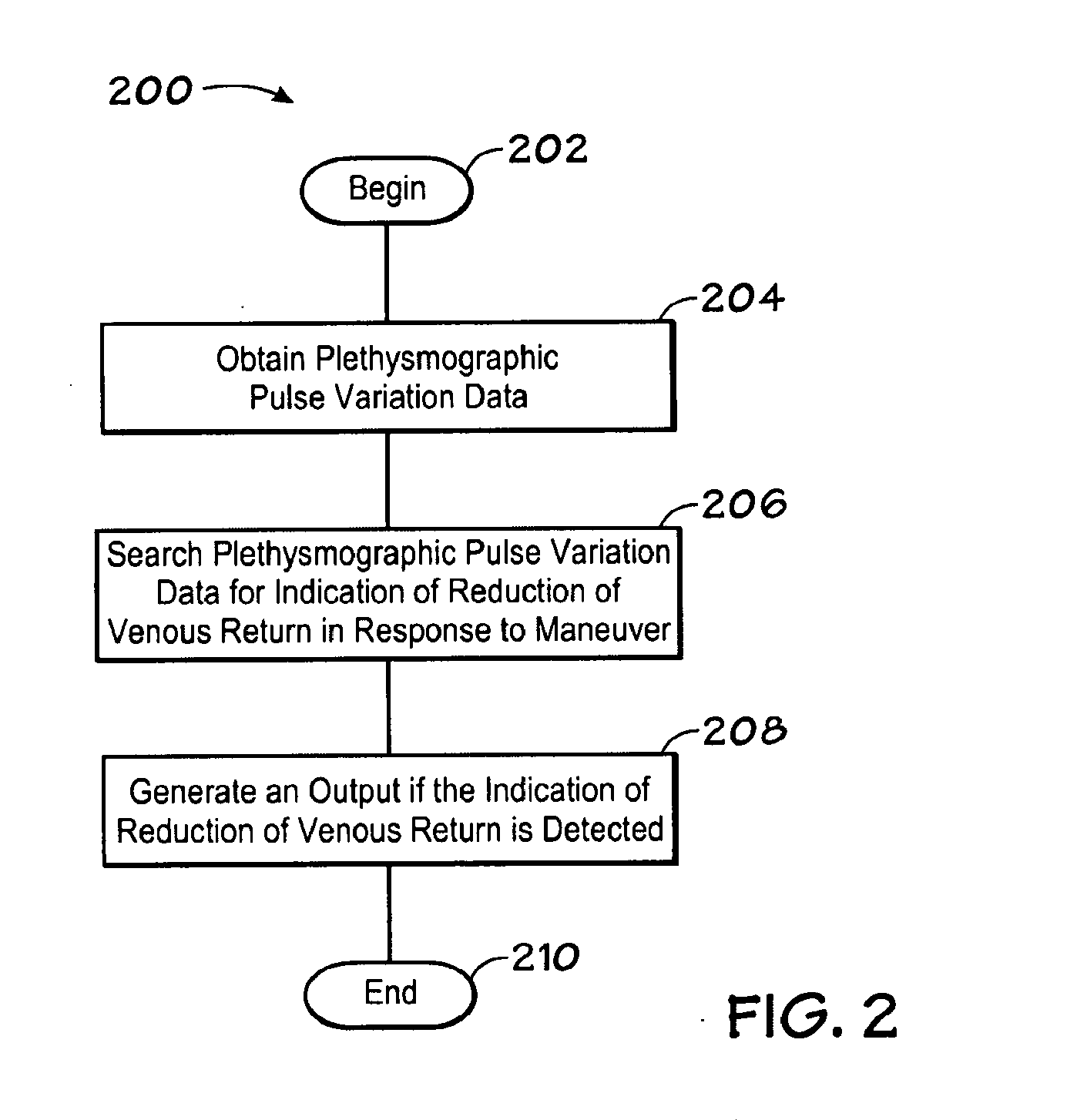
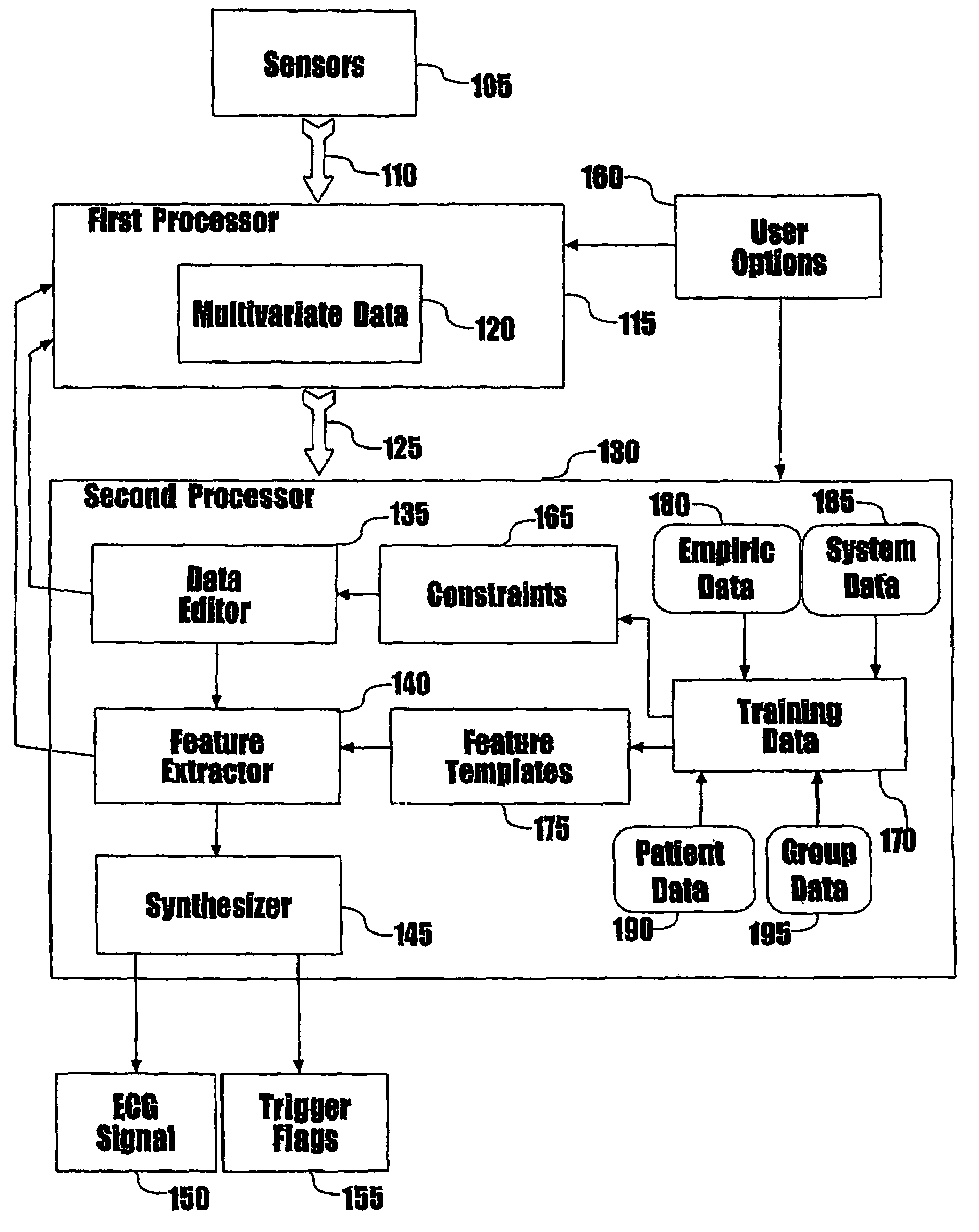
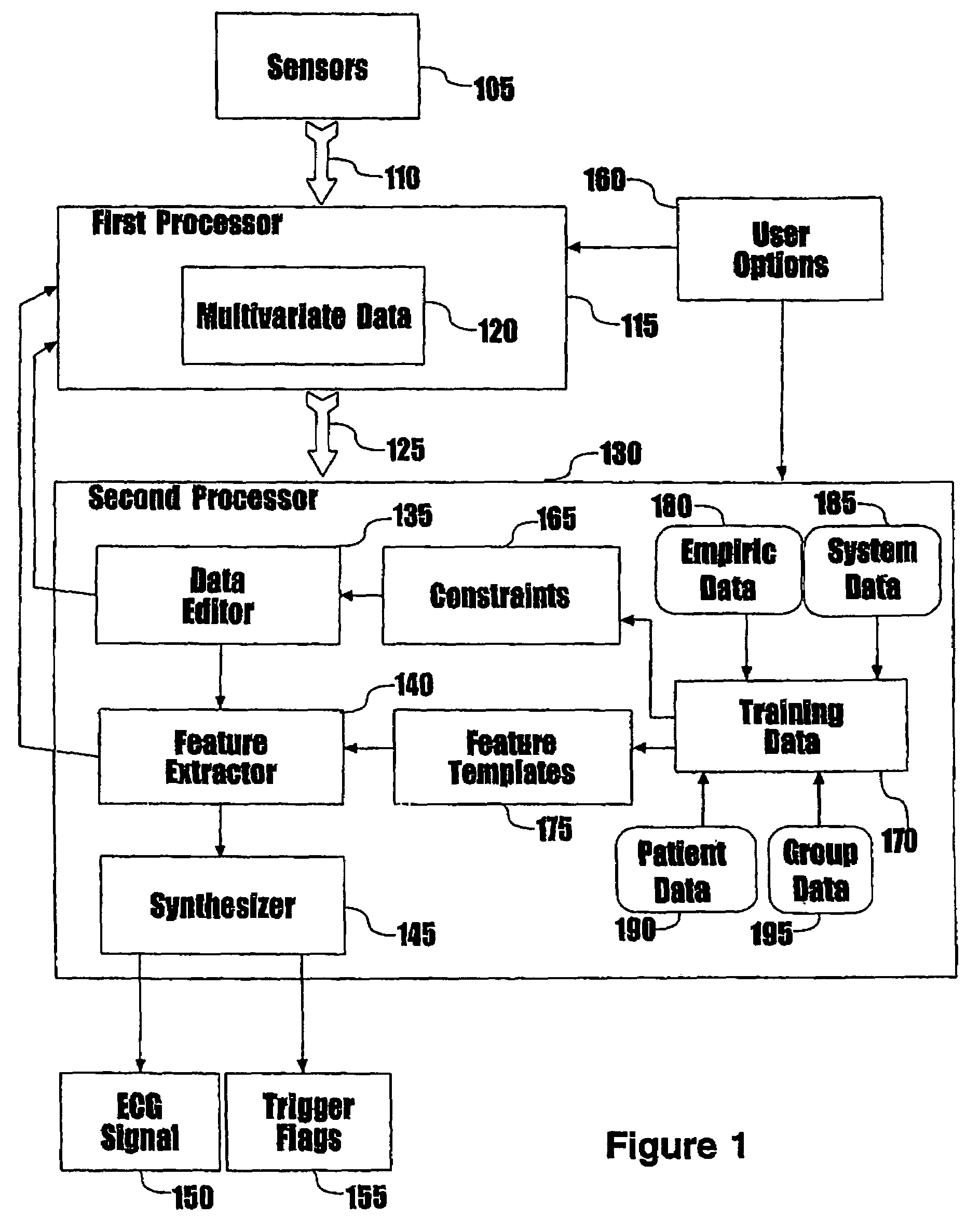
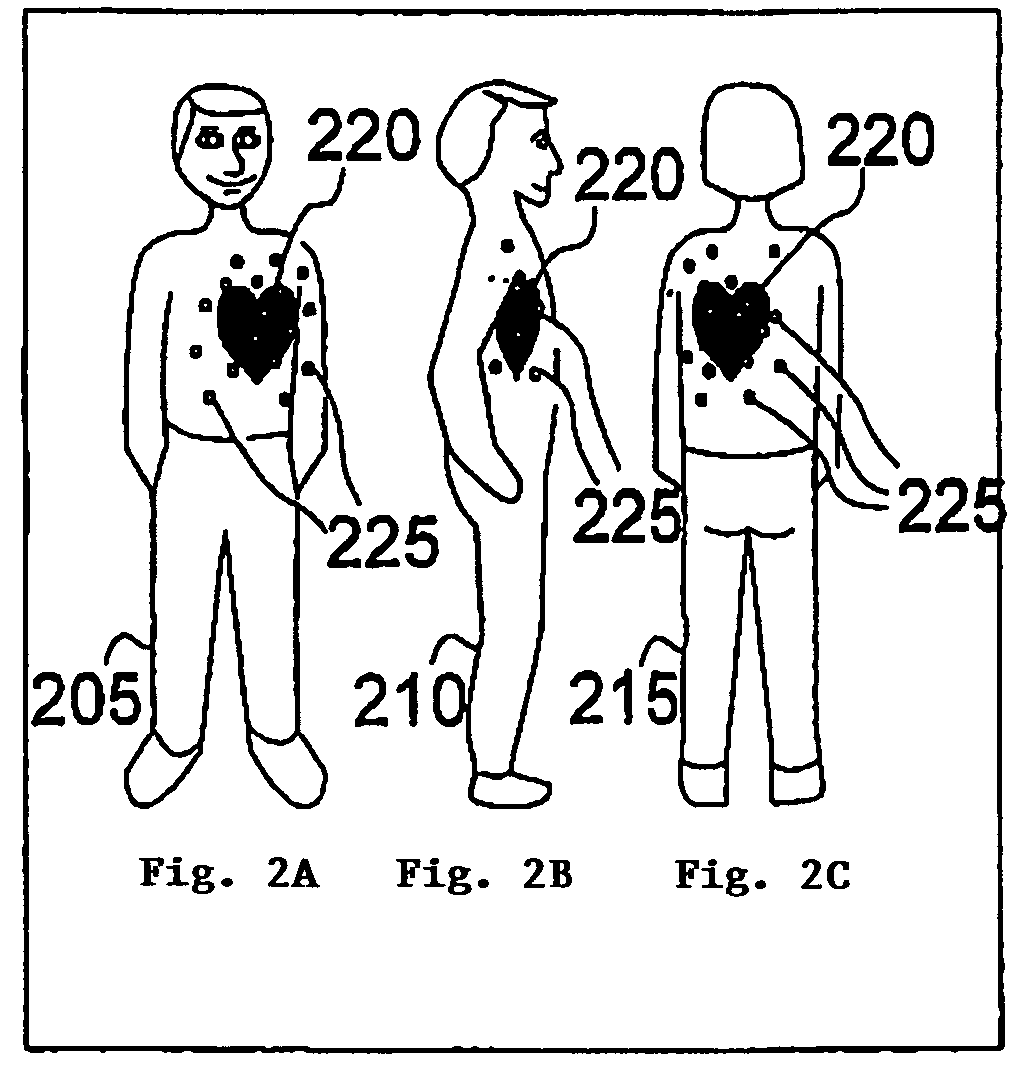
Method of and system for signal separation during multivariate physiological monitoring
InactiveUS7572231B2Quick placementThe process is simple and fastMedical data miningElectrocardiographyRespiratory triggeringPosterior chest
Multiple electrode contacts make electrical connections to the anterior and / or posterior chest for multivariate characterization of the electrical activation of the heart. A central processing unit derives synthetic composite electrographic signals as well as flag signals for specific purposes. A preferred embodiment uses this system to trigger or gate magnetic resonance imaging, eliminating or reducing problems from small or inverted R-waves, lead detachment, noise, flow signal, gradient changes, and rhythm changes, more reliably flagging the onset of electrical activation of the ventricles. Additional derived data are ST-segment shifts, filling times, and respiratory cycle. Filling times may be used for greatly improved imaging in the presence of rhythm disturbances, such as atrial fibrillation. Respiratory cycle may be used as a respiratory trigger to control for the effects of breathing on the heart position and image quality.
Owner:PEARLMAN JUSTIN D
Reducing inappropriate delivery of therapy for suspected non-lethal arrhythmias
ActiveUS20110172727A1Reducing inappropriate delivery of therapyAvoid delayElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsMedical deviceMedical treatment
An implantable medical device (IMD) identifies suspected non-lethal ventricular arrhythmia, and takes one or more actions in response to the identification to avoid or delay delivery of a defibrillation or cardioversion shock. The IMD employs number of intervals to detect (NID) thresholds for detection of ventricular arrhythmias. When a NID threshold is met, the IMD determines whether the ventricular rhythm is a suspected non-lethal rhythm despite satisfying a NID threshold. In some embodiments, the IMD increases the NID threshold, i.e., extends the time for detection, in response to identifying a rhythm as a suspected non-lethal rhythm, and monitors subsequent ventricular beats to determine if the increased NID threshold is met before detecting a ventricular arrhythmia and delivering therapy. The IMD can determine whether a rhythm is a suspected non-lethal arrhythmia by, for example, comparing the median ventricular cycle length (VCL) to the median atrial cycle length (ACL).
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
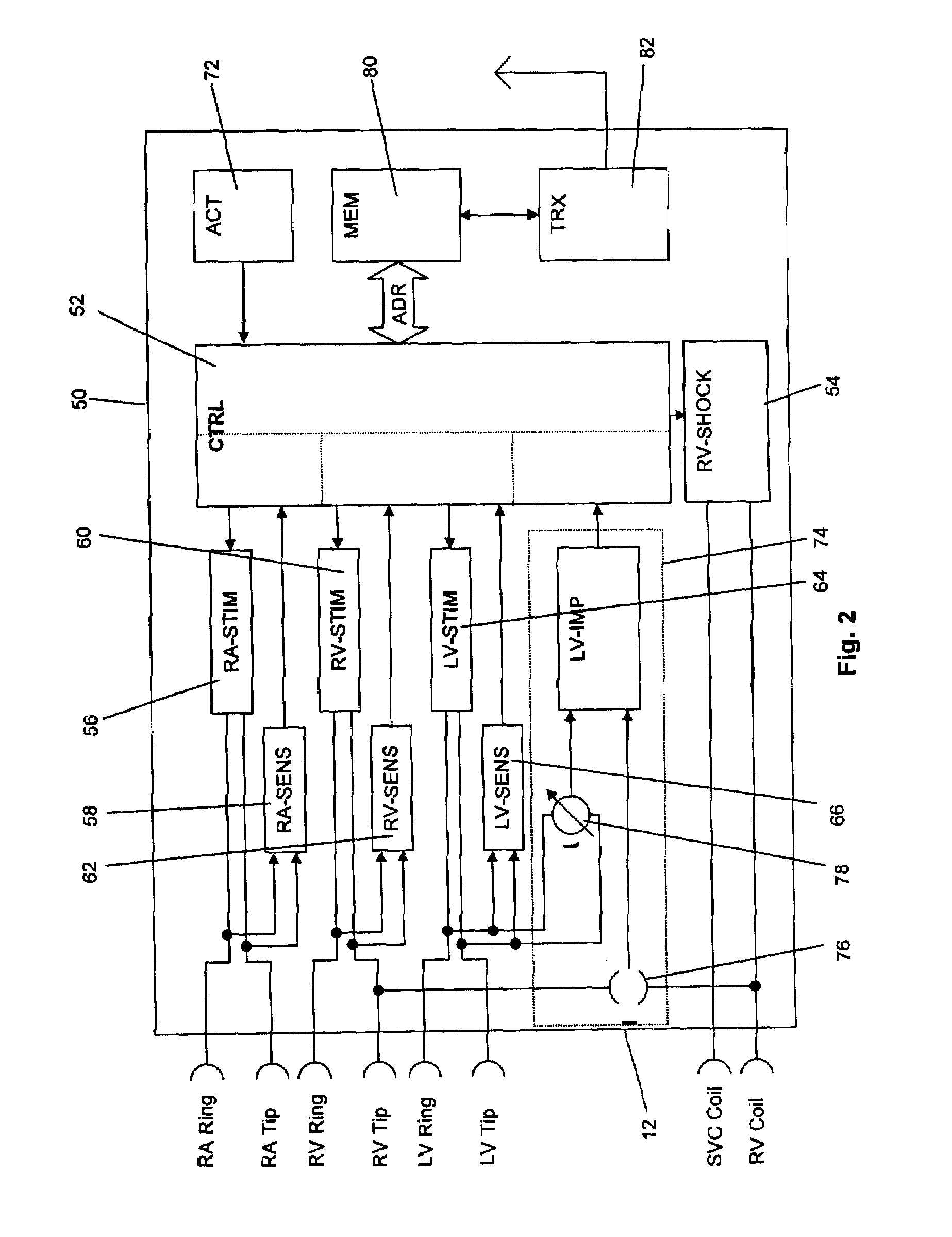
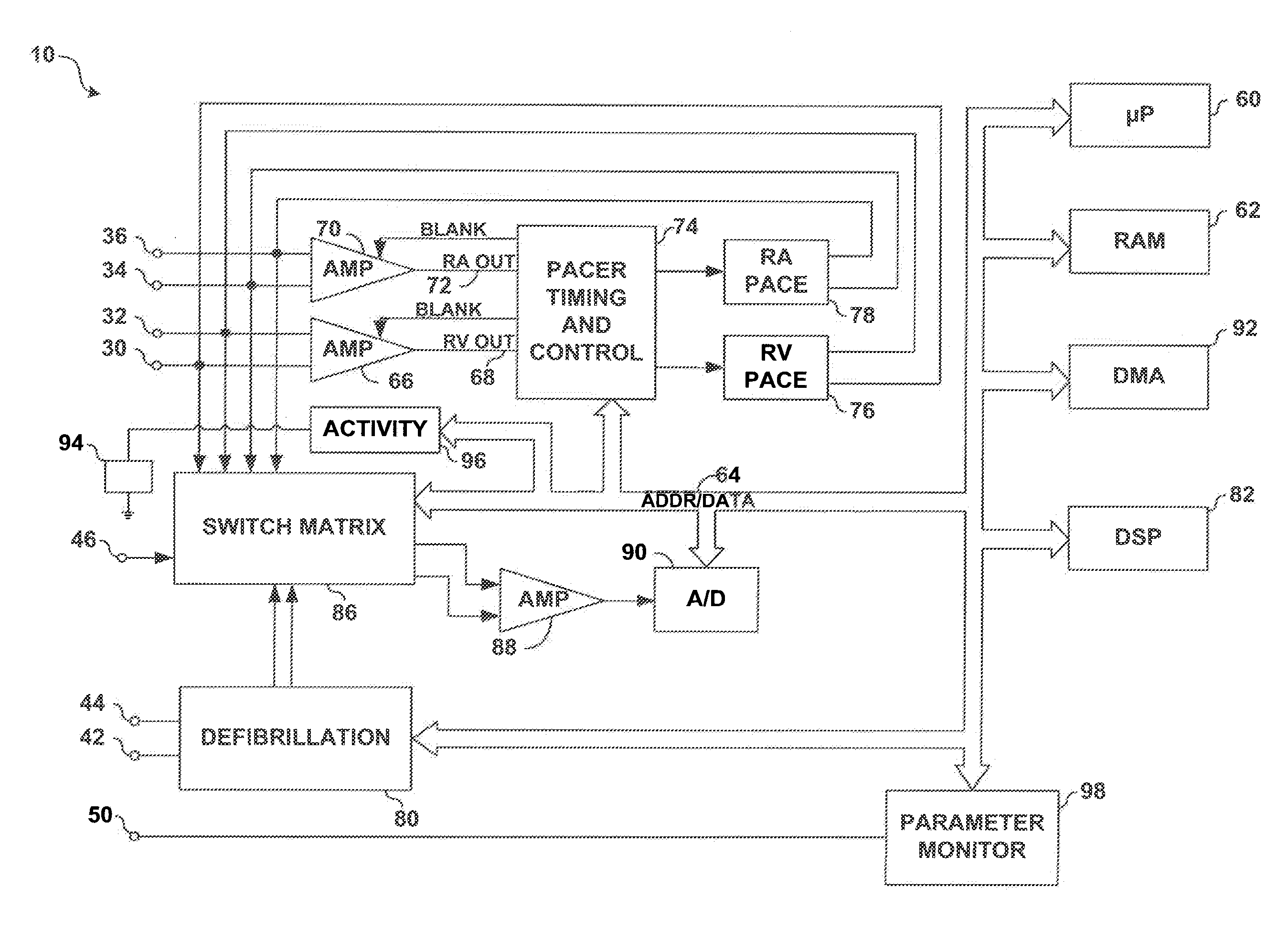
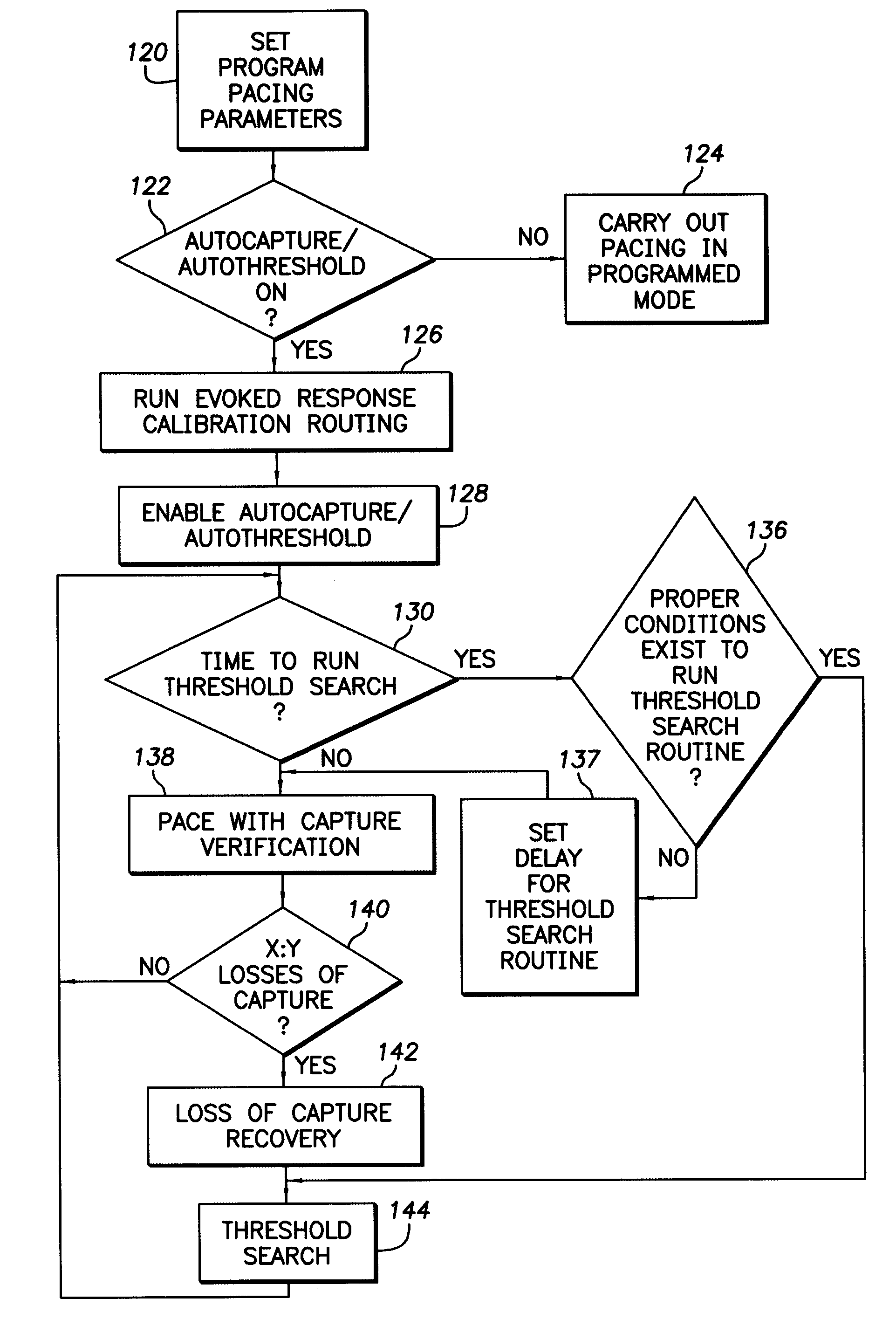
Implantable cardiac stimulation device having autocapture/autothreshold capability
An improved system and method for performing autocapture / autothreshold detection in an implantable cardiac stimulation device or any device capable of stimulating some organ or tissue in the body. In some existing systems, loss-of-capture and capture decisions are based upon two consecutive cardiac events. However, such systems may be subject to subthreshold stimulation pulses that capture and lose capture on alternating pulses, trigeminy PVC sequences, or the like that require a higher stimulation pulse amplitude but cannot make this determination due to the two consecutive event requirement. Accordingly, in the present invention, the determination of whether there is a loss-of-capture is determined only according to paced events, i.e., ignoring intrinsic and PVC beats. Furthermore, the loss-of-capture determination is based upon X out of the last Y beats, where Y is greater than 2 and X is less than Y. Accordingly, consecutive loss-of-capture events are no longer required in determining the threshold level. In a further aspect, a preferred embodiment monitors cardiac events to detect a sequence of patterns that could indicate a trigeminy pattern and, if detected, the pacing rate is increased to attempt to break the pattern and thus permit the threshold level to be detected.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
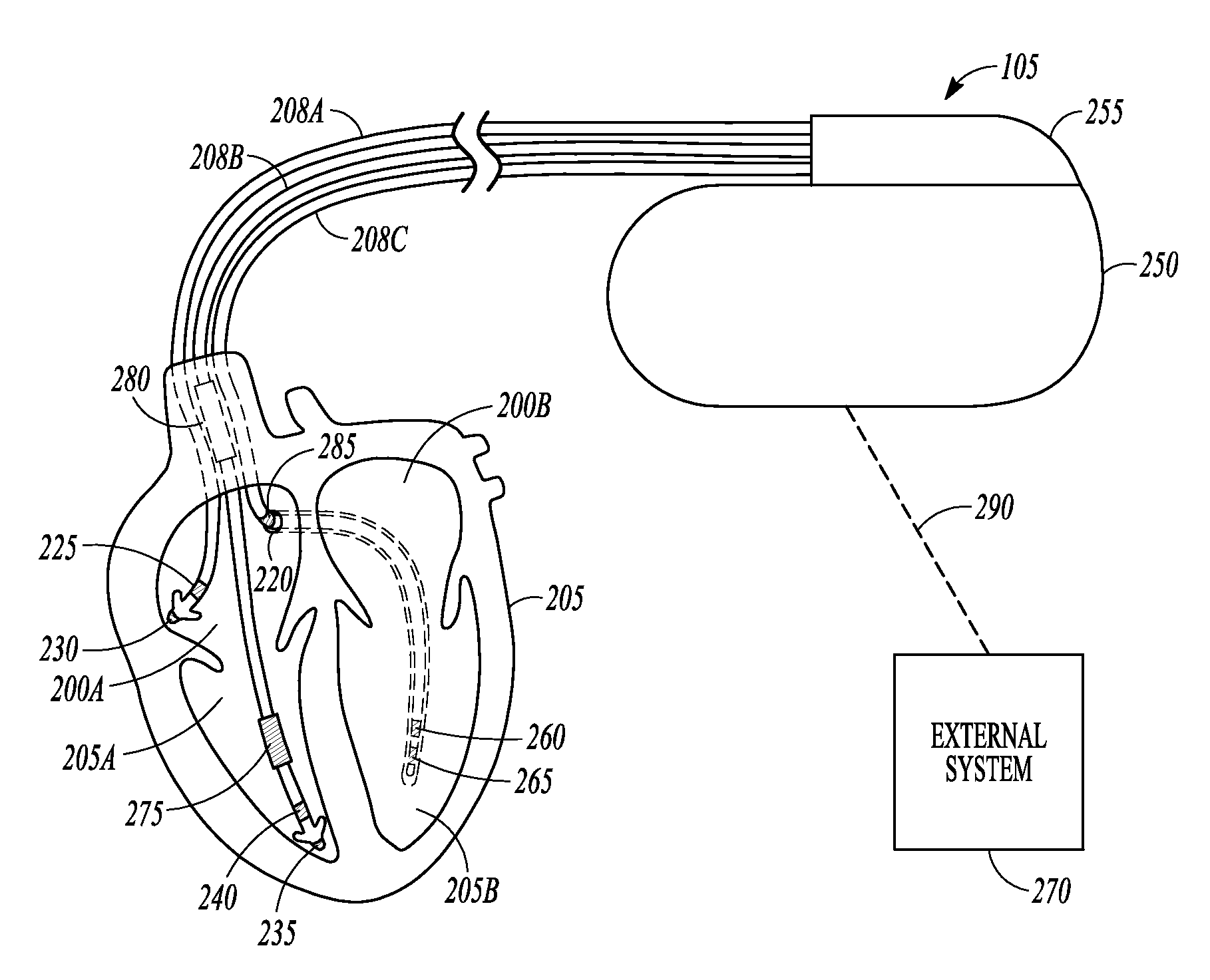
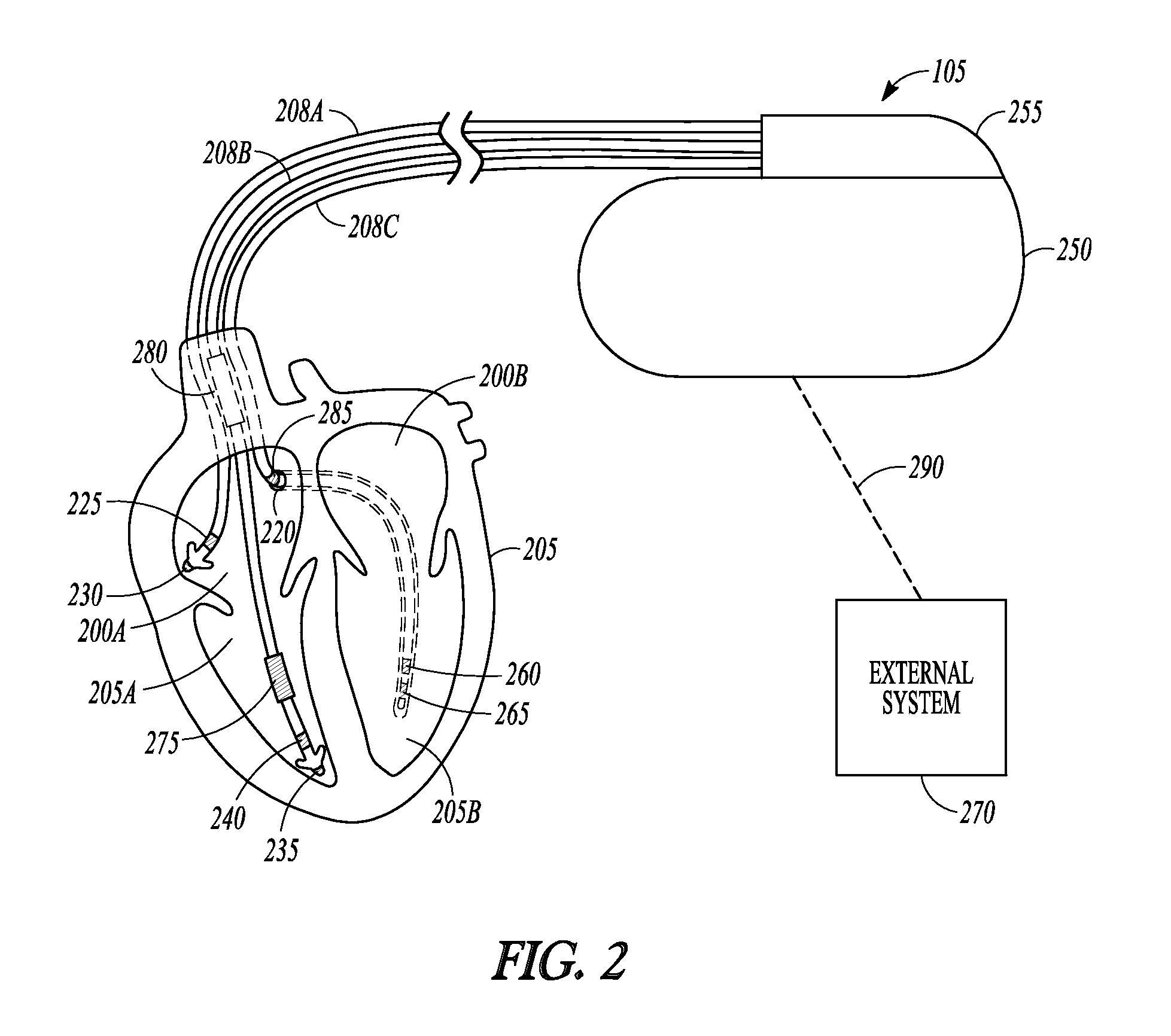
Rhythm discrimination using information indicative of lead motion
Systems and methods for rhythm discrimination using the motion of an implantable lead are described. In an example, an implantable medical device can include a receiver circuit configured to be electrically coupled to an implantable lead and be configured to obtain information indicative of a movement of the implantable lead due at least in part to a motion of a heart. The device can include an arrhythmia detection circuit configured to determine an arrhythmia status using the information indicative of the movement of the implantable lead and an arrhythmia classification circuit configured to determine one or more of a location or a type of an arrhythmia, using the information indicative of the movement of the implantable lead, when the arrhythmia status indicates that an arrhythmia is occurring or has occurred.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Systems and methods for cardiac rhythm variability analysis
Systems and methods are provided for the study of the cardiac rhythm variability. These systems and methods include the recording of the electrocardiogram (EKG), with subsequent calculation of the duration of the beat-to-beat intervals (i.e., R-R intervals), drawing up of the rhythmograms, and additional systems and methods that include determination of, throughout all observation times within particular intervals included in the recording periods, the average values of the informational entropy of the beta-distribution (AE) of the R-R intervals, the differences between the maximum and minimum values of the informational entropy of the beta-distribution (MDE) of the R-R intervals, the root-mean-square deviations of the informational entropy of the beta-distribution (RMSDE) of the R-R intervals, and / or variation factors of the informational entropy of the beta-distribution (VFE) by means of calculation of the informational entropy of the beta-distribution of the R-R intervals.
Owner:INFOTRANS US
Apparatus for inducing energies of alpha rhythm to the human body
Alpha rhythm brain waves are related to mental and physical relaxation and healing. Based on the studies of bionics, this invention relates to inducing oscillatory alpha rhythm to the human body, and relates to the means of the alpha rhythm machine applied to human body. Research of the alpha rhythm of human brain wave patterns and EEG has indicated special recorded data of alpha rhythm brain waveform which is the bearing of the proper biological information of relaxing and healing. The apparatus was developed and built to construct and release the simulated human brain alpha rhythm signals which are at the frequencies ranging 8 Hz–14 Hz and at the amplitudes altered in high or low. Both the frequencies and the amplitudes are changing at a non-stationary random order in the duration of the event, respectively. The electrical signals are transformed via a transducer, into three forms of energy, 1, alpha rhythm electromagnetic energy and alpha rhythm interfering static magnetic energy; 2, alpha rhythm sub-audio acoustic oscillatory energy; and 3, alpha rhythm mechanical vibrational energy. The combining energies from the apparatus can benefit the whole human body or only the area affected by illness, for example, treating men's prostate problems or treating sleep disorders.
Owner:WANG XIAOMING +2
Treatment of cardiac arrhythmia utilizing ultrasound
A noninvasive or minimally invasive treatment of cardiac arrhythmia such as supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias, specifically atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia, by treating the tissue with heat produced by ultrasound, including High Intensity Focused Ultrasound or HIFU, emitted without respect to the timing or phase of the cardiac cycle, intended to have a biological and / or therapeutic effect, so as to interrupt or remodel the electrical substrate in the tissue area that supports arrhythmia.
Owner:桑那丽声有限公司
Implantable medical device and method for LV coronary sinus lead implant site optimization
InactiveUS7844335B2Ease of evaluationTransvascular endocardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsCoronary sinusMedical device
A device is connected to electrode leads which performs intracardiac impedance measurements, conducts a transient pacing protocol, analyses the impedance measurements, and generates an LV lead position quality factor. The transient pacing protocol includes a repeated change (“transitions”) between ventricular intrinsic rhythm and biventricular paced rhythm and may also include a variation of the atrioventricular delay (AVD) and / or the interventricular delay (VVD). The quality factor expresses the degree to which hemodynamic properties have improved due to BiV stimulation for the current LV lead position compared to intrinsic ventricular rhythm.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Implantable medical device with ventricular pacing protocol
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Therapy-selection methods for implantable heart monitors
InactiveUS7440799B2Identify and treat abnormal rhythmic conditions both efficiently and accuratelyHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsFibrillationHeart monitoring
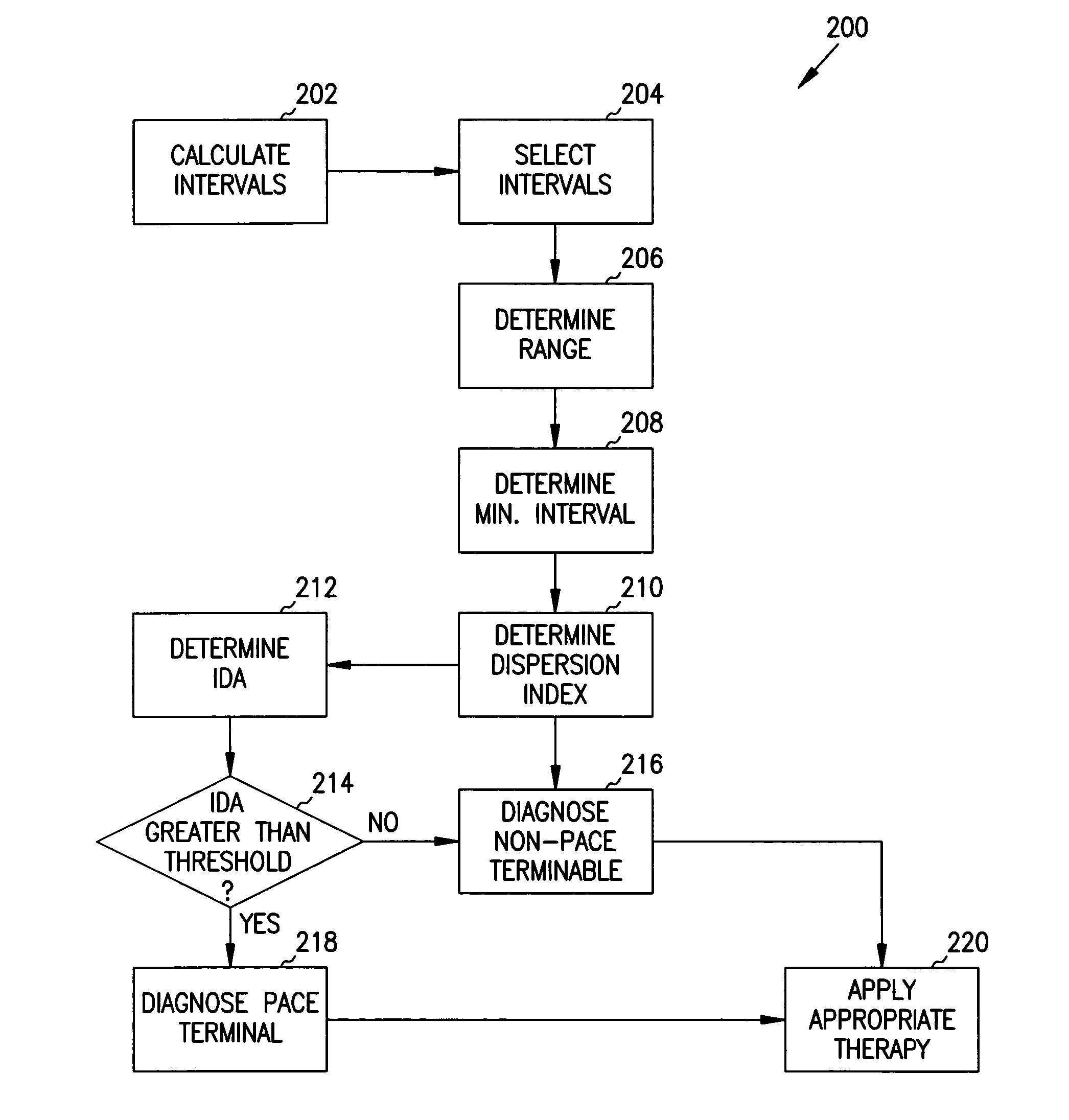
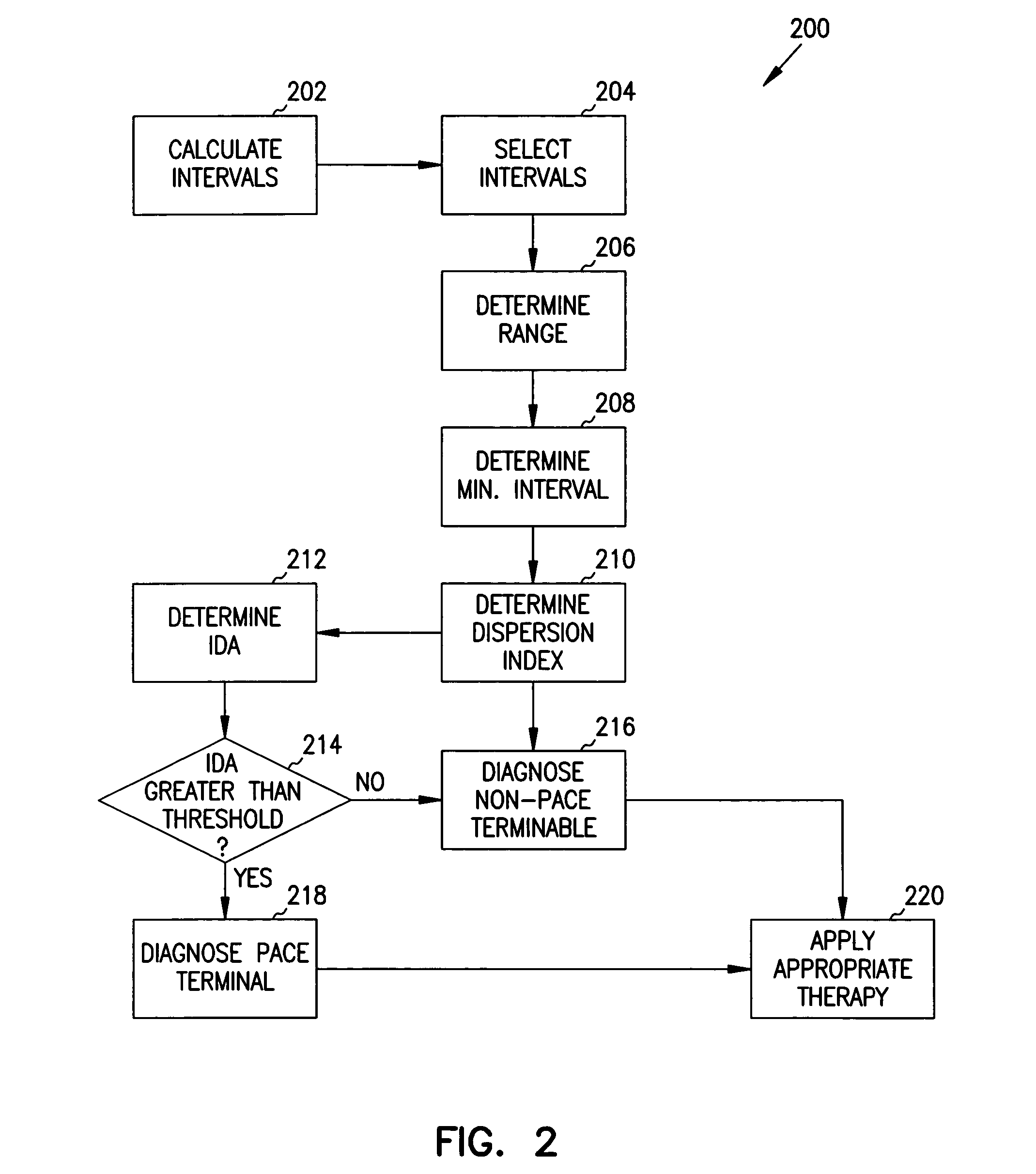
Miniature heart-monitoring devices, such as defibrillators and cardioverters, are implanted in humans to detect and correct abnormal heart rhythms Microprocessors and stored instructions, or algorithms within these devices govern how they interpret and react to abnormal heart rhythms. Algorithms that are too simple lead to unnecessary shocking of the heart, while those that are too complex consume considerable battery power. Accordingly, the inventor devised a relatively simple yet accurate algorithm for determining appropriate therapy options. One version of the algorithm computes three statistics—a range statistic, a minimum interval statistic, and a dispersion index—from a set of depolarization intervals. A scalar interval dispersion assessment, based on the three statistics, is then compared to a threshold to identify a rhythm as a flutter or fibrillation.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com