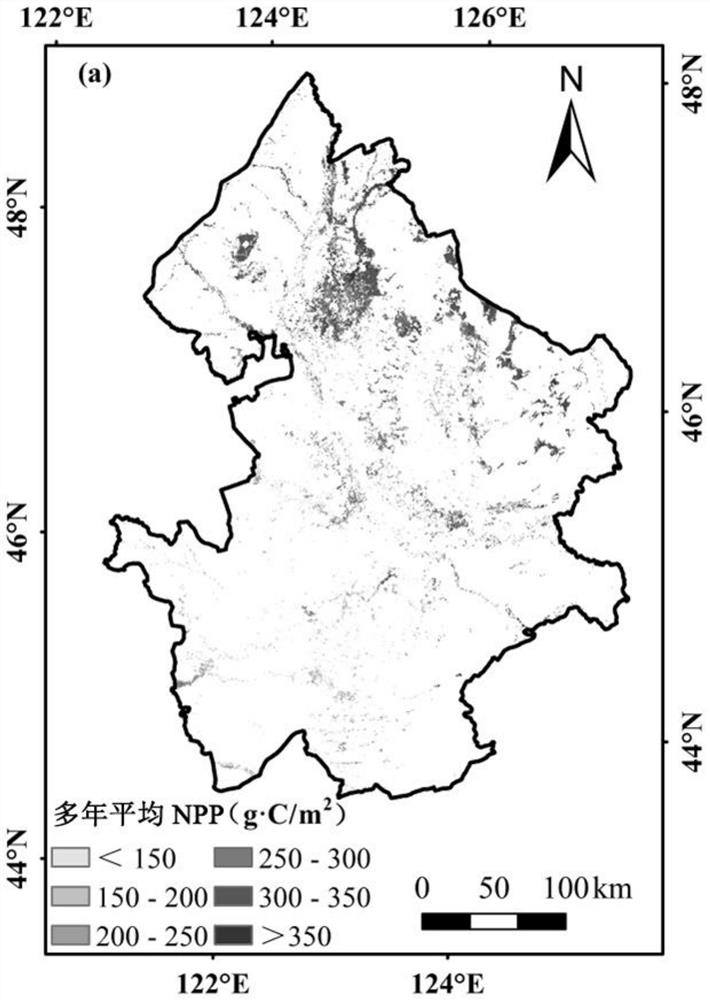
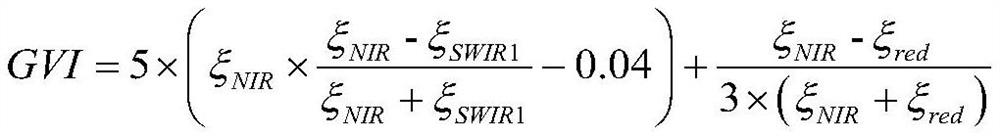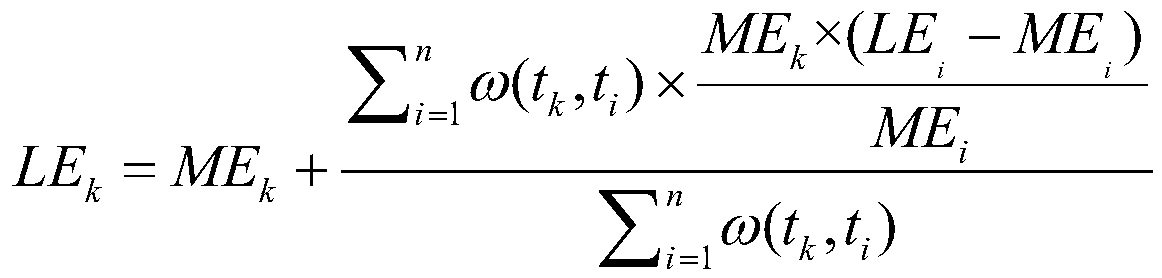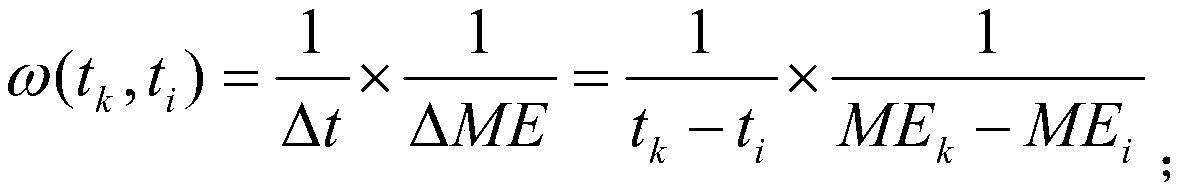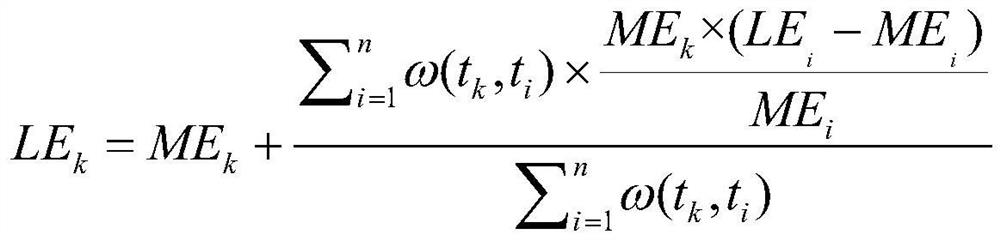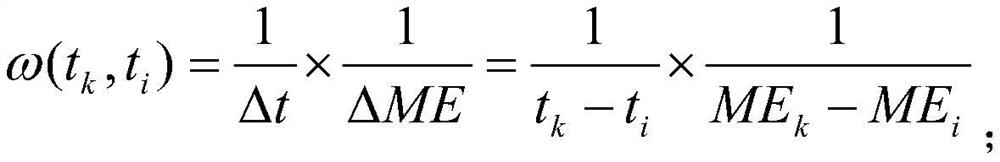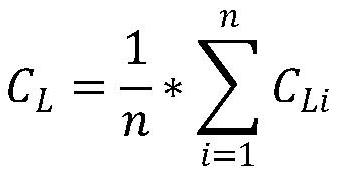Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Vegetation remote sensing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
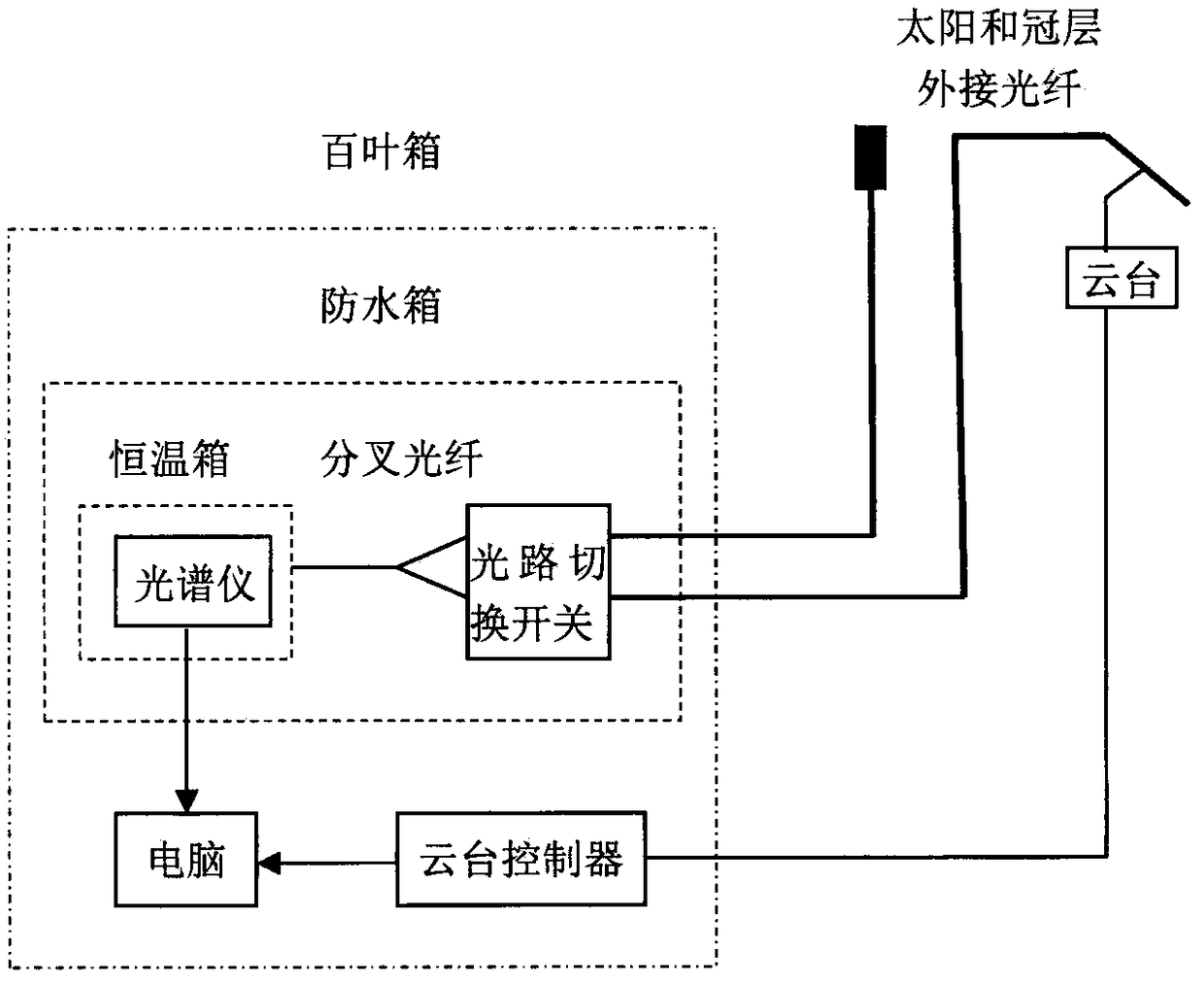
Remote sensing of vegetation is mainly performed by obtaining the electromagnetic wave reflectance information from canopies using passive sensors. It is well known that the reflectance of light spectra from plants changes with plant type, water content within tissues, and other intrinsic factors [10].
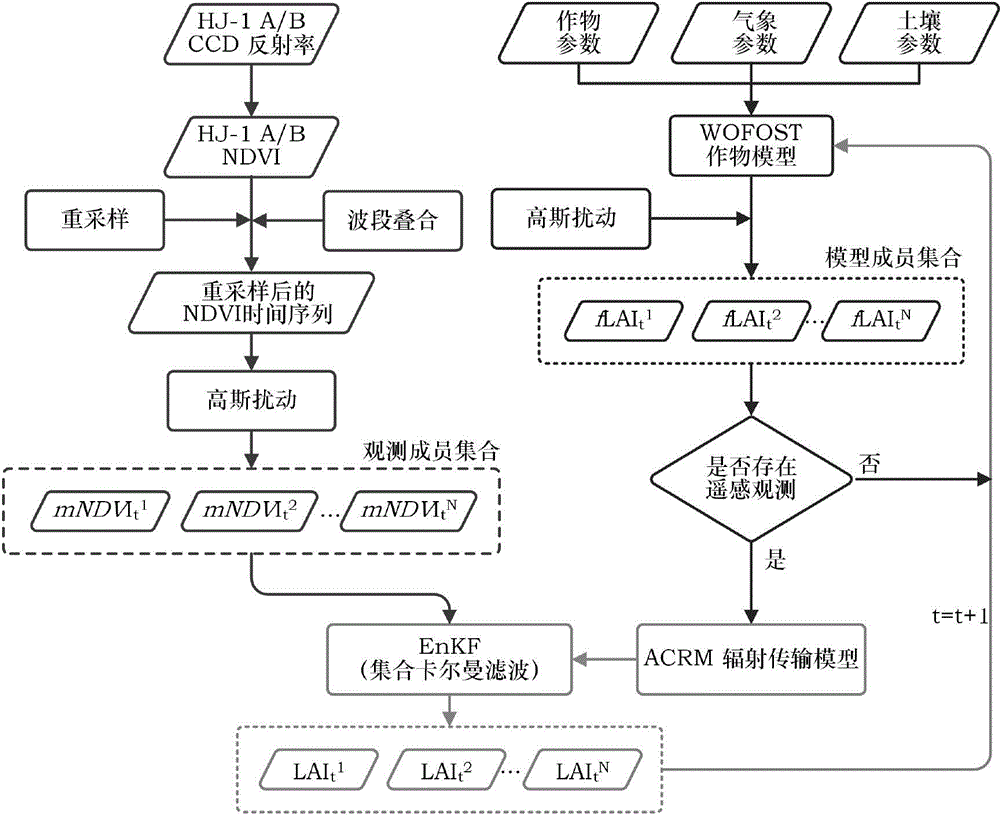
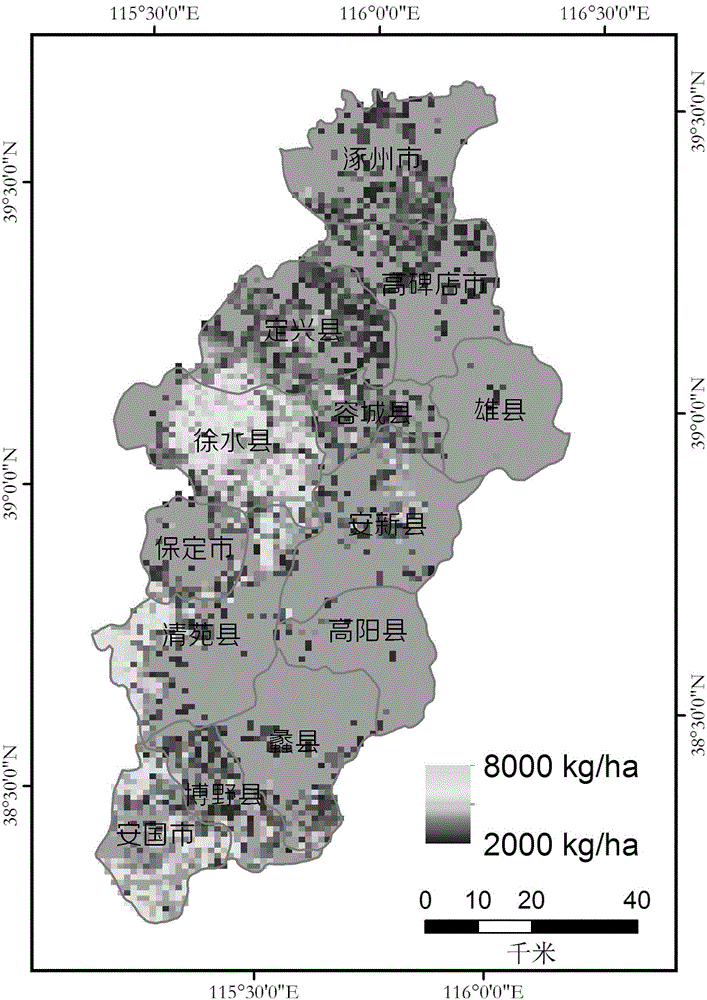
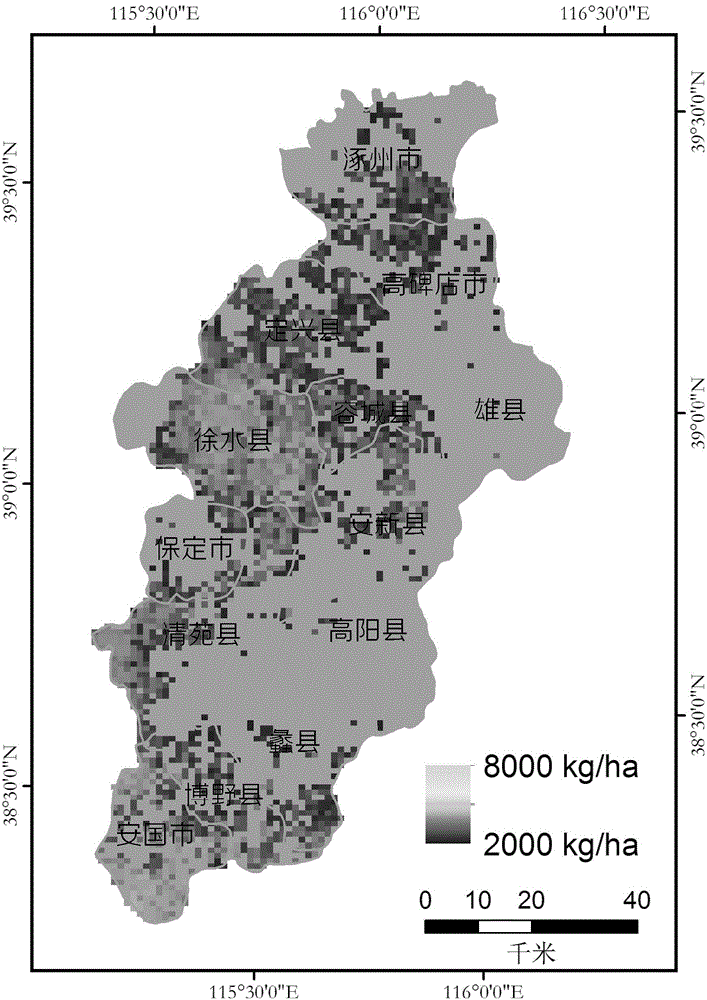
Regional crop yield estimation method based on ensemble Kalman filter assimilation
InactiveCN103955860AHigh precisionAssimilation realizationData processing applicationsSensing dataEstimation methods
The invention provides a regional crop yield estimation method based on ensemble Kalman filter assimilation. The advantages of remote sensing data and crop models are combined, EVIs generally used in vegetation remote sensing are used as observational variables, LAIs are used as assimilation variables, optimization adjustment is carried out on the model LAIs through an ensemble Kalman filter algorithm, a PROSAIL model is used as an observational operator, the problem that the observational variables and state variables are inconsistent is solved, assimilation of remote sensing information and the models is achieved, and errors due to the fact that inversion is carried out on the LAIs through reflectivity are avoided. Compared with the yield of crop with unassimilated EVIs, the RMSE of the yield of crop with the assimilated EVIs is reduced, the determination coefficient R2 is improved obviously, estimation precision of the crop model yield is obviously improved after assimilation, and the yield space distribution trend is consistent with the statistical yield.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
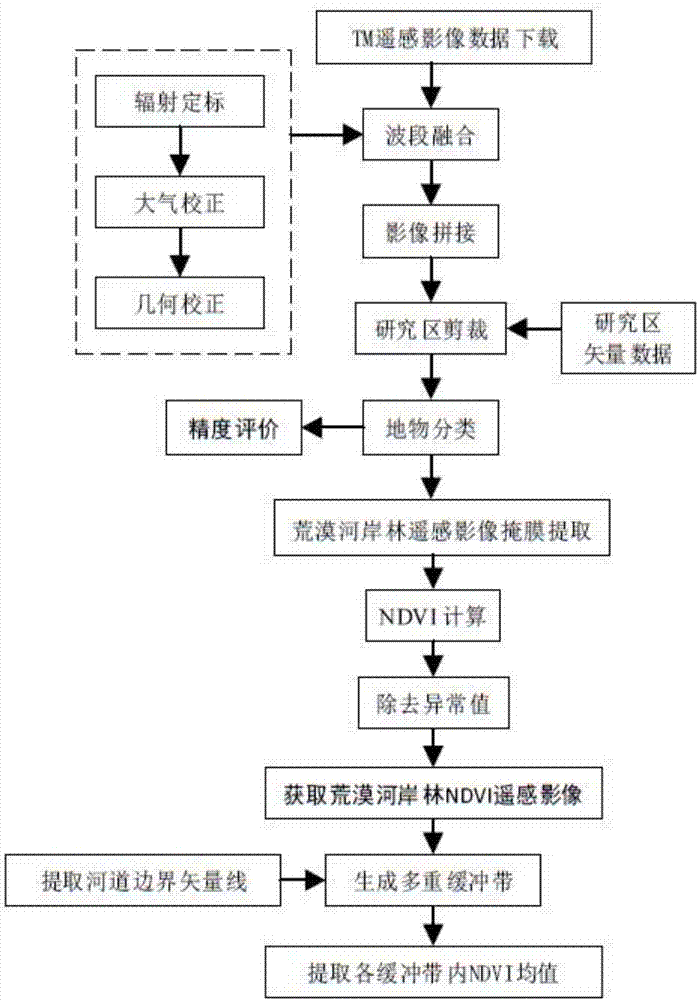
Desert riparian forest spatial distribution obtaining method based on GIS buffer area analysis
ActiveCN107145872ADynamic MonitoringImprove efficiencyImage enhancementDrawing from basic elementsVegetationSensing data
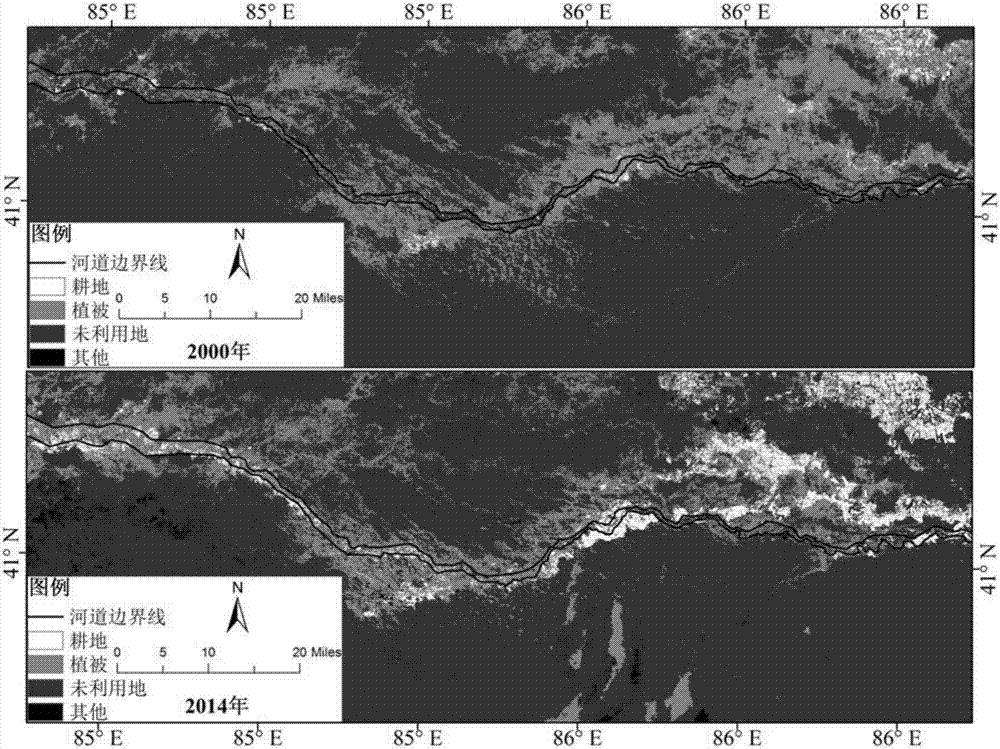
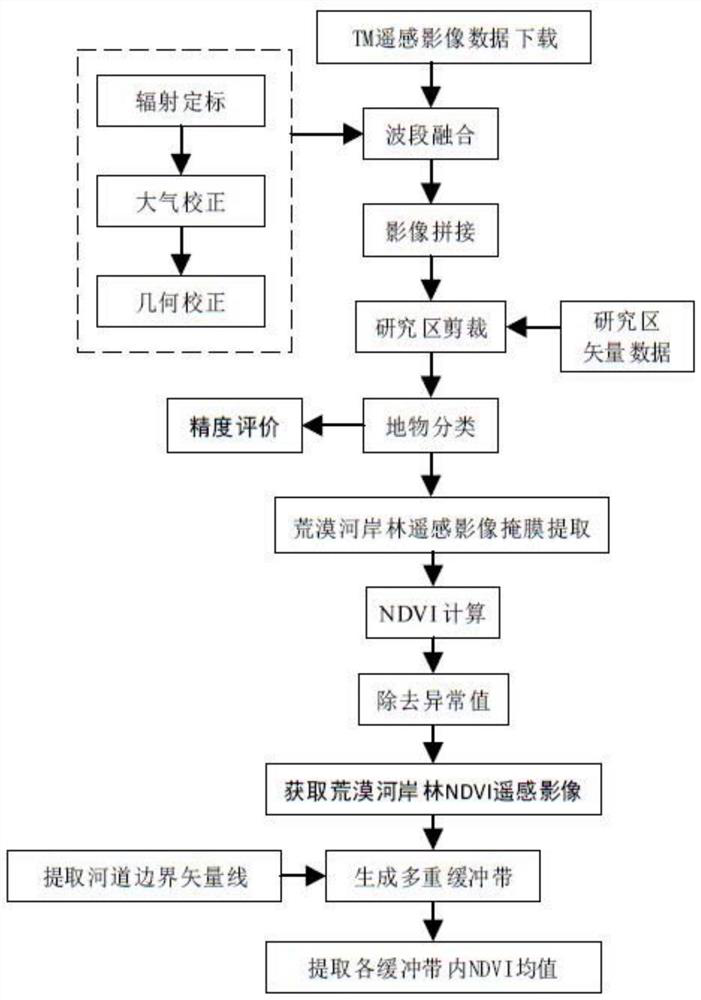
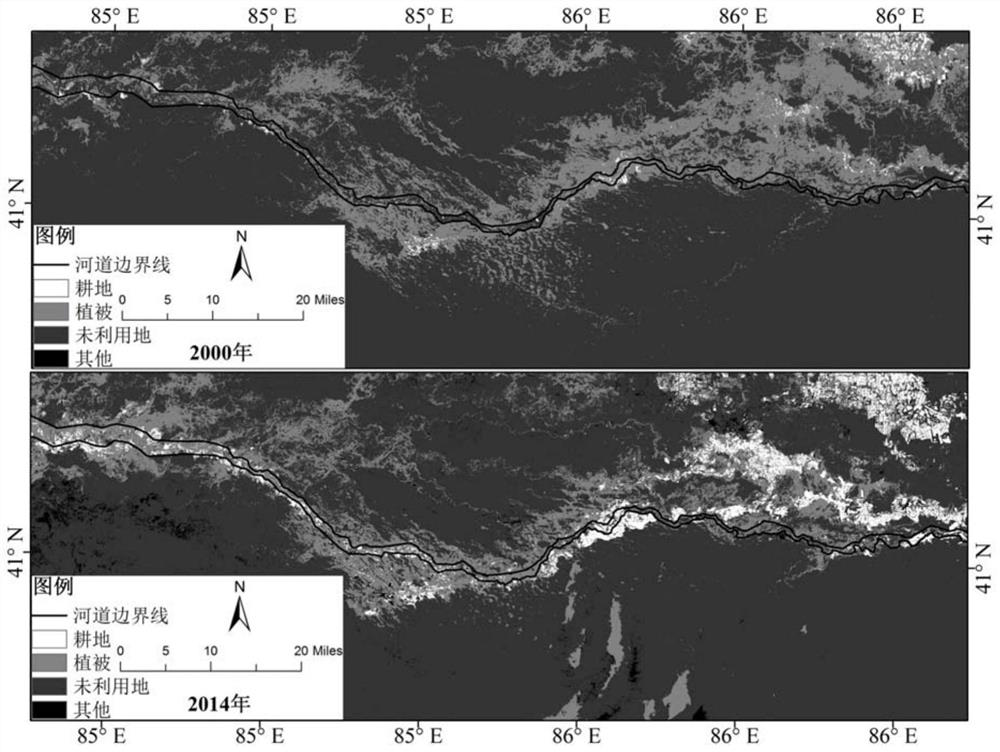
The invention discloses a desert riparian forest spatial distribution obtaining method based on GIS buffer area analysis, wherein the method belongs to the field of drought area vegetation remote sensing technology. The method comprises the following steps of a first step, downloading a TM remote sensing image of a location with a drought area river, performing image preprocessing, remote sensing interpretation and NDVI calculation on the remote sensing image, and obtaining NDVI remote sensing data of the desert riparian forest; a second step, extracting a riverbank boundary vector line, and performing unified registering and correction on the remote sensing image in a GIS platform; a third step, generating a riverway peripheral multiple-buffer-area vector picture according to a research requirement; and a fourth step, overlapping the multiple-buffer-area vector picture and the NDVI remote sensing data of the desert riparian forest, extracting an NDVI mean value in each buffer area, using a vertical riverawy distance as an independent variable and using the NDVI mean value as a dependent variable, and performing desert riparian forest spatial distribution structure analysis by means of curve fitting. The desert riparian forest spatial distribution obtaining method supplies a beneficial reference for determining continuous gradient distribution of the desert riparian forest and the protecting range thereof.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Optical synthesis aperture image-forming system based on optical fiber array
InactiveCN101299067APrecise length adjustmentPrecisely adjust the lengthElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptical elementsHigh resolution imagingPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
The present invention provides a novel optical synthesis aperture imaging system based on the optical fiber array. The high-resolution image can be obtained by the imaging technique of synthesizing a plurality of small apertures to a synthesis aperture. The acquired accomplishment of optical synthesis aperture imaging in the high resolution imaging displays that the technique has a wide developing prospect. The invention receives the optical wave radiated from the target by a Cassegrain telescope array. The optical fiber is coupled in a single-mode polarization-preserving fiber for transmitting. An optical fiber collimator array is used for leading to coherent imaging of the light beam. The phase error compensation is executed through a piezoelectric ceramic phase modulator and an optical fiber delay line. The whole set of equipment goes for miniaturization and lightening, and can be applied in the fields of astronomical measurement, remote sensing the plant cover, monitoring the environment and disaster and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
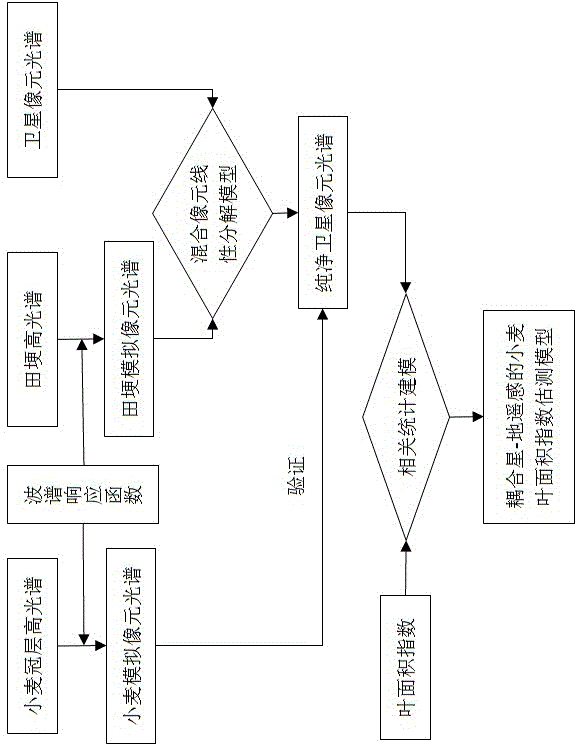
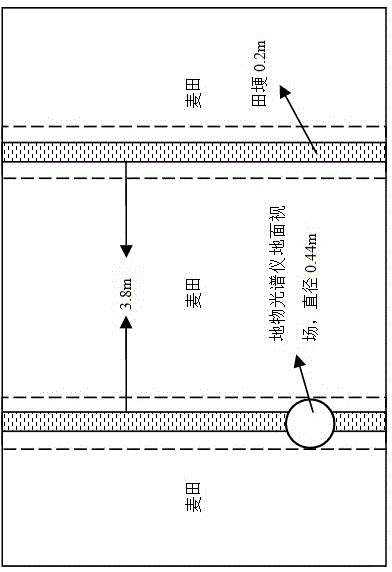
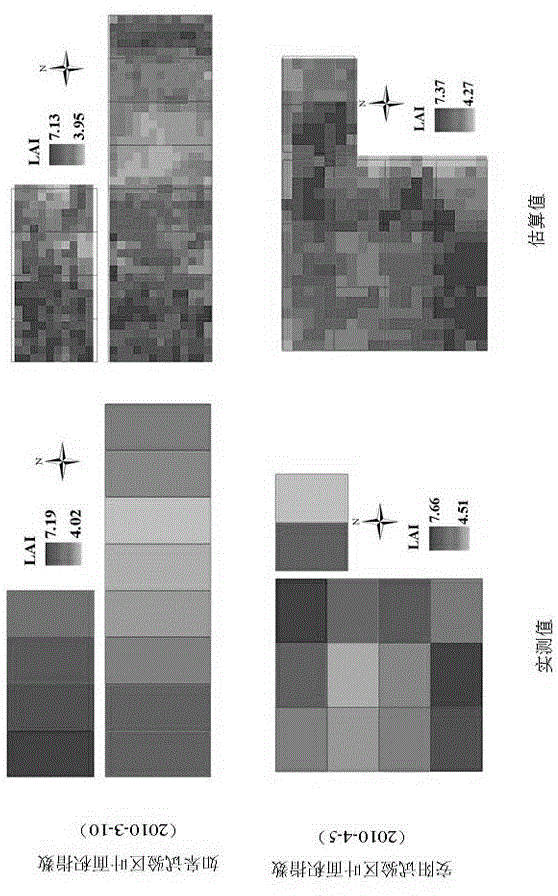
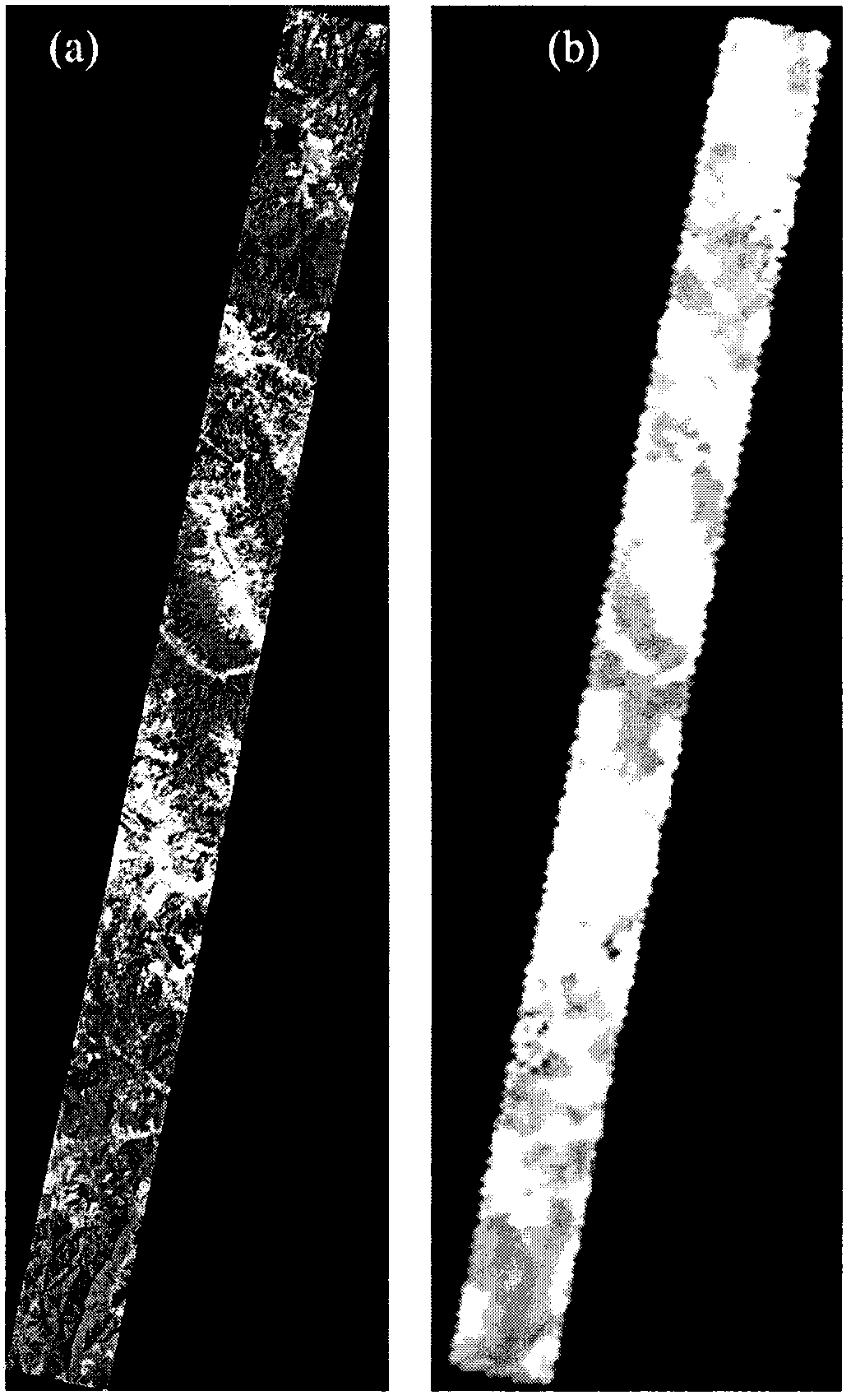
Wheat LAI (leaf area index) estimation method coupled with satellite-ground remote sensing
InactiveCN104567754AAvoid defectsAchieve real-time acquisitionUsing optical meansDecompositionEstimation methods
The invention relates to the field of agricultural vegetation remote sensing, particularly to a wheat LAI (leaf area index) estimation method coupled with satellite-ground remote sensing. The method comprises steps as follows: 1) acquiring two different scales of canopy spectrum information, namely, a wheat ground high-spectrum and an SPOT-5 image; 2) fitting a wheat canopy high-spectrum and a ridge high-spectrum with a satellite sensor wave spectrum response function; 3) extracting a pure satellite pixel spectrum on the basis of a mixed pixel linear decomposition model; 4) meanwhile, verifying the pure satellite pixel spectrum by the aid of a synchronous wheat simulation pixel spectrum; 5) constructing a wheat LAI monitoring model coupled with satellite-ground remote sensing with related statistical methods. The method overcomes defects of existing ground remote sensing point scales and satellite remote sensing mixed pixels and is higher in precision and accuracy of estimation of wheat LALs at different nitrogen application levels in different ecological regions in particular, wheat LAI growth information is acquired in real time, and wide application of remote sensing based crop growth remote sensing monitoring technologies is facilitated.
Owner:INST OF AGRI ECONOMICS & INFORMATION HENAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Leaf reflectance satellite remote sensing extraction method for eliminating influence of vegetation canopy structure and earth surface background
The invention provides a leaf reflectance satellite remote sensing extraction method for eliminating influence of vegetation canopy structures and earth surface backgrounds and belongs to the field ofresearch on vegetation remote sensing retrieval parameter methods. The method comprises the following steps: by using a 4-Scale model, confirming visual probability (PT) of sun leaves corresponding to a remote sensing image pixel spectrum and visual probability (PG) of a lighting background; calculating an angle index (AI) of the spectrum, performing related analysis on PT and PG, and establishing an estimation model based on Al, PT and PG; by taking a leaf area index (LAI), PT and PT as three retrieval items, establishing a checking table (related to wavelengths) for multi-time scattering factors M in a simulation manner by using the 4-Scale model; finally, by using the established estimation model and the checking table, calculating average leaf reflectance of remote sensing image vegetation pixels. By adopting the method provided by the invention, reflection spectrums of leaves can be extracted through remote sensing images; compared with an optimal iterative computation method, the method is high in calculation efficiency, and compared with a table checking method with multiple steps of checking, the method is relatively simple in calculation process and relatively high in efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
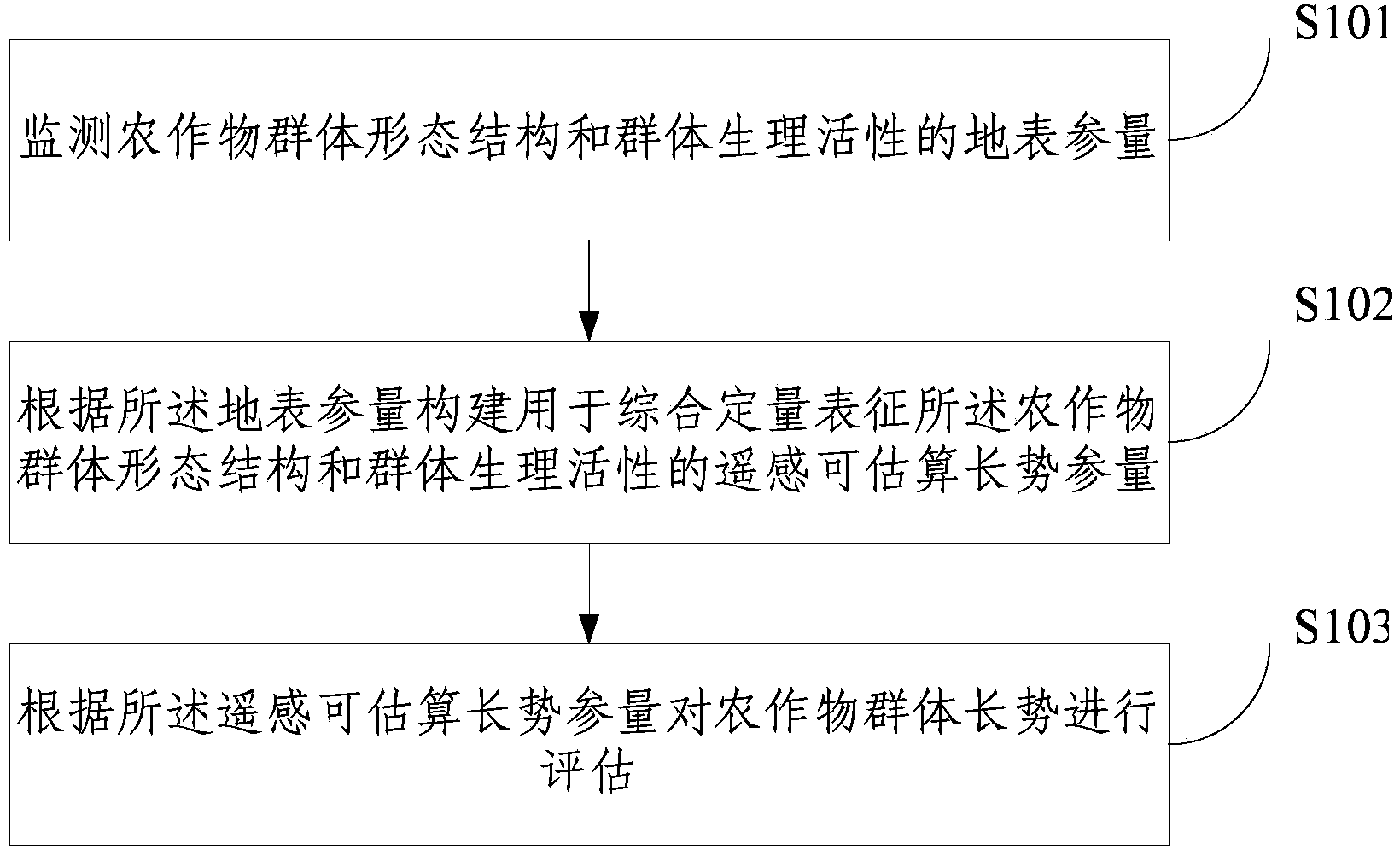
Multi-space-scale self-adaptive monitoring method and device for population growth of crops
InactiveCN103839184AIncrease spaceImprove portabilityData processing applicationsMeasurement devicesVegetationSelf adaptive
The invention relates to a multi-space-scale self-adaptive monitoring method and device for the population growth of crops. The method includes the following steps that surface parameters of the population morphological structure and the population physiological activity of the crops are monitored; remote-sensing parameters capable of estimating the growth are established according to the surface parameters and used for comprehensively and quantitatively representing the population morphological structure and the population physiological activity of the crops; the population growth of the crops is estimated according to the remote-sensing parameters capable of estimating the growth. The remote-sensing parameters capable of estimating the growth are established by combining agricultural knowledge and a vegetation remote sensing response mechanism and can be used for comprehensively and quantitatively representing the population morphological structure and the population physiological activity of the crops, a threshold valve division strategy with the space scale self-adaptive capacity is made according to the remote-sensing parameters capable of estimating the growth, space scale universality and transferability of the quantitative threshold value division method are expanded, and the advantage of comprehensively and quantitatively classifying the population growth conditions of the crops is achieved.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
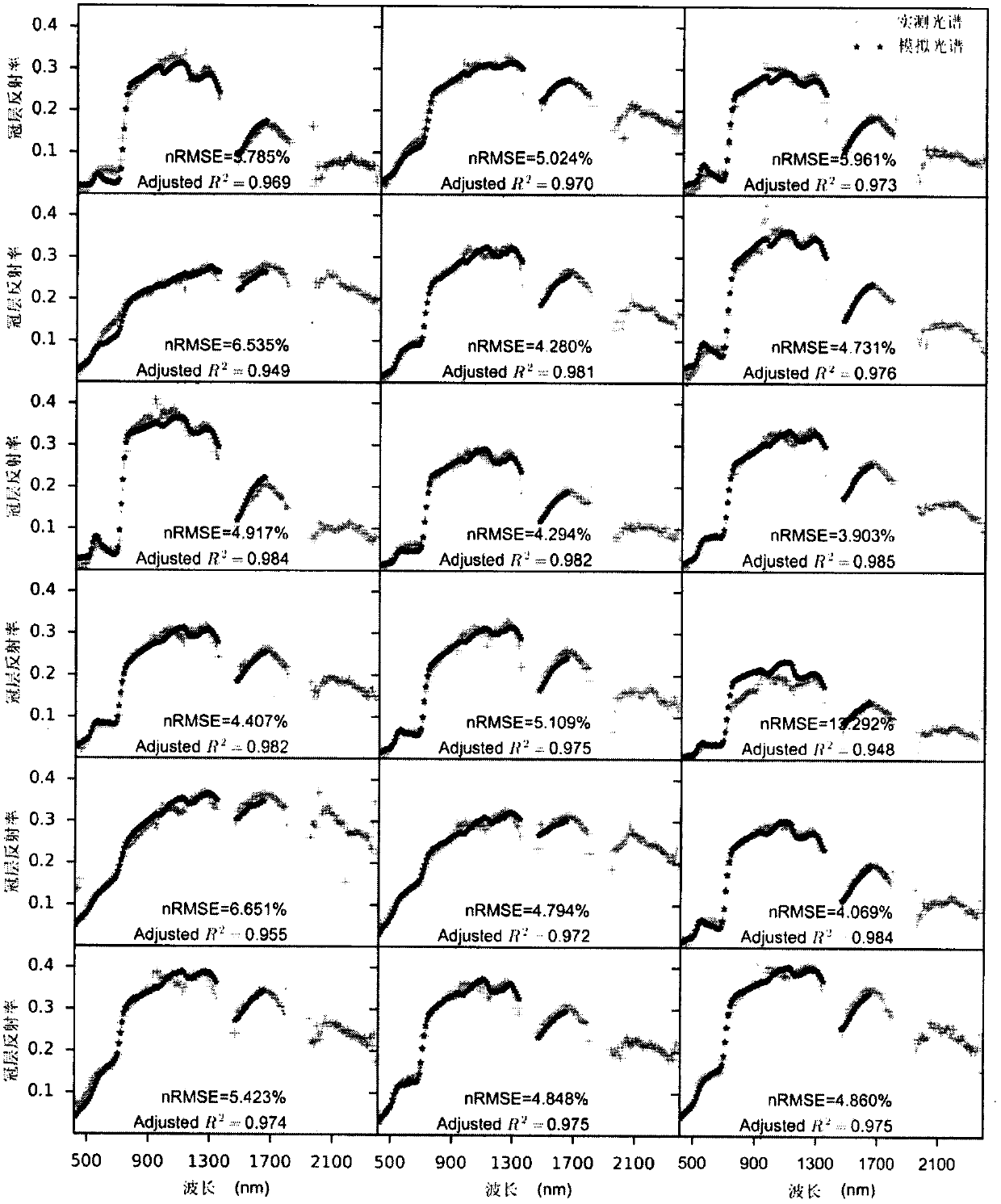
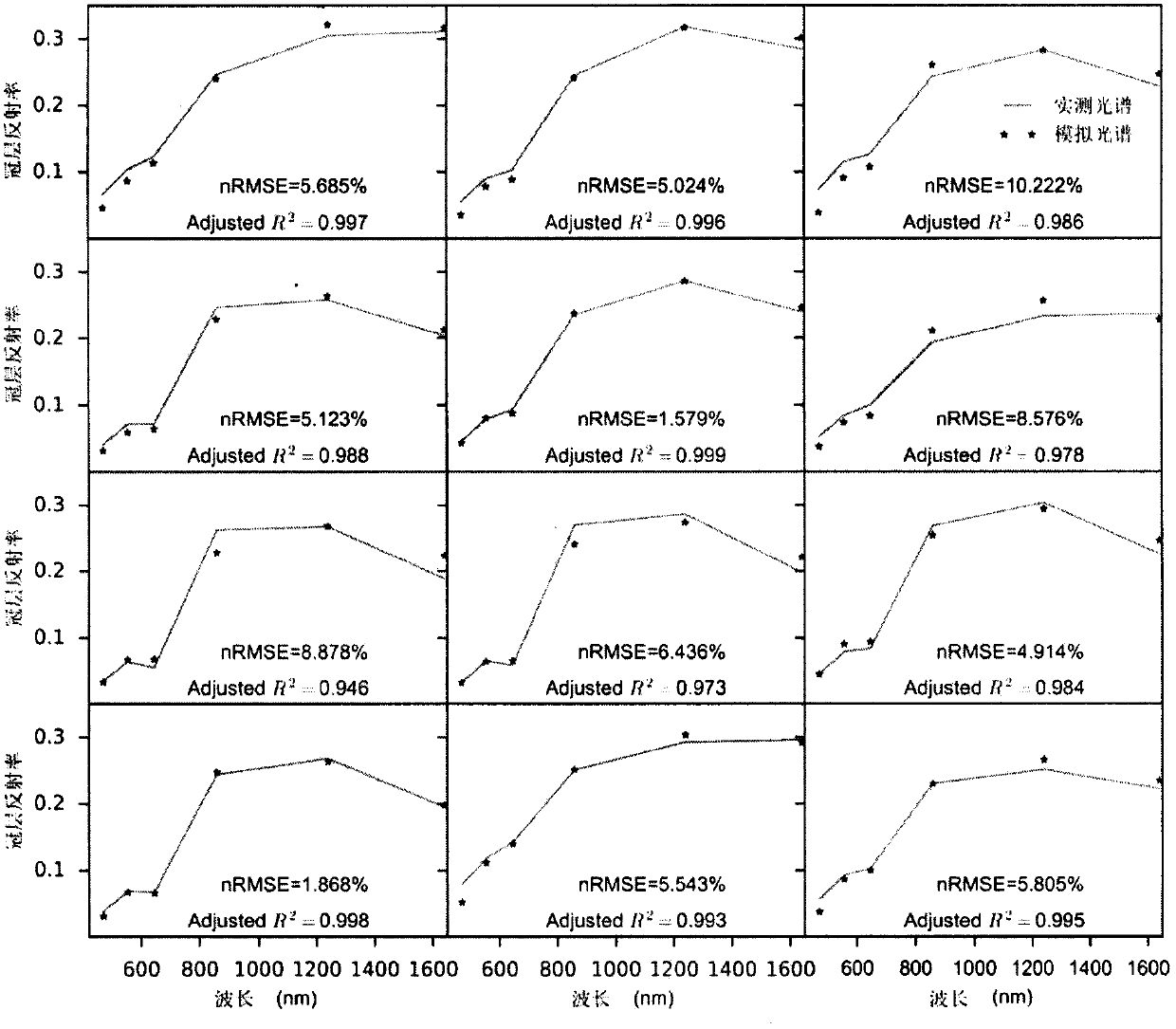
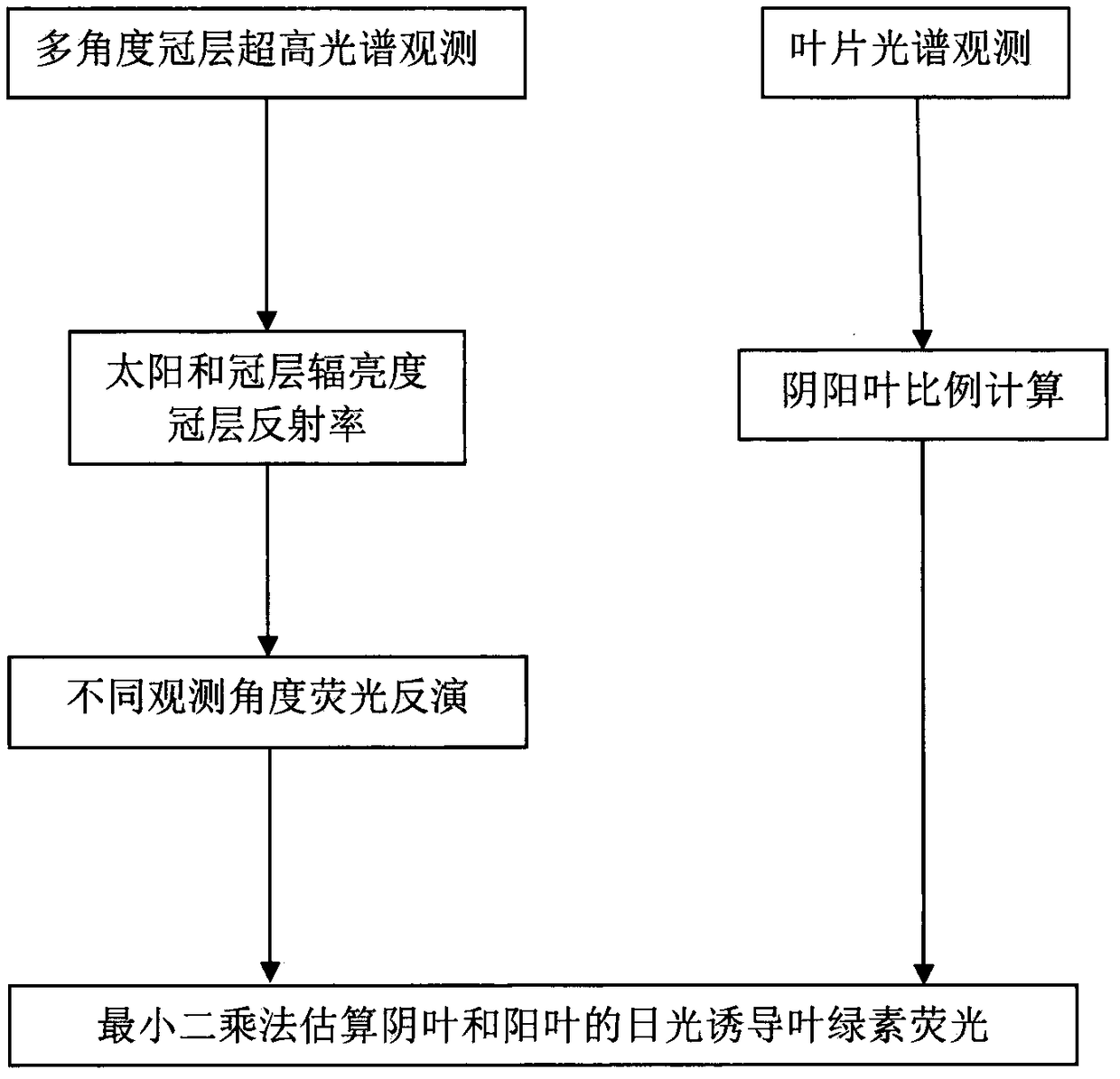
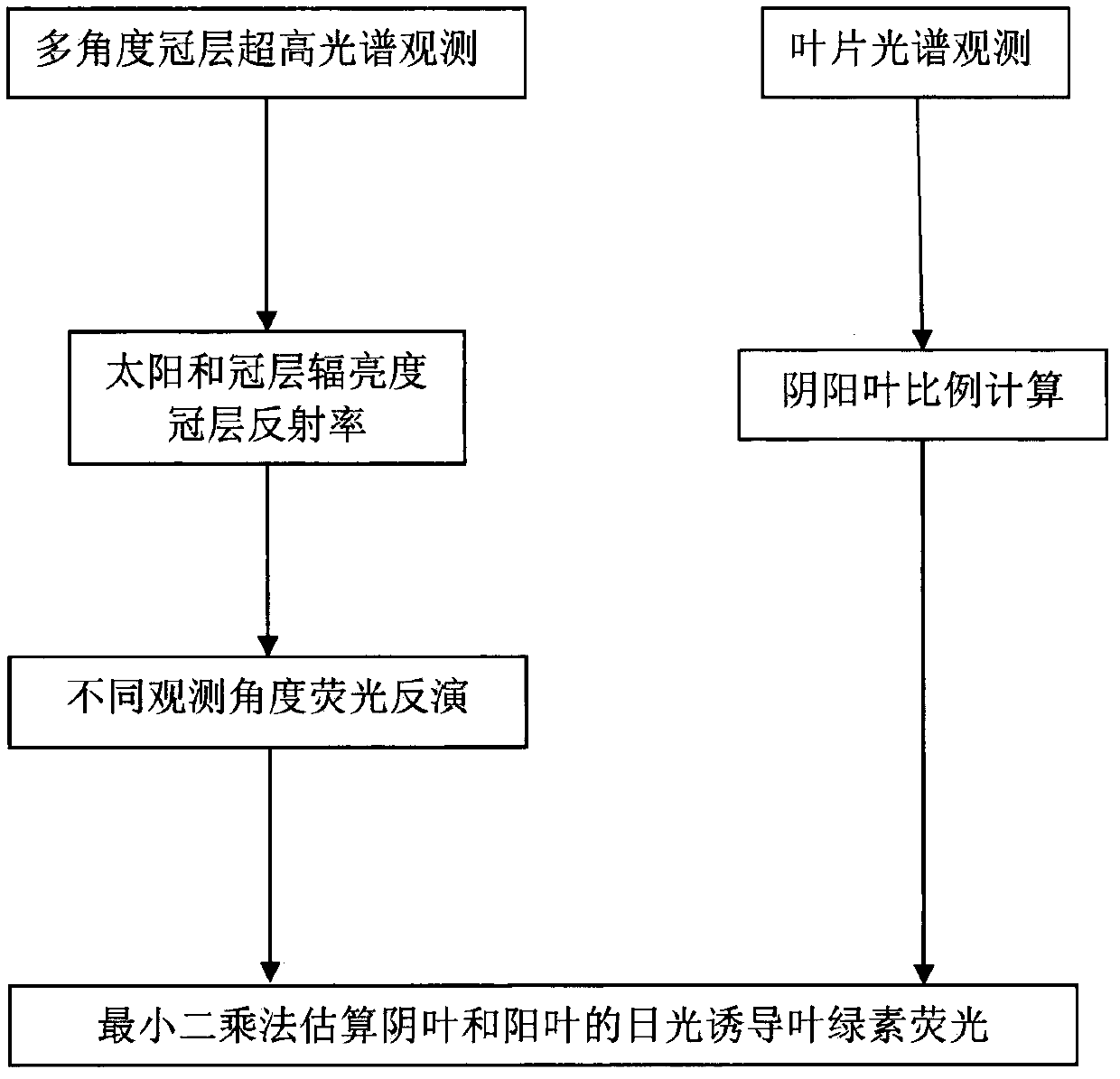
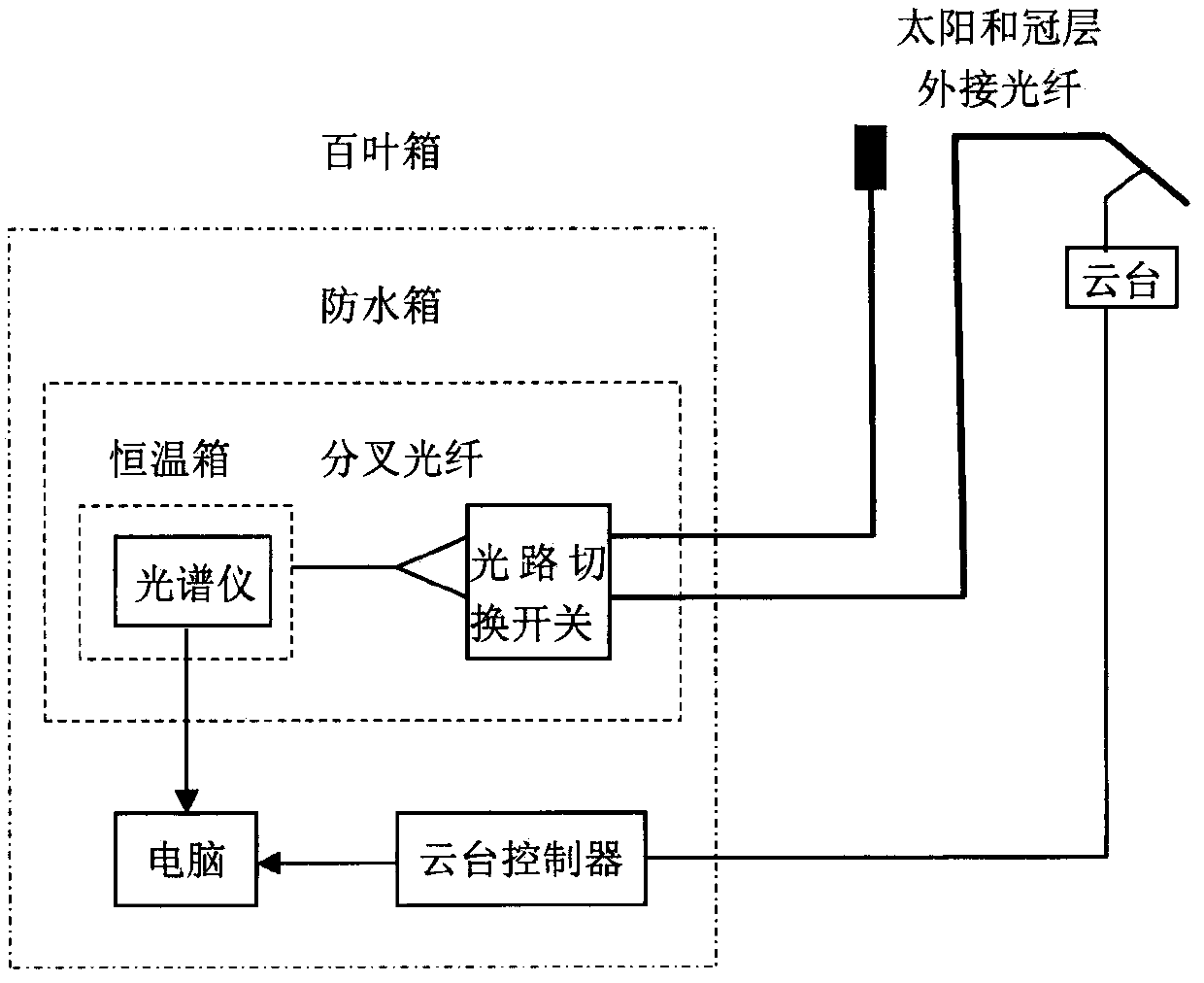
Method for multi-angle observing and precisely inverting sunlight induced chlorophyll fluorescence of shade/sun leaf of vegetation
The invention provides a method of utilizing a multi-angle observation system to obtain the vegetation canopy spectroscopic data to precisely inverting sunlight induced chlorophyll fluorescence of shade / sun leaves of a canopy, and belongs to the research field of vegetation remote sensing inversion parameter obtaining methods. The method comprises following steps: establishing a multi-angle super-hyperspectral observing system; obtaining multi-angle super-hyperspectral data; calculating the solar incident angle and canopy reflection brightness; calculating the reflection rate and inverted chlorophyll fluorescence; using a leaf clamp to observe the leaf reflection rate; utilizing the ratio of canopy reflection rate to leaf reflection rate, under the assistance of a geometrical optical model, calculating the ratio of shade / sun leaves from different observation angles, and obtaining the fluorescence of the sun leaves and shade leaves through fitting of least square method. The provided method can obtain continuous multi-angle vegetation canopy super-hyperspectral data, is used to invert chlorophyll fluorescence, can simply and effectively calculate the ratio of sun leaves and shade leaves of a canopy from different observation angles and solar incident angles based on the leaf reflection rate and a geometrical optical model, calculates the fluorescence of the sun leaves and shadeleaves, and improves the precision of monitoring the primary productivity of a land.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
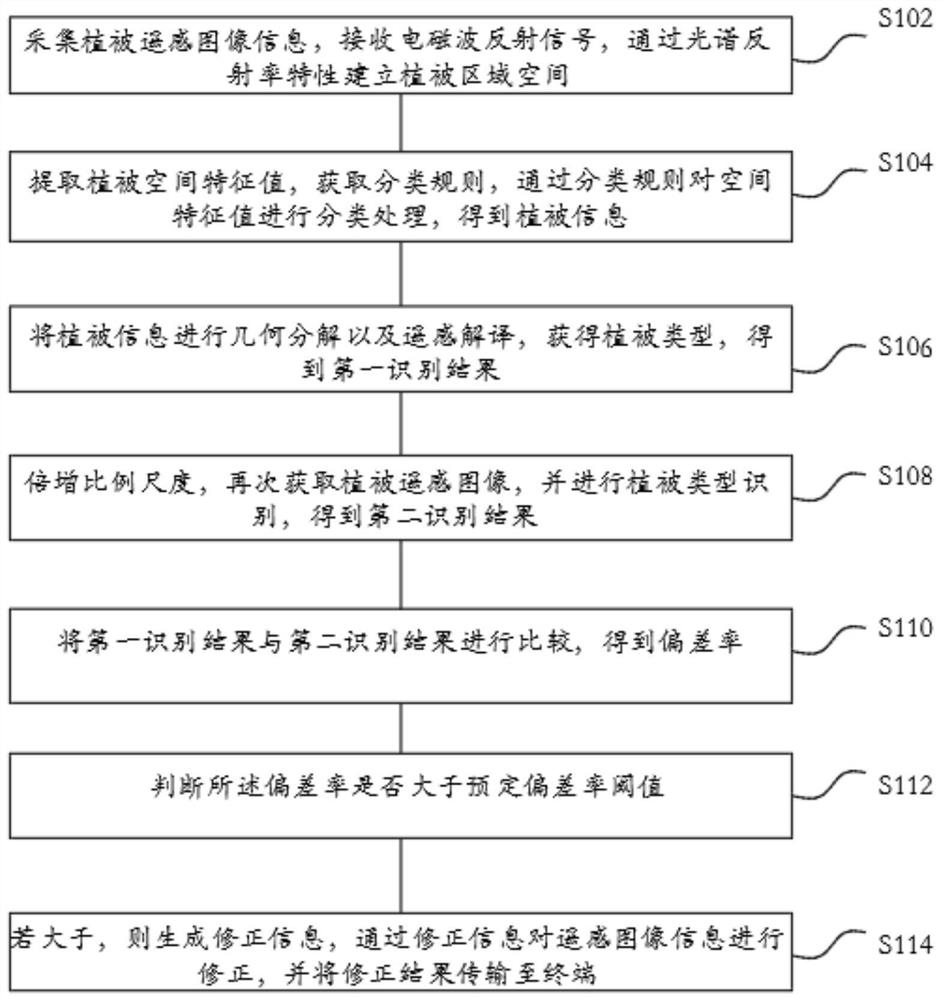
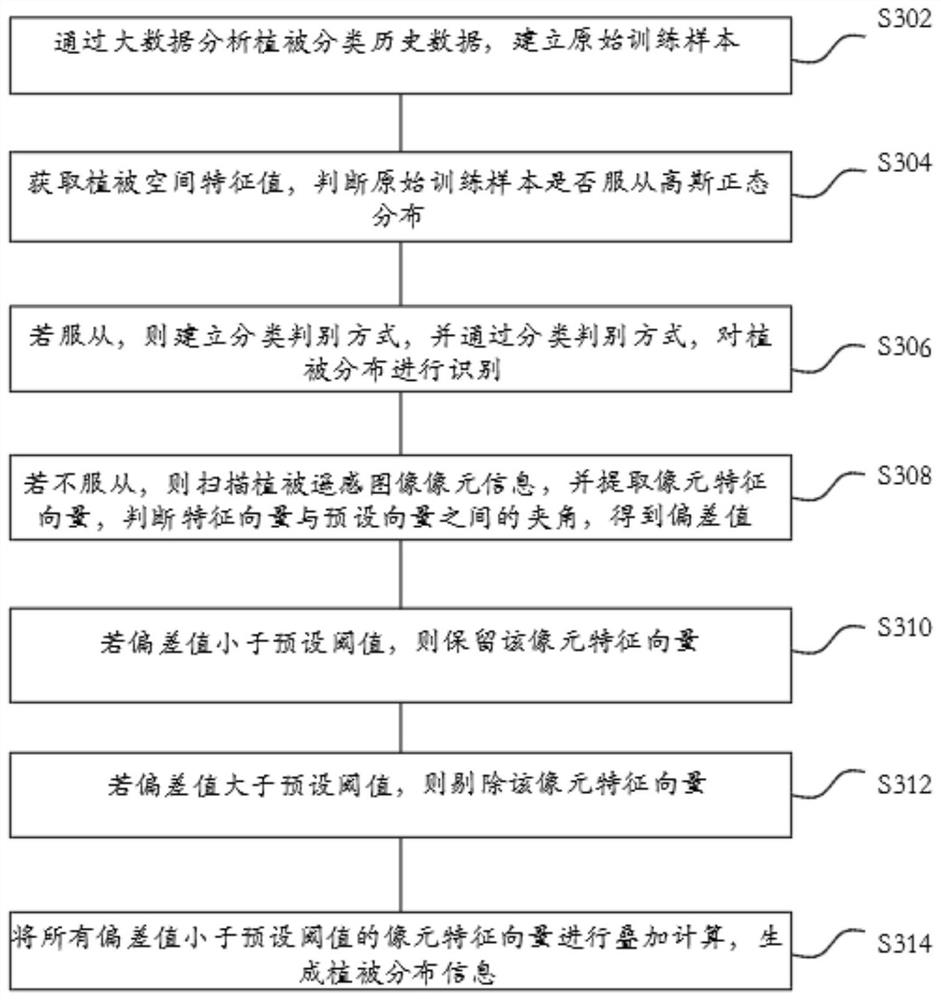
Earth surface vegetation identification method and system based on unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing technology, and readable storage medium
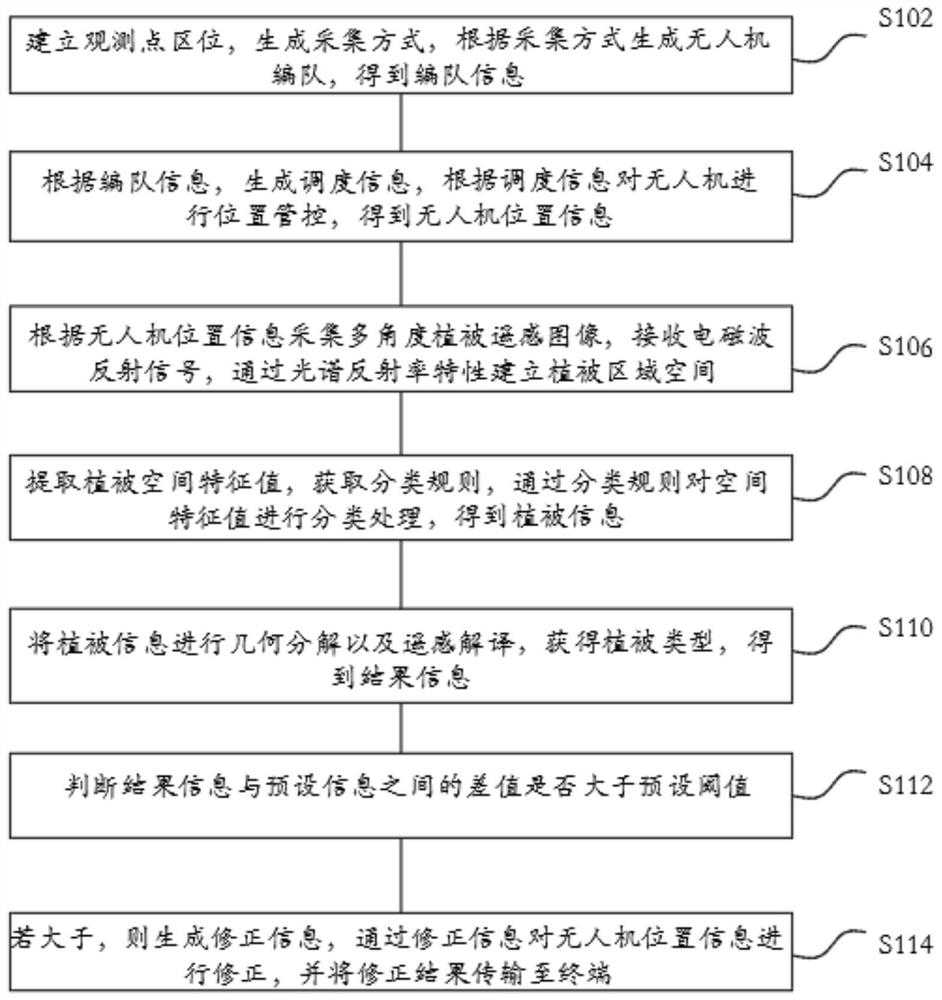
InactiveCN112445241AImprove recognition accuracyHigh precisionPosition/course control in three dimensionsObservation pointUncrewed vehicle
The invention relates to an unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing technology-based surface vegetation identification method and system, and a readable storage medium. The method comprises the steps of establishing an observation point location, generating an acquisition mode, generating an unmanned aerial vehicle formation according to the acquisition mode, and obtaining formation information; generating scheduling information according to the formation information, and performing position management and control on the unmanned aerial vehicle according to the scheduling information to obtainunmanned aerial vehicle position information; collecting a multi-angle vegetation remote sensing image according to the unmanned aerial vehicle position information, receiving an electromagnetic wavereflection signal, and establishing a vegetation region space through spectral reflectivity characteristics; extracting vegetation space characteristic values, obtaining classification rules, and performing classification processing on the space characteristic values through the classification rules to obtain vegetation information; carrying out geometric decomposition and remote sensing interpretation on the vegetation information to obtain a vegetation type and result information; judging whether a difference value between the result information and preset information is greater than a preset threshold value; and if yes, generating correction information, collecting the position information of the unmanned aerial vehicle through the correction information, and transmitting a correction result to the terminal.
Owner:广东竞合基业科技服务有限公司
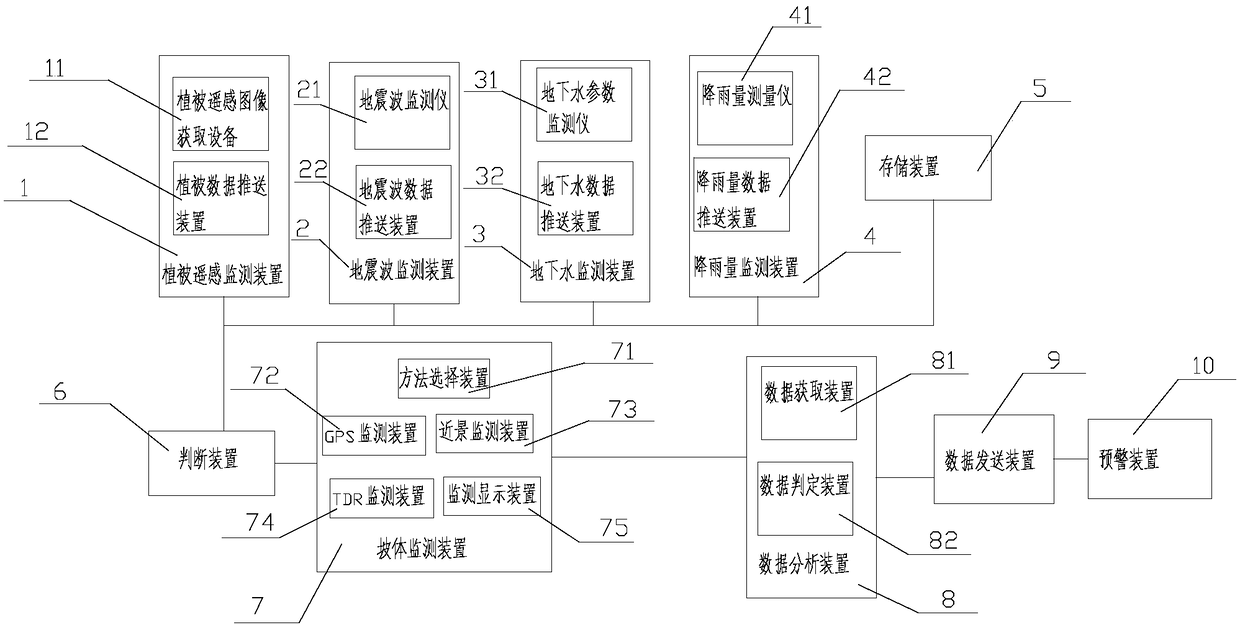
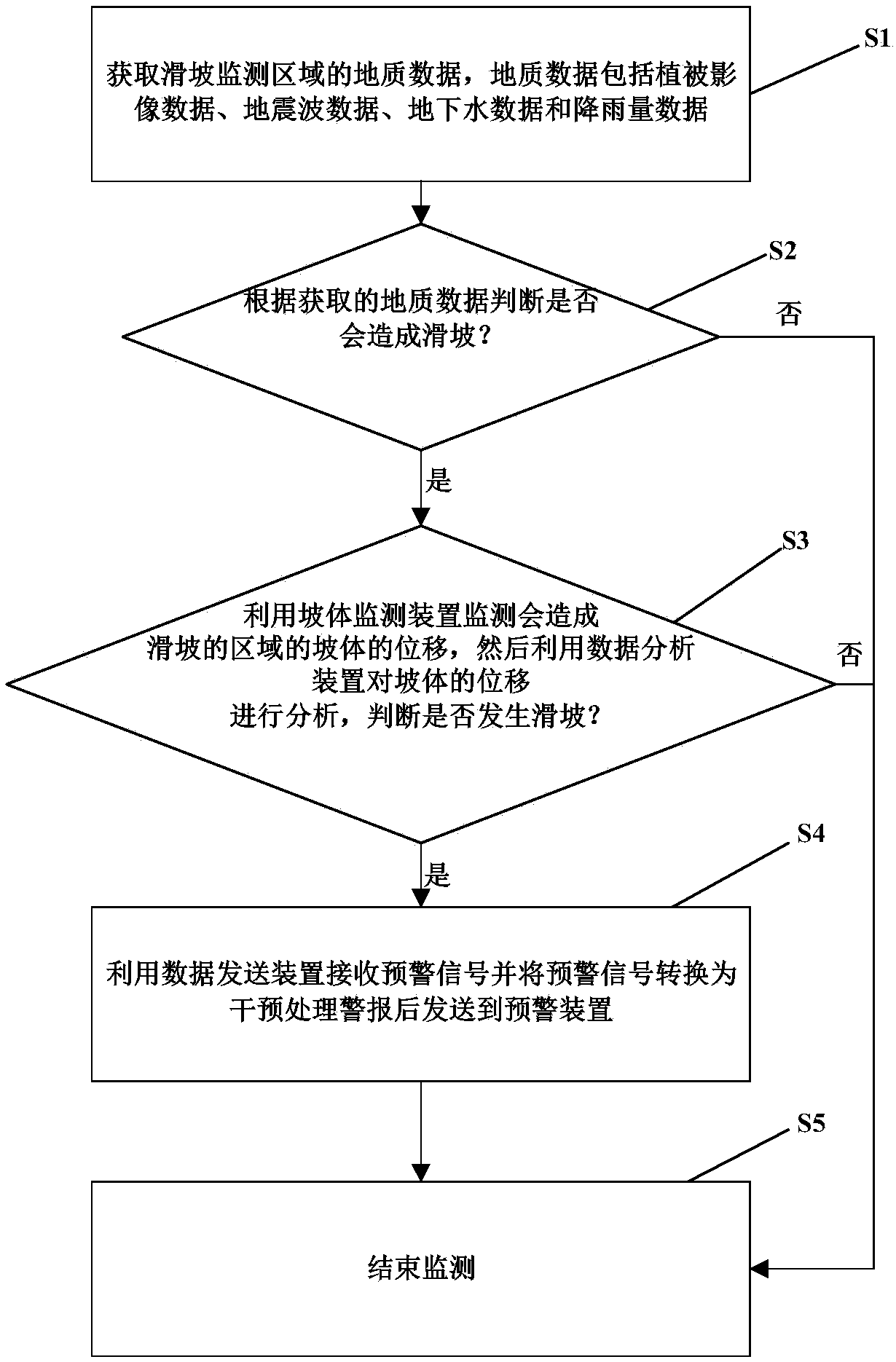
Landslide disaster monitoring device and monitoring method thereof
The invention provides a landslide disaster monitoring device, which comprises a vegetation remote sensing monitoring device, a seismic wave monitoring device, a groundwater monitoring device, a rainfall monitoring device, a determining device, a slope monitoring device, a data analysis device, a data transmitting device and an early warning device. The invention also provides a monitoring methodfor the landslide disaster monitoring device. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring the geological data of a landslide monitoring area, the geological data including vegetation image data, seismic wave data, groundwater data and rainfall data; determining whether a landslide may occur according to the geological data, if so, using the slope monitoring device to monitor the displacement of the slope that may cause the landslide, using the data analysis device to analyze the displacement of the slope to determine whether a landslide occurs, and if a landslide occurs, enabling the data analysis device to give an early warning signal; and receiving the early warning signal by the data transmitting device and converting the early warning signal into an intervention processing alarm and transmitting the intervention processing alarm to the early warning device. The landslide disaster monitoring device has high monitoring efficiency.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Vegetation distribution identification method and system based on unmanned aerial vehicle, and readable storage medium
InactiveCN112396019AImprove recognition accuracyHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionUncrewed vehicleClassification rule
The invention relates to a vegetation distribution identification method and system based on an unmanned aerial vehicle, and a readable storage medium. The method comprises the steps of collecting vegetation remote sensing image information, receiving an electromagnetic wave reflection signal, and establishing a vegetation region space through spectral reflectivity characteristics; extracting vegetation space characteristic values, obtaining classification rules, and performing classification processing on the space characteristic values through the classification rules to obtain vegetation information; carrying out geometric decomposition and remote sensing interpretation on the vegetation information to obtain a vegetation type, and obtaining a first identification result; multiplying the proportion scale, obtaining a vegetation remote sensing image again, and performing vegetation type identification to obtain a second identification result; comparing the first identification resultwith the second identification result to obtain a deviation ratio; and judging whether the deviation rate is greater than a preset deviation rate threshold, if so, generating correction information,correcting the remote sensing image information through the correction information, and transmitting a correction result to the terminal.
Owner:佛山市墨纳森智能科技有限公司
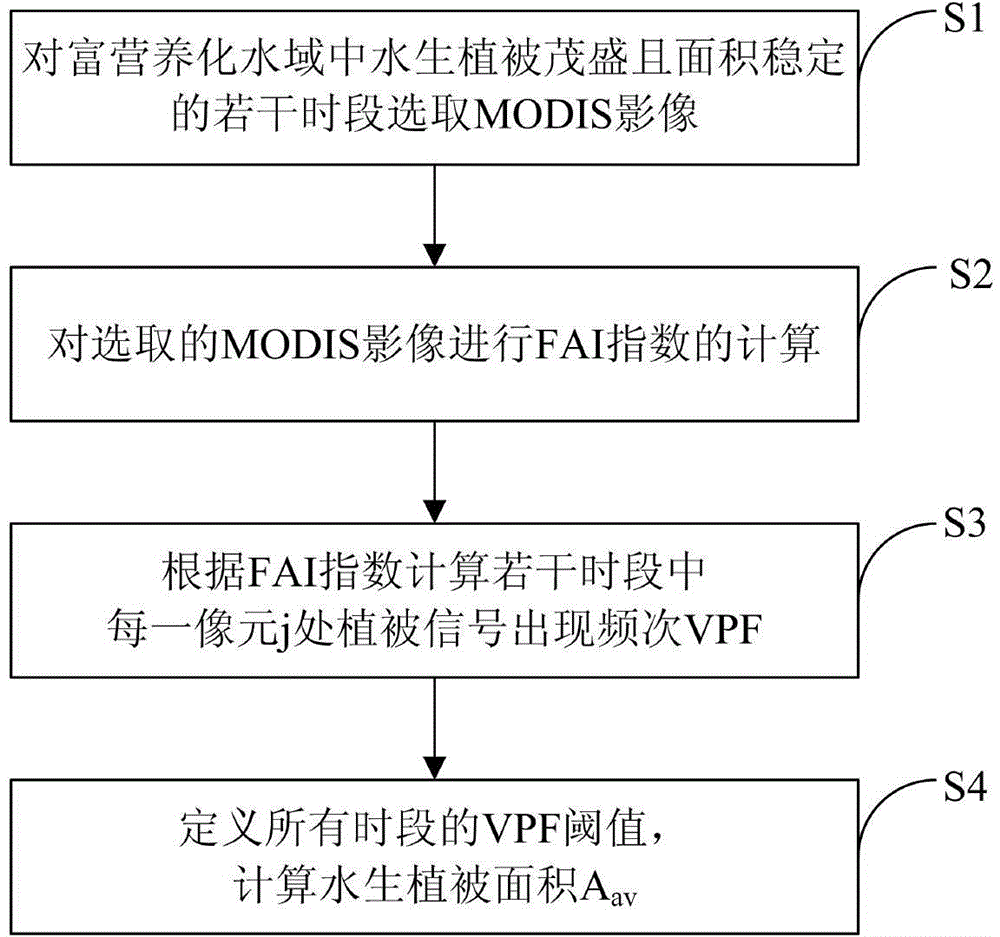
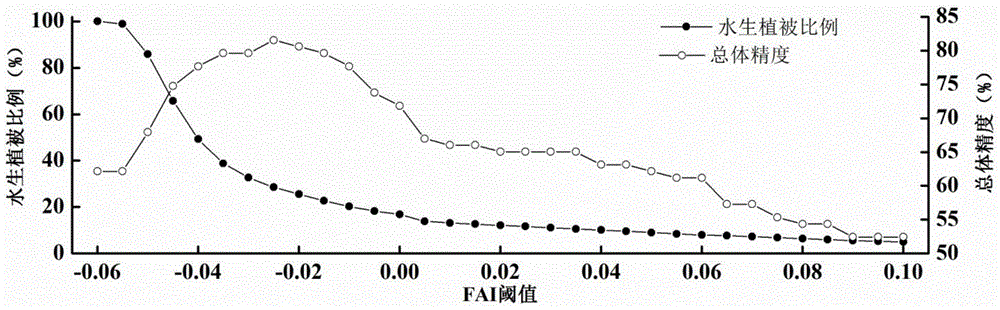
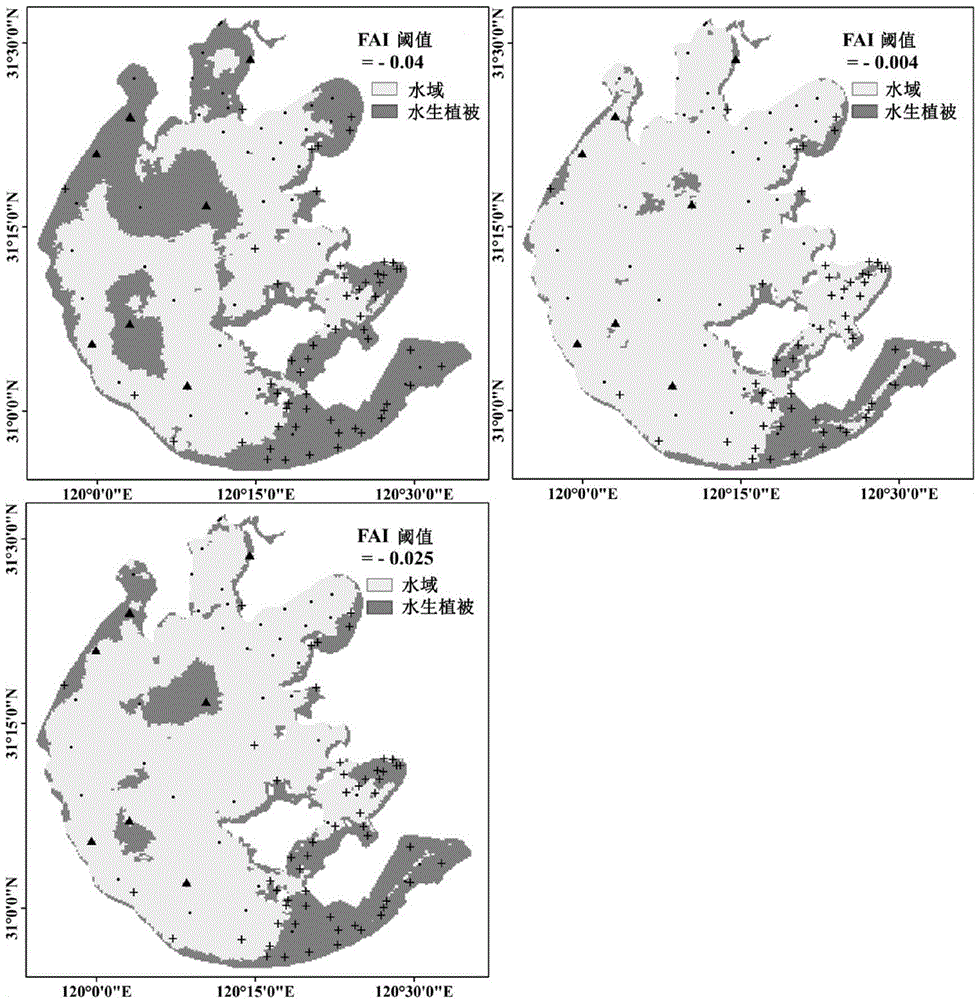
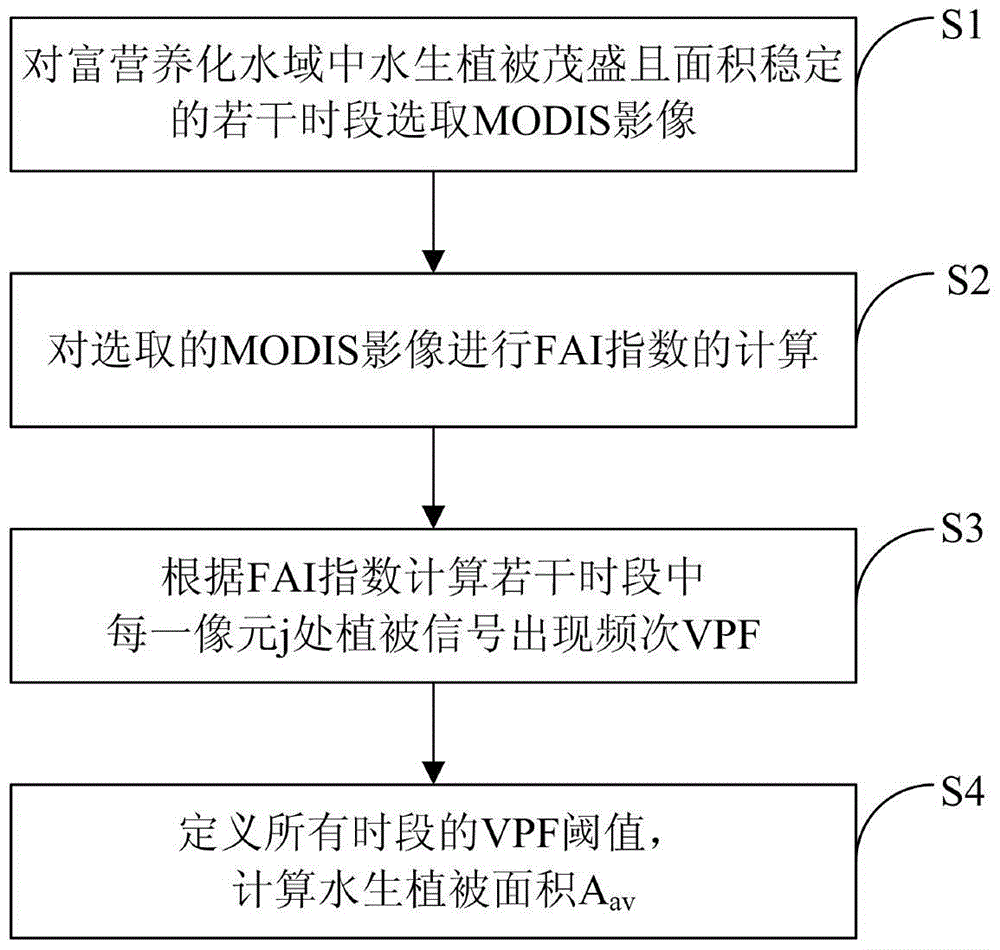
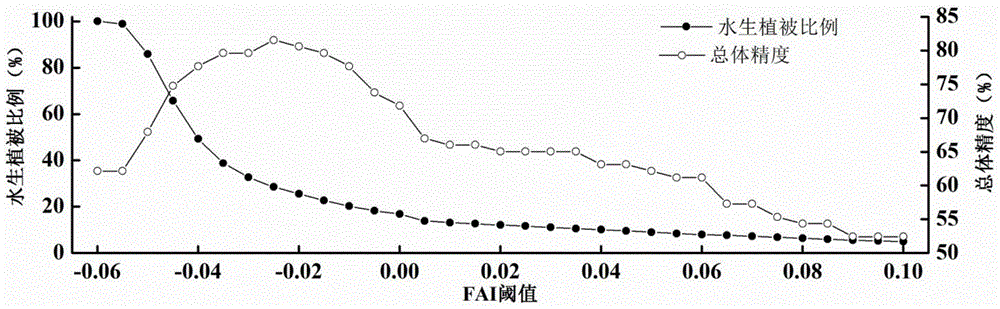
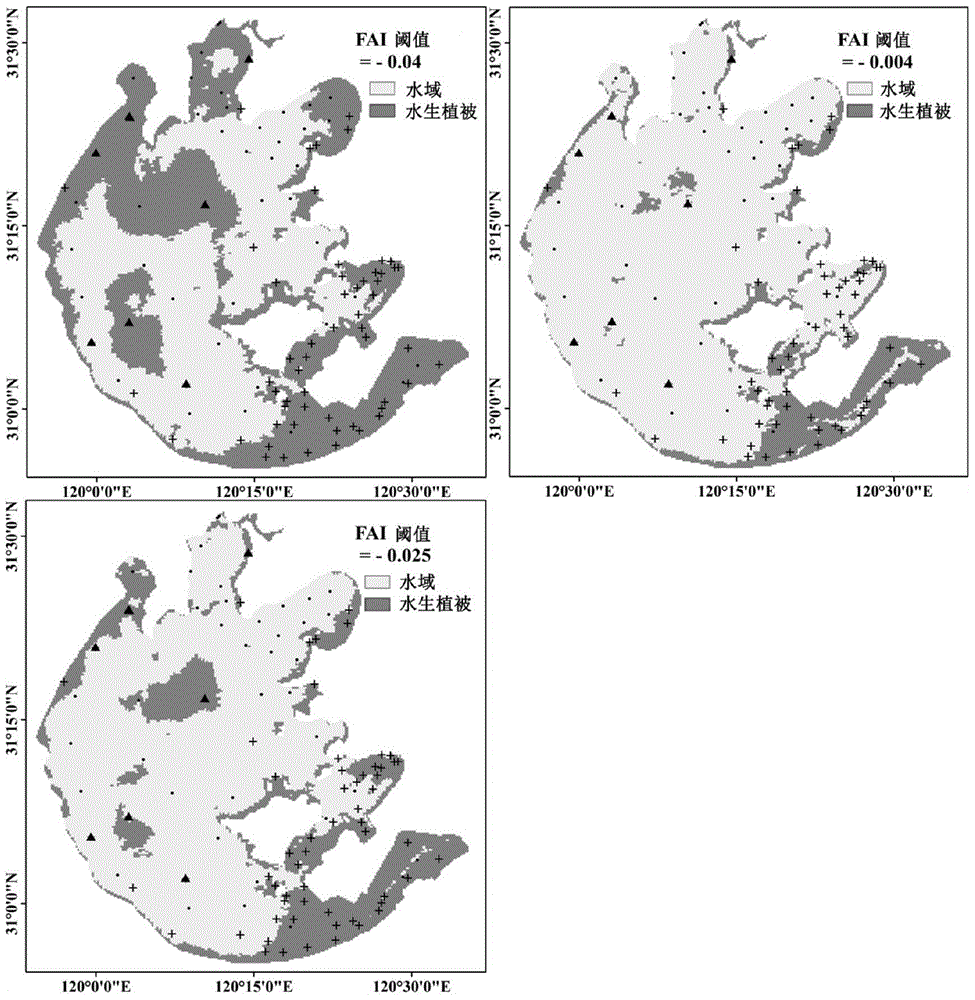
Eutrophic water aquatic vegetation remote sensing extraction method based on alga index frequency method
ActiveCN104596448AEfficient removalSimple and fast operationUsing optical meansSatellite imageModerate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer
The invention provides an eutrophic water aquatic vegetation remote sensing extraction method based on an alga index frequency method. The eutrophic water aquatic vegetation remote sensing extraction method includes S1, selecting MODIS (moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer) images of eutrophic water with aquatic vegetation luxuriant and area stable at different periods; S2, subjecting the MODIS images selected to FAI (floating alga index) calculation; S3, according to the FAI, calculating VPF (vegetation signal appearance frequency) of pixels j at the periods; S4, defining VPF threshold values of all periods and calculating the aquatic vegetation area Aav. The eutrophic water aquatic vegetation remote sensing extraction method has the advantages that the influence of floating alga to aquatic vegetation remote sensing inversion is eliminated, and by integrating typical period dividing, frequency judgment and satellite image judgment, the influence of the floating alga and perennial alga bloom areas to the accurate aquatic vegetation area remote sensing inversion is eliminated.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
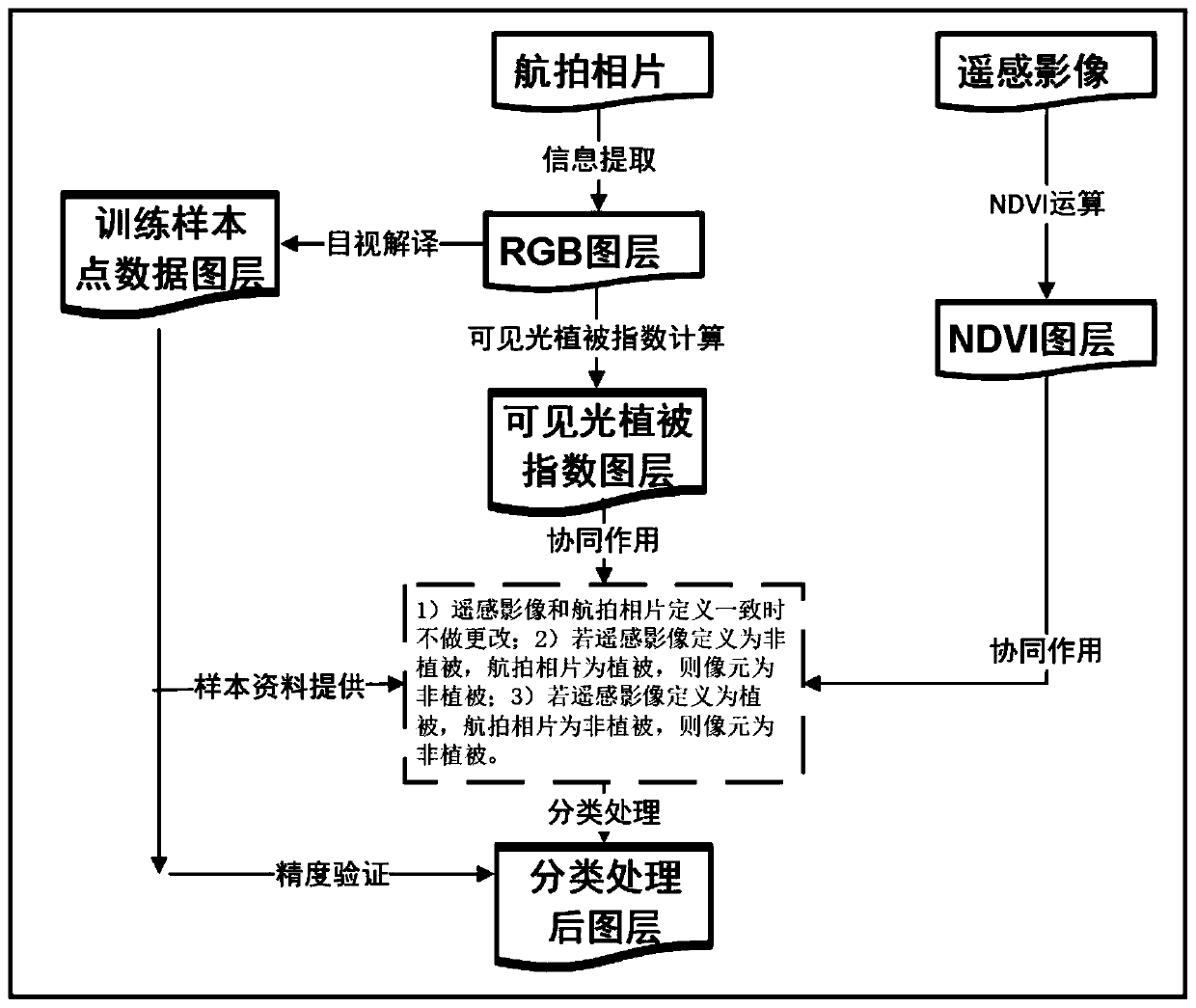
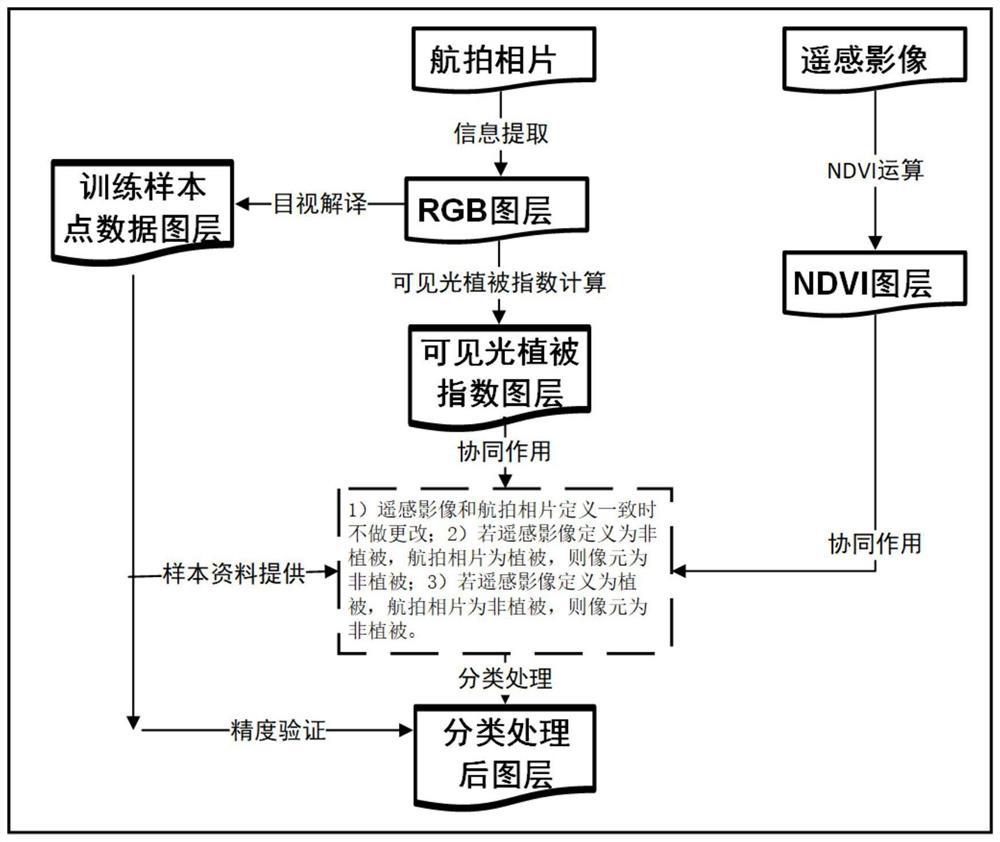
Aerial photo vegetation information extraction method cooperating with remote sensing image
ActiveCN110533052AExtraction is fast and relatively accurateExpand the scope of remote sensing applicationsMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionVegetationImaging processing
The invention discloses an aerial photo vegetation information extraction method cooperating with a remote sensing image, and relates to the technical field of image processing, and aims to establishan effective vegetation remote sensing monitoring method by extracting vegetation information through aerial photos containing visible light wave bands and remote sensing images so as to be applied toplant identification research of destination aerial photos and extract the vegetation information quickly and relatively accurately.
Owner:GUIZHOU INST OF PRATACULTURE
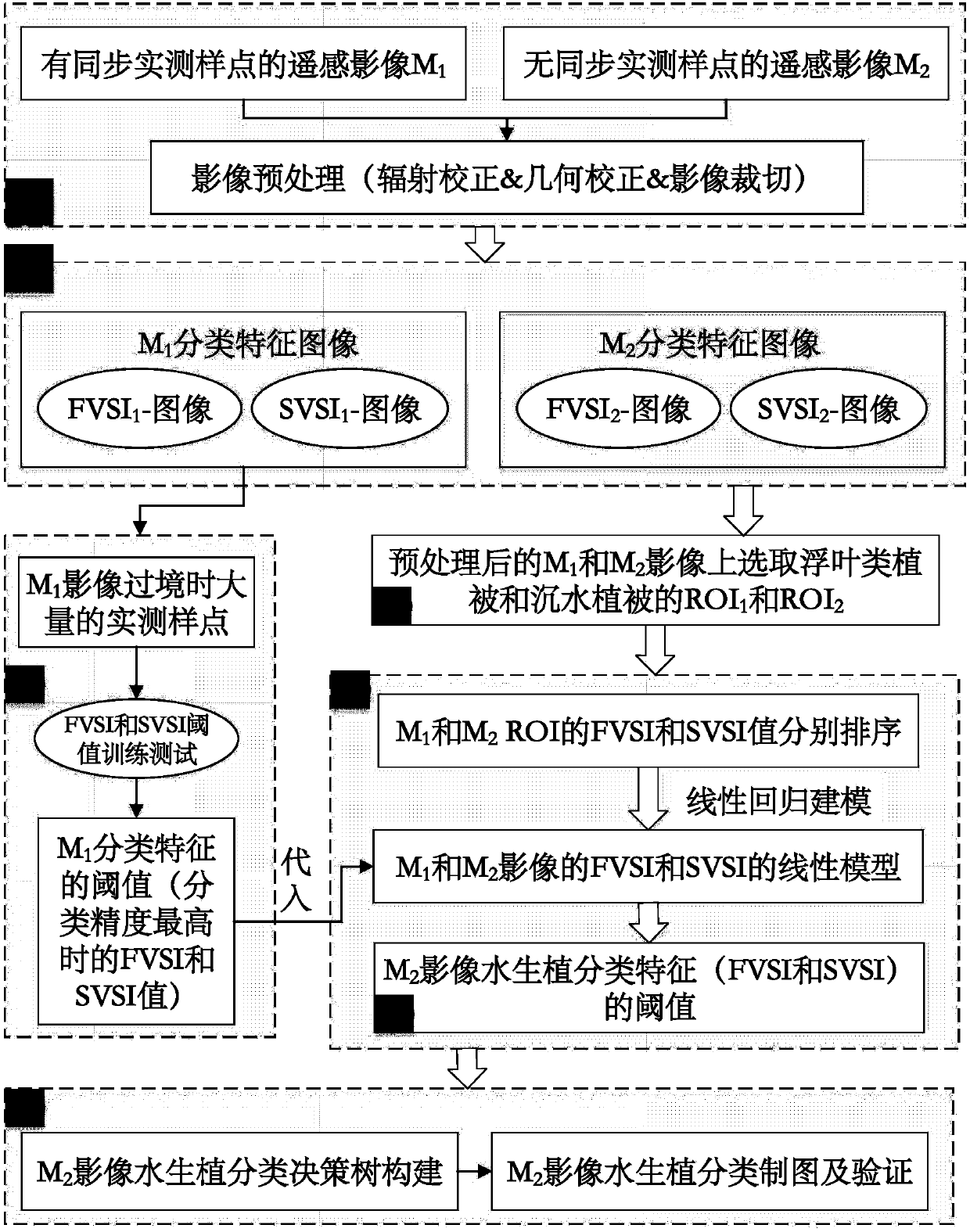
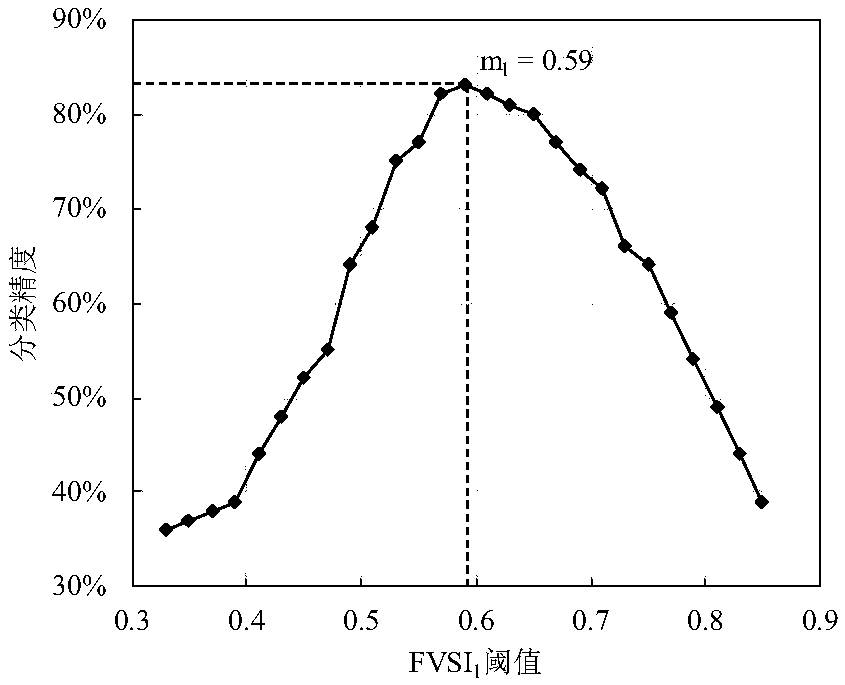
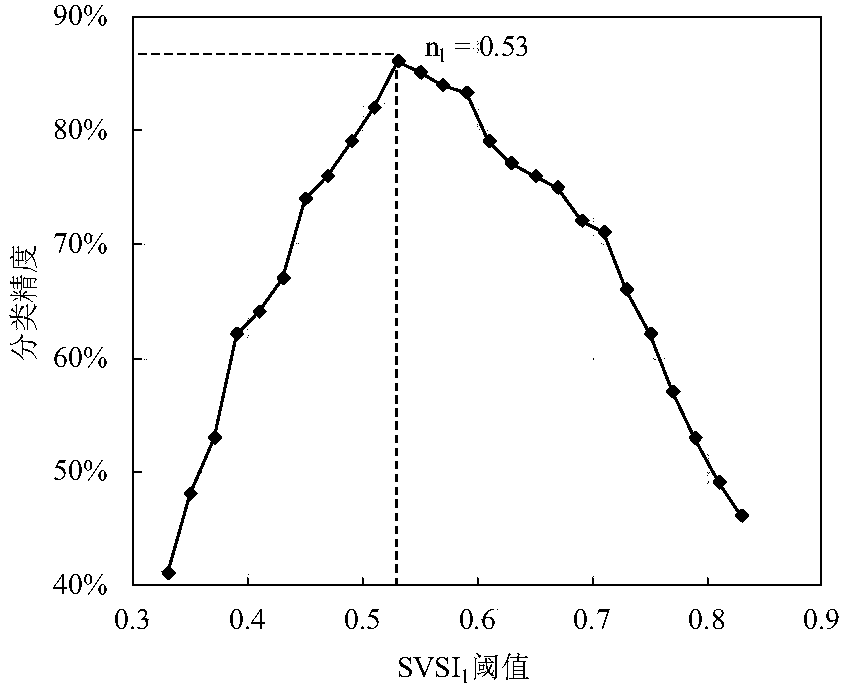
Aquatic vegetation remote-sensing classification threshold calculating method based on spectrum index ordering method
The invention provides an aquatic vegetation remote-sensing classification threshold calculating method based on a spectrum index ordering method. Pixel spectrum indexes of the same natural object incertain area in two images are ordered, a spectrum index related linear model is obtained by fitting, classification thresholds of the image spectrum indexes with synchronous actual measurement samplepoints are substituted into the linear model, and the classification threshold of the spectrum index without synchronous actual measurement sample points can be calculated. The method can be used todetermine the classification threshold of the spectrum index during remote-sensing classification of aquatic vegetation without a lot of images, especially historical images, of synchronous actual measurement point, support is provided for reconstruction of spatial distribution data of the aquatic vegetation of shallow-water lakes, especially shallow-water lakes with eutrophication, and ecologicalrestoration of the lakes and salvage of aquatic plants can be guided.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
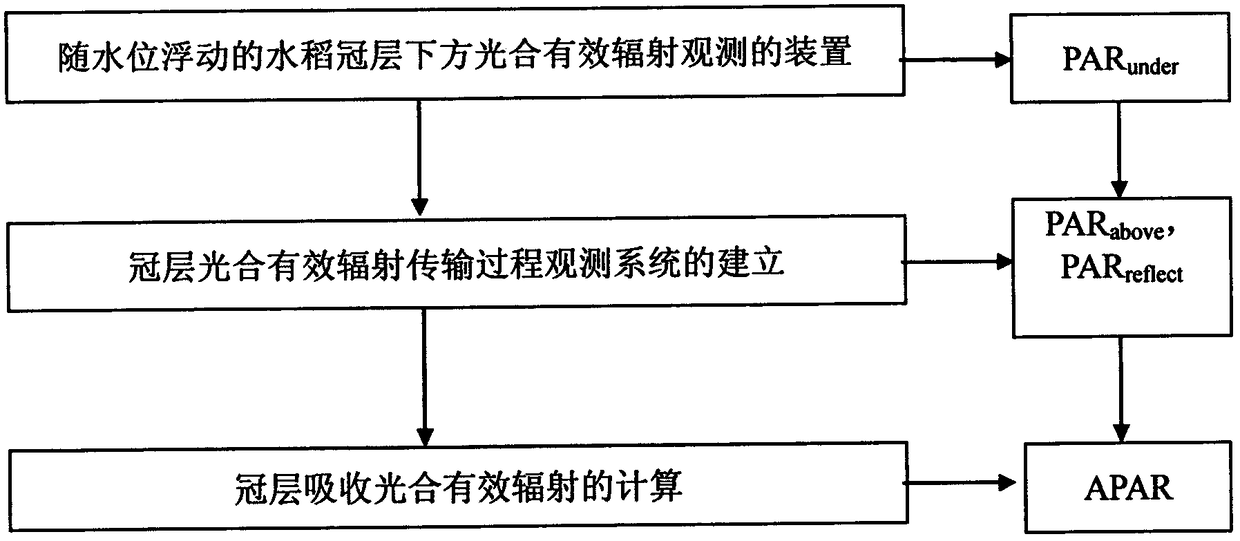
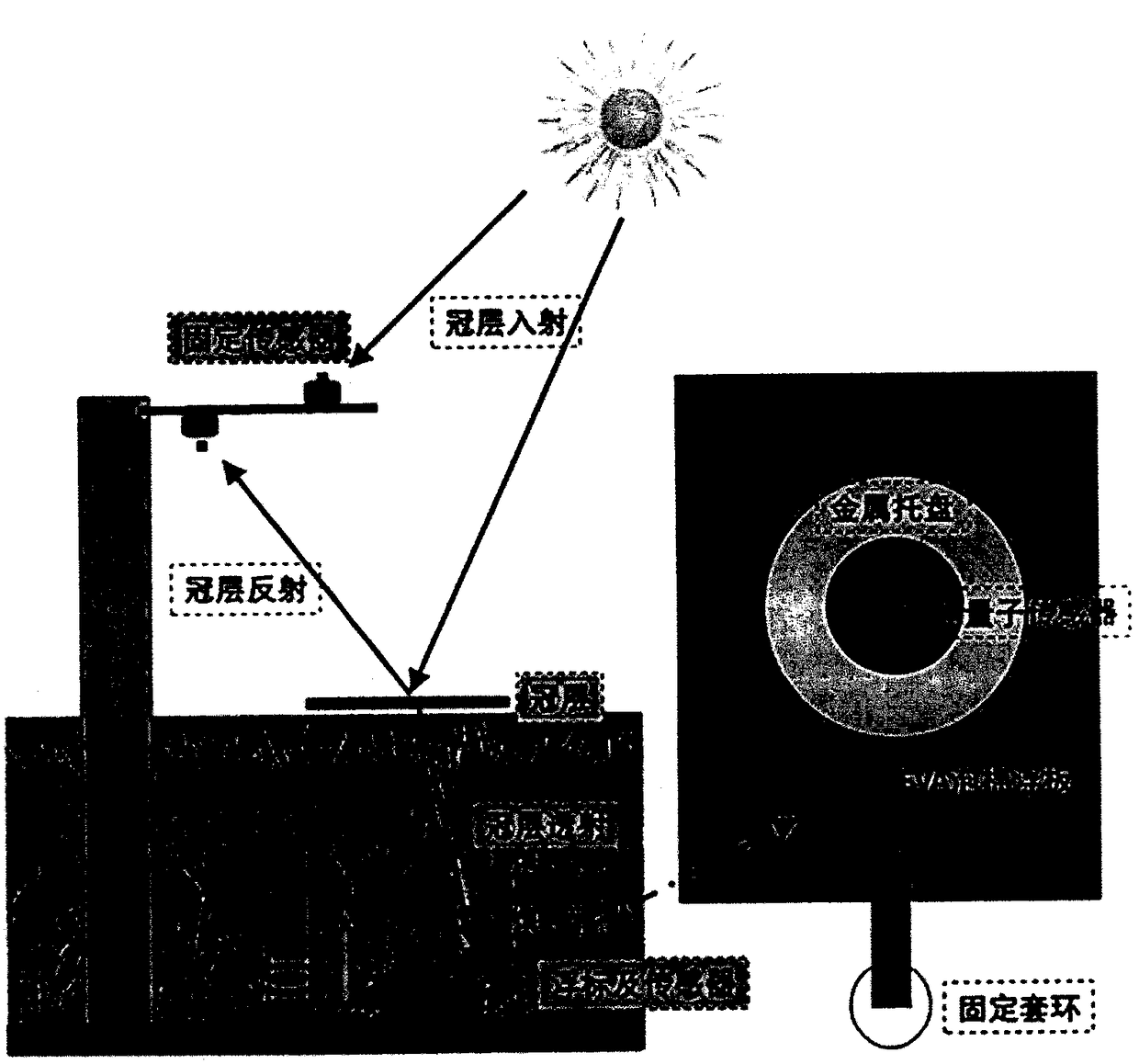
Rice canopy absorbed photosynthetic effective radiation continuous observation method
InactiveCN108871561AImprove accuracyAnalysis by material excitationPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsEnergy balancingLight energy
The invention relates to a method that uses a multi-layer compound canopy radiation continuous observation system to obtain radiation data on the rice canopy and below the canopy, thus calculating therice canopy photosynthetic effective radiation; the method belongs to the vegetation remote sensing inversion parameter obtaining method research field, and comprises the following steps: designing and building an escape photosynthetic effective radiation observation device below the rice canopy and changing with the rice field water level; building a canopy photosynthetic effective radiation transmission process observation system; calculating the canopy photosynthetic effective radiation absorption. The method uses the plant canopy light energy transmission process energy balance as the basis, obtains incoming, reflection and escape energy data in a plant canopy photosynthetic effective radiation transmission process, thus simply, directly and effectively calculating the canopy absorbedphotosynthetic effective radiation; the method can de directly applied in the ecological system plant productivity estimation studies.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
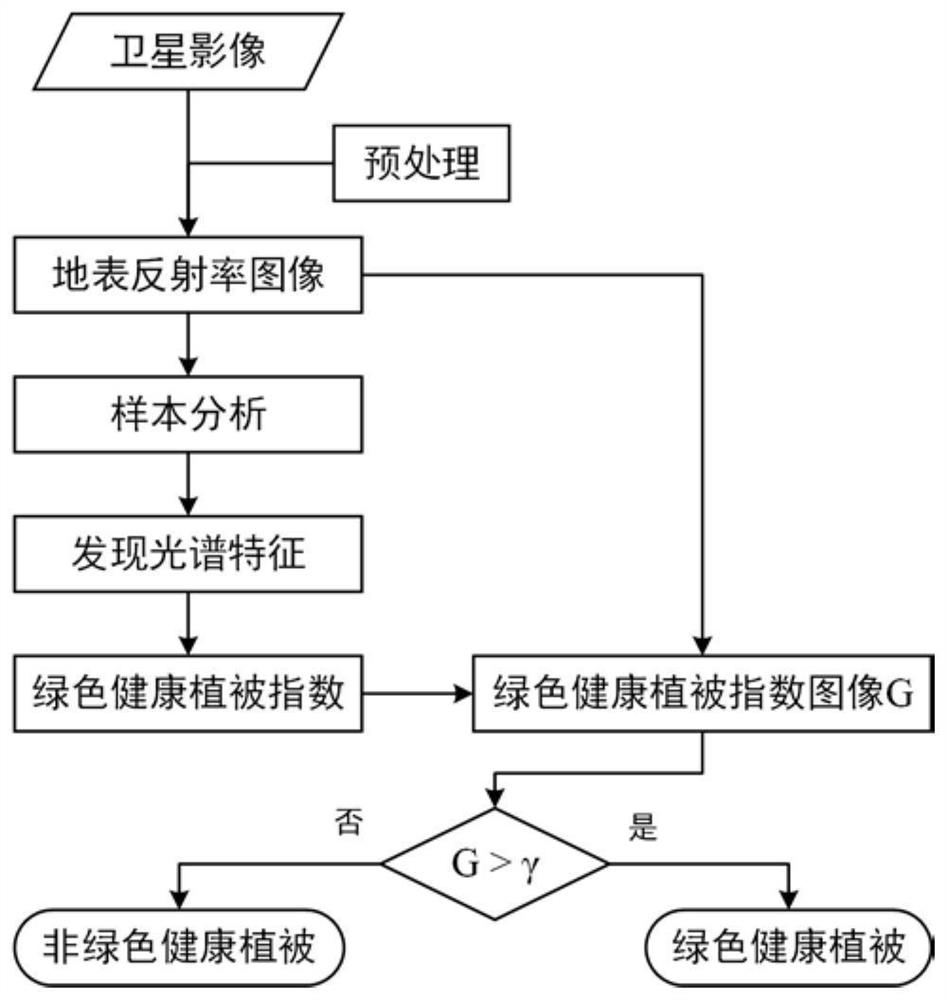
Method for constructing green and healthy vegetation remote sensing recognition index
PendingCN114519821AEnhance image informationImage information suppressionCharacter and pattern recognitionICT adaptationVegetationSoil science
The invention provides a green healthy vegetation remote sensing recognition index construction method, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring a surface reflectance image of an optical satellite image through a cloud platform, and acquiring spectral information of green healthy vegetation, withered and fallen vegetation and other ground feature samples by utilizing spectral acquisition software; the spectral difference between the green healthy vegetation and the withered and fallen vegetation and other ground objects in the satellite image is analyzed to obtain that the green healthy vegetation shows high reflectivity in a near-infrared band and shows low reflectivity in a red band and a short-wave infrared band, and accordingly, a green healthy vegetation remote sensing index algorithm is constructed, and the green healthy vegetation remote sensing index is calculated. And determining a green healthy vegetation index to identify a threshold value of the green healthy vegetation. According to the method, the technical problem that the green and healthy vegetation and the withered and deciduous vegetation are difficult to accurately distinguish is solved, and a technical scheme and theoretical support are provided for realizing green and healthy vegetation spatial distribution drawing, disease and pest monitoring and the like.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
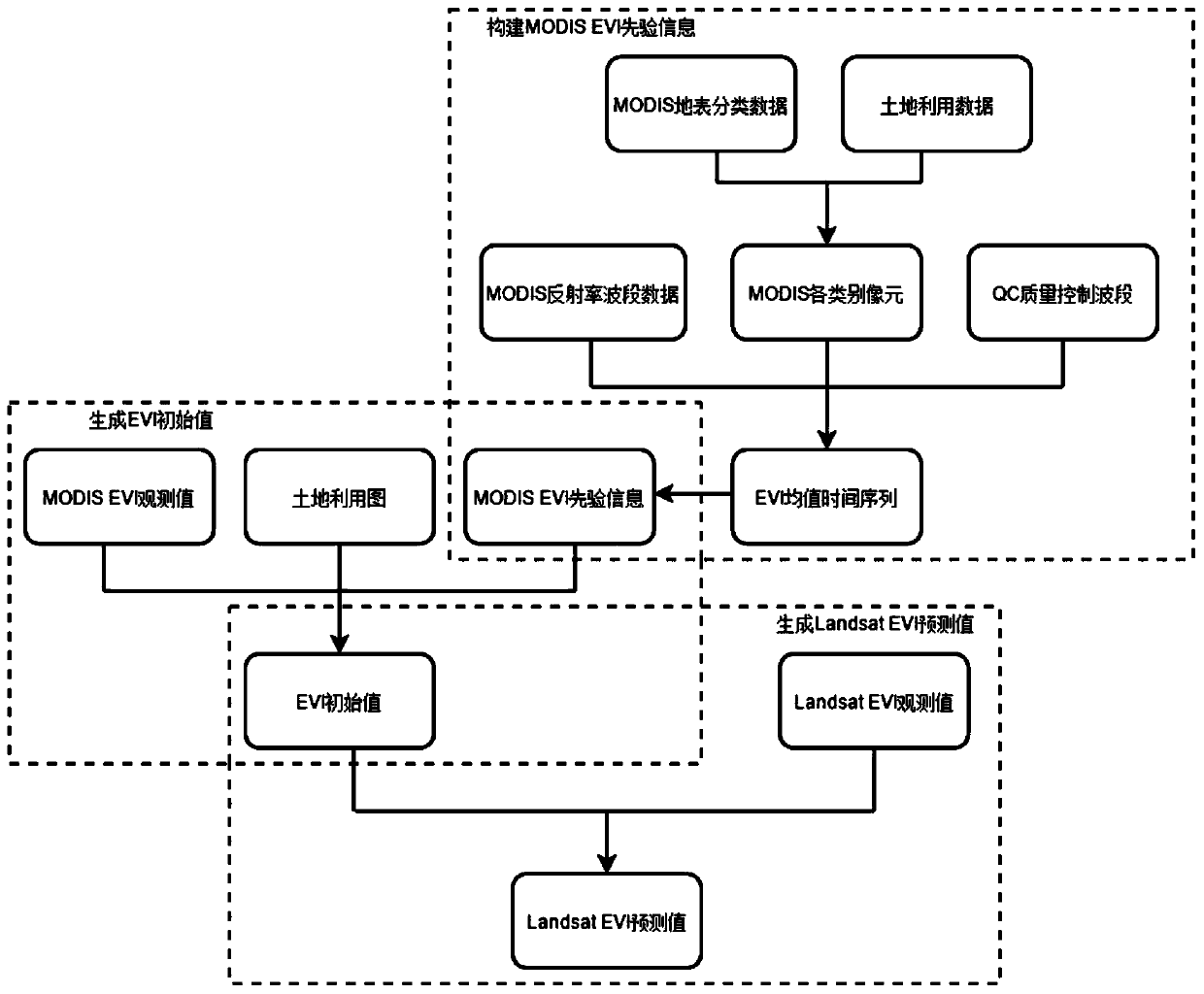
Method model for obtaining EVI index based on Bayesian theory
ActiveCN110147832AImprove time resolutionIn line with the law of growthCharacter and pattern recognitionTemporal resolutionDecomposition
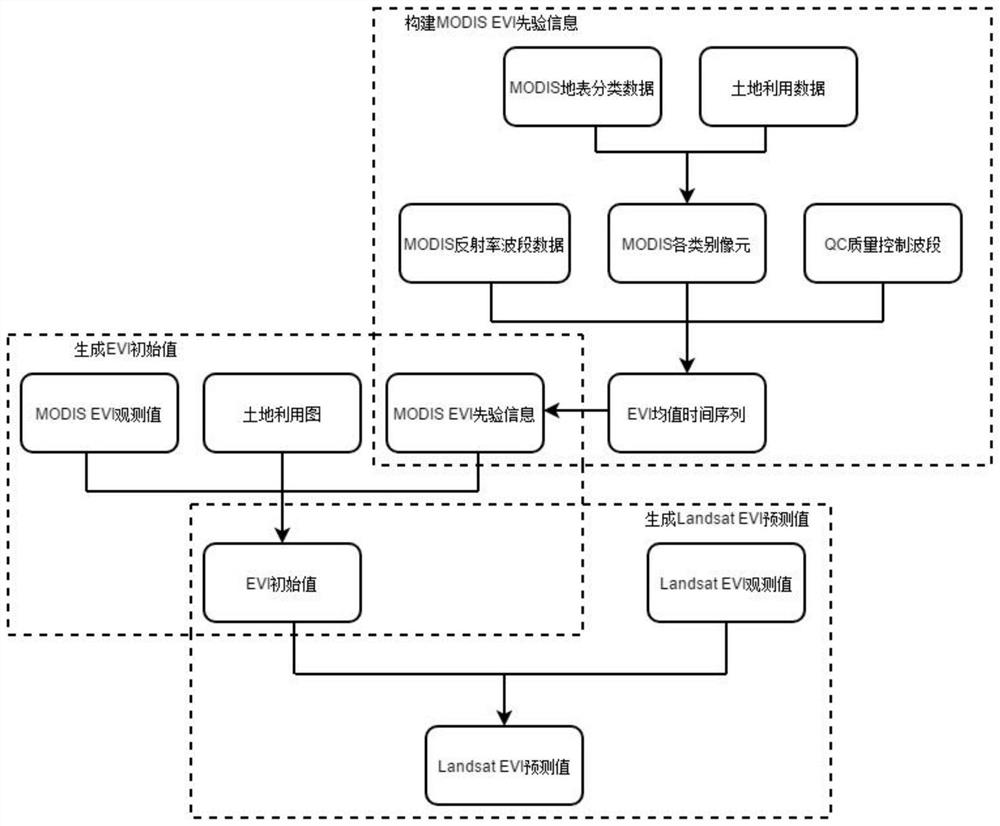
The invention belongs to the technical field of vegetation remote sensing, and discloses a method model for obtaining an EVI index based on the Bayesian theory, and the method model comprises the following generation steps: (1) building MODIS EVI priori information: carrying out the spatial superposition of MODIS surface classification data and land utilization data, and carrying out the judgmentand extraction of all types of pixels of an MODIS of each land type; obtaining an EVI mean time sequence by combining the MODIS reflectivity band data and the QC quality control band of the MODIS reflectivity band data; performing filtering reconstruction; (2) generating an EVI initial value: introducing the MODIS EVI prior information by utilizing a Bayesian theory; carrying out mixed pixel decomposition on the MODIS EVI priori information and the MODIS EVI observation value in combination with a land utilization map; and (3) generating a Landsat EVI predicted value, using an EVI data prediction model, and using the Landsat EVI observed value at the pairing moment to reconstruct the EVI initial value. Based on the Bayesian theory, Landsat high-spatial-resolution data and MODIS high-time-resolution data are fused, and finally the EVI data with high spatial-temporal resolution are obtained.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for calculating vegetation indexes based on mixed vegetation indexes
ActiveCN110634077AIncreased sensitivityMake up for insensitivityData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionVegetationVegetation Index
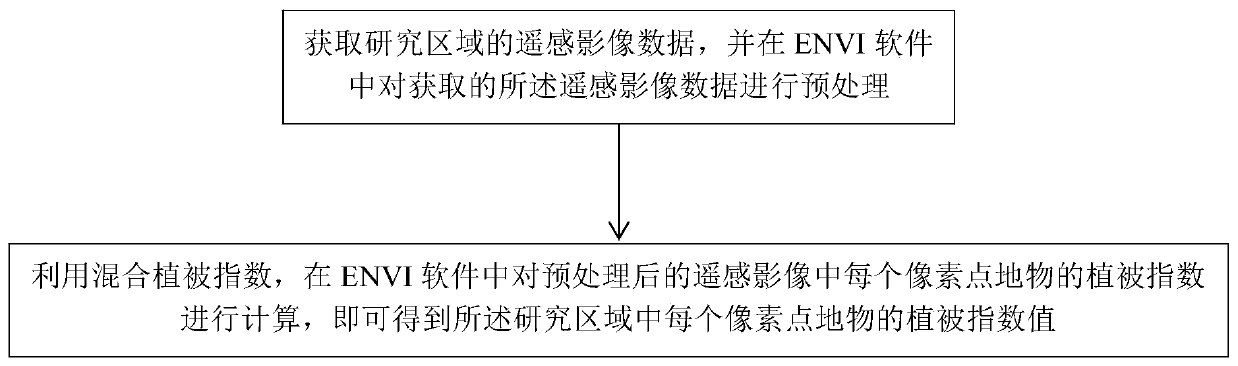
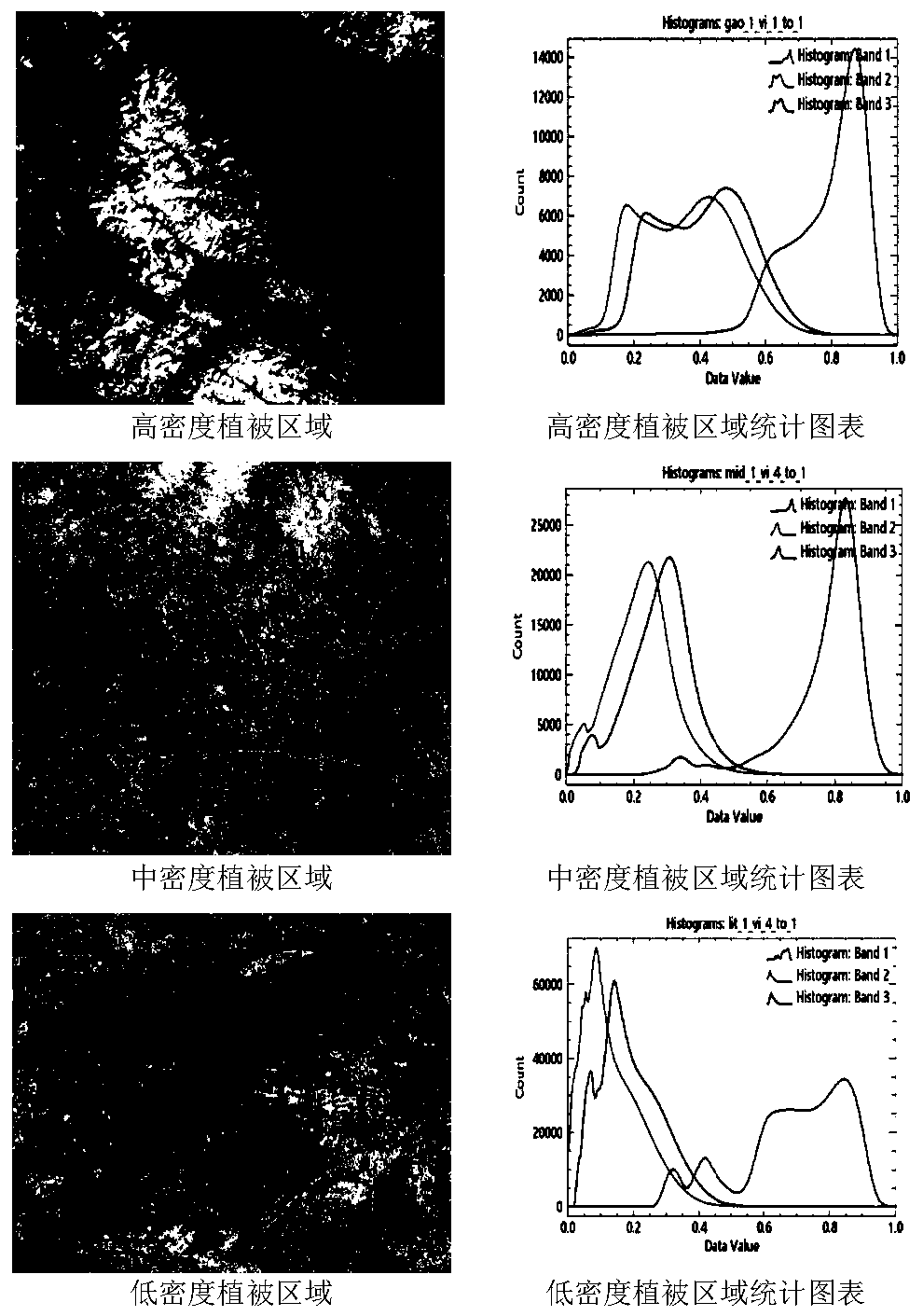
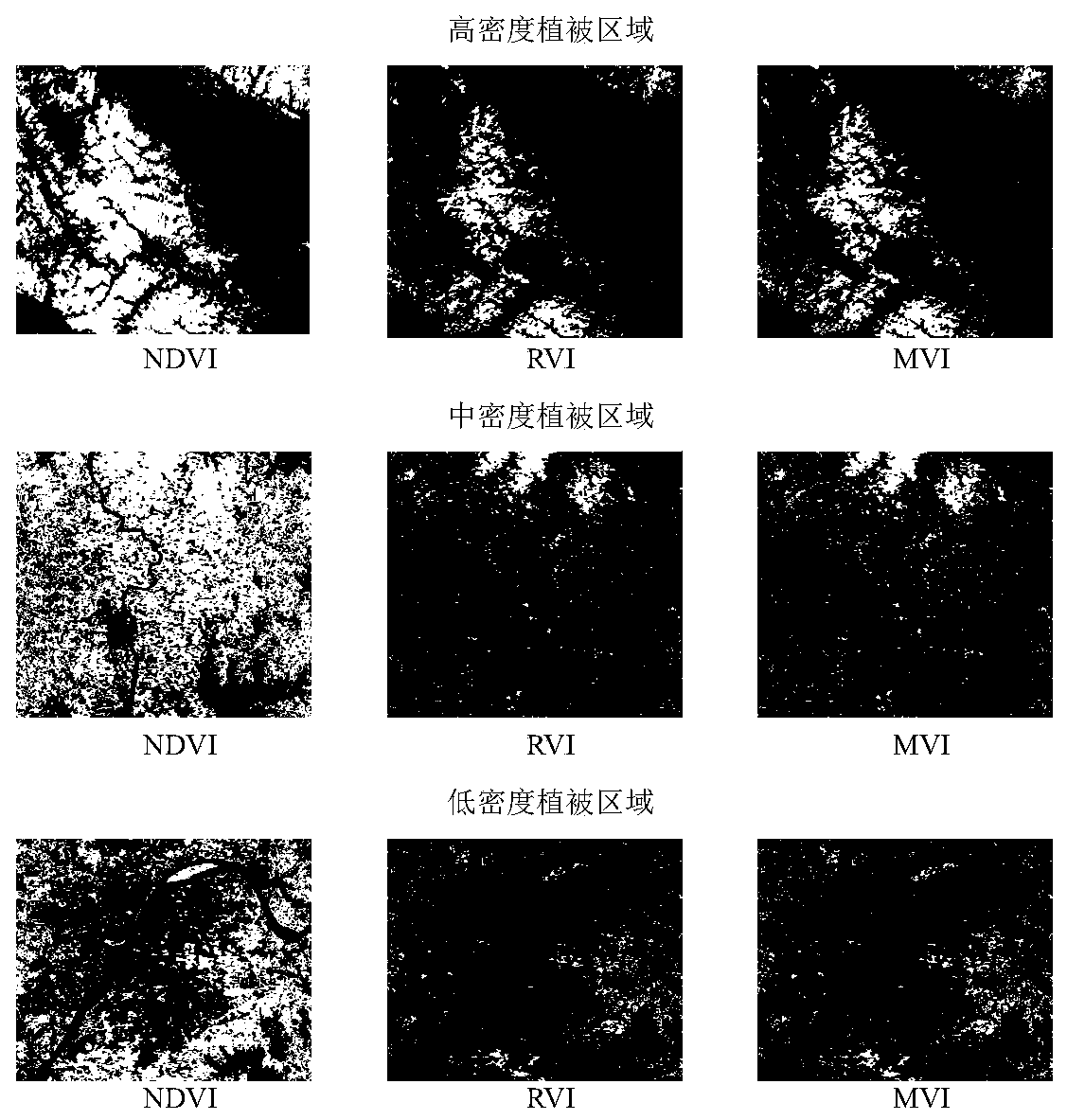
The invention relates to the field of vegetation remote sensing, in particular to a method for calculating a vegetation index based on a mixed vegetation index, which mainly comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring remote sensing image data of a research area, and preprocessing the acquired remote sensing image data in ENVI software; and S2, calculating the vegetation index of the ground object of each pixel point in the preprocessed remote sensing image in ENVI software by utilizing the mixed vegetation index, so as to obtain the vegetation index value of the ground object of each pixel point in the research area. The mixed vegetation index provided by the invention has high sensitivity to vegetation state change in a wider vegetation coverage range, and makes up for the defect of insensitivity of NDVI calculation in a high vegetation coverage area and RVI calculation in a low vegetation coverage area.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
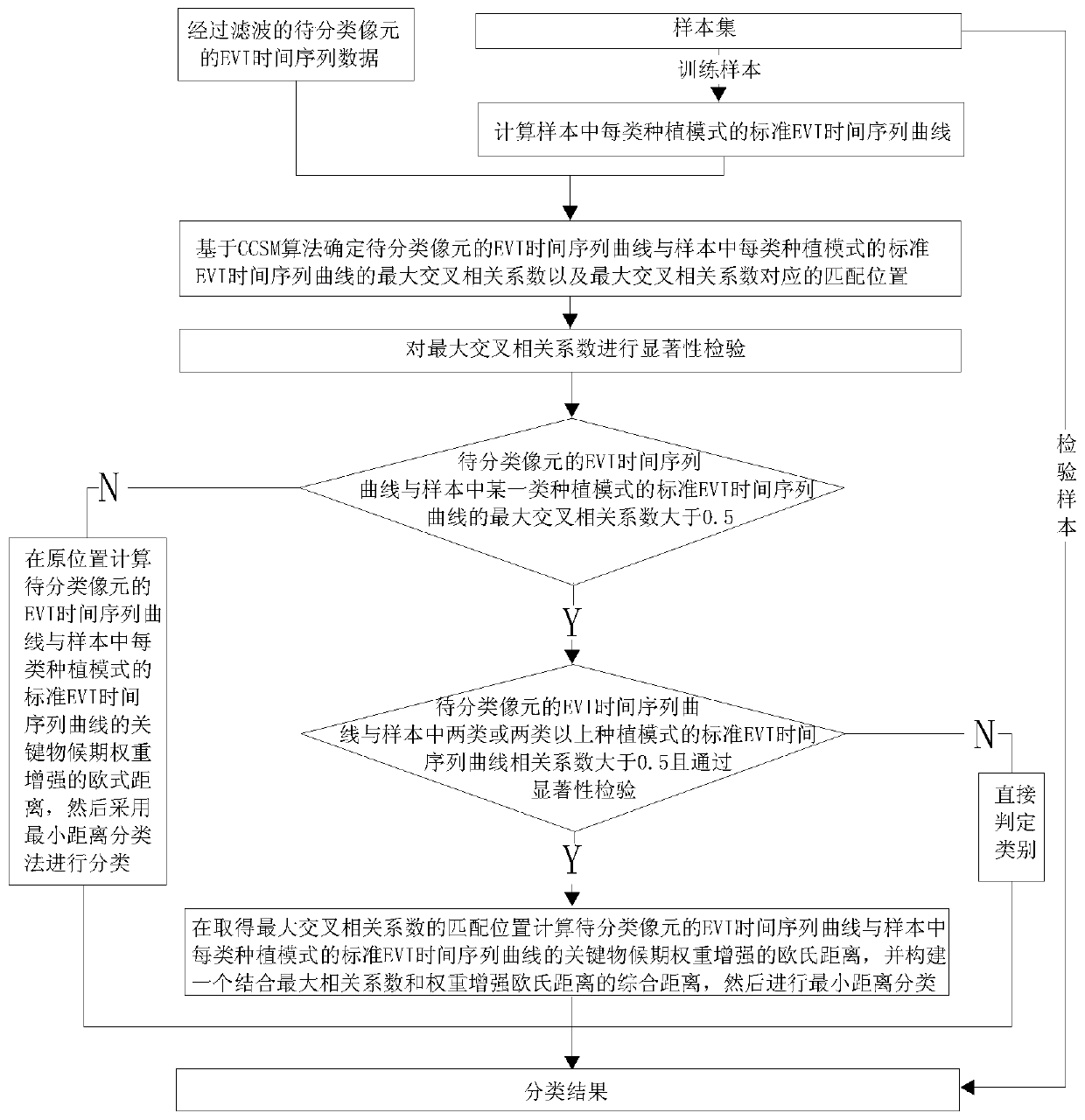
Crop planting pattern classification method and system considering phenological characteristics
ActiveCN109919207BEliminate the effect of classificationEfficient use ofCharacter and pattern recognitionSoil scienceComputer vision
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
A Method for Obtaining Spatial Distribution of Desert Riparian Forest Based on GIS Buffer Analysis
ActiveCN107145872BDynamic MonitoringImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisBuffer stripVegetation
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
A multi-angle observation method for accurate inversion of sunlight-induced chlorophyll fluorescence in shade and sun leaves of vegetation
Owner:NANJING UNIV
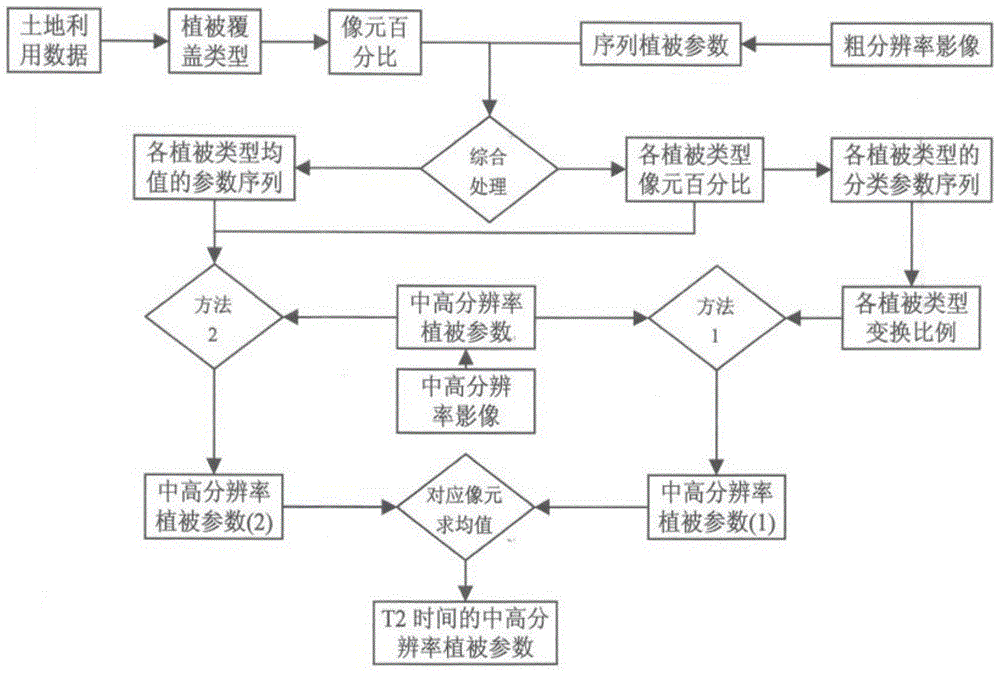
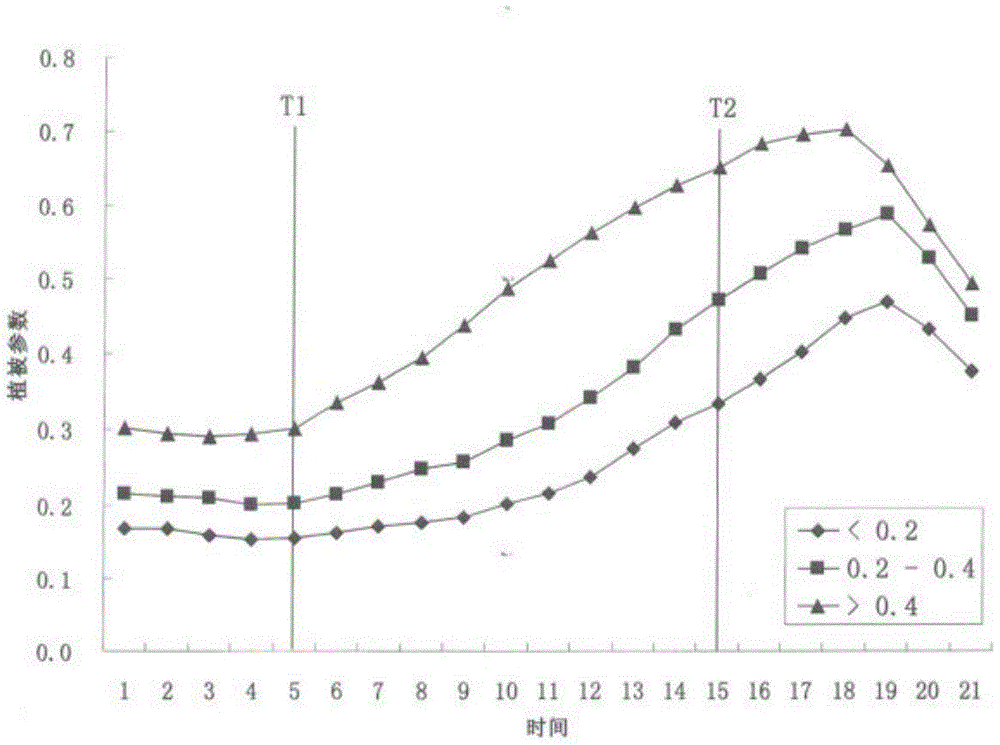
A Fitting Method of Vegetation Parameters Based on Medium and High Resolution Remote Sensing
ActiveCN103729835BImprove time resolutionRich remote sensing research methodsImage enhancementSensing dataImage resolution
The invention discloses a vegetation parameter fitting method based on middle-high resolution remote sensing. Due to the facts that used coarse resolution remote sensing data can be acquired easily, time resolution is very high, free shared data and products can be obtained, and the growth and development law difference of different vegetation types and the growth and development law difference in the vegetation of the same type are also used, when a study urges for the vegetation parameter in certain time, however, only the remote sensing data in another time can be acquired, through the method, the vegetation remote sensing parameter in the needed time can be simulated, and remote sensing study methods are enriched. For the reason that the middle-high resolution remote sensing is used for regional scale study, through the method, remote sensing data acquired at the study area in different time can be unified to the time which is needed by the study, and therefore the remote sensing data covering the entire study area in the same time can be acquired. Cloudless middle-high resolution remote sensing data in the needed time can reappear, and thus necessary data support can be provided for vegetation remote sensing correlation study work such as ecological remote sensing, environmental remote sensing and agricultural remote sensing.
Owner:河南河大资产经营有限公司
A Method Model for Obtaining Evi Index of High Spatiotemporal Time Series Based on Bayesian Theory
ActiveCN110147832BImprove time resolutionIn line with the law of growthCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmHigh temporal resolution
The invention belongs to the technical field of vegetation remote sensing, and discloses a method model based on Bayesian theory to obtain high time-series EVI index, comprising the following generation steps: (1) constructing MODIS EVI prior information: combining MODIS surface classification data and land use data in Superimpose in space, judge and extract MODIS pixels of each category; combine MODIS reflectance band data and its QC quality control band to obtain EVI mean time series; carry out filter reconstruction; (2) generate EVI initial value: use Bay The Yasian theory introduces the MODIS EVI prior information; combined with the land use map, the MODIS EVI prior information and the MODIS EVI observation value are decomposed into mixed pixels; (3) Generate Landsat EVI prediction value and use EVI data to predict The model uses the Landsat EVI observations at paired moments to reconstruct the initial value of EVI. Based on Bayesian theory, the present invention fuses Landsat high spatial resolution data and MODIS high temporal resolution data, and finally obtains EVI data with high temporal and spatial resolution.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
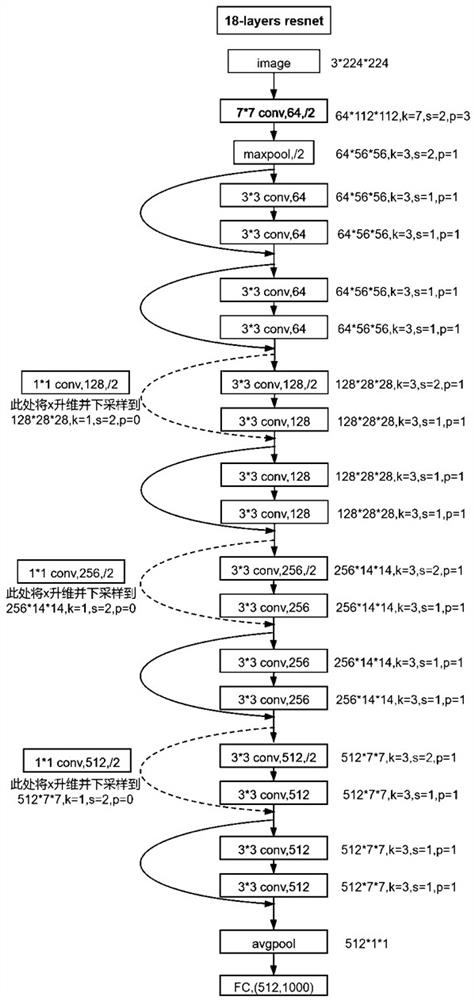
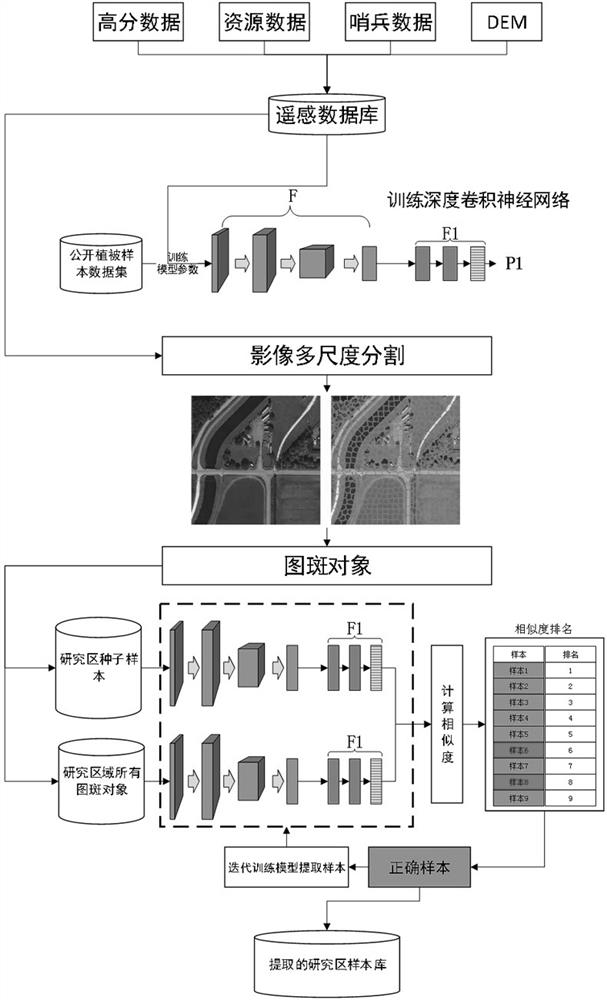
Semi-automatic vegetation remote sensing sample selection method based on convolutional neural network
PendingCN113989506ASolve the scarcityHigh degree of automationCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setNetwork output
The invention provides a semi-automatic vegetation remote sensing sample selection method based on a convolutional neural network. The method comprises the following steps of S1, constructing a multi-source multi-temporal remote sensing database, S2, dividing vegetation in the research area into m vegetation groups, S3, constructing a deep residual network, and changing the number of network output categories into m, S4, using the public vegetation sample data set to train a deep residual network, and enabling model parameters to be suitable for vegetation group classification, S5, segmenting the image of the research area into vegetation group pattern spots by adopting a multi-scale segmentation algorithm, S6, selecting n representative samples of m vegetation types, and taking m*n samples as seed samples of sample selection, S7, calculating network output of all individual pattern spots in the research area, and S8, calculating network output of the seed sample. The problem of sample scarcity in mountainous area vegetation classification is solved to a certain extent.
Owner:FUZHOU PLANNING DESIGN & RES INST
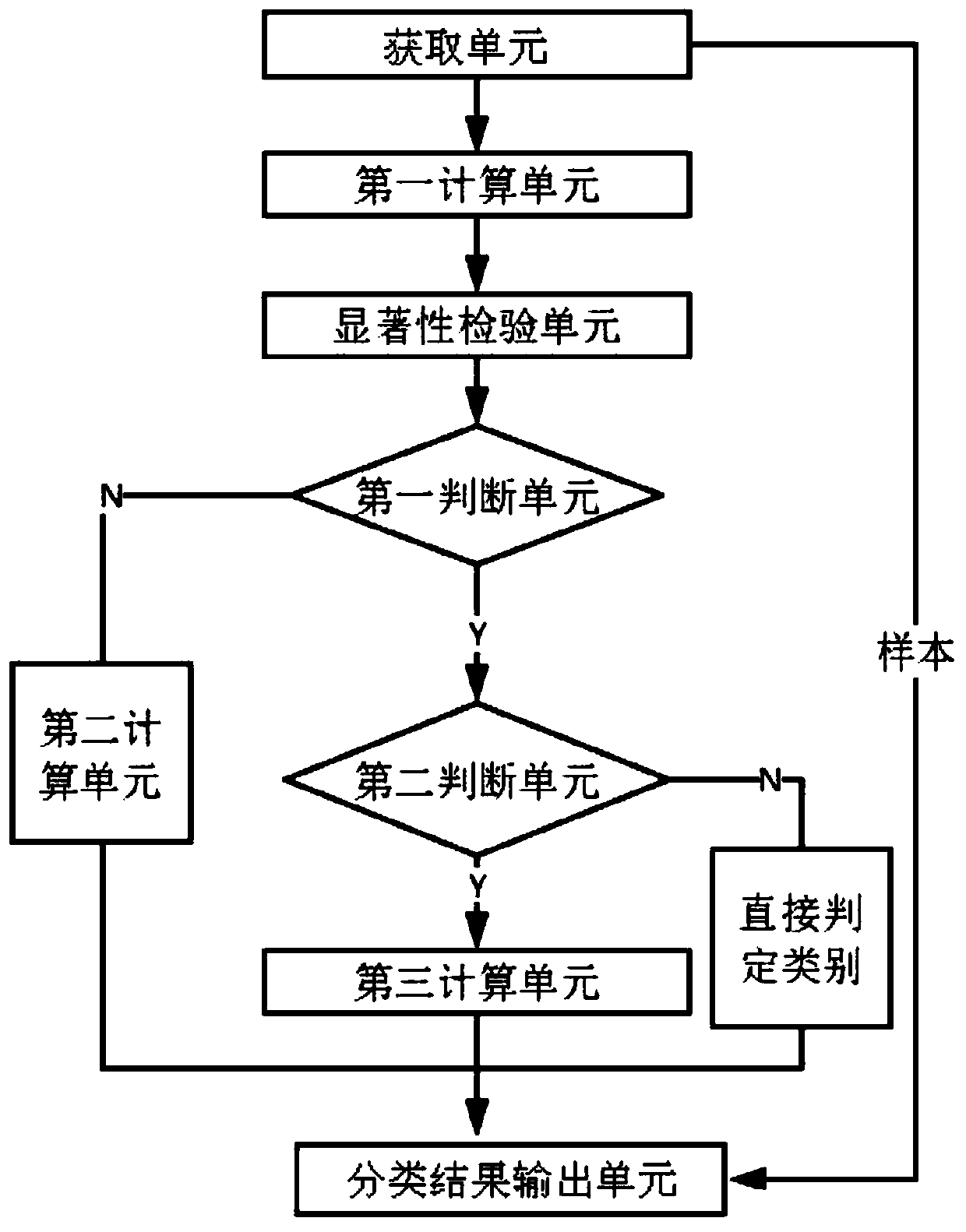
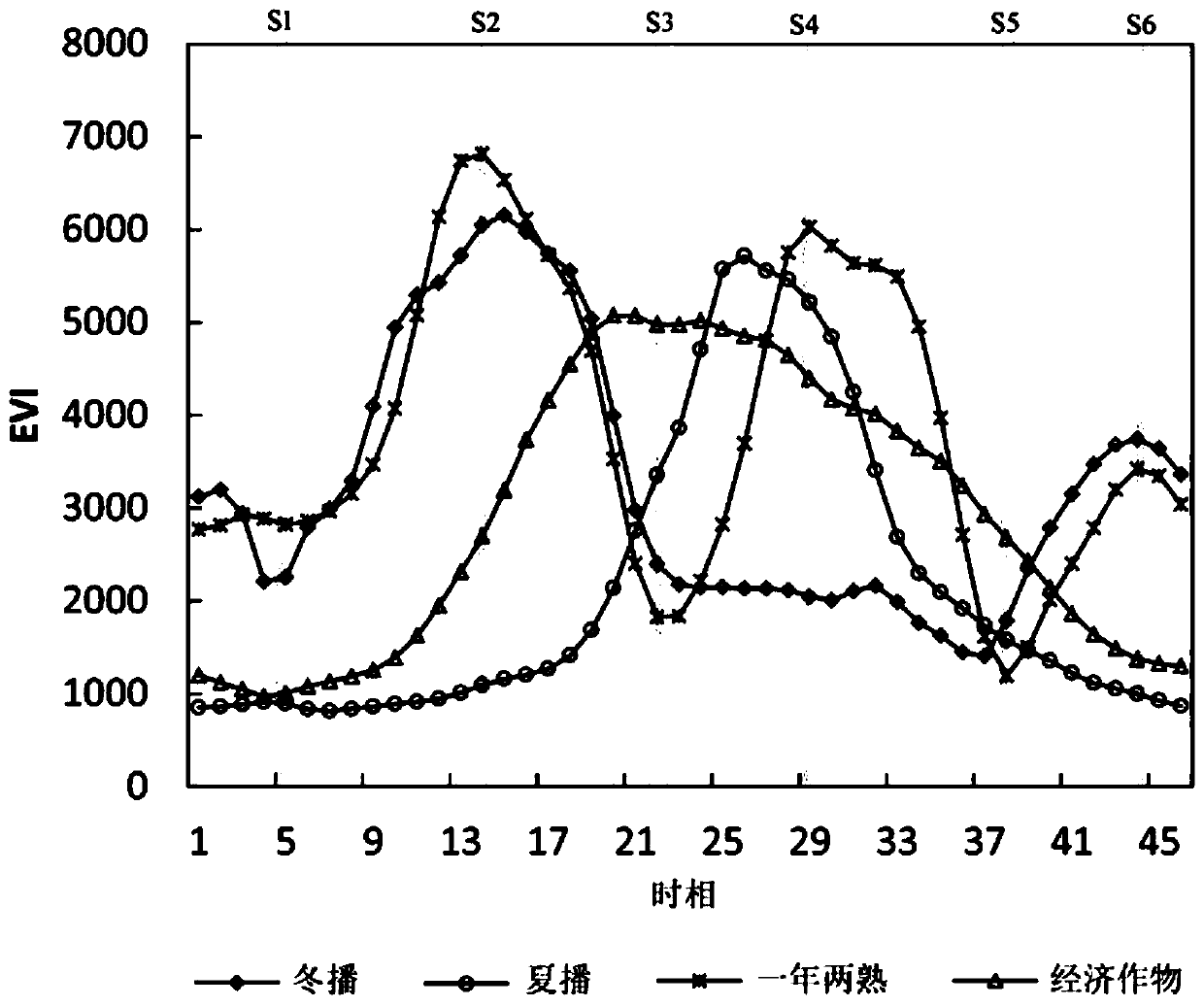
A crop planting mode classification method and system considering phenological characteristics
ActiveCN109919207AEliminate the effect of classificationEfficient use ofCharacter and pattern recognitionClassification methodsComputer science
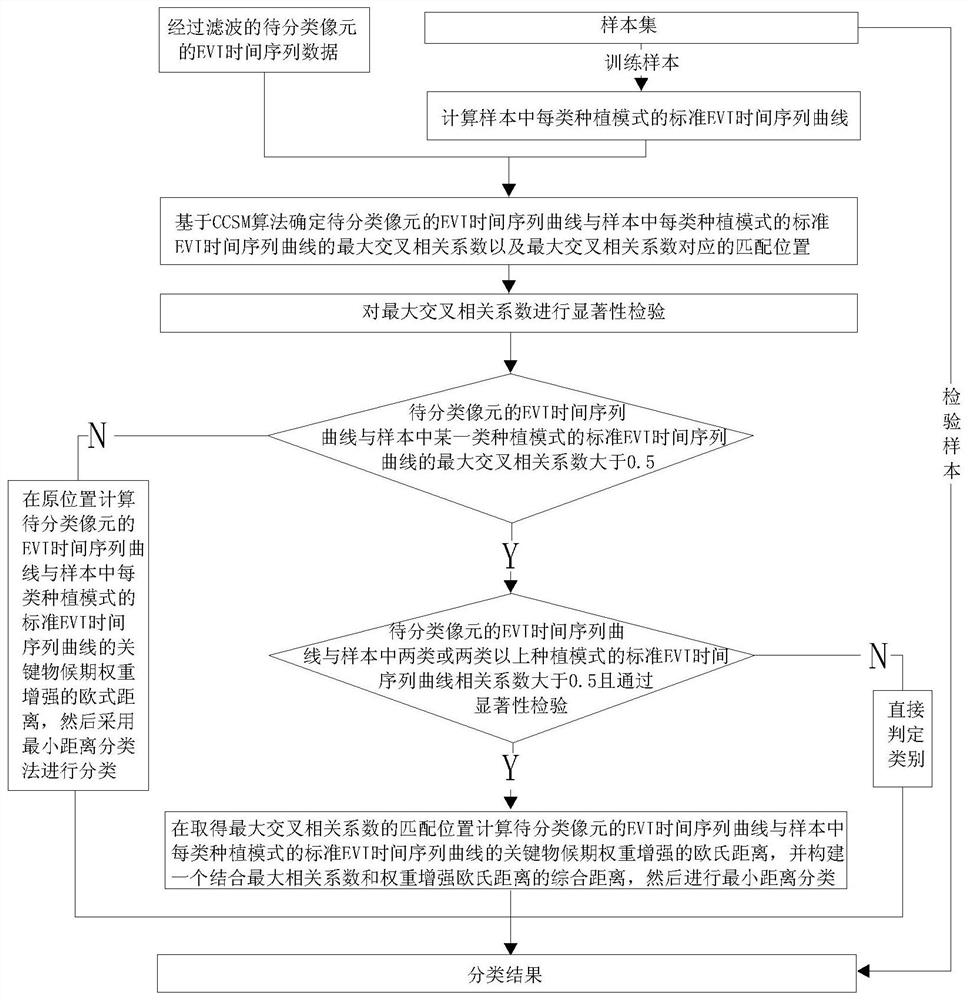
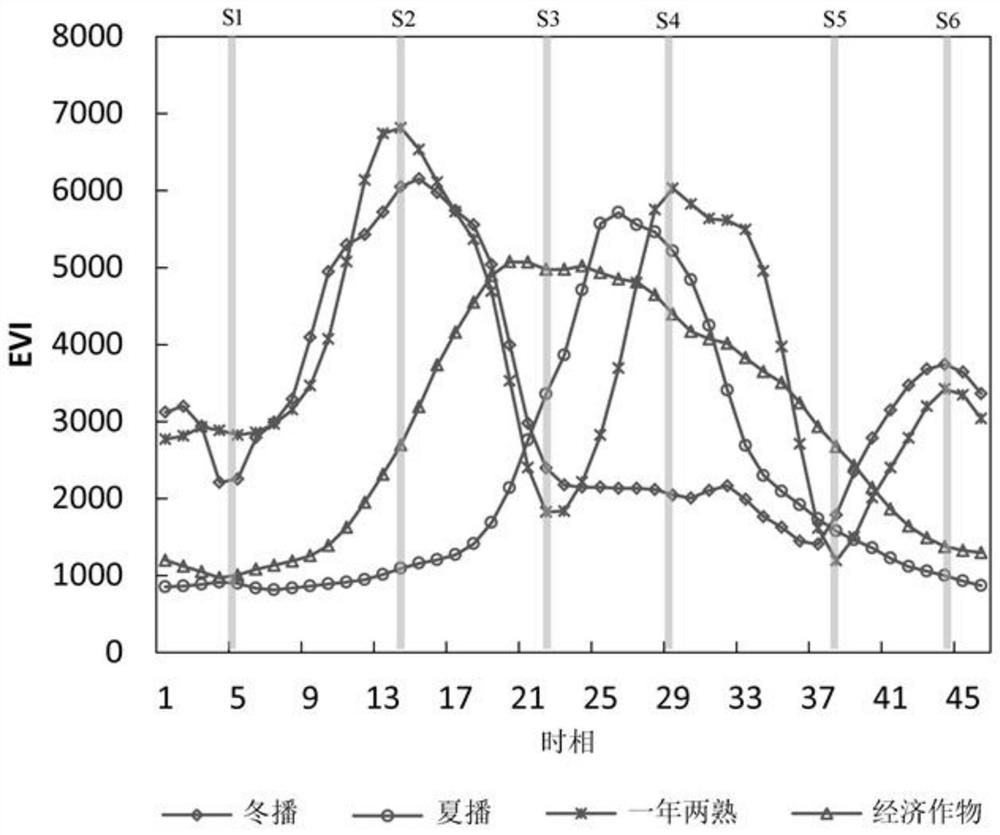
The invention provides a crop planting mode classification method and system considering phenological characteristics, and relates to the field of vegetation remote sensing. By fully utilizing the effect of the difference of the key phenological period EVI time sequence curve in identifying the planting mode type and enhancing the weight of the key phenological period, the information of the key phenological period can be effectively utilized, the information of the non-key phenological period can be inhibited, and the crop planting mode classification precision can be improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
A Method of Extracting Vegetation Information from Aerial Photographs Based on Collaborative Remote Sensing Images
ActiveCN110533052BExtraction is fast and relatively accurateExpand the scope of remote sensing applicationsMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionVegetationImaging processing
The invention discloses a method for extracting vegetation information from aerial photographs of cooperative remote sensing images, and relates to the technical field of image processing. An effective method for vegetation remote sensing monitoring is established by using aerial photographs and remote sensing images containing visible light bands to extract vegetation information. , to be applied to the plant identification research of destination aerial photos, to extract vegetation information quickly and relatively accurately.
Owner:GUIZHOU INST OF PRATACULTURE
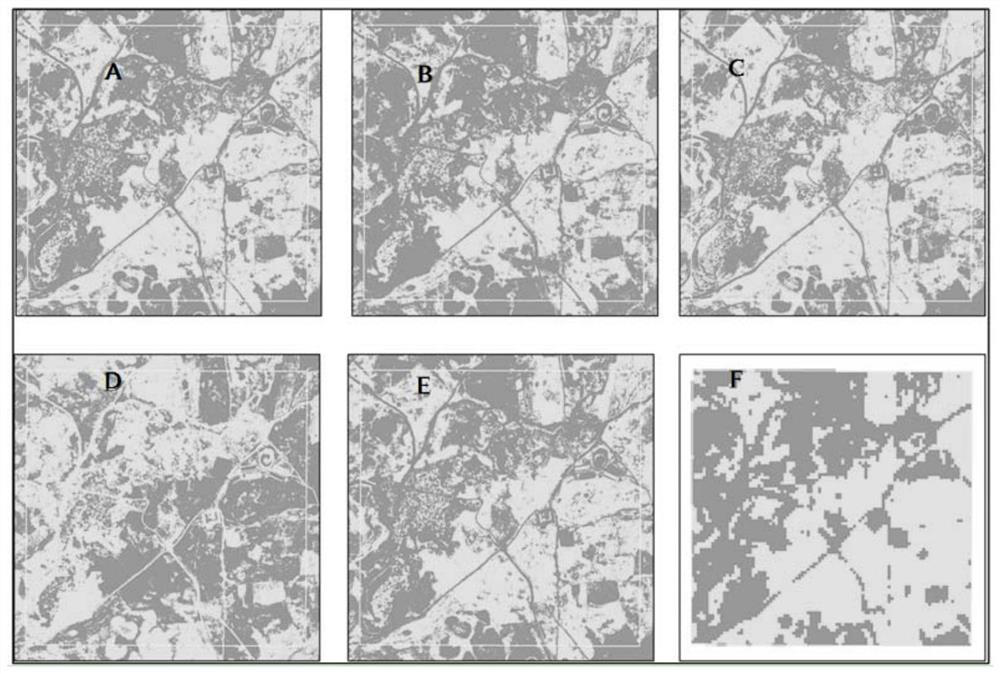
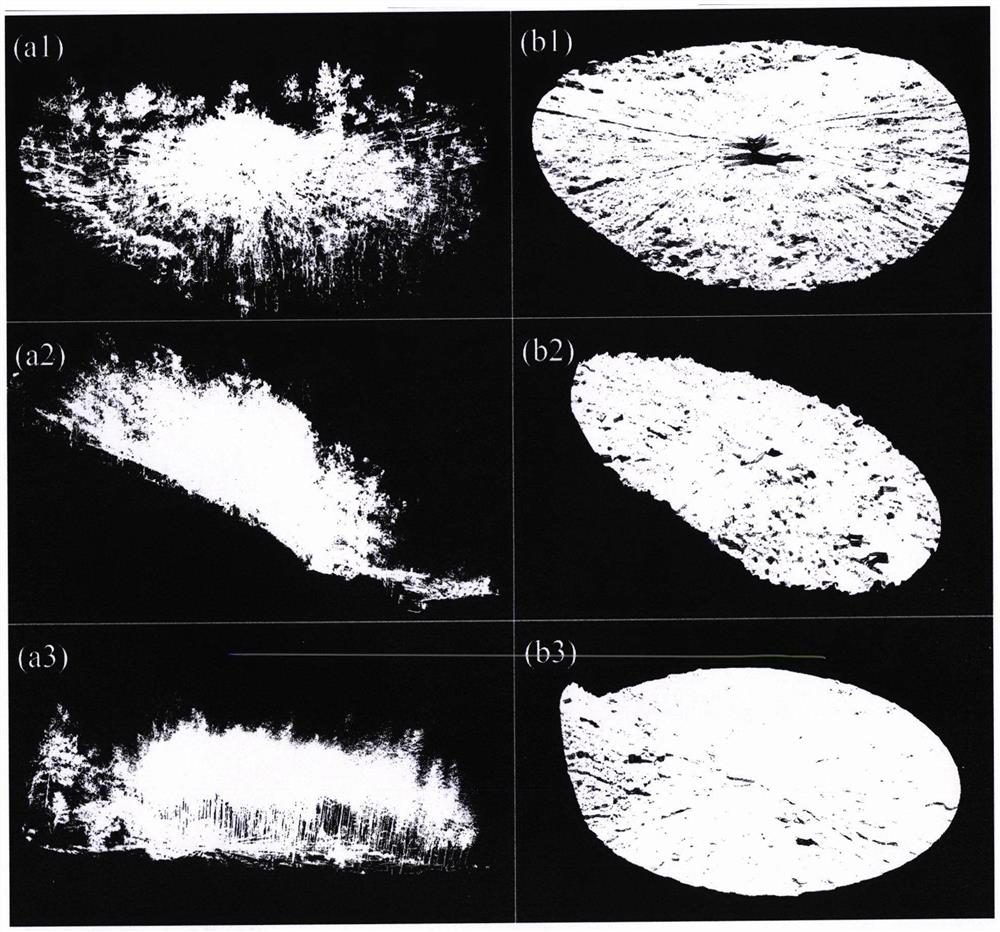
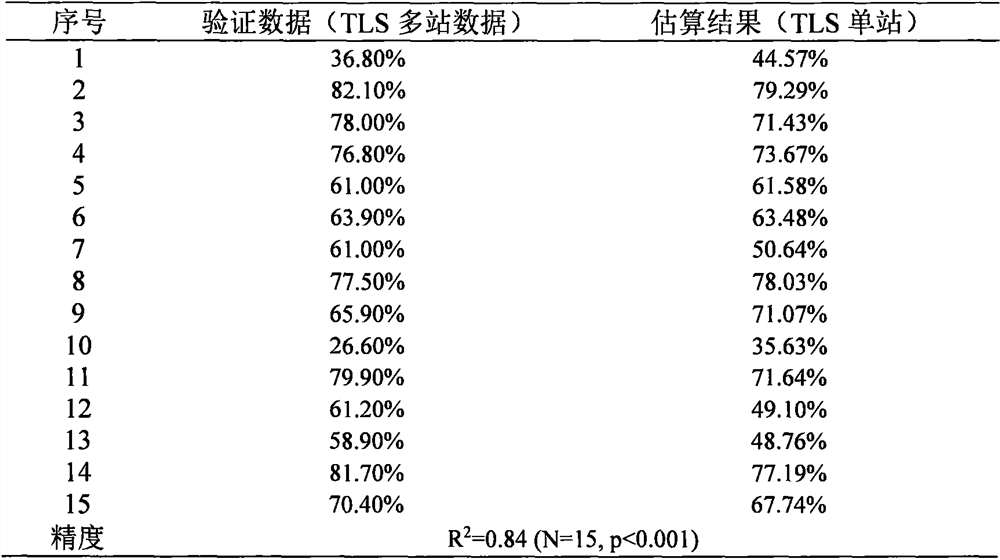
Method for extracting under-forest vegetation coverage under complex terrain condition by using ground laser radar data
PendingCN112859108AElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationSoil scienceVegetation remote sensing
The invention provides a method for extracting under-forest vegetation coverage under a complex terrain condition by using ground laser radar data, belongs to the research field of a vegetation remote sensing inversion parameter method, and aims to solve the problem that the under-forest vegetation coverage cannot be rapidly and effectively extracted under the complex terrain condition at present. According to the method, a ground point is extracted via height information, and on the basis of the ground point, the coverage of the vegetation under the forest is estimated by using a directional slicing method. The method can be used to accurately extract the coverage of the vegetation under the forest under the complex terrain condition, is high in precision, and is has great significance in recognition of erosion of soil under the forest and research of forest carbon cycle.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
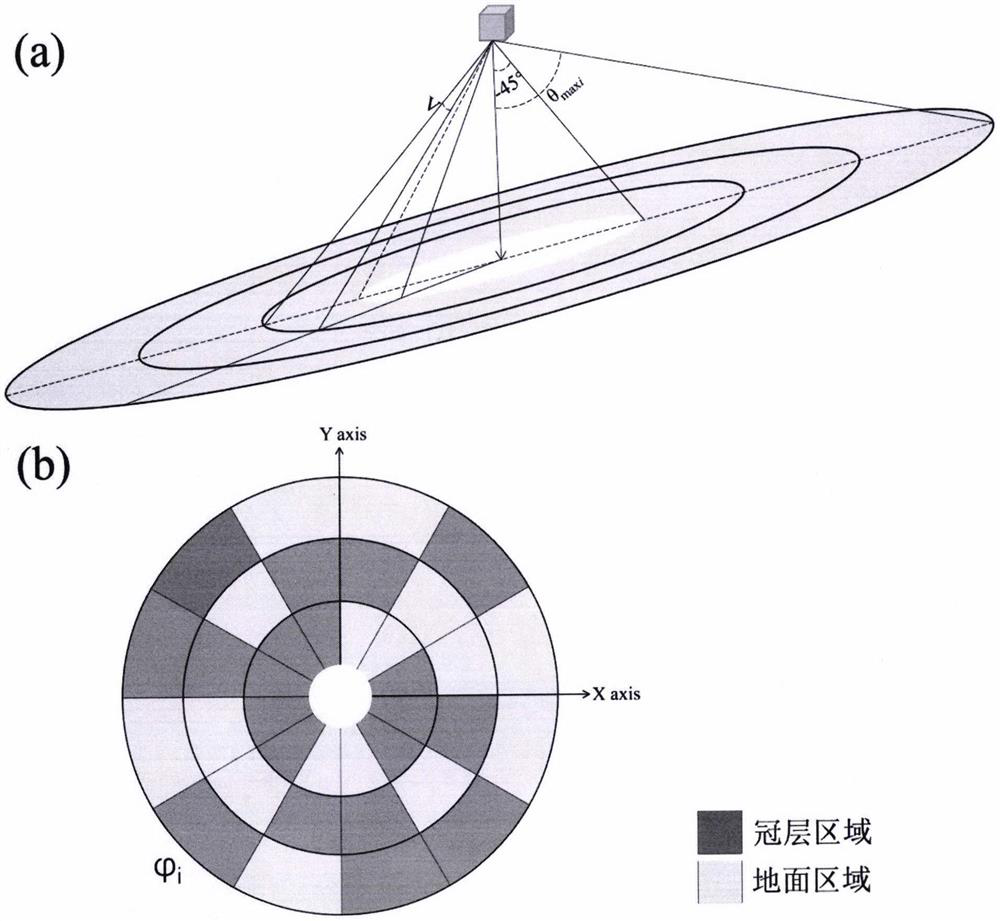
A model to describe the distribution of photosynthetically active radiation in forests using 3D point cloud data
The invention provides a model for depicting the distribution of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) in a forest by using three-dimensional point cloud data, which belongs to the research field of vegetation remote sensing modeling. Aiming at the problem that the three-dimensional distribution of forest canopy PAR cannot be effectively estimated by using lidar data on a fine scale at present, the present invention proposes a forest PAR three-dimensional spatiotemporal distribution estimation model based on the forest ground lidar data obtained from multiple stations. The model separately considers direct solar and scattered PAR transport in the forest, while taking into account the effects of element angles. The model constructed by the invention can quantitatively describe the three-dimensional space-time distribution of PAR in the forest on a fine scale, with high precision, which is helpful for the research on the physiological process of the forest.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A Satellite Remote Sensing Extraction Method of Leaf Albedo to Eliminate the Effects of Vegetation Canopy Structure and Surface Background
The invention provides a leaf reflectance satellite remote sensing extraction method for eliminating influence of vegetation canopy structures and earth surface backgrounds and belongs to the field ofresearch on vegetation remote sensing retrieval parameter methods. The method comprises the following steps: by using a 4-Scale model, confirming visual probability (PT) of sun leaves corresponding to a remote sensing image pixel spectrum and visual probability (PG) of a lighting background; calculating an angle index (AI) of the spectrum, performing related analysis on PT and PG, and establishing an estimation model based on Al, PT and PG; by taking a leaf area index (LAI), PT and PT as three retrieval items, establishing a checking table (related to wavelengths) for multi-time scattering factors M in a simulation manner by using the 4-Scale model; finally, by using the established estimation model and the checking table, calculating average leaf reflectance of remote sensing image vegetation pixels. By adopting the method provided by the invention, reflection spectrums of leaves can be extracted through remote sensing images; compared with an optimal iterative computation method, the method is high in calculation efficiency, and compared with a table checking method with multiple steps of checking, the method is relatively simple in calculation process and relatively high in efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for predicting net primary productivity of vegetation in regional marsh wetland
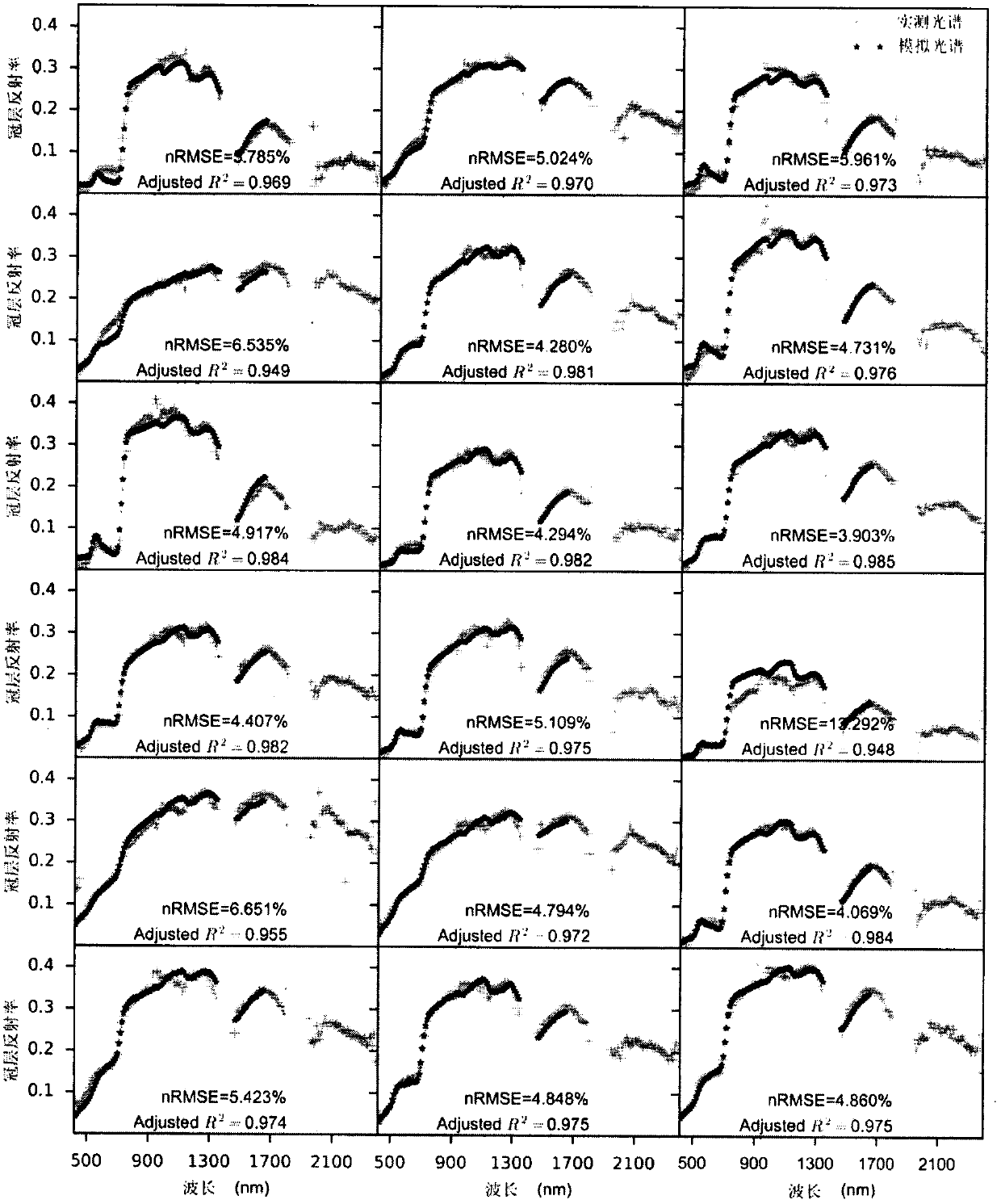
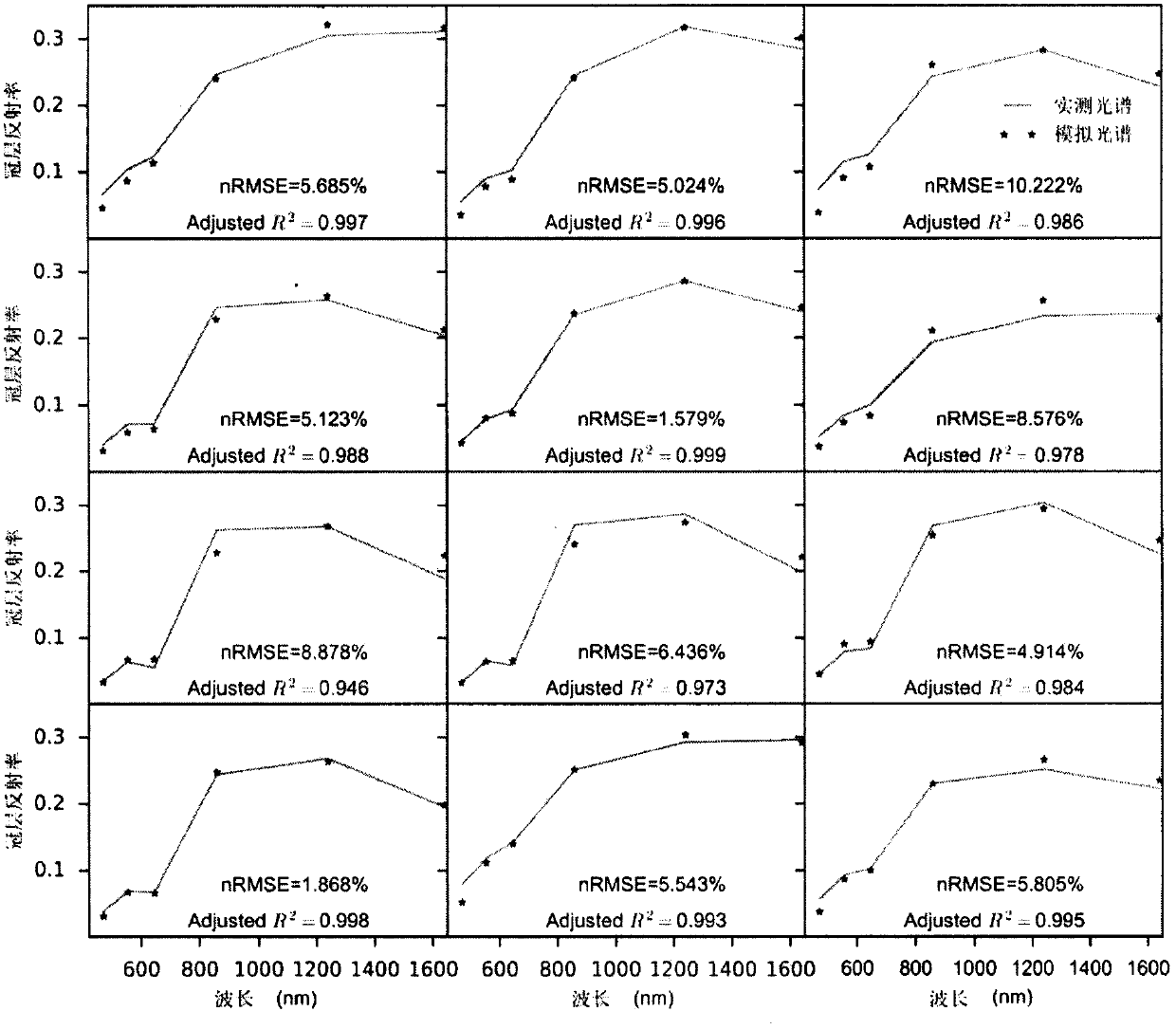
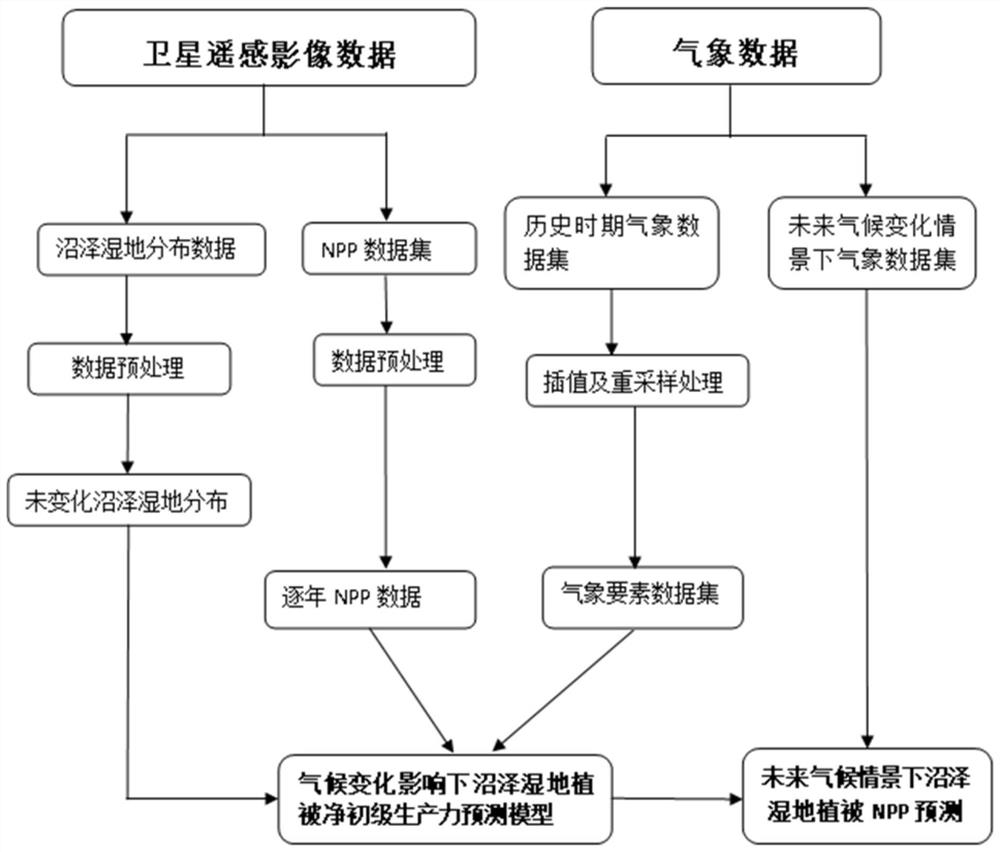
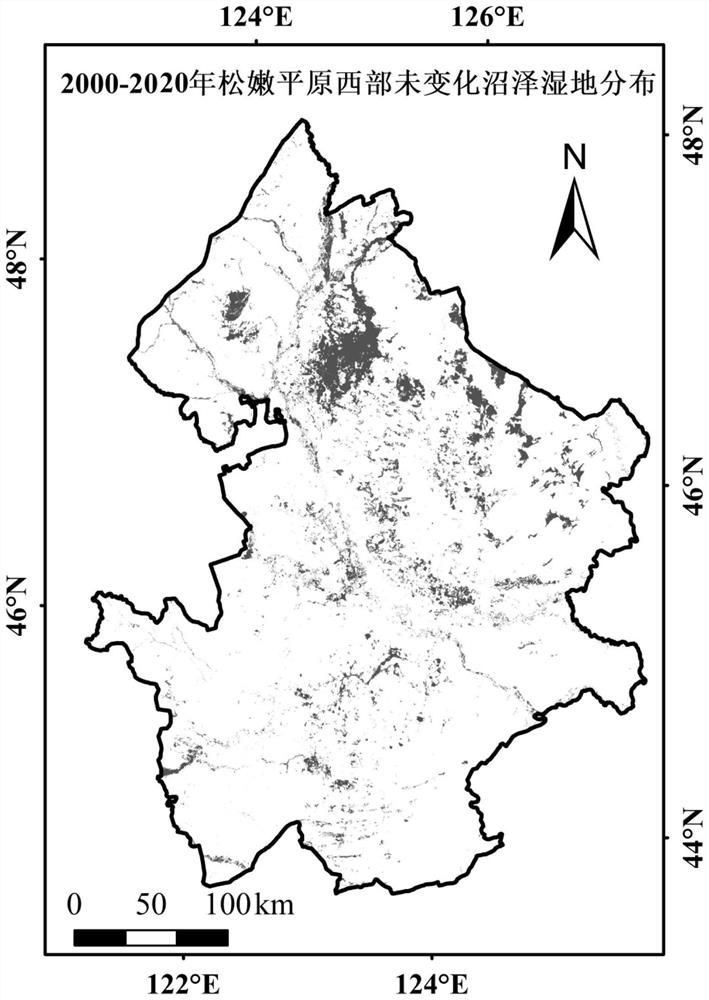
PendingCN113887841AAccurate predictionForecastingComplex mathematical operationsMarshMarsh vegetation
The invention discloses a method for predicting the net primary productivity of vegetation in a regional marsh wetland, and relates to a method for predicting the net primary productivity of future regional marsh wetland vegetation under the influence of climate change. The invention aims to solve the problem that the prior art means cannot accurately predict the net primary productivity of future marsh wetland vegetation. The method comprises the following steps: selecting unchanged marsh wetland distribution within a certain research time period as a research area; acquiring and preprocessing remote sensing data and meteorological data of marsh wetland vegetation in the research area; interpolating the meteorological data, and resampling; extracting net primary productivity and meteorological element values corresponding to all marsh vegetation pixels in the research area; constructing a prediction model; and predicting the net primary productivity of the marsh wetland vegetation in the future by using the prediction model in combination with meteorological data in a future climate change scene. The net primary productivity of the marsh vegetation under the influence of future climate change is predicted by utilizing the advantages that the remote sensing data is large in spatial scale and easy to obtain and combining the existing meteorological data.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Remote sensing extraction method of aquatic vegetation in eutrophic water based on algae index frequency method
ActiveCN104596448BEfficient removalSimple and fast operationUsing optical meansSatellite imageModerate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer
The invention provides an eutrophic water aquatic vegetation remote sensing extraction method based on an alga index frequency method. The eutrophic water aquatic vegetation remote sensing extraction method includes S1, selecting MODIS (moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer) images of eutrophic water with aquatic vegetation luxuriant and area stable at different periods; S2, subjecting the MODIS images selected to FAI (floating alga index) calculation; S3, according to the FAI, calculating VPF (vegetation signal appearance frequency) of pixels j at the periods; S4, defining VPF threshold values of all periods and calculating the aquatic vegetation area Aav. The eutrophic water aquatic vegetation remote sensing extraction method has the advantages that the influence of floating alga to aquatic vegetation remote sensing inversion is eliminated, and by integrating typical period dividing, frequency judgment and satellite image judgment, the influence of the floating alga and perennial alga bloom areas to the accurate aquatic vegetation area remote sensing inversion is eliminated.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com