Method for predicting net primary productivity of vegetation in regional marsh wetland
A technology of net primary productivity and wetland vegetation, applied in the direction of forecasting, complex mathematical operations, data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to accurately predict the net primary productivity of swamp wetland vegetation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
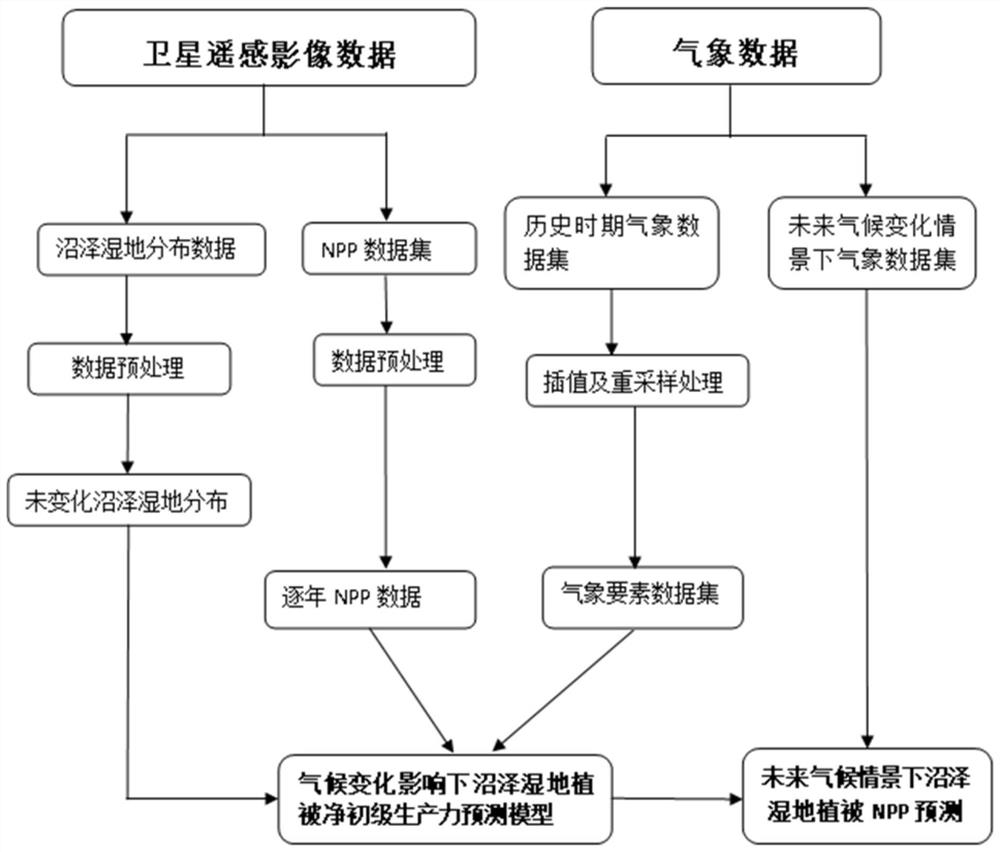
[0031] Specific implementation mode one: the steps of a method for predicting the net primary productivity of regional swamp wetland vegetation in this implementation mode are as follows:
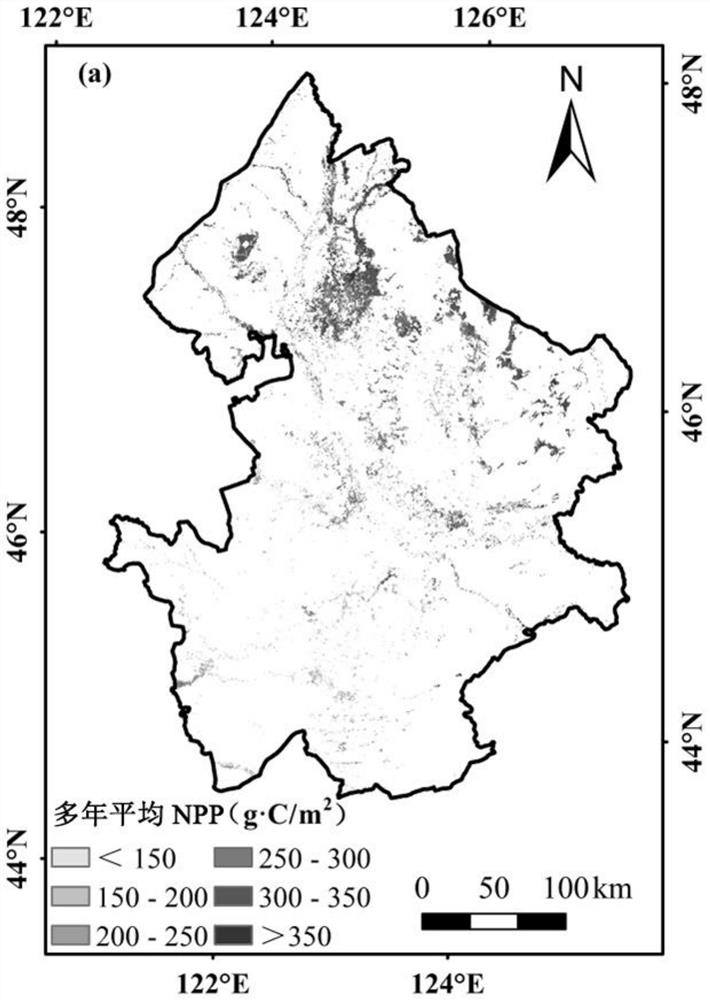
[0032] Step 1. Obtain two phases of swamp and wetland distribution data sets, NPP data sets, and monthly observation meteorological data sets of meteorological stations within a period of time covering the study area, and preprocess the NPP data sets;
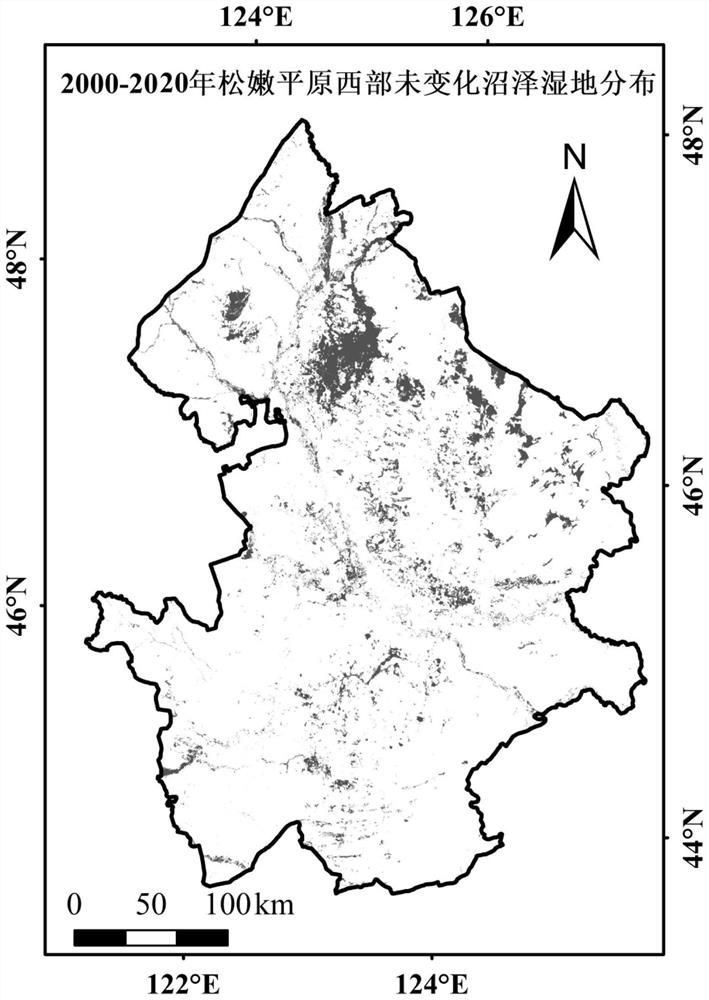
[0033] Step 2. Based on the distribution data of the two phases of swamp wetlands, extract the distribution of swamp wetlands that have not changed during the research period, and use them as the scope of the research area;
[0034] Step 3. Using the ordinary Kriging interpolation method, interpolation and resampling are carried out on the monthly observation meteorological data sets of the meteorological stations in the study time period, so as to obtain the monthly meteorological data sets of each meteorological element with the same resolu...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in Step 1, the year-by-year NPP data set is preprocessed in the form of format conversion and reprojection to unify it into the same coordinate system and projection. Others are the same as the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0041] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one or two is that step six: through multivariate stepwise regression analysis pixel by pixel, construct the net primary productivity prediction model of swamp wetland vegetation under the influence of climate change, select the fitting The model with the highest coefficient value is used as the final prediction model, and the formula is as follows:
[0042] NPP=a 0 +a 1 x 1 +a 2 x 2 +a 3 x 3 +…+a n x n Formula 1)
[0043] where x 1 , x 2 , x 3 ,...x n are the values of a certain meteorological element in a certain month during the research period, a 1 , a 2 , a 3 ,...a n are the corresponding coefficients, a 0 is a constant term. Others are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com