Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
78 results about "Telescope mount" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
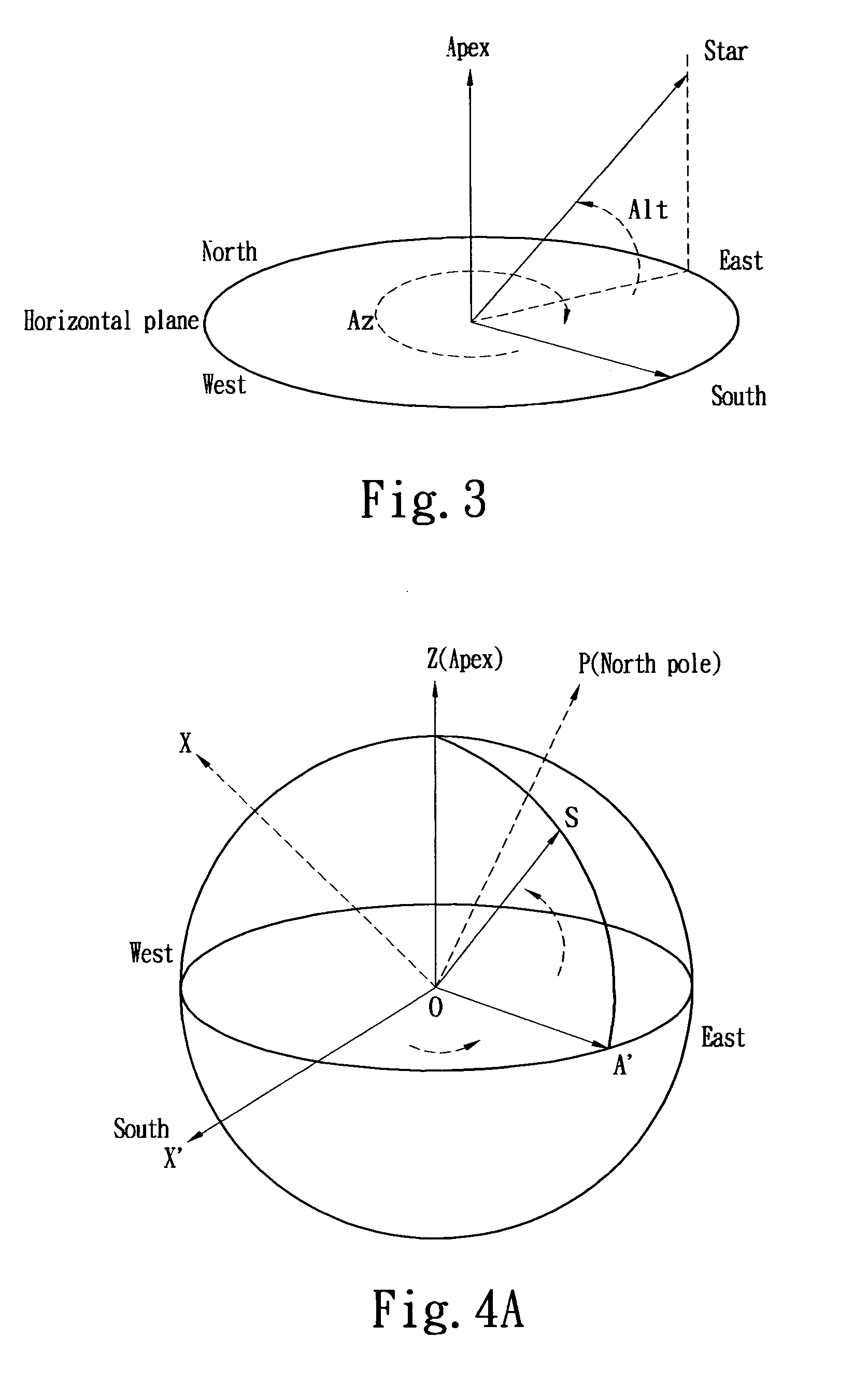
A telescope mount is a mechanical structure which supports a telescope. Telescope mounts are designed to support the mass of the telescope and allow for accurate pointing of the instrument. Many sorts of mounts have been developed over the years, with the majority of effort being put into systems that can track the motion of the fixed stars as the Earth rotates.
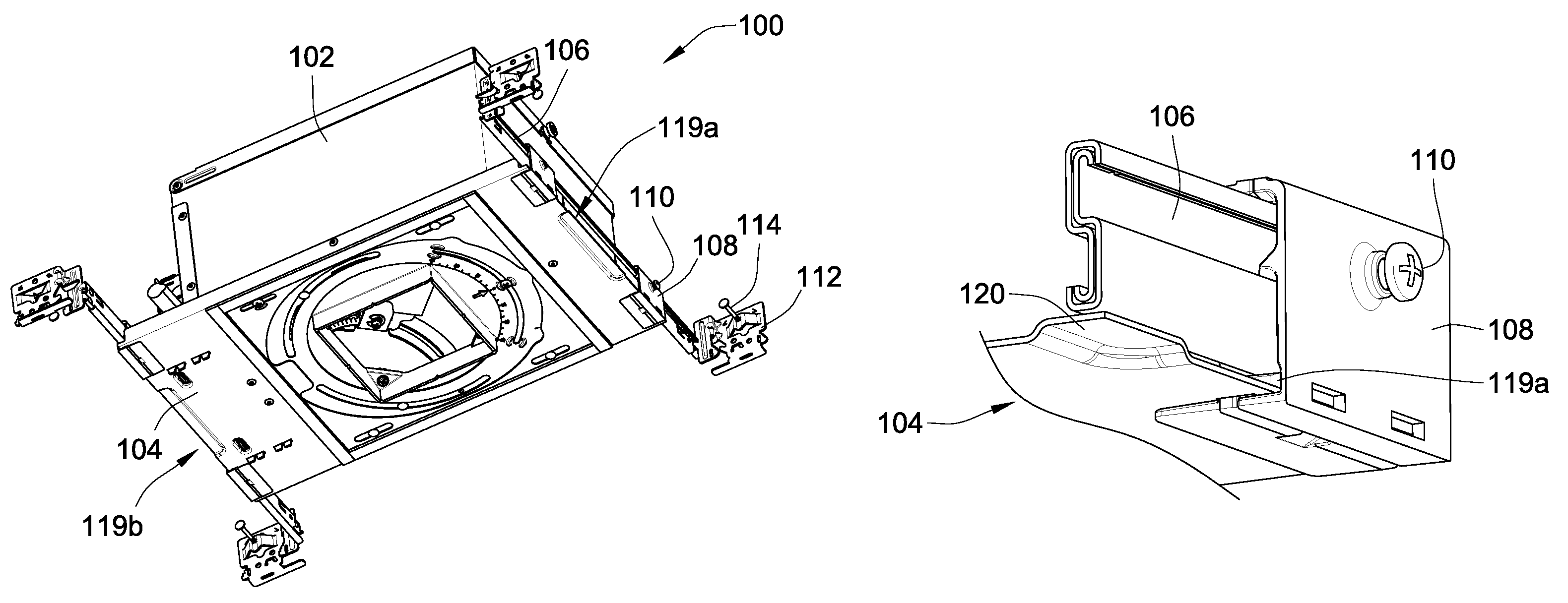
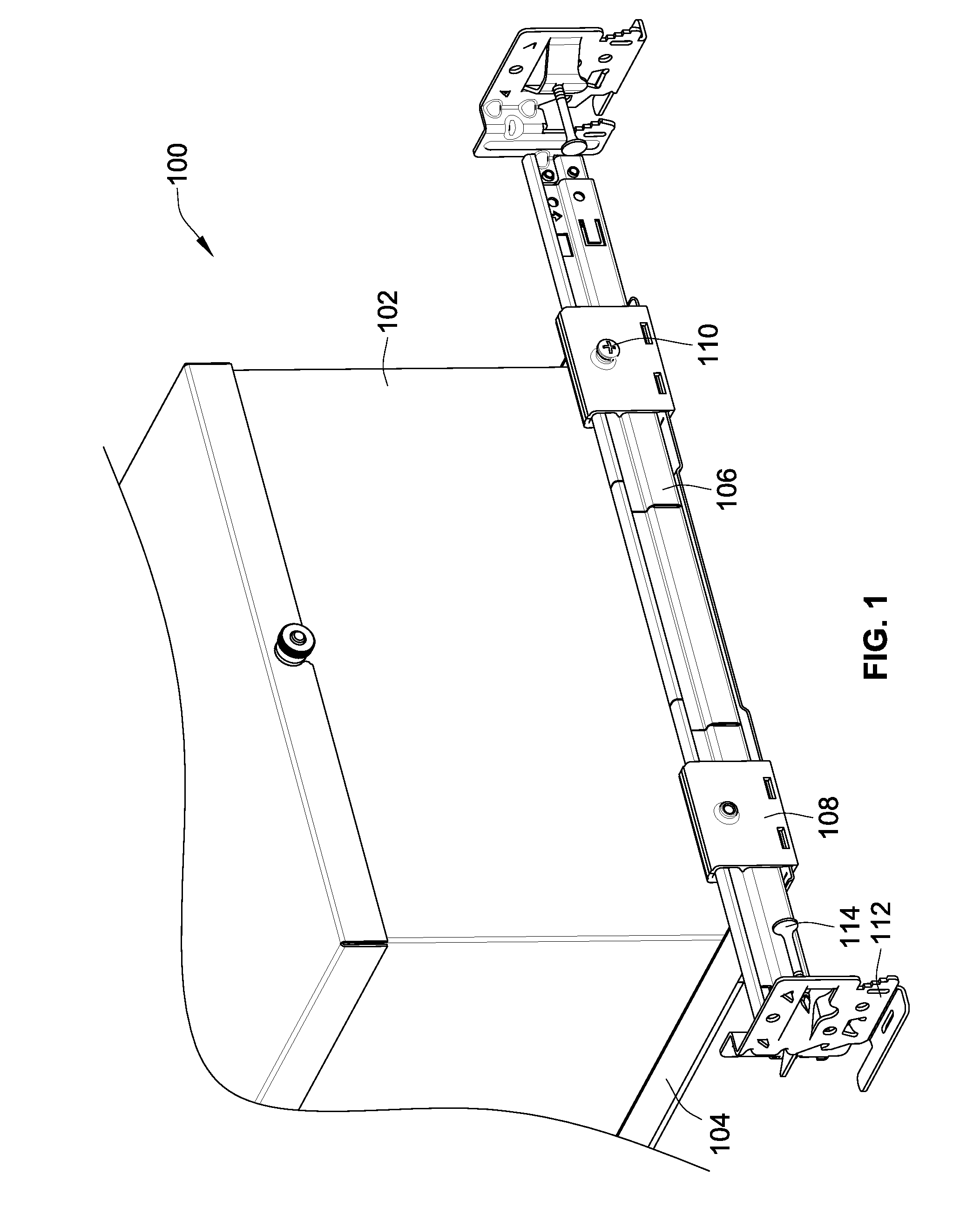
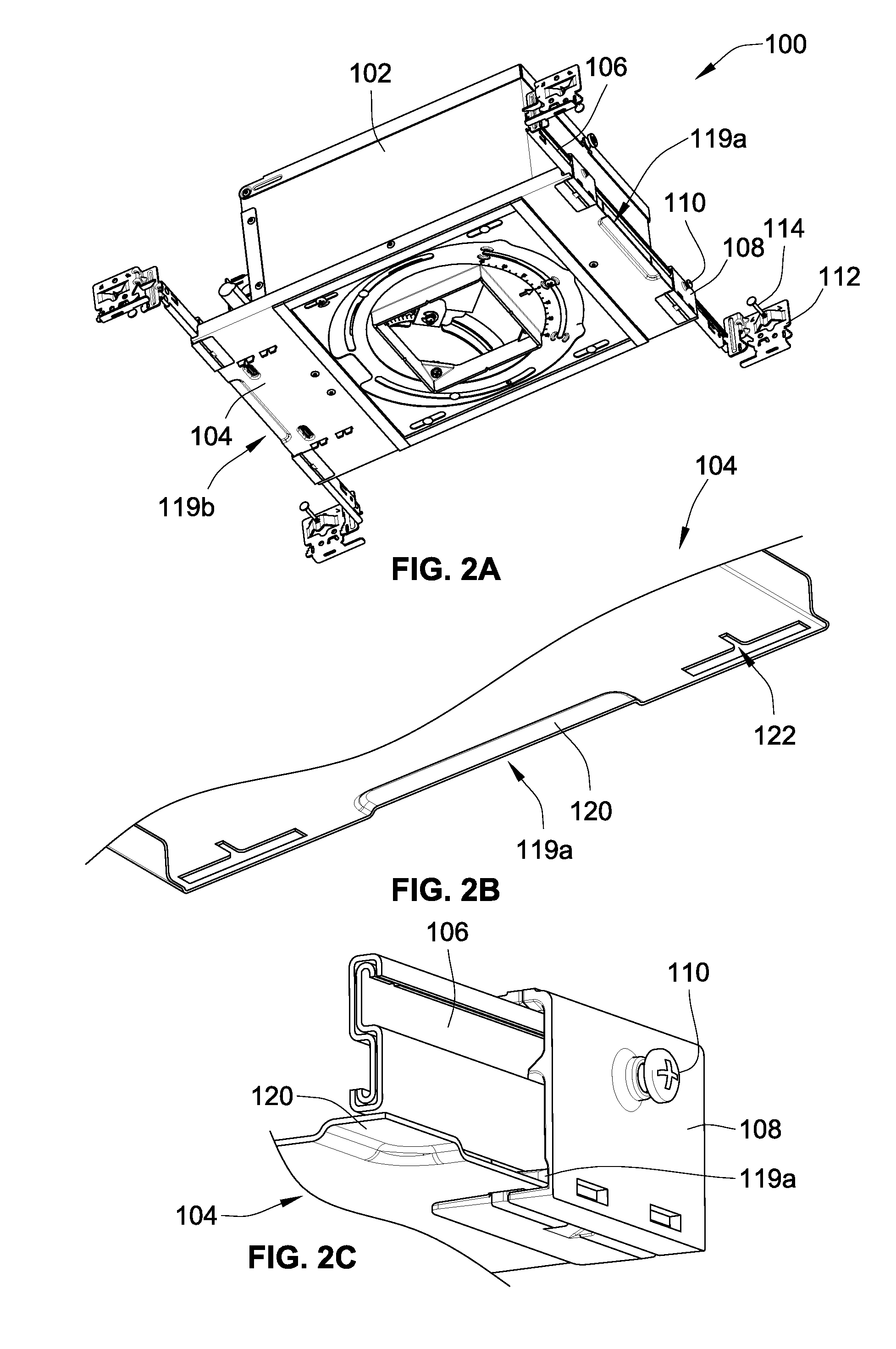
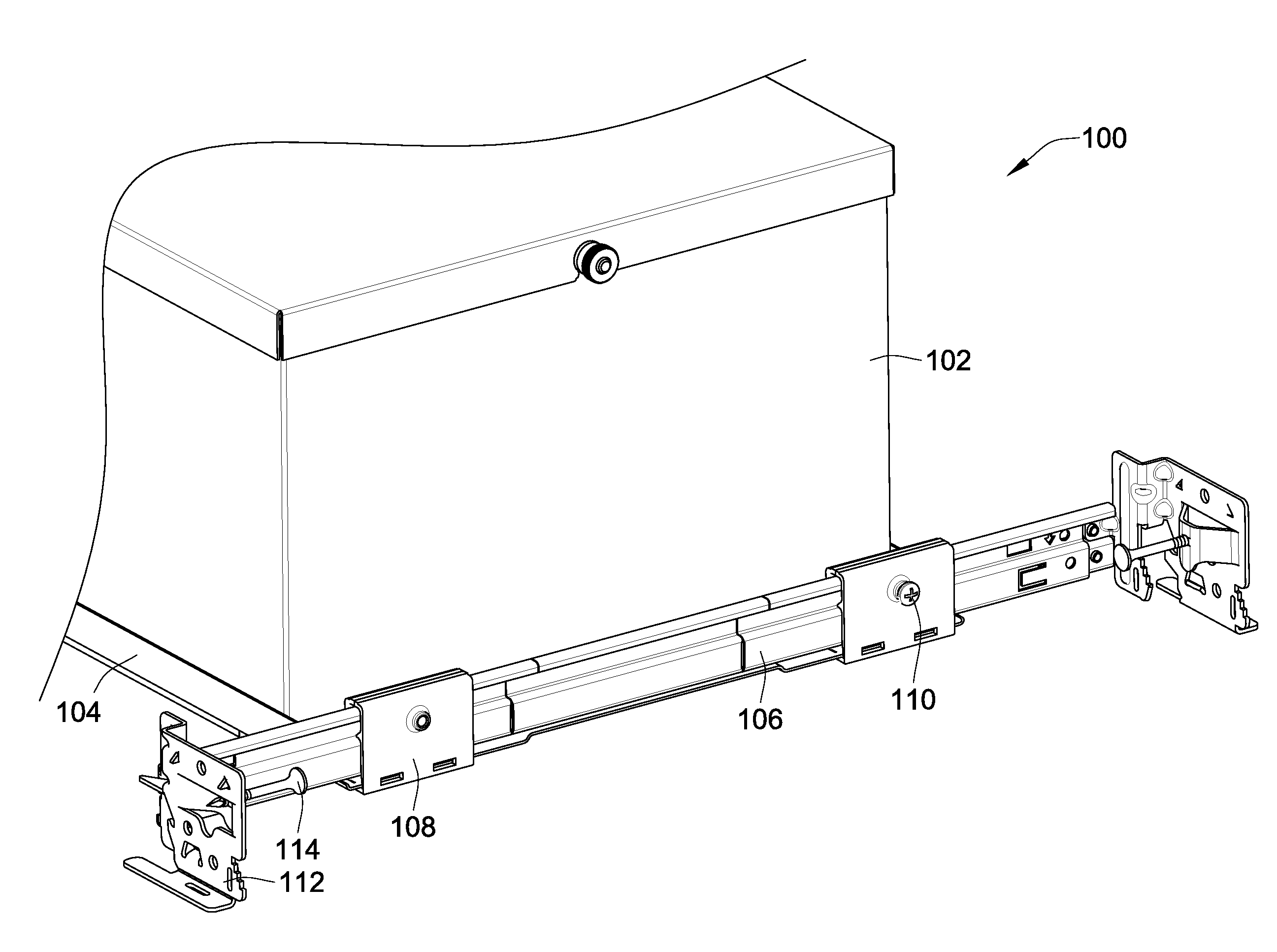
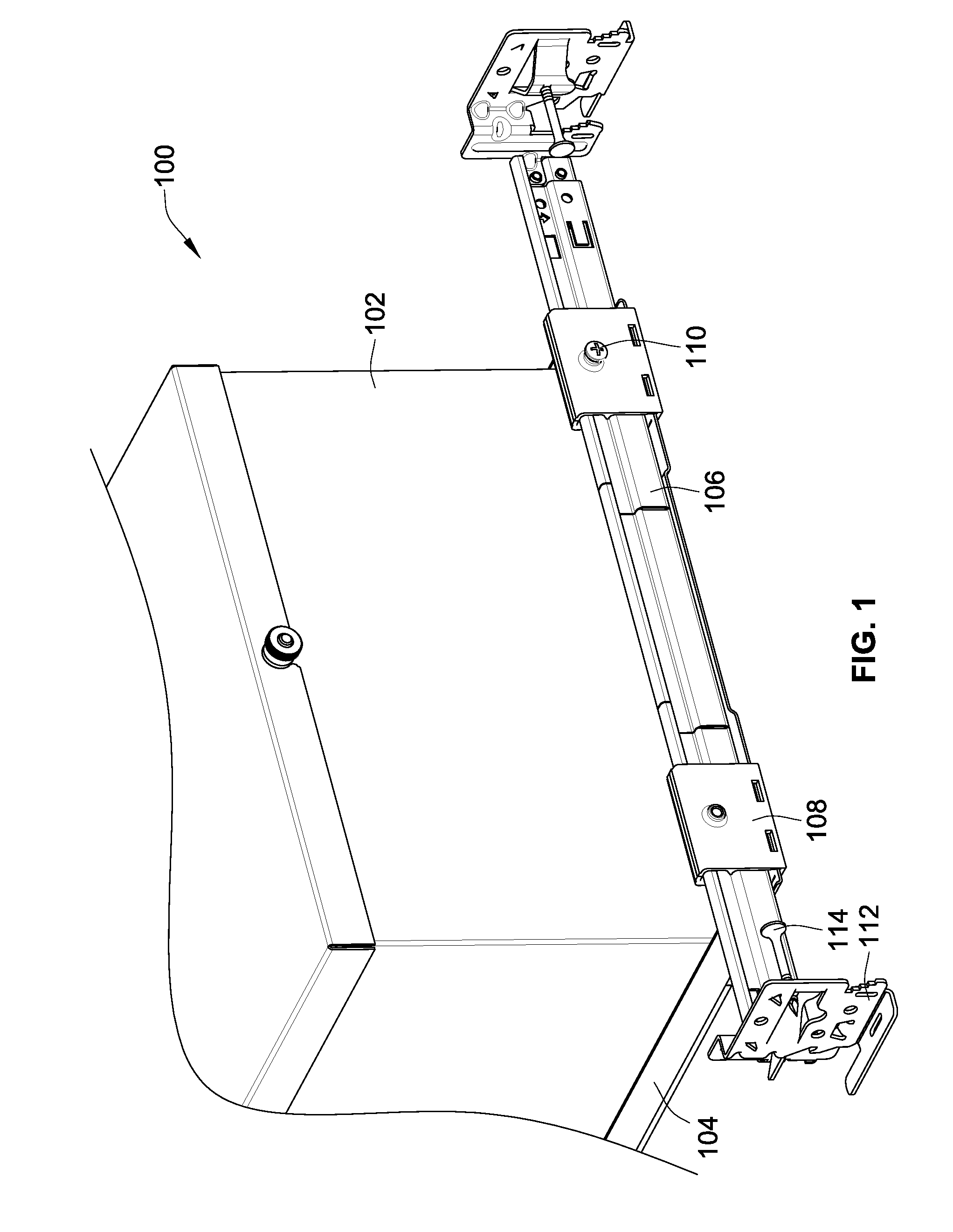
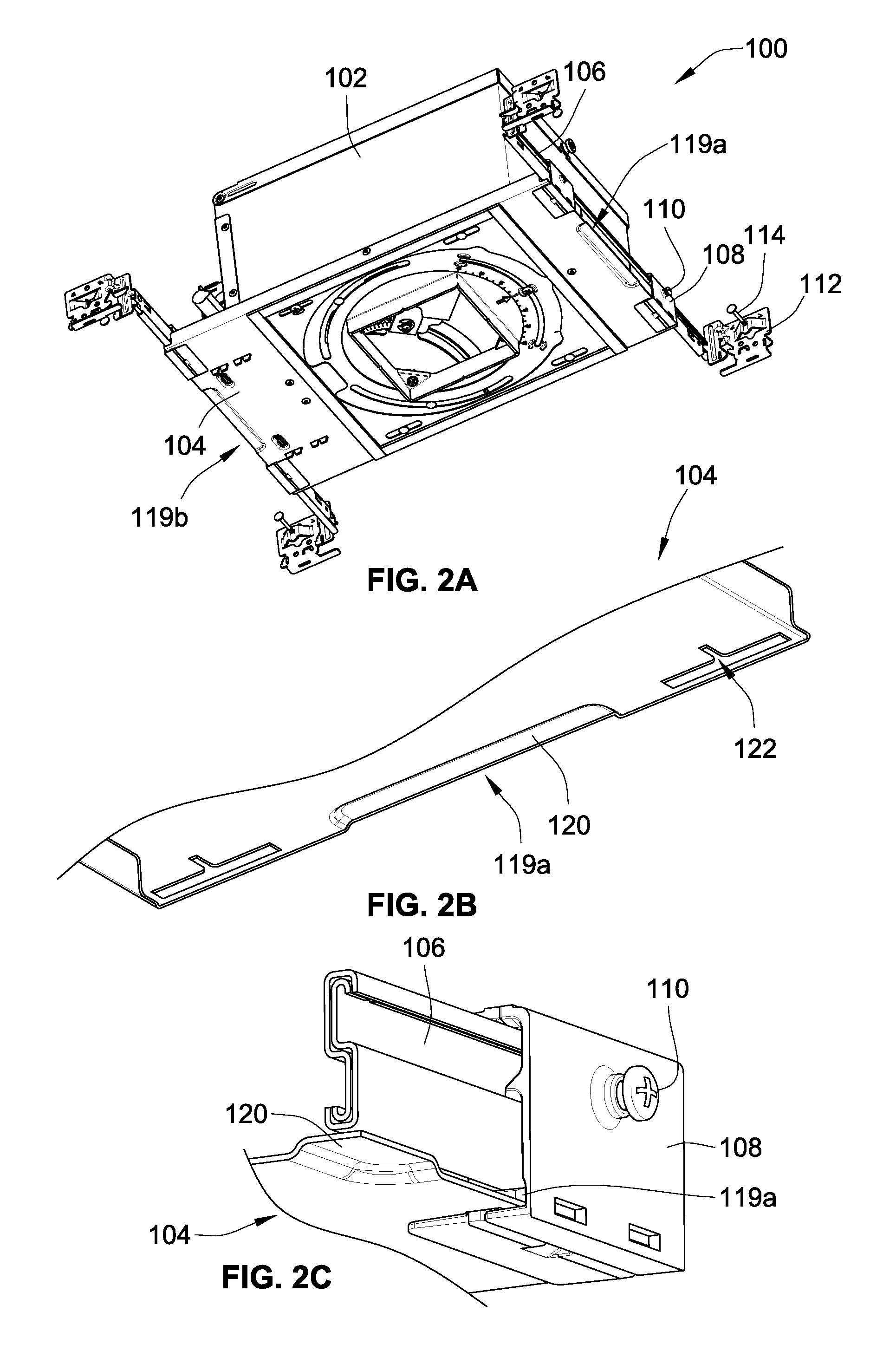
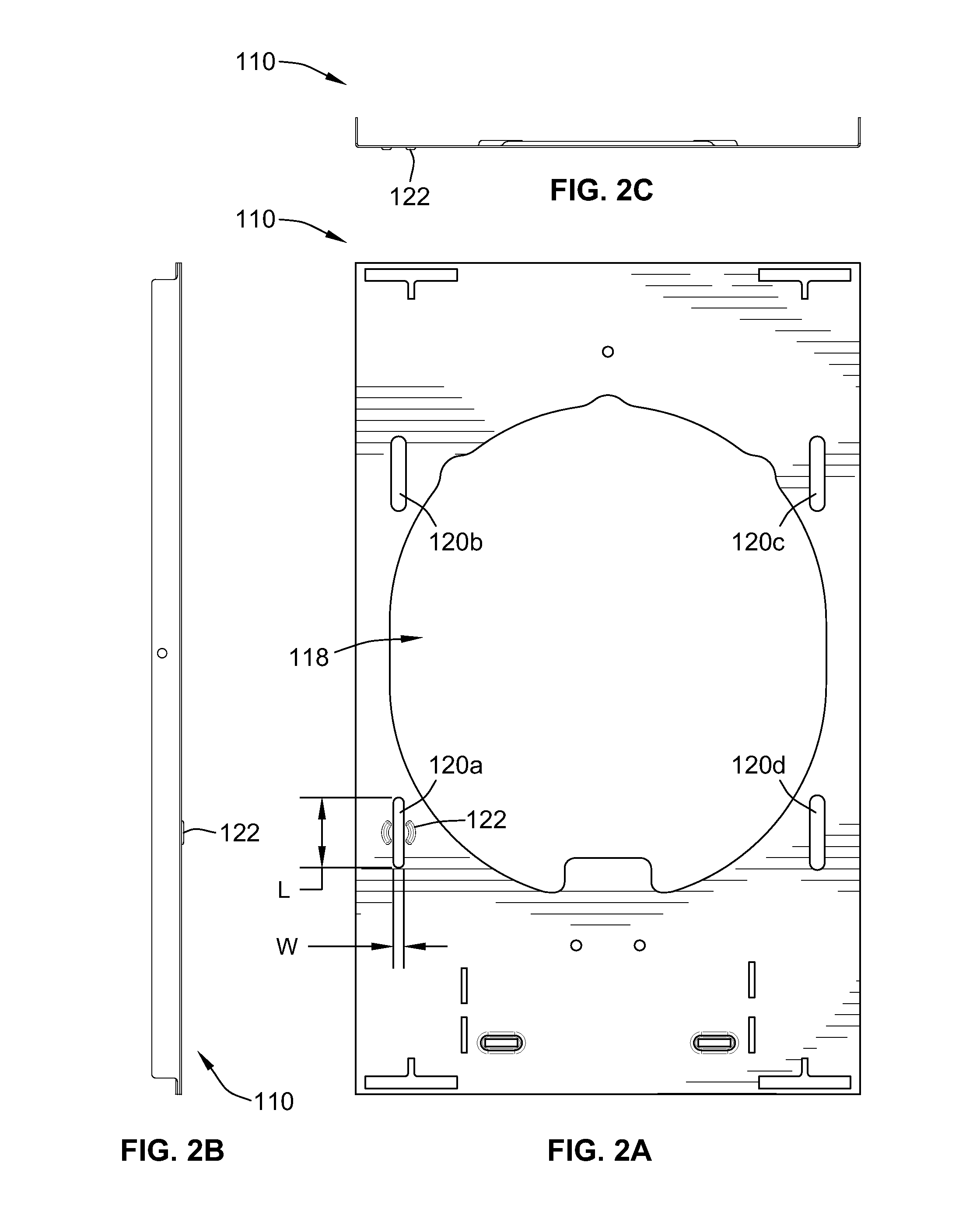
Telescoping mounting system for a recessed luminaire
ActiveUS8038113B2Improves installation and adjustmentEasy to participateLighting support devicesCurtain suspension devicesMechanical engineeringTelescope mount
A lighting assembly for a recessed luminaire includes a plaster frame for supporting the recessed luminaire and a pair of telescoping bars for attaching the plaster frame to framing support members. The telescoping bars include a first bar and a second bar, each of the bars having a generally S-shaped cross-sectional profile that is defined by a center curve joining a first area and a second area, which are generally hook-shaped and extend perpendicularly from the center curve in opposing directions. The first area of the first bar is overlappingly positioned at least in part within the second area of the second bar, and the first area of the second bar is overlappingly positioned at least in part within the second area of the second bar whereby the first and second bars are mated in an inverted and opposed adjacent relationship allowing sliding extension of the bars.
Owner:ABL IP HLDG
Telescoping mounting system for a recessed luminaire
ActiveUS20110226919A1Improve installationEasy to adjustLighting support devicesCurtain suspension devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A lighting assembly for a recessed luminaire includes a plaster frame for supporting the recessed luminaire and a pair of telescoping bars for attaching the plaster frame to framing support members. The telescoping bars include a first bar and a second bar, each of the bars having a generally S-shaped cross-sectional profile that is defined by a center curve joining a first area and a second area, which are generally hook-shaped and extend perpendicularly from the center curve in opposing directions. The first area of the first bar is overlappingly positioned at least in part within the second area of the second bar, and the first area of the second bar is overlappingly positioned at least in part within the second area of the second bar whereby the first and second bars are mated in an inverted and opposed adjacent relationship allowing sliding extension of the bars.
Owner:ABL IP HLDG
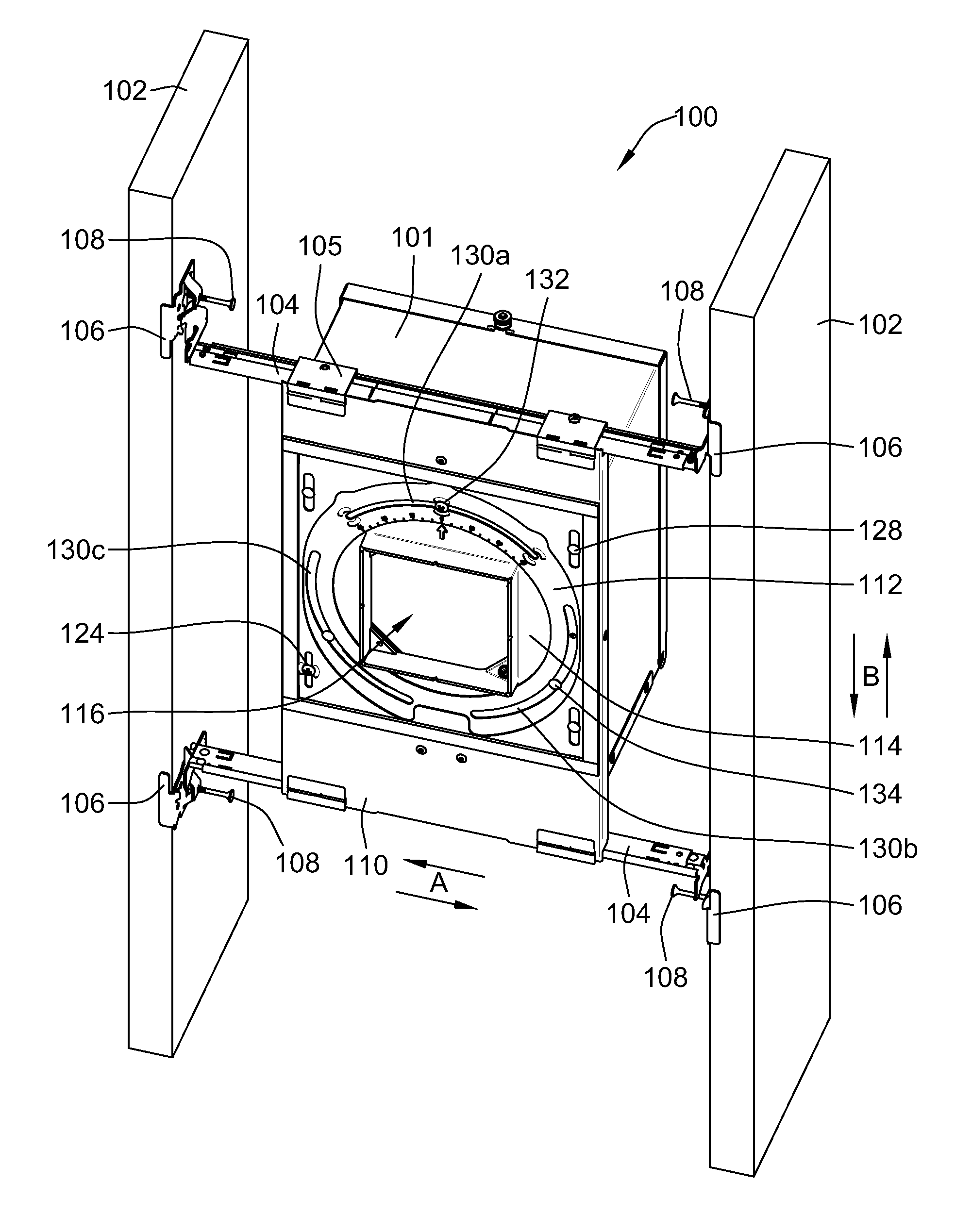
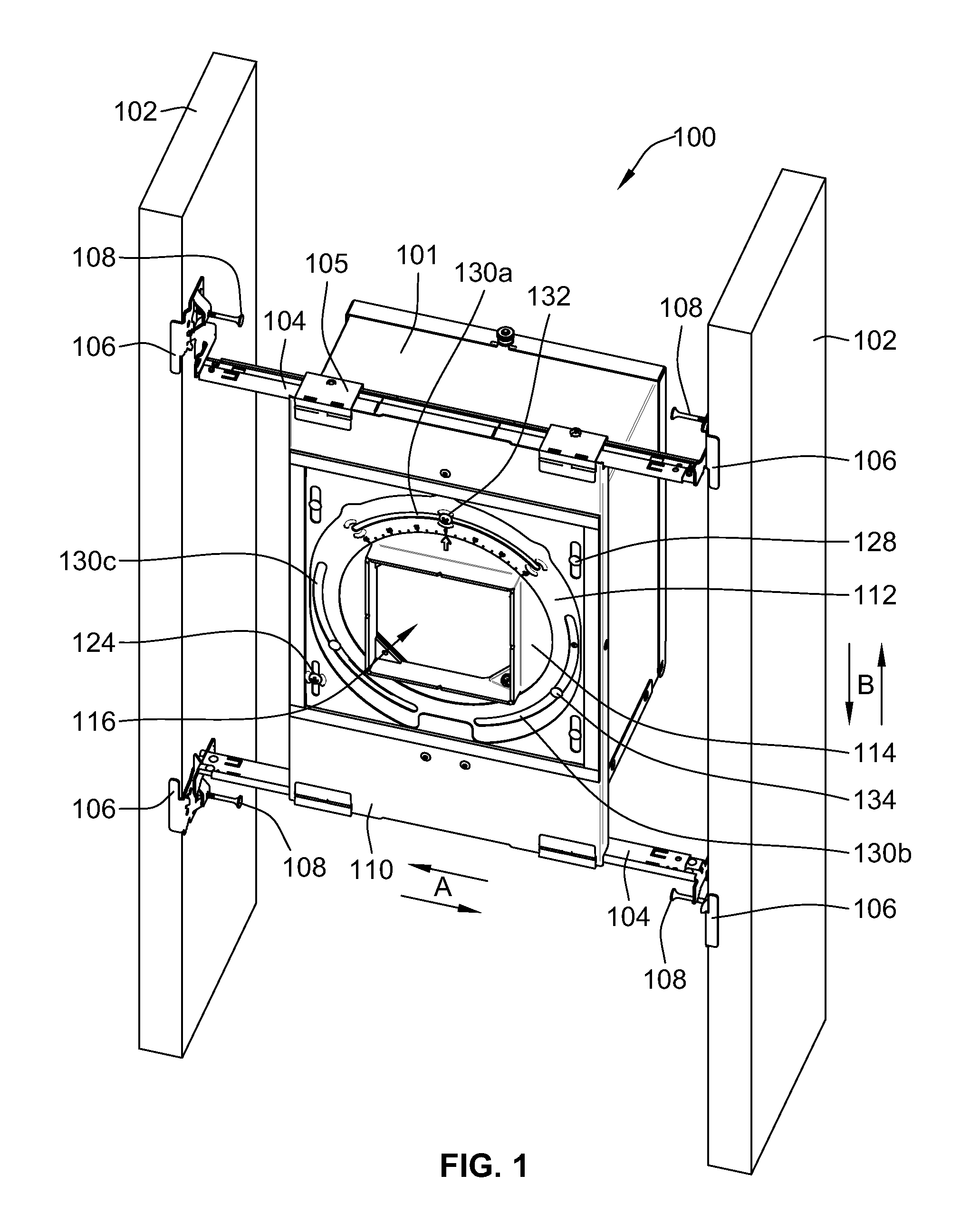
Translating aperture adjustment for a recessed luminaire
ActiveUS8277090B2Improve adjustabilityPrevent movementLighting support devicesProtective devices for lightingLinear motionTelescope mount
A mounting assembly includes a stationary plate for supporting and linearly adjusting a recessed fixture in a parallel direction relative to structural framing members. Telescoping mounting bars are fixed to a building structure and allow adjustability of the stationary plate in a direction generally perpendicular to structural framing members. An adjustable plate has a plurality of linear guides received in a linear movable manner within a corresponding one of linear guide slots of the stationary plate. A linear locking member is adjustably secured in one of the linear guide slots such that linear movement of the adjustable plate is prevented relative to the stationary plate when the linear locking member is in a locked position, linear movement of the adjustable plate being allowed relative to the stationary plate in a direction parallel to the structural framing members when the linear locking member is in an adjustable position.
Owner:ABL IP HLDG
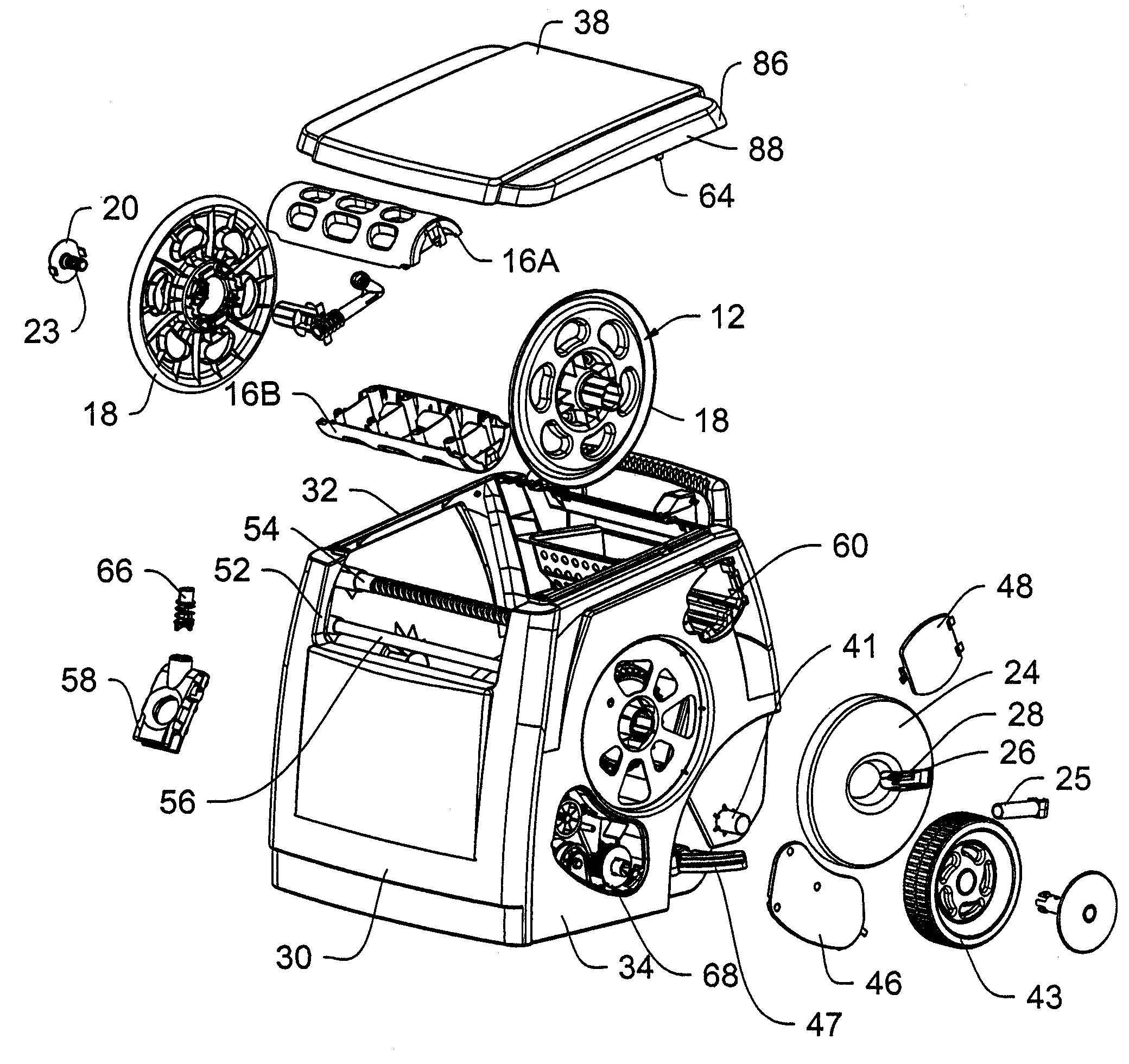
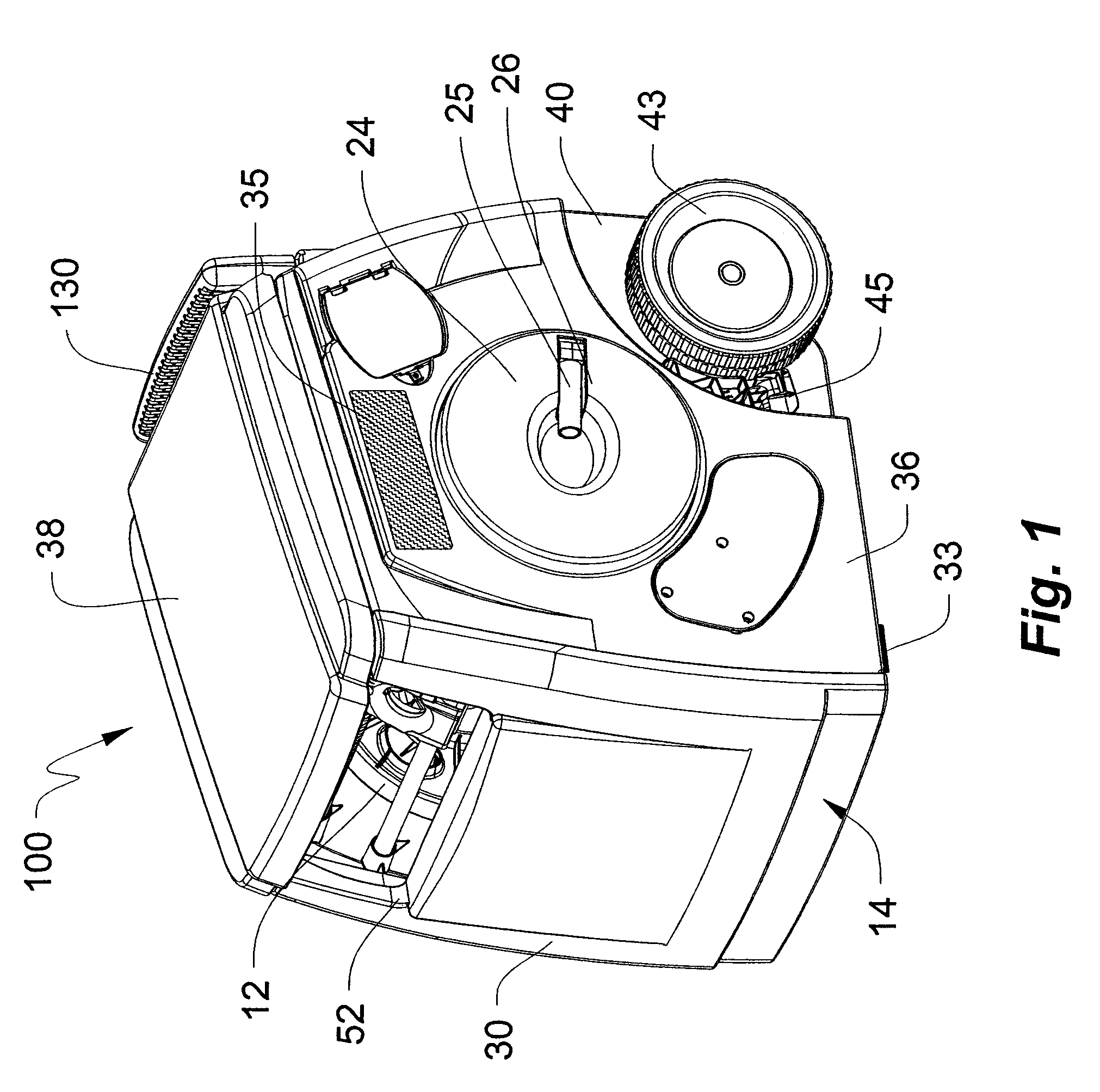
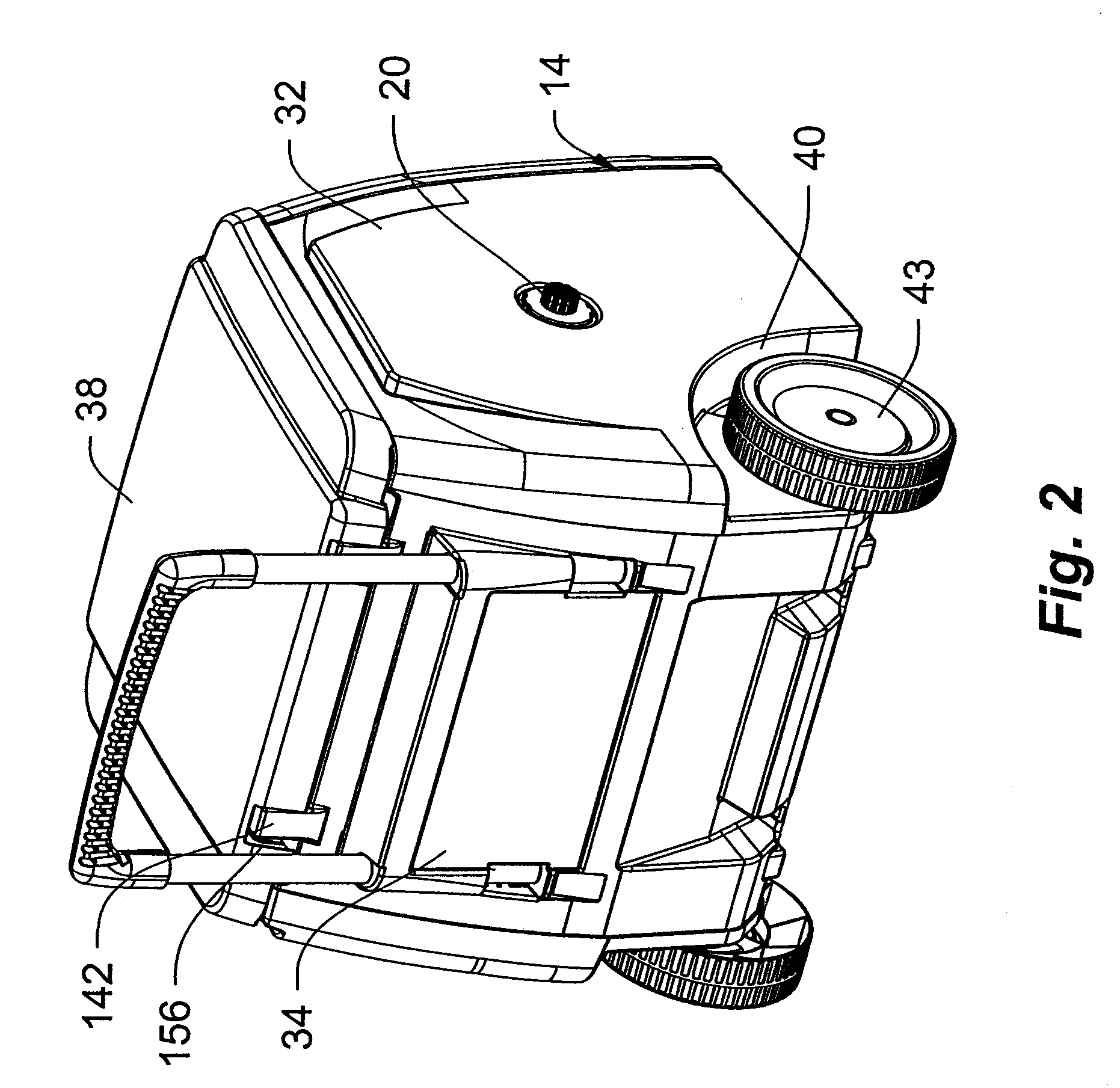
Direct current powered hose rewinding apparatus
InactiveUS20050017117A1Reducing RPM outputIncreasing motor torqueFire rescueThin material handlingEngineeringConductor Coil
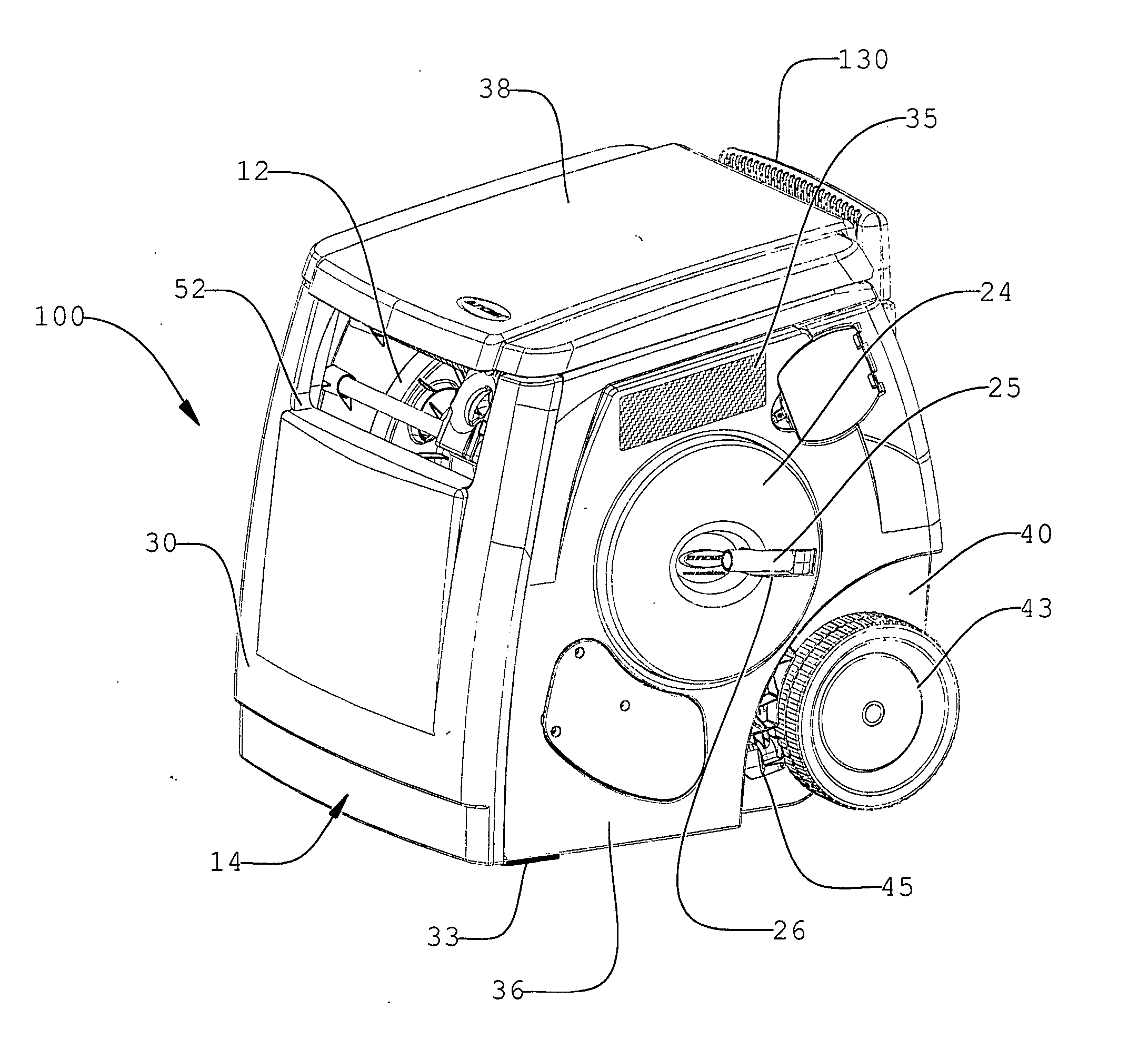
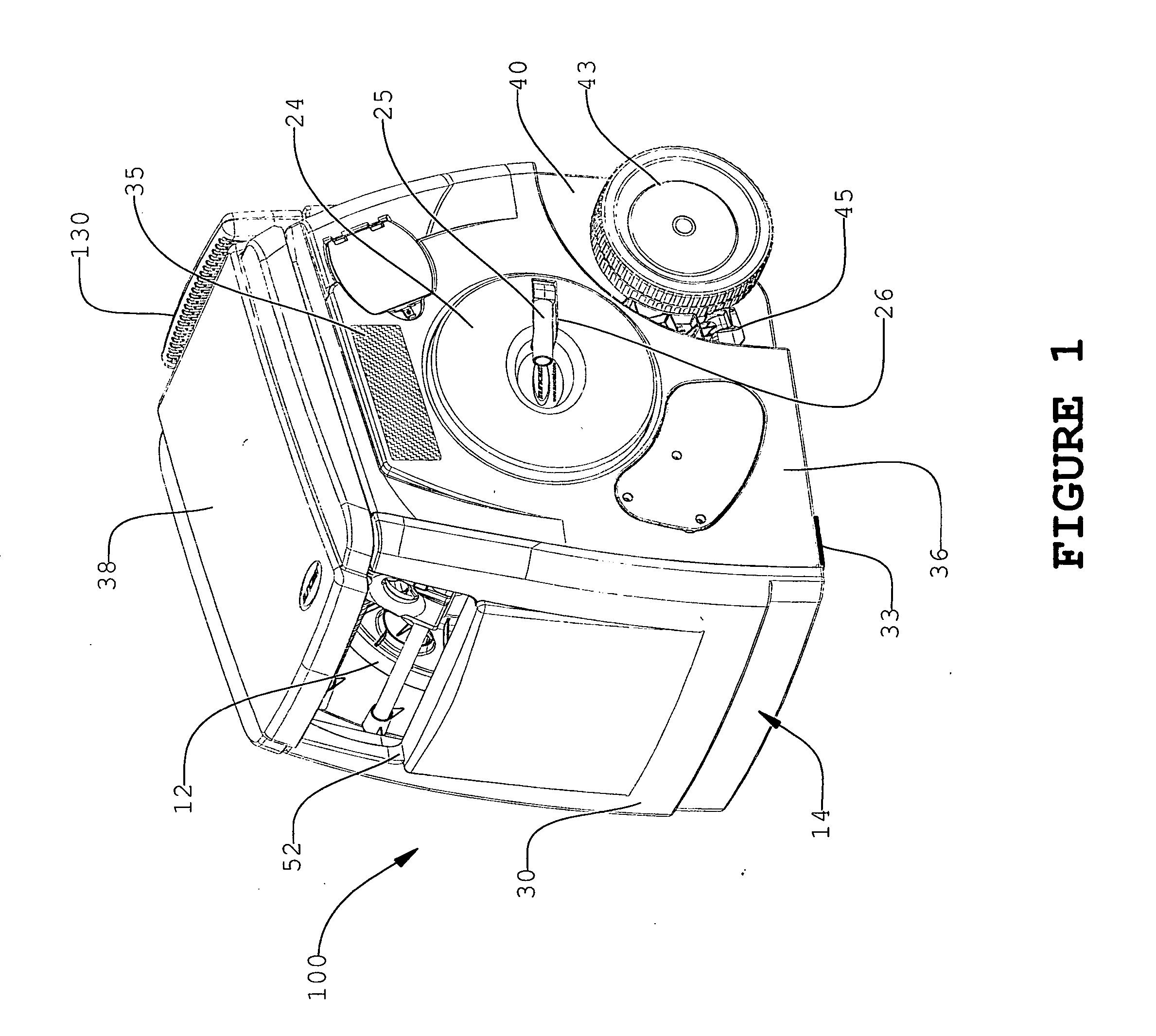
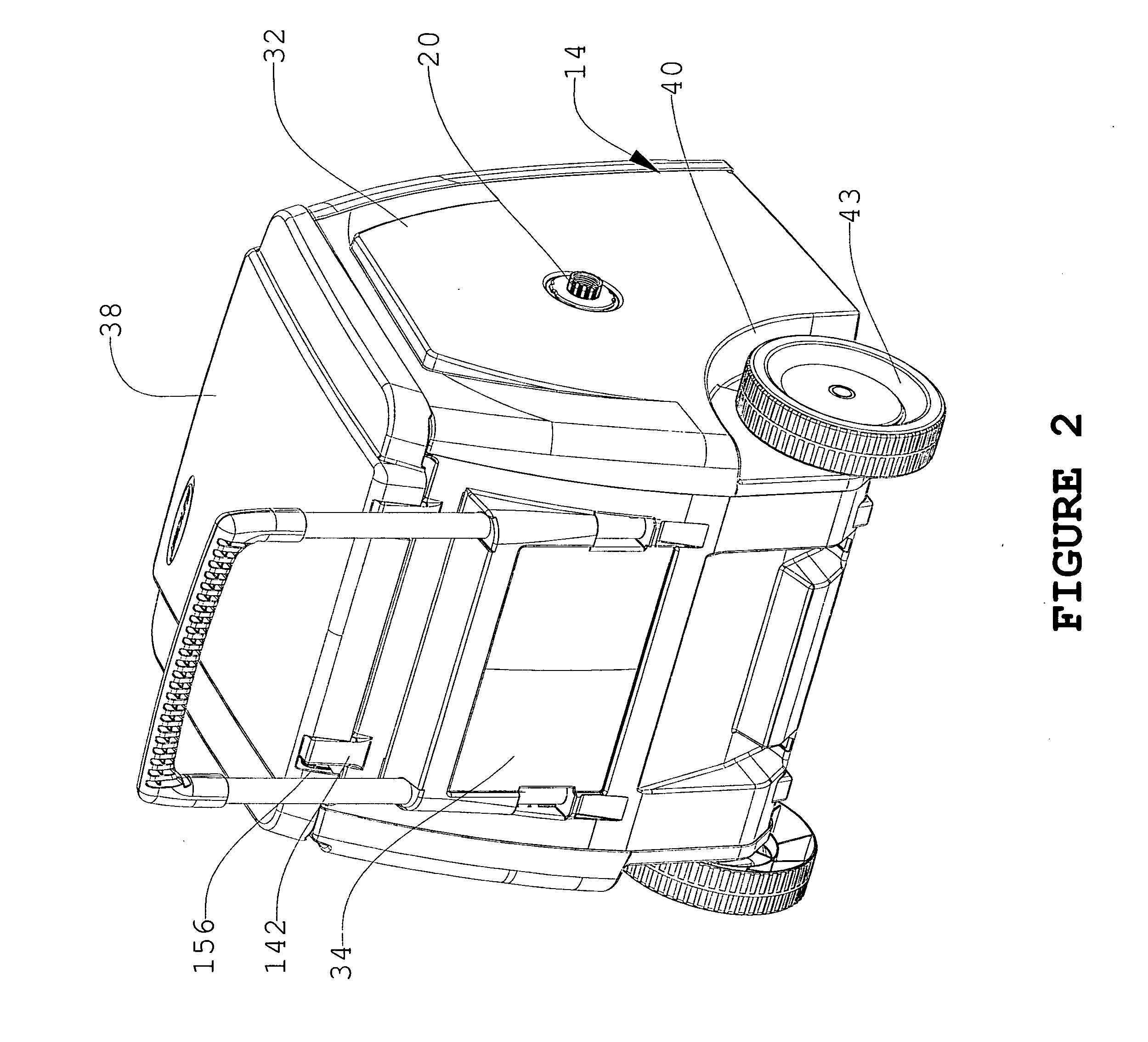
The present invention relates to portable hose carts for handling and storage of flexible hoses, such as garden or air hoses. The cart is primarily constructed of plastic components having a centrally rotatable spool for winding of the flexible hose, an enclosure for supporting the spool, wheels at one end of the base of the enclosure, and a handle assembly for tilting the frame onto the wheels to facilitate moving the device. The handle assembly is telescoping mounted and includes a handle mounted near the top of the handle assembly. The spool is rotatable by either a direct current powered motor or a folding manual crank. Power from the electrical motor is transferred to the spool via an infinitely adjustable torque transfer assembly. When the cover is in the open position, the direct current motor is operationally locked out, and when the cover is rotated into the closed position, the direct current motor is operable. The device may further include a reciprocating guide assembly that operates during rotation of the spool to rewind the hose into a compact configuration.
Owner:SUNCAST
Direct current powered hose rewinding apparatus
InactiveUS7316368B2Promote sportsEasy to transportFire rescueThin material handlingEngineeringMobile device
The present invention relates to portable hose carts for handling and storage of flexible hoses, such as garden or air hoses. The cart is primarily constructed of plastic components having a centrally rotatable spool for winding of the flexible hose, an enclosure for supporting the spool, wheels at one end of the base of the enclosure, and a handle assembly for tilting the frame onto the wheels to facilitate moving the device. The handle assembly is telescoping mounted and includes a handle mounted near the top of the handle assembly. The spool is rotatable by either a direct current powered motor or a folding manual crank. Power from the electrical motor is transferred to the spool via an infinitely adjustable torque transfer assembly. When the cover is in the open position, the direct current motor is operationally locked out, and when the cover is rotated into the closed position, the direct current motor is operable. The device may further include a reciprocating guide assembly that operates during rotation of the spool to rewind the hose into a compact configuration.
Owner:SUNCAST
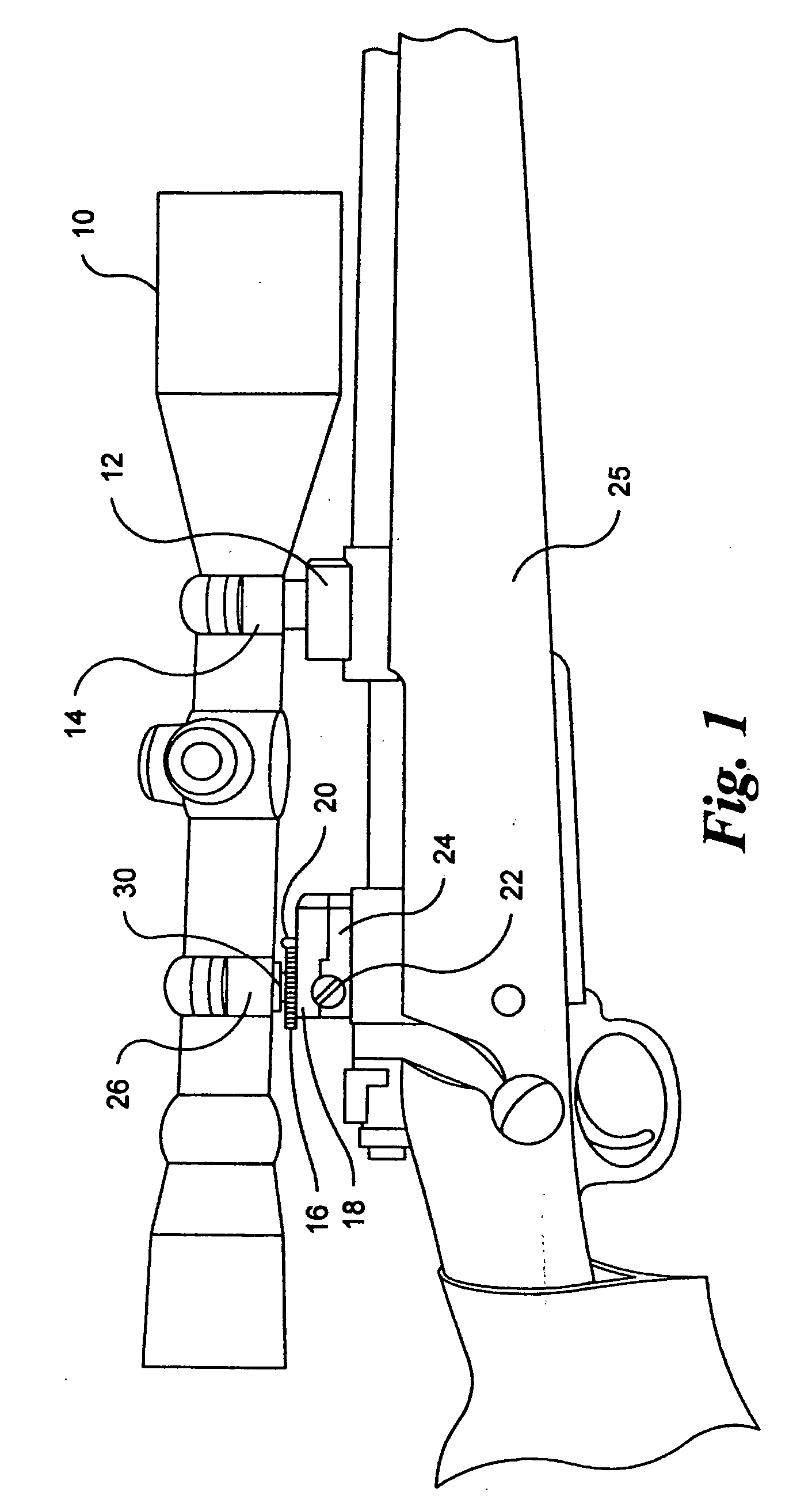
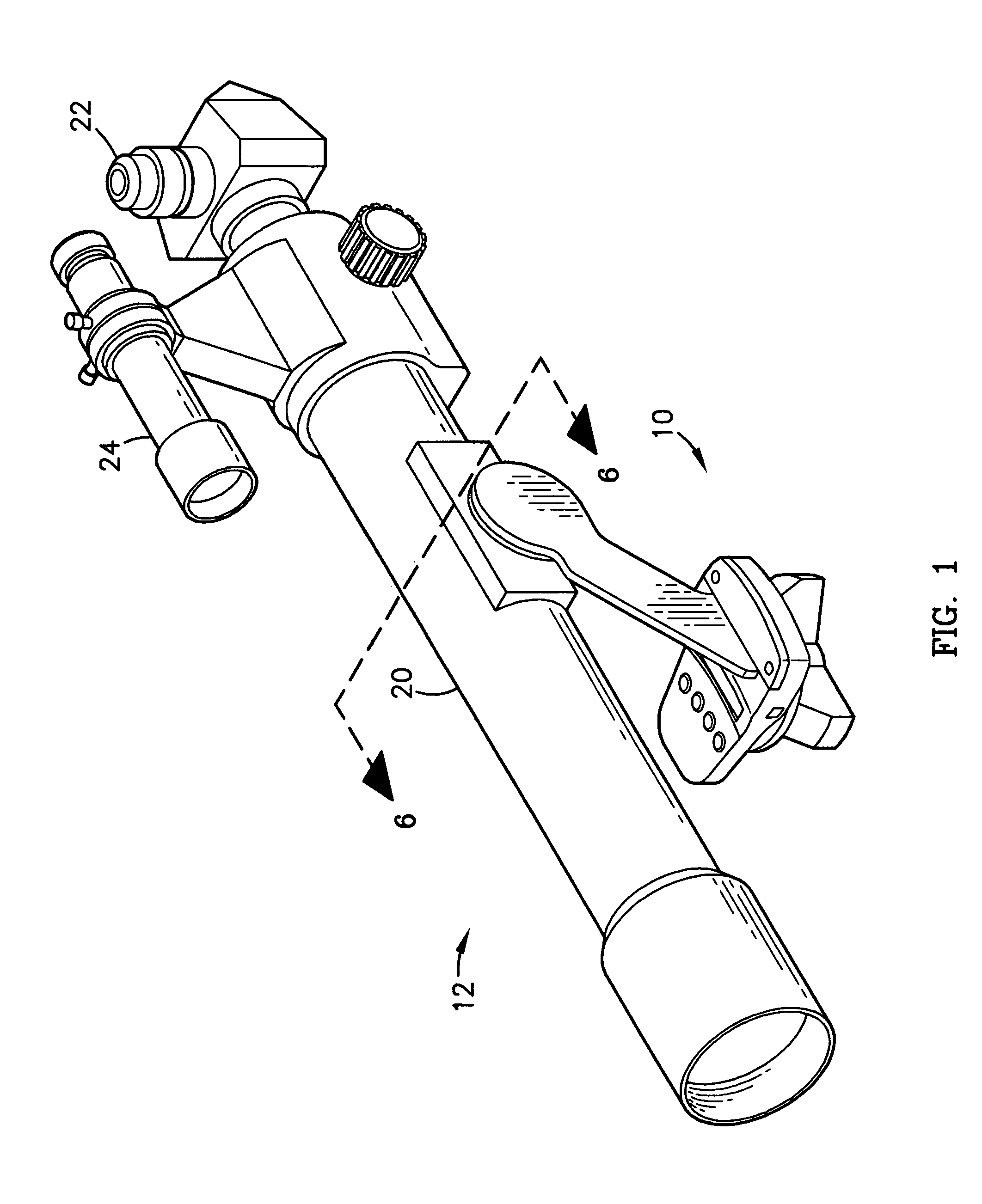
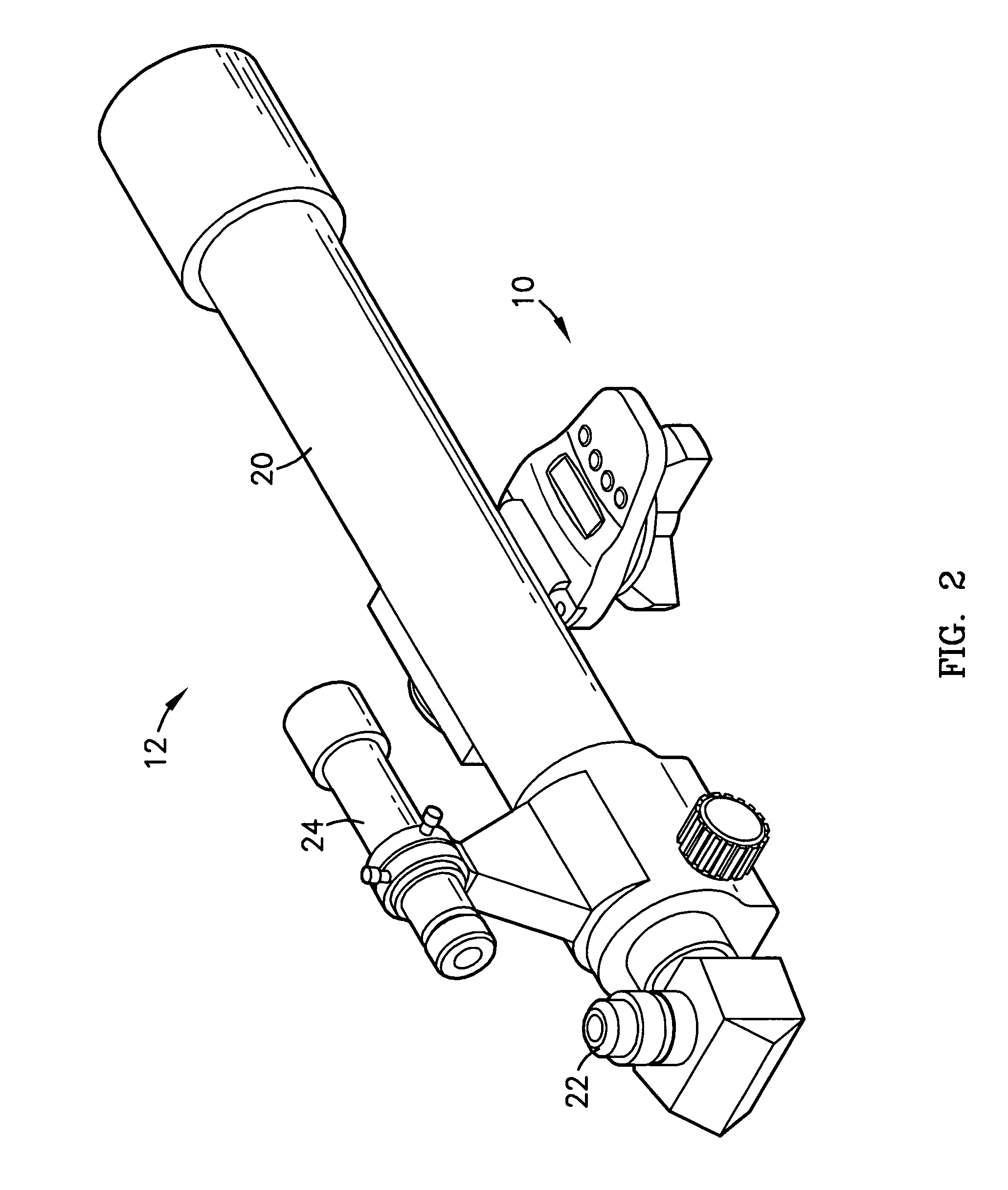
External adjustable telescopic scope device
An adjustable scope mounting device for adjusting a scope mounted on a gun. The scope utilizes opposite threaded screws for elevational adjustment and further includes a windage adjustment.
Owner:ROBERT NILS PENNEY
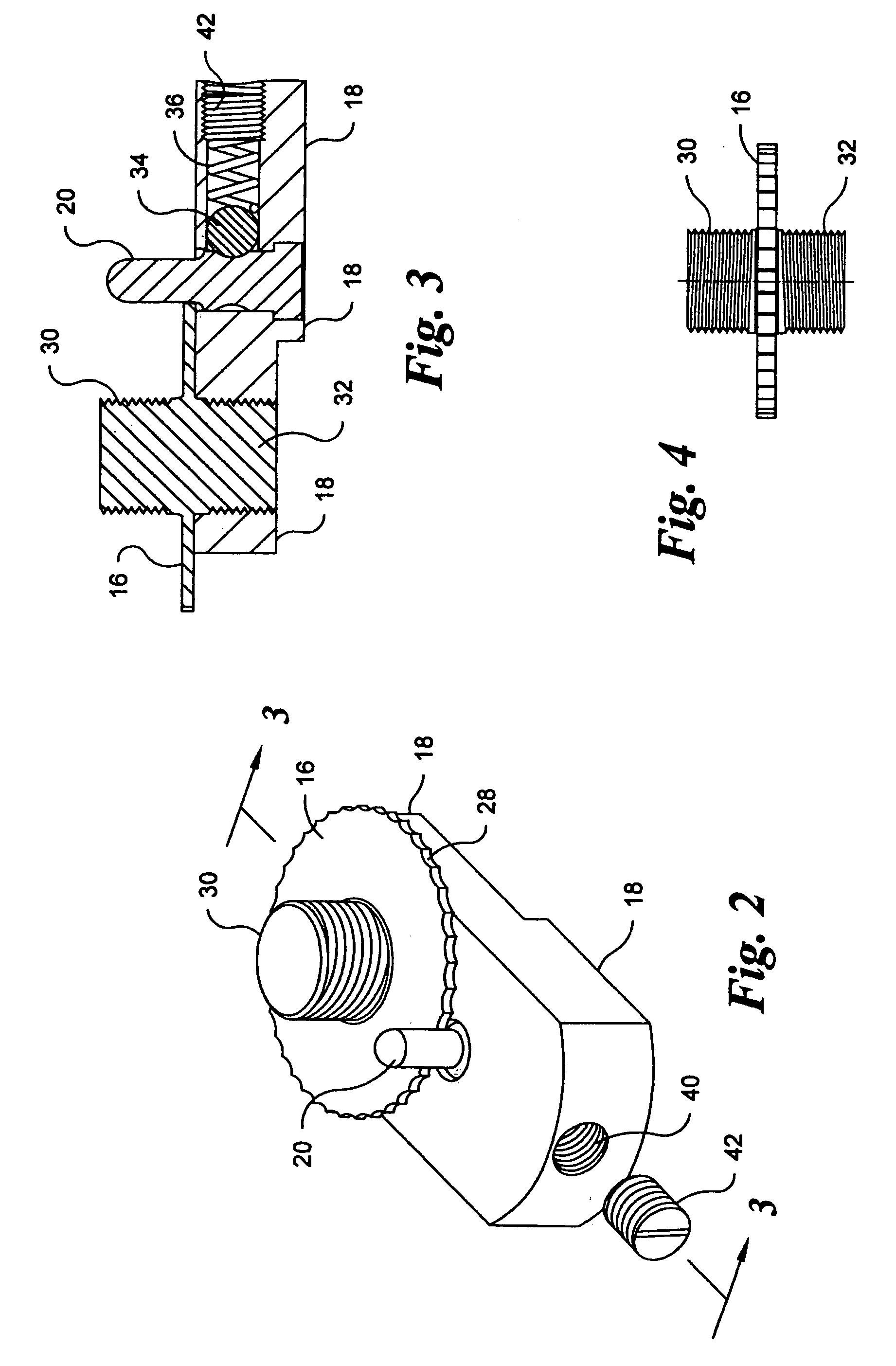
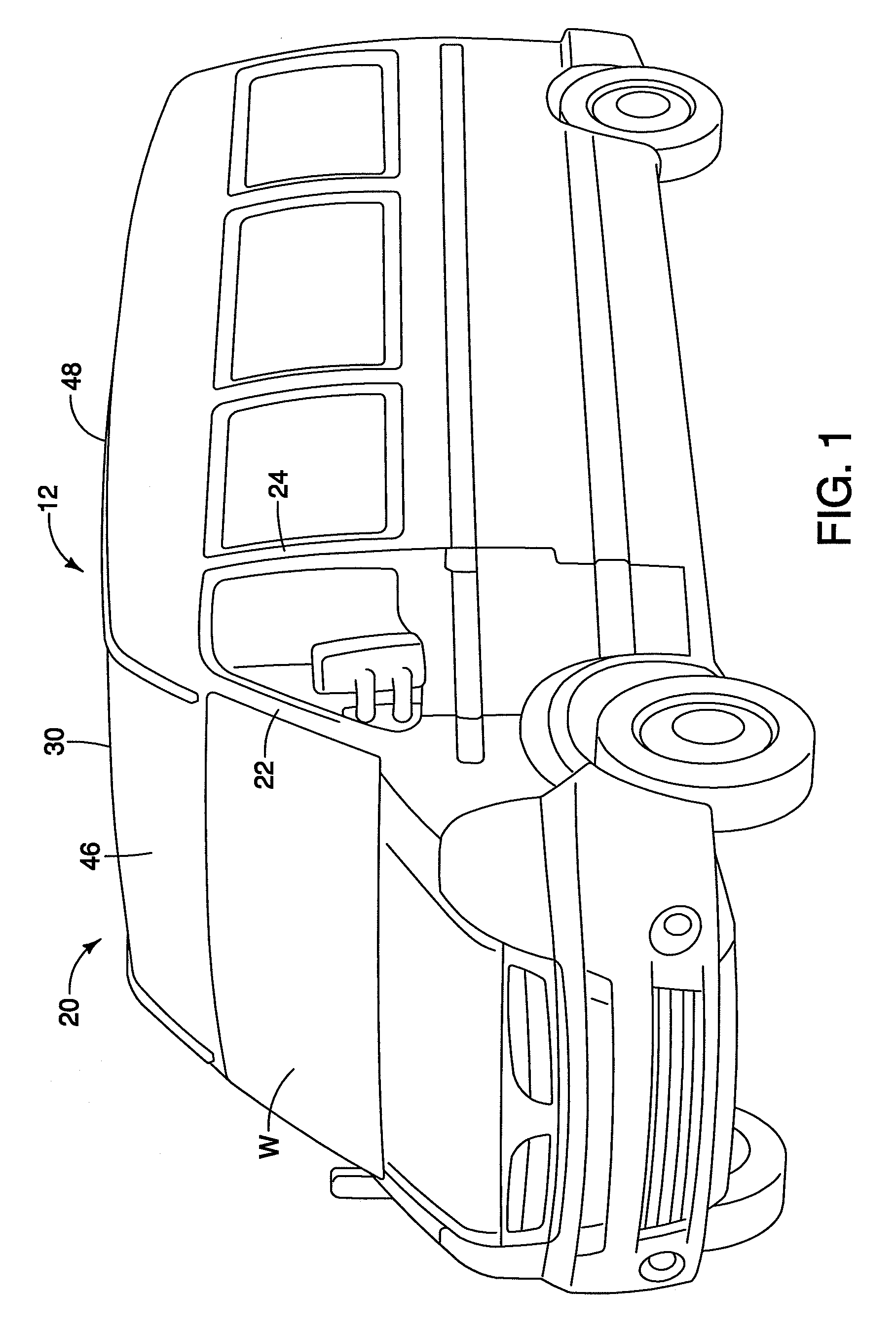
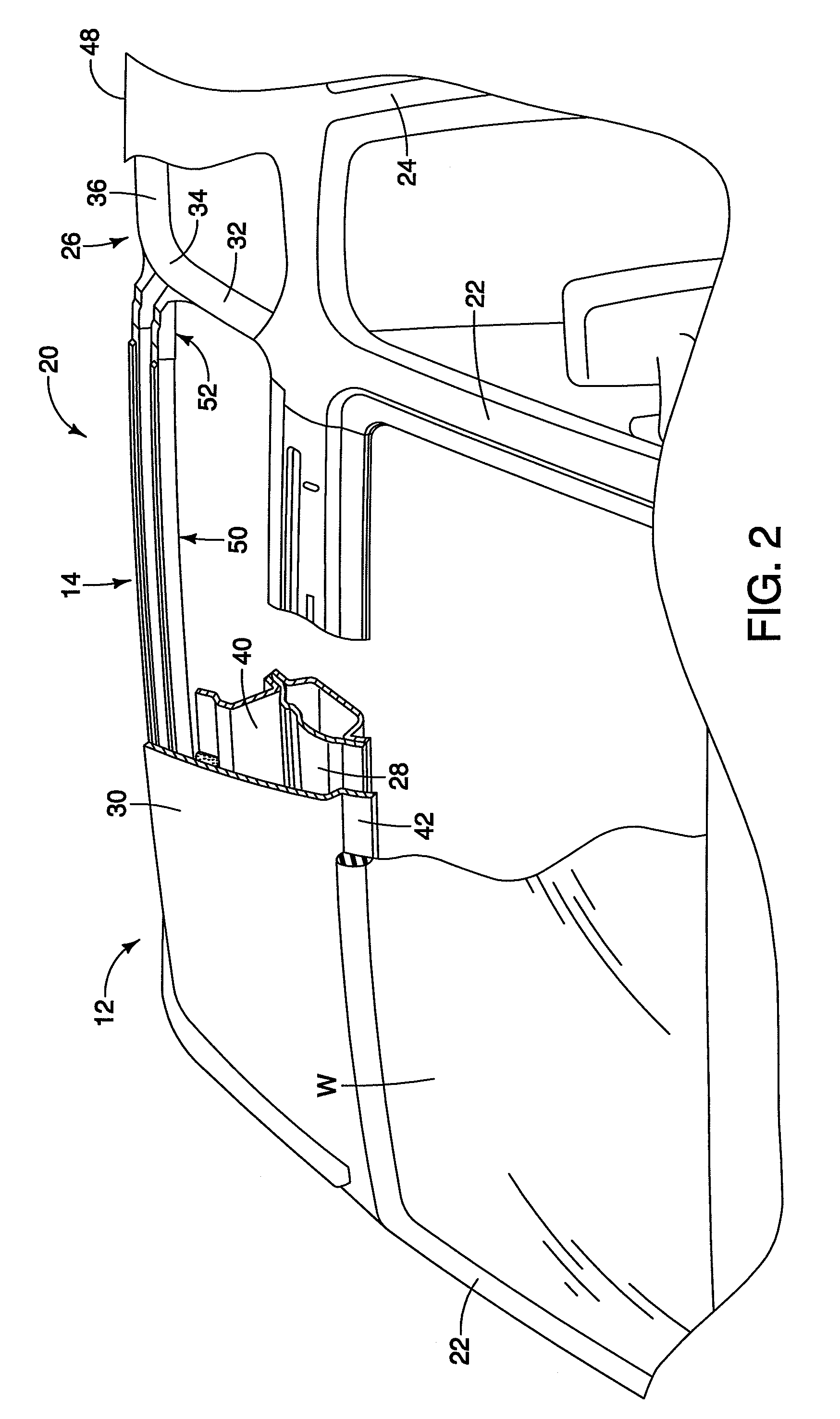
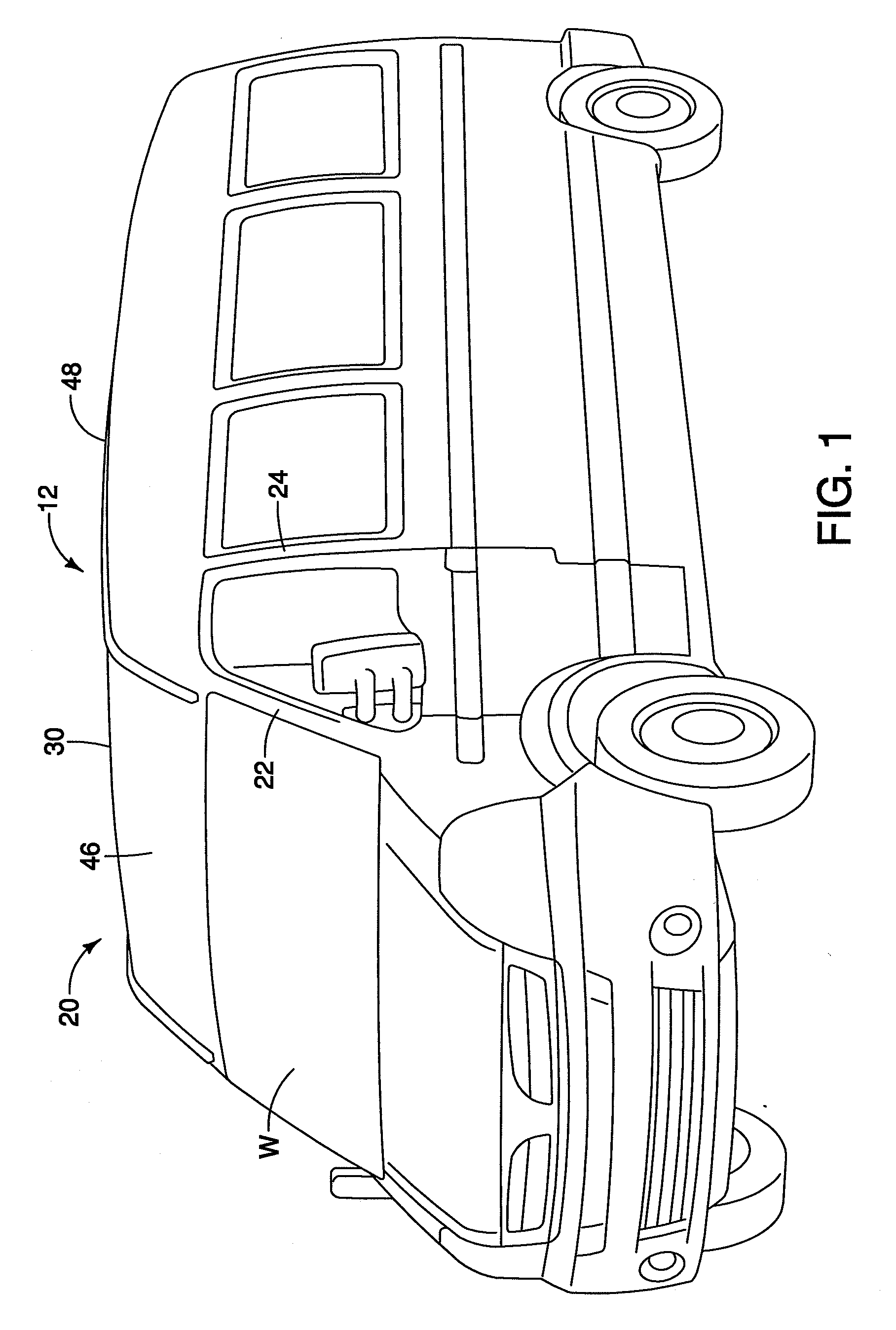
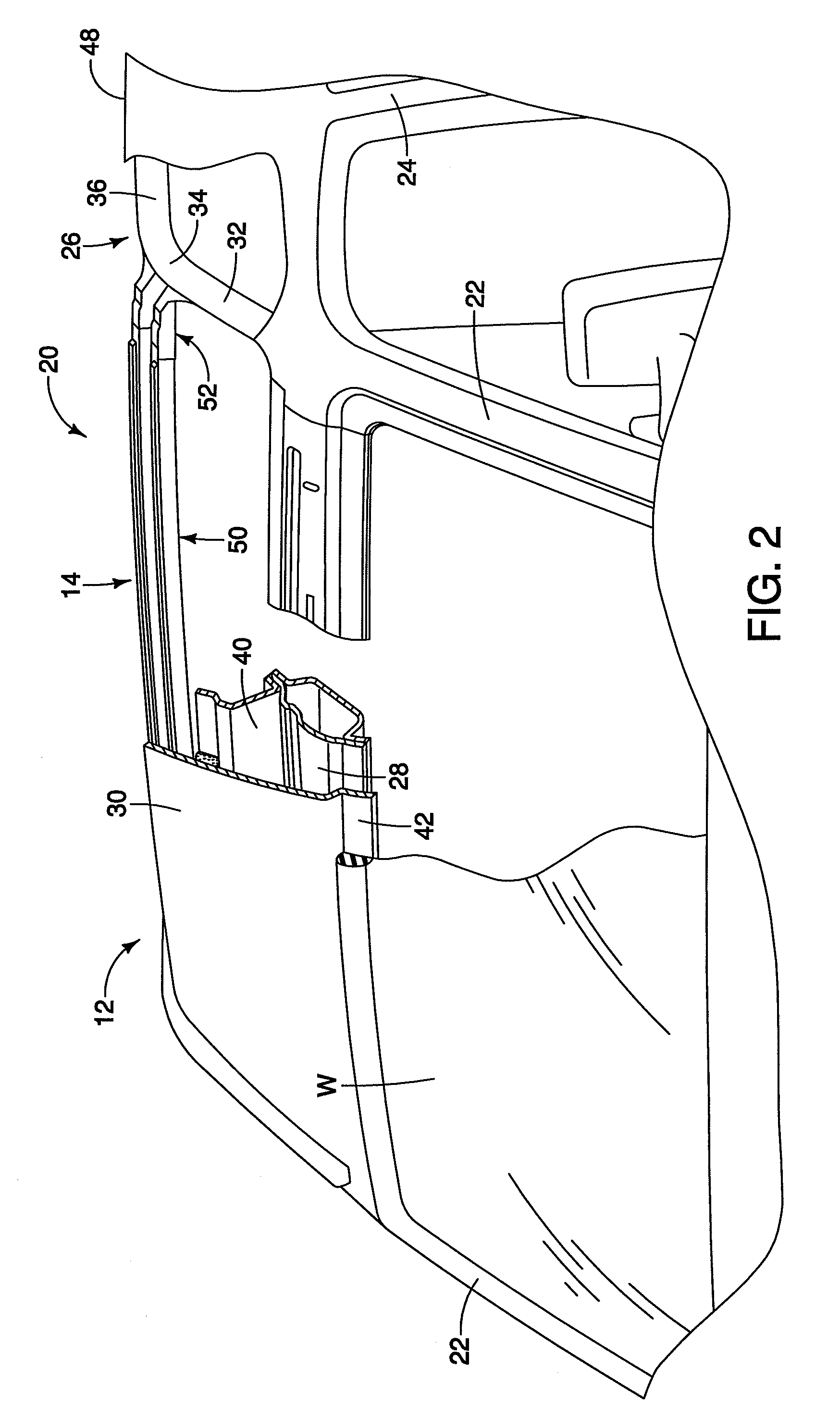
Vehicle roof bow assembly
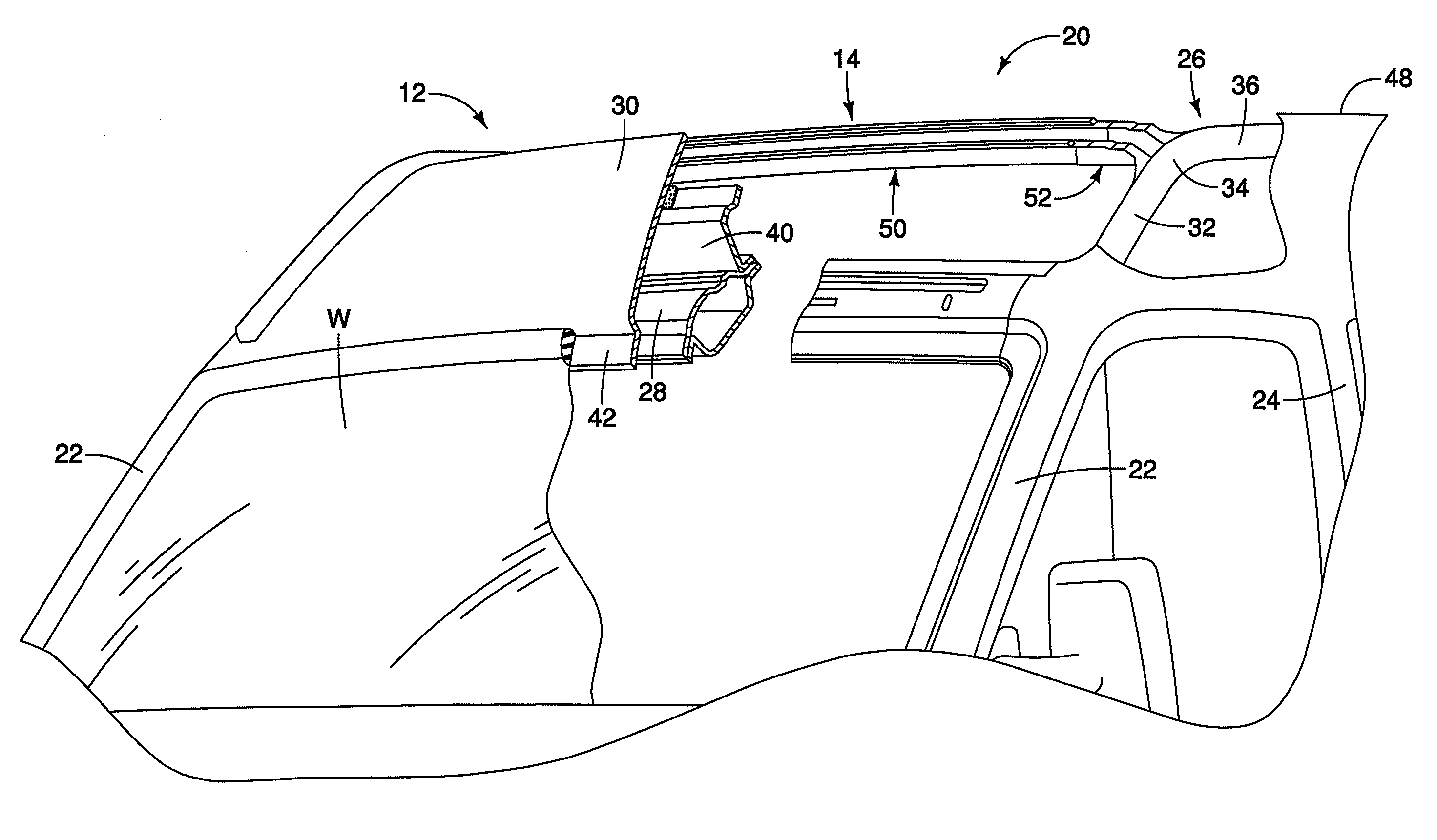
A vehicle roof bow assembly includes a roof bow member and a pair of telescoping mounting brackets. The roof bow member is configured to extend in a lateral side-to-side direction along an underside of a vehicle roof panel. The telescoping mounting brackets each have a first end and a second end with the first end having a side rail attachment flange configured for rigid attachment to a first vehicle roof side rail and a roof panel attachment flange configured for rigid attachment to the vehicle roof panel and the second end being attached to the roof bow member. The telescoping mounting brackets are disposed at opposite ends of the roof bow member.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
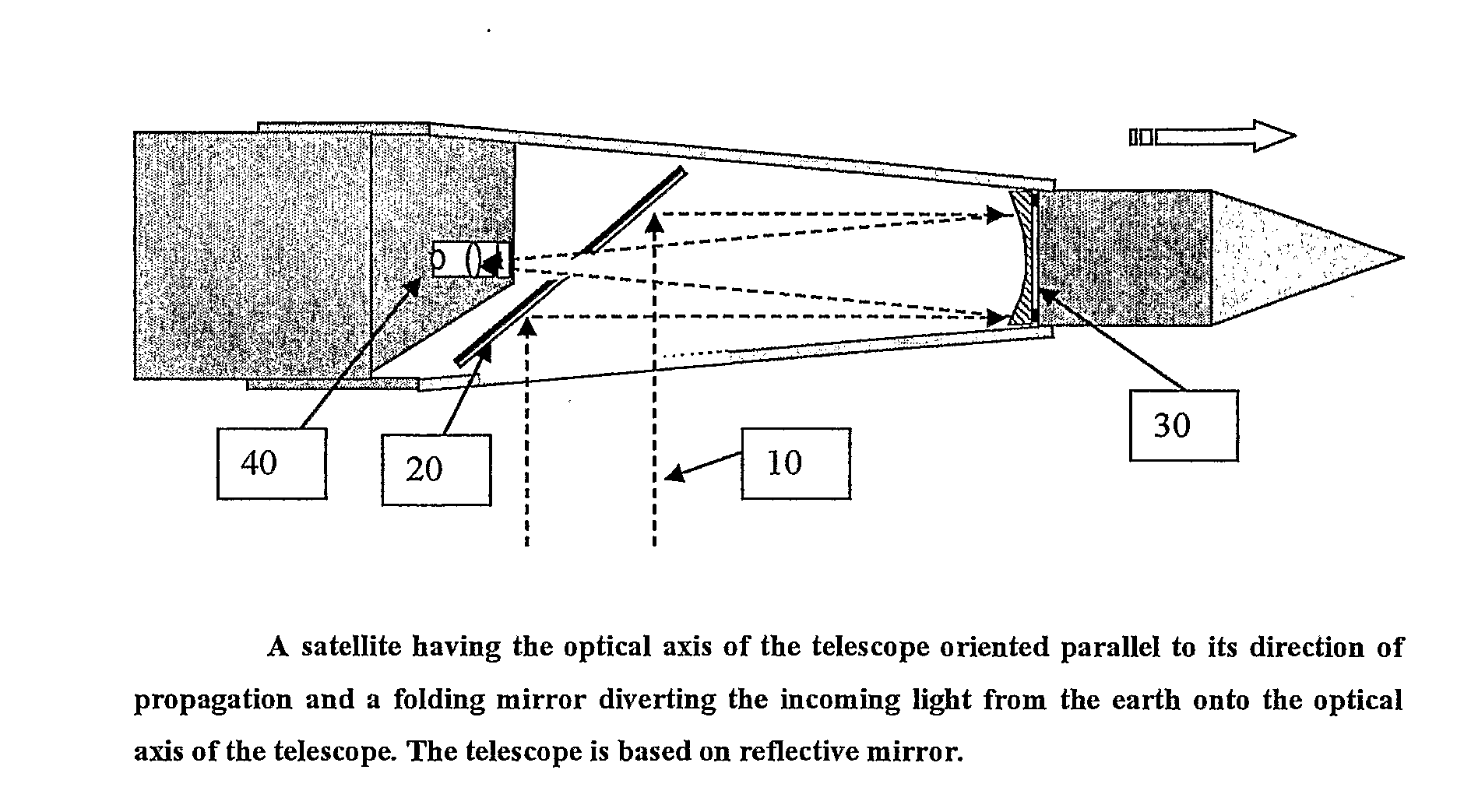
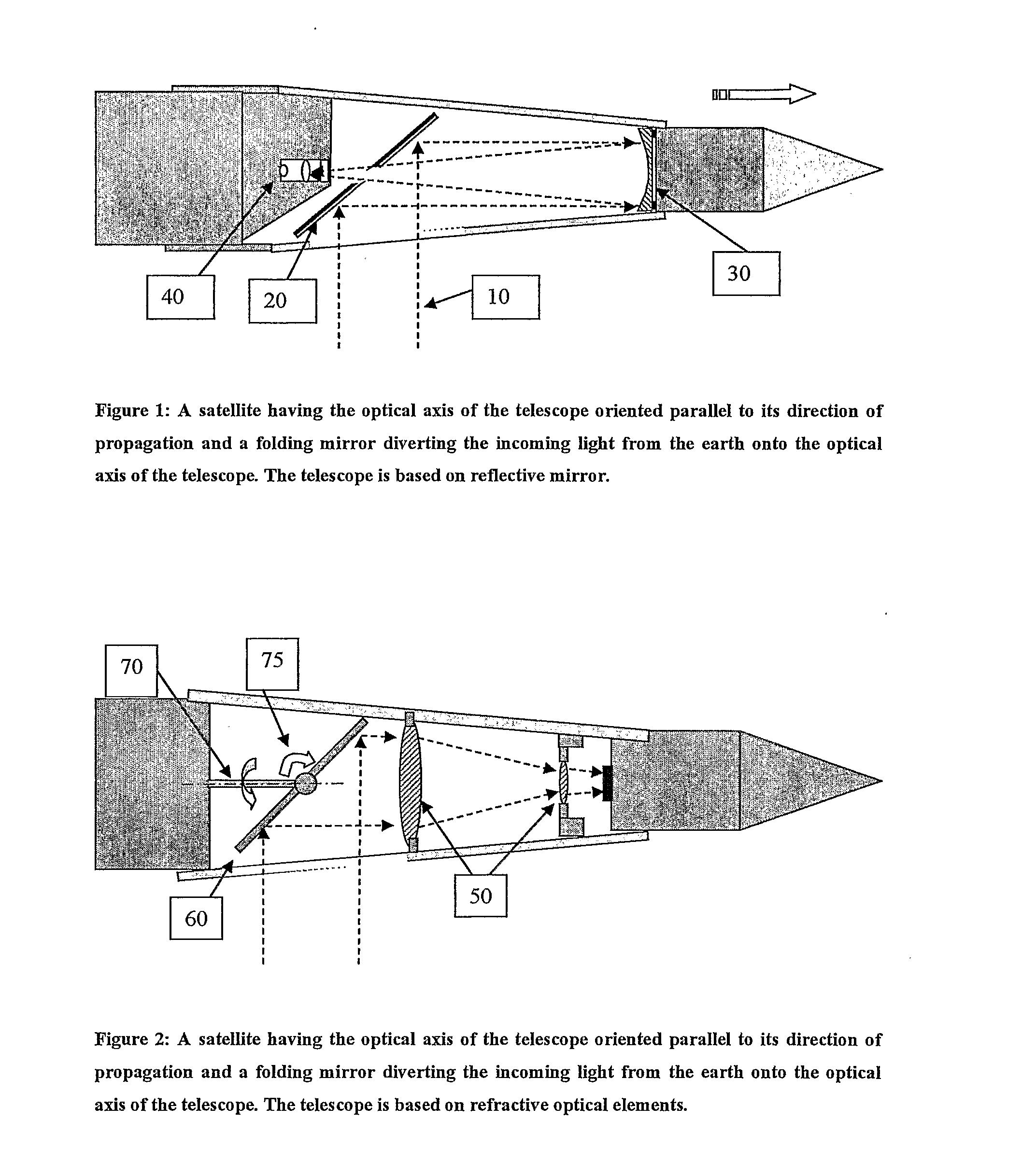
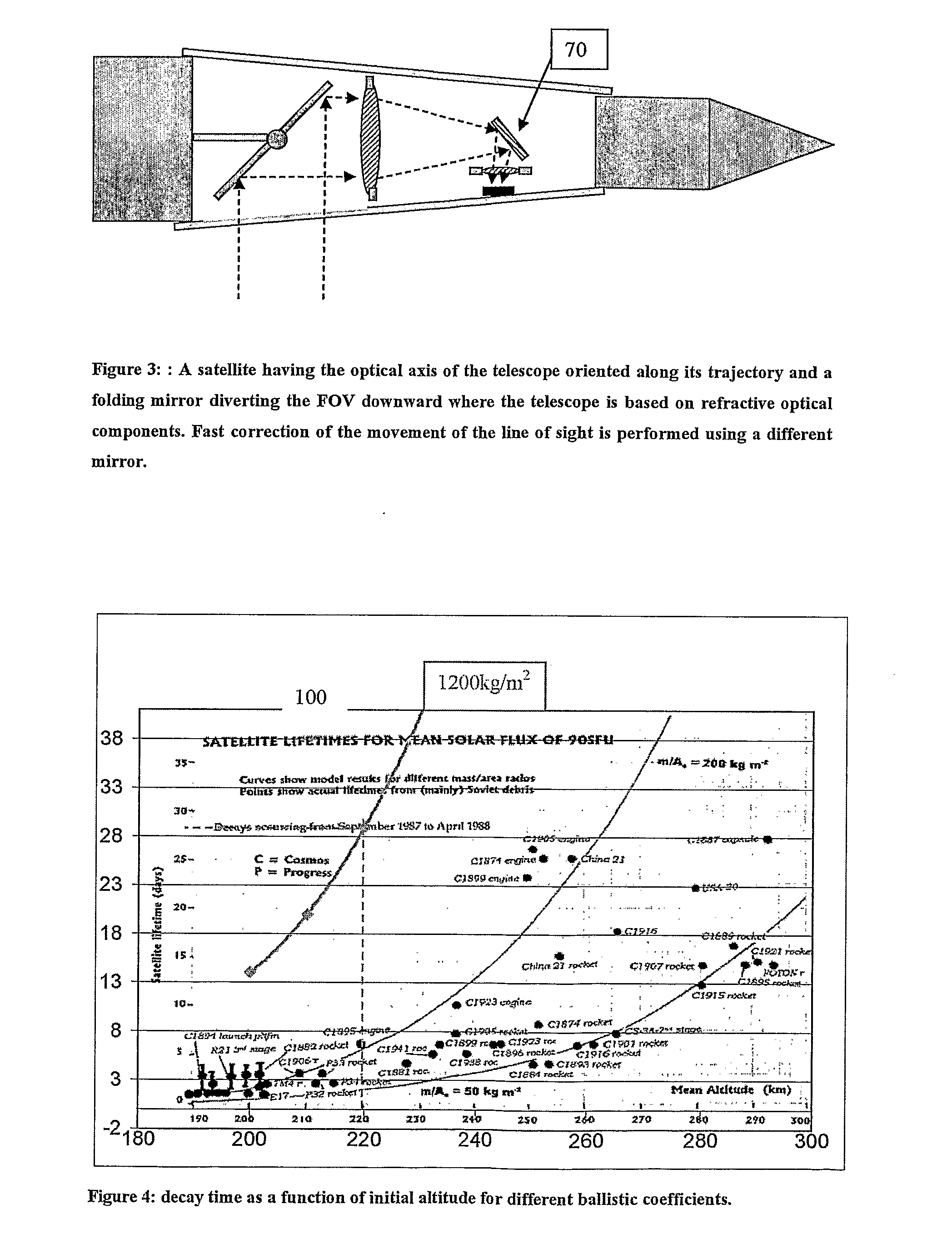
Low orbit missile-shaped satellite for electro-optical earth surveillance and other missions
InactiveUS20090251773A1Image obtainedCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusSurgeryOptical axisThermosphere
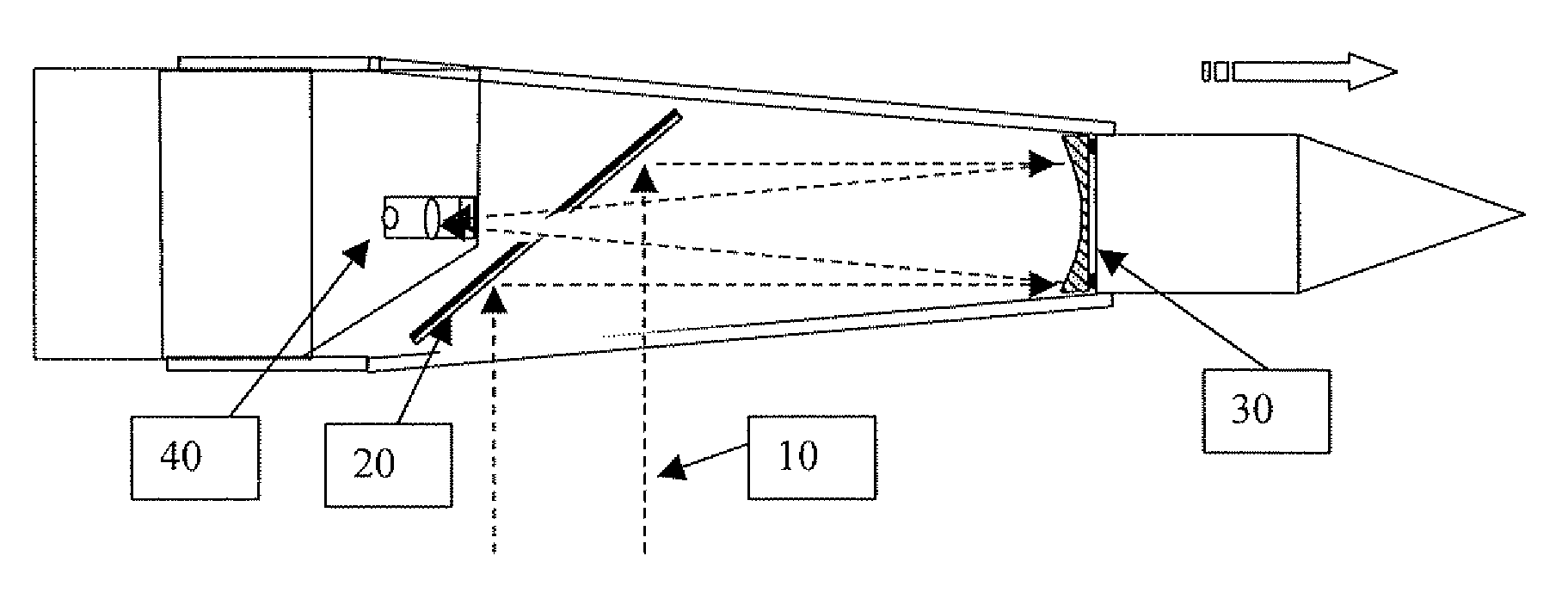
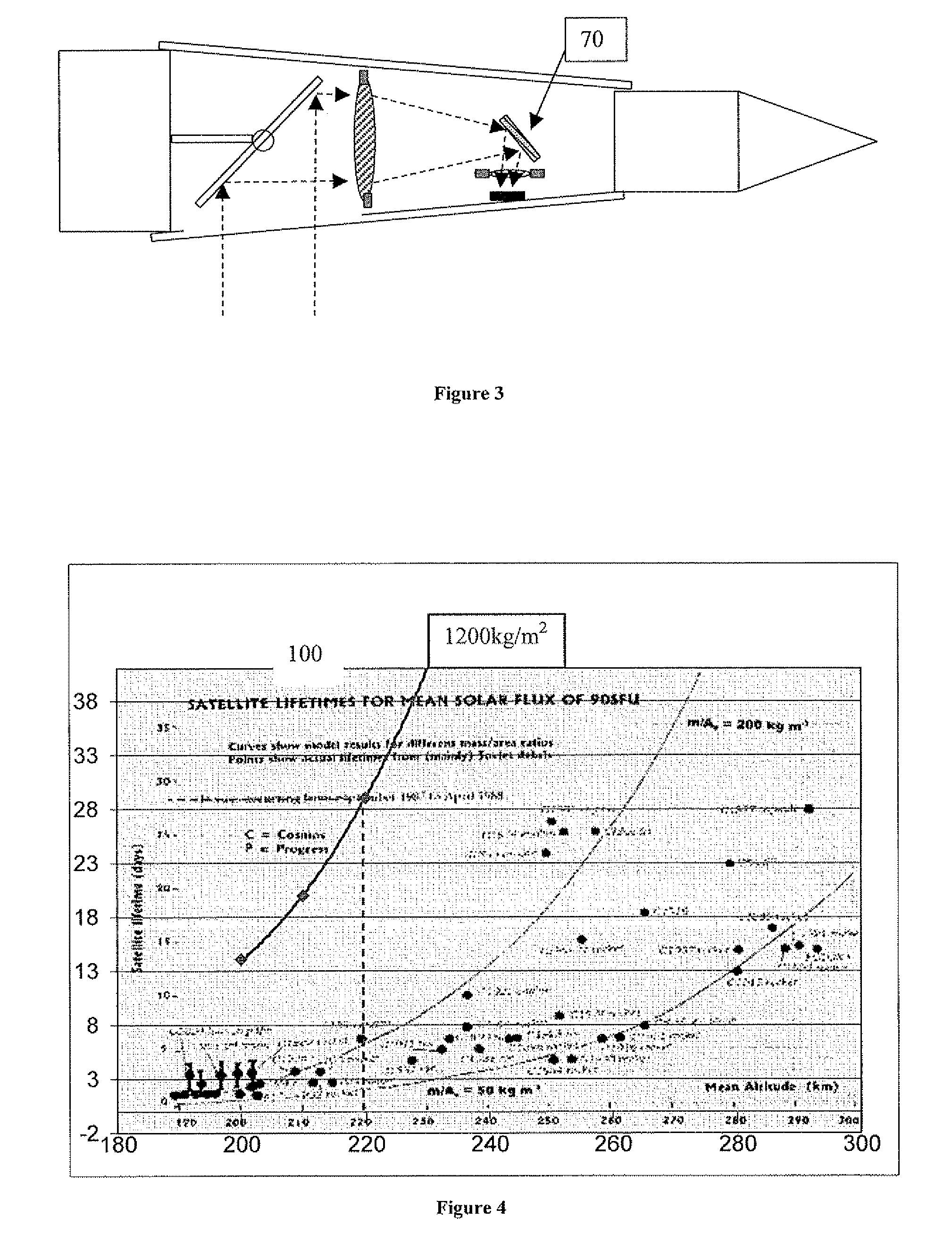
A low orbit optical imaging satellite has a long thin satellite body housing an optical telescope arrangement. A major part of the telescope arrangement has its optical axis roughly parallel to the direction of elongation and includes a mirror arrangement deployed to direct a line of sight of the optical telescope out sideways from the direction of elongation. The transverse dimensions of the satellite body are preferably minimized to be close to the optical aperture dimension of the optical telescope, thereby providing a high ballistic coefficient and high orbit lifetime for orbits in the low thermosphere.
Owner:RAFAEL ADVANCED DEFENSE SYSTEMS
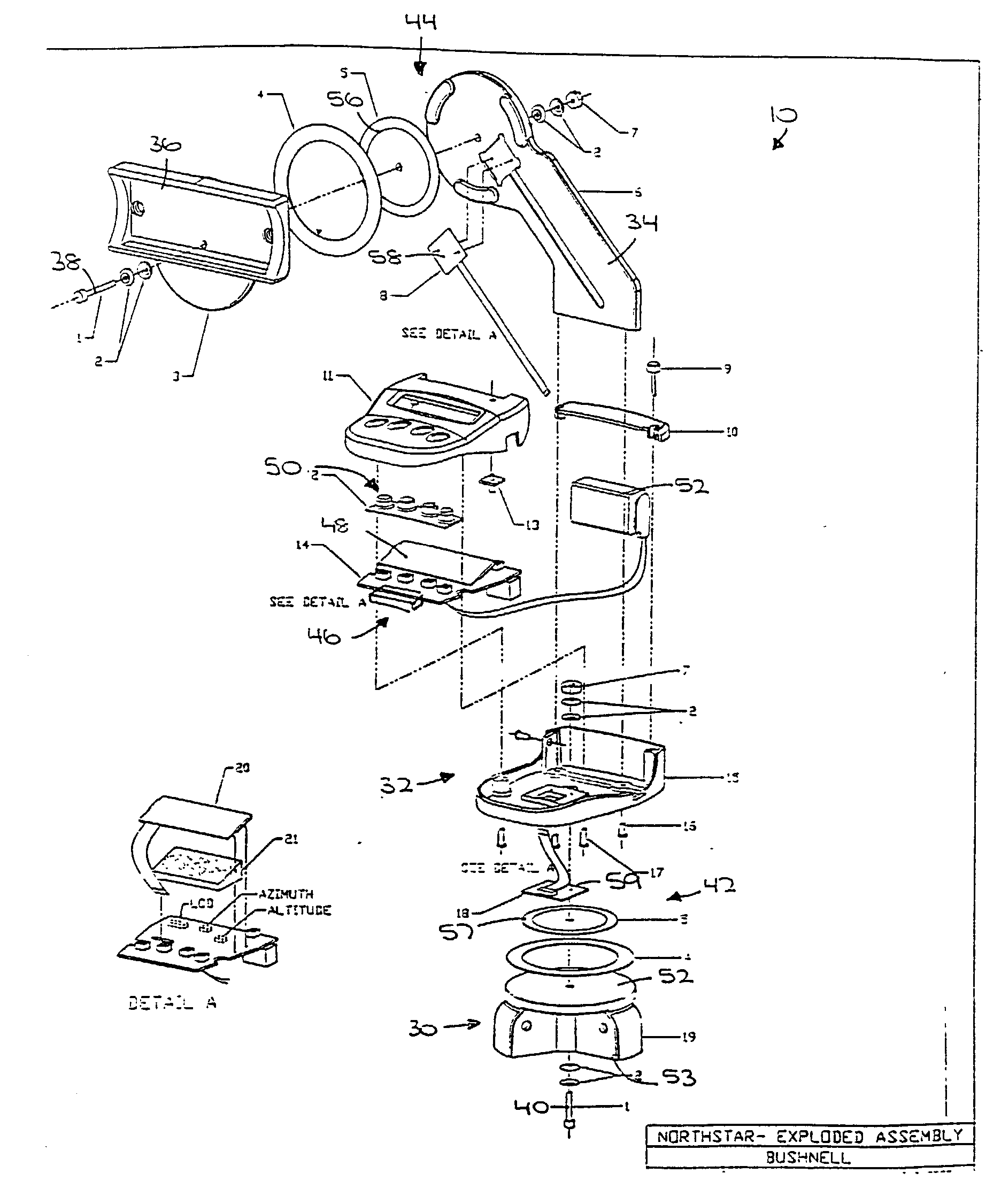
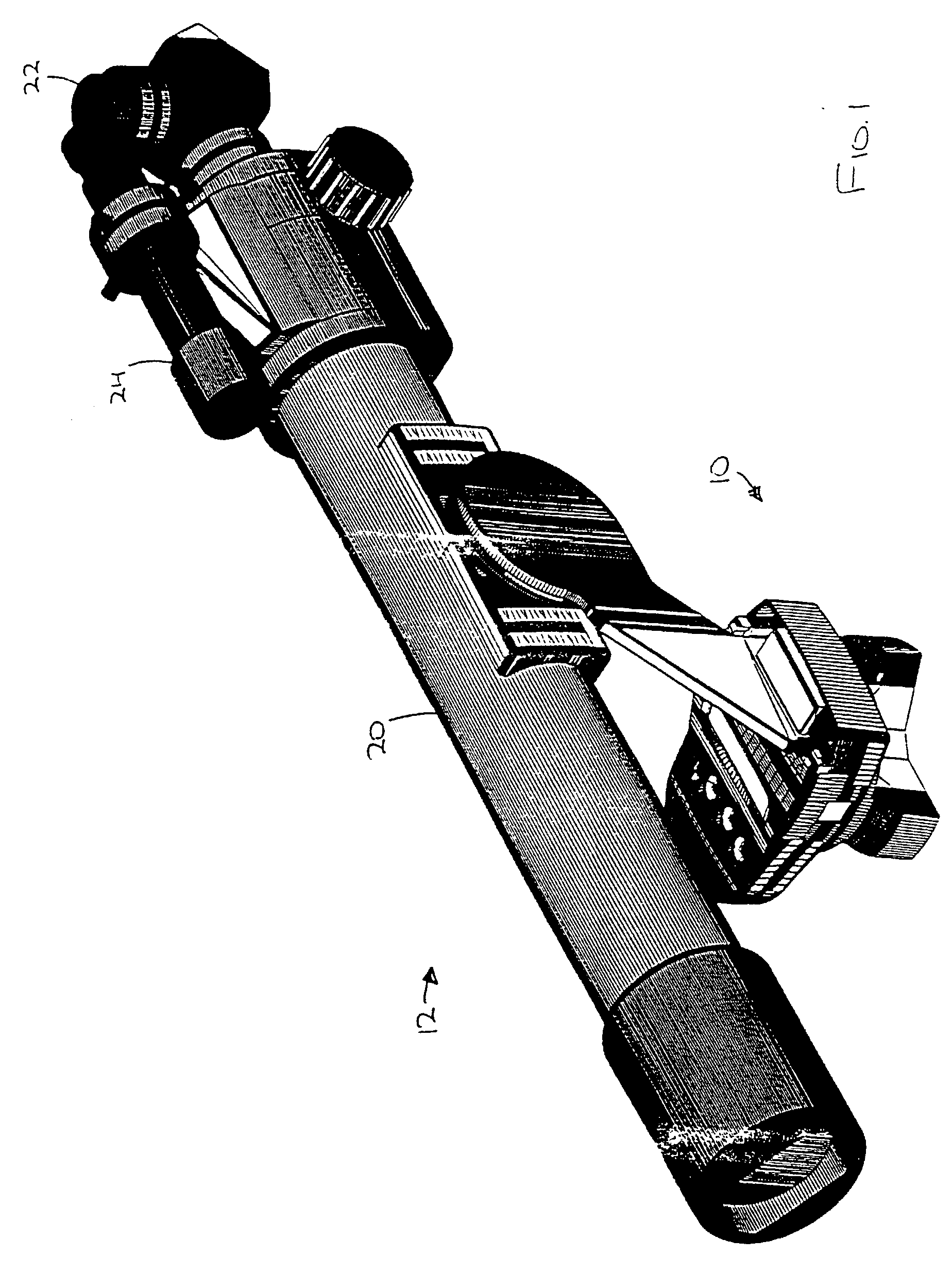
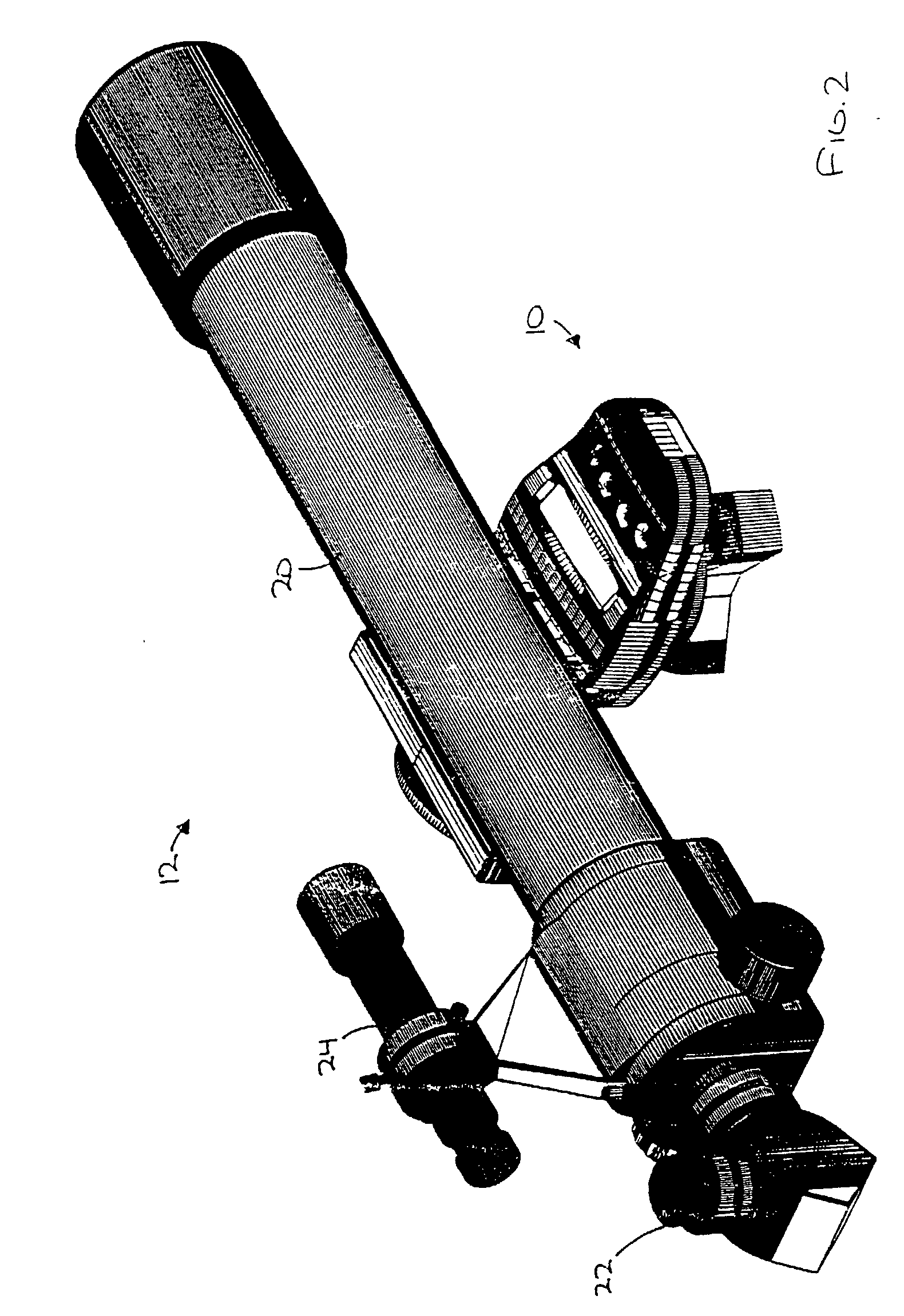
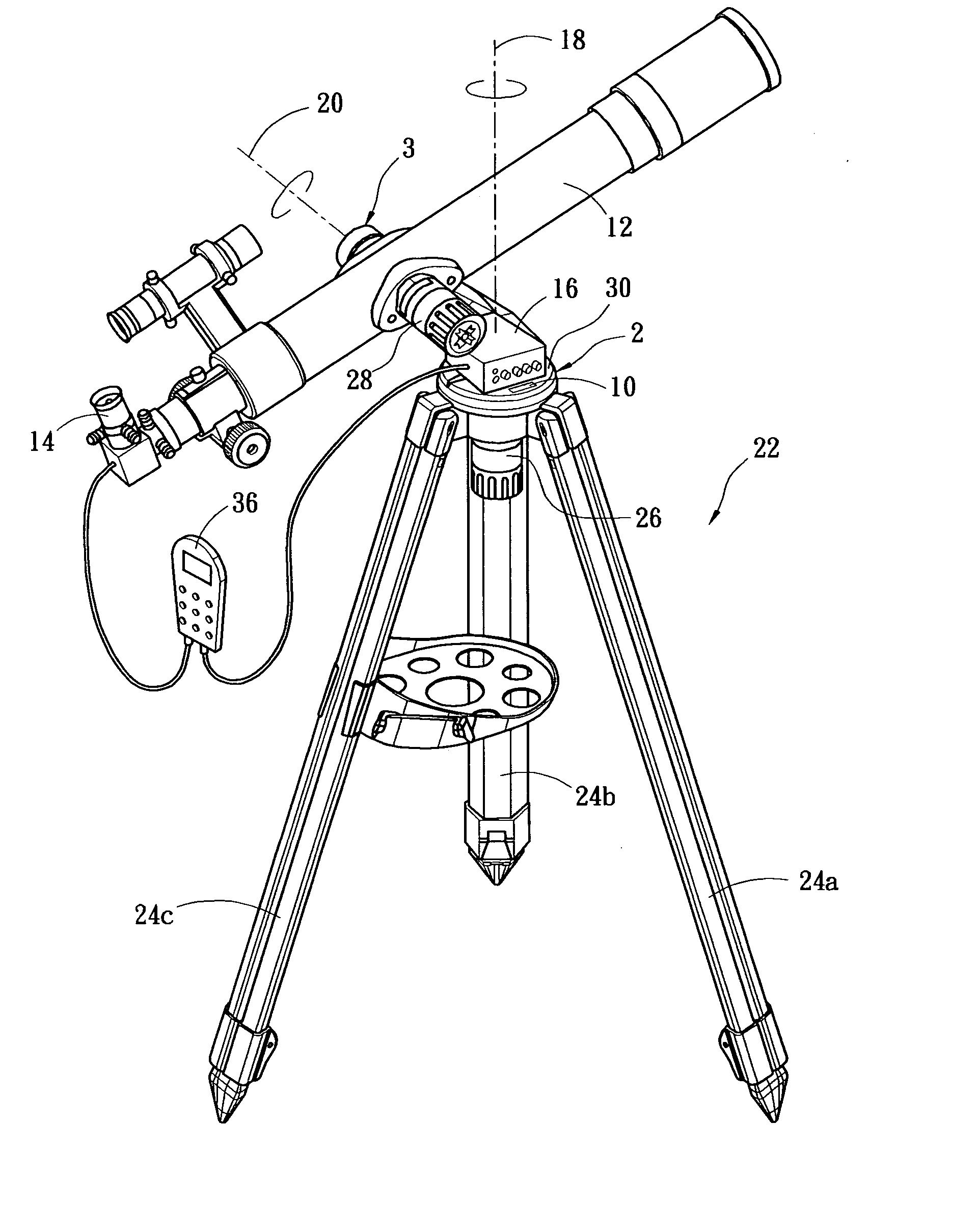
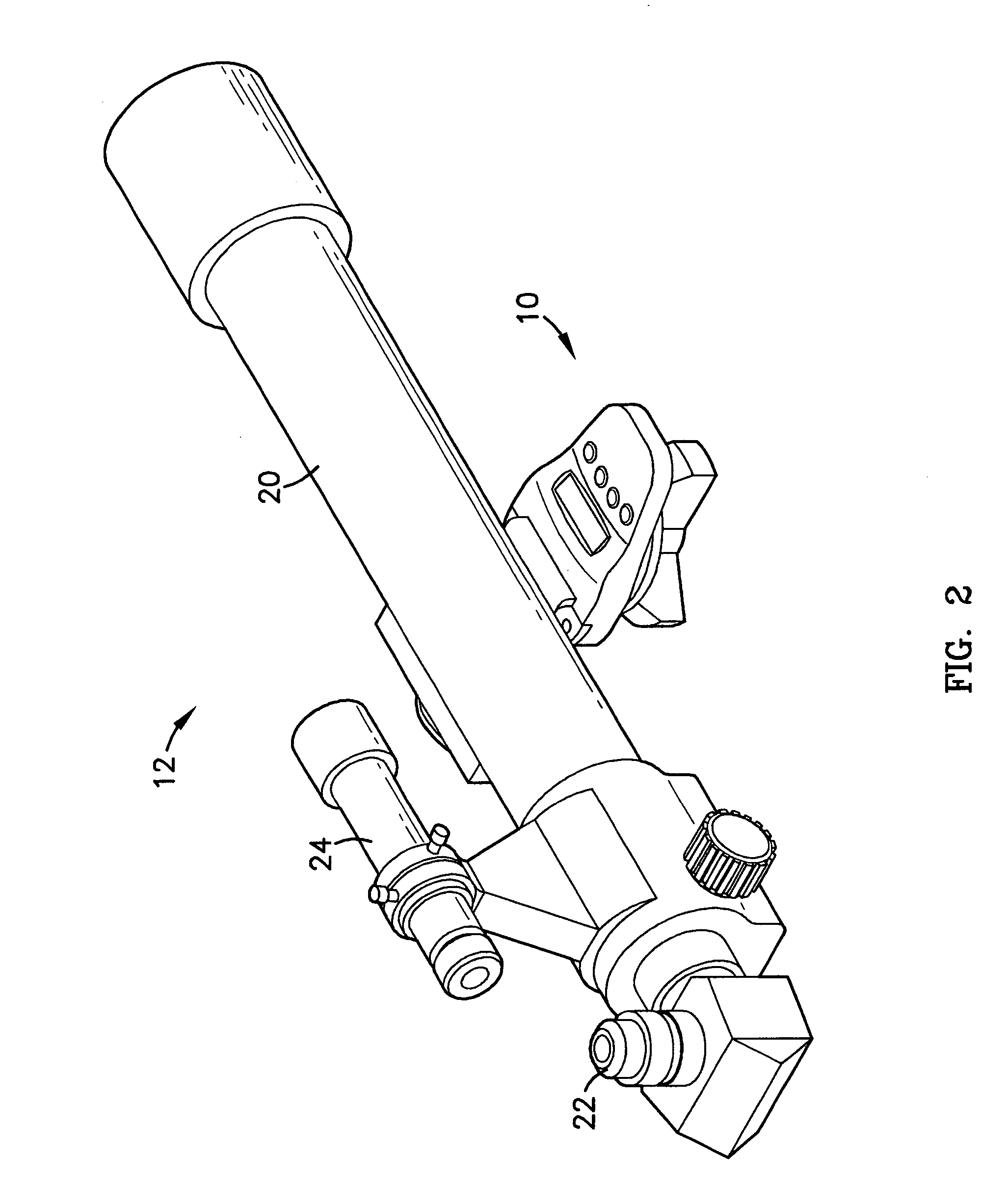
Portable telescope mount with integral locator using magnetic encoders for facilitating location of objects and positioning of a telescope
A portable altitude / azimuth telescope mount having an integral locator system with a magnetic encoder mechanism for facilitating location of astronomical objects and telescope positioning for observation thereof. A microprocessor receives signals from the encoder mechanism and translates such into position data for display. The locator system also includes a database of astronomical objects, including their locations and other relevant information.
Owner:BUSHNELL CORPORATION
Daytime stellar imager for attitude determination
InactiveUS7447591B2Efficient use ofImprove accuracyPosition fixationNavigation by astronomical meansJet aeroplaneCelestial navigation
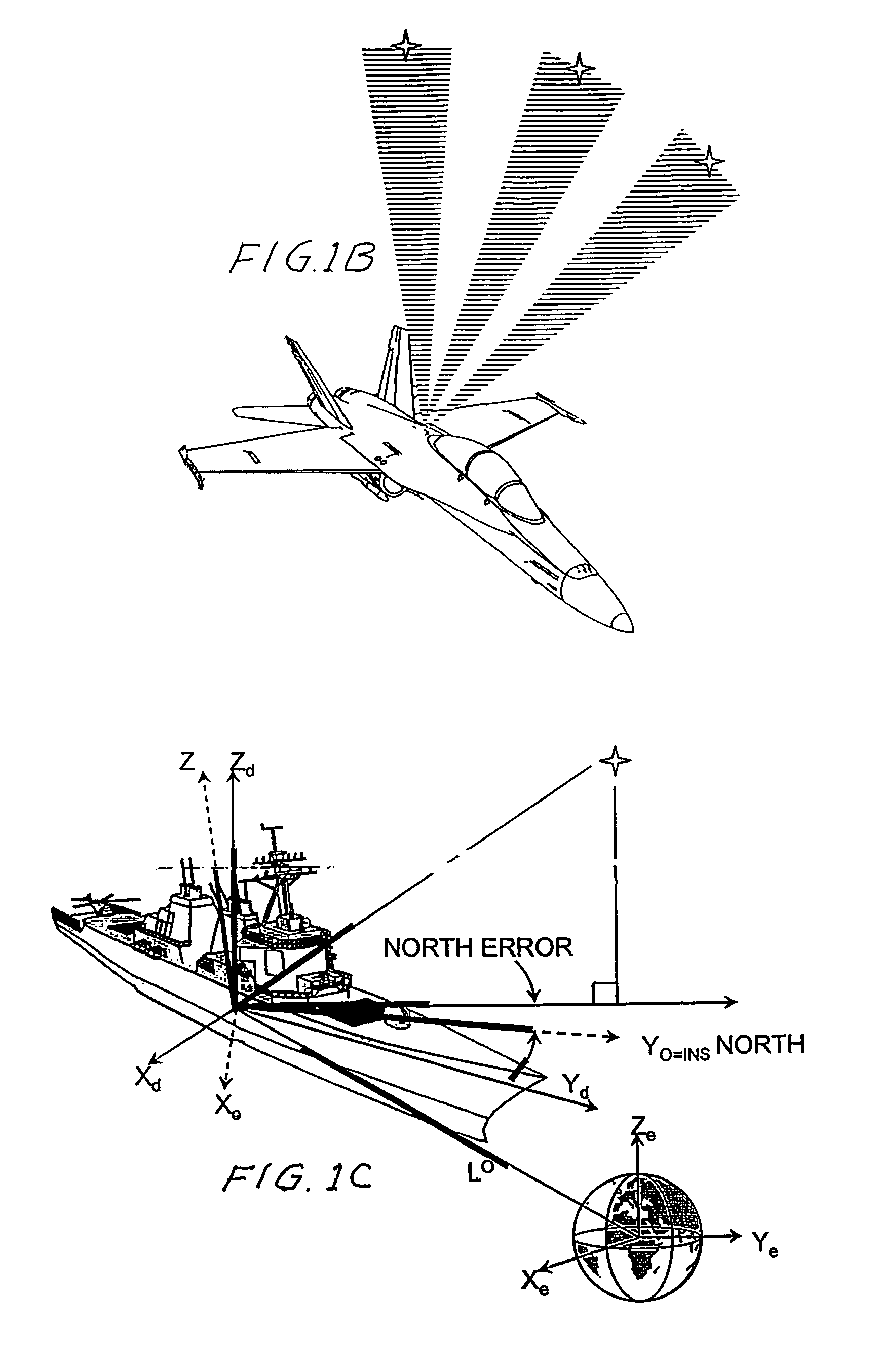
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. One or more telescopes mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane and directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Telescope optics focus (on to a pixel array of a sensor) H-band or K-band light from one or more stars in multiple telescopic fields of view. Each system also includes a GPS sensor and a computer processor having access to catalogued infrared star charts. The processor for each system is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, position and timing information from the GPS sensor, and the catalogued star charts information to determine orientation (attitude) of the platform.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
All-day multifunctional telescope device capable of being both used for solar active region observation and night astronomical observation
ActiveCN103901601AReduce the temperatureSeeing effect controlTelescopesTemperature controlControl system
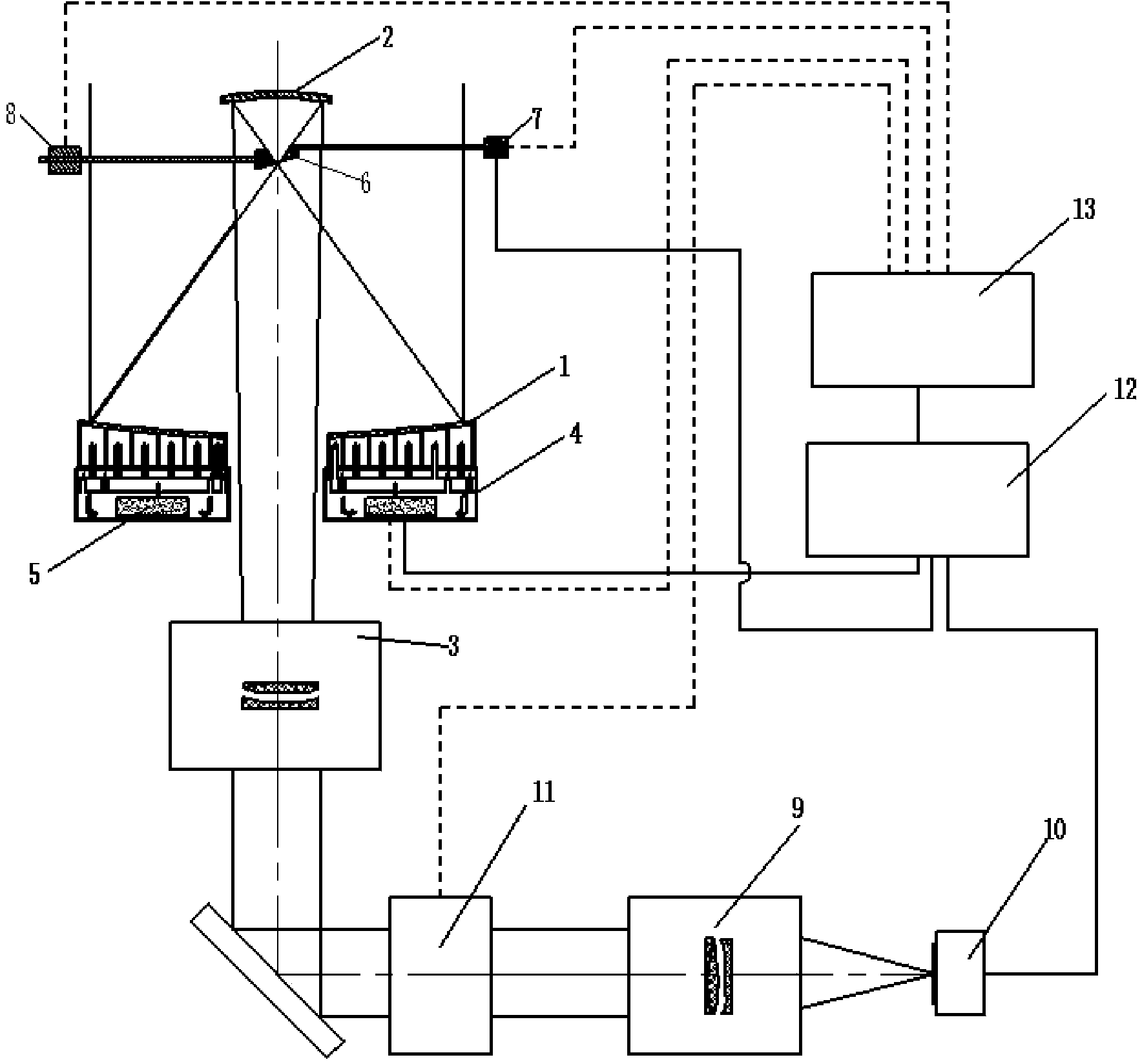
An all-day multifunctional telescope device capable of being both used for solar active region observation and night astronomical observation comprises an optical telescope system, a lightweight cellular main lens and temperature control system, a thermovision field diaphragm and temperature control system, a thermovision field diaphragm adjusting structure, an achromatic imaging system, a light filter, a rotating rack and a data processing and control system. According to the all-day multifunctional telescope device capable of being both used for solar active region observation and night astronomical observation, under the condition that cost and system complexity are not obviously increased, the effective observation time of the telescope device is changed to achieve daytime and night continuous observation from only daytime or night observation, the effective observation time is effectively prolonged, the observation efficiency is improved, important reference is provided for development of telescopes, in particular to development of large-diameter telescopes, and the innovativeness and practicability are achieved.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vehicle roof bow assembly
InactiveUS20090206636A1Superstructure subunitsLoading-carrying vehicle superstructuresEngineeringFlange
A vehicle roof bow assembly includes a roof bow member and a pair of telescoping mounting brackets. The roof bow member is configured to extend in a lateral side-to-side direction along an underside of a vehicle roof panel. The telescoping mounting brackets each have a first end and a second end with the first end having a side rail attachment flange configured for rigid attachment to a first vehicle roof side rail and a roof panel attachment flange configured for rigid attachment to the vehicle roof panel and the second end being attached to the roof bow member. The telescoping mounting brackets are disposed at opposite ends of the roof bow member.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
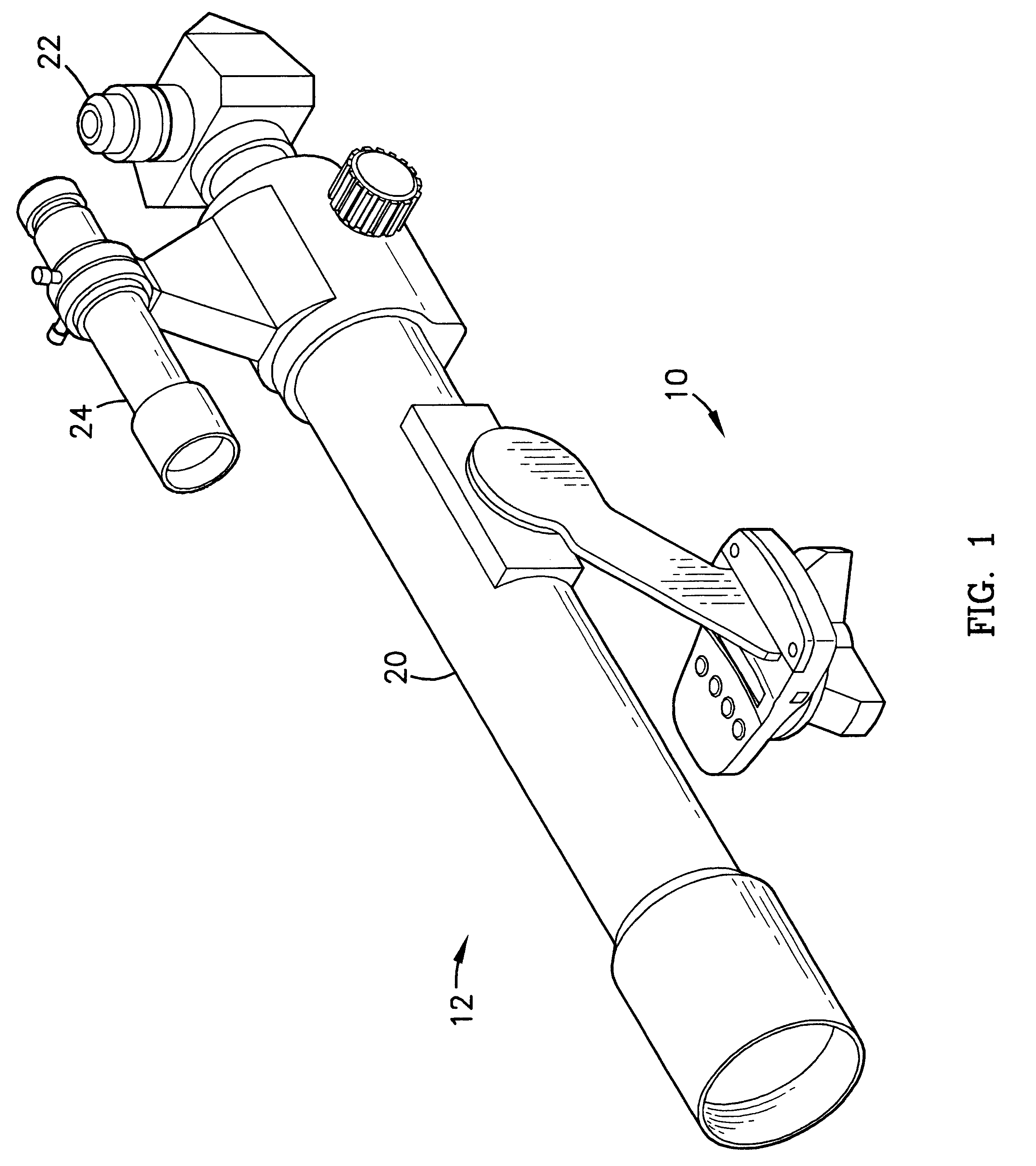
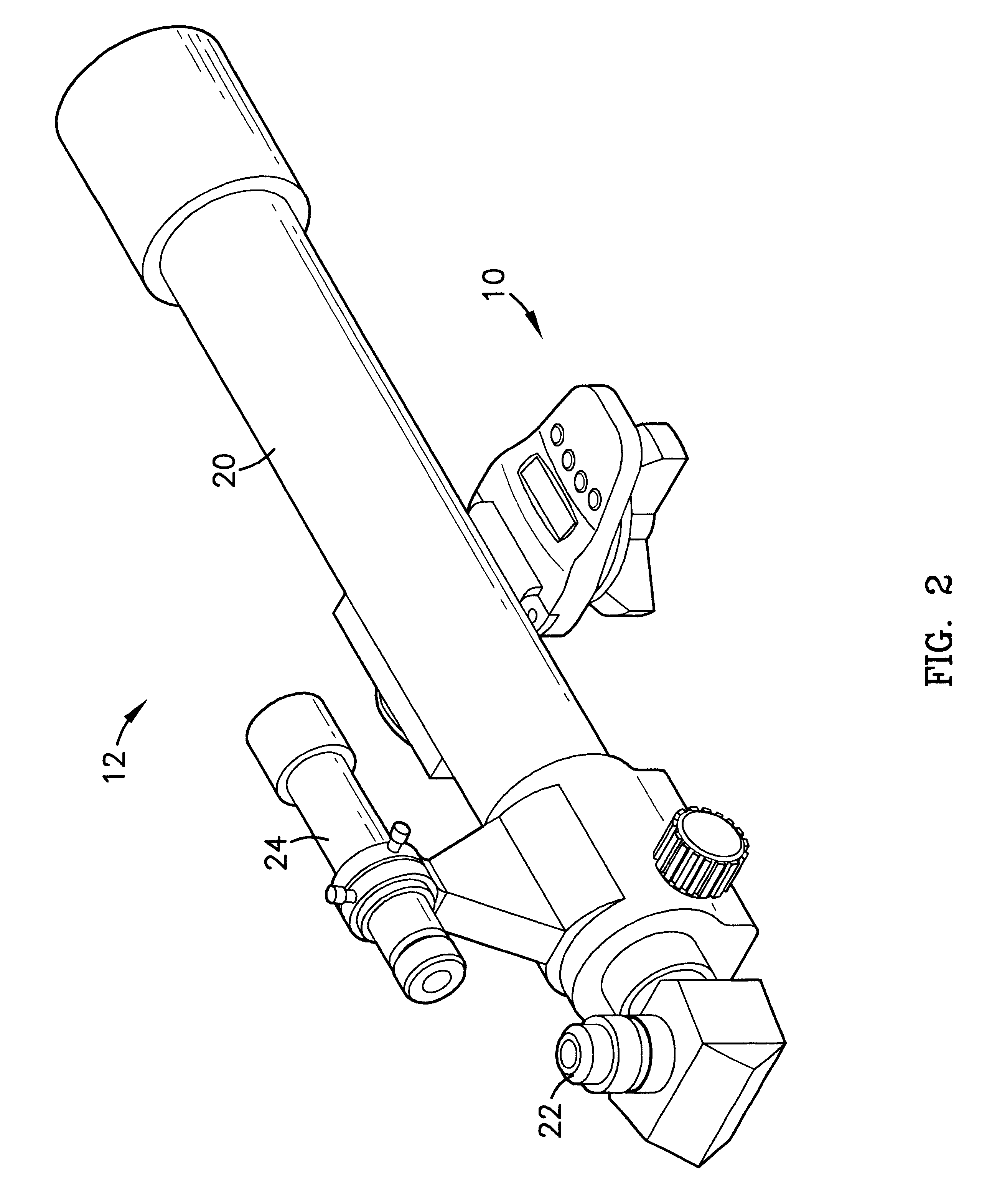
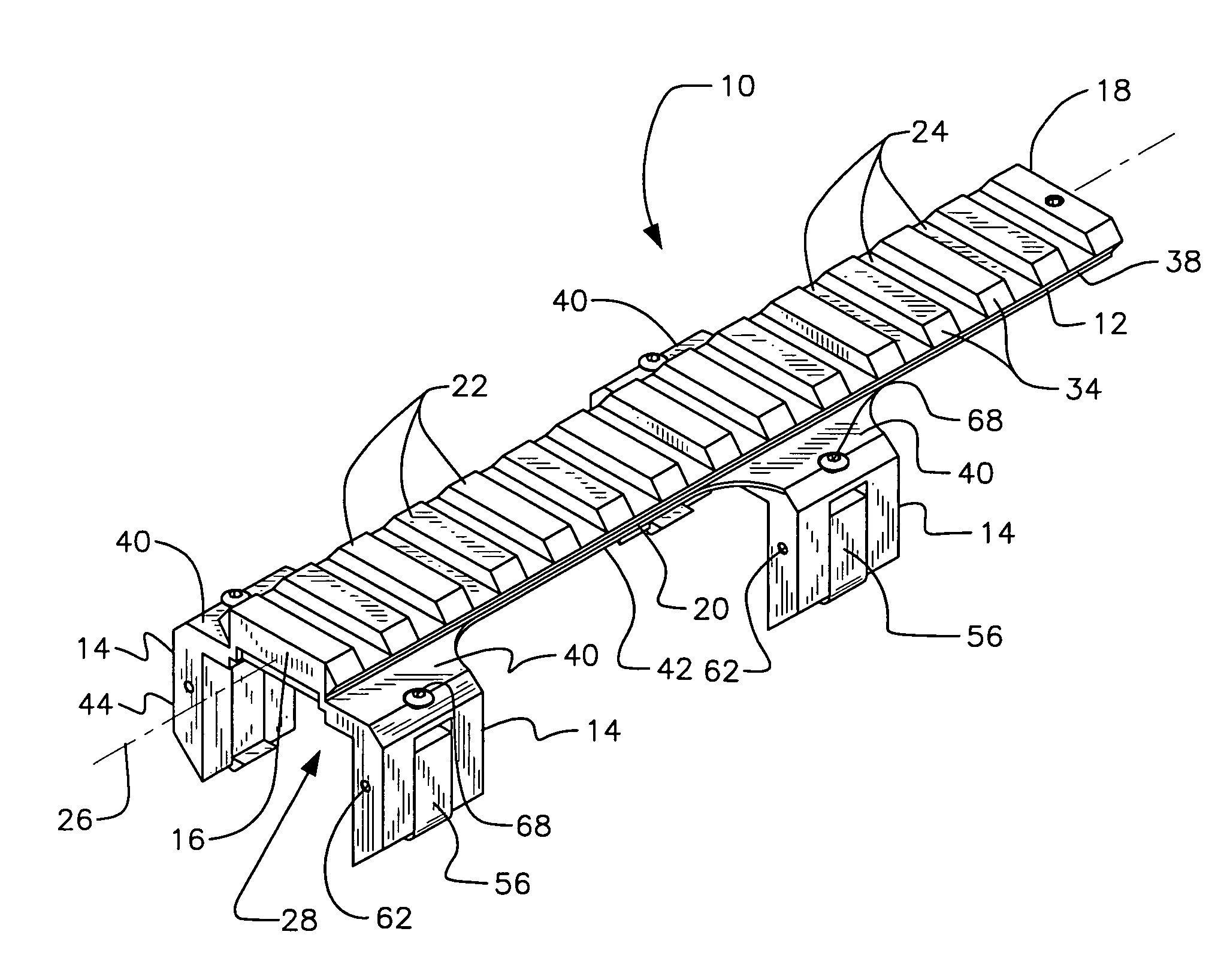
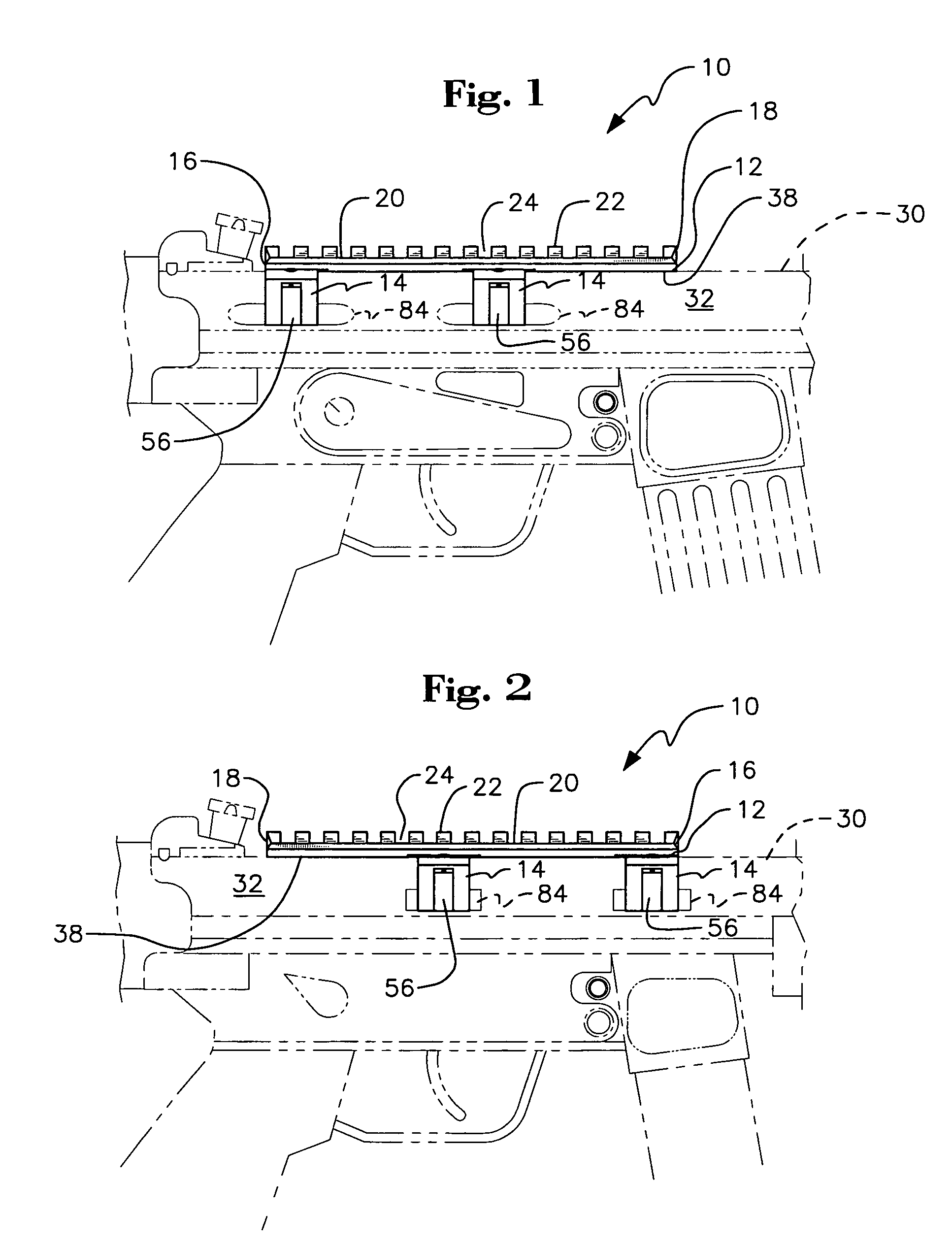
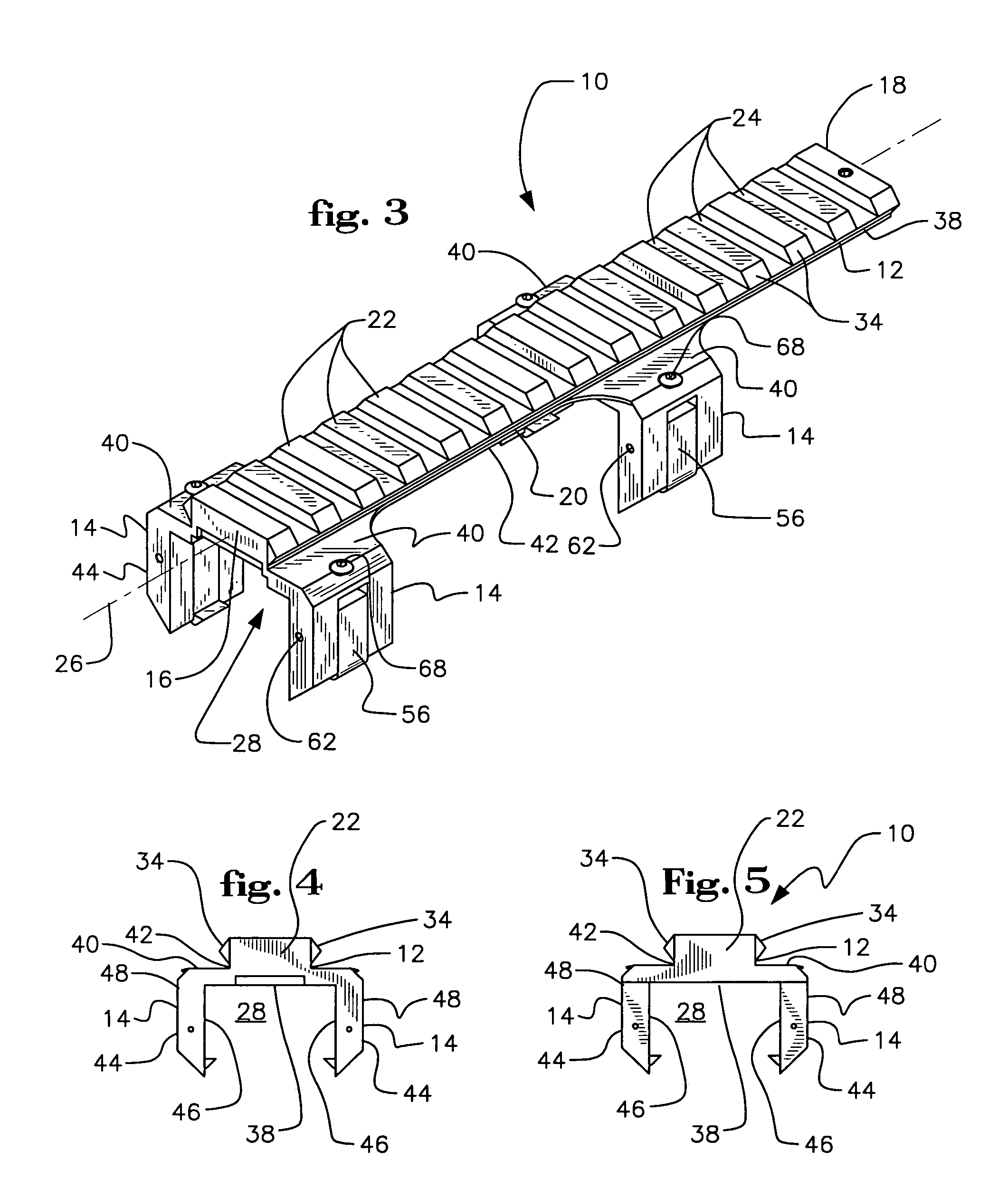
Reversible weapon telescope mount
A low profile, reversible weapon telescope mount is provided. The mount has a longitudinal planar top support having a series of ridges and recesses disposed thereupon in an alternating and parallel orientation to that of a central axis of the support. Attached to opposed peripheral side edges of the support are four downwardly depending legs. The support and legs form a channel of the scope mount that surrounds a top end of a weapon receiver, such as a rifle, such that a bottom surface of the top planar support rests upon a top surface of the receiver. Each leg has a movable guide finger supported in a vertical channel formed in each leg. Each guide finger has an inwardly extending ledge member for grabbing outwardly extending flanges of the rifle receiver. The finger is guided up and down by an pin inserted through the leg and finger when a screw, acting upon the finger is tightened or loosened. The mount can be reversed so that its front end is closer to the head of the user of the weapon while still permitting a telescope to be mounted thereupon.
Owner:FROST MICHAEL
Portable telescope mount with integral locator using magnetic encoders for facilitating location of objects and positioning of a telescope
A portable altitude / azimuth telescope mount having an integral locator system with a magnetic encoder mechanism for facilitating location of astronomical objects and telescope positioning for observation thereof. A microprocessor receives signals from the encoder mechanism and translates such into position data for display. The locator system also includes a database of astronomical objects, including their locations and other relevant information.
Owner:BUSHNELL
Synthetic aperture type high-resolution imaging telescope device based on bright source
InactiveCN103558684ALow costAchieving Sparse Synthetic ApertureTelescopesHigh resolution imagingPlane mirror
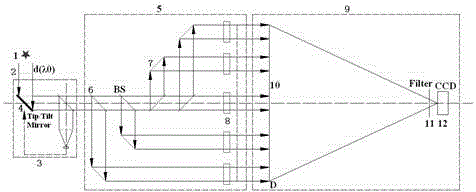
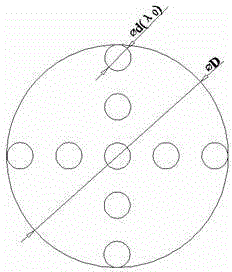
The invention discloses a synthetic aperture type high-resolution imaging telescope device based on a bright source. The synthetic aperture type high-resolution imaging telescope device is composed of a receiving pupil whose diameter d is matched with the current observatory address seeing, a synthetic aperture type optical imaging system and a telescope imaging system having a main mirror diameter of D. A sparse aperture array and delay line compensators are arranged in the synthetic aperture type optical imaging system. The sparse aperture array includes a plurality of sub-mirrors having an aperture of d which are distributed in a plurality of multistage two-dimensional spaces. The sub-mirrors comprise a spectroscope, a transmitting mirror and a plane mirror. The delay line compensators are arranged on the output optical path of each sub-mirror separately. The plurality of sub-mirrors are used to acquire nearly-complete real-time UV plane coverage on a focal plane through the multistage spectral arrangement according to the energy ratio. The delay line compensators are used to compensate the optical path difference of each aperture to acquire the outgoing diffraction limit wavefront on the sparse aperture array longest baseline D and output the outgoing diffraction limit wavefront to the telescope imaging system having a main mirror diameter of D. According to the invention, advantages of low cost and simple system can be realized, and high time and space resolution diffraction limit imaging can be obtained on a real-time basis.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ASTRONOMICAL OPTICS & TECH NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSE
Method for automatically aligning telescope
A manual controller commands a telescope mount to automatically track a specific bright star after the image of the star is located to center of an electronic eyepiece and a timer is started. The average moving speed of the bright star is calculated after a predetermined elapsed time to acquire the right ascension (RA) and the declination (DEC) coordinates of this bright star. Subsequently, the RA and DEC coordinates are compared with pre-stored data contained within a database used to identify the bright star. The celestial sphere coordinates of the telescope can be determined after a minimum of one bright star is identified. In the auto-tracking procedure, the manual controller controls movement of telescope by feedbacks of the drifting speed and direction of the specific bright star in an electronic eyepiece for the purpose of keeping the specific bright star in the center of the electronic eyepiece.
Owner:NANTONG SCHMIDT OPTO ELECTRICAL TECH CO LTD
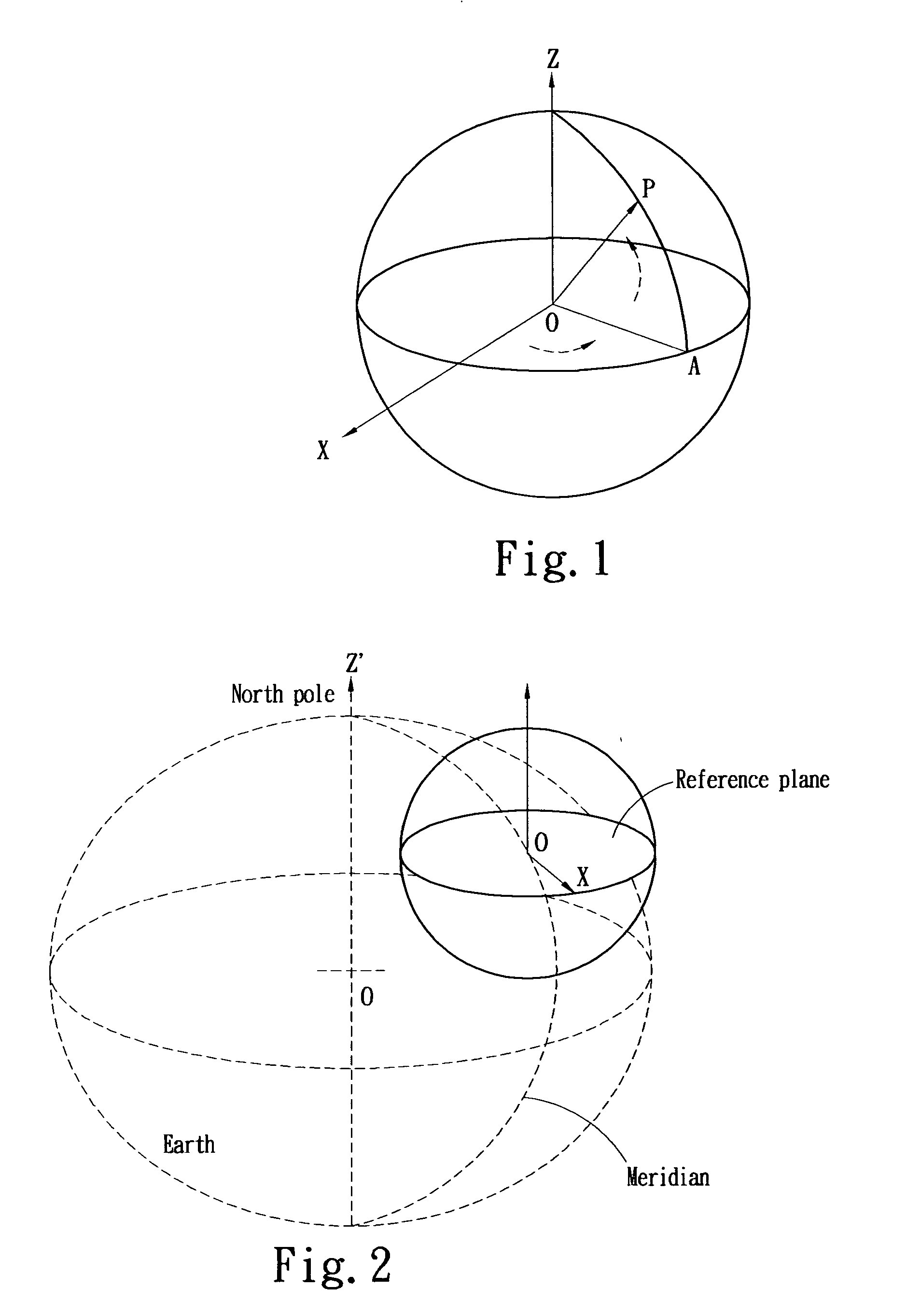
Accurate Telescope Tracking System with a Calibrated Rotary Encoder
InactiveUS20130265639A1Improve accuracyExpensive encoderComputer controlTelescopesMicrocontrollerEarth's rotation
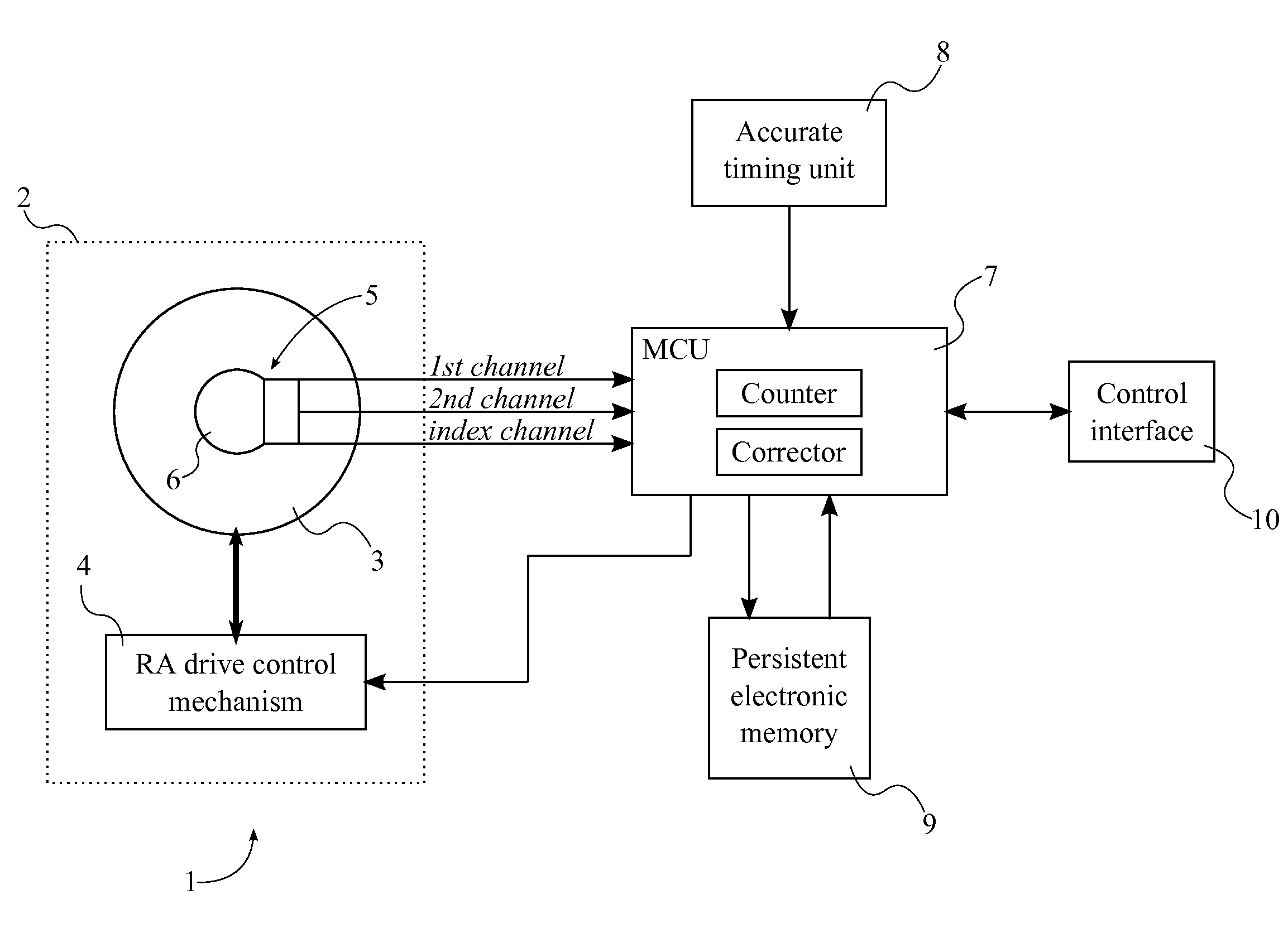
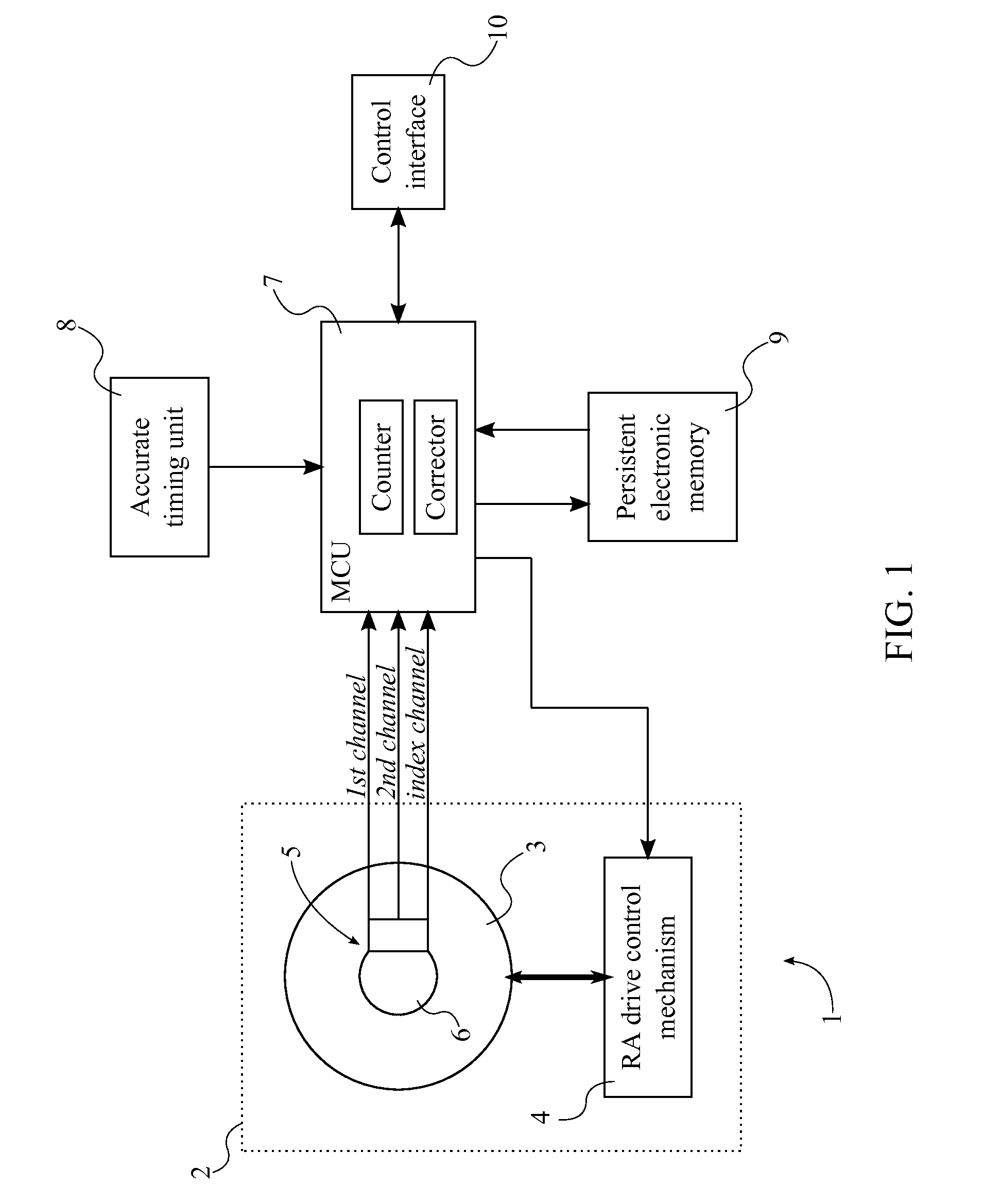
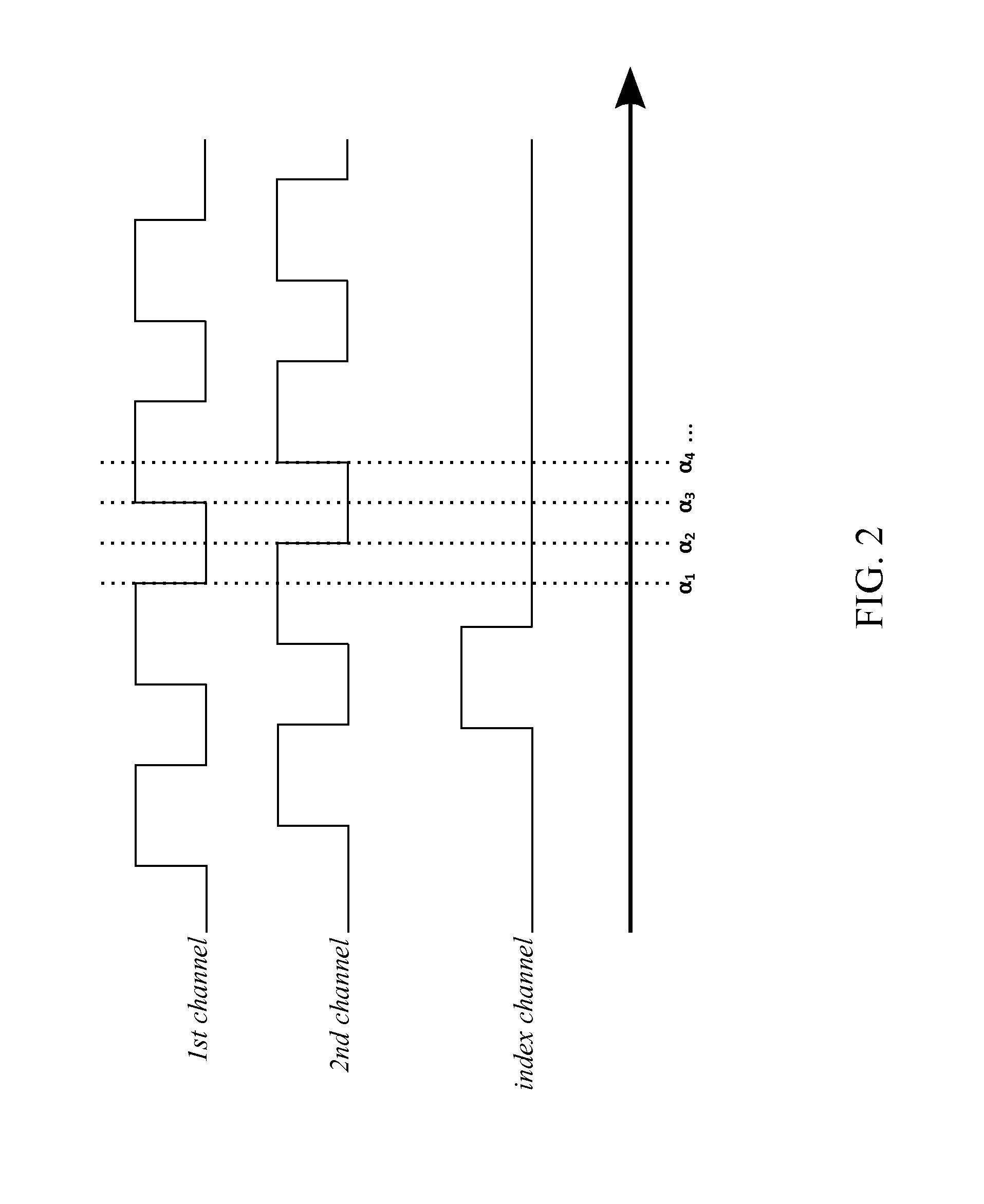
A system with a calibrated rotary encoder can be used for accurate telescope tracking along the Right Ascension (RA) rotation axis. The system includes an incremental quadrature optical encoder, a microcontroller unit (MCU), a timer, an electronic memory, and a control interface. The rotor of the encoder is coaxially attached to the RA drive shaft of the telescope mount in order to send angular position data for the RA drive shaft to the MCU. The MCU evaluates the angular position data for errors and send corrections to the control mechanism of the RA drive shaft. The electronic memory stores calibrated reference data, which is compared to the angular position data by the MCU. The calibrated reference data can be found by measuring the movement of a reference star across an image. The system can also calculate an accurate visible speed for the Earth's rotation in a desired direction.
Owner:BATCHVAROV ANDREY BORISSOV
Telescope based calibration of a three dimensional optical scanner
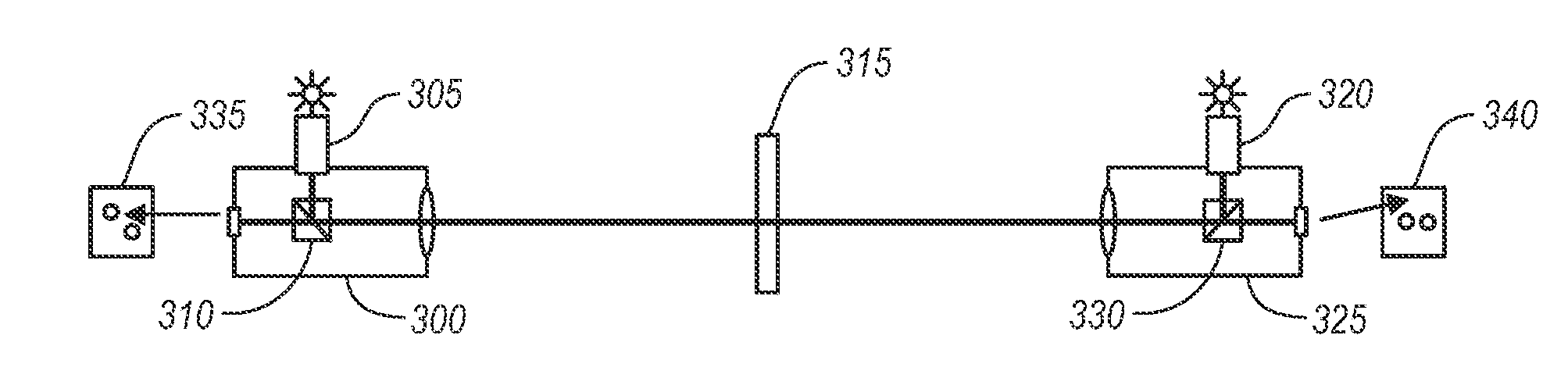
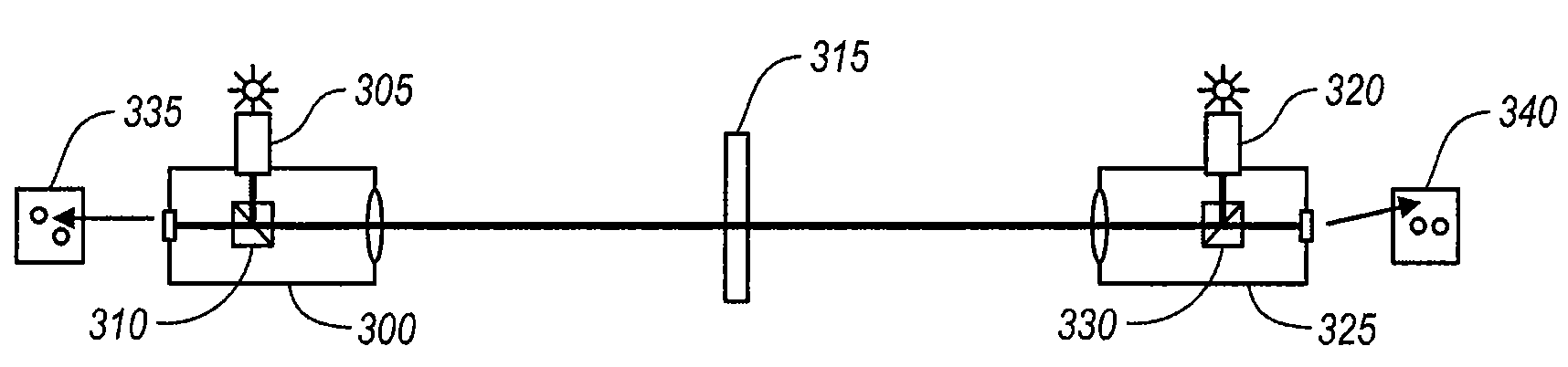
An embodiment of the invention includes using a set of telescopes to calibrate a three dimensional optical scanner. Three separate calibrations are disclosed for a survey grade calibration: (1) angular calibration, implemented using at least one anti-podal pair of telescopes, (2) range calibration, implemented using at least one telescope mounted fiber recirculator, and (3) tilt calibration, implemented using at least one pair of telescopes not mounted in anti-podal configuration and an integral tilt table. Methods for aligning or measuring the mis-alignment between anti-podal telescope pairs are also described.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
Telescope mount having locator system and drive mechanism for locating objects and positioning telescope
A portable altitude / azimuth telescope mount having an integral locator system with a magnetic encoder mechanism for facilitating location of astronomical objects and telescope positioning for observation thereof. A microprocessor receives signals from the encoder mechanism and translates such into position data for display. The locator system also includes a database of astronomical objects, including their locations and other relevant information. The mount is preferably provided with a drive mechanism adapted to allow for automatically or manually positioning the telescope to view astronomical objects and for automatically repositioning or steering the telescope in order to track the astronomical objects during extended viewing. When moved manually, components of the drive act as a clutch mechanism that effectively disengages the drive motor to avoid damage. An instance of the drive may be provided for each axis of movement.
Owner:BUSHNELL CORPORATION
Disc based alt-azimuth telescope mount
A disc-based altitude-azimuth telescope mount for mounting and adjusting a telescope along altitude and azimuth axes. The telescope mount includes an azimuth disc assembly for facilitating adjustment of the telescope along the azimuth axis and an altitude disc assembly for facilitating adjustment of the telescope along the altitude axis. A friction adjusting mechanism operably engages the azimuth disc assembly and the altitude disc assembly to prevent inadvertent movement of the telescope along both axes. A digital setting circle may be operably connected to the disc assemblies to facilitate automatic adjustment of the telescope, as desired.
Owner:PETERS JR LYAL T
Technique for Telescope Polar Alignment
A polar scope for a telescope mount includes a reticle having a pattern with multiple markings that allows users to accurately position pole stars for precise polar alignment. A system and mount may be provided including a polar scope of this kind. The polar scope may be provided with a controller that calculates the apparent position of a pole star, while accounting for errors, such as proper motion, precession of the earth's axis, and / or atmospheric refraction.
Owner:XU NING +1
Telescope mount having locator system and drive mechanism for locating objects and positioning telescope
InactiveUS7046438B2Low costReduce weightProgramme controlComputer controlRelevant informationDrive motor
A portable altitude / azimuth telescope mount having an integral locator system with a magnetic encoder mechanism for facilitating location of astronomical objects and telescope positioning for observation thereof. A microprocessor receives signals from the encoder mechanism and translates such into position data for display. The locator system also includes a database of astronomical objects, including their locations and other relevant information. The mount is preferably provided with a drive mechanism adapted to allow for automatically or manually positioning the telescope to view astronomical objects and for automatically repositioning or steering the telescope in order to track the astronomical objects during extended viewing. When moved manually, components of the drive act as a clutch mechanism that effectively disengages the drive motor to avoid damage. An instance of the drive may be provided for each axis of movement.
Owner:BUSHNELL CORPORATION
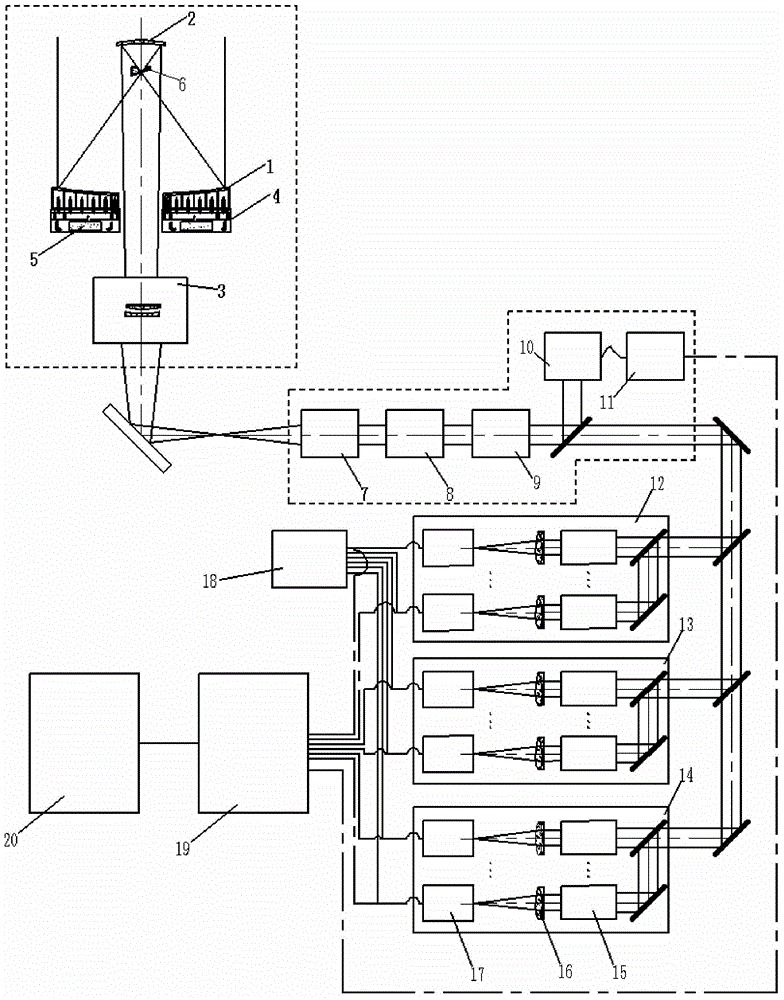
Solar active region high-resolution tomographic imaging telescope device
ActiveCN105022157AImprove imaging effectImprove resolutionTelescopesSolar ActivitiesSolar atmosphere
The invention provides a solar active region high-resolution tomographic imaging telescope device comprising an optical telescope system, a solar self-adaptive optical system, a multispectral tomographic imaging system and an image restoration and data fusion system. The relation between the solar radiation spectrum and solar atmosphere height is utilized, the multispectral tomographic imaging system is additionally arranged, and a solar self-adaptive optical technology and an image restoration technology are combined so that solar active region high-resolution and high-contrast tomographic imaging observation can be realized finally. The solar active region high-resolution tomographic imaging telescope device has high innovativeness and practicality and has an important effect in research of solar activity development and evolution.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Adjustable GPS/sonar mount
The present invention includes a folding and telescoping mounting stand apparatus for mounting a Global Positioning System (GPS) / sonar device on a boat, comprising a first outer tubing attached to a base plate which is secured to a deck of a boat, a first inner tubing having a bottom end and a top end, wherein the bottom end is placed in and attached to the first outer tubing by a pin and a first knob and the top end is placed in and attached to a second outer tubing by an intermediate tubing, a second inner tubing attached to a top tube by a second knob, wherein the combination of the second inner tubing and the top tube are placed in the second outer tubing and held in place with a spring plunger, a board connected to a rod and wherein the rod is secured to the top tube and the second inner tubing with the second knob, wherein the inner tubing is raised to a desired height when the spring plunger is pulled and the board is lifted upward; and the apparatus having an upper body above the first outer tubing that is folded down by releasing the first knob and pulling upward on the board until the upper body is 1″ above the first outer tubing and then folding the upper body forward to the deck.
Owner:ROBICHAUX JR ELMO
Device for improving rotary table chopper Q-switch laser performance and a Q-switch laser
ActiveCN104701717AHigh beam qualityPrevent breakdownOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionResonant cavityLight beam
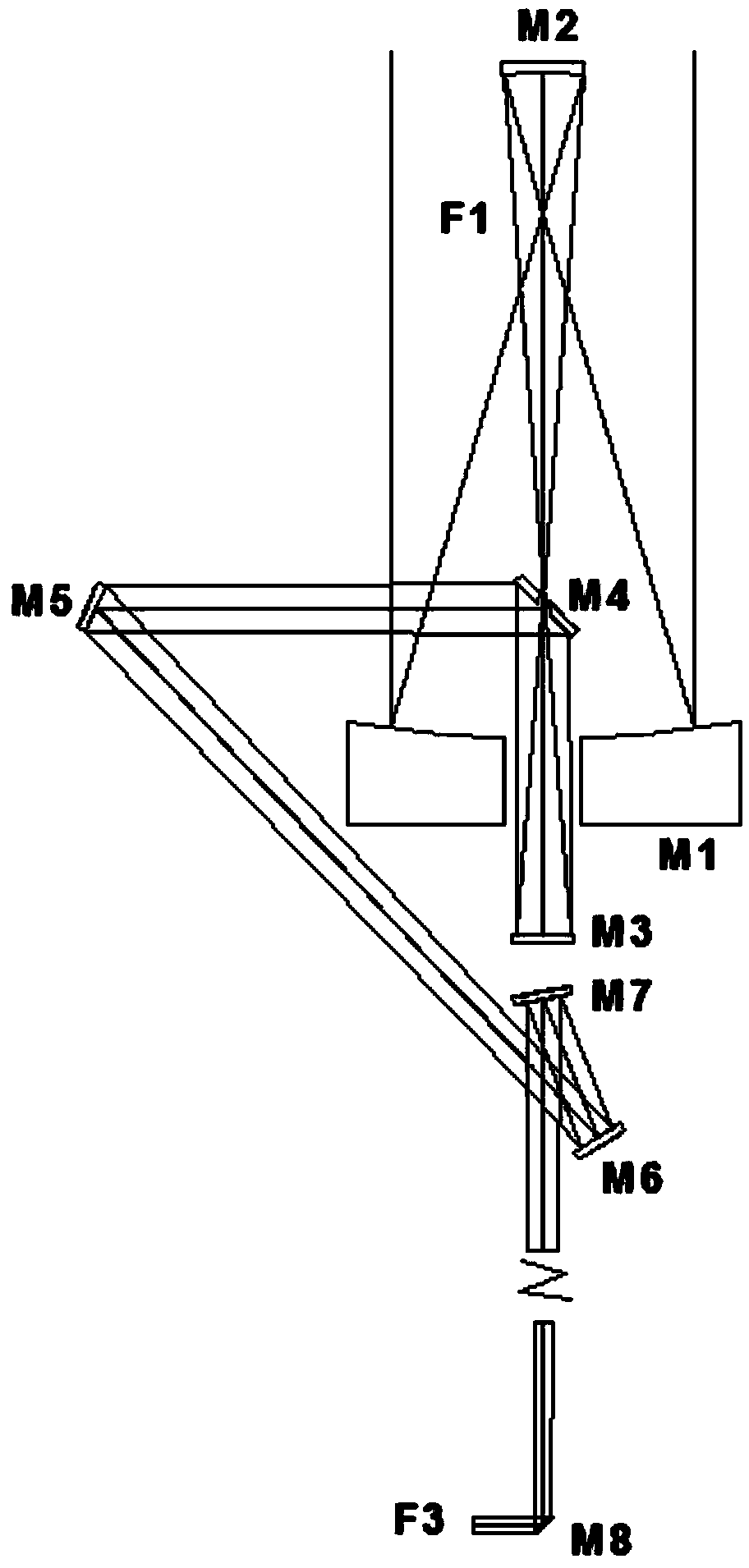
The invention discloses a device for improving rotary table chopper Q-switch laser performance and a Q-switch laser. The device comprises Galileo telescope units located inside or outside a resonant cavity and a rotary table chopper Q-switched component located inside the resonant cavity and used for performing Q-switch on a compressed laser beam; when the number of laser media is one, the first Galileo telescopic unit is located inside the resonant cavity and used for compressing the diameter of the compressed laser beam so as to reduce Q-switching time and enhance Q-switch effect; when the number of the laser media is more than one, the second Galileo telescopic unit located outside the resonant cavity is shared by various laser resonant cavities and used for subjecting the Q-switch laser to beam combination, and superposition output of incoherent light wave is realized; when the number of the laser media is more than one which is an even number, superposition output of quasi-coherent light wave is realized by the aid of a polyhedron prism and the third Galileo telescopic unit located in the laser resonant cavity. The device is of active effects on narrow pulse width and large-energy Q-switch laser generated by the aid of a shopper rotary table.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
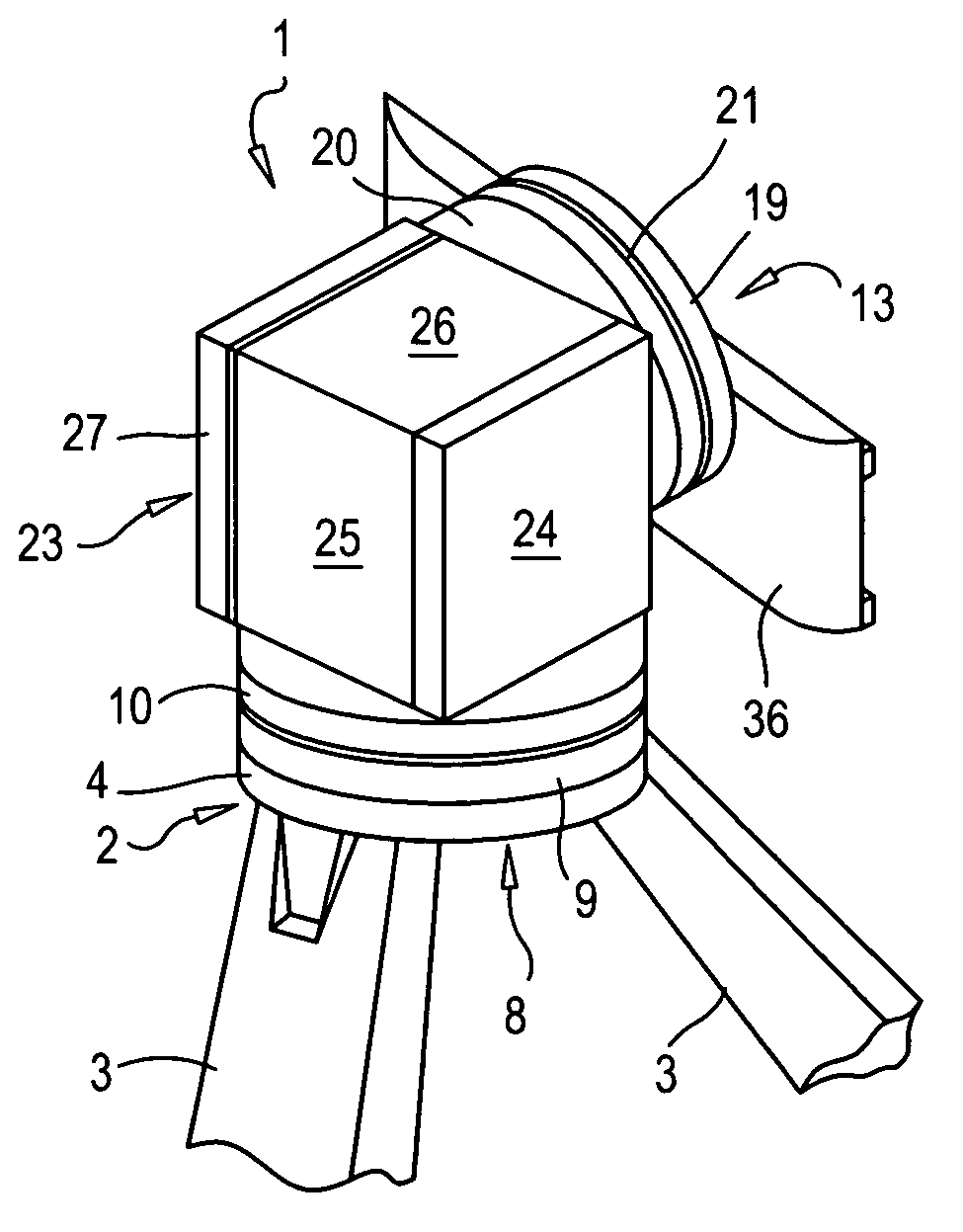
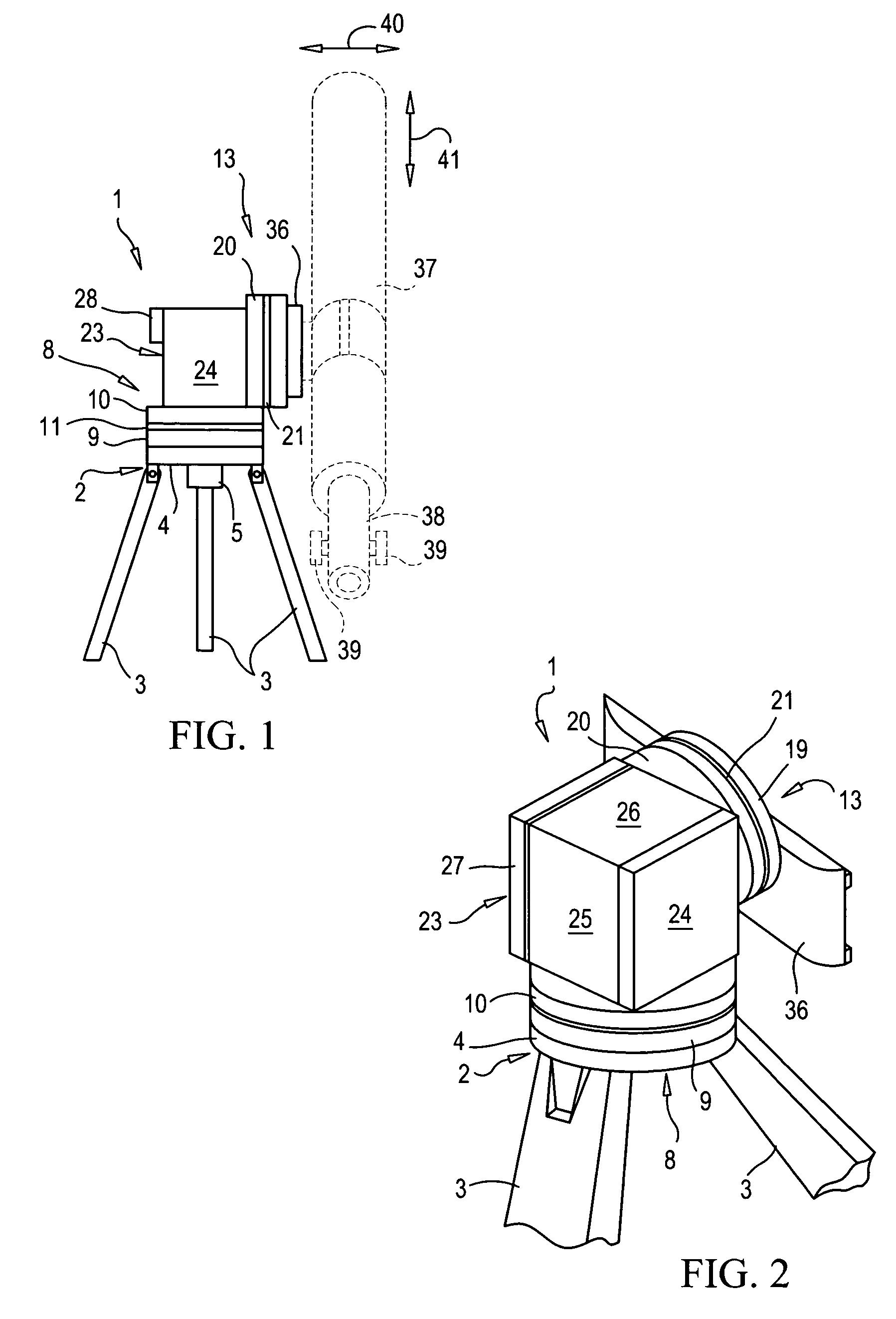
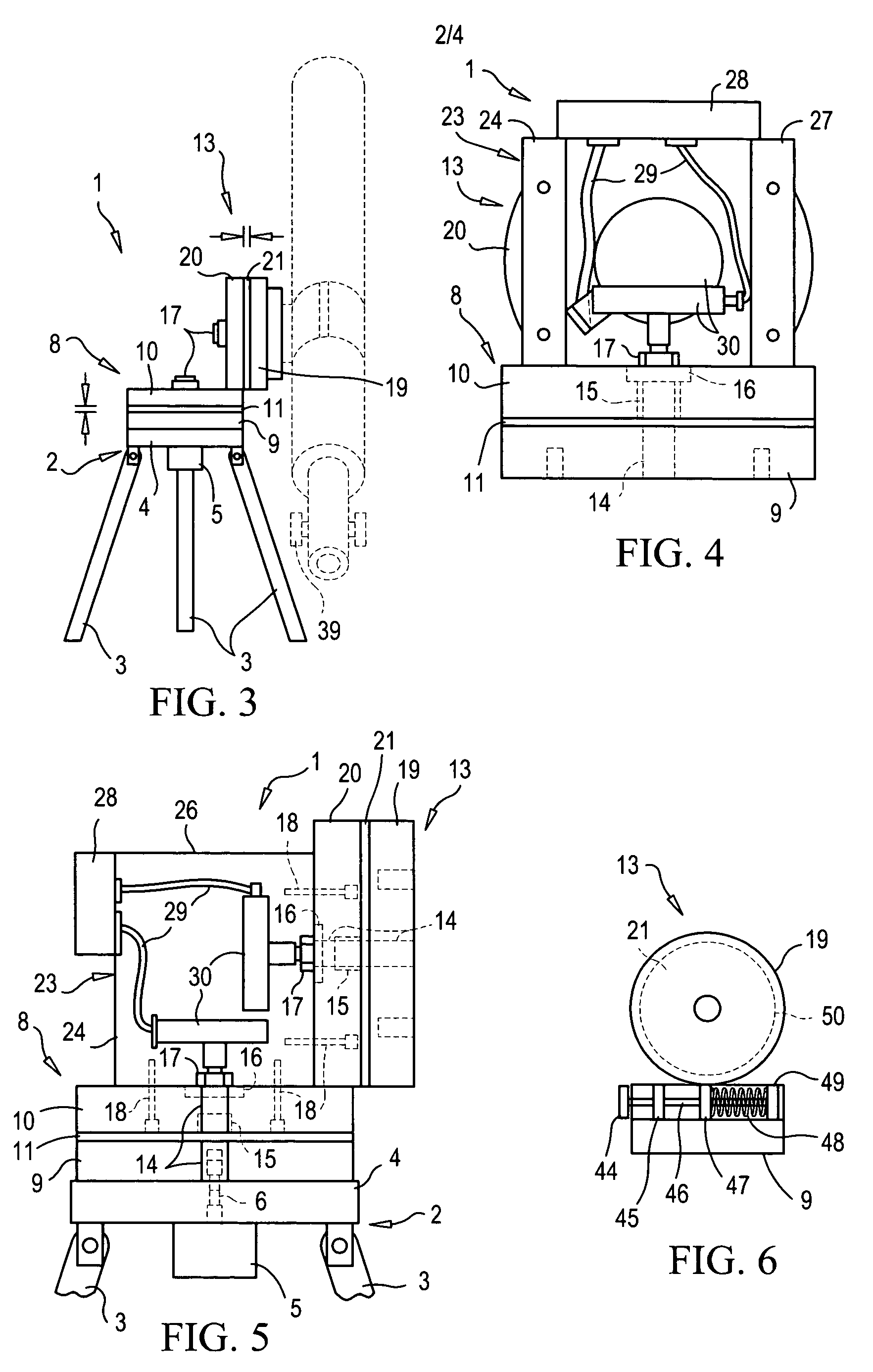
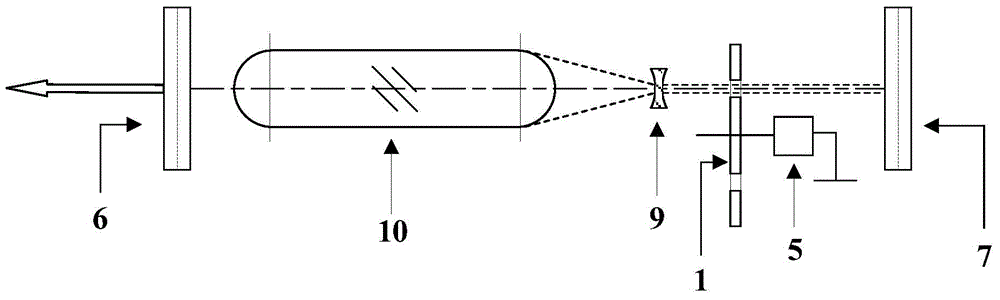
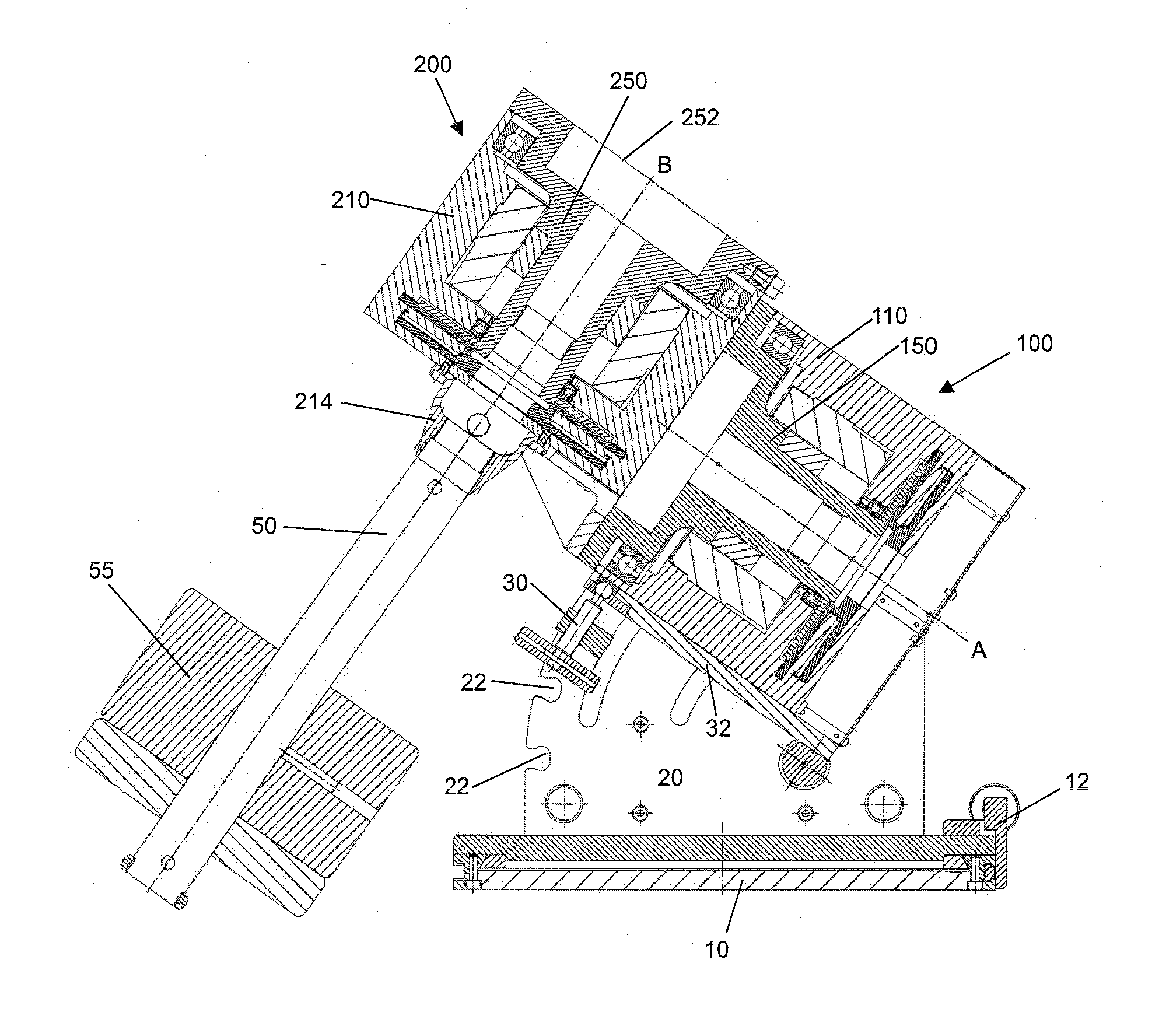
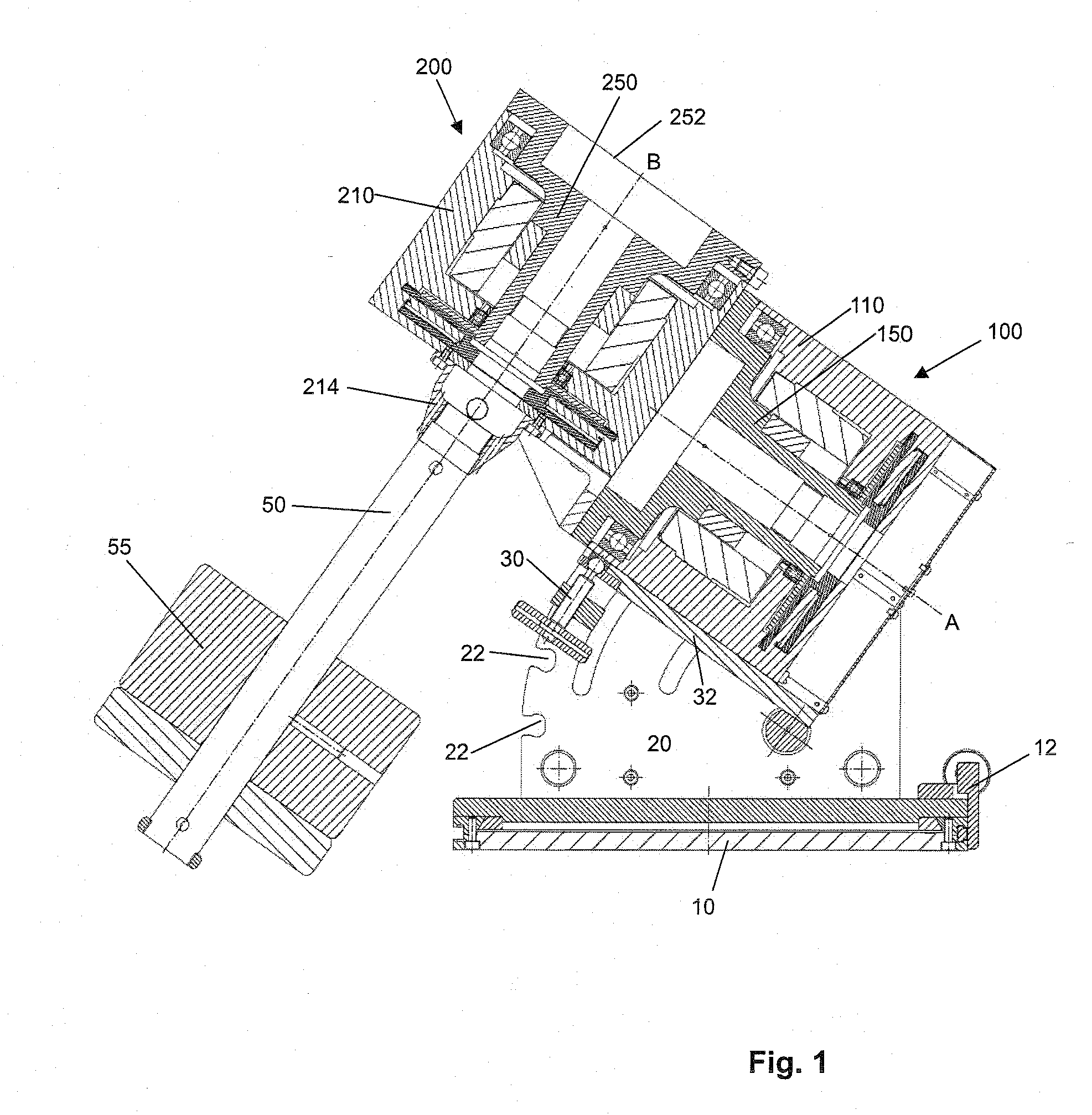
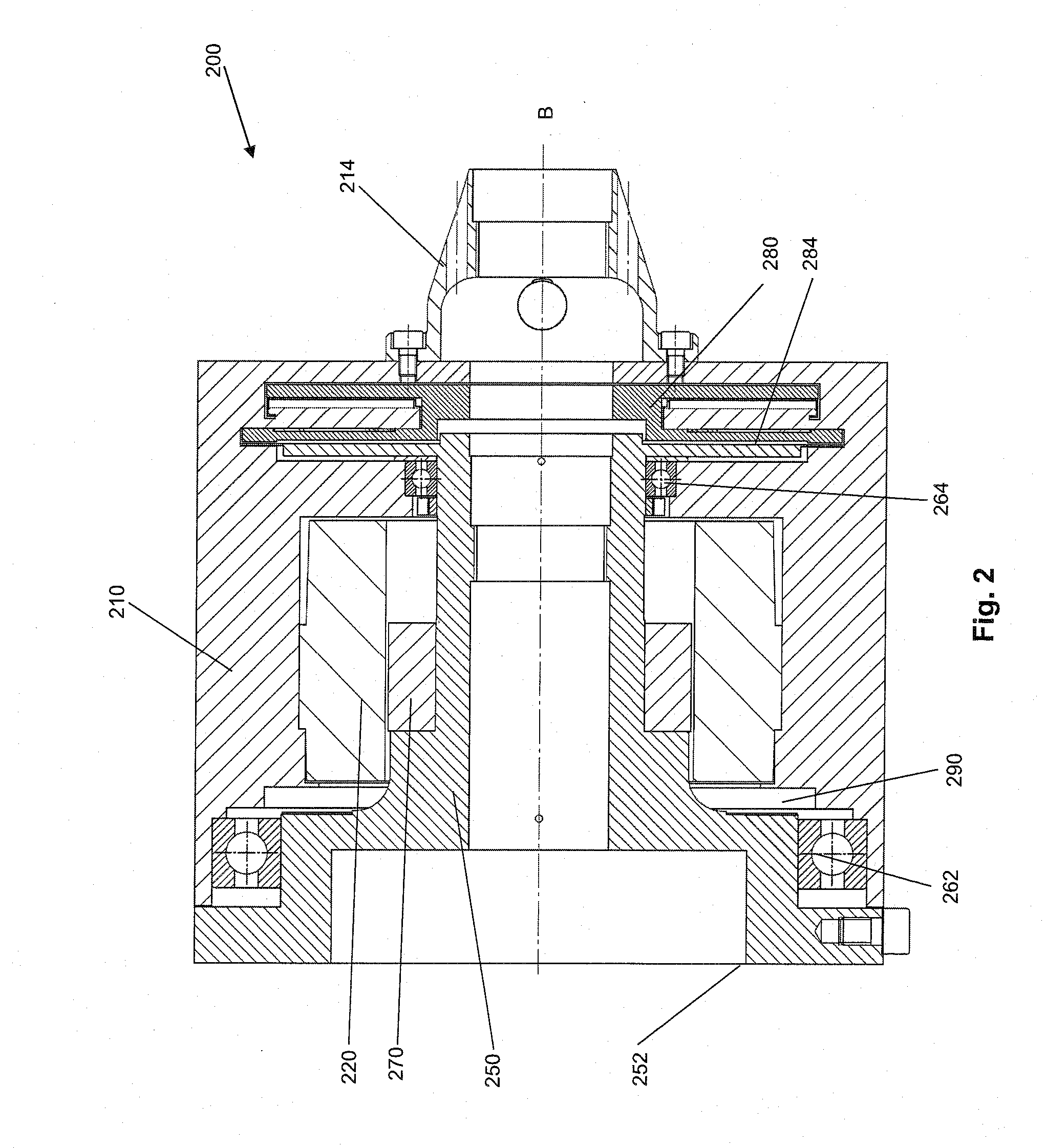
Telescope Mount
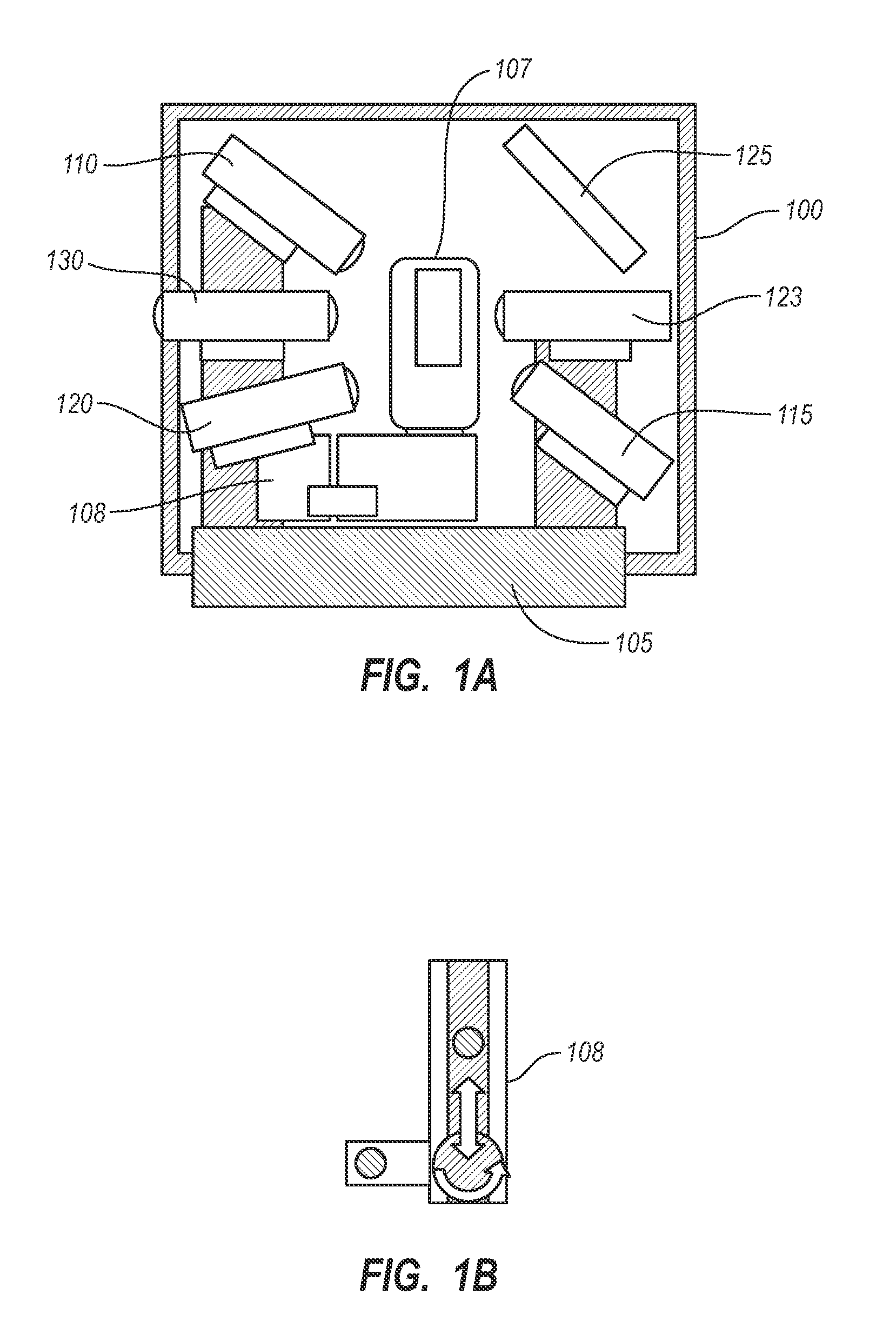
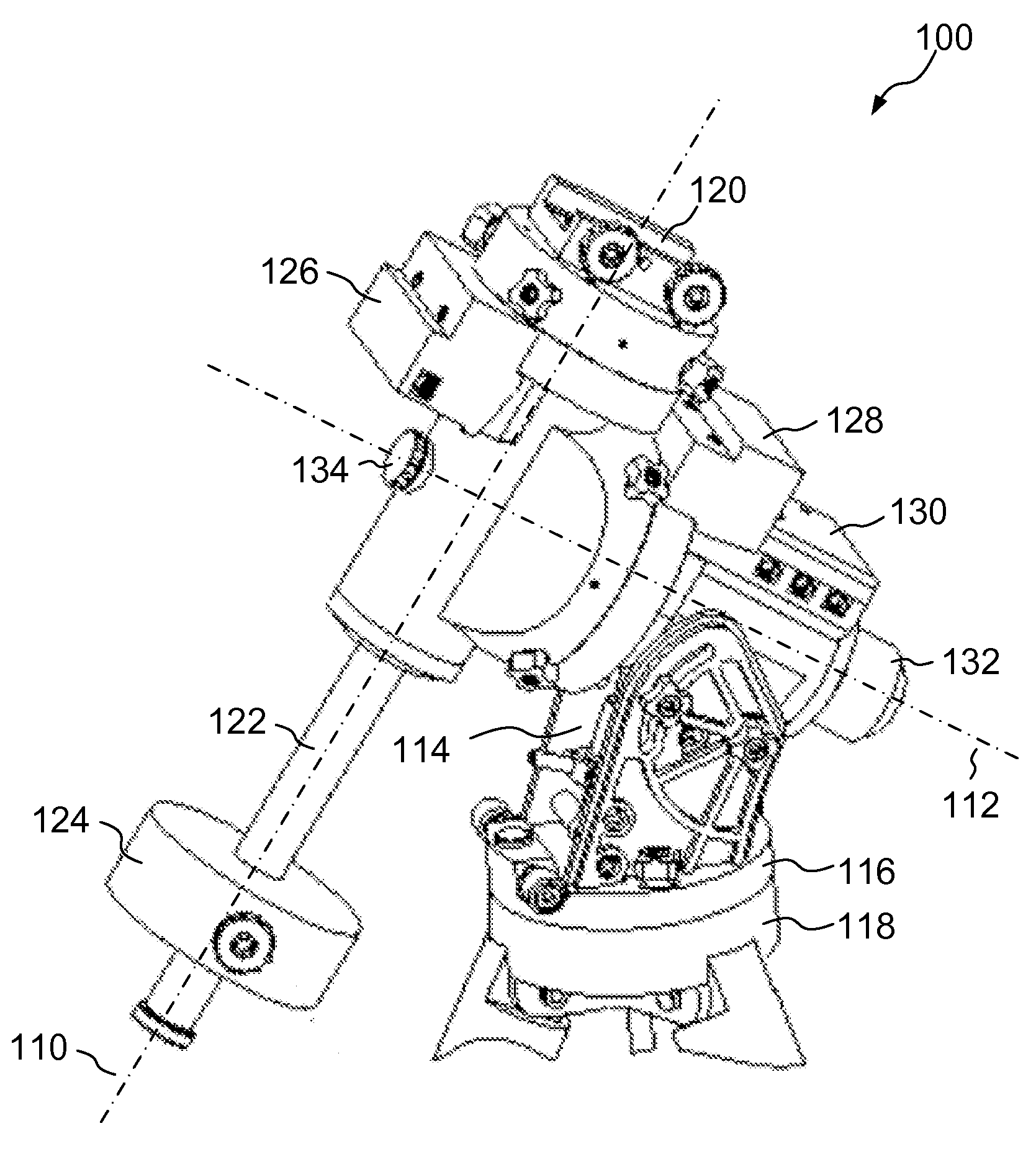
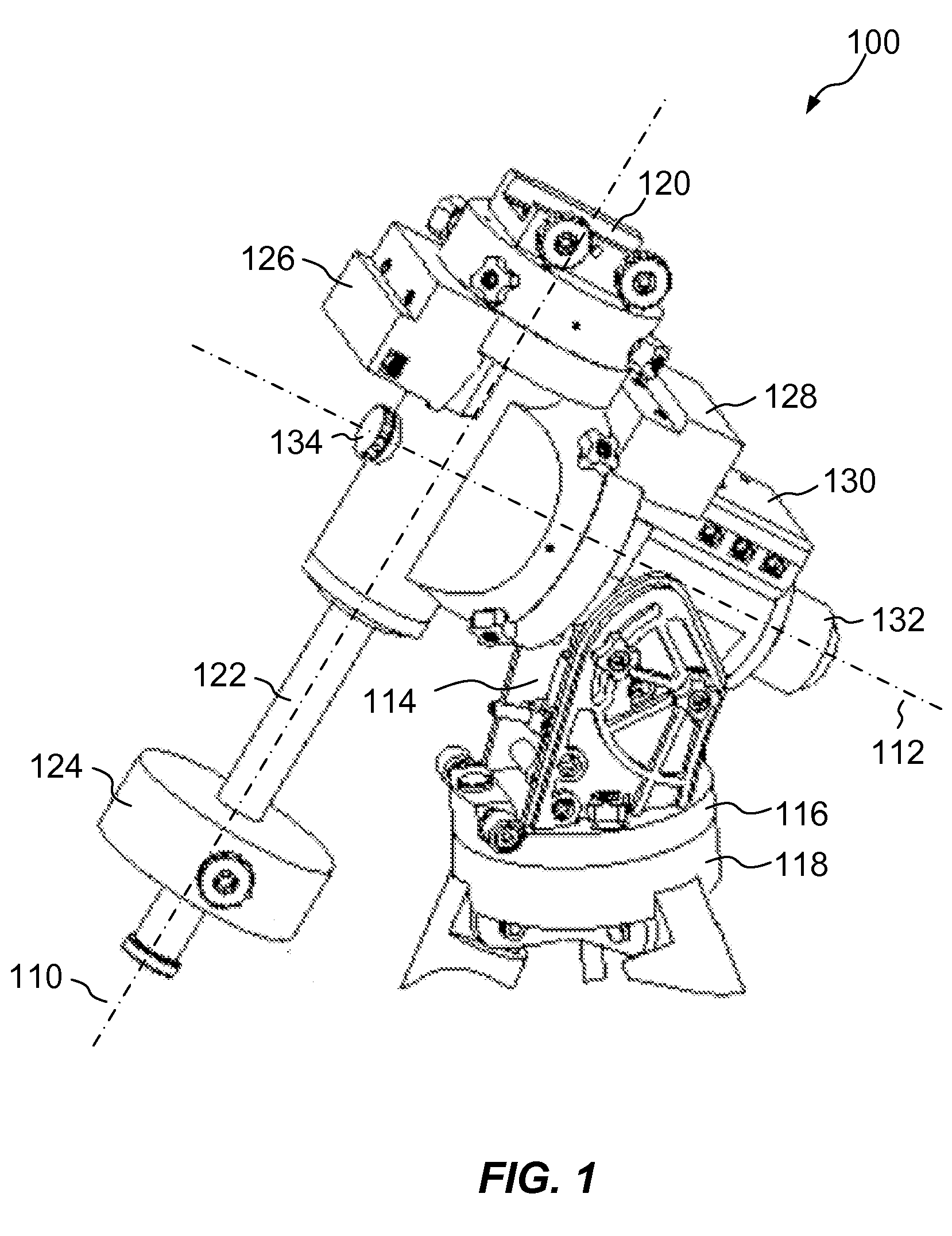
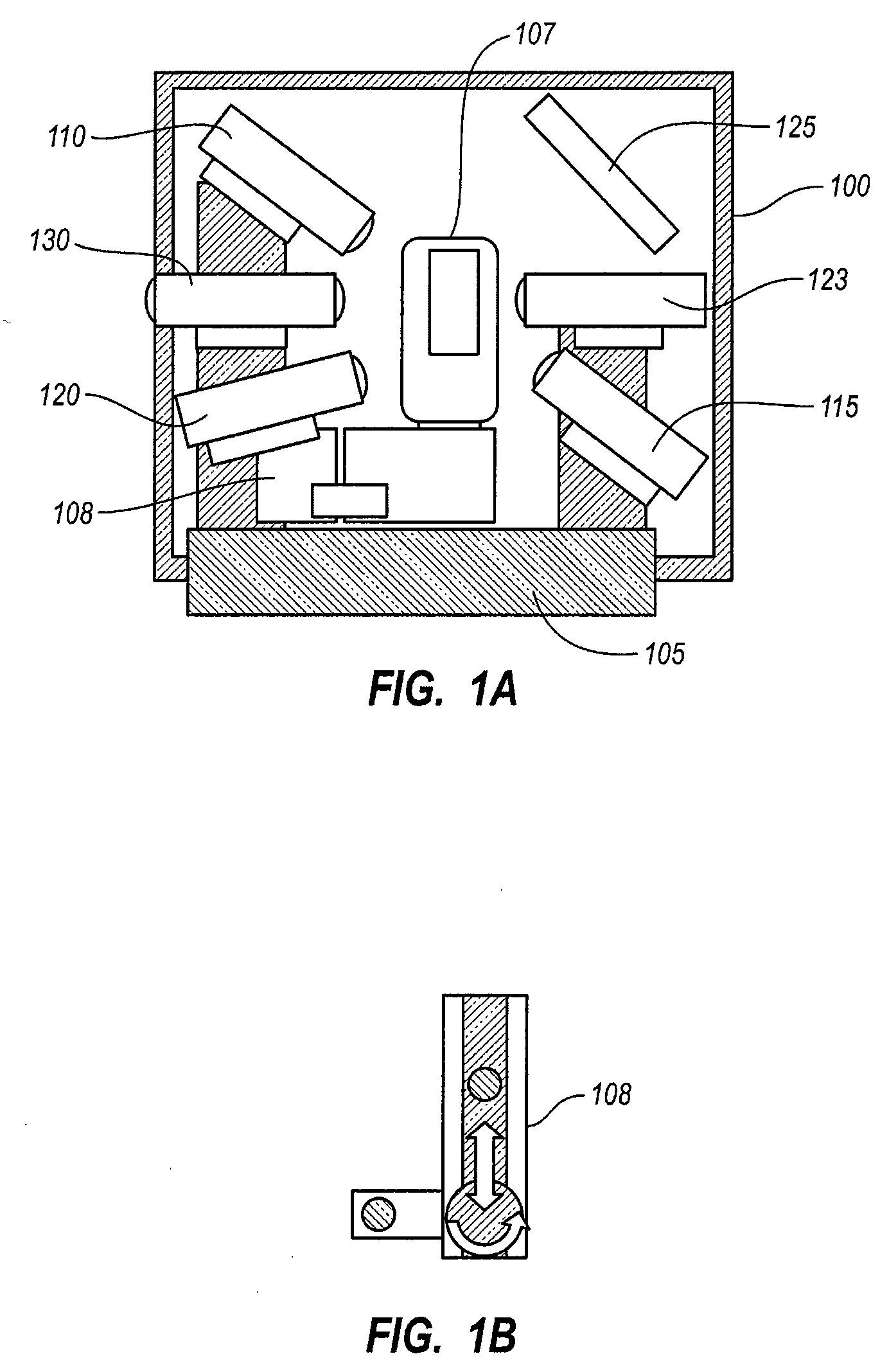
InactiveUS20080062515A1Mounting or exchanging of the telescope optics is much easier and fasterEasy fast exchangeTelescopesDrive shaftTelescope mount
Apparatus for the rotatable mount of a telescope having at least two axes being substantially orthogonal to each other, wherein the telescope is rotatable about at least a first axis of the two orthogonal axes by at least a first rotation device, the rotation device comprising a first working shaft and a first driven shaft of a first drive wherein the respective axis of the first working shaft and the first driven shaft are aligned and formed integrally.
Owner:ANIOL PETER +1
Telescope based calibration of a three dimensional optical scanner
An embodiment of the invention includes using a set of telescopes to calibrate a three dimensional optical scanner. Three separate calibrations are disclosed for a survey grade calibration: (1) angular calibration, implemented using at least one anti-podal pair of telescopes, (2) range calibration, implemented using at least one telescope mounted fiber recirculator, and (3) tilt calibration, implemented using at least one pair of telescopes not mounted in anti-podal configuration and an integral tilt table. Methods for aligning or measuring the mis-alignment between anti-podal telescope pairs are also described.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
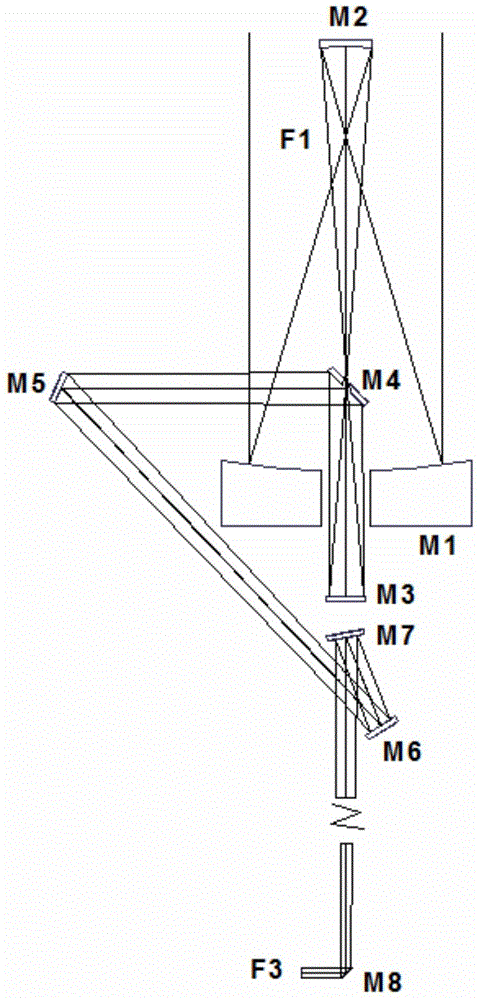
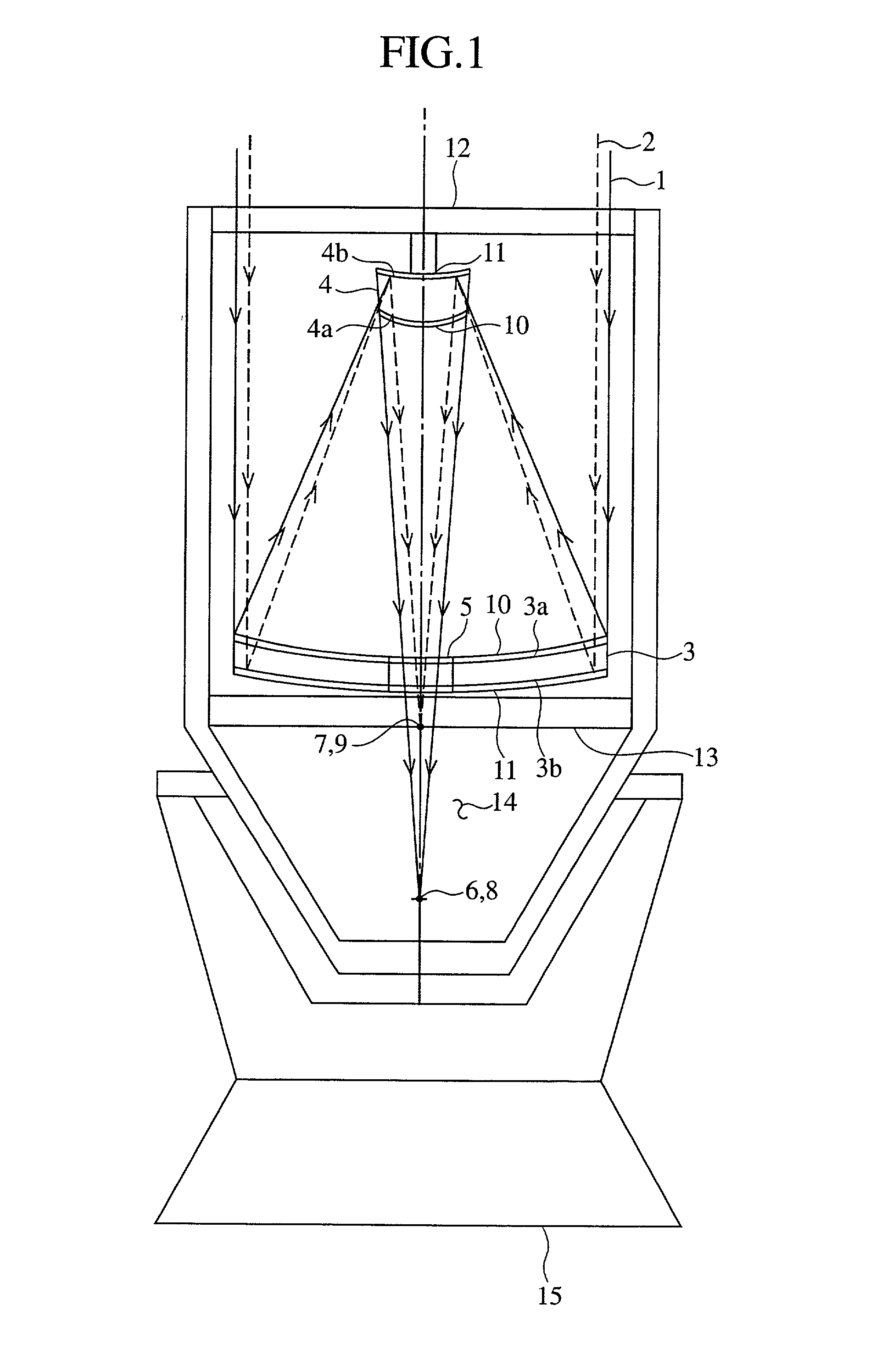
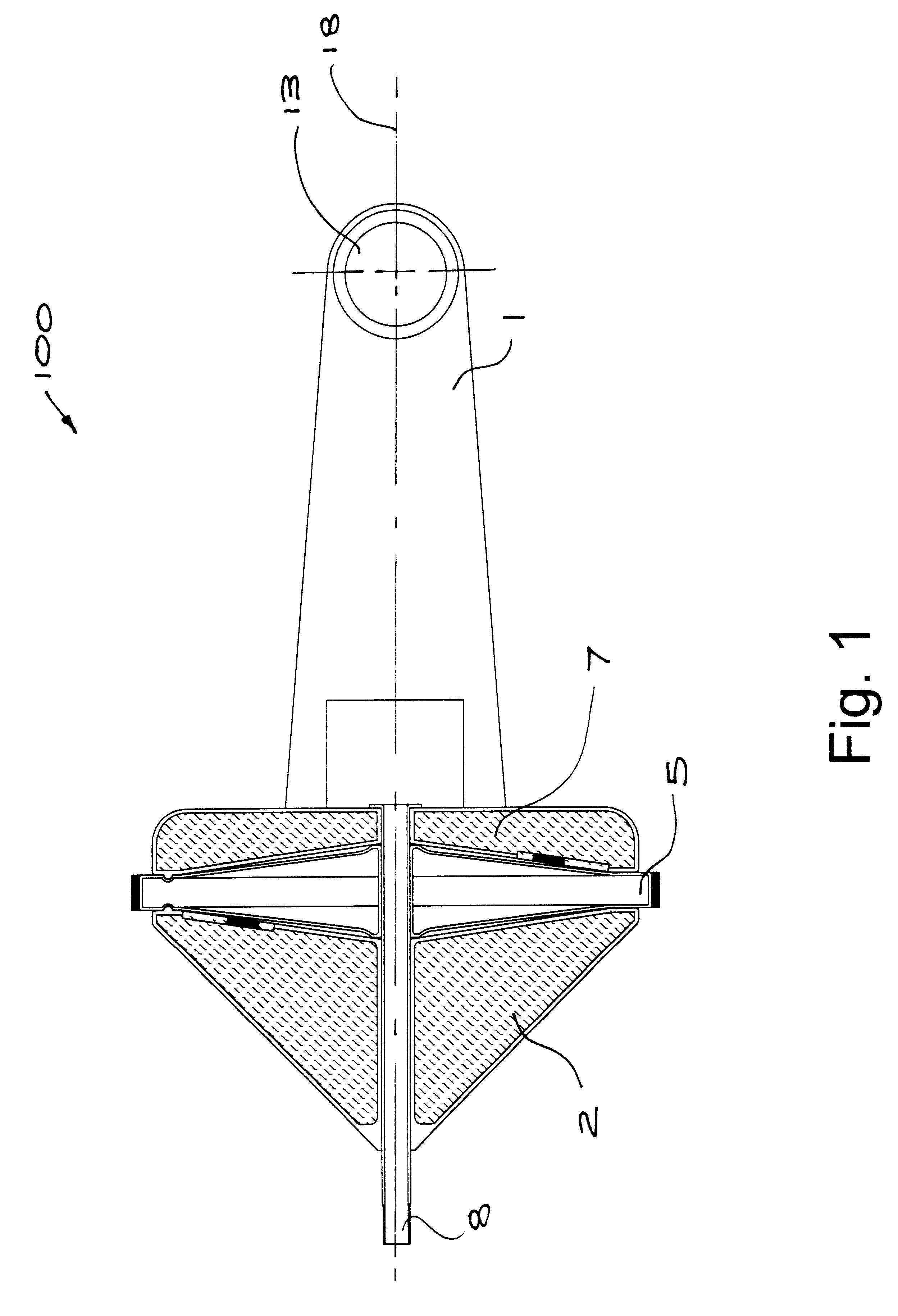
Multi-frequency telescope apparatus for celestial observations using reflecting telescope
A telescope apparatus for celestial observations by a reflecting telescope which is provided with: a first reflecting mirror 3 having its surface 3a coated over the entire area thereof with a grid-like metallic film 10 that reflects radio waves 1 but permits the passage therethrough of infrared and visible rays 2 and having its back 3b coated over the entire area thereof with a full-face metallic film that reflects both of the radio waves 1 and the infrared and visible rays 2; and a second reflecting mirror 4 having its surface 4a coated over the entire area thereof with the grid-like metallic film 10 that reflects the radio waves 1 but permits the passage therethrough of the infrared and visible rays 2 and having its back 4b coated over the entire area thereof with the full-face metallic film 11 that reflects both of the radio waves 1 and the infrared and visible rays.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Low orbit missile-shaped satellite for electro-optical earth surveillance and other missions
A low orbit optical imaging satellite has a long thin satellite body housing an optical telescope arrangement. A major part of the telescope arrangement has its optical axis roughly parallel to the direction of elongation and includes a mirror arrangement deployed to direct a line of sight of the optical telescope out sideways from the direction of elongation. The transverse dimensions of the satellite body are preferably minimized to be close to the optical aperture dimension of the optical telescope, thereby providing a high ballistic coefficient and high orbit lifetime for orbits in the low thermosphere.
Owner:RAFAEL ADVANCED DEFENSE SYSTEMS
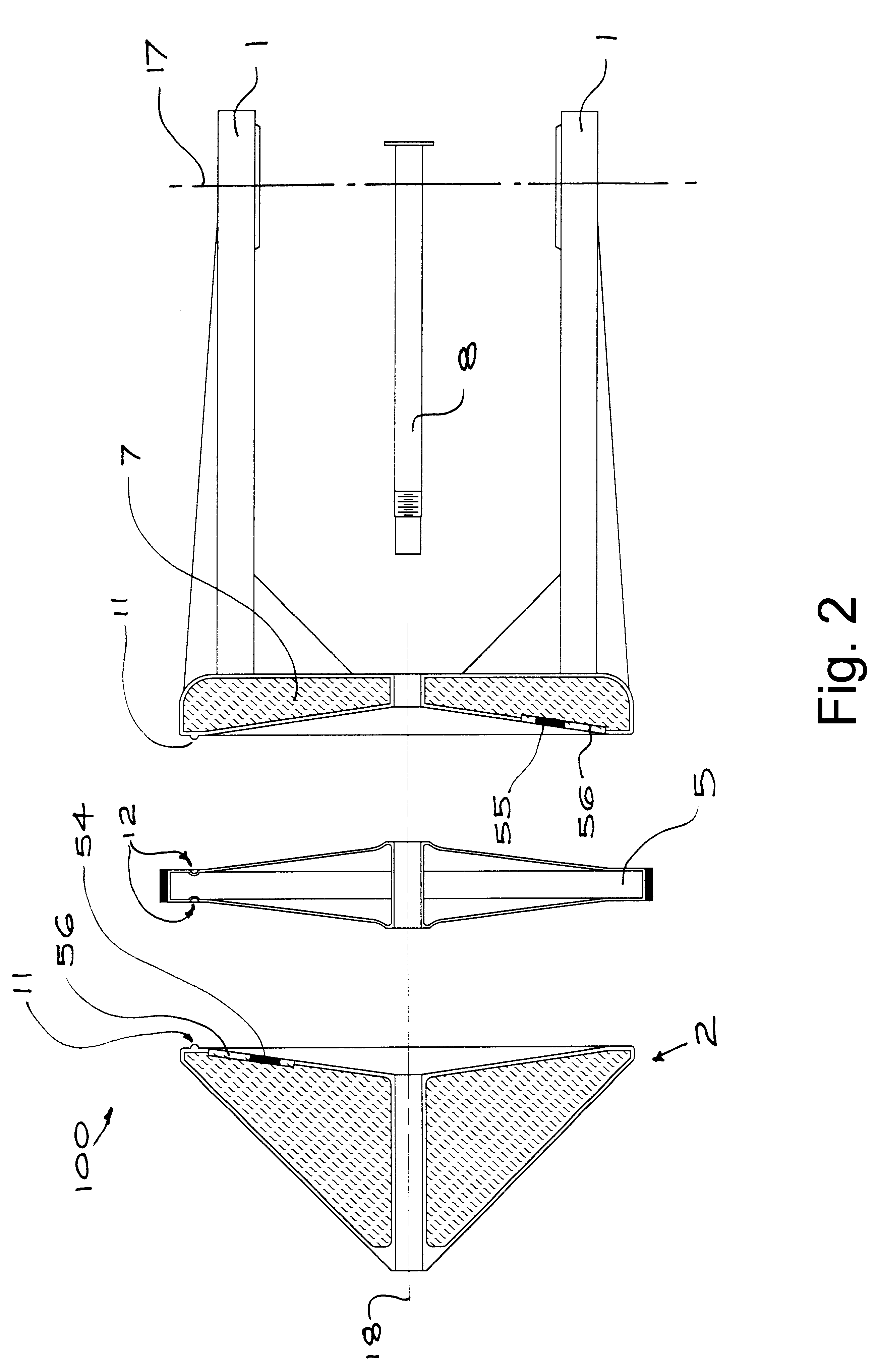
Telescope mount
A support for a telescope includes cavities for holding ballast material for improved stability. The cavities are provided in a fork to which the telescope is mounted, the fork is fixed to a ground-engaging frame for rotation about an axis of the fork. The cavity includes a lowermost conical section having an axis aligned with the axis of rotation.
Owner:BELCHER MICHAEL JOHN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com