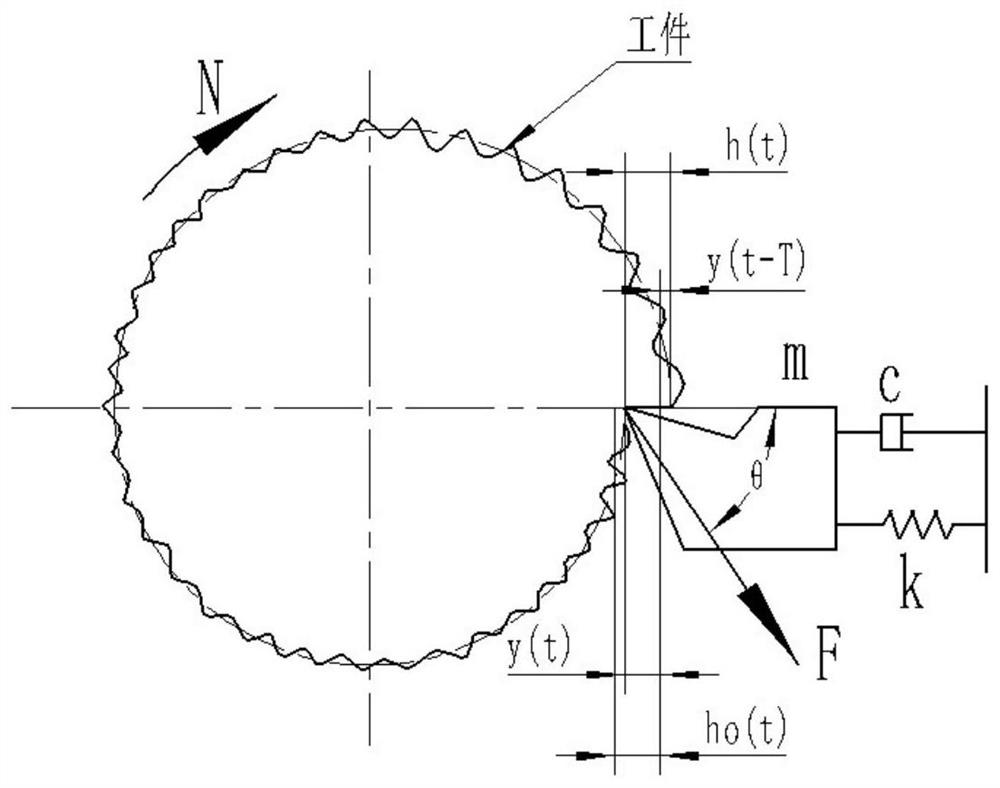
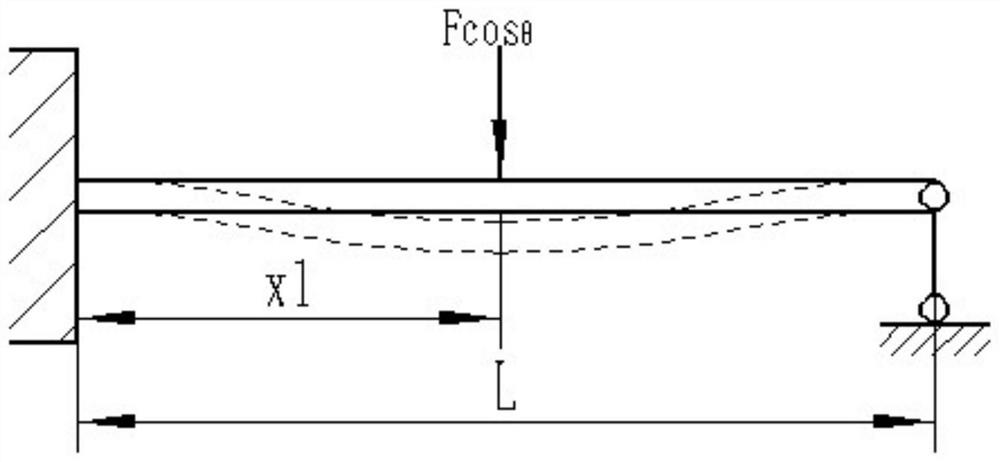
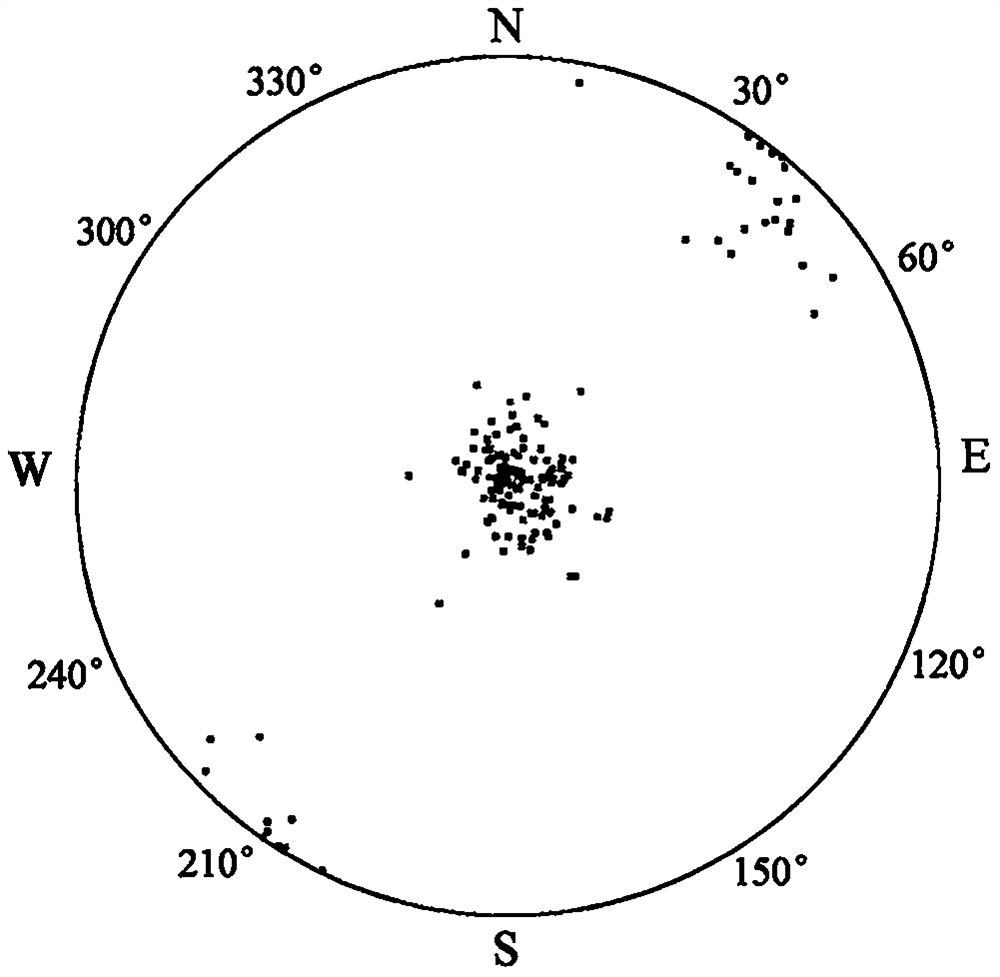
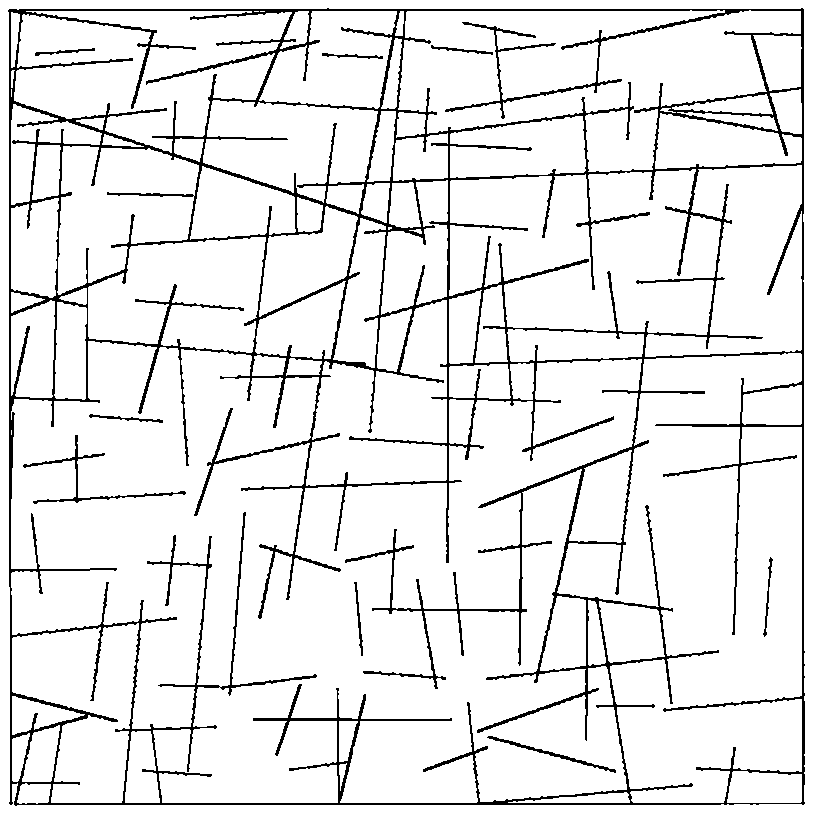
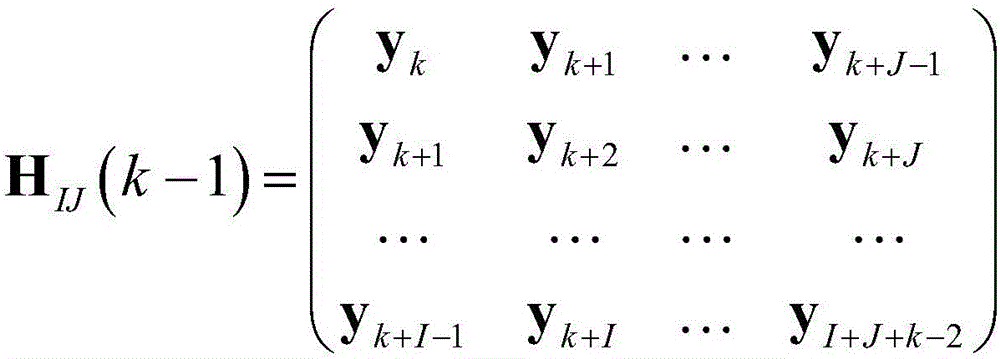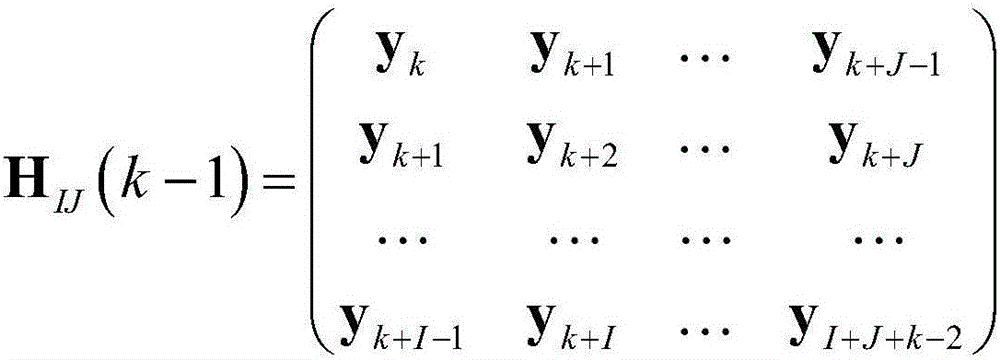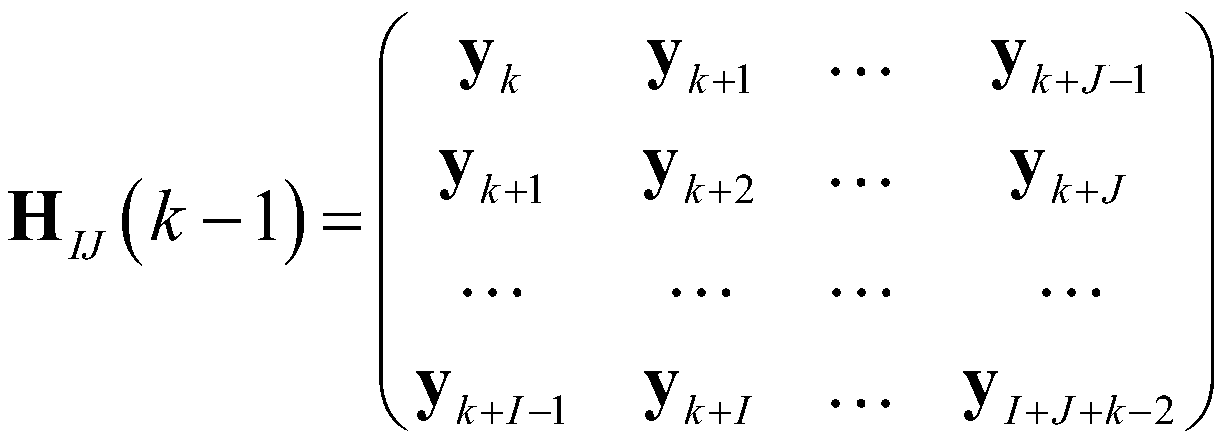Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Stability diagram" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bridge structure modal parameter authenticity and falsity discrimination method and terminal device
InactiveCN108318129AImprove discrimination accuracySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementTerminal equipmentCorrelation function
The invention belongs to the bridge monitoring technical field and provides a bridge structure modal parameter authenticity and falsity discrimination method and a terminal device. The method includesthe following steps that: the monitoring data of the structure of a bridge under an environmental excitation condition are obtained through data acquisition devices disposed in a plurality of measuring points of the bridge; the NExT (natural excitation technique) is adopted, at first, the cross power spectrum density function of the monitoring data is calculated, and Fourier inverse transformation is performed on the cross power spectrum density function, so that the cross-correlation function of the monitoring data is obtained, the cross-correlation function is adopted as the input data of amodal parameter identification algorithm, so that modal parameter identification can be carried out, and a stability diagram can be drawn; the auto-power spectrum density function and cross-power spectrum density function of the monitoring data of the measuring points are calculated, the auto-power spectra and cross-power spectra of all the measuring points are summated, and the auto-spectra andthe cross spectra are summated in the same order of magnitude, so that the sum function of the power spectra can be obtained; and a diagram of the sum function, and true and false modal parameters canbe discriminated according to the stability diagram of the sum function. According to the method, the stability diagram method and a power spectrum summation peak method are combined to perform bridge structure modal parameter authenticity and falsity discrimination, so that discrimination accuracy can be improved.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG TIEDAO UNIV
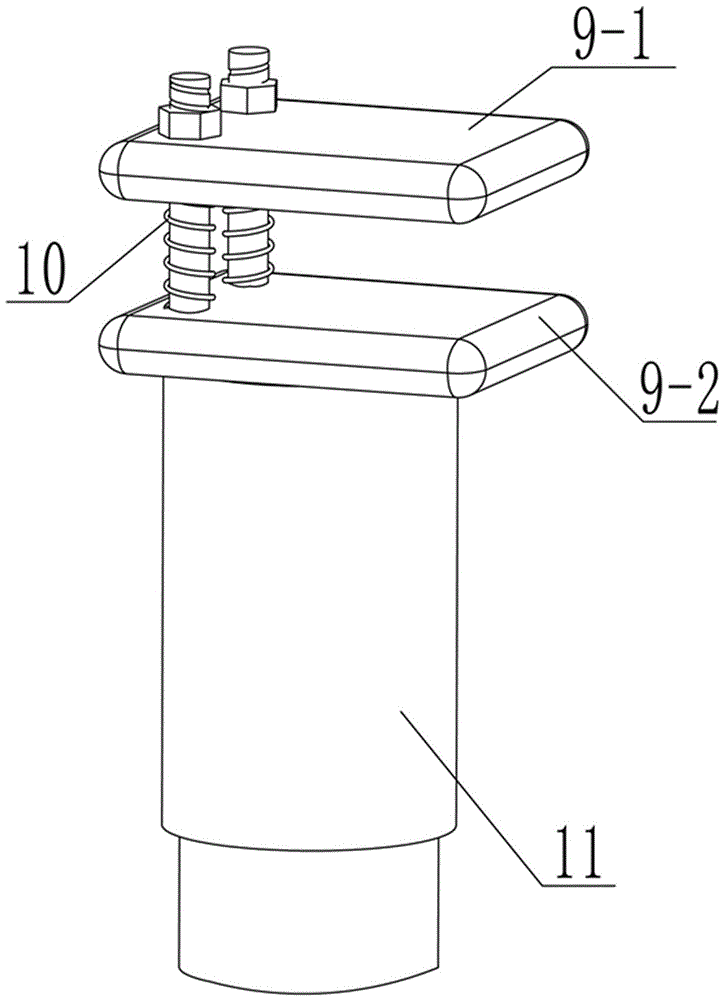
Supporting device and machining precision improving method for thin-wall part
InactiveCN104708458AEffective support and fixationExact modal parametersMilling equipment detailsPositioning apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
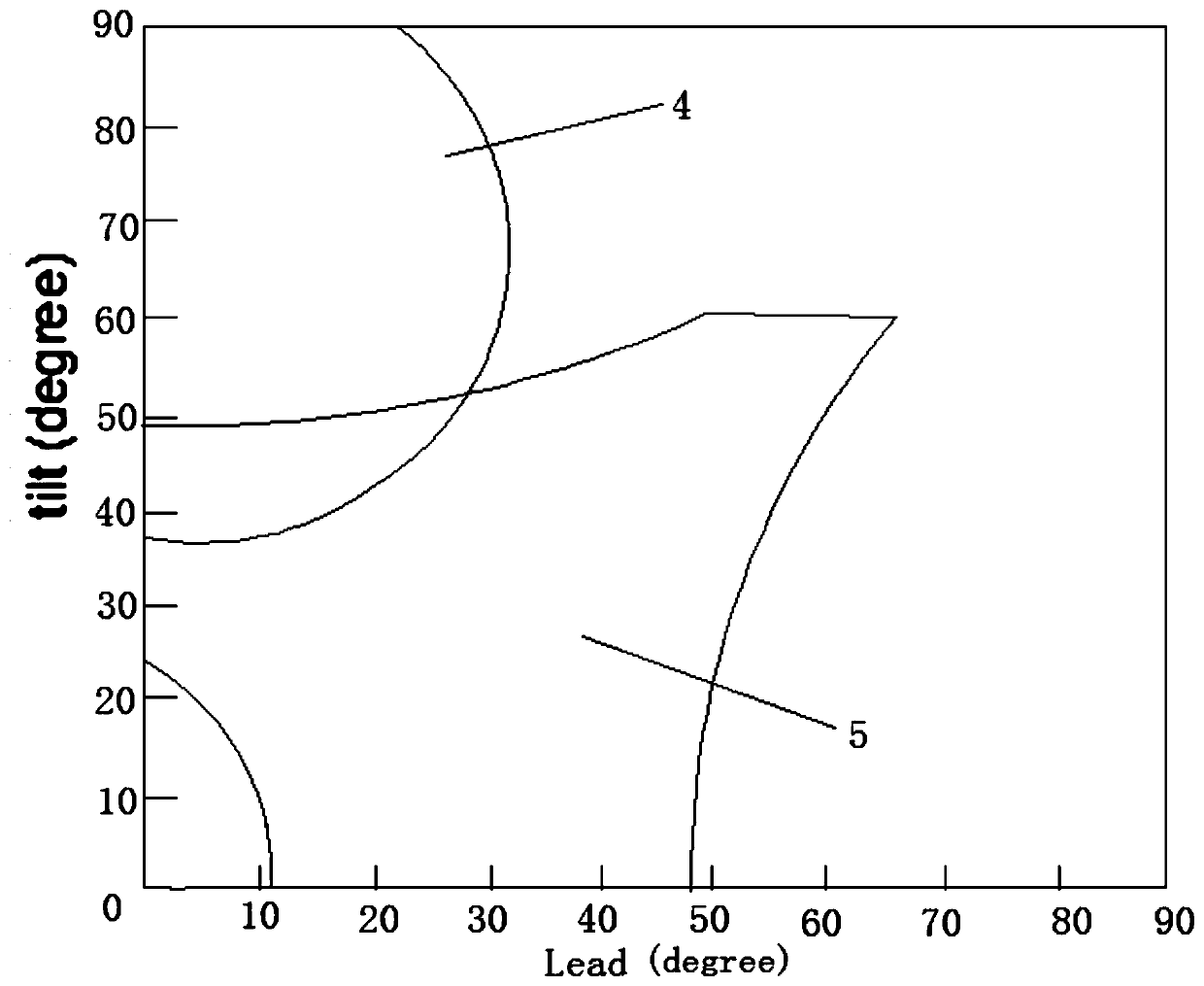
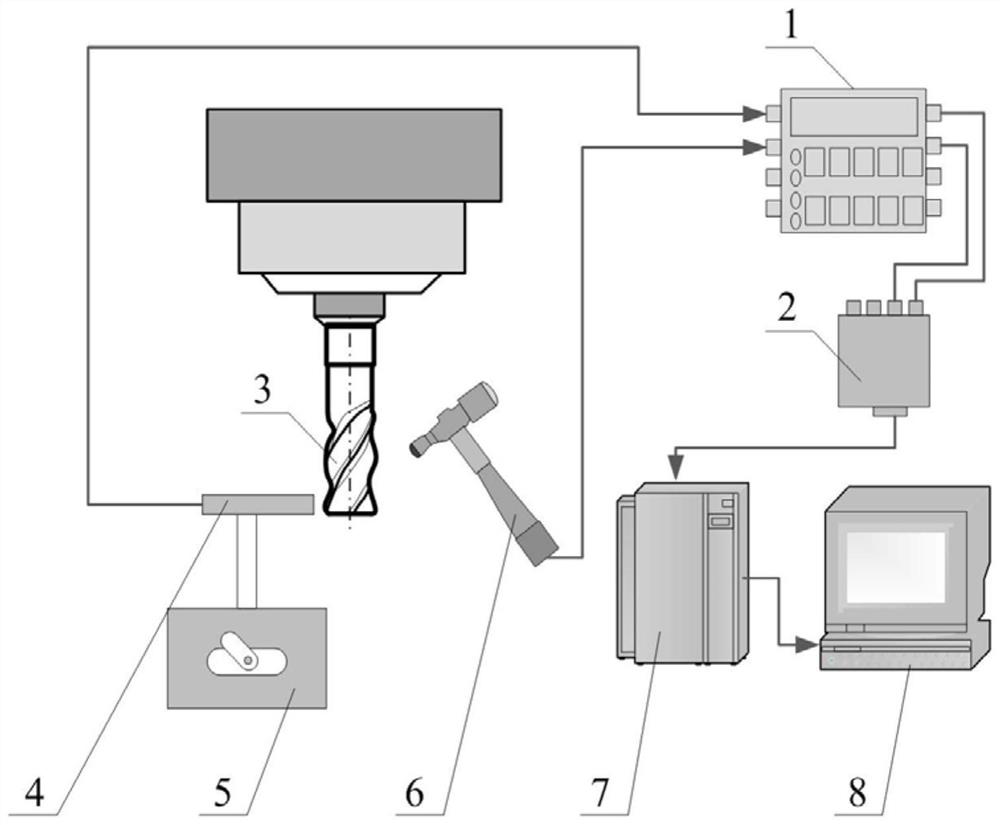
The invention relates to the field of advanced manufacturing, in particular to a supporting device and a machining precision improving method for a thin-wall part. Matching buckles are matched with ring ways and slide ways so that supporting postures of different space shapes can be completed on a supporting table, a thin-wall part can be fixedly supported effectively, and more precise modal parameters can be obtained through clamping conducted through the supporting device. Under the circumstance that boundary limiting conditions such as the cut-in angle, the cut-out angle and the cutting thickness are considered sufficiently, a numerical integration method is used for iterative operation, a vibration displacement simulating diagram is obtained by subdividing the rotating speed of a main shaft and the axial cutting depth within a certain range, a milling stability diagram is finally obtained, simulation precision is improved, and machining quality is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
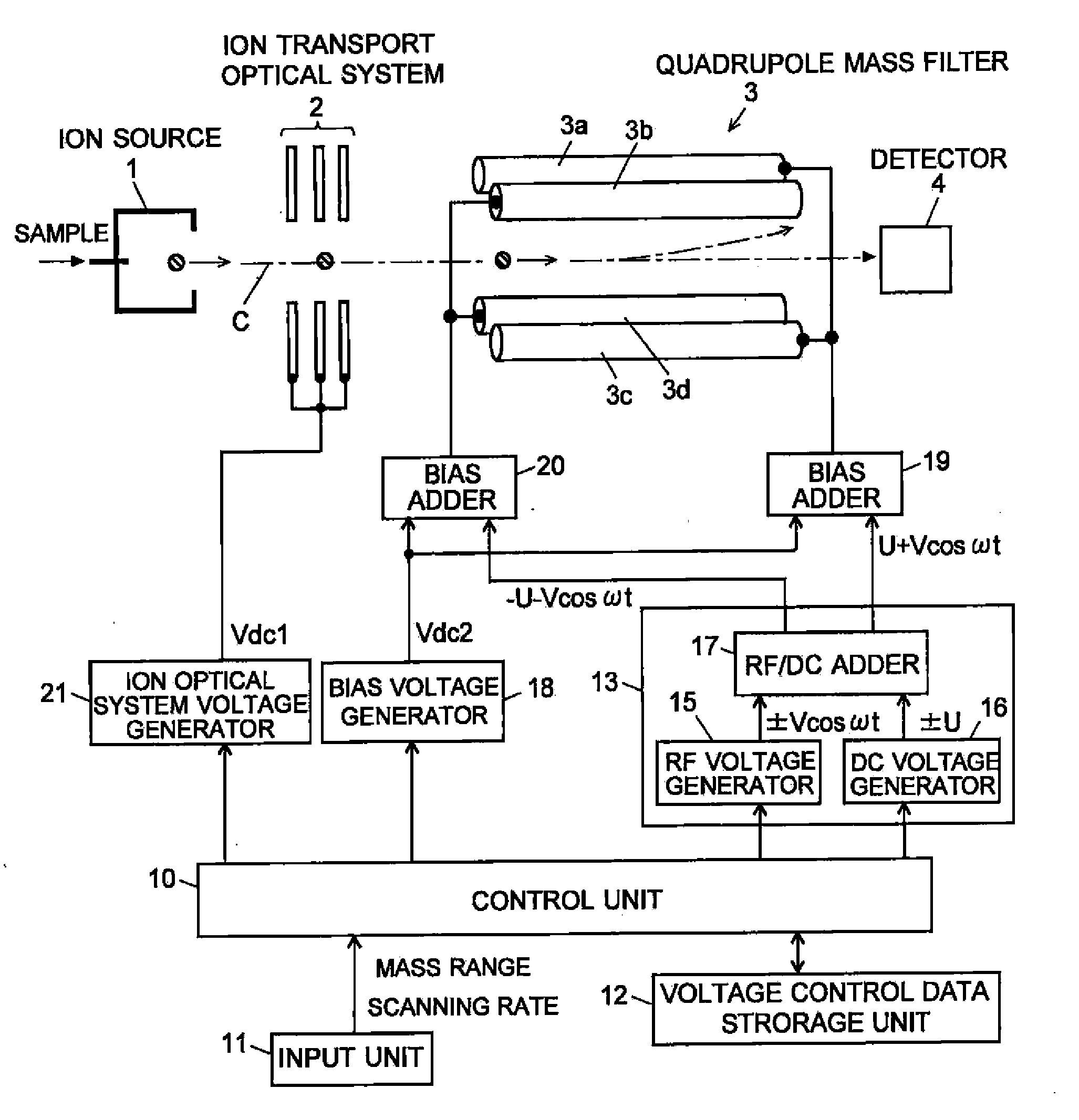
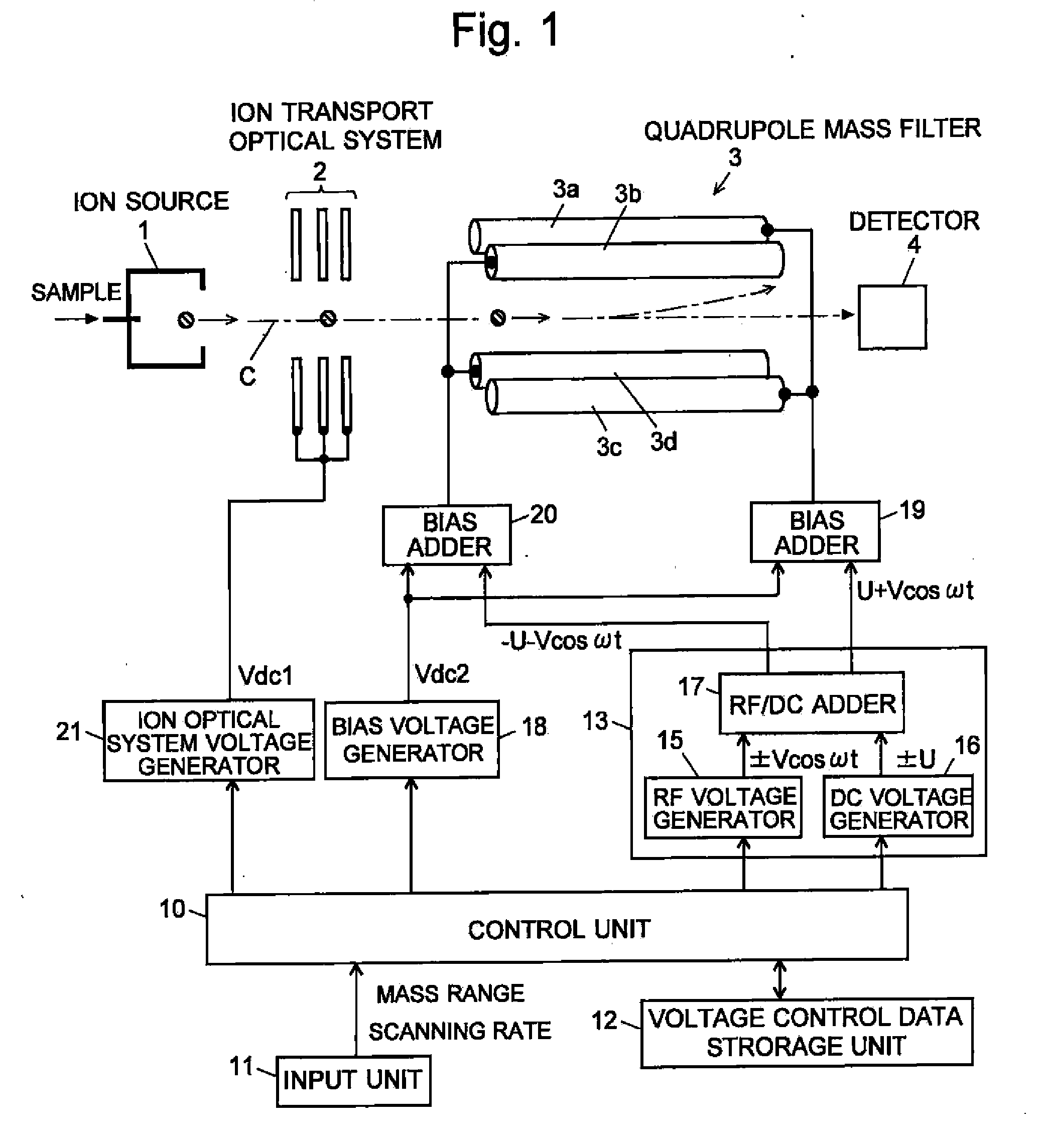
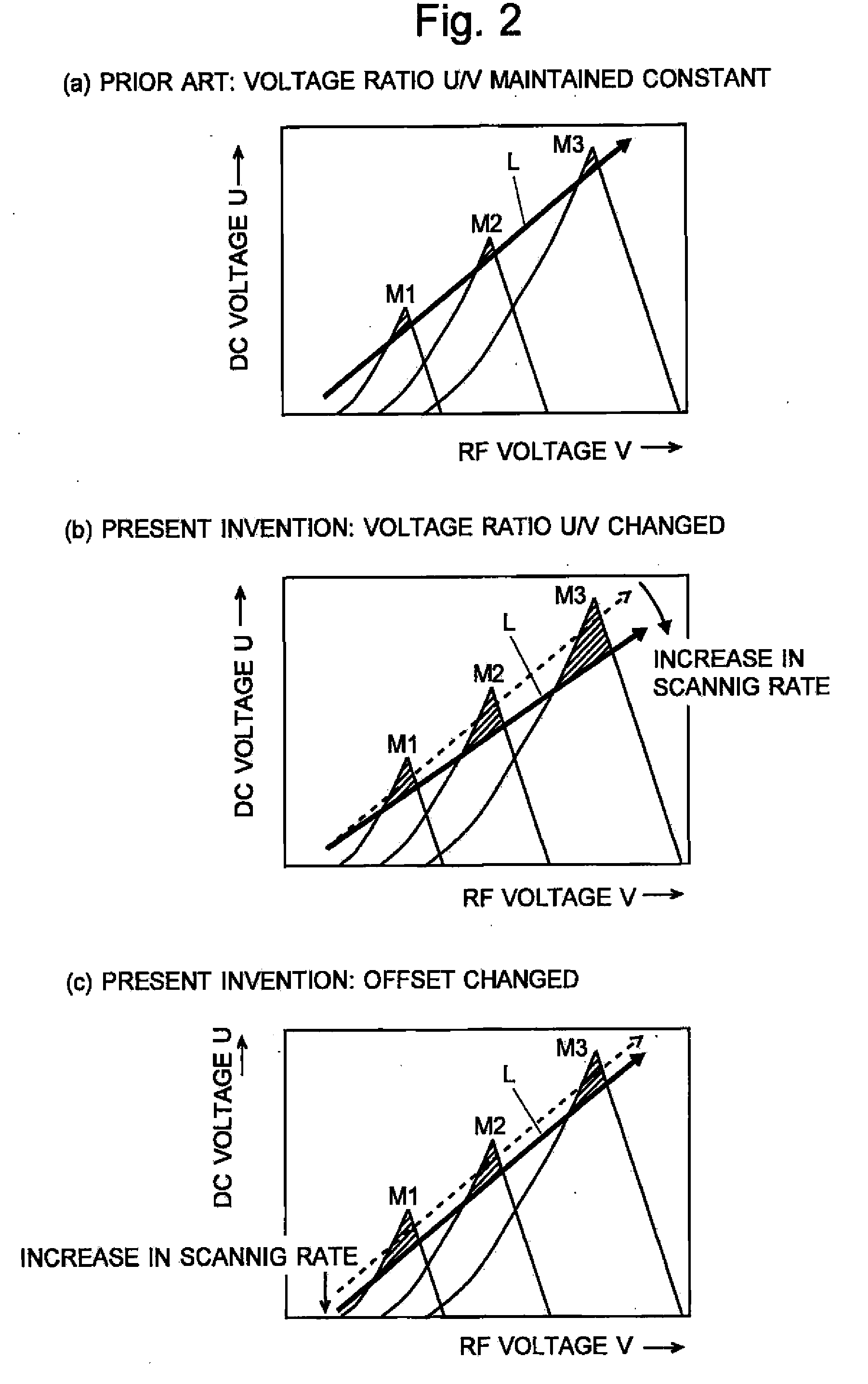
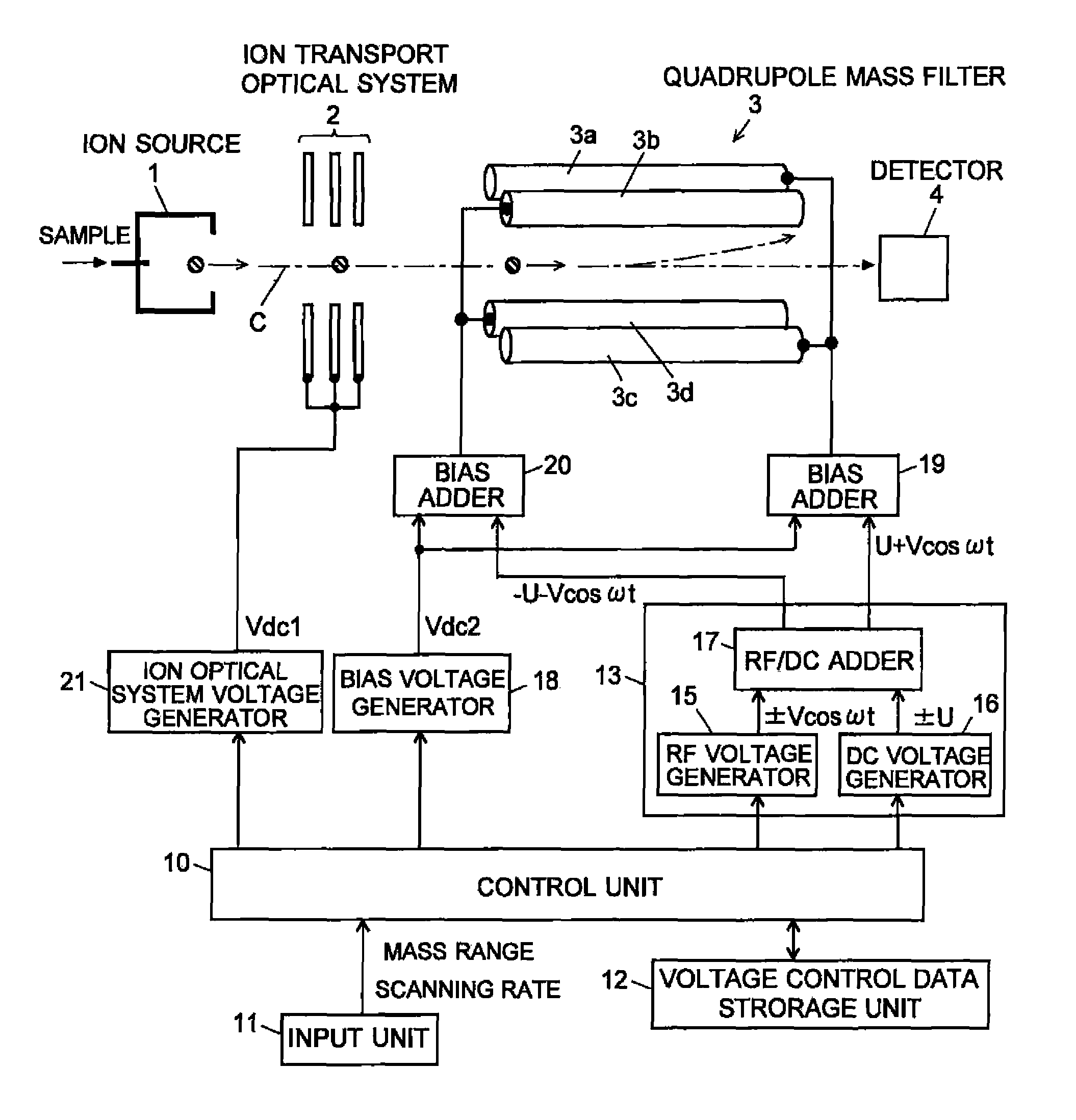
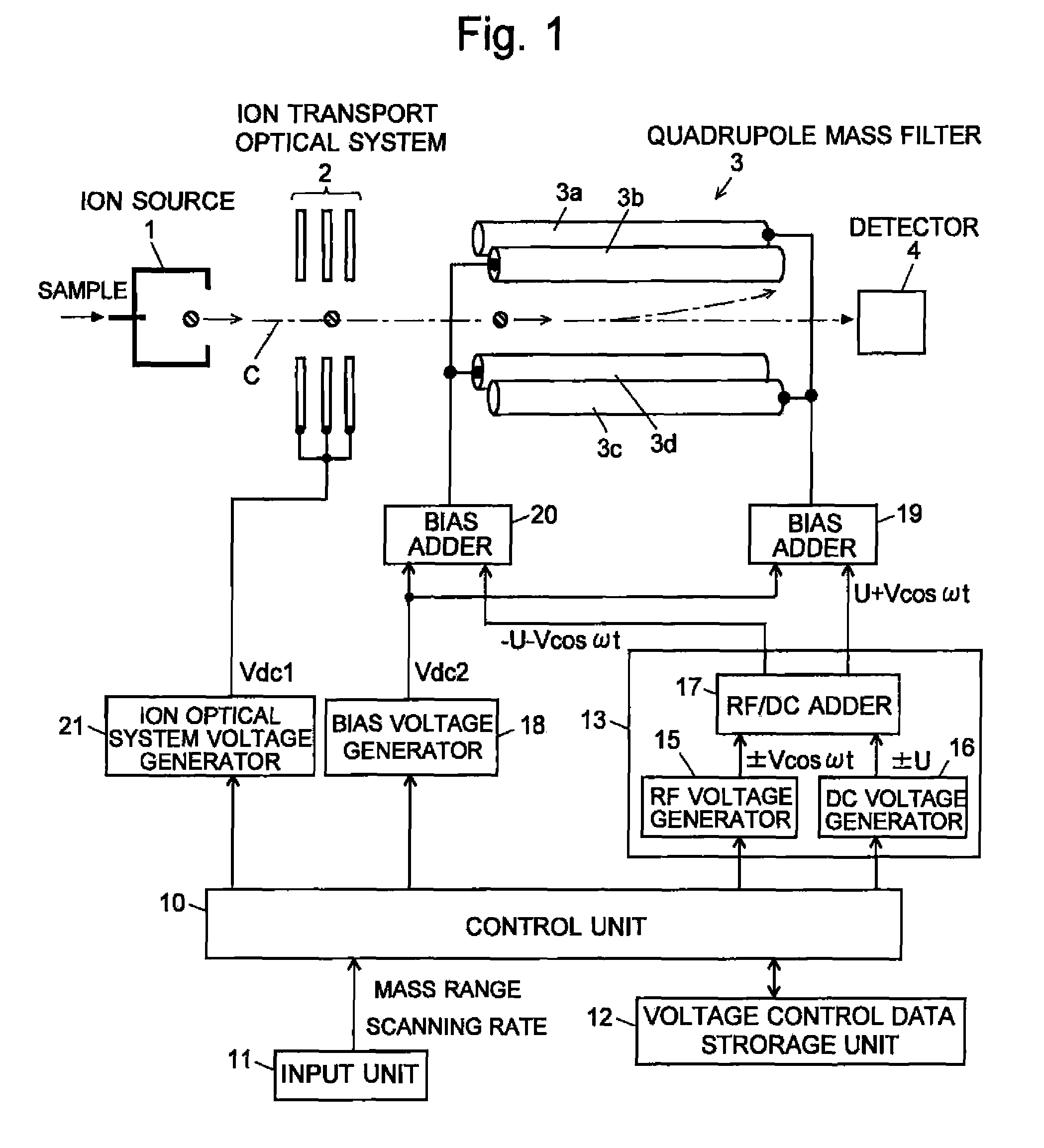
Quadropole Mass Spectrometer
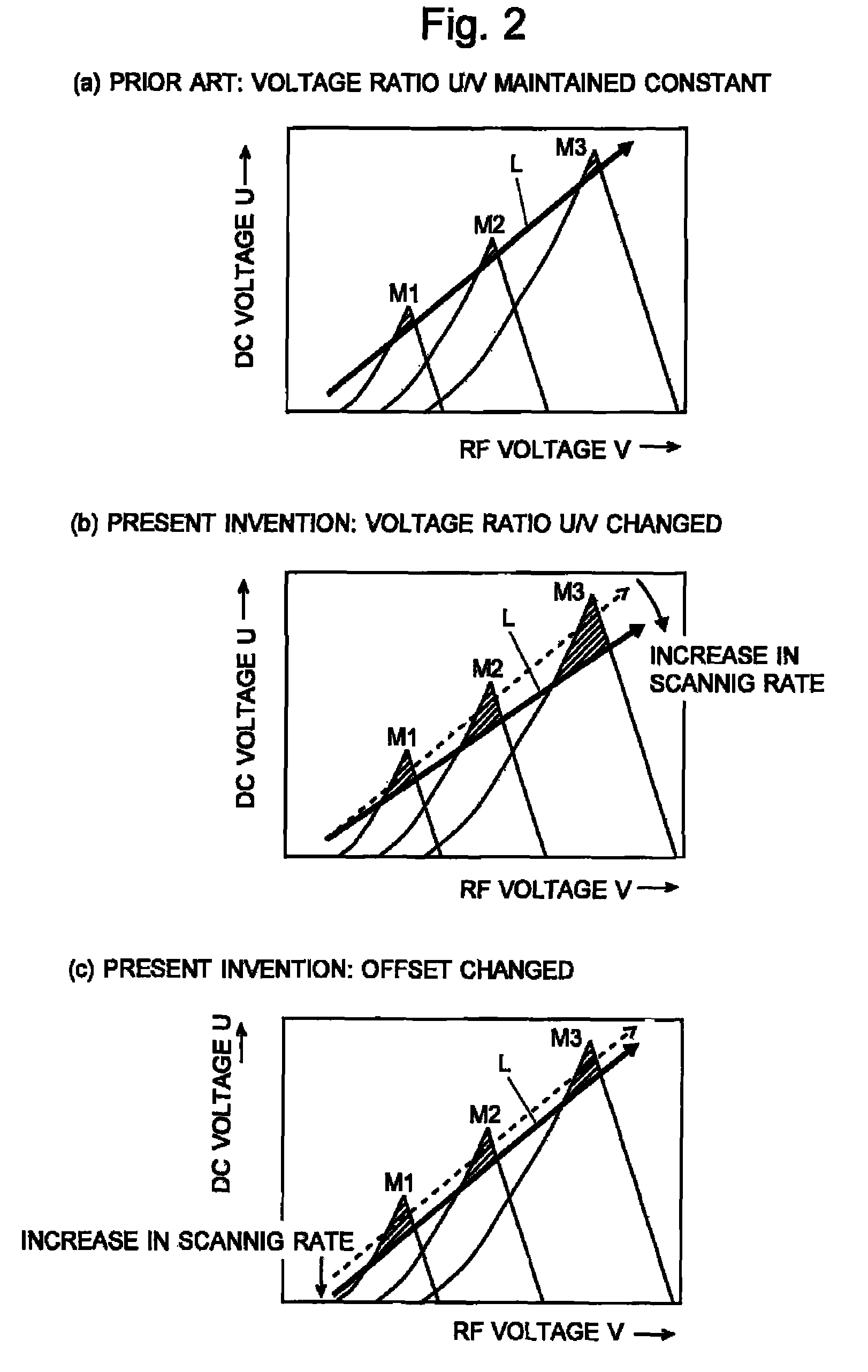
ActiveUS20110062325A1High detection sensitivityConstantStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationVoltage ratioRadio frequency
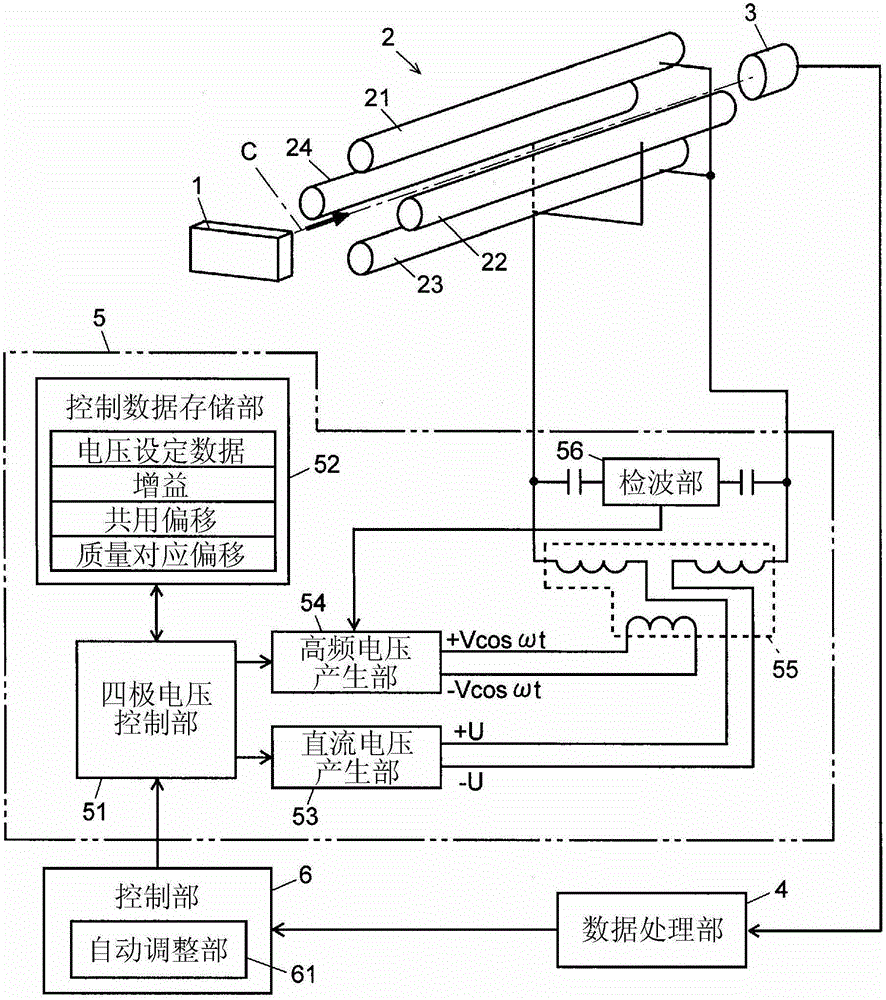
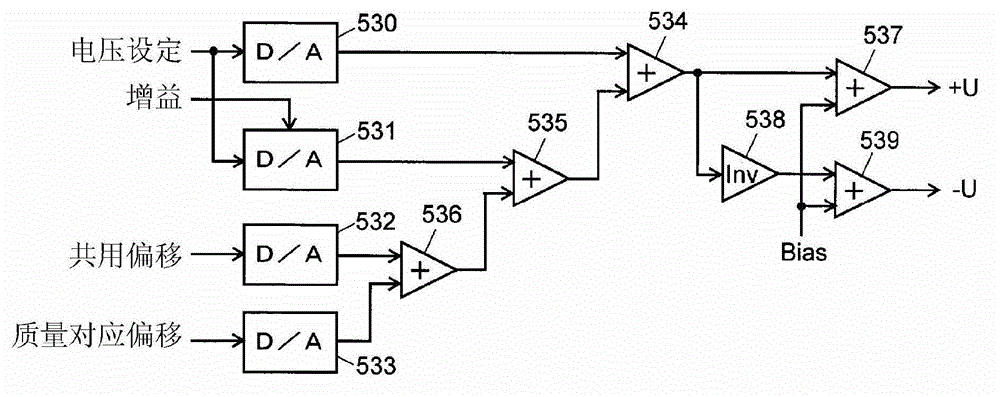
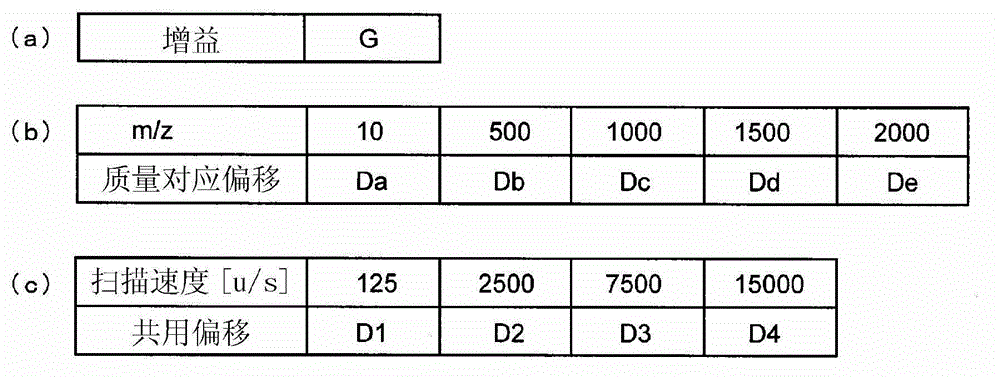
If a scanning rate of a mass scanning is set to be high, the amount of change in an applied voltage between a time of an incidence of a certain ion into a quadrupole mass filter and a time of an emission of the ion therefrom increases. This leads to a change in the condition of a passage of ions, causing the amount of ions to decrease and thereby deteriorating detection sensitivity. In order to avoid this problem, according to the present invention, the values of direct current voltage U and an amplitude V of radio-frequency voltage, both voltages being applied to rod electrodes during a mass scanning, are respectively determined so that a voltage ratio U / V of the voltage U to the amplitude V becomes smaller as the scanning rate becomes higher. Accordingly, in a stability diagram based on the Mathieu equation, the inclination of line L indicating the change in the applied voltage during the mass scanning becomes gradual and the amount of ions passing through the quadrupole mass filter increases particularly when the mass is high.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Method of identifying false mode of engineering structure
InactiveCN106777763AAccurate discriminationGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsData selectionData profiling
The invention belongs to the technical field of engineering structure monitoring data analysis, mainly relates to a method of identifying false mode of an engineering structure and particularly provides a structure false mode identifying method based on different data selection characteristic system realization algorithms. Truncation order nt is judged preliminarily, data selection is changed according to the truncation order nt, a data movement stability diagram is drawn, and a structure false mode is identified accurately from the data movement stability diagram. The influence of an environment upon frequency is observed by changing data selection, the influence of the environment upon a true mode may be reflected directly, and the false mode may be identified accurately.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
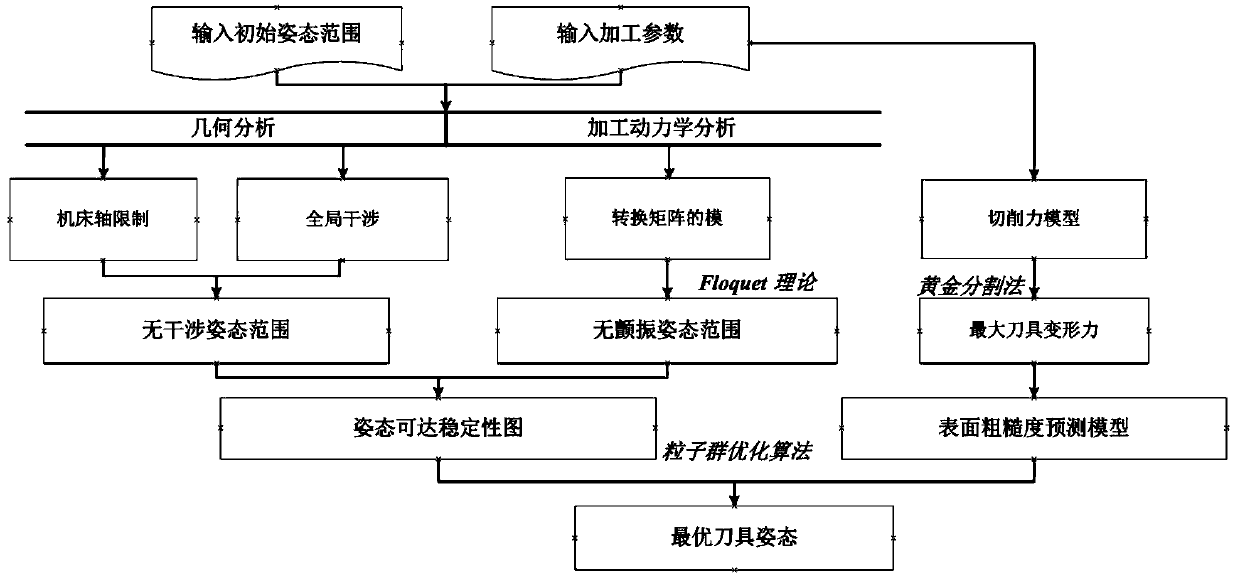
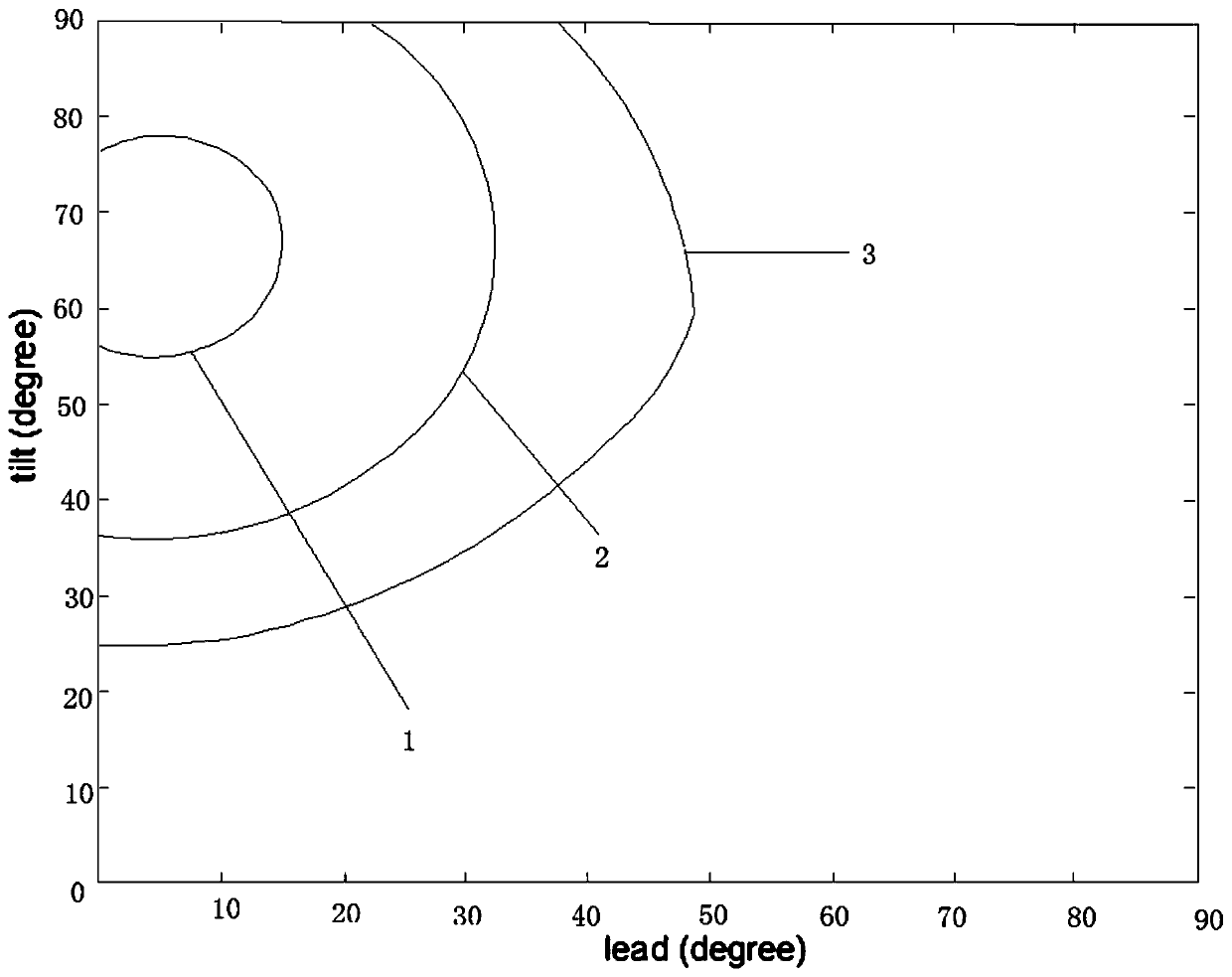
Cutter pose optimization method
ActiveCN110405533AImprove surface propertiesAvoid interferenceAutomatic control devicesFeeding apparatusSurface roughnessEngineering
The invention discloses a cutter pose optimization method specifically comprising the steps that S1, the accessibility range of a cutter under the limit of a machine tool shaft is determined; S2, global-interference-free pose range of the cutter is obtained; S3, the flutter-free pose range of the cutter is obtained; S4, a cutter pose accessibility stability diagram is built; and S5, on the basis of S4, the optimal cutter pose is obtained with a surface roughness prediction model as a fitness function. According to the cutter pose optimization method, the surface roughness prediction model of aworkpiece serves as the fitness function, the optimal cutter pose is obtained, interference and flutter in the machining process are avoided, surface performance of the workpiece is also improved, and significance is achieved for route planning.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Surrounding rock stability evaluation method based on photogrammetry, BQ and improved Mathews stability diagram
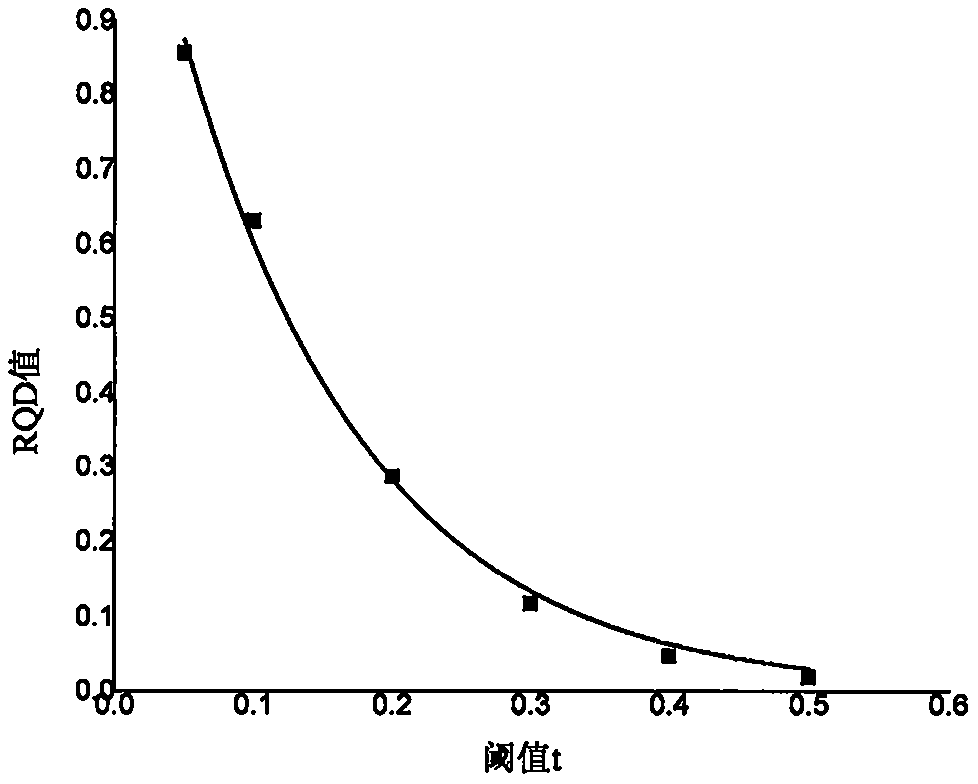
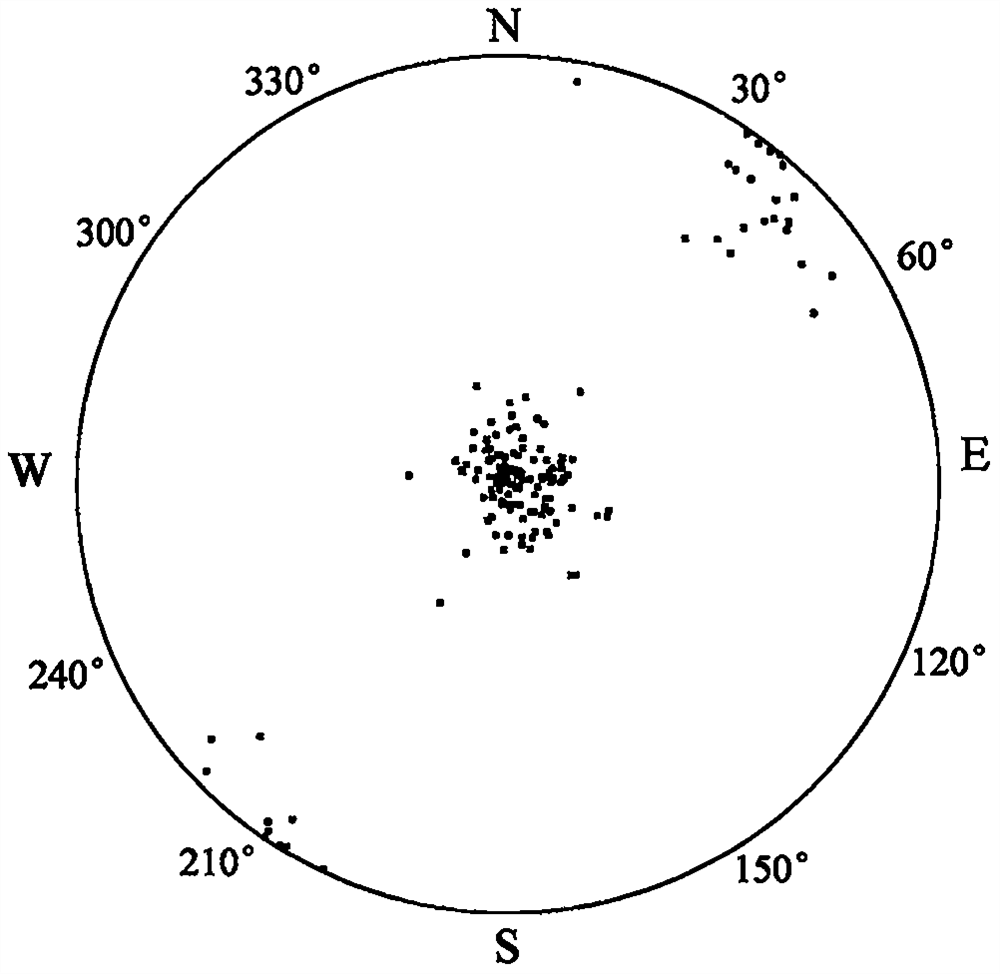
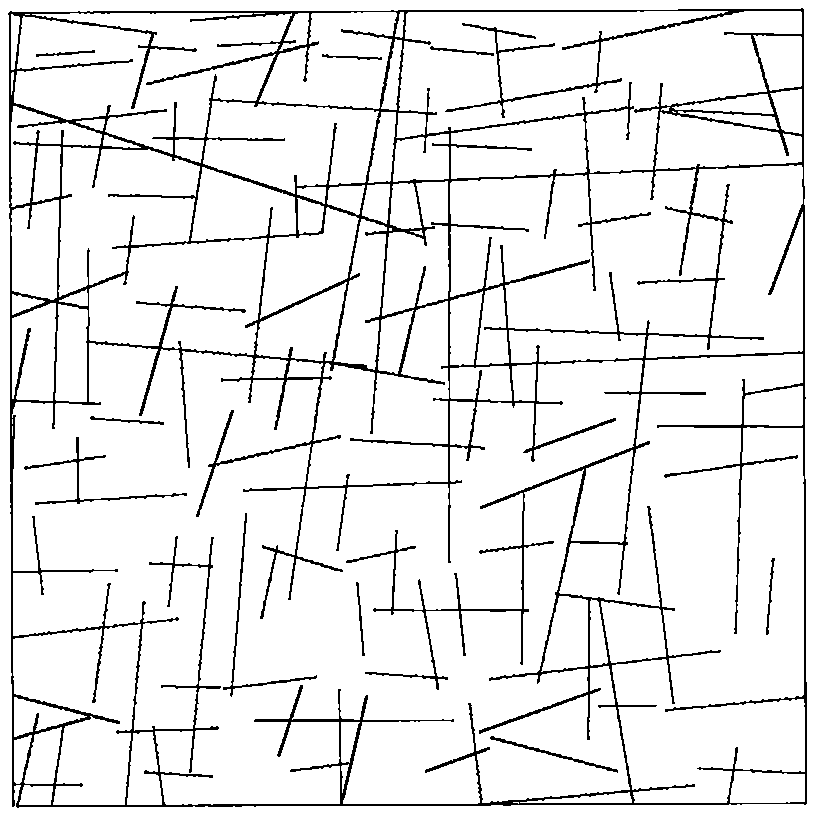
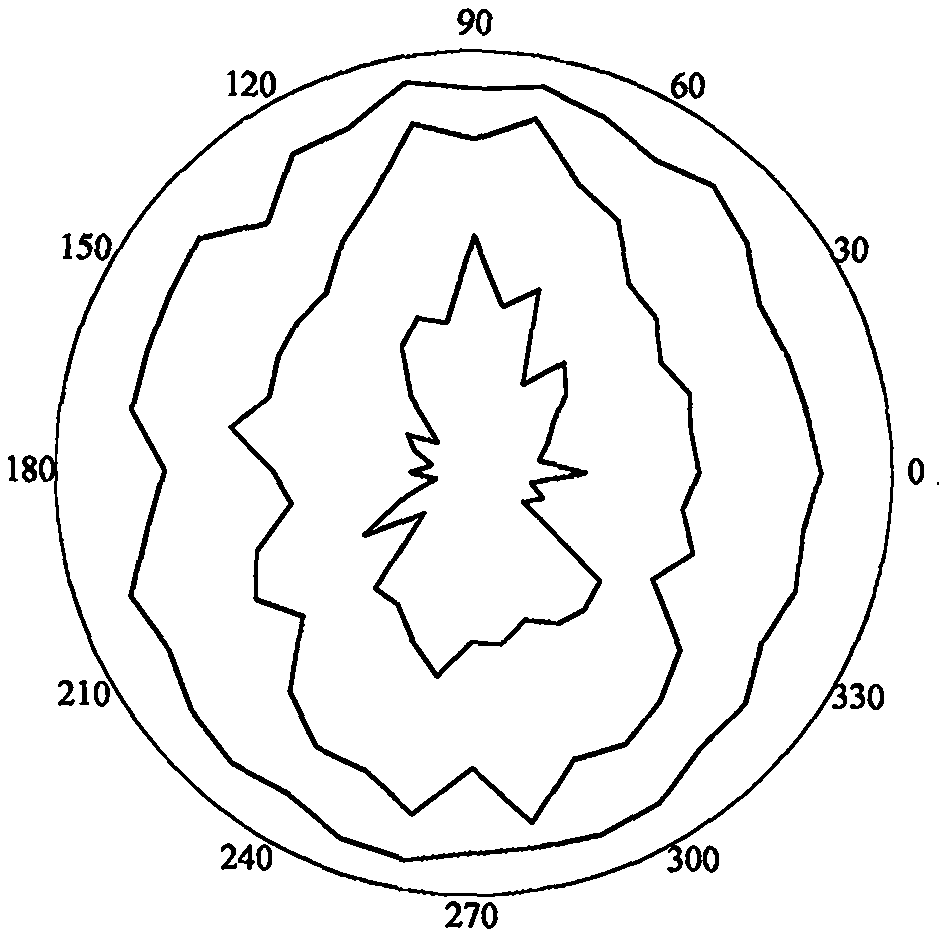
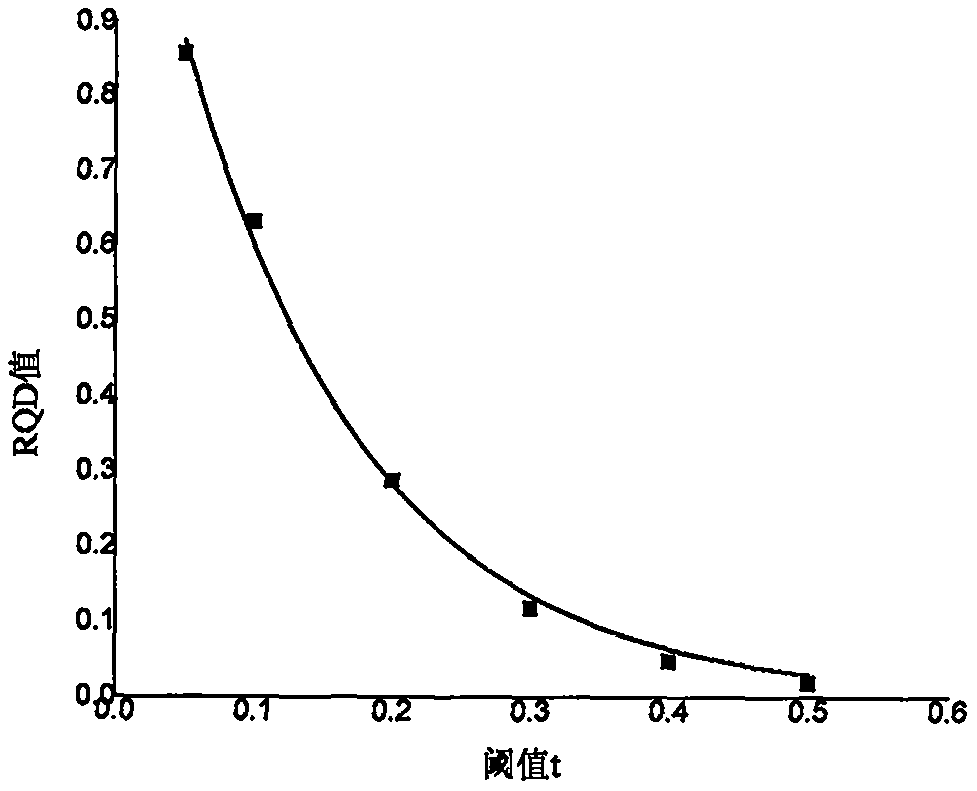
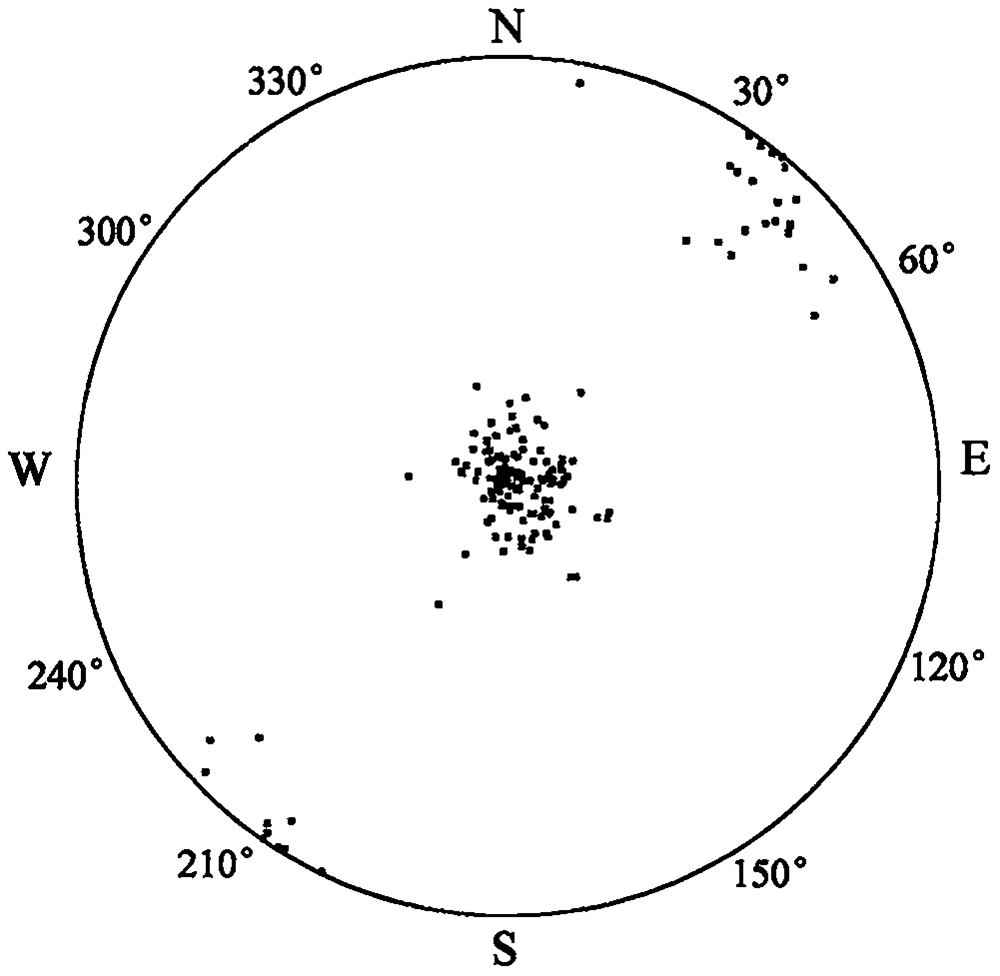
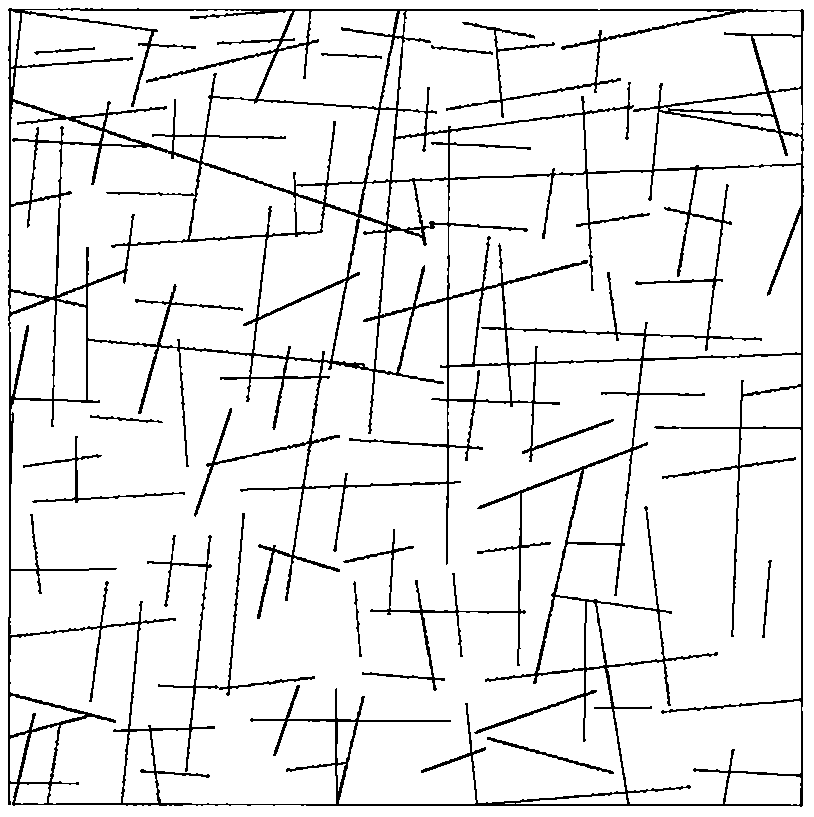
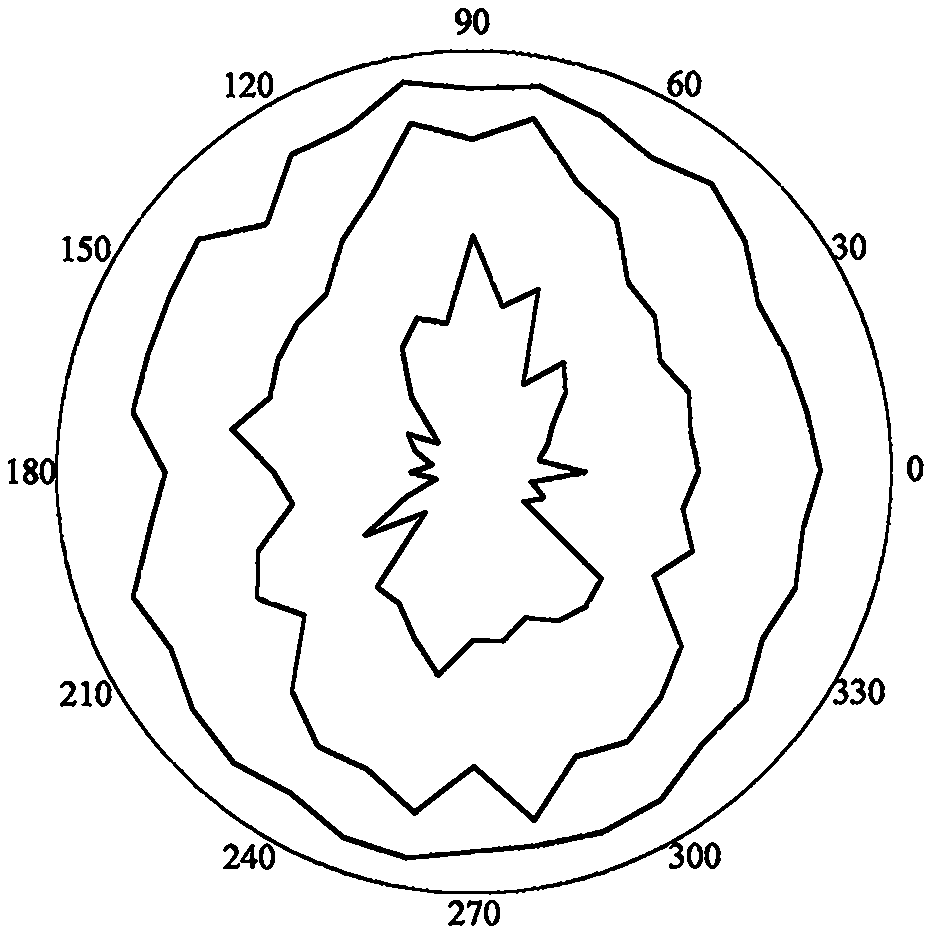
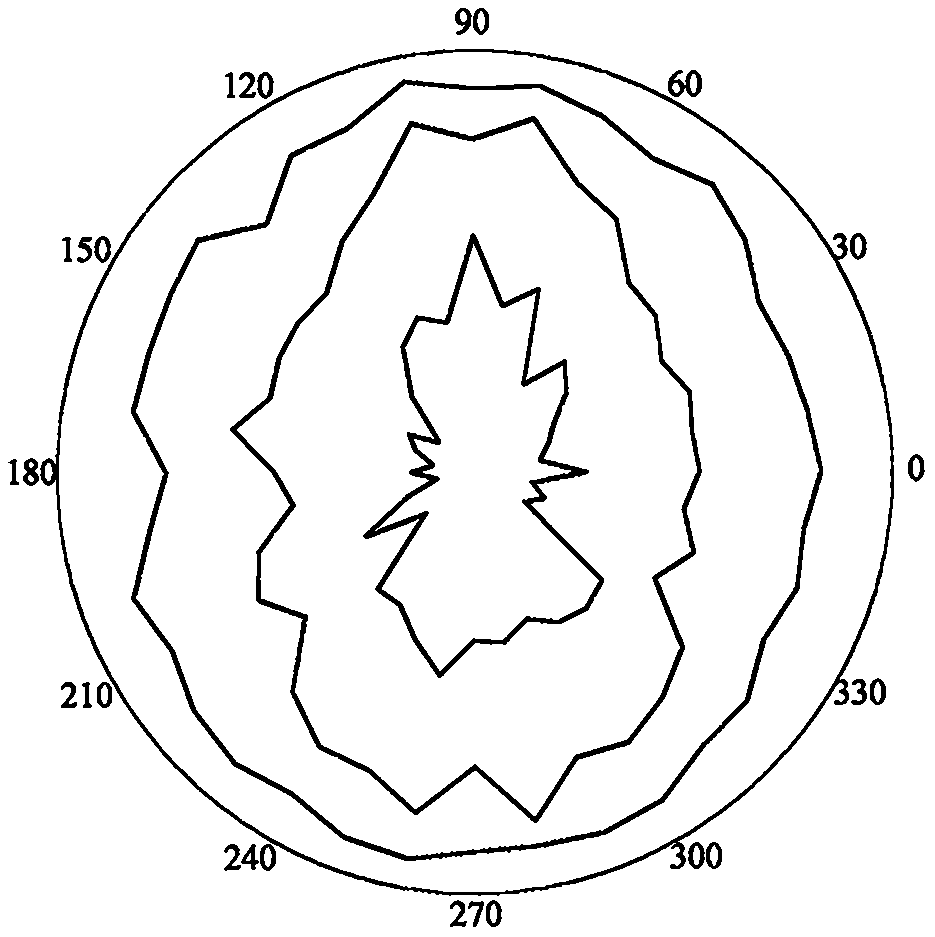
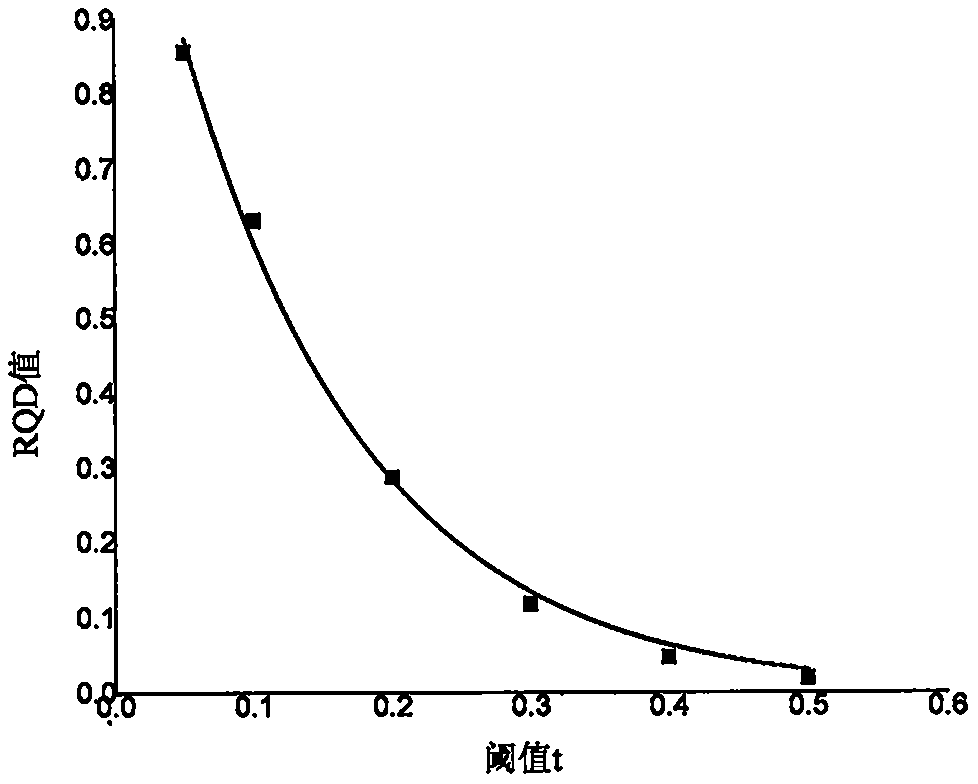
A surrounding rock stability evaluation method based on photogrammetry, BQ and an improved Mathews stability diagram belongs to the field of goaf stability evaluation, and comprises the following steps: (1) quickly acquiring structural plane digital photogrammetry; (2) performing structural plane fuzzy equivalent clustering analysis; (3)performing rock mass quality calculation based on a BQ index;(4) generating and sectioning a rock mass three-dimensional fracture network model; (5) drawing an RQDt anisotropy diagram; (6) performing an optimal threshold t solving method based on BQ inversion;(7) performing an RQDt anisotropy solving method; (8) performing a crustal stress measurement method; (9) performing an improved method of a Mathews stability graph method; (10) improving a Mathews stability diagram evaluation method; (11) performing a surrounding rock stability analysis method; and (12) performing a goaf stability evaluation method. According to the invention, improvement of a Mathews stability diagram method considering RQDt anisotropy and ground stress fitting is realized, and surrounding rock stability evaluation based on the improved Mathews stability diagram method andnumerical simulation is realized. The method is clear and suitable for goaf surrounding rock stability evaluation.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Surrounding rock stability evaluation method based on laser scanning, BQ and improved Mathews stability diagram
InactiveCN112200419AImprovement of Surrounding Rock Stability Evaluation MethodFast cluster analysisGeometric CADDrawing from basic elementsLaser scanningEngineering
The invention discloses a surrounding rock stability evaluation method based on laser scanning, BQ and an improved Mathews stability diagram, and belongs to the field of goaf stability evaluation, andthe method comprises the following steps: (1) quick obtaining of structural surface three-dimensional laser scanning; (2) structural plane clustering analysis; (3) rock mass quality calculation basedon a BQ index; (4) generating and sectioning of a rock mass three-dimensional fracture network model; (5) drawing of an RQDt anisotropy diagram; (6) an optimal threshold t solving method based on BQinversion; (7) an RQDt anisotropy solving method; (8) a crustal stress measurement method; (9) an improved method of a Mathews stability graph method; (10) an improved Mathews stability diagram evaluation method; (11) a surrounding rock stability analysis method; and (12) a goaf stability evaluation method. According to the method, improvement of a Mathews stability diagram method considering RQDtanisotropy and ground stress fitting is realized, and surrounding rock stability evaluation based on the improved Mathews stability diagram method and numerical simulation is realized. The method isclear and suitable for goaf surrounding rock stability evaluation.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
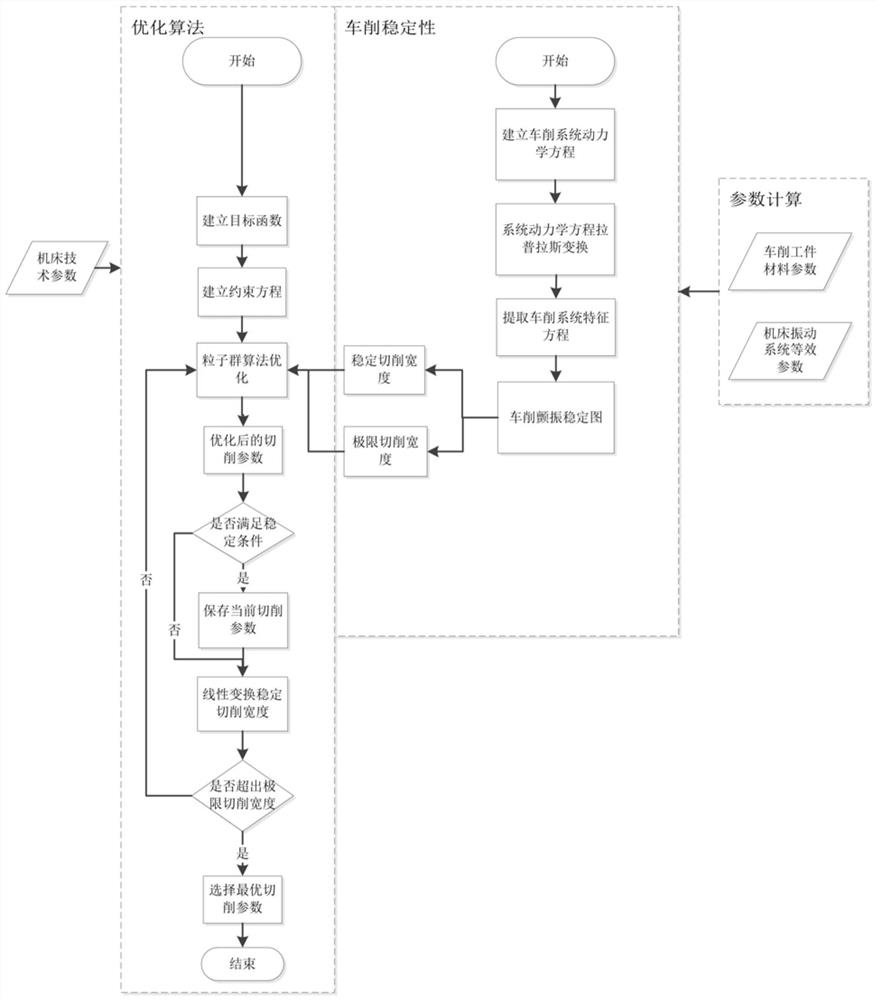
Turning flutter cutting parameter optimization method and system based on workpiece deformation
ActiveCN112859590AImproved value conservativeConvenient timeAdaptive controlStructural engineeringMachine tool
The invention discloses a turning flutter cutting parameter optimization method and system based on workpiece deformation. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) establishing a workpiece-tool turning flutter model; and (2) obtaining limit cutting width and stable cutting width through a turning flutter stability diagram. 3) establishing an objective function by using the machining cost of a machine tool, the machining quality of a workpiece and cutting efficiency, establishing a constraint equation by using the surface quality of the workpiece, the power of the machine tool and the service life of a cutter, and performing particle swarm optimization by using back engagement, the revolution of a main shaft and a feed amount as optimization parameters; and 4) carrying out linear transformation stable cutting width iterative solution to obtain an optimal cutting parameter. According to the method, the deformation problem in workpiece machining is considered, the problem that selected turning machining parameters at present are conservative can be solved, the machining efficiency is improved, the workpiece surface machining quality is improved, and meanwhile the flutter problem caused by adopting improper cutting parameters is avoided.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Improved Mathews stability diagram evaluation method based on photogrammetry, BQ, RQDt and crustal stress
InactiveCN112200417ARealize BQ index classificationRealize generationGeometric CADDrawing from basic elementsNetwork modelDigital photogrammetry
The invention discloses an improved Mathews stability diagram evaluation method based on photogrammetry, BQ, RQDt and crustal stress, and belongs to the field of Mathews stability diagram evaluation methods, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) quickly obtaining structural plane digital photogrammetry; (2) conducting structural plane fuzzy equivalent clustering analysis; (3) conducting rock mass quality calculation based on a BQ index; (4) generating and sectioning a rock mass three-dimensional fracture network model; (5) drawing an RQDt anisotropy diagram; (6) solving an optimalthreshold t based on BQ inversion; (7) solving an RQDt under anisotropy conditions; (8) measuring a crustal stress; (9) improving a Mathews stability graph method; and (10) conducting evaluation basedon an improved Mathews stability diagram. According to the method, photogrammetry, fuzzy equivalence analysis, a BQ theory, a fracture network model, a generalized RQD theory and a crustal stress measurement method are combined, and improved Mathews stability diagram method mine room stability evaluation considering RQDt anisotropy and crustal stress fitting is achieved. The method is clear and suitable for evaluating the stability of the mine room surrounding rock.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
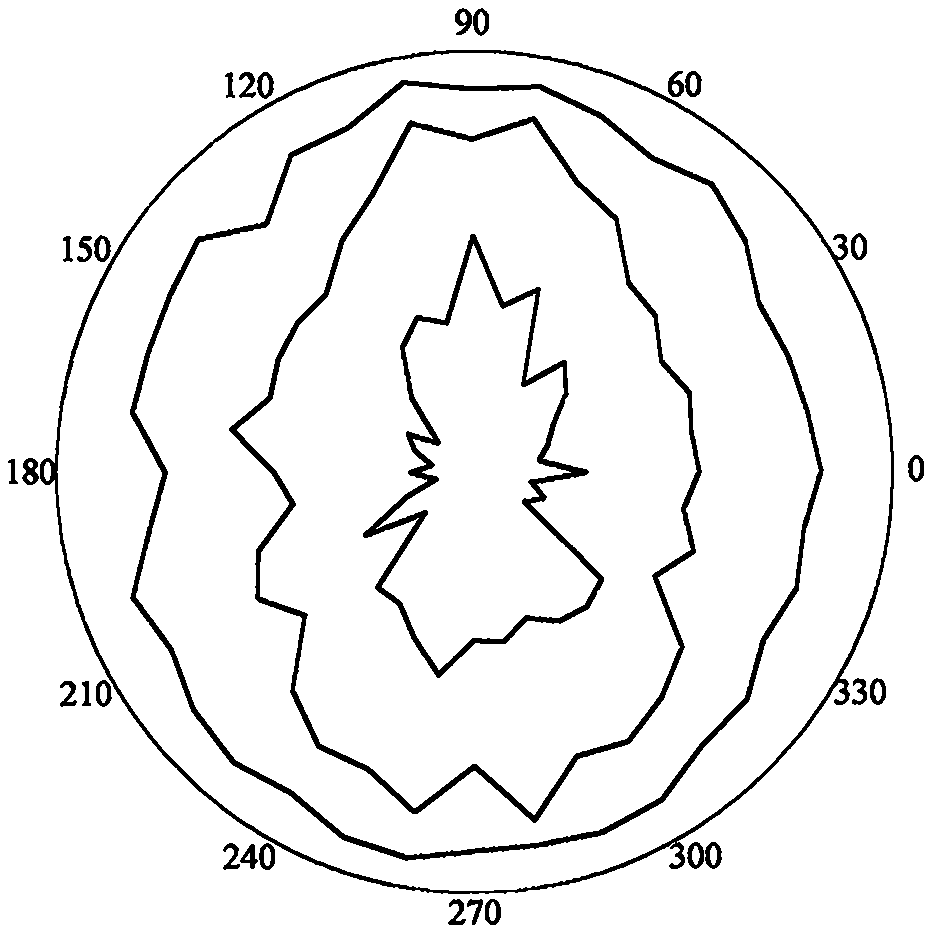
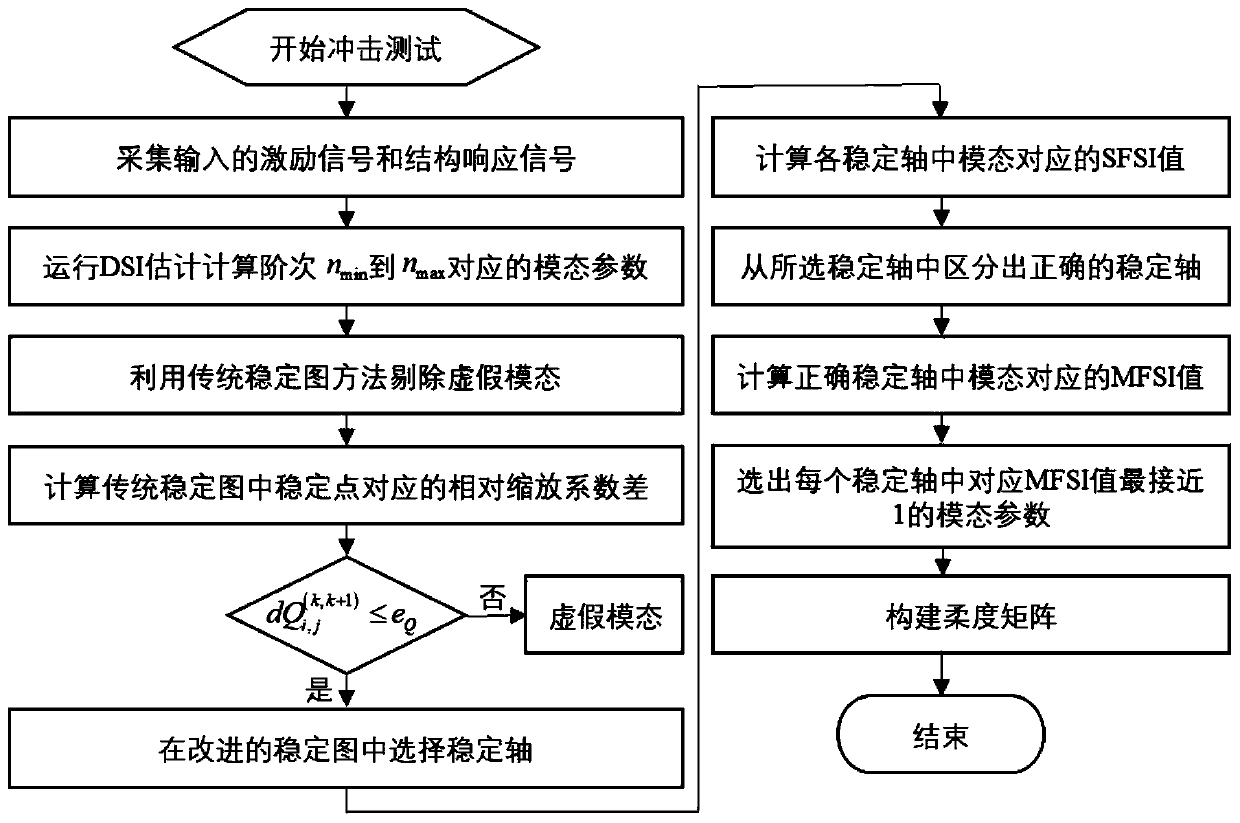
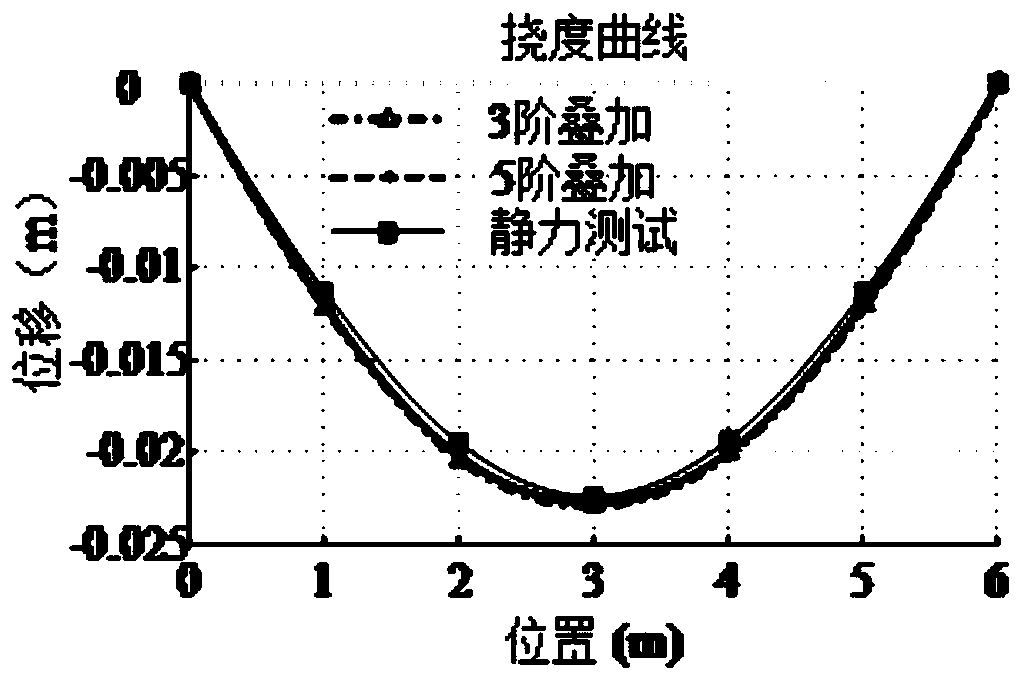
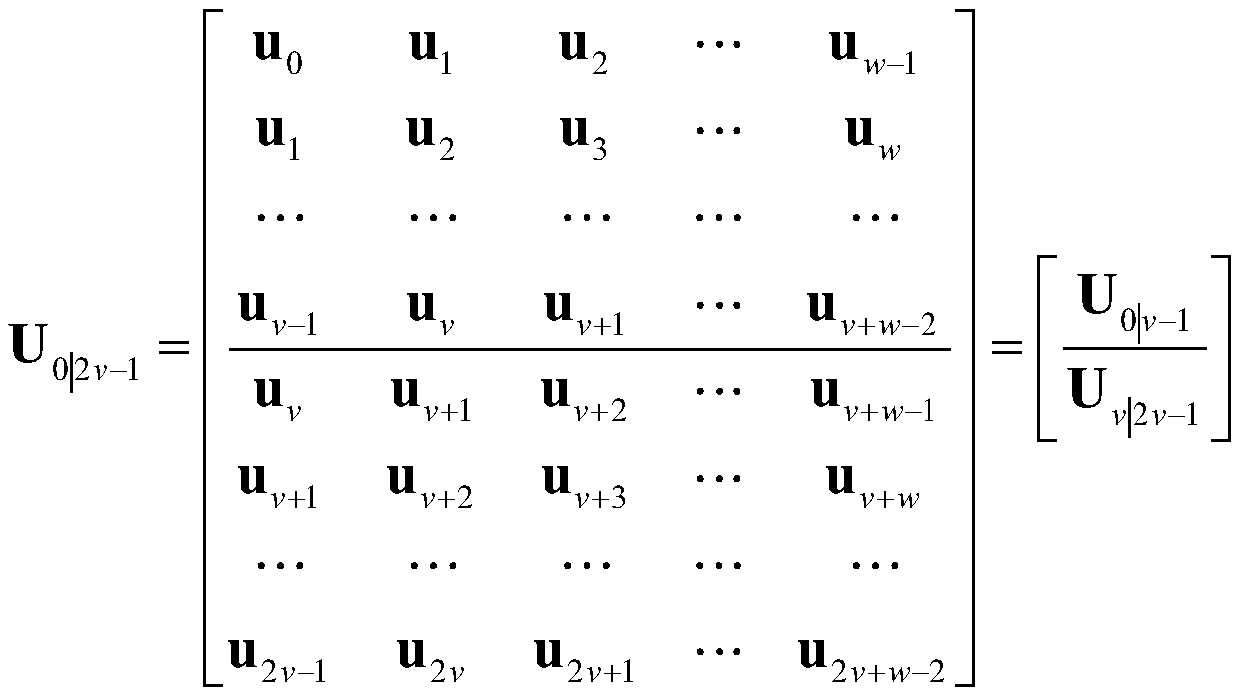
Physical mode extraction method for engineering structure flexibility identification
ActiveCN111274630AGood choiceAccurate compliance informationGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationAlgorithmState space
The invention belongs to the technical field of engineering structure detection data analysis, and provides a physical mode extraction method for engineering structure flexibility identification. According to the method, basic modal parameters and modal scaling coefficients are calculated from state space models of different orders through a determination-random subspace identification method. Andthen, adding the relative zoom coefficient tolerance as a new modal index into the classic stability diagram, thereby obtaining a clearer stability diagram. And calculating a single-order modal frequency domain similarity index by utilizing the single-order frequency response function and the actually measured frequency response function to judge whether the selected stable axis is correct or not. Then, calculating a multi-order modal frequency domain similarity index by utilizing a low-order superposition frequency response function and an actually measured frequency response function, and further determining a physical modal in each stable axis; and finally, calculating a flexibility matrix by utilizing the identified modal parameters, and achieving the purpose of predicting the displacement of the structure under the action of any static load.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Broaching machining stability monitoring method and system
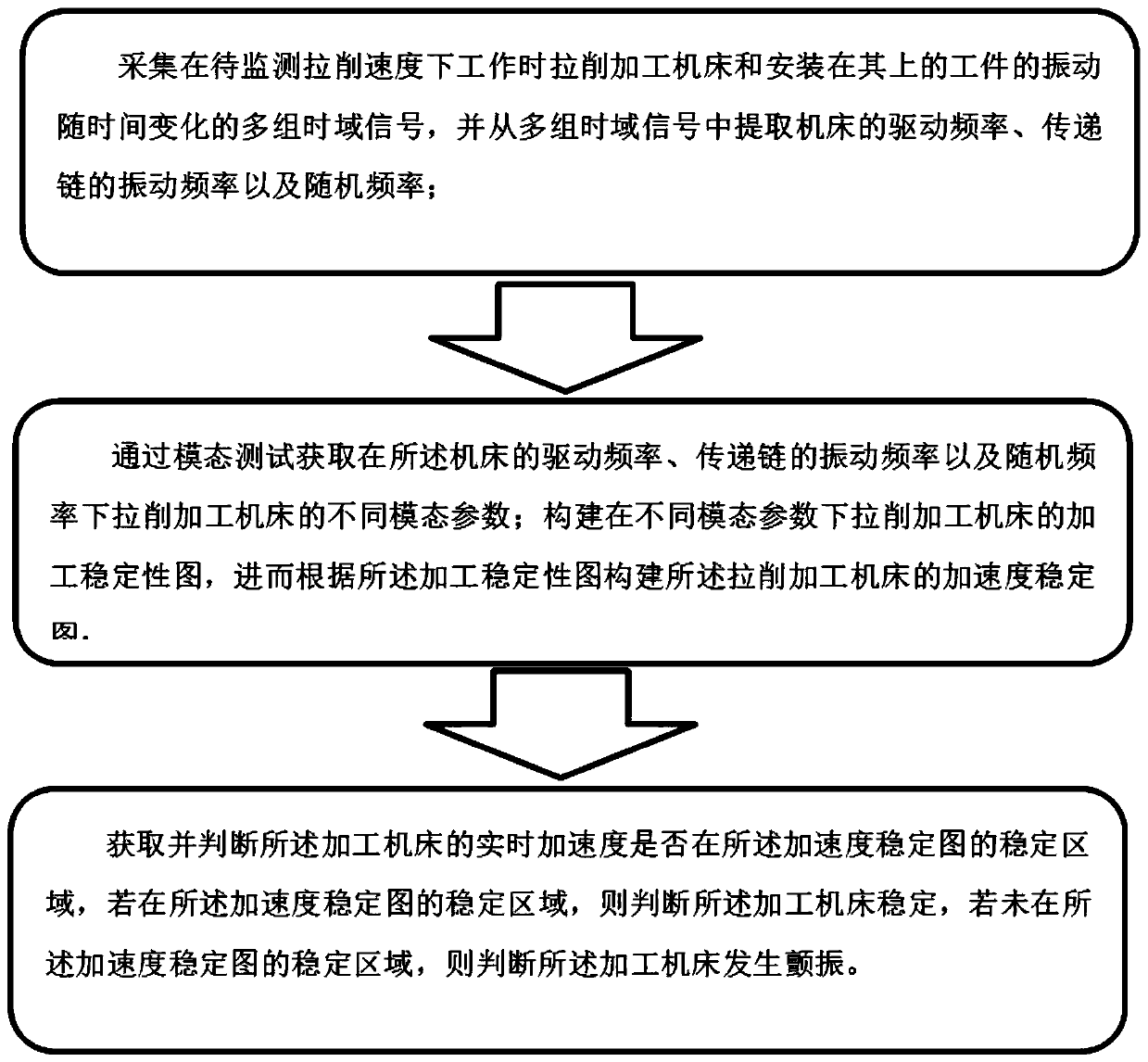
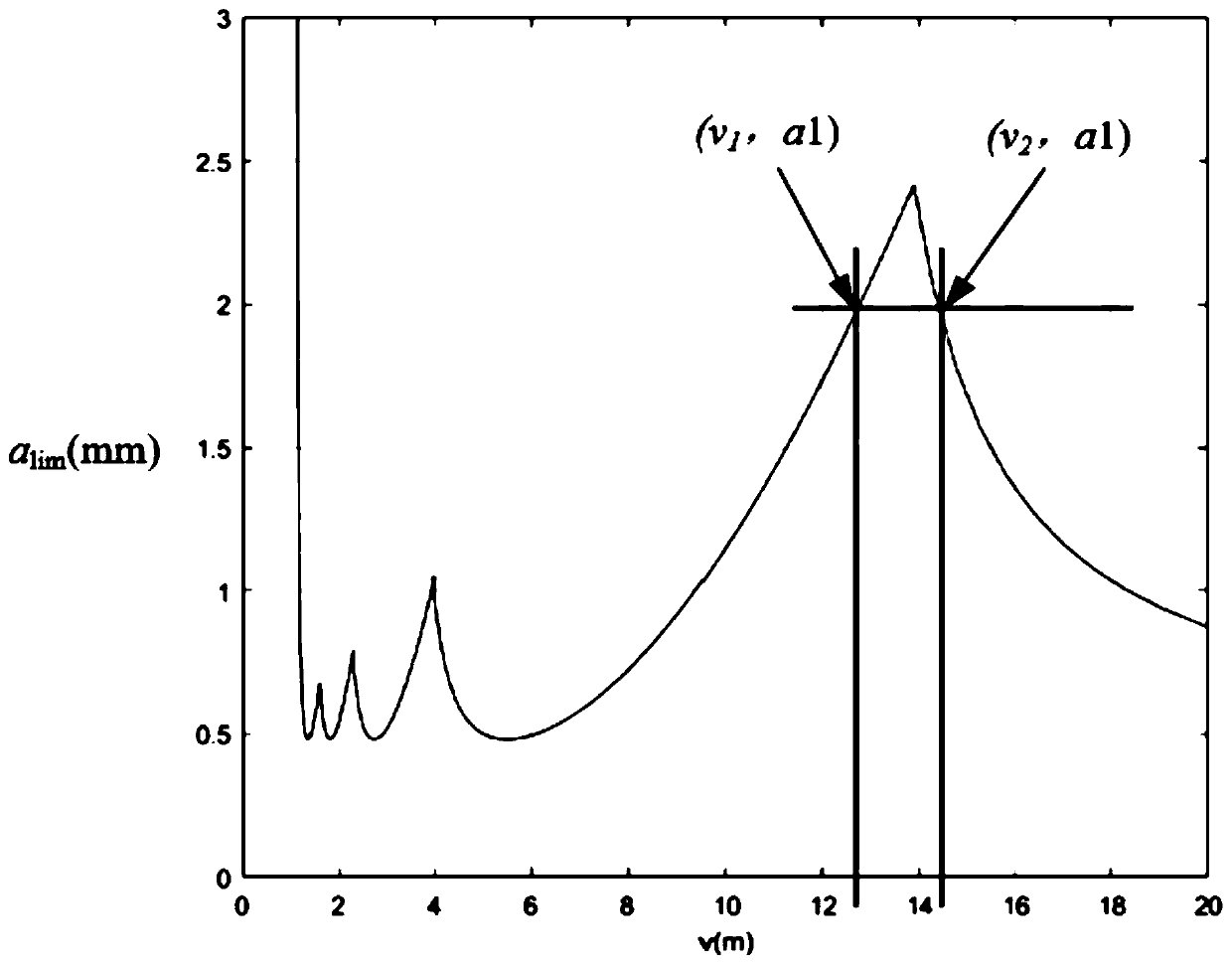
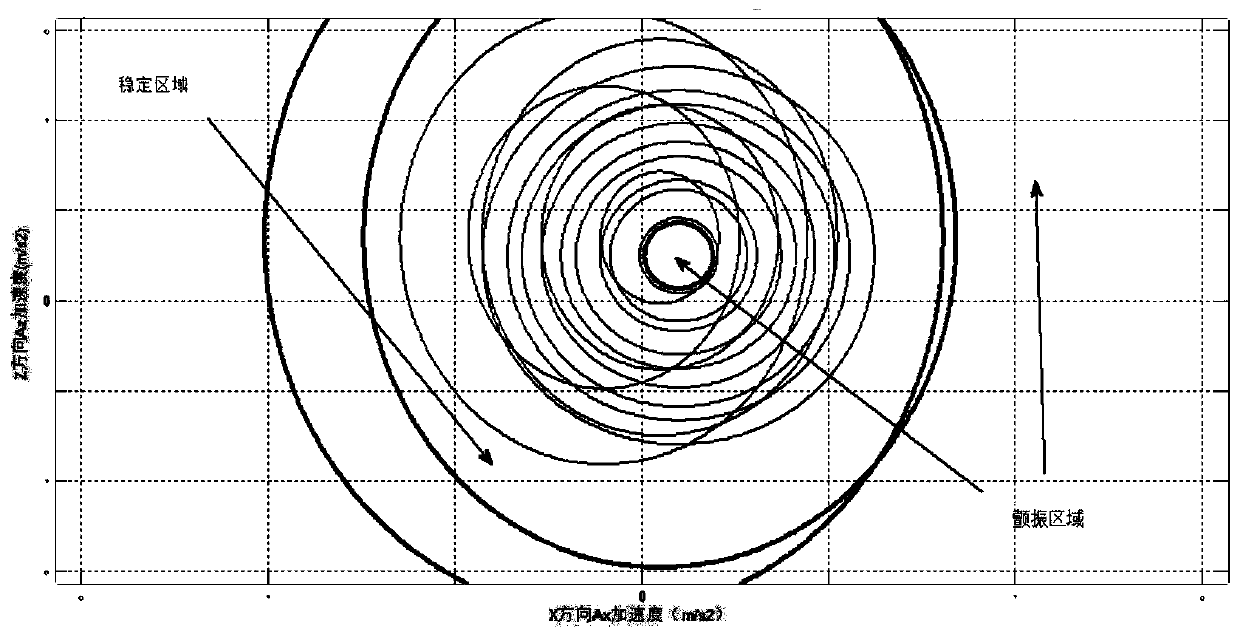
ActiveCN111230590AMonitor stabilityEffective monitoring of stabilityBroaching accessoriesMeasurement/indication equipmentsTime domainModal testing
The invention discloses a broaching machining stability monitoring method and a broaching machining stability monitoring system. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a plurality of groups of time-domain signals about vibration, changing with time, of a broaching machine tool and a workpiece when the broaching machine tool works at a to-be-monitored broaching speed so as to extract the driving frequency of the machine tool and the vibration frequency and random frequency of a transmission chain from the plurality of groups of time-domain signals; acquiring different modal parameters of the broaching machine tool under the driving frequency and the vibration frequency and random frequency of the transmission chain by virtue of a modal test; building an acceleration stability diagram of the broaching machine tool under different modal parameters; judging whether the real-time acceleration of the broaching machine tool is within a stability region of the acceleration stability diagram or not; if the real-time acceleration of the broaching machine tool is within the stability region of the acceleration stability diagram, judging that the broaching machine tool is stable; if the real-time acceleration of the broaching machine tool is not within the stability region of the acceleration stability diagram, judging that the broaching machine tool will generate flutter,thereby effectively monitoring the stability of the broaching machine tool, discovering the flutter phenomenon of the broaching machine tool in time and solving the problem about deviation of relativepositions of a cutter and the workpiece due to vibration of an existing system.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Improved Mathews stability diagram evaluation method based on laser scanning, BQ, RQDt and crustal stress
InactiveCN112150002AFast cluster analysisRealize BQ index classificationGeometric CADDrawing from basic elementsLaser scanningNetwork model
The invention discloses an improved Mathews stability diagram evaluation method based on laser scanning, BQ and RQDt anisotropy, and belongs to the field of Mathews stability diagram evaluation methods, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) quickly obtaining three-dimensional laser scanning of a structural plane; (2) performing structural plane clustering analysis; (3) performing rockmass quality calculation based on a BQ index; (4) generating and sectioning a rock mass three-dimensional fracture network model; (5) drawing an RQDt anisotropy diagram; (6) performing an optimal threshold t solving method based on BQ inversion; (7) performing an RQDt anisotropy solving method; (8) performing an improved method of a Mathews stability graph method; and (9) improving a Mathews stability diagram evaluation method. According to the invention, three-dimensional laser scanning, structural plane clustering analysis, a BQ theory, a fracture network model and a generalized RQD theory are combined, and improved Mathews stability diagram method mine room stability evaluation considering RQDt anisotropism is achieved. The method is clear and suitable for evaluating the stability of the mine room surrounding rock.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Quadropole mass spectrometer
ActiveUS8188426B2High detection sensitivityConstantStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationVoltage ratioRadio frequency
If a scanning rate of a mass scanning is set to be high, the amount of change in an applied voltage between a time of an incidence of a certain ion into a quadrupole mass filter and a time of an emission of the ion therefrom increases. This leads to a change in the condition of a passage of ions, causing the amount of ions to decrease and thereby deteriorating detection sensitivity. In order to avoid this problem, according to the present invention, the values of direct current voltage U and an amplitude V of radio-frequency voltage, both voltages being applied to rod electrodes during a mass scanning, are respectively determined so that a voltage ratio U / V of the voltage U to the amplitude V becomes smaller as the scanning rate becomes higher. Accordingly, in a stability diagram based on the Mathieu equation, the inclination of line L indicating the change in the applied voltage during the mass scanning becomes gradual and the amount of ions passing through the quadrupole mass filter increases particularly when the mass is high.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
A Method for Improving Machining Accuracy of Supporting Device for Thin-walled Parts
InactiveCN104708458BEffective support and fixationExact modal parametersMilling equipment detailsPositioning apparatusEngineeringProcessing accuracy
The invention relates to the field of advanced manufacturing, in particular to a supporting device and a machining precision improving method for a thin-wall part. Matching buckles are matched with ring ways and slide ways so that supporting postures of different space shapes can be completed on a supporting table, a thin-wall part can be fixedly supported effectively, and more precise modal parameters can be obtained through clamping conducted through the supporting device. Under the circumstance that boundary limiting conditions such as the cut-in angle, the cut-out angle and the cutting thickness are considered sufficiently, a numerical integration method is used for iterative operation, a vibration displacement simulating diagram is obtained by subdividing the rotating speed of a main shaft and the axial cutting depth within a certain range, a milling stability diagram is finally obtained, simulation precision is improved, and machining quality is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Improvement method of Mathews stability diagram method based on BQ and RQDt anisotropy
InactiveCN112200422ARealize BQ index classificationRealize generationGeometric CADDrawing from basic elementsComputational physicsNetwork model
An improvement method of a Mathews stability diagram method based on BQ and RQDt anisotropy belongs to the field of method improvement of the Mathews stability diagram method, and comprises the following steps: (1) rock mass quality calculation based on a BQ index; (2) generating and sectioning of a rock mass three-dimensional fracture network model; (3) drawing of an RQDt anisotropy diagram; (4)an optimal threshold t solving method based on BQ inversion; (5) an RQDt anisotropy solving method; and (6) an improved method of a Mathews stability diagram method. According to the method, the BQ theory, the fracture network model, the generalized RQD theory and inversion calculation are combined, the optimal threshold t and anisotropy of RQDt are solved, and the Mathews stability diagram methodconsidering anisotropy of RQDt is improved. The method provided by the invention is clear and is suitable for improving a Mathews stability diagram method.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Surrounding rock stability dynamic evaluation method based on photogrammetry, BQ and numerical simulation
A surrounding rock stability dynamic evaluation method based on photogrammetry, BQ and numerical simulation belongs to the field of goaf stability evaluation, and comprises the following steps: (1) quickly obtaining structural plane digital photogrammetry; (2) conducting structural plane fuzzy equivalent clustering analysis; (3) conducting rock mass quality calculation based on a BQ index; (4) generating and sectioning a rock mass three-dimensional fracture network model; (5) drawing an RQDt anisotropy diagram; (6) solving an optimal threshold t based on BQ inversion; (7) solving an RQDt underanisotropy conditions; (8) measuring a crustal stress; (9) improving a Mathews stability graph method; (10) conducting evaluation based on the improved Mathews stability diagram; (11) dynamically analysing the surrounding rock stability; and (12) dynamically evaluating the goaf stability. The goaf surrounding rock stability dynamic evaluation method realizes goaf surrounding rock stability dynamic evaluation based on combination of an improved Mathews stability graph method and numerical simulation. The method is clear, and is suitable for dynamic evaluation of goaf surrounding rock stability.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Quadrupole mass analyzer
ActiveCN103069540BUniform mass resolutionRegulation stabilityStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRadio frequencyStandard samples
Owner:SHIMADZU SEISAKUSHO CO LTD
Goaf stability dynamic evaluation method based on photogrammetry, BQ and numerical simulation
A goaf stability dynamic evaluation method based on photogrammetry, BQ and numerical simulation belongs to the field of goaf stability evaluation, and comprises the following steps: (1) quick obtaining of structural plane digital photogrammetry; (2) structural plane fuzzy equivalent clustering analysis; (3) rock mass quality calculation based on a BQ index; (4) generating and sectioning of a rockmass three-dimensional fracture network model; (5) drawing of an RQDt anisotropy diagram; (6) an optimal threshold t solving method based on BQ inversion; (7) an RQDt anisotropy solving method; (8) animproved method of a Mathews stability graph method; (9) an improved Mathews stability diagram evaluation method; (10) a surrounding rock stability dynamic analysis method; and (11) a goaf stabilitydynamic evaluation method. According to the method, solving of RQDt anisotropism and improvement of a Mathews stability diagram method are achieved, and goaf surrounding rock stability dynamic evaluation combining the improved Mathews stability diagram method and numerical simulation is achieved. The method is clear, and is suitable for dynamic evaluation of goaf surrounding rock stability.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Goaf stability evaluation method based on photogrammetry, BQ and improved Mathews stability diagram
InactiveCN112200432AImproved Evaluating Method of Gap StabilityGeometric CADDrawing from basic elementsNetwork modelDigital photogrammetry
A goaf stability evaluation method based on photogrammetry, BQ and an improved Mathews stability diagram belongs to the field of goaf stability evaluation, and comprises the following steps: (1) quickacquiring of structural plane digital photogrammetry; (2) structural plane fuzzy equivalent clustering analysis; (3) rock mass quality calculation based on a BQ index; (4) generating and sectioning of a rock mass three-dimensional fracture network model; (5) drawing of an RQDt anisotropy diagram; (6) an optimal threshold t solving method based on BQ inversion; (7) an RQDt anisotropy solving method; (8) an improved method of a Mathews stability graph method; (9) an improved Mathews stability diagram evaluation method; (10) a surrounding rock stability analysis method; and (11) a goaf stabilityevaluation method. According to the method, the optimal threshold t of the RQDt, the anisotropism solving of the RQDt and the improvement of the Mathews stability diagram method are realized, and thegoaf surrounding rock stability evaluation combining the improved Mathews stability diagram method and numerical simulation is realized. The method is clear and suitable for goaf surrounding rock stability evaluation.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Improved method of Mathews stability diagram method based on laser scanning, BQ and RQDt anisotropism
InactiveCN112150005AFast cluster analysisRealize BQ index classificationGeometric CADDrawing from basic elementsLaser scanningNetwork model
The invention relates to an improved method of a Mathews stability diagram method based on laser scanning and BQ and RQDt anisotropy, and belongs to the field of improvement method of the Mathews stable diagram method. The improved method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining structural plane three-dimensional laser scanning rapidly; (2) performing structural plane clustering analysis; (3)performing rock mass quality calculation based on a BQ index; (4) generating and sectioning a rock mass three-dimensional fracture network model; (5) drawing an RQDt anisotropy diagram; (6) performingan optimal threshold t solving method based on BQ inversion; (7) performing an RQDt anisotropy solving method; and (8) performing an improved method of a Mathews stability diagram method. According to the invention, three-dimensional laser scanning, structural plane clustering analysis, a BQ theory, a fracture network model and a generalized RQD theory are combined, solving of the optimal threshold t of RQDt and anisotropy of RQDt is achieved, and improvement of a Mathews stability diagram method is achieved. The method provided by the invention is clear and is suitable for improving a Mathews stability diagram method.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Surrounding rock stability evaluation method based on BQ and improved Mathews stability diagram method
InactiveCN112200427AImprovement of Surrounding Rock Stability Evaluation MethodRealize BQ index classificationGeometric CADDrawing from basic elementsClassical mechanicsEngineering
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Improved Mathews stability diagram evaluation method based on photogrammetry, BQ and RQDt anisotropy
InactiveCN112150003ARealize BQ index classificationRealize generationGeometric CADDrawing from basic elementsNetwork modelThresholding
The invention discloses an improved Mathews stability diagram evaluation method based on photogrammetry, BQ and RQDt anisotropy, and belongs to the field of Mathews stability diagram evaluation methods, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) quickly obtaining structural plane digital photogrammetry; (2) performing structural plane fuzzy equivalent clustering analysis; (3) performing rock mass quality calculation based on a BQ index; (4) generating and sectioning a rock mass three-dimensional fracture network model; (5) drawing an RQDt anisotropy diagram; (6) performing an optimal threshold t solving method based on BQ inversion; (7) performing an RQDt anisotropy solving method; (8) performing an improved method of a Mathews stability graph method; and (9) improving a Mathews stability diagram evaluation method. According to the invention, photogrammetry, fuzzy equivalence analysis, a BQ theory, a fracture network model and a generalized RQD theory are combined, and improvedMathews stability graph method mine room stability evaluation considering RQDt anisotropism is achieved. The method is clear and suitable for evaluating the stability of the mine room surrounding rock.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Goaf stability evaluation method based on laser scanning, BQ and improved Mathews stability diagram
InactiveCN112200420AImproved Evaluating Method of Gap StabilityFast cluster analysisGeometric CADDrawing from basic elementsLaser scanningComputational physics
The invention discloses a goaf stability evaluation method based on laser scanning, BQ and an improved Mathews stability diagram, and belongs to the field of goaf stability evaluation, and the methodcomprises the following steps: (1) quick obtaining of structural surface three-dimensional laser scanning; (2) structural plane clustering analysis; (3) rock mass quality calculation based on a BQ index; (4) generating and sectioning of a rock mass three-dimensional fracture network model; (5) drawing of an RQDt anisotropy diagram; (6) an optimal threshold t solving method based on BQ inversion; (7) an RQDt anisotropy solving method; (8) an improving method of a Mathews stability graph method; (9) an improved Mathews stability diagram evaluation method; (10) a surrounding rock stability analysis method; and (11) a goaf stability evaluation method. According to the method, the optimal threshold t of the RQDt, the anisotropism solving of the RQDt and the improvement of the Mathews stabilitydiagram method are realized, and the goaf surrounding rock stability evaluation combining the improved Mathews stability diagram method and numerical simulation is realized. The method is clear and suitable for goaf surrounding rock stability evaluation.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Milling stability prediction method and system and storage medium
PendingCN112417616AAvoid the influence of dynamic characteristicsFast convergenceGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationProcess engineeringMachining
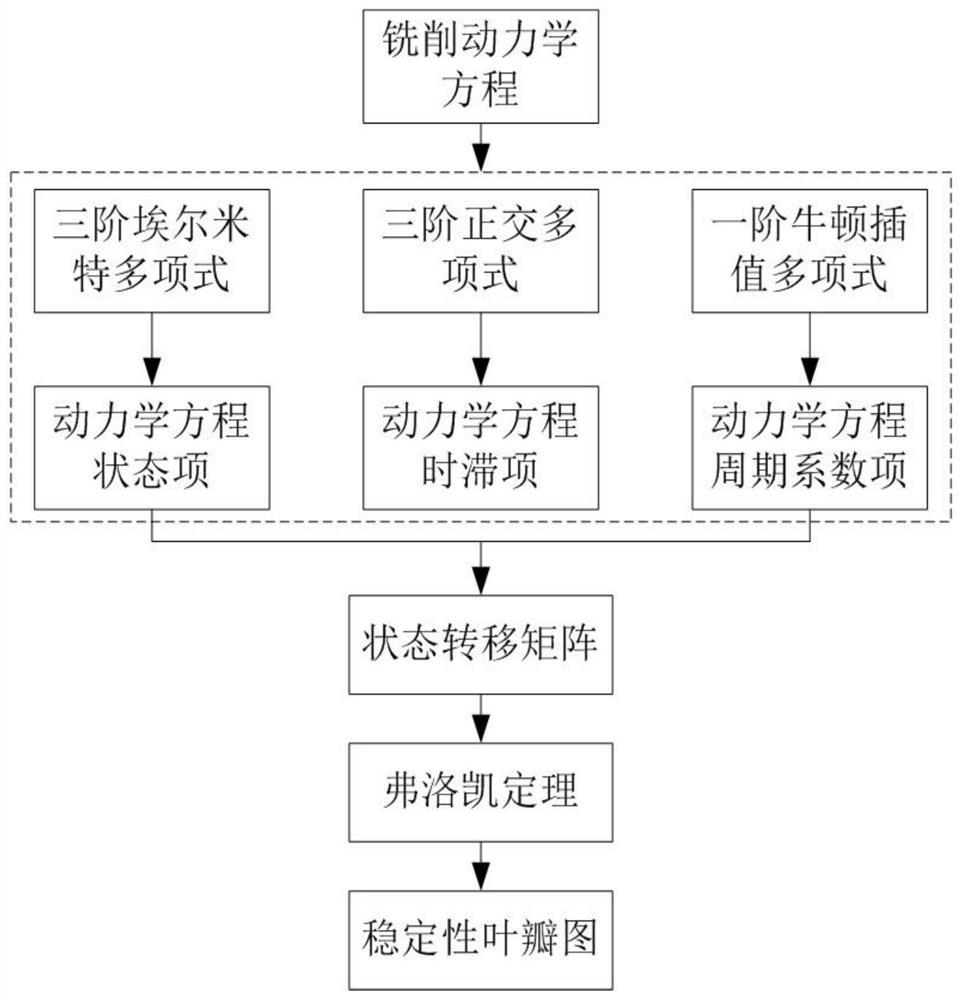
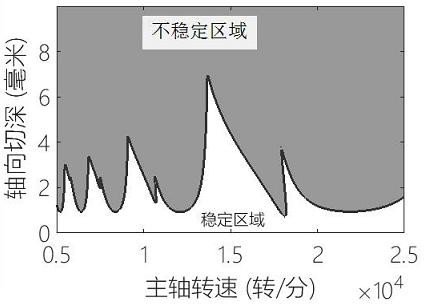
The invention relates to a milling stability prediction method and system and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps: establishing a single-degree-of-freedom milling kinetic model; performing integral solving on the milling state equation; obtaining a state transition matrix through the milling state equation after integral solving; obtaining a stability lobe graph of the milling system,and completing stability prediction. According to the method, the stability lobe diagram of the milling process can be accurately obtained, and the stability diagram is used for selecting stable machining parameters. The method can be widely applied to the field of milling stability prediction in machining.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
Improved method of Mathews stability diagram method based on photogrammetry, BQ, RQDt and crustal stress
InactiveCN112150004ARealize BQ index classificationRealize generationGeometric CADDrawing from basic elementsAlgorithmNetwork model
The invention relates to an improved method of a Mathews stability diagram method based on photogrammetry, BQ, RQDt and crustal stress, and belongs to the field of improvement of the Mathews stable diagram method, which comprises the following steps: (1) quickly obtaining structural plane digital photogrammetry; (2) performing structural plane fuzzy equivalent clustering analysis; (3) performing rock mass quality calculation based on a BQ index; (4) generating and sectioning a rock mass three-dimensional fracture network model; (5) drawing an RQDt anisotropy diagram; (6) performing an optimalthreshold t solving method based on BQ inversion; (7) performing an RQDt anisotropy solving method; (8) performing a crustal stress measurement method; and (9) performing an improved method of a Mathews stability diagram method. According to the invention, photogrammetry, fuzzy equivalence analysis, a BQ theory, a fracture network model, a generalized RQD theory and a crustal stress measurement method are combined, the optimal threshold t of RQDt and anisotropy of RQDt are solved, and method improvement of a Mathews stable graph method is achieved. The method provided by the invention is clearand is suitable for improving a Mathews stability diagram method.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Improved Mathews stability diagram evaluation method based on BQ and RQDt anisotropy
InactiveCN112200425ARealize BQ index classificationRealize generationGeometric CADDrawing from basic elementsNetwork modelGeophysics
An improved Mathews stability diagram evaluation method based on BQ and RQDt anisotropy belongs to the field of Mathews stability diagram evaluation methods, and comprises the following steps: (1) rock mass quality calculation based on BQ indexes; (2) generating and sectioning of a rock mass three-dimensional fracture network model; (3) drawing of an RQDt anisotropy diagram; (4) an optimal threshold t solving method based on BQ inversion; (5) an RQDt anisotropy solving method; (6) an improved method of a Mathews stability diagram method; and (7) an improved Mathews stability diagram evaluationmethod. According to the method, the BQ theory, the fracture network model, the generalized RQD theory and inversion calculation are combined, the optimal threshold t of the RQDt and the anisotropy of the RQDt are solved, and the improved Mathews stability diagram method mine room stability evaluation considering the anisotropy of the RQDt is achieved. The method is clear and suitable for evaluating the stability of the mine room surrounding rock.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
A milling stability domain prediction method based on cotes numerical integration
ActiveCN111611725BReduce the number of calculationsImprove computing efficiencyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationState spaceEngineering
The invention discloses a milling stable domain determination method based on Cotes numerical integration, which establishes a milling dynamics differential equation in the form of a state space considering the regeneration effect: the continuous time in a cycle t Represented as a discrete time node: calculate the equation expression in the interval: calculate the equation about the state item, and obtain the state transition matrix of the system within one cycle, and finally take the spindle speed as the abscissa, and the axial depth of cut as the ordinate A plot is made to obtain a stability diagram. When selecting the milling processing parameters, in the stable area below the black curve, select the corresponding spindle speed and axial depth of cut for milling processing, that is, chatter-free cutting can be obtained. The invention reduces the number of calculations of the exponential matrix and the state transition matrix, so that the calculation efficiency is greatly improved compared with the discrete method; and due to the mathematical approximation error reaching O ( h 6 ), the calculation accuracy is also greatly improved compared with the frequency domain method and the discrete method.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Goaf stability dynamic evaluation method based on laser scanning, BQ and numerical simulation
InactiveCN112200431AFast cluster analysisGeometric CADDrawing from basic elementsLaser scanningStructural engineering
A goaf stability dynamic evaluation method based on laser scanning, BQ and numerical simulation belongs to the field of goaf stability evaluation, and comprises the following steps: (1) quick acquiring of structural surface three-dimensional laser scanning; (2) structural plane clustering analysis; (3) rock mass quality calculation based on a BQ index; (4) generating and sectioning of a rock massthree-dimensional fracture network model; (5) drawing of an RQDt anisotropy diagram; (6) an optimal threshold t solving method based on BQ inversion; (7) an RQDt anisotropy solving method; (8) an improved method of a Mathews stability graph method; (9) an improved Mathews stability diagram evaluation method; (10) a surrounding rock stability dynamic analysis method; and (11) a goaf stability dynamic evaluation method. According to the method, the optimal threshold t of the RQDt, the anisotropism solving of the RQDt and the improvement of the Mathews stability diagram method are realized, and the goaf surrounding rock stability dynamic evaluation combining the improved Mathews stability diagram method and the numerical simulation is realized. The method is clear and suitable for dynamic evaluation of goaf surrounding rock stability.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Goaf stability dynamic evaluation method based on BQ and numerical simulation
InactiveCN112200416ARealize BQ index classificationRealize generationGeometric CADDrawing from basic elementsClassical mechanicsStructural engineering
A goaf stability dynamic evaluation method based on BQ and numerical simulation belongs to the field of goaf stability evaluation, and comprises the following steps: (1) performing rock mass quality calculation based on a BQ index; (2) generating and sectioning a rock mass three-dimensional fracture network model; (3) drawing an RQDt anisotropy diagram; (4) providing an optimal threshold t solvingmethod based on BQ inversion; (5) performing an RQDt anisotropy solving method; (6) performing an improved method of a Mathews stability diagram method; (7) improving a Mathews stability diagram evaluation method; (8) performing a surrounding rock stability dynamic analysis method; and (9) performing a goaf stability dynamic evaluation method. According to the invention, the optimal threshold t of the RQDt, the anisotropism solution of the RQDt and the improvement of the Mathews stability diagram method are realized, and the goaf surrounding rock stability dynamic evaluation combining the improved Mathews stability diagram method and the numerical simulation is realized. The invention is clear and suitable for dynamic evaluation of goaf surrounding rock stability.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
An Accurate Discrimination Method for False Modes of Engineering Structures
InactiveCN106777763BAccurate discriminationGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsData selectionSimulation
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com