A milling stability domain prediction method based on cotes numerical integration
A technology of numerical integration and stable domain, applied in geometric CAD, electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as high calculation efficiency, high calculation accuracy, and large calculation time consumption, so as to reduce calculation times, calculate Effects of improved accuracy and increased computational efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
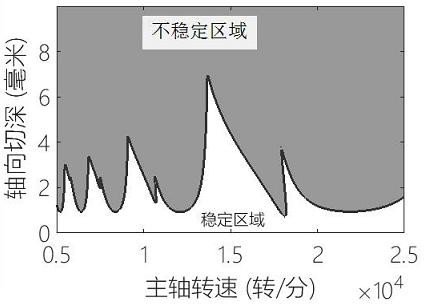
[0079] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with drawings and embodiments. see Figure 1 to Figure 3 , a method for determining the stable region of milling based on Cotes numerical integration, the specific steps are as follows:
[0080] Step 1: Establish the milling dynamics differential equation in state space form considering regeneration effect:
[0081]
[0082] Specific steps are as follows:
[0083] S01: The milling dynamics differential equation of n degrees of freedom considering the regenerative effect can be expressed as:
[0084]
[0085] Among them, M, C and K are the modal mass matrix, modal damping matrix and modal stiffness matrix of the tool system with n degrees of freedom, q(t) is the vibration displacement vector of the tool with n degrees of freedom, K c (t) is the dynamic milling force matrix suffered by the system, t is the continuous time, T is the cutting cycle of a single tooth, a p is the axial depth of cut;...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com