Goaf stability dynamic evaluation method based on laser scanning, BQ and numerical simulation
A technology of numerical simulation and laser scanning, applied in CAD numerical modeling, testing material strength using stable tension/pressure, 3D modeling, etc. method, cannot reflect RQD anisotropy, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0238] The present invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
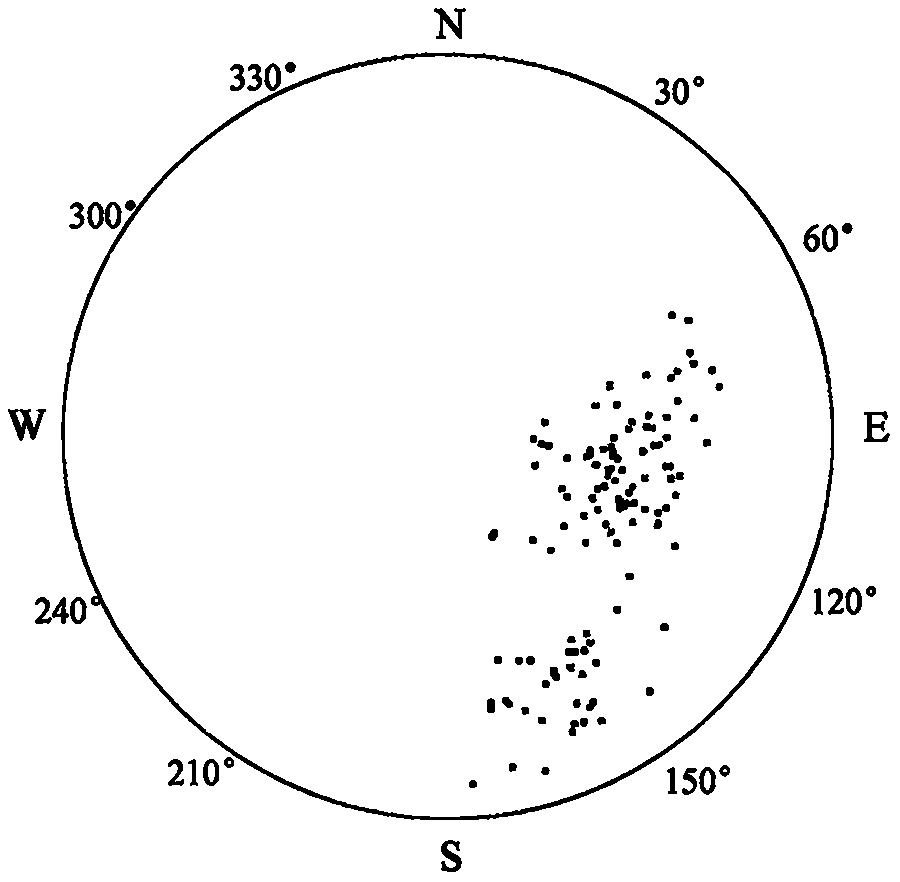
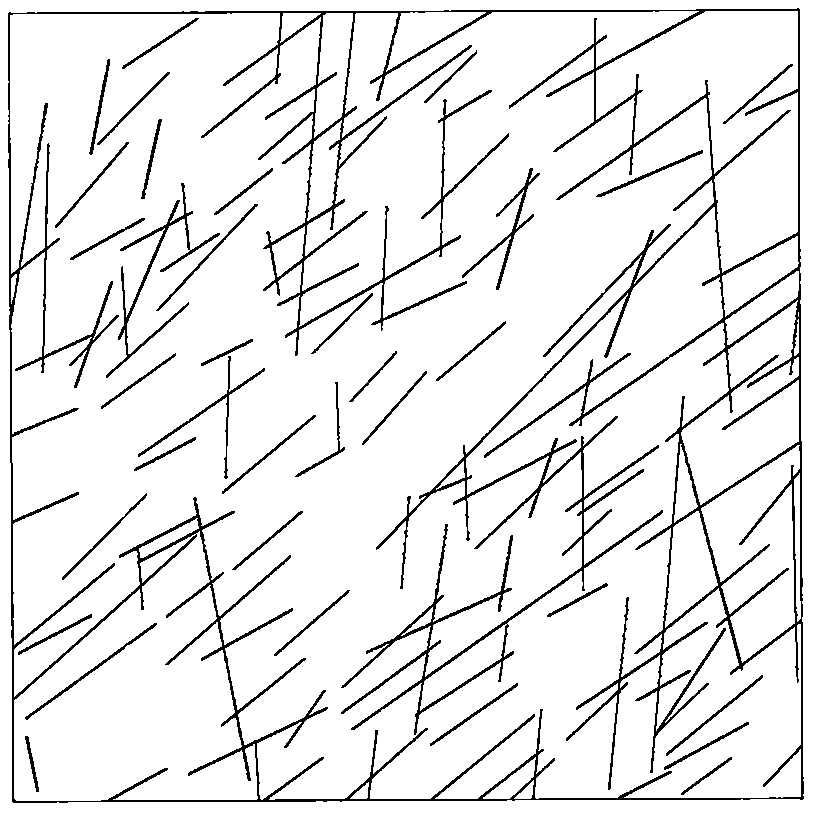
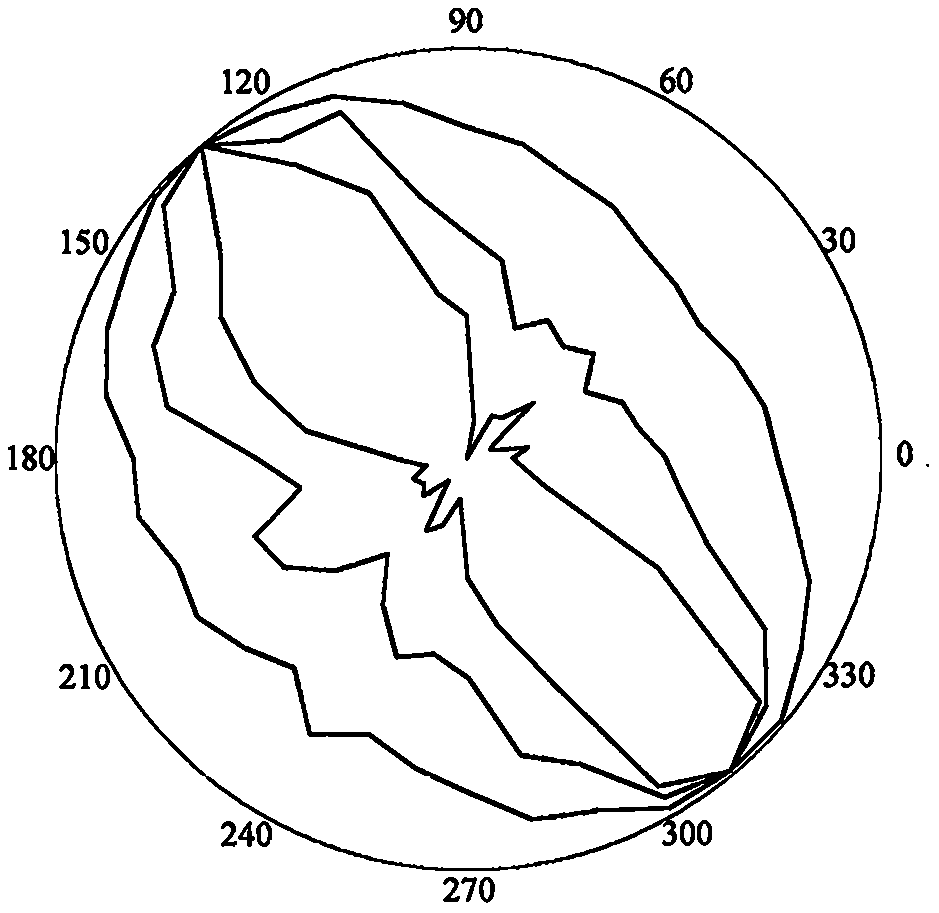
[0239] refer to Figure 1 to Figure 6 , a dynamic evaluation method for void stability based on laser scanning, BQ, and numerical simulation, including the following steps:
[0240] 1) Rapid acquisition of structural plane 3D laser scanning, the process is as follows:
[0241] 1.1: According to the scanning target and site conditions, select the location of the scanning machine and set up a tripod. During the erection, it is necessary to ensure that the instrument can completely obtain the three-dimensional point cloud information of the slope rock mass according to a certain scanning route, and at the same time, the tripod table should be ensured as much as possible. level, and place control targets;
[0242] 1.2: Place the scanner host on the tripod table, fix the knob, center the bubble of the host by coarsely adjusting the tripod and fine-tuning the scanner base, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com