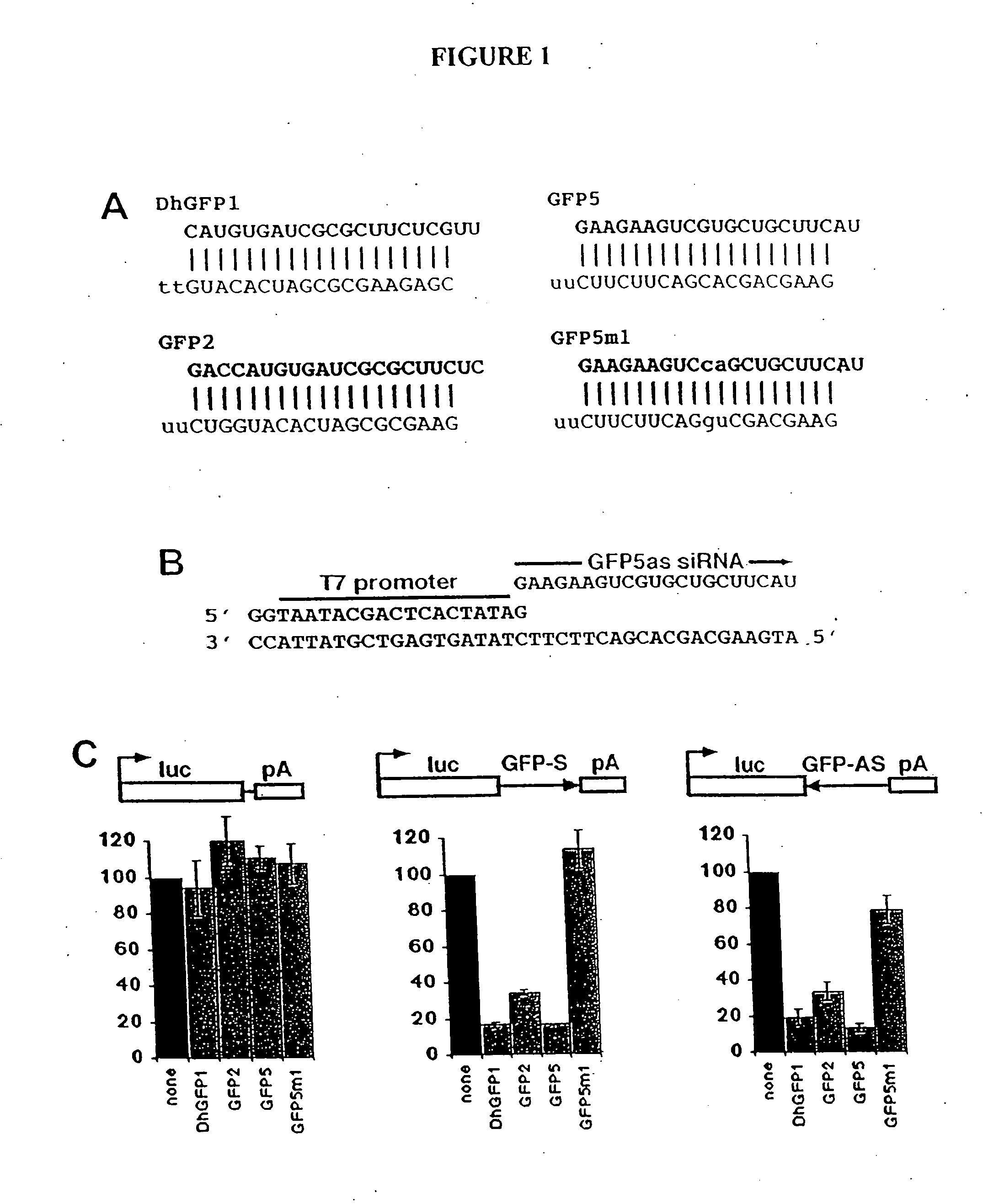
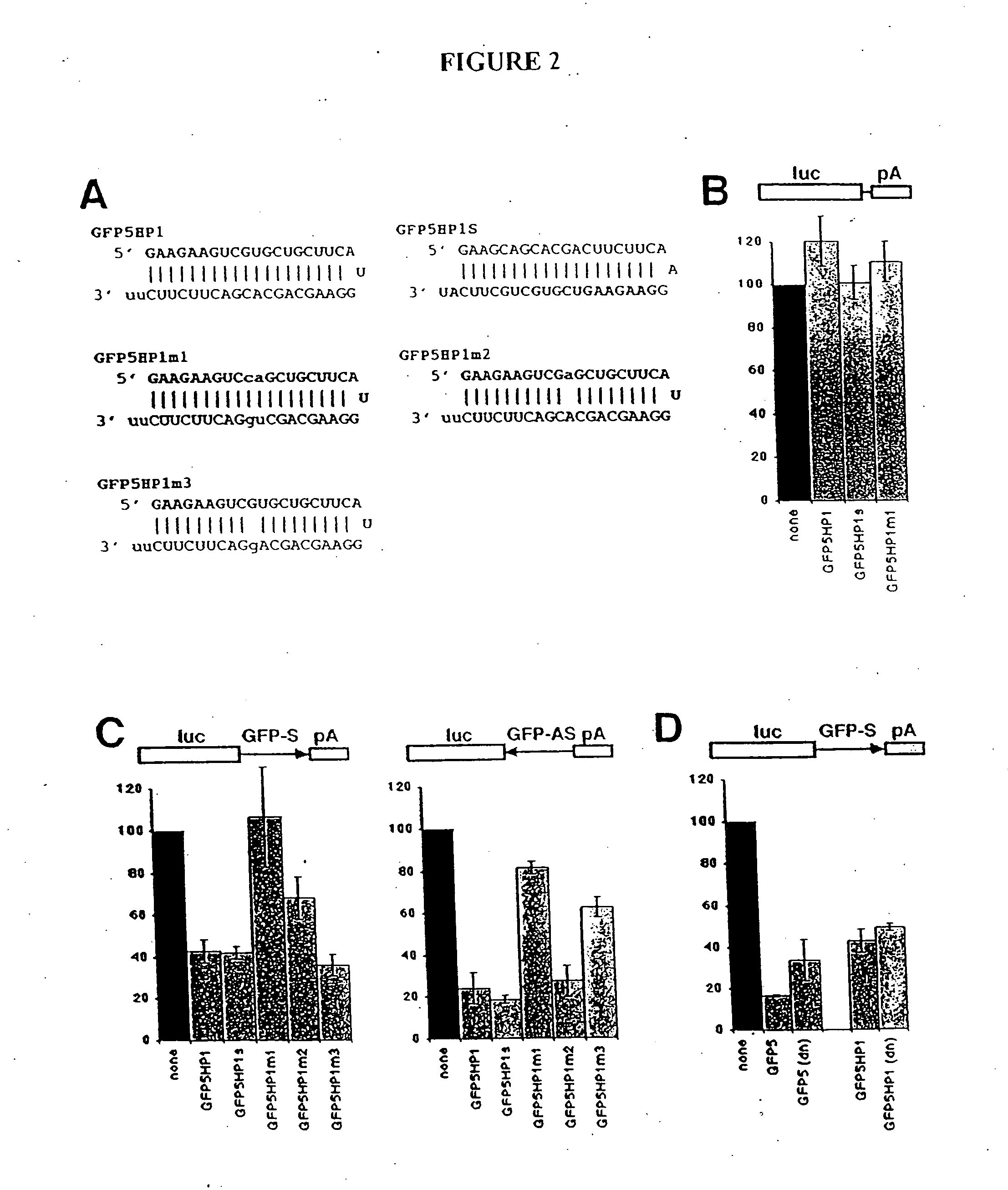
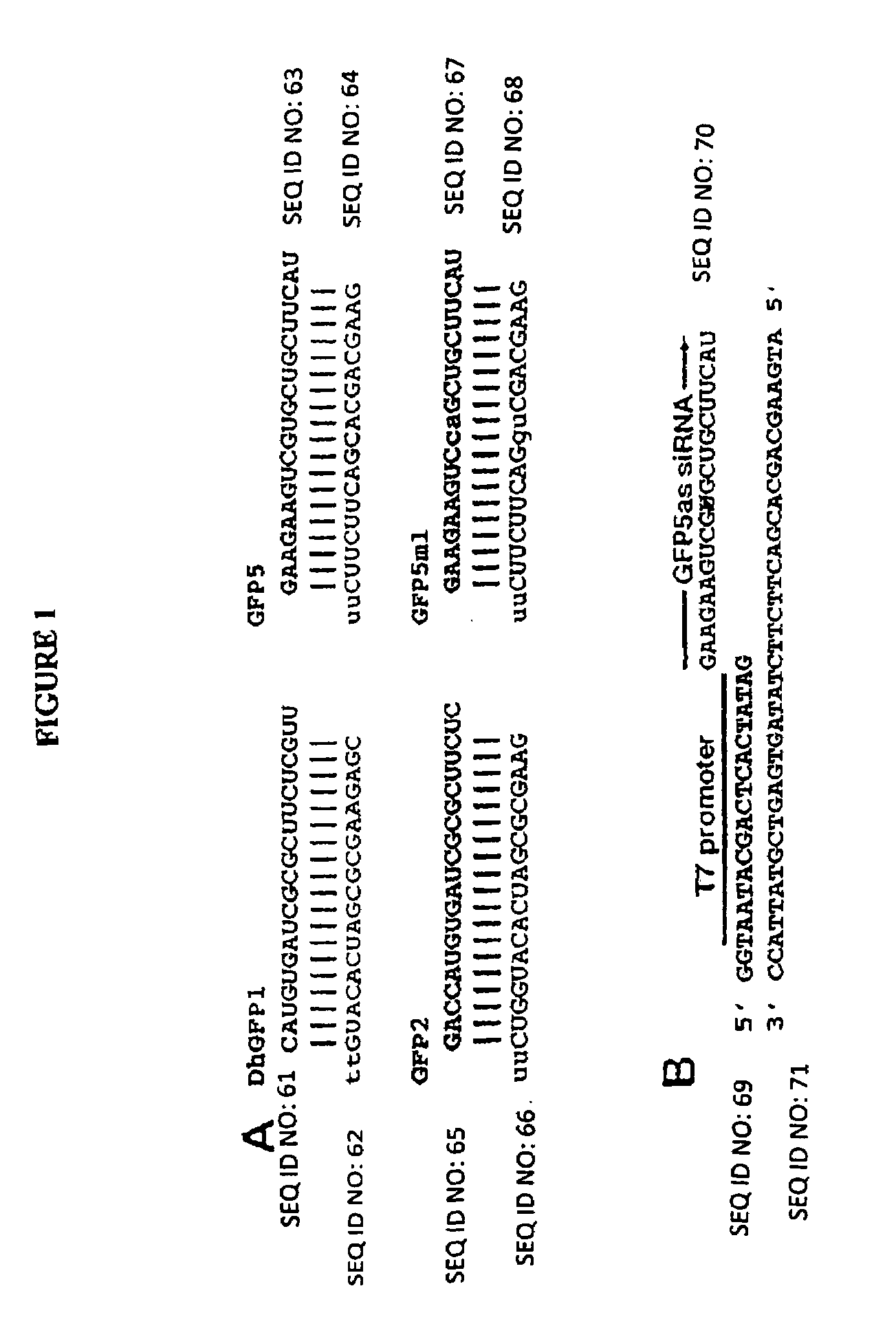
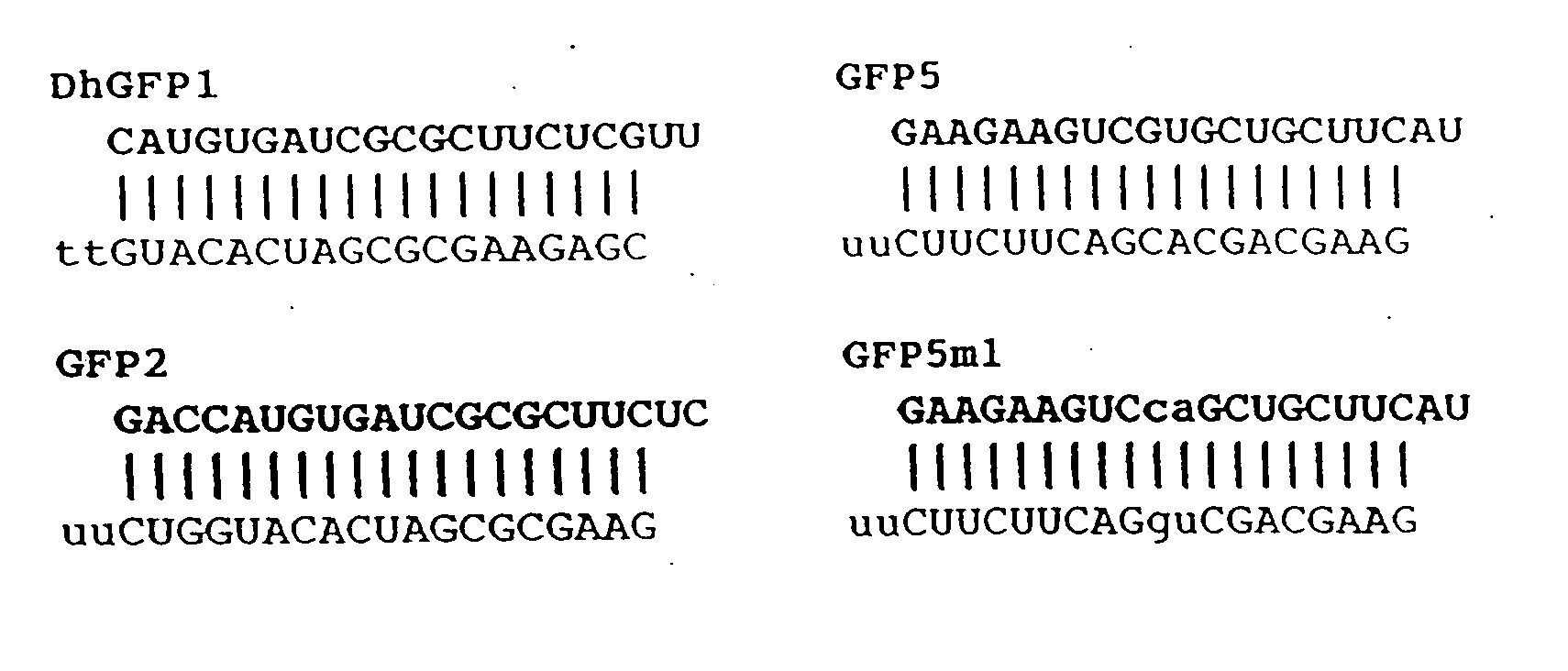Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
55 results about "RNA silencing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
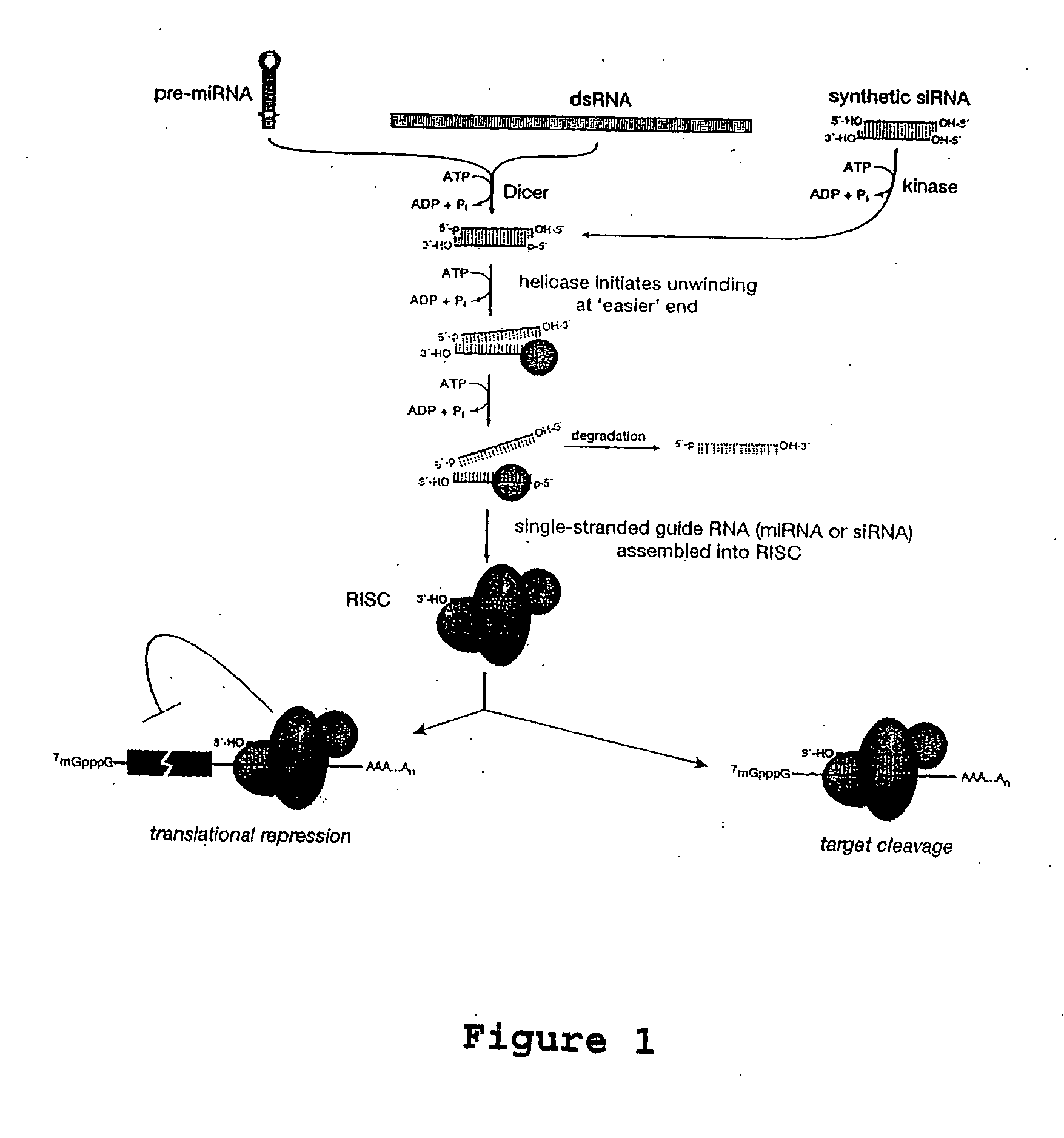
RNA silencing or RNA interference refers to a family of gene silencing effects by which gene expression is negatively regulated by non-coding RNAs such as microRNAs. RNA silencing may also be defined as sequence-specific regulation of gene expression triggered by double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). RNA silencing mechanisms are highly conserved in most eukaryotes. The most common and well-studied example is RNA interference (RNAi), in which endogenously expressed microRNA (miRNA) or exogenously derived small interfering RNA (siRNA) induces the degradation of complementary messenger RNA. Other classes of small RNA have been identified, including piwi-interacting RNA (piRNA) and its subspecies repeat associated small interfering RNA (rasiRNA).
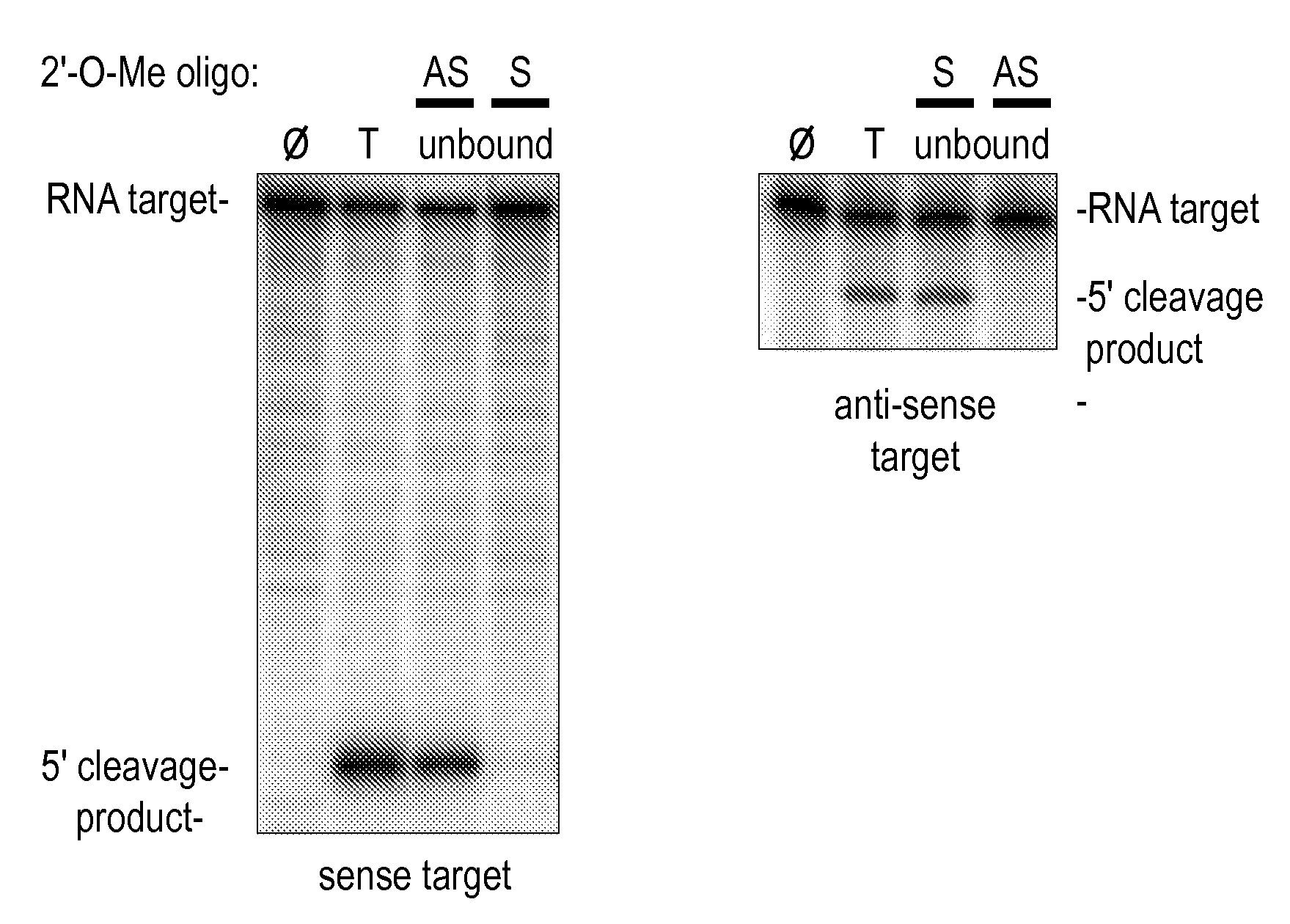
Sequence-specific inhibition of small RNA function
ActiveUS20050227256A1Suitable for useOrganic active ingredientsActivity regulationRegulatory rnaCytokine
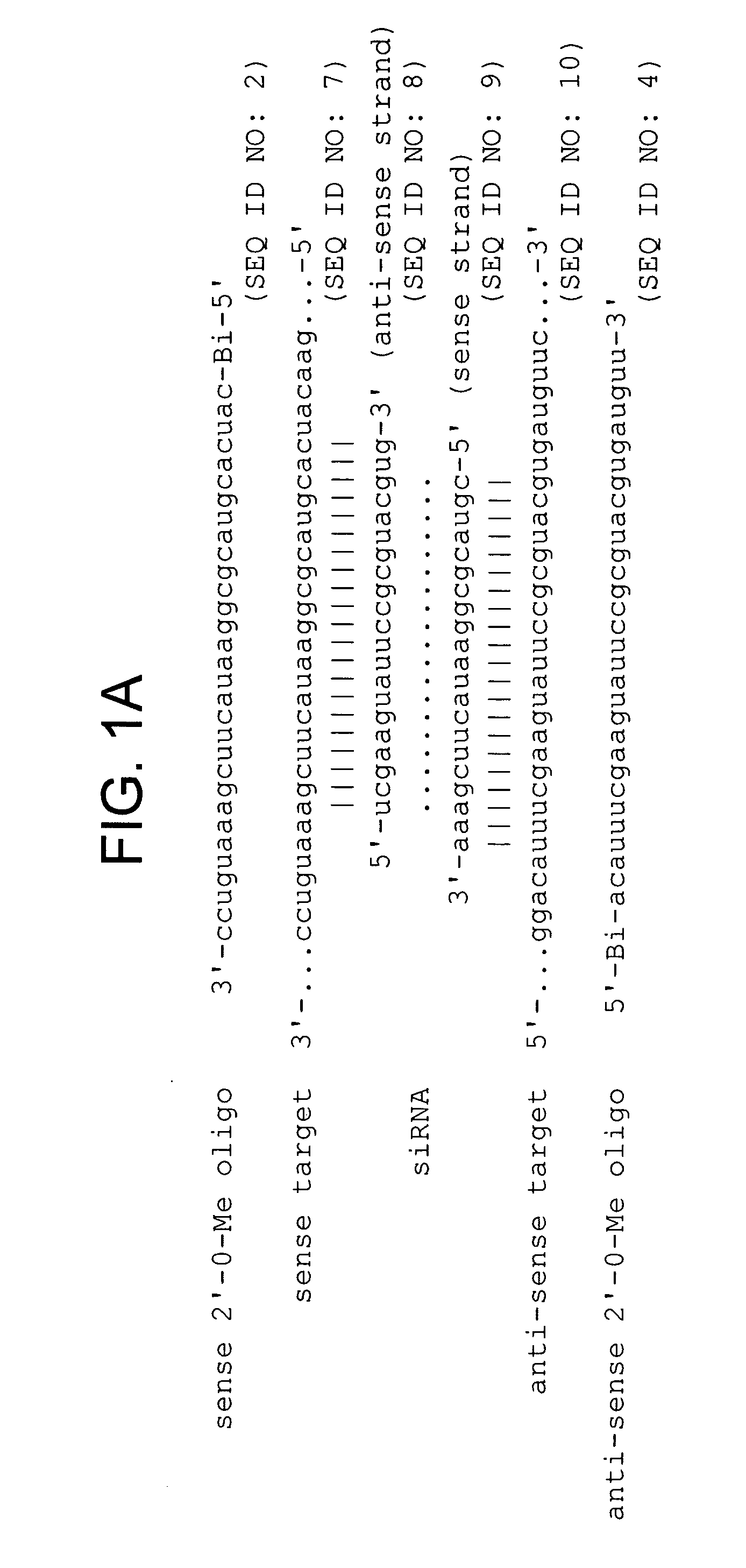
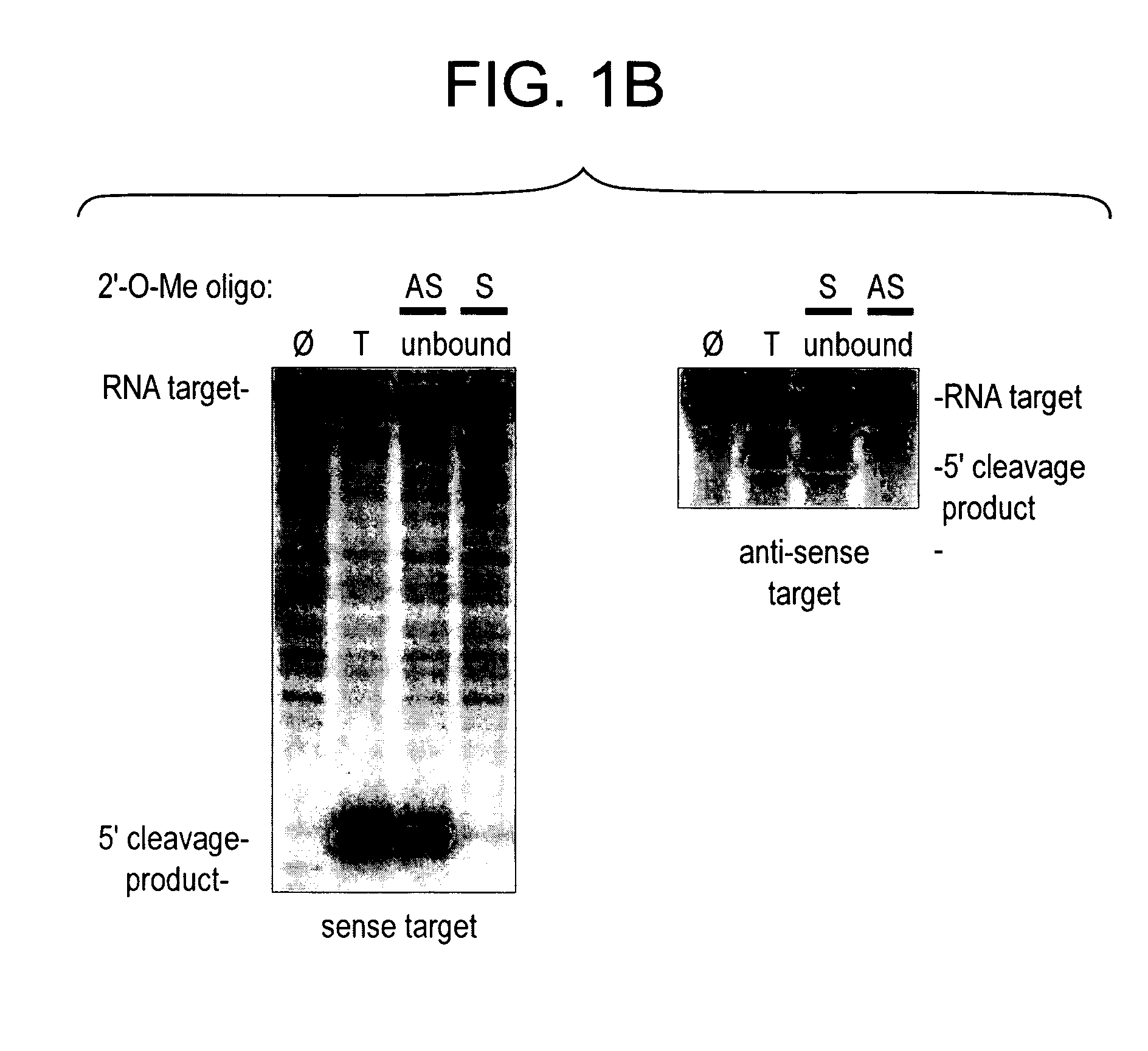
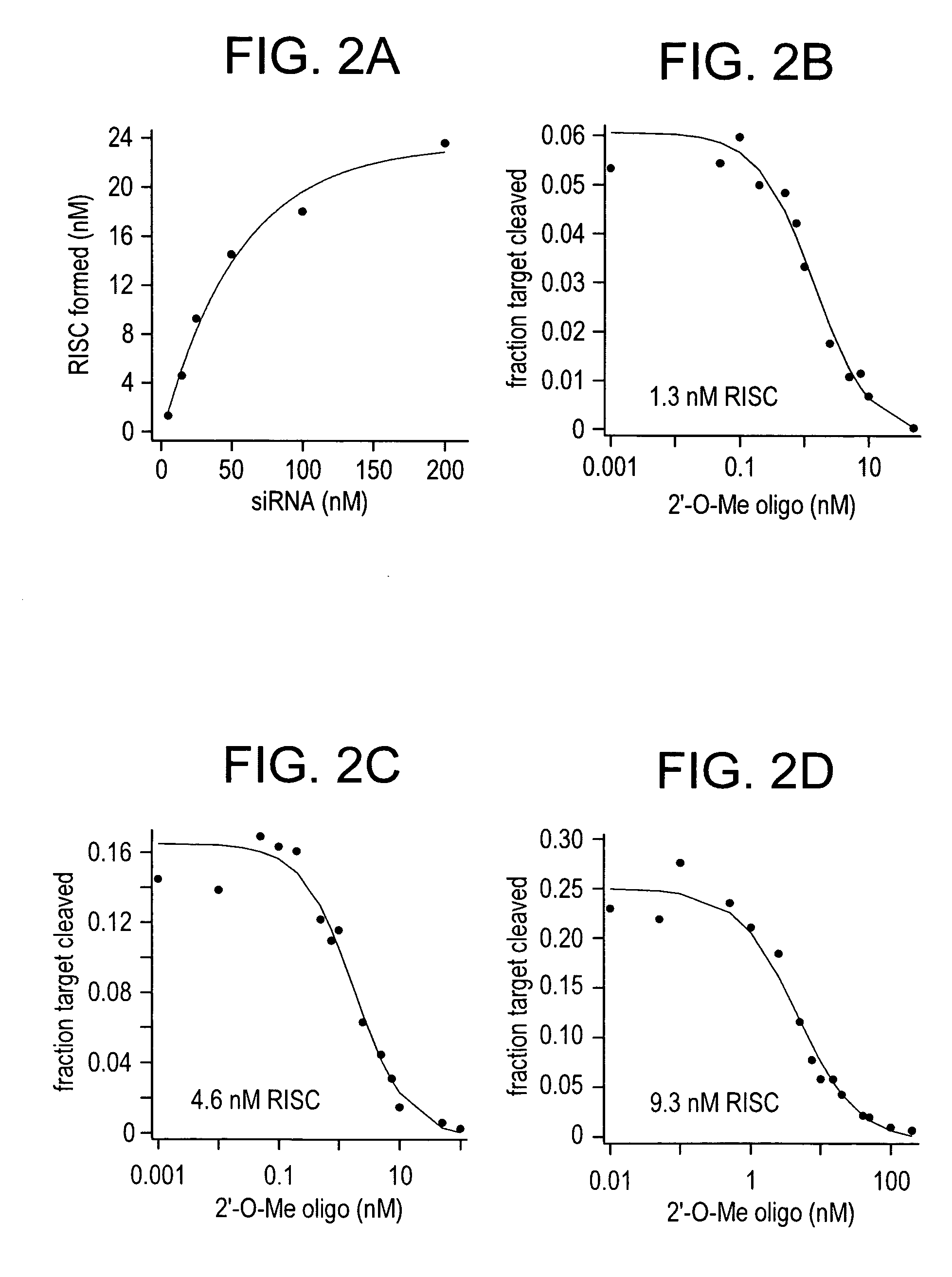
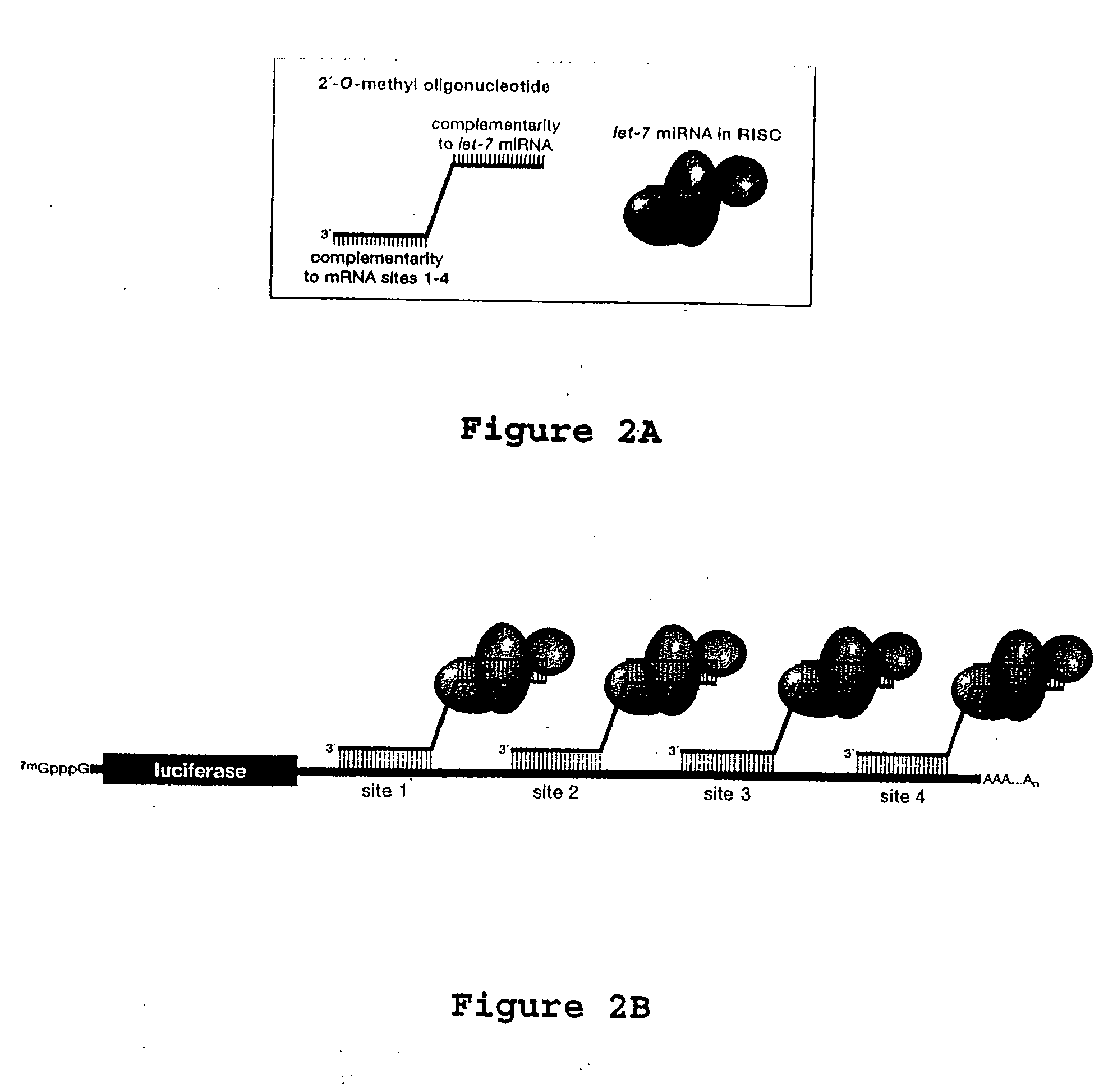
The present invention relates to the discovery of a method for inhibiting RNA silencing in a target sequence-specific manner. RNA silencing requires a set of conserved cellular factors to suppress expression of gene-encoded polypeptide. The invention provides compositions for sequence-specific inactivation of the RISC component of the RNA silencing pathway, and methods of use thereof. The RISC inactivators of the present invention enable a variety of methods for identifying and characterizing miRNAs and siRNAs, RISC-associated factors, and agents capable of modulating RNA silencing. Therapeutic methods and compositions incorporating RISC inactivators and therapeutic agents identified through use of RISC inactivators are also featured.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF
Dual functional oligonucleotides for use in repressing mutant gene expression
InactiveUS20050256072A1Improve in vivo stabilityNervous disorderSugar derivativesHuntingtons choreaHuntington's disease
The present invention is based, in part, on the discovery that endogenous mRNAs can be recruited for translational repression of target mRNAs. The RNA-silencing agents and the methods described herein, thereby provide a means by which to treat genetic (e.g., genetic neurodegenerative diseases such as Huntington's Disease) or non-genetic diseases by, for example, blocking the synthesis of proteins that contribute to the diseases. Accordingly the RNA-silencing agents of the present invention have an mRNA targeting moiety, a linking moiety, and an mRNA recruiting moiety.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Compositions and methods for enhancing discriminatory RNA interference
InactiveUS20070259827A1Improved allelic discriminationImprove discriminationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNon targetedGenetic disorder
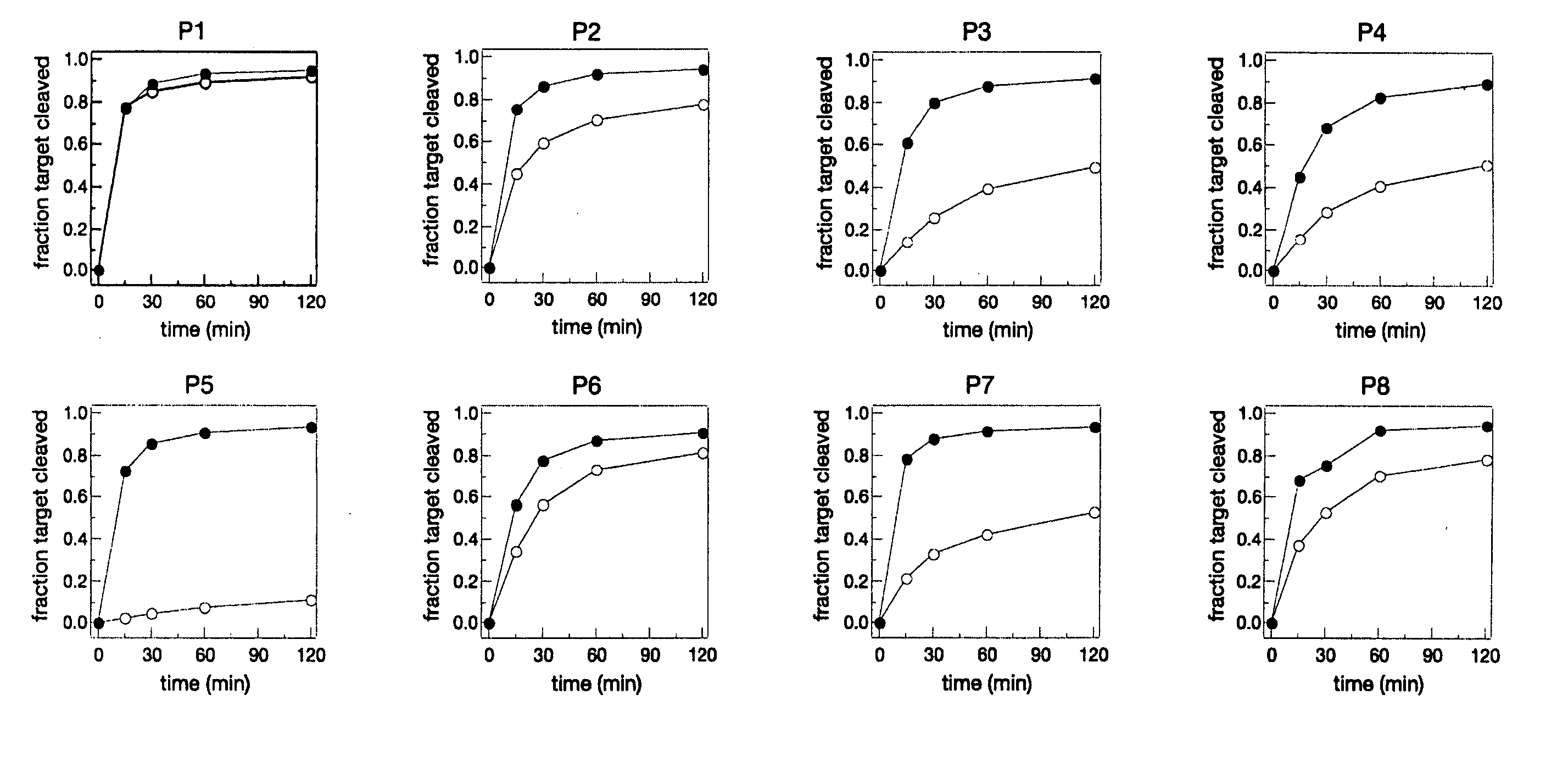
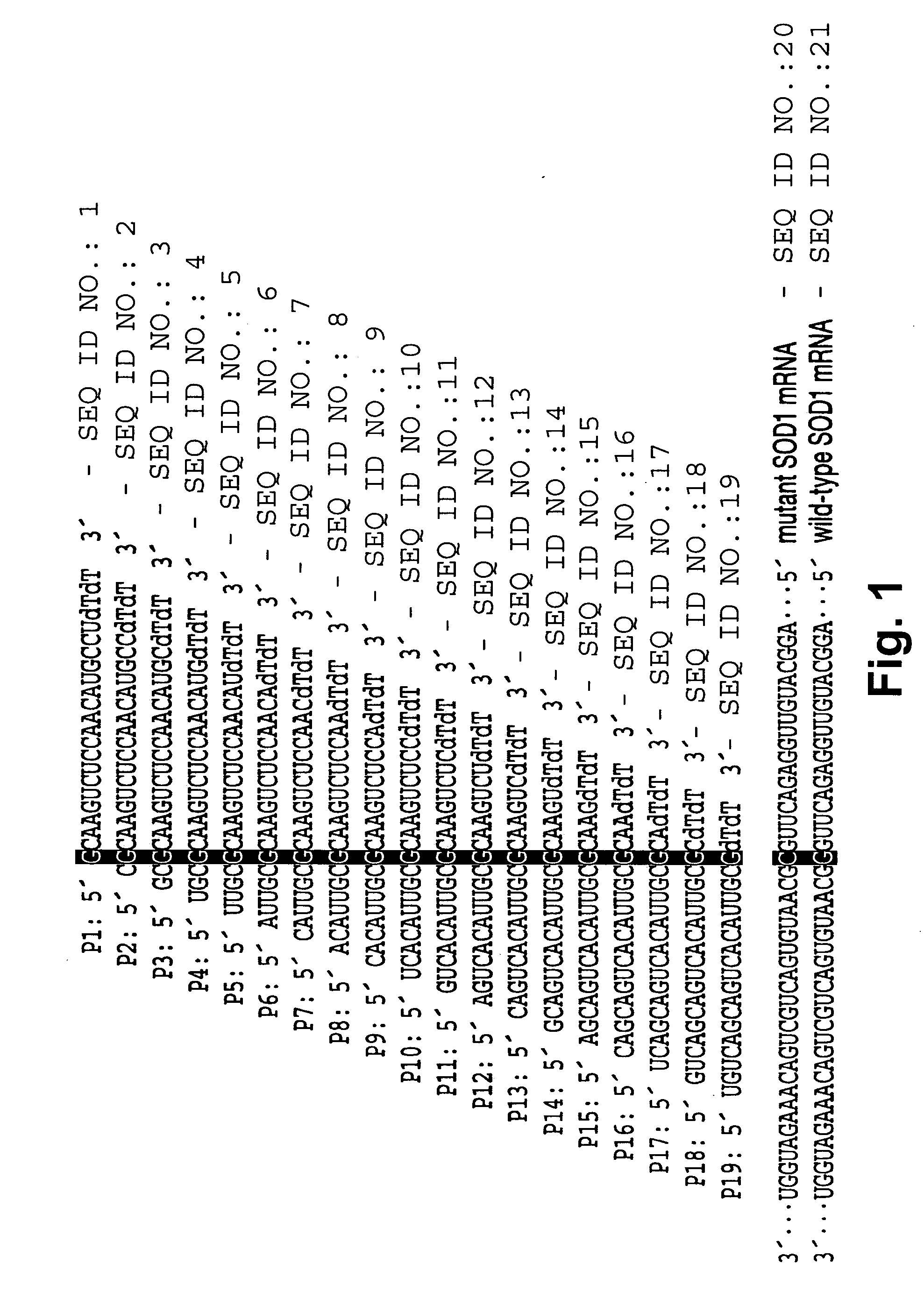
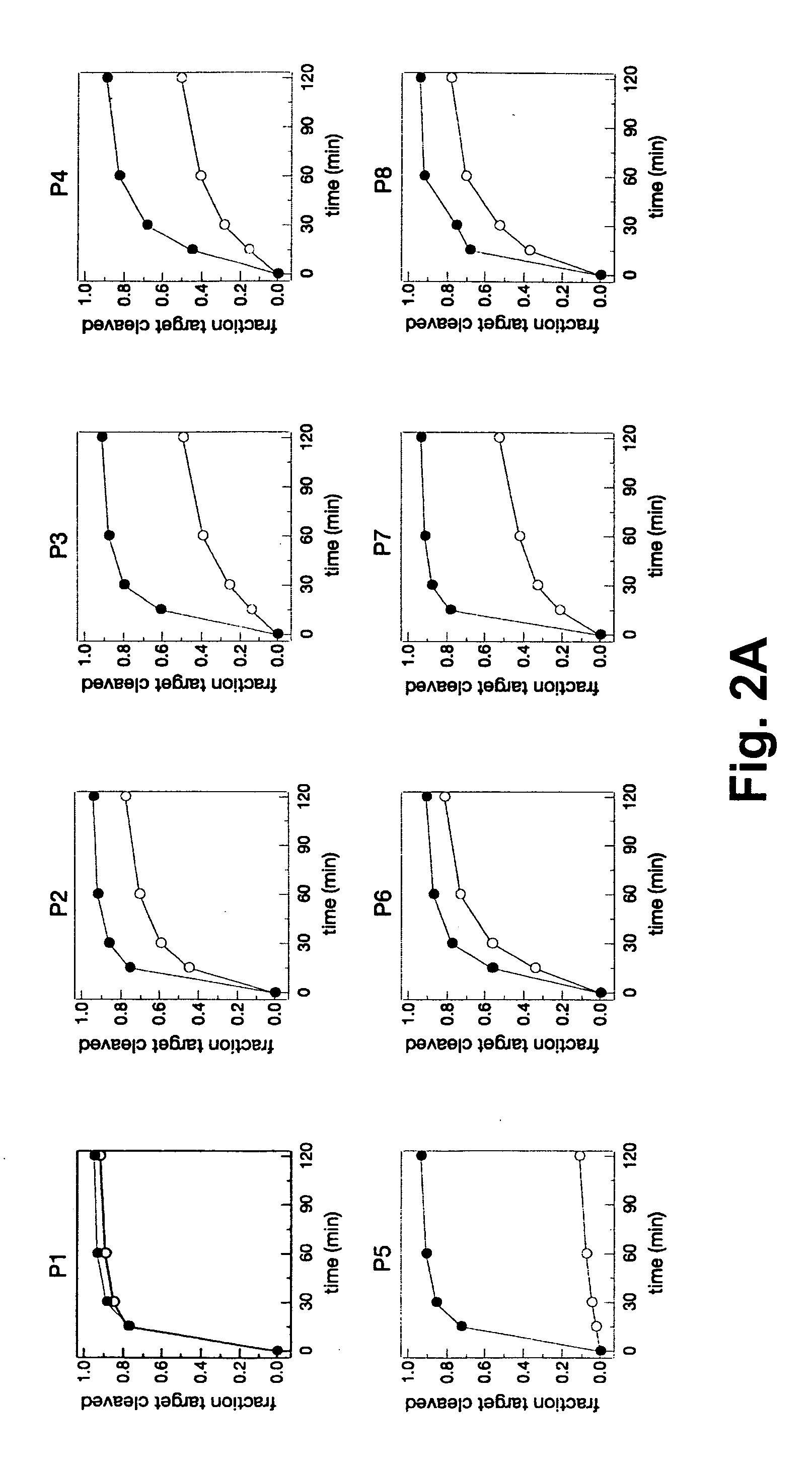
The present invention provides methods for enhancing discriminatory RNA silencing by RNA silencing agents. In particular, the invention provides methods for generating RNA silencing agents which can discriminate between target and non-target mRNAs that differ in sequence by only one nucleotide. Also provided are improved RNA silencing agents with enhanced discriminatory RNA silencing, e.g., single nucleotide discriminatory RNA silencing. The compositions and methods of the invention are useful in therapeutic strategies for treating genetic disorders associated with dominant, gain-of-function gene mutations.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS +1
MicroRNA vectors
InactiveUS20060063174A1Genetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementGene silencingIn vivo
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
MicroRNA vectors
InactiveUS7387896B2Genetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementIn vivoRegulator gene
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Dual functional oligonucleotides for use as anti-viral agents
InactiveUS20060293267A1Improve in vivo stabilitySugar derivativesActivity regulationTarget mrnaViral infection
The present invention is based, in part, on the discovery that endogenous mRNAs, such as viral miRNAs, can be recruited for translational repression of target mRNAs, such as viral target mRNAs. The RNA-silencing agents and the methods described herein, thereby provide a means of treating viral infections, of treating diseases or disorders caused by viral infections, or for preventing viral propagation. The RNA-silencing agents of the present invention have an mRNA targeting moiety, a linking moiety, and a viral miRNA recruiting moiety.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF
Conserved HBV and HCV sequences useful for gene silencing
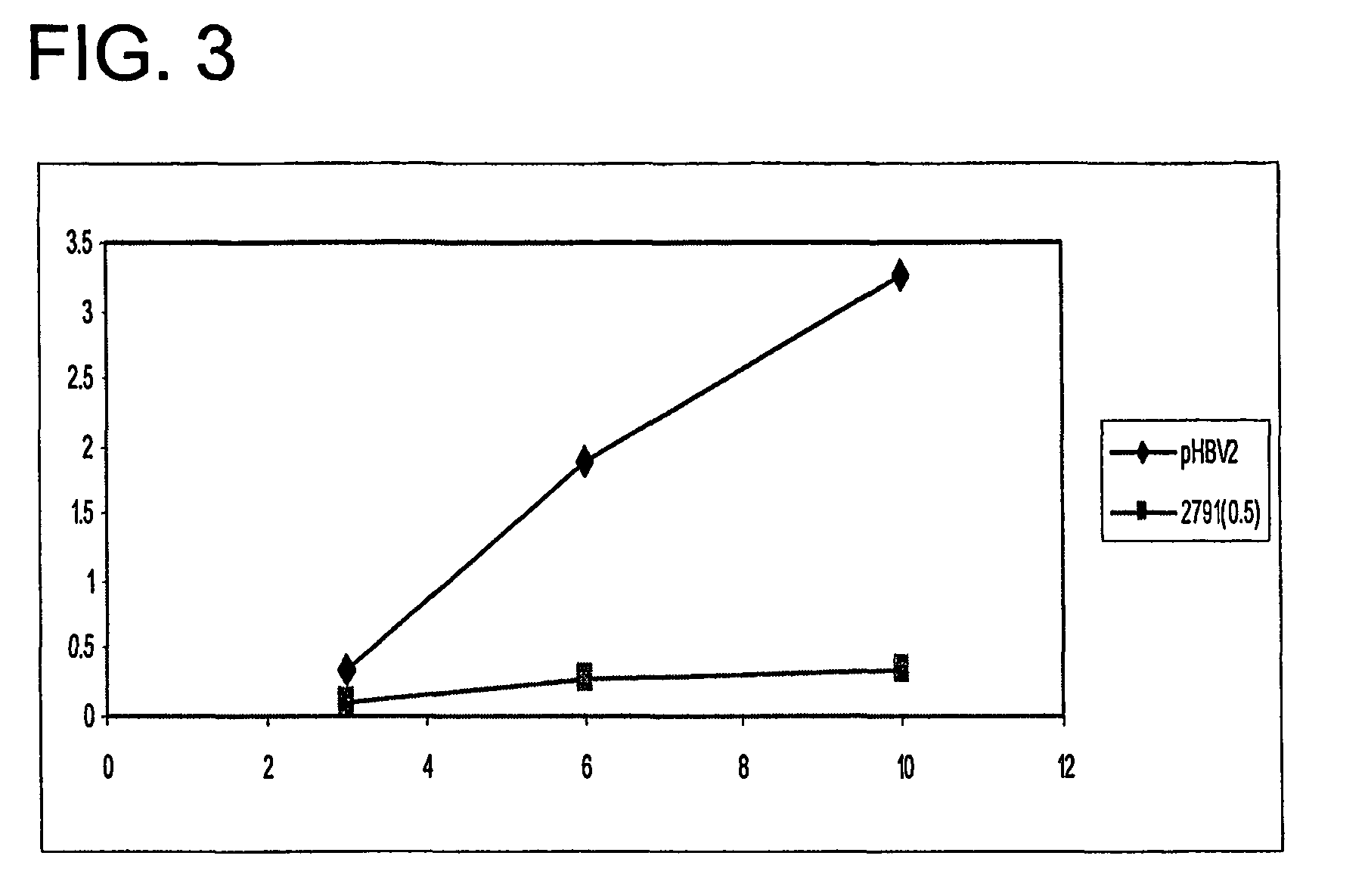
Conserved consensus sequences from known hepatitis B virus strains and known hepatitis C virus strains, which are useful in inhibiting the expression of the viruses in mammalian cells, are provided. These sequences are useful to silence the genes of HBV and HCV, thereby providing therapeutic utility against HBV and HCV viral infection in humans.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
Compositions for bacterial mediated gene silencing and methods of using the same
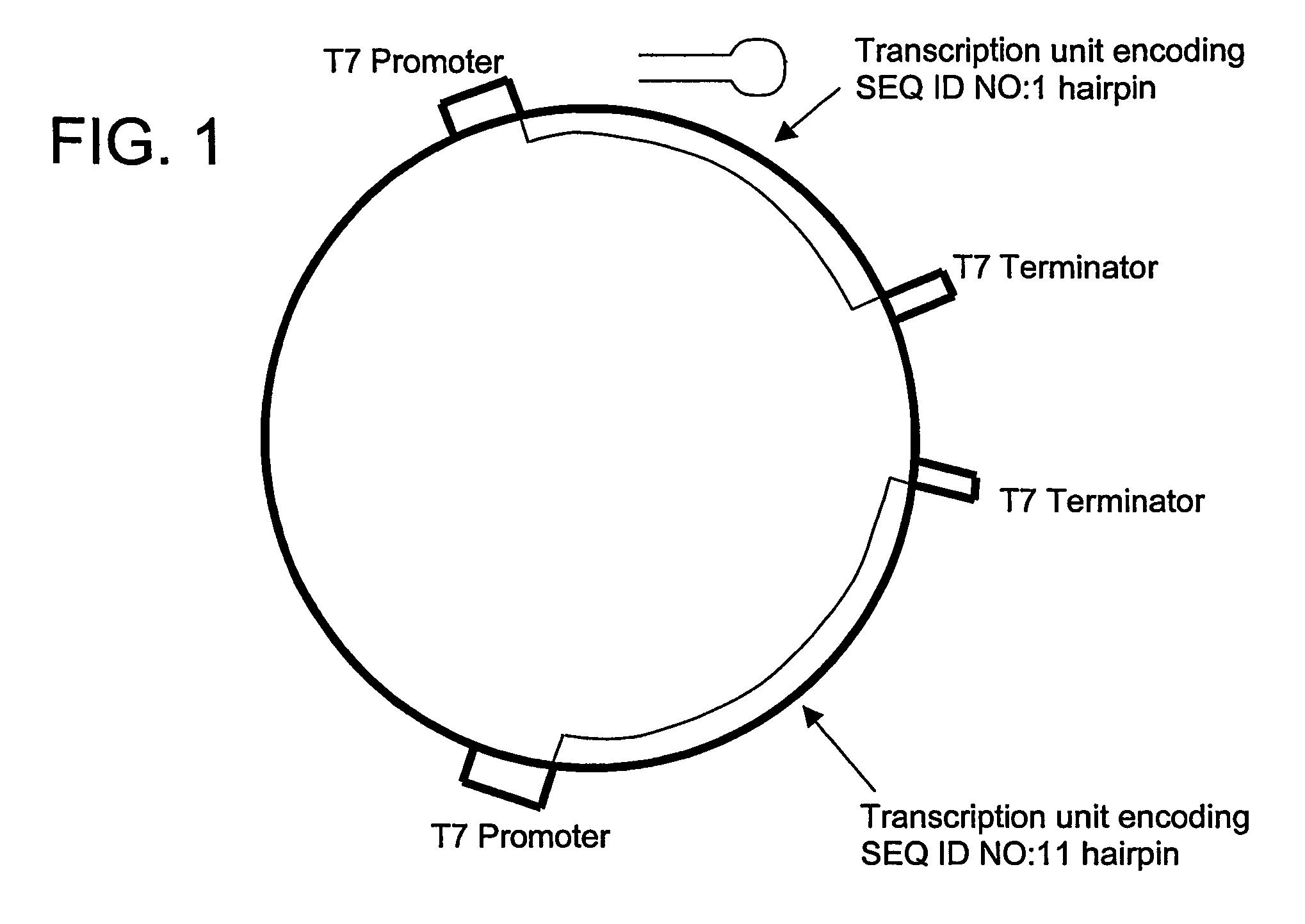
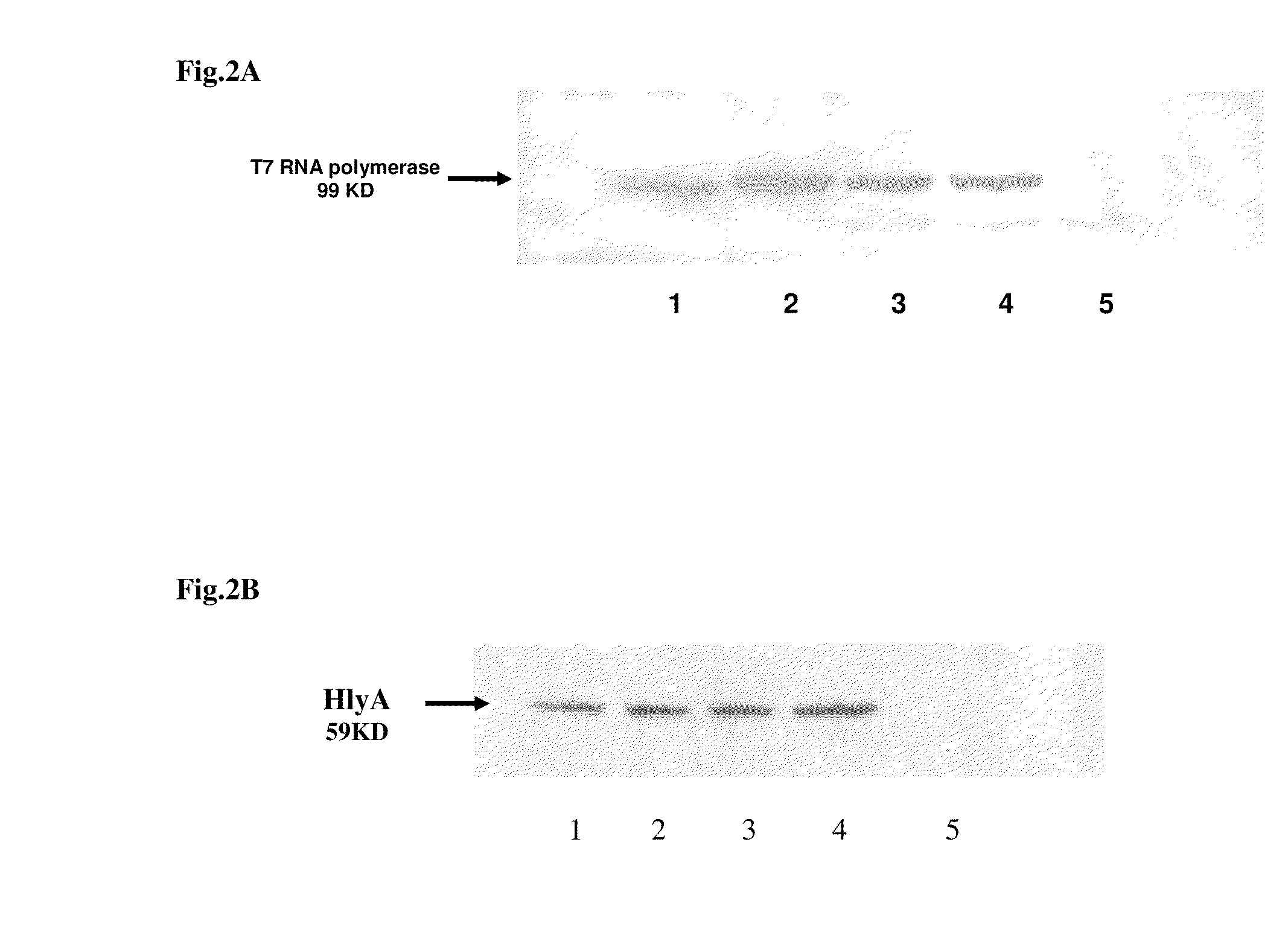
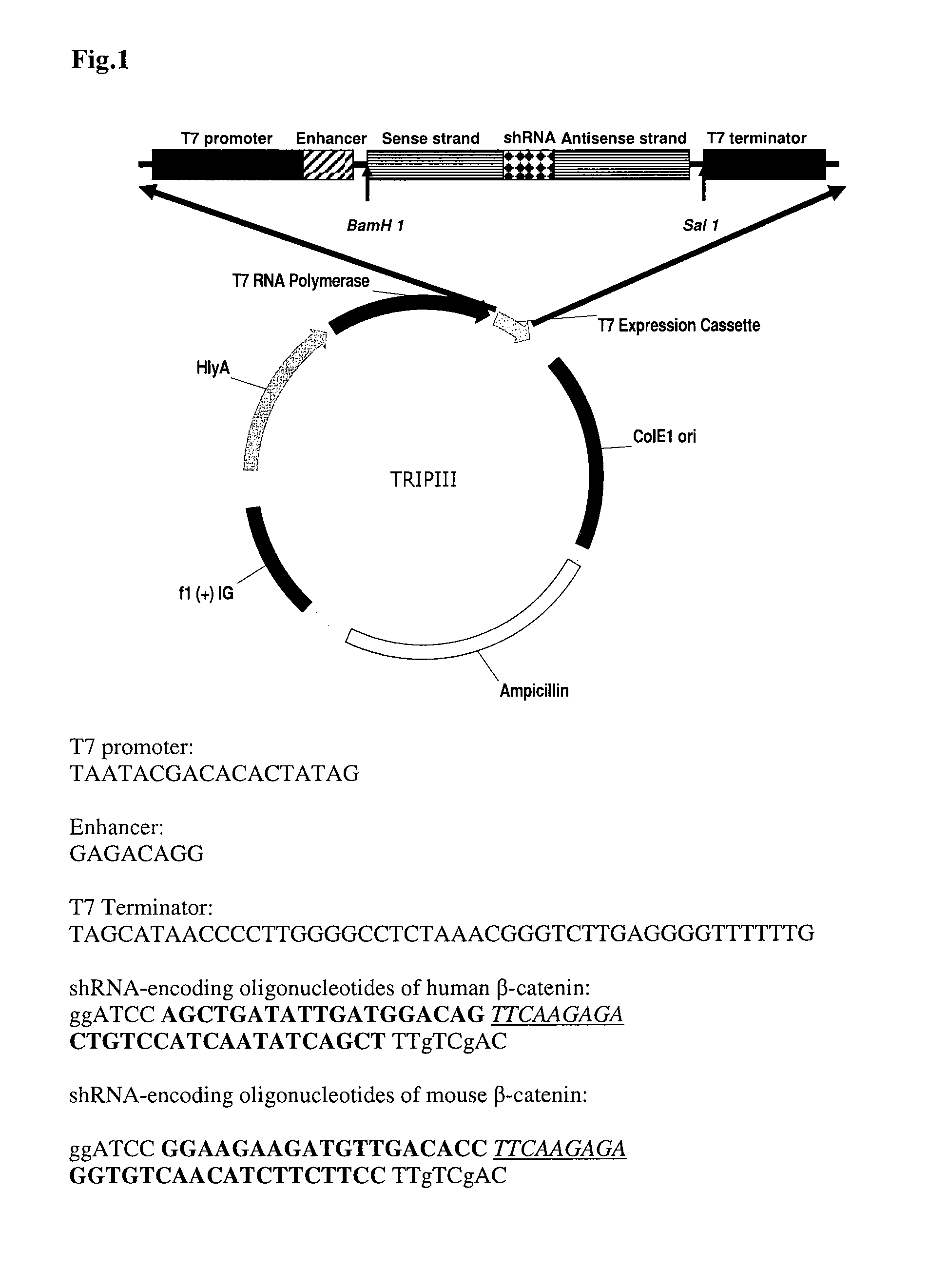
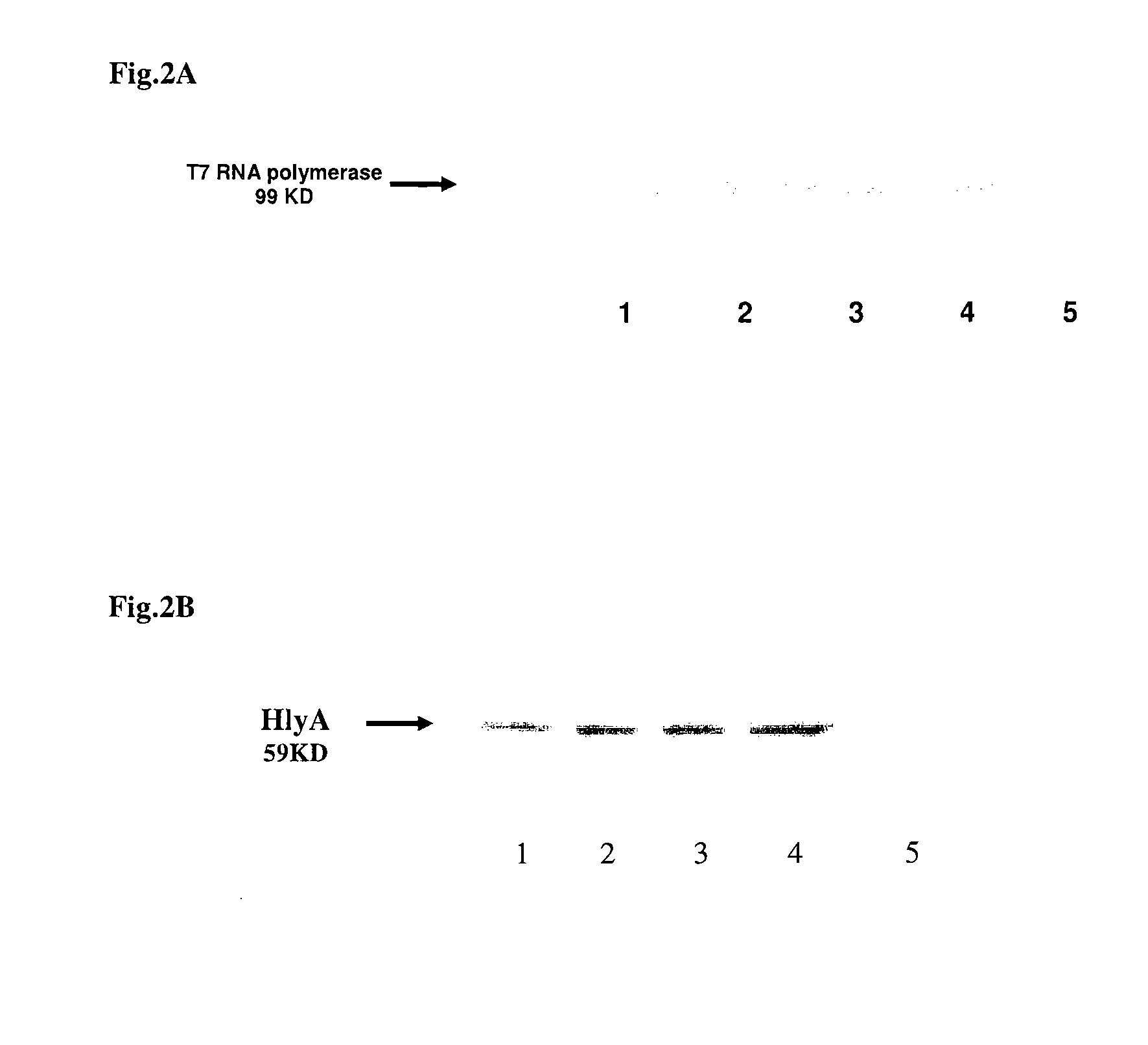
The invention features compositions and methods for delivering small interfering (siRNAs), e.g., shRNAs, to host cells using non-pathogenic strains of Salmonella bacteria containing nucleic acid expression constructs encoding shRNAs. In this process, shRNA expressed by the Salmonella silences or knocks down genes of interest (target genes) inside target cells. The nucleic acid expression constructs of the invention include an RNA polymerase (e.g., a T7 polymerase), an RNA polymerase promoter (e.g., a T7 polymerase promoter), and an RNA polymerase terminator (e.g., a T7 polymerase terminator). The Salmonella bacteria can also include, on the same or different nucleic acid construct, an endosomal release factor (e.g., HlyA).
Owner:GUO HONGNIAN +2
Polygalacturonase arrestin gene CaPGIP1 and disease resistance technology thereof
InactiveCN102250921AImprove disease resistanceReduced disease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationNicotiana tabacumPentagalacturonic acid
The invention belongs to the field of plant biotechnology, in particular provides a polygalacturonase arrestin gene CaPGIP1 cloned from hot pepper, the gene can specially inhibit the activity of polygalacturonase (PGs) secreted by pathogenic bacteria. The invention provides the function verification techniques based on the coding of the gene, such as protein making, enzyme activity testing, gene silencing, transgenic excessive expression and the like and the application of the techniques. Based on the gene and protein operation technology, the CaPGIP1 gene is proved to effectively participate in the defense reaction of hot pepper under the induction of a stress facto, and can inhibit the activity of polygalacturonase (PGs) secreted by various pathogenic bacteria. The gene silence and transgenic technology are further used for proving that the silence or less expression of the gene in the hot pepper reduces the disease resistance of a host, and the excessive expression of the gene in the transgenic tobacco can enhance the resistance; therefore, the gene codes an important disease-resistance related protein. The invention provides an important technological reserve for transforming the polygalacturonase arrestin (PGIP) gene and cultivating a new disease-resistant variety.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
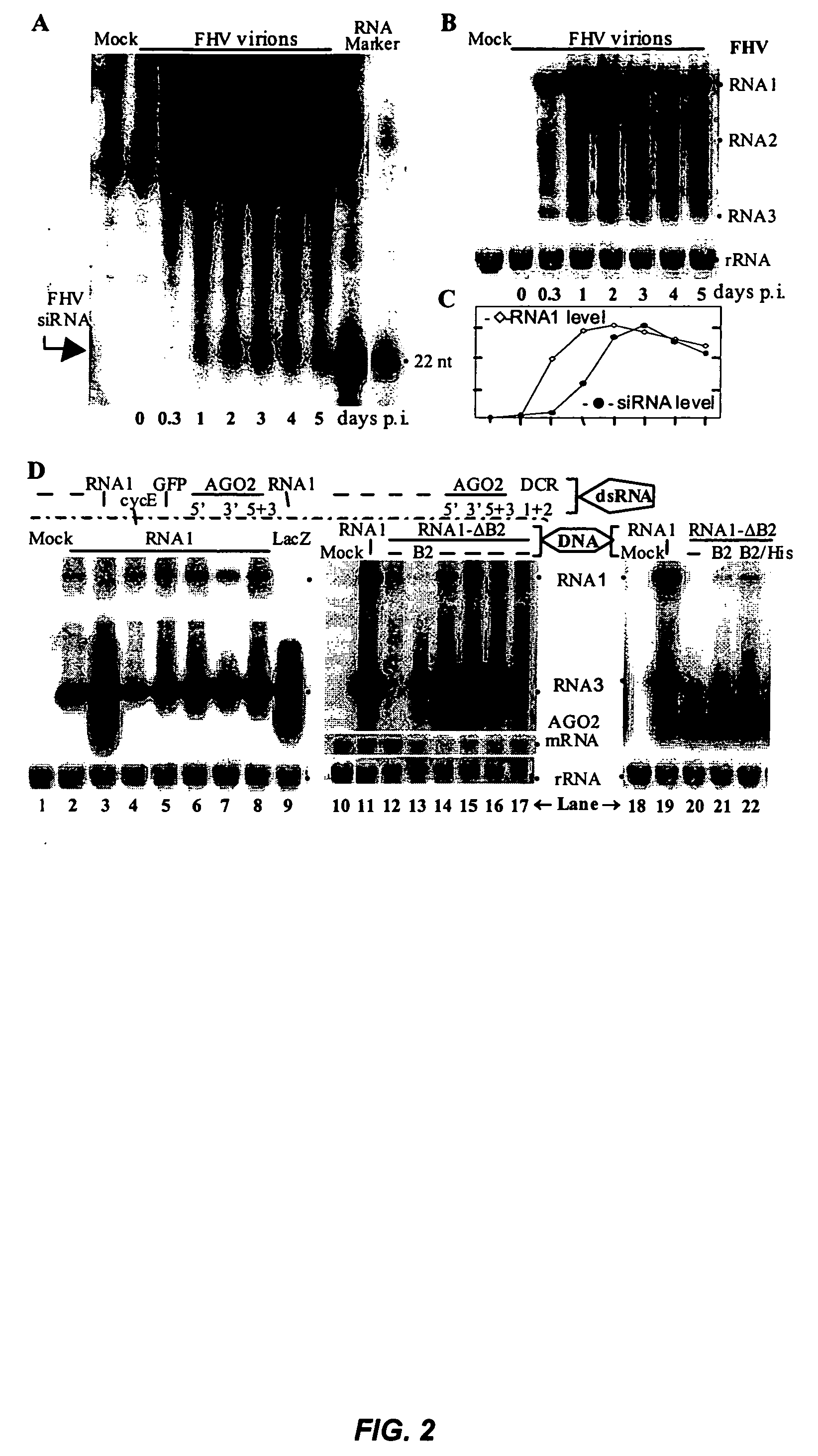
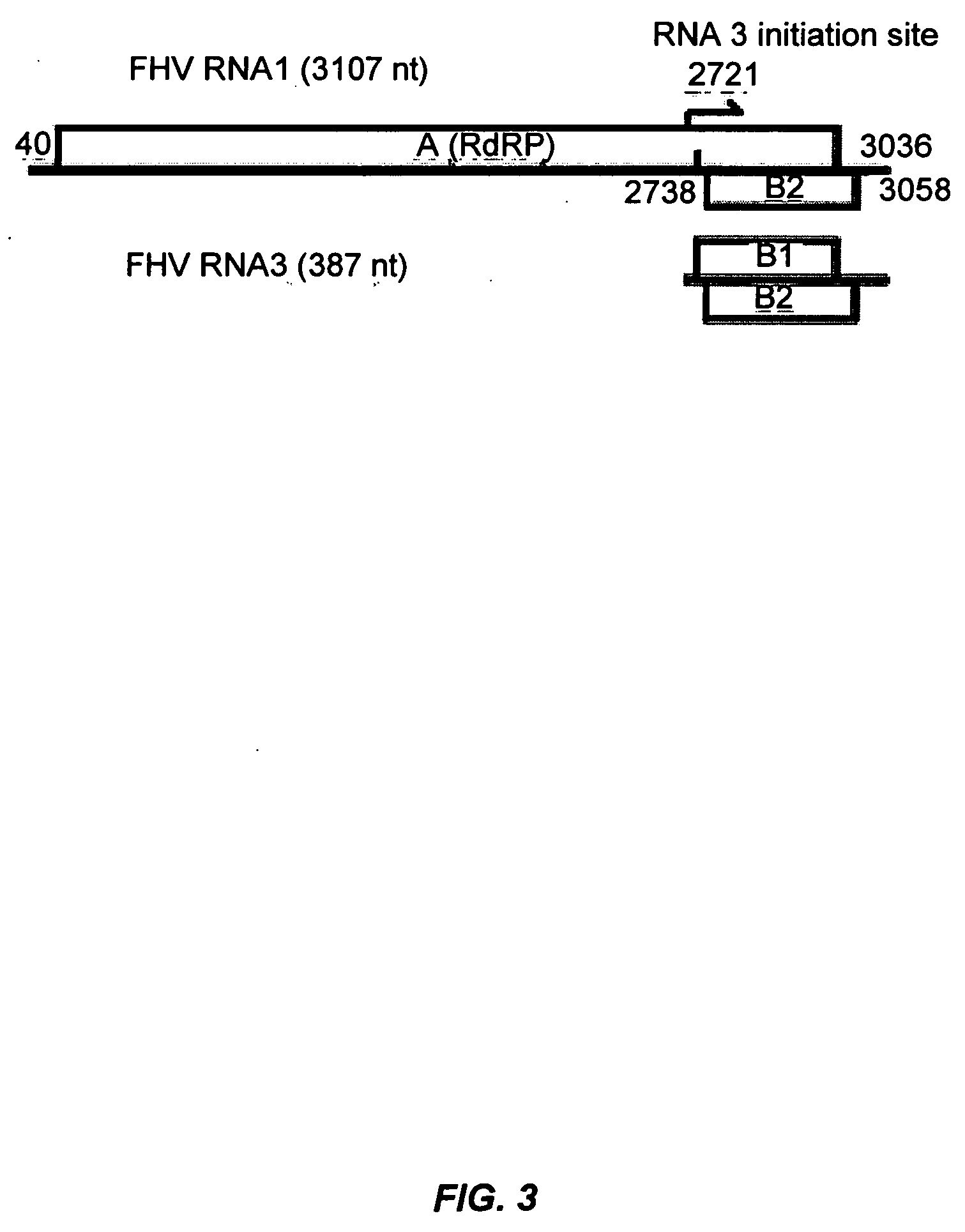
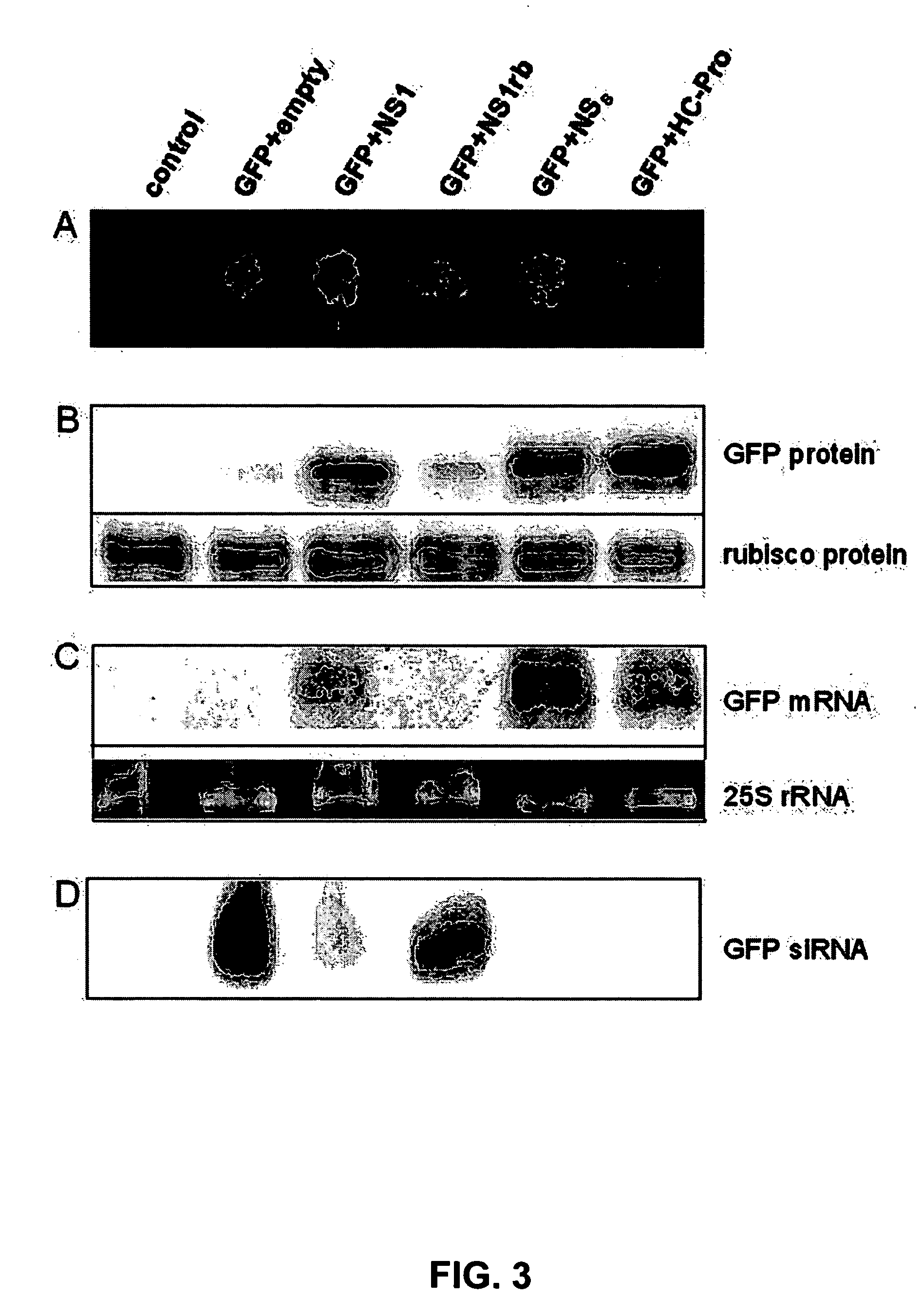
RNA silencing in animals as an antiviral defense
InactiveUS20060094055A1Inhibit expressionAvoid virus infectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideSequence analysisSuppressor
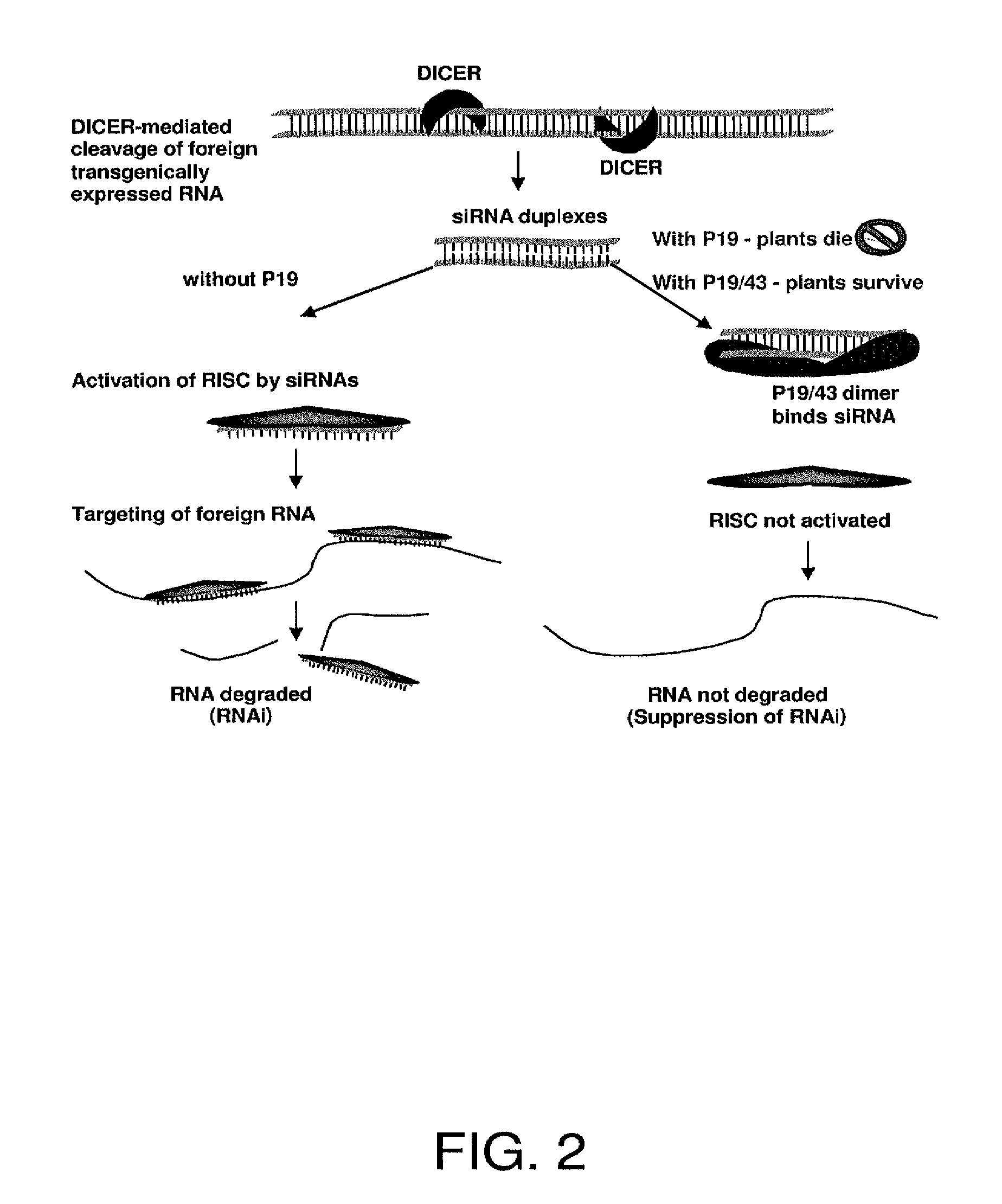
The present invention provides recombinant DNA constructs for inactivation of viral or endogenous genes in a cell, wherein the construct comprises viral sequence sufficient to activate RNA silencing. In another aspect, the invention provides methods for identifying RNA silencing suppressors by sequence analysis and functional tests. In yet another aspect, the invention provides a method for identifying inhibitors of RNA silencing suppressors. In still other aspects, the invention comprises methods for identifying genes in the antiviral RNA silencing pathway, enhancers of the antiviral pathway, and methods of treating or preventing viral infections using enhancers of the pathway.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Delivery method
The present invention relates, in general, to RNA silencing and, in particular, to a method of effecting targeted delivery of an RNA silencing moiety using a targeting moiety that binds to a cell surface receptor and mediates internalization of the RNA silencing moiety to be accessible to Dicer. Also provided is a chimeric nucleic acid molecule comprised of a targeting moiety and an RNA silencing moiety, wherein the targeting moiety is an aptamer and the RNA silencing moiety comprises a Dicer substrate.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Gene relevant to papillary thyroid tumors
The invention relates to a gene relevant to papillary thyroid tumors and an application thereof. According to the base sequence of the gene, real-time and quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primers are designed and synthesized; the expression level of long-chain non-coding RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) transcribed by the gene is detected in a papillary thyroid carcinoma clinical case specimen; the result shows remarkable reducing of the expression level of the long-chain non-coding RNA in papillary thyroid tumor tissues and the long-chain non-coding RNA of the gene silencing can remarkably promote the growth of thyroid cancer cells. The gene relevant to the papillary thyroid tumors is expected to prepare preparations used in papillary thyroid carcinoma auxiliary diagnosis, gene therapy, curative effect prediction or prognosis.
Owner:BOZHOU CITY THE NEW HEALTH TECH CO LTD
Una oligomers having reduced off-target effects in gene silencing
InactiveUS20150307881A1Reduced off-target effect in gene silencingReduce off-target effectsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderOligomerGene silencing
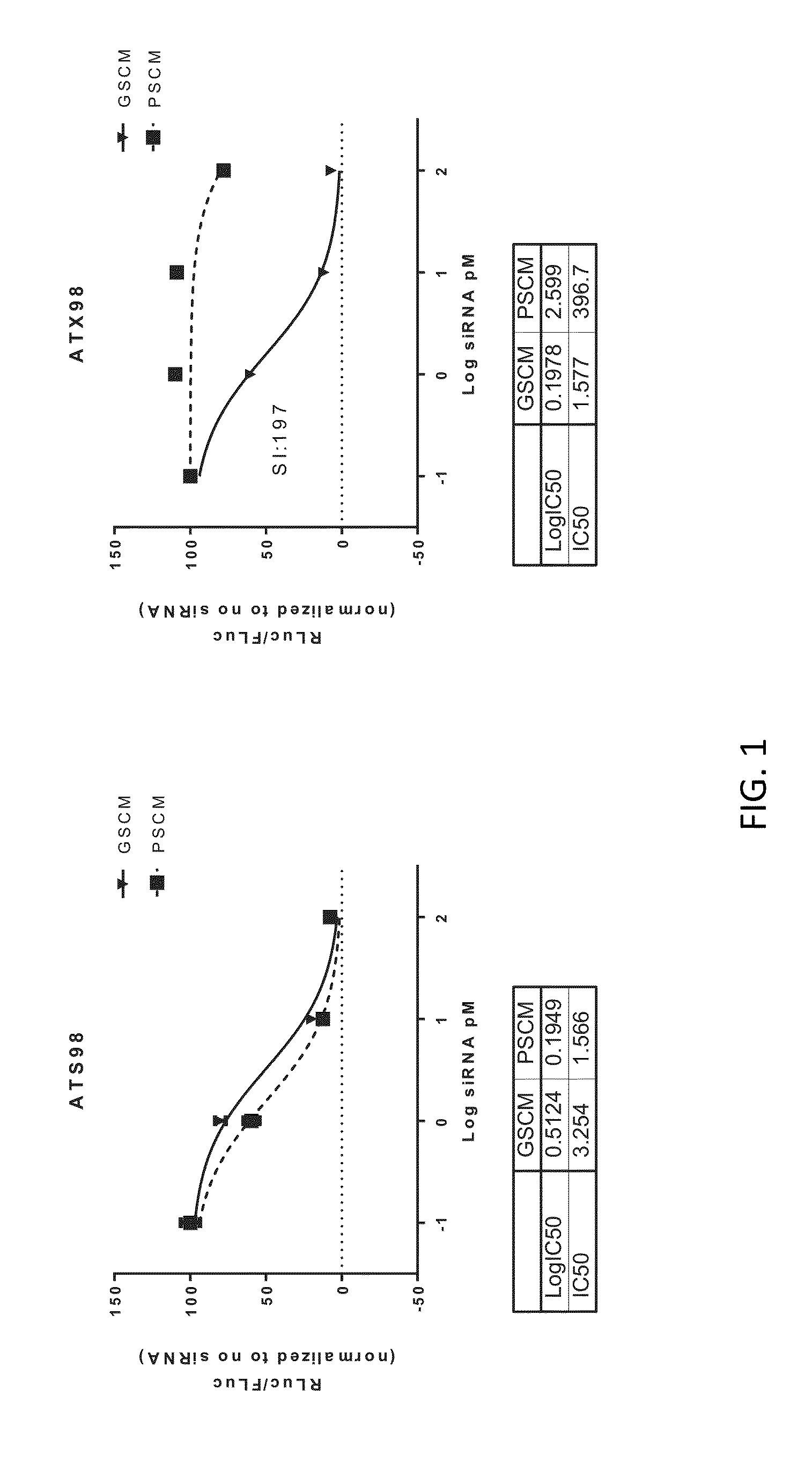
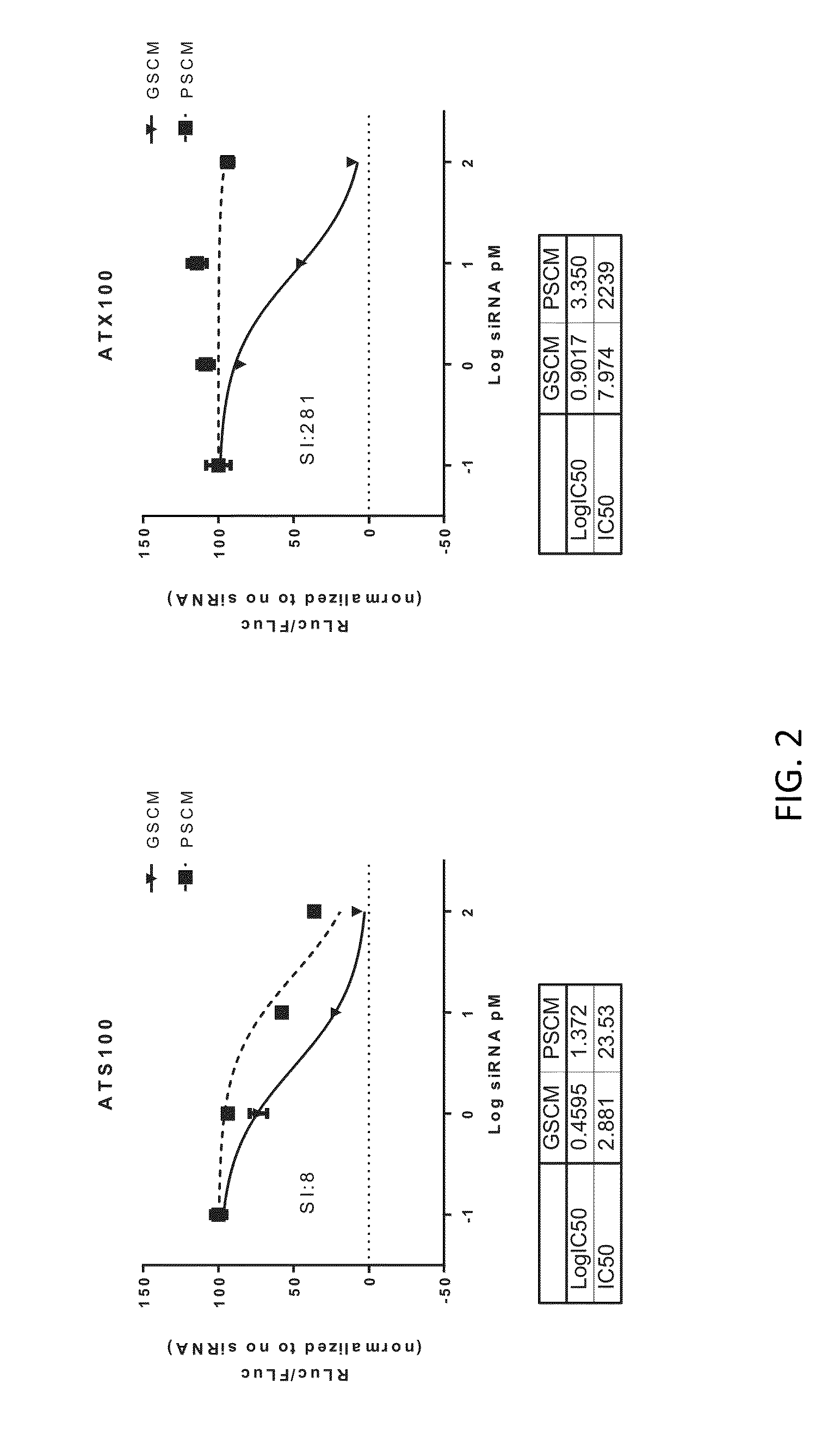
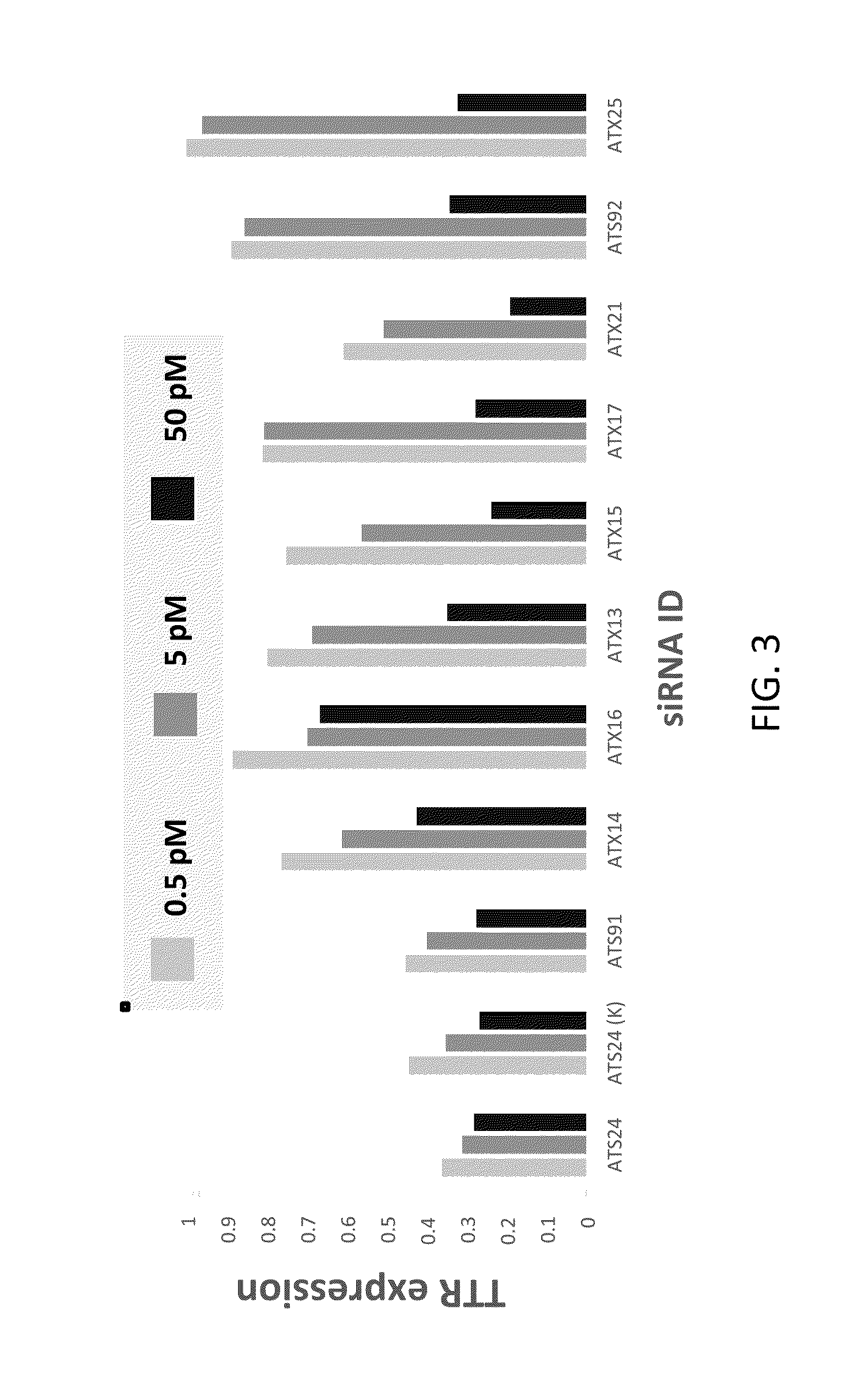
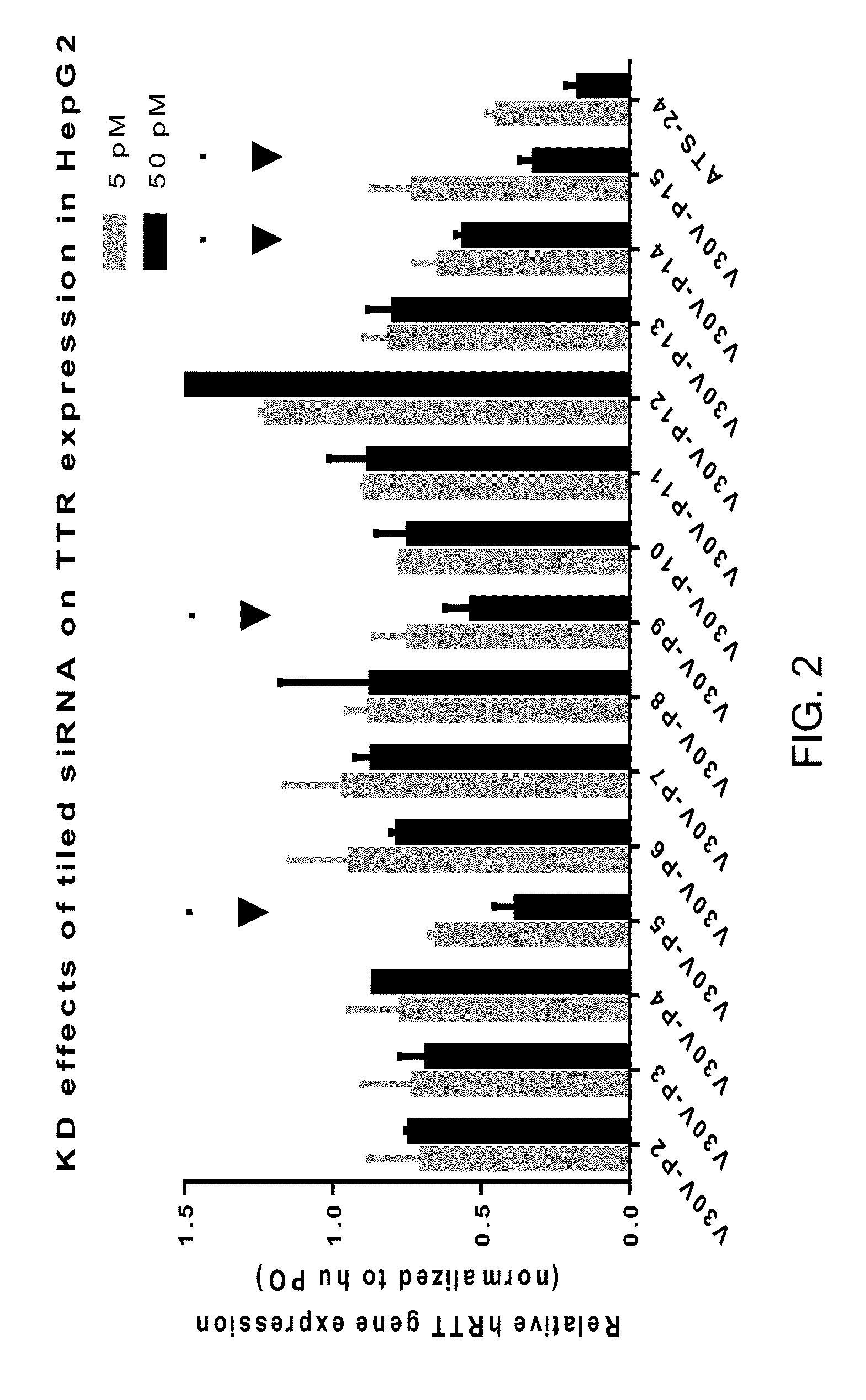
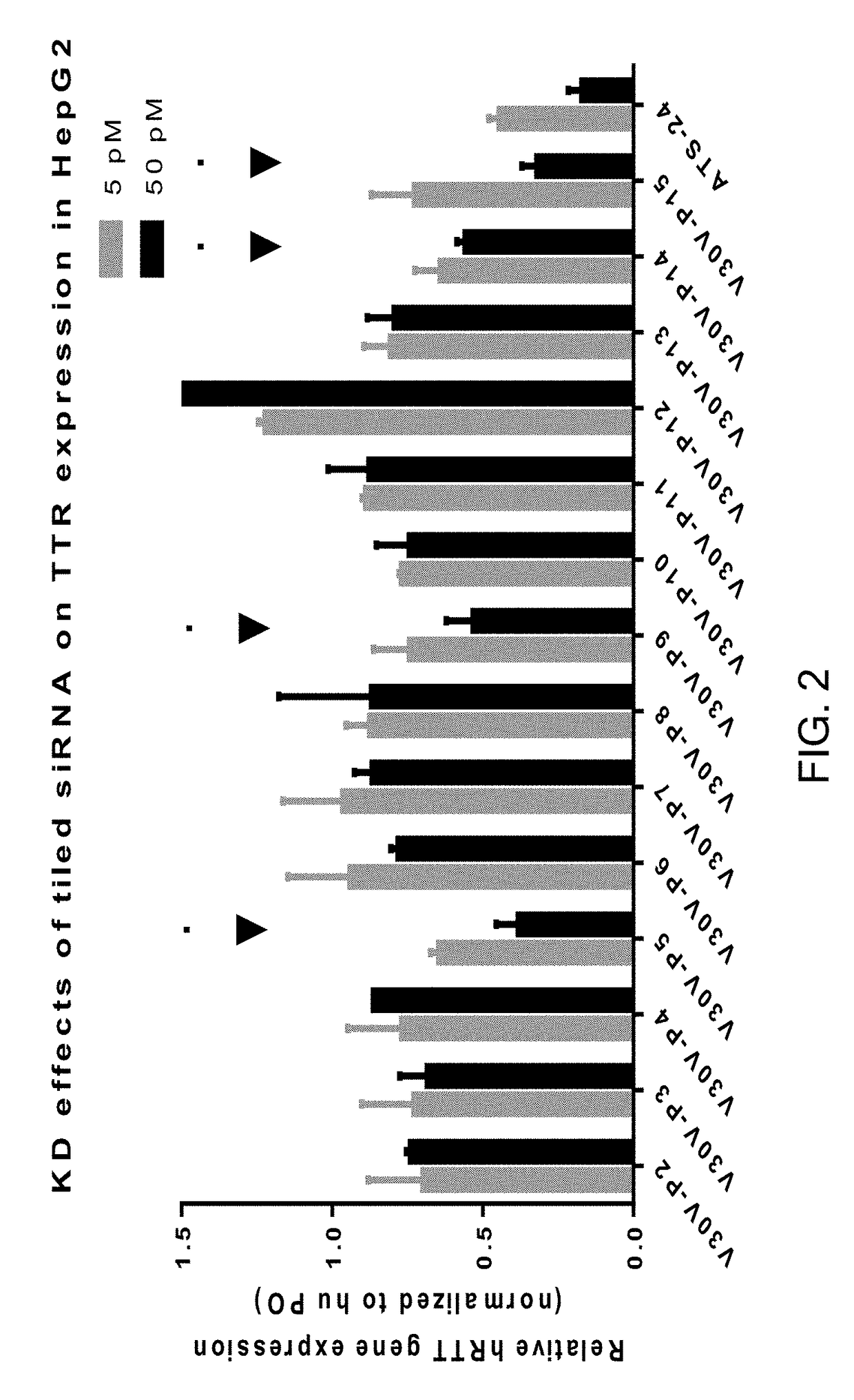
This invention provides UNA oligomers for gene silencing with reduced off-target effects. The UNA oligomers can have a first strand and a second strand, each of the strands being 19-29 monomers in length, the monomers being UNA monomers and various nucleic acid monomers. Embodiments include pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating or preventing TTR-related amyloidosis with reduced off-target effects by administering a UNA oligomer to a subject.
Owner:ARCTURUS THERAPEUTICS
Transthyretin allele selective una oligomers for gene silencing
This invention provides UNA oligomers for selectively inhibiting V30M TTR expression, which can be used in treating amyloidosis. The UNA oligomers can have a first strand and a second strand, each of the strands being 19-29 monomers in length, the monomers being UNA monomers and nucleic acid monomers. Embodiments include pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating or preventing TTR-related amyloidosis by administering a UNA oligomer to a subject.
Owner:ARCTURUS THERAPEUTICS
Transthyretin allele selective UNA oligomers for gene silencing
ActiveUS9982259B2Reduces peripheral neuropathyOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderOligomerGene silencing
This invention provides UNA oligomers for selectively inhibiting V30M TTR expression, which can be used in treating amyloidosis. The UNA oligomers can have a first strand and a second strand, each of the strands being 19-29 monomers in length, the monomers being UNA monomers and nucleic acid monomers. Embodiments include pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating or preventing TTR-related amyloidosis by administering a UNA oligomer to a subject.
Owner:ARCTURUS THERAPEUTICS
Expressional enhancers from viruses
InactiveUS20050260166A1Suppression problemHigh expressionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsSuppressorVirus
The present invention discloses that vertebrate viruses encode RNA silencing suppressors / expressional enhancers which enable them to overcome host intracellular defense responses. This has paved the way for the development of protein production systems and for production systems of (recombinant) virus particles, and of vaccines directed against vertebrate viruses.
Owner:PHYTOVATION BV
Methods for determining specificity of RNA silencing and for genetic analysis of the silenced gene or protein
InactiveUS20060287272A1Microbiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsProtein targetMutated protein
Methods and kits for determining the specificity of siRNAs for their targets are provided. Also provided is a method for performing genetic analysis of the target protein or gene using different versions of a synthetic gene to complement the phenotype induced by RNAi-mediated silencing of the target protein and / or gene of interest. Finally, a method for treating genetic disorders associated with production of mutated proteins is also disclosed.
Owner:BOYCE THOMPSON INST FOR PLANT RES
Sequence-specific inhibition of small RNA function
The present invention relates to the discovery of a method for inhibiting RNA silencing in a target sequence-specific manner. RNA silencing requires a set of conserved cellular factors to suppress expression of gene-encoded polypeptide. The invention provides compositions for sequence-specific inactivation of the RISC component of the RNA silencing pathway, and methods of use thereof. The RISC inactivators of the present invention enable a variety of methods for identifying and characterizing miRNAs and siRNAs, RISC-associated factors, and agents capable of modulating RNA silencing. Therapeutic methods and compositions incorporating RISC inactivators and therapeutic agents identified through use of RISC inactivators are also featured.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
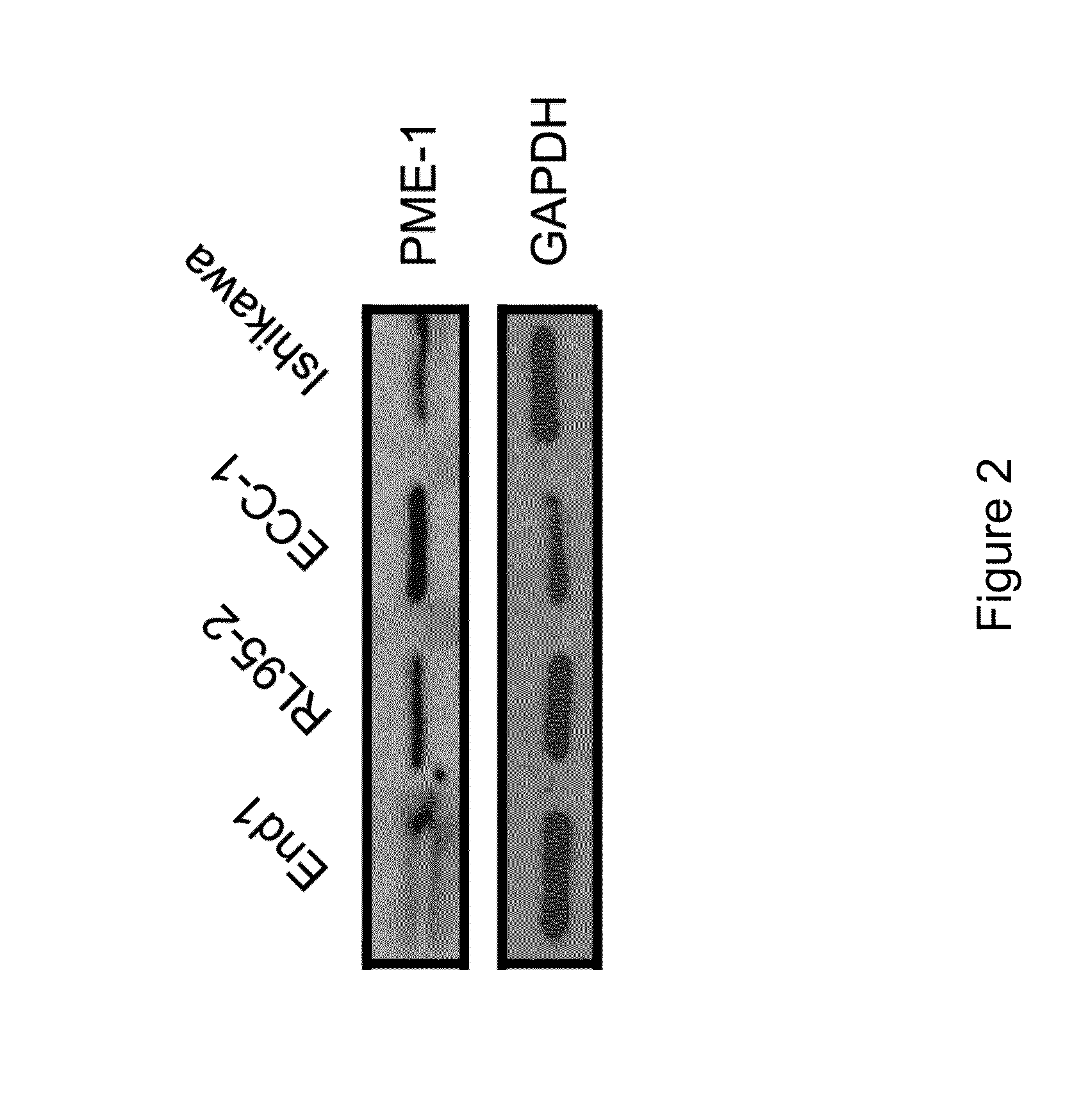
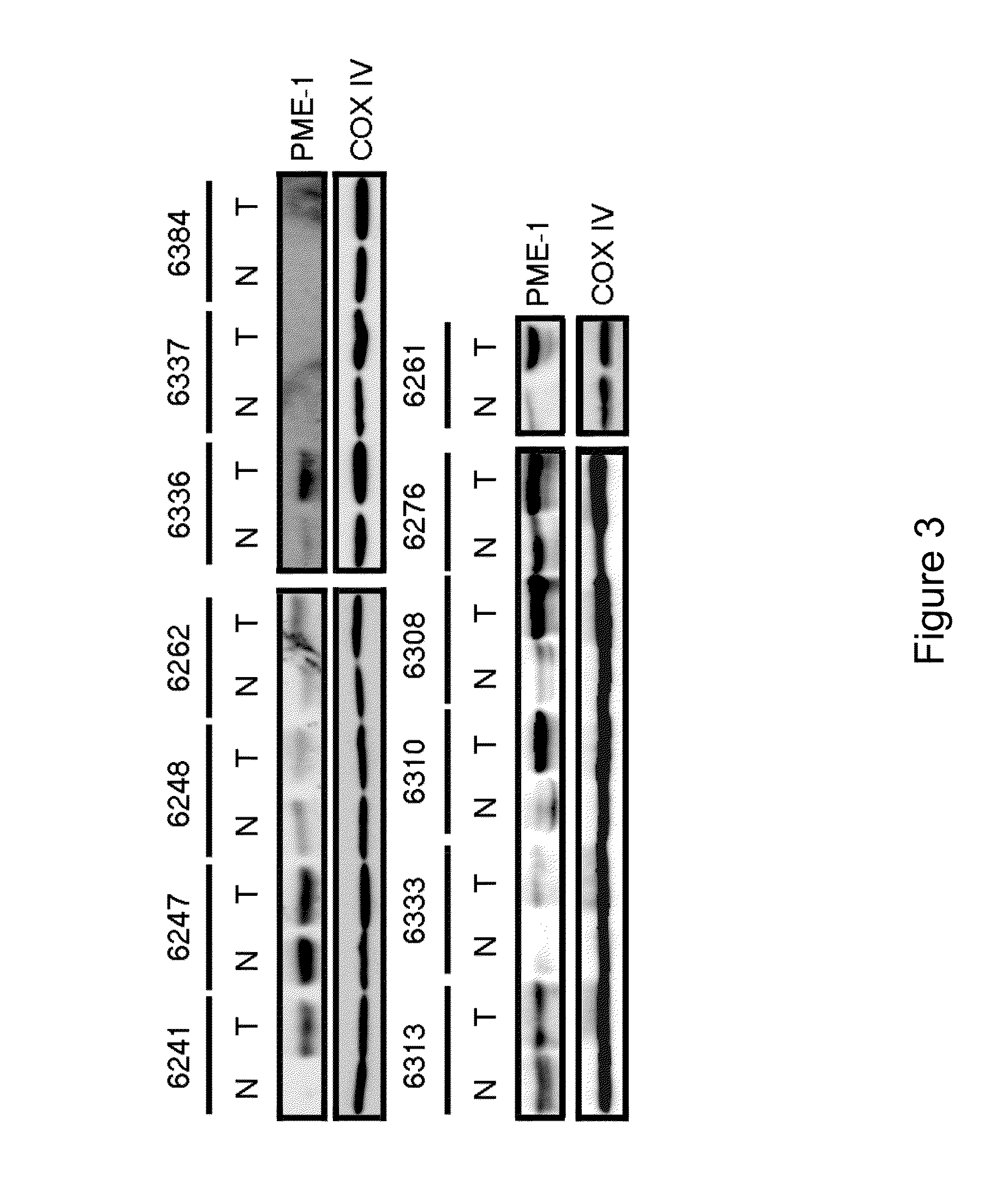
PME-1 as a biomarker to predict and diagnose an increased risk of endometrial cancer and gene silencing of PME-1 to inhibit epithelial to mesenchymal transition
InactiveUS20140323546A1Improve expression levelIncreased riskOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesIncreased riskGene silencing
Disclosed are methods of attenuating activity of the PME-1 gene. siRNAs or shRNAs are used to target against PME-1, thereby reducing the PME-1 mRNA. It is disclosed that the siRNAs or shRNAs targeted against PME-1 attenuate the epithelial to mesenchymal transition, thereby inhibit endometrial cancer development. A kit containing siRNA or shRNA reagents for attenuating the PME-1 gene expression is also disclosed.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
Preparation method for plant mutant
The invention discloses a preparation method for a plant mutant. The preparation method comprises the following steps that T1, a CRISPR / cas9 gene knockout vector is constructed, and a CYP78A13 gene isknocked out; T2, agrobacterium is transformed; T3, gene knockout detection is carried out; and T4, phenotype identification is carried out on a transgenic plant. According to the preparation method for the plant mutant, a rice cell nucleus fertility gene serves as a target gene, gene knockout is carried out by using CRISPR / cas9 gene silencing, the function is lost after gene silencing, a cell isdeveloped into a complete plant, but the complete plant does not have pollen which is developed to have normal functions, and the plant mutant can be taken as a research object and used for creating asterile line.
Owner:QINGDAO YUANCE GRP CO LTD
RNA silencing in animals as an antiviral defense
InactiveUS20150267203A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseSequence analysisSuppressor
The present invention provides recombinant DNA constructs for inactivation of viral or endogenous genes in a cell, wherein the construct comprises viral sequence sufficient to activate RNA silencing. In another aspect, the invention provides methods for identifying RNA silencing suppressors by sequence analysis and functional tests. In yet another aspect, the invention provides a method for identifying inhibitors of RNA silencing suppressors. In still other aspects, the invention comprises methods for identifying genes in the antiviral RNA silencing pathway, enhancers of the antiviral pathway, and methods of treating or preventing viral infections using enhancers of the pathway.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions for bacterial mediated gene silencing and methods of using the same
The invention features compositions and methods for delivering small interfering (siRNAs), e.g., shRNAs, to host cells using non-pathogenic strains of Salmonella bacteria containing nucleic acid expression constructs encoding shRNAs. In this process, shRNA expressed by the Salmonella silences or knocks down genes of interest (target genes) inside target cells. The nucleic acid expression constructs of the invention include an RNA polymerase (e.g., a T7 polymerase), an RNA polymerase promoter (e.g., a T7 polymerase promoter), and an RNA polymerase terminator (e.g., a T7 polymerase terminator). The Salmonella bacteria can also include, on the same or different nucleic acid construct, an endosomal release factor (e.g., HlyA).
Owner:GUO HONGNIAN +2
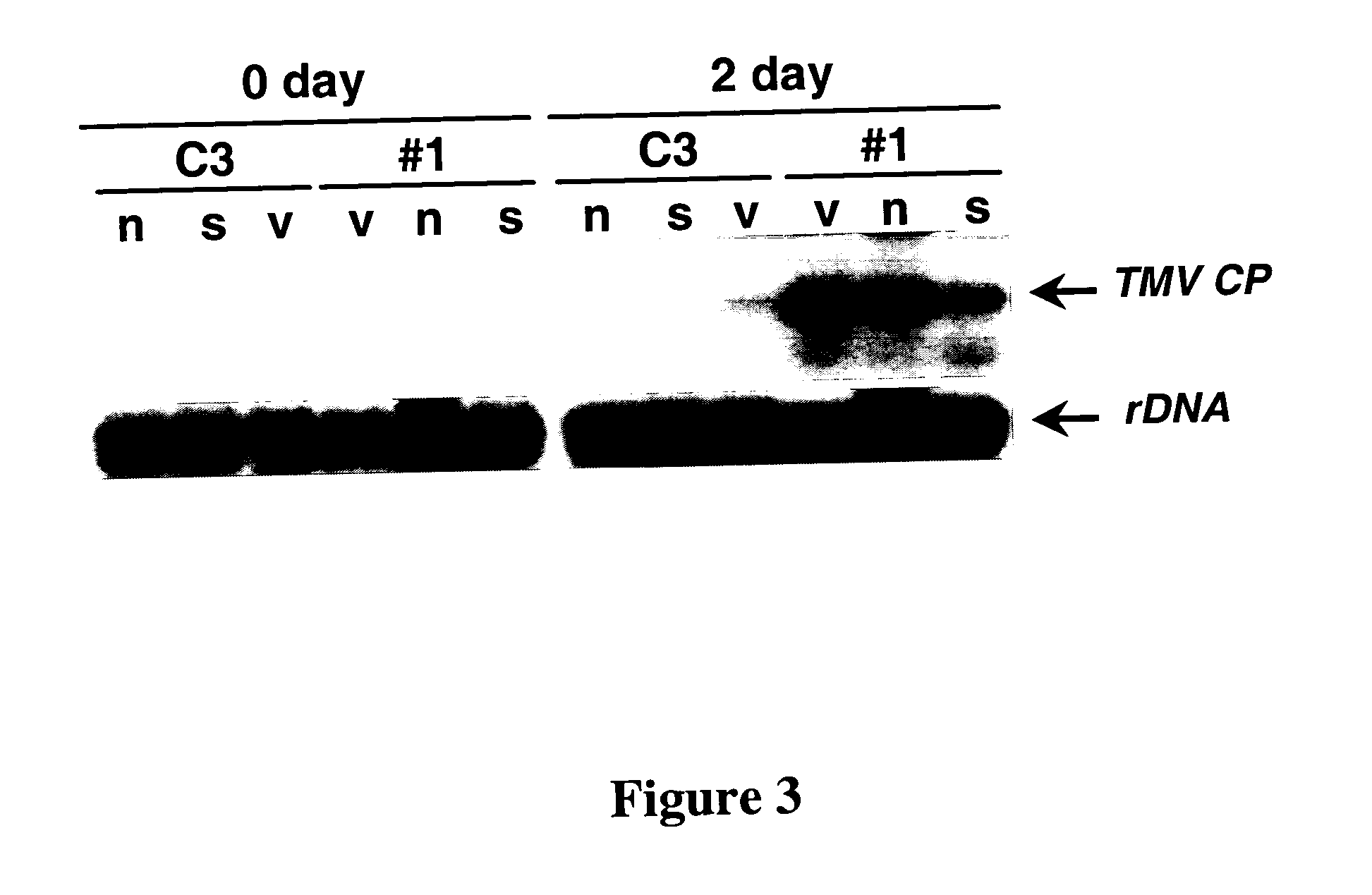
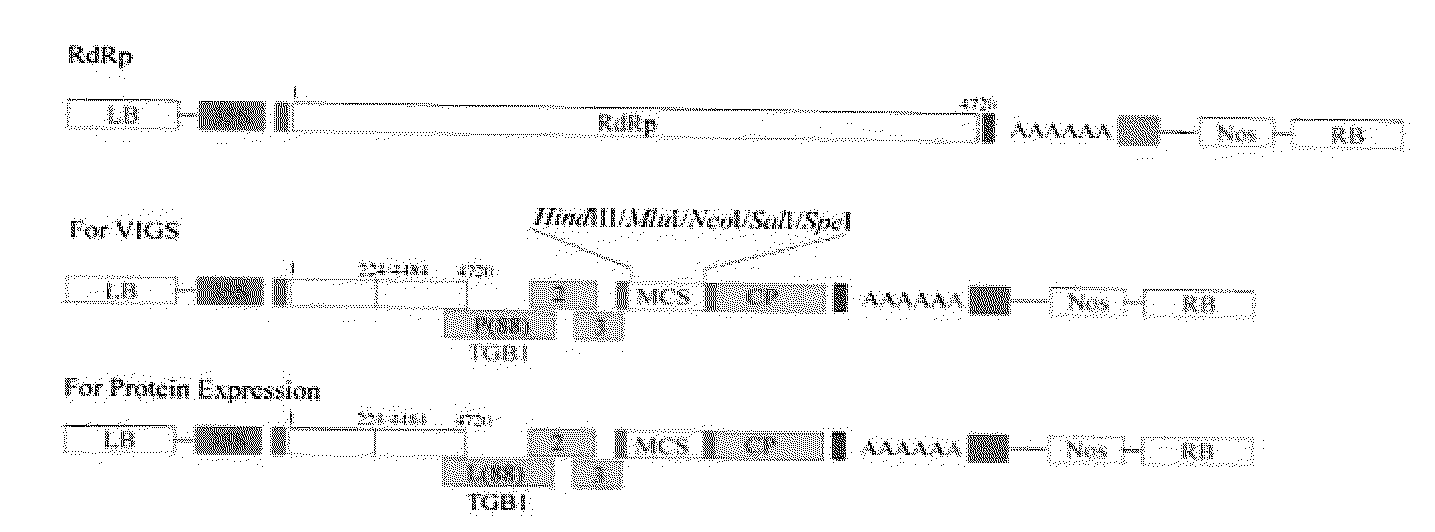
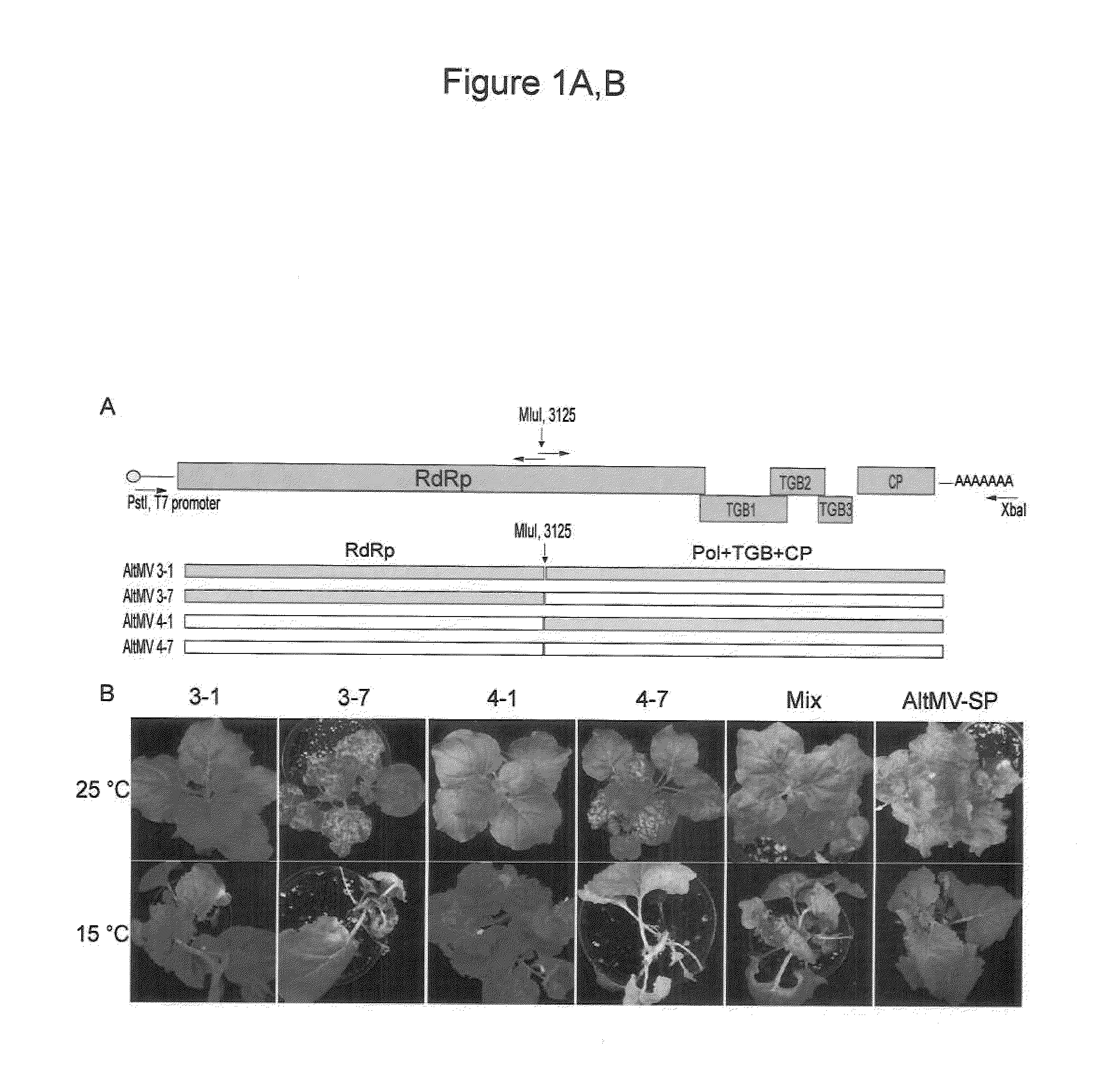
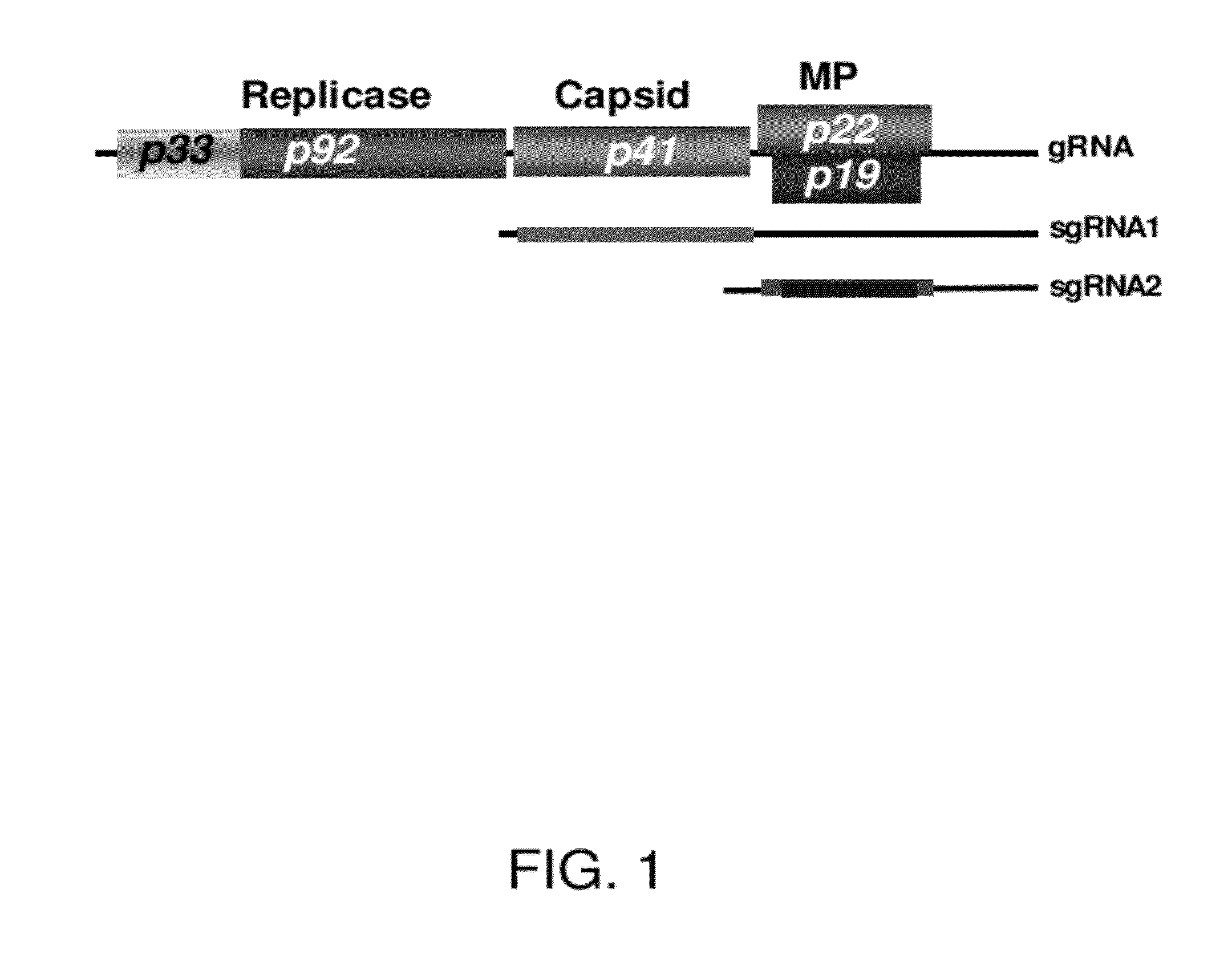
Infectious Plant Viral Vector and An Artificial Bipartite Plant Viral Vector An Infectious Plant Viral Vector and An Artificial Bipartite Plant Viral Vector
InactiveUS20110154538A1High level of proteinImprove transcription efficiencySsRNA viruses positive-senseOther foreign material introduction processesCoat proteinIn vivo
We have developed a versatile plant viral vector system based on Alternanthera mosaic virus (AltMV), suitable for infection by agroinfiltration or in vivo T7 transcripts from the same clone; agroinfection is enhanced by coinfiltration of a T7 RNA polymerase construct. Variants adapted for efficient protein expression, or for virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS), are based on a specific amino acid substitution (L88P) in the triple gene block 1 (TGB1) protein affecting RNA silencing suppression. A bipartite delivery system developed for AltMV delivers replicase (RdRp) functions separately from movement and encapsidation (TGB and coat protein, CP) functions by agroinfiltration, resulting in precise recombination of RdRp and TGB-CP constructs in planta. The bipartite delivery system has potential for high throughput protein expression or VIGS with the appropriate TGB1 variant, for hosts including Nicotiana benthamiana and Arabidopsis thaliana. Equivalent TGB1 substitutions in other potexviruses also reduced RNA silencing suppression, demonstrated with Potato virus X.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Methods and Compositions of Improved Modified siRNA
ActiveUS20150322431A1Improve efficacyImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSmall interfering RNACancer research
Chemically modified small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) that include both phosphorodithioate modifications (PS2-RNA) and 2′-O-methyl modifications (MePS2) provide improved RNA silencing. Specific chemically modified siRNA that show enhanced silencing of RNAs involved in resistance to chemotherapeutic agents are provided.
Owner:AM BIOTECH
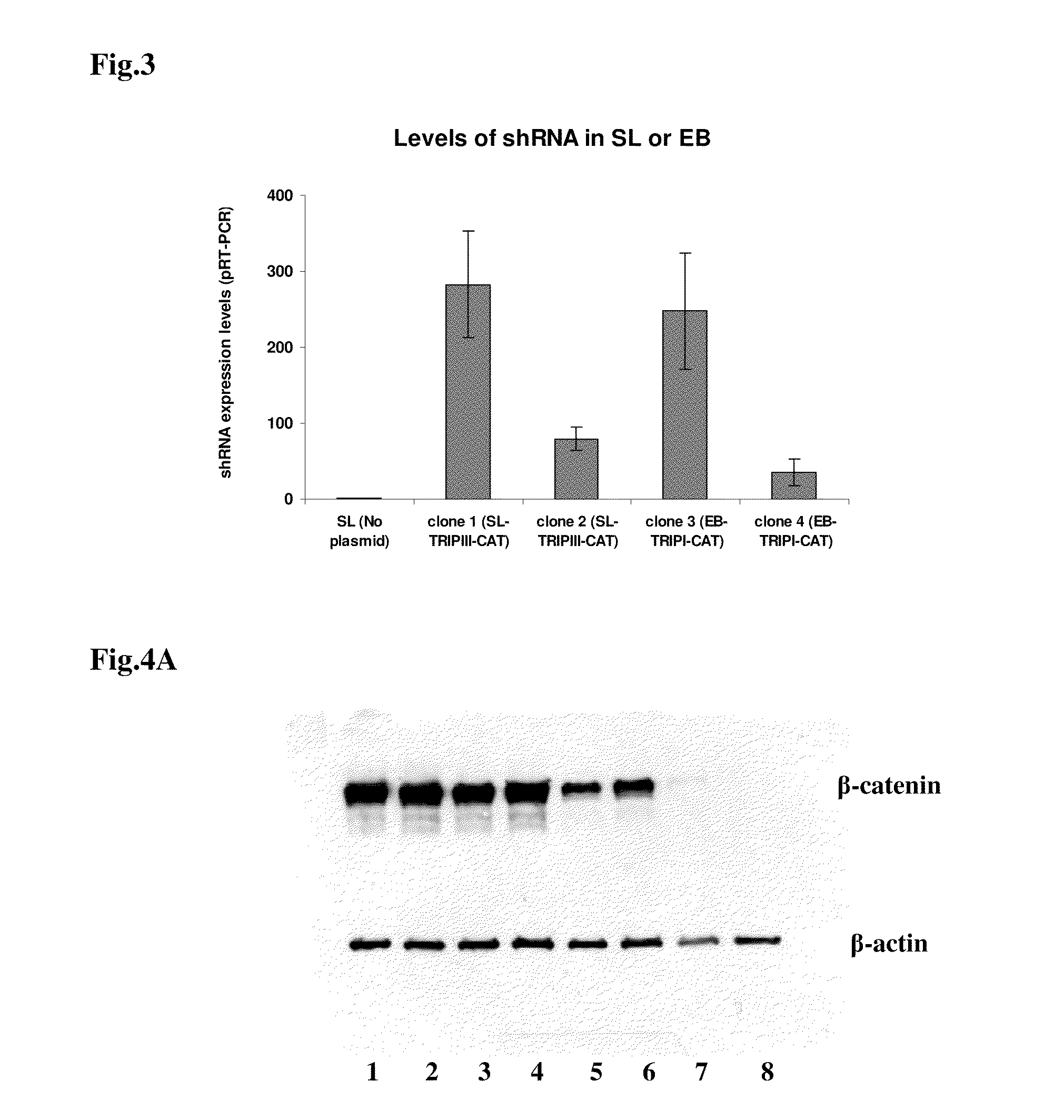
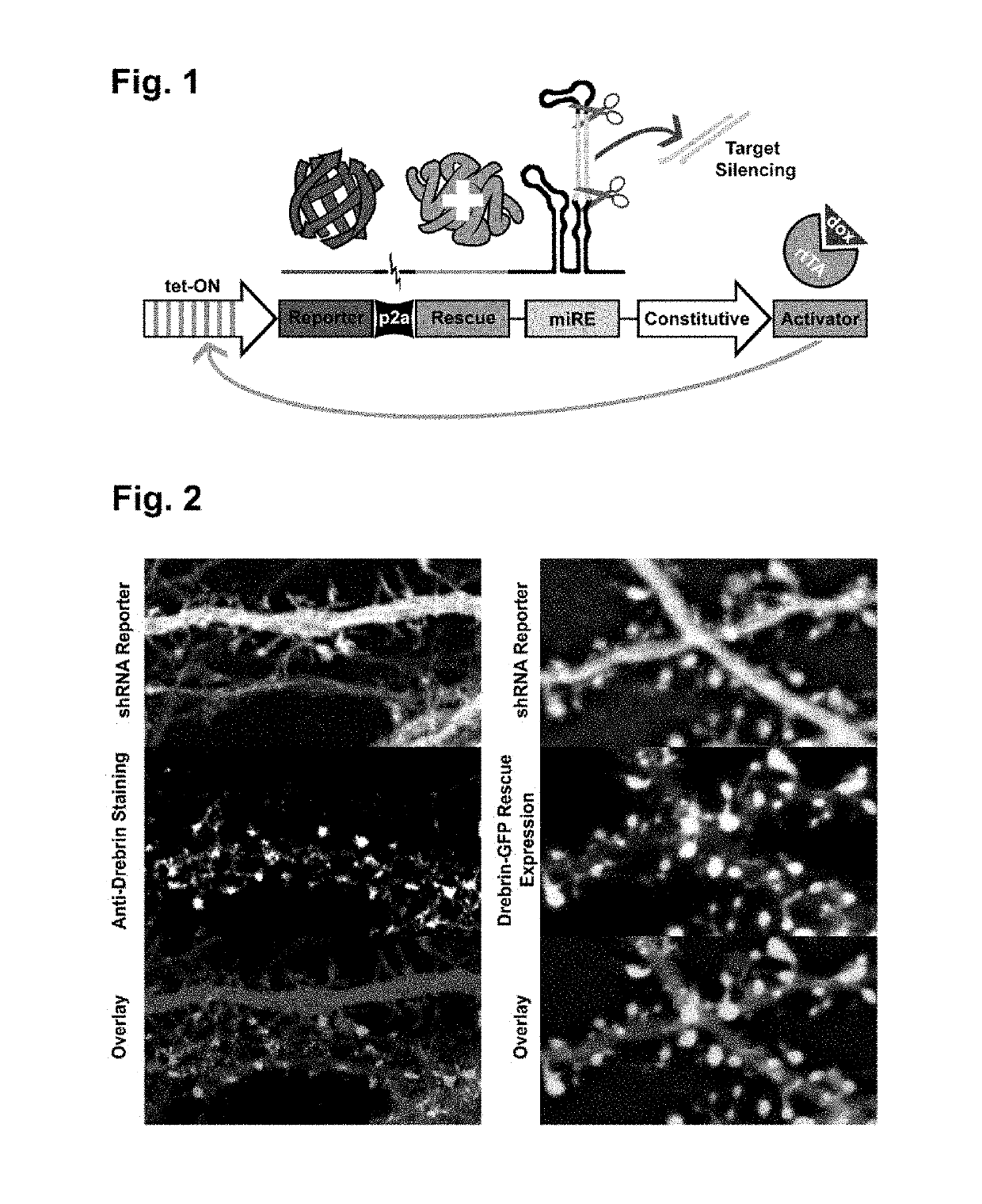
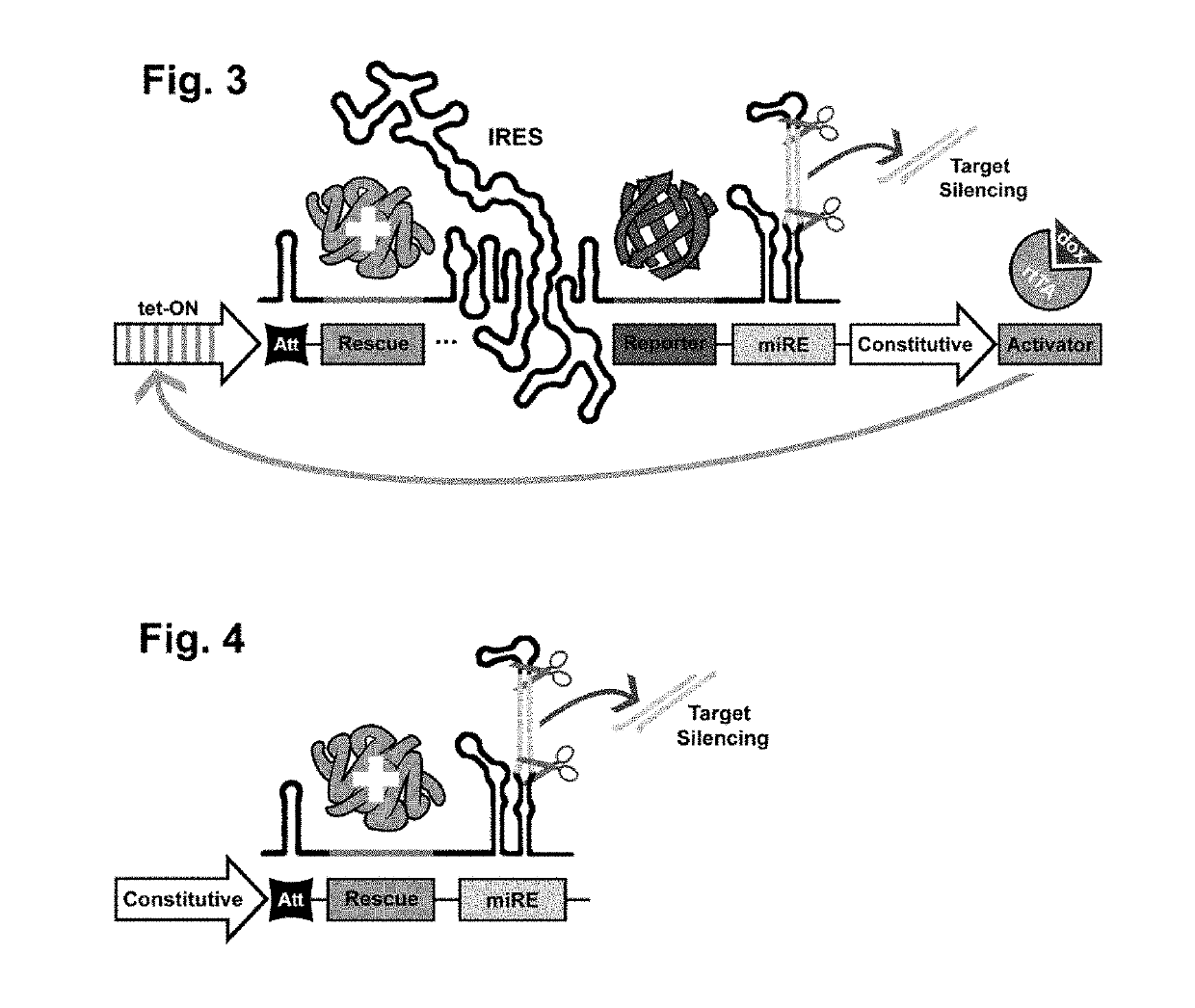
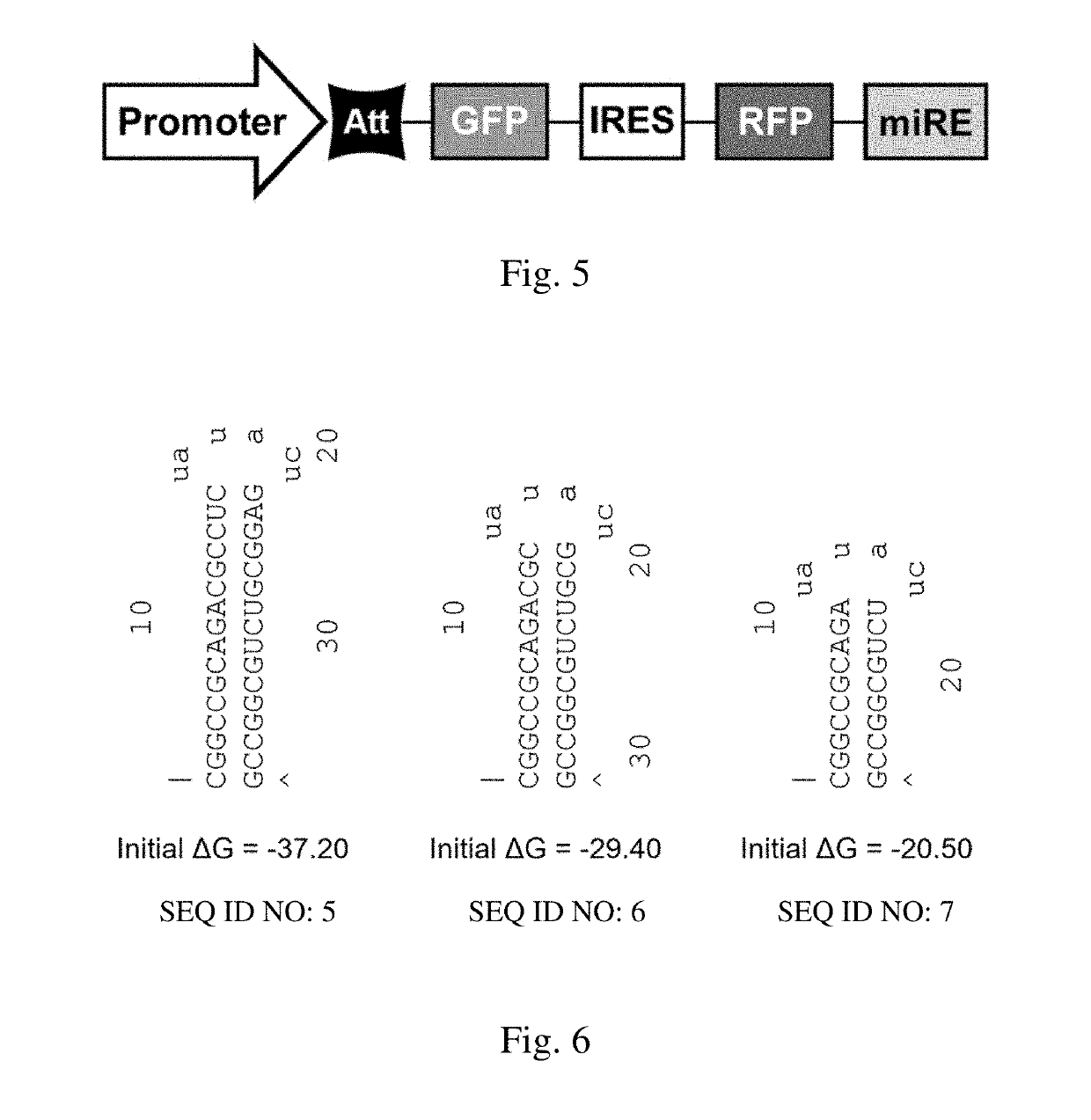
Vector for gene silencing and replacement and methods of use thereof
An expression cassette for gene silencing and replacement, including, in operable communication, a promoter, an expression attenuator, a nucleotide sequence encoding a gene for a replacement target protein, and an shRNA sequence for knockdown of an endogenous variant of the target protein, wherein the promoter, the expression attenuator, the nucleotide sequence encoding the gene for the replacement target protein, and the shRNA are expressed as a single transcript. Also included are expression vectors and cells. Also included are methods of silencing and replacement of a target gene in a cell in culture by transforming the cells with the expression vectors described herein. Also included are minimal expression cassettes suitable for therapeutic methods.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Enhancing expression of value-added genes by transgenic expression of tombusvirus-based P19 gene mutants
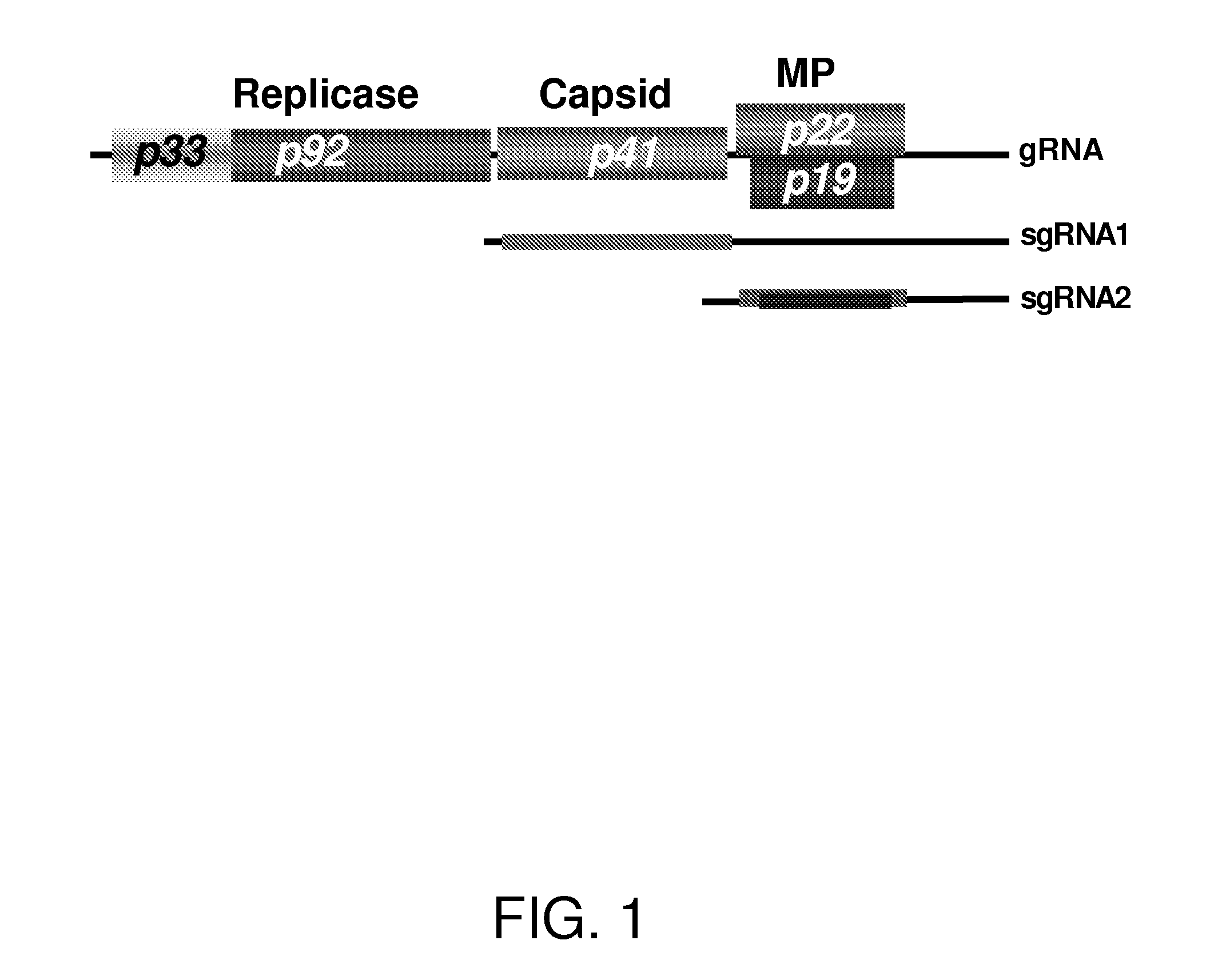
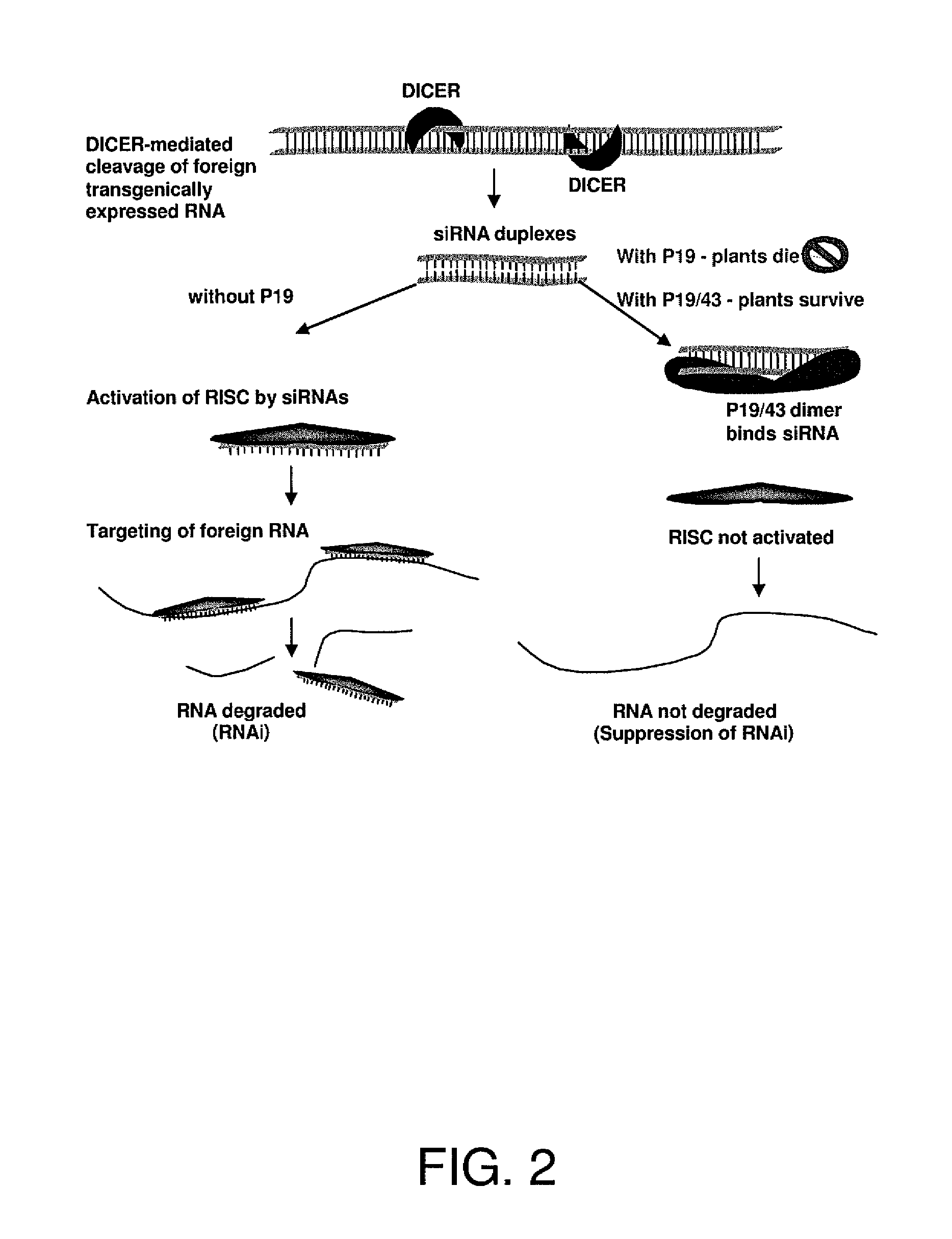
ActiveUS8222488B2Robust and readily applicable enhancerLow toxicitySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesMutated proteinGene product
A method of enhancing expression of at least one desired gene product in a plant, comprises transgenically introducing a Tombusvirus p19 / R43W mutant gene (SEQ. ID NO: 3) into the plant, expressing at least one desired gene product in the plant, wherein expression of said product is susceptible to RNA silencing; and co-expressing the transgenically introduced p19 / R43W, to produce an amount of P19 / R43W mutant protein (SEQ. ID NO: 4) sufficient to suppress silencing of expression of said desired gene product.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Maize microrna sequences
InactiveUS20110083232A1Raise the possibilitySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesRNA SequenceMicroRNA
Methods and compositions useful in target sequence suppression and target sequence validation are described. Polynucleotide constructs useful for gene silencing, as well as cells, plants and seeds comprising the polynucleotides and a method for using microRNAs to silence a target sequence are also described.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Modified human cmv promoters that are resistant to gene silencing
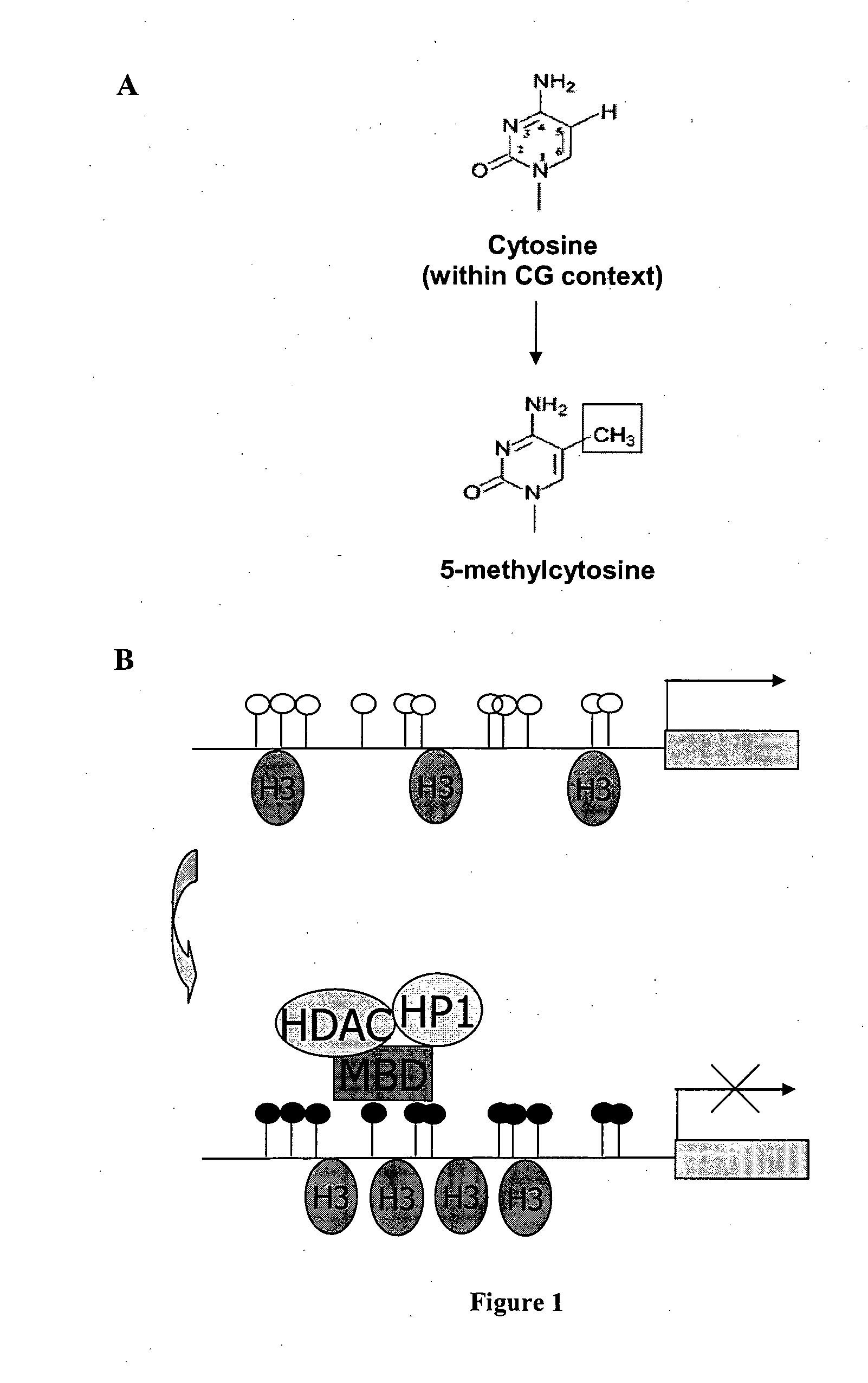
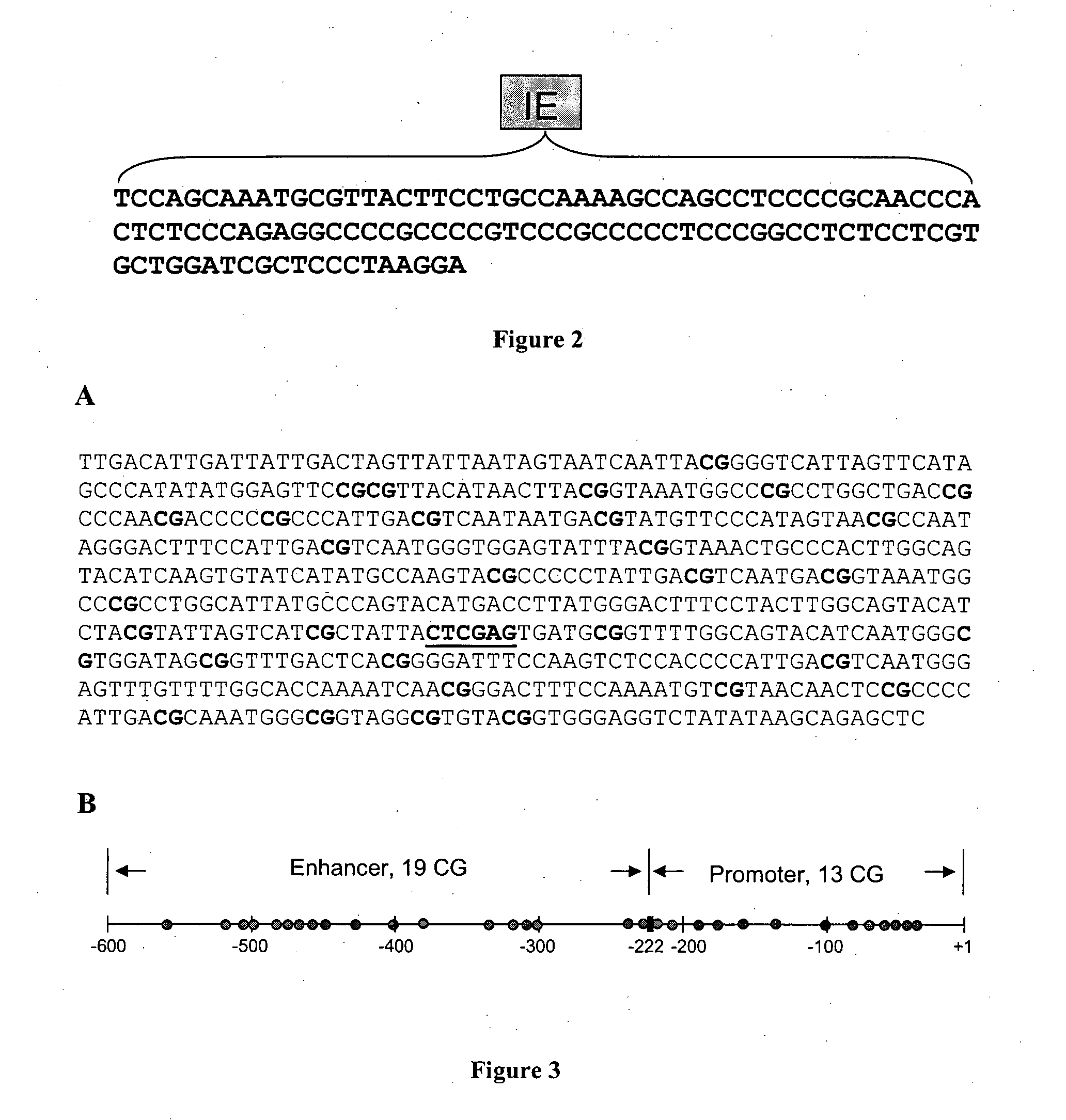
InactiveUS20140017726A1High expressionVectorsGenetic material ingredientsAdenine phosphoribosyltransferaseGene silencing
The invention relates to a nucleic acid molecule comprising a functional promoter of a herpesvirus, a functional enhancer of a herpesvirus, and one or more internal elements of the CpG island of the aprt (adenine phosphoribosyl transferase) gene and / or a functional variant thereof. A method of producing a desired polypeptide using the nucleic acid molecule, a vector and a host cell containing the nucleic acid molecule are also disclosed.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Small molecule inhibitors of RNA silencing
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Enhancing expression of value-added genes by transgenic expression of tombusvirus-based p19 gene mutants
ActiveUS20100269220A1Robust and readily applicable enhancerLow toxicitySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesMutated proteinGene product
A method of enhancing expression of at least one desired gene product in a plant, comprises transgenically introducing a Tombusvirus p19 / R43W mutant gene (SEQ. ID NO: 3) into the plant, expressing at least one desired gene product in the plant, wherein expression of said product is susceptible to RNA silencing; and co-expressing the transgenically introduced p19 / R43W, to produce an amount of P19 / R43W mutant protein (SEQ. ID NO: 4) sufficient to suppress silencing of expression of said desired gene product.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com