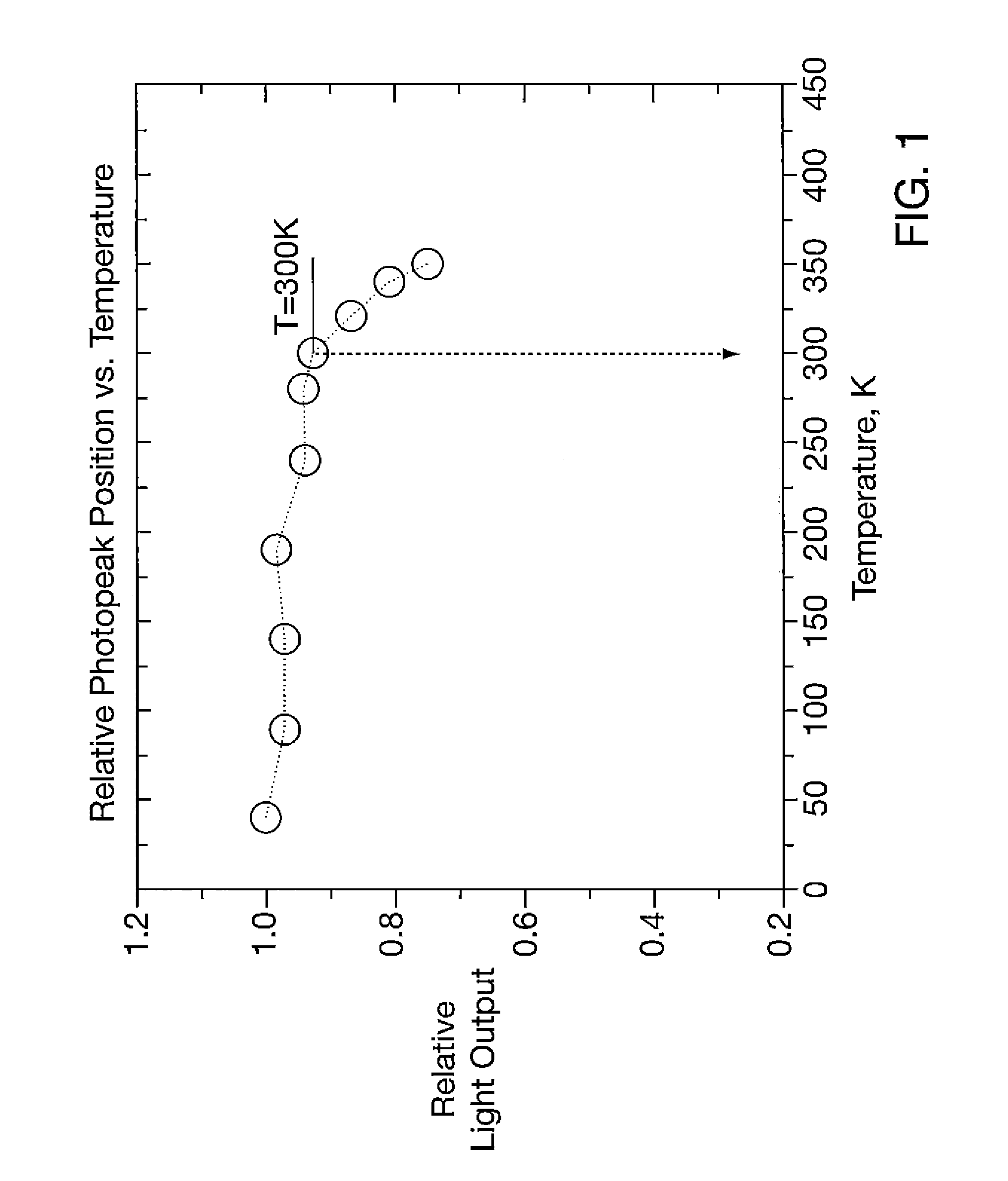
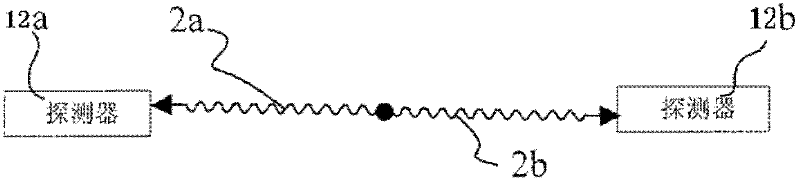
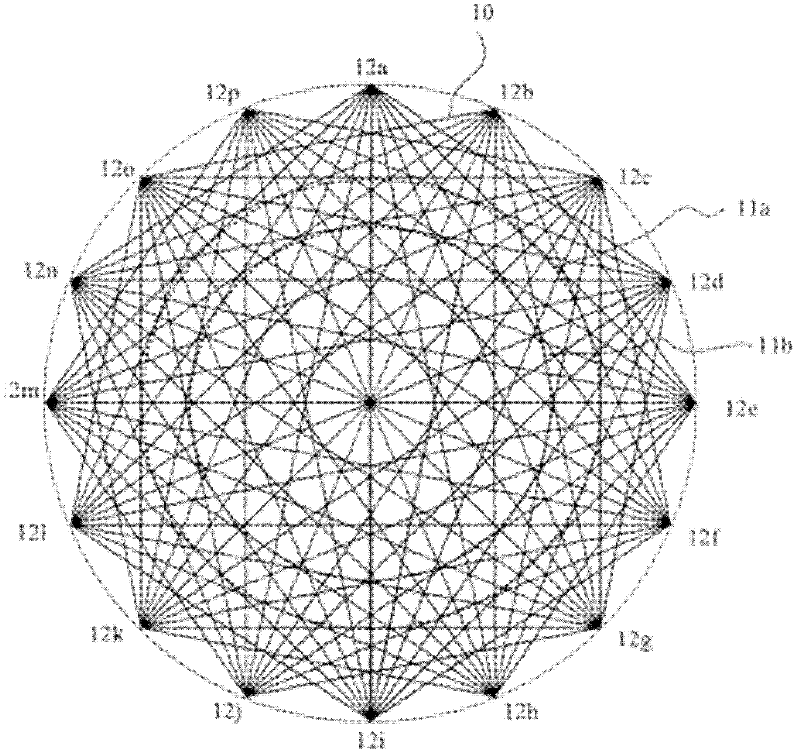
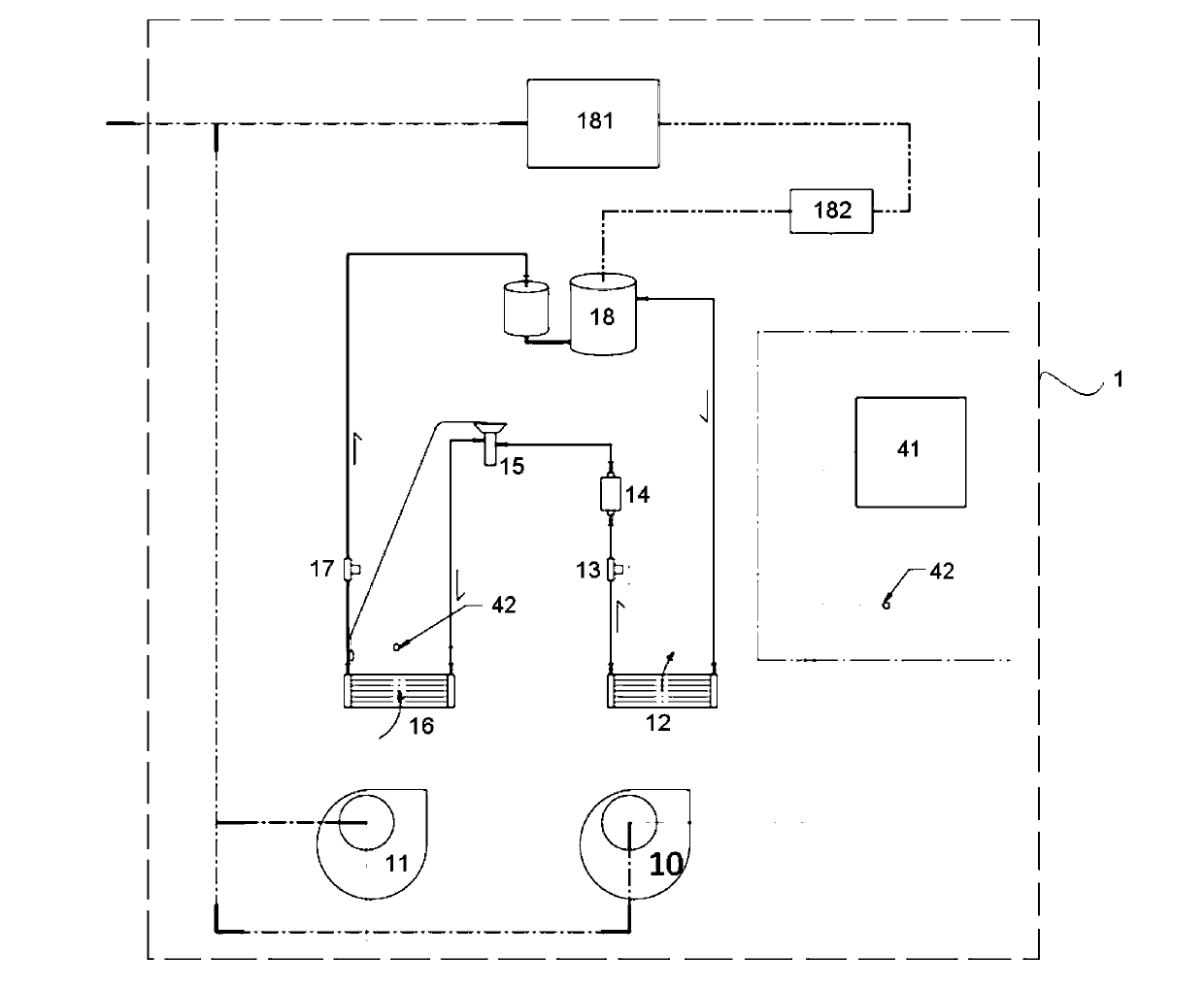
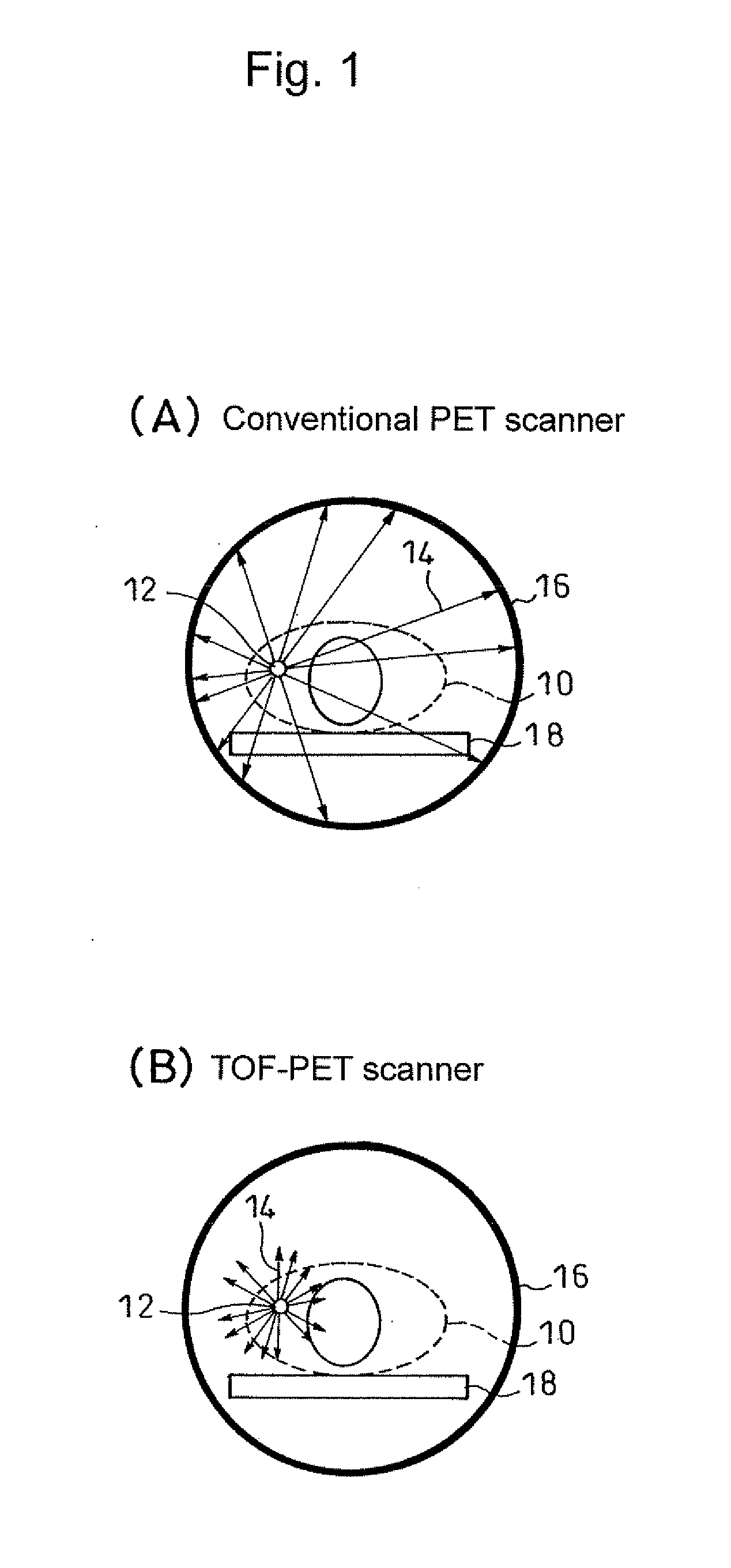
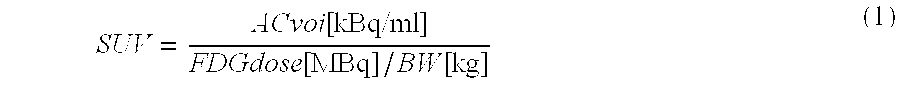Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49 results about "Positron emission tomography scanner" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is an imaging test that allows your doctor to check for diseases in your body. The scan uses a special dye containing radioactive tracers.
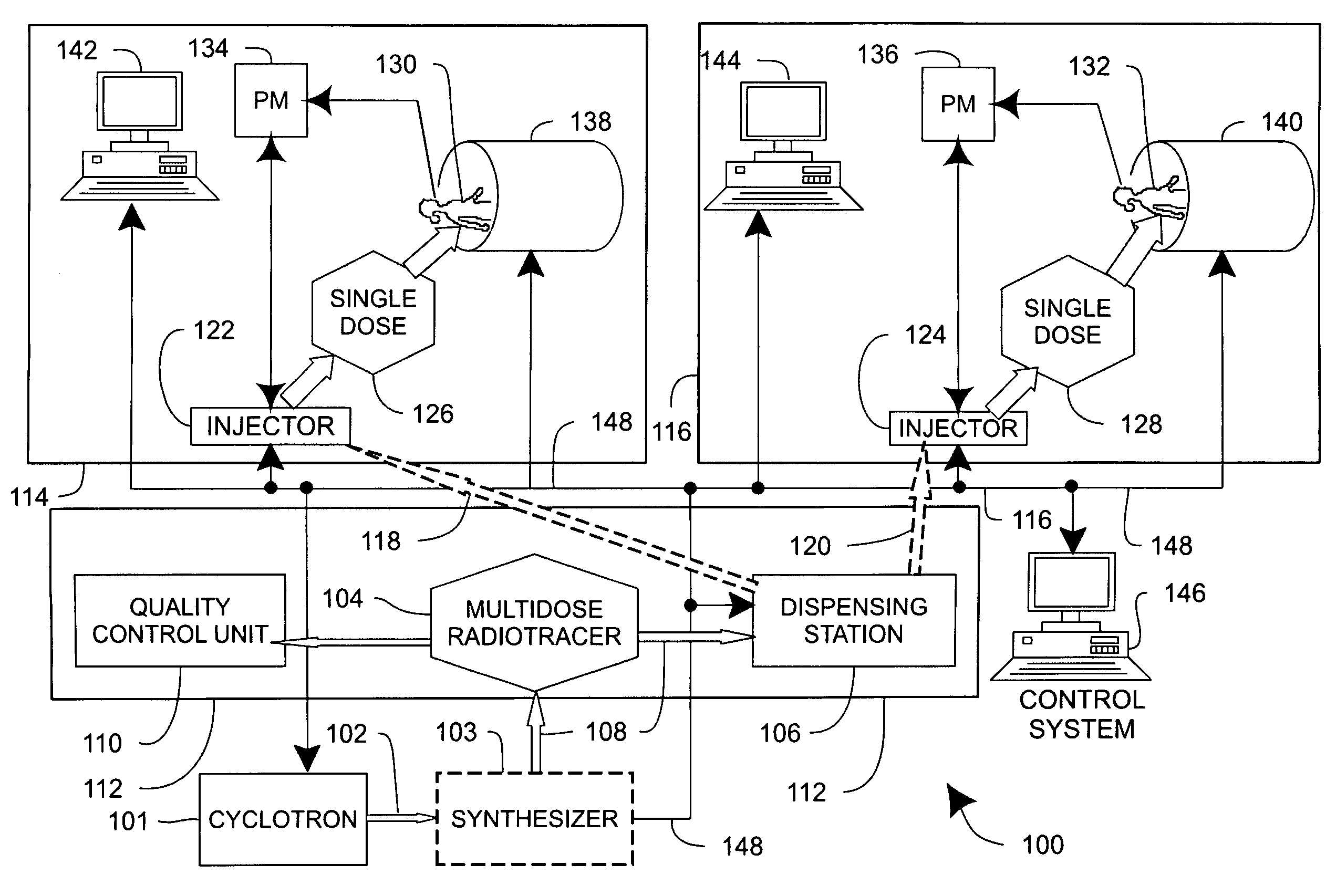
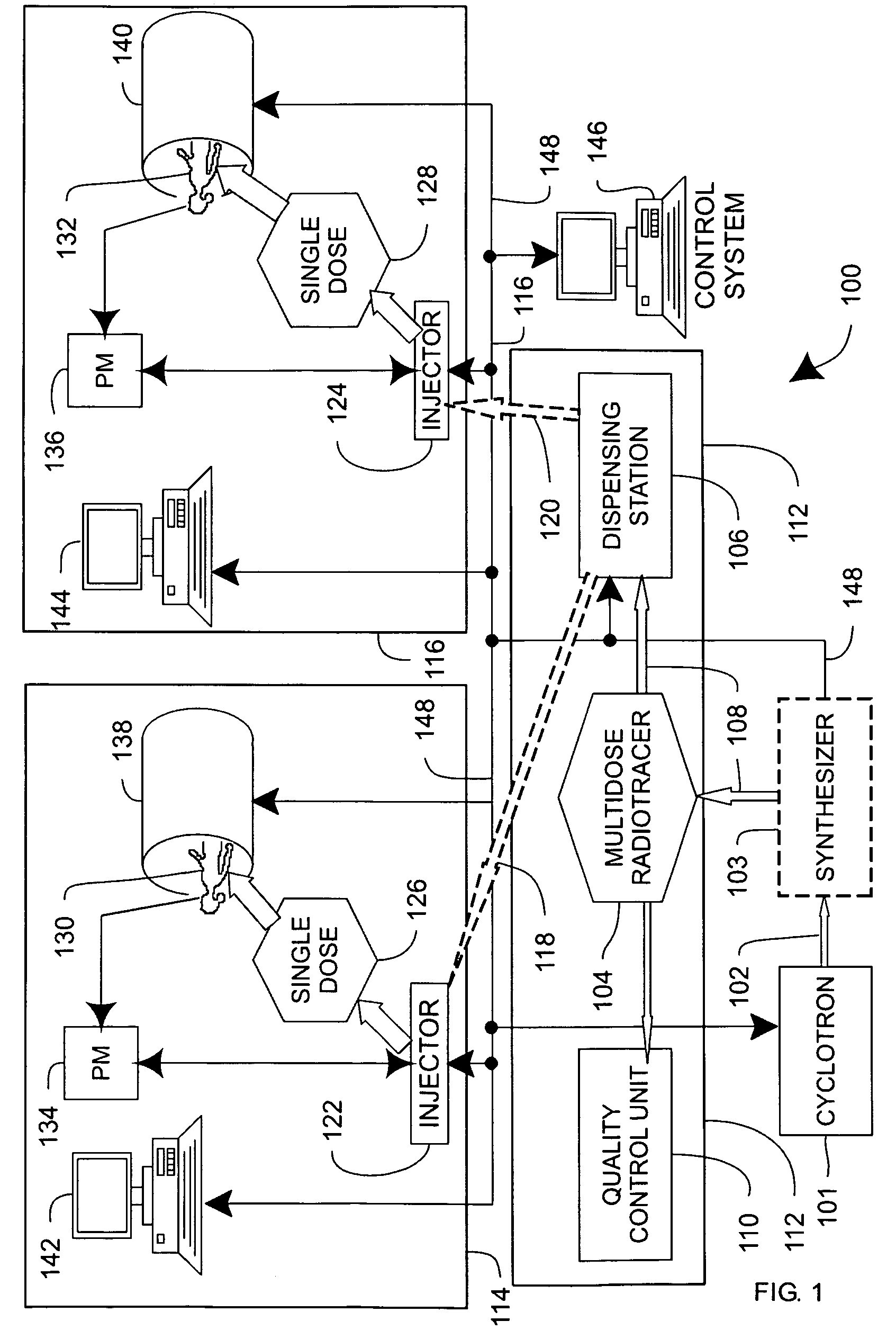
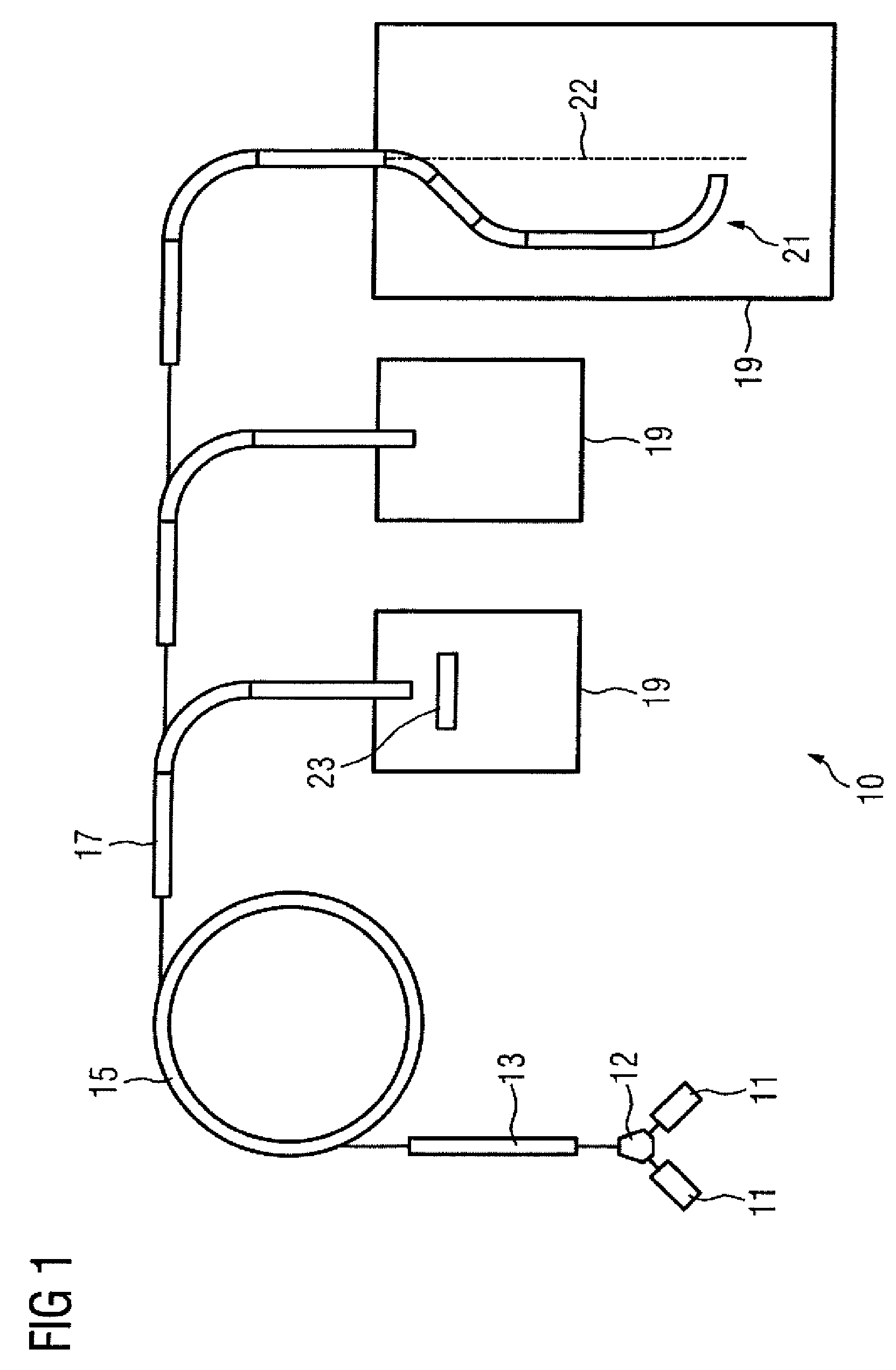
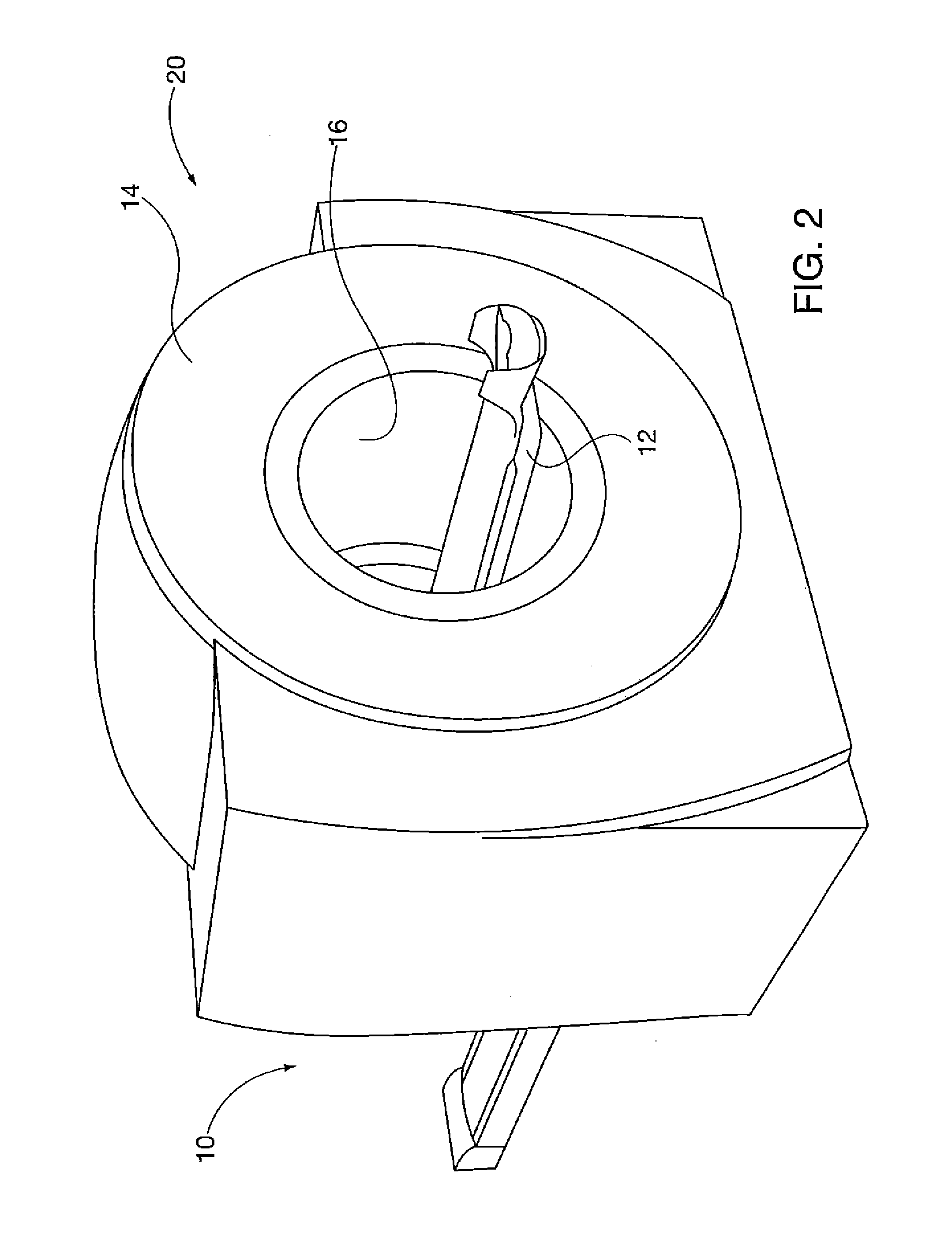
Systems, methods and apparatus for preparation, delivery and monitoring of radioisotopes in positron emission tomography
ActiveUS7734331B2Economy of scaleImprove distributionMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDrug and medicationsRadioactive tracerQuality control
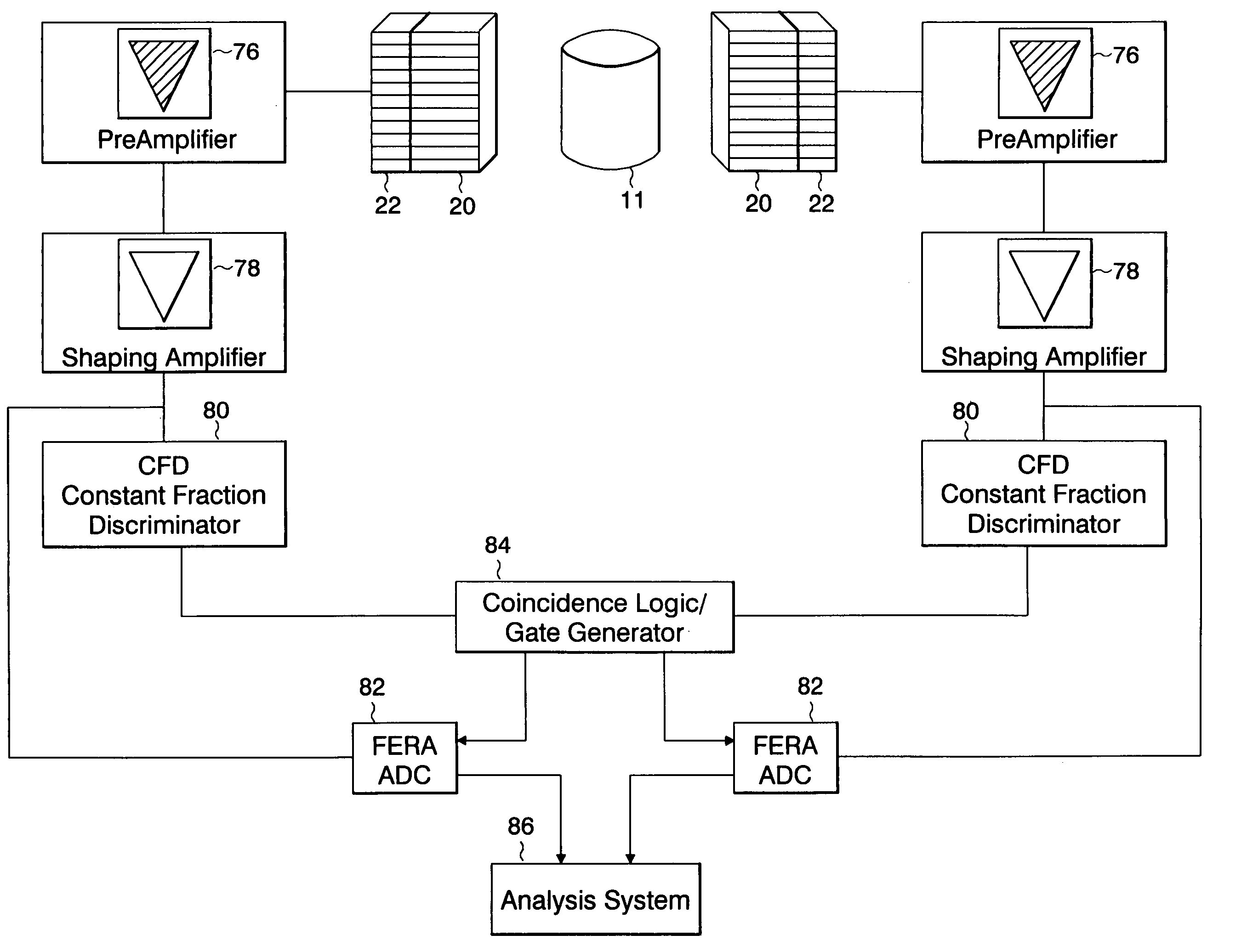
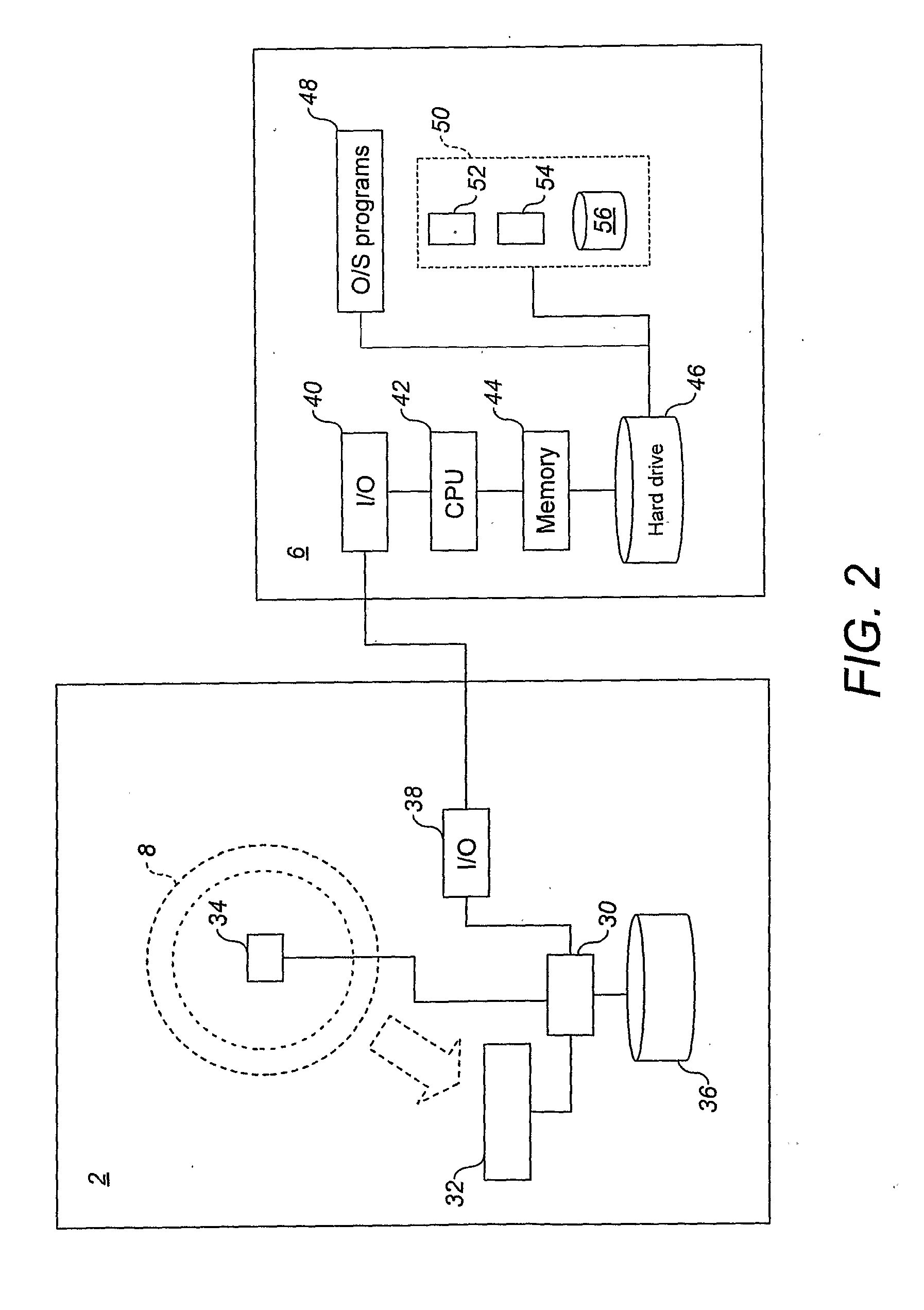
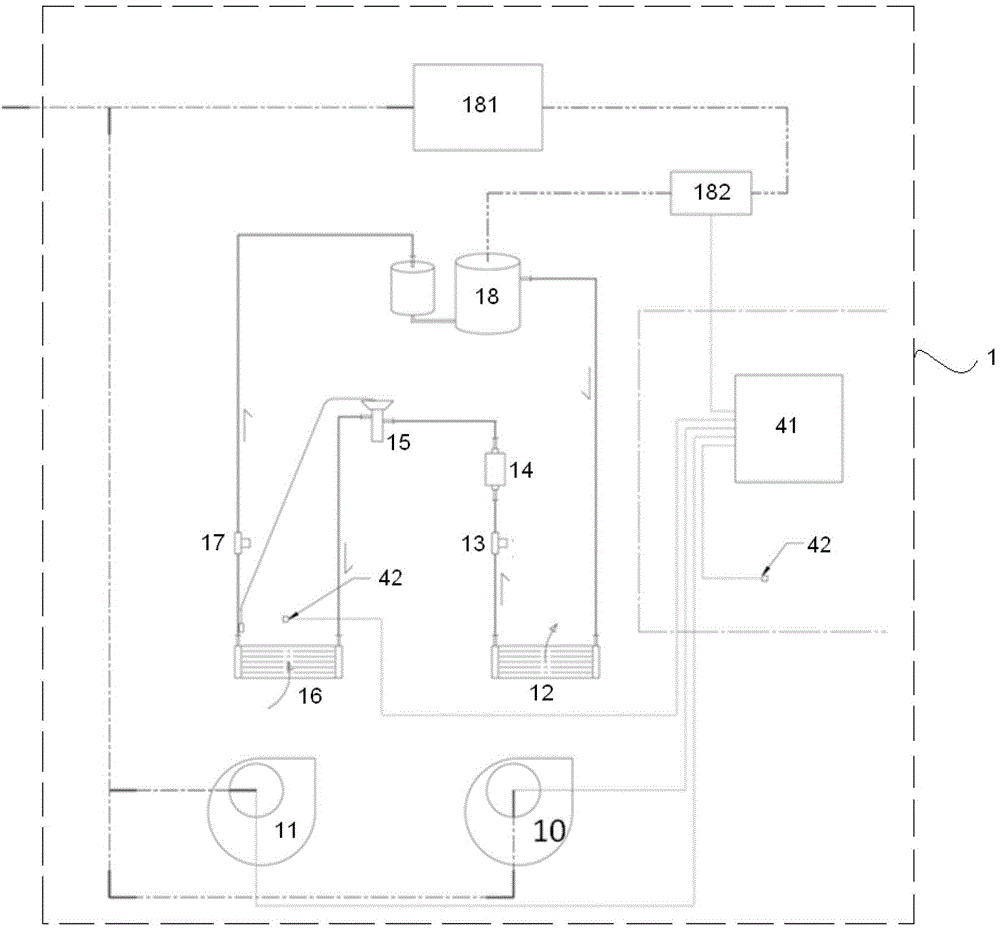
In one aspect, systems, methods and apparatus are provided through which a dispensing station dispenses a large quantity of a radiotracer to one or more positron emission tomography imaging stations. In some aspects a quality control unit verifies the quality of the radiotracer. In some embodiments, components of the system are coupled by a local area network. In some aspects, each positron emission tomography imaging station includes an injector system, a physiological monitoring device, and a positron emission tomography scanner. All of the devices can be controlled by a computer system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
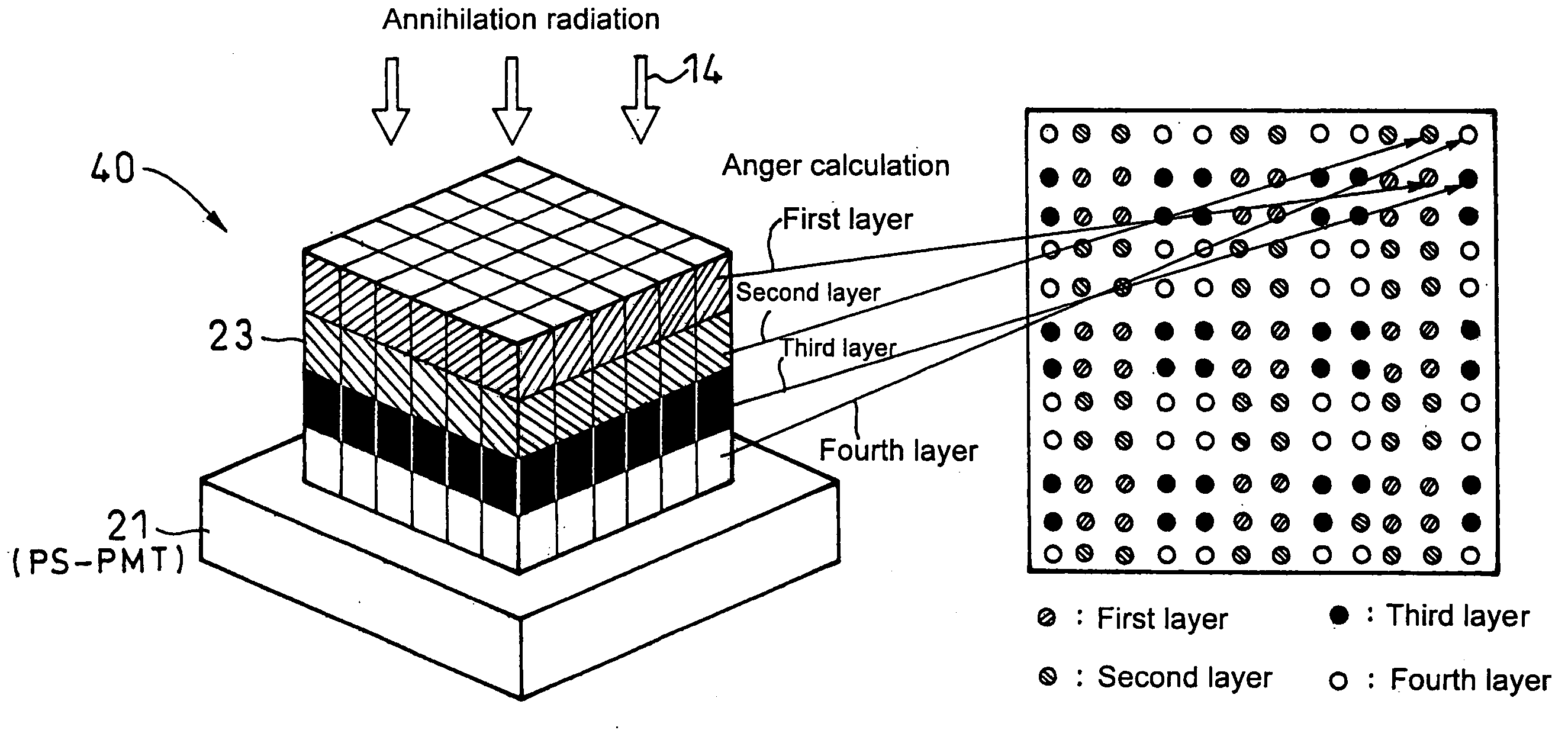
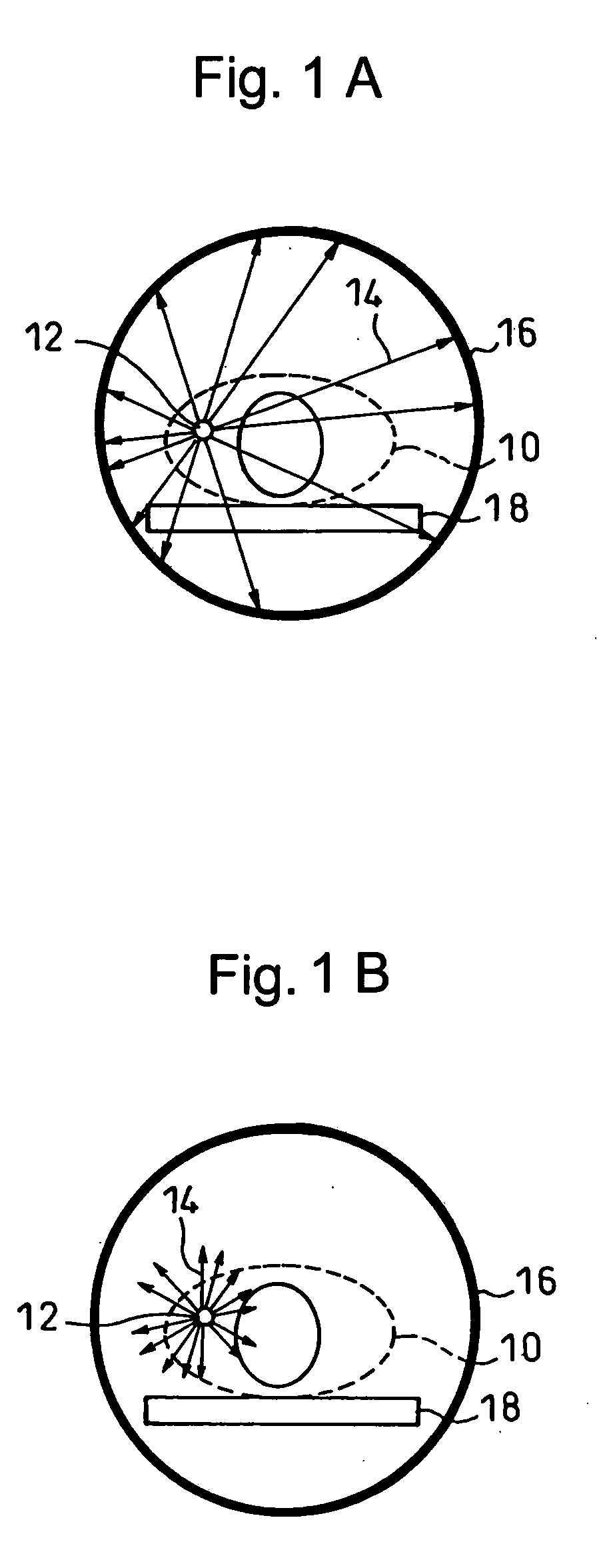
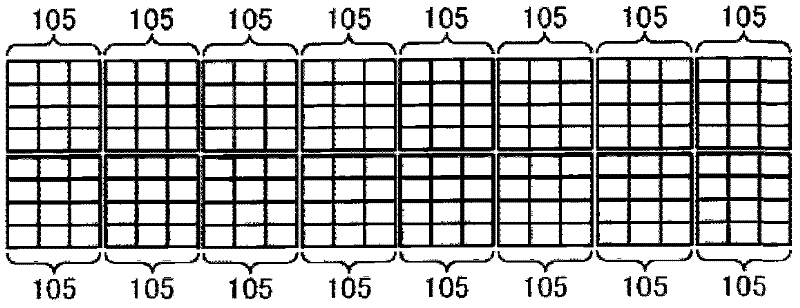
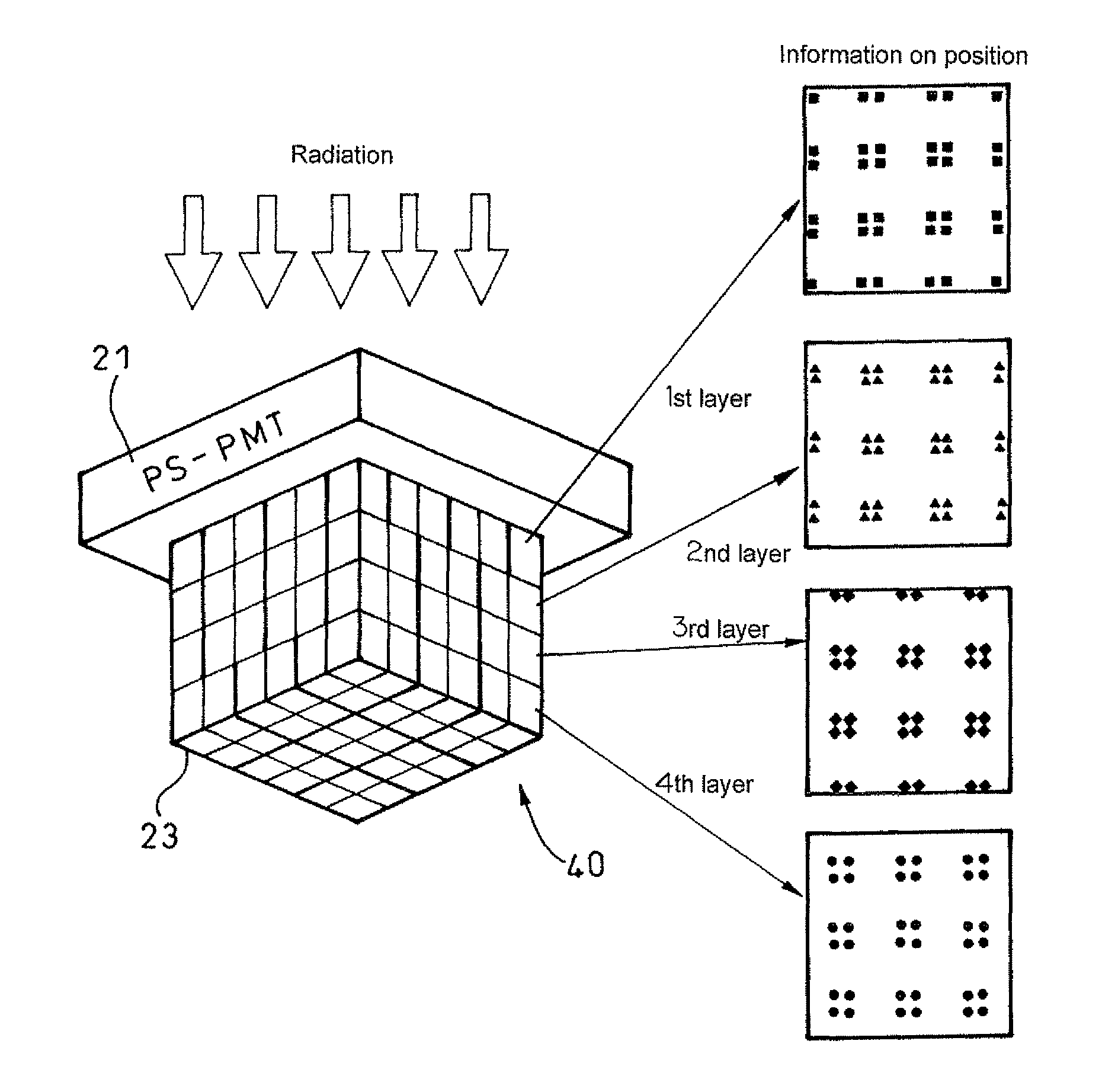
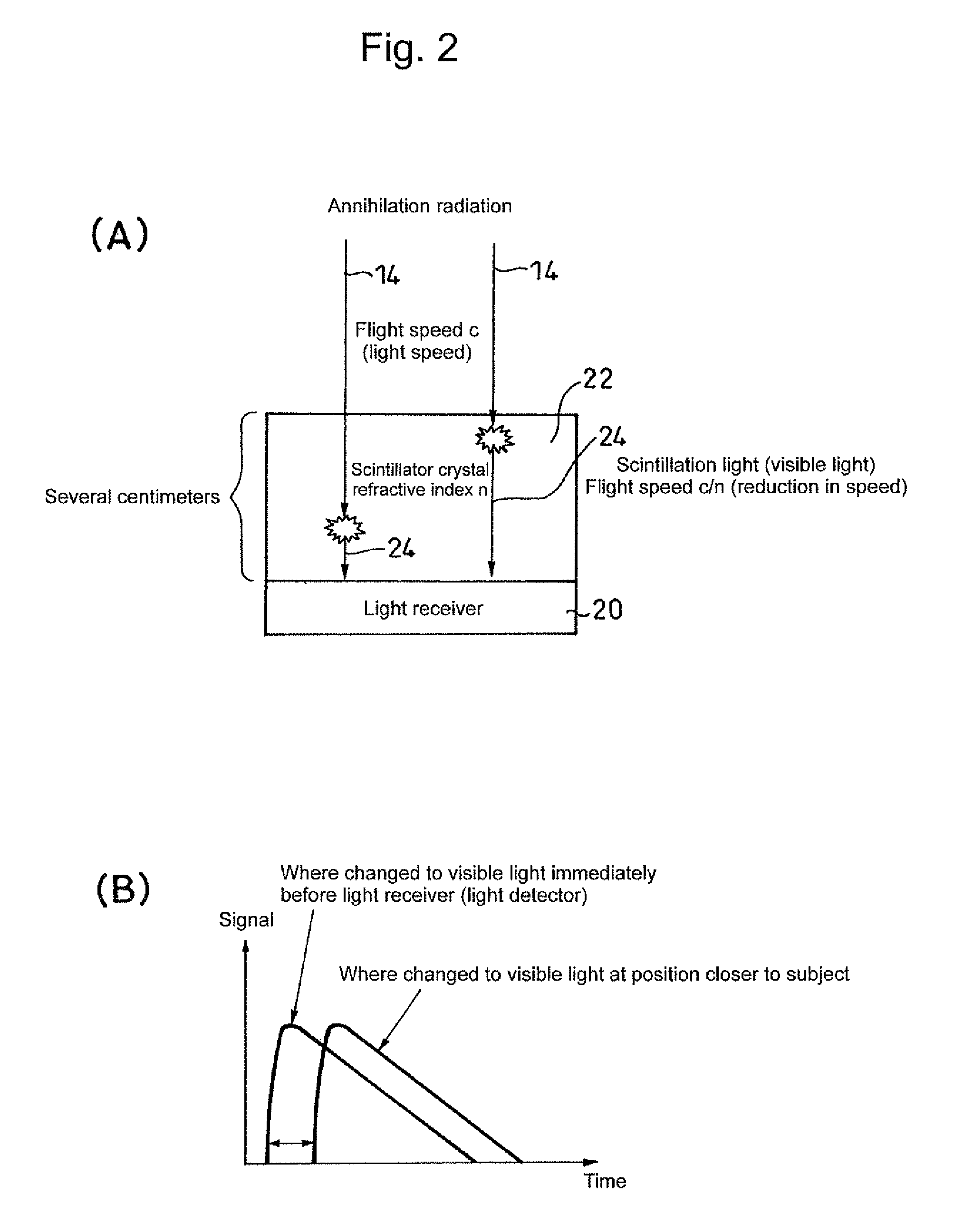
Positron emission tomography scanner and radiation detector
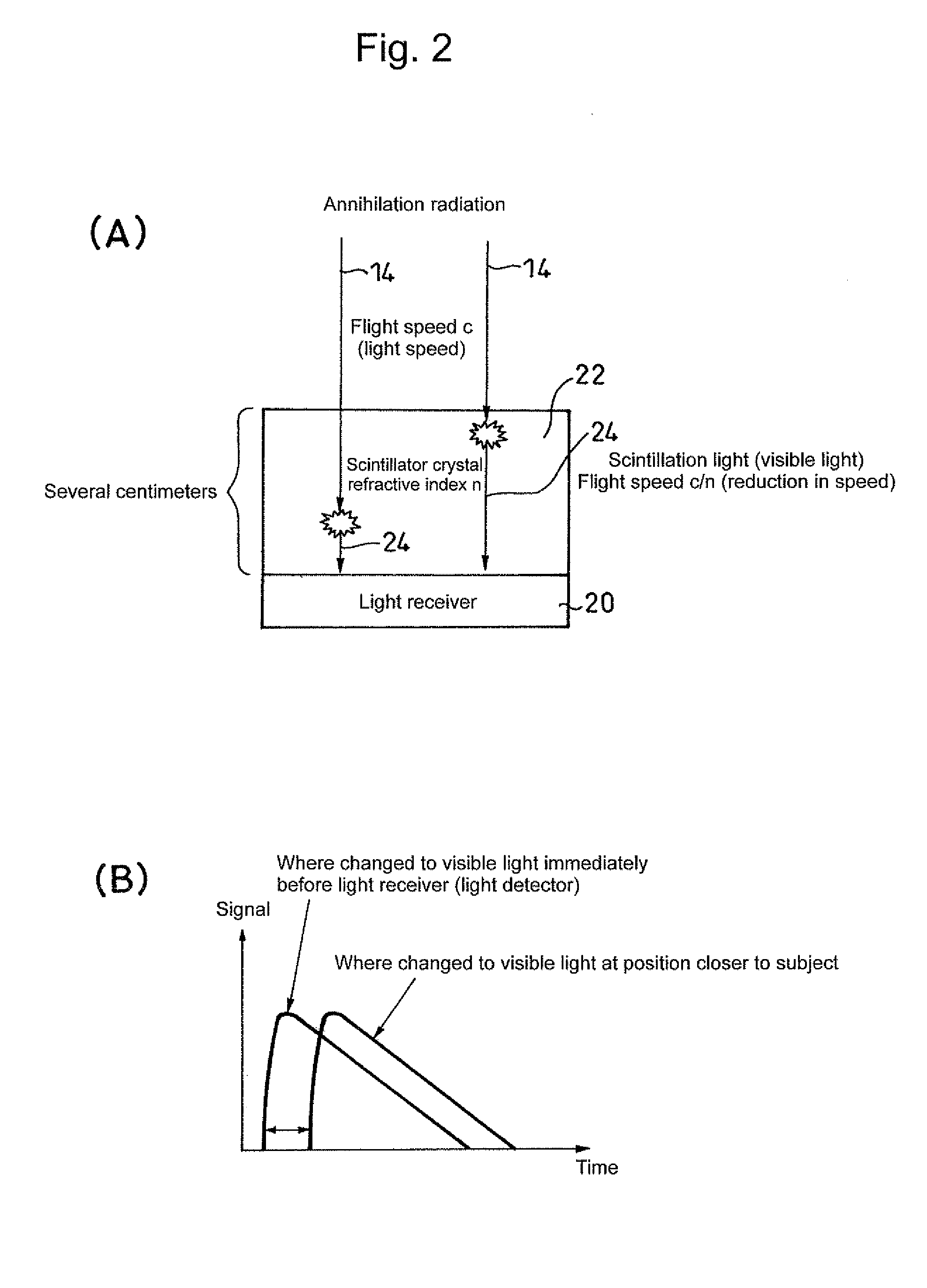
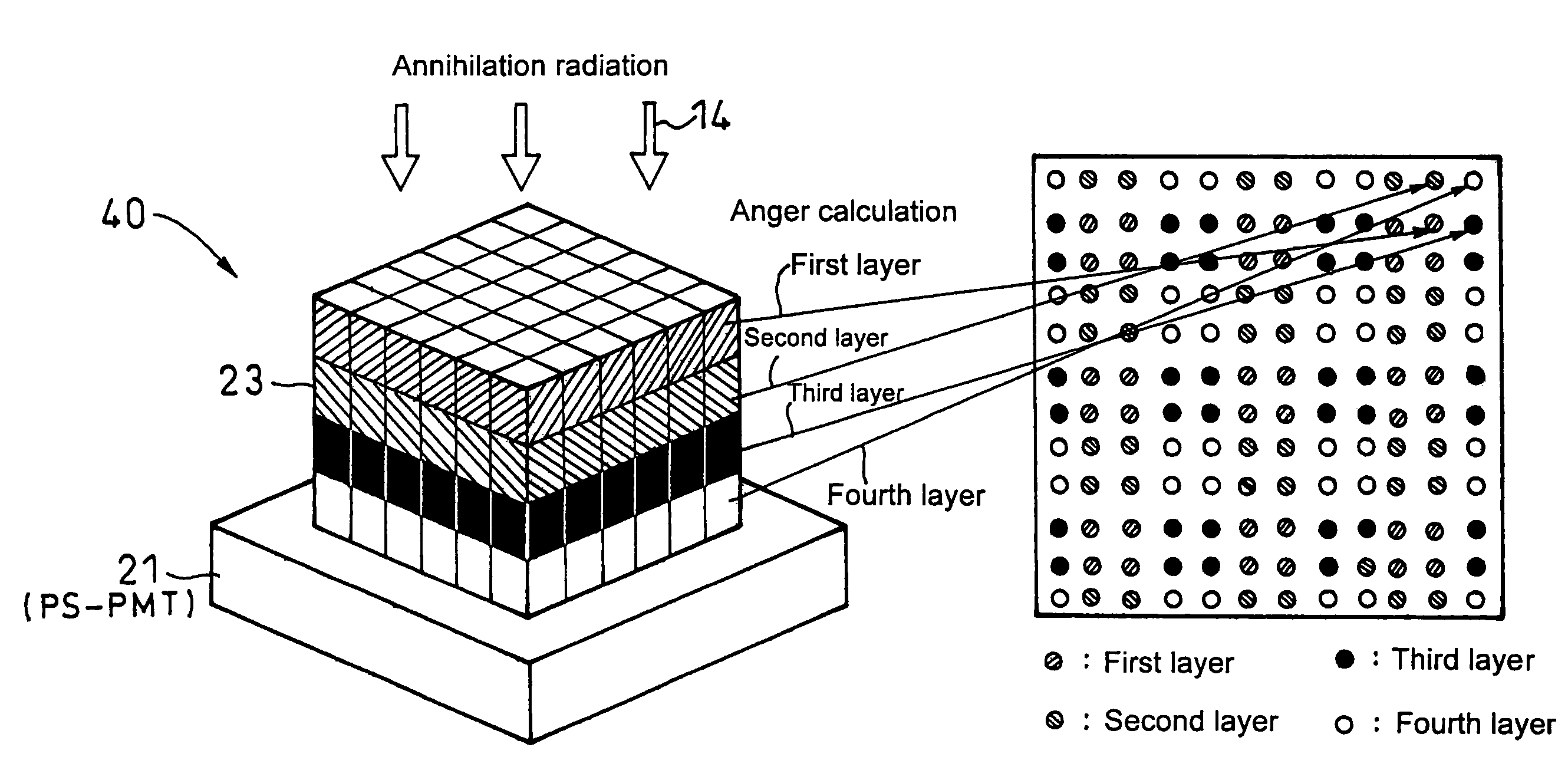
InactiveUS20090159804A1Improve accuracyRaise the ratioMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyAnnihilation radiationCompanion animal
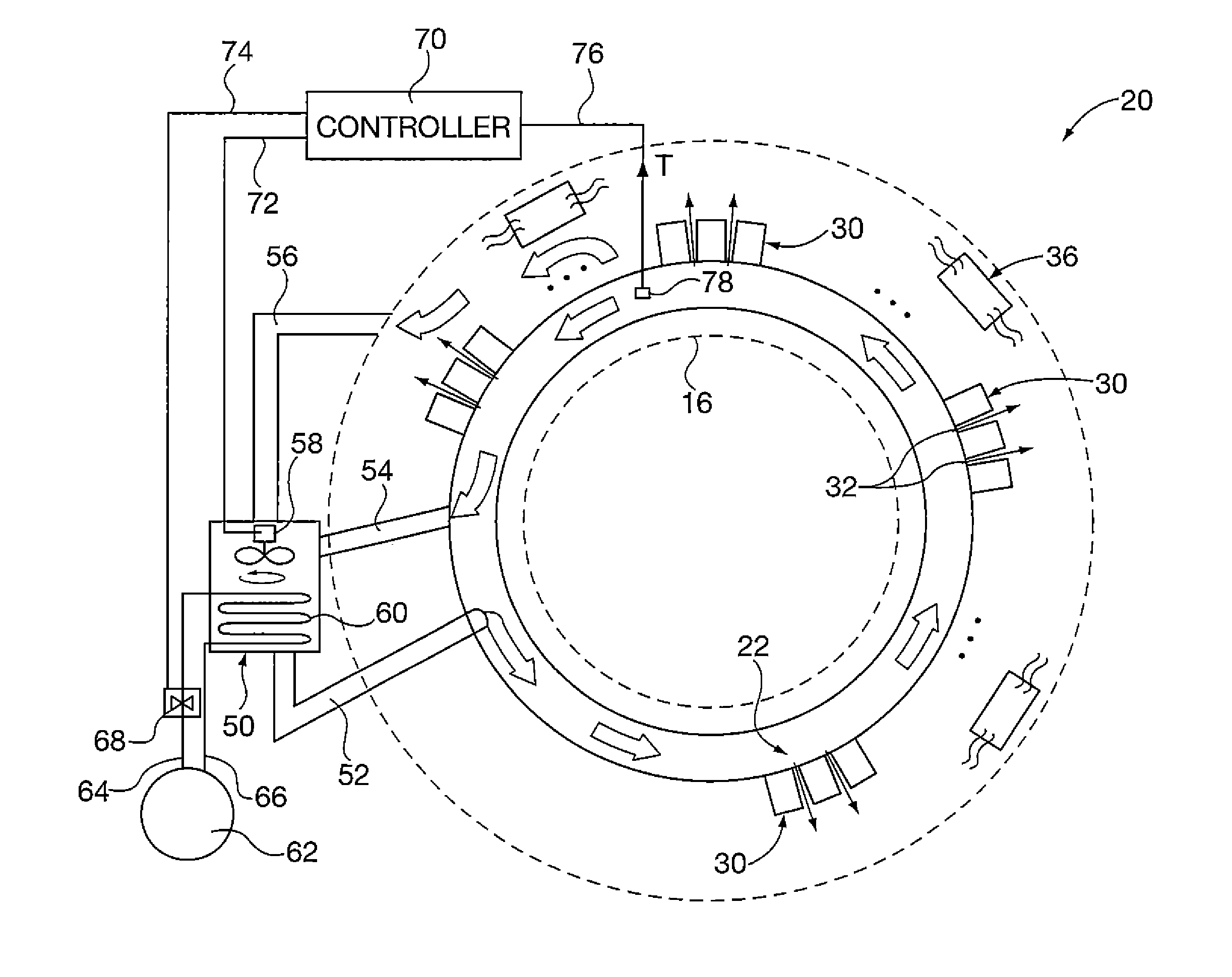
A positron emission tomography (PET) scanner is provided which uses information on the time-of-flight difference (TOF) between annihilation radiations for image reconstruction. The scanner has detection time correction information (memory) corresponding to information on coordinates in a radiation detection element (e.g., scintillator crystal), in the depth and lateral directions, at which an interaction has occurred between an annihilation radiation and the crystal. Reference is made to the detection time correction information, thereby providing information on time-of-flight difference with improved accuracy. As such, an improved signal to noise ratio and spatial resolution are provided for image reconstruction using time-of-flight (TOF) difference.
Owner:NAT INST FOR QUANTUM & RADIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
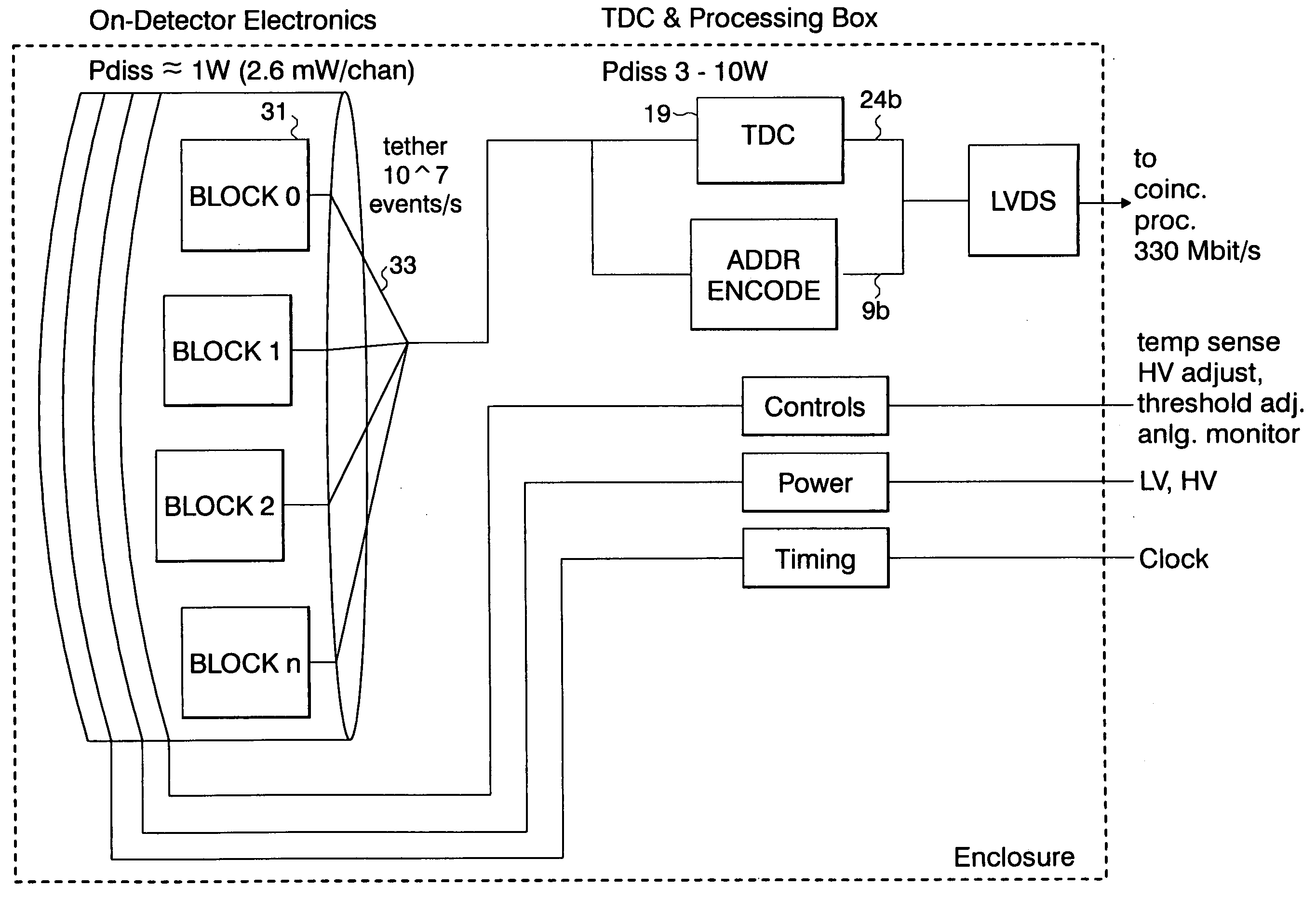
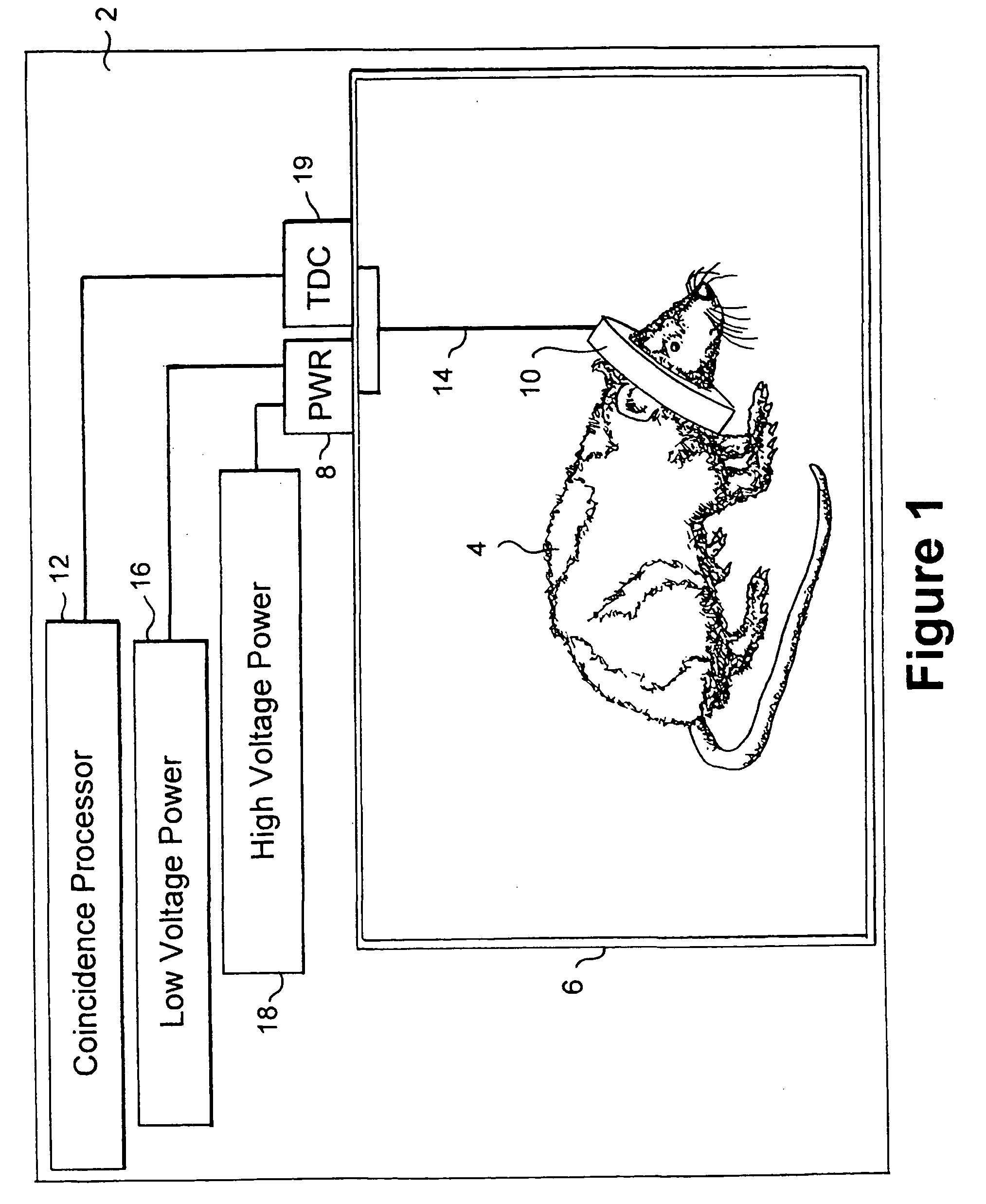
Compact conscious animal positron emission tomography scanner
ActiveUS20050082486A1Reduce power consumptionMagnetic measurementsHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSerial transferEngineering
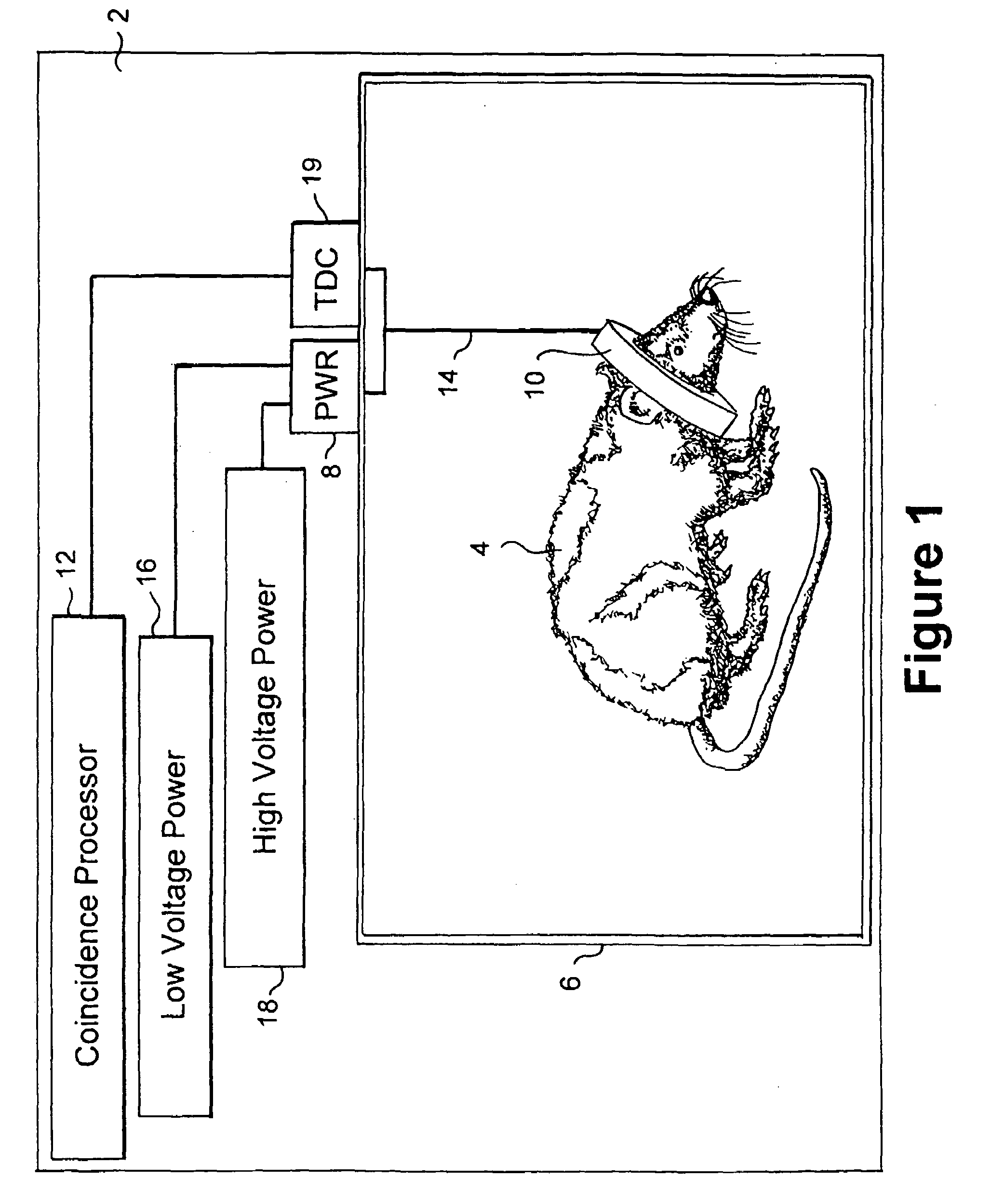
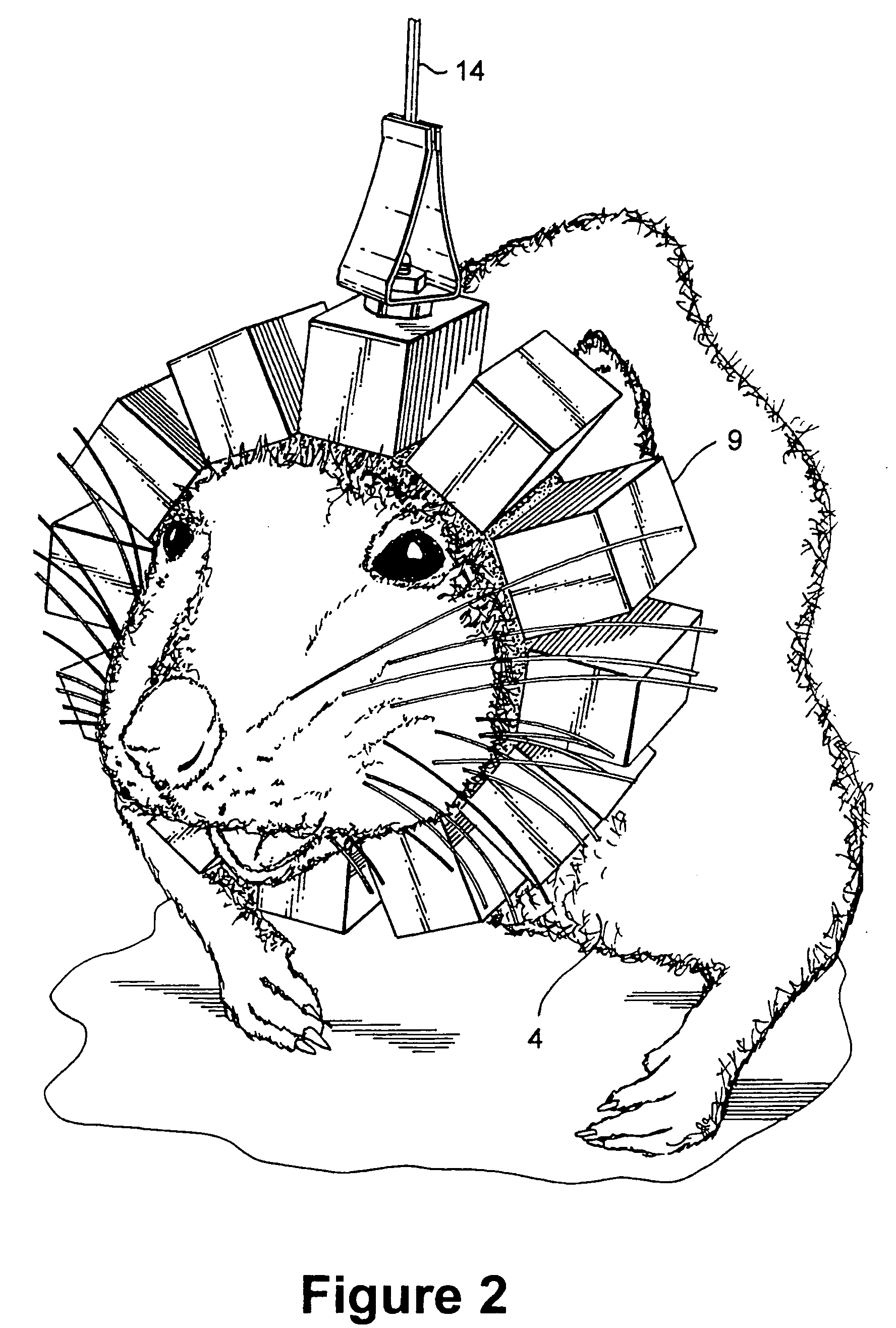
A method of serially transferring annihilation information in a compact positron emission tomography (PET) scanner includes generating a time signal for an event, generating an address signal representing a detecting channel, generating a detector channel signal including the time and address signals, and generating a composite signal including the channel signal and similarly generated signals. The composite signal includes events from detectors in a block and is serially output. An apparatus that serially transfers annihilation information from a block includes time signal generators for detectors in a block and an address and channel signal generator. The PET scanner includes a ring tomograph that mounts onto a portion of an animal, which includes opposing block pairs. Each of the blocks in a block pair includes a scintillator layer, detection array, front-end array, and a serial encoder. The serial encoder includes time signal generators and an address signal and channel signal generator.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Calibrating a positron emission tomography scanner
A method for calibrating a positron emission tomography scanner of a radiation therapy device is provided. The method includes applying at least one defined radiation dose in a sample body; measuring the activity generated by the radiation dose using the positron emission tomography scanner; and calibrating the positron emission tomography scanner based on the measured activity.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST PARTICLE THERAPY GMBH & CO KG
Method and apparatus for increasing spatial resolution of a pet scanner
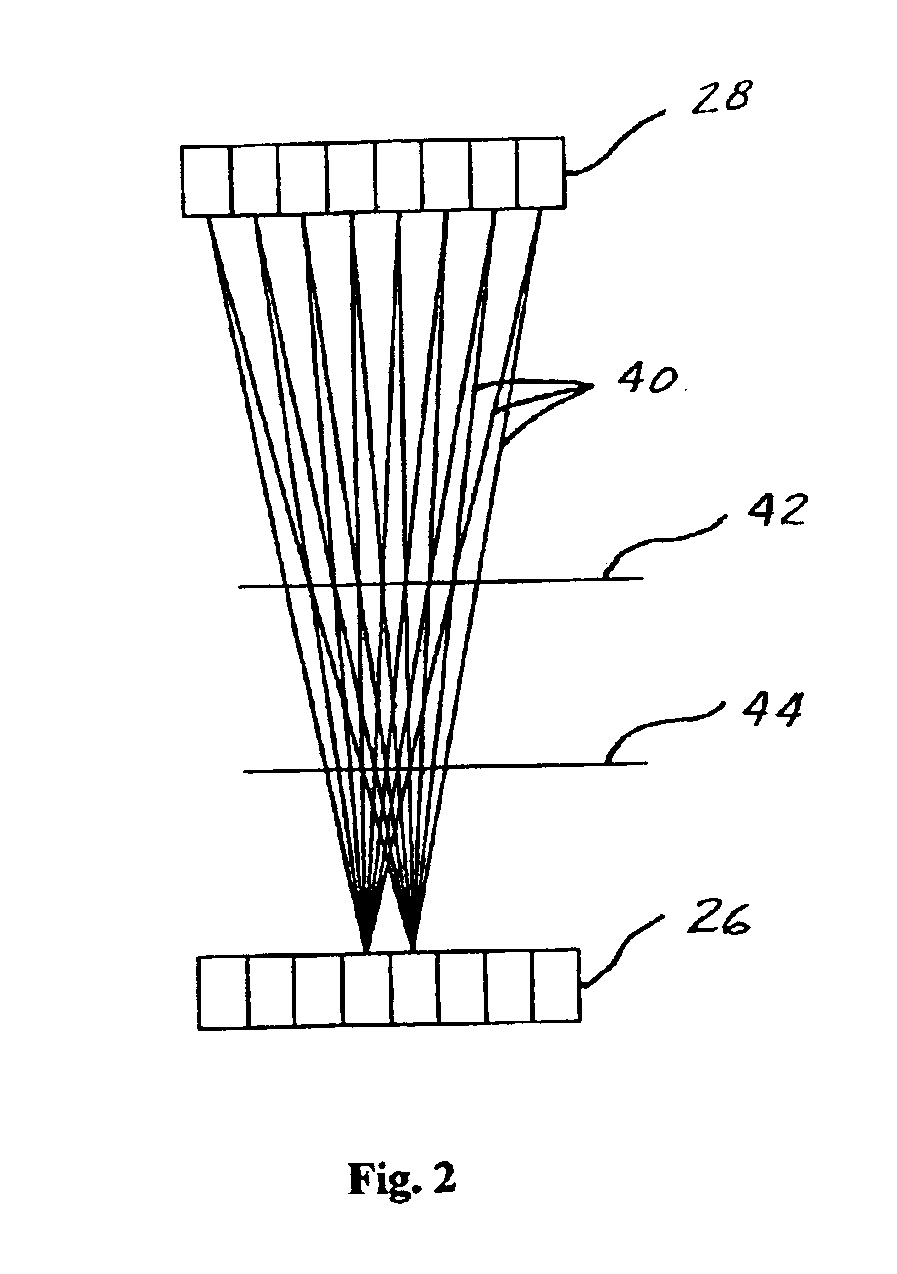
InactiveUS6946658B2Improve imaging resolutionImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementDetector arrayElectron
A method and apparatus for increasing the resolution of a Positron Emission Tomography scanner. The method and apparatus comprise elements and acts for centering a region of interest of an object at a point between first and second detector arrays which is at least about ten percent closer to the first detector array than to the second detector array.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Positron emission tomography scanner and conformity judgment and selection method
ActiveCN102631212AAvoid processing powerSpeed blockComputerised tomographsTomographyTime informationGamma photon
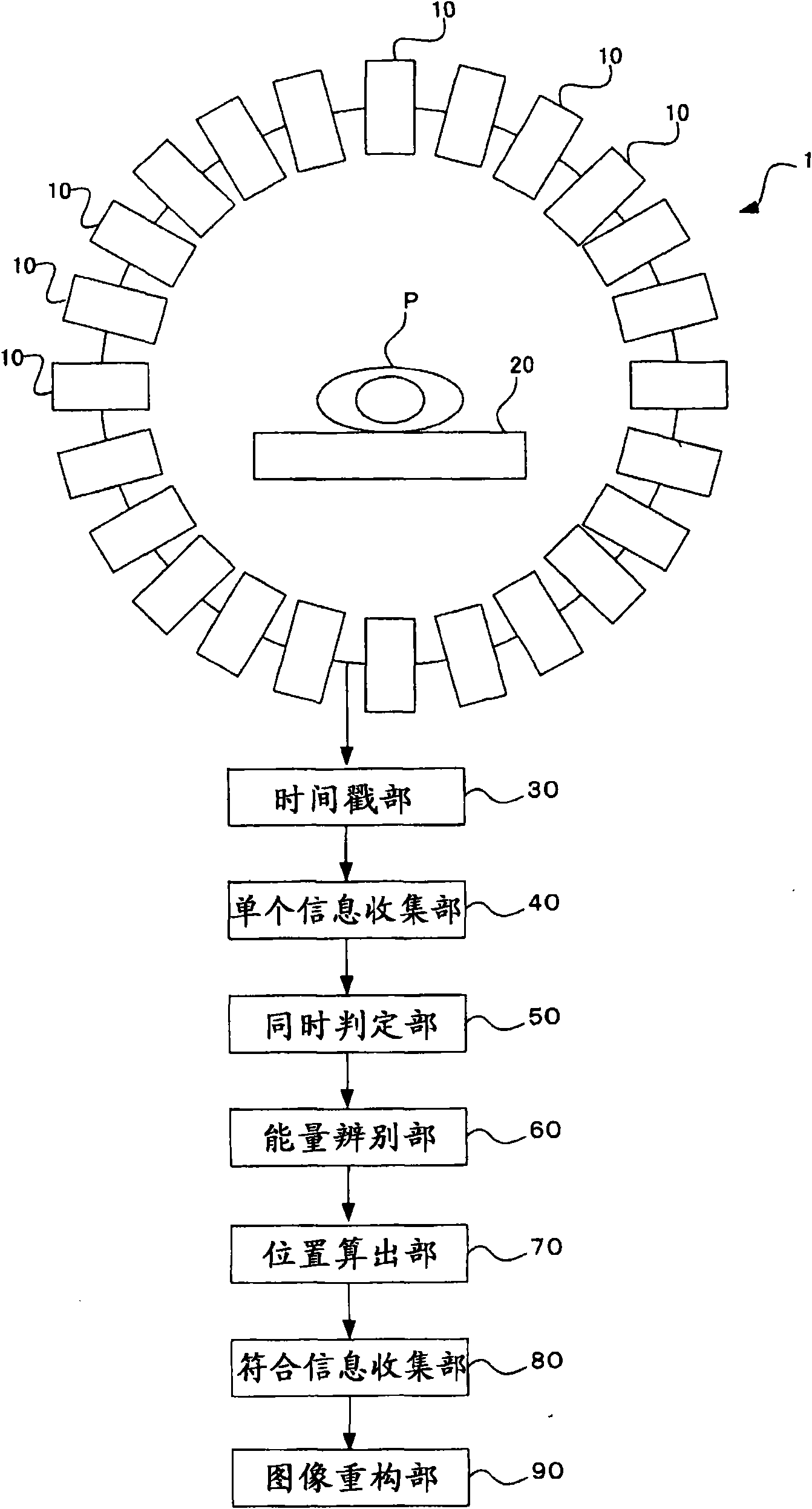
The invention relates to a positron emission tomography scanner and a conformity judgment and selection method. The scanner comprises a plurality of detectors. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring instance information of each detector; storing the instance information in the corresponding storage space; taking the time information of each instance information as address information of the storage space; acquiring a plurality of sign information according to each instance information, wherein each sign information shows times of detecting gamma photons in corresponding time; acquiring judgment and selection information according to each sign information, wherein the judgment and selection information represents the times of detecting the gamma photons in a preset conformed time window from the corresponding time information; ranking each judgment and selection according to the corresponding time information; checking the ranked judgment and selection information by utilizing sequence checking features in sequence; identifying the storage space that the conformed instance corresponds to; and outputting the instance information in the storage space that the conformed instance corresponds to. The positron emission tomography scanner and the conformity judgment and selection method provided by the invention have the advantages of rapid and efficient conformity judgment and selection and wide application range.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
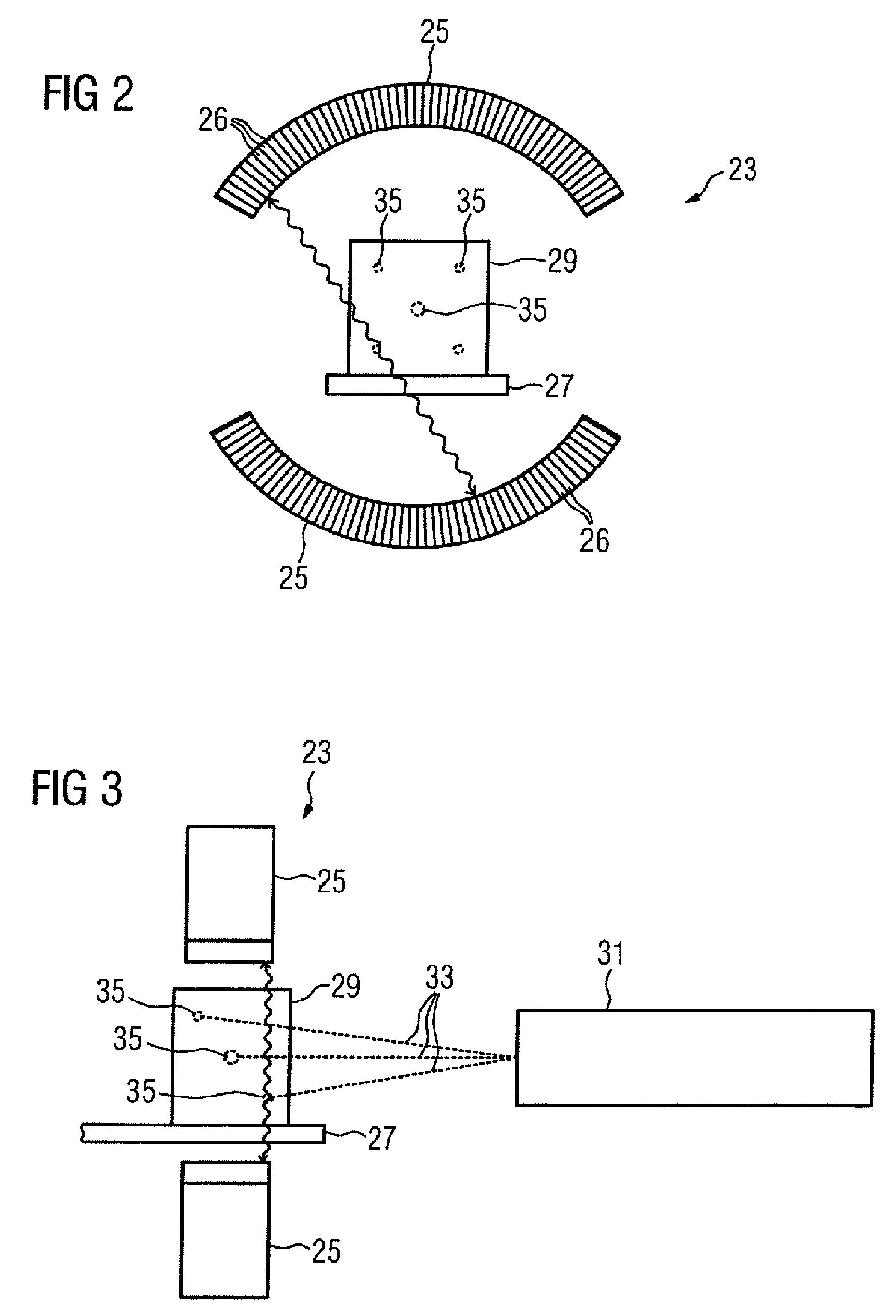
Detector arrangement for a tomographic imaging apparatus, particularly for a positron emission tomograph
InactiveUS20110198504A1Short decay timeEasy to detectMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementPhotodetectorScintillator
The invention relates to a detector arrangement (21) for a tomographic imaging apparatus, particularly for a positron emission tomograph. The detector arrangement (21) according to the invention includes at least two sandwiched pairs of a scintillator (22-24) and an associated photodetector (25-27), wherein the pairs are sandwiched along a direction of detection.
Owner:BERGEN TEKNOLOGIOVERFORING
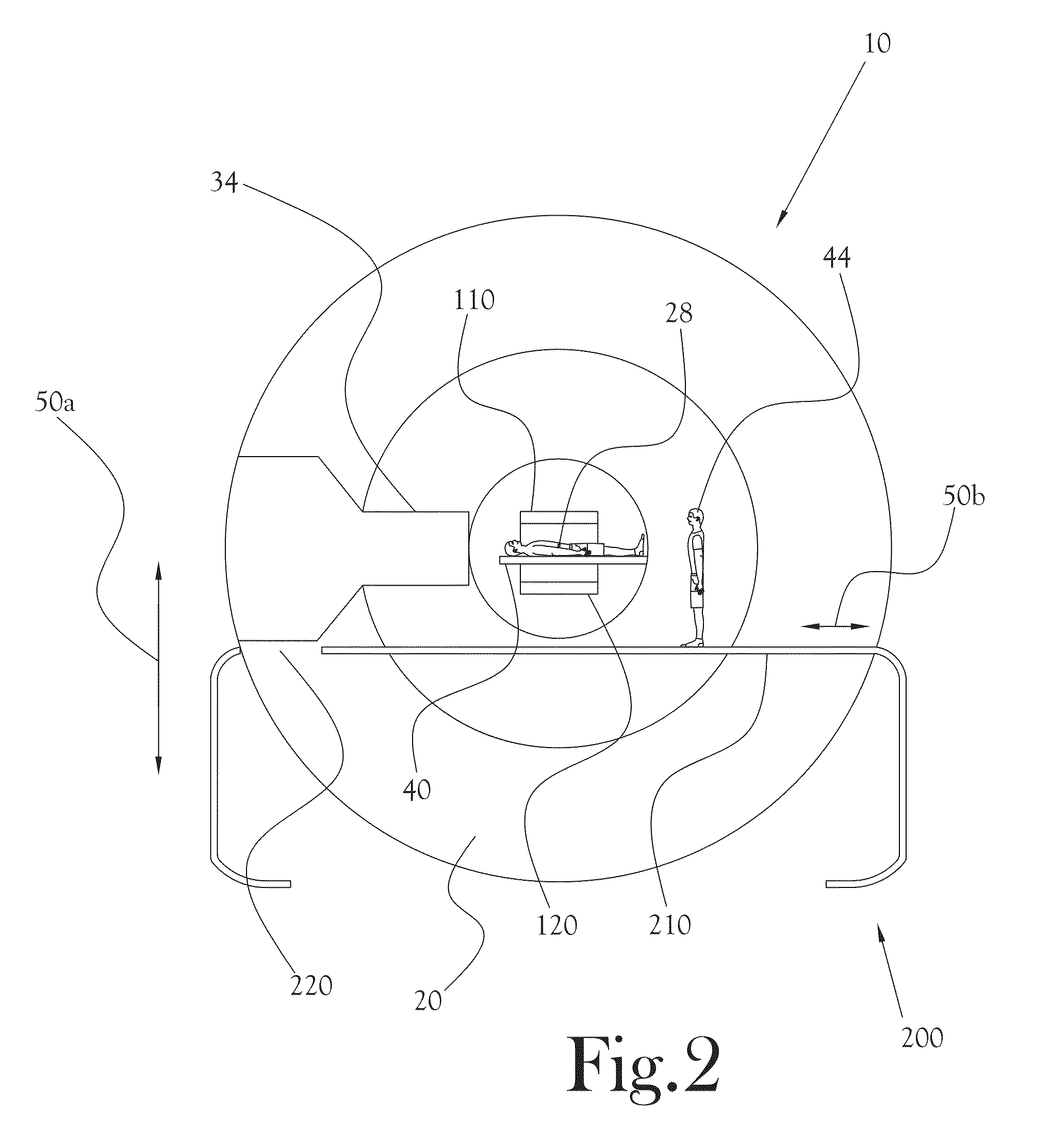
Apparatus and methods for cooling positron emission tomography scanner detector crystals
InactiveUS20130119259A1Sensitivity is increased and stabilizedWeaken energyMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyFractographyCompanion animal
Detector crystals in a positron emission tomography (PET) apparatus gantry are cooled by directing cooling gas flow into a cooling duct bounded by the crystals and a cover defining the patient scanning field within the gantry. The cooling gas cools the crystals. Cooling gas may also be directed radially outwardly from the cooling duct into spatial gaps defined between detector enclosures that include the crystals, further isolating heat generated by other components within gantry from the detector crystals. Cooling gas is provided by a cooling system that may be incorporated within the gantry, external the gantry or a combination of both. Cooling gas can be provided by directing air within the gantry in contact with internal gantry cooling tubes and routing cooled air directly into the cooling duct with a powered fan.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Positron emission tomography guided proton therapy
Systems and methods of treating a patient, including a proton treatment system having a proton delivery unit to direct protons to a target area of a patient, the proton treatment system including a positron emission tomography (PET) system having a detector unit to scan for radiotracers introduced into a patient's body, a processing unit to generate location information corresponding to a target area of the patient based on a scanned radiotracer, a guidance unit to receive the location information from the PET system and to instruct the proton delivery unit to direct protons to the target area according to the location information.
Owner:PRONOVA SOLUTIONS
Calibrating a Positron Emission Tomography Scanner
A method for calibrating a positron emission tomography scanner of a radiation therapy device is provided. The method includes applying at least one defined radiation dose in a sample body; measuring the activity generated by the radiation dose using the positron emission tomography scanner; and calibrating the positron emission tomography scanner based on the measured activity.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST PARTICLE THERAPY GMBH & CO KG
Compact conscious animal positron emission tomography scanner
ActiveUS7126126B2Reduce power consumptionMagnetic measurementsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringTime signal
A method of serially transferring annihilation information in a compact positron emission tomography (PET) scanner includes generating a time signal for an event, generating an address signal representing a detecting channel, generating a detector channel signal including the time and address signals, and generating a composite signal including the channel signal and similarly generated signals. The composite signal includes events from detectors in a block and is serially output. An apparatus that serially transfers annihilation information from a block includes time signal generators for detectors in a block and an address and channel signal generator. The PET scanner includes a ring tomograph that mounts onto a portion of an animal, which includes opposing block pairs. Each of the blocks in a block pair includes a scintillator layer, detection array, front-end array, and a serial encoder. The serial encoder includes time signal generators and an address signal and channel signal generator.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Positron emission tomography scanner and coincidence judging and selecting method therein
The invention relates to a positron emission tomography scanner and a coincidence judging and selecting method therein. The positron emission tomography scanner comprises a detecting ring, wherein the detecting ring consists of a plurality of detectors. The coincidence judging and selecting method comprises the following steps of: judging whether each detector is correlated to opposite detectors, acquiring correlation data according to each judgment result, and judging the two detectors to be correlated to each other if a time difference of a single event respectively detected by the two detectors stays within a coincidence time window, wherein the opposite detectors of any detector refer to the detectors in a sector area with a preset angle by adopting the detector as a center; and judging whether the two detectors are exclusively correlated to each other according to the correlation data and judging the single event detected by the two exclusively-correlated detectors to be a coincidence event. The positron emission tomography scanner and the coincidence judging and selecting method have advantages of rapidness in coincidence judging and selection, high efficiency and wide application range.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
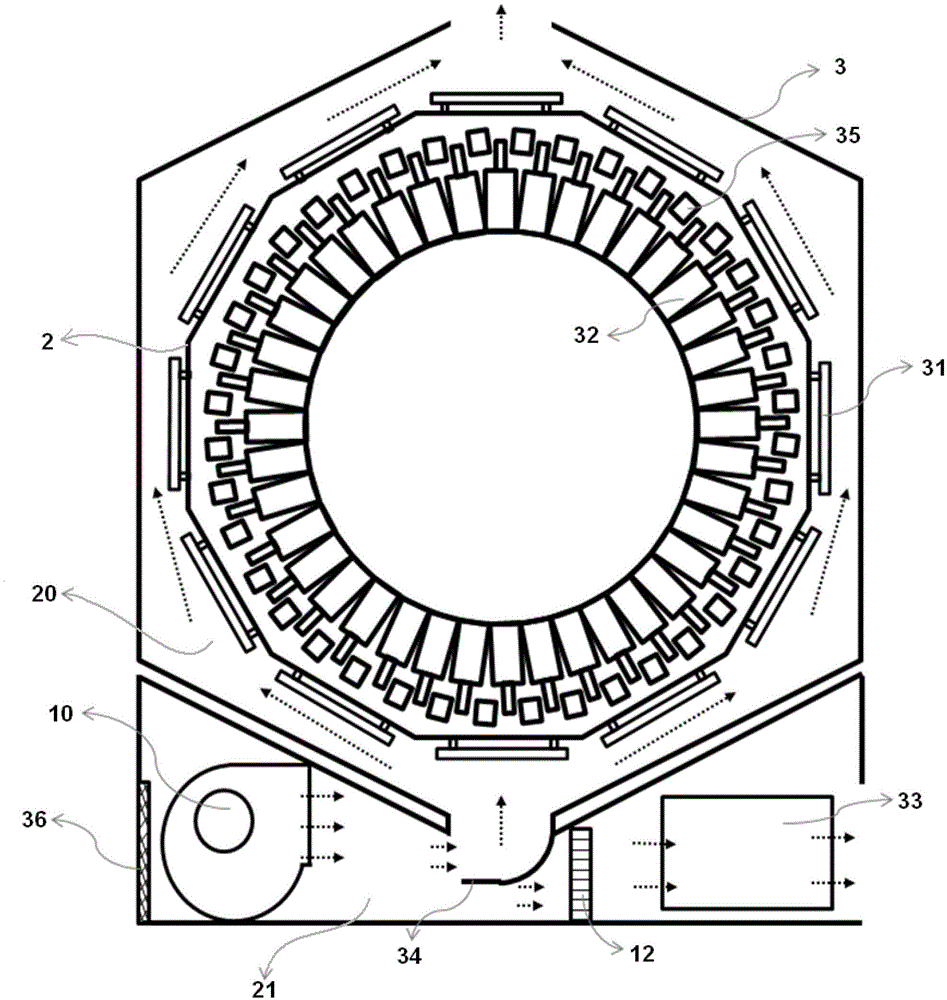
Cooling system of positron emission tomography scanner
ActiveCN103860187AAvoid driftingImprove stabilityComputerised tomographsTomographyInlet channelImaging quality
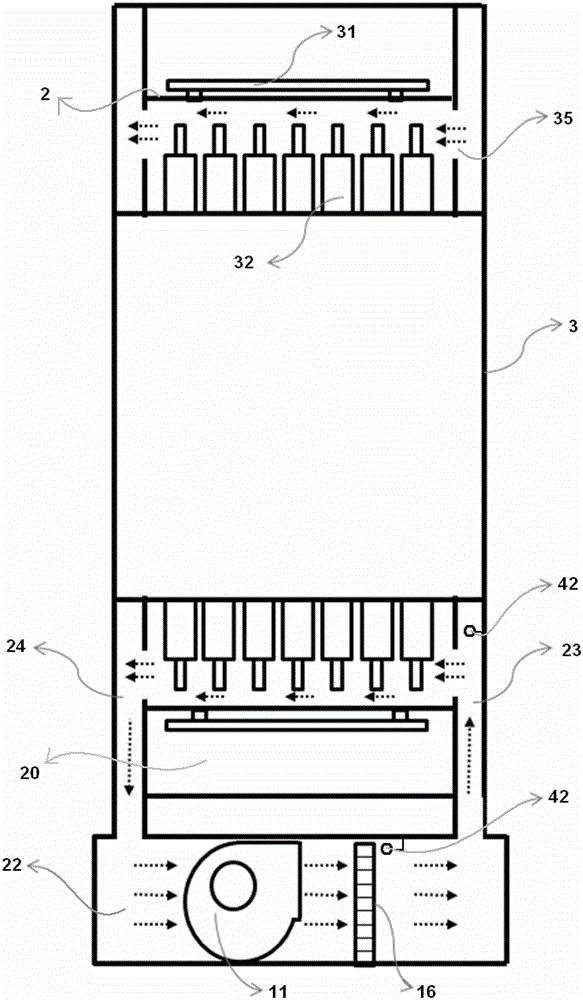
The invention discloses a cooling system of a positron emission tomography scanner. The positron emission tomography scanner comprises a peripheral electronics plate, a detector module and a bottom electronics plate; the cooling system comprises a cooling device, a peripheral cooling air channel, an inner chamber cooling air channel and a bottom cooling air channel; the inner chamber cooling air channel is a chamber body and comprises an air inlet channel and an air return channel; the peripheral electronics plate is located in the peripheral cooling air channel; the detector module is located between the air inlet channel and the air return channel; the bottom electronics plate is located in the bottom cooling air channel; the cooling device is used for conveying cooled air flow to the peripheral cooling air channel, the inner chamber cooling air channel and the bottom cooling air channel so as to cool the peripheral electronics plate, the detector module and the bottom electronics plate. According to the cooling system of the positron emission tomography scanner, ventilation cooling is performed on the peripheral electronics plate and the bottom electronics plate, the low-temperature and stable inner chamber cooling air channel is provided for the detector module, and accordingly the stability and the imaging quality of the system are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
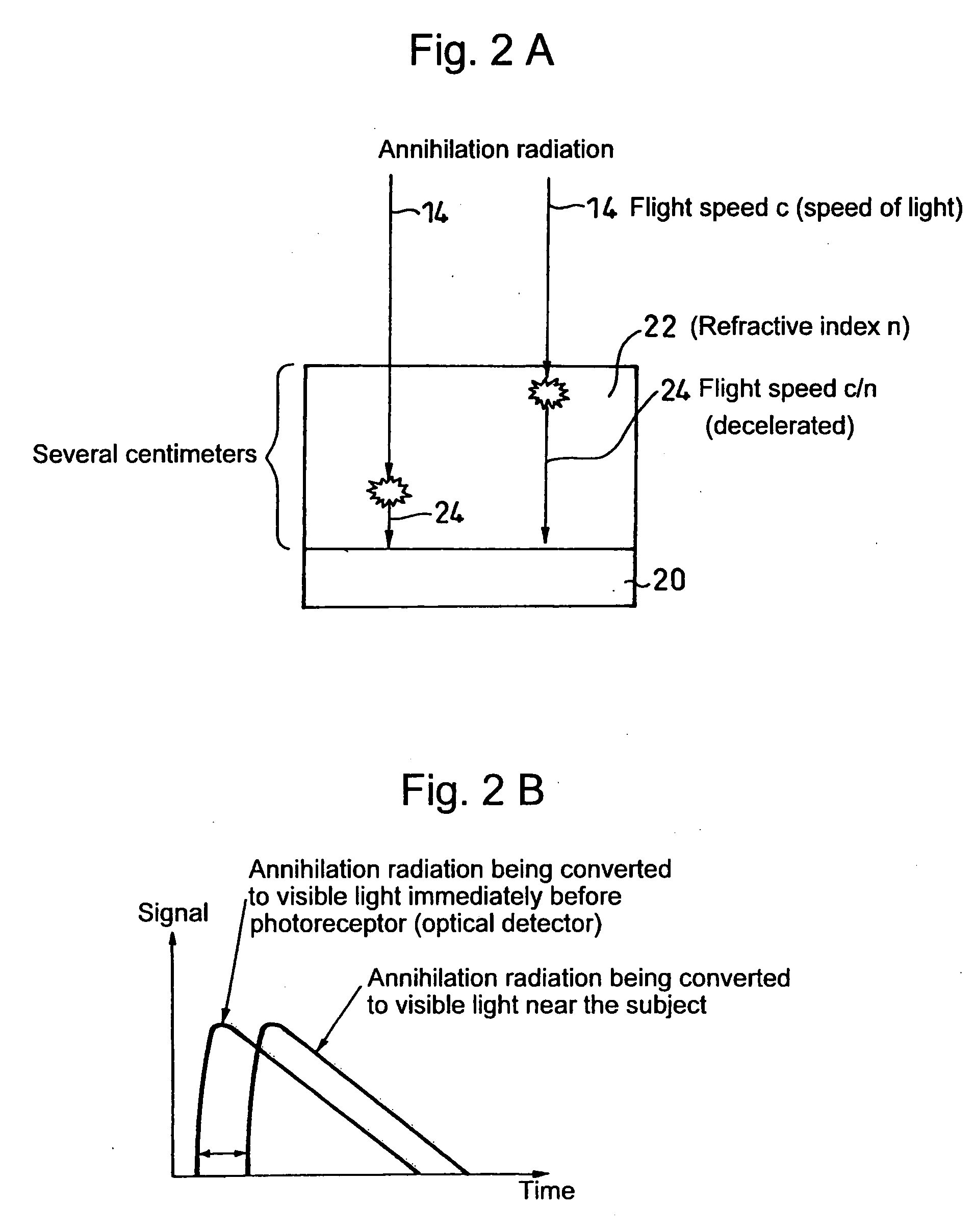
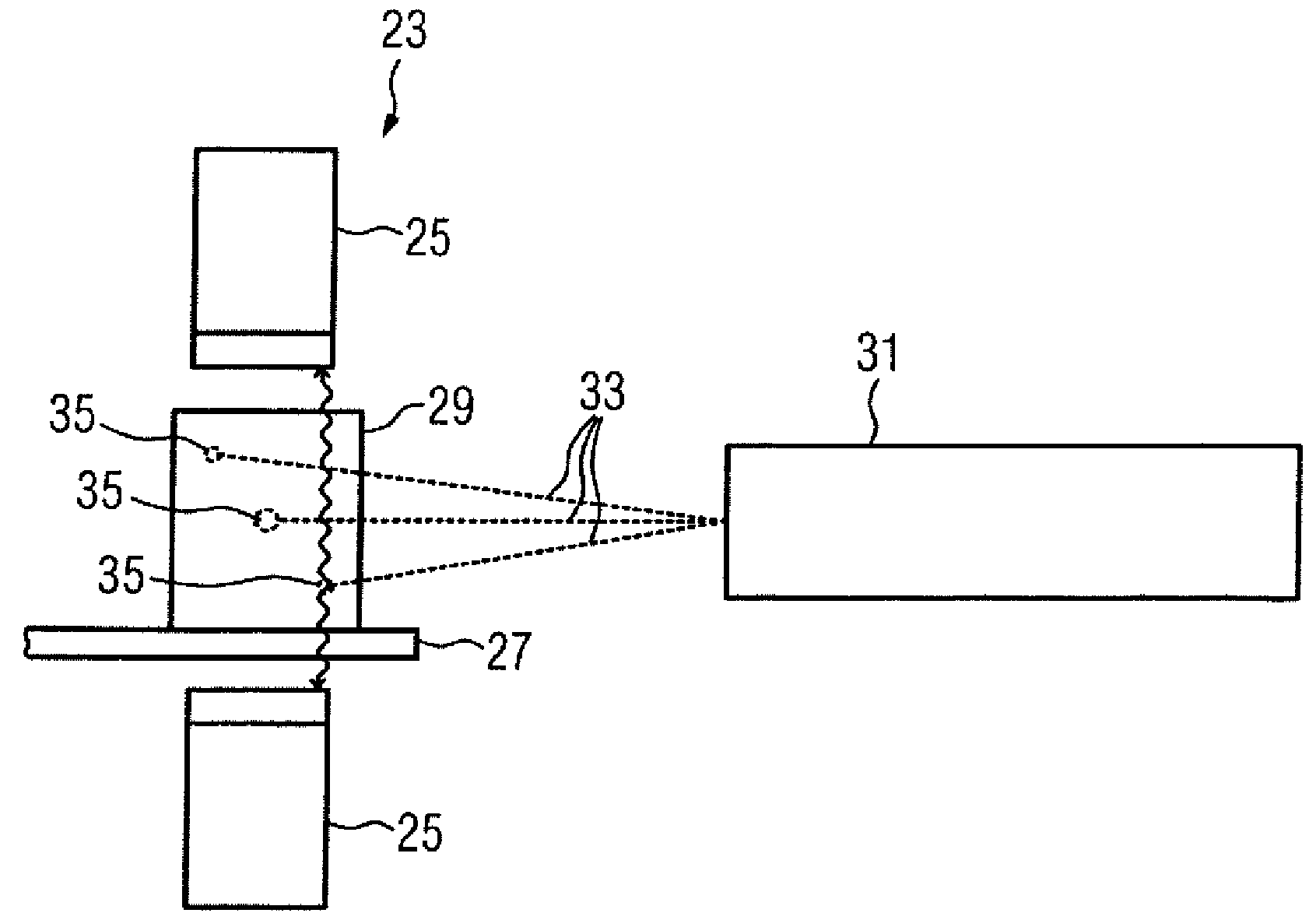
Method for detecting radiation, device thereof, and positron emission tomography scanner
InactiveUS20110001049A1High measurement accuracyResolution timeMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyScintillatorElectron
A light receiver for detecting incident time is installed on the side of a radiation source of a scintillator (including a Cherenkov radiation emitter), and information (energy, incident time, an incident position, etc.) on radiation made incident into the scintillator is obtained by the output of the light receiver. It is, thereby, possible to identify an incident position and others of radiation into the scintillator at high accuracy.
Owner:NAT INST FOR QUANTUM & RADIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
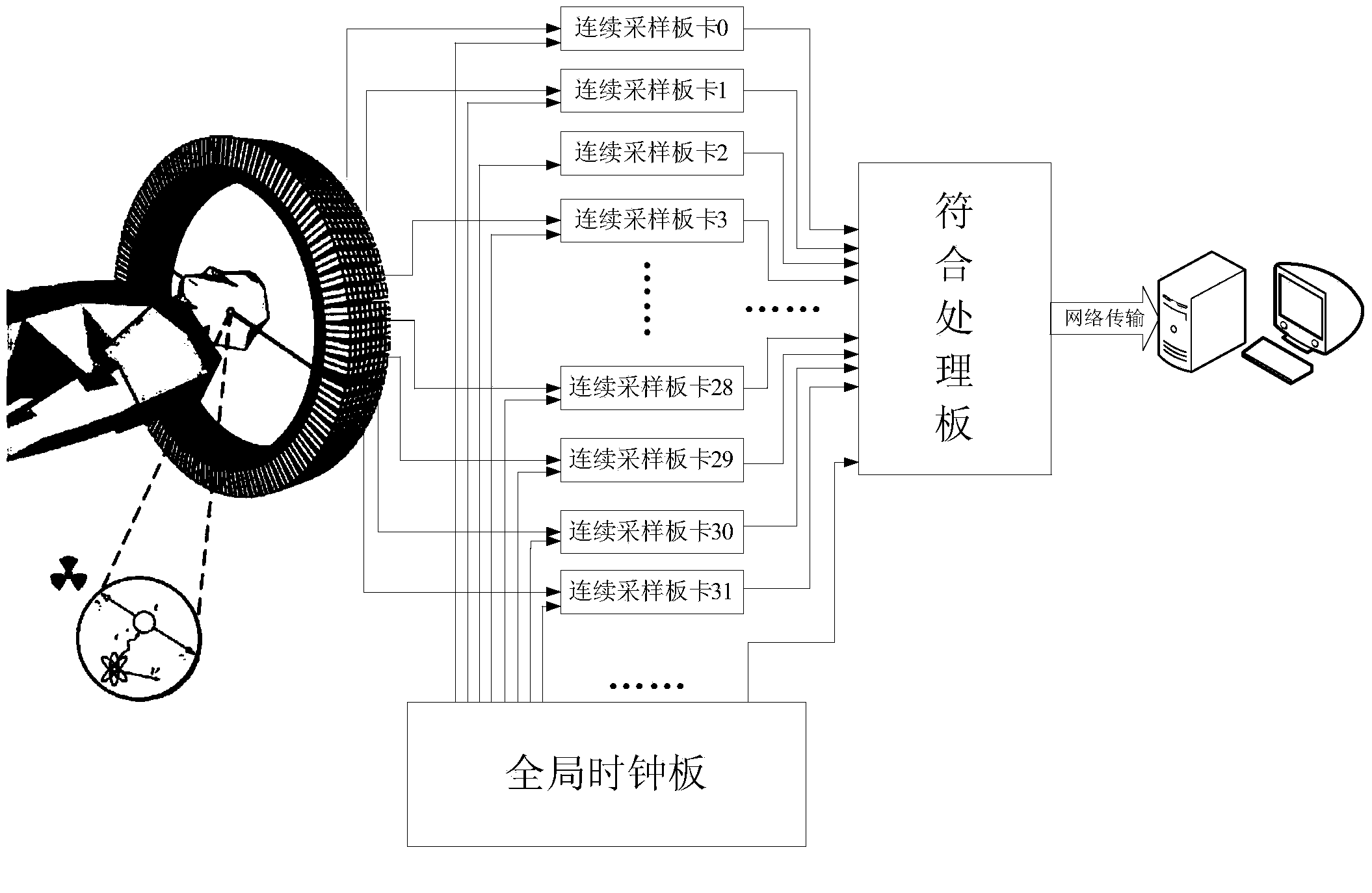
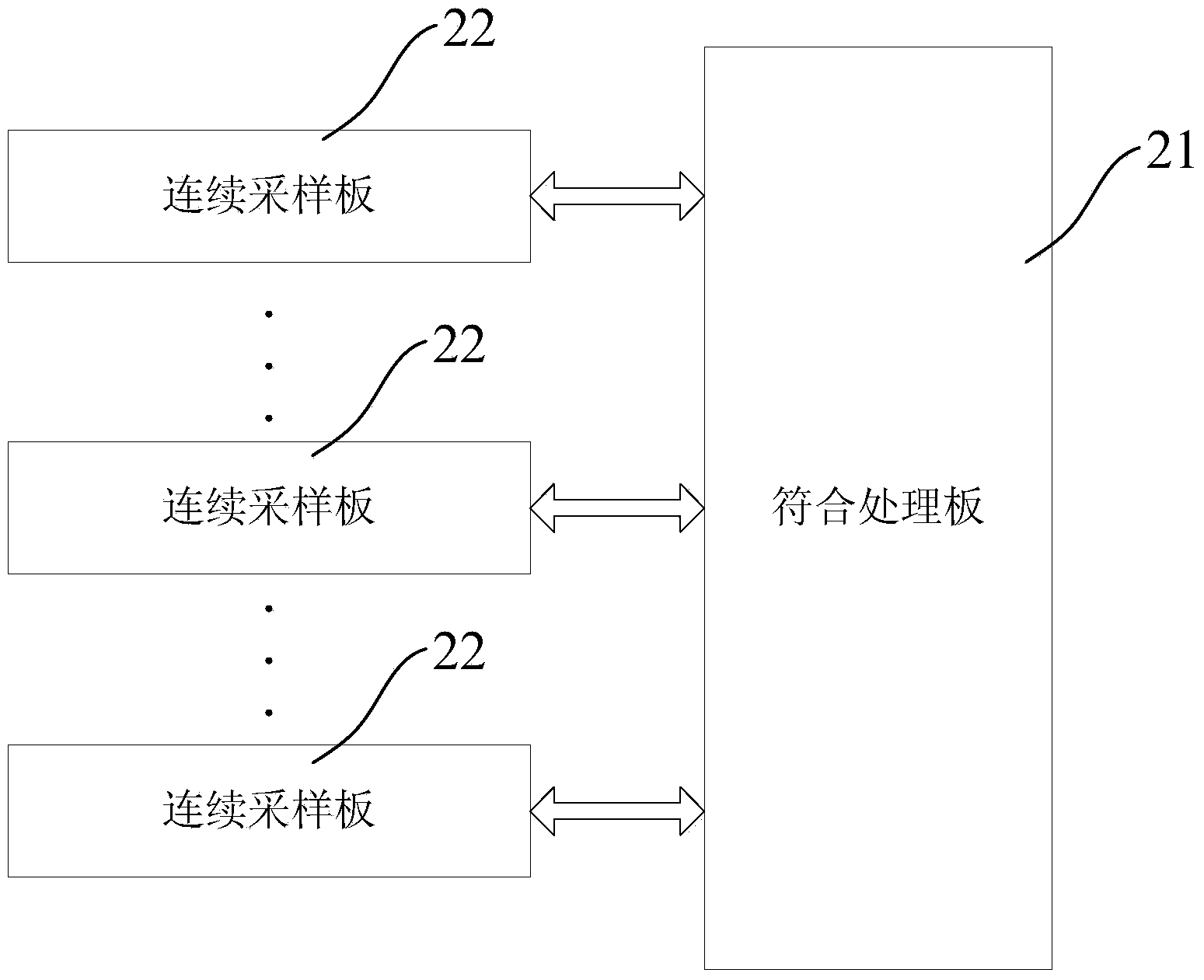
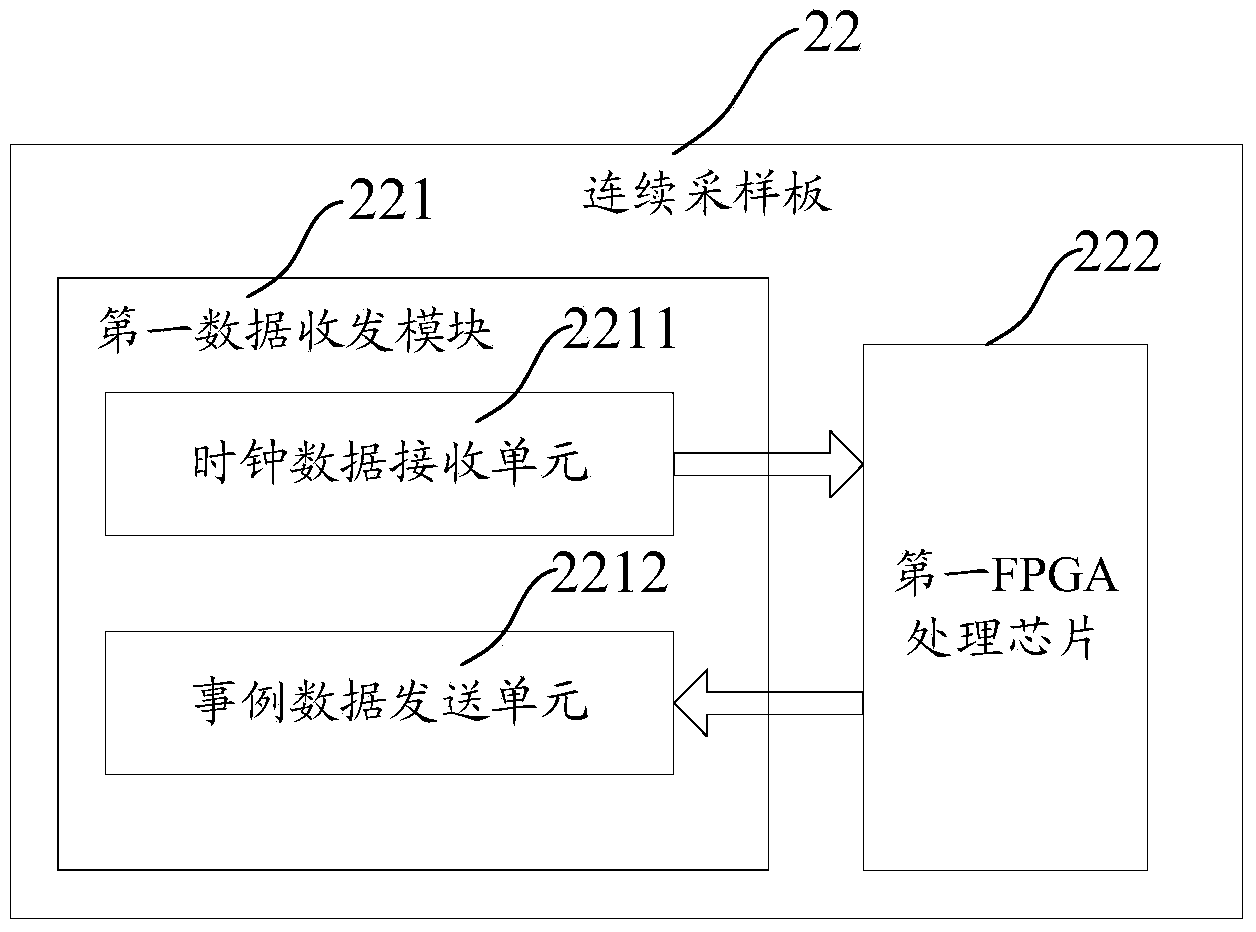
Clock synchronization control method and system and positron emission tomography scanner
The invention relates to a clock synchronization control method, a clock synchronization control system and a positron emission tomography scanner. The clock synchronization control system comprises a coincidence processing module CPM and a plurality of continuous sampling modules CSM respectively connected with the coincidence processing module, wherein the coincidence processing module is used for fanning local crystal oscillators, as source clocks, out through multiple routes, correspondingly sending multiple routes of fan-out clock data to each continuous sampling module and receiving, judging and selecting example data sent by each continuous sampling module; each continuous sampling module is used for receiving the multiple routes of clock data sent by the coincidence processing module, recovering the source clocks according to the received clock data, taking the recovered clock as main working clock sampling example data and sending the collected example data to the coincidence processing module. According to the clock synchronization control system, bidirectional data transmission is realized between the continuous sampling modules and the coincidence processing module, a global clock module does not need to be singly arranged, and the global clock distribution of each continuous sampling module is realized through the coincidence processing module, so that the system structure is simplified.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Positron emission tomography apparatus and nuclear medical image generating method
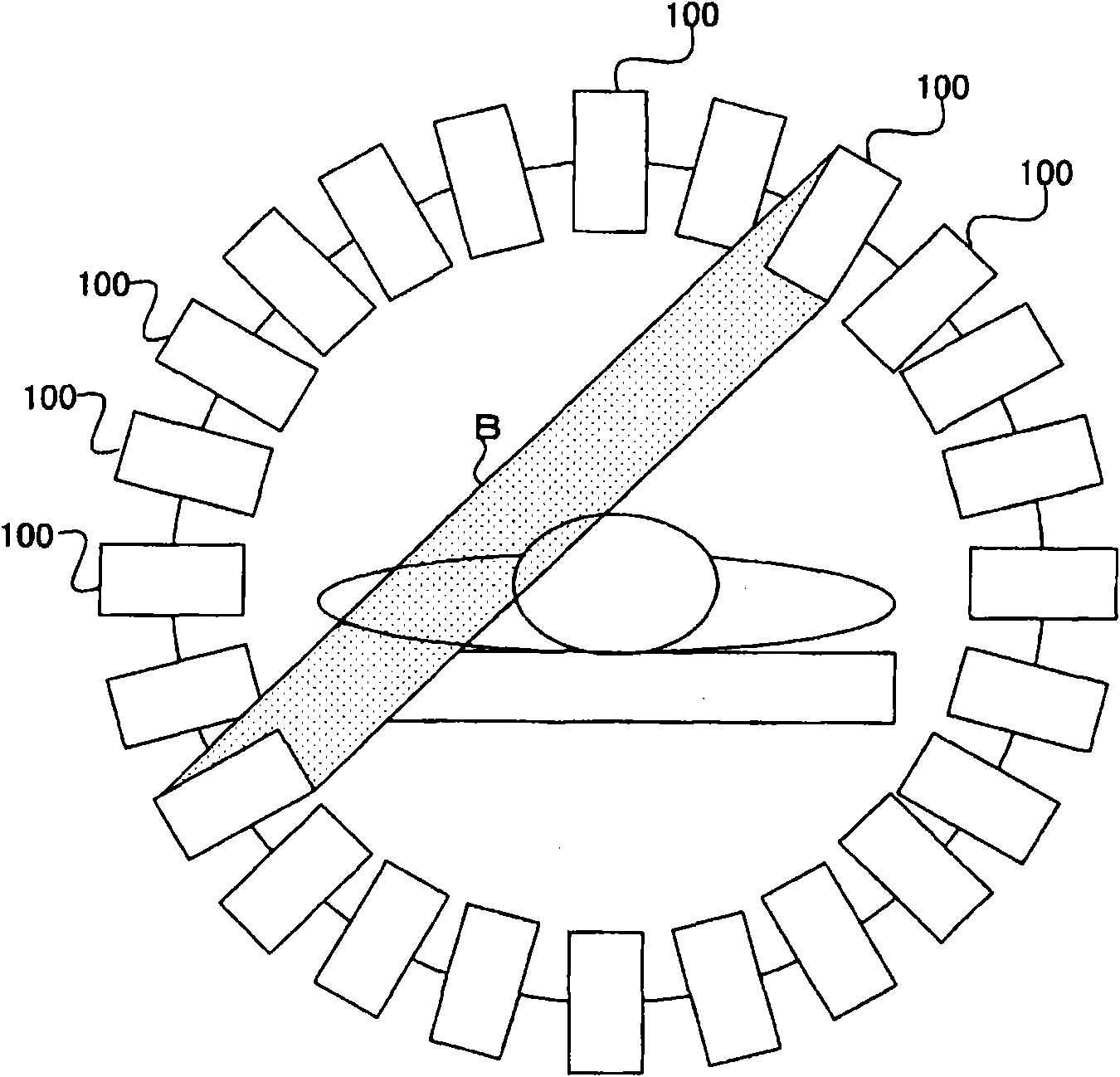
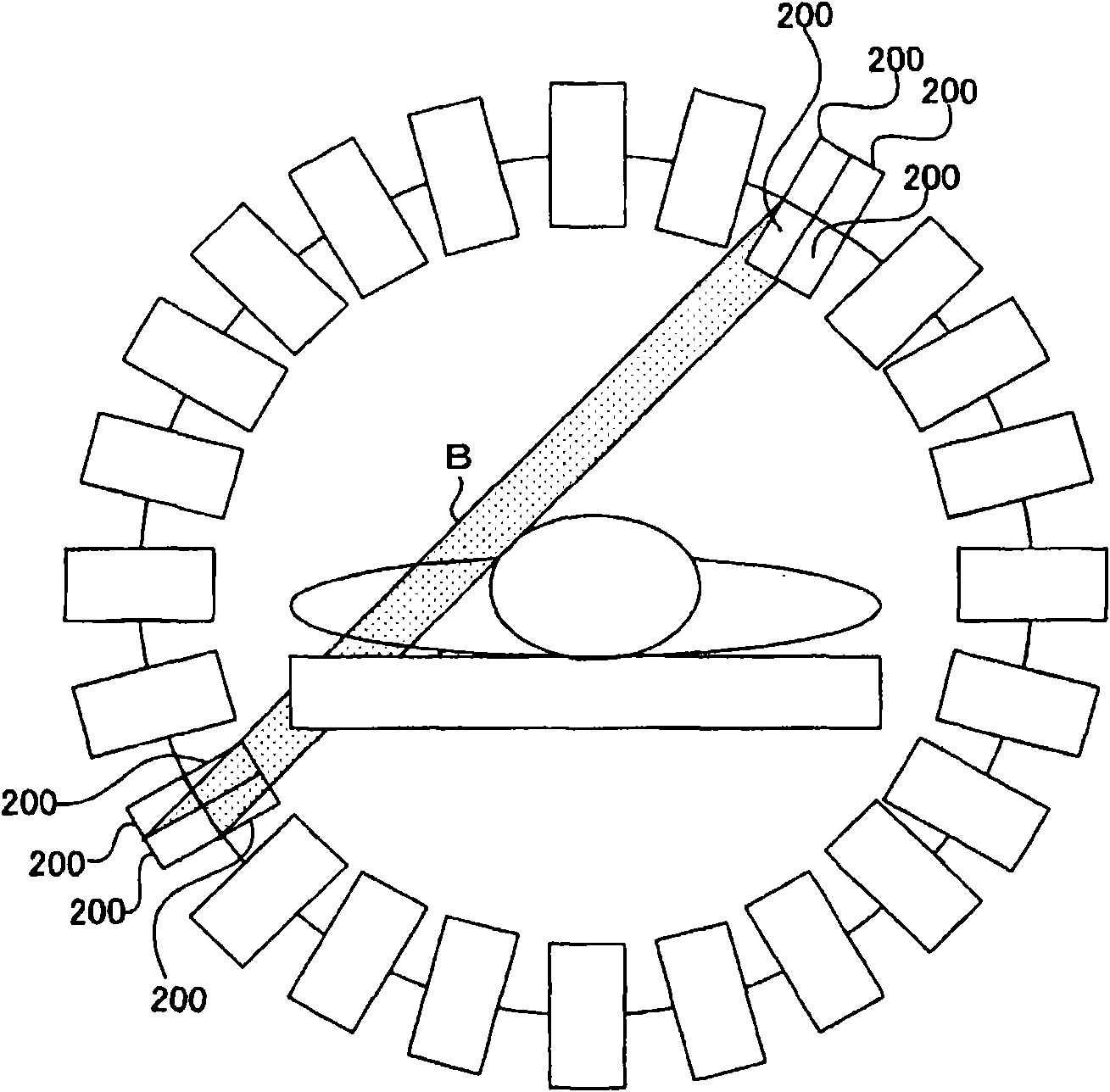
The invention provides a positron emission tomography apparatus and a nuclear medical image generating method. In a case that a gamma ray has entered into a plurality of scintillators adjacent to each other simultaneously, a detector detects the gamma ray having entered simultaneously. A position calculator calculates the ratio of wave heights representing the energies of the detected gamma ray. The position calculator obtains a trajectory of such a gamma ray that a ratio of distances passed by the gamma ray inside the plurality of scintillators, respectively, coincides with the ratio of the wave heights. The position calculator obtains an intersection between the boundary of the plurality of scintillators and the trajectory, as a passing position of the gamma ray. A reconstructing part executes a back projection process with the trajectory passing through the calculated passing position as a projection position.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Generating detector efficiency estimates for a pet scanner
InactiveUS20060249682A1Material analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentBlank ScanDetector array
Detector efficiency data is generated for a positron emission tomography scanner (2) including a single photon source by conducting a blank scan acquisition procedure using the single photon source. The acquired detection count data is processed using an efficiency estimation algorithm to calculate data efficiencies of individual detectors in the detector array (8). In one embodiment, the detection count data is output as artificial coincidence count data and the efficiency estimation algorithm operates on the artificial coincidence count data. The method can be used in a non-rotating scanner or a rotating scanner.
Owner:HAMMERSMITH IMANET
Method of and software for calculating a scatter estimate for tomographic scanning and system for tomographic scanning
InactiveUS20100086101A1Improve fitImprove stabilityReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTomographyPositron emission tomographic
The method calculates a scatter estimate for scatter correction of detection data from a subject in a positron emission tomographic scanner. The detection data represent the scattered events and unscattered events of annihilation photons emitted in the subject. The method uses the following steps:determine an estimate of the unscattered events;determine a simulation of the scattered events;determine a value of a scaling factor by fitting the sum of the estimate of the unscattered events and a product of the scaling factor and the simulation of the scattered events to the detection data; anddetermine the scatter estimate as the product of the scaling factor having said value and the simulation of the scattered events.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Method and apparatus for increasing spatial resolution of a pet scanner
InactiveUS20060027755A1Improve imaging resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementDetector arrayTomography
A method and apparatus for increasing the resolution of a Positron Emission Tomography scanner. The method and apparatus comprise elements and acts for centering a region of interest of an object at a point between first and second detector arrays at least about ten percent closer to the first detector array than to the second detector array.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
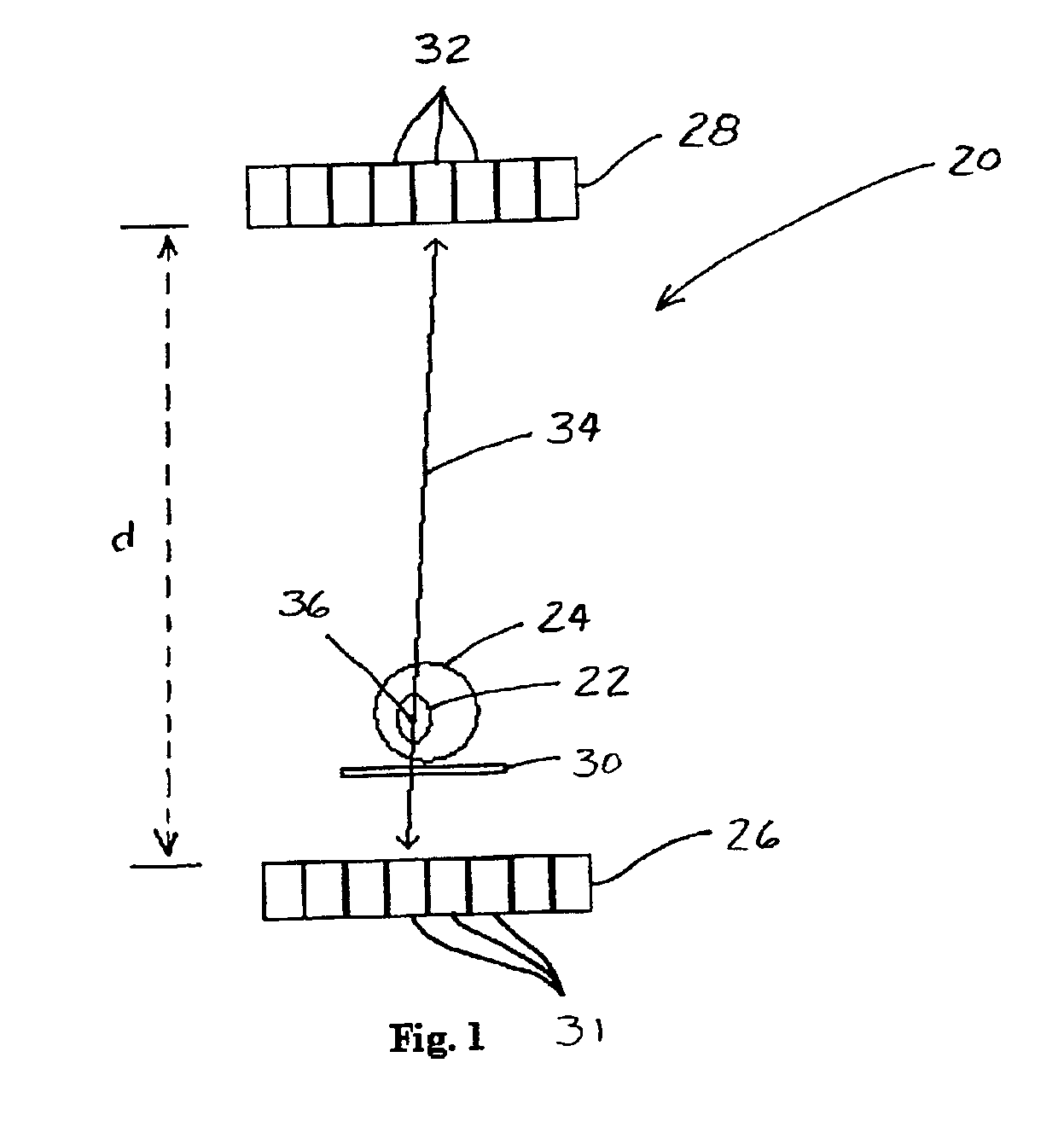
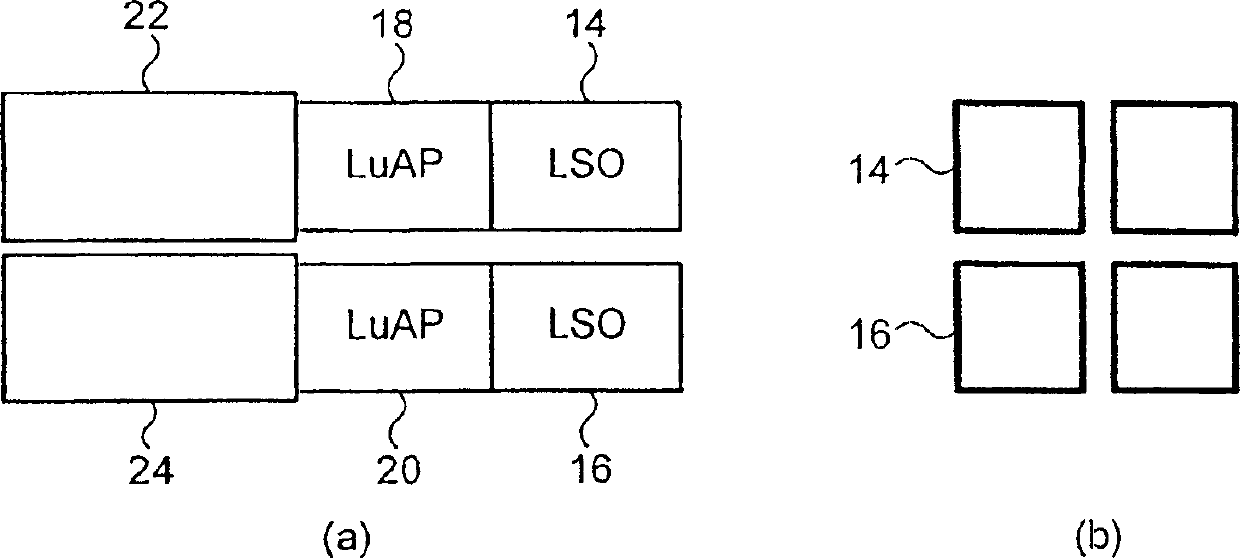
PET scanner
A positron emission camera comprising a plurality of scintillators, wherein the scintillators comprise LuAlO3:Ce (LuAP) based crystals (18,20). In particular, the scintillation crystals (18,20) are LuAP and / or LuYAP.
Owner:EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH
Method for determining radiation attenuation in positron emission tomography
InactiveCN102293662AImproved radiation attenuationExact radiation attenuationReconstruction from projectionComputerised tomographsRadiation attenuationElectron
A method is disclosed for determining radiation attenuation as a result of an object in a positron emission tomography scanner. In at least one embodiment, a phantom object is arranged in the positron emission tomography scanner during the method. First raw radiation data of the phantom object is acquired while the object is not arranged in the positron emission tomography scanner. A first image of the phantom object is calculated from the first raw radiation data. The object then is arranged in the positron emission tomography scanner (2) and preliminary radiation attenuation of the object is identified. Second raw radiation data of the phantom object is acquired while the object is arranged in the positron emission tomography scanner. A second image of the phantom object is calculated from the second raw radiation data taking into account the preliminary radiation attenuation. The radiation attenuation is determined on the basis of the first image and the second image.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
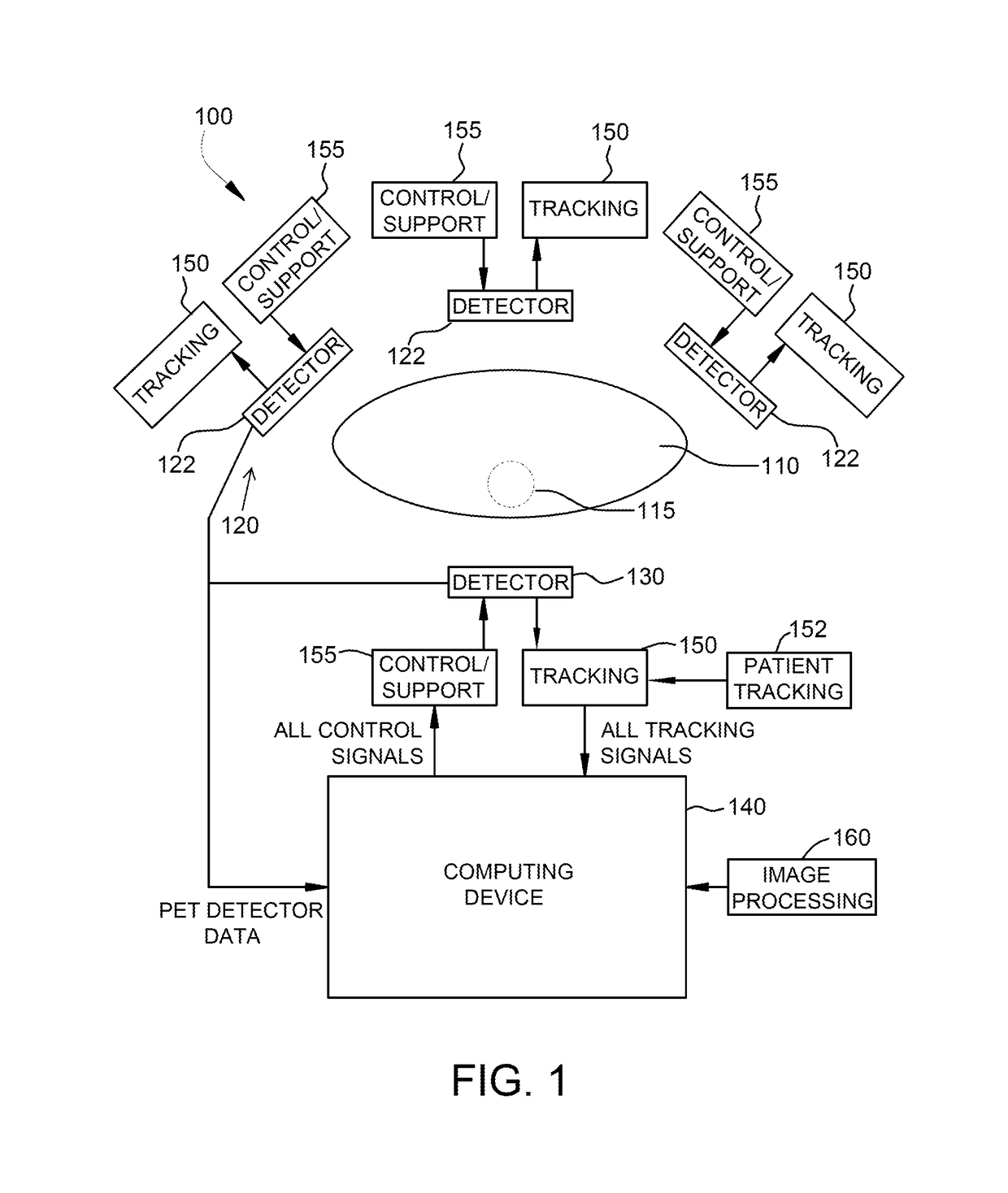
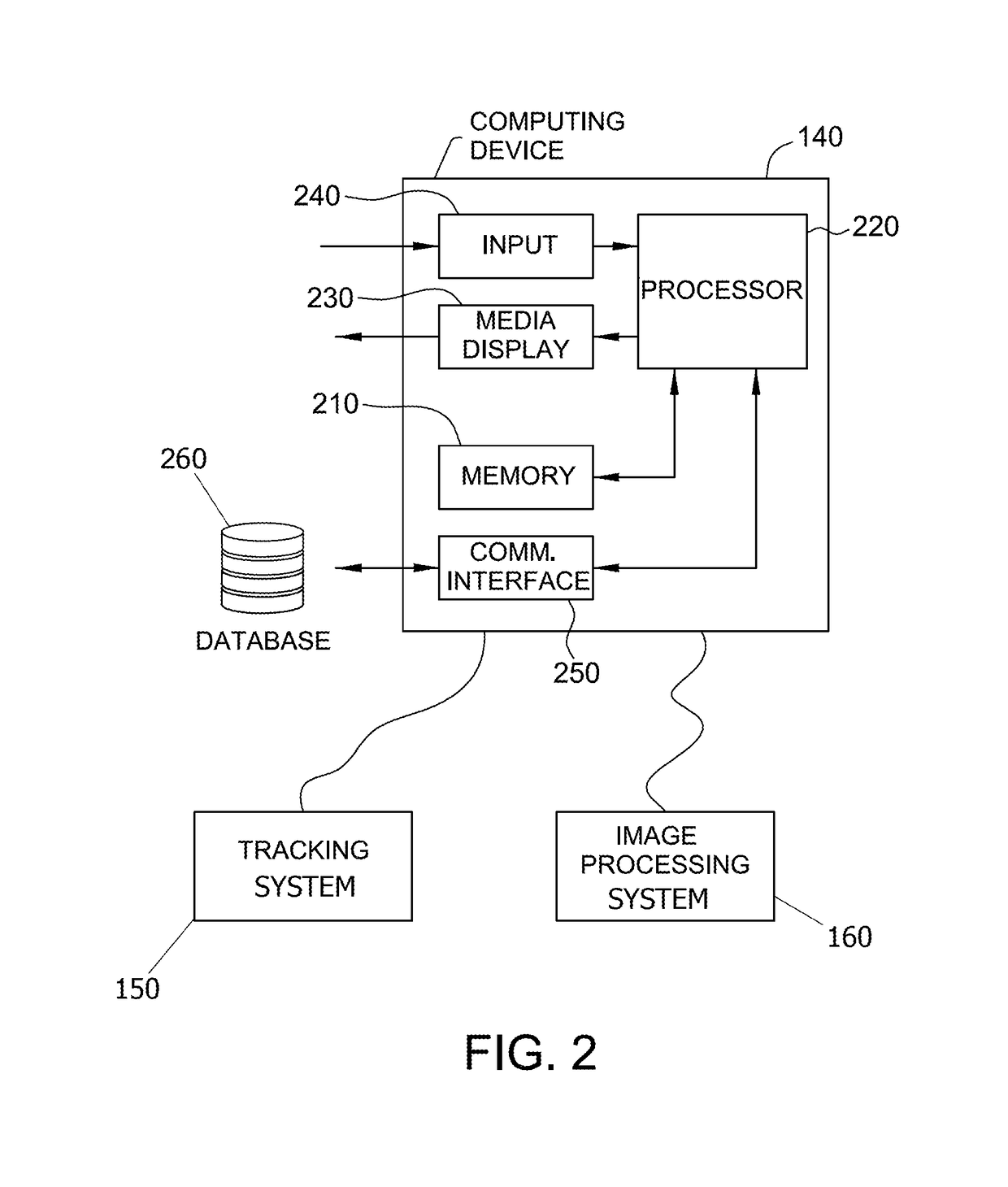
Systems and methods for point-of-care positron emission tomography
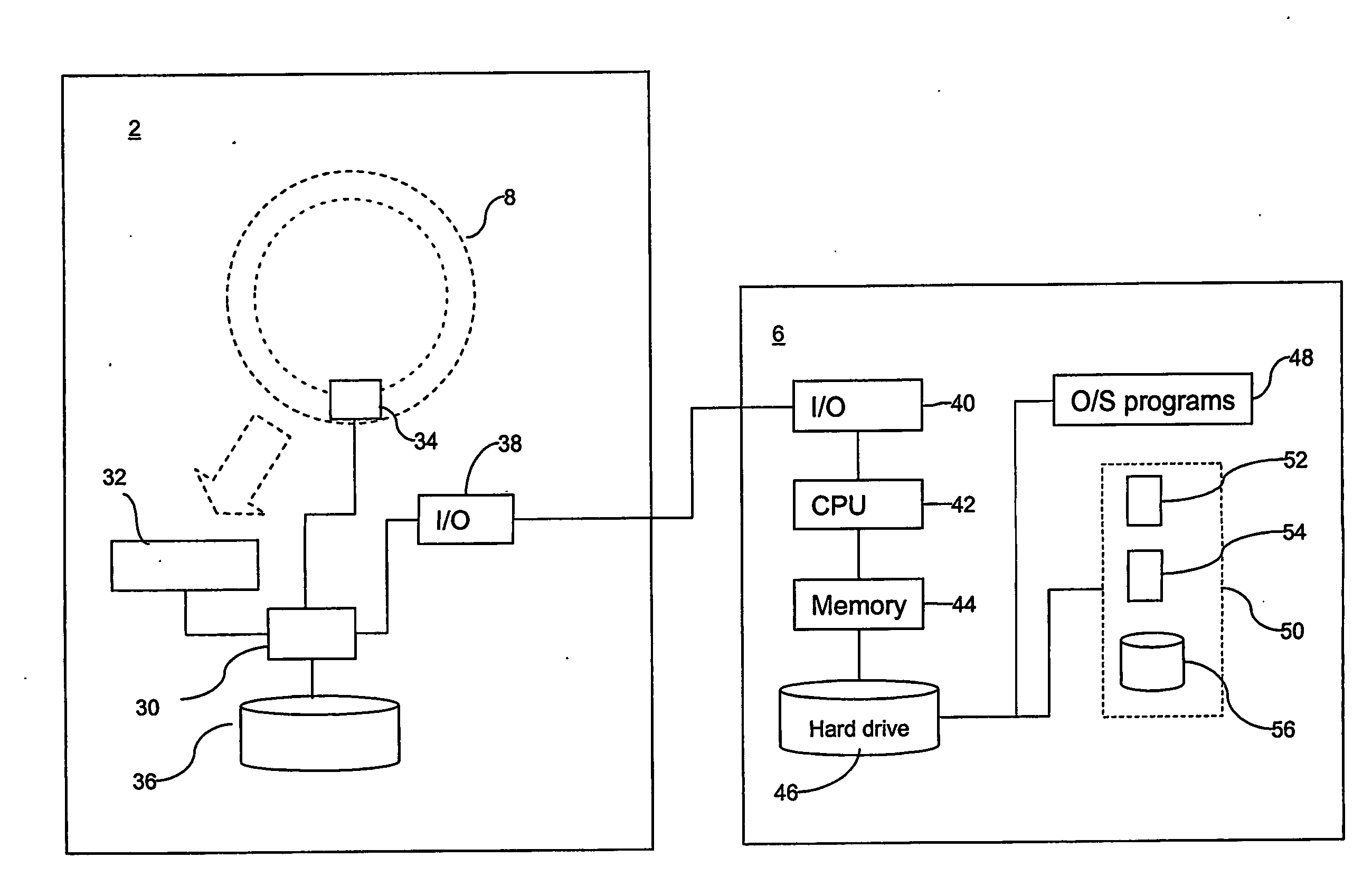
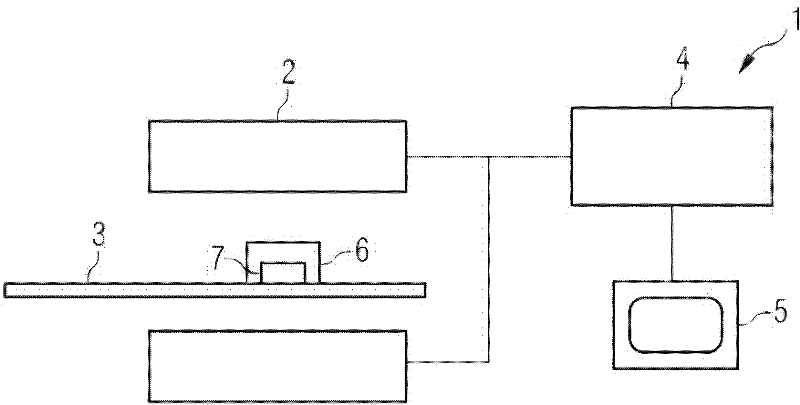
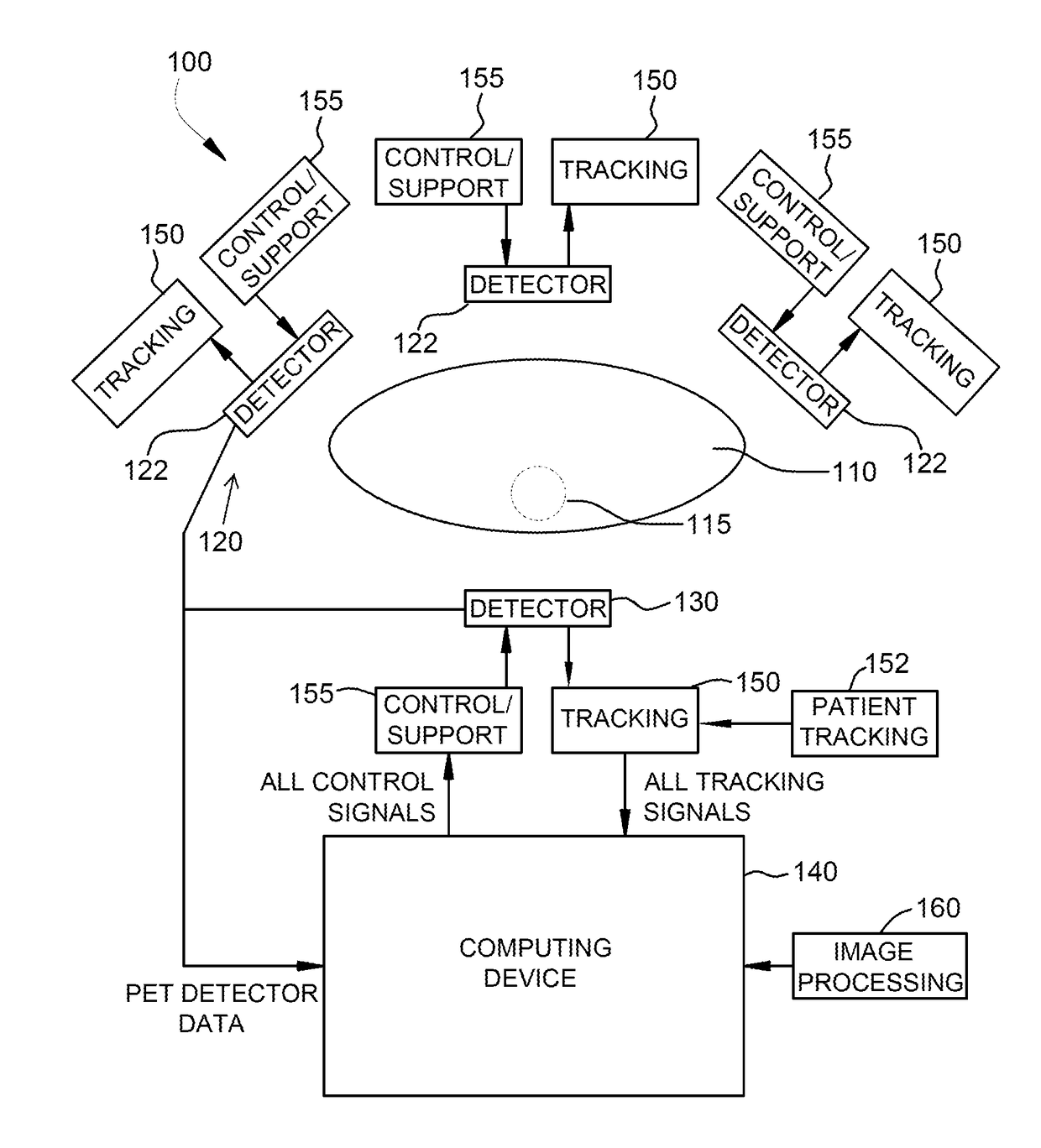
A positron emission tomography (PET) system is provided. The system includes a first detector panel including a first array of detectors, a second detector panel including a second array of detectors, said second detector panel being moveable relative to a point between the first detector panel and the second detector panel, a tracking system configured to detect a position of said second detector panel relative to the first detector panel while imaging a subject, a computing device in communication with the first detector panel, the second detector panel, and the tracking system, the computing device configured to receive coincidence data from the first and second detector panels, receive position data from the tracking system, wherein each coincidence datum of the received coincidence data is associated with a unique position datum of the received position data, and reconstruct a plurality of images based on the received coincidence data and the received position data.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
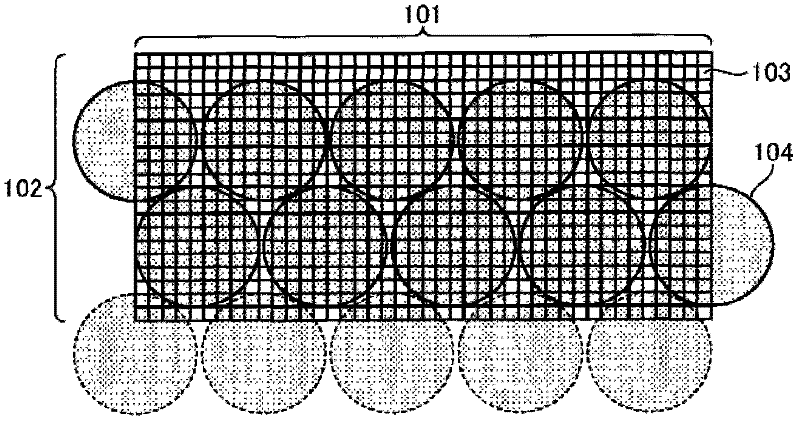
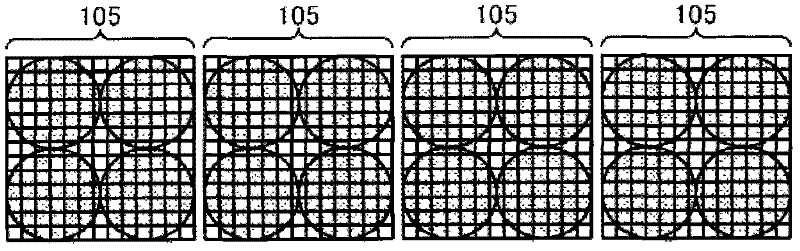
Positron emission tomography detector module, radiation detector, positron emission tomography scanner system, method of processing signals, and method of manufacturing radiation detector module
ActiveCN102455432AIncrease expansionLow costX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentScintillation crystalsSignal processing
A PET detector module according to one embodiment includes an array of scintillation crystal elements and a plurality of photosensors. The array includes a plurality of substantially optically isolated sub-arrays. The photosensors are arranged to cover the array and configured to receive light emitted from the array. The sub-arrays are optically isolated so that light emitted from an individual scintillation crystal located in a corresponding sub-array is concentrated so as to be primarily received only by those photosensors that cover the corresponding sub-array. At least one photosensor, which receives light emitted from crystals in a first sub-array, also receives light emitted from crystals in one and only one sub-array that is adjacent to the first sub-array.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method for detecting radiation, device thereof, and positron emission tomography scanner
InactiveUS9029789B2High measurement accuracyResolution timeMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyScintillatorElectron
A light receiver for detecting incident time is installed on the side of a radiation source of a scintillator (including a Cherenkov radiation emitter), and information (energy, incident time, an incident position, etc.) on radiation made incident into the scintillator is obtained by the output of the light receiver. It is, thereby, possible to identify an incident position and others of radiation into the scintillator at high accuracy.
Owner:NAT INST FOR QUANTUM & RADIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Cooling system of positron emission tomography scanner
ActiveCN103860187BAvoid driftingImprove stabilityComputerised tomographsTomographyInlet channelImaging quality
The invention discloses a cooling system of a positron emission tomography scanner. The positron emission tomography scanner comprises a peripheral electronics plate, a detector module and a bottom electronics plate; the cooling system comprises a cooling device, a peripheral cooling air channel, an inner chamber cooling air channel and a bottom cooling air channel; the inner chamber cooling air channel is a chamber body and comprises an air inlet channel and an air return channel; the peripheral electronics plate is located in the peripheral cooling air channel; the detector module is located between the air inlet channel and the air return channel; the bottom electronics plate is located in the bottom cooling air channel; the cooling device is used for conveying cooled air flow to the peripheral cooling air channel, the inner chamber cooling air channel and the bottom cooling air channel so as to cool the peripheral electronics plate, the detector module and the bottom electronics plate. According to the cooling system of the positron emission tomography scanner, ventilation cooling is performed on the peripheral electronics plate and the bottom electronics plate, the low-temperature and stable inner chamber cooling air channel is provided for the detector module, and accordingly the stability and the imaging quality of the system are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Apparatus and methods for cooling positron emission tomography scanner detector crystals
InactiveUS8481949B2Sensitivity is increased and stabilizedWeaken energyMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyFractographyCompanion animal
Detector crystals in a positron emission tomography (PET) apparatus gantry are cooled by directing cooling gas flow into a cooling duct bounded by the crystals and a cover defining the patient scanning field within the gantry. The cooling gas cools the crystals. Cooling gas may also be directed radially outwardly from the cooling duct into spatial gaps defined between detector enclosures that include the crystals, further isolating heat generated by other components within gantry from the detector crystals. Cooling gas is provided by a cooling system that may be incorporated within the gantry, external the gantry or a combination of both. Cooling gas can be provided by directing air within the gantry in contact with internal gantry cooling tubes and routing cooled air directly into the cooling duct with a powered fan.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method of and software for calculating a scatter estimate for tomographic scanning and system for tomographic scanning
InactiveUS7902511B2Reduce quality problemsImprove accuracyReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyPositron emission tomographic
The method calculates a scatter estimate for scatter correction of detection data from a subject in a positron emission tomographic scanner. The detection data represent the scattered events and unscattered events of annihilation photons emitted in the subject. The method uses the following steps:determine an estimate of the unscattered events;determine a simulation of the scattered events;determine a value of a scaling factor by fitting the sum of the estimate of the unscattered events and a product of the scaling factor and the simulation of the scattered events to the detection data; anddetermine the scatter estimate as the product of the scaling factor having said value and the simulation of the scattered events.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
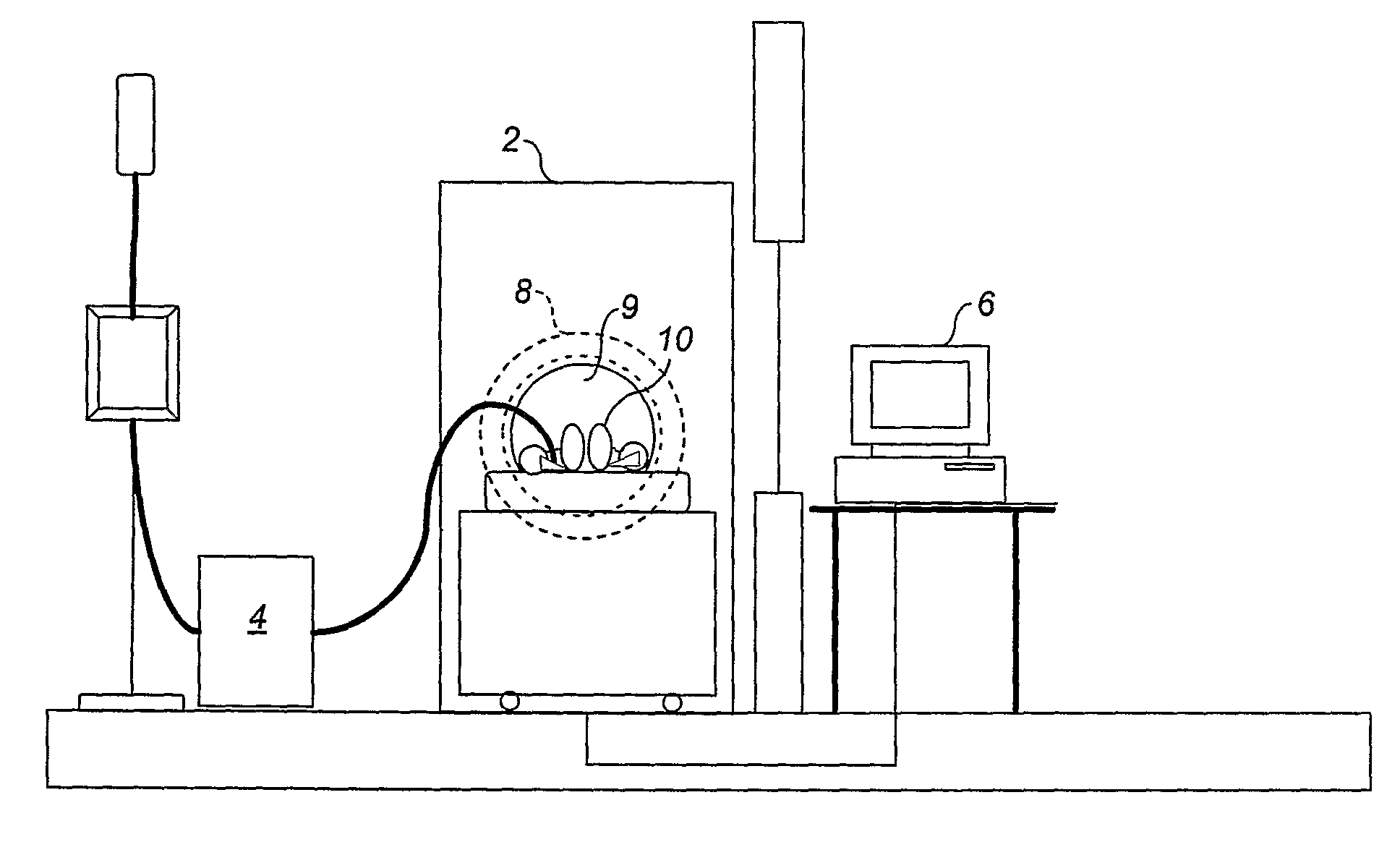
Alignment of positron emission tomographs by virtual tomographs
ActiveUS20130202172A1Increase the importanceImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionQuantitative assessmentImaging data
Positron emission tomography, possibly in combination with computed tomography, allows in addition to medical diagnostic imaging the quantitative determination of various parameters. Quantitative measurements using tomographs exhibit a severe and unavoidable dependency on the imaging properties of the respective tomograph, which makes quantitative assessment of the results difficult. This relates particularly to multicentric medical studies, which obligatorily require quantitative comparability of the data measured by the participating centers. The methods claimed herein include the definition of a virtual tomograph with defined imaging properties. The claimed methods also cover determination of the imaging properties of different tomographs on the basis of suitable reference measurements and possibly by using a calibration phantom. Based on the definition of the virtual tomograph and the determination of the imaging properties of different tomographs, the methods according to the invention then allow conversion and subsequently standardized and quantitatively comparable representation of the image data recorded by the different tomographs or systems as if all measurements were acquired equally by the virtual system. The method according to the invention therefore supports the quantitative evaluation of image data in multicentric studies.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BERN +1
Positron emission tomography scanner and radiation detector
InactiveUS7671339B2Improve accuracyRaise the ratioMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyAnnihilation radiationCompanion animal
Owner:NAT INST FOR QUANTUM & RADIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
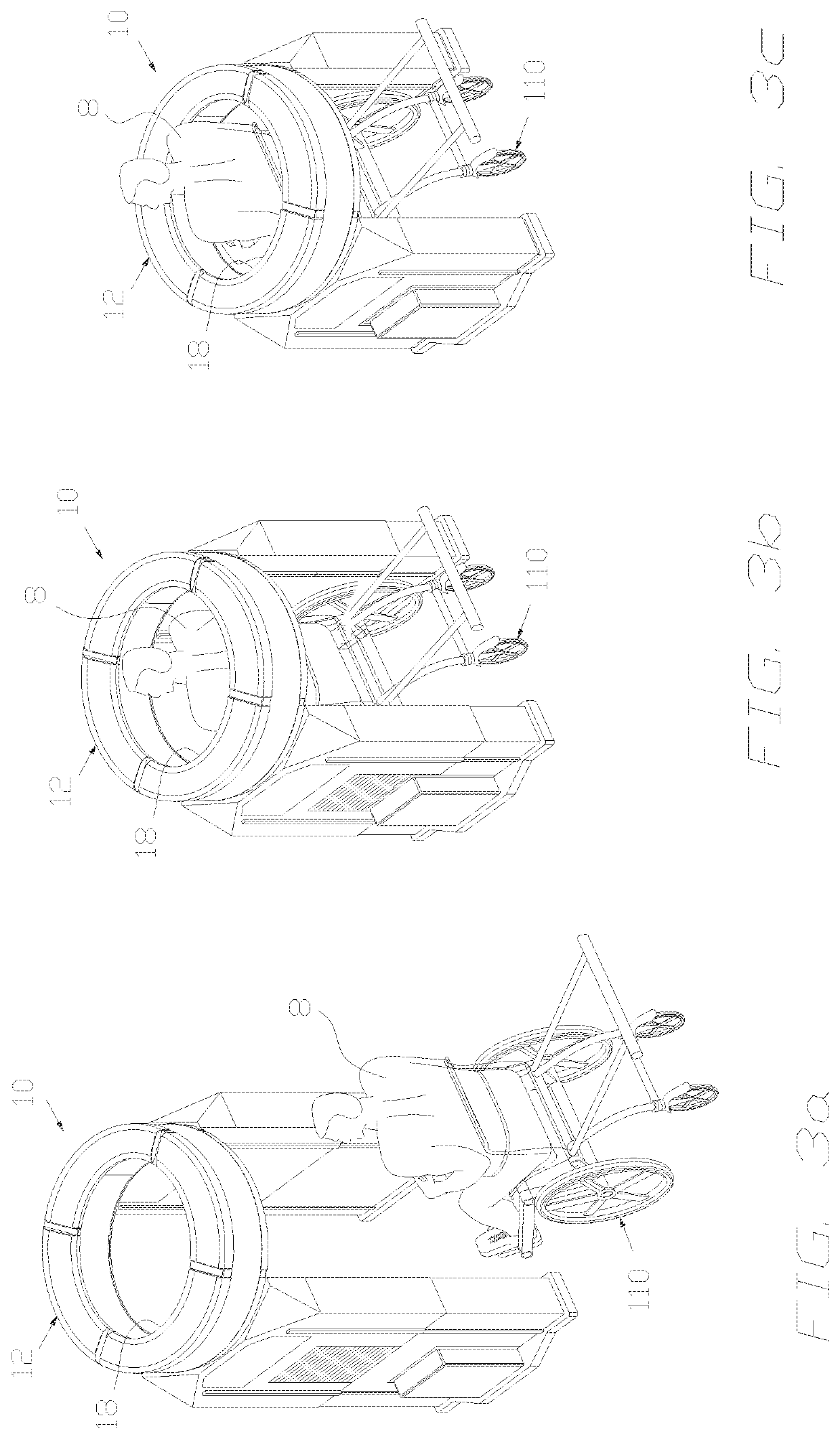
Portable positron emission tomography scanner having a rotatable detector ring which can be rotated 90 degrees for imaging a patient in a vertical or horizontal configuration
ActiveUS10653374B1Reduce system footprintComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringTomographyHorizontal orientation
A portable positron emission tomography (PET) scanner includes a rotatable scan detector ring which can be rotated 90 degrees for imaging a patient in a vertical or horizontal orientation. In the vertical orientation, a patient can be standing or seating such that the aperture of the scan detector ring is raised to allow the patient to be within the scanning region and lower to perform the image scanning on the patient. In the horizontal orientation, a patient must be lying down on a platform whereby the platform is moved within the aperture of the scan detector ring to perform the image scanning on the patient. In this horizontal orientation, the scan detector ring is also stowed and secured to be moved to other scanning locations.
Owner:PRESCIENT IMAGING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com