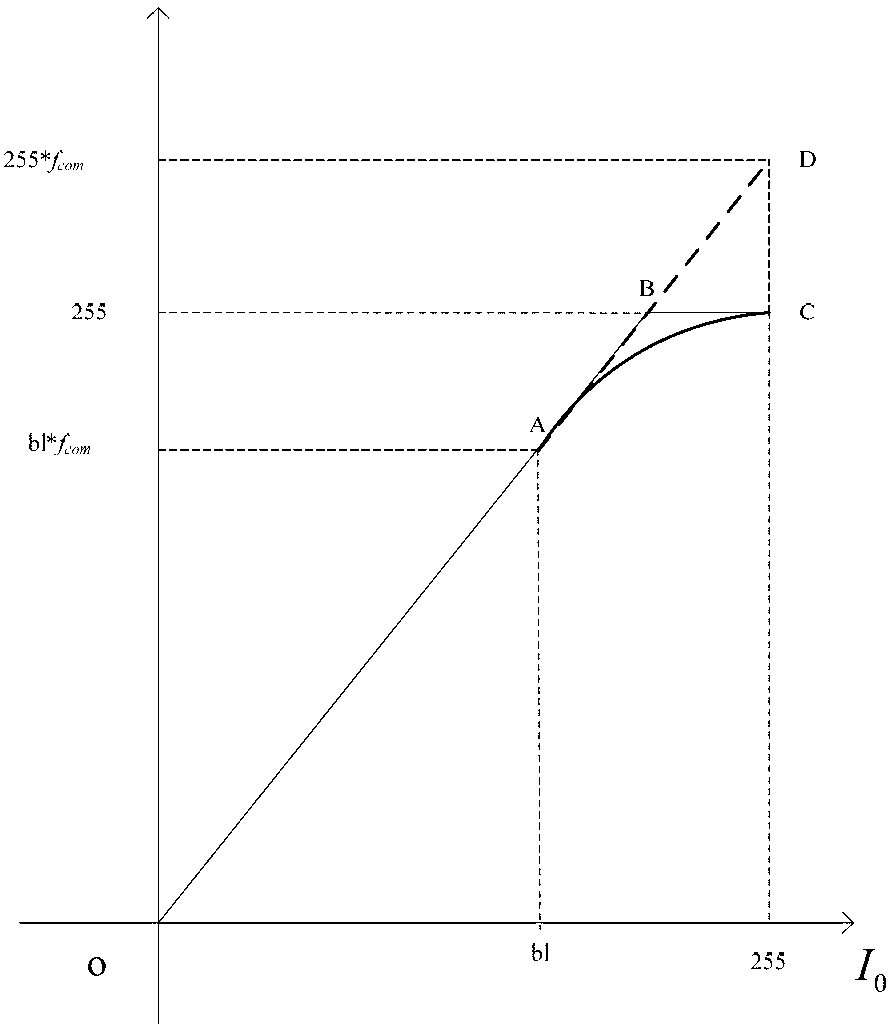Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
817 results about "Pixel brightness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
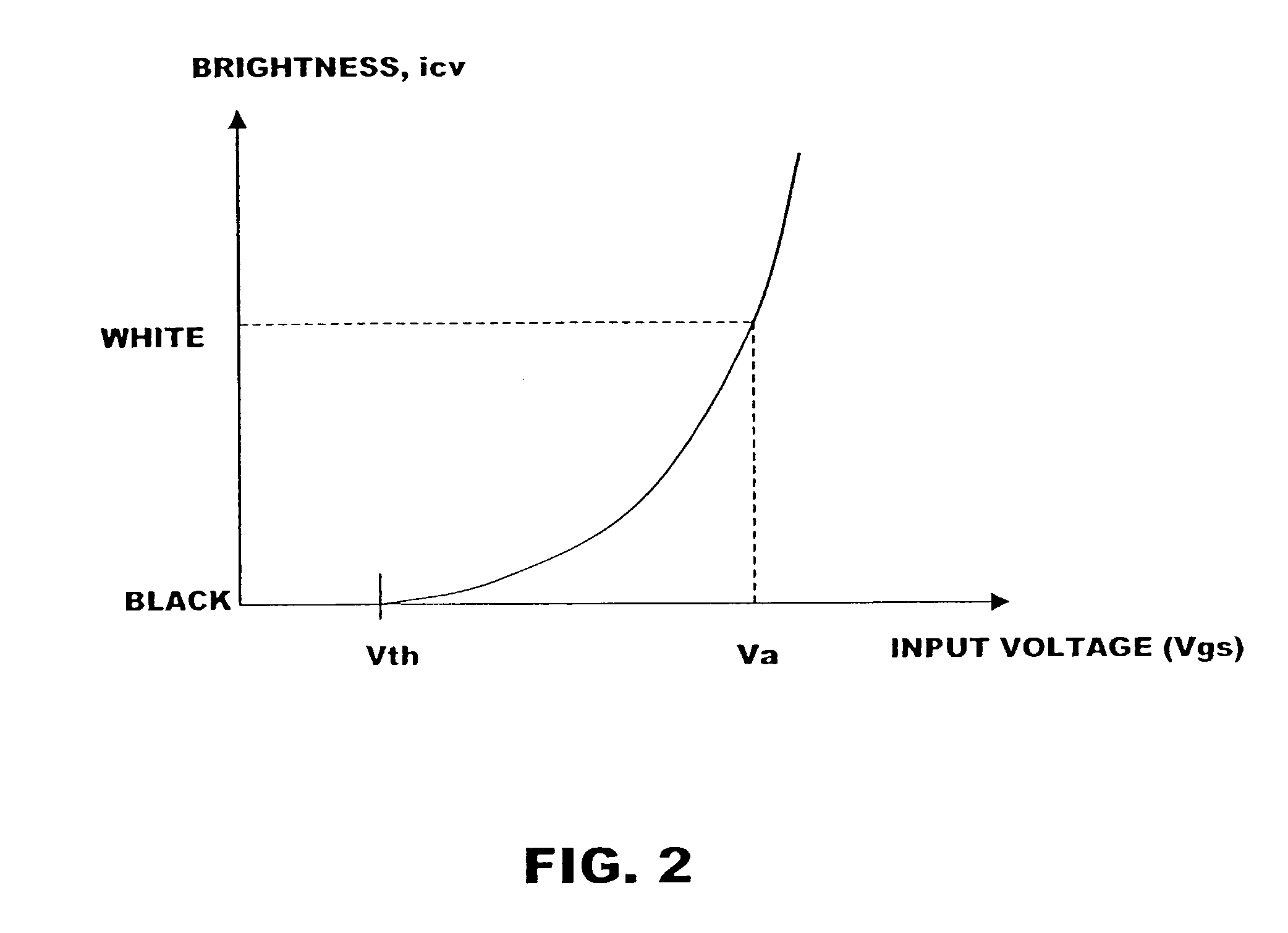
Brightness resolution. Definition: A measure of how fully a pixel in a digital image represents (digitally) the brightness (which is analogue) of the corresponding point in the original image.
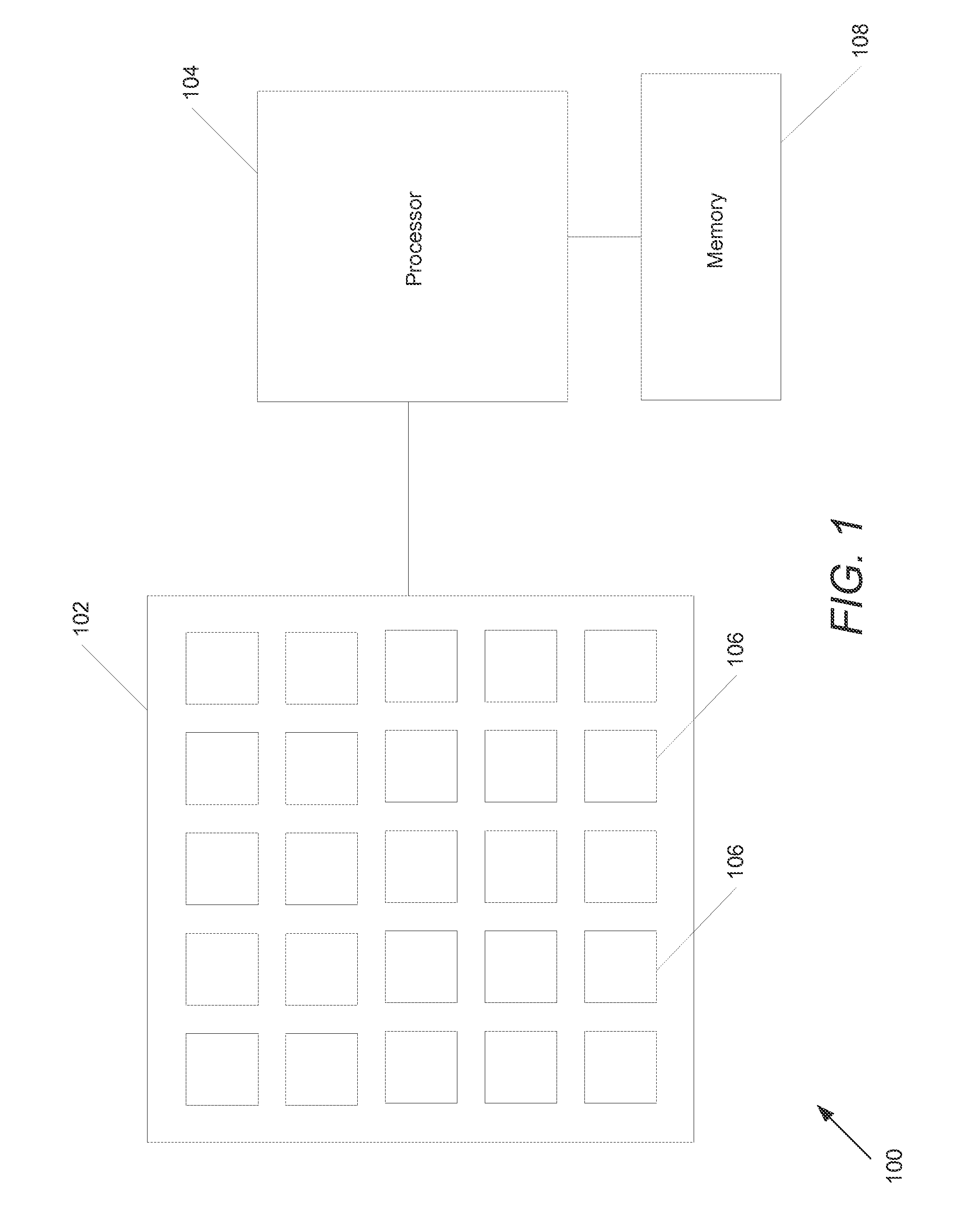
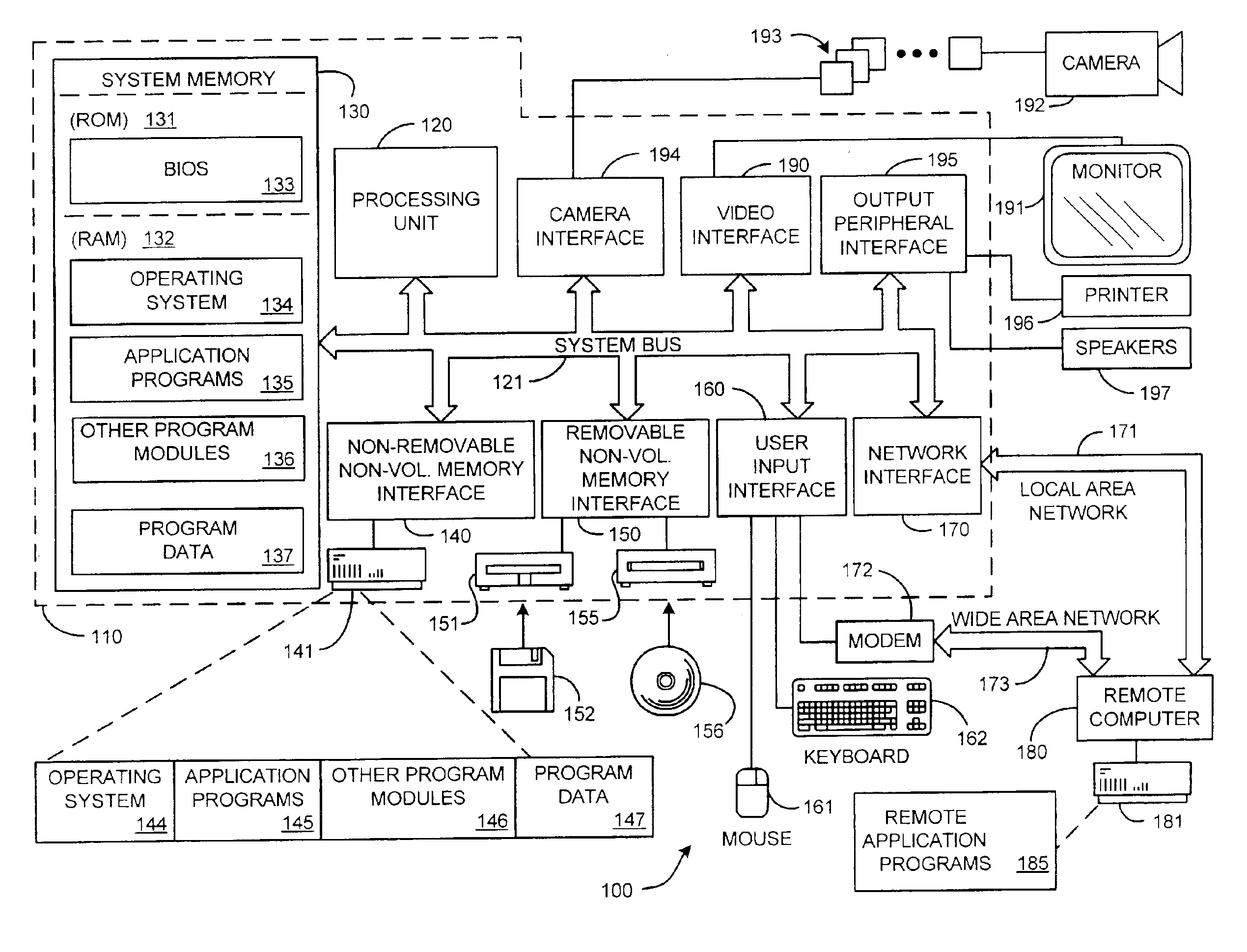
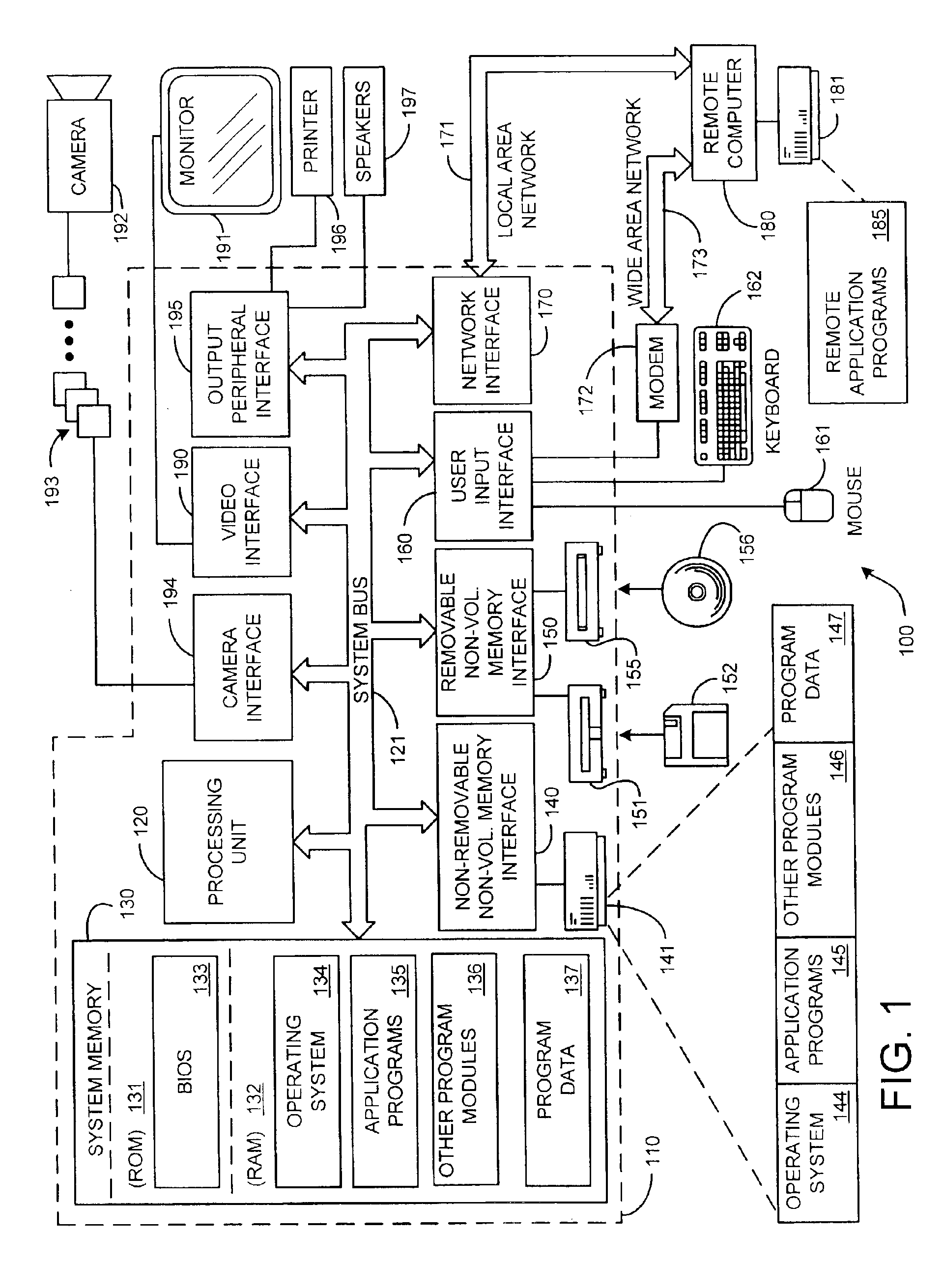
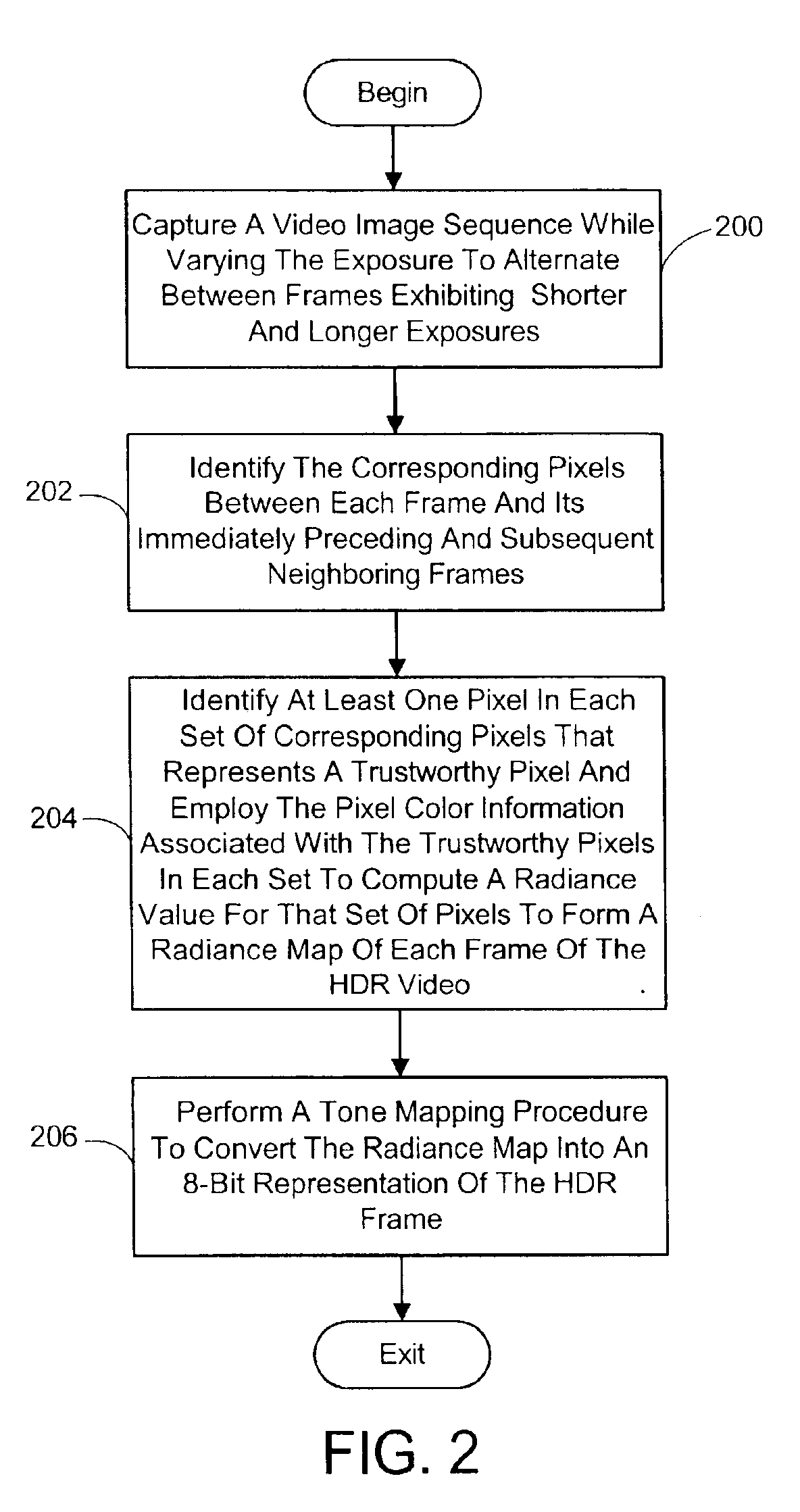
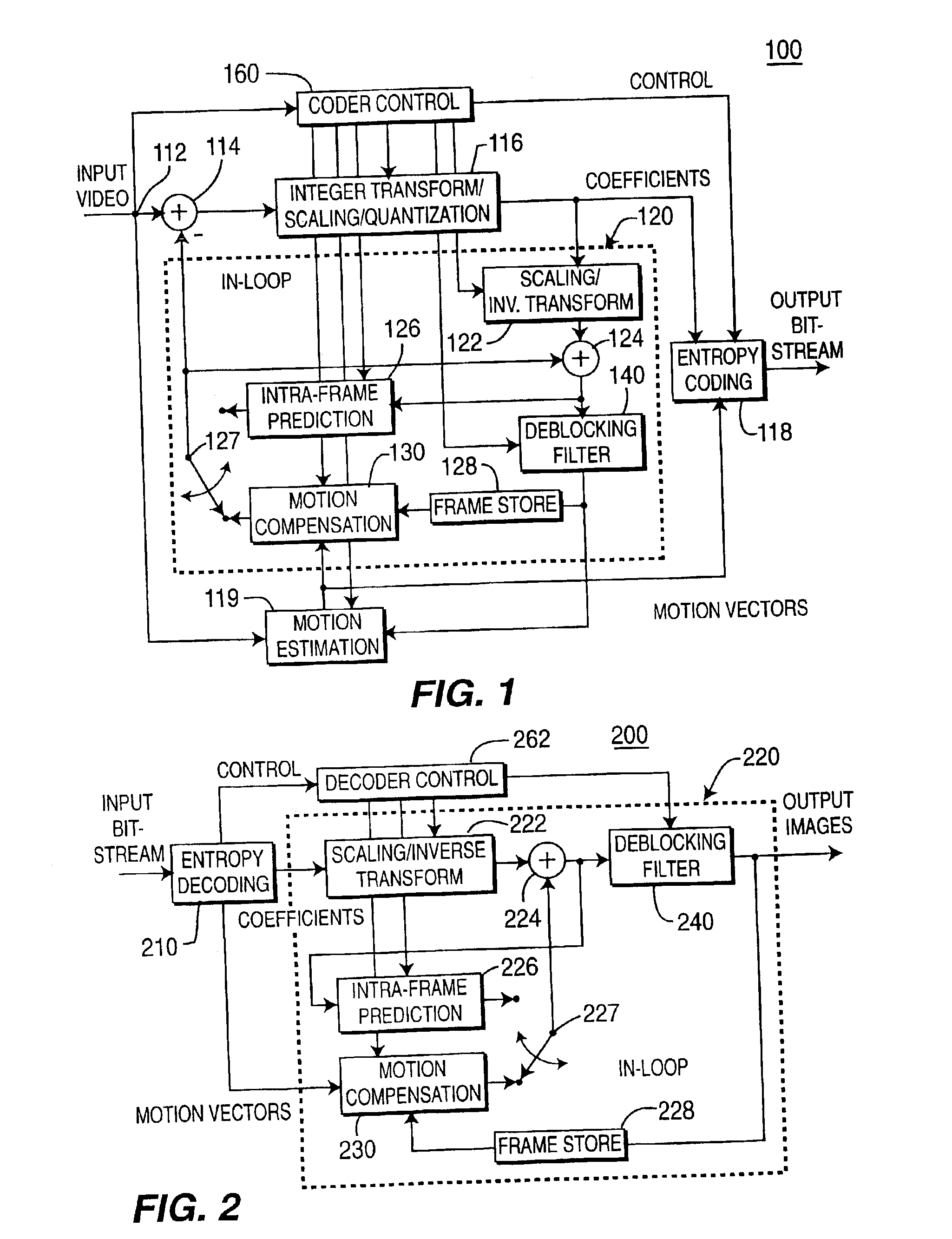
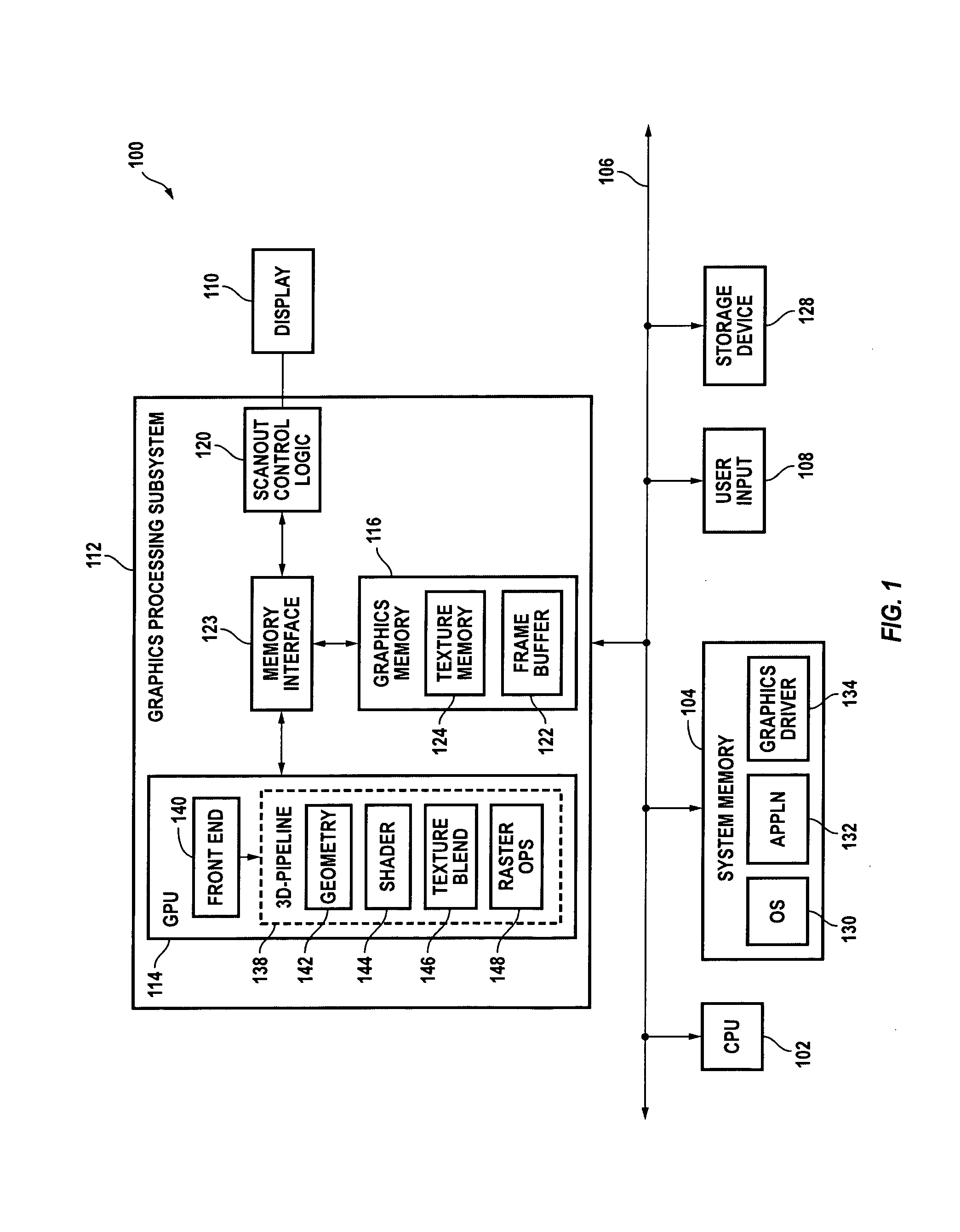
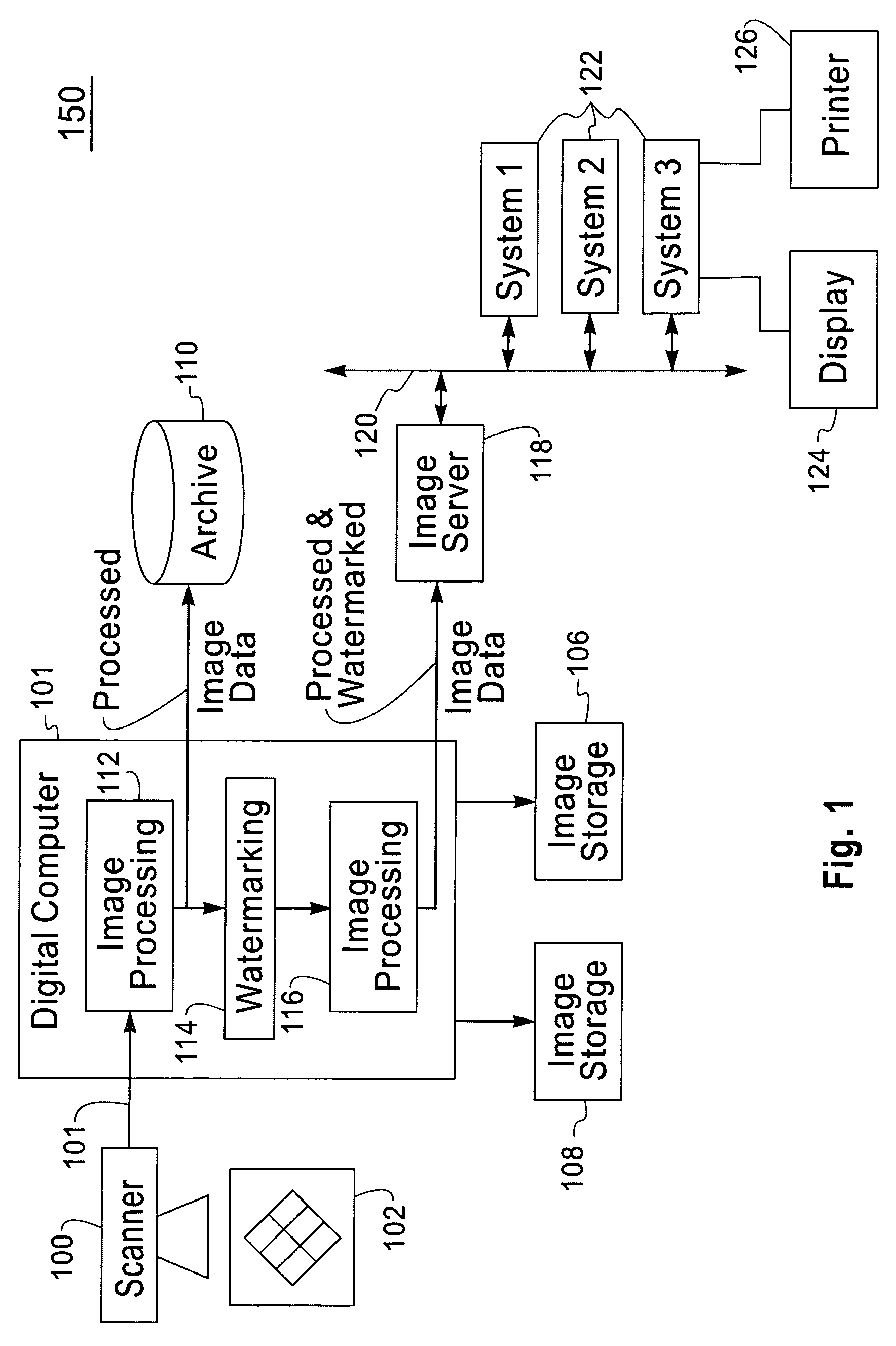
System and process for generating high dynamic range video
InactiveUS6879731B2Minimizing any discontinuityTelevision system detailsImage enhancementTone mappingRadiance
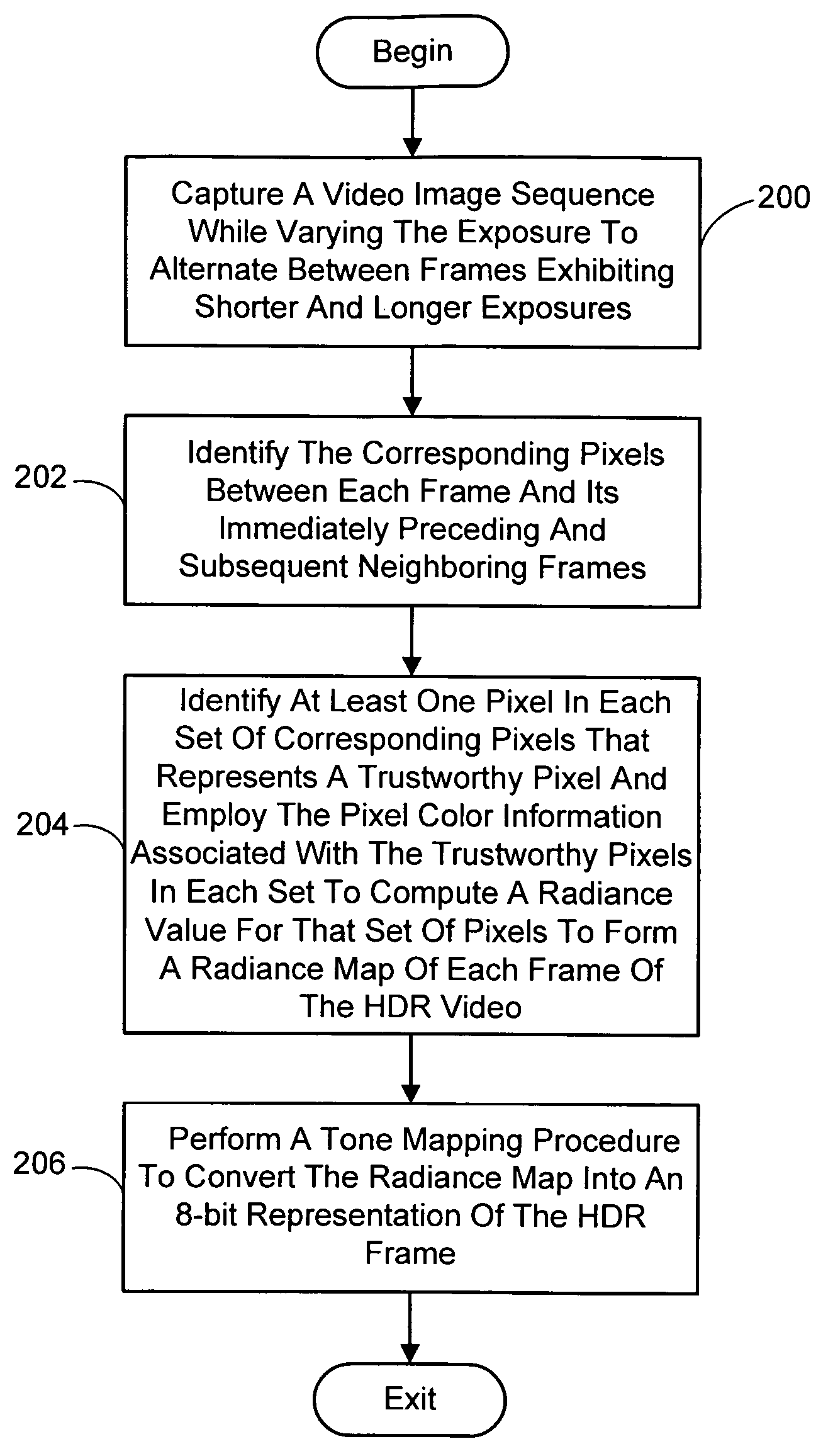
A system and process for generating High Dynamic Range (HDR) video is presented which involves first capturing a video image sequence while varying the exposure so as to alternate between frames having a shorter and longer exposure. The exposure for each frame is set prior to it being captured as a function of the pixel brightness distribution in preceding frames. Next, for each frame of the video, the corresponding pixels between the frame under consideration and both preceding and subsequent frames are identified. For each corresponding pixel set, at least one pixel is identified as representing a trustworthy pixel. The pixel color information associated with the trustworthy pixels is then employed to compute a radiance value for each pixel set to form a radiance map. A tone mapping procedure can then be performed to convert the radiance map into an 8-bit representation of the HDR frame.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Chiplet display device with serial control
ActiveUS8803857B2Higher-performance pixel circuit and image quality and digital controlElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesImaging qualityDisplay device
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
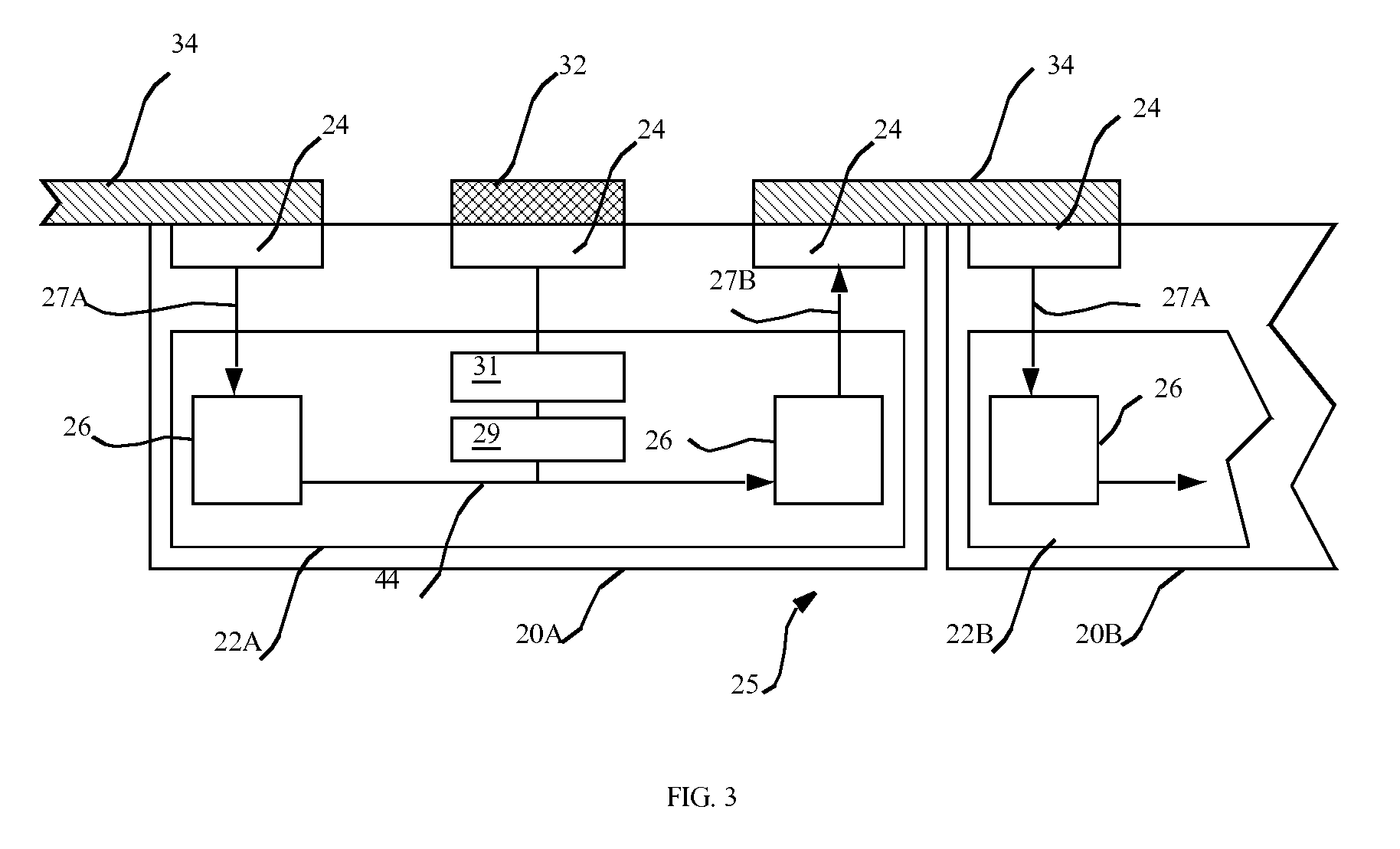
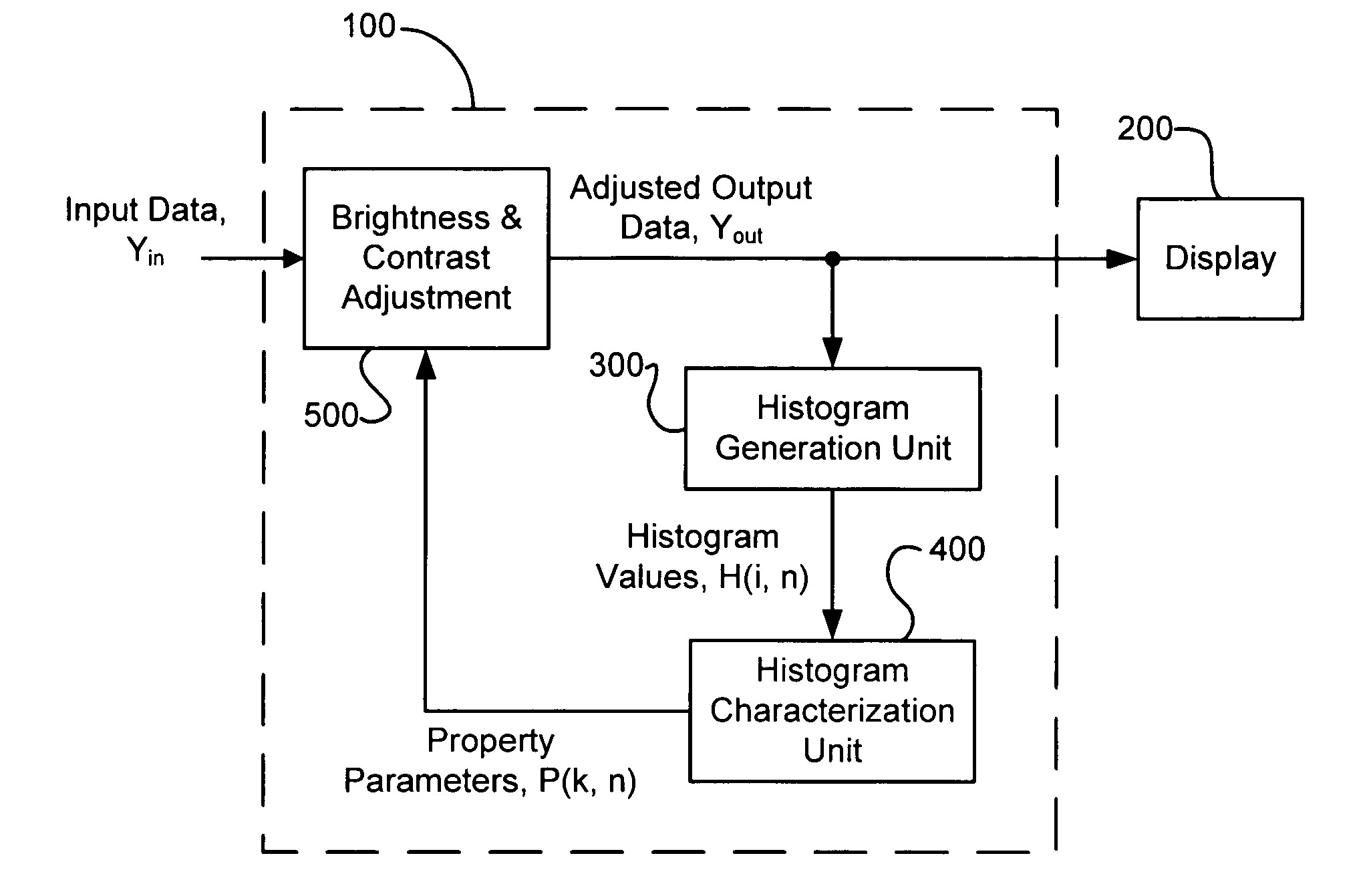
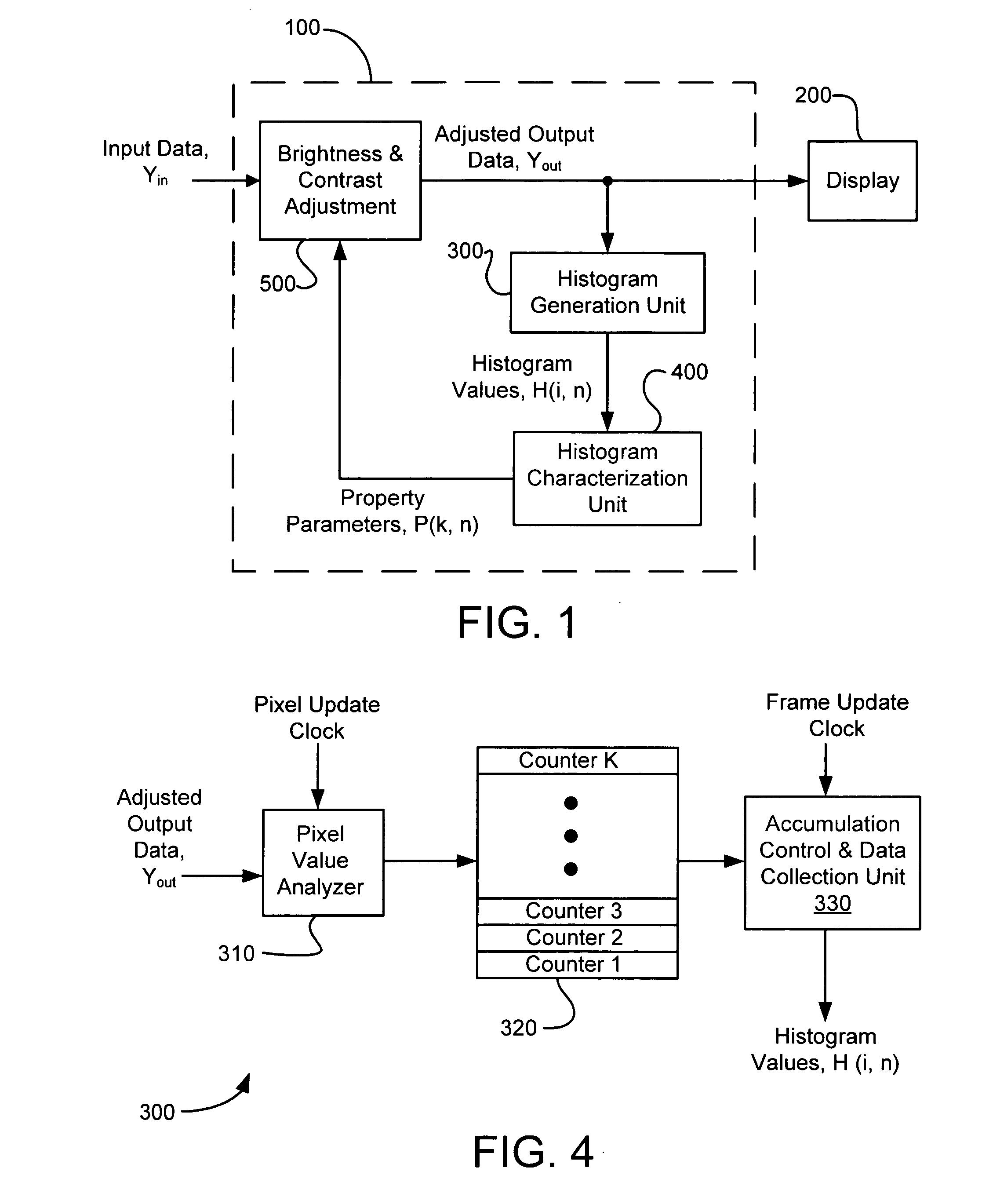
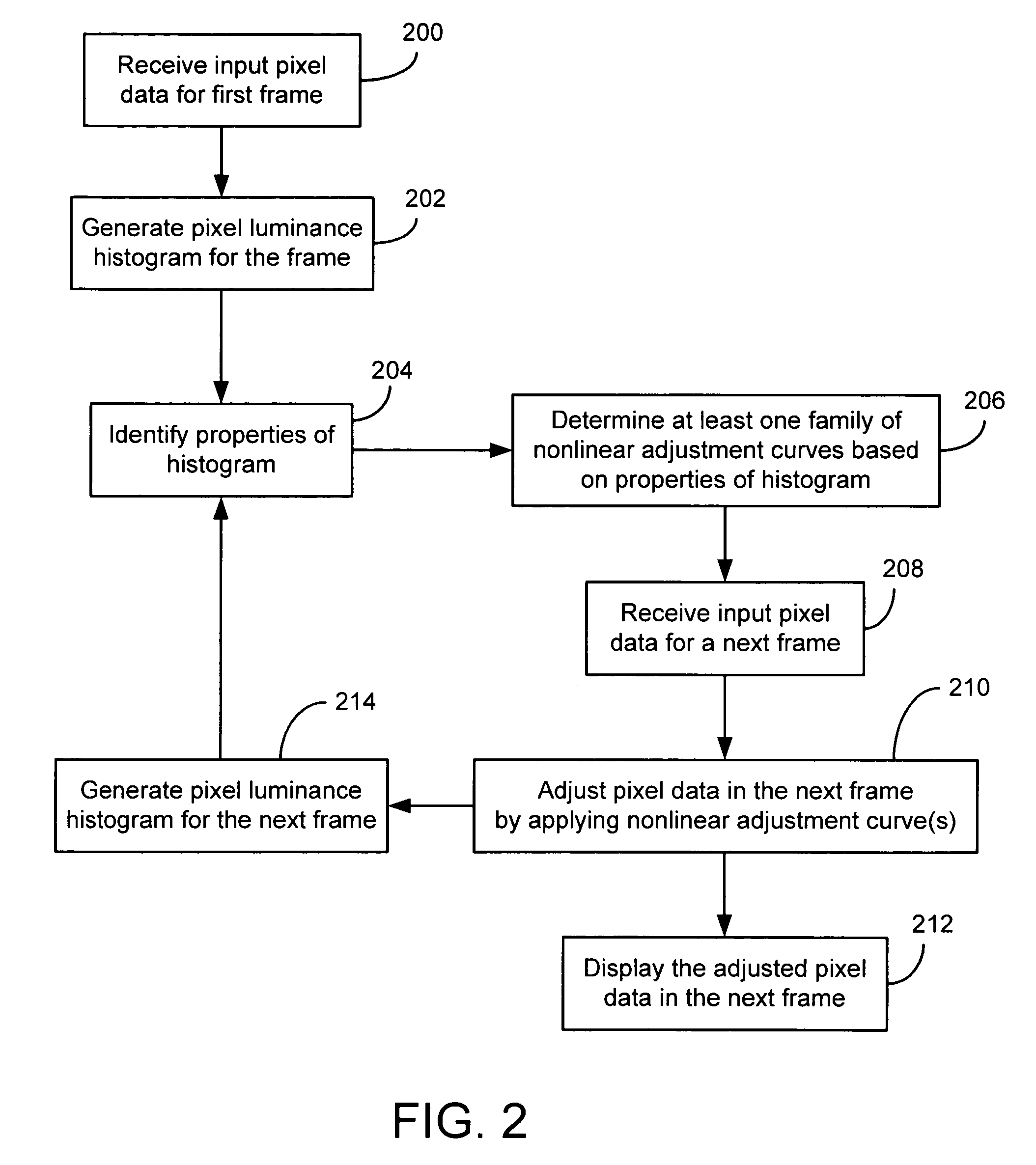
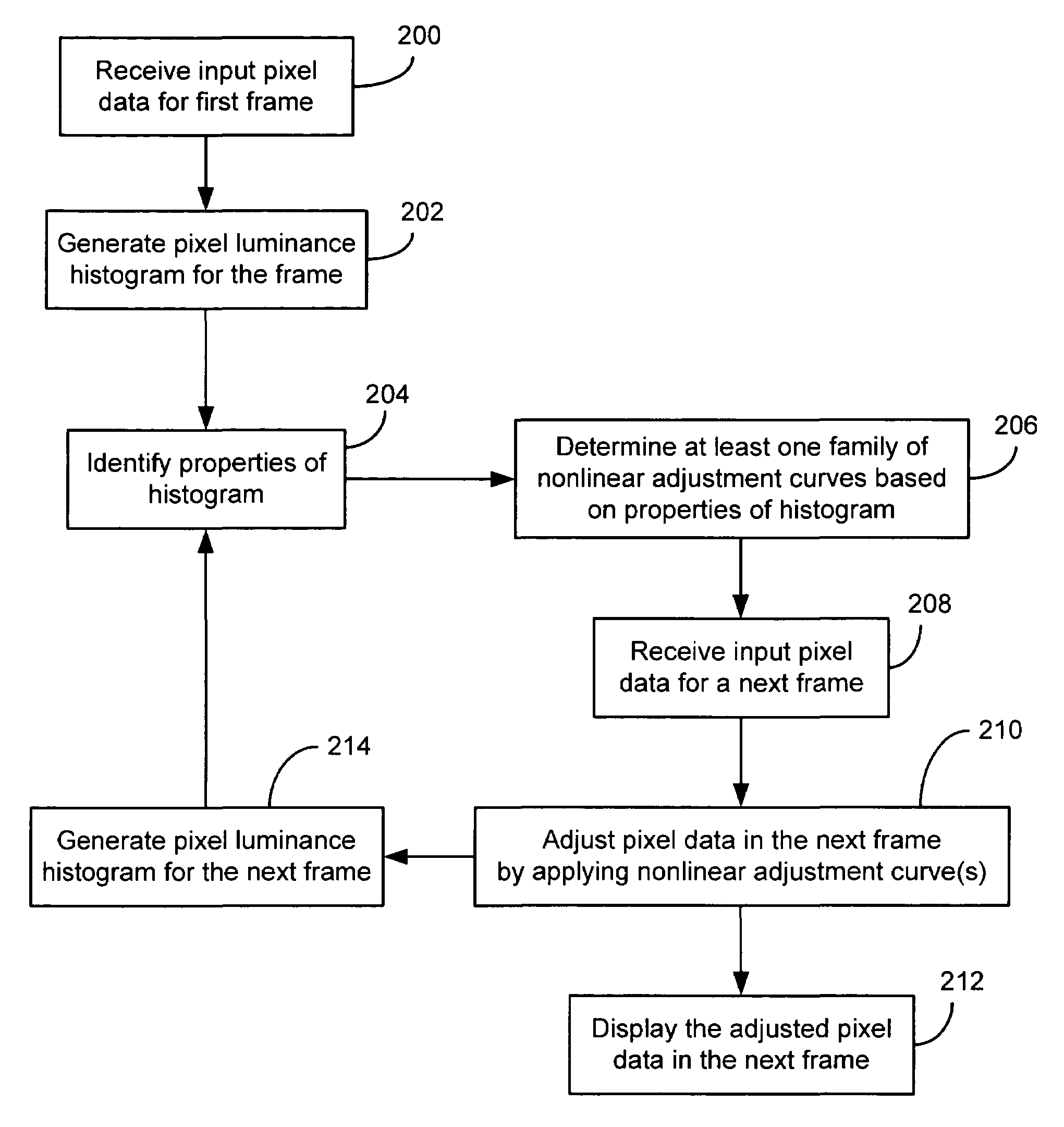
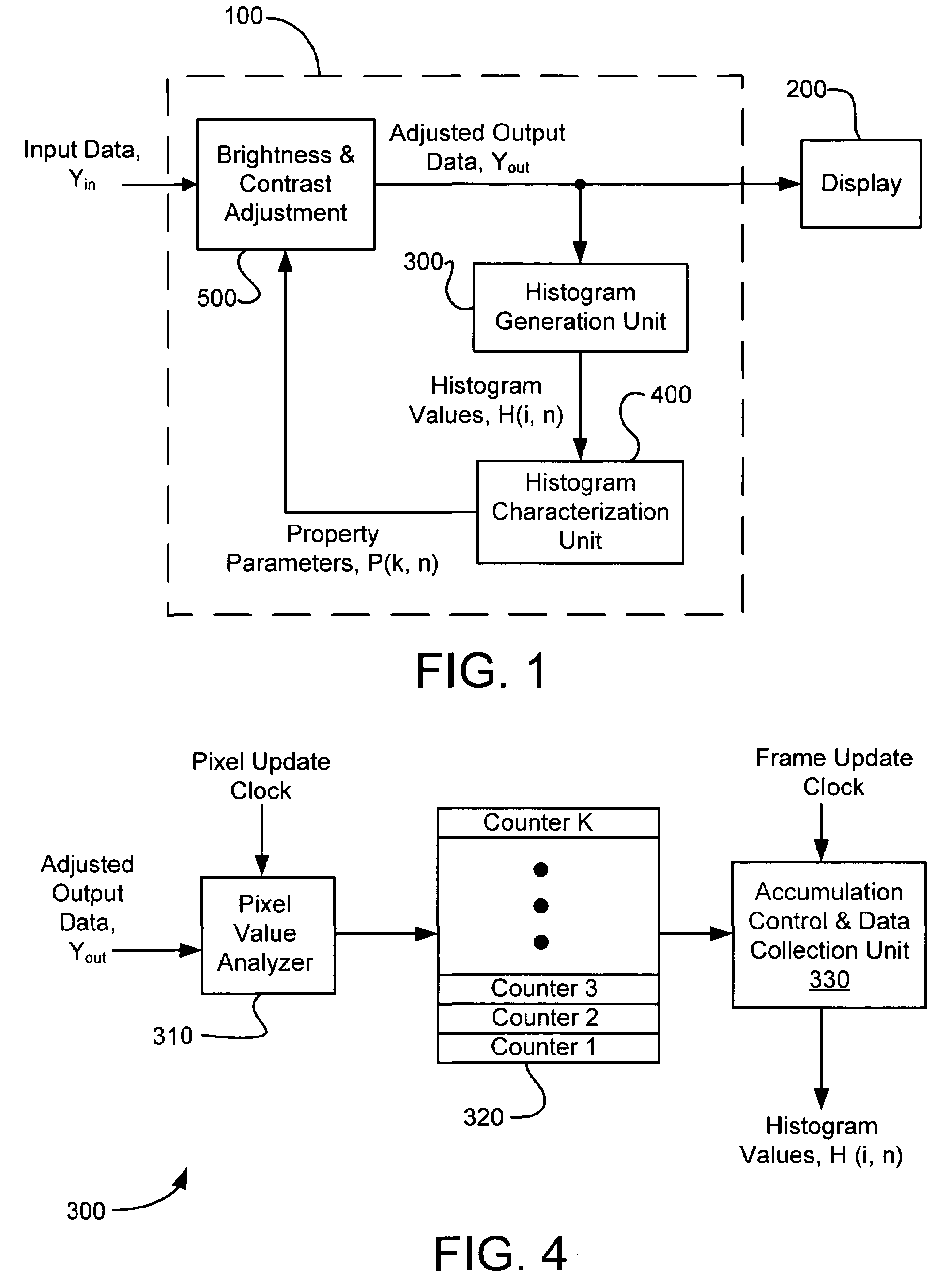
Method and system for automatic brightness and contrast adjustment of a video source
InactiveUS20060268180A1Increase contrastTelevision system detailsImage enhancementFrame basedPixel brightness
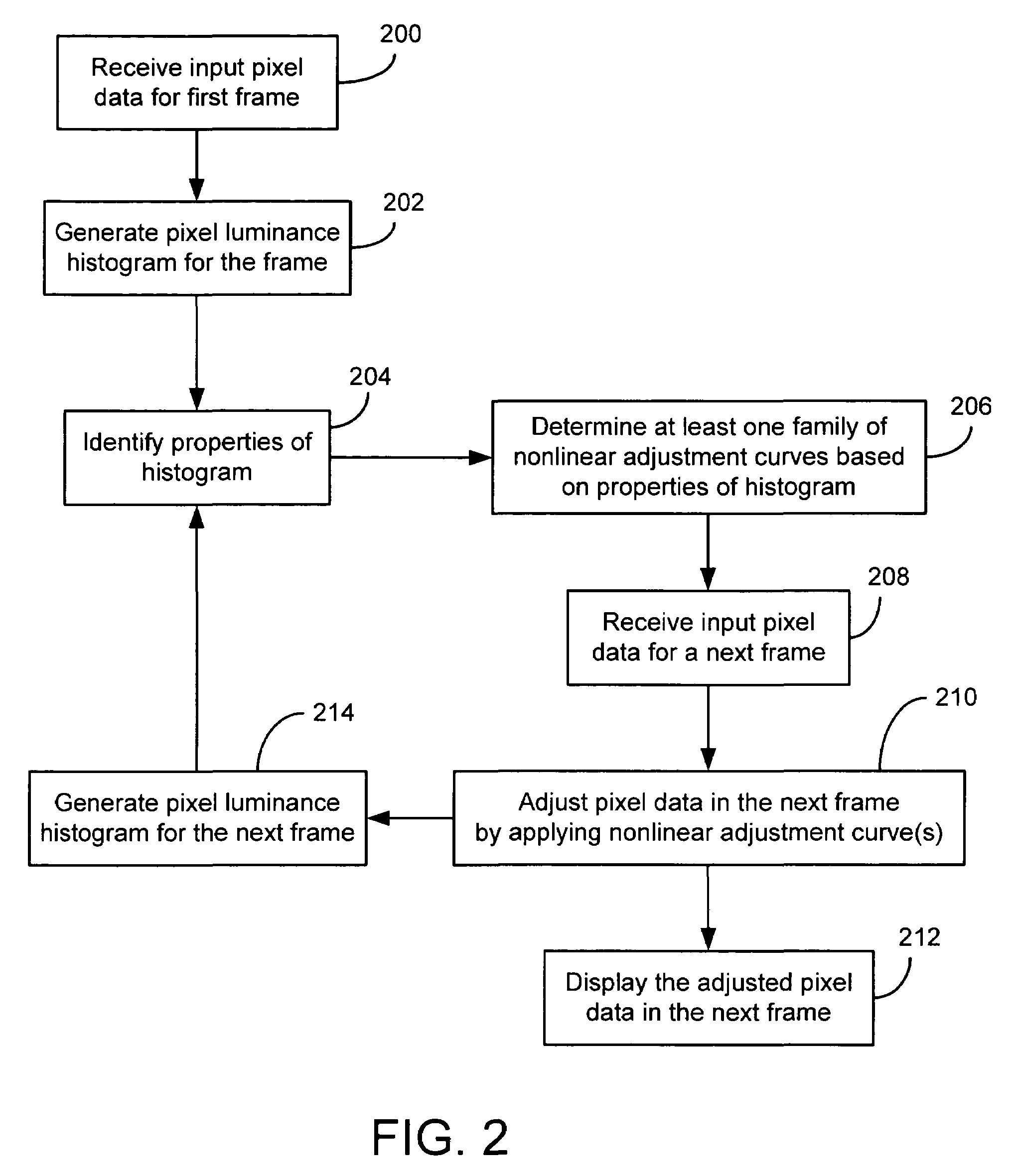
An image brightness and contrast management module for automatically adjusting brightness and contrast of an input video signal includes a histogram generation unit that generates a pixel luminance histogram based on pixel luminance values in a frame, whereby the histogram shows a distribution of luminance values in the frame and indicates the dynamic range and the dominant luminance value(s) for the frame. The module includes a histogram characterization unit that uses the pixel luminance histogram to identify which of a plurality of brightness / contrast properties is exhibited in the frame. The module also includes a brightness and contrast adjustment unit that nonlinearly adjusts, in real-time, the pixel luminance values in a next frame based on the identified brightness / contrast properties exhibited in the preceding frame. In this manner, bright or dark dominant areas of an image are stretched to enhance the contrast of the dominant luminance values without blackening the darker portions or saturating the brighter portions of the image.
Owner:CORONA
Method and apparatus for obtaining high dynamic range images
InactiveUS7084905B1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsLight sensingImage resolution
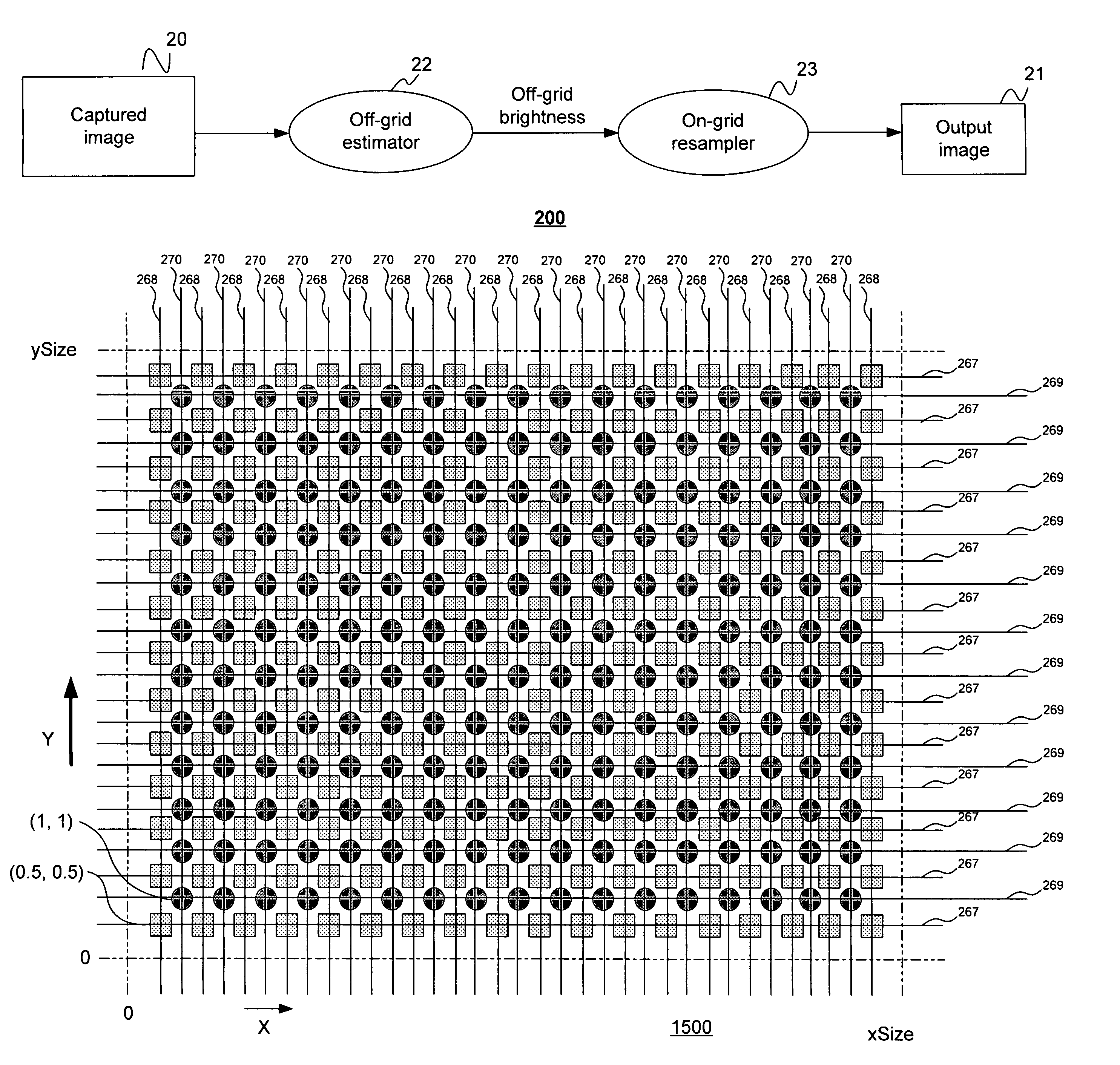
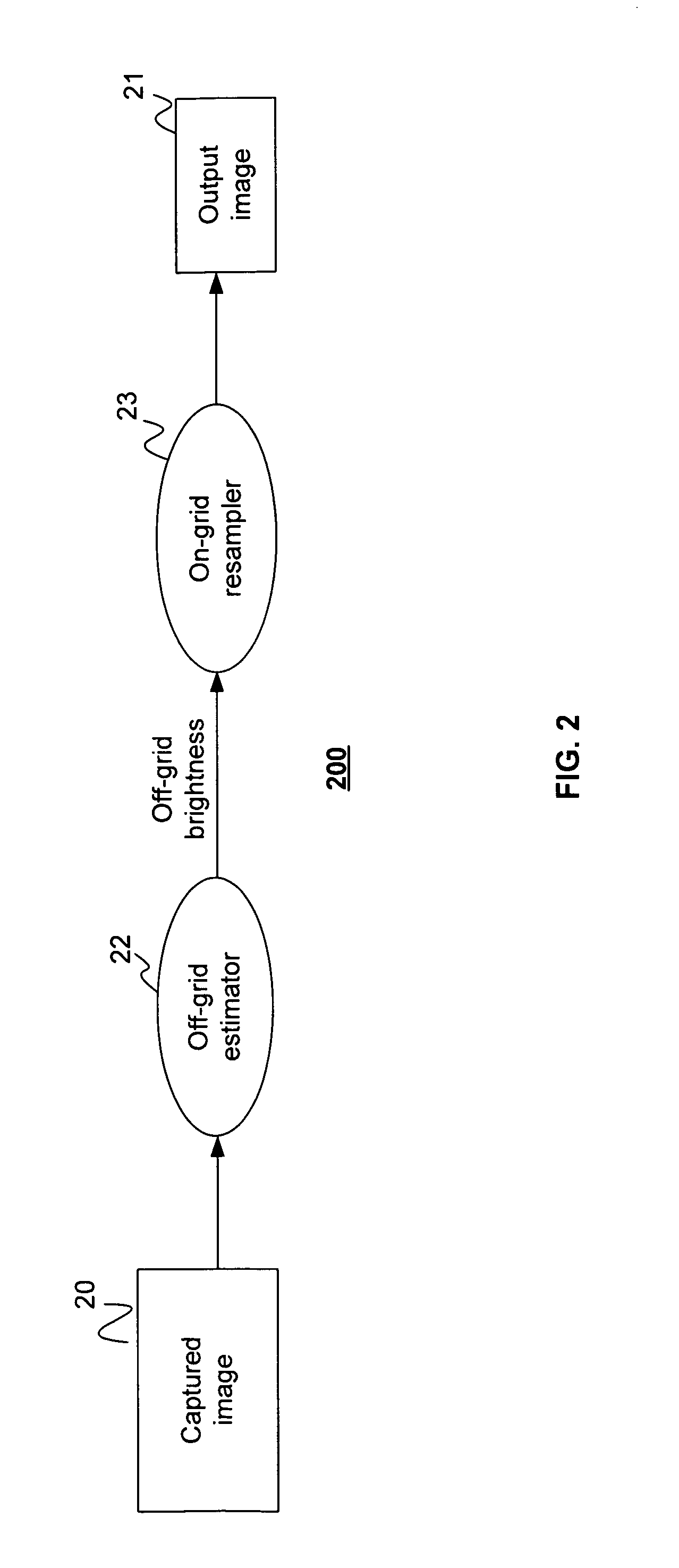
Disclosed are method and apparatus for obtaining relatively high dynamic range images using a relatively low dynamic range image sensor without significant loss of resolution. The image sensor has an array of light-sensing elements with different sensitivity levels in accordance with a predetermined spatially varying sensitivity pattern for the array of light-sensing elements. An image of a scene is captured with the image sensor and stored as brightness values at respective pixel positions in a linear or two-dimensional uniform grid. The brightness values of the captured image at the pixel positions are then used to estimate the brightness values at off-grid positions of a uniform off-grid array located at respective interstices of the pixel position grid. The estimated off-grid brightness values are either used directly as the pixel brightness values of a relatively high dynamic output image or interpolated to derive resampled on-grid brightness values at the pixel positions of the pixel position grid to provide a relatively high dynamic range output image. Alternatively, the brightness values of the captured image are interpolated by an on-grid interpolation filter to derive pixel brightness values of a relatively high dynamic range output image, each pixel brightness value of the output image being derived from a corresponding plurality of the captured image brightness values. In each instance, either the captured image brightness values or the pixel brightness values of the output image may be compensated for non-linearities of the radiometric response function of the light-sensing elements of the image sensor.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Penlight and touch screen data input system and method for flat panel displays
System, device, and method for receiving or sensing touch or light input to an emissive display such as to a OLED display using the same or different sensors as are used to sense and maintain a pixel luminance. Penlight and touch screen data input system and method for display. A sidelight illuminated display and touch panel input device. Method and device for reading display pixel emission and ambient luminance levels. Emissive display having sensing for luminance stabilization and user light or touch screen input. Method and device for emissive display using shielded or partially shielded sensors. Emissive pixel display device characterized in that photon sensors are disposed within pixels and operated to sense photons emitted by emitter within pixel and ambient photons emitted by sources outside pixel, sensed internally emitted photons being for luminance feedback control and sensed ambient photons being used to detect external light source or sources.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Emissive display device having sensing for luminance stabilization and user light or touch screen input
InactiveUS20050200292A1Solid-state devicesElectric light circuit arrangementPhotonic sensorDisplay device
System, device, and method for receiving or sensing touch or light input to an emissive display such as to a OLED display using the same or different sensors as are used to sense and maintain a pixel luminance. Penlight and touch screen data input system and method for display. A sidelight illuminated display and touch panel input device. Method and device for reading display pixel emission and ambient luminance levels. Emissive display having sensing for luminance stabilization and user light or touch screen input. Method and device for emissive display using shielded or partially shielded sensors. Emissive pixel display device characterized in that photon sensors are disposed within pixels and operated to sense photons emitted by emitter within pixel and ambient photons emitted by sources outside pixel, sensed internally emitted photons being for luminance feedback control and sensed ambient photons being used to detect external light source or sources.
Owner:LEADIS TECH
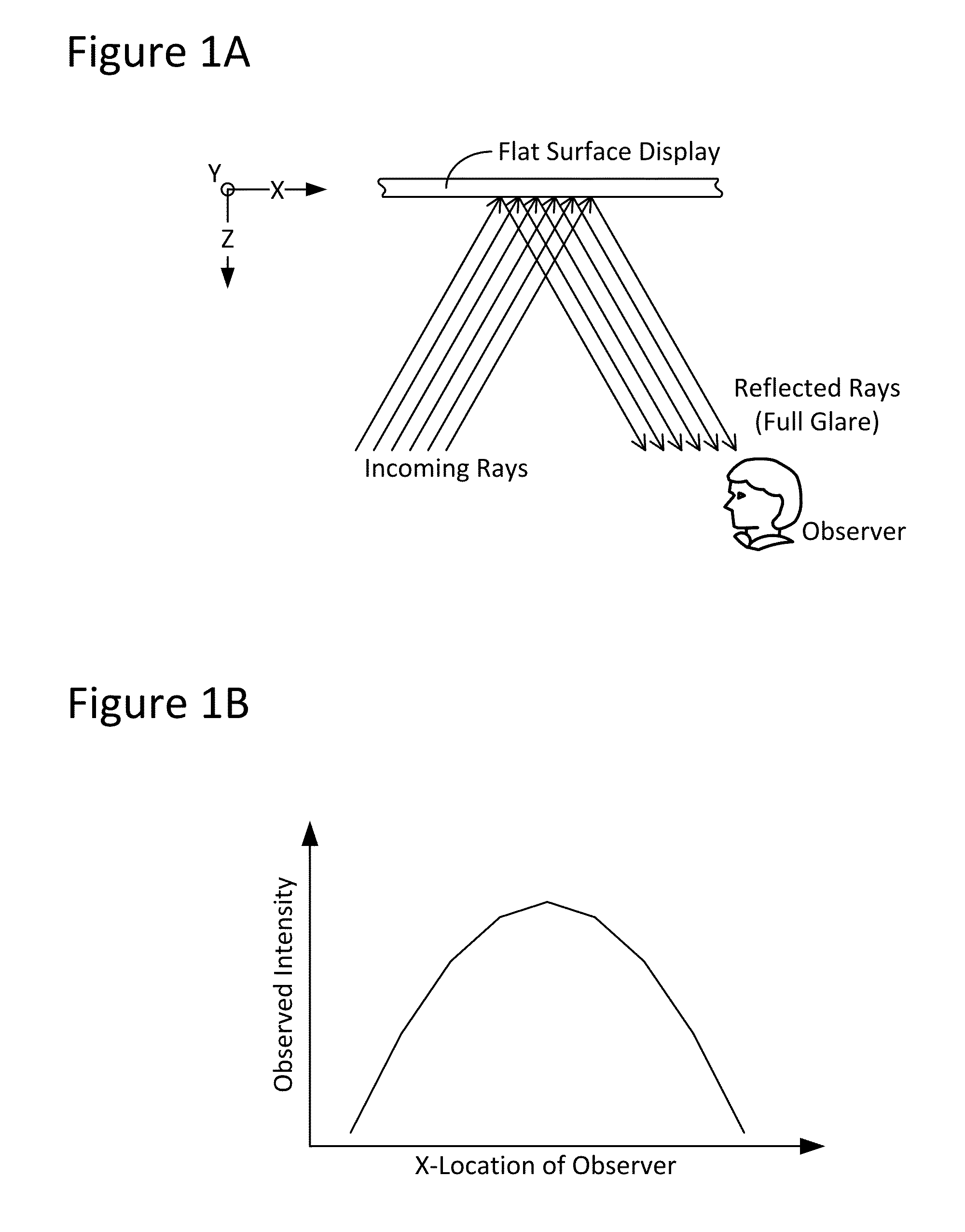
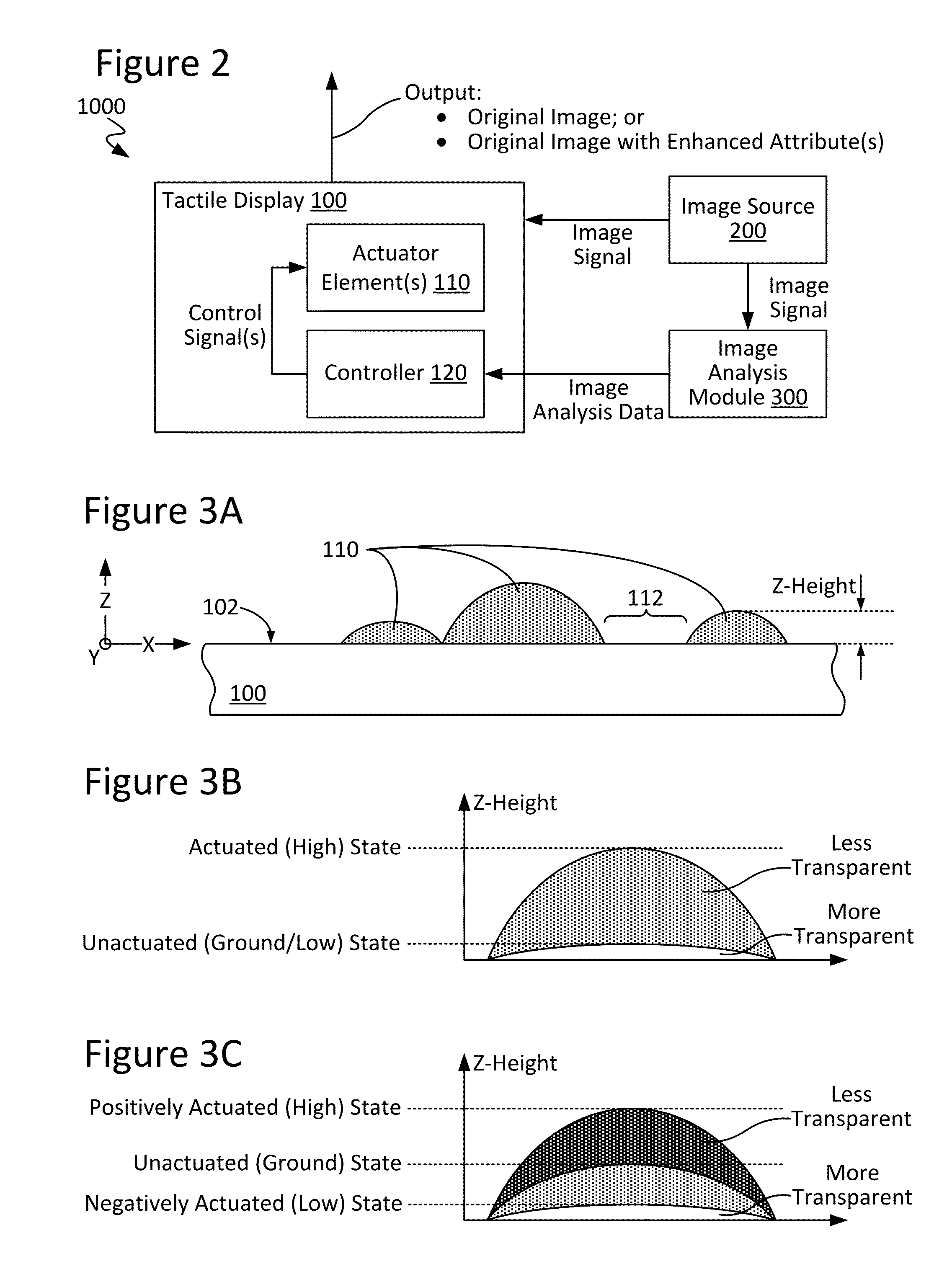
Techniques for image enhancement using a tactile display
Techniques are disclosed for enhancing the quality of a displayed image using a tactile or other texture display. In particular, the disclosed techniques leverage active-texture display technology to enhance the quality of graphics by providing, for example, outlining and / or shading when presenting a given image, so as to create the effect of increased contrast and image quality and / or to reduce observable glare. These effects can be present even at high viewing angles and in environments of high light reflection. To these ends, one or more graphics processes, such as edge-detection and / or shading, may be applied to an image to be displayed. In turn, an actuator element (e.g., microelectromechanical systems, or MEMS, devices) of the tactile display may be manipulated (e.g., in Z-height) to provide fine-grain adjustment of image attributes such as: pixel brightness / intensity; pixel color; edge highlighting; object outlining; effective shading; image contrast; and / or viewing angle.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Systems and methods for reducing motion blur in images or video in ultra low light with array cameras
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Luminance control method for display screen
ActiveCN101383139ASolve glareProblems that are unclear to the solverCathode-ray tube indicatorsPixel brightnessComputer science
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
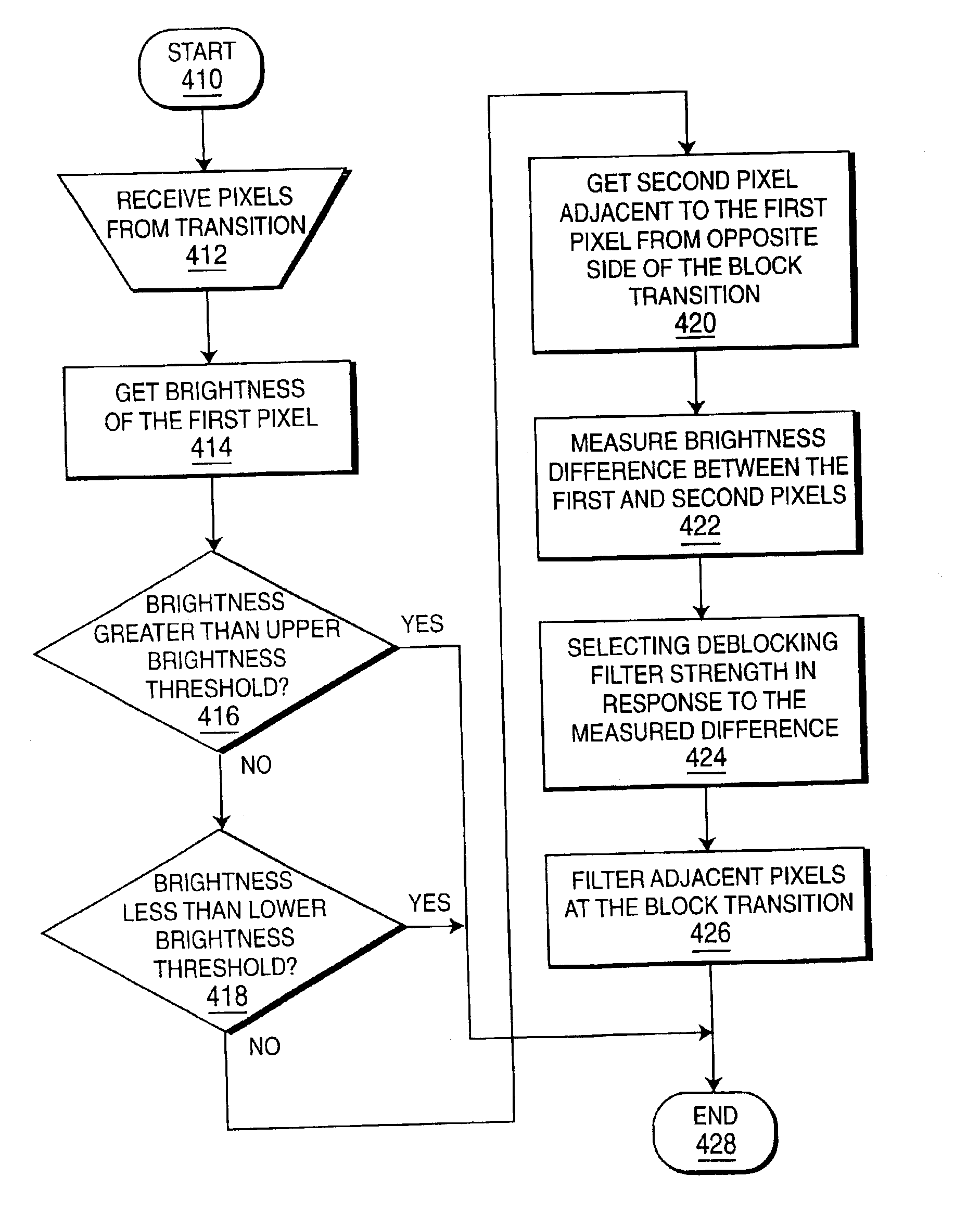
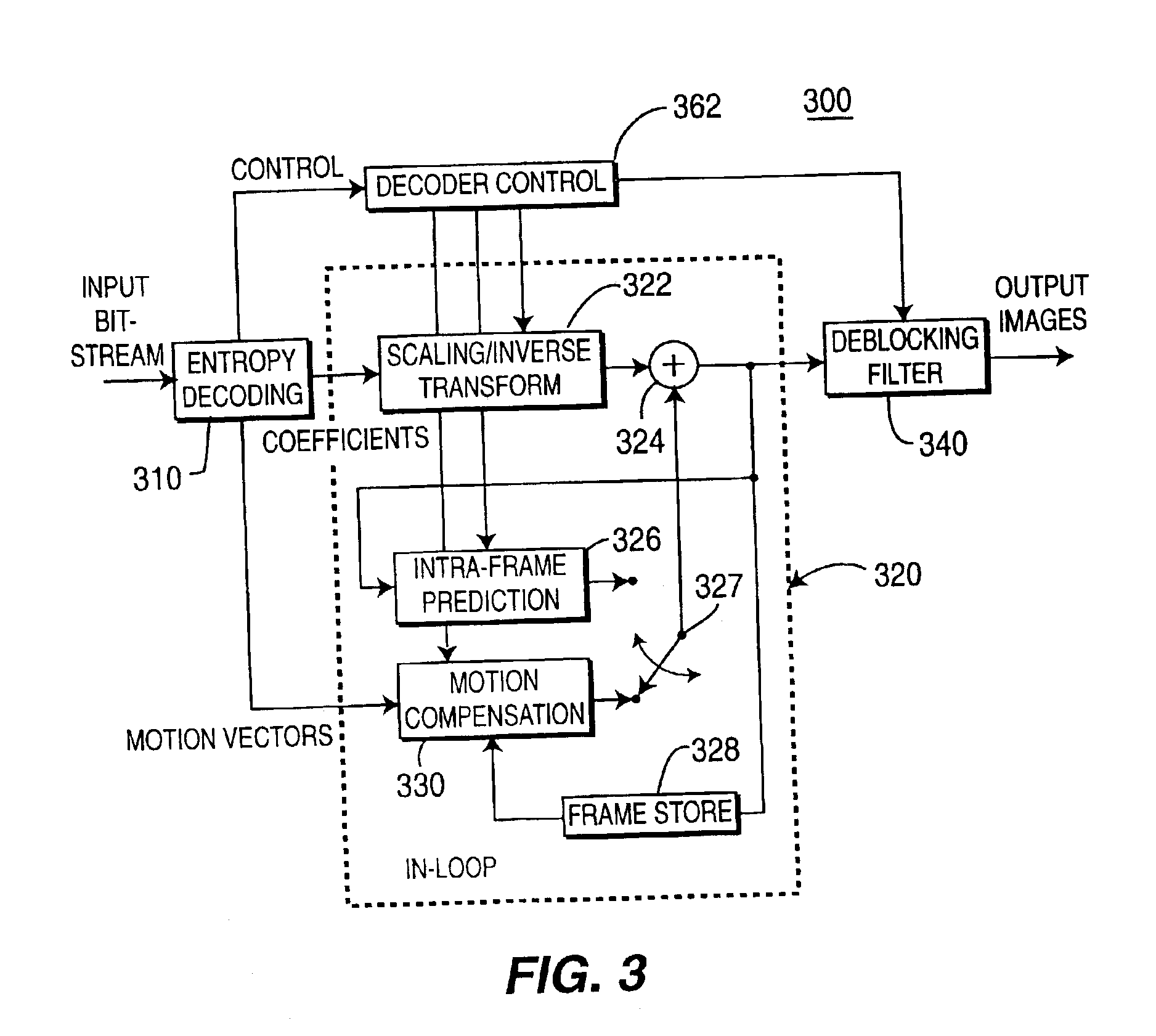
Deblocking filter conditioned on pixel brightness
InactiveUS6907079B2Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionBlock transformDeblocking filter
An encoder, decoder, and corresponding method are disclosed for encoding pixel data as a plurality of block transform coefficients and decoding encoded block transform coefficients to provide reconstructed pixel data, the encoder and / or decoder includes a conditional deblocking filter for filtering only block transitions meeting pre-selected pixel brightness level criteria, where the conditional deblocking filter method includes receiving at least one first pixel adjacent to a block transition, providing a signal indicative of the brightness of the at least one first pixel, comparing the brightness signal with at least one of an upper brightness threshold and a lower brightness threshold, and conditionally filtering a plurality of adjacent pixels including the first pixel at the block transition in response to the brightness comparison.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
System and process for generating high dynamic range video
InactiveUS20050047676A1Minimizing any discontinuityTelevision system detailsImage enhancementTone mappingRadiance
A system and process for generating High Dynamic Range (HDR) video is presented which involves first capturing a video image sequence while varying the exposure so as to alternate between frames having a shorter and longer exposure. The exposure for each frame is set prior to it being captured as a function of the pixel brightness distribution in preceding frames. Next, for each frame of the video, the corresponding pixels between the frame under consideration and both preceding and subsequent frames are identified. For each corresponding pixel set, at least one pixel is identified as representing a trustworthy pixel. The pixel color information associated with the trustworthy pixels is then employed to compute a radiance value for each pixel set to form a radiance map. A tone mapping procedure can then be performed to convert the radiance map into an 8-bit representation of the HDR frame.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
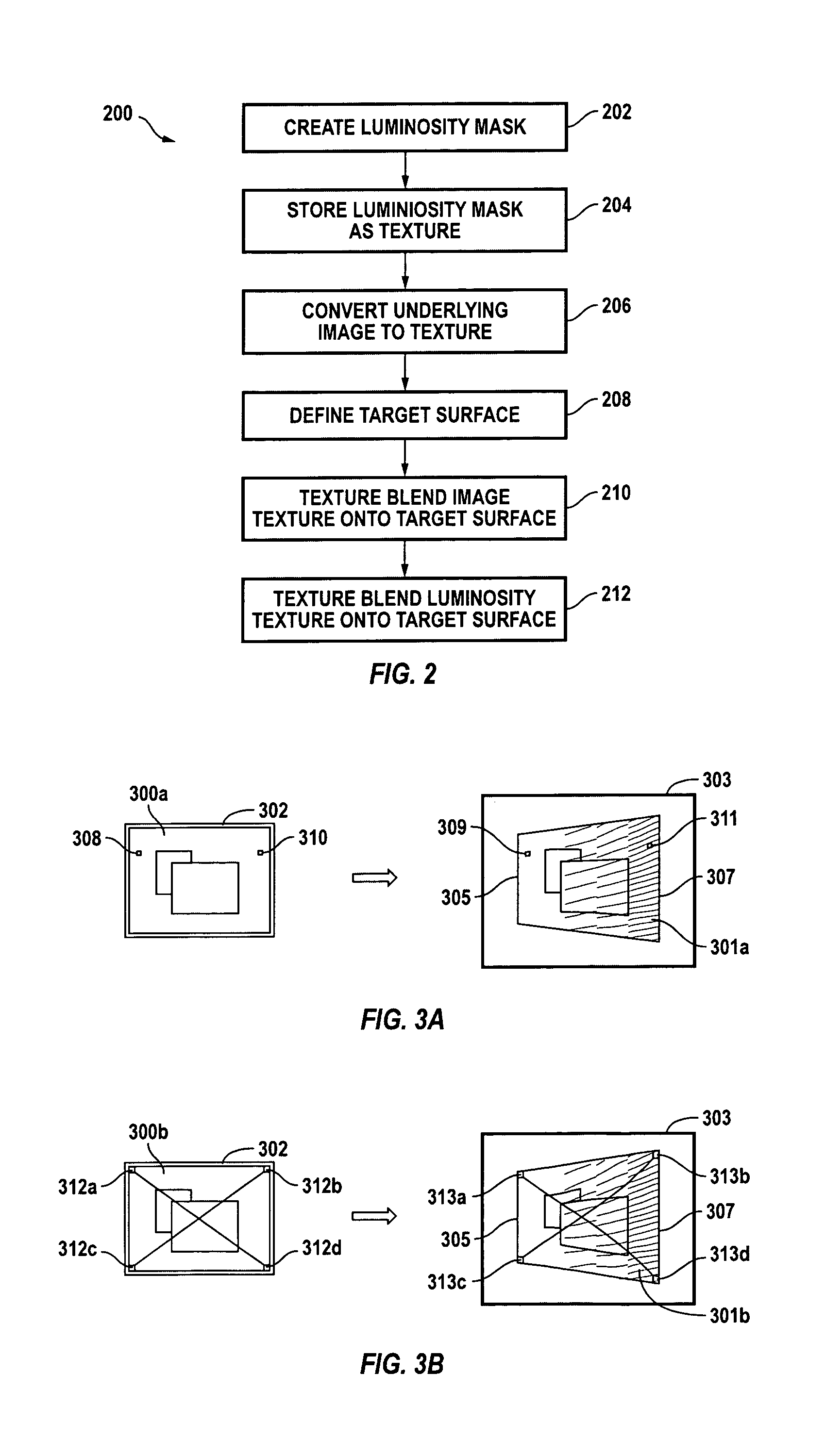
Per-pixel output luminosity compensation
ActiveUS7336277B1Television system scanning detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionTarget surfaceComputer graphics (images)
Per-pixel luminosity adjustment uses a luminosity mask applied as a texture. In one embodiment, a luminosity texture is defined. Pixel data of an underlying image is converted to an image texture. The image texture is blended onto a target surface. The luminosity texture is also blended onto the target surface, thereby generating luminosity compensated pixel data for the image.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
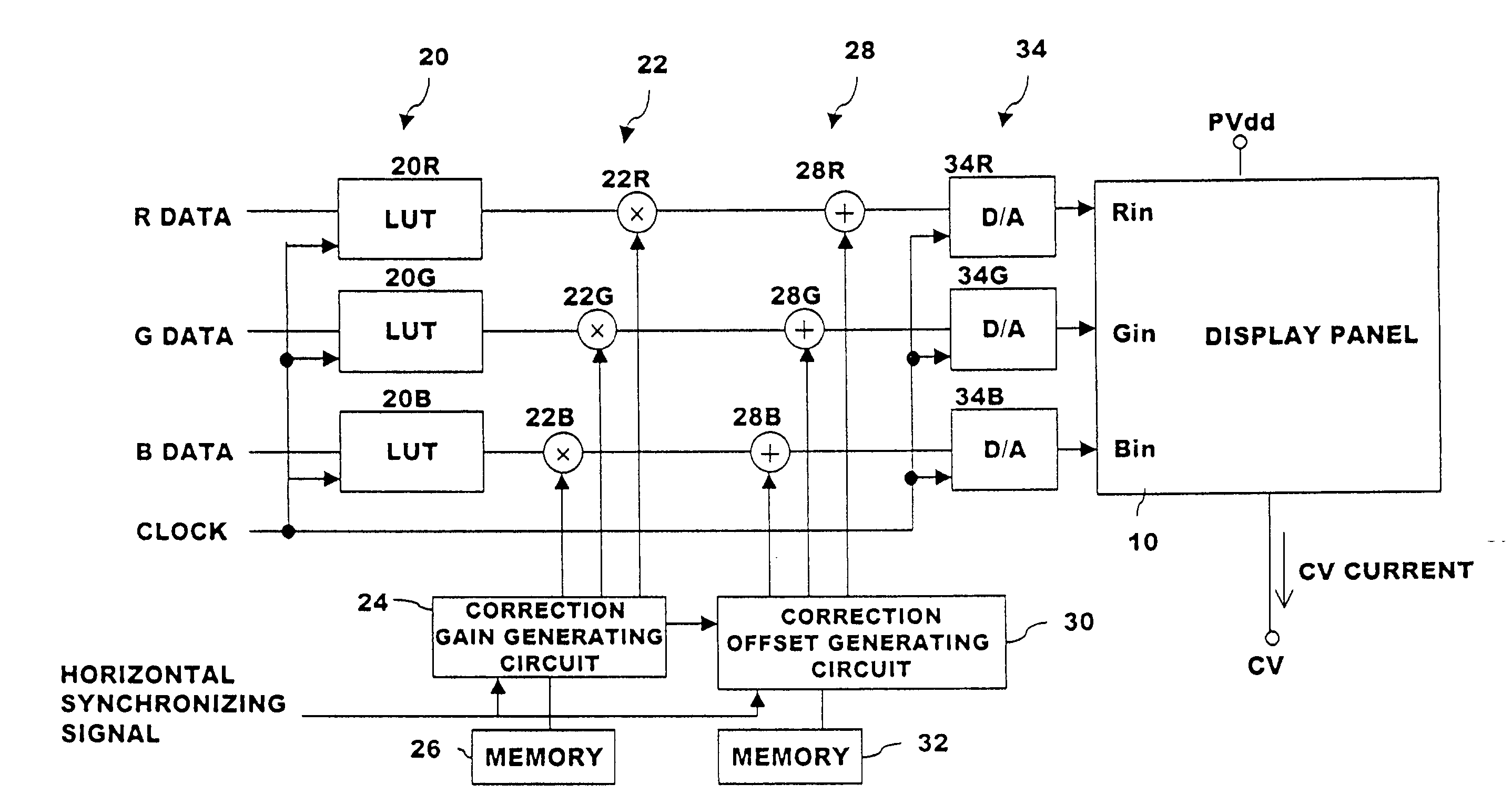
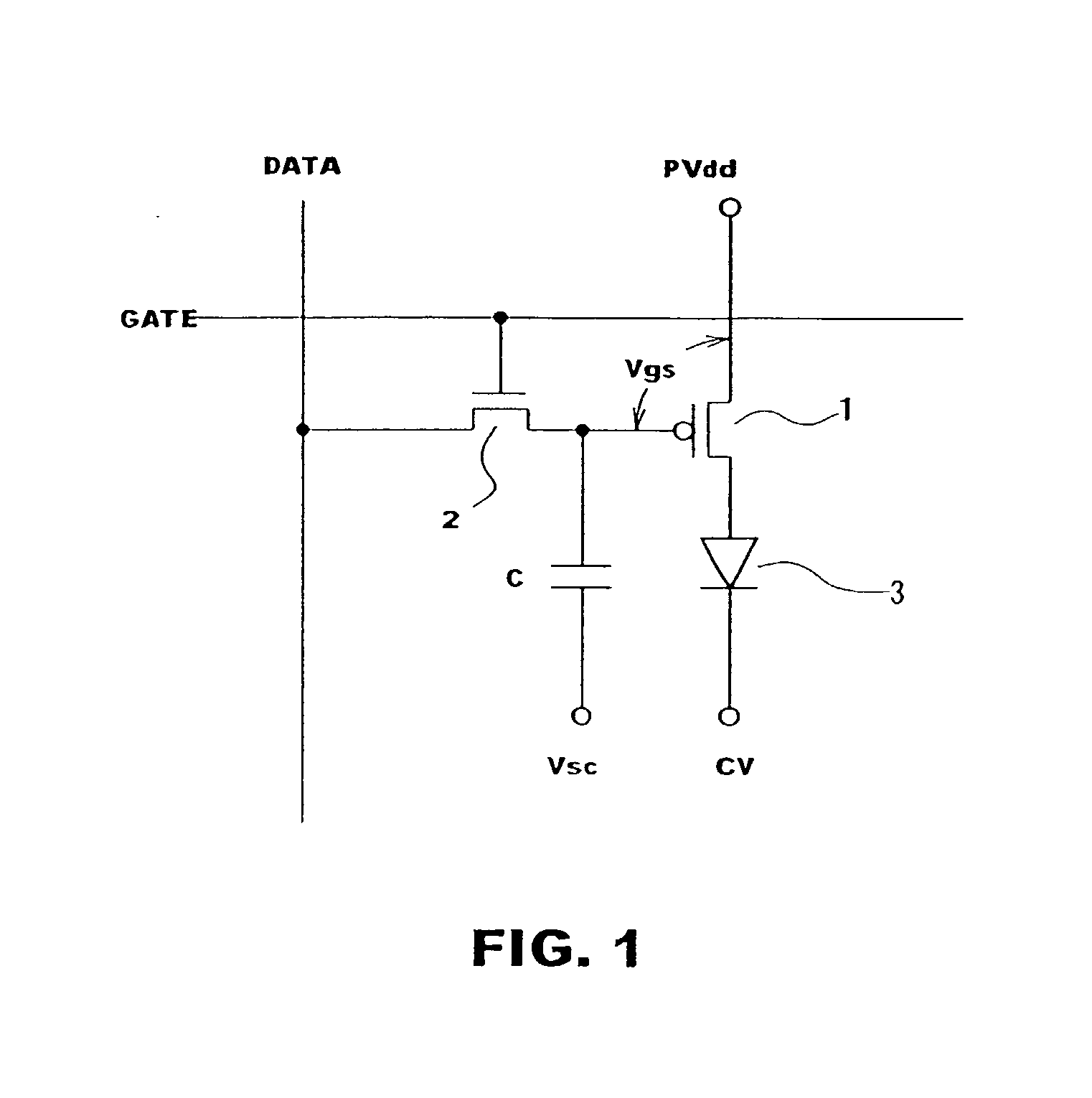
Organic electrolimunescent display apparatus
ActiveUS20070210996A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentDisplay device
An organic EL display apparatus including in each display pixel an organic EL element. A drive transistor supplies a drive current that depends on brightness data and having the display pixels arranged in a matrix form. The display includes a correction gain storage unit for storing display pixel positions and a correction gain for correcting the slope of the brightness-data-based drive current of the drive transistors in the display pixels; and a correction unit for correcting pixel-by-pixel brightness data depending on the pixel position using the correction gain stored in the correction gain storage unit into brightness data for the pixel to generate corrected brightness data, each of the display pixels is displayed by driving its drive transistor in response to the data generated by the correction gain storage unit and the correction unit and supplying the corresponding organic EL element with the drive current.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
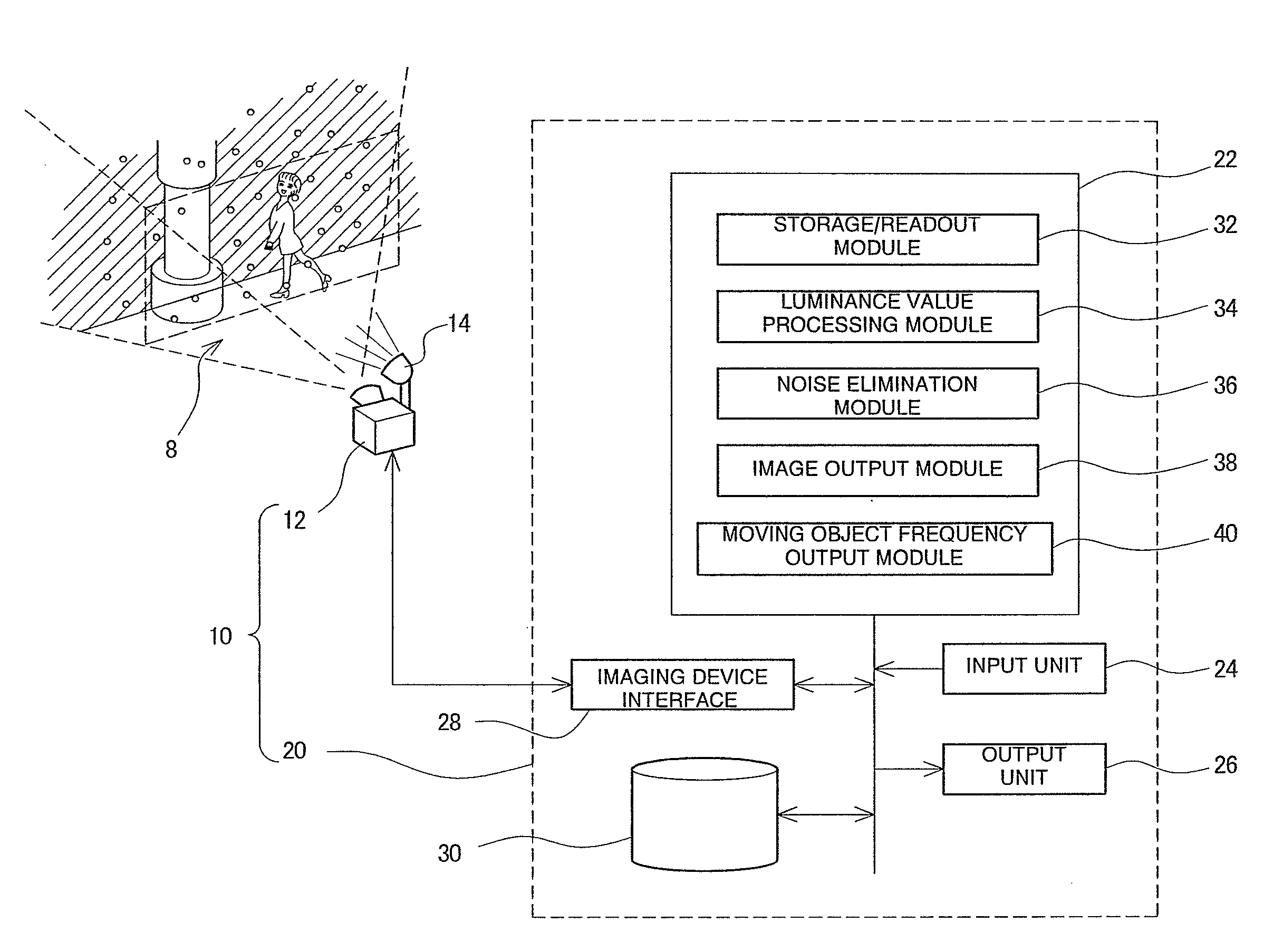
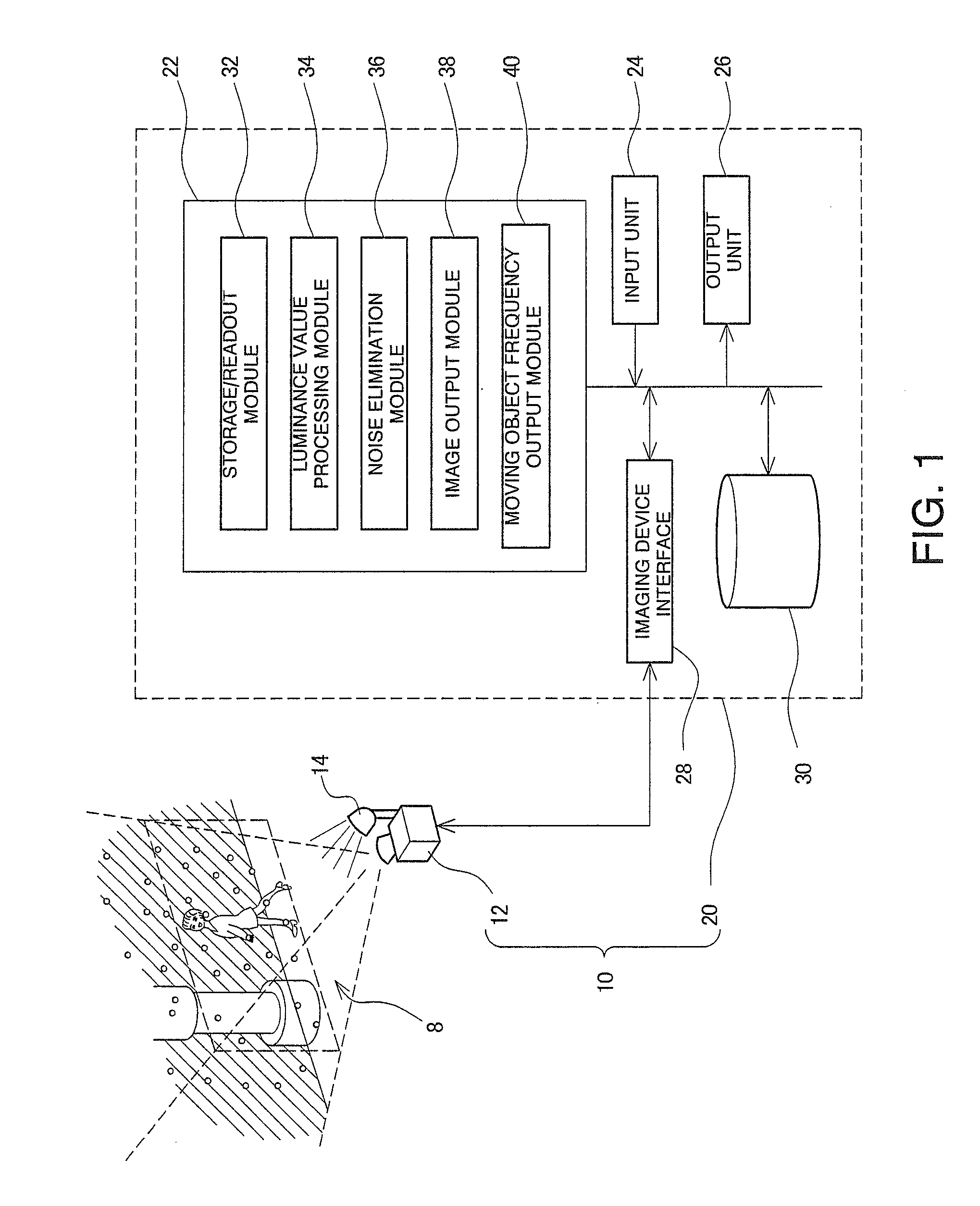
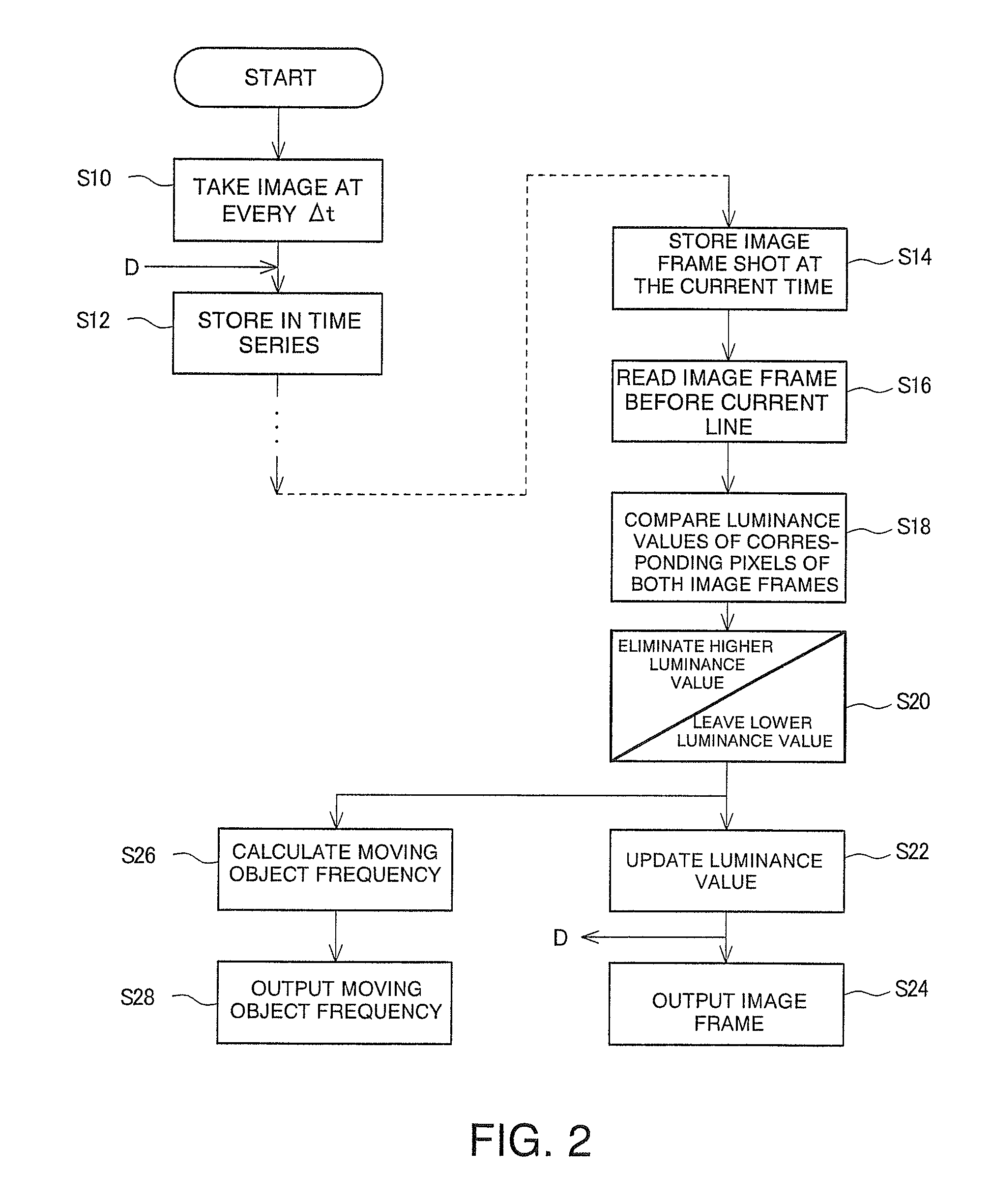
Moving Object Noise Elimination Processing Device and Moving Object Noise Elimination Processing Program
InactiveUS20100141806A1Brightness value increasedCancel noiseImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionPixel brightness
A moving object noise elimination processing device and a moving object noise elimination processing program are provided for making it possible to effectively eliminate a noise due to a moving object in front of a photographing object with a relatively simple method. A moving object noise elimination process involves first photographing an image every predetermined sampling interval Δt and the photographed images are stored in association with time (S10, S12). Next, with respect to the currently photographed image frame data and the previously photographed image frame data, each corresponding pixel brightness value is compared (S14, S16, S18). For each pixel, the one with a higher brightness value is then eliminated as a noise and that with lower brightness value is left (S20). The brightness value in each pixel of the image frame is updated with the left brightness value in each pixel and the updated one is output (S22, S24). Further, a moving object frequency is calculated from a ratio of the total number of data to the number of data with the eliminated brightness values and the calculated one is output (S26, S28).
Owner:HOKKAIDO UNIVERSITY +1
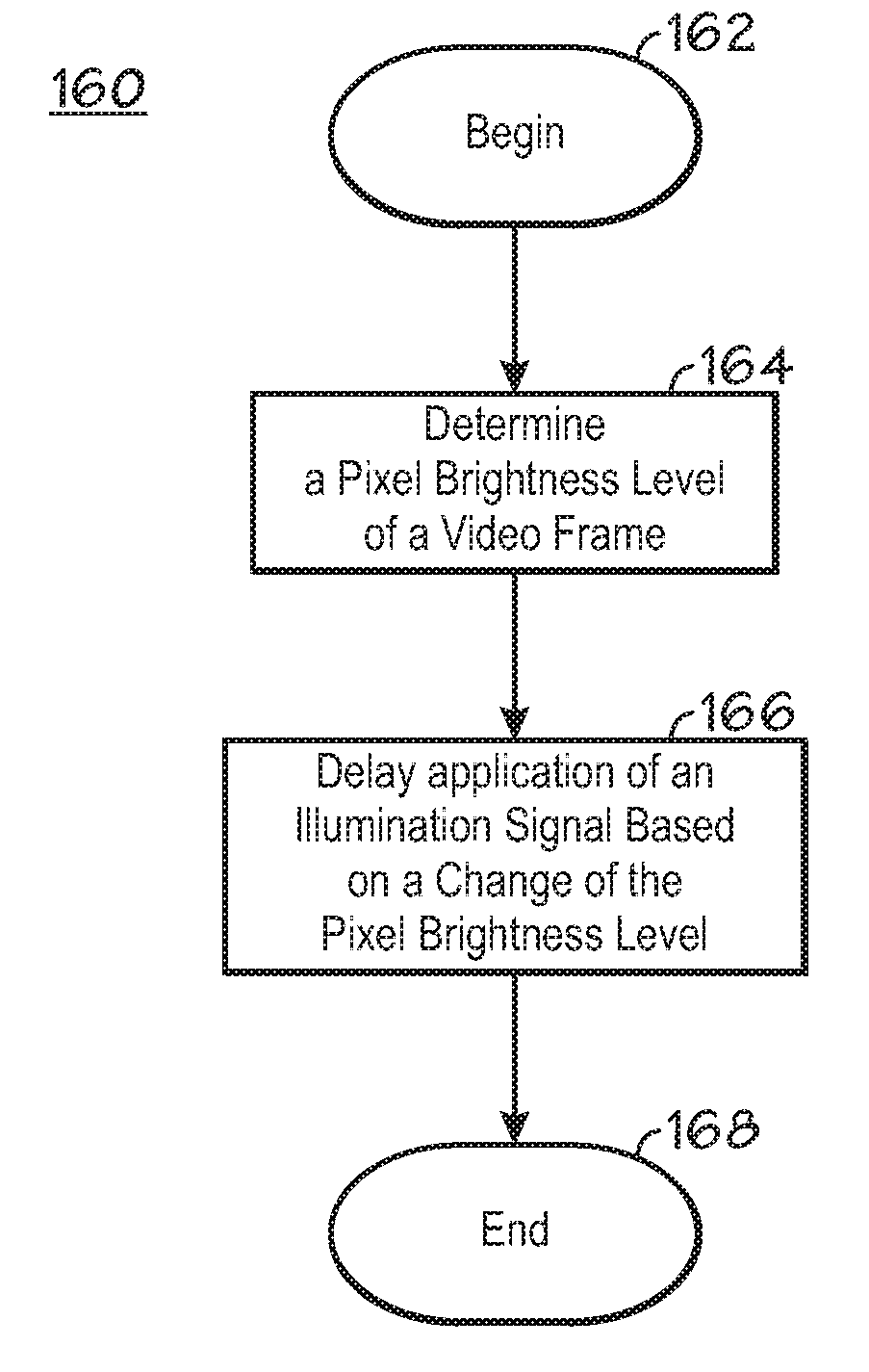
Contrast Ratio Enhancement System Using Asymmetrically Delayed Illumination Control
InactiveUS20090015602A1Increase contrastCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceContrast enhancement
The disclosed embodiments relate to a system and method that enhance contrast ratio of a display device using asymmetrically delayed illumination signal control. An exemplary embodiment comprises determining a pixel brightness level for a video frame, and delaying application of the illumination signal based on a change of the pixel brightness level.
Owner:TTE TECH INC
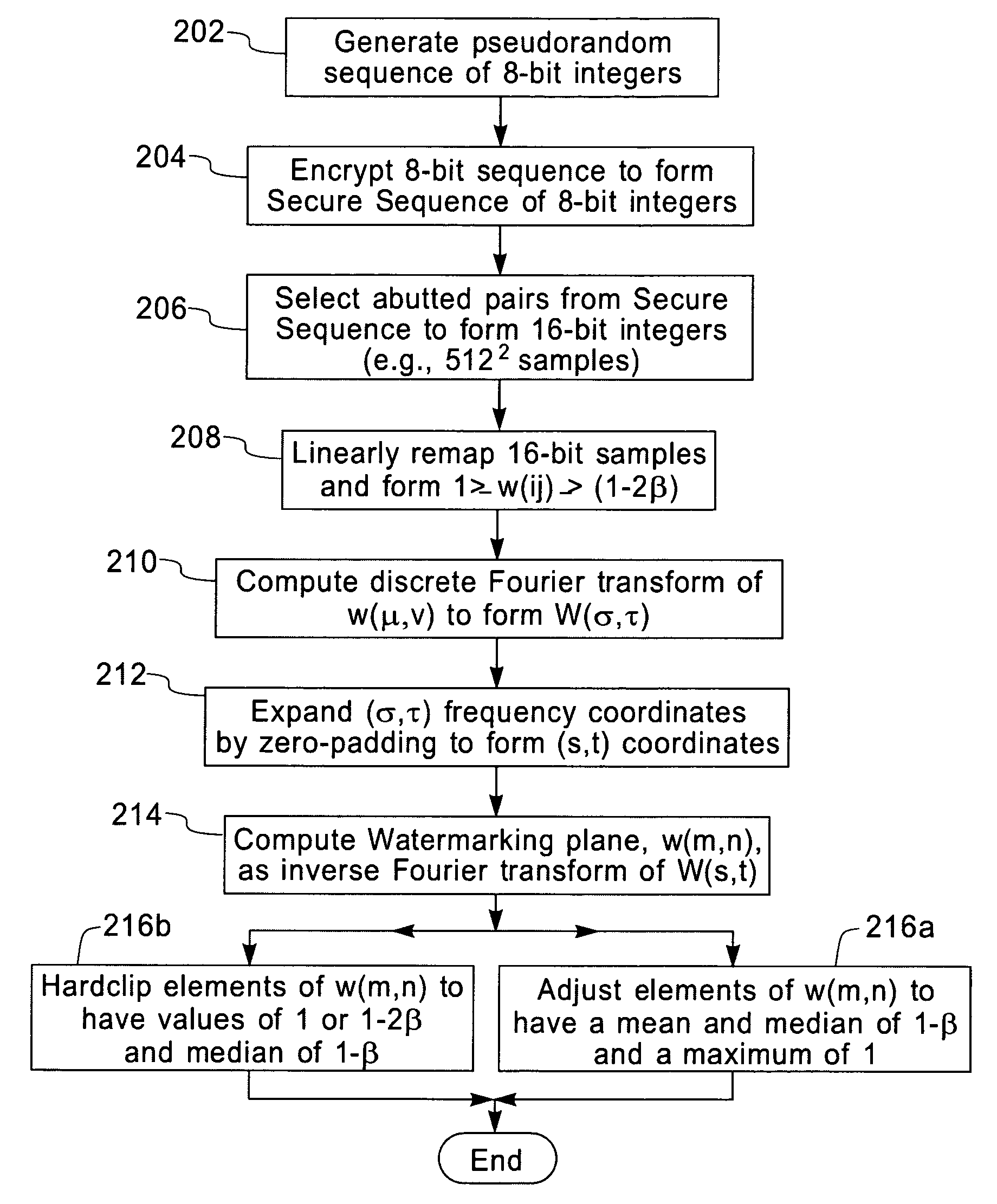
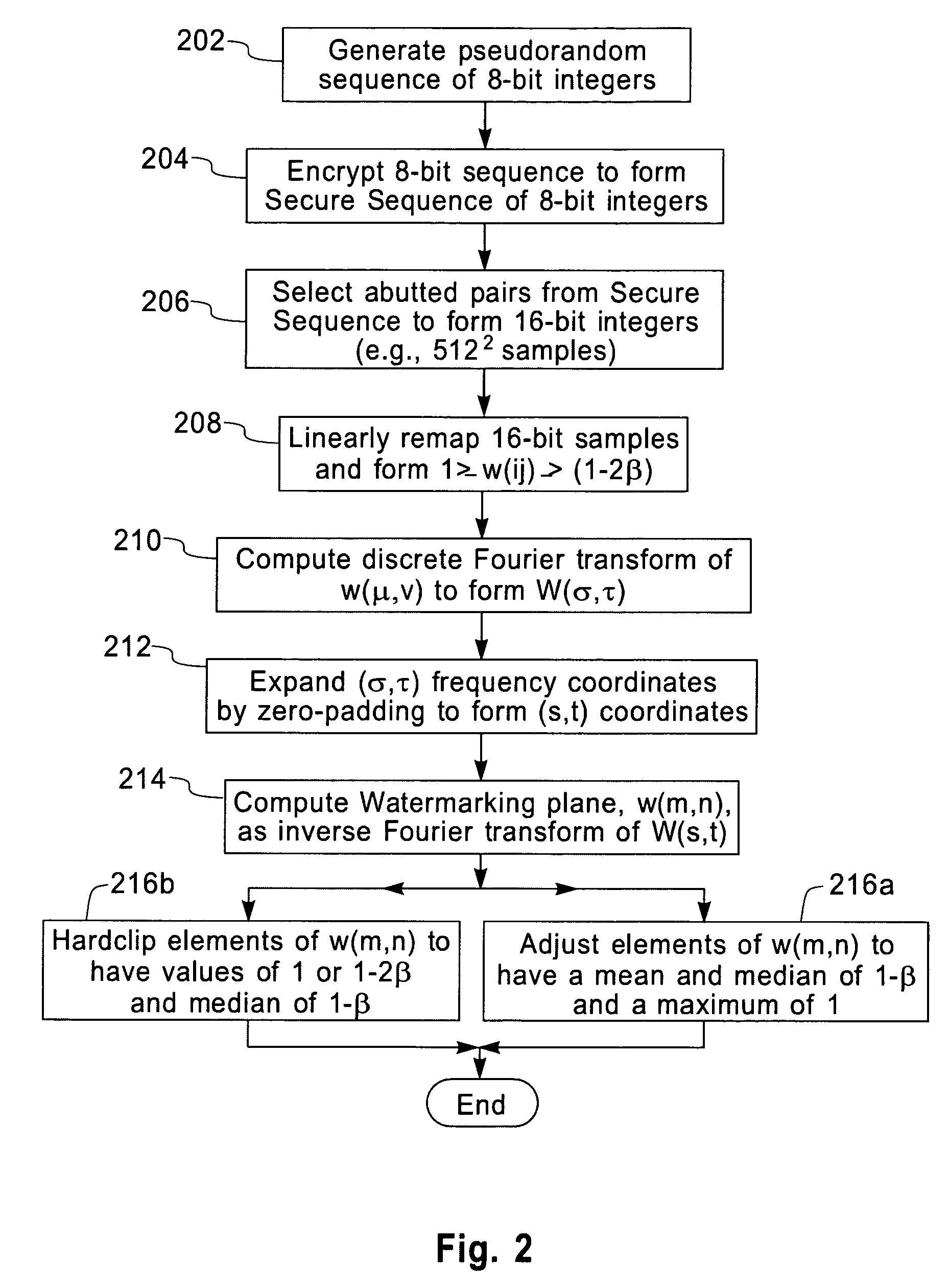
Protecting images with an image watermark
InactiveUS7130442B2Improve detection rateCharacter and pattern recognitionSecret communicationPixel brightnessLightness
A robust means of watermarking a digitized image with a highly random sequence of pixel brightness multipliers is presented. The random sequence is formed from ‘robust-watermarking-parameters’ selected and known only by the marker and / or the marking entity. A watermarking plane is generated having an element array with one-to-one element positional correspondence with the pixels of the digitized image being marked. Each element of the watermarking plane is assigned a random value dependent upon a robust random sequence and a specified brightness modulation strength. The so generated watermarking plane is imparted onto the digitized image by multiplying the brightness value or values of each pixel by its corresponding element value in the watermarking plane. The resulting modified brightness values impart the random and relatively invisible watermark onto the digitized image. Brightness modulation is the essence of watermark imparting. Detection of an imparted watermark requires knowing the watermarking plane with which the watermark was imparted. Regeneration of the watermarking plane requires knowledge of the robust-marking-parameters used in its formulation. This is generally only known to the marker and / or marking entity. Once regenerated, the watermarking plane is used together with a verifying image located in a ‘visualizer’ to demonstrate the existence of the watermark. The process of watermark detection is enhanced by application of a blurring filter to the marked image before detection is attempted.
Owner:RPX CORP
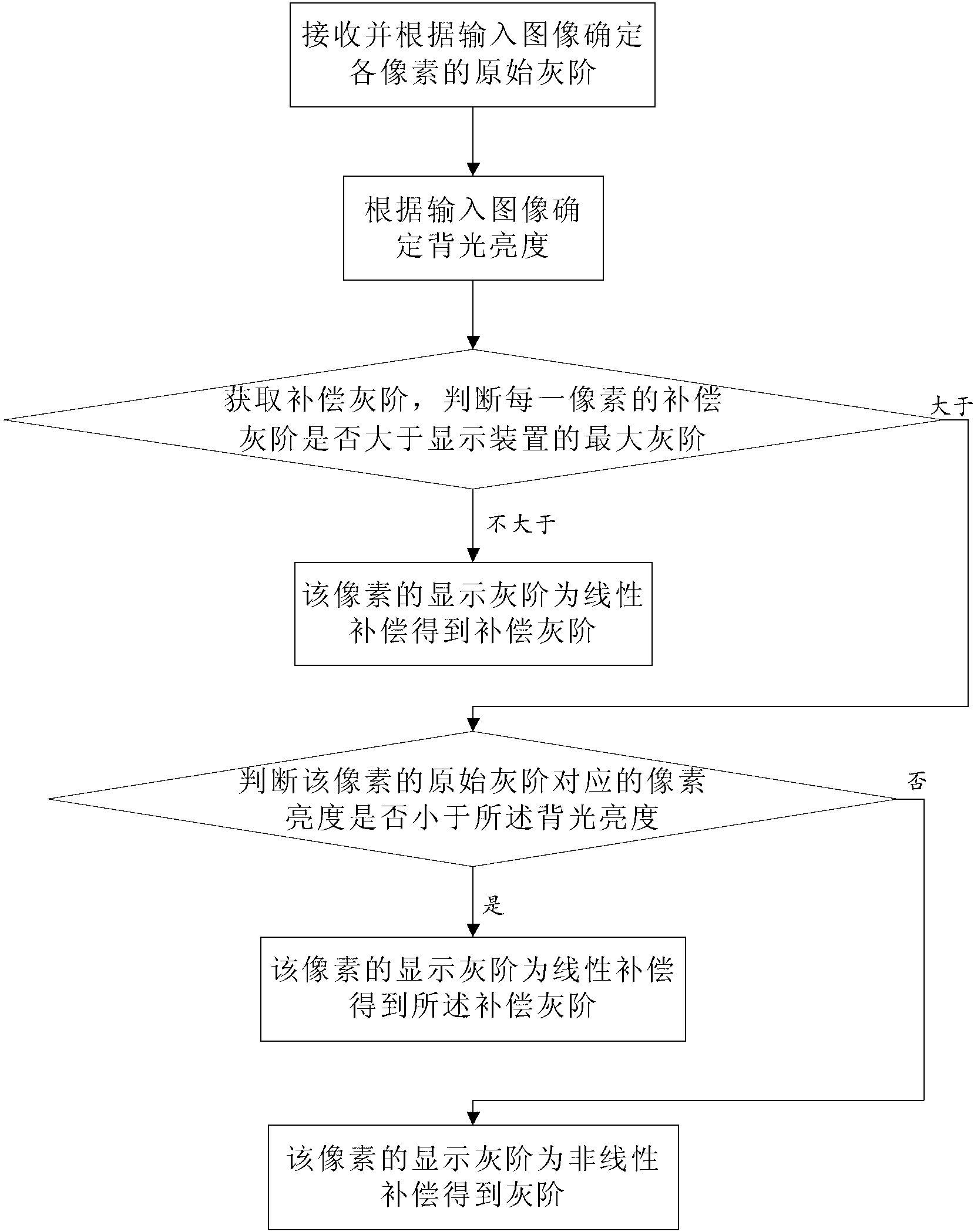
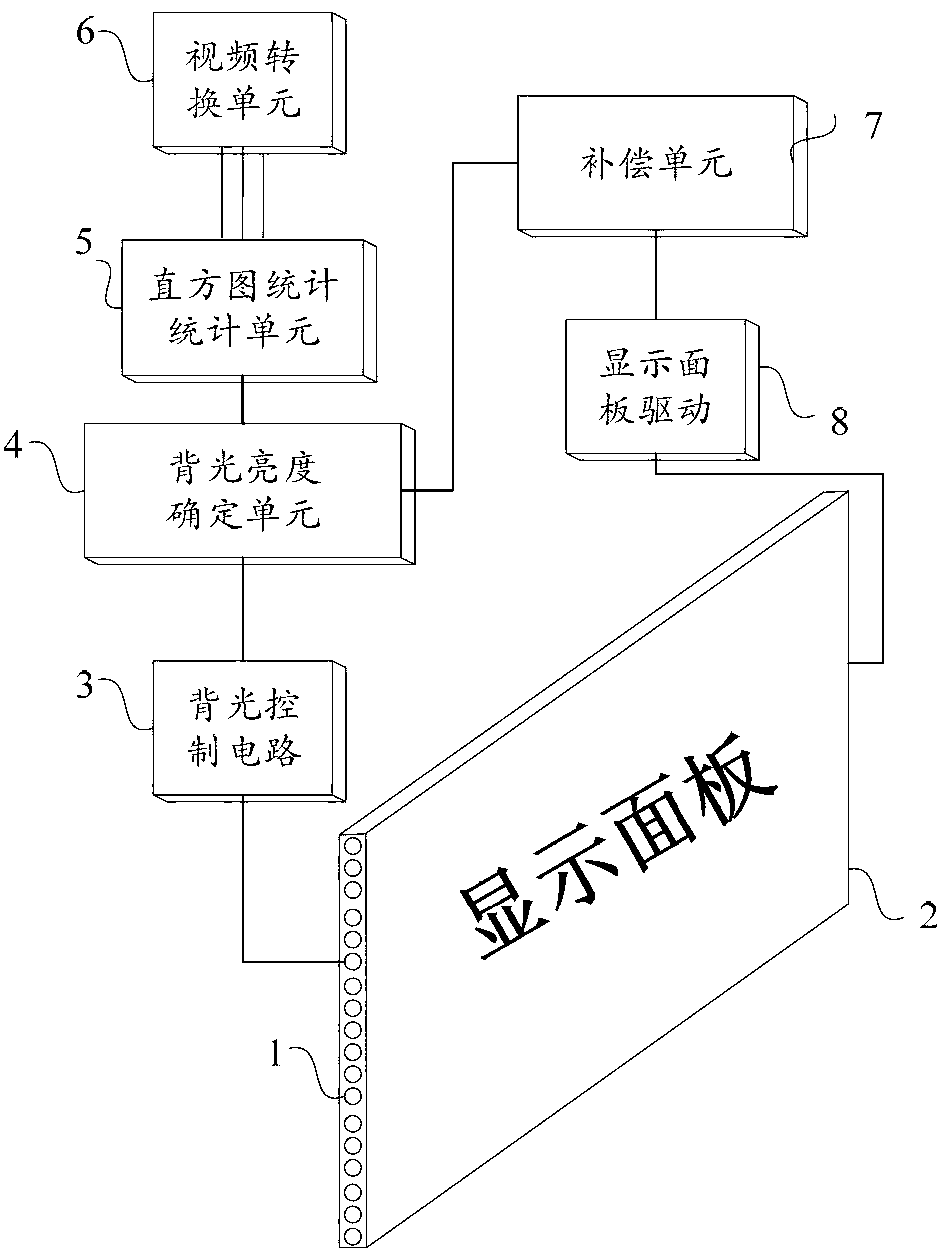
Backlight brightness compensation method and display device
ActiveCN103310765ASimple structureSmall distortionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay devicePixel brightness
The invention discloses a backlight brightness compensation method and a display device and aims to solve such problems that image distortion is serious and display effect is poor in the prior art. The backlight brightness compensation method includes: receiving, and determining original gray scales of pixels according to an input image; determining backlight brightness according to the input image; linearly compensating the original gray scales according to a compensation factor fcom so as to obtain compensated gray scale of each pixel; judging whether the compensated gray scale of each pixel is larger than the maximum gray scale of the display device or not; if not, determining that the display gray scale of the pixel is the compensated gray scale; if yes, judging whether pixel brightness corresponding to the original gray scale of the pixel is smaller than the backlight brightness or not; if smaller, determining that the display gray scale of the pixel is the compensated gray scale; if not smaller, determining that the display gray scale of the pixel is the gray scale obtained by linearly compensating the original gray scale according to the compensation factor fcom. The backlight brightness compensation method and the display device have the advantages that image displaying effect is good, resolution is high, the structure is simple and production cost is low.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
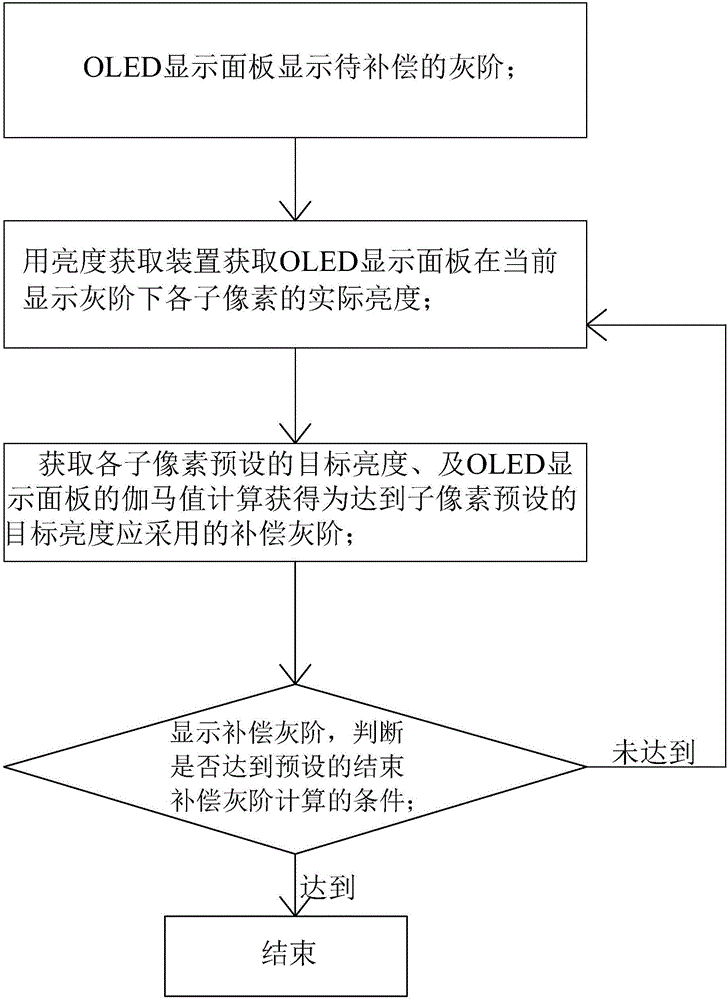
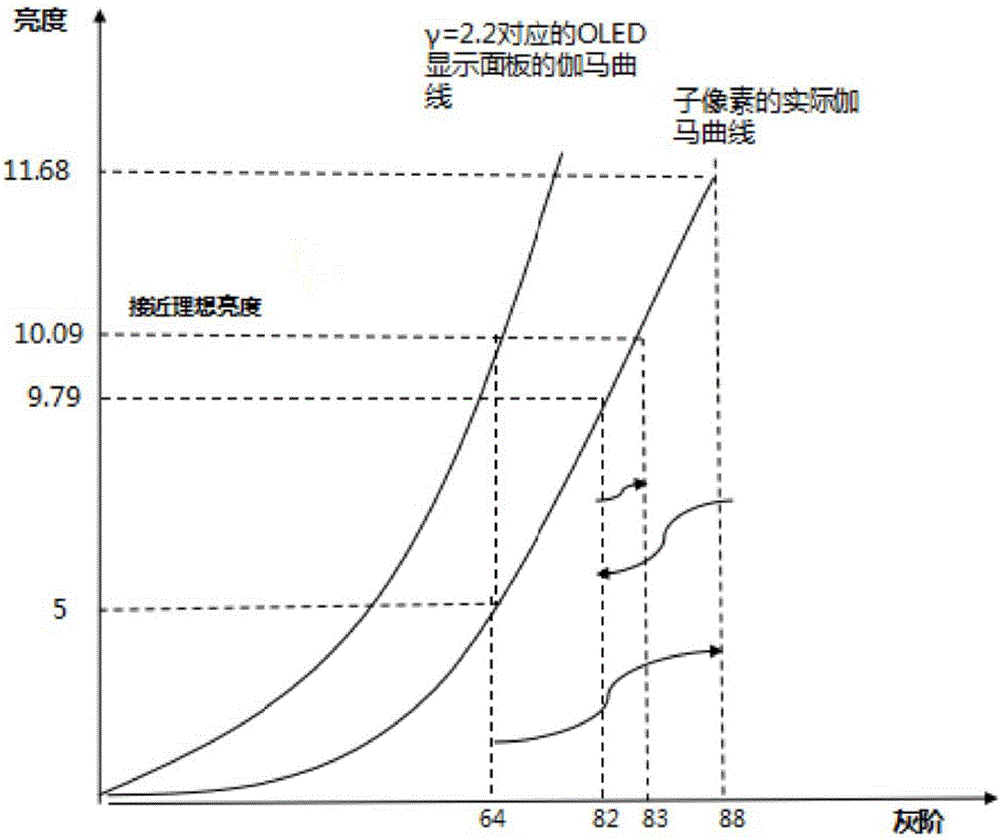
Method for eliminating Mura of OLED display panel
ActiveCN105741763AUniform brightnessImprove display qualityStatic indicating devicesPixel brightnessComputer science
The invention provides a method for eliminating Mura of an Organic Light Emitting Display (OLED) display panel. The method includes the steps of: firstly calculating and obtaining gray scale compensation should be adopted according to the target brightness and the actual brightness of each sub-pixel, current display gray scale, and a gamma value of the OLED display panel; the making the OLED display panel display the currently obtained compensation gray scale; and judging whether a preset compensation gray scale calculation-ending condition is reached, if the preset compensation gray scale calculation-ending condition is not reached, and obtaining the actual brightness of the sub-pixels in the compensation gray scale; and calculating again and obtaining the compensation gray scale should be adopted next time, and continuously carrying out iterative computation, until the preset compensation gray scale calculation-ending condition is reached. Compared with the prior art, the method for eliminating the Mura of the OLED display panel makes the sub-pixel brightness furthermore approach the target brightness through the compensation gray scale obtained by multiple iterative computations, can fast and effectively eliminate the Mura of the OLED display panel, ensures the brightness uniformity of the OLED display panel, and raises the display quality of the OLED display panel.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
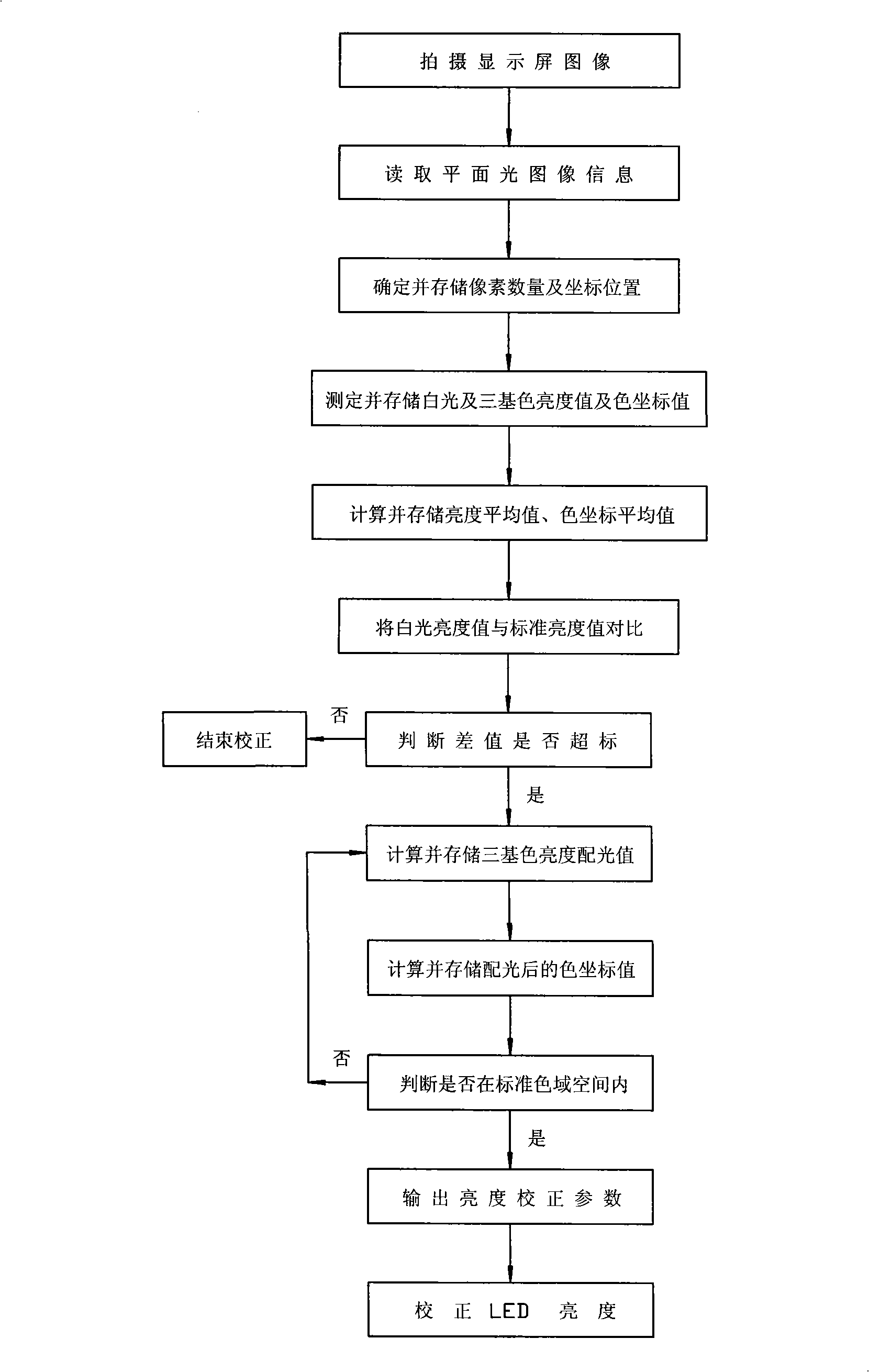
On-line brightness correcting and color gamut optimizing method for full-color LED display screen
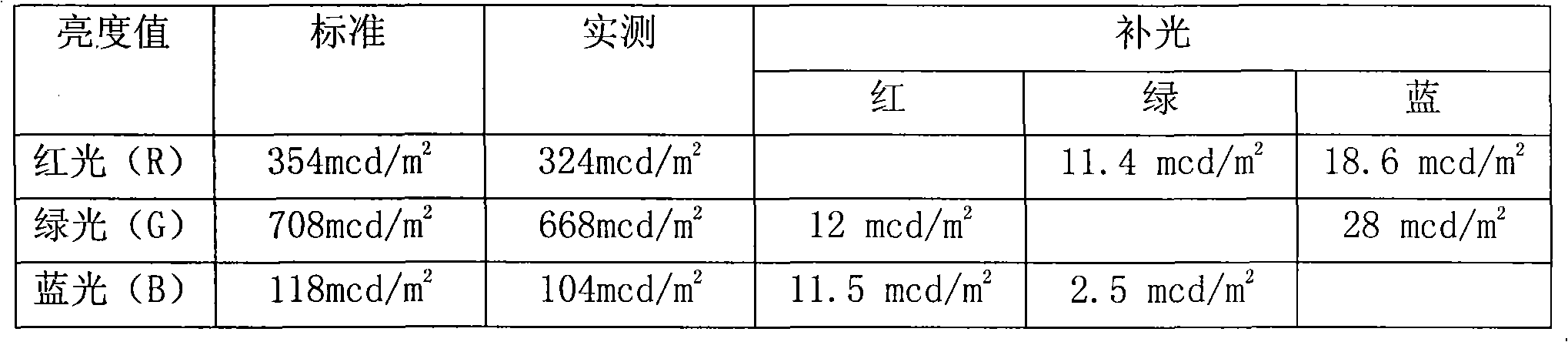
The invention discloses a method for regulating online brightness and optimizing color range of a full-color LED display screen, which has the specific steps that: the white balance images and the RGB tricolor images of the full-color LED display screen are shot to obtain plane light images; the information of the plane light images is read; the number of pixels and each pixel position coordinate are determined and stored; the white light of the selected pixel, a tricolor brightness value and a color coordinate value are measured and stored; the pixel brightness and color coordinate mean value are computed and stored; the white light brightness value of the pixel is compared with a standard brightness value to judge whether difference value is out of limits. If the difference value is not out of limits, the regulation stops; if the difference value is out of limits, the following steps are carried out: the tricolor brightness light distribution value of the selected pixel is computed and stored; the color coordinate value of G(x, y), R(x, y), B(x, y) is computed after the light distribution and is judged whether within the standard color range or not; if not, the steps of g and h are repeated; if so, brightness regulation parameter is output to regulate the LED brightness of the selected pixel in the standard color range.
Owner:DALIAN DAMING TECH
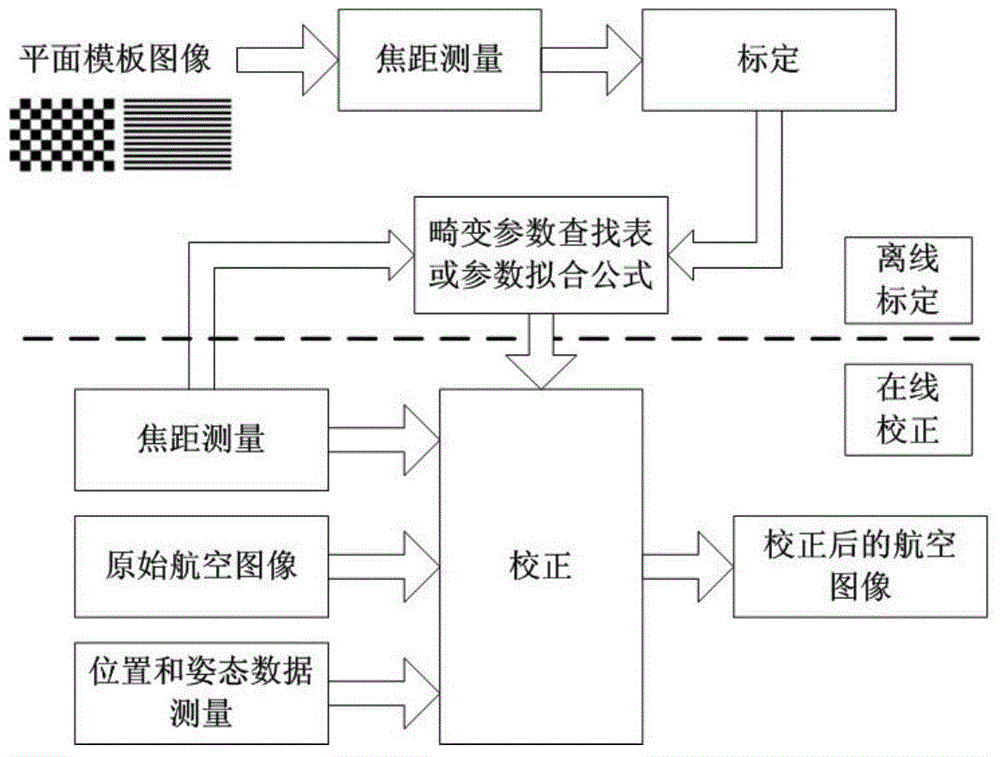
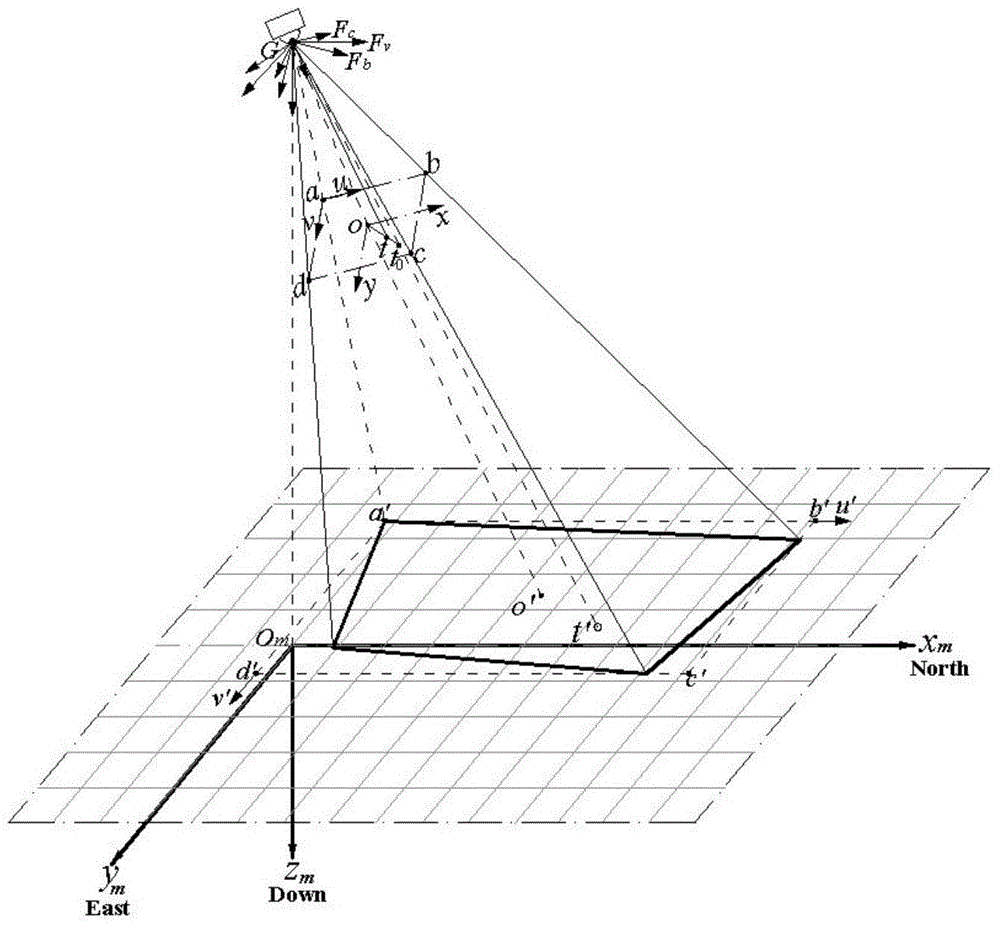
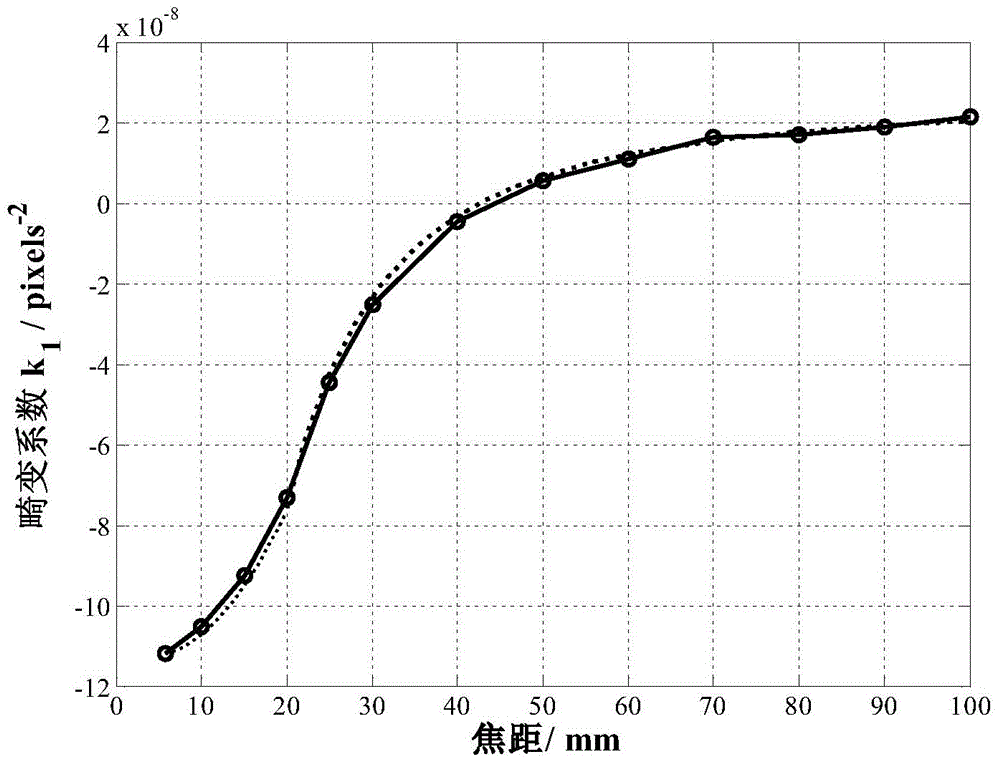
Digital image correction method for continuous variable-focal-length optical imaging system
InactiveCN104835159AGet rid of dependencyReduce processingImage analysisNonlinear distortionProjection image
The invention discloses a digital image correction method for a continuous variable-focal-length optical imaging system. The digital image correction method comprises the steps of acquiring planar template images which are photographed by an image camera in a plurality of discrete focal lengths, performing off-line calibration on a distortion parameter which corresponds with each focal length of a variable-focal-length lens; performing curve fitting on the distortion parameter which corresponds with each focal length for obtaining a fitting formula or establishing a distortion parameter lookup table; according to the actual operation focal length of the image camera, obtaining a lens distortion parameter which corresponds with the actual operation focal length through the distortion parameter lookup table or calculation by the fitting formula; and constructing a projection conversion relationship from an image camera coordinate system to a map coordinate system according to position gesture data and the lens distortion parameter in imaging of the image camera, and performing resampling on the pixel brightness value after coordinate conversion for obtaining an orthographic projection image after correction on the squint deformation and lens distortion. The digital image correction method realizes a purpose of simultaneous correction for squint trapezoidal distortion and variable-focal-length nonlinear distortion in the variable-focal-length imaging system.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
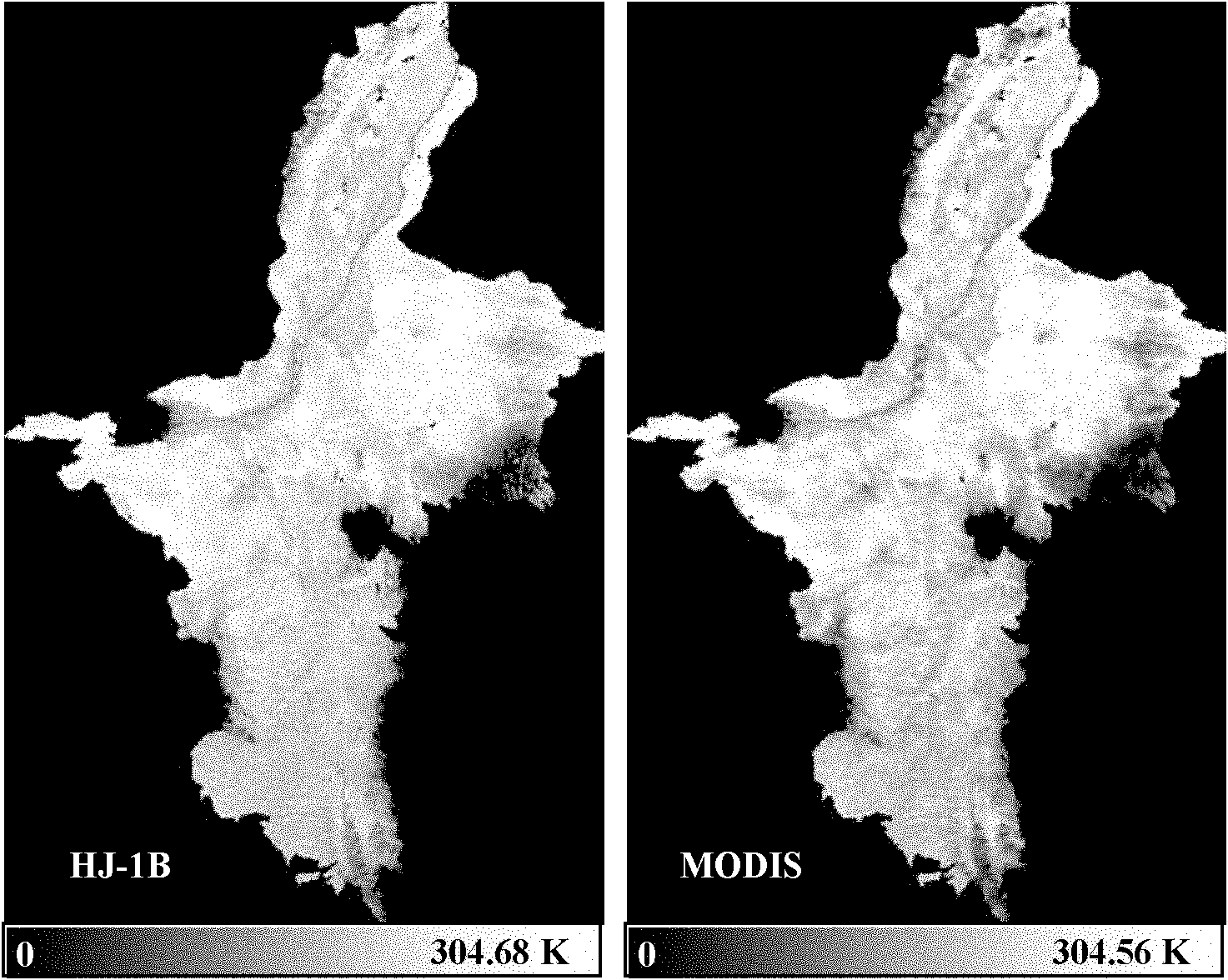
Environmental satellite 1-based surface temperature single-window inversion method
InactiveCN102103203AAchieve inversionWave based measurement systemsPyrometry using electric radation detectorsPixel brightnessAtmospheric correction
The invention discloses an environmental satellite 1-based surface temperature single-window inversion method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, acquiring remote sensing data of an environmental satellite 1B, namely an HJ-1B satellite, of the surface of a region to be tested, preprocessing the remote sensing data to acquire image data and converting a pixel brightness digital number (DN) value of the image data into radiance; 2, performing atmospheric correction on the image data by using an image-based continental offshore stratigraphic test (COST) atmospheric correction model; 3, estimating emissivity epsilon of the surface of the region to be tested by a normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) threshold method; and 4, inverting the surface temperature by a single-window algorithm according to calculation results obtained in the steps 1 to 3. In the method, the image-based COST model atmospheric correction method and the surface temperature single-window algorithm with no need of an atmospheric water vapor content parameter are applied to the HJ-1B satellite remote sensing data, so that the inversion of the surface temperature is realized.
Owner:SATELLITE ENVIRONMENT CENT MINIST OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
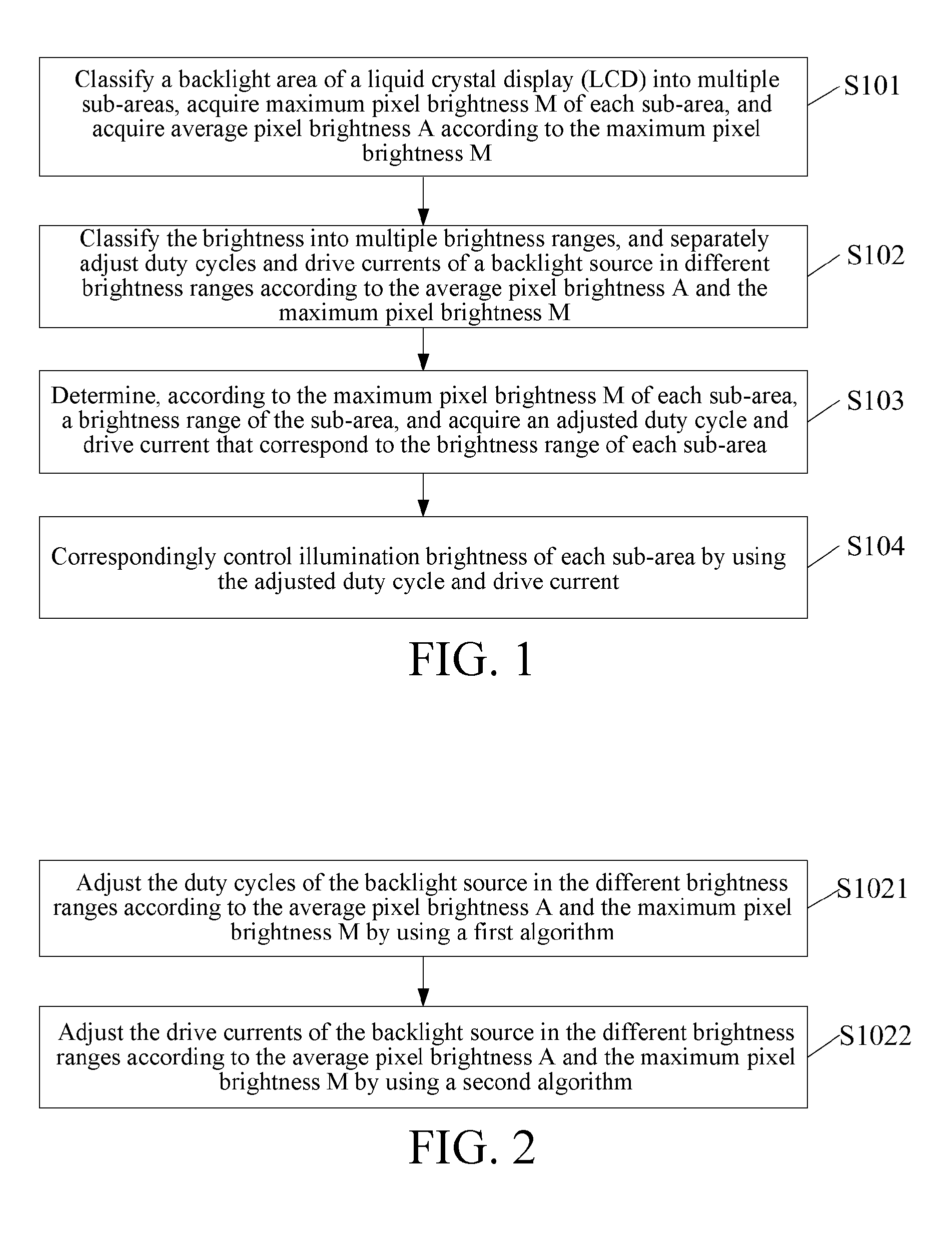
Backlight brightness adjustment method and apparatus
ActiveUS20160335957A1Enlarge range of illumination brightnessIncrease contrastStatic indicating devicesDriving currentPower flow
Disclosed are a backlight brightness adjustment method and apparatus. The backlight brightness adjustment method includes the following steps: dividing a backlight area of a liquid crystal display (LCD) into multiple sub-areas, acquiring maximum pixel brightness M of each sub-area, and acquiring average pixel brightness A according to the maximum pixel brightness M; classifying the brightness into multiple brightness ranges, and separately adjusting duty cycles and drive currents of a backlight source in different brightness ranges according to the average pixel brightness A and the maximum pixel brightness M; determining, according to the maximum pixel brightness M of each sub-area, a brightness range of the sub-area, and acquiring an adjusted duty cycle and drive current that correspond to the brightness range of each sub-area; and correspondingly controlling illumination brightness of each sub-area by using the adjusted duty cycle and drive current. The present invention improves contrast of an LCD.
Owner:SHENZHEN SKYWORTH RGB ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for automatic brightness and contrast adjustment of a video source
InactiveUS7352410B2Increase contrastImage enhancementTelevision system detailsFrame basedPixel brightness
An image brightness and contrast management module for automatically adjusting brightness and contrast of an input video signal includes a histogram generation unit that generates a pixel luminance histogram based on pixel luminance values in a frame, whereby the histogram shows a distribution of luminance values in the frame and indicates the dynamic range and the dominant luminance value(s) for the frame. The module includes a histogram characterization unit that uses the pixel luminance histogram to identify which of a plurality of brightness / contrast properties is exhibited in the frame. The module also includes a brightness and contrast adjustment unit that nonlinearly adjusts, in real-time, the pixel luminance values in a next frame based on the identified brightness / contrast properties exhibited in the preceding frame. In this manner, bright or dark dominant areas of an image are stretched to enhance the contrast of the dominant luminance values without blackening the darker portions or saturating the brighter portions of the image.
Owner:CORONA
Method for eliminating Mura of OLED display panel
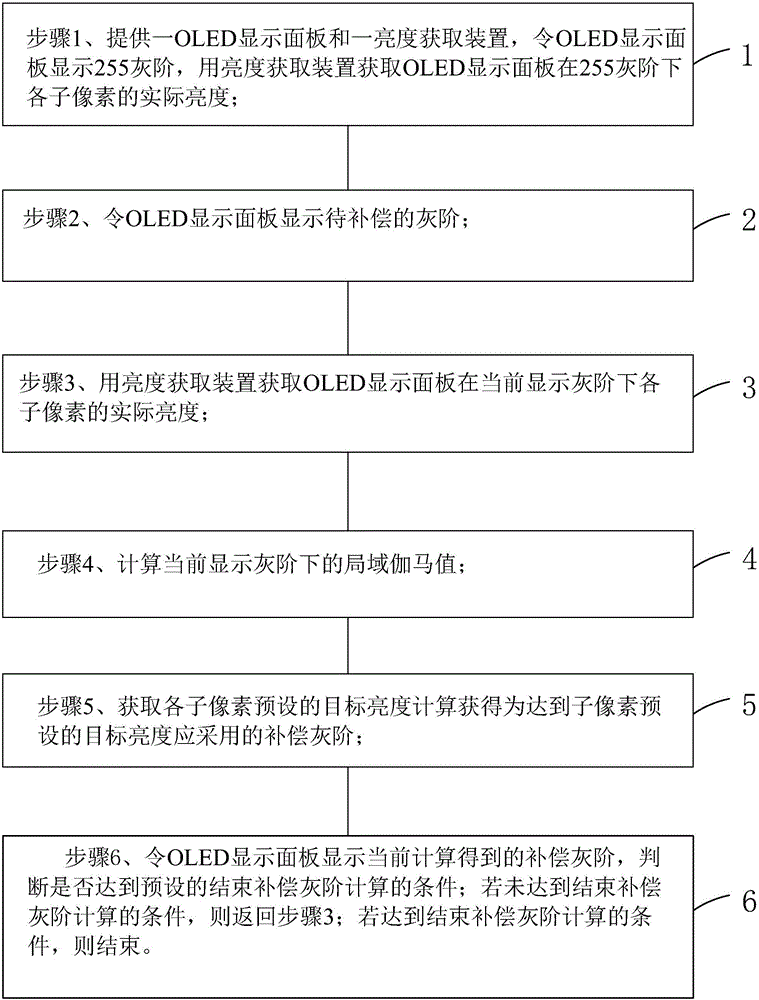
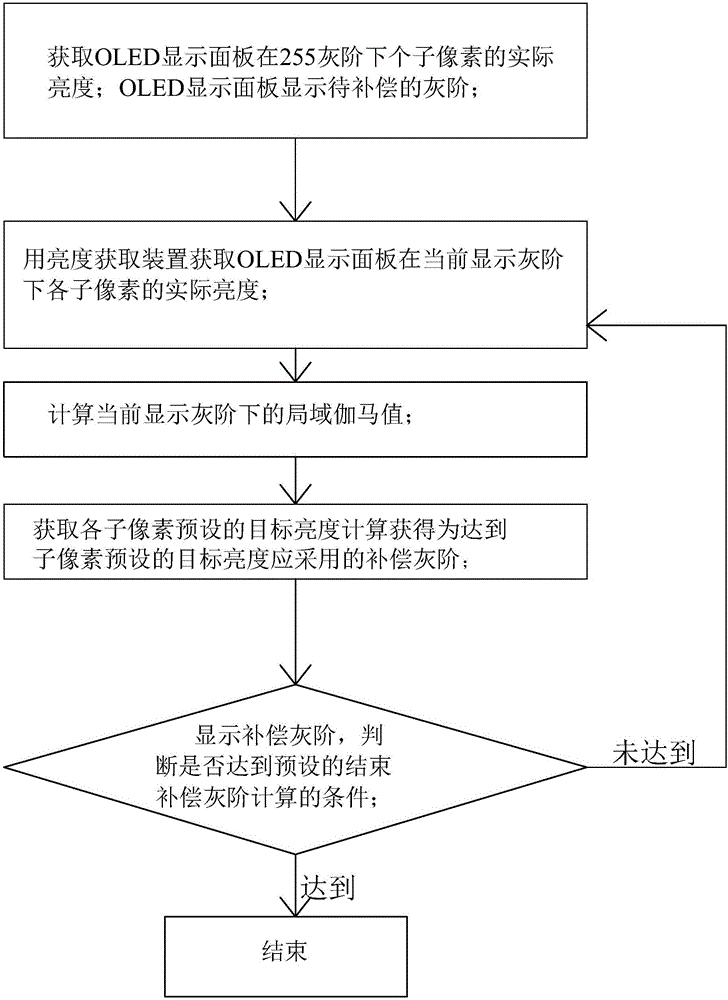
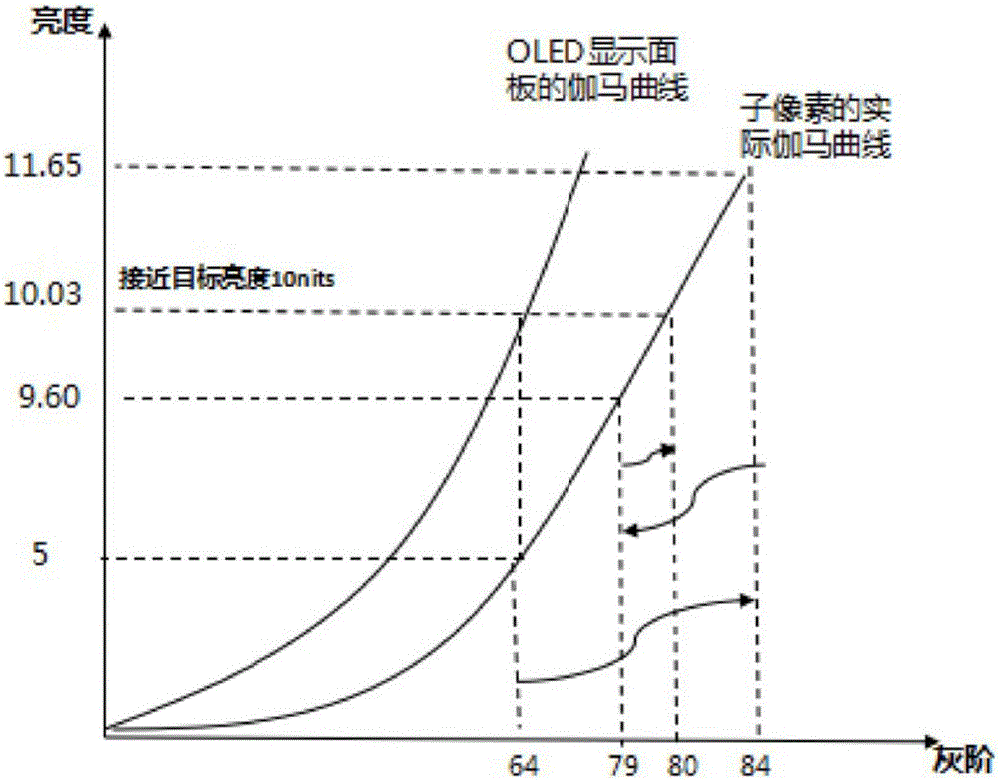
ActiveCN105741764AUniform brightnessImprove display qualityStatic indicating devicesGray levelPixel brightness
The invention provides a method for eliminating Mura of an Organic Light Emitting Display (OLED) display panel. The method includes the steps of: firstly calculating and obtaining gray scale compensation should be adopted according to the target brightness of each sub-pixel, the actual brightness in the 255 gray scale, and a local gamma value in the current display gray scale; then making the OLED display panel display the currently obtained compensation gray scale; and judging whether a preset compensation gray scale calculation-ending condition is reached, if the preset compensation gray scale calculation-ending condition is not reached, and obtaining the actual brightness of the sub-pixels in the compensation gray scale; calculating again and obtaining the local gamma value in the current display gray scale and the next compensation gray scale should be adopted; and continuously carrying out iterative computation, until the preset compensation gray scale calculation-ending condition is reached. Compared with the prior art, the method for eliminating the Mura of the OLED display panel makes the sub-pixel brightness further approach the target brightness through the compensation gray scale obtained by multiple iterative computations, can fast and effectively eliminate the Mura of the OLED display panel, ensures the brightness uniformity of the OLED display panel, and raises the display quality of the OLED display panel.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
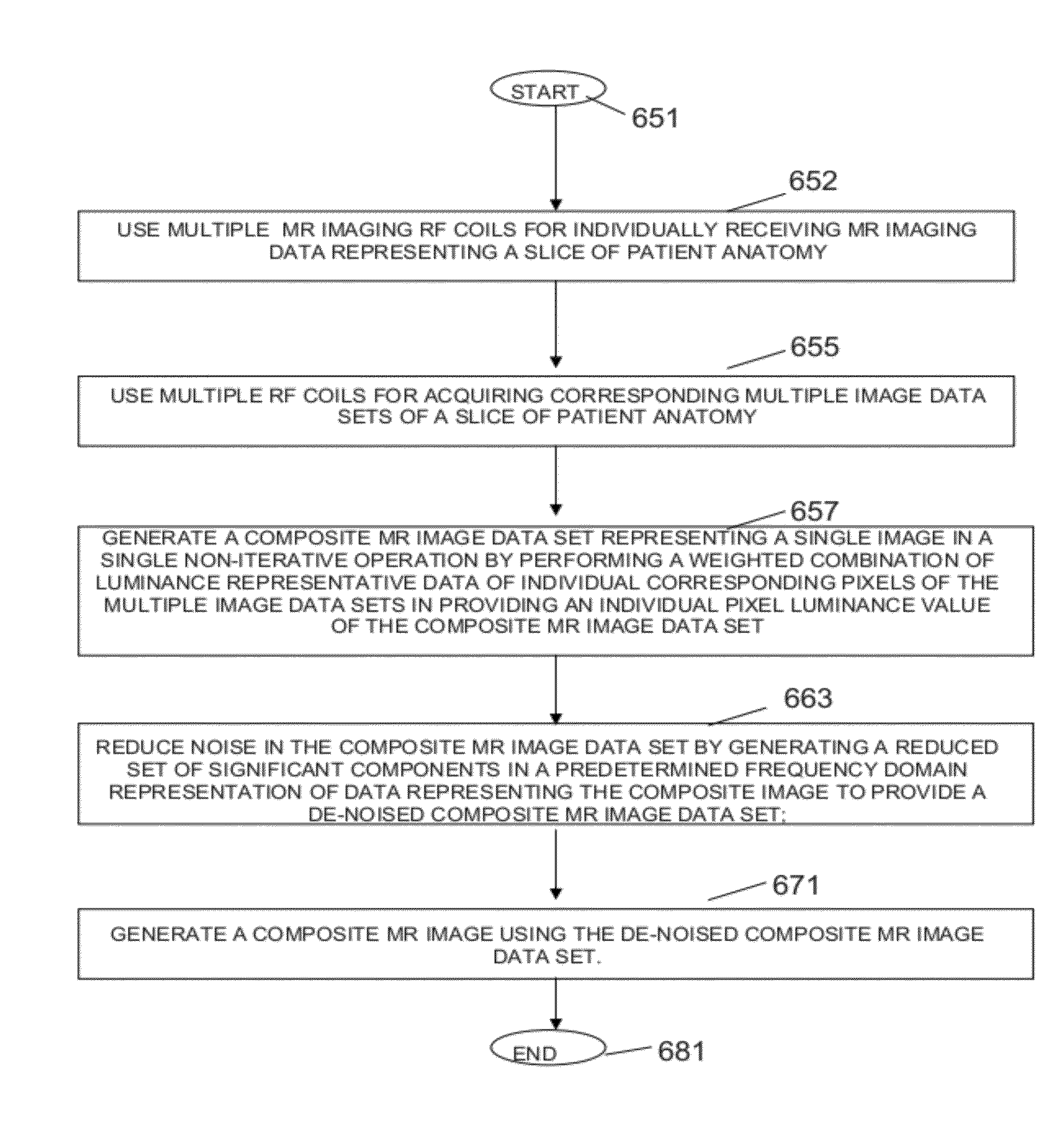
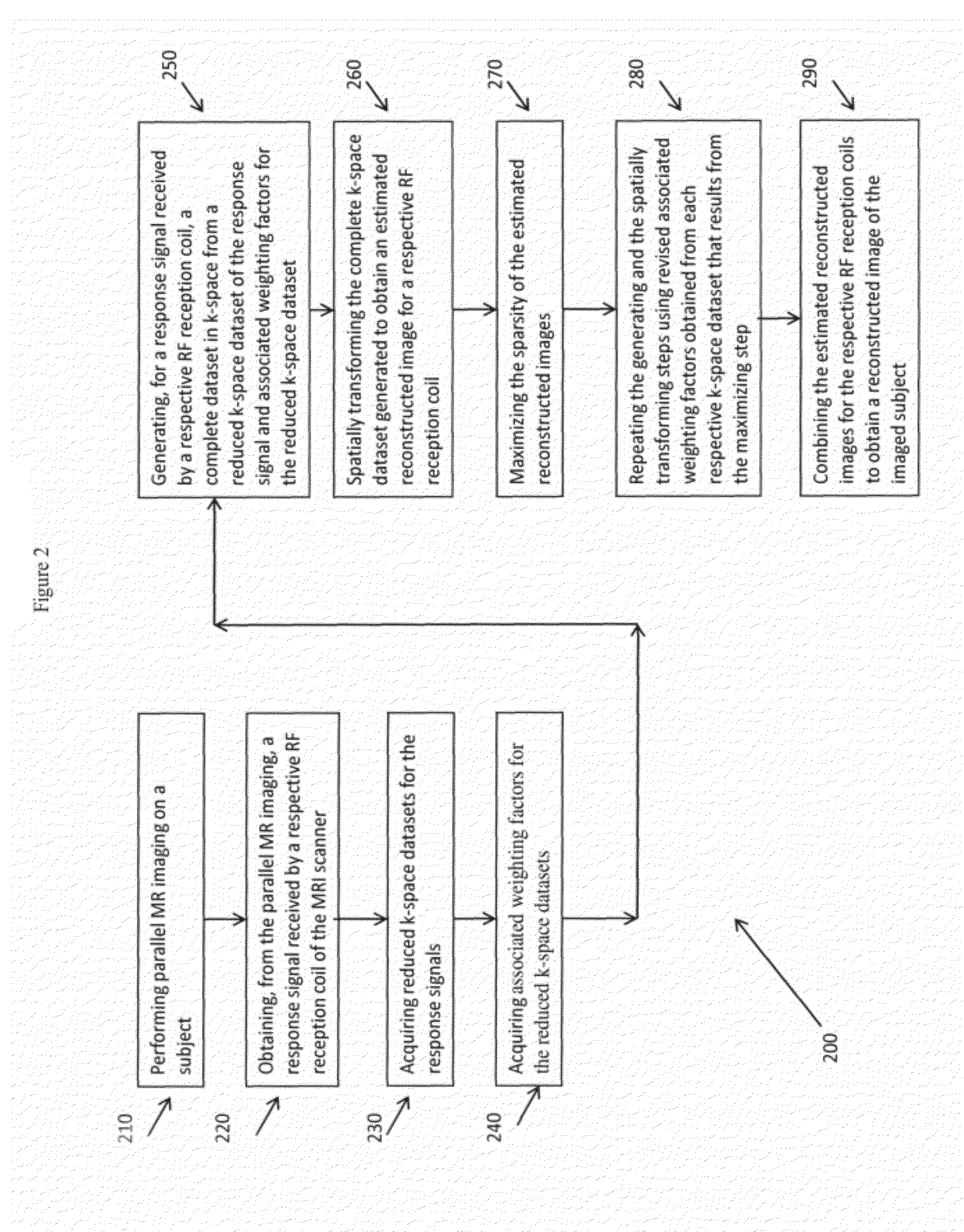
System for Accelerated MR Image Reconstruction
ActiveUS20120081114A1Maximizing sparsityReduce noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionData setSingle image
An MR imaging system uses the multiple RF coils for acquiring corresponding multiple image data sets of the slice. An image data processor comprises at least one processing device conditioned for, generating a composite MR image data set representing a single image in a single non-iterative operation by performing a weighted combination of luminance representative data of individual corresponding pixels of the multiple image data sets in providing an individual pixel luminance value of the composite MR image data set. The image data processor reduces noise in the composite MR image data set by generating a reduced set of significant components in a predetermined transform domain representation of data representing the composite image to provide a de-noised composite MR image data set. An image generator comprises at least one processing device conditioned for, generating a composite MR image using the de-noised composite MR image data set.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
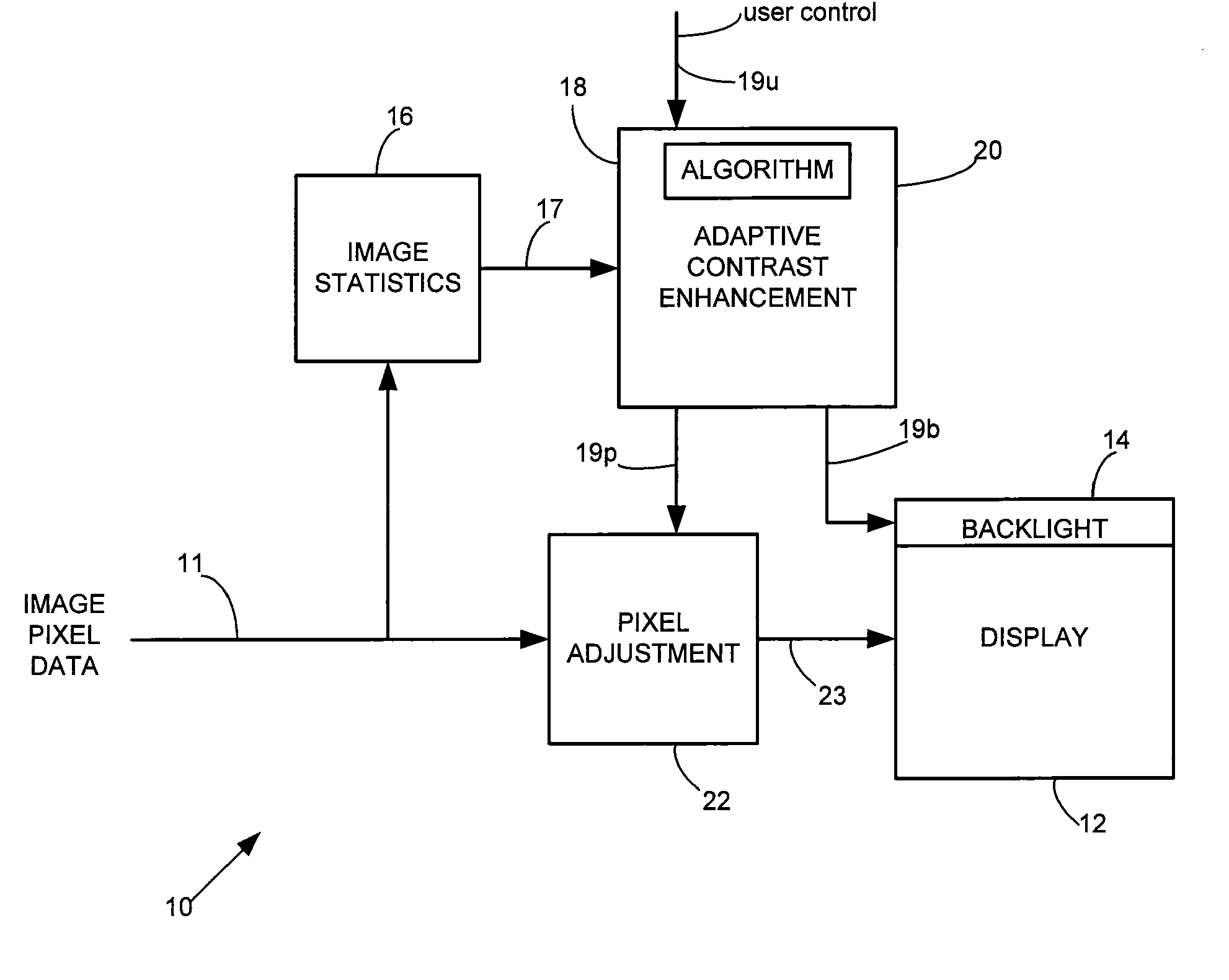
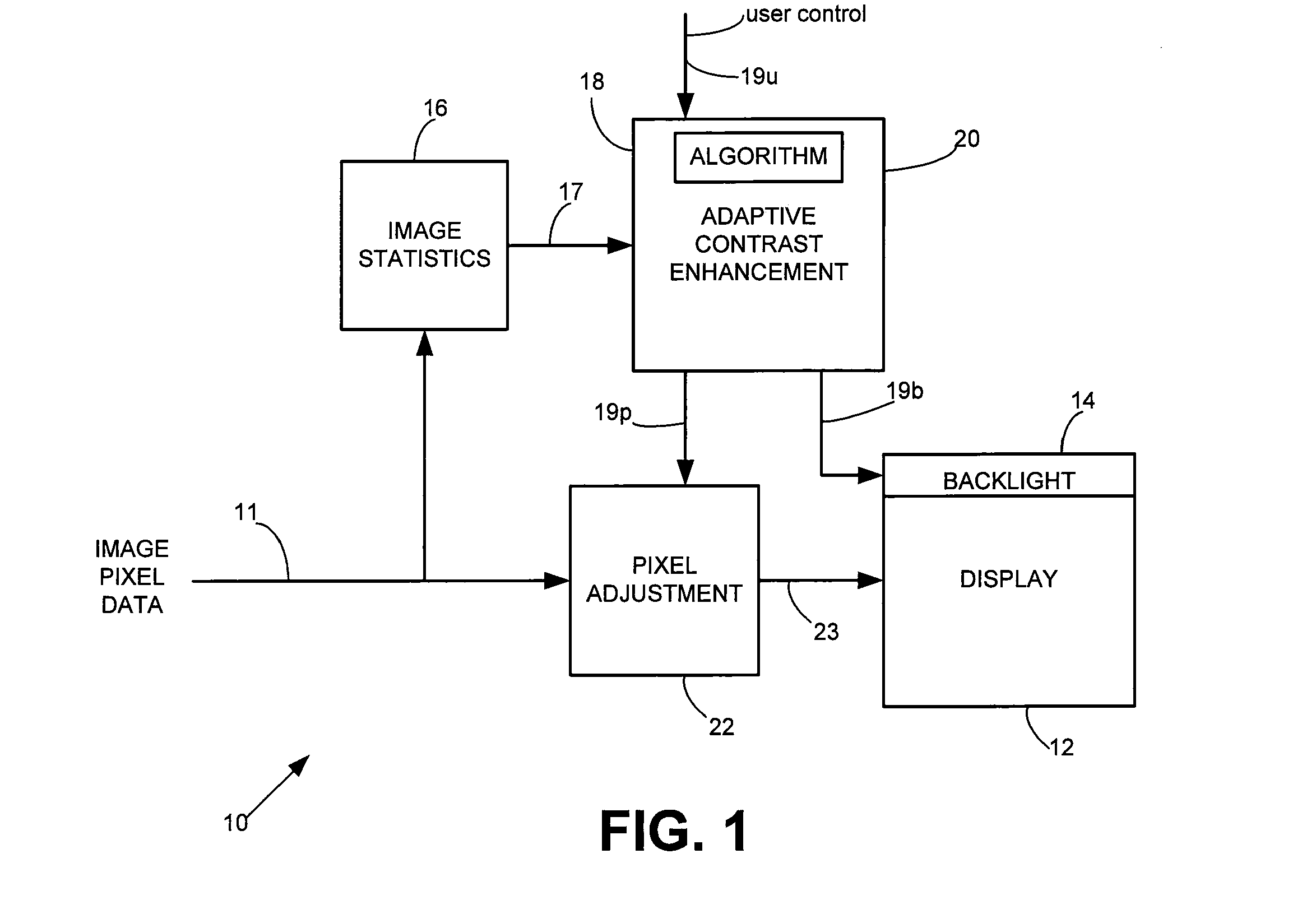
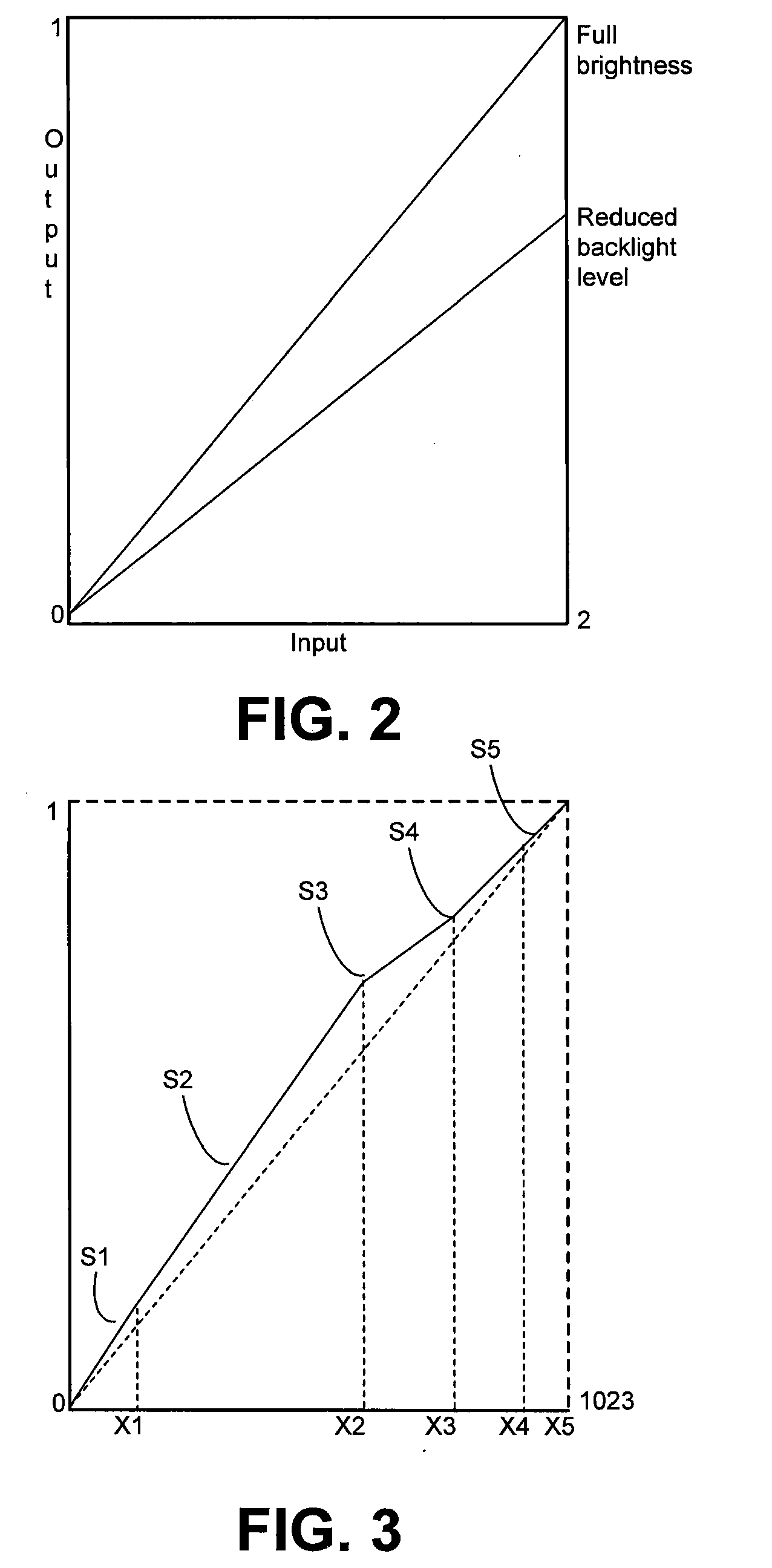
System and Method for Providing Control Data for Dynamically Adjusting Lighting and Adjusting Video Pixel Data for a Display to Substantially Maintain Image Display Quality While Reducing Power Consumption
InactiveUS20120075353A1Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsControl data
System and method for providing control data for dynamically adjusting lighting and adjusting video pixel data for a display to substantially maintain image display quality while reducing power consumption. In accordance with one or more embodiments, image statistics, e.g., histogram data representing luma values corresponding to pixels for a video frame, are analyzed to determine whether the pixels represent one or more of a plurality of images which includes an image containing primarily natural imagery, an image containing primarily graphics imagery, and an image containing a combination of at least respective portions of natural and graphics imagery. Based on such analysis, control data are provided to enable light source brightness reduction by one of a plurality of percentages and pixel brightness increases, e.g., in accordance with one of a plurality of multiple-segment piecewise linear curves defined in accordance with respective segment slopes, thresholds, and threshold offsets in accordance with whether the incoming pixel data primarily represents a natural image, primarily represents a graphics image, or represents a combination of natural and graphics images.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
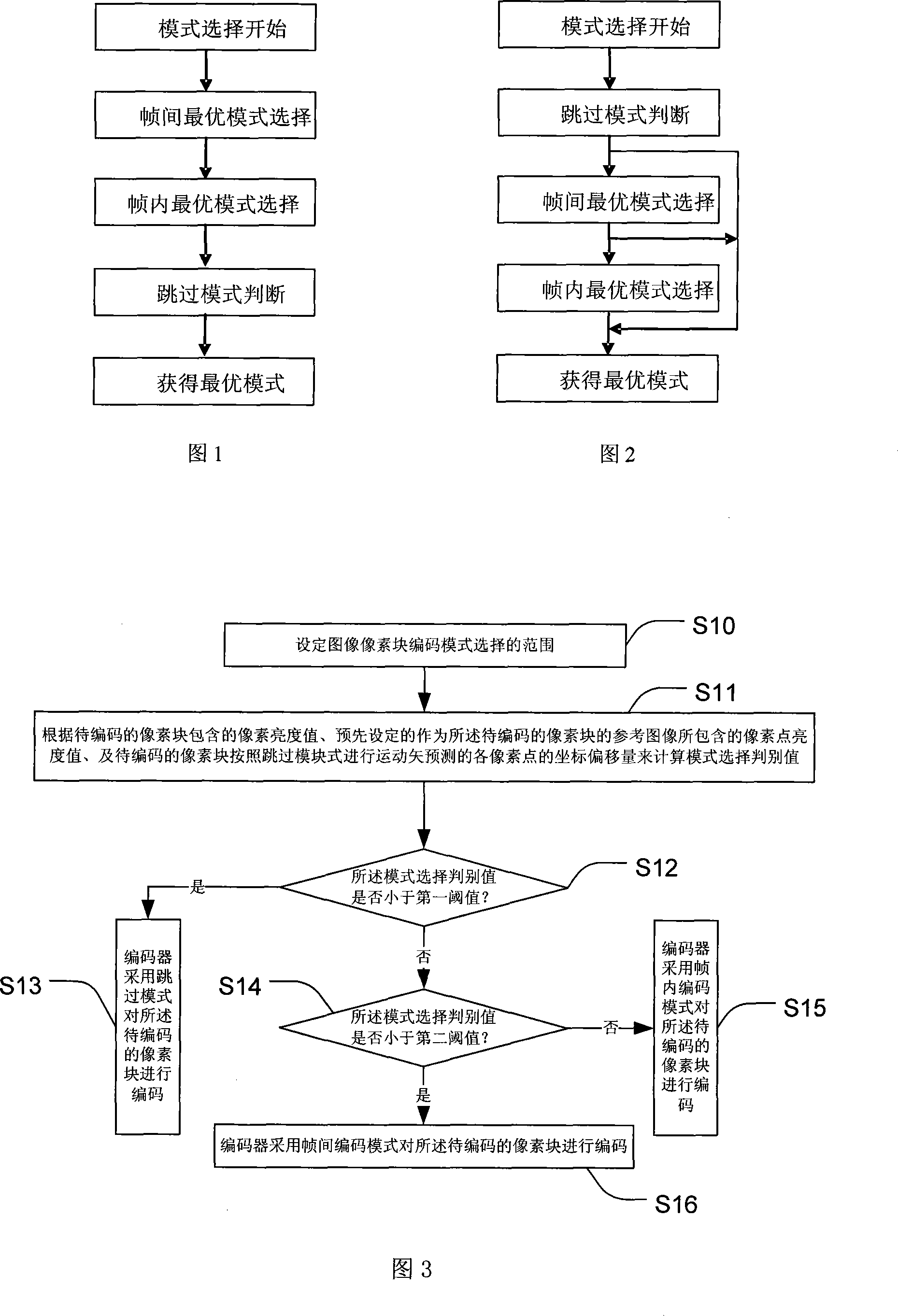
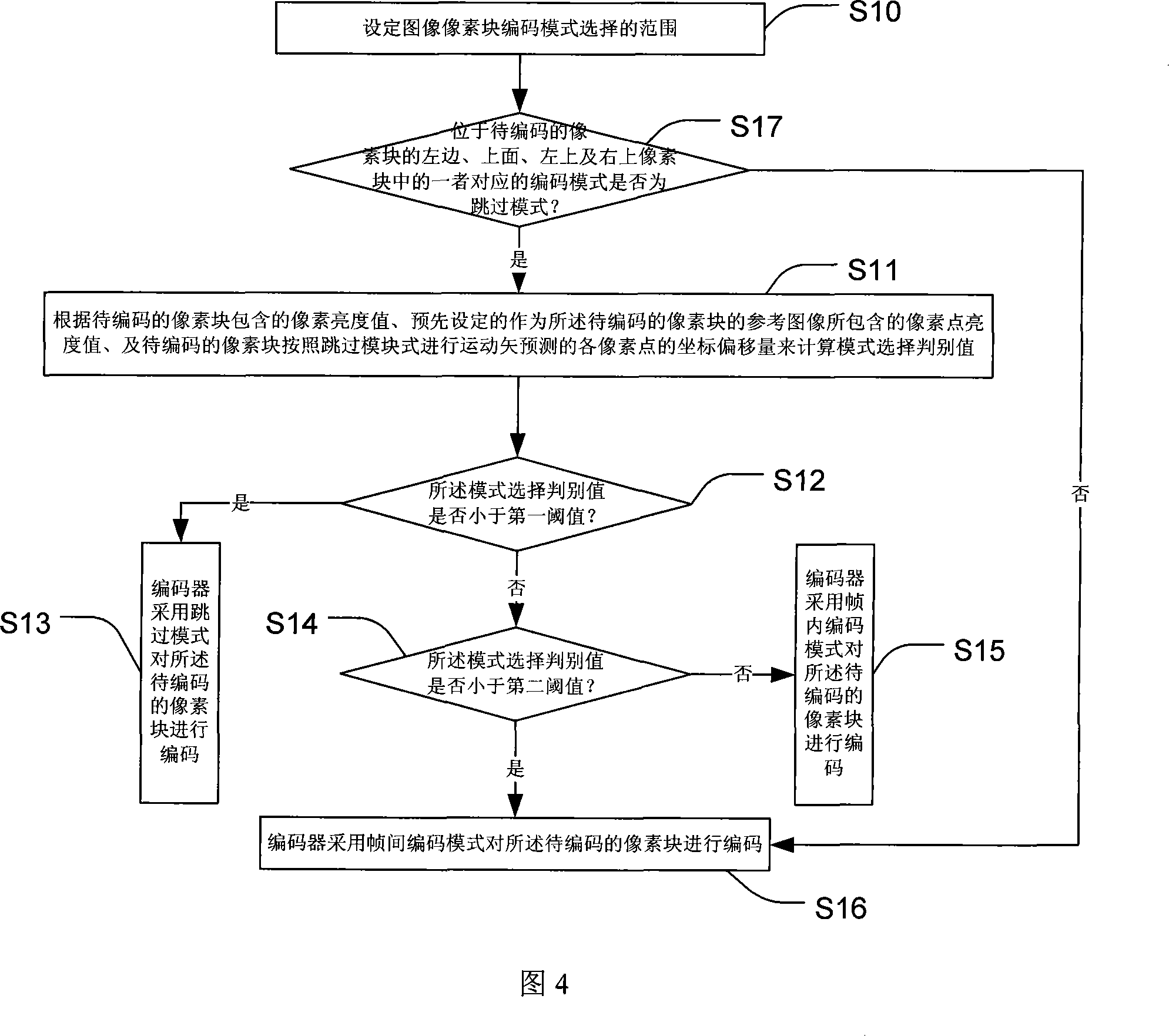
A quick selecting method of the encode mode of image pixel block for the encoder
ActiveCN101217663AImprove encoding speedEliminate redundant calculationsTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationInterframe codingBlock code
The invention relates to a fast selecting method for image pixel block coding mode, which is used in a coder. The selection scope of the image pixel block coding mode, which comprises at least one coding mode in a frame, a coding mode between frames and a skipping mode, is set firstly; next, a mode selection judging value is calculated according to a pixel brightness value contained in a pixel block needing to be coded, a pixel point brightness value that is preset and contained in a reference image of the pixel block needing to be coded and coordinate offset of every pixel point done with motion vector prediction by the pixel block needing to be coded according to a skipping mode; finally, according to the mode selection judging value and the comparison of a first threshold value and a second threshold value, the optimum coding mode of the pixel block needing to be coded is selected from the selection scope, therefore the redundant calculation can be eliminated to the utmost extend in a macro block coding mode to effectively improve the coding speed of the coder.
Owner:SHANGHAI AVCON INFORMATION TECH
AMOLED display panel brightness compensation method and device
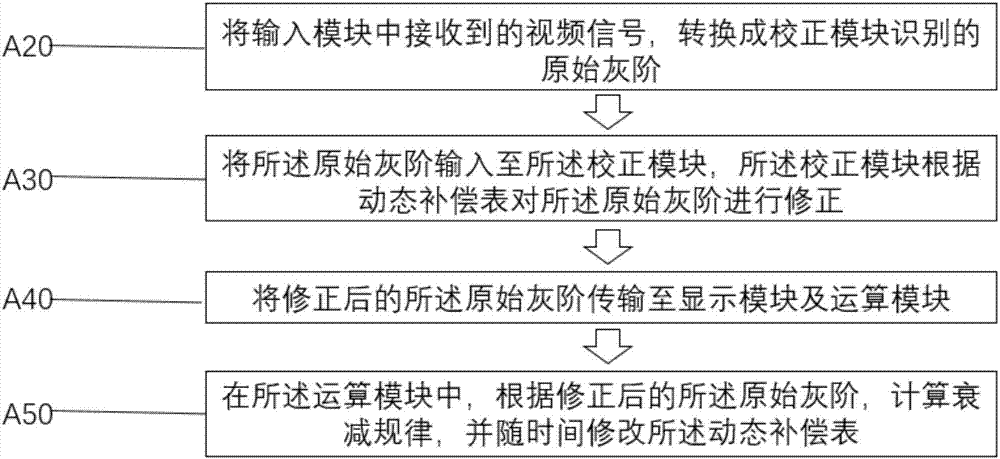
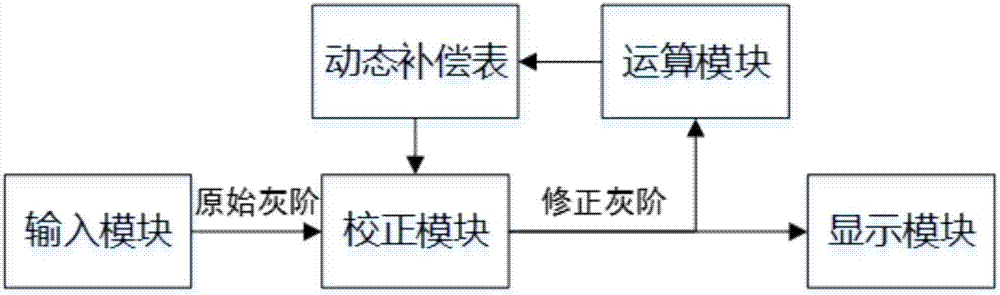
ActiveCN107274834ASimple structureEasy to operateStatic indicating devicesUltrasound attenuationDisplay device
The invention provides an AMOLED display panel brightness compensation method and device. The method is concise in step. The device is simple in structure and easy to operate. The aging test is performed on a display panel in advance and the attenuation law of the sub-pixel brightness along with grayscale and time is obtained, the compensation data are calculated and a dynamic compensation table is generated; and the inputted original grayscale is corrected in a correction module according to the dynamic compensation table, the sub-pixel brightness is compensated and the display panel is enabled to be normal in display. The beneficial effects are that aging of the TFT in the displayer and attenuation of the OLED luminous efficiency can be compensated without arranging the circuit or the sensor for detecting the luminous state in the display panel.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS SEMICON DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
System and process for generating high dynamic range video
InactiveUS20050243177A1Minimizing any discontinuityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsTone mappingRadiance
A system and process for generating High Dynamic Range (HDR) video is presented which involves first capturing a video image sequence while varying the exposure so as to alternate between frames having a shorter and longer exposure. The exposure for each frame is set prior to it being captured as a function of the pixel brightness distribution in preceding frames. Next, for each frame of the video, the corresponding pixels between the frame under consideration and both preceding and subsequent frames are identified. For each corresponding pixel set, at least one pixel is identified as representing a trustworthy pixel. The pixel color information associated with the trustworthy pixels is then employed to compute a radiance value for each pixel set to form a radiance map. A tone mapping procedure can then be performed to convert the radiance map into an 8-bit representation of the HDR frame.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
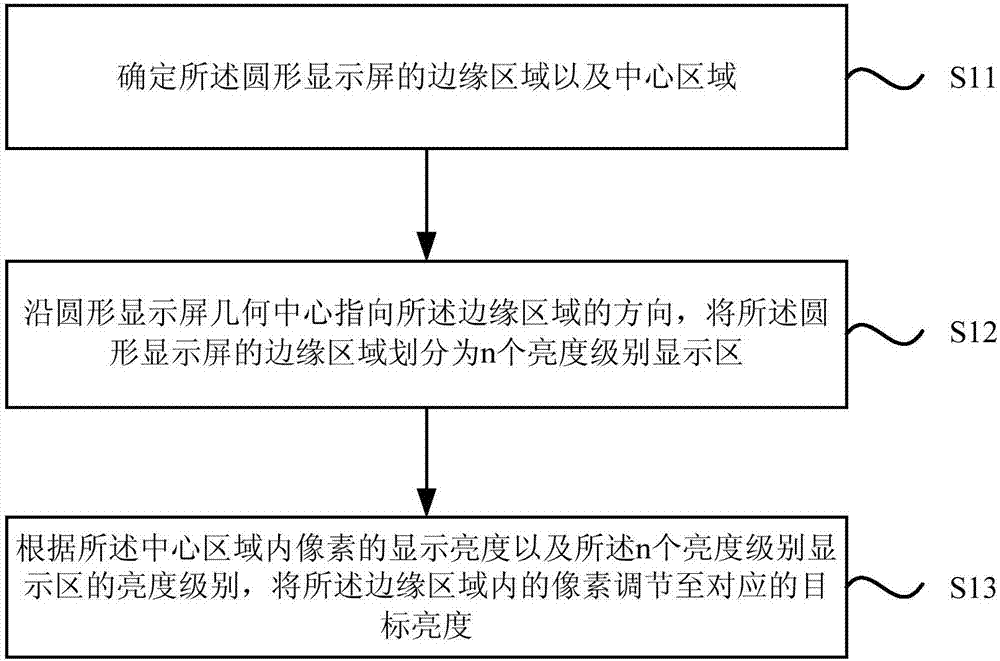
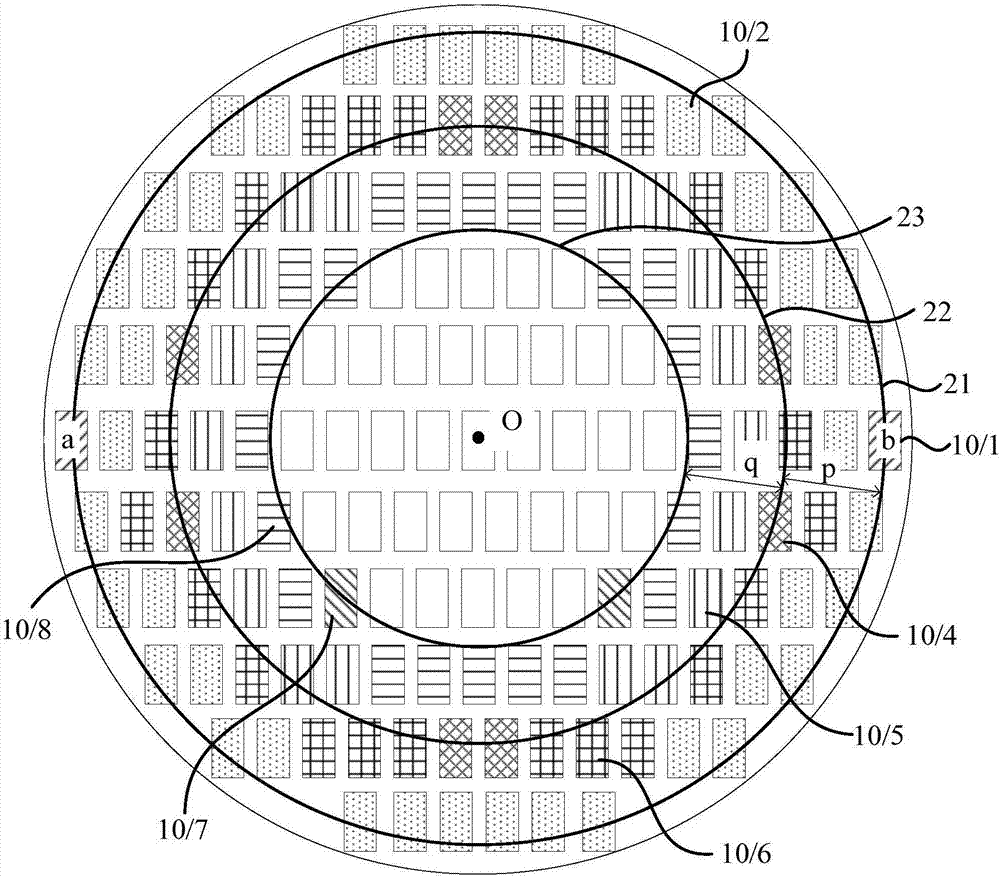
Method for improving edge display effect of circular display screen
ActiveCN107103893AReduce brightnessCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Pixel brightness
The invention discloses a method for improving the edge display effect of a circular display screen. The method includes: determining the edge area and the central area of the circular display screen; dividing the edge area of the circular display screen into display areas of n brightness levels along a direction pointing from the geometrical center to the edge area; adjusting pixels in the edge area to corresponding target brightness according to the display brightness of pixels in the central area and the brightness levels of the display areas. By the method, the brightness of the pixels in the edge area is allowed to be lower than that of the central area, the brightness of the pixels in the display areas in the edge area sequentially decreases along the direction pointing from the central area to the edge area, and the problems of edge aliasing, color edges and bright edges of the circular display screen are improved.
Owner:WUHAN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com