Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
59 results about "Fine-needle aspirate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is a diagnostic procedure used to investigate lumps or masses. In this technique, a thin (23-25 gauge), hollow needle is inserted into the mass for sampling of cells that, after being stained, will be examined under a microscope (biopsy).
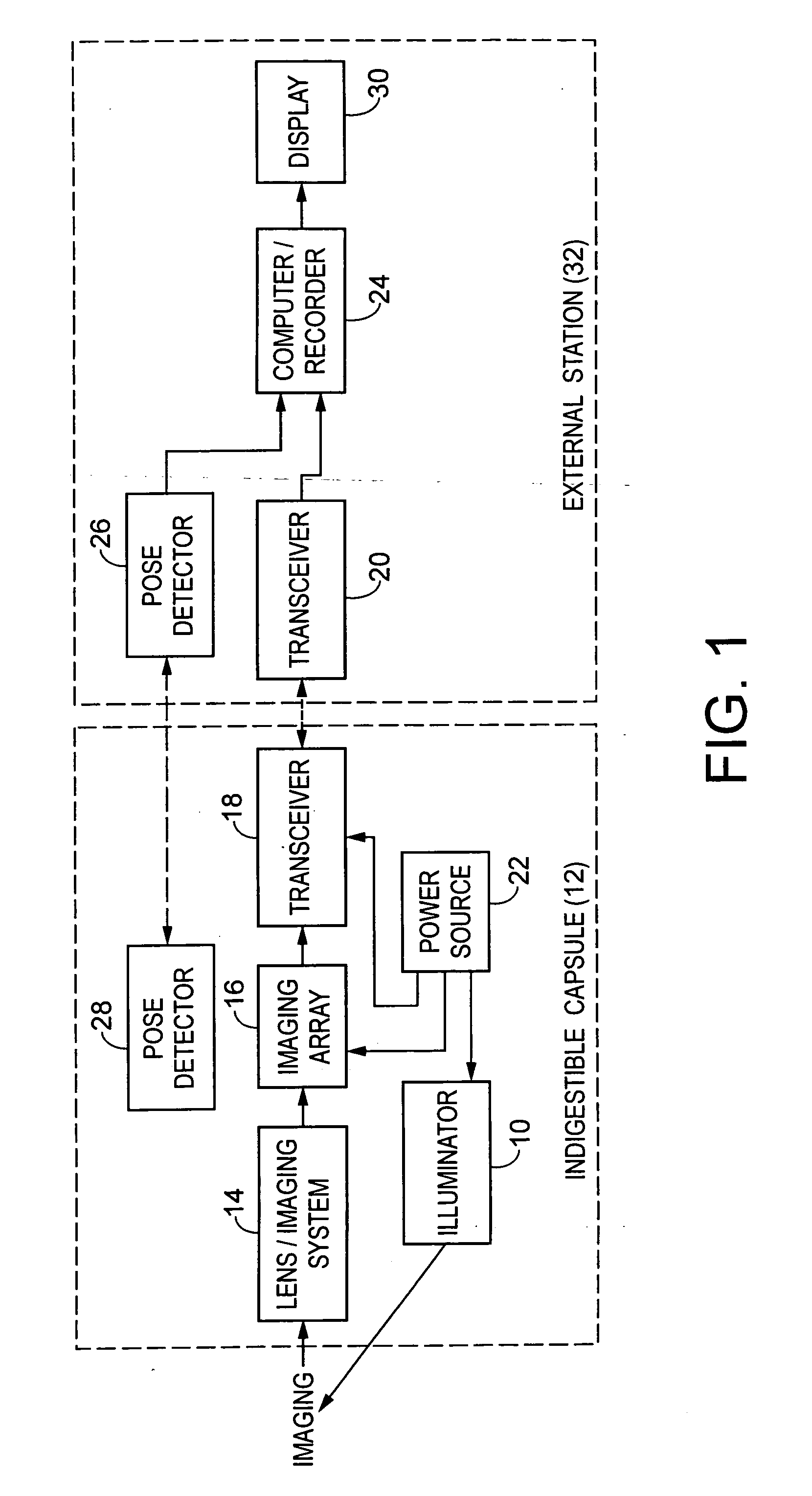
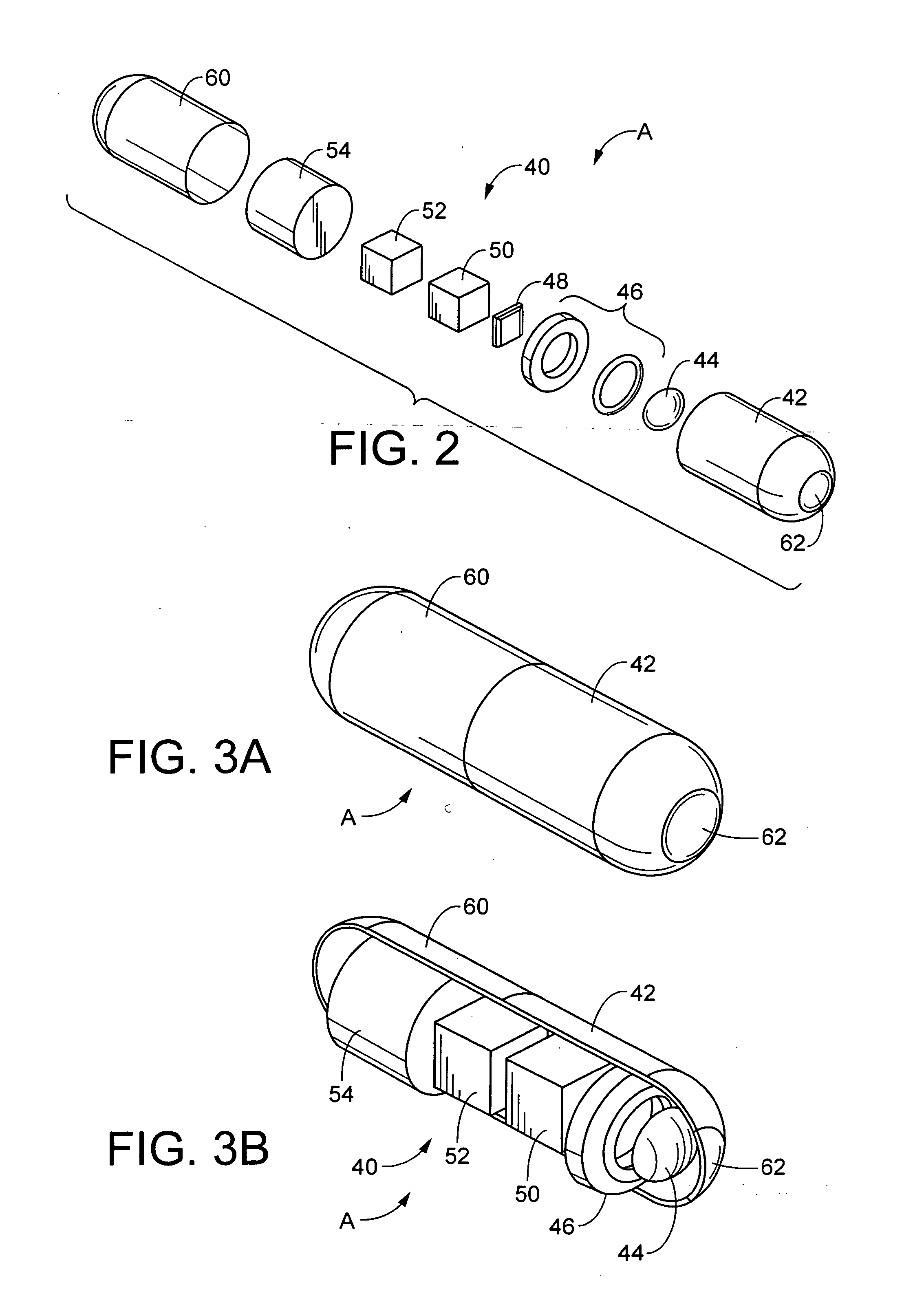
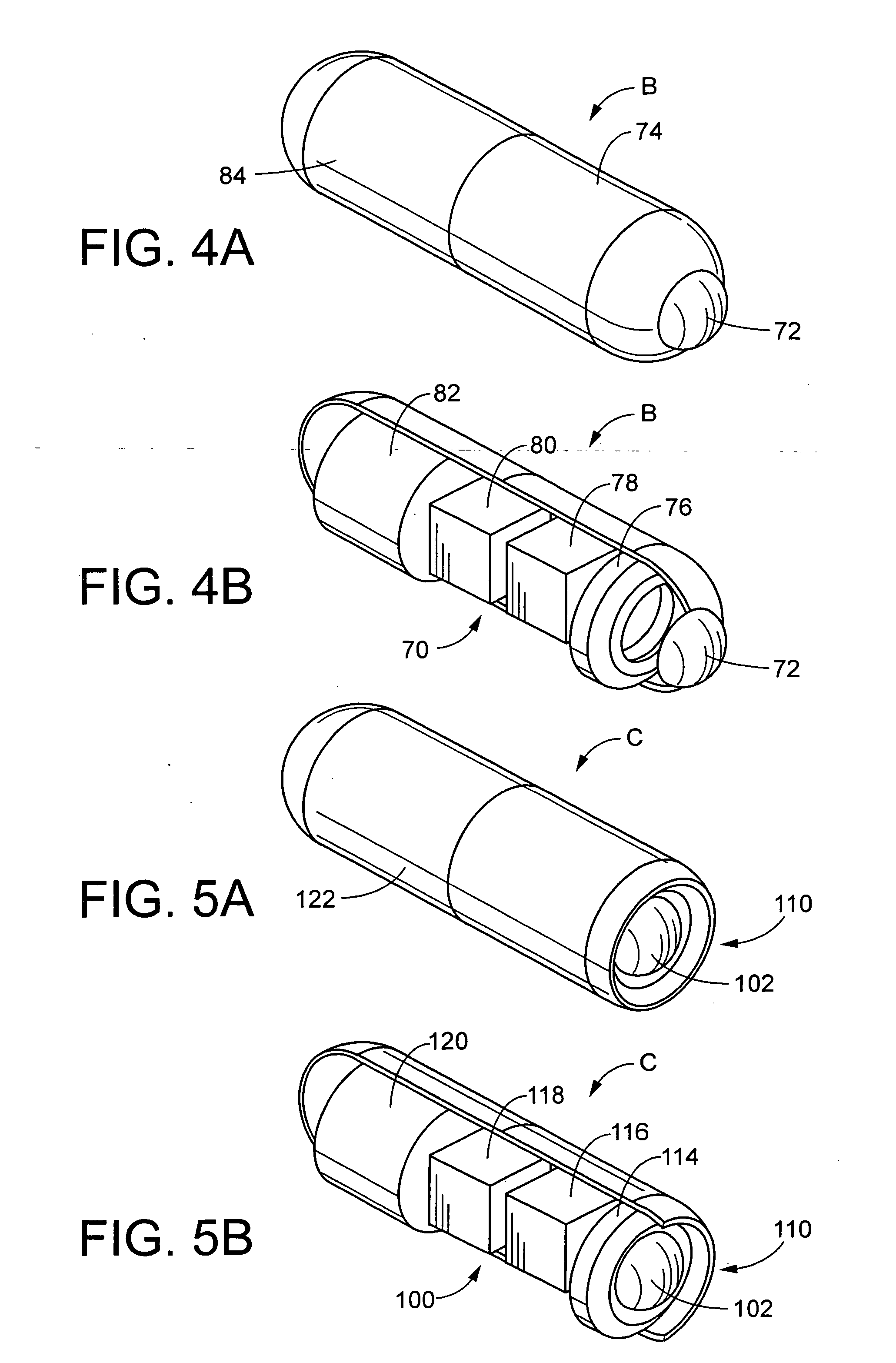
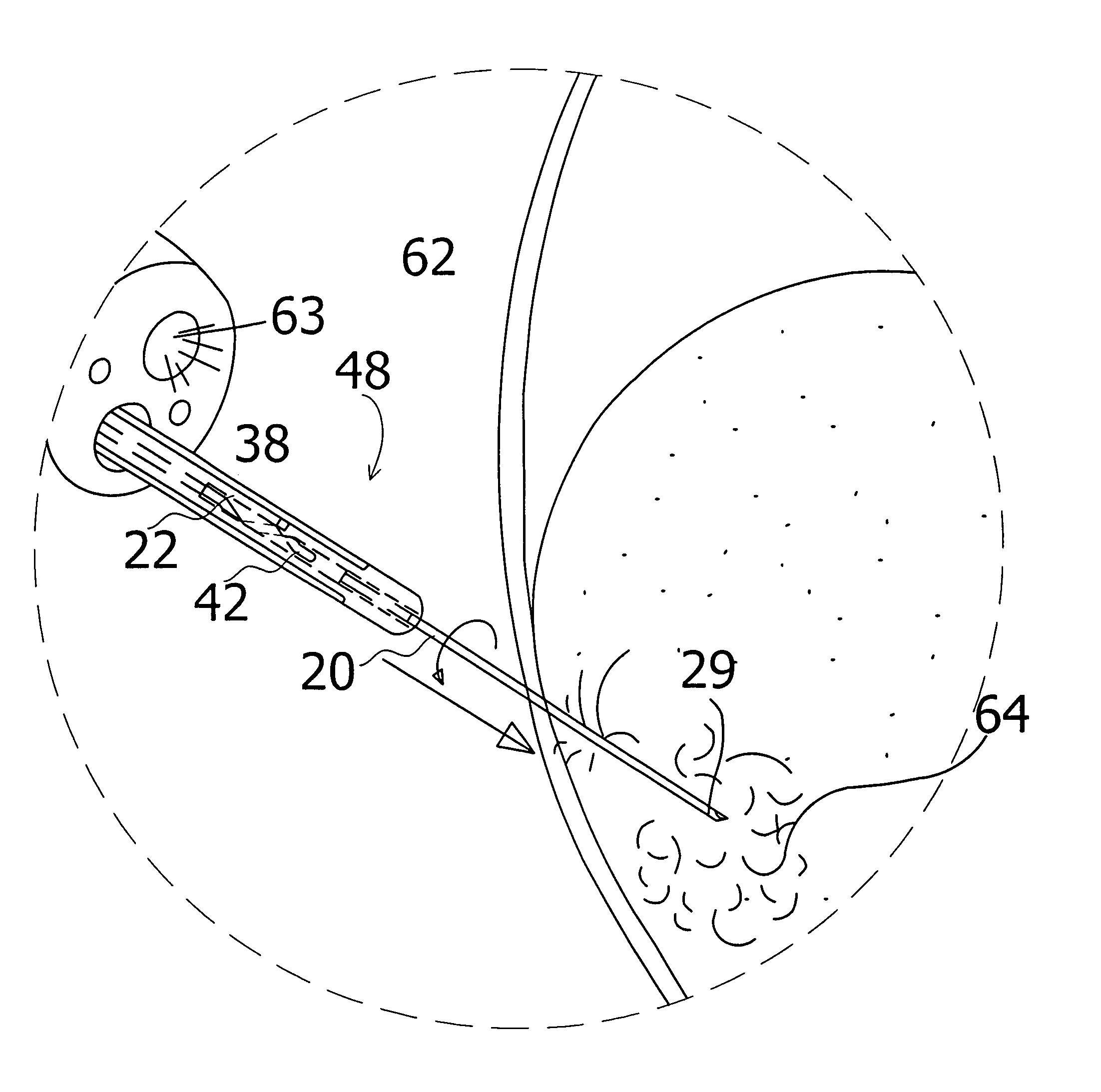
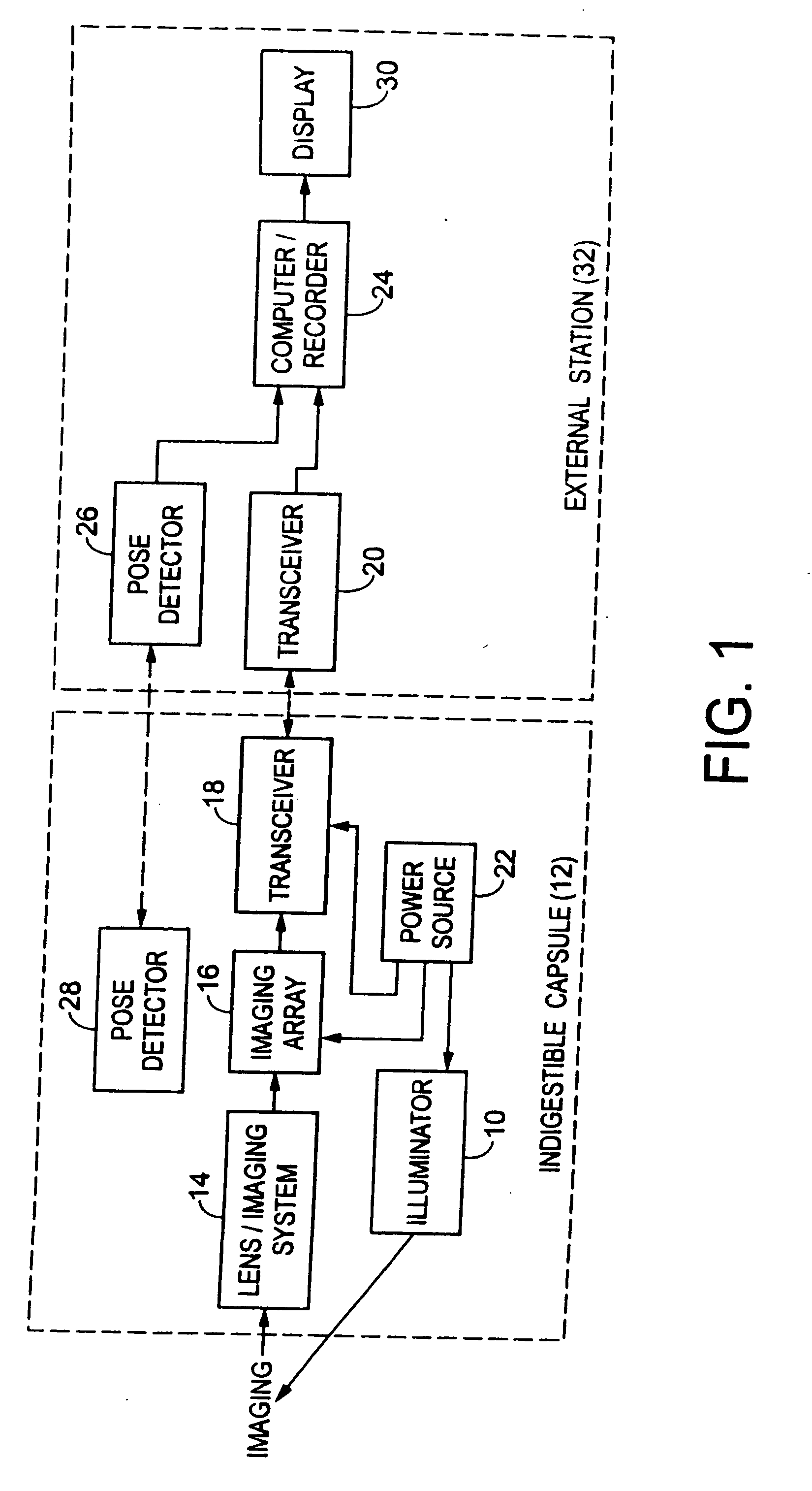
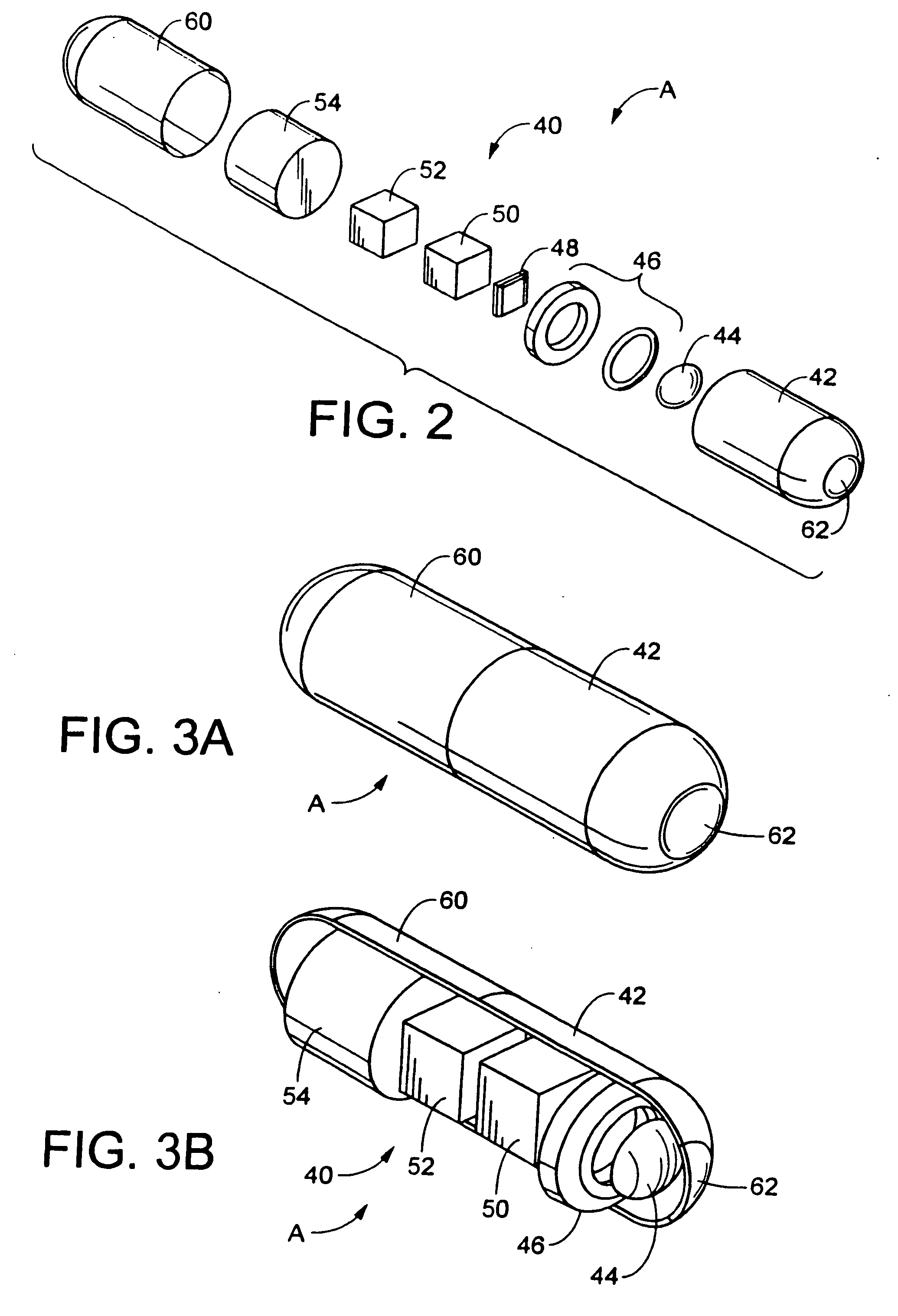
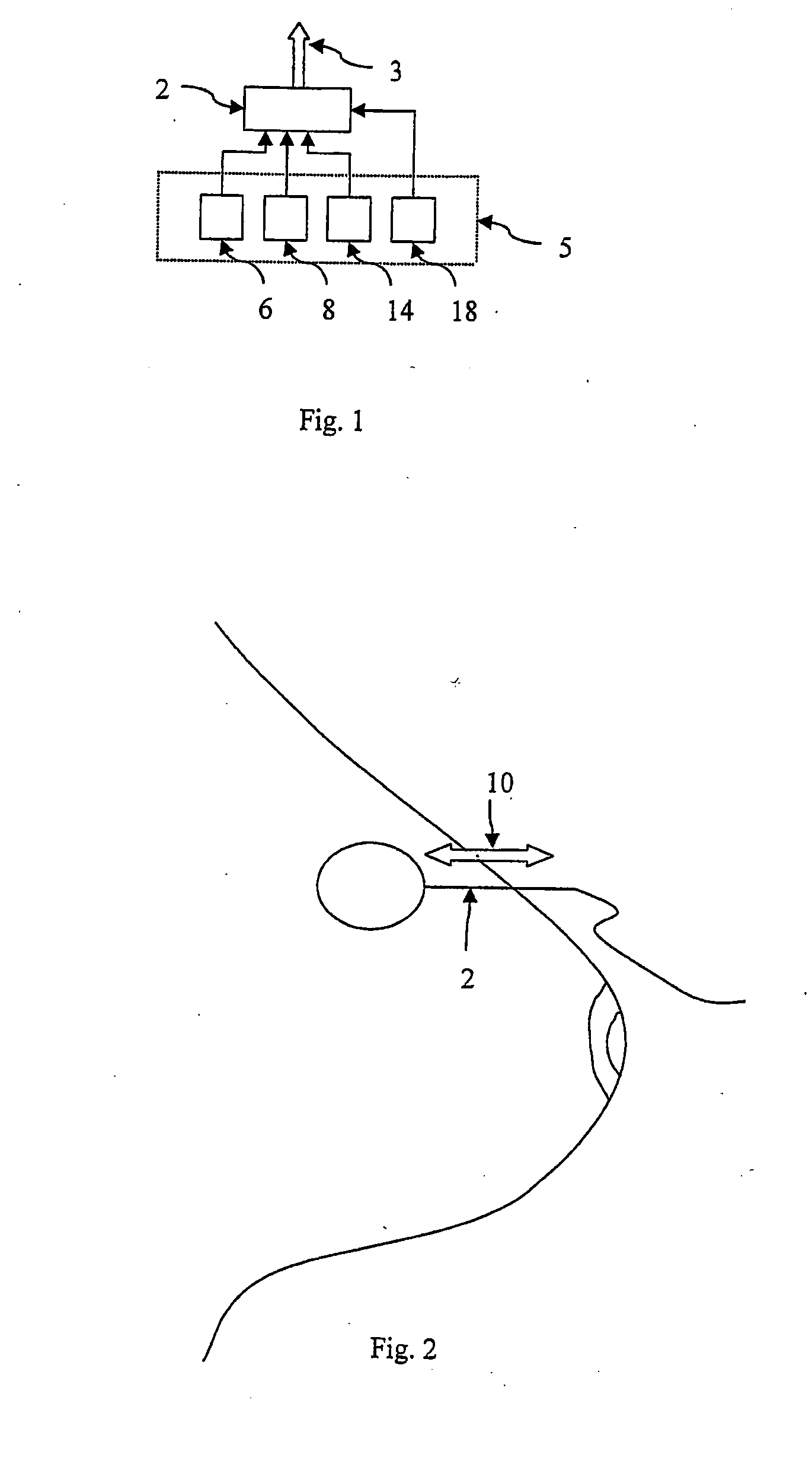
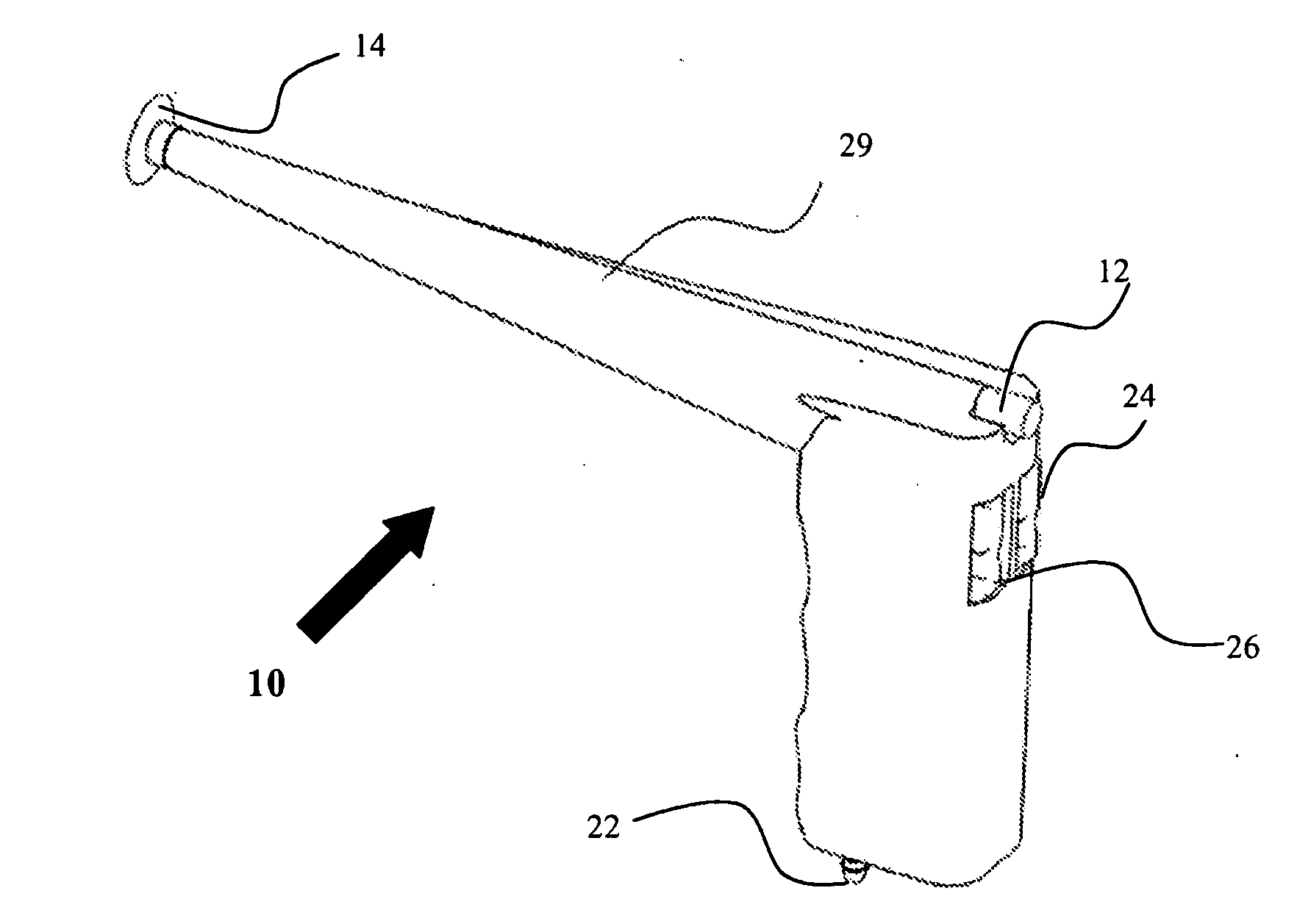
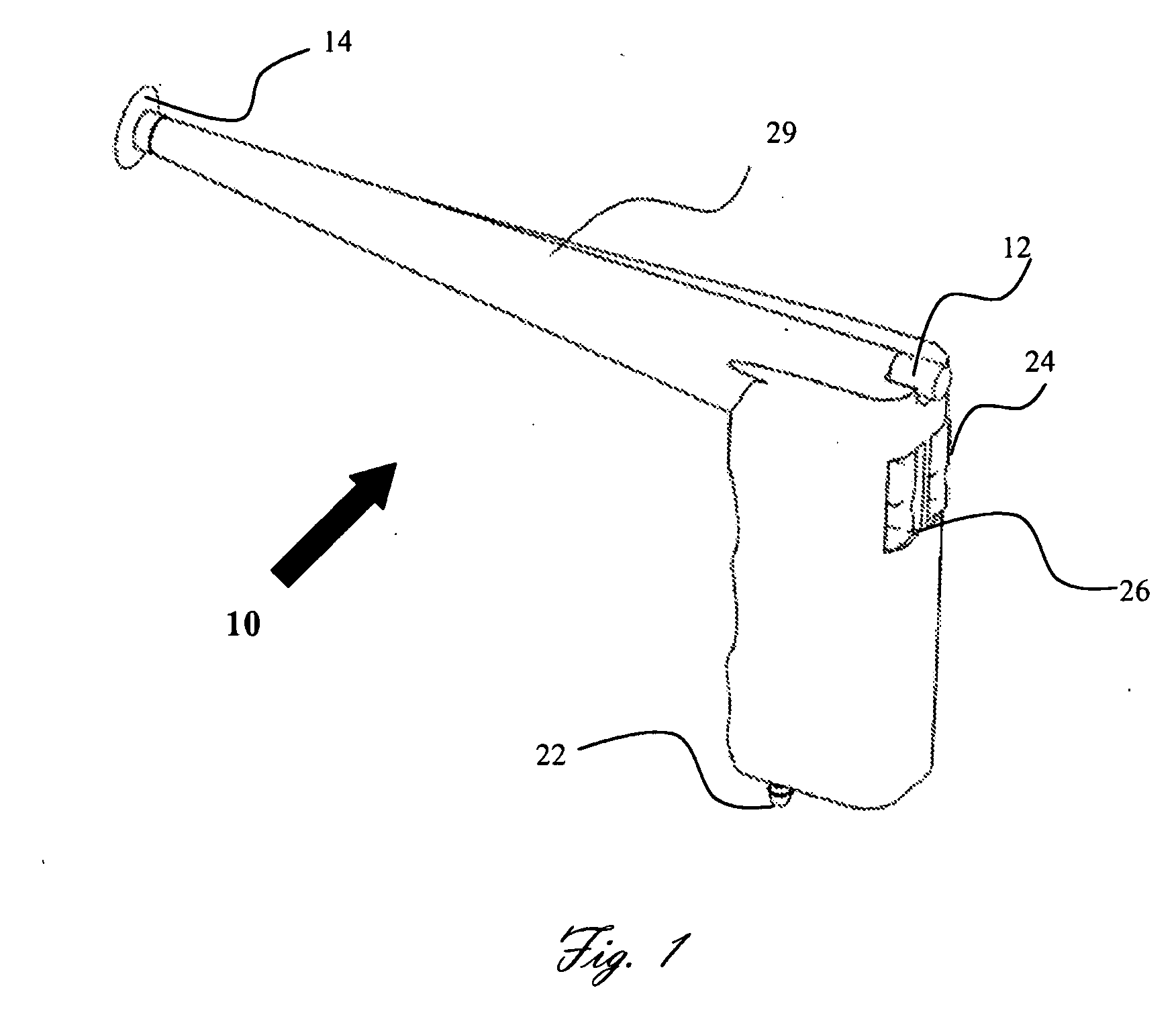
Miniature ingestible capsule
Owner:NAIR PADMANABHAN P +1
Rotating fine needle for core tissue sampling
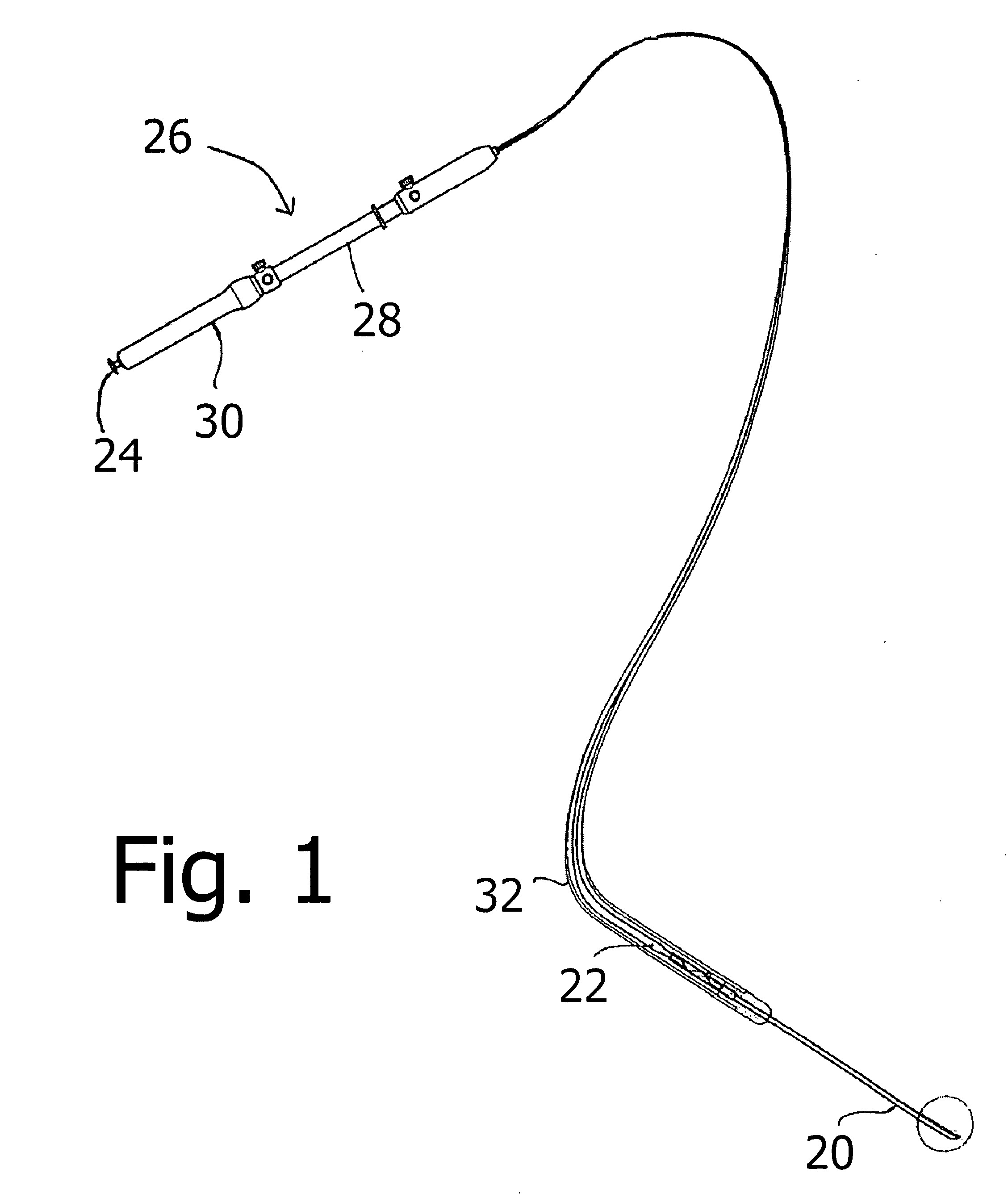
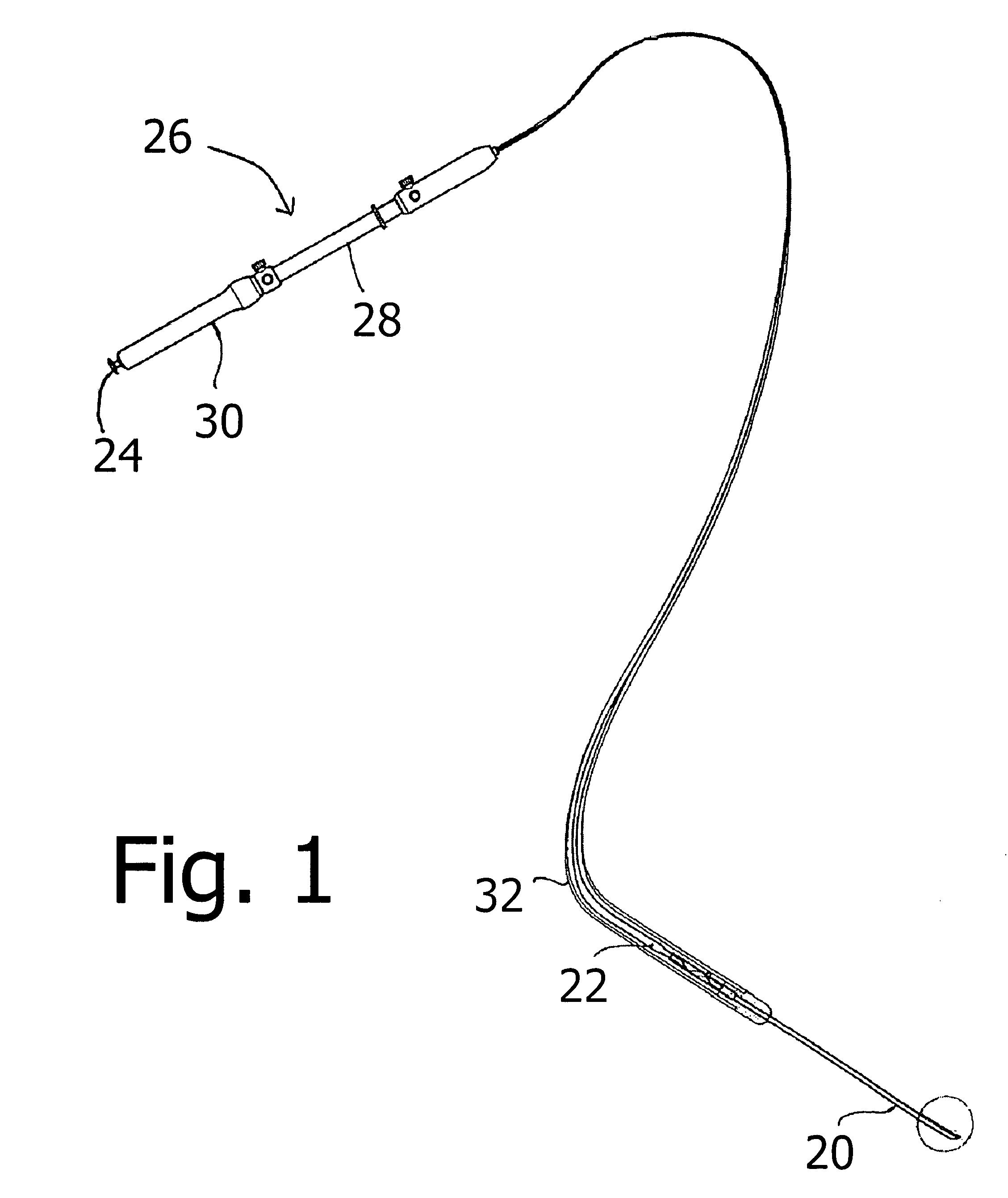
ActiveUS20060116605A1Easy to collectSmall diameterSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSurgical siteEcho endoscopie
A medical instrument usable with an ultrasound-endoscope for performing a needle biopsy on a patient's internal body tissues usable at a surgical site not visible to the unaided eye or viewed endoscopically, comprises an elongate tubular member with a hollow needle element connected at its distal end, a sheath member housing said tubular member and needle element, an actuator subassembly with a shifter member operatively connected to elongate tubular member's proximal end, and a distal camming subassembly, said subassembly enabling a rotating motion of said needle member while handle actuator is moved in the forward direction. Upon inserting an ultrasound-endoscope into a patient and locating a mass, the fine needle with sharply pointed spoon shaped distal end is inserted into the mass aided by endoscopic and ultrasonographic guidance. Once in the mass, a camming action is initiated, causing rotation of the fine needle within the mass, resulting in a scooped out core biopsy. This instrument enables the performance of a fine needle aspiration requiring only one or two needle introductions, with a resultant core biopsy substantial enough for diagnostic purposes.
Owner:GRANIT MEDICAL INNOVATION
Rotating fine needle for core tissue sampling
ActiveUS7722549B2Minimal numberSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSurgical siteEndoscopy
A medical instrument usable with an ultrasound-endoscope for performing a needle biopsy on a patient's internal body tissues usable at a surgical site not visible to the unaided eye or viewed endoscopically, comprises an elongate tubular member with a hollow needle element connected at its distal end, a sheath member housing said tubular member and needle element, an actuator subassembly with a shifter member operatively connected to elongate tubular member's proximal end, and a distal camming subassembly, said subassembly enabling a rotating motion of said needle member while handle actuator is moved in the forward direction. Upon inserting an ultrasound-endoscope into a patient and locating a mass, the fine needle with sharply pointed spoon shaped distal end is inserted into the mass aided by endoscopic and ultrasonographic guidance. Once in the mass, a camming action is initiated, causing rotation of the fine needle within the mass, resulting in a scooped out core biopsy. This instrument enables the performance of a fine needle aspiration requiring only one or two needle introductions, with a resultant core biopsy substantial enough for diagnostic purposes.
Owner:GRANIT MEDICAL INNOVATION
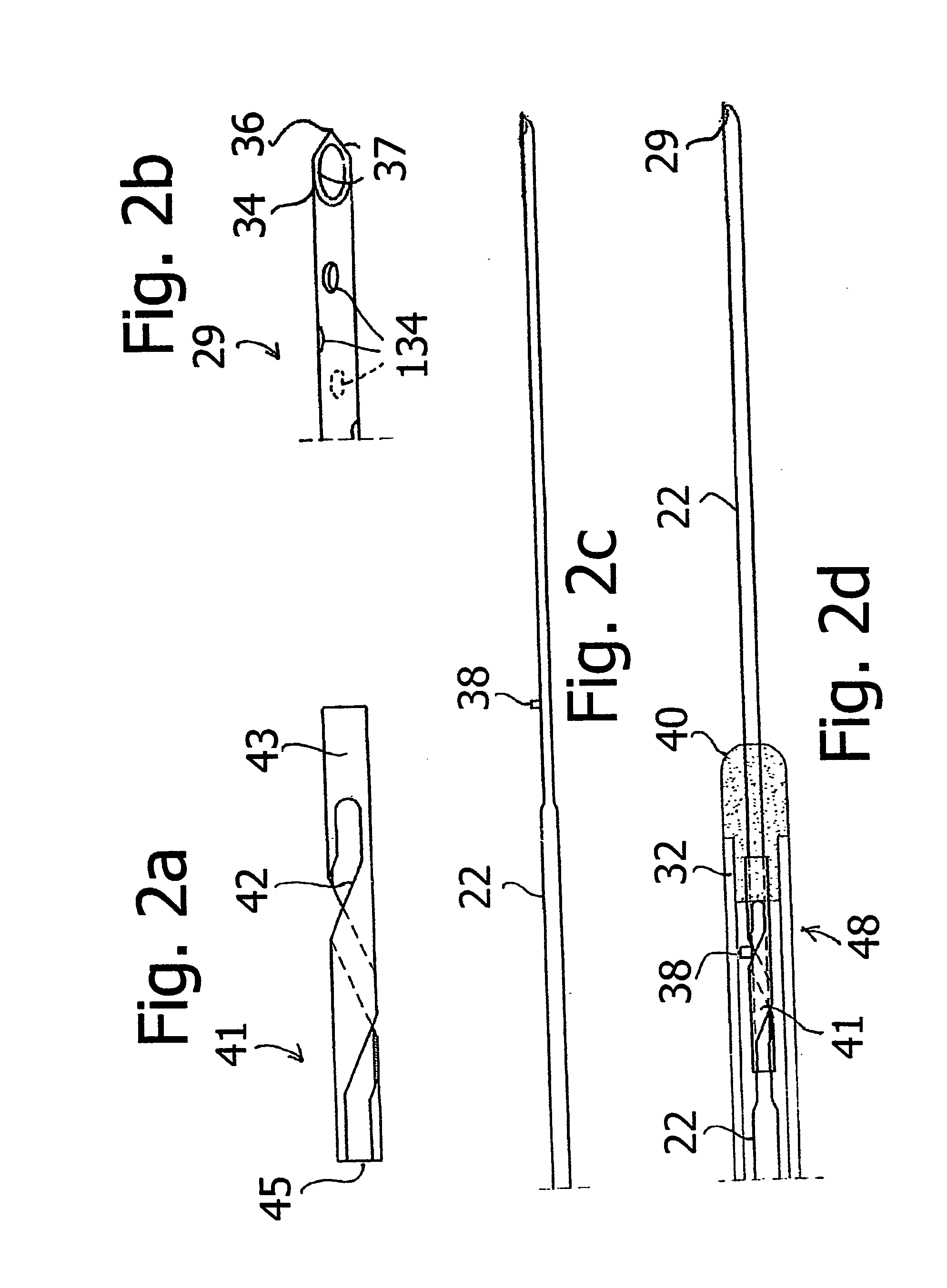
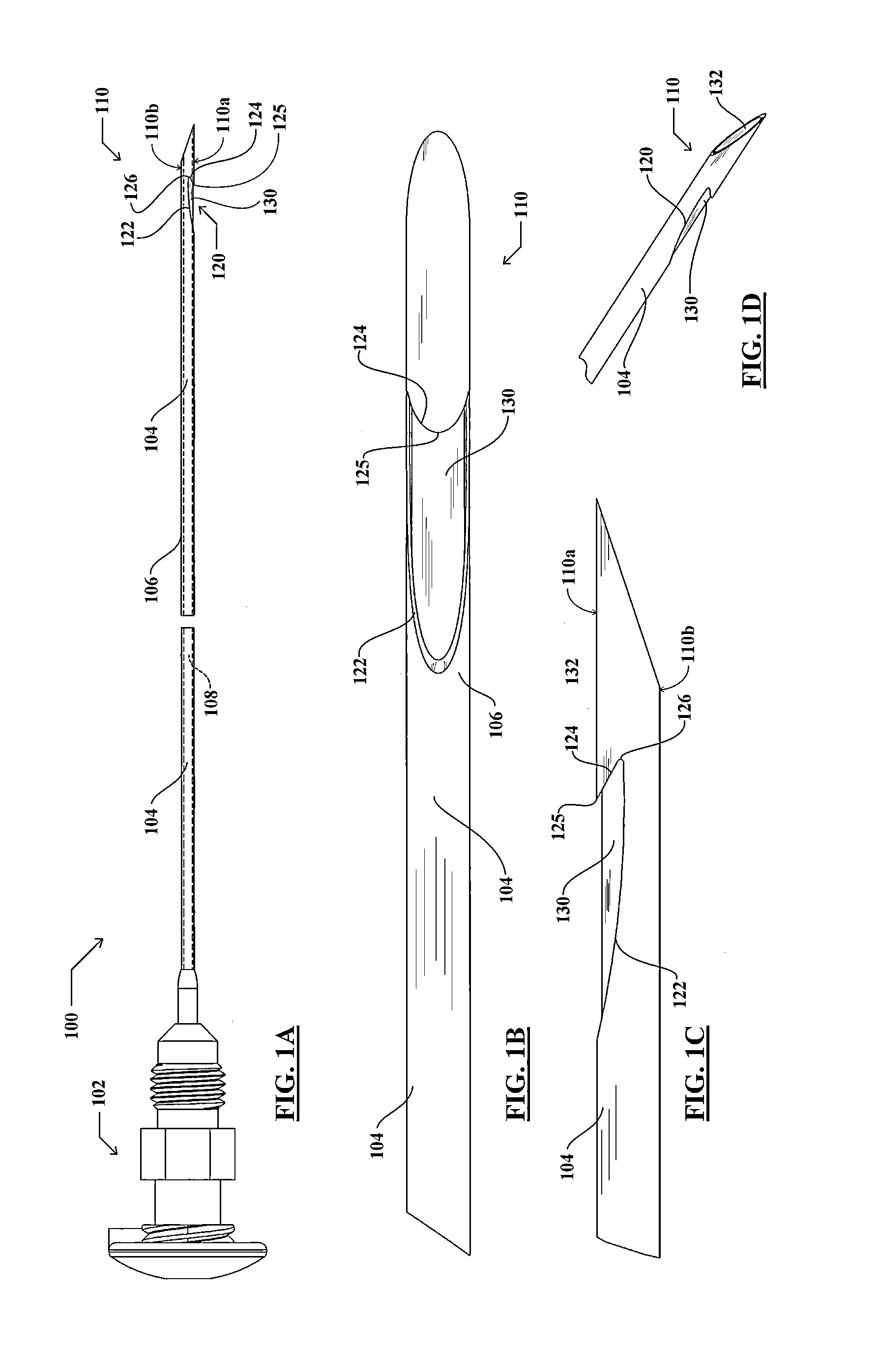
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy needle
ActiveUS20120253228A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesTissue CollectionEndoscope
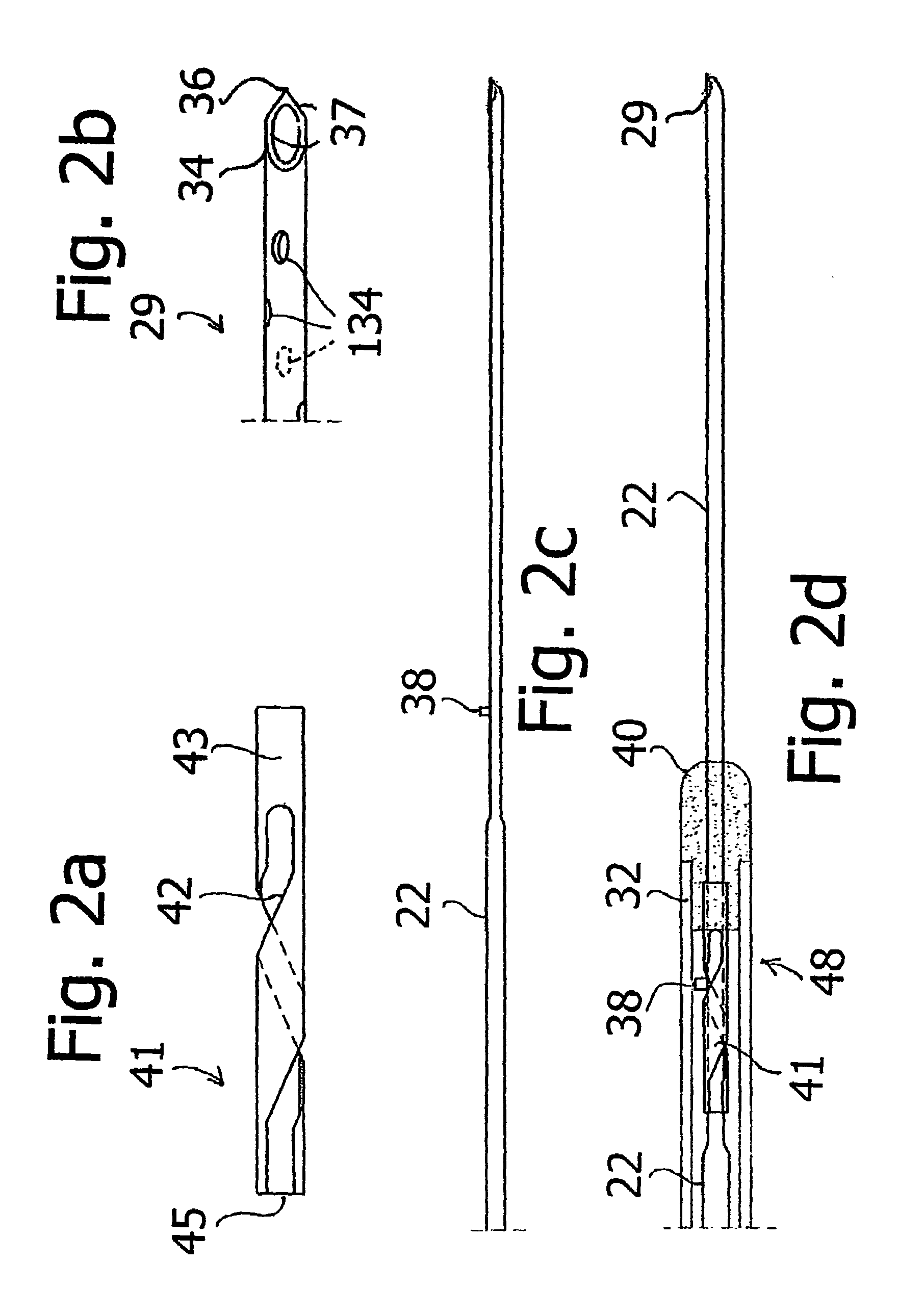
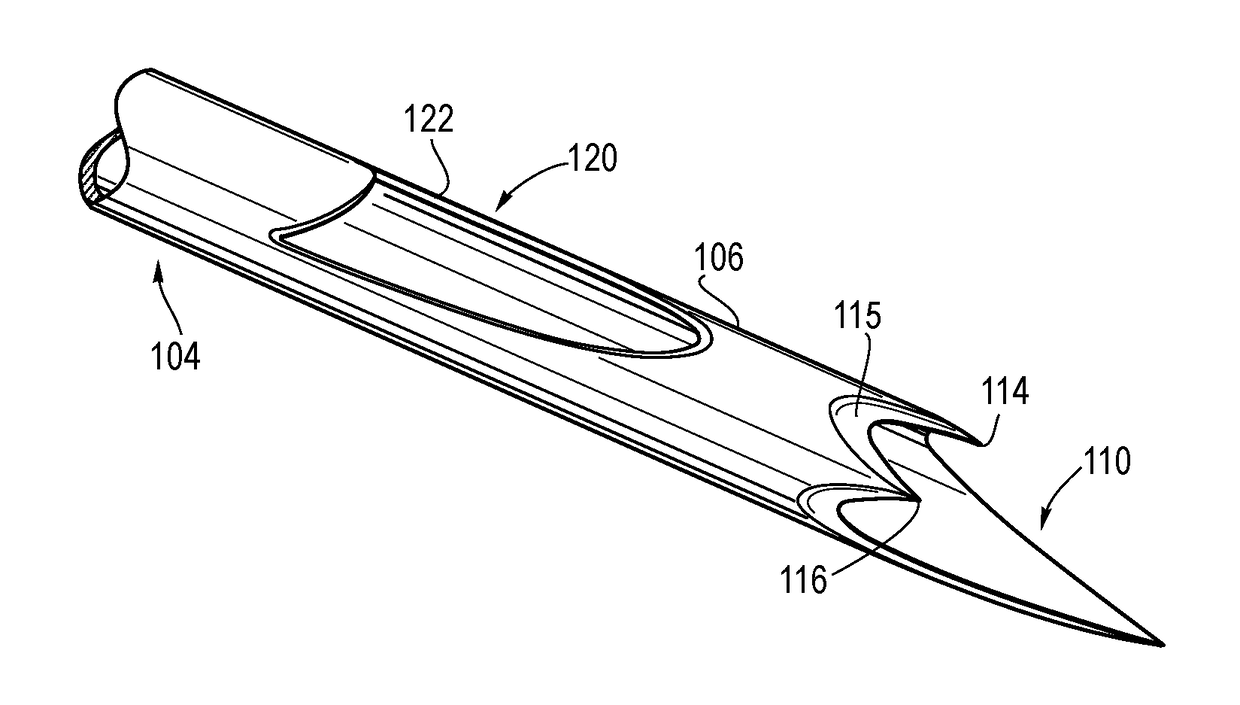
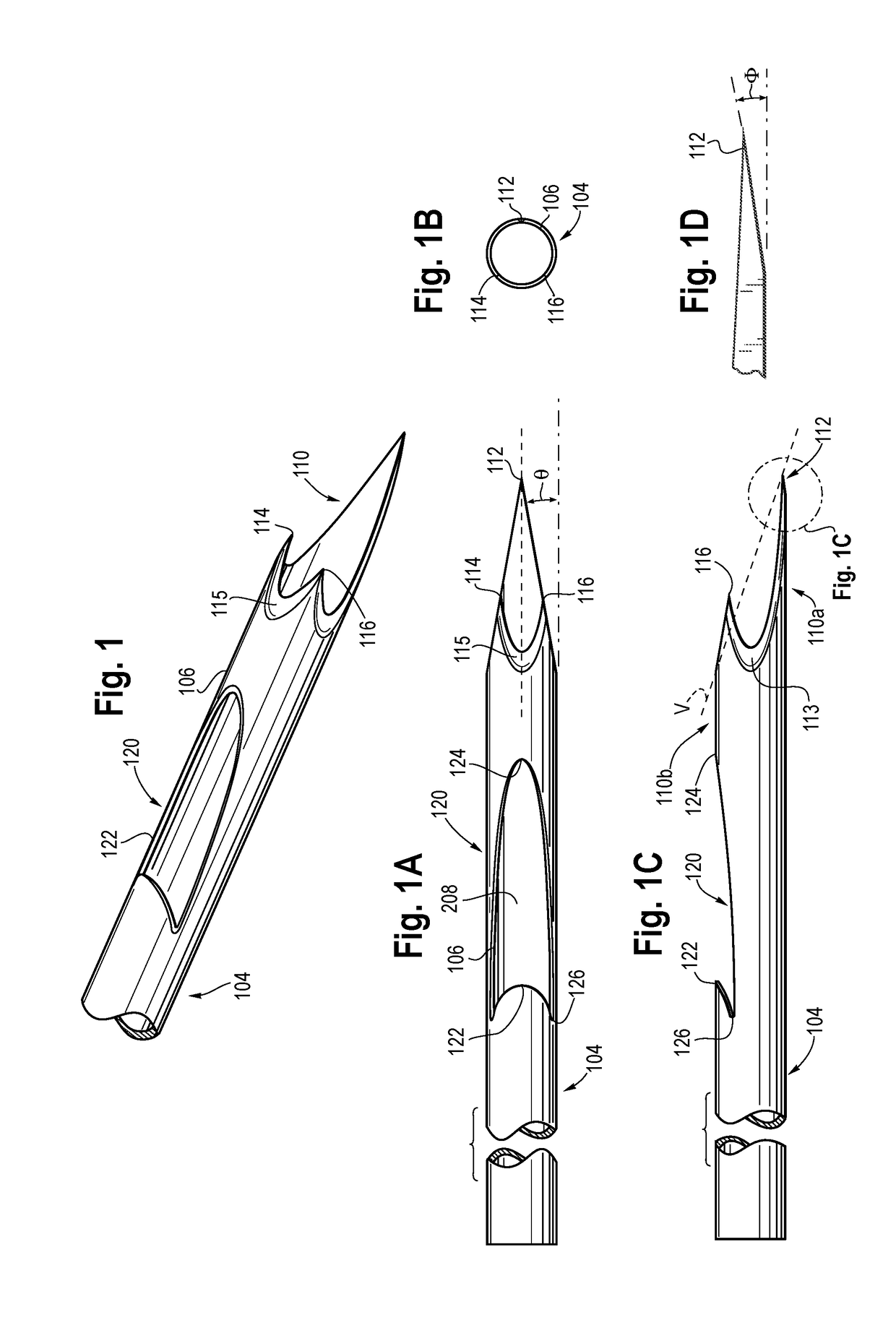
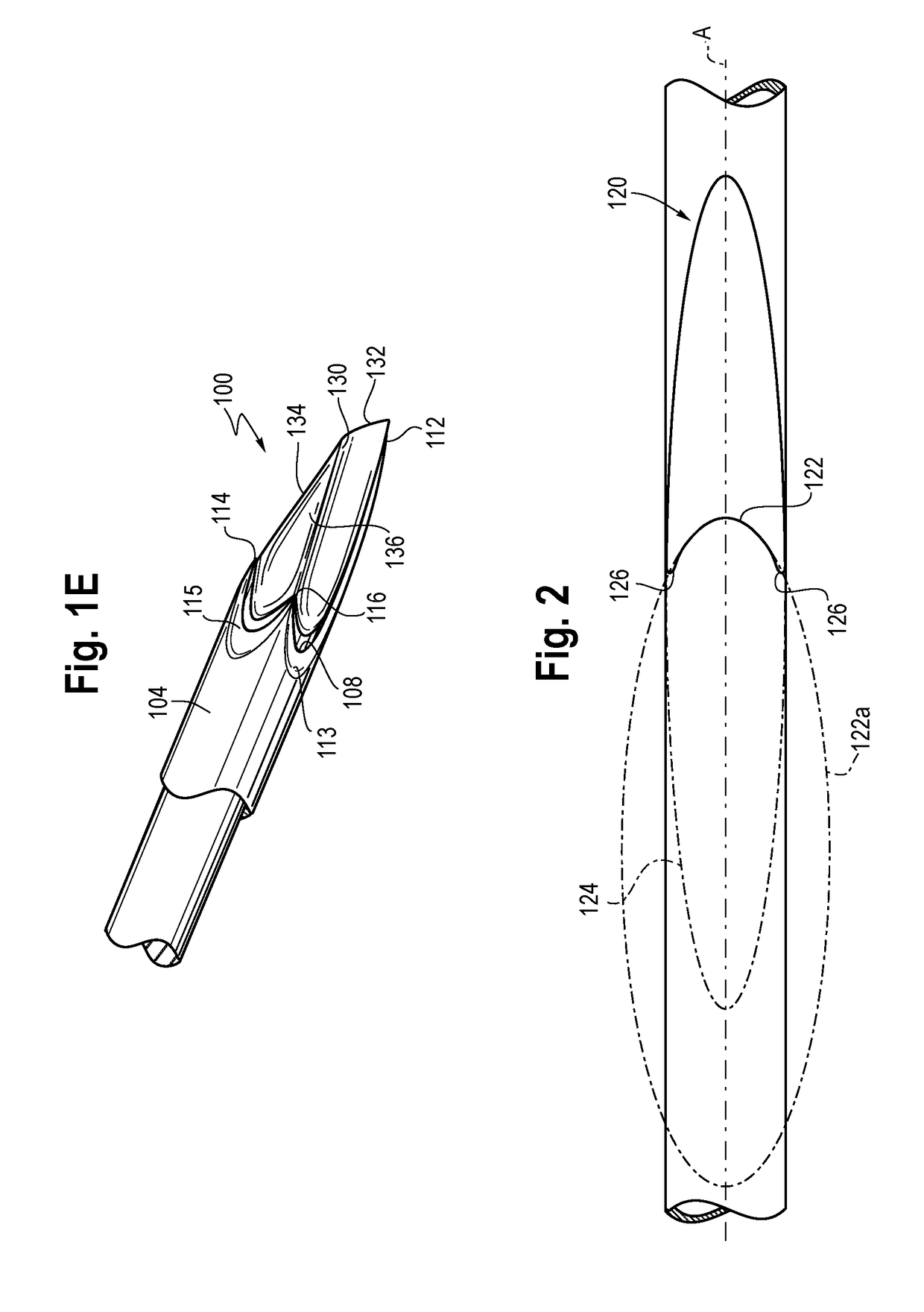
A notched tissue-collection needle configured similarly to a fine-needle-aspiration needle is provided with a cutting edge disposed in the notch and configured to excise tissue into the notch for collection. A stylet may be provided through a lumen of the needle during introduction into a patient body. The needle may be provided with echogenicity-enhancing features.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Biopsy method
A biopsy method is disclosed. The biopsy method can be used to provide a fine needle aspiration sample and a core biopsy sample. The biopsy method can include adjusting a sample port length without removing the biopsy device from the patient.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
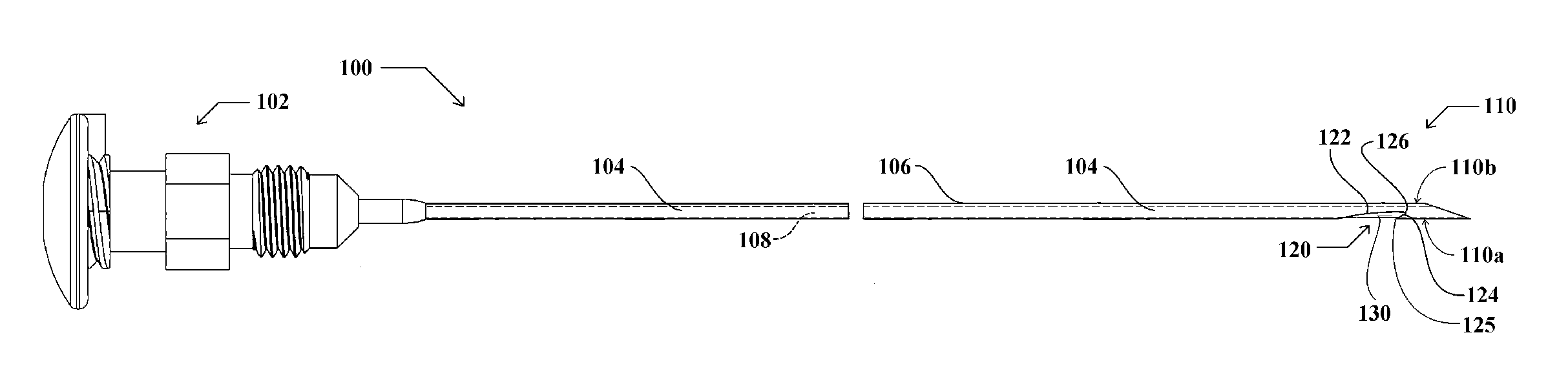
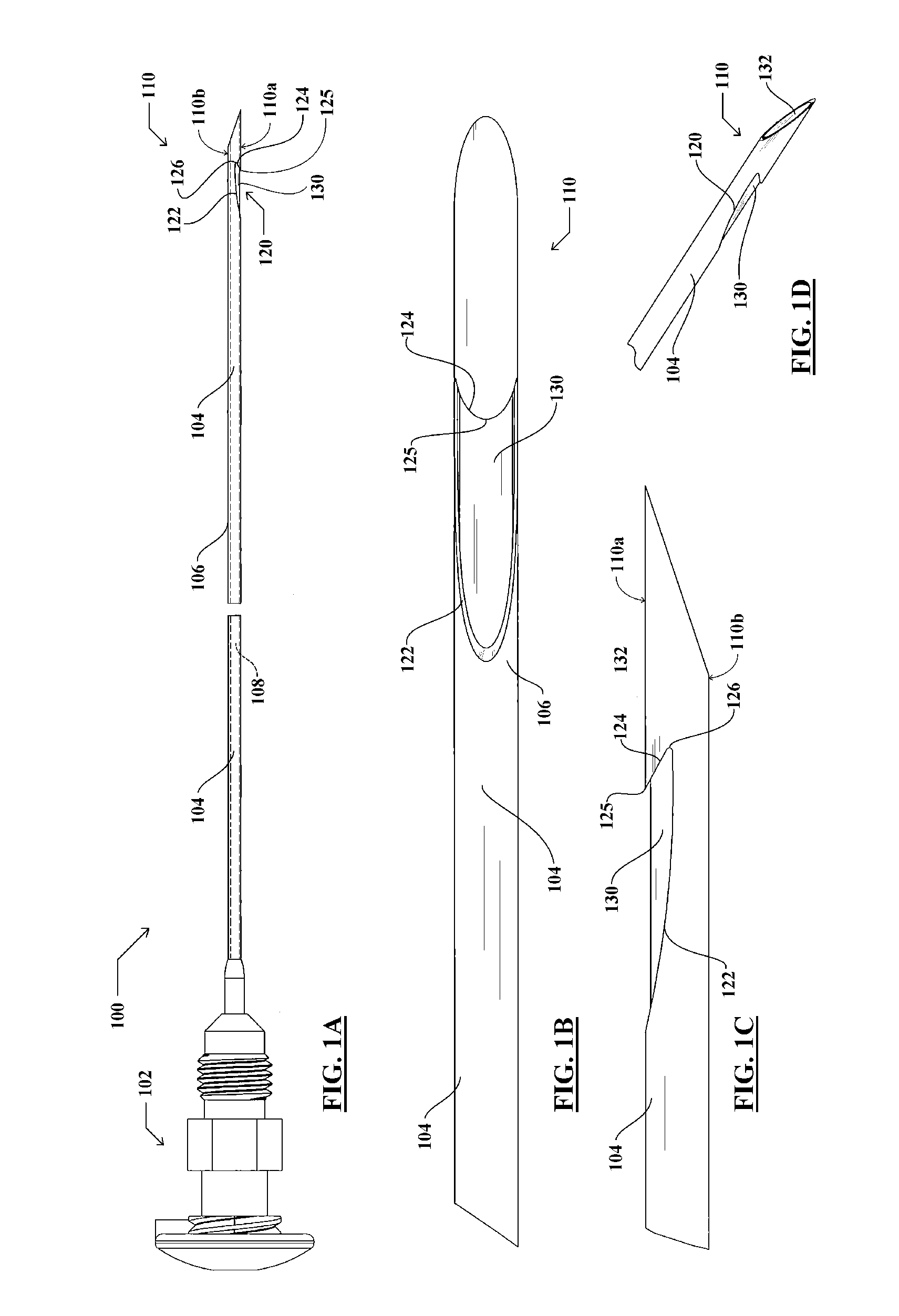
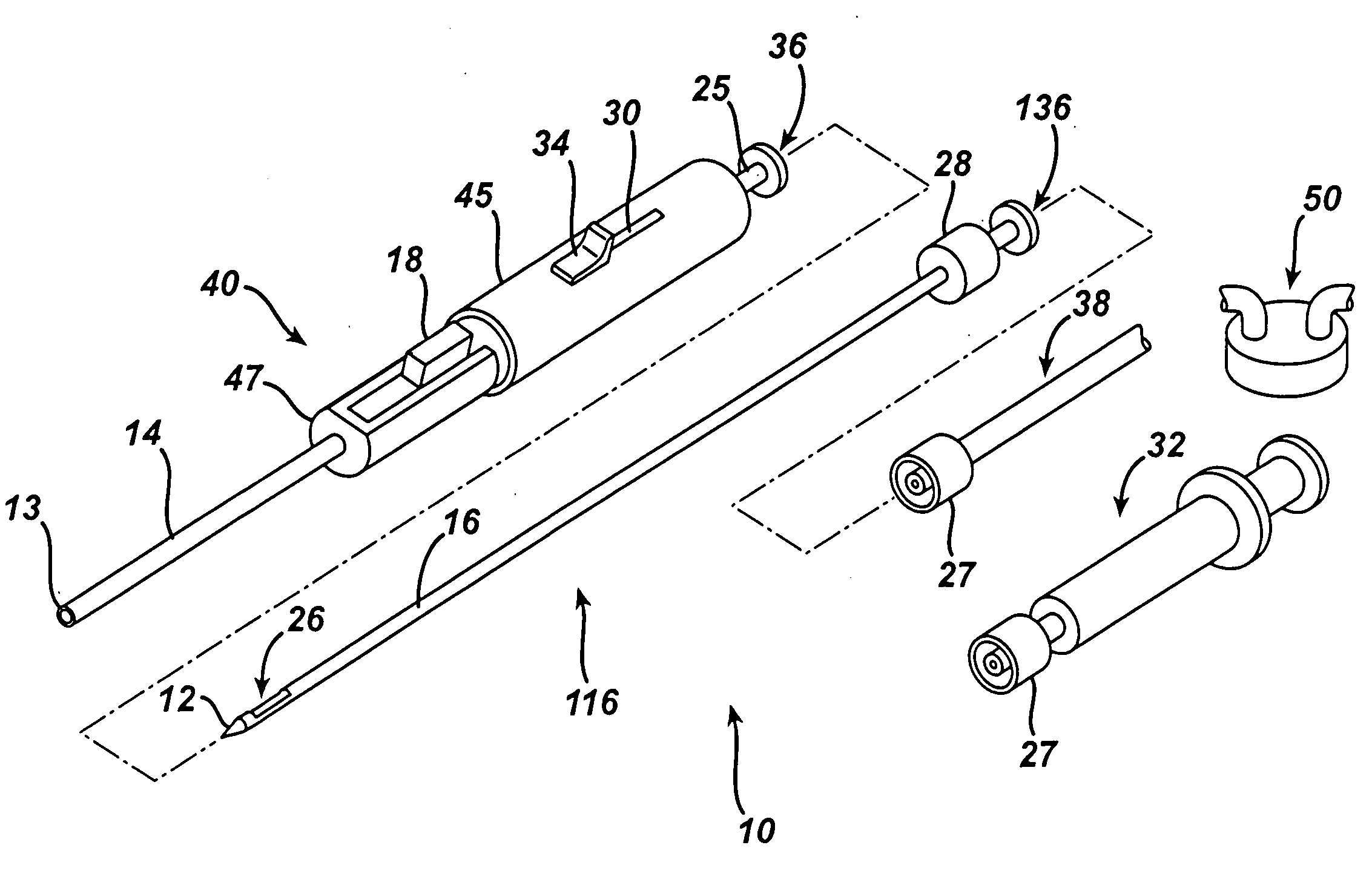
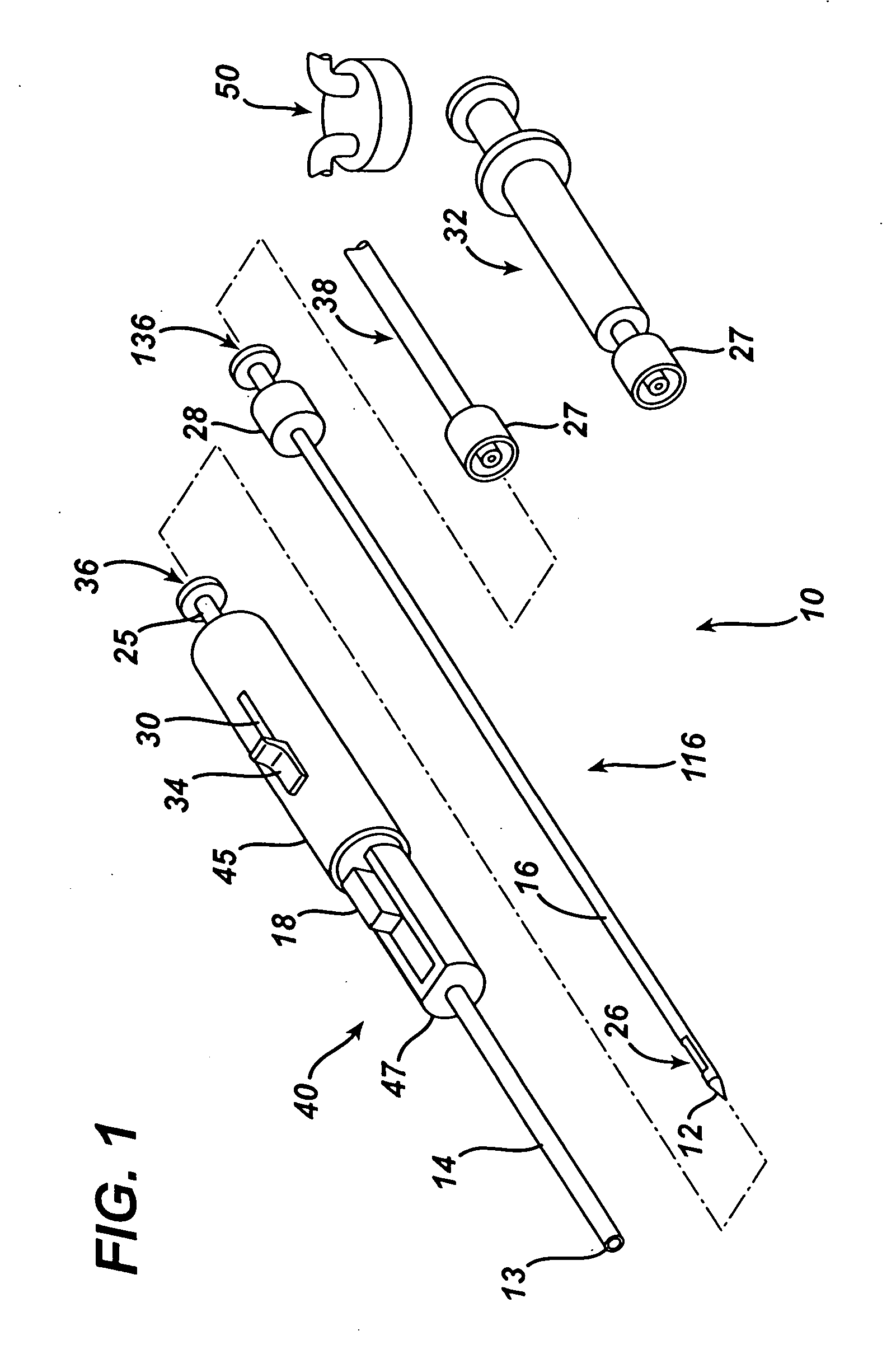
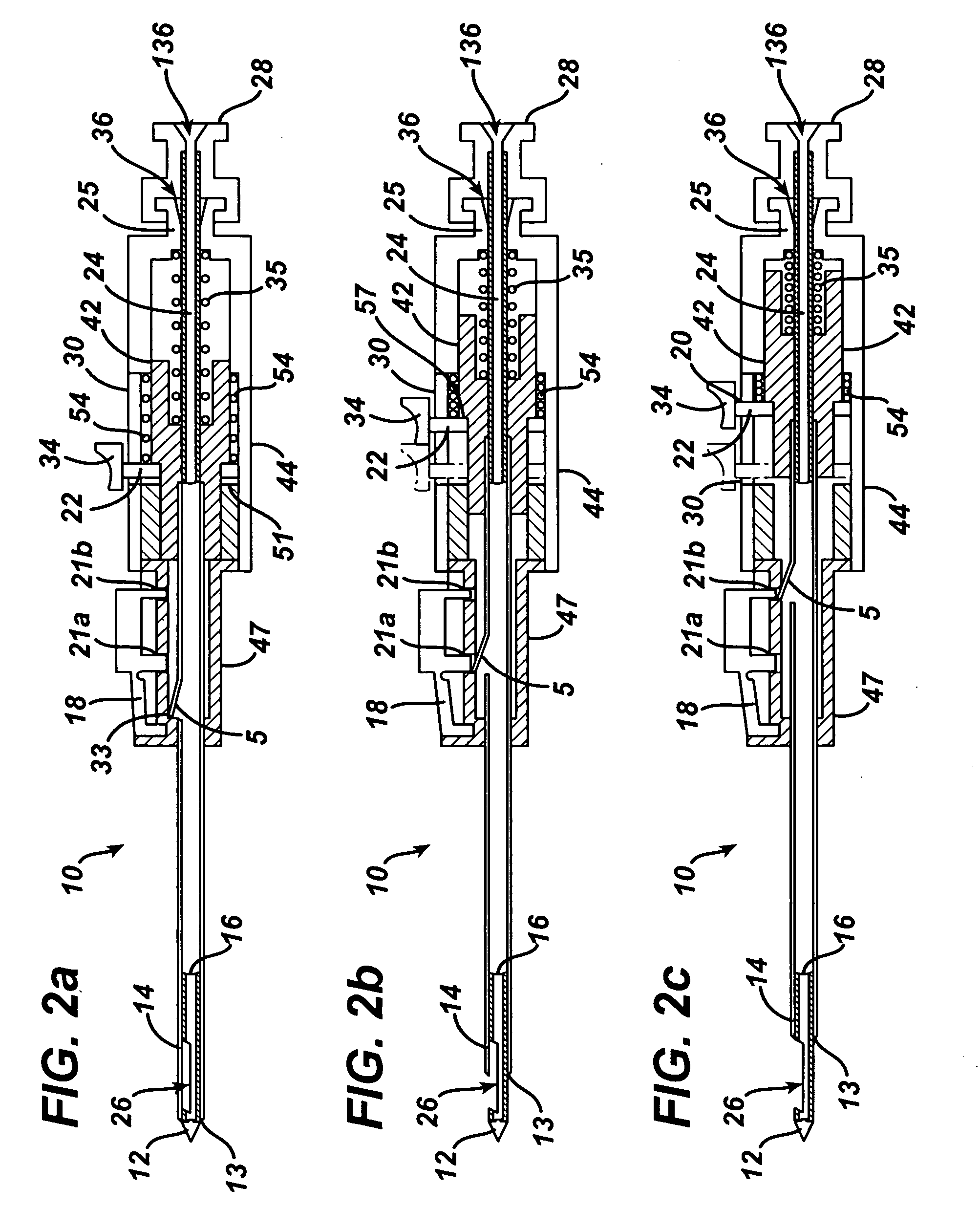
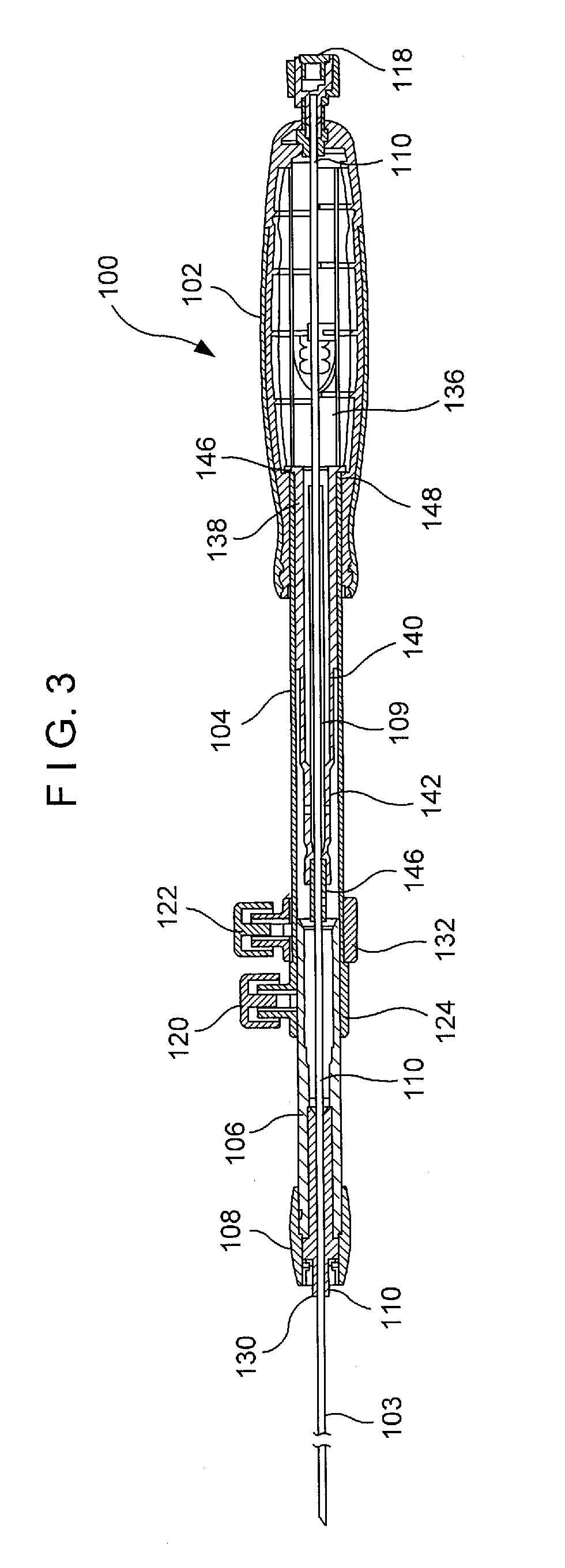
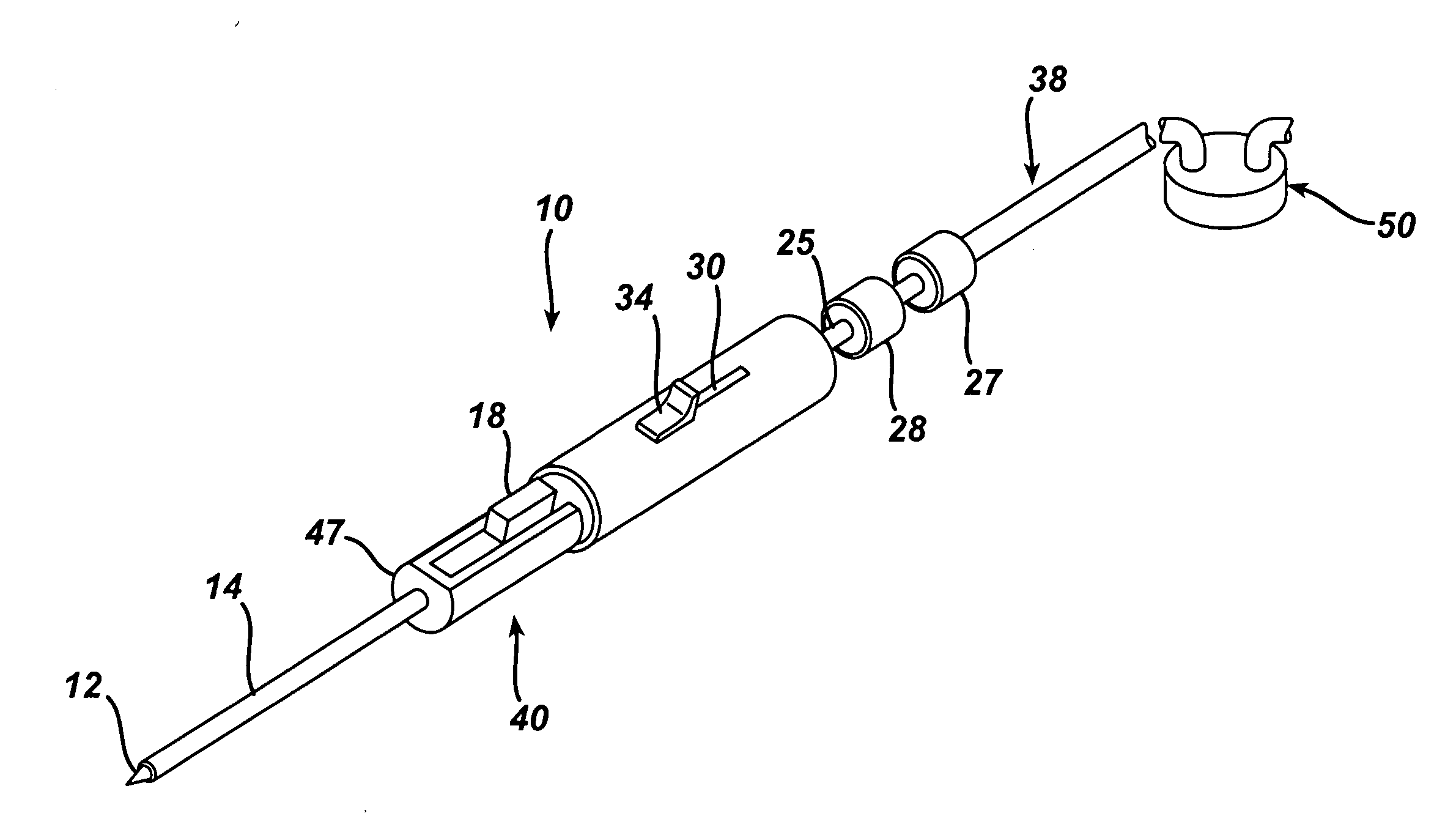
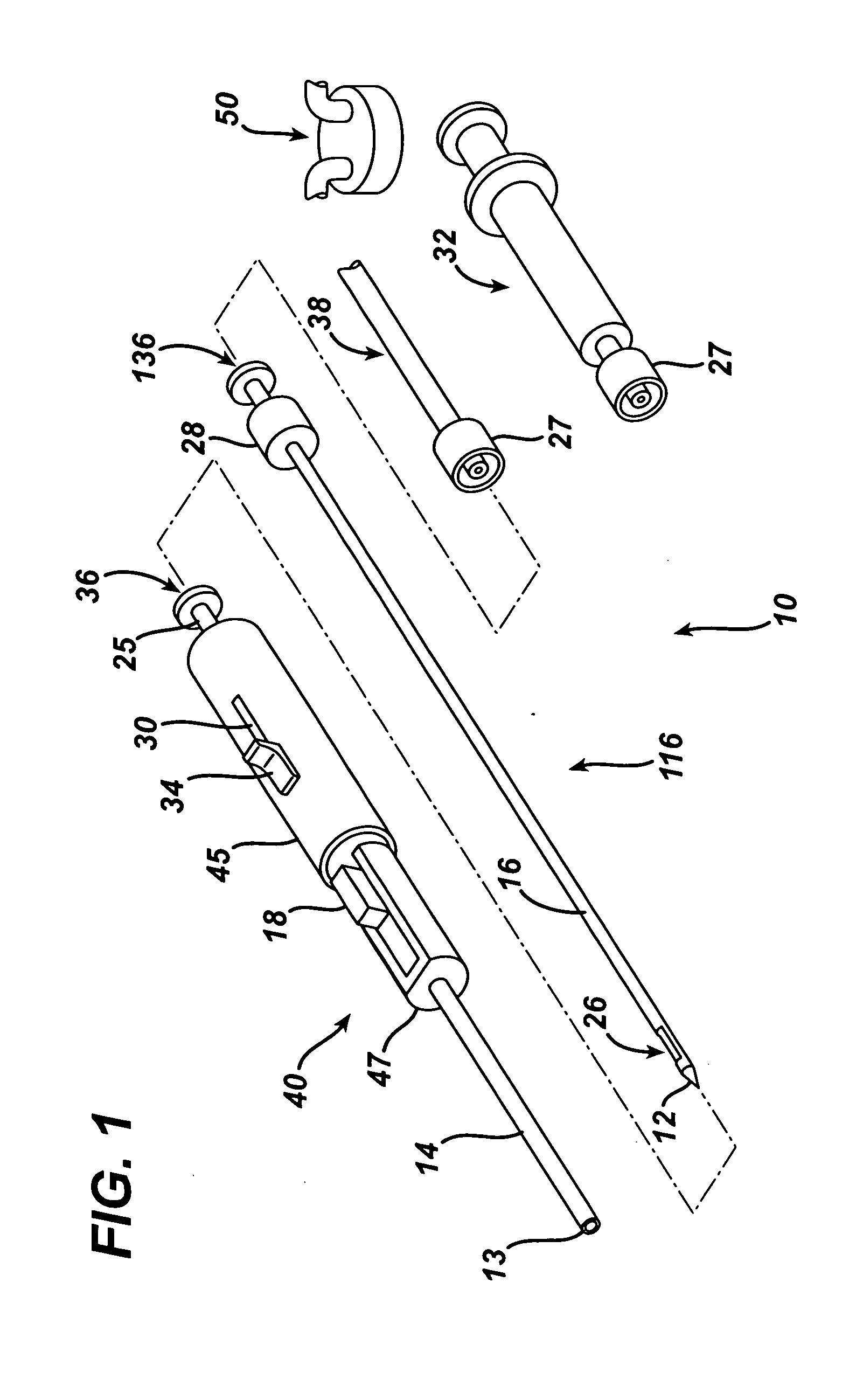
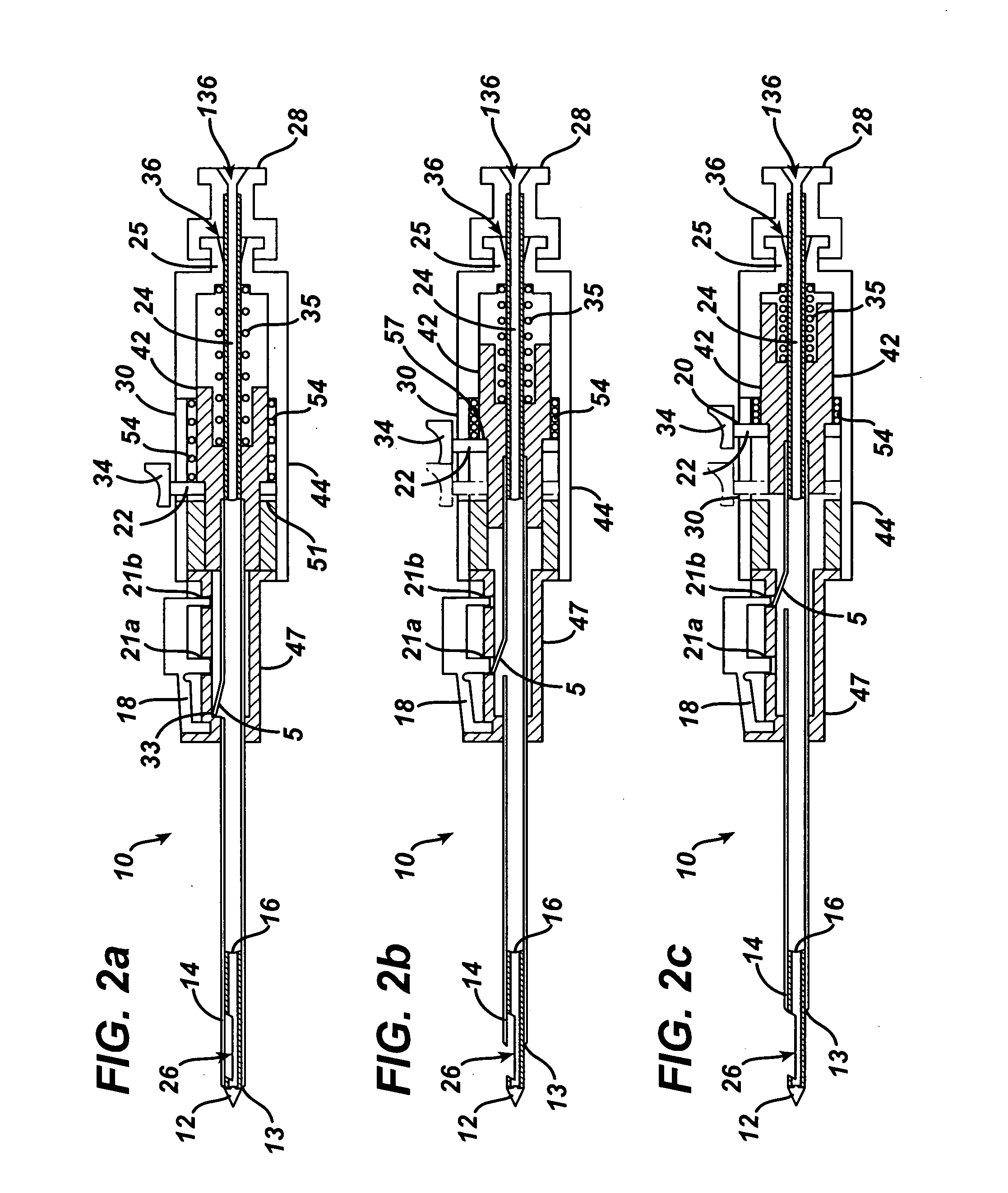
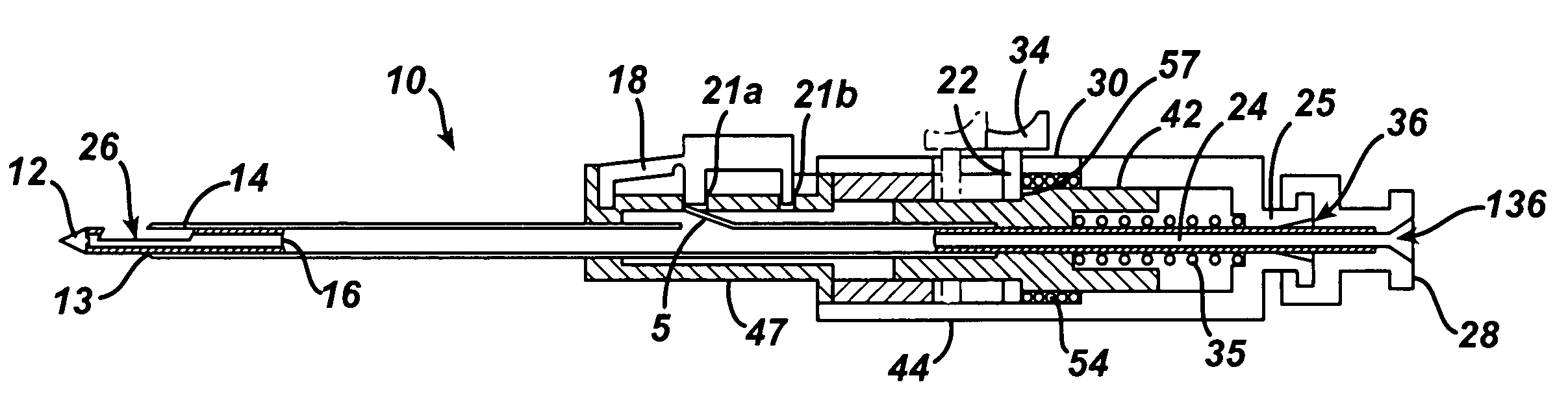
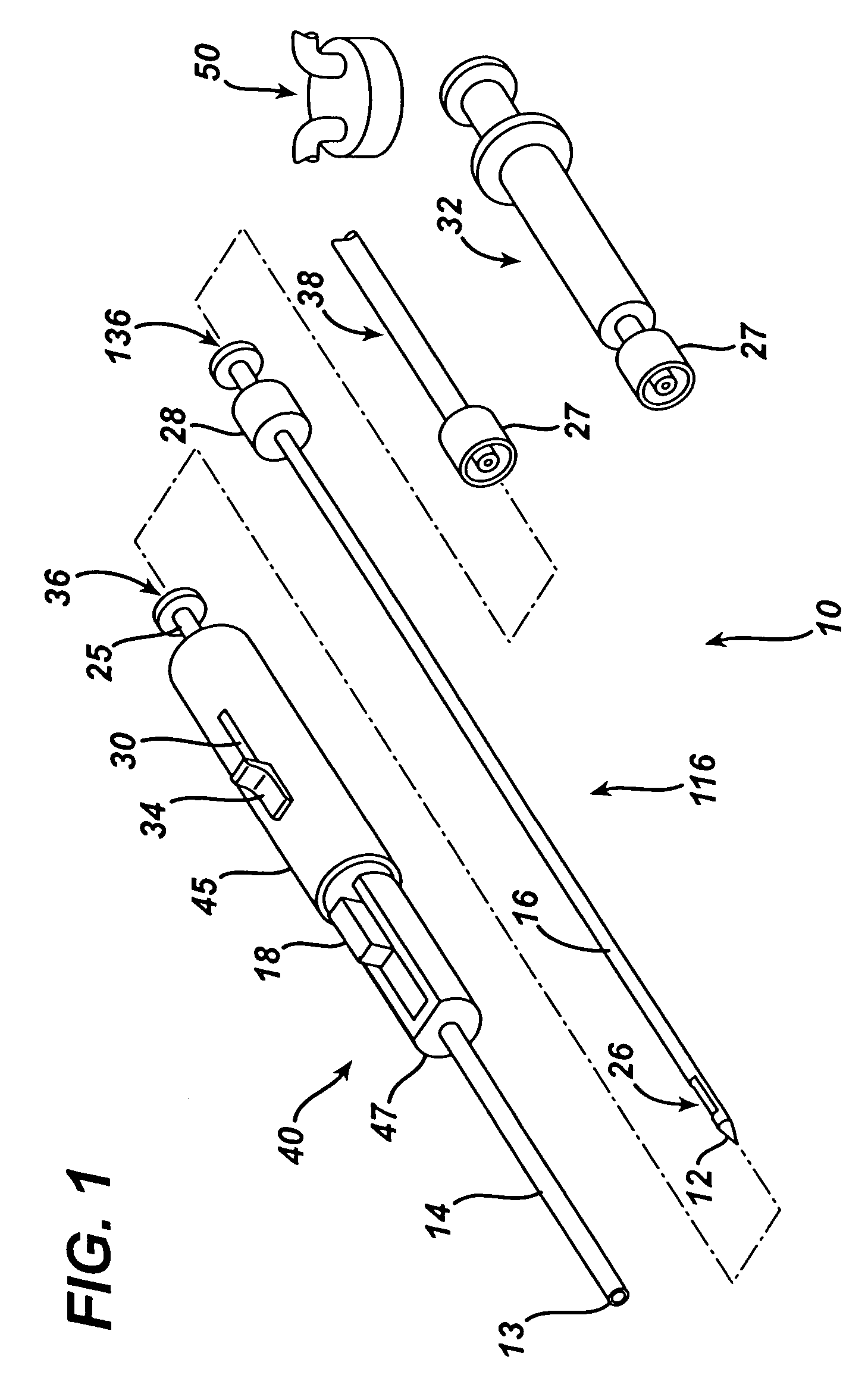
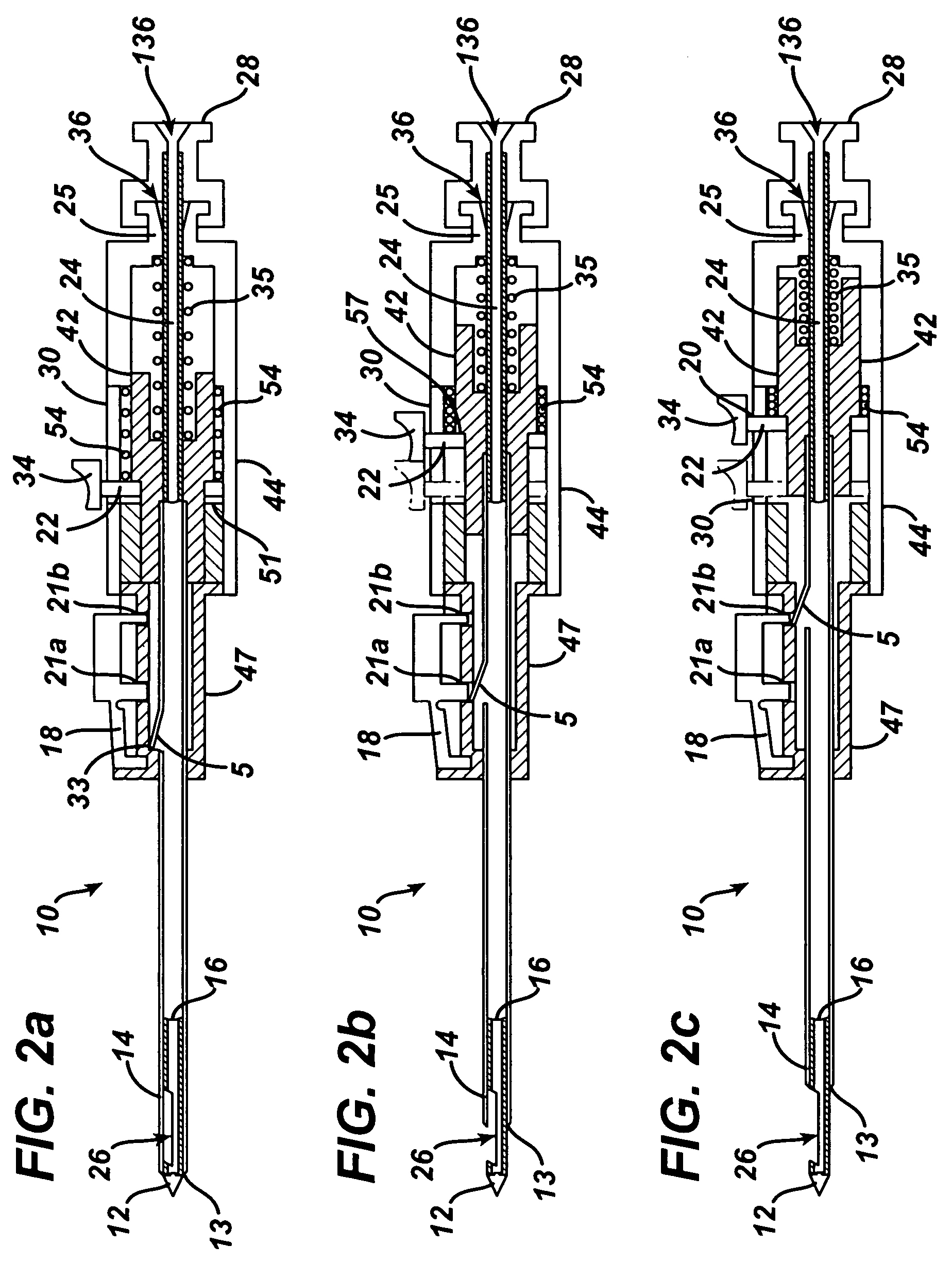
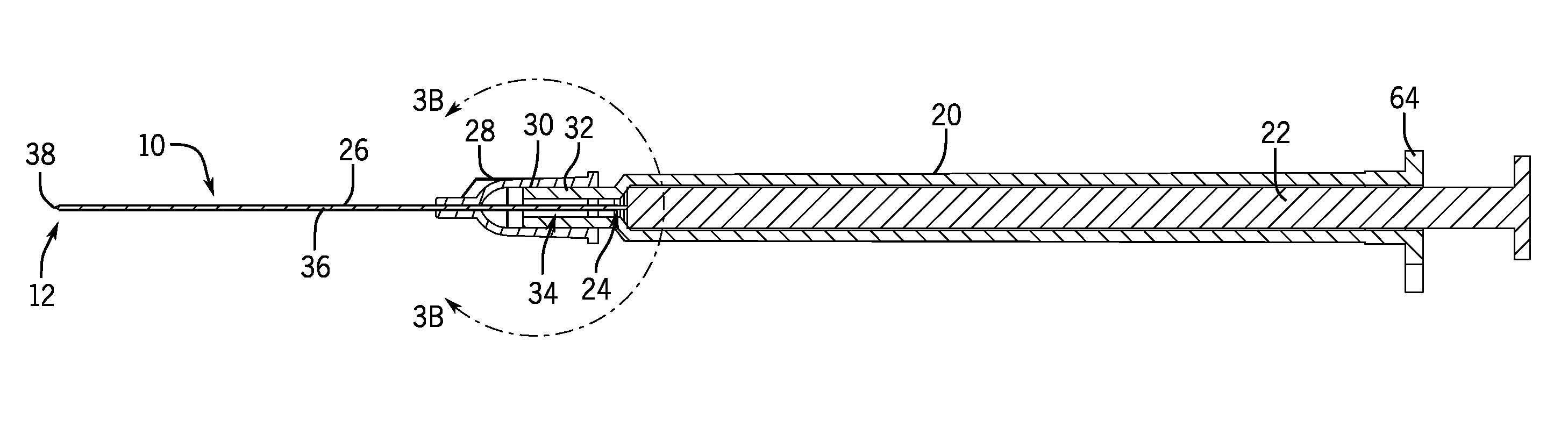
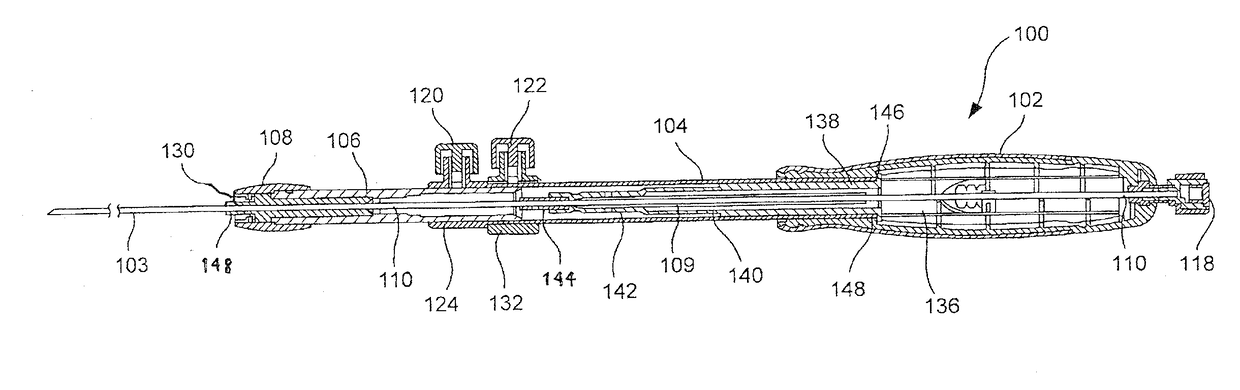
Endoscopic Ultrasound Fine Needle Aspiration Device
A handle for a medical device comprises a proximal segment defining a proximal lumen extending therethrough and sized and shaped to receive an endoscopic medical device therein. A medial segment is received within a distal portion of the proximal segment and has an outer diameter smaller than an inner diameter thereof. A medial lumen extends through the proximal segment and is open to the proximal lumen. A distal segment is received within a distal portion of the medial segment and defines a distal lumen extending therethrough open to the medial lumen. The distal segment has an outer diameter smaller than an inner diameter of the medial segment. The medial segment includes a first movement limiting mechanism limiting movement of an endoscopic medical device inserted therethrough along an axis of the distal lumen and a second movement limiting mechanism limiting advancement of an endoscope attached to the distal body portion.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Biopsy device
InactiveUS20070208272A1Safer procedureSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsRadiologyOuter Cannula
A biopsy device is disclosed. The biopsy device disclosed includes an outer cutting cannula and an inner cannula. The inner cannula has a side sample port for receiving a biopsy sample. The outer cannula can be selectively positioned with respect to the side port to provide fine needle aspiration sampling or, alternatively, core biopsy sampling.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Biopsy method
A biopsy method is disclosed. The biopsy method can be used to provide a fine needle aspiration sample and a core biopsy sample. The biopsy method can include adjusting a sample port length without removing the biopsy device from the patient.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
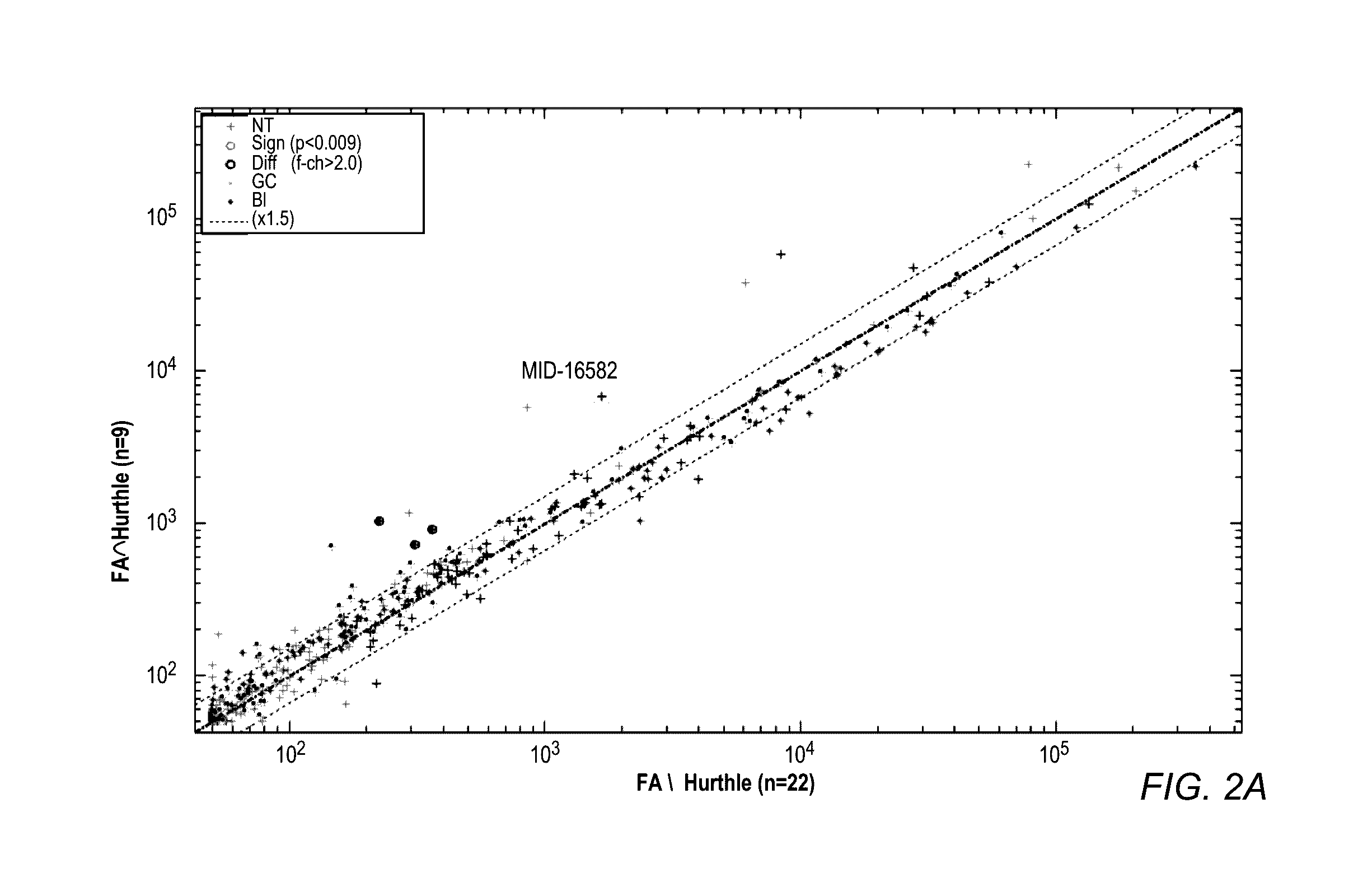
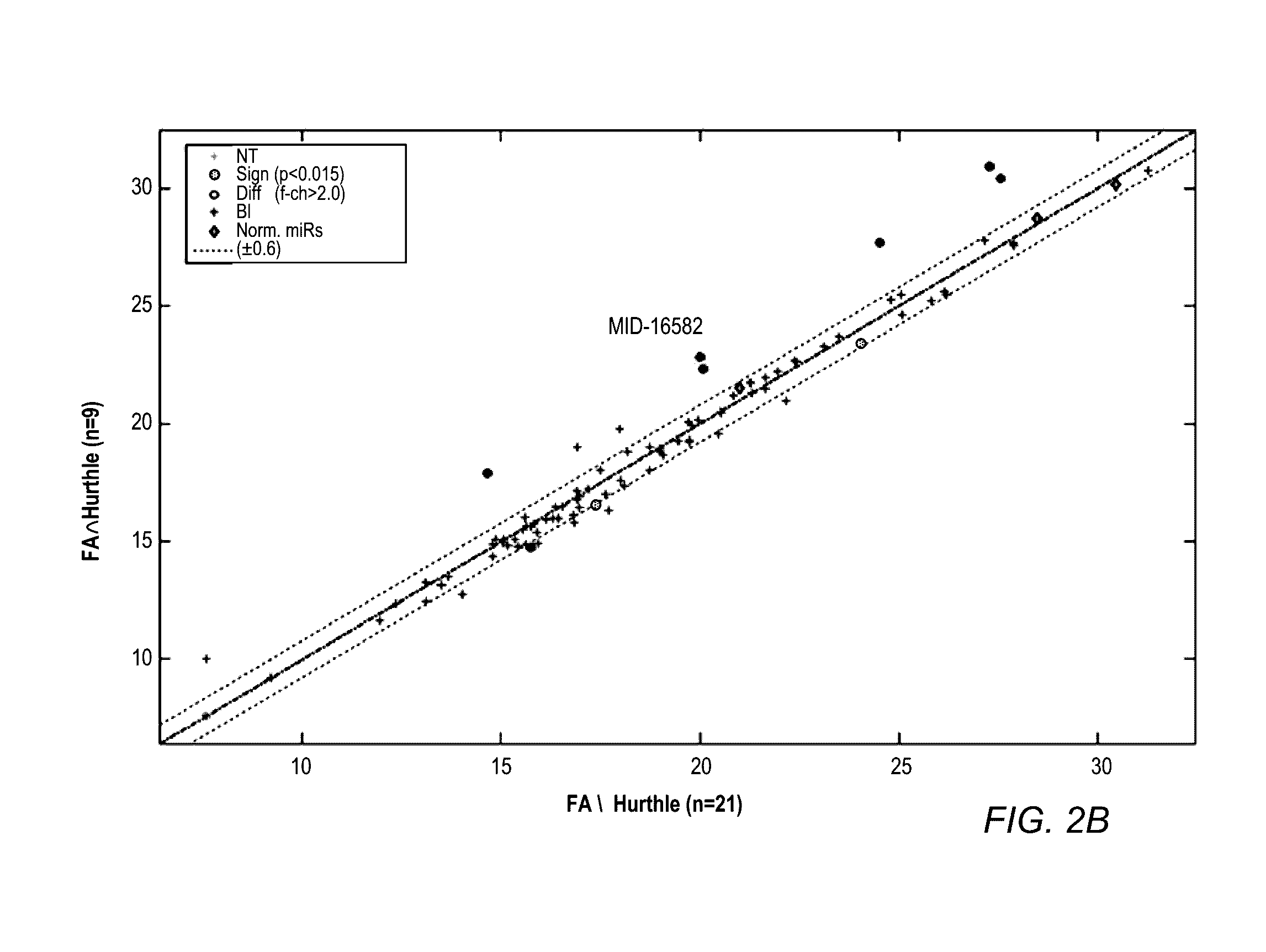
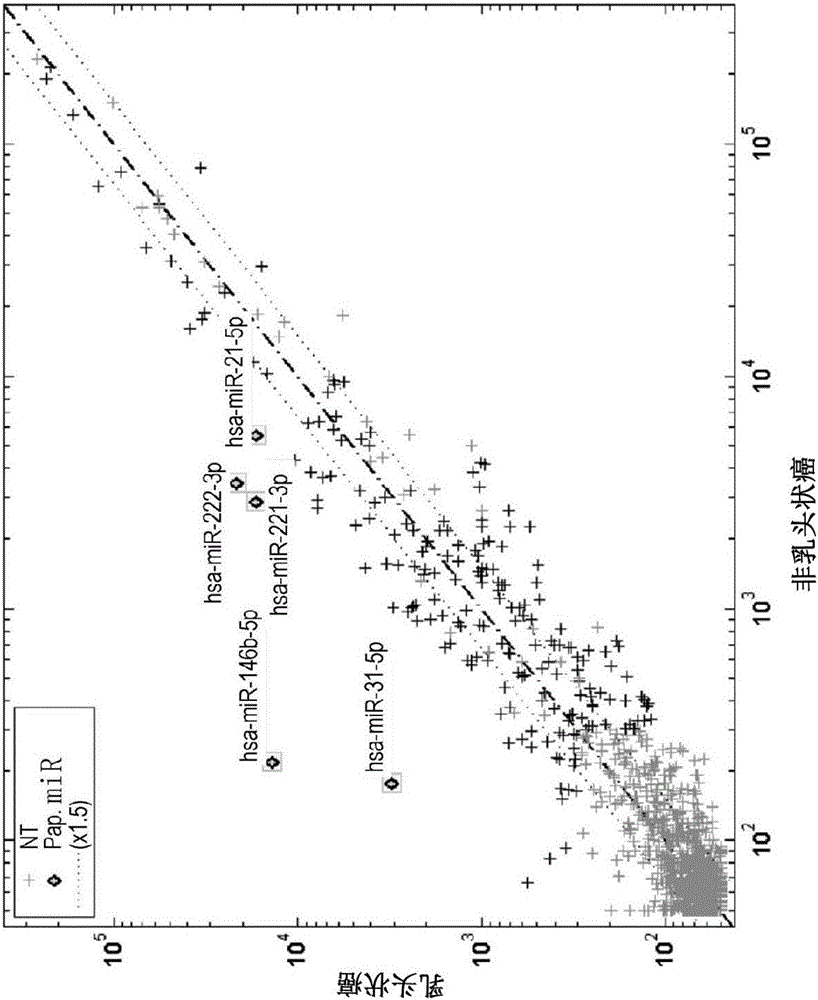
Mirna expression signature in the classification of thyroid tumors
The present invention provides a method for classification of thyroid tumors through the analysis of the expression patterns of specific microRNAs in fine needle aspiration samples. Thyroid tumor classification according to a microRNA expression signature allows optimization of diagnosis and treatment, as well as determination of signature-specific therapy.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
MiRNA expression signature in the classification of thyroid tumors
The present invention provides a method for classification of thyroid tumors through the analysis of the expression patterns of specific microRNAs in fine needle aspiration samples. Thyroid tumor classification according to a microRNA expression signature allows optimization of diagnosis and treatment, as well as determination of signature-specific therapy.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
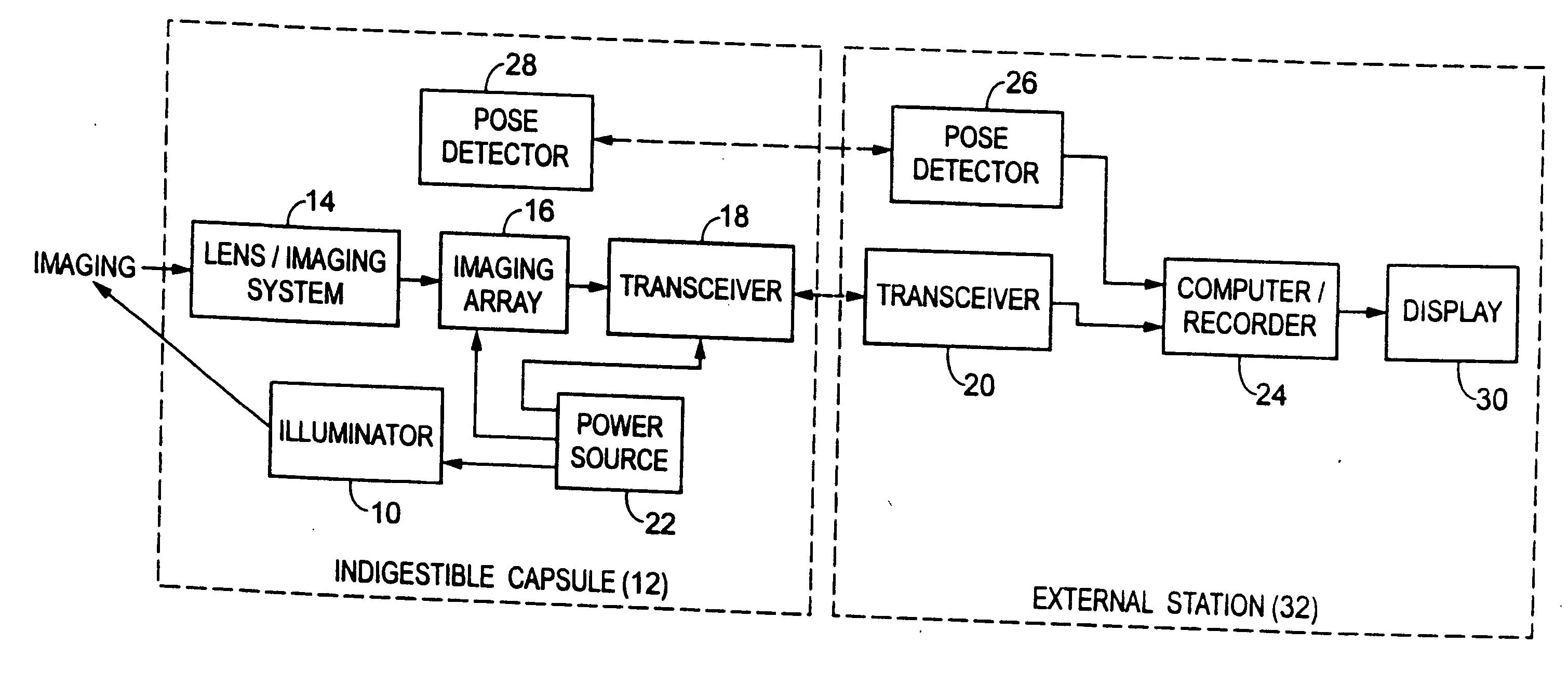
Miniature ingestible capsule
ActiveUS20110065987A1Improve and enhance visualizationSlow motionSurgeryEndoscopesMotor controlBiopsy forceps
A miniature ingestible capsule has multiple therapeutic or diagnostic operations that can be performed. These functions are controlled by a combination of an outside control, a pose beacon and through information relayed from an imagining array and transmitter. These functions can be in a separate capsule without an imaging array or within the same capsule with an imaging array. Typically, there is one function performed in addition to imaging. These functions can include suction and spray capabilities, ultrasound sensor, lithotripsy, laser, heat, electrocautery, BICAP, biopsy forceps, a needle knife snare cautery (cold and hot with continuous or pulsed current for cutting and coagulation), with a basket, and fine needle aspiration with various wheels and fins and motors controlled externally and other tools to be used in humans. All of these tools can be attached to a retractable arm. Also, they can be used on an elevator device that lifts them, allowing for an extra 180° of movement.
Owner:MICROGIZZMOS LLC
Endoscopic biopsy needle with coil sheath
ActiveUS20140257136A1Large outer diameterHigh strengthSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsTissue CollectionEndoscope
A notched tissue-collection needle configured similarly to a fine-needle-aspiration needle is provided with a cutting edge disposed in the notch and configured to excise tissue into the notch for collection. A stylet may be provided through a lumen of the needle during introduction into a patient body. The needle may be provided with echogenicity-enhancing features. A coated-wire sheath through which the needle is slidably disposed includes an overcoating that is thicker along a distal length and thinner along a proximal length.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
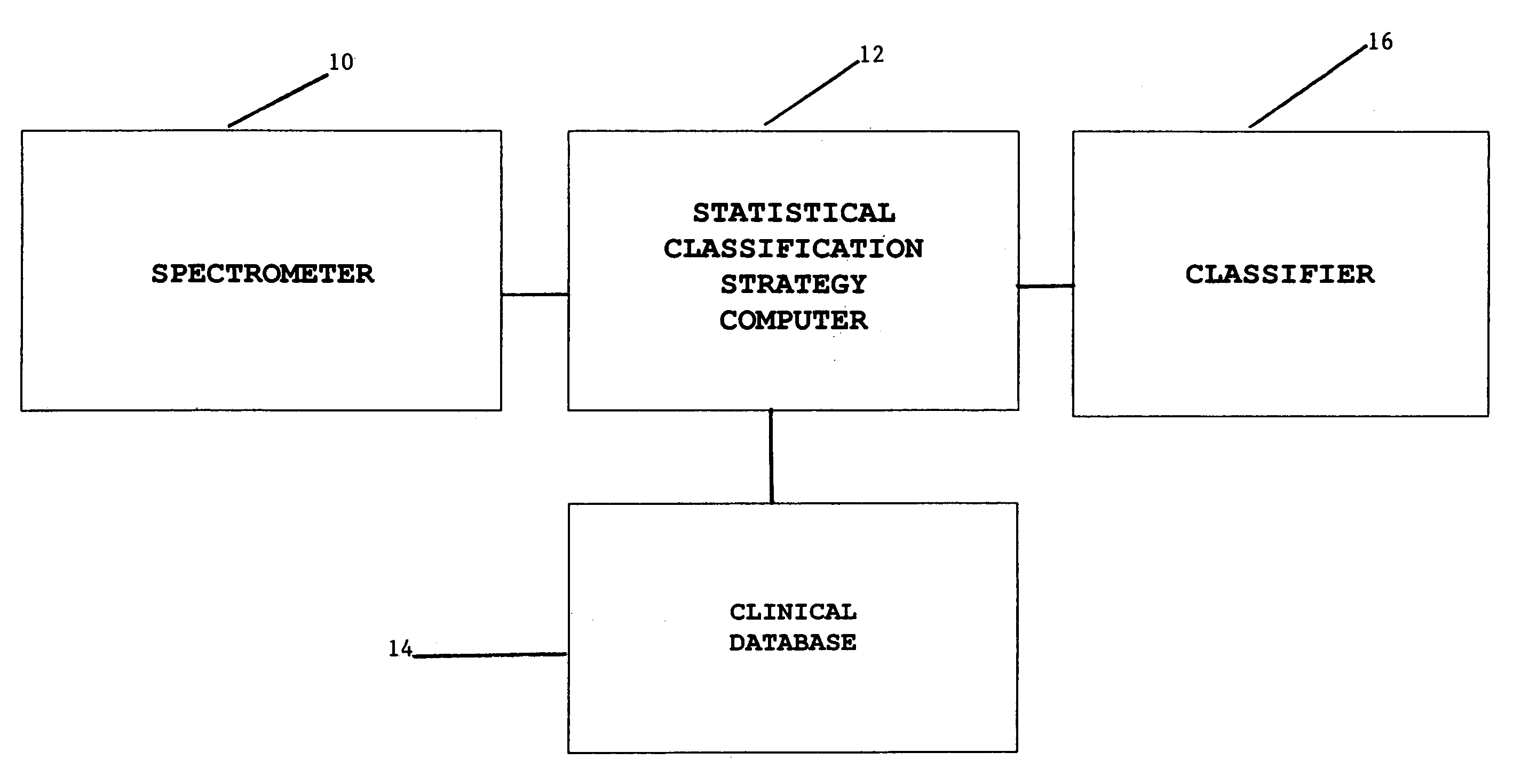
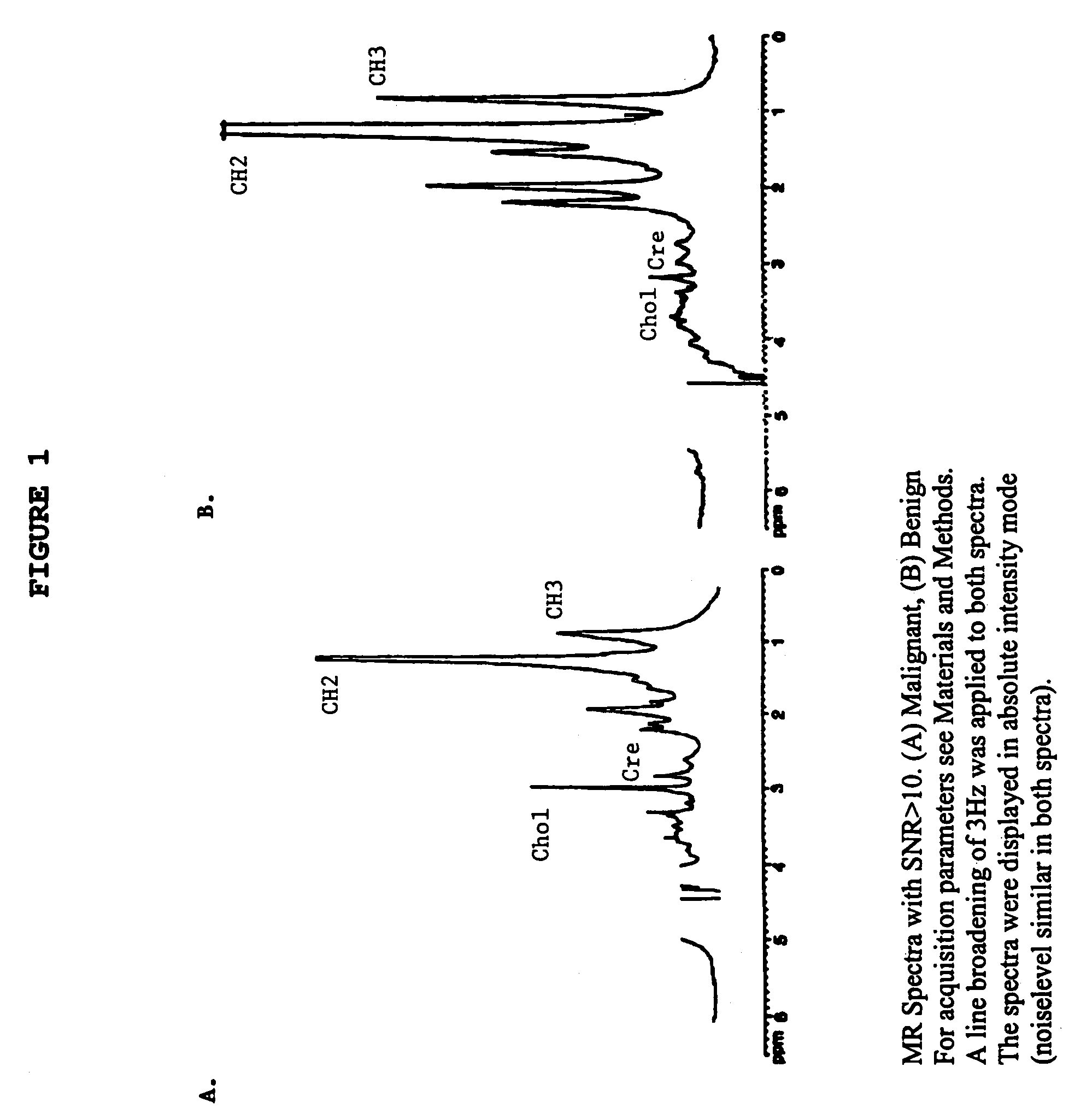
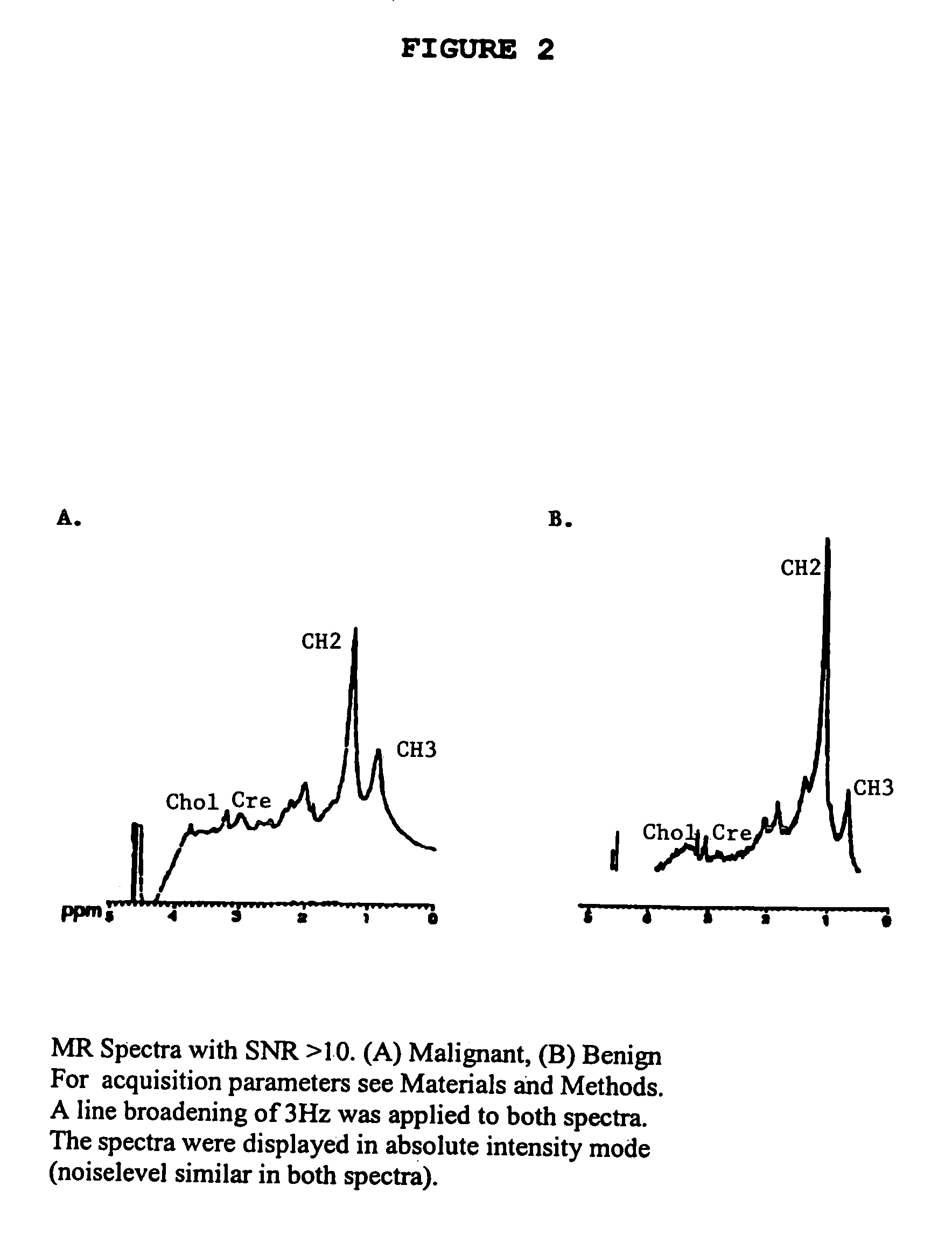
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy to classify tissue
InactiveUS7335511B2Reliable determinationComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyClassification methodsTumor vessel
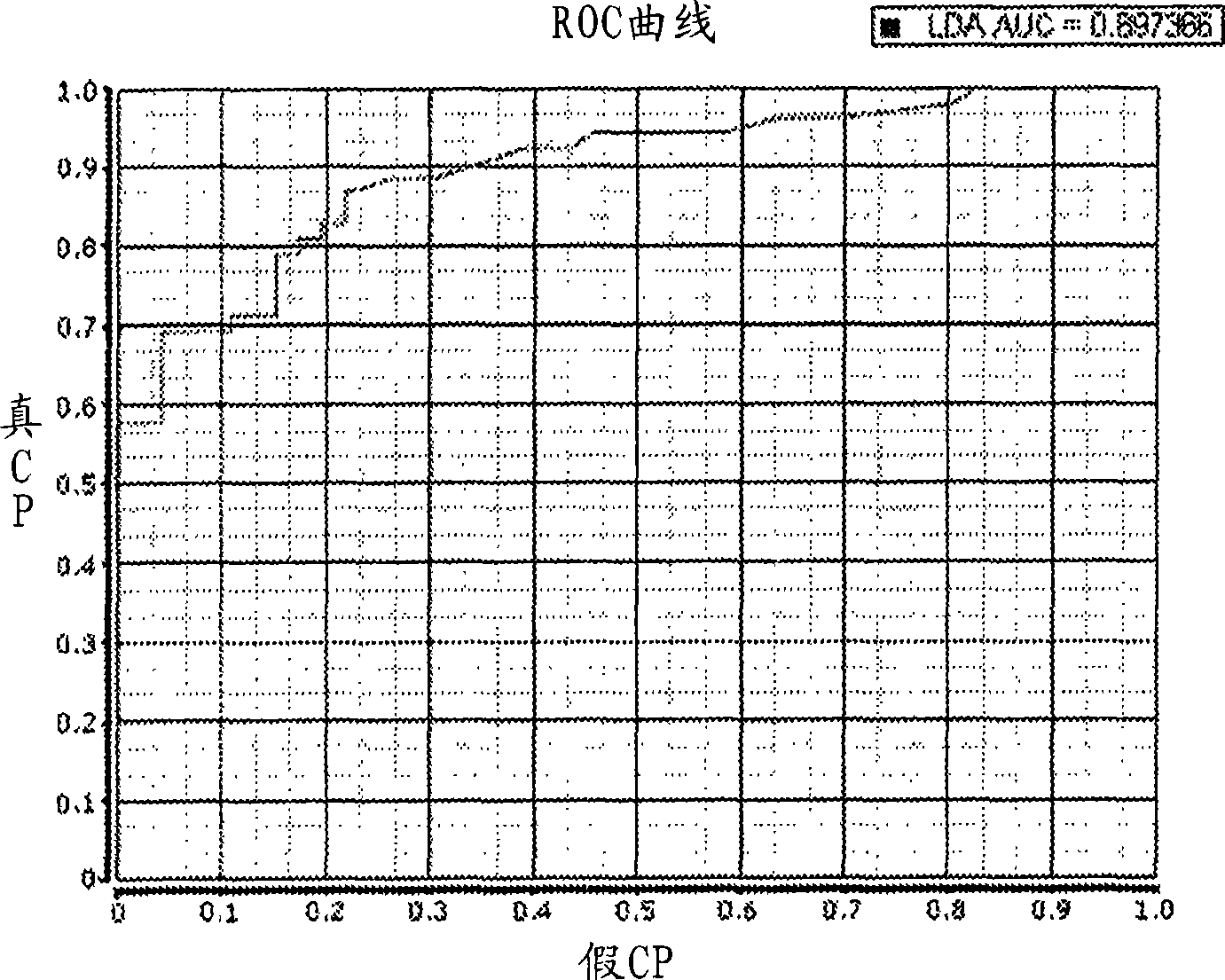
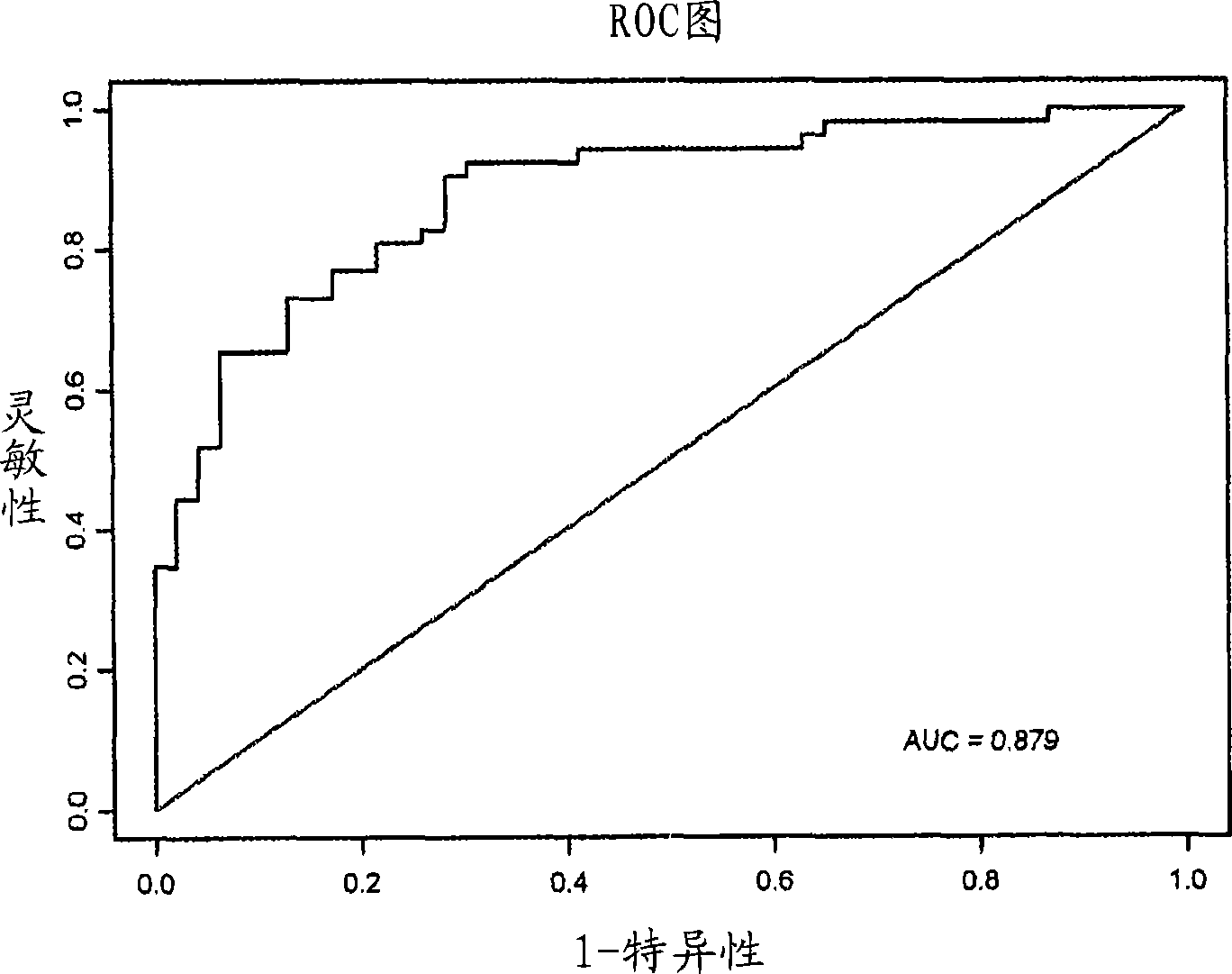
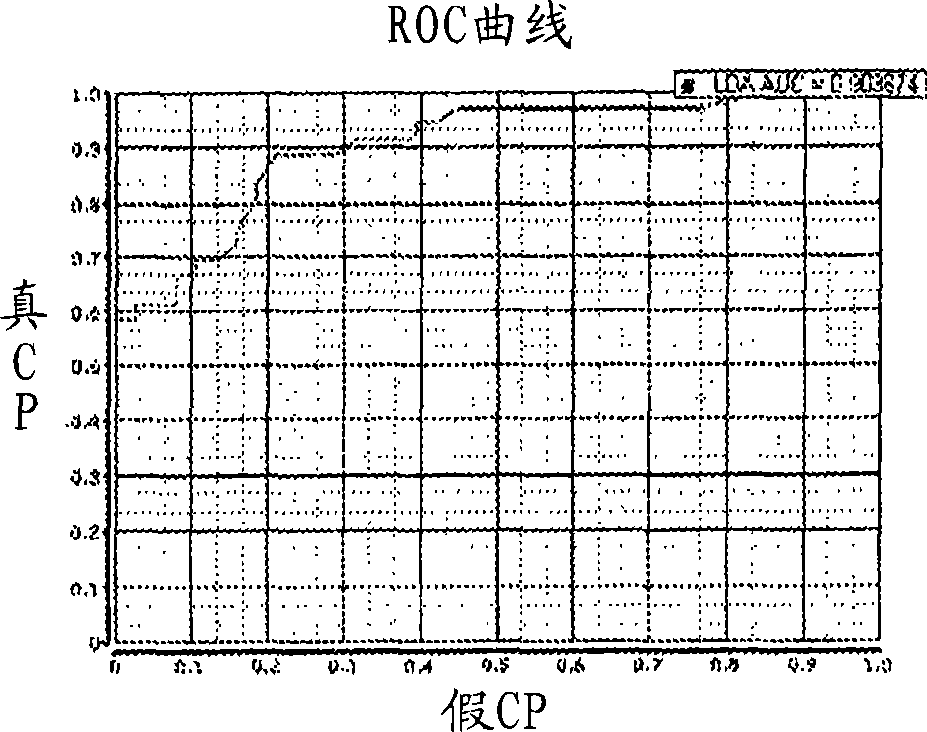
Robust classification methods analyze magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) data (spectra) of fine needle aspirates taken from breast tumors. The resultant data when compared with the histopathology and clinical criteria provide computerized classification-based diagnosis and prognosis with a very high degree of accuracy and reliability. Diagnostic correlation performed between the spectra and standard synoptic pathology findings contain detail regarding the pathology (malignant versus benign), vascular invasion by the primary cancer and lymph node involvement of the excised axillary lymph nodes. The classification strategy consisted of three stages: pre-processing of MR magnitude spectra to identify optimal spectral regions, cross-validated Linear Discriminant Analysis, and classification aggregation via Computerised Consensus Diagnosis. Malignant tissue was distinguished from benign lesions with an overall accuracy of 93%. From the same spectrum, lymph node involvement was predicted with an accuracy of 95% and tumor vascularisation with an overall accuracy of 92%.
Owner:SYDNEY UNIV OF
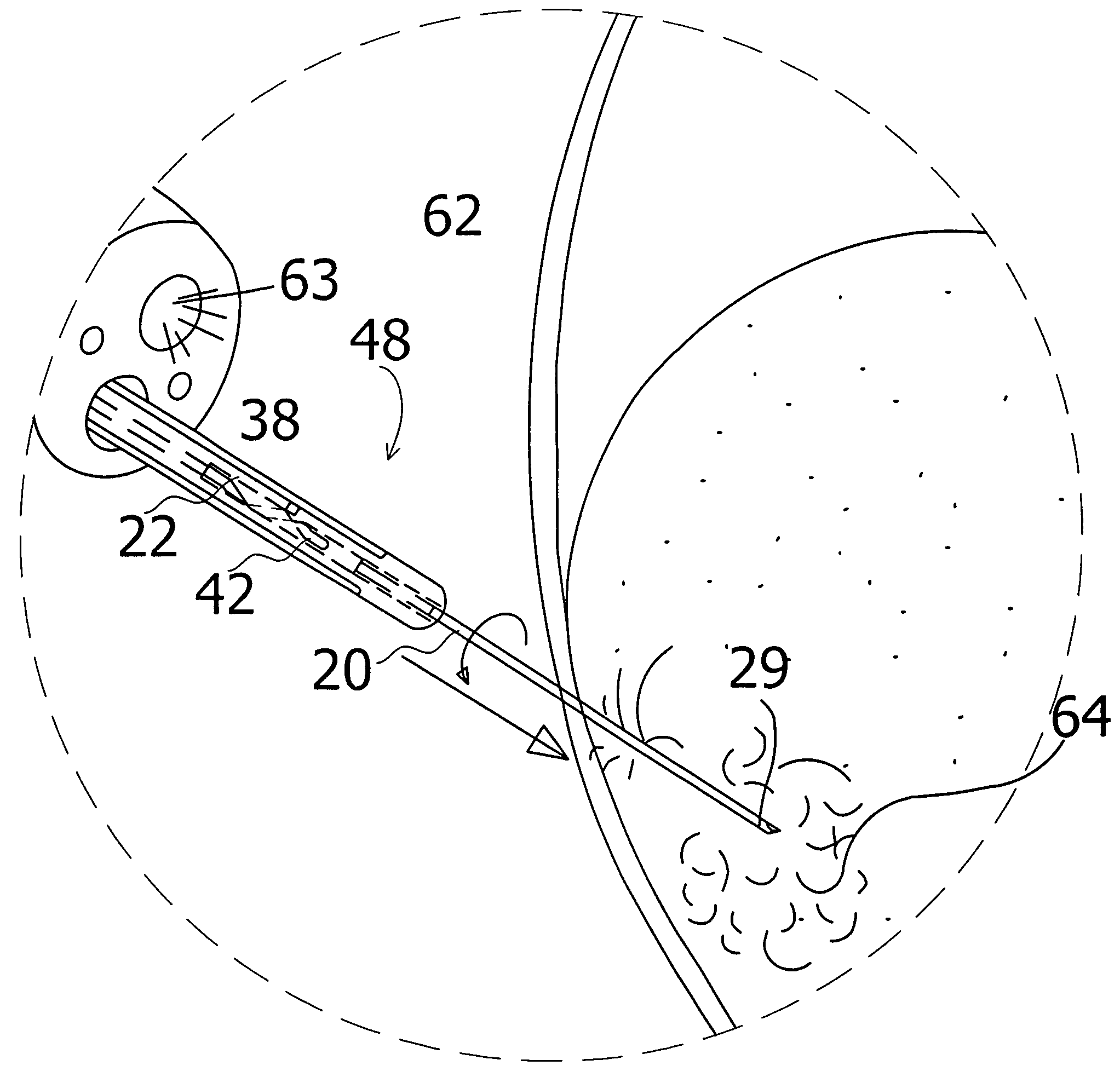
Arrangement for cell sampling
InactiveUS7871383B2Improve permeabilityLow anatomical distortion and dislocationSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsFibrous TumorWilms' tumor
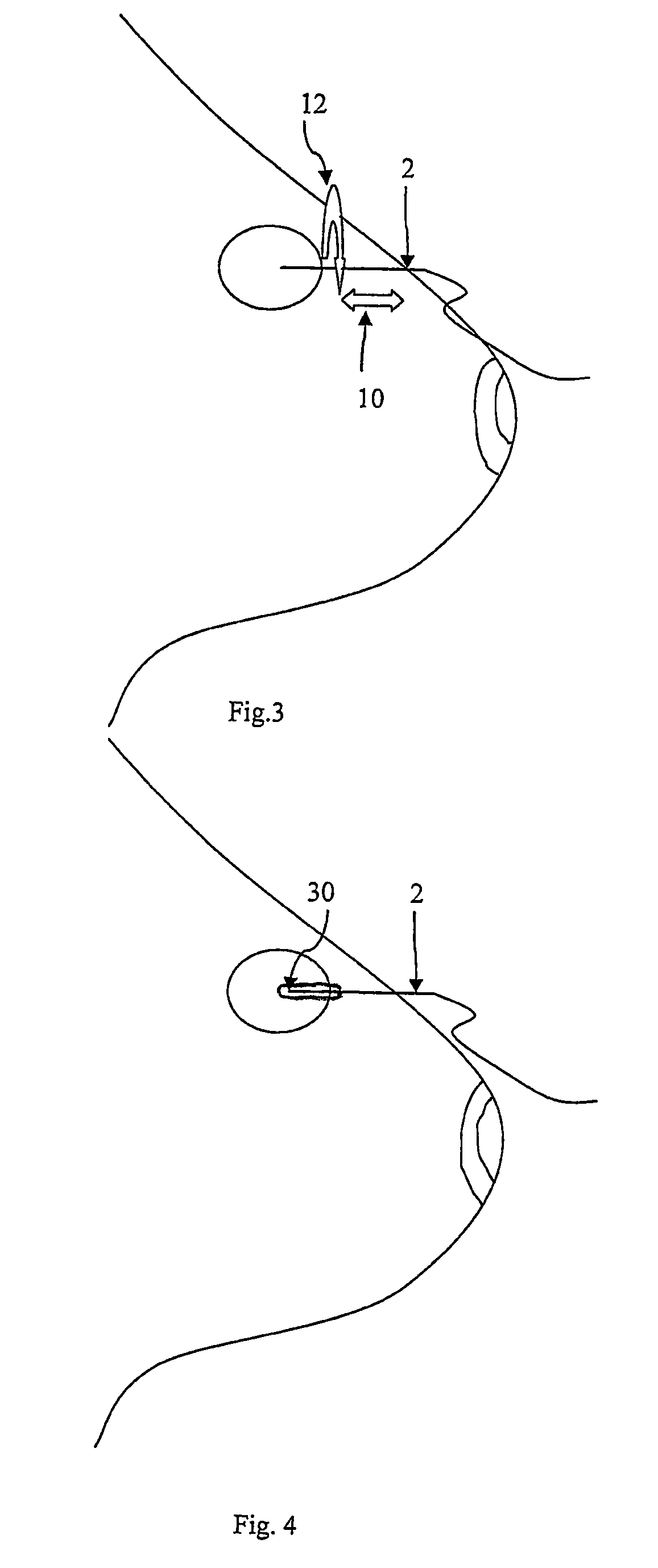
An arrangement for taking a sample of cells from a suspicious lesion or a tumor with the so called fine needle aspiration technique, provides a good penetration of tumors, especially small and / or hard fibrous tumors, and in the meantime yielding an increased amount of cells in the sample, by applying a longitudinal movement to the needle when the needle is penetrating the tumor and by applying both a rotational and a longitudinal movement to the needle when the needle is positioned inside the tumor. The arrangement is further provided with heat generating elements in order to apply a short pulse of heat to the needle in order to lower the risk for the tumor to spread.
Owner:VIBRATECH AB
Endoscopic tri-point biopsy needle
ActiveUS20180228476A1Surgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsIntact tissueTissue Collection
A tri-point tissue-collection needle configured similarly to a fine-needle-aspiration needle is configured to excise intact tissue cores for collection. The distal tip is configured with three beveled points separated by cutting edges, where a single longer / more distal point is trailed by and circumferentially separated from a symmetrical pair of points, providing a bilaterally symmetrical needle cannula distal end. A stylet may be provided through a lumen of the needle during introduction into a patient body, where the distal end surface of the stylet may be configured to complement the tri-point needle end configuration.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Thyroid fine needle aspiration molecular assay
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
Dispensable continuous negative-pressure puncture outfit
ActiveCN101716087APrecise positioningImproving the accuracy level of cytopathological diagnosisSurgical needlesSuction devicesStops deviceSurgery
Owner:余小蒙
MIRNA expression signature in classification of thyroid tumors
InactiveCN106460053AMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsRna expressionThyroid tumors
The present invention provides a method for classification of thyroid tumors through the analysis of the expression patterns of specific microRNAs in fine needle aspiration samples. Thyroid tumor classification according to a microRNA expression signature allows optimization of diagnosis and treatment, as well as determination of signature-specific therapy.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
Arrangement For Cell Sampling
InactiveUS20080058671A1Reduce riskIncrease cell concentrationSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsRadiologyEngineering
An arrangement for taking a sample of cells from a suspicious lesion or a tumour with the so called fine needle aspiration technique, provides a good penetration of tumours, especially small and / or hard fibrous tumours, and in the meantime yielding an increased amount of cells in the sample, by applying a longitudinal movement to the needle when the needle is penetrating the tumour and by applying both a rotational and a longitudinal movement to the needle when the needle is positioned inside the tumour. The arrangement is further provided with heat generating elements in order to apply a short pulse of heat to the needle in order to lower the risk for the tumour to spread.
Owner:VIBRATECH AB
Compositions and methods for DNA and RNA extraction from tissue samples
Methods and reagents are provided for the rapid extraction of nucleic acids from a cell or tissue sample. In certain embodiments the sample comprises a formalin fixed paraffin embedded sample (e.g., aFFPET sample), or a fine needle aspirate and / or a cell / tissue smear. In some embodiments, the methods comprise incubating one or more sections of said tissue sample in a lysis solution comprising a buffer sufficient to maintain the pH of said solution at a pH ranging from about pH 4 to about pH 9; a chaotropic agent; a chelating agent; and a detergent; where the incubating is at a temperature ranging from about 50 DEG C to about 100 DEG C; and recovering the nucleic acid from said lysis solution.
Owner:CEPHEID INC
Extraction method of genome DNA and RNA from fine needle aspiration material
The invention discloses a method for extracting genome DNA and RNA from a fine needle aspiration biopsy material. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing a turbine mixer to mix a cell lysis solution and a sample of a trace of biopsy material, implementing simultaneous extraction of DNA and RNA, and substituting the conventional liquid nitrogen grinding or mechanical pulverization method which can only extract the DNA and RNA respectively as the loss of the sample during the operation process is high. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in operation steps, low in cost, low in required sample capacity, short in experiment operating time, and capable of effectively preventing degradation of the DNA and RNA; the concentration, the purity and the integrity of the extracted DNA and RNA can meet the follow-up analytic requirement on genomics in various aspects.
Owner:天津迈安诊生物技术有限公司 +1
All-in-one optical microscopic handle
InactiveUS20110130679A1Improved needle penetrationEasy to handleSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsNeedle insertionElectron
The present invention discloses an all-in-one fine needle aspiration means (FNA) for precision guidance and improved control of needle for ease of insertion, manipulation and efficient extraction of sample and a method thereof. Said FNA comprises means selected from a mechanically or electronically stabilized effecter; a mechanical or automated needle insertion and manipulation mechanism; optical means; a mechanical or automated vacuum or suction mechanism; and a biopsy collection receptacle.
Owner:BRESLAUER REUVEN +1
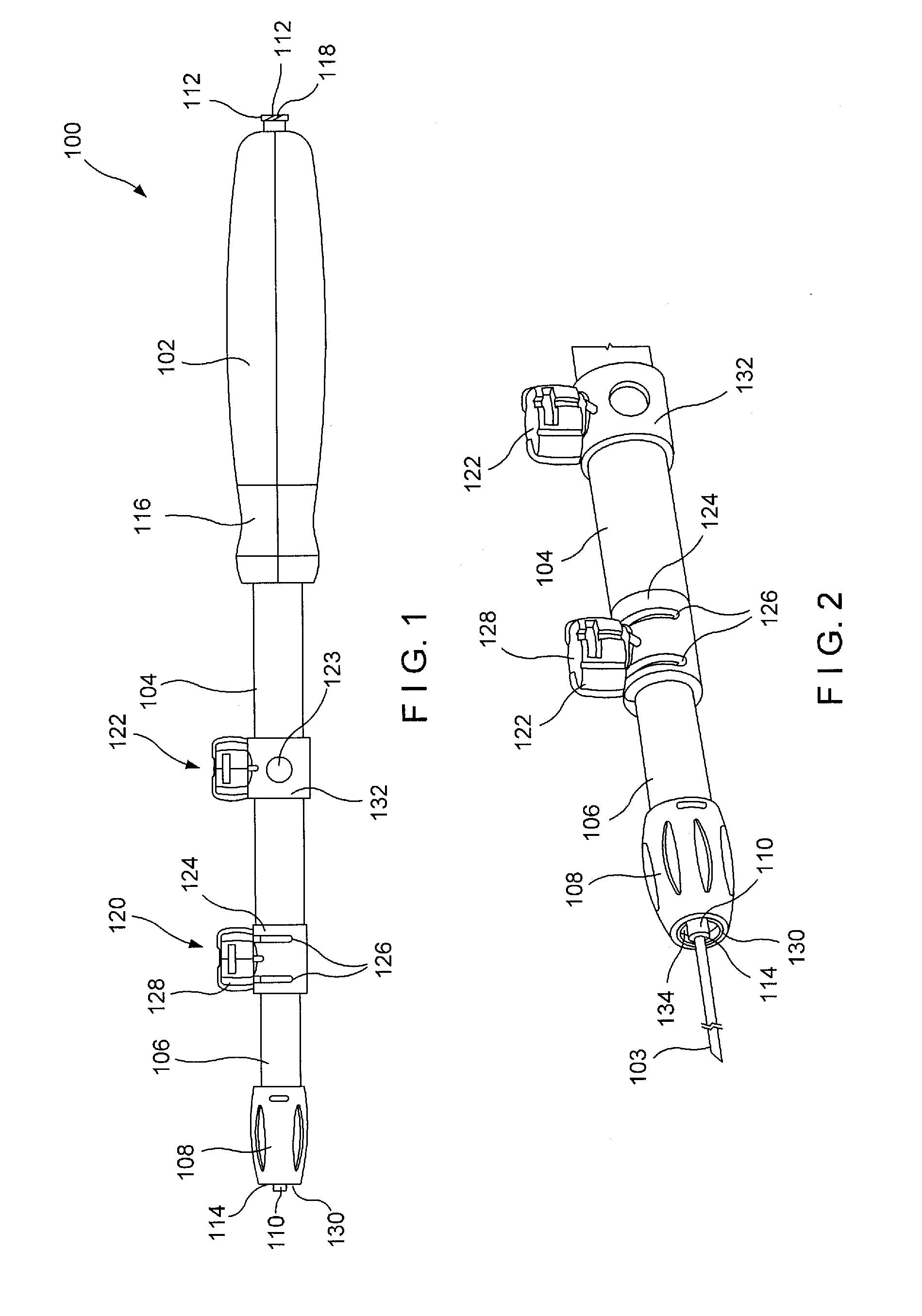
System and method for fine needle aspiration
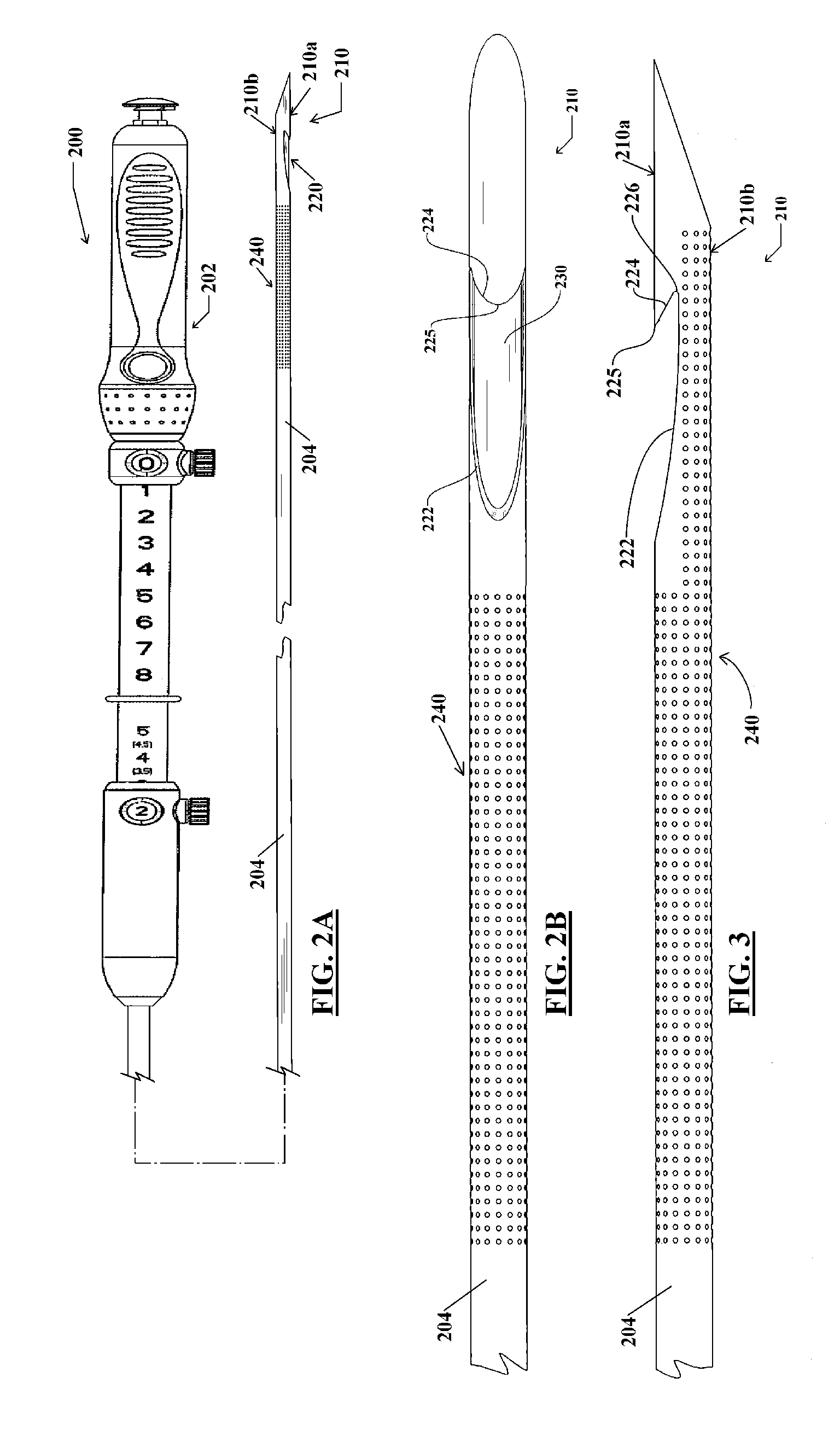
InactiveUS20150005662A1Improving fine needle aspirationPromote absorptionSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsVertical edgeBiomedical engineering
A system and method for fine needle aspiration includes a plurality of components. A device includes a body unit, a trigger unit, and at least one gear. The body unit is configured to hold a syringe, and the trigger unit is configured to laterally move relative to the body unit in order to extend and retract a plunger within the syringe. The at least one gear is configured to engage the syringe so that lateral movement of the trigger unit causes rotation of the syringe. A needle includes a distal tip with a vertical edge extending from a distal end to a proximal end, and a curved edge running from the distal end to the proximal end. A syringe kit includes a stylet connected to the plunger. The stylet includes an outer diameter equal to an inner diameter of the needle.
Owner:BRIK ROBERT +7
Flared Needle for EUS Fine Needle Aspiration Device
InactiveUS20110046512A1Increase the diameterSmall outer diameterSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsDistal portionTissue sample
A device for gathering tissue samples includes a needle defining a distal tissue penetrating tip. The needle includes an increased diameter proximal portion extending proximally from the distal tip. An outer diameter of the distal tip is smaller than an outer diameter of the proximal portion. The needle defines a lumen extending therethrough from a distal opening in the distal tip thereof to a proximal opening at a proximal end thereof. The lumen includes a distal portion having a first inner diameter and a proximal portion having a second diameter greater than the first diameter. The device also includes a stylet slidably received within the lumen. An outer diameter of a distal portion of the stylet is substantially equal to the inner diameter of the distal portion of the lumen so that, when the stylet is in an extended position extending to the distal opening of the lumen, the lumen is substantially sealed thereby, and when, in a retracted position in which a distal end of the stylet is received within the proximal portion of the lumen, an annular space surrounding the stylet defines an aspiration path for samples exiting the distal portion of the lumen.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided notched biopsy needle
A notched tissue-collection needle configured similarly to a fine-needle-aspiration needle is provided with a cutting edge disposed in the notch and configured to excise tissue into the notch for collection. A stylet may be provided through a lumen of the needle during introduction into a patient body. The needle may be provided with echogenicity-enhancing features.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Fine needle arrangement for cell sampling
InactiveUS20100160828A1Reduce riskIncrease cell concentrationSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsCouplingLesion
Fine needle arrangement for taking a sample of cells from suspicious lesions by using fine needle aspiration (FNA) technique, including a tubular needle member (1), a storage compartment (2) enclosing a chamber, and a coupling (3) to which a connector may be attached. The chamber is configured with a gradually increasing cross-sectional area from the distal part of the chamber to the proximal part of the chamber, such that the chamber has no residual spaces where cell samples may be trapped, and that an efficient air streaming is achieved.
Owner:NEODYNAMICS
Methods for lung cancer classification
ActiveUS20140309123A1Accurate classificationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningFine needle biopsyFormalin fixed paraffin embedded
The present invention provides specific nucleic acid sequences for use in the identification, classification and diagnosis of various sub-types of lung cancers. The present invention permits one to accurately classify lung cancers based on their miR expression profile without further manipulation. Using microRNA microarray data generated from over two hundred formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) resection samples, fine needle aspiration (FNA) samples and fine needle biopsy (FNB) samples of primary lung cancer, microRNA expression profiles were identified that differ significantly for various sub-types of lung cancer.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
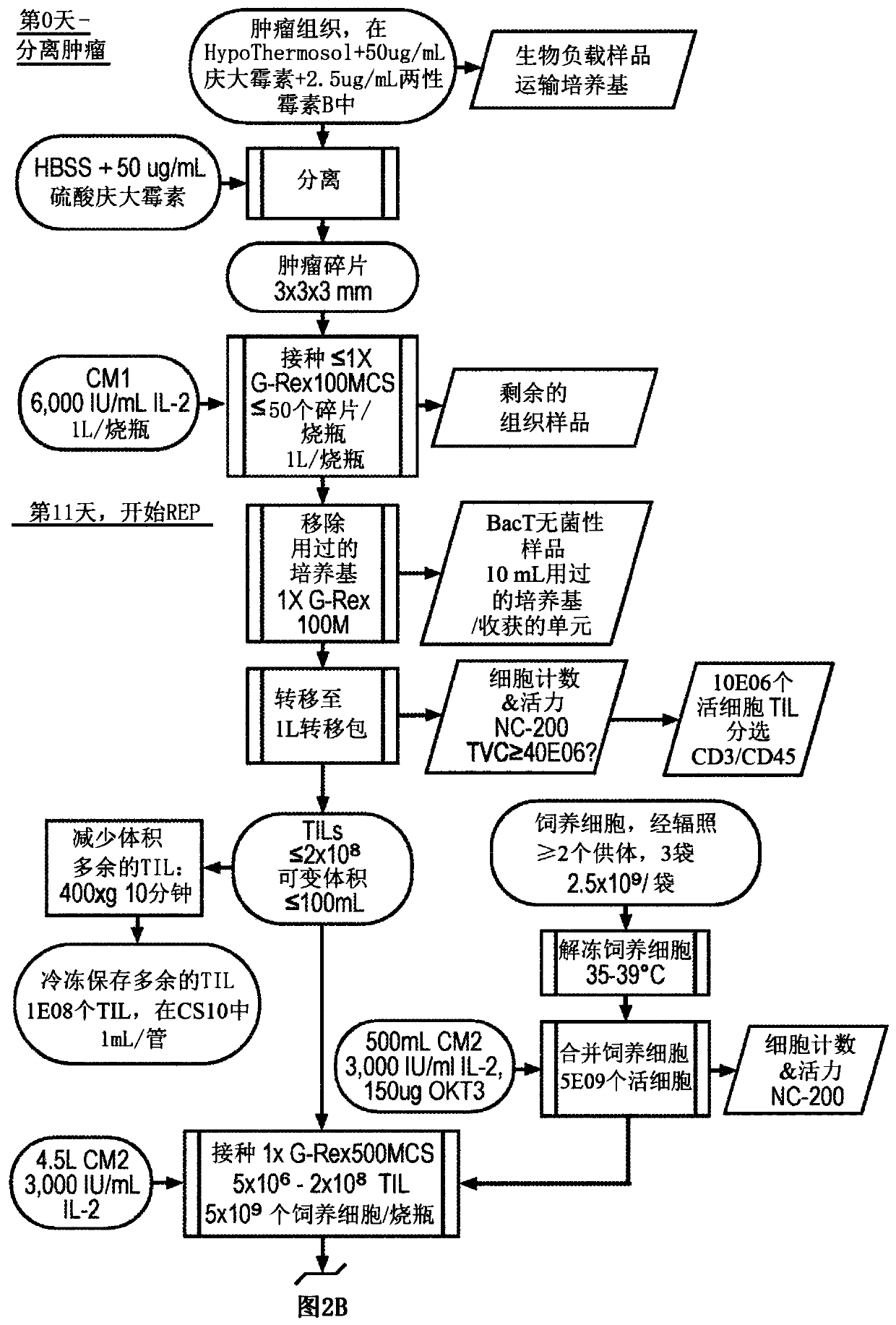
Til expansion from fine needle aspirates and small biopsies
The present disclosure provides methods for expanding TIL populations from fine needle aspirates (FN As) or small biopsies which contain low numbers of TILs, using the methods disclosed herein including in a closed system that leads to improved phenotype and increased metabolic health of the TILs in a shorter time period.
Owner:IOVANCE BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Endoscopic Ultrasound Fine Needle Aspiration Device
A handle for a medical device includes a proximal segment defining a proximal lumen extending therethrough and sized and shaped to receive an endoscopic medical device therein. A medial segment is received within a distal portion of the proximal segment and has an outer diameter smaller than an inner diameter thereof. A medial lumen extends through the proximal segment and is open to the proximal lumen. A distal segment is received within a distal portion of the medial segment and defines a distal lumen extending therethrough open to the medial lumen. The distal segment has an outer diameter smaller than an inner diameter of the medial segment. The medial segment includes a first movement limiting mechanism limiting movement of an endoscopic medical device inserted therethrough along an axis of the distal lumen and a second movement limiting mechanism limiting advancement of an endoscope attached to the distal body portion.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Preparation method for thyroid and mammary fine needle aspiration cell tissue blocks
ActiveCN109975090ASimple structureNo privacy involvedPreparing sample for investigationHydrothoraxThyroid
The invention provides a preparation method for thyroid and mammary fine needle aspiration cell tissue blocks. The method includes the following steps: a, performing centrifugation on hydrothorax or ascites in advance, and obtaining hydrothorax or ascites supernatant; b, taking the hydrothorax or ascites supernatant to inject into a centrifuge tube; c, injecting a fine needle punctured thyroid andmammary specimen into the centrifuge tube, and then immediately taking 95% of ethanol to inject into the centrifuge tube; and d, performing centrifugation on the centrifuge tube and abandoning the supernatant so that cell sediment can be obtained, adding 4% of neutral buffer formaldehyde fixative, and adopting a paraffin tissue specimen processing program to perform conventional embedding after the cell sediment in the centrifuge tube is solidified. The preparation method can guarantee that tissue fragments and free-floating single cells are not lost; and cytoplasm is good in form and structure preservation, can be sliced continuously or for many times, and is suitable for a plurality of dyeing, and therefore, diagnosis efficacy can be enhanced.
Owner:马晓丽
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com