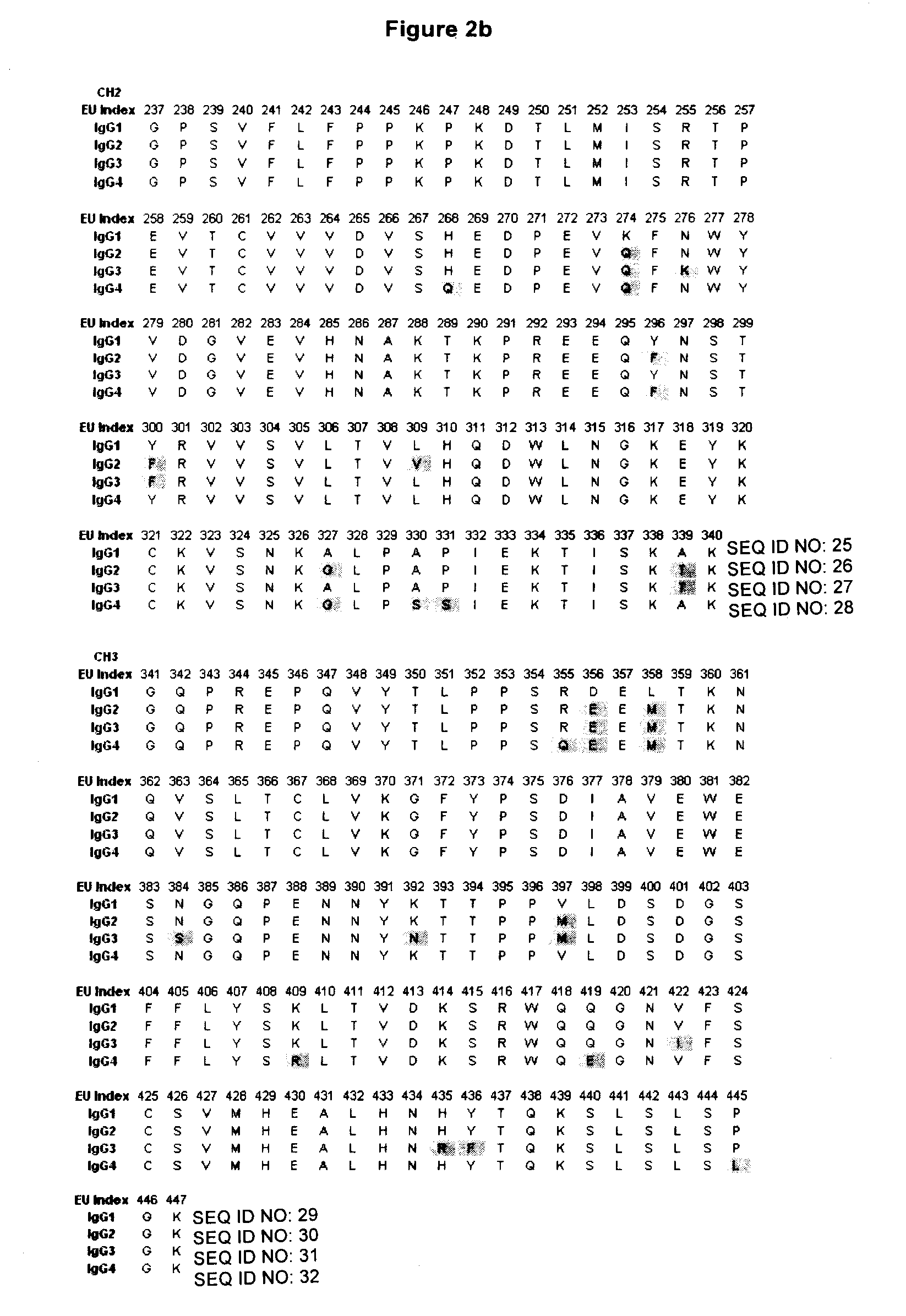
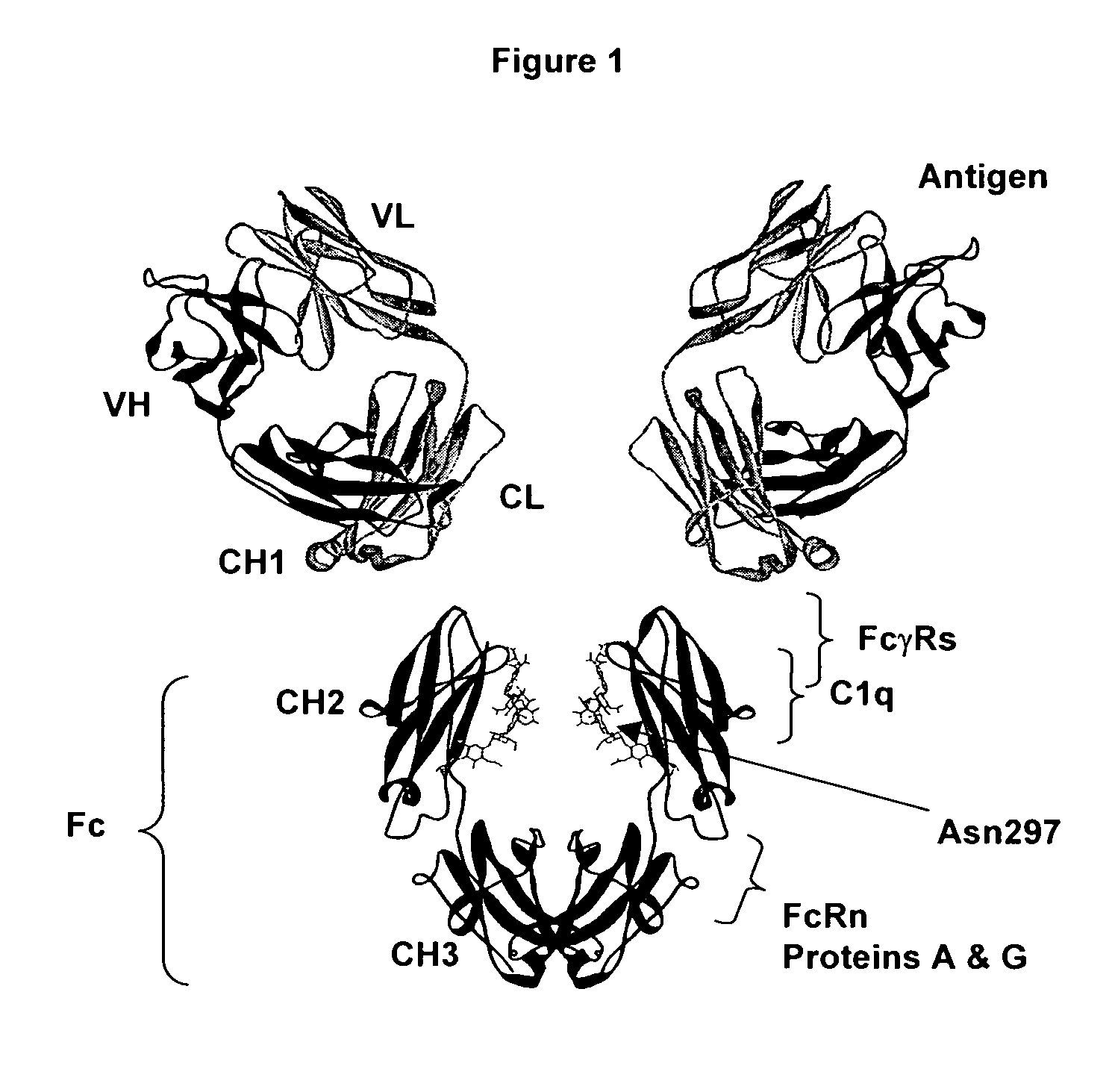
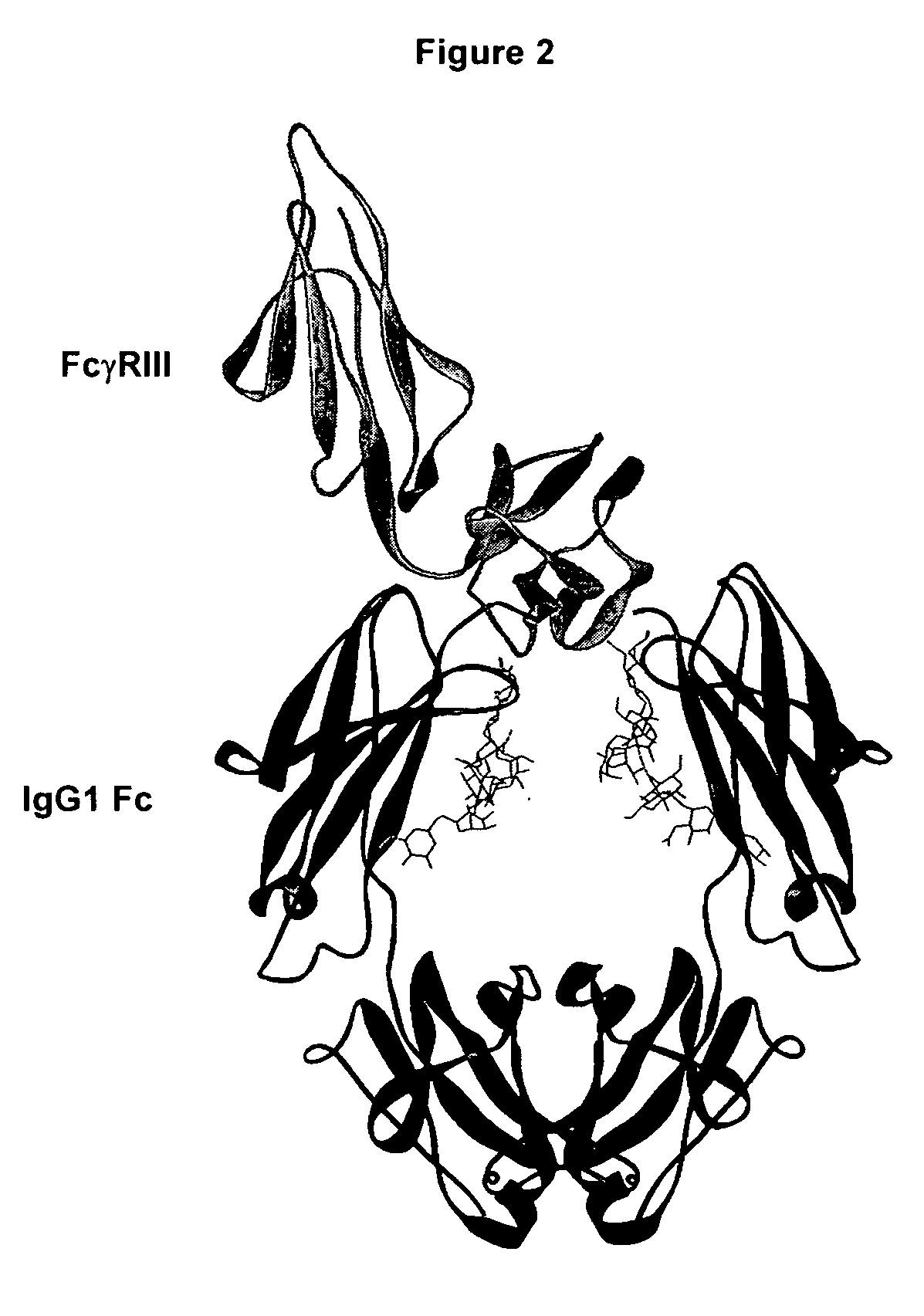
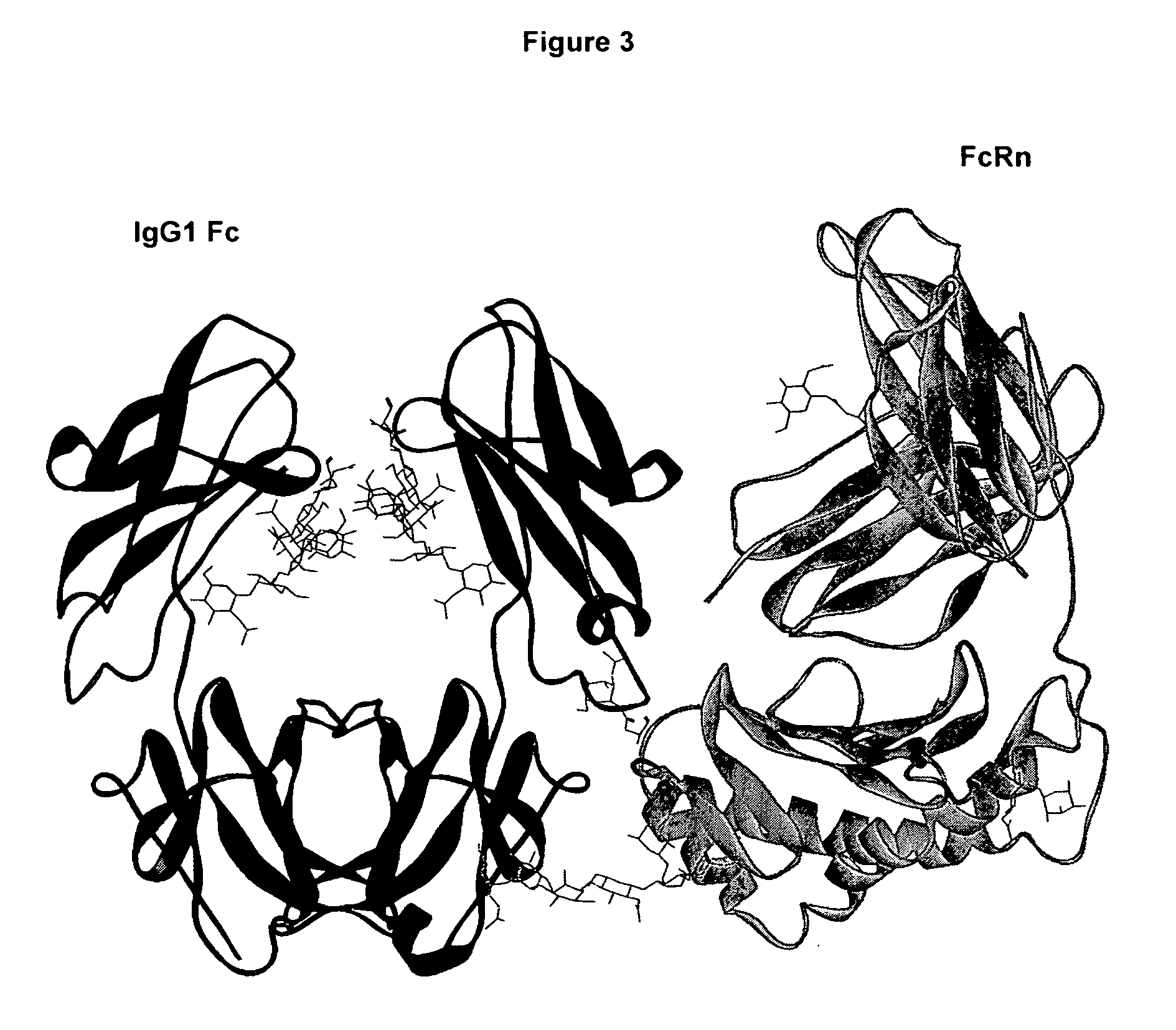
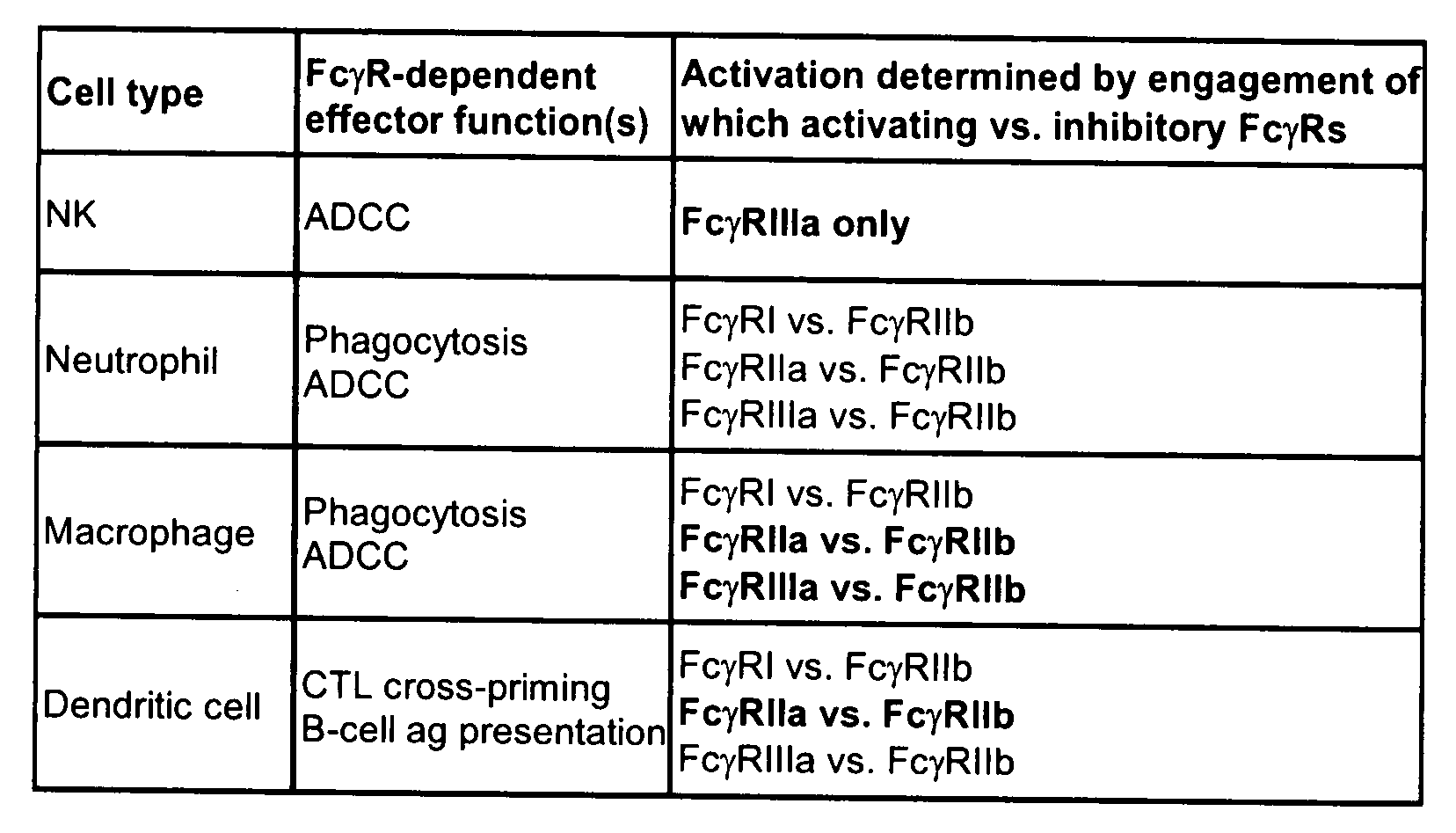
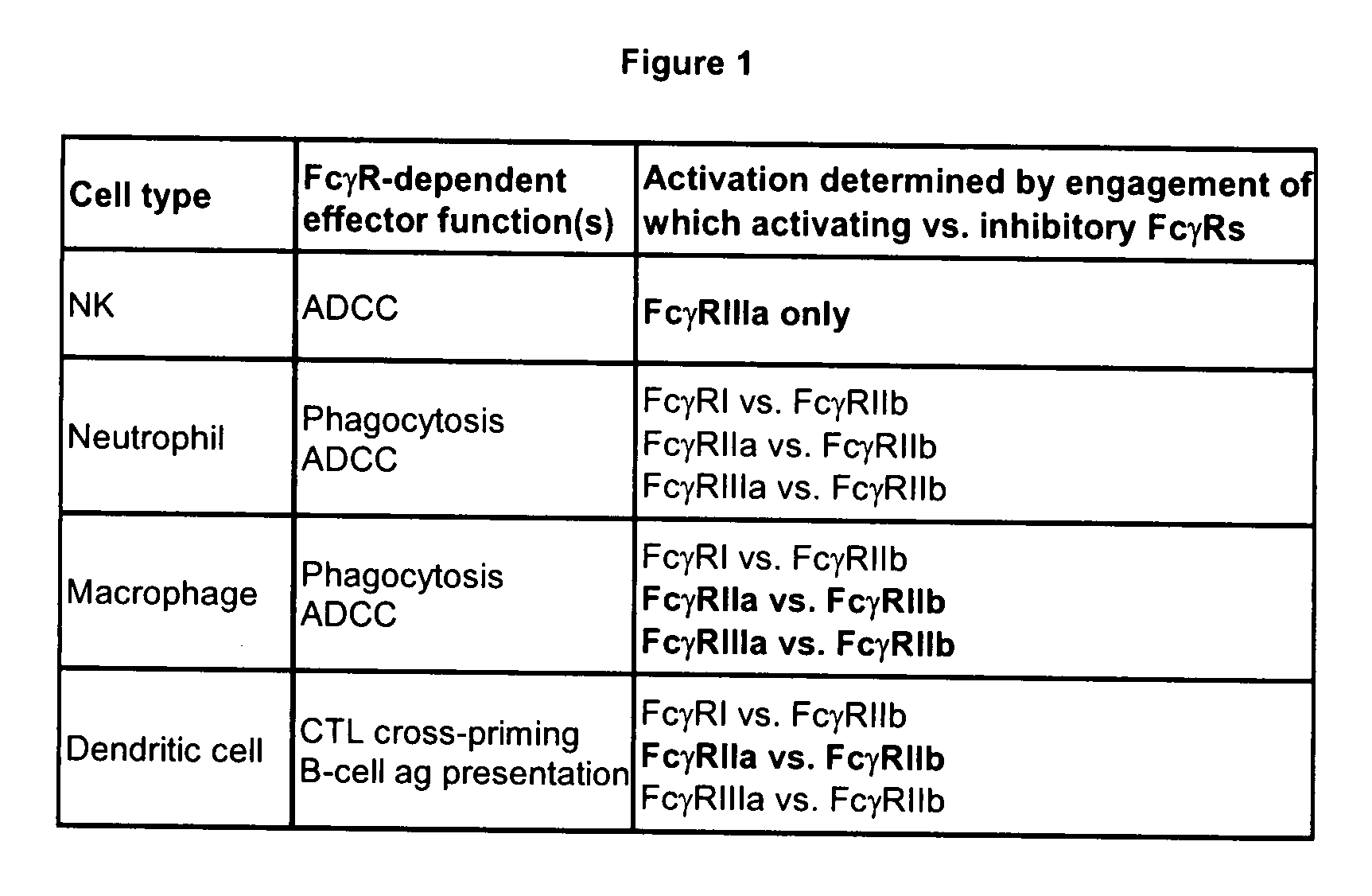
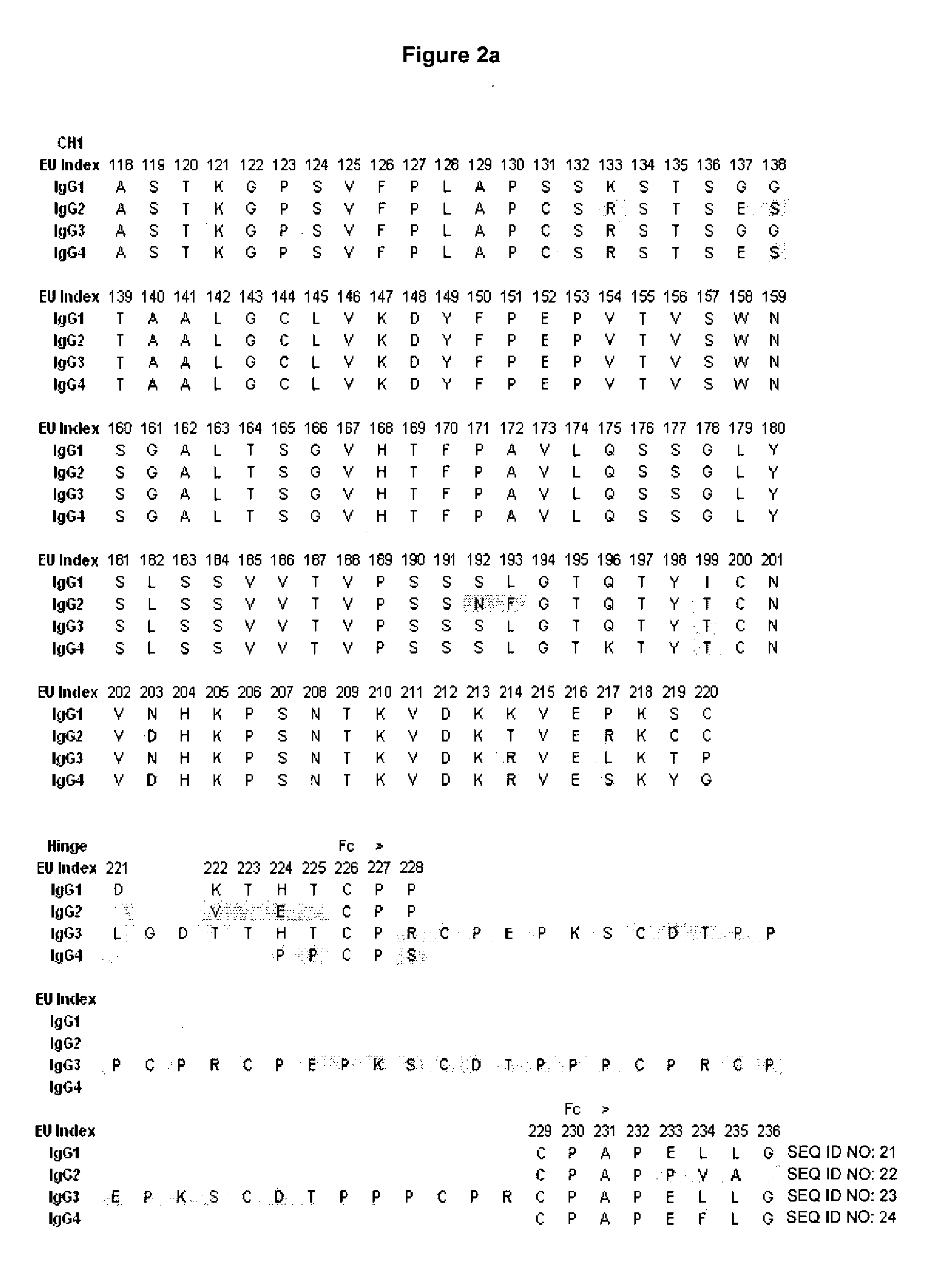
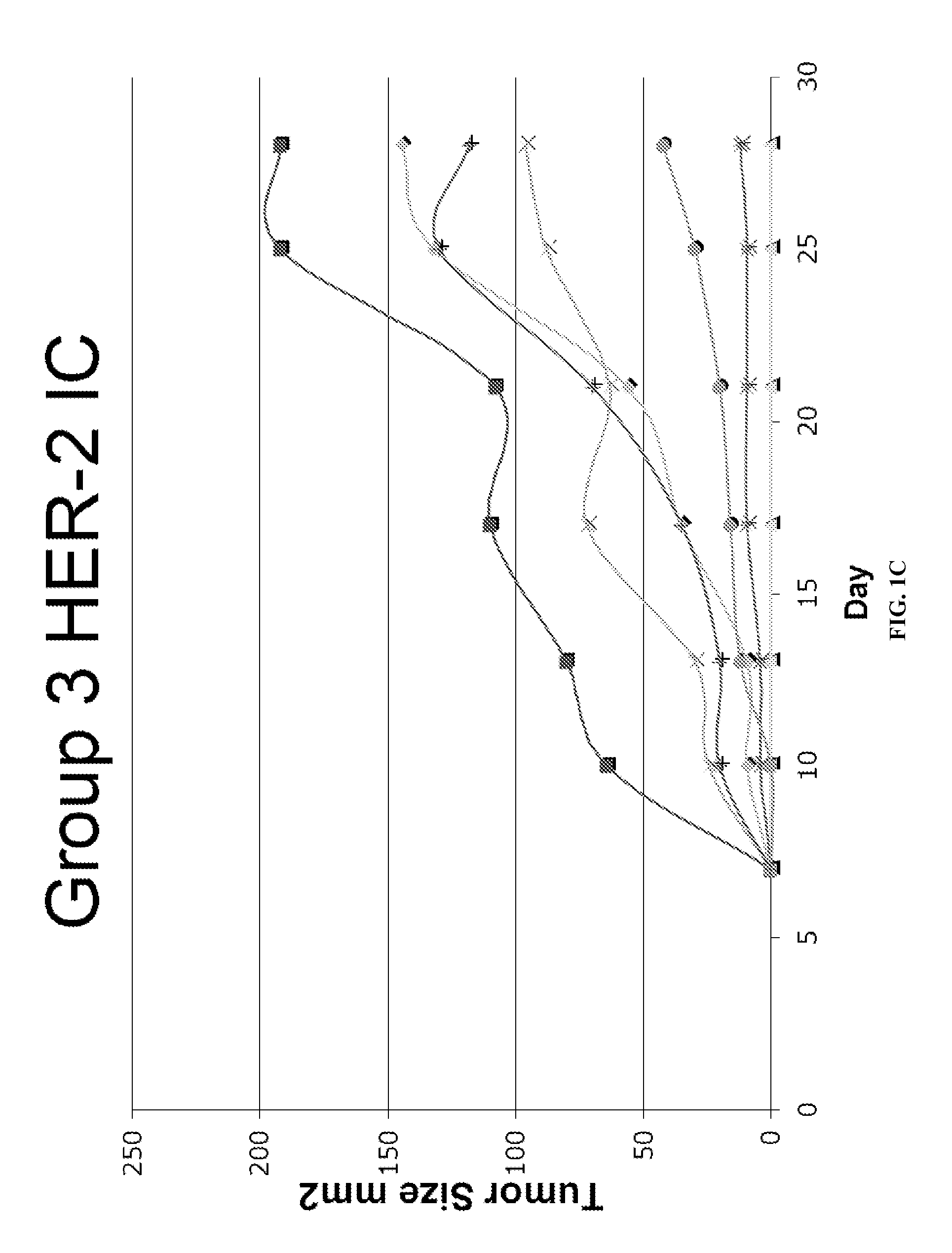
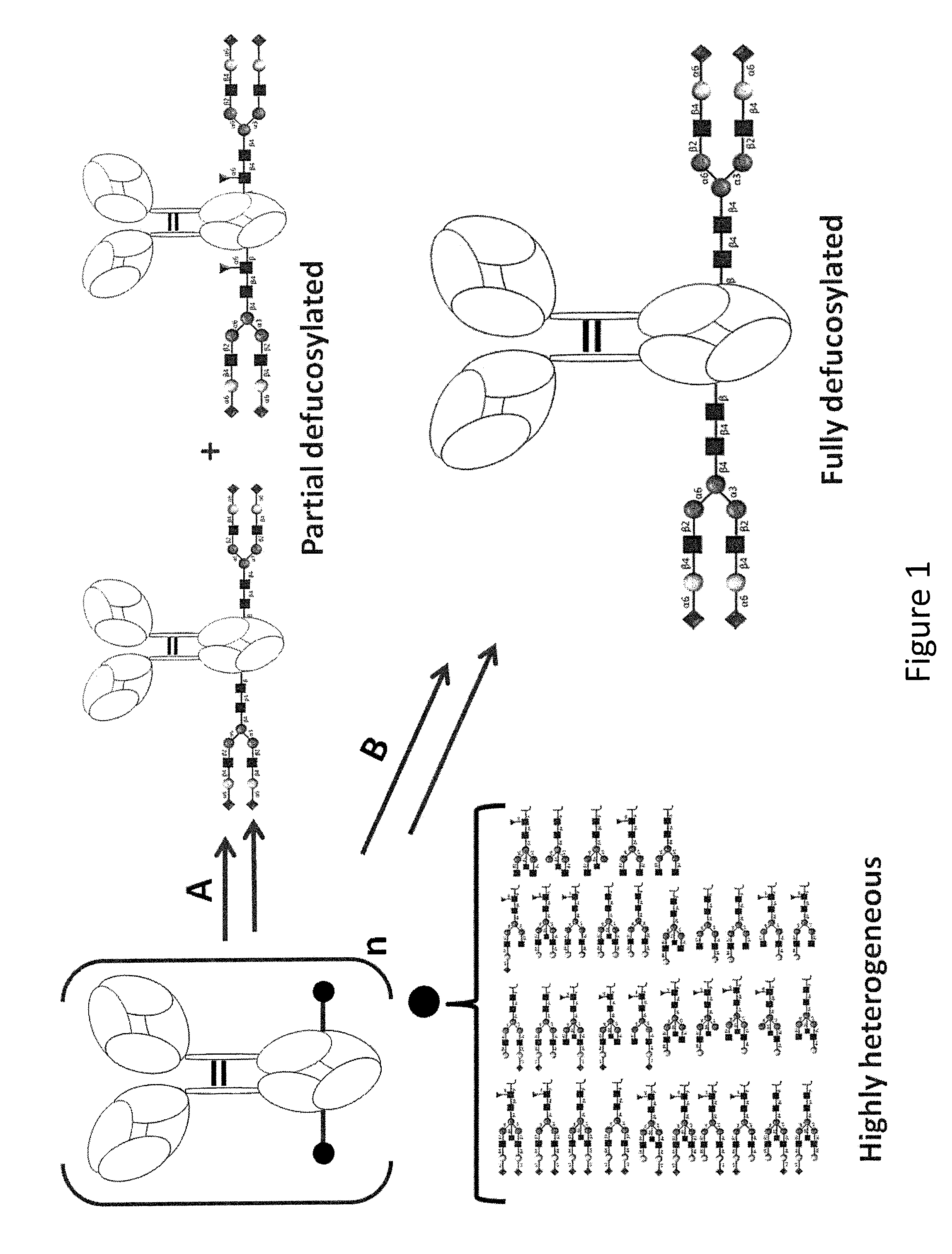
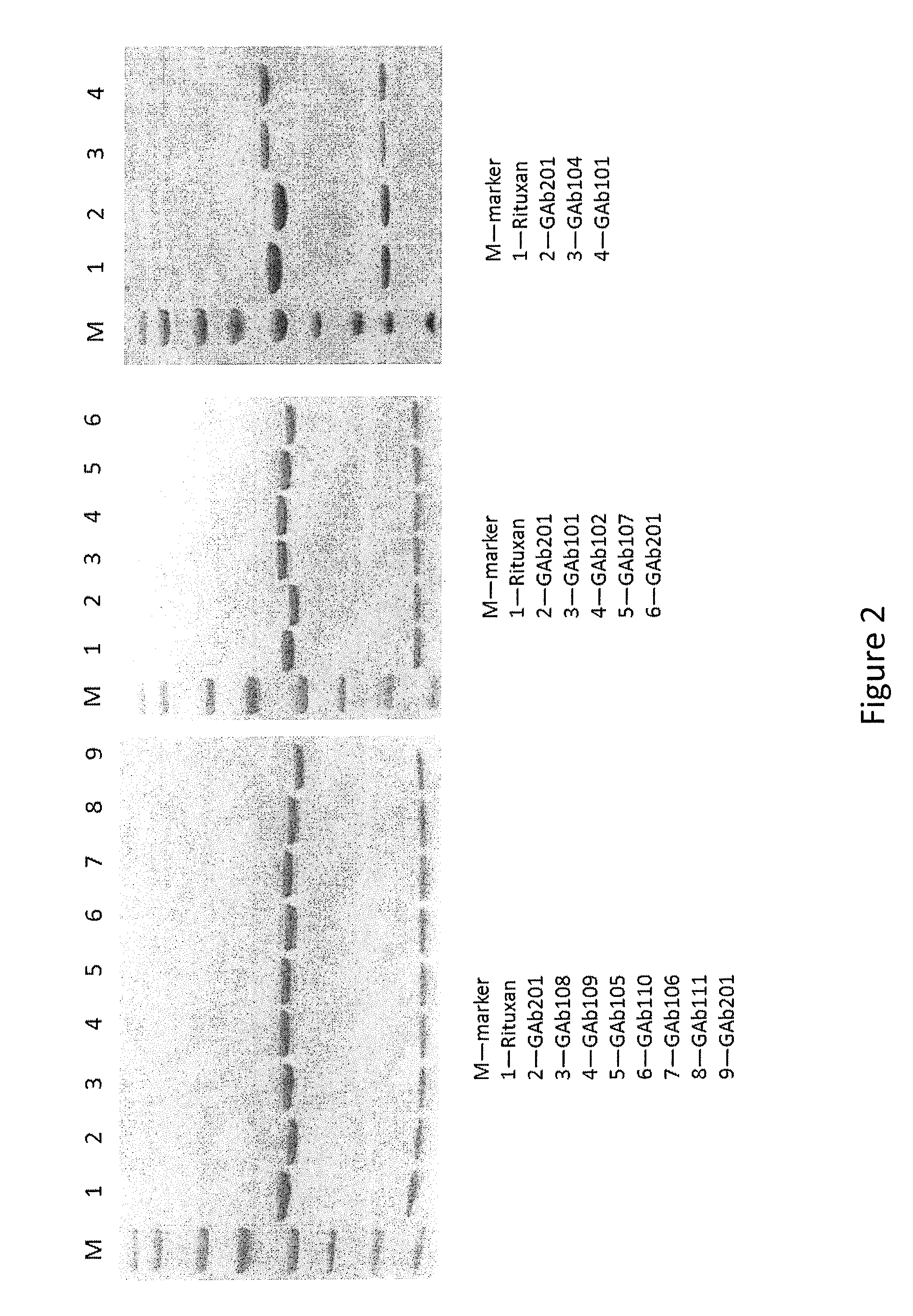
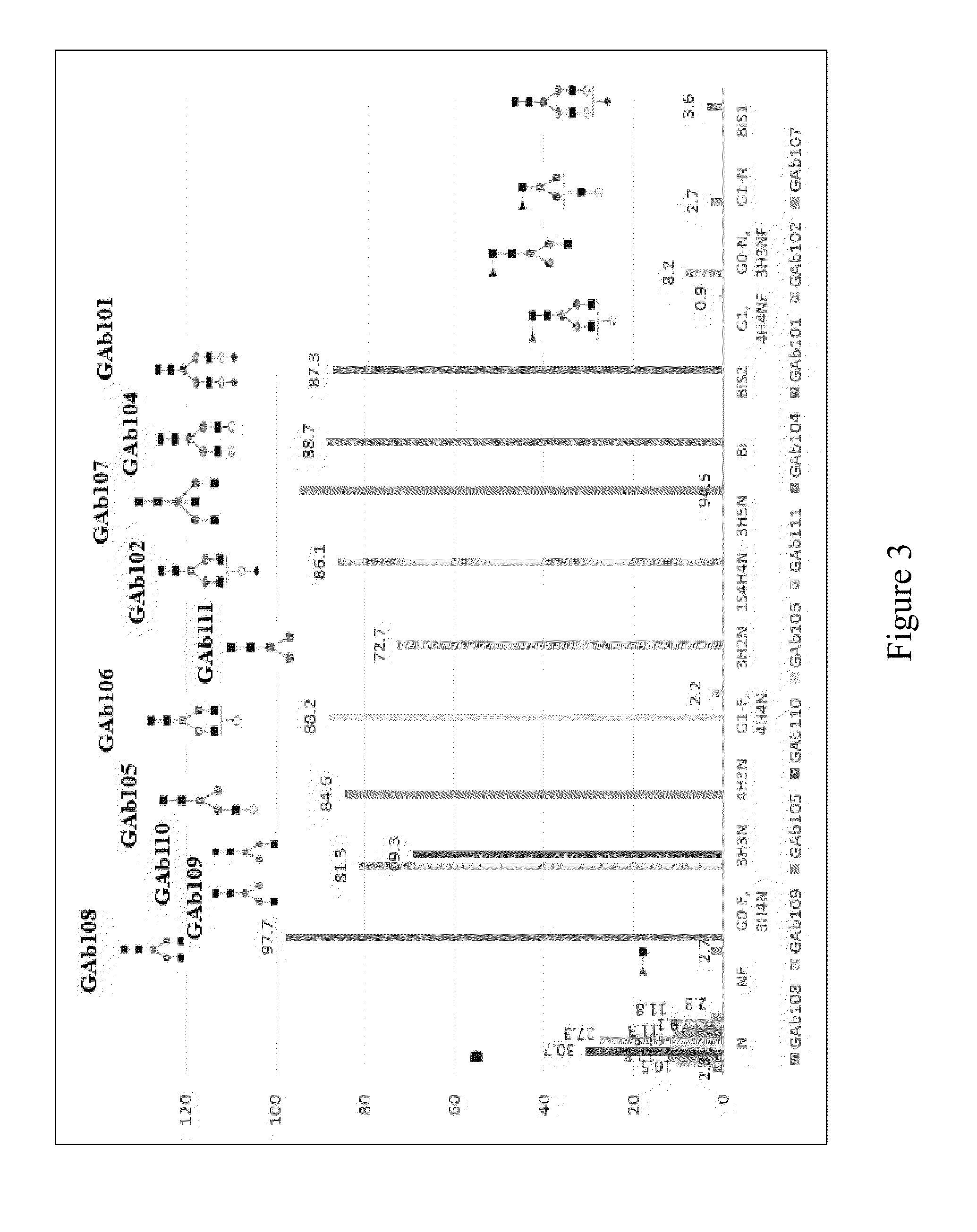
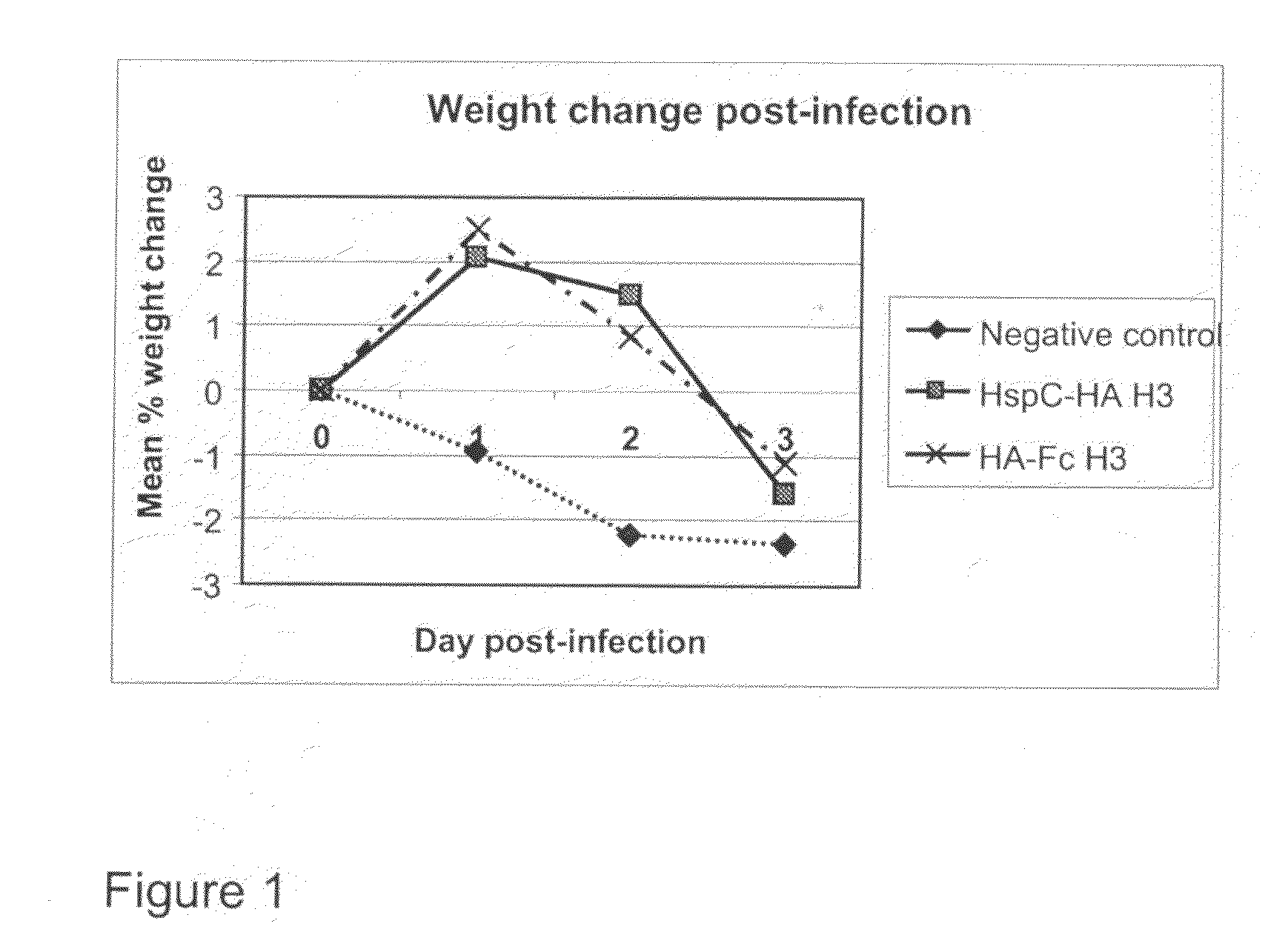
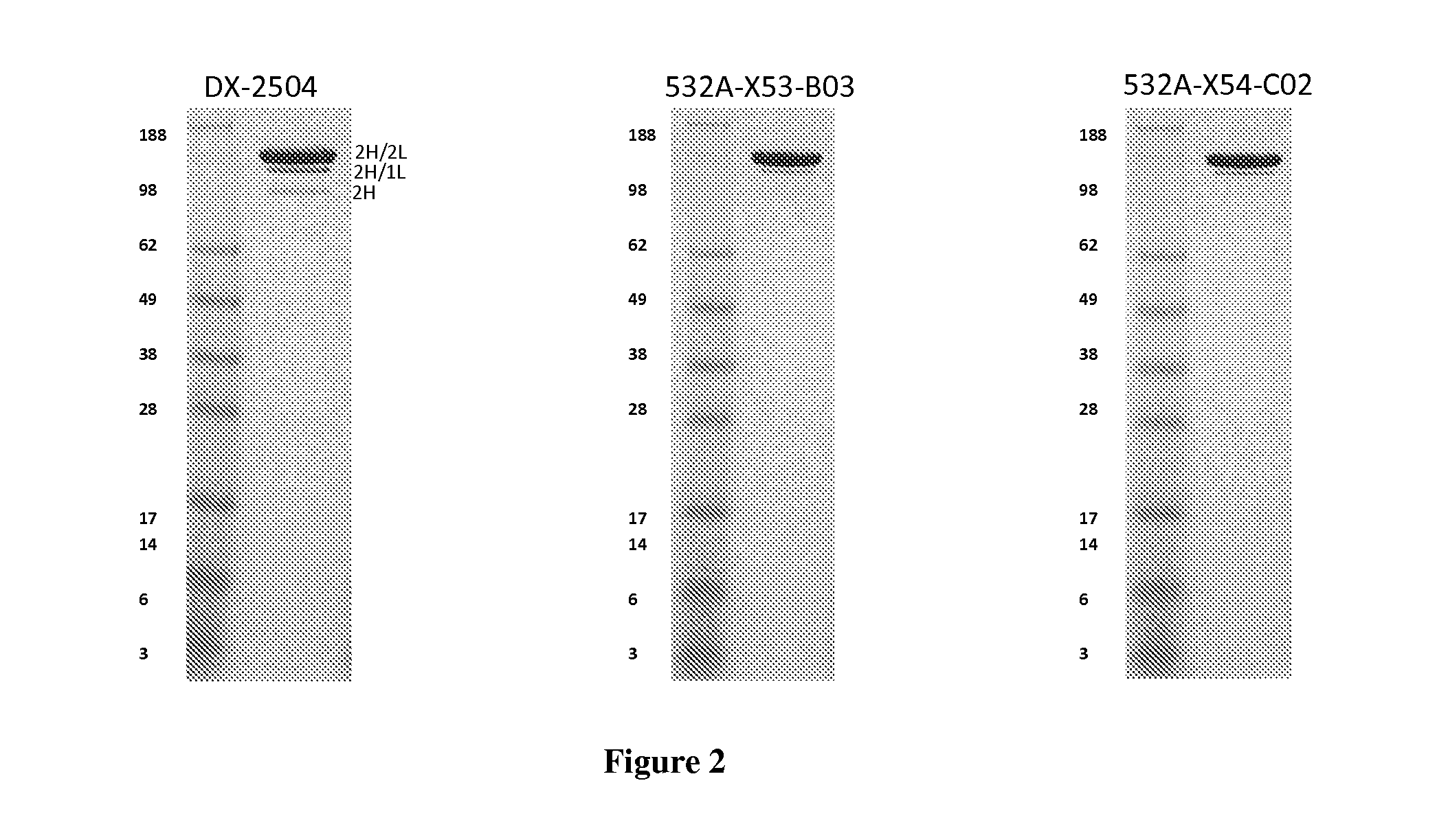
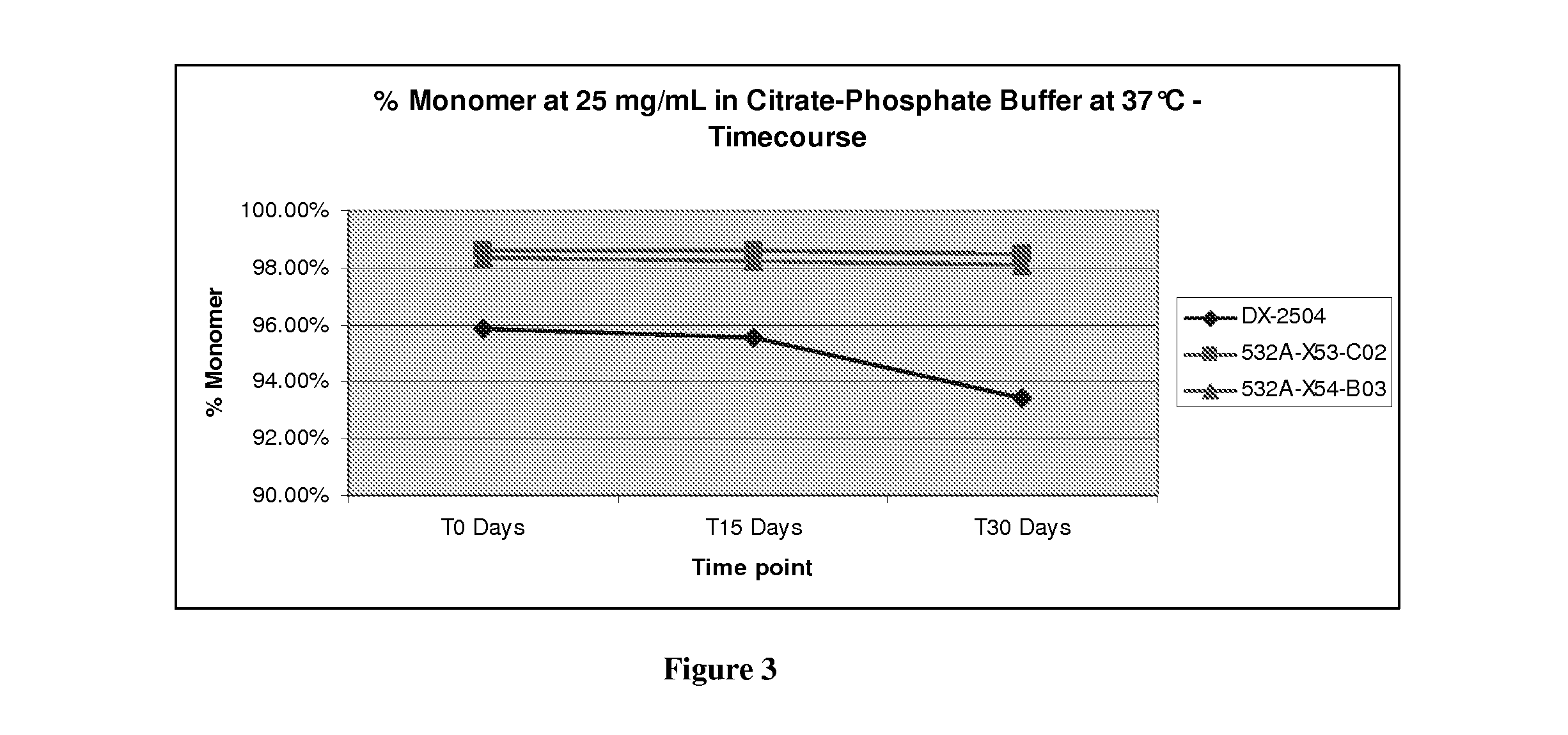
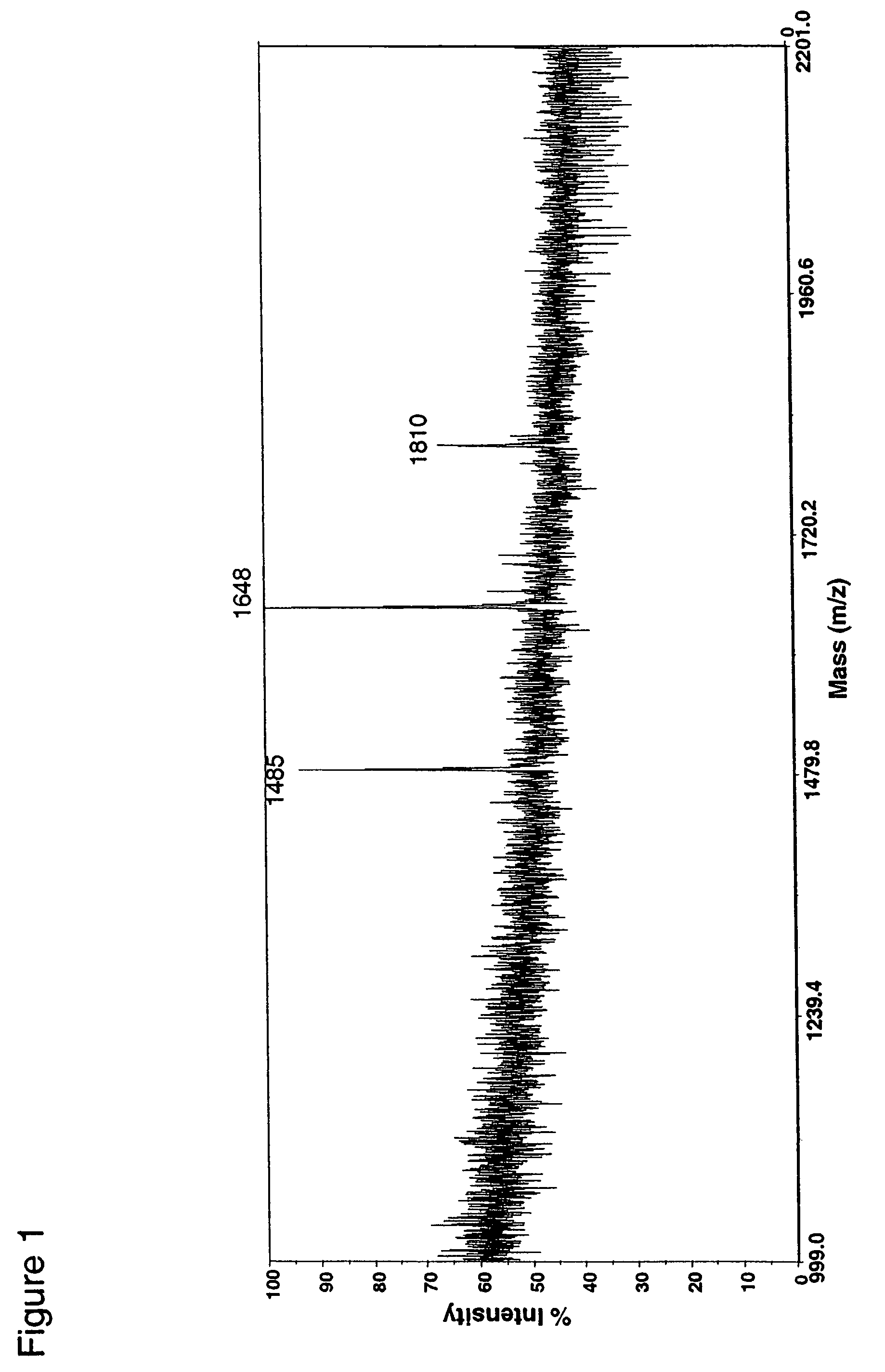
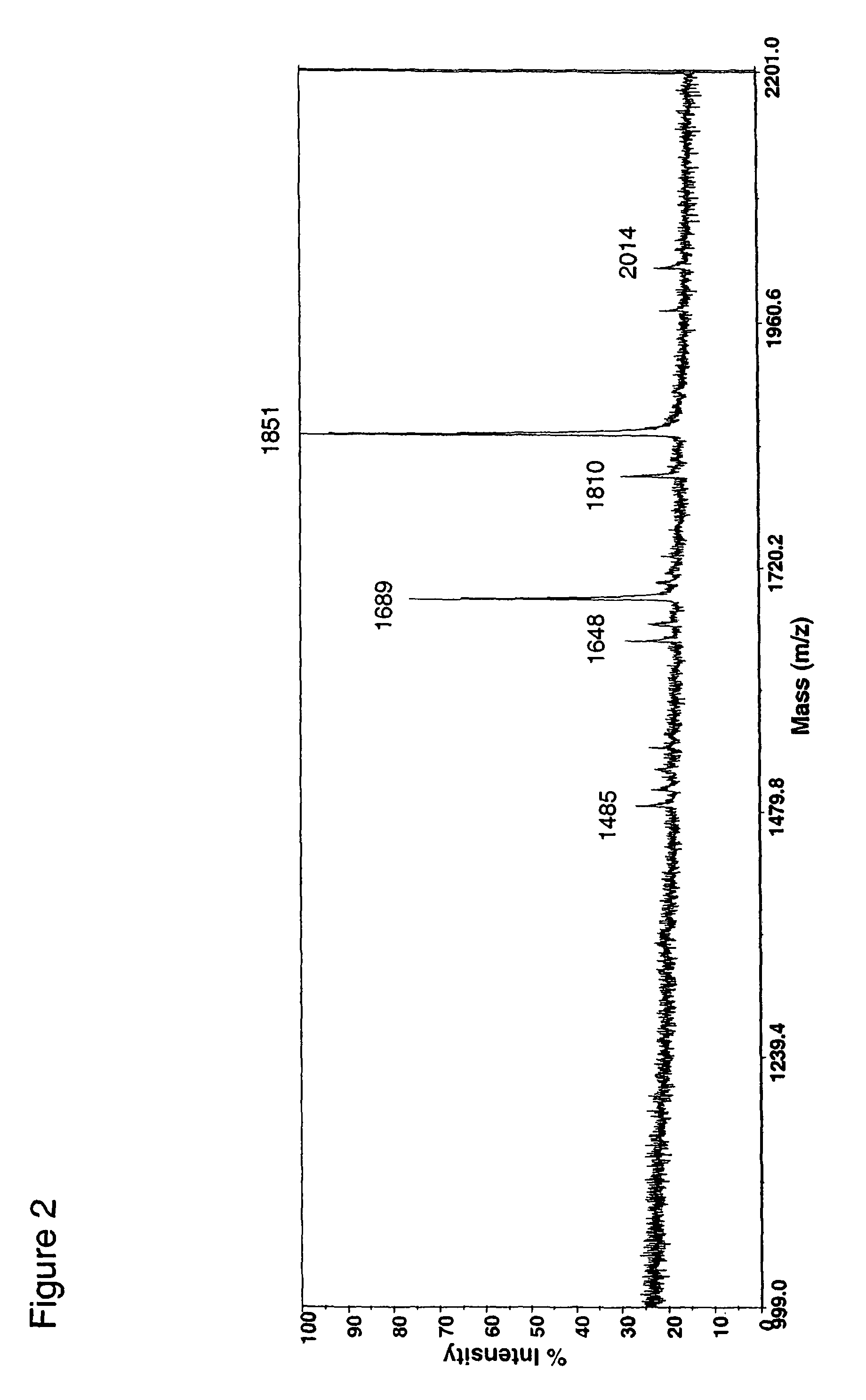
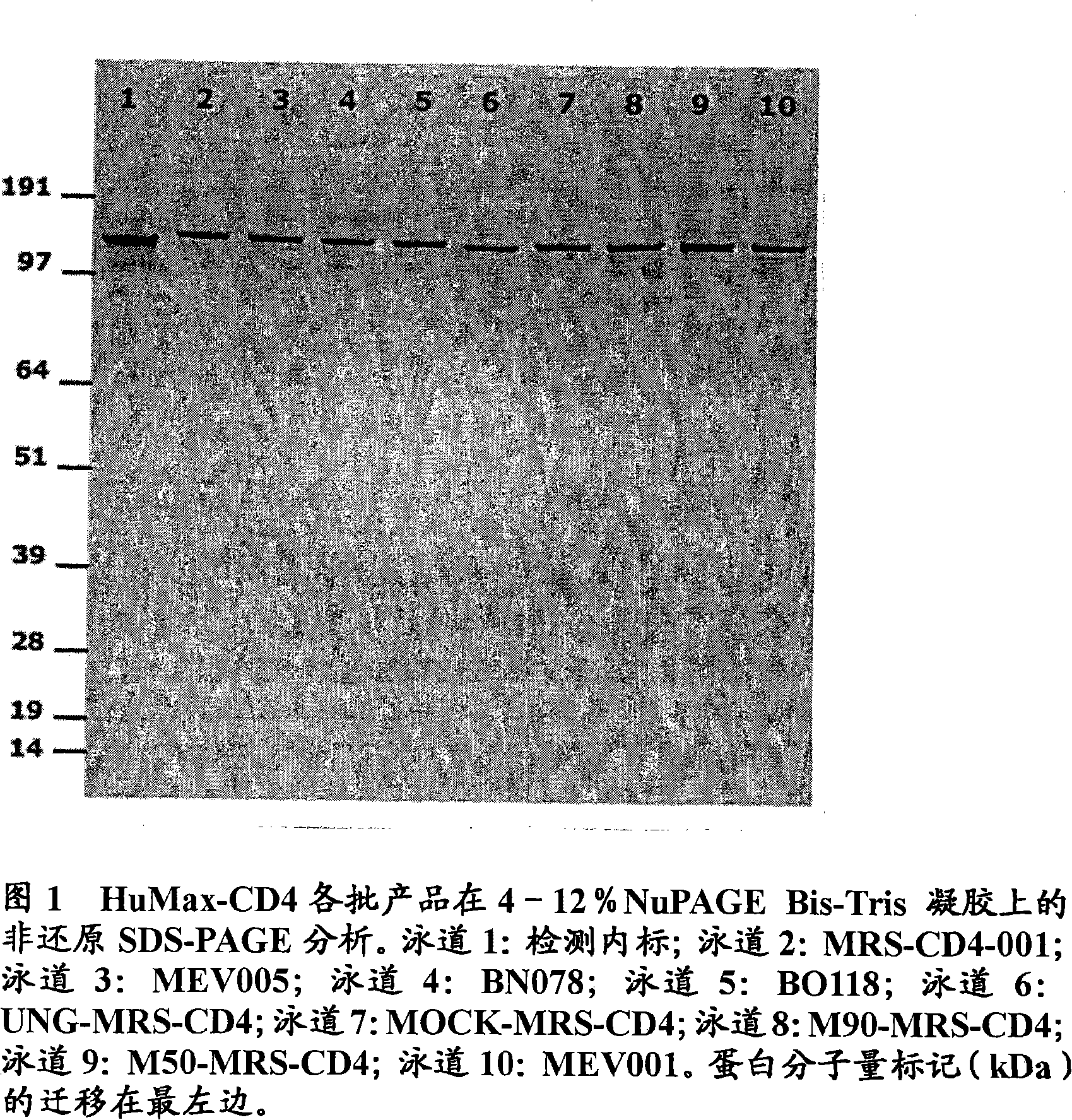
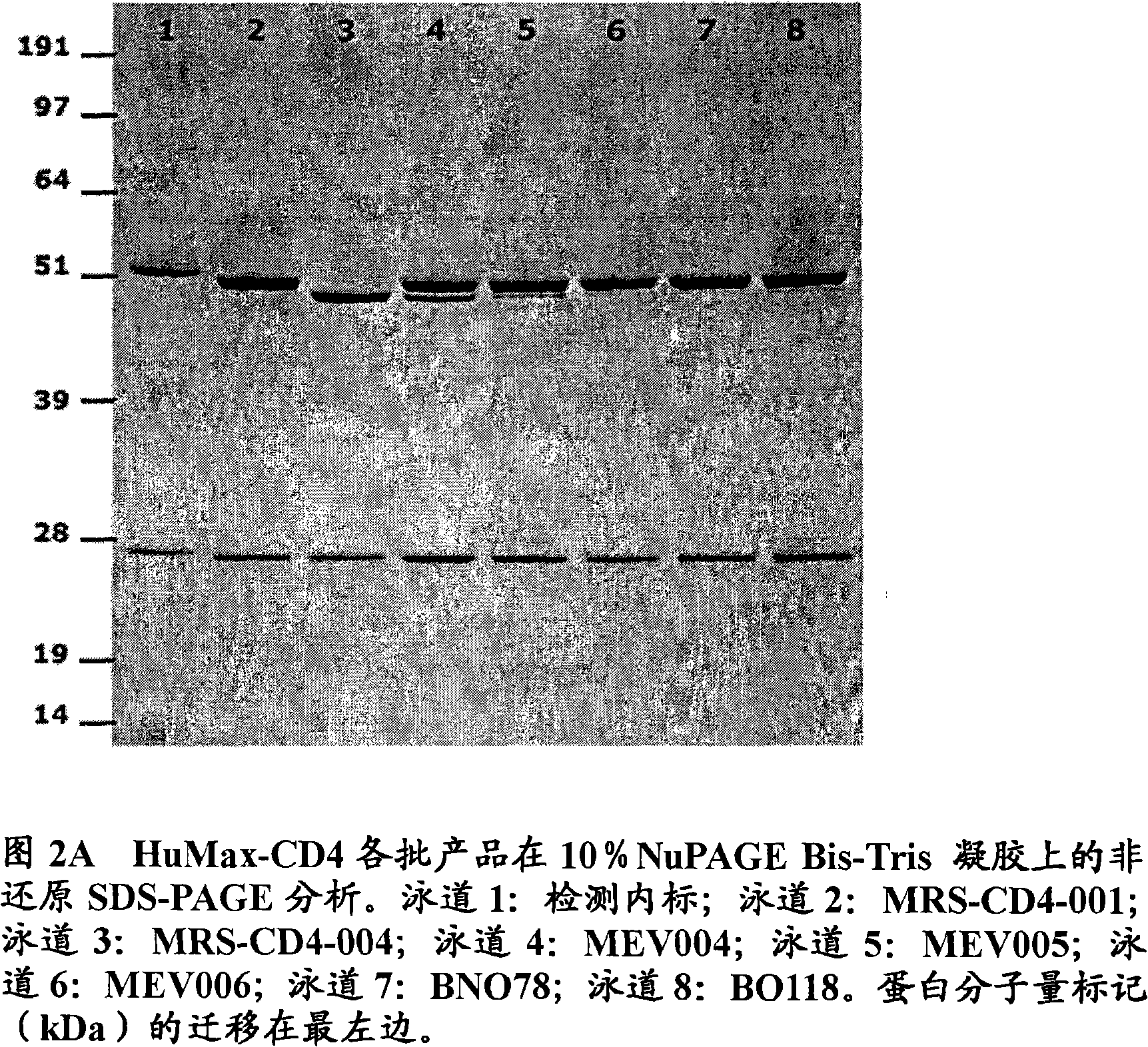
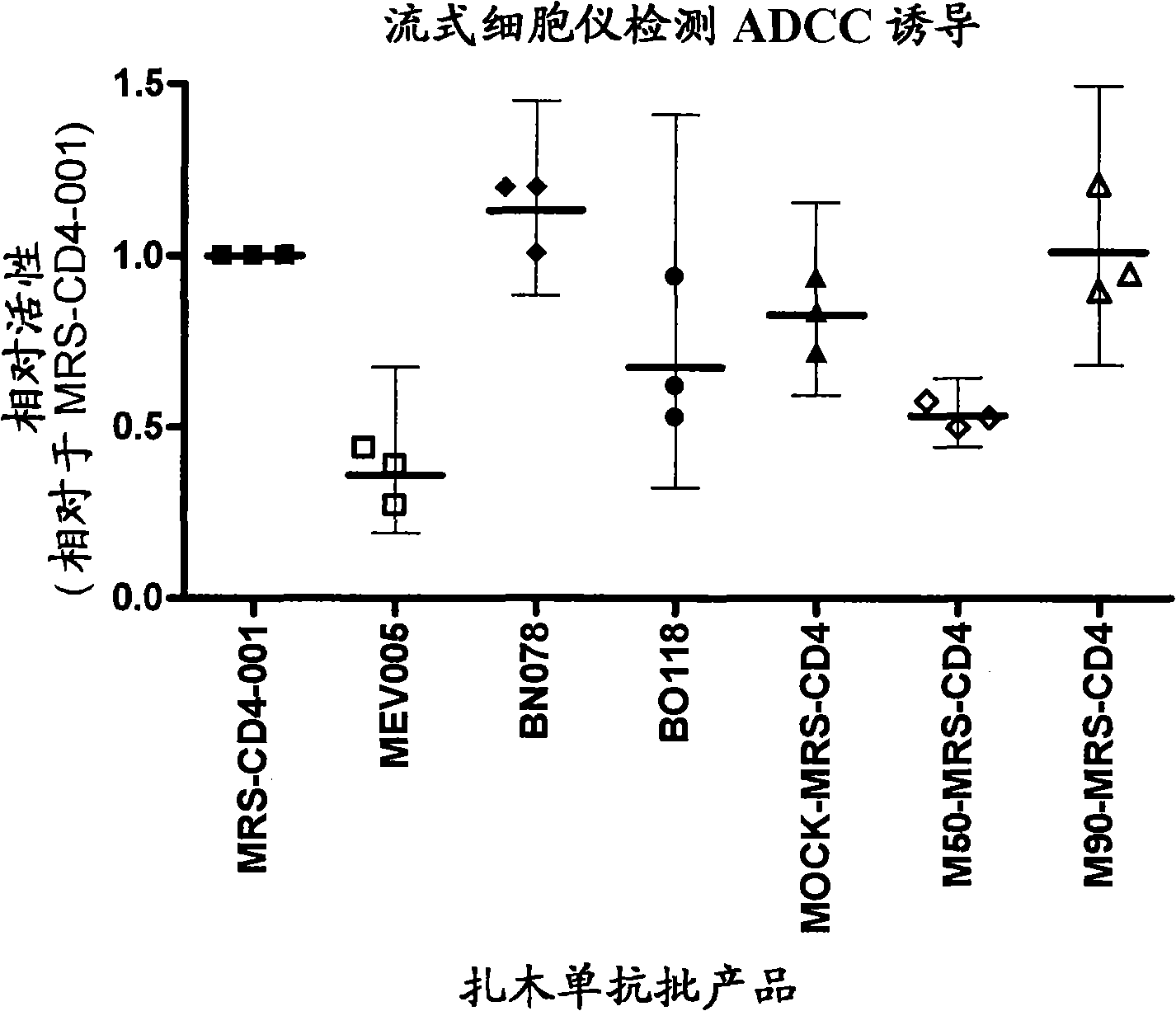
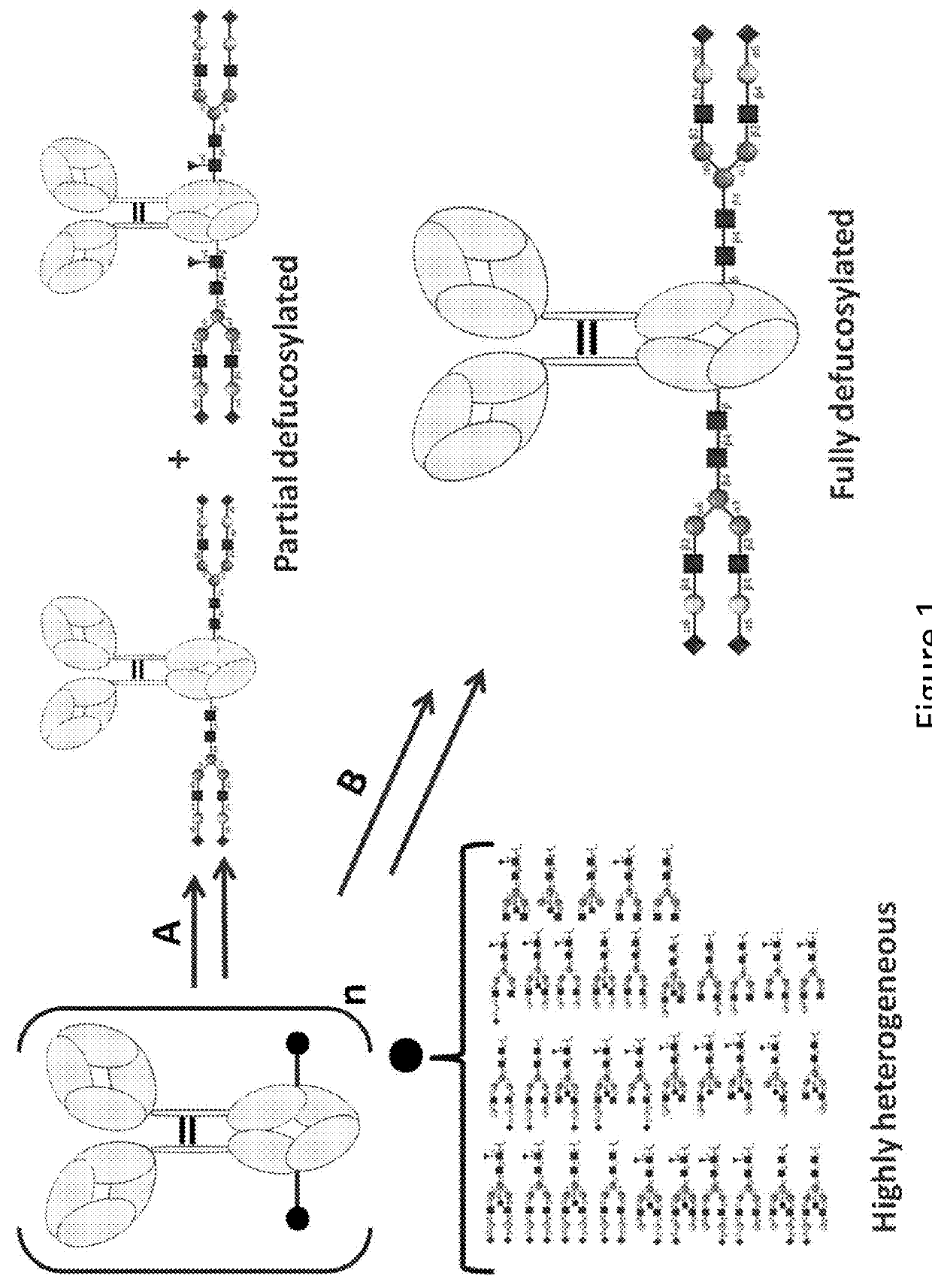
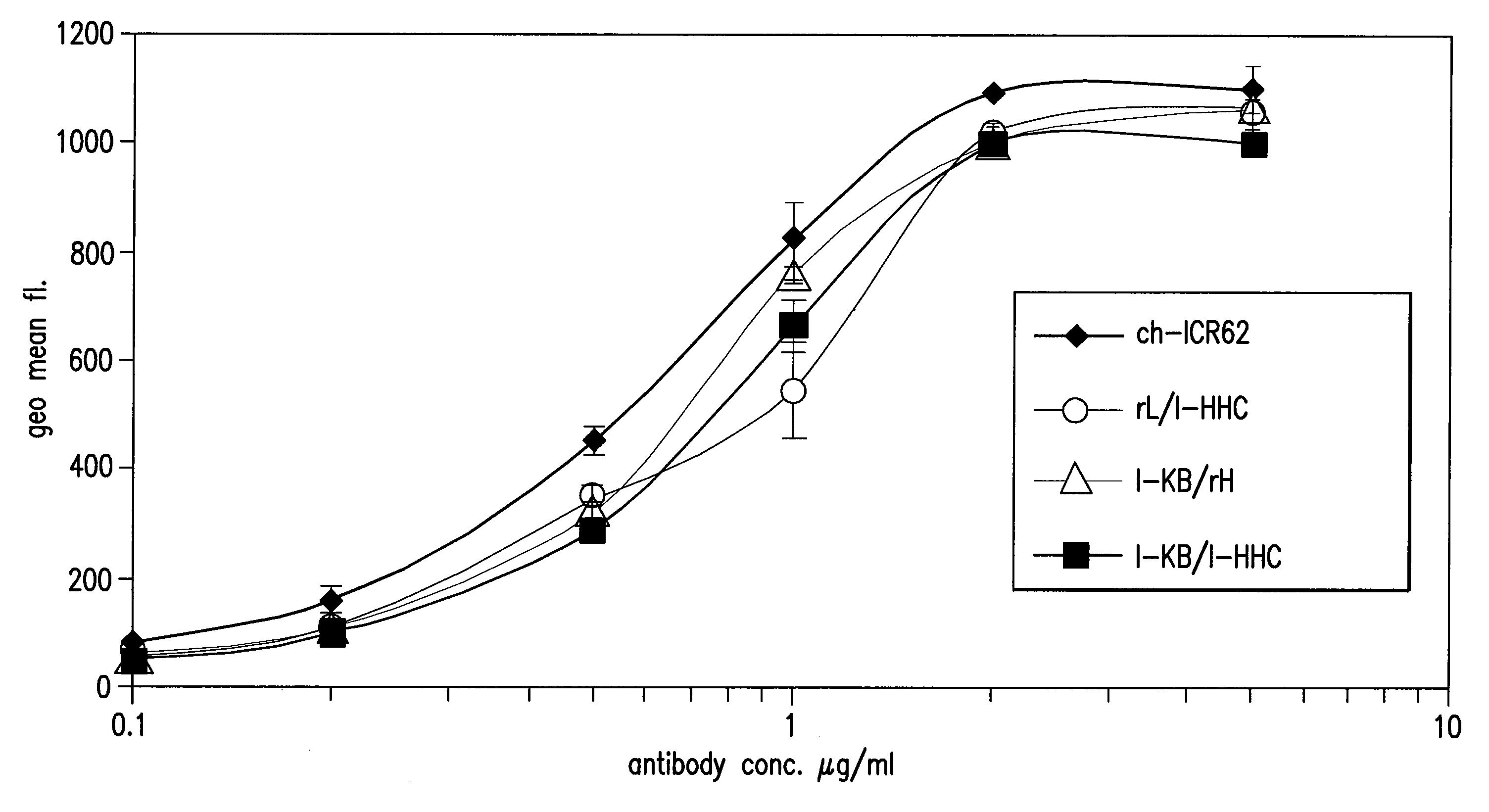
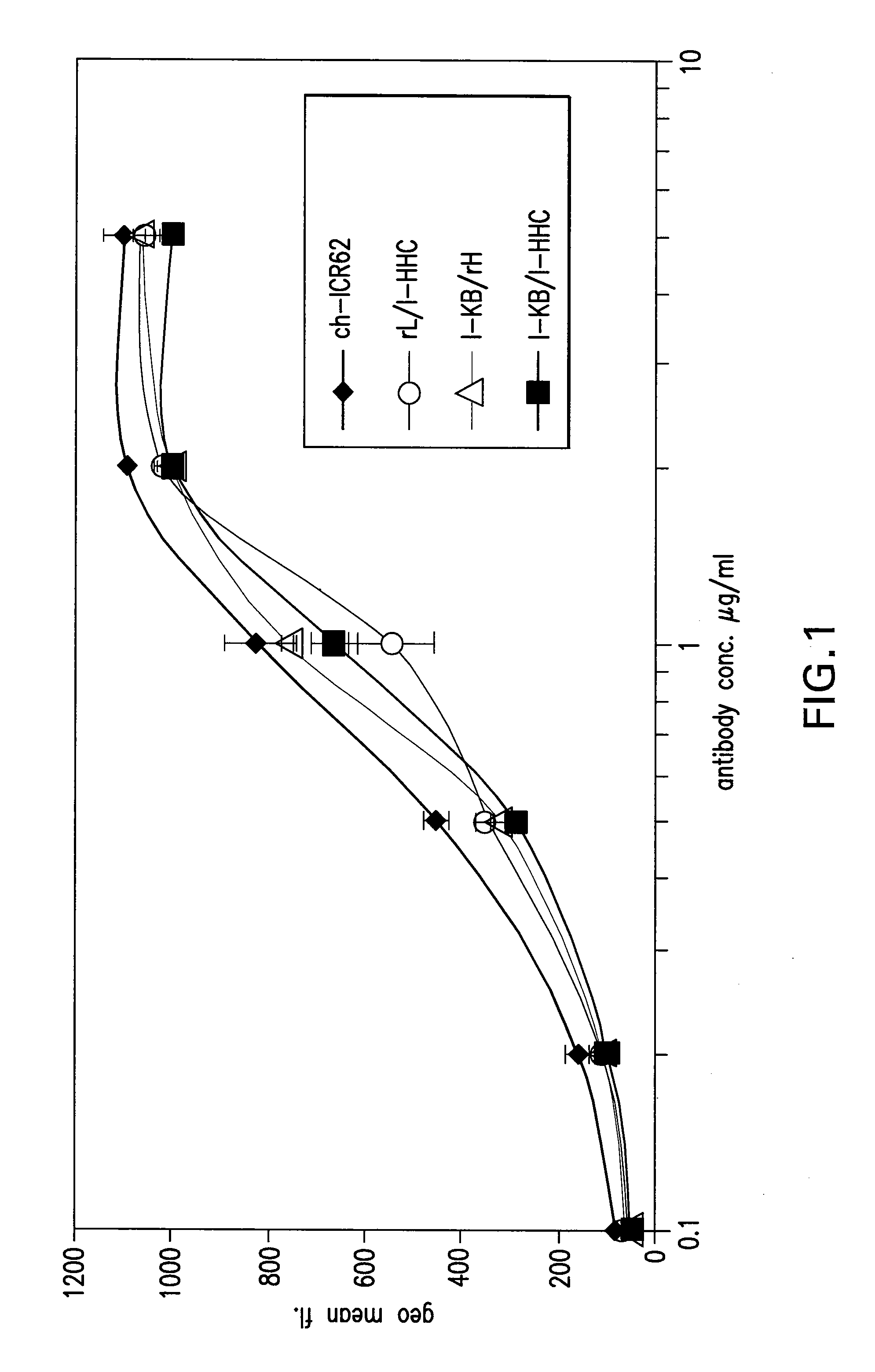
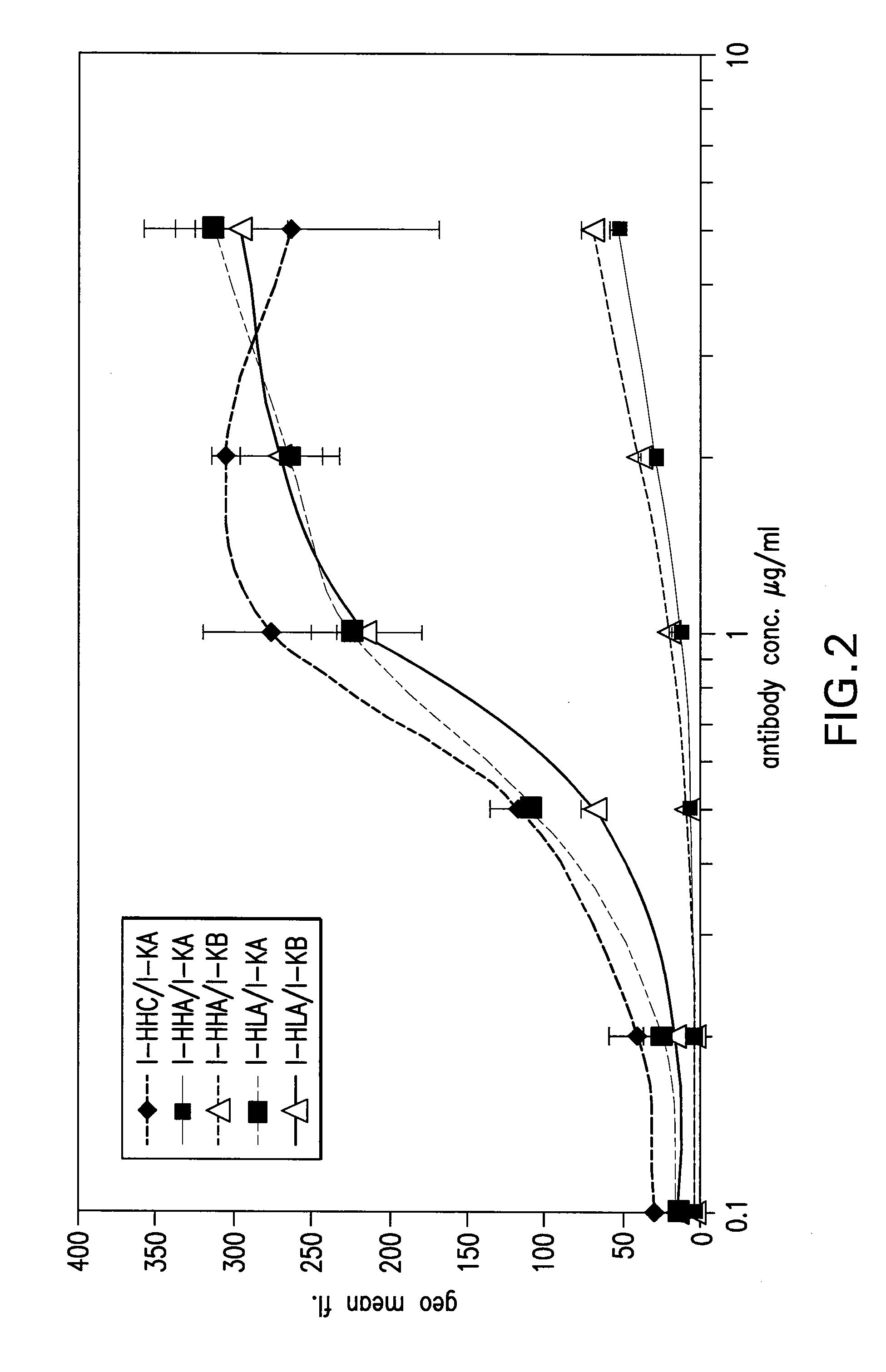
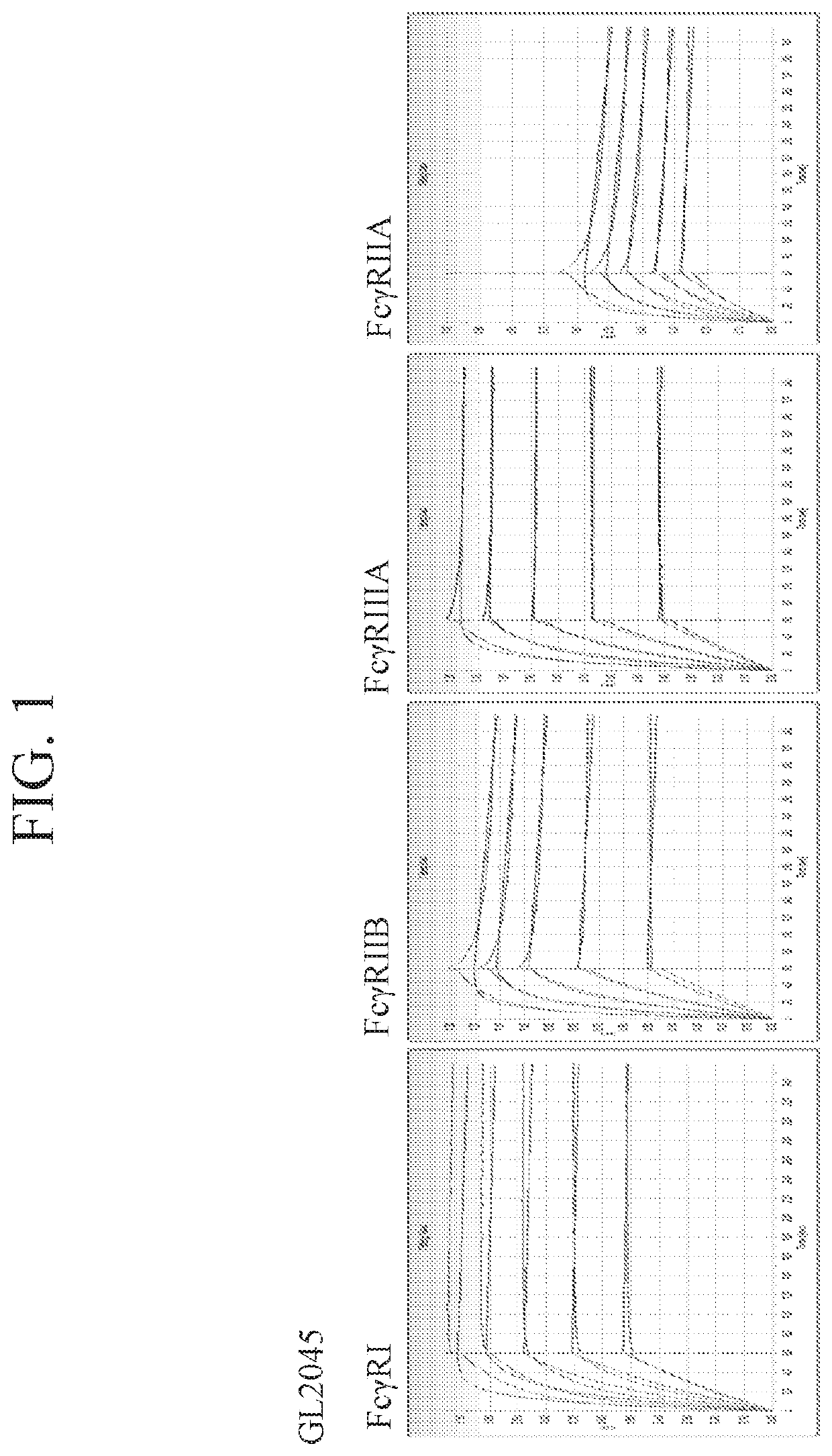
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58 results about "Fc receptor binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
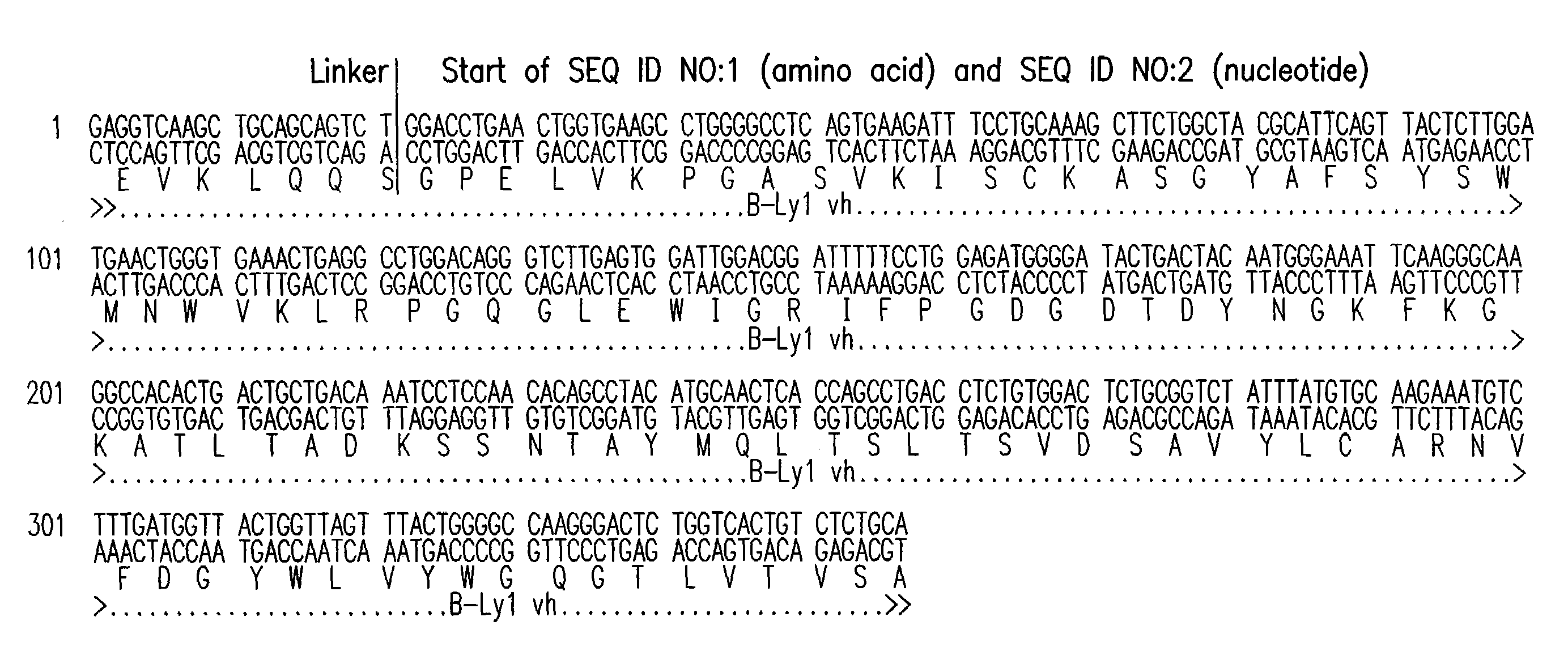
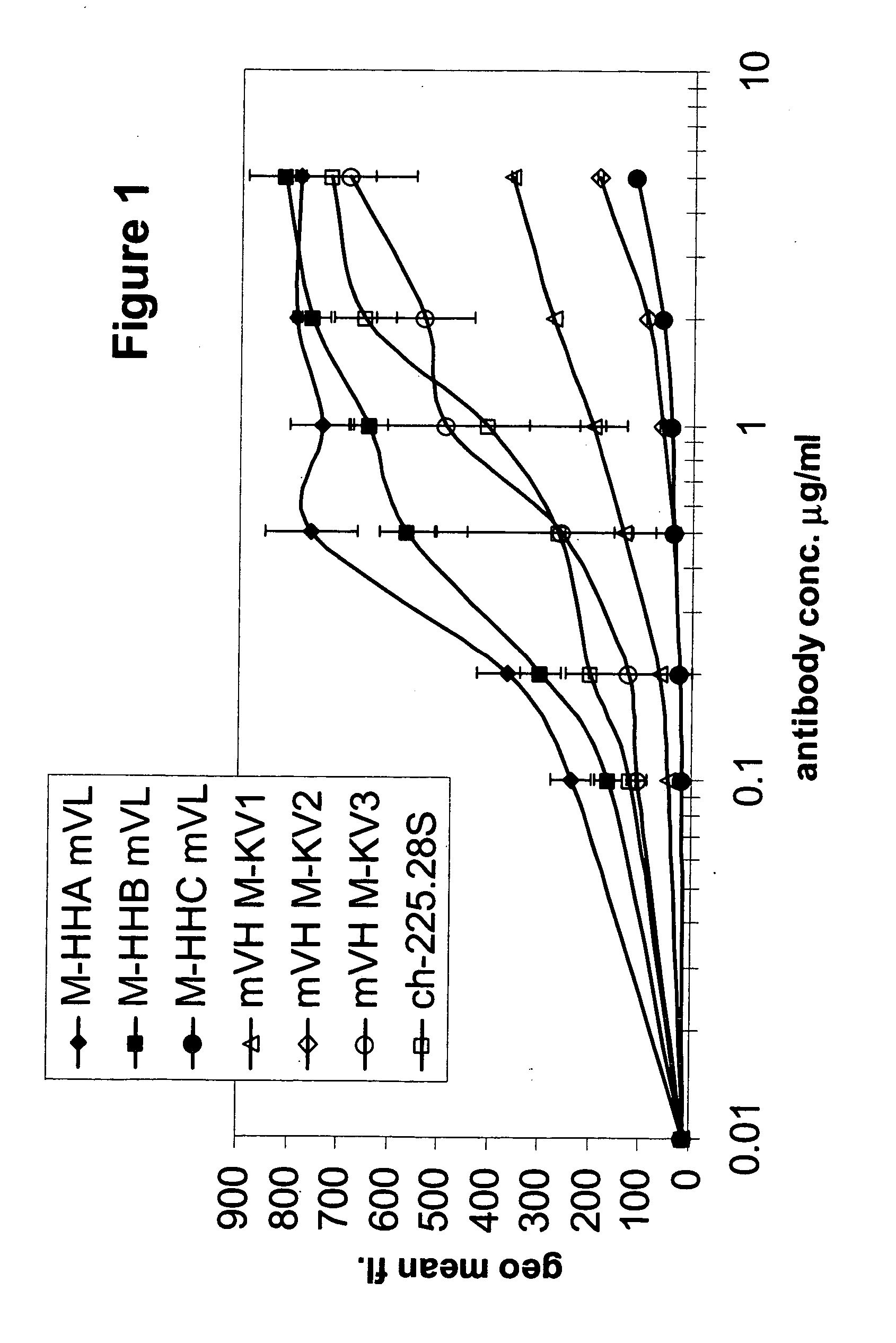
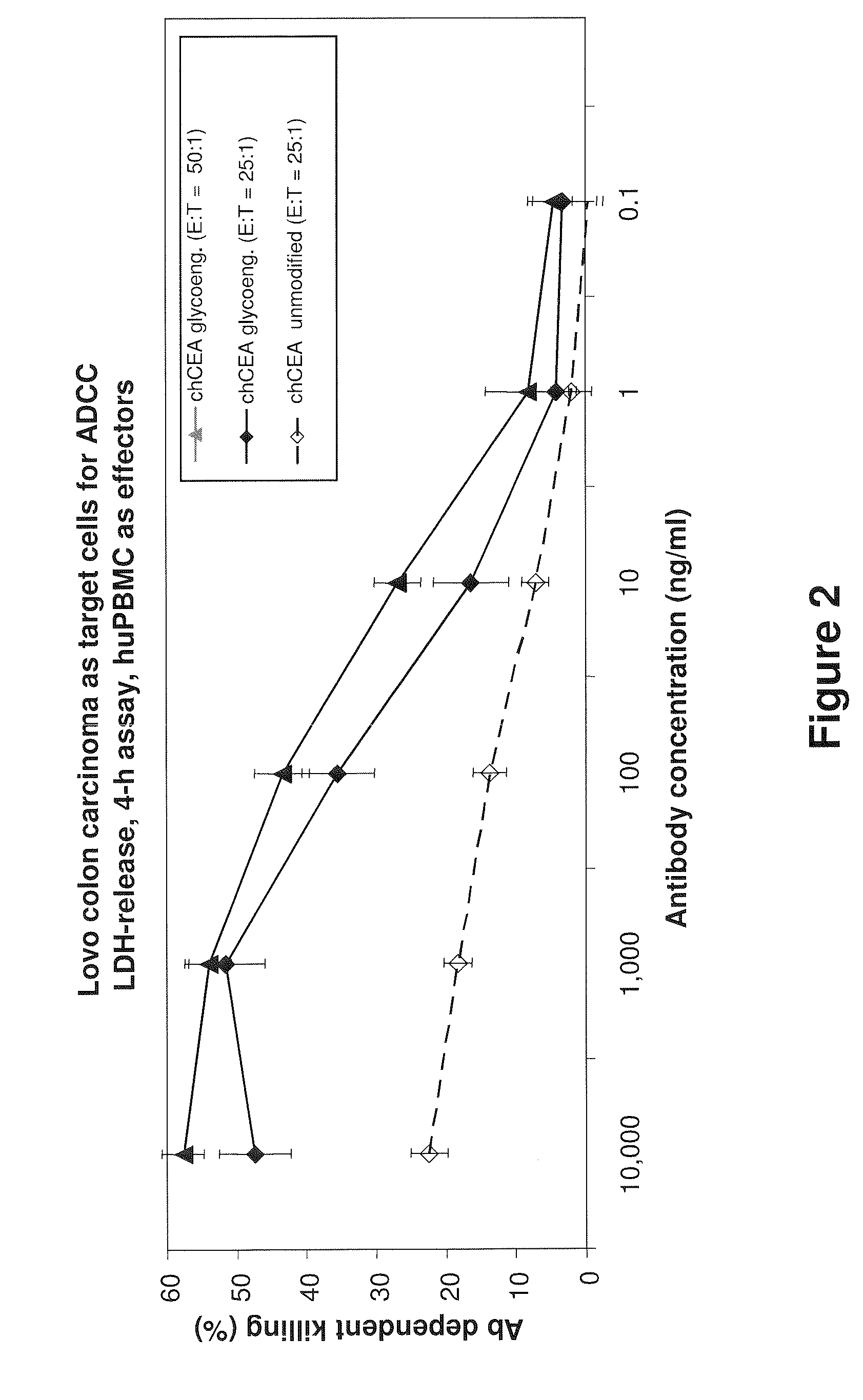
Antigen binding molecules with increased Fc receptor binding affinity and effector function
The present invention relates to antigen binding molecules (ABMs). In particular embodiments, the present invention relates to recombinant monoclonal antibodies, including chimeric, primatized or humanized antibodies specific for human CD20. In addition, the present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding such ABMs, and vectors and host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The invention further relates to methods for producing the ABMs of the invention, and to methods of using these ABMs in treatment of disease. In addition, the present invention relates to ABMs with modified glycosylation having improved therapeutic properties, including antibodies with increased Fc receptor binding and increased effector function.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Fc Variants With Optimized Fc Receptor Binding Properties
InactiveUS20070148170A1High affinityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsFc receptorFc(alpha) receptor
The present invention relates to Fc variants with optimized Fc receptor binding properties, methods for their generation, Fc polypeptides comprising Fc variants with optimized Fc receptor binding properties, and methods for using Fc variants with optimized Fc receptor binding properties.
Owner:XENCOR
Fc polypeptides with novel Fc ligand binding sites
The present invention relates to Fc polypeptides with novel Fc receptor binding sites, and their application, particularly for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:XENCOR
Immunoglobulin constant region fc receptor binding agents
ActiveUS20100239633A1Wide applicationPathological conditionAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseFc(alpha) receptor
IVIG replacement compounds are derived from recombinant and / or biochemical creation of immunologically active biomimetic(s). These replacement compounds are then screened in vitro to assess each replacements compound's efficiency at modulating immune function. Particular replacement compounds are selected for further in vivo validation and dosage / administration optimization. Finally, the replacement compounds are used to treat a wide range of diseases, including inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:GLIKNIK +1
Fc variants with optimized Fc receptor binding properties
InactiveUS20080206867A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTissue cultureFc(alpha) receptorFc receptor
The present invention relates to Fc variants with optimized Fc receptor binding properties, methods for their generation, Fc polypeptides comprising Fc variants with optimized Fc receptor binding properties, and methods for using Fc variants with optimized Fc receptor binding properties.
Owner:DESJARLAIS JOHN R +5
Antibodies comprising chimeric constant domains
ActiveUS9359437B2Hybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFc(alpha) receptorFc receptor
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Antigen binding molecules with increased Fc receptor binding affinity and effector function
The present invention relates to antigen binding molecules (ABMs). In particular embodiments, the present invention relates to recombinant monoclonal antibodies, including chimeric, primatized or humanized antibodies specific for human CD20. In addition, the present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding such ABMs, and vectors and host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The invention further relates to methods for producing the ABMs of the invention, and to methods of using these ABMs in treatment of disease. In addition, the present invention relates to ABMs with modified glycosylation having improved therapeutic properties, including antibodies with increased Fc receptor binding and increased effector function.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Methods for converting or inducing protective immunity
InactiveUS20090214533A1Reduced activityReduce functionAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsRegulatory T cellImmune complex deposition
The invention is based in part on the finding that suppressing regulatory T cell function is needed in order to convert passive immunity into active antigen-specific immunity. Generally, the methods of the invention comprise at least the combination of: (1) increasing the amount of immune complexes in the subject, wherein the immune complex comprises a target antigen and a immunoglobulin molecule comprising (i) a variable region specific to the target antigen and (ii) a Fc receptor binding region; and (2) inhibiting regulatory T cell function or decreasing / depleting the regulatory T cell population in the subject.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Anti-cd20 glycoantibodies and uses thereof
InactiveUS20150344585A1Increase healing valueEnhanced ADCC activityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsFc(alpha) receptorFc receptor
The present disclosure relates to a novel class of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies comprising a homogeneous population of anti-CD20 IgG molecules having the same N-glycan on each of Fc. The antibodies of the invention can be produced from anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies by Fc glycoengineering. Importantly, the antibodies of the invention have improved therapeutic values with increased ADCC activity and increased Fc receptor binding affinity compared to the corresponding monoclonal antibodies that have not been glycoengineered.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
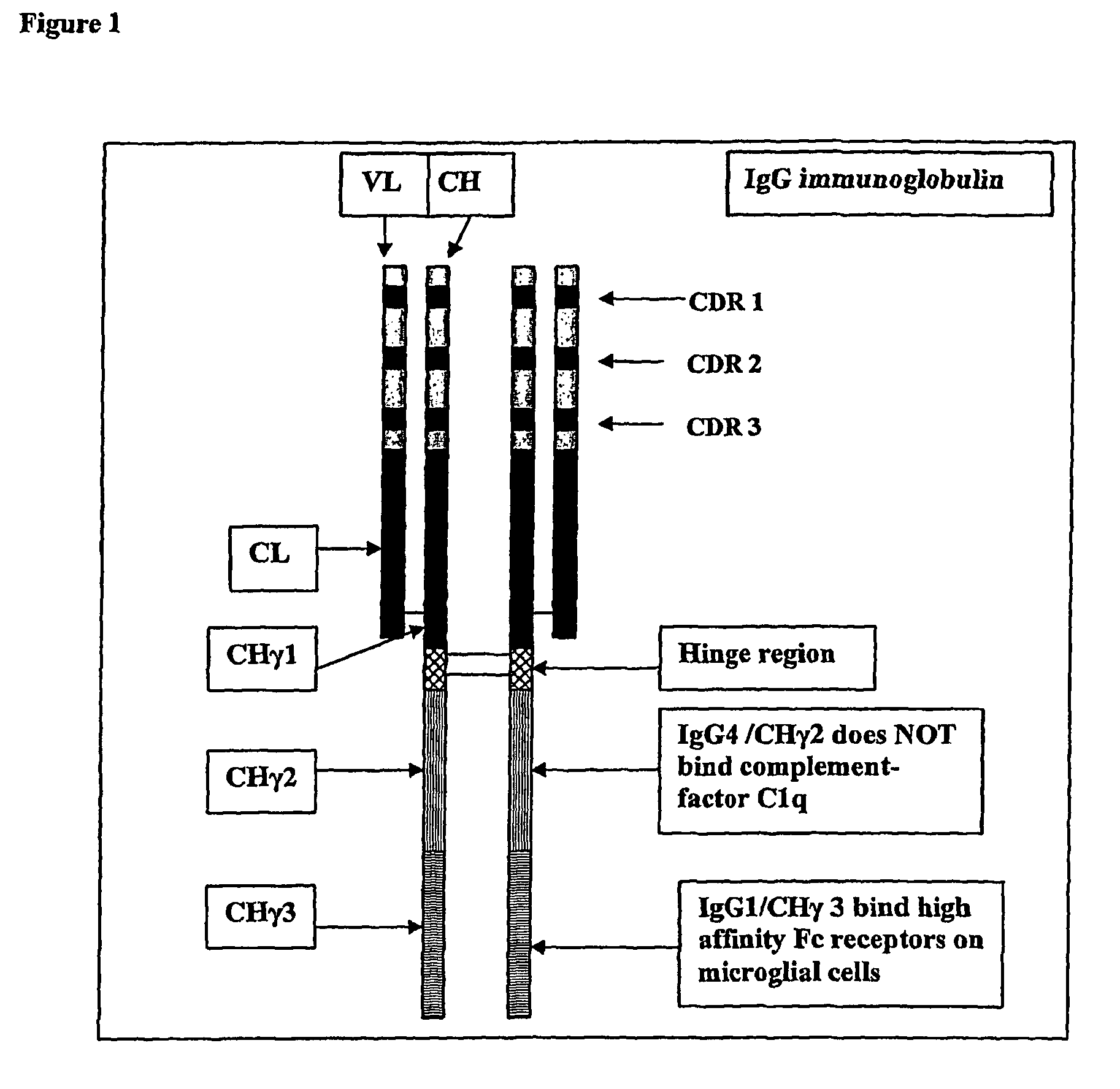
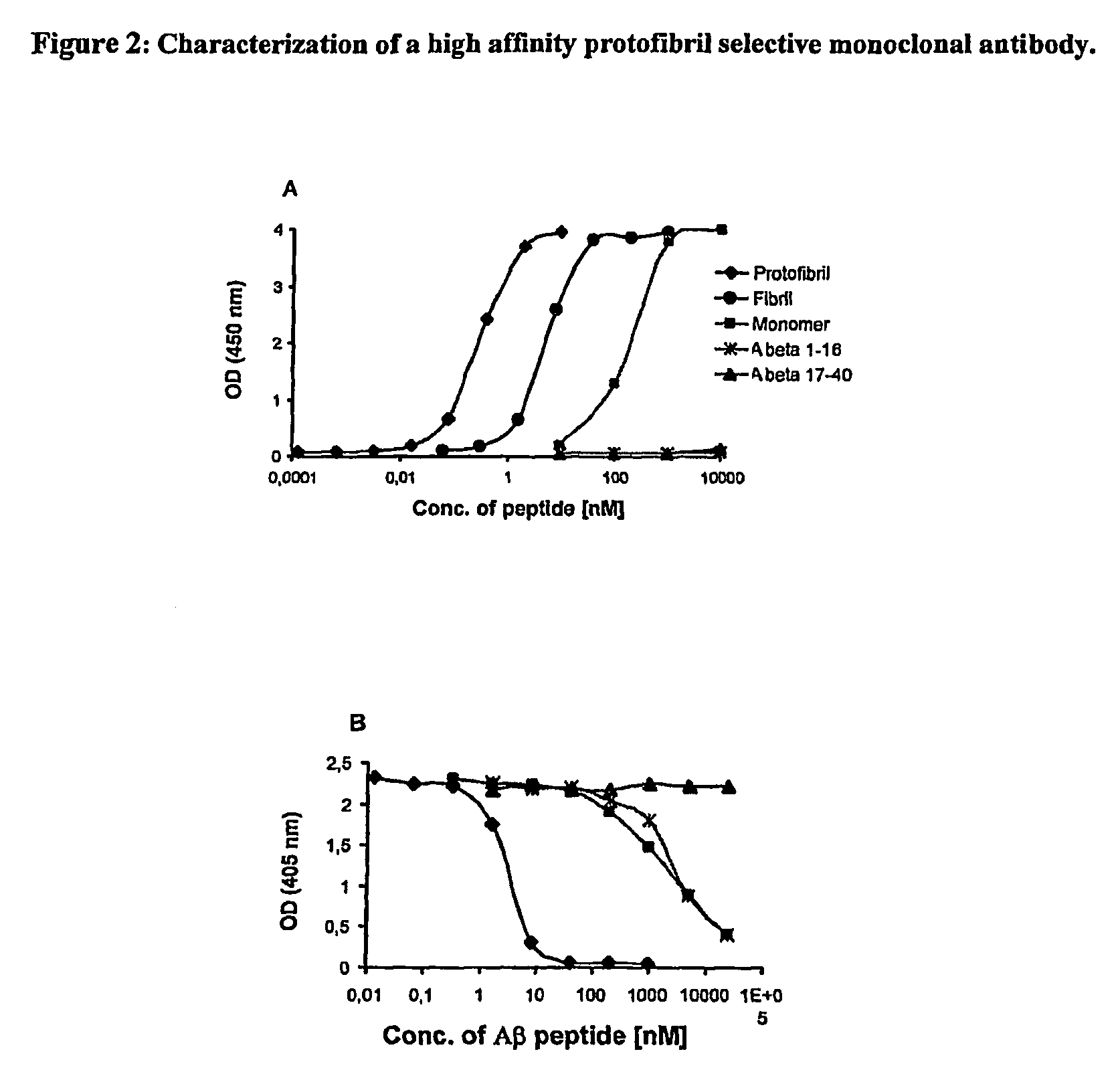
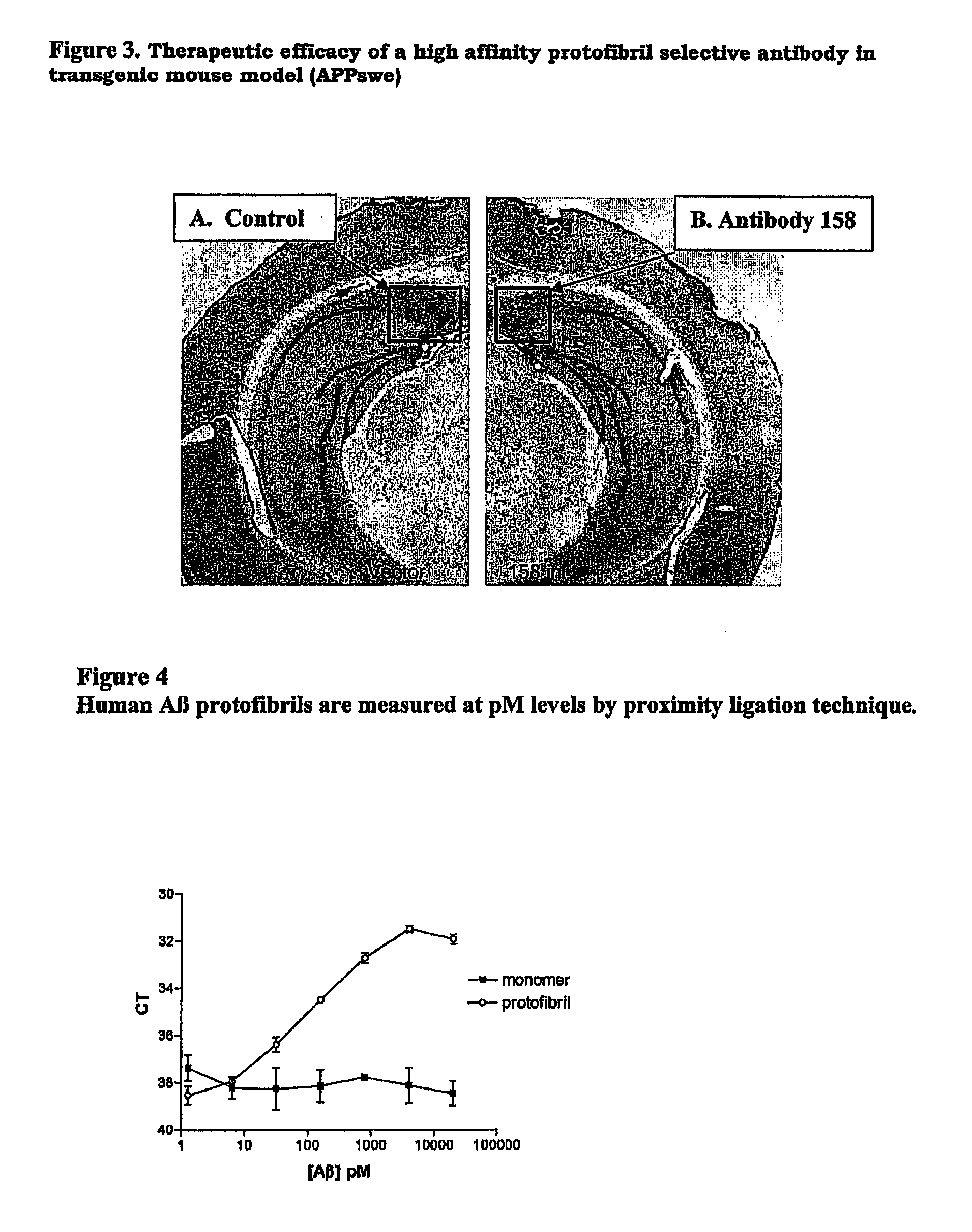
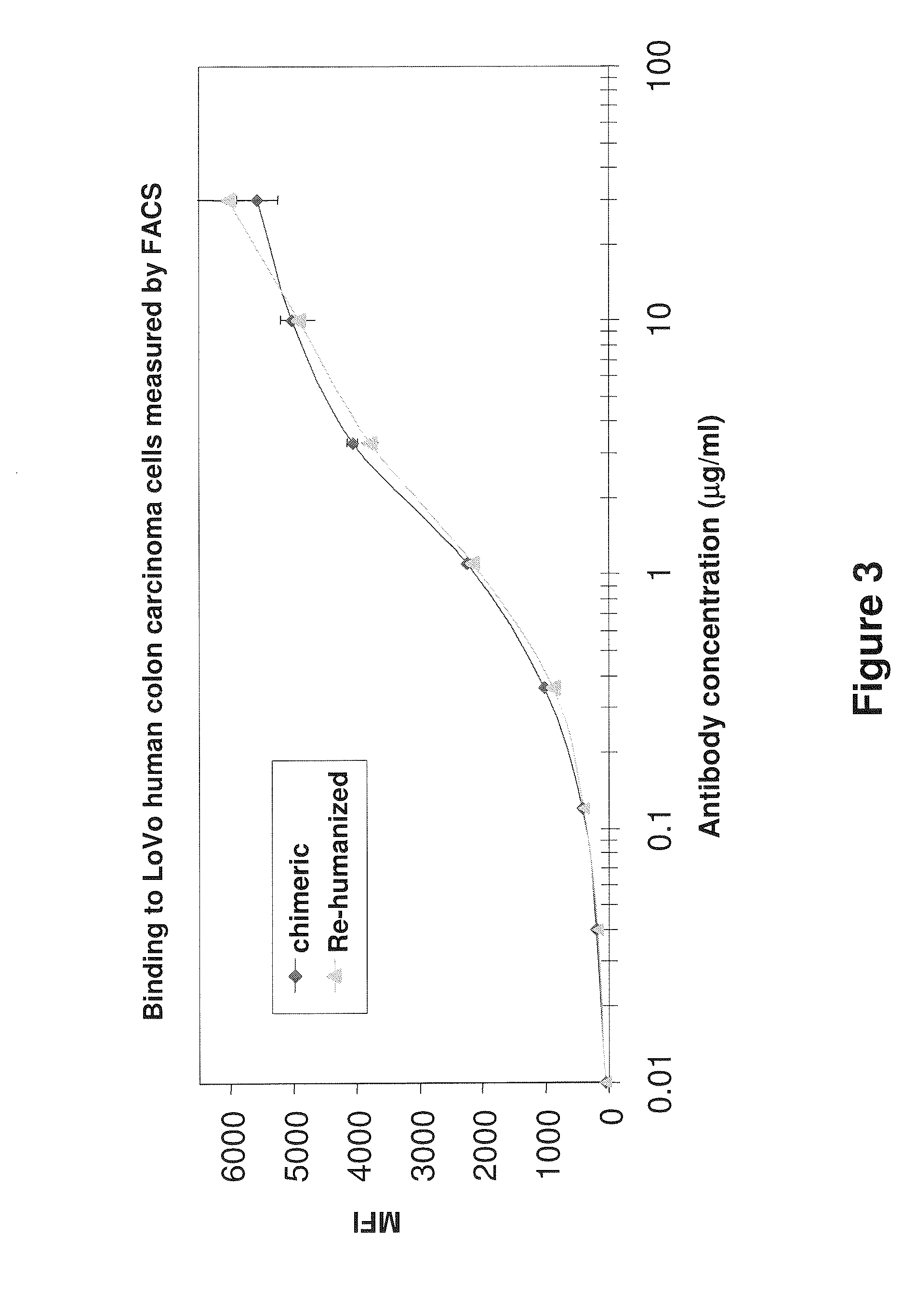
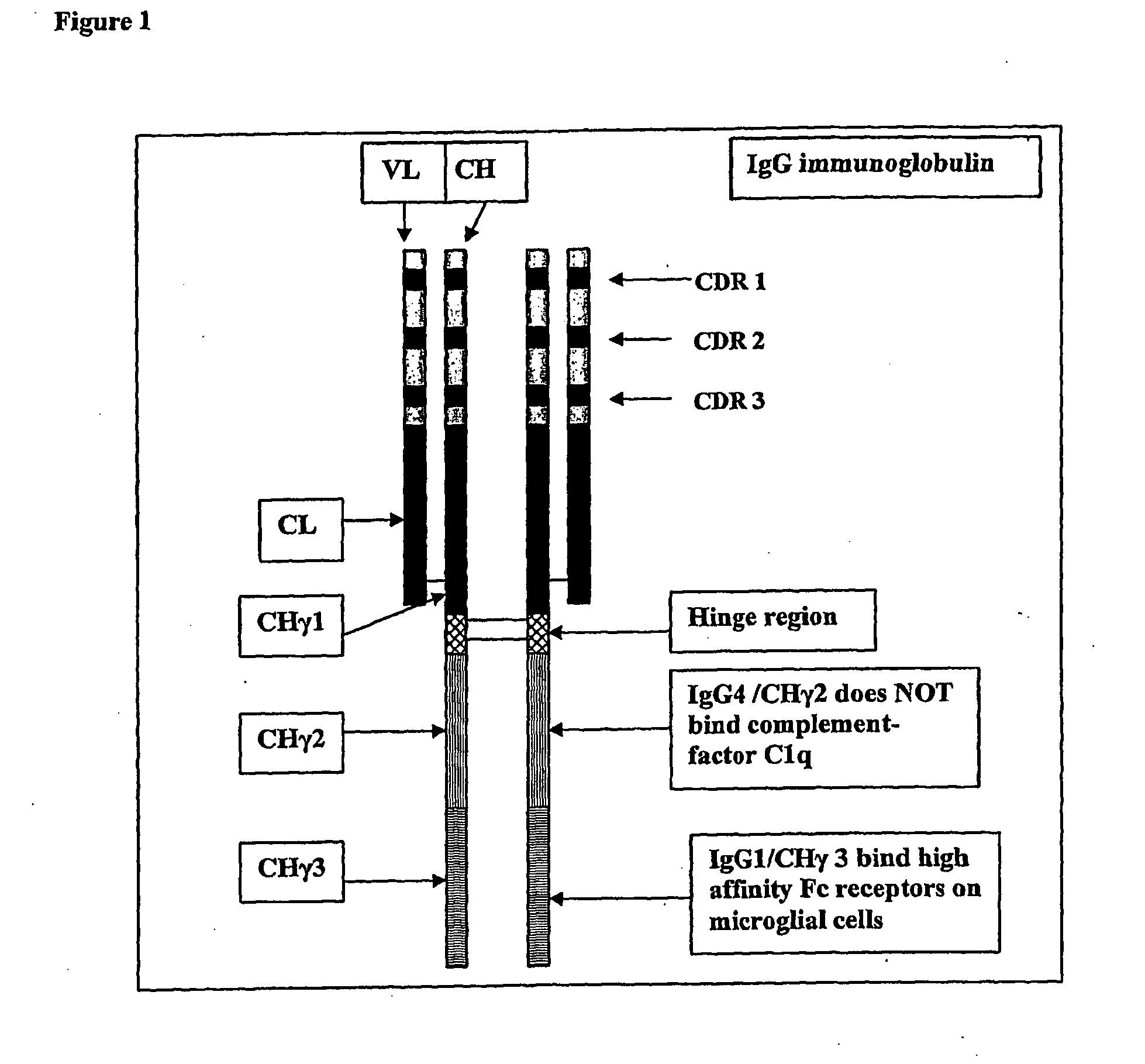
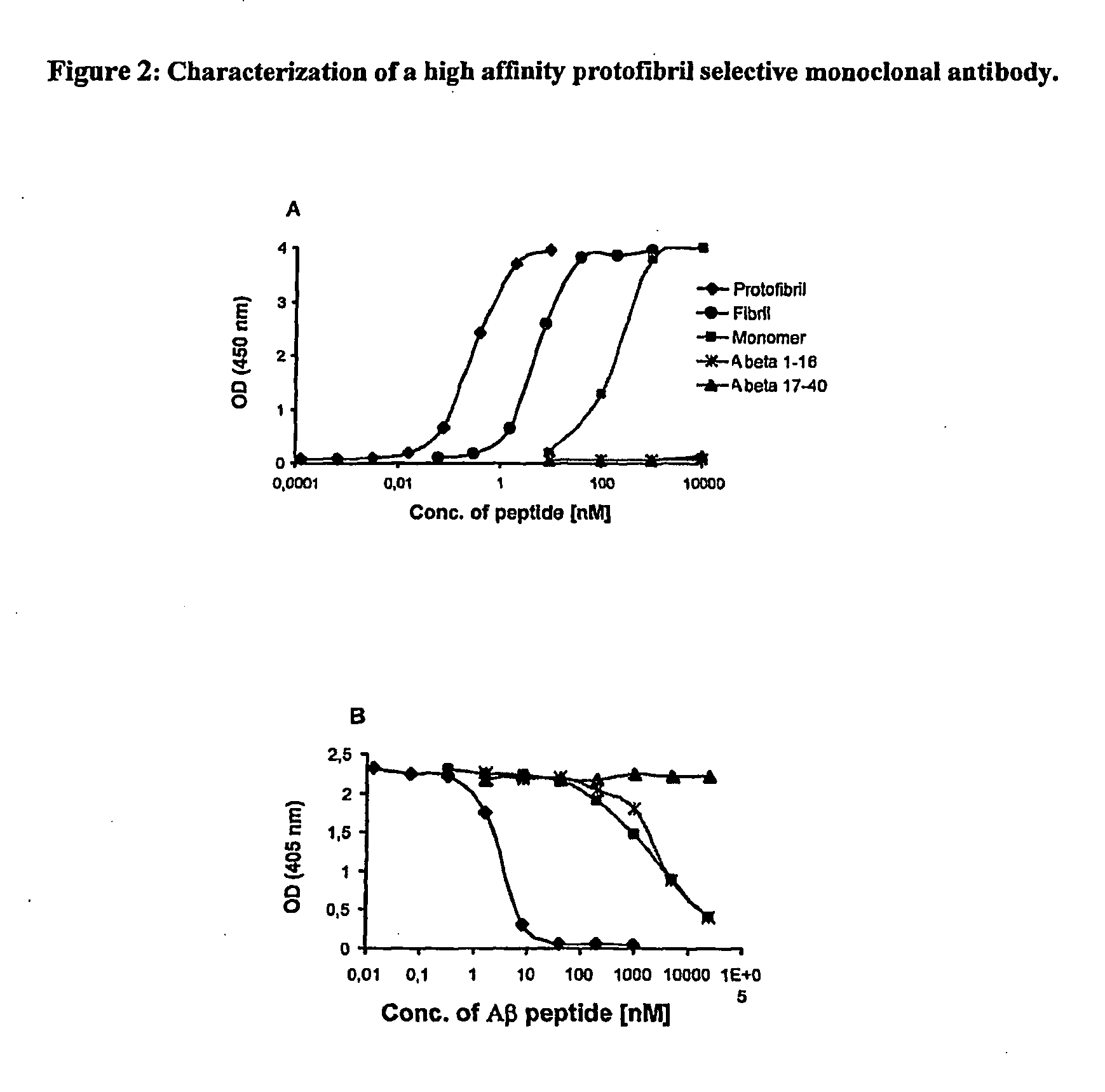
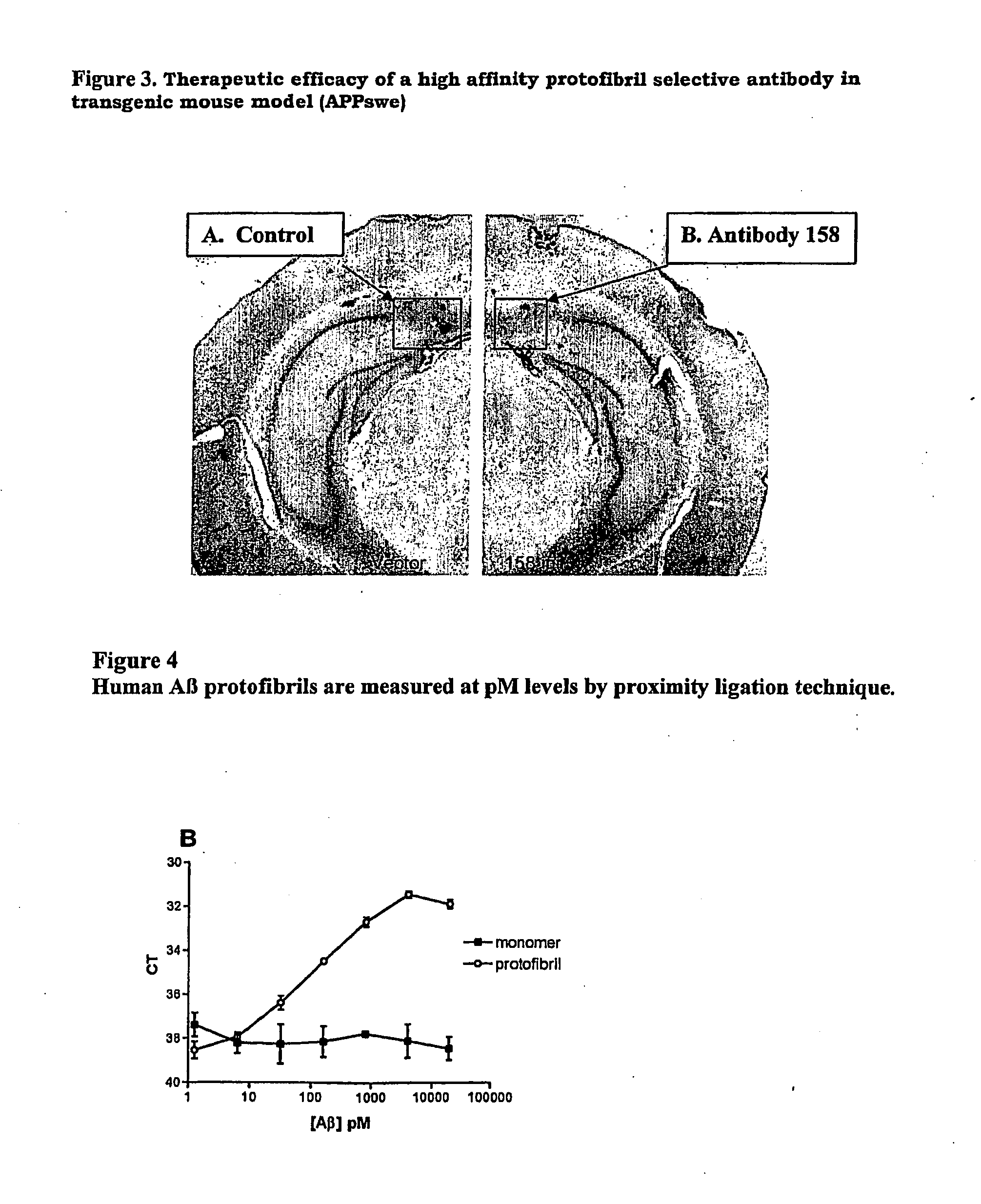
Protofibril selective antibodies and the use thereof
ActiveUS8025878B2Reduce complement factor C1q bindingReduce activationAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderDiseaseHigh affinity antibody
The present invention pertains to the prevention, treatment and diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases, in particular Alzheimer's disease, and other similar disease. More specifically to high affinity antibodies selective for amyloid beta protein (Aβ) in its protofibril conformation and of IgG class and IgG1 or IgG4 subclass or combinations thereof or mutations thereof, retaining high Fc receptor binding and low C1(C1q) binding, effective in clearance of Aβ protofibrils and with reduce risk of inflammation.
Owner:BIOARCTIC AB
Antigen binding molecules directed to MCSP and having increased Fc receptor binding affinity and effector function
InactiveUS20060223096A1High affinityFunction increaseImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTissue cultureHumanized antibodyDisease cause
The present invention relates to antigen binding molecules (ABMs). In particular embodiments, the present invention relates to recombinant monoclonal antibodies, including chimeric, primatized or humanized antibodies specific for human MCSP. In addition, the present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding such ABMs, and vectors and host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The invention further relates to methods for producing the ABMs of the invention, and to methods of using these ABMs in treatment of disease. In addition, the present invention relates to ABMs with modified glycosylation having improved therapeutic properties, including antibodies with increased Fc receptor binding and increased effector function.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
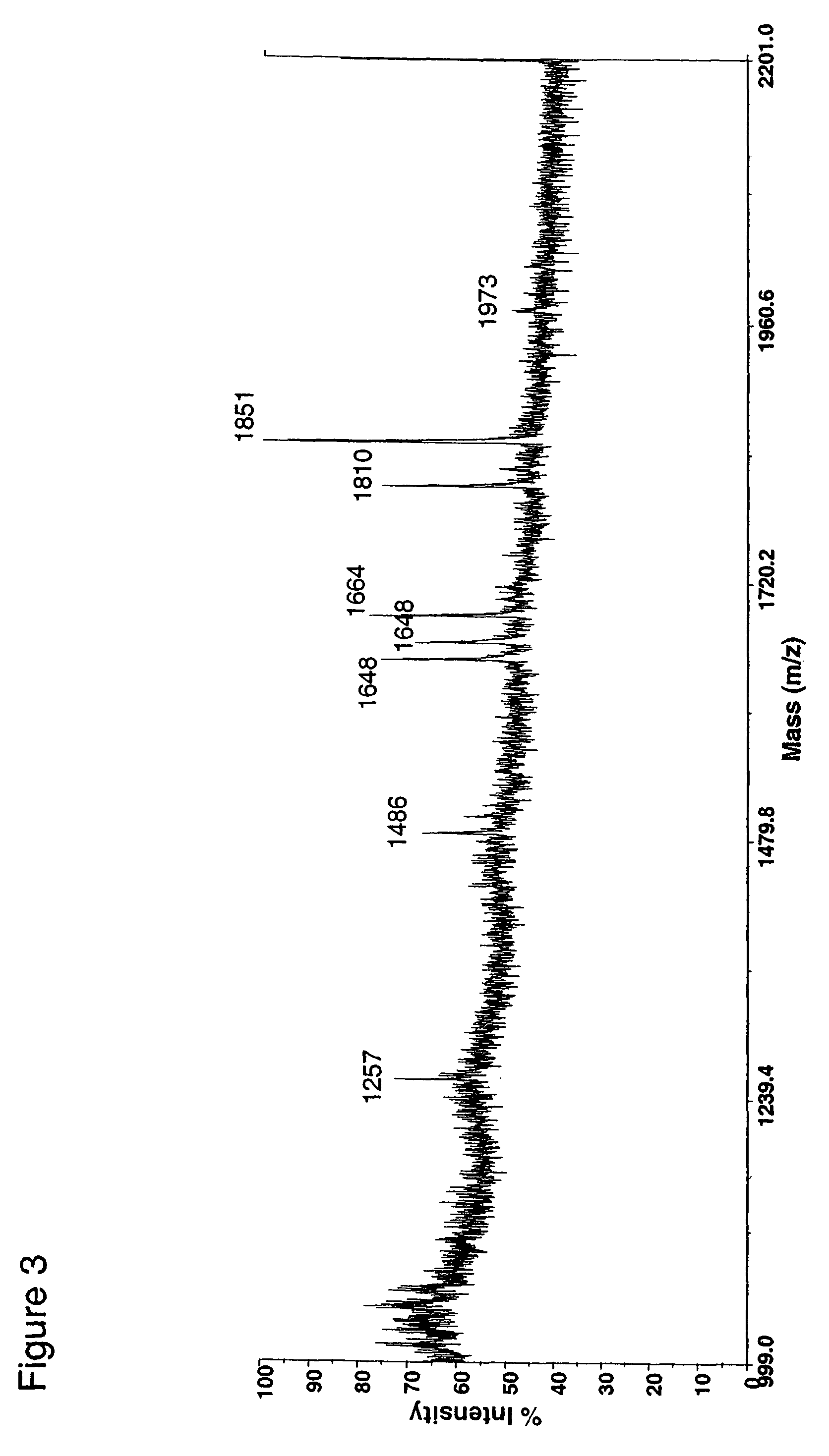
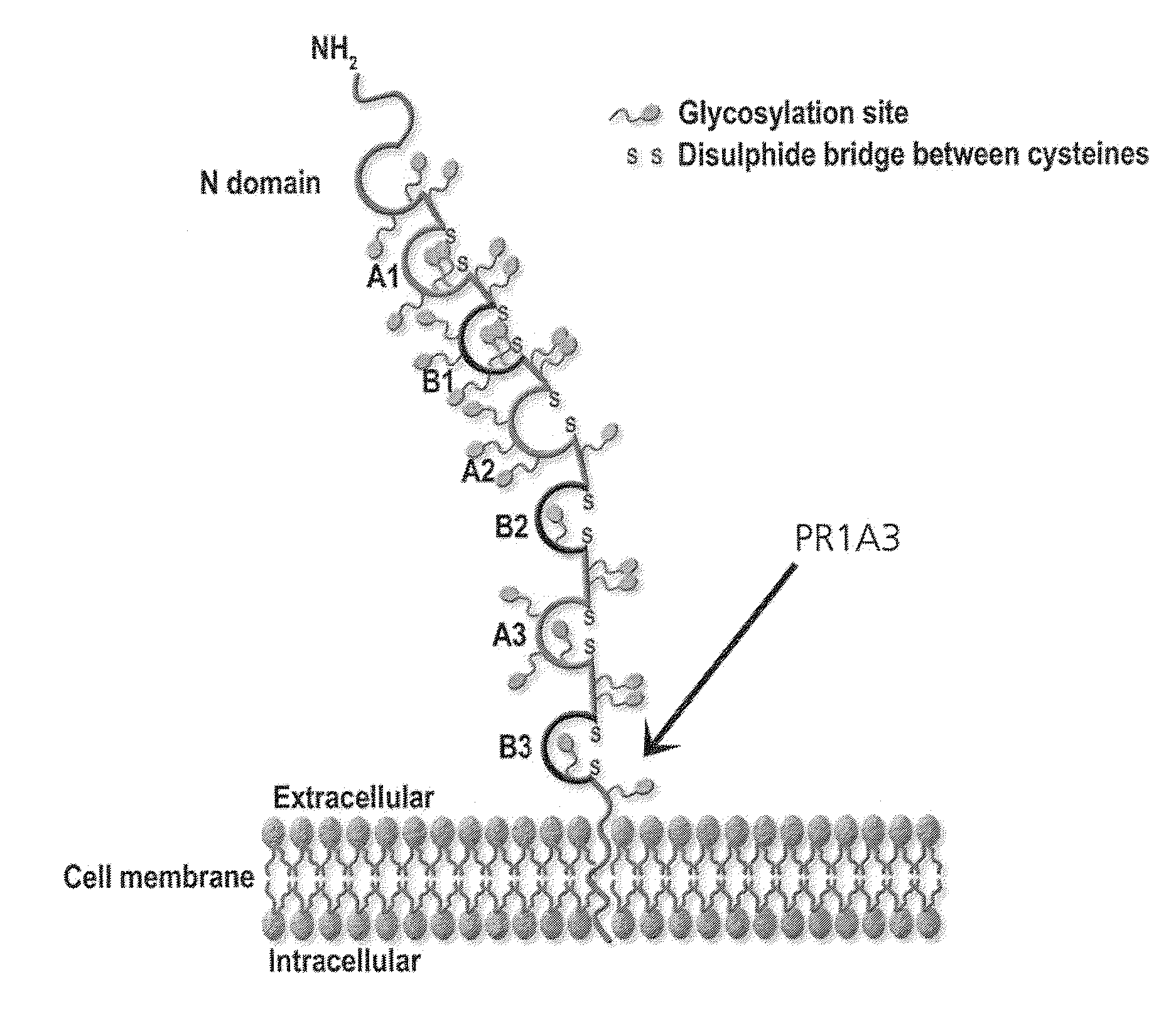
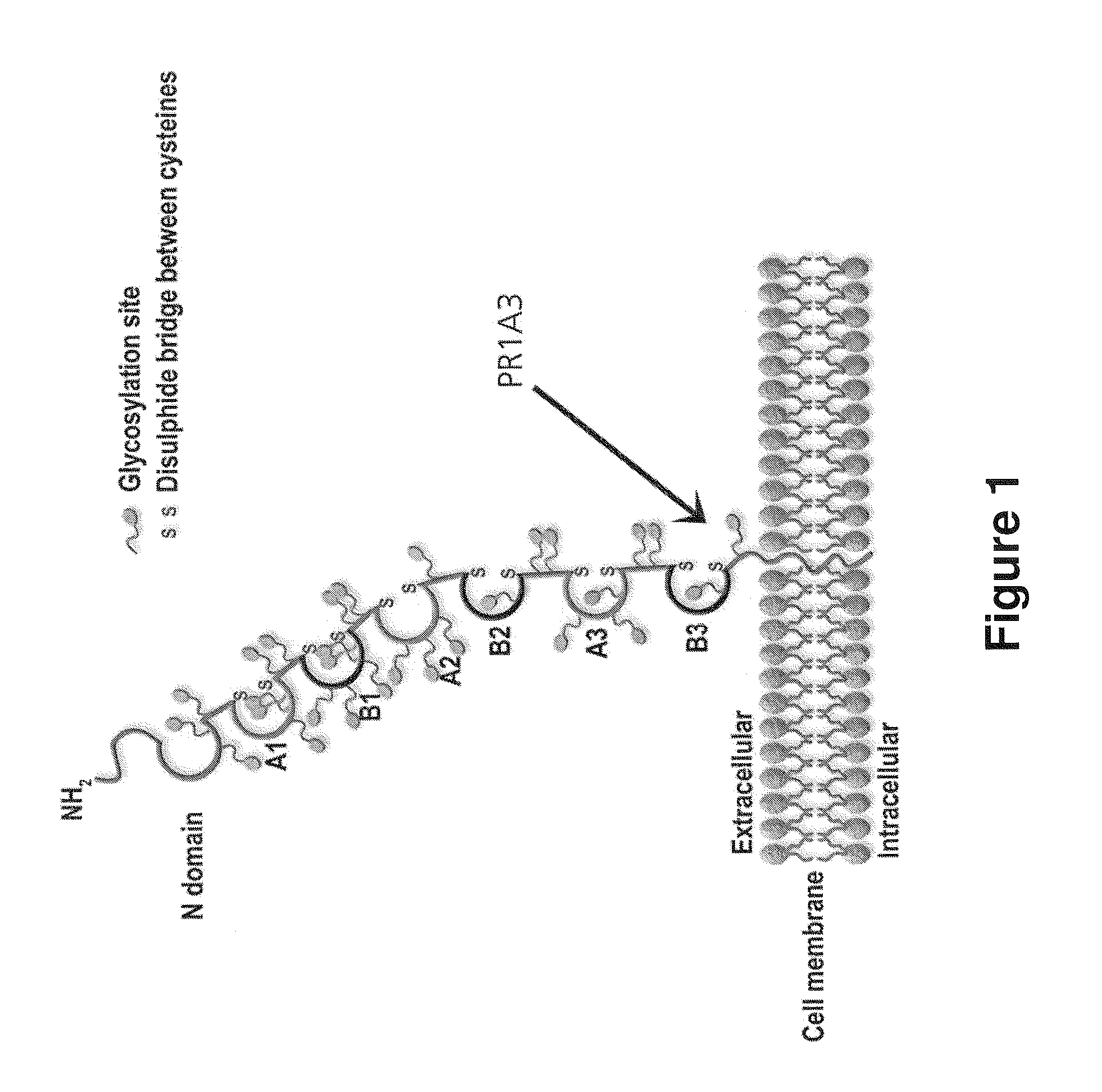
Antibodies to carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), methods of making same, and uses thereof
The present invention relates to antigen binding molecules (ABMs). In particular embodiments, the present invention relates to recombinant monoclonal antibodies, including chimeric, primatized or humanized antibodies or variants thereof specific for cell surface or membrane bound human CEA. In addition, the present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding such ABMs, and vectors and host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The invention further relates to methods for producing the ABMs of the invention, and to methods of using these ABMs in treatment of disease. In addition, the present invention relates to ABMs with modified glycosylation having improved therapeutic properties, including antibodies with increased Fc receptor binding and increased effector function.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Protofibril selective antibodies and the use thereof
ActiveUS20090258009A1Lower Level RequirementsSevere side-effectsAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderHigh affinity antibodyInflammation
The present invention pertains to the prevention, treatment and diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases, in particular Alzheimer's disease, and other similar disease. More specifically to high affinity antibodies selective for amyloid beta protein (Aβ) in its protofibril conformation and of IgG class and IgG1 or IgG4 subclass or combinations thereof or mutations thereof, retaining high Fc receptor binding and low C1(CIq) binding, effective in clearance of Aβ protofibrils and with reduce risk of inflammation.
Owner:BIOARCTIC AB
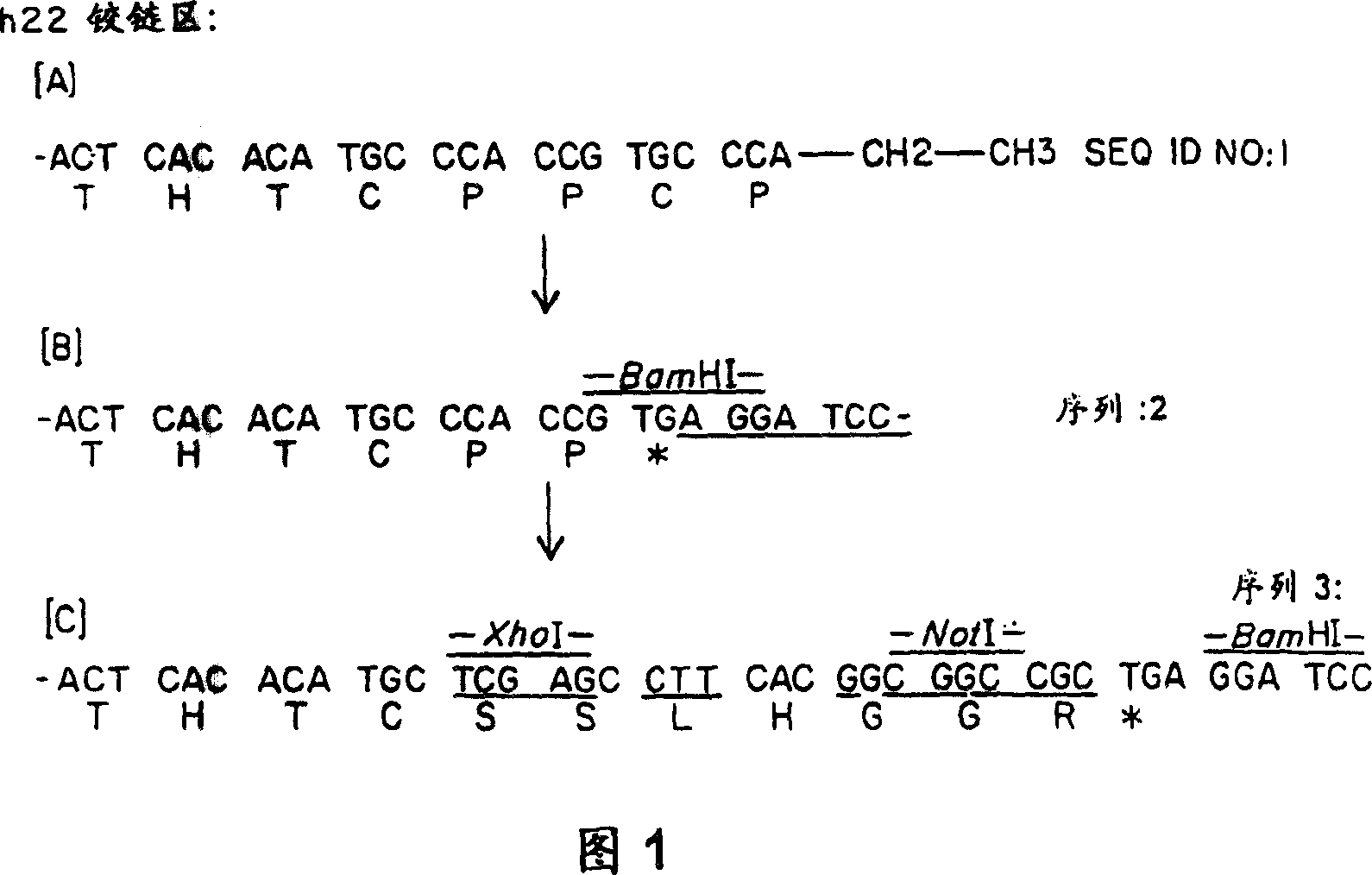
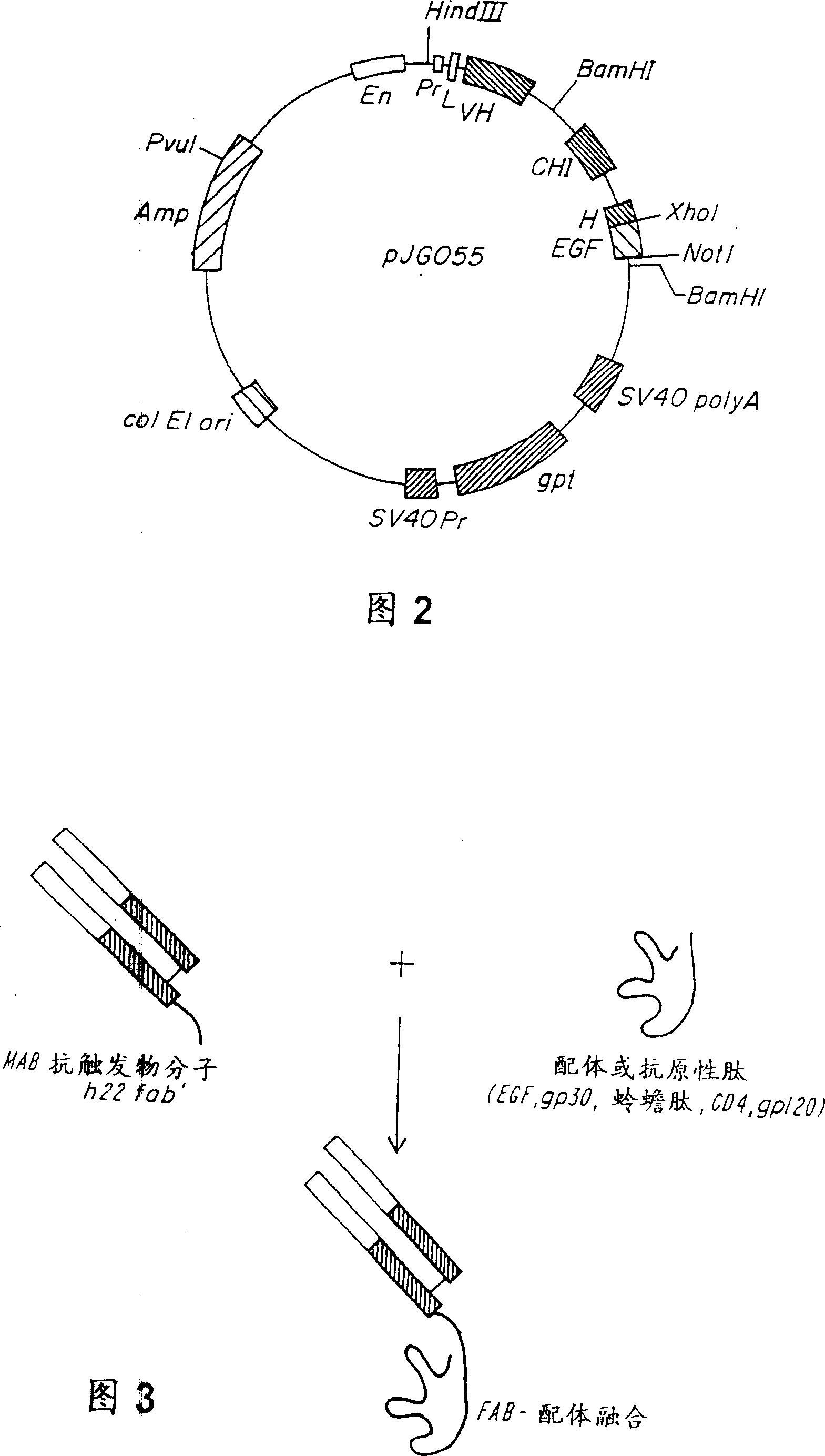
Fusion Protein Comprising an Fc Receptor Binding Polypeptide and an Antigenic Polypeptide for Mediating an Immune Response
InactiveUS20090186025A1Prevent and treat diseaseStrong pathogenicityAntibacterial agentsVirusesFc(alpha) receptorDisease
The present invention provides a fusion protein comprising an Fc receptor binding polypeptide and an antigenic polypeptide. The fusion peptide may further comprise a linker sequence or hinge portion which joins the Fc receptor biding polypeptide and the antigenic polypeptide. The Fc receptor binding polypeptide typically comprises the CH2 constant domain of a human IgG immunoglobulin. The antigenic polypeptide can be any polypeptide which induces an immune response. Administration of the fusion protein to a subject results in a cytotoxic T lymphocyte response being induced against the antigenic polypeptide provided within the fusion protein. The invention further extends to methods for the treatment of a disease condition in a subject using the fusion proteins of the invention.
Owner:IMMUNOBIOLOGY LTD
Immunomodulatory proteins
InactiveUS20150218236A1Easy to assembleSenses disorderNervous disorderFc(alpha) receptorCysteine thiolate
A method for treatment of a mammalian subject for an autoimmune or inflammatory disease, the method comprising: administering to the mammalian subject an effective amount of a polymeric protein comprising five, six or seven polypeptide monomer units; wherein each polypeptide monomer unit comprises an Fc receptor binding portion comprising two immunoglobulin G heavy chain constant regions; wherein each immunoglobulin G heavy chain constant region comprises a cysteine residue which is linked via a disulfide bond to a cysteine residue of an immunoglobulin G heavy chain constant region of an adjacent polypeptide monomer unit; wherein the polymeric protein does not comprise a further immunomodulatory portion; or an antigen portion that causes antigen-specific immunosuppression when administered to the mammalian subject.
Owner:LIVERPOOL SCHOOL OF TROPICAL MEDICINE
Immunoglobulin constant region fc receptor binding agents
InactiveUS20120309941A1Wide applicationPathological conditionAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFc(alpha) receptorAutoimmune condition
Owner:GLIKNIK +1
Method for determining the glycosylation of an antibody
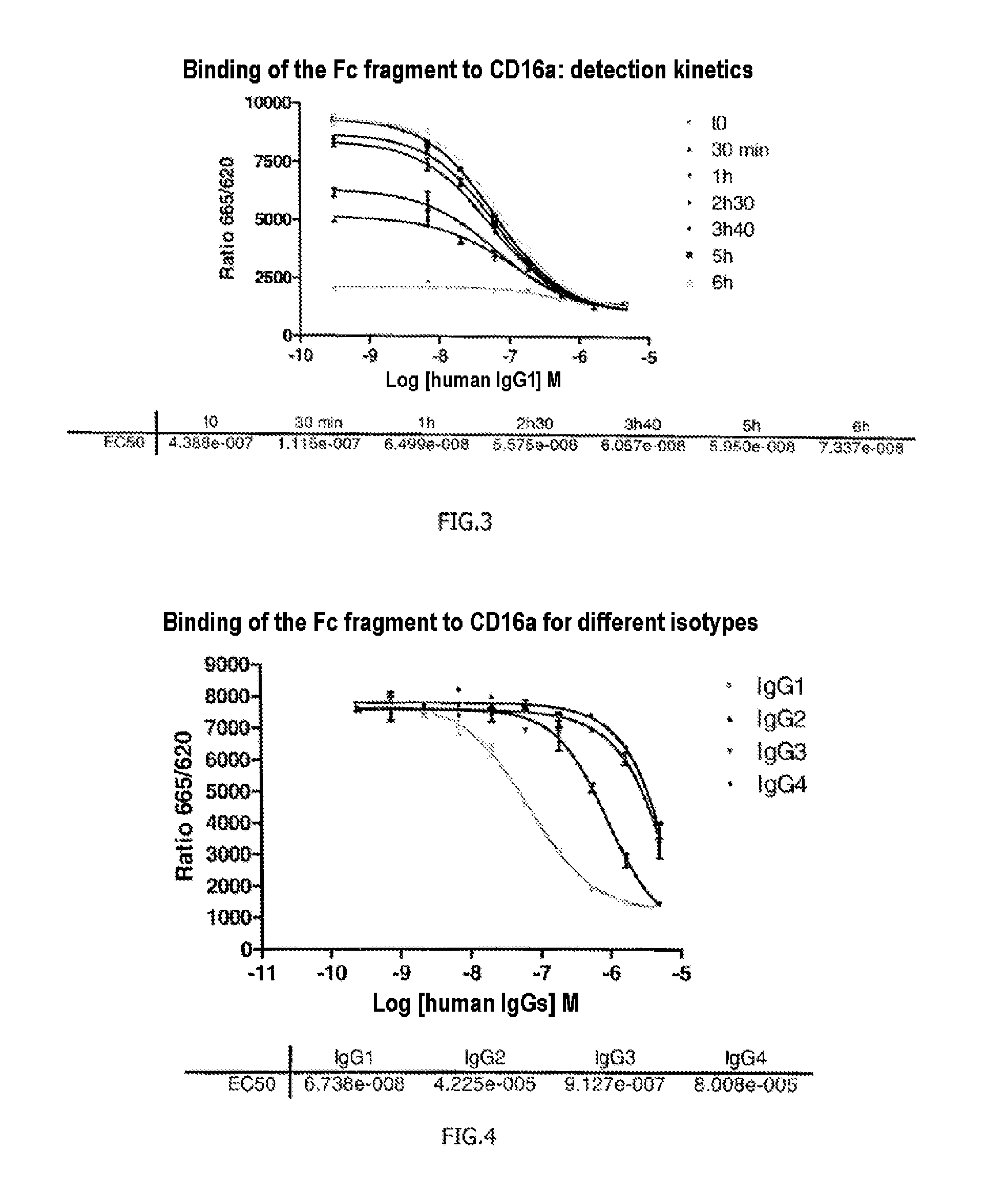
ActiveUS20150024410A1Easy to testBiological testingDetection of post translational modificationsFc(alpha) receptorFc receptor
The invention relates to a method for detecting the binding of an antibody to an Fc receptor present on the surface of a cell as well as to a method for determining the level of glycosylation of an antibody. The invention also relates to a reagent kit for carrying out these methods.
Owner:CISBIO BIOASSAYS
Antigen binding molecules that bind EGFR, vectors encoding same, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20080095770A1Enhance effector functionGood curative effectAnimal cellsSugar derivativesHumanized antibodyDisease cause
The present invention relates to antigen binding molecules (ABMs). In particular embodiments, the present invention relates to recombinant monoclonal antibodies, including chimeric, primatized or humanized antibodies specific for human EGFR. In addition, the present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding such ABMs, and vectors and host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The invention further relates to methods for producing the ABMs of the invention, and to methods of using these ABMs in treatment of disease. In addition, the present invention relates to ABMs with modified glycosylation having improved therapeutic properties, including antibodies with increased Fc receptor binding and increased effector function.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Fc receptor binding proteins
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Fusion constructs and use of same to produce antibodies with increased Fc receptor binding affinity and effector function
ActiveUS8367374B2Function increaseIncreased Fc receptor bindingAntibacterial agentsHydrolasesFc receptorReceptor for activated C kinase 1
The present invention relates to the field of glycosylation engineering of proteins. More particularly, the present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules, including fusion constructs, having catalytic activity and the use of same in glycosylation engineering of host cells to generate polypeptides with improved therapeutic properties, including antibodies with increased Fc receptor binding and increased effector function.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Antibodies to Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA), Methods of Making Same, and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20110104148A1Increase heightGood curative effectBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCarcinoembryonic antigen
The present invention relates to antigen binding molecules (ABMs). In particular embodiments, the present invention relates to recombinant monoclonal antibodies, including chimeric, primatized or humanized antibodies or variants thereof specific for cell surface or membrane bound human CEA. In addition, the present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding such ABMs, and vectors and host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The invention further relates to methods for producing the ABMs of the invention, and to methods of using these ABMs in treatment of disease. In addition, the present invention relates to ABMs with modified glycosylation having improved therapeutic properties, including antibodies with increased Fc receptor binding and increased effector function.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Potency assays for antibody drug substance binding to FC receptor
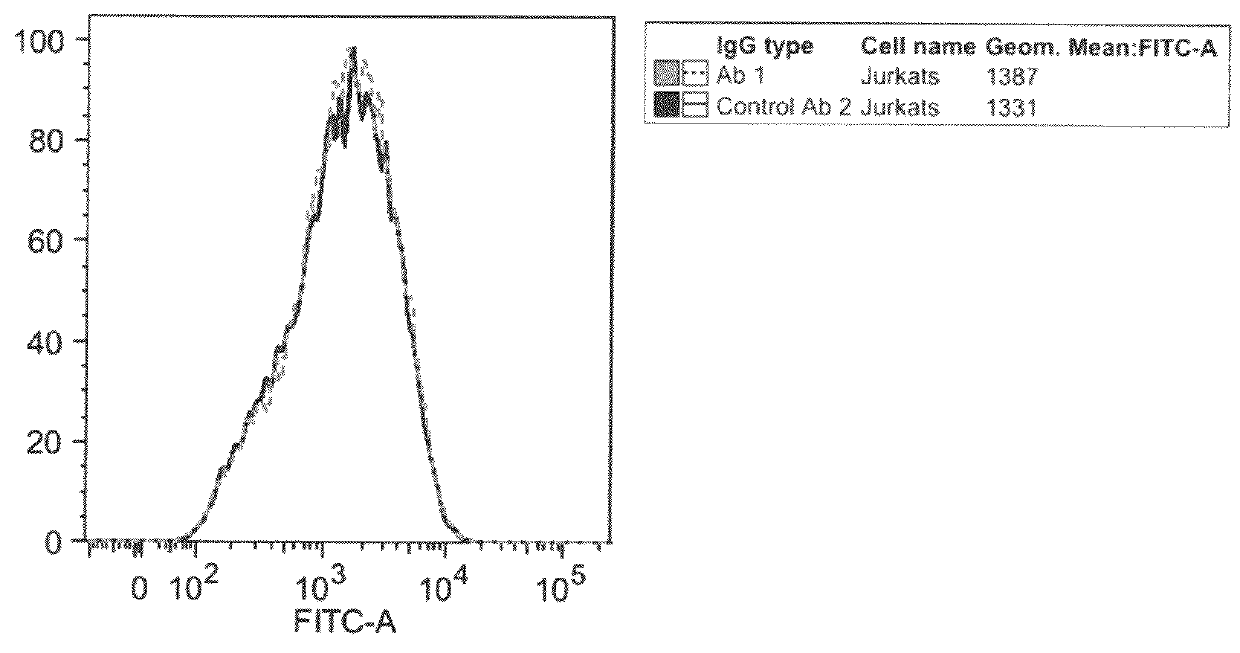
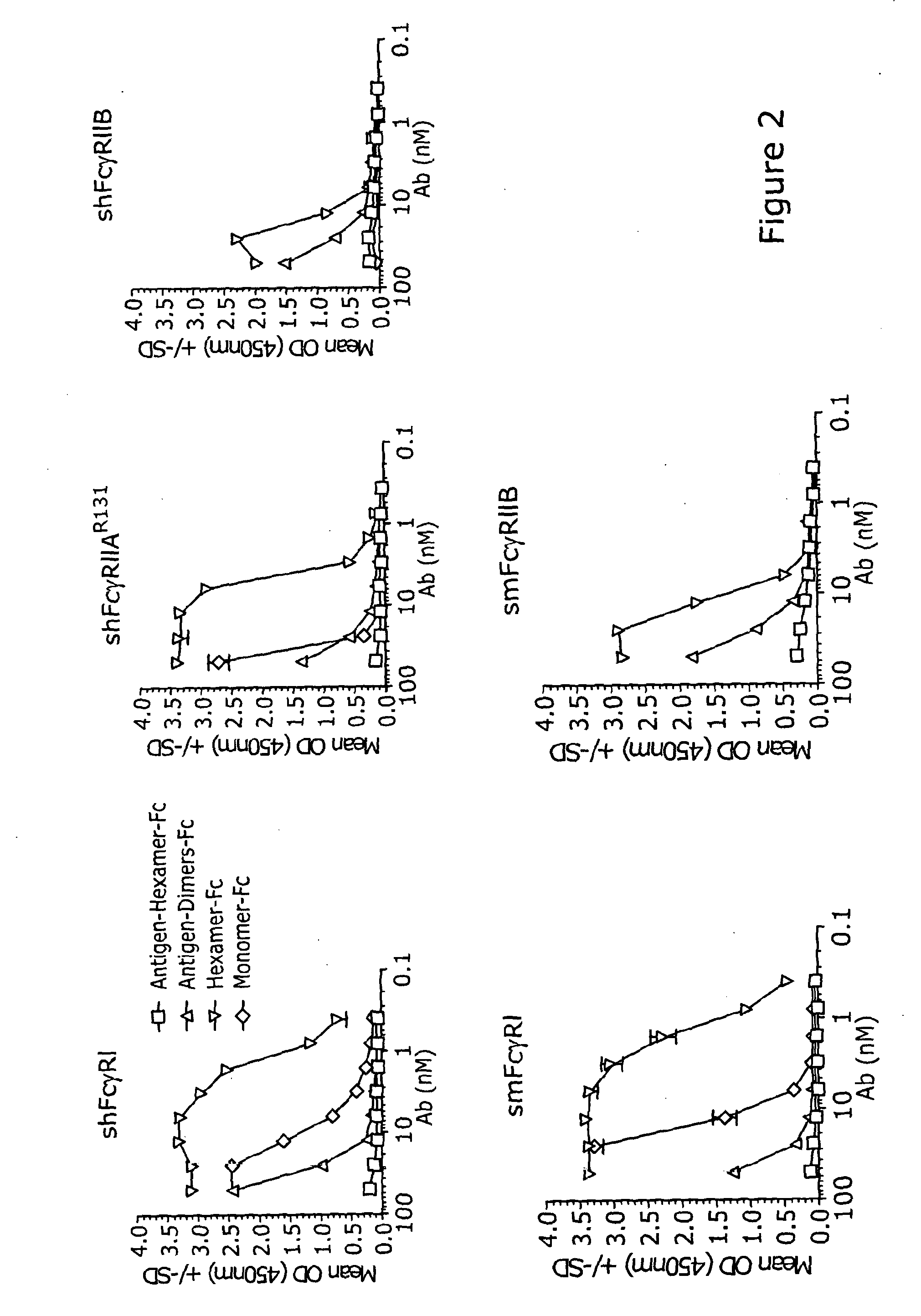
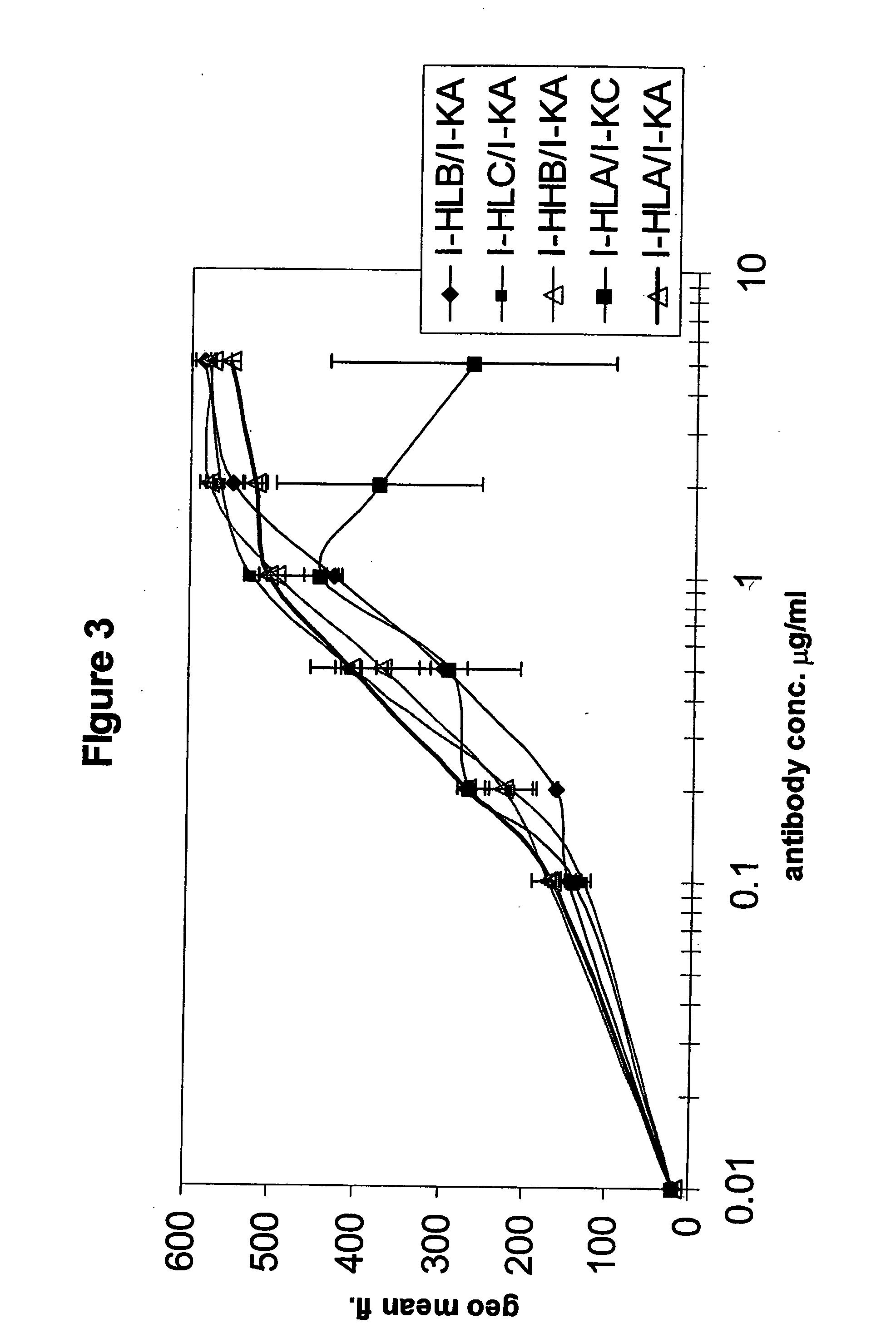
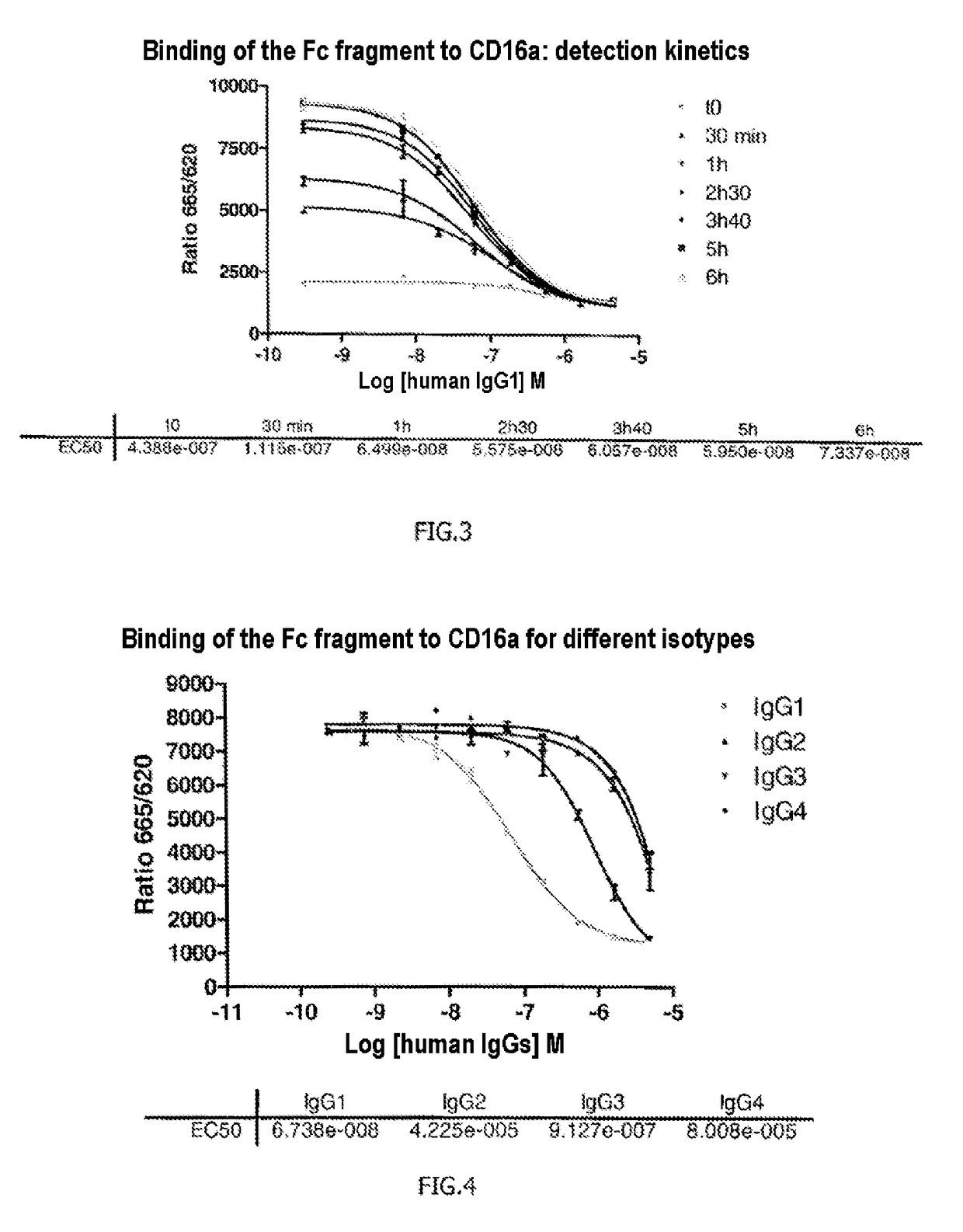
The invention relates to a method of characterizing an antibody, which method is suitable as a potency assay for batch release of a pharmaceutical composition comprising an antibody, specifically for use when applying for marketing authorization for said pharmaceutical composition. The assay provided is a method for determining the potency of a drug product comprising an FcR binding peptide, wherein at least one mechanism of action of the FcR binding peptide of the drug product is mediated through the binding of the FcR binding peptide of the drug product to a Fc receptor, wherein said method comprises determining the binding of the FcR binding peptide of the drug product to an Fc receptor.
Owner:GENMAB AS
Anti-HER2 glycoantibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS10005847B2Increase healing valueHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFc(alpha) receptorFc receptor
The present disclosure relates to a novel class of anti-HER2 monoclonal antibodies comprising a homogeneous population of anti-HER2 IgG molecules having the same N-glycan on each of Fc. The antibodies of the invention can be produced from anti-HER2 monoclonal antibodies by Fc glycoengineering. Importantly, the antibodies of the invention have improved therapeutic values with increased ADCC activity and increased Fc receptor binding affinity compared to the corresponding monoclonal antibodies that have not been glycoengineered.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Antigen binding molecules that bind EGFR, vectors encoding same, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20060269545A1Enhance effector functionGood curative effectBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseHumanized antibody
The present invention relates to antigen binding molecules (ABMs). In particular embodiments, the present invention relates to recombinant monoclonal antibodies, including chimeric, primatized or humanized antibodies specific for human EGFR. In addition, the present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding such ABMs, and vectors and host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The invention further relates to methods for producing the ABMs of the invention, and to methods of using these ABMs in treatment of disease. In addition, the present invention relates to ABMs with modified glycosylation having improved therapeutic properties, including antibodies with increased Fc receptor binding and increased effector function.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Detection method for serum specificity IgE biological activity and kit adopted by same
InactiveCN103823069AAssess the risk of allergiesAssessing Clinical EffectsBiological material analysisBiological testingFc(alpha) receptorCross-link
The invention provides a detection method for serum specificity IgE biological activity and a kit adopted by the same. The detection method comprises the following steps: adopting a KU812 cell system as indicate cells to induce expression of IgE-Fc receptors; incubating serum of a subject and the KU812 cells to facilitate the combination of sIgE to be detected in the serum and the IgE-Fc receptors on the surfaces of the KU812 cells; adding specific allergens combined with the sIgE on the surfaces of the KU812 cells in order to cross-link the receptors and activate the KU812 cells for degranulation and histamine releasing, and simultaneously promoting CD63 molecules in the cells to be transferred onto the surfaces of the cell membranes; marking anti-CD63 antibodies by fluoresceins for cell immunostaining; adopting a flow cytometry to detect the percentage of the expressing CD63 cells in order to finally determine the activated intensity of the KU812 cells. The detection method has the benefits that the detection method can be used for evaluating the risk degree of allergy when patients contact the allergens, as well as evaluating the clinical effects of specific desensitization treatment.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Method for determining the glycosylation of an antibody
ActiveUS9880176B2Biological testingDetection of post translational modificationsFc(alpha) receptorFc receptor
The invention relates to a method for detecting the binding of an antibody to an Fc receptor present on the surface of a cell as well as to a method for determining the level of glycosylation of an antibody.The invention also relates to a reagent kit for carrying out these methods.
Owner:CISBIO BIOASSAYS
Antigen binding molecules that bind EGFR, vectors encoding same, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20080286277A1High affinityFunction increaseAnimal cellsSugar derivativesDiseaseHumanized antibody
The present invention relates to antigen binding molecules (ABMs). In particular embodiments, the present invention relates to recombinant monoclonal antibodies, including chimeric, primatized or humanized antibodies specific for human EGFR. In addition, the present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding such ABMs, and vectors and host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The invention further relates to methods for producing the ABMs of the invention, and to methods of using these ABMs in treatment of disease. In addition, the present invention relates to ABMs with modified glycosylation having improved therapeutic properties, including antibodies with increased Fc receptor binding and increased effector function.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
No mitogen activity anti CD3 small molecular antibody designing method
InactiveCN1891716AMitogen activity was not apparentMitogen activity is evidentMetabolism disorderAntinoxious agentsAmyotrophic lateral sclerosisOrgan transplantation
The invention relates to an engineering method for constructing mini-antibody of non-mitogen anti-human CD3 and its usage. The antibody of CD3 with a minibody structure is constructed by CH1, CH2 region, which contains Fc receptor binding site in the structures without antibodies. The antibody can bind with the antigenic specificity of CD3 of T achroacytes' surface and can initiate immunosuppressive function and meanwhile, there is no obvious activity for promoting the mitogen. The antibody can be used for the prevention and treatment about acute rejection in organ transplantation and the treatment about type I diabetes, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis of spinal cord and other autoimmune diseases.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
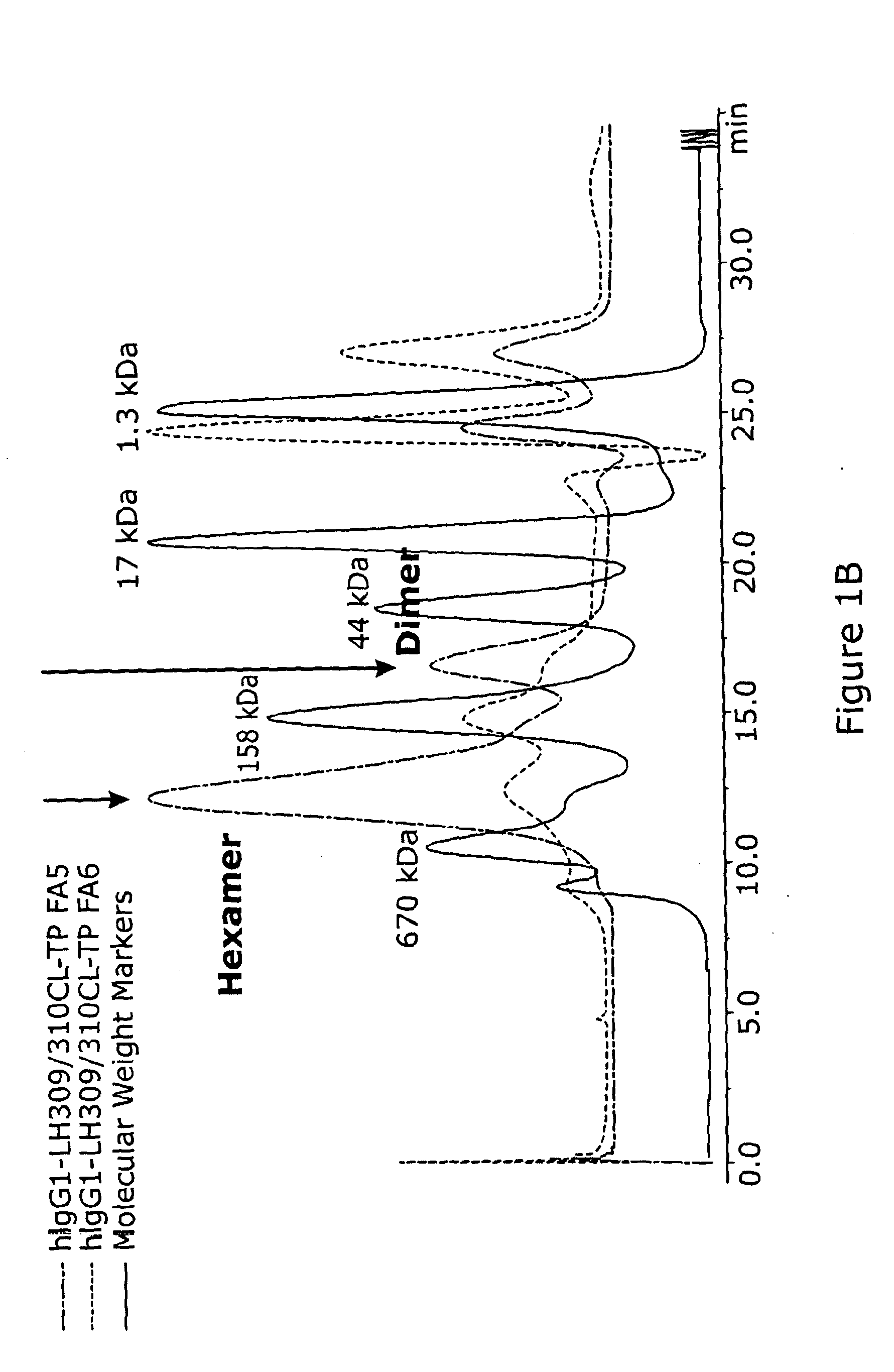
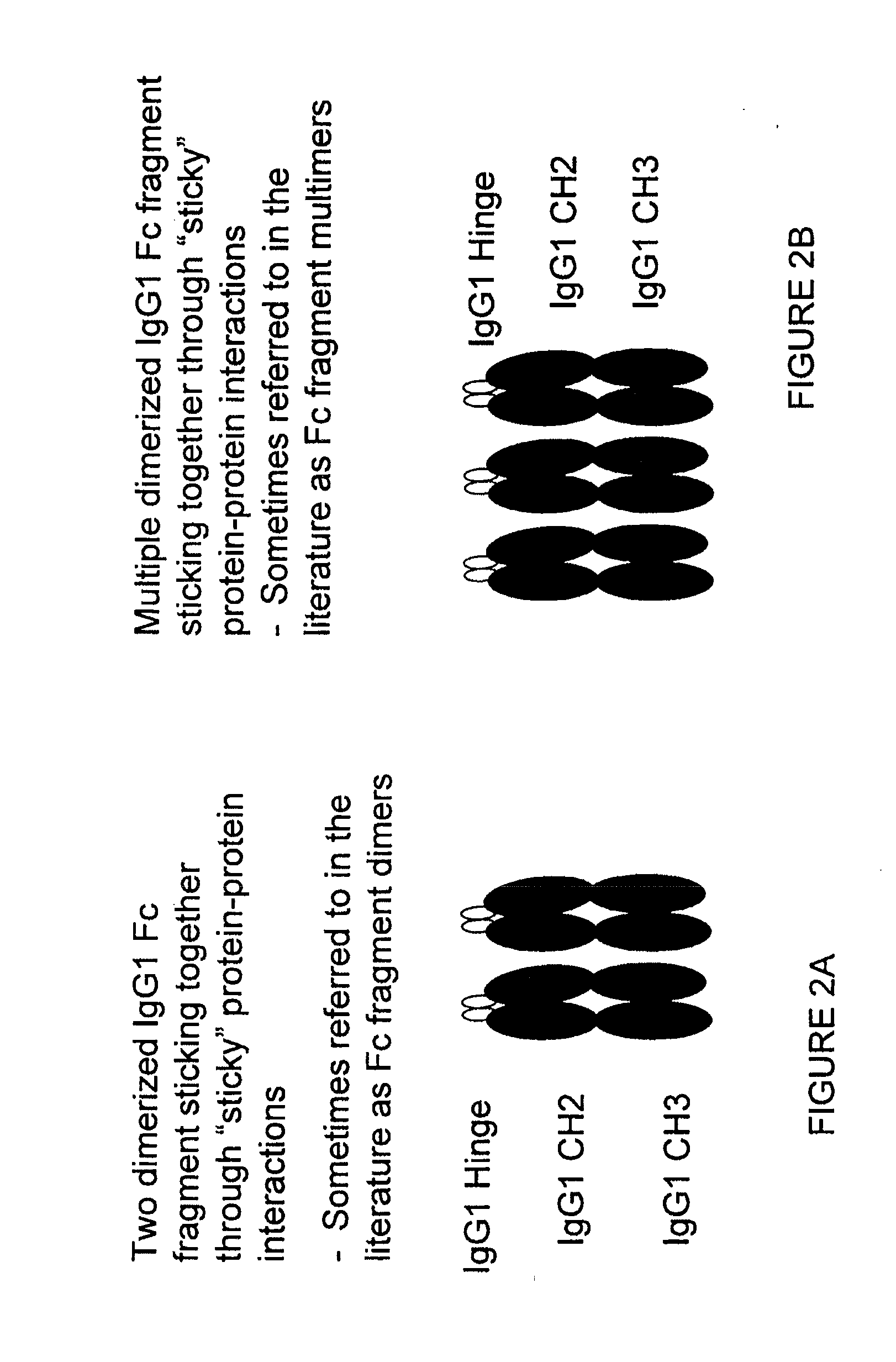
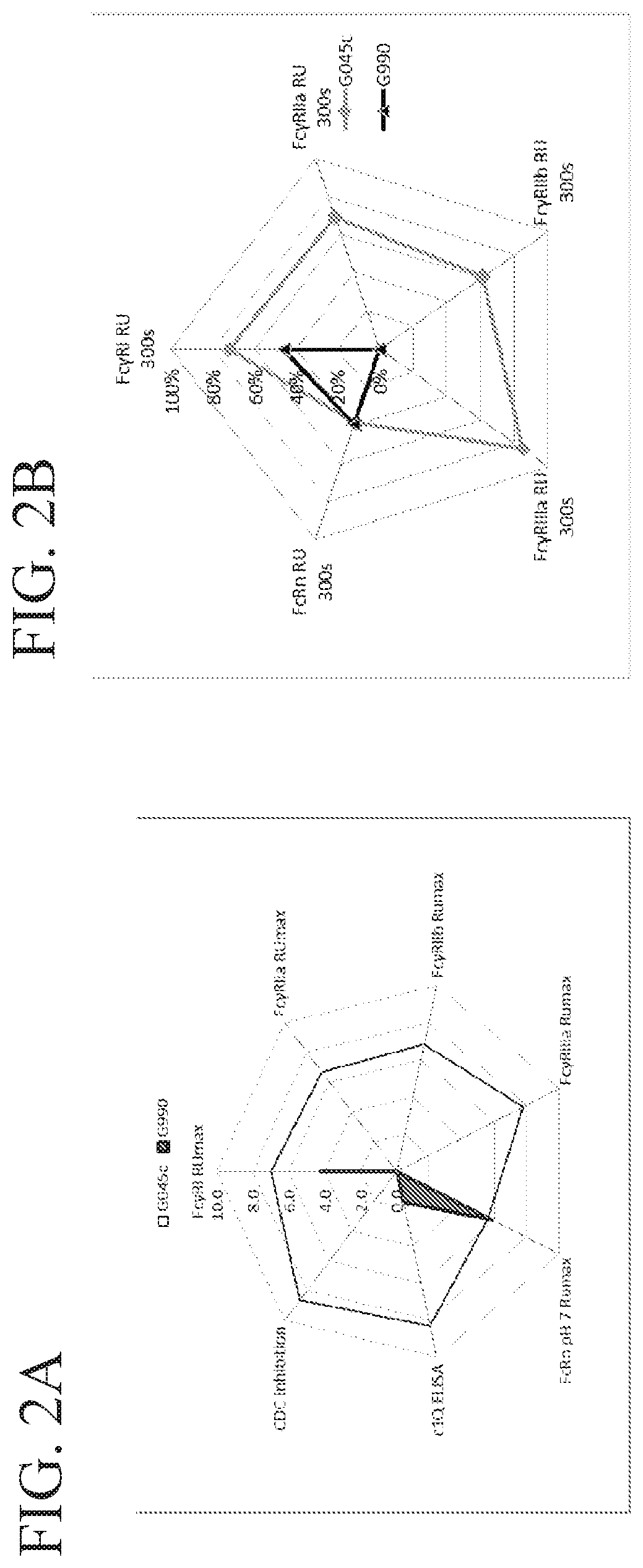
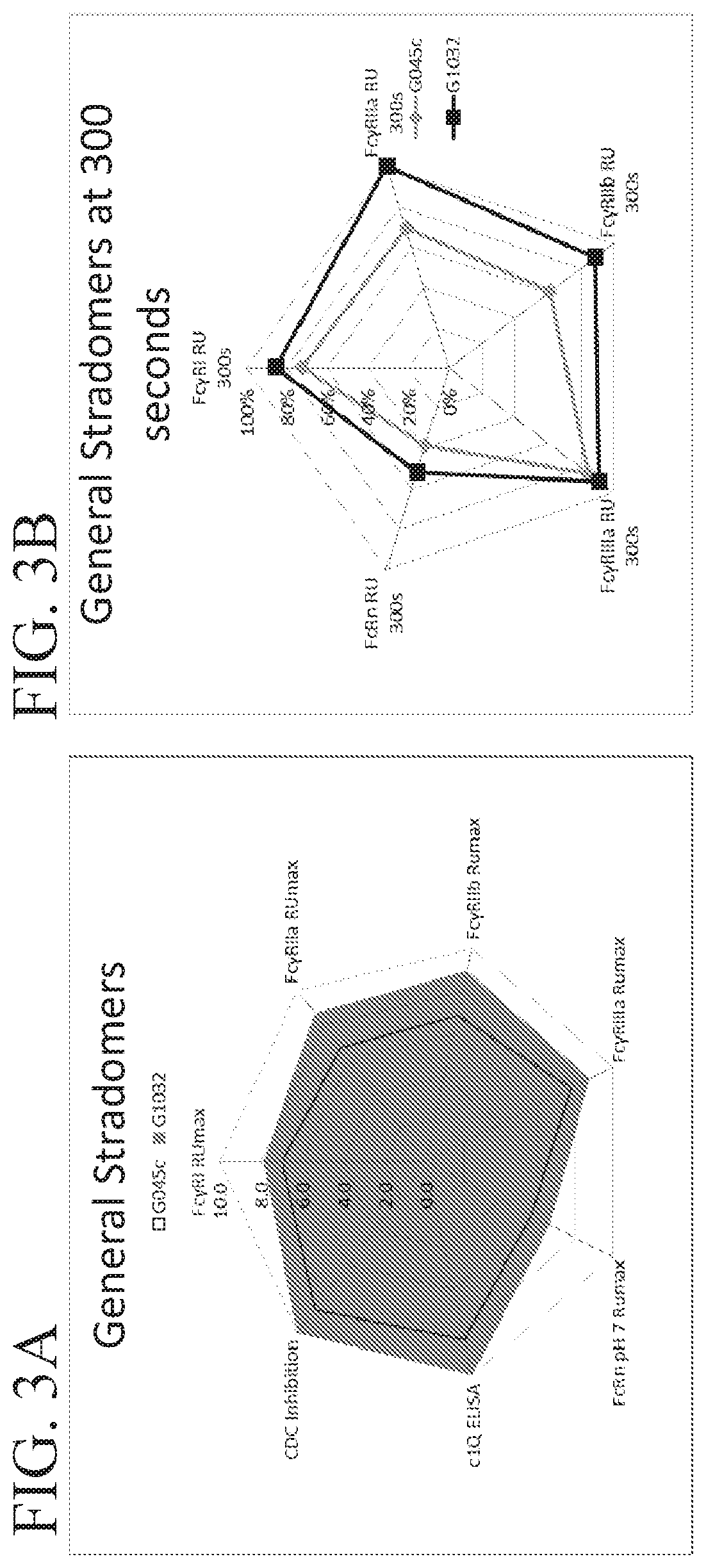
Fusion proteins of human protein fragments to create orderly multimerized immunoglobulin fc compositions with enhanced fc receptor binding
InactiveUS20190389941A1Retained and enhanced bindingEnhanced multimerizationSenses disorderNervous disorderDiseaseHuman proteins
The current invention involves a series of fully recombinant multimerized forms of immunoglobulin Fc which thereby present polyvalent immunoglobulin Fc to immune cell receptors. The fusion proteins exist as both homodimeric and highly ordered multimeric fractions, termed stradomers. The invention involves fusion proteins that bind to FcγRs and complement and that are useful in the treatment and prevention of disease.
Owner:GLIKNIK
Therapeutic compounds comprised of anti-fc receptor binding agents
InactiveCN101092453AHigh affinityImprove featuresPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFc receptorFc(alpha) receptor
Multispecific multivalent molecules which are specific to an Fc receptor (FcR), and therapeutic uses and methods for making the molecules are described.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com