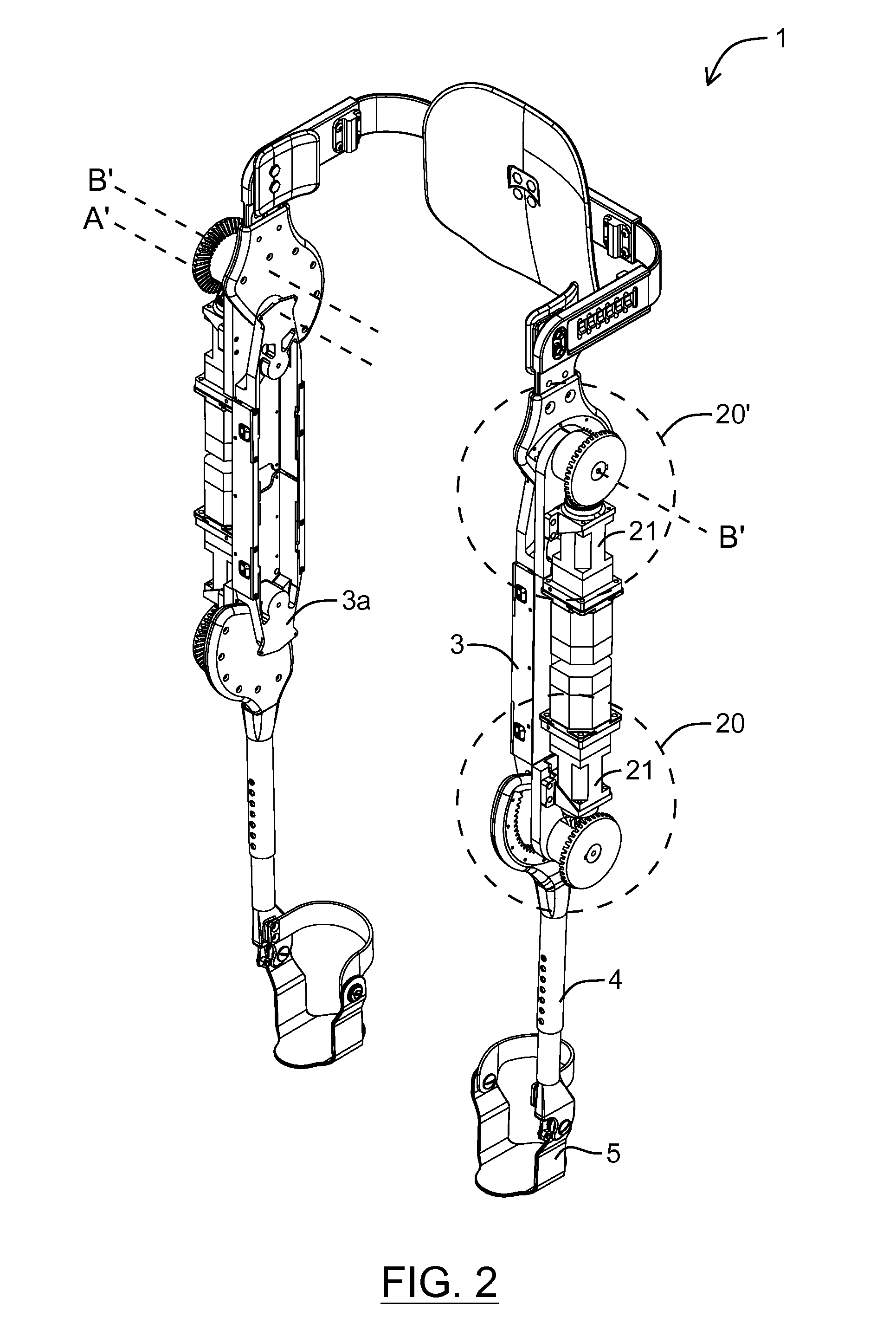
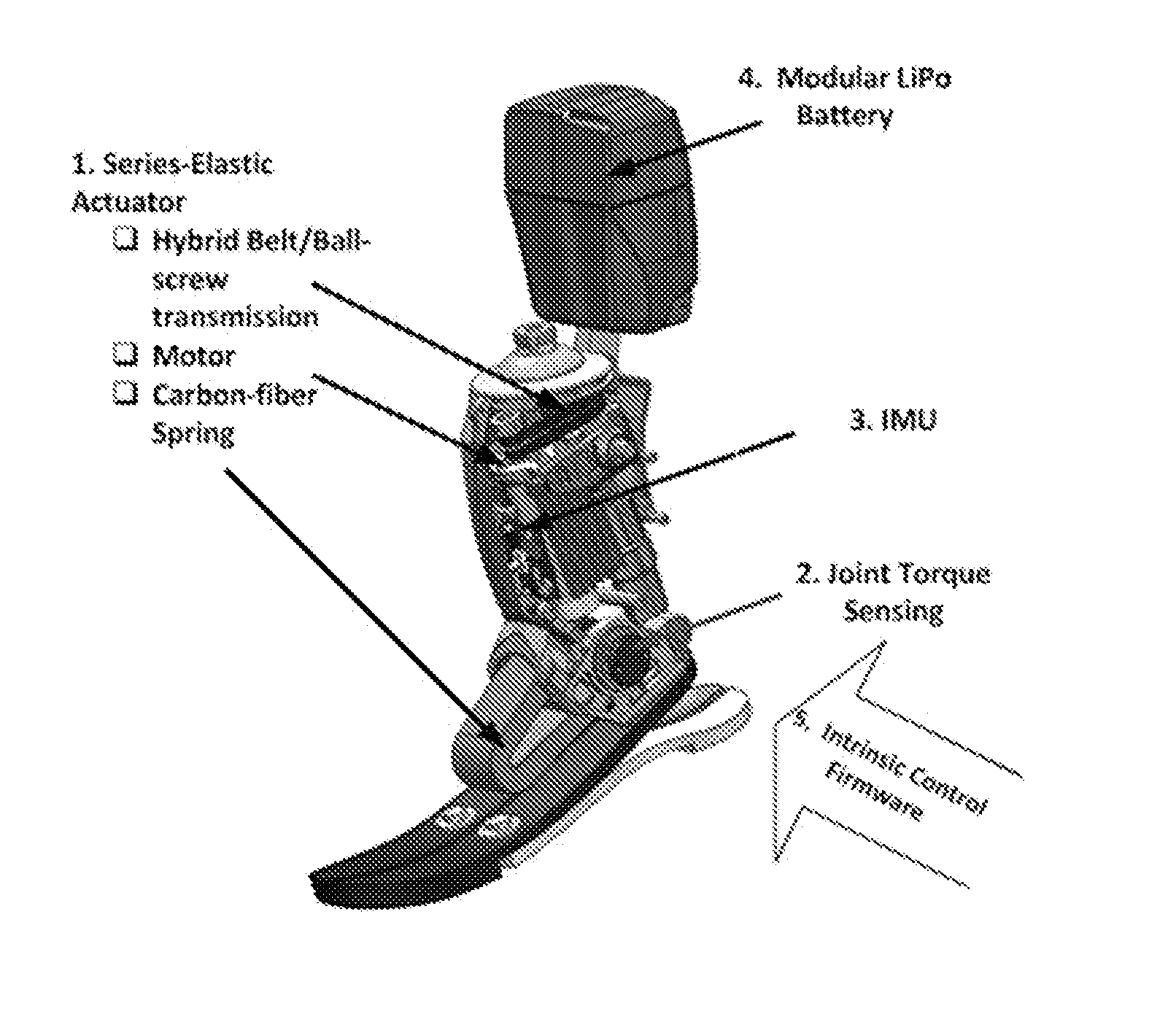
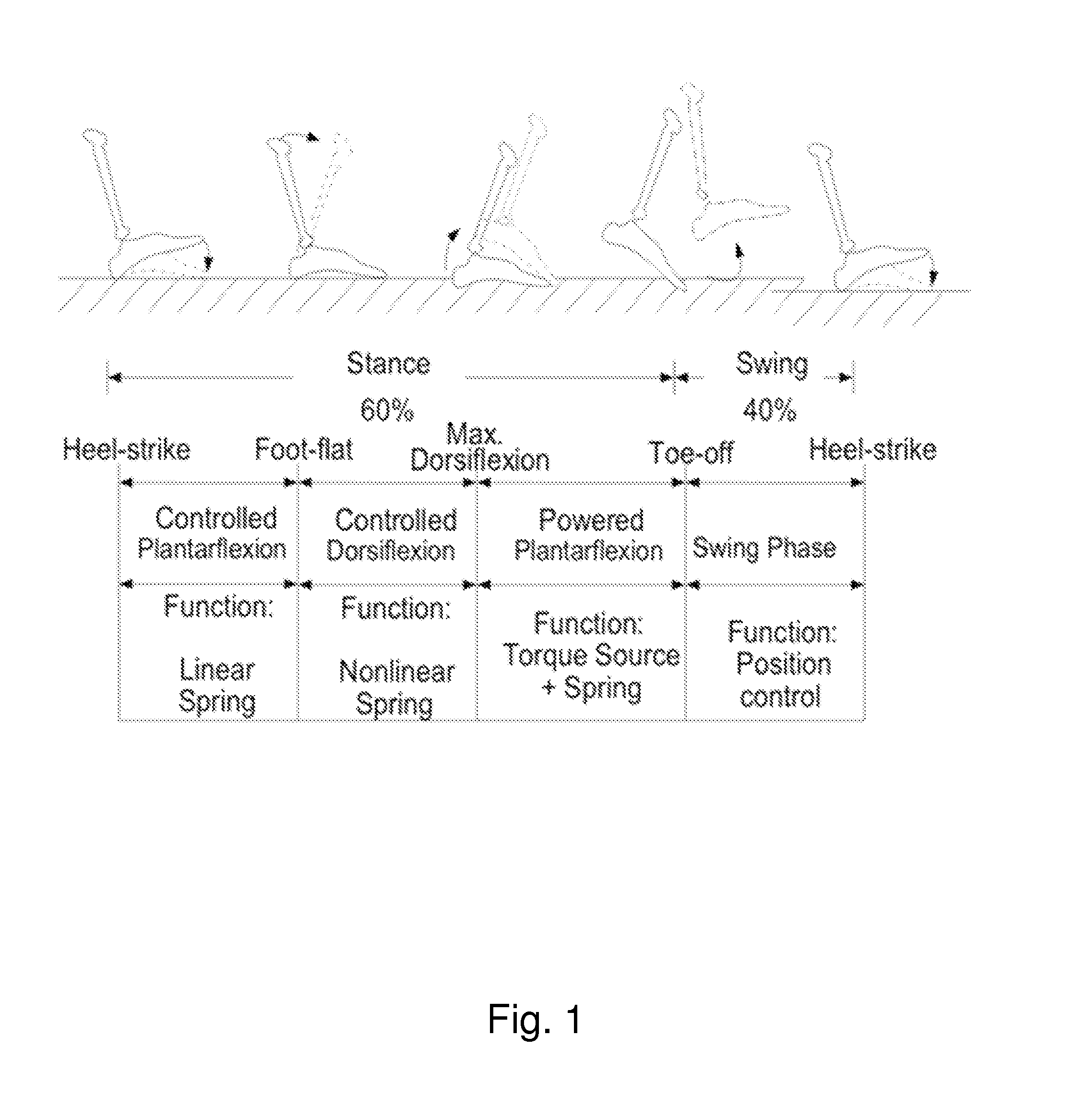
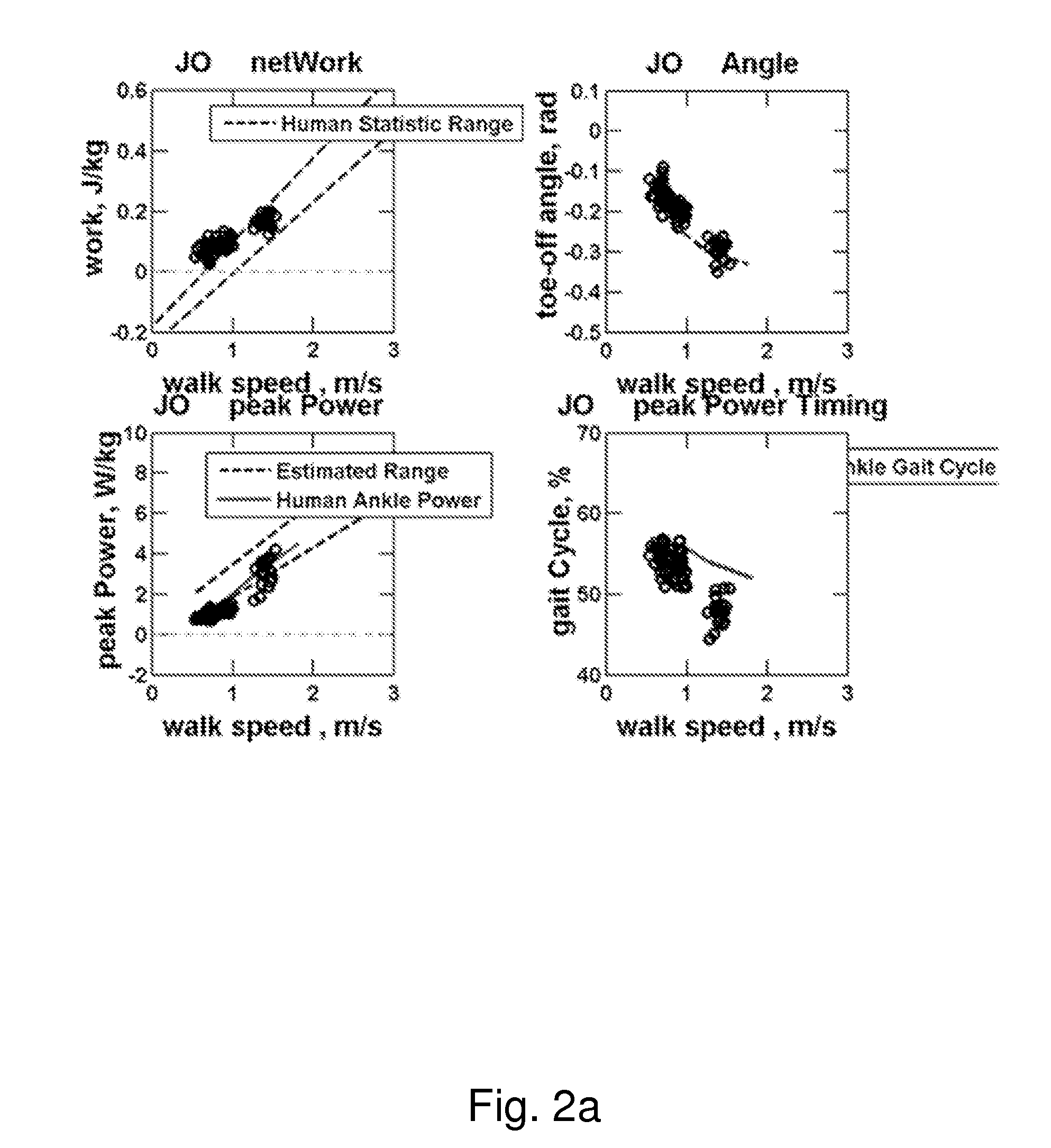
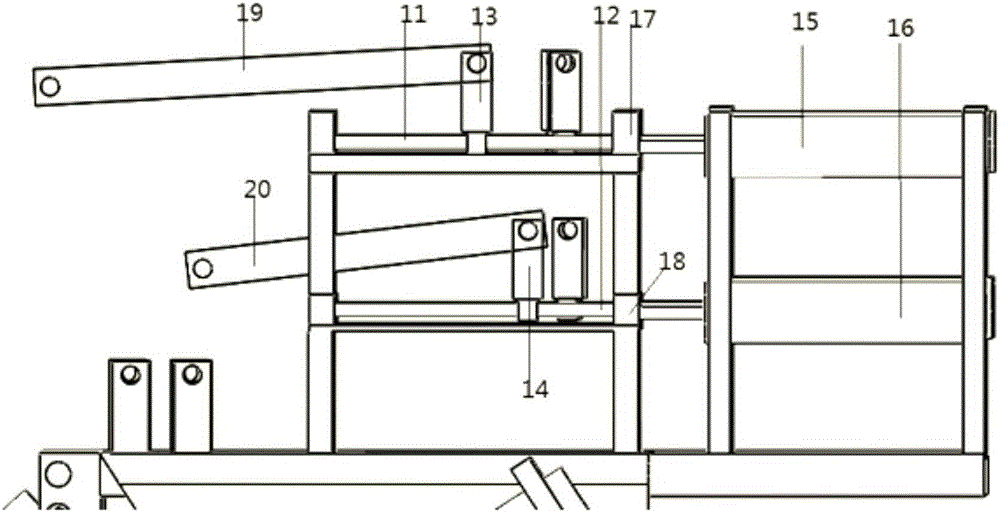
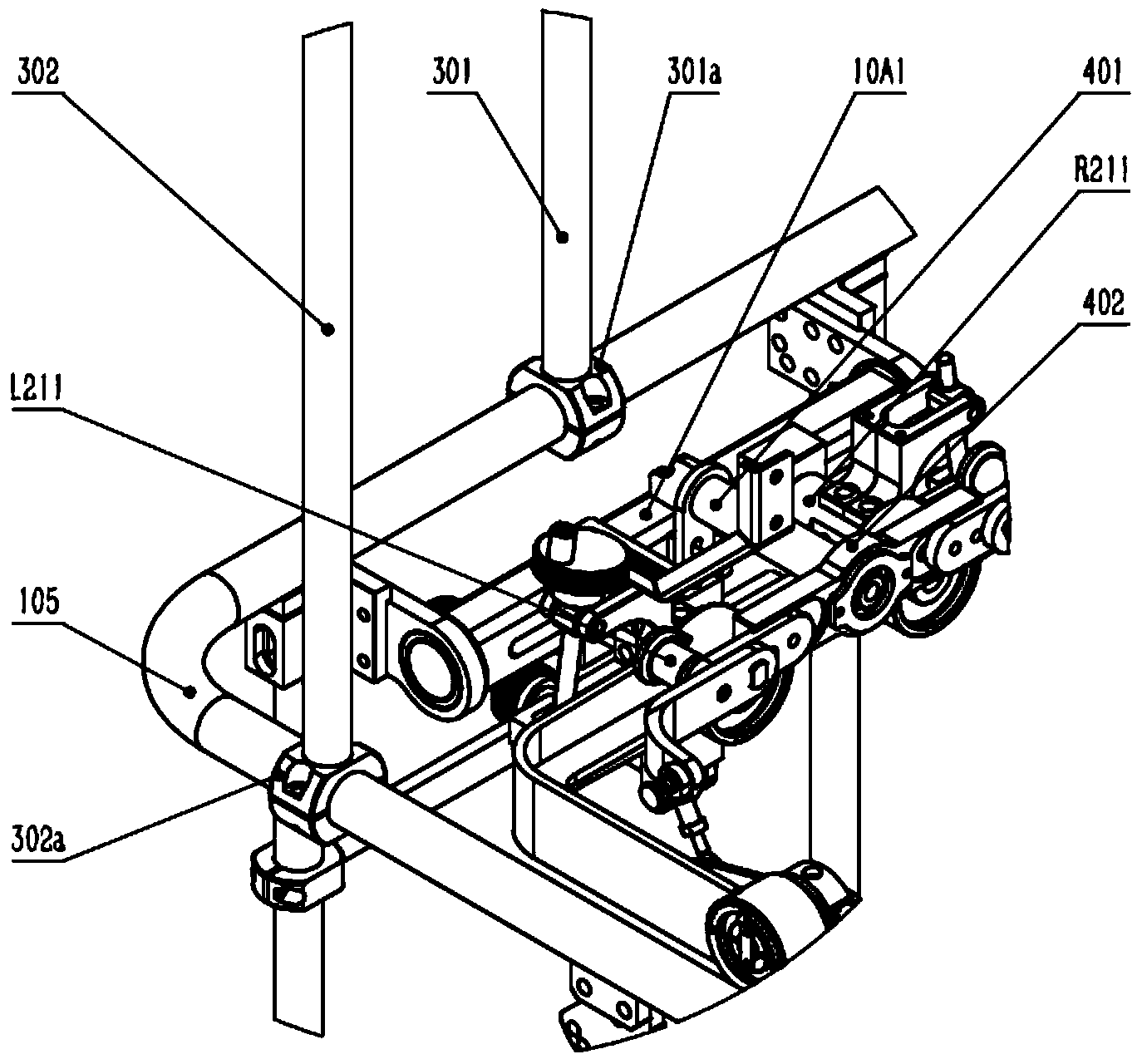
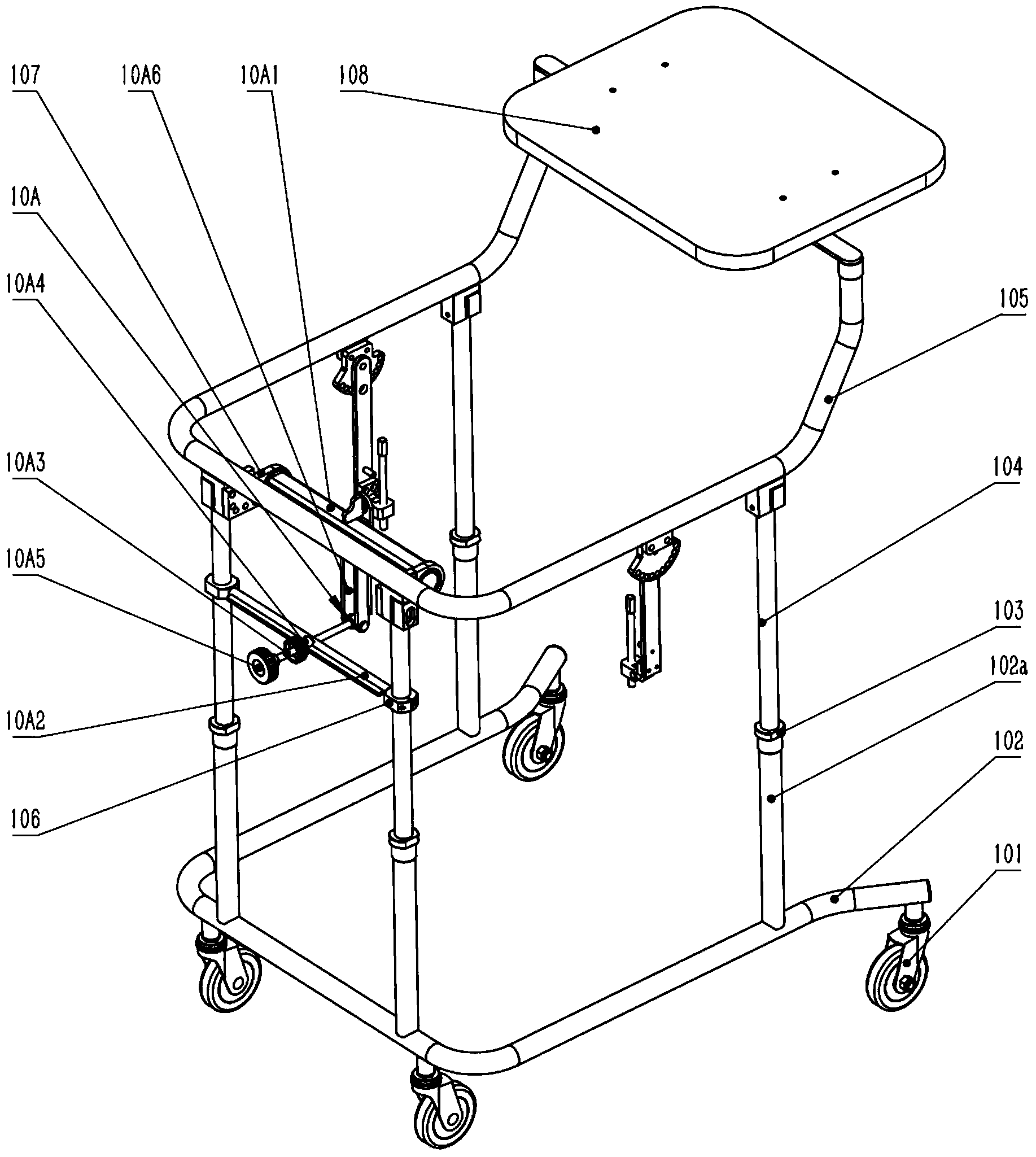
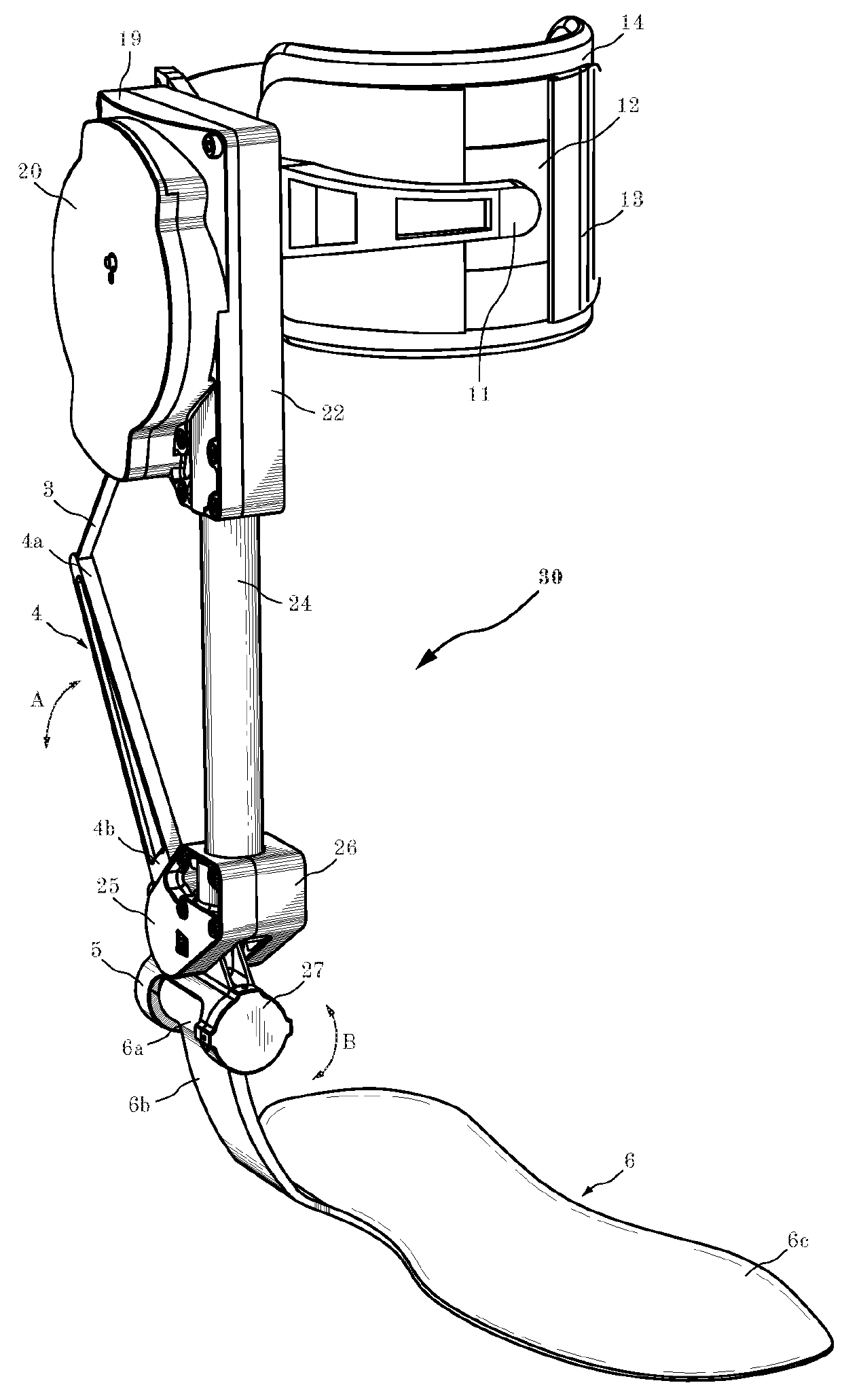
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
284 results about "Exoskeleton Device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
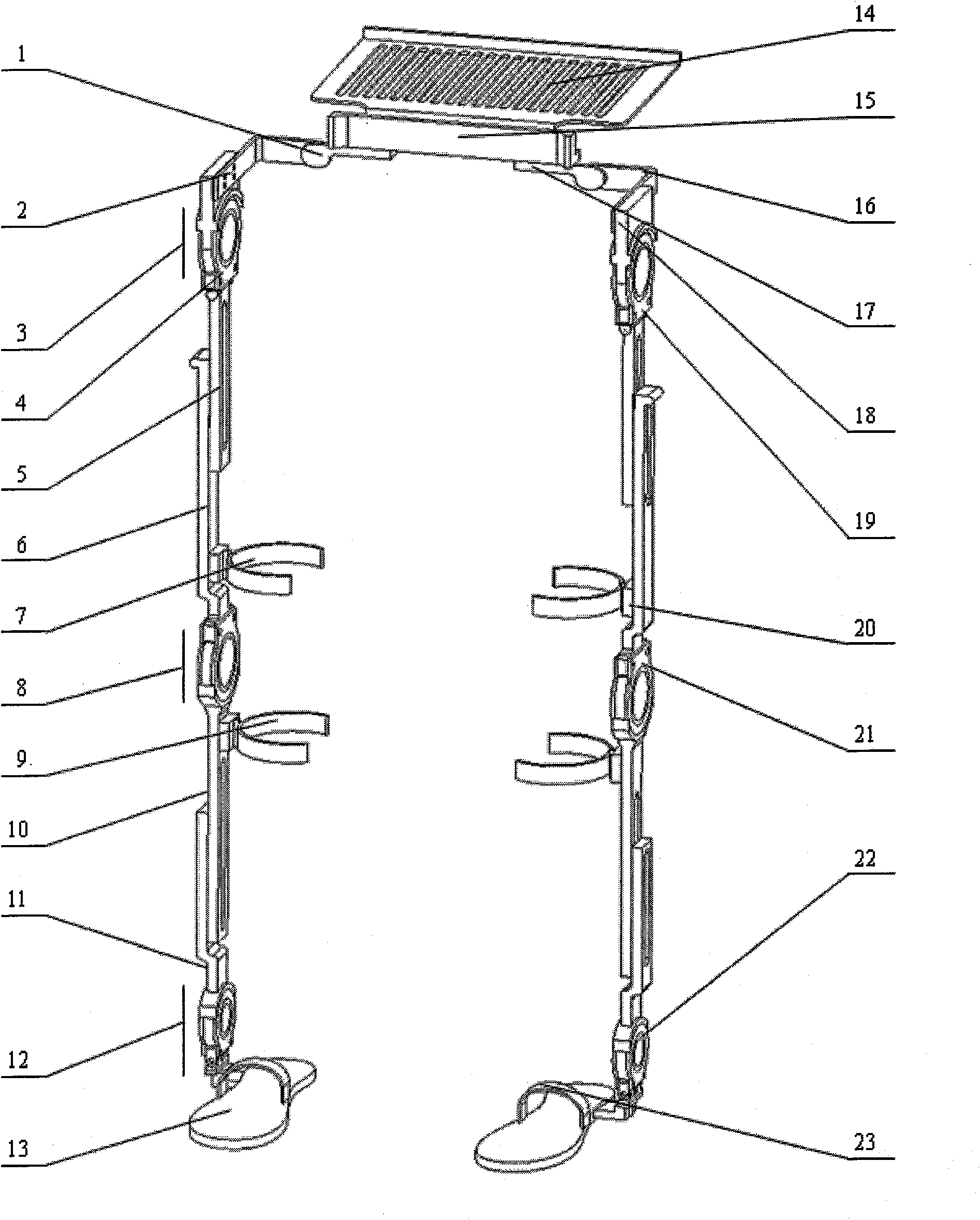
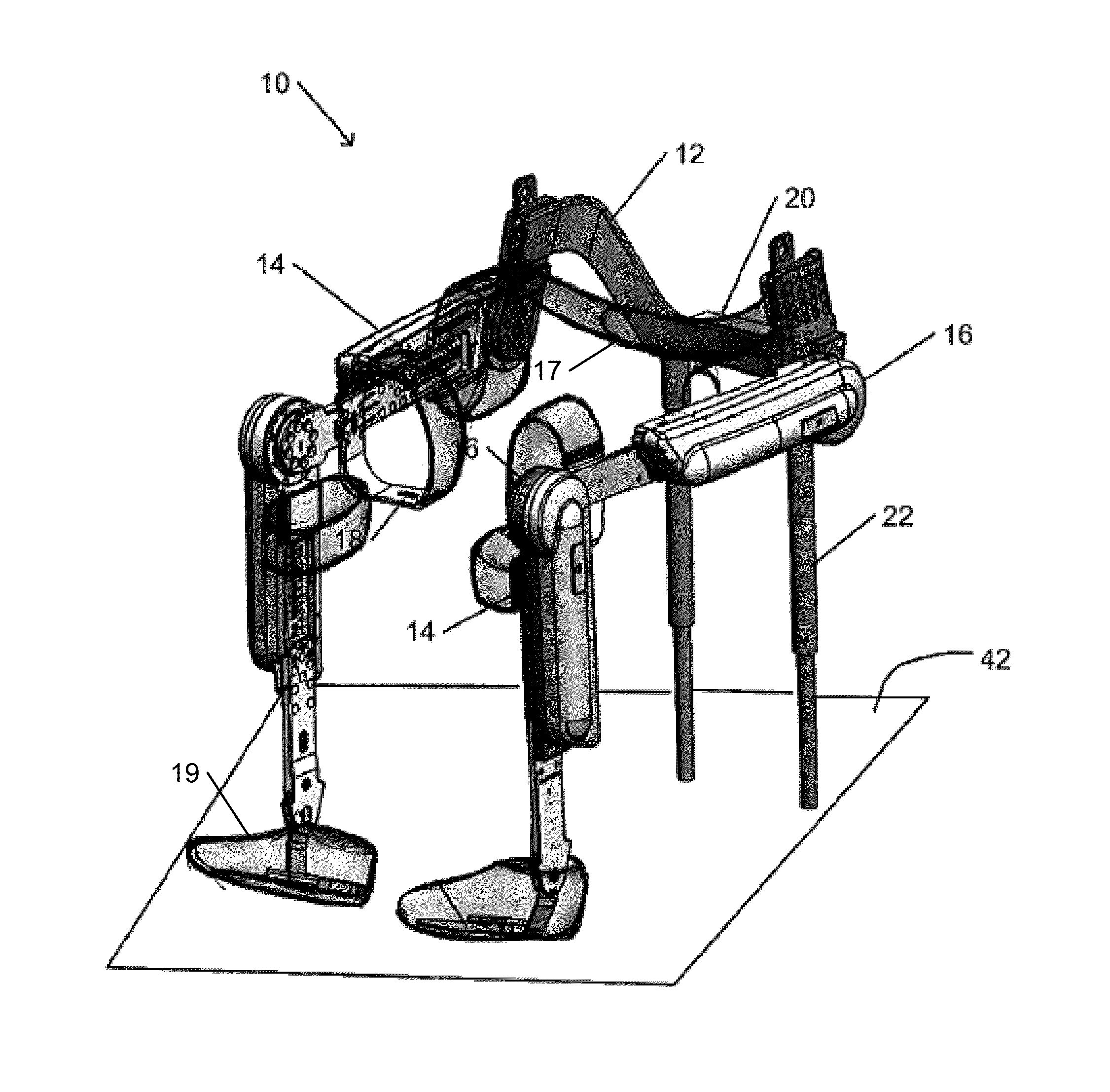
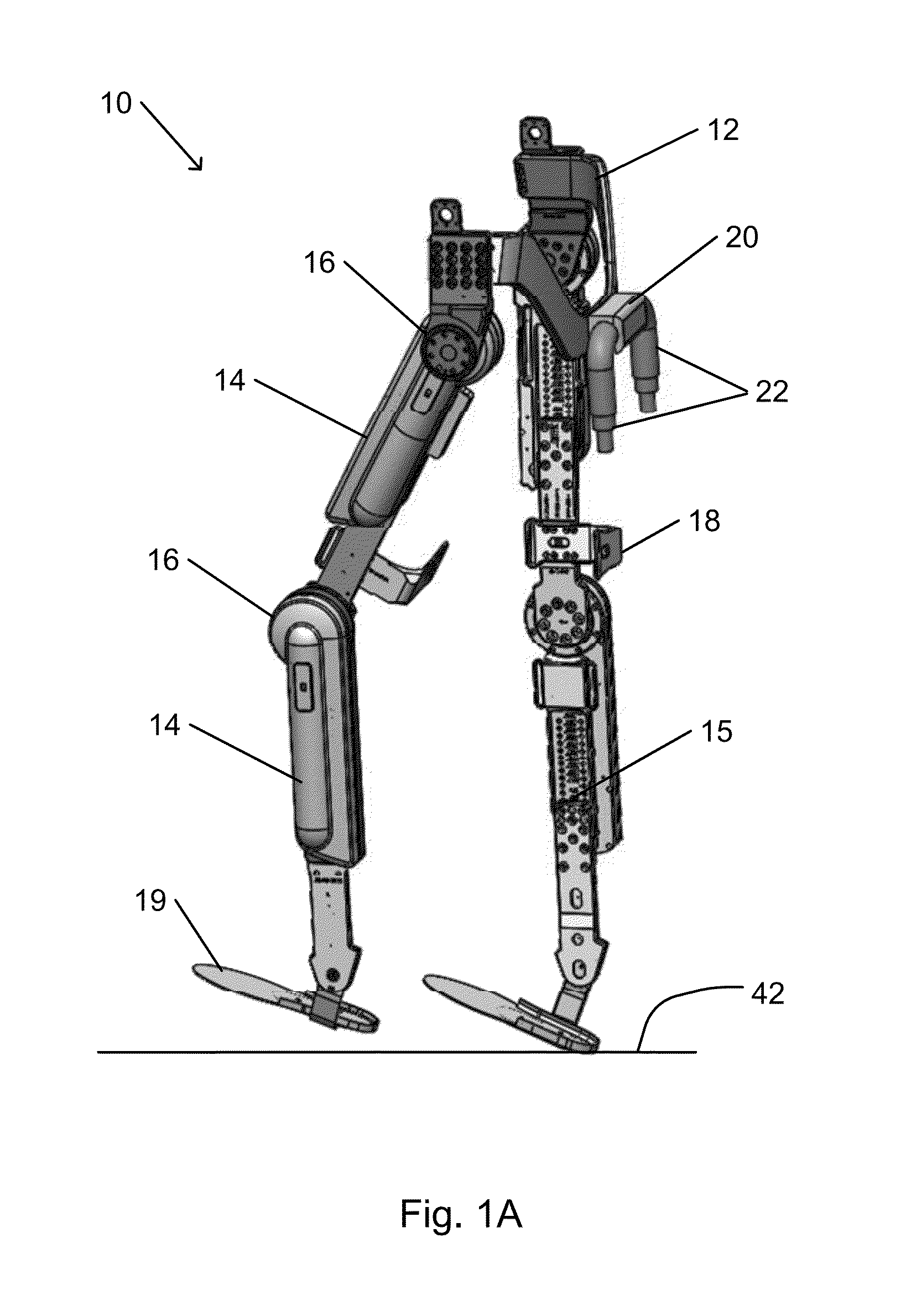
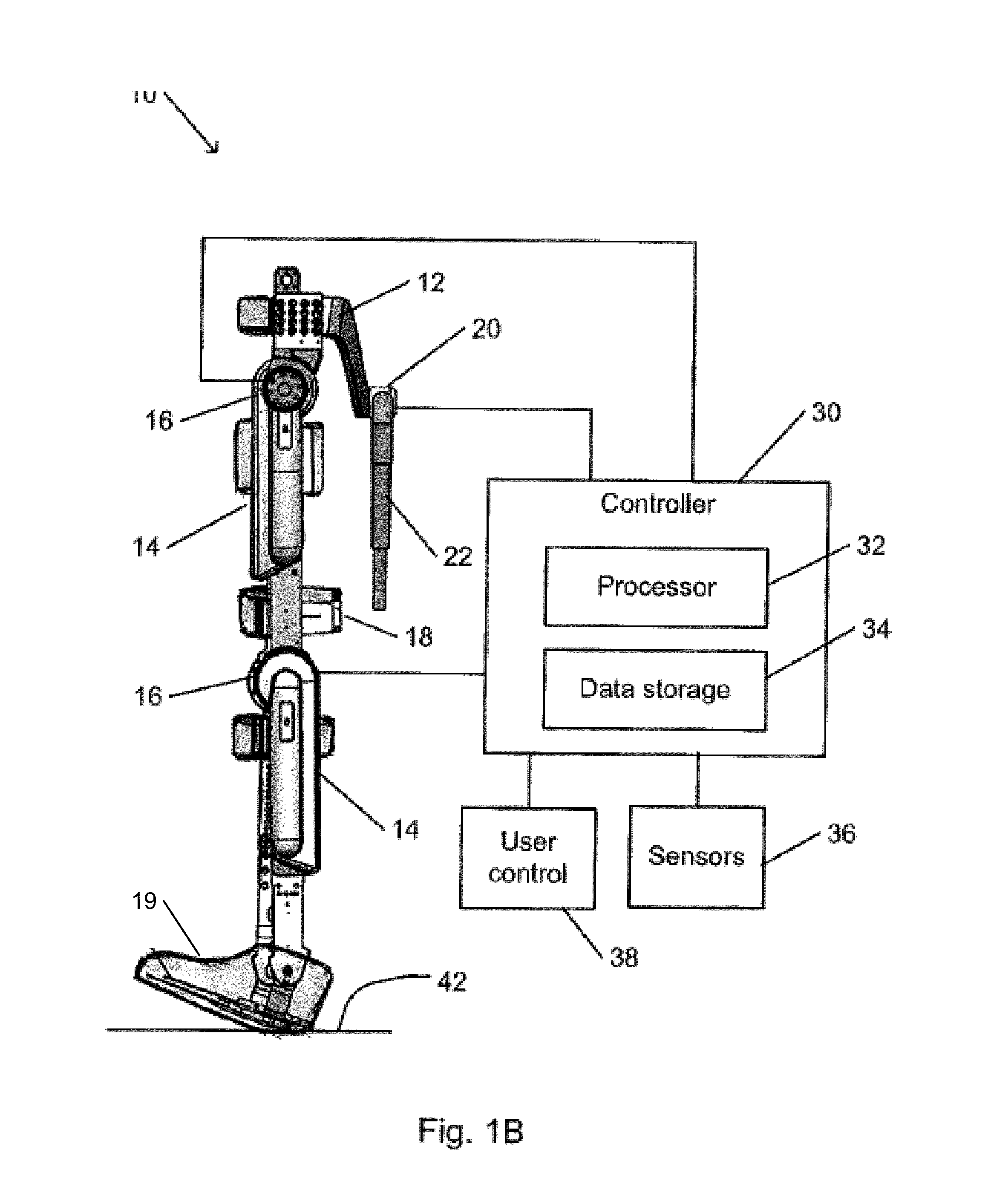
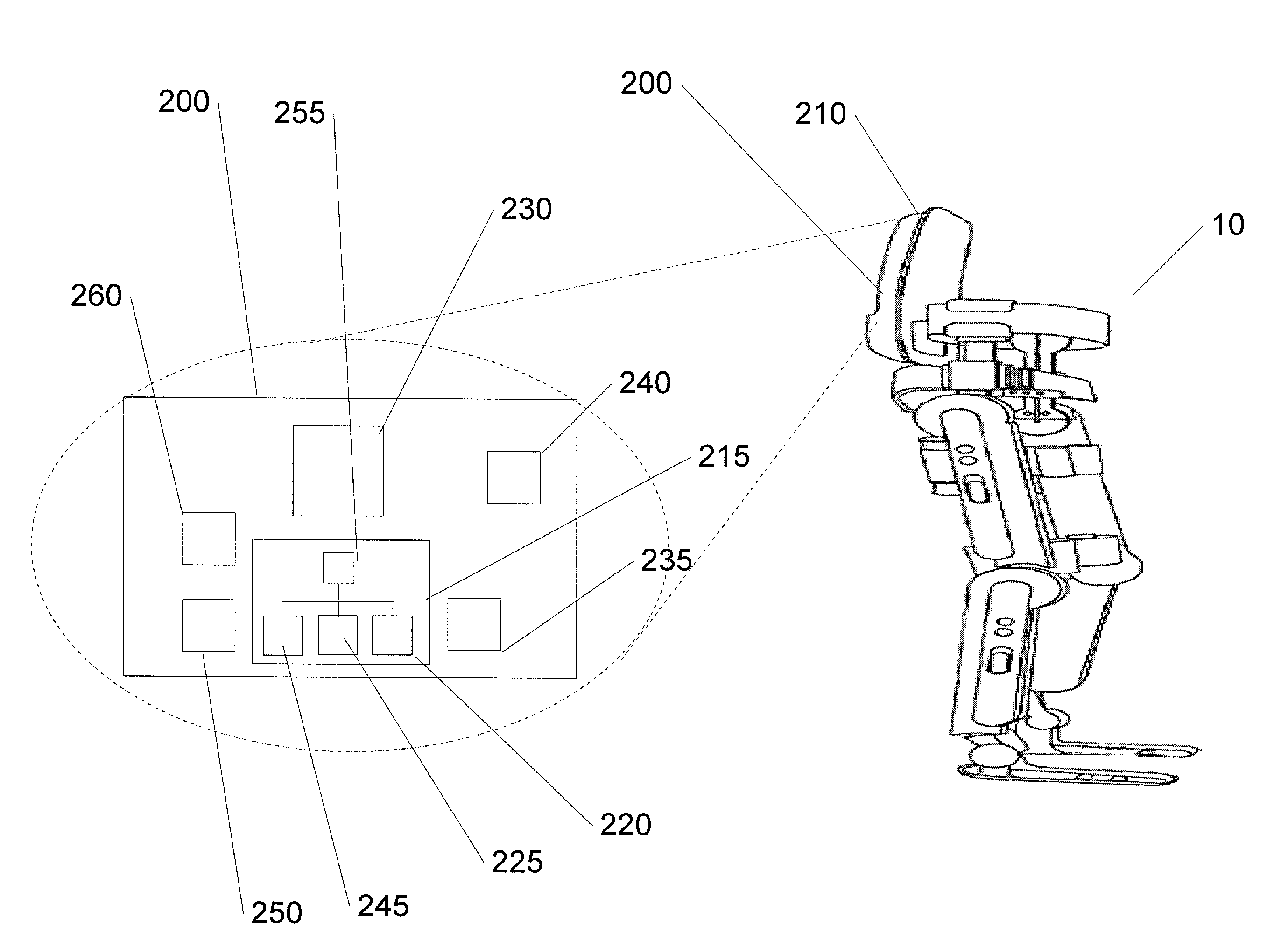
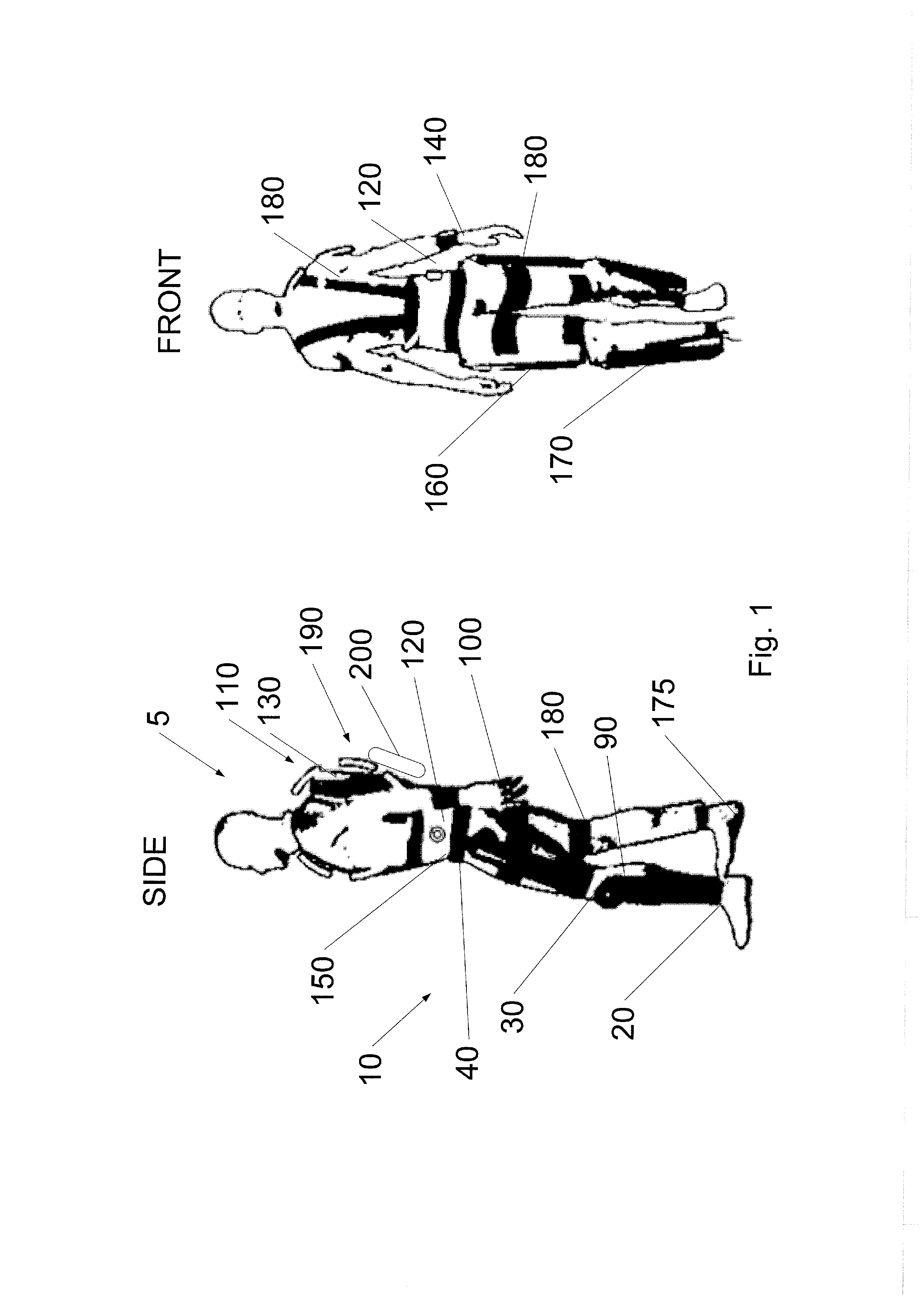
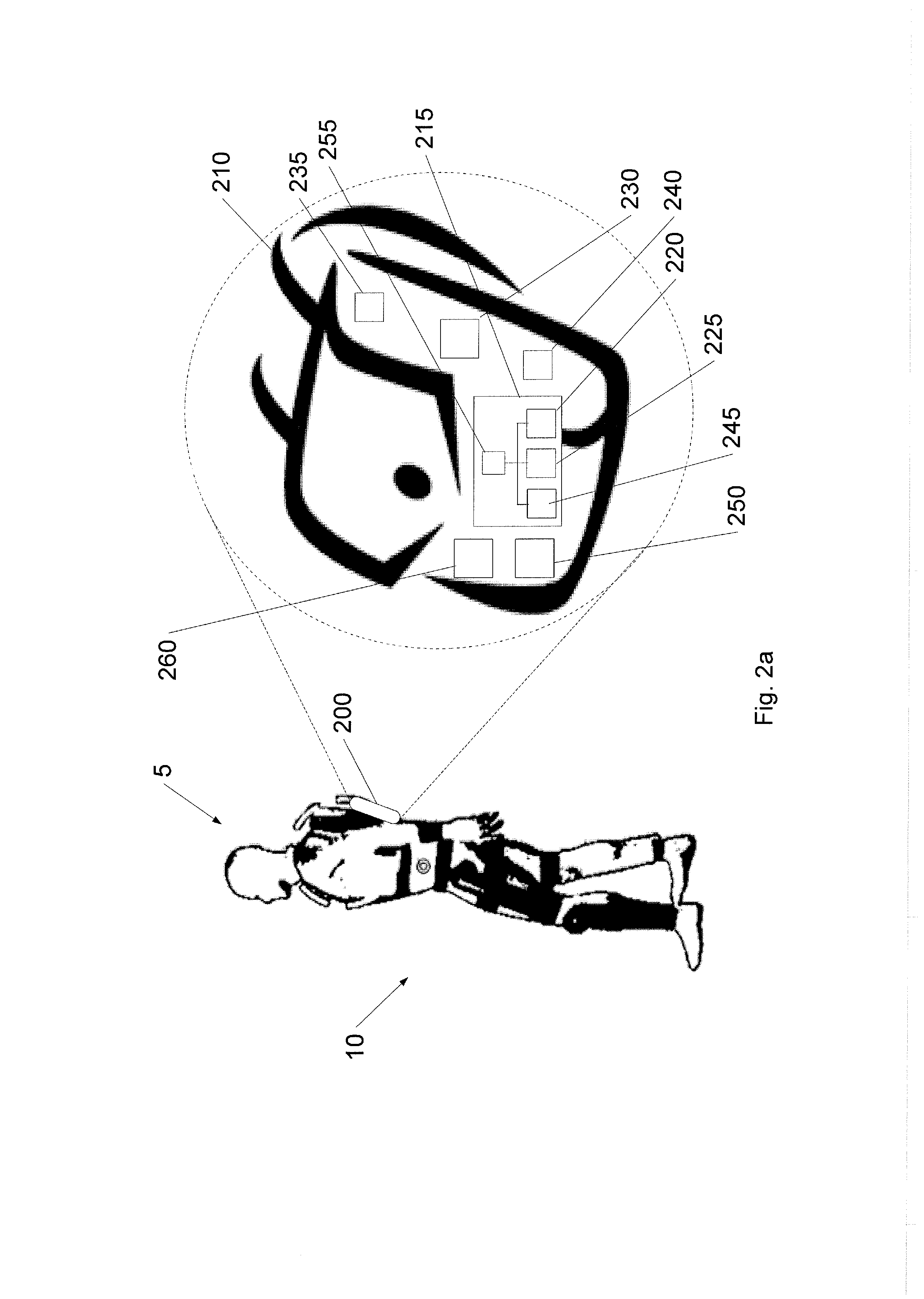
Device designed to wear externally to support muscular skeletal system in various movements such as RANGE OF MOTIONS; WEIGHT-BEARING; GAIT; and LOCOMOTION.
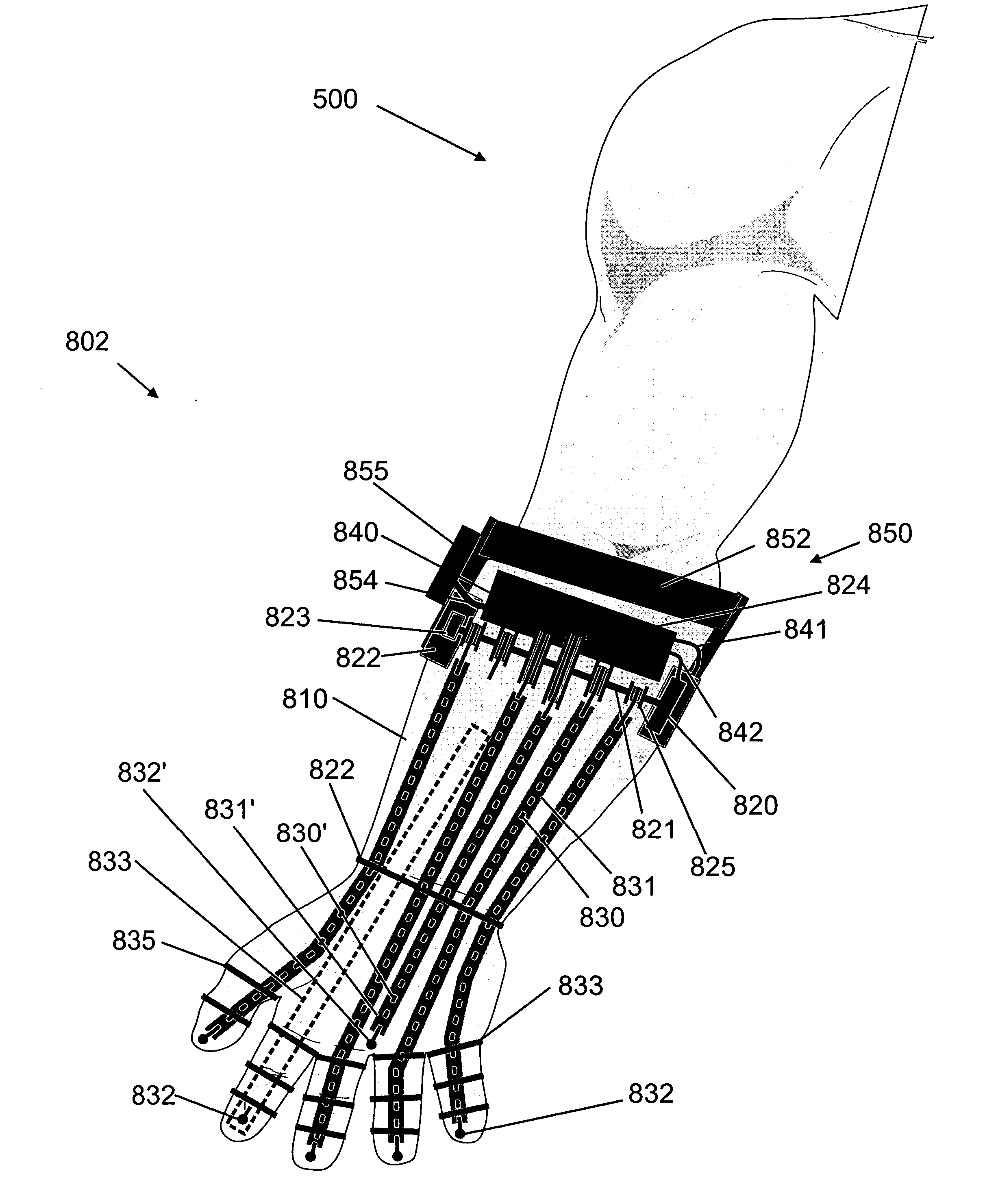
Limb and digit movement system
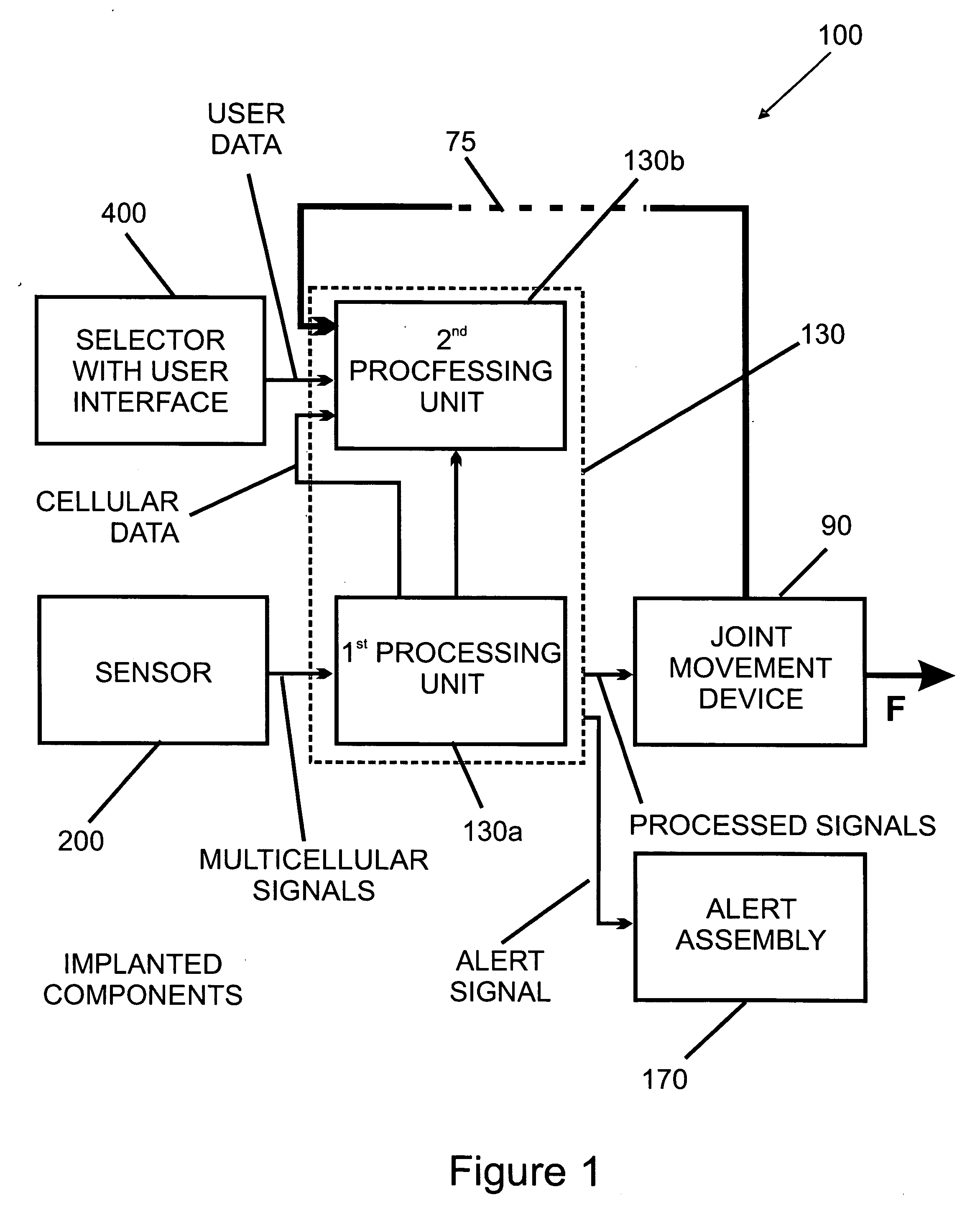
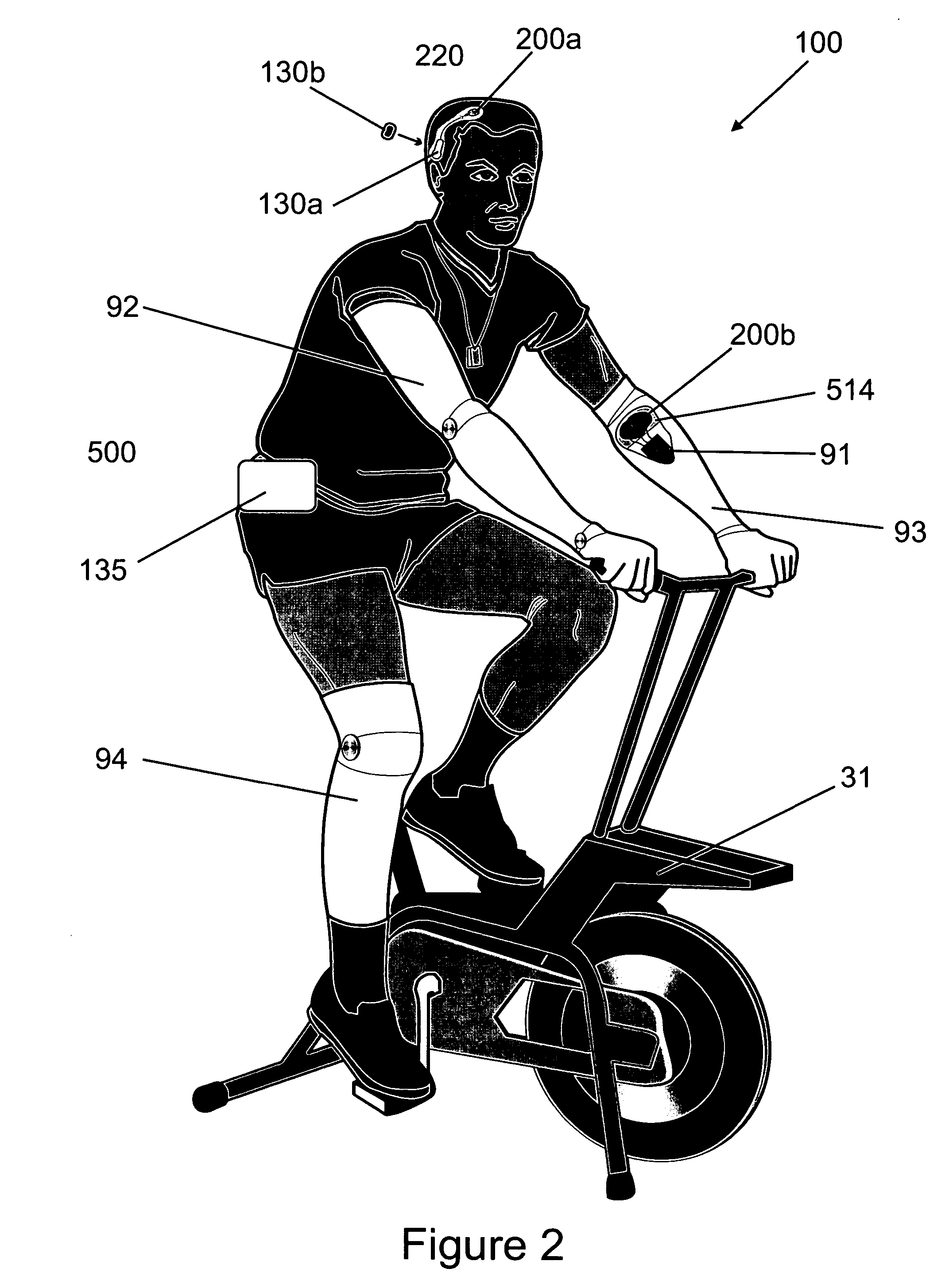
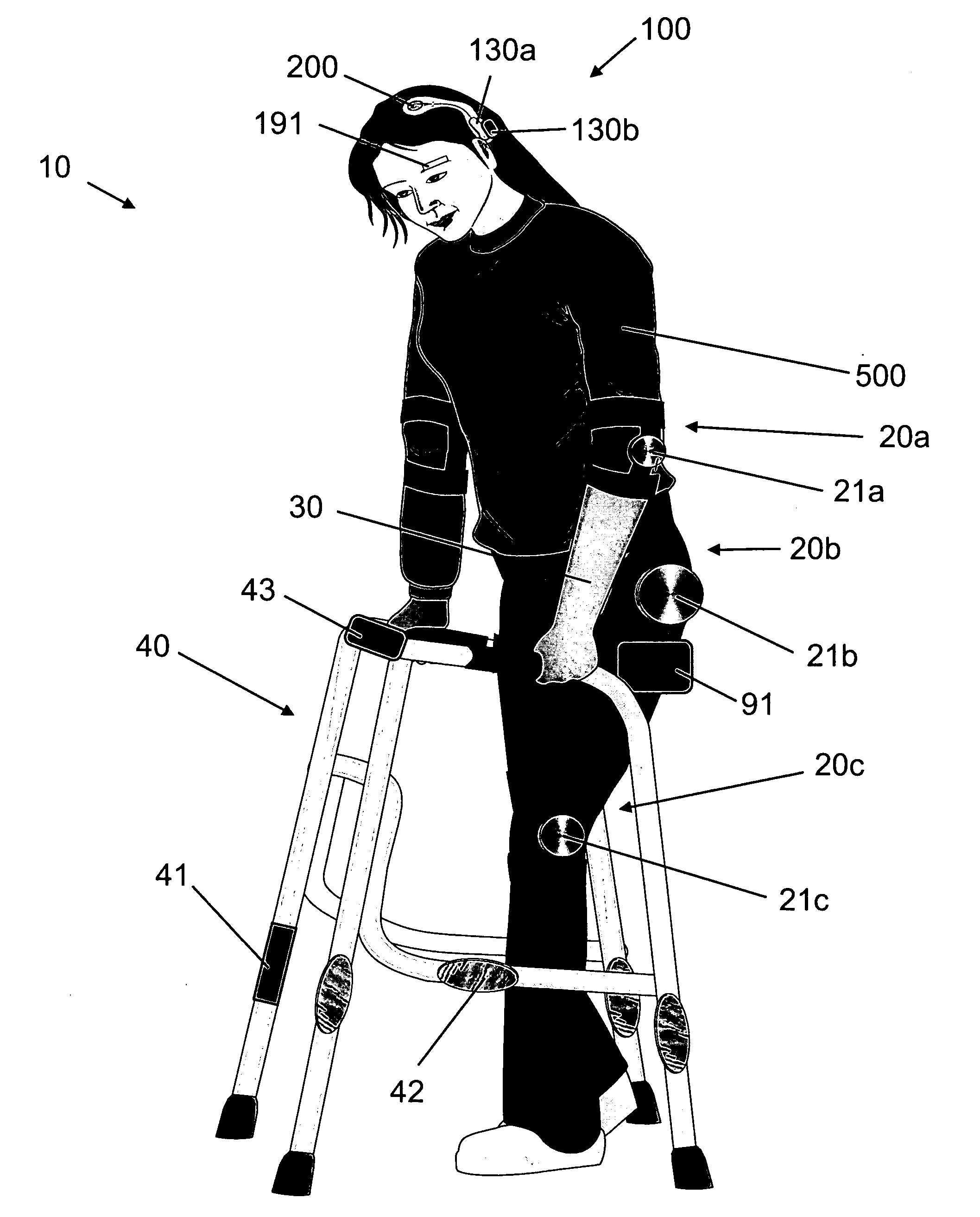
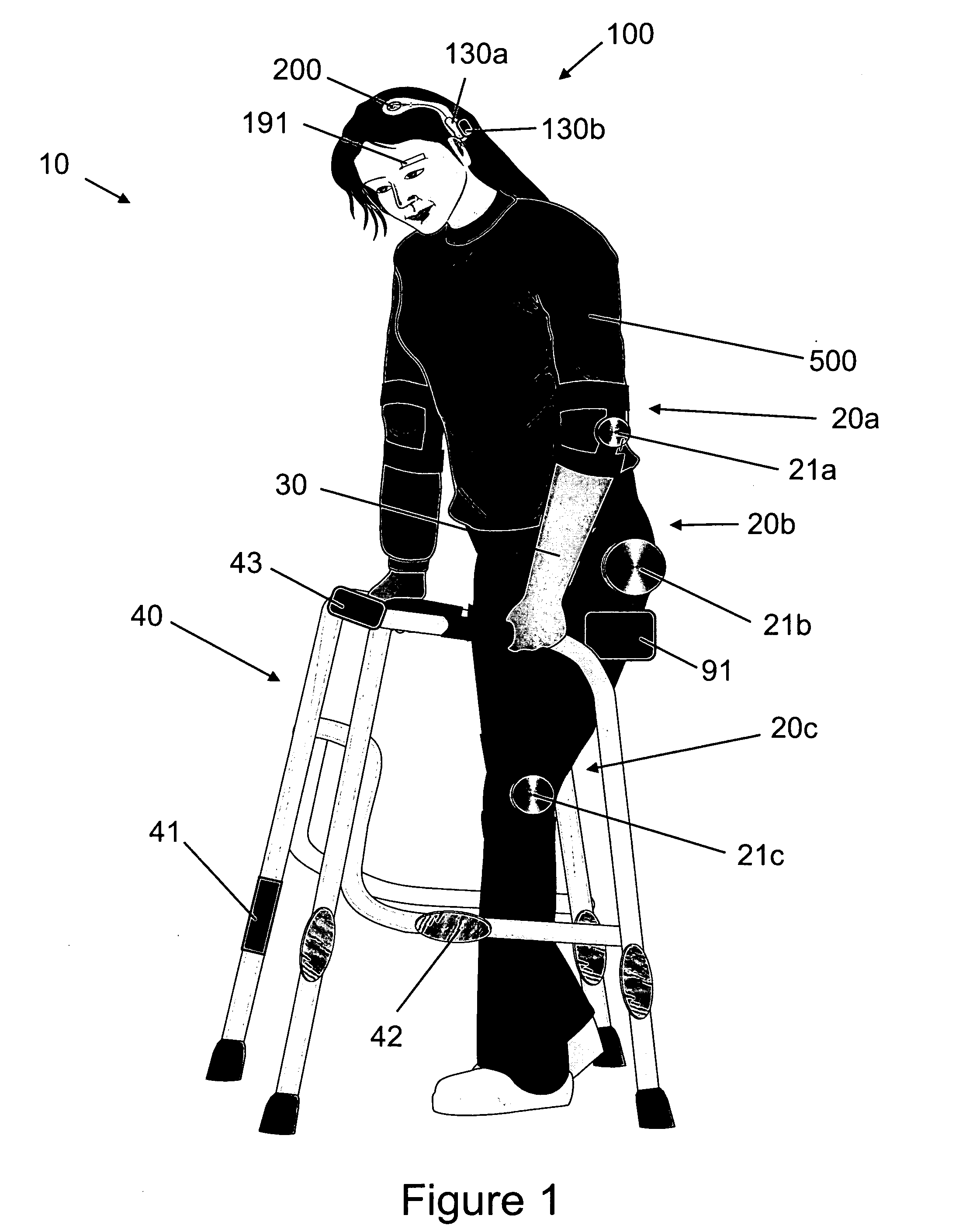
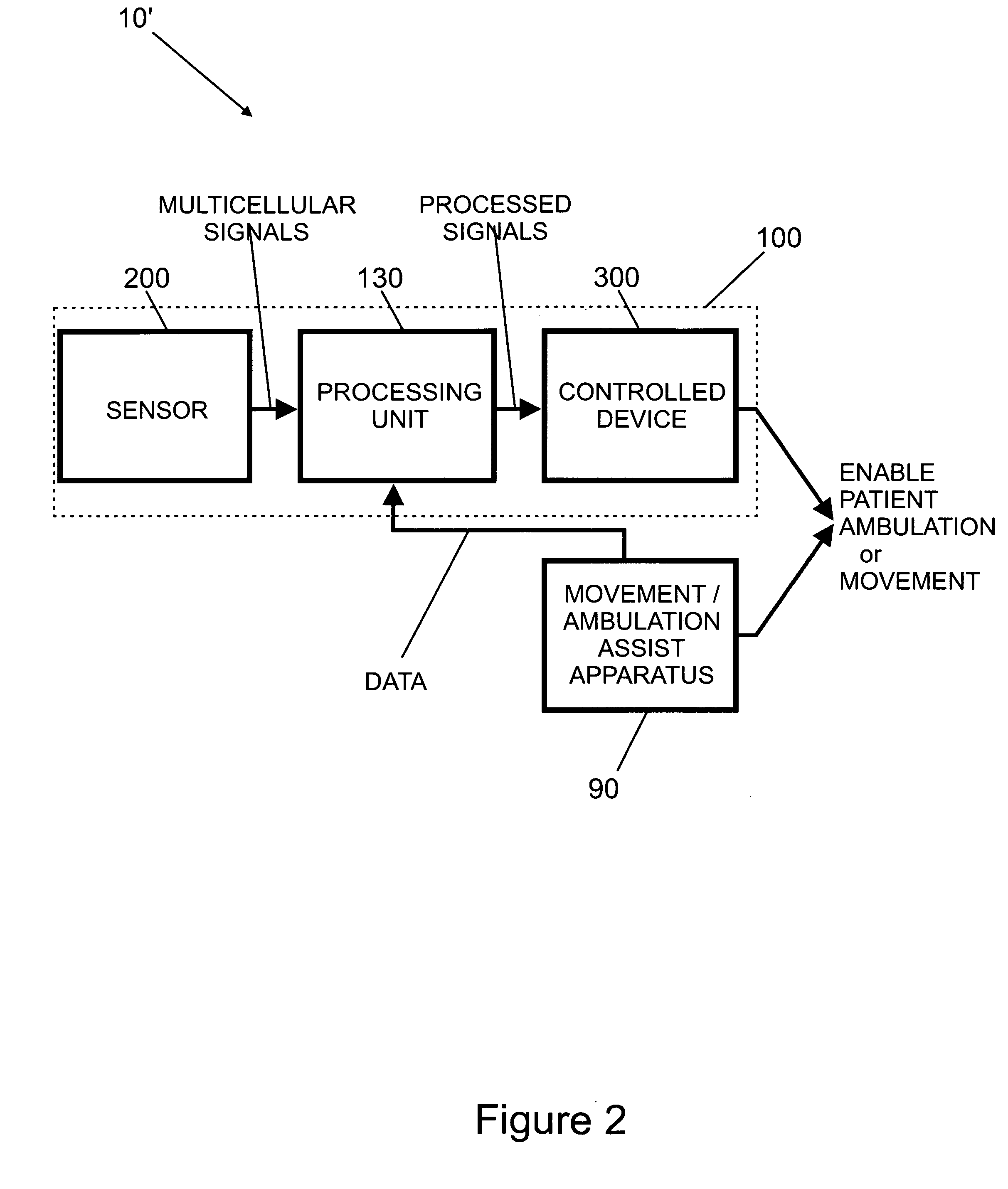
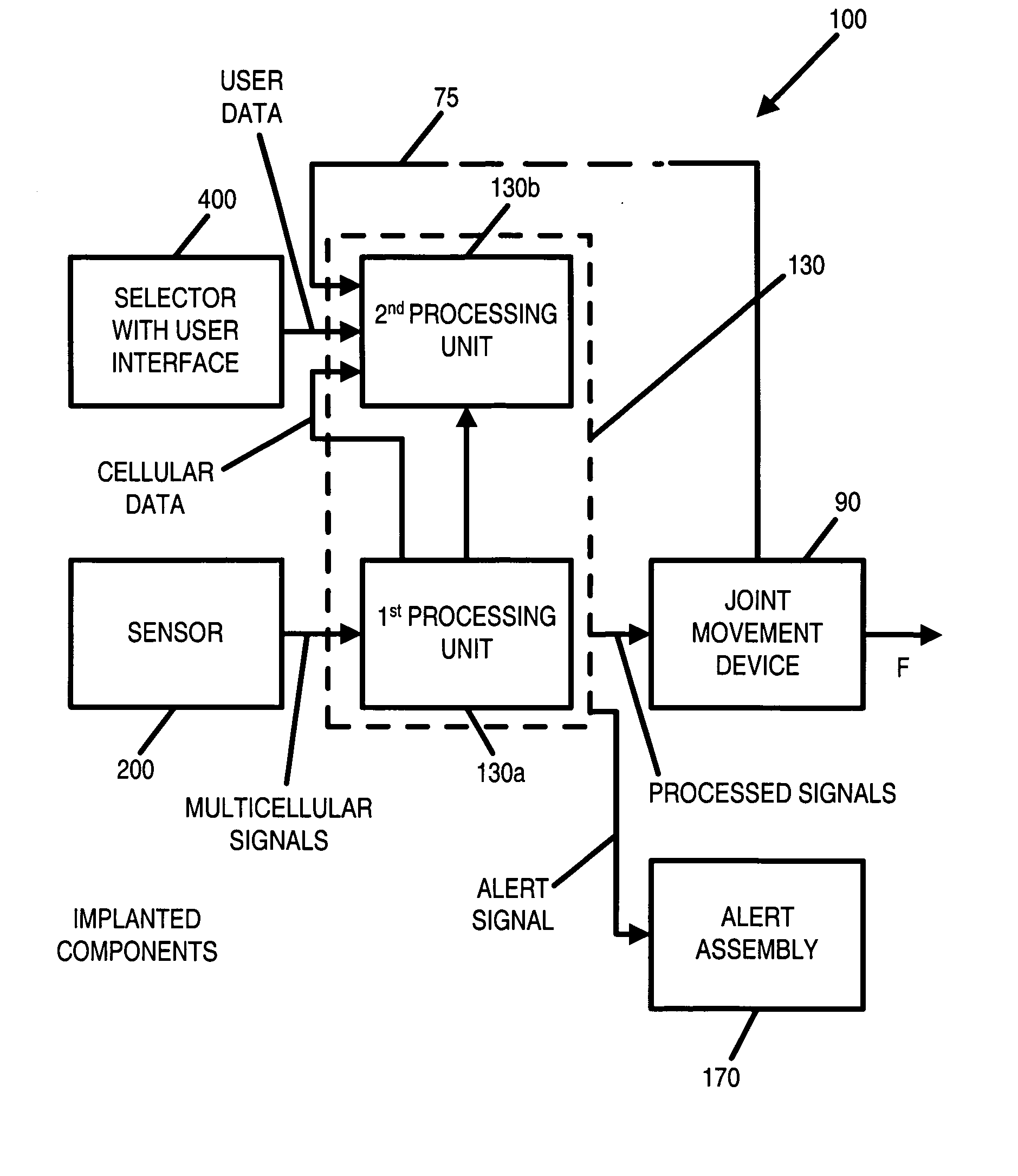
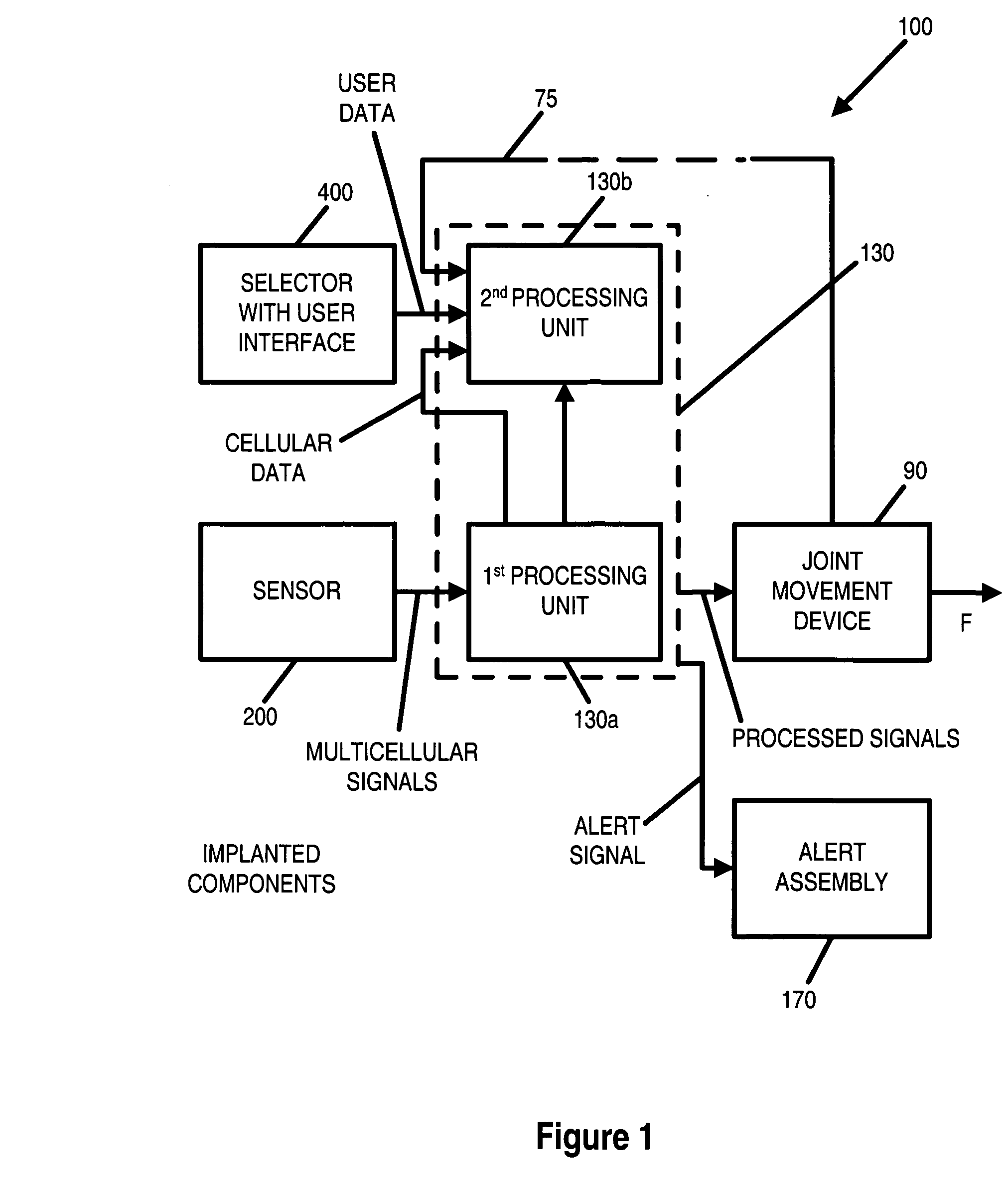
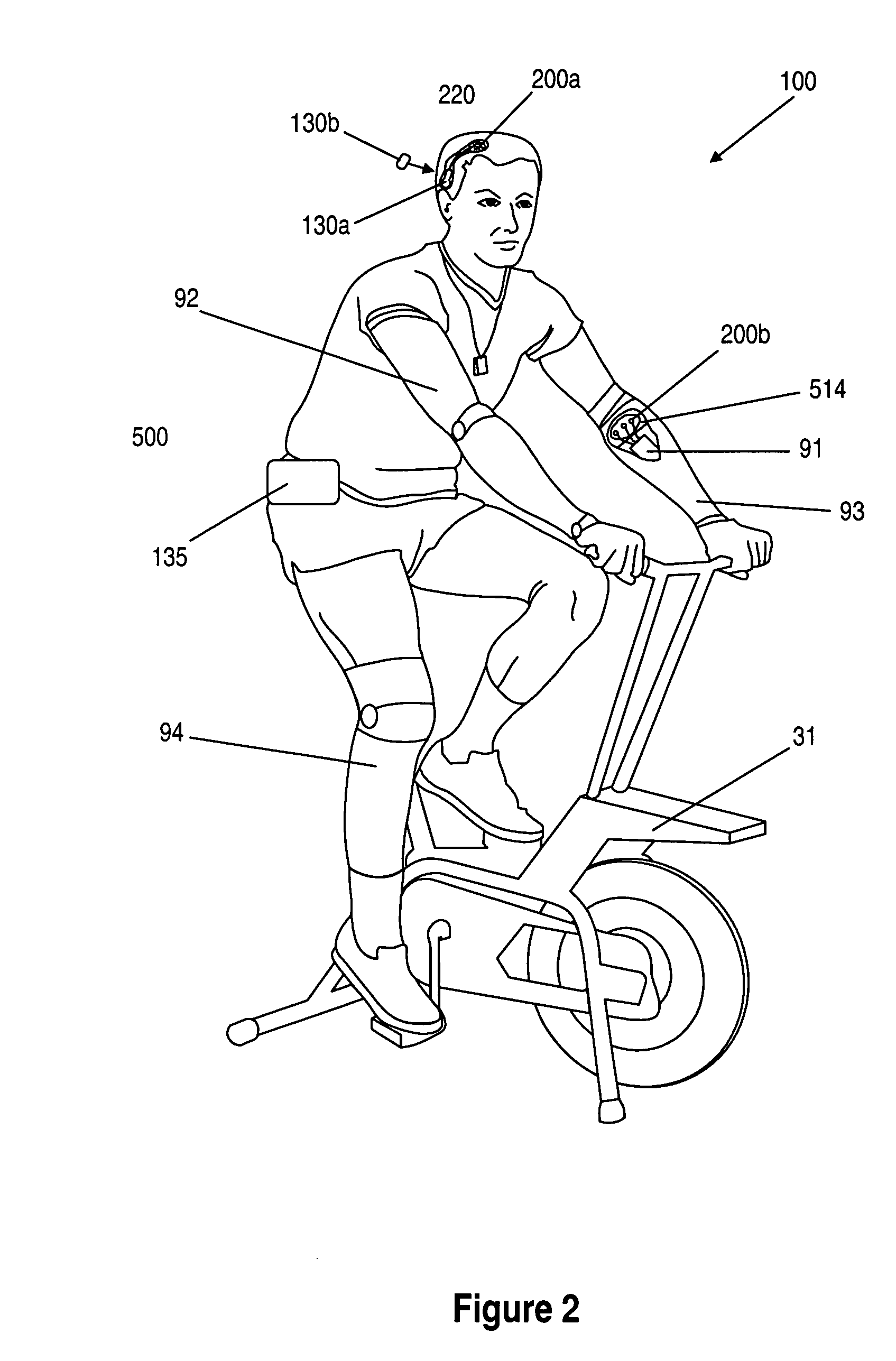
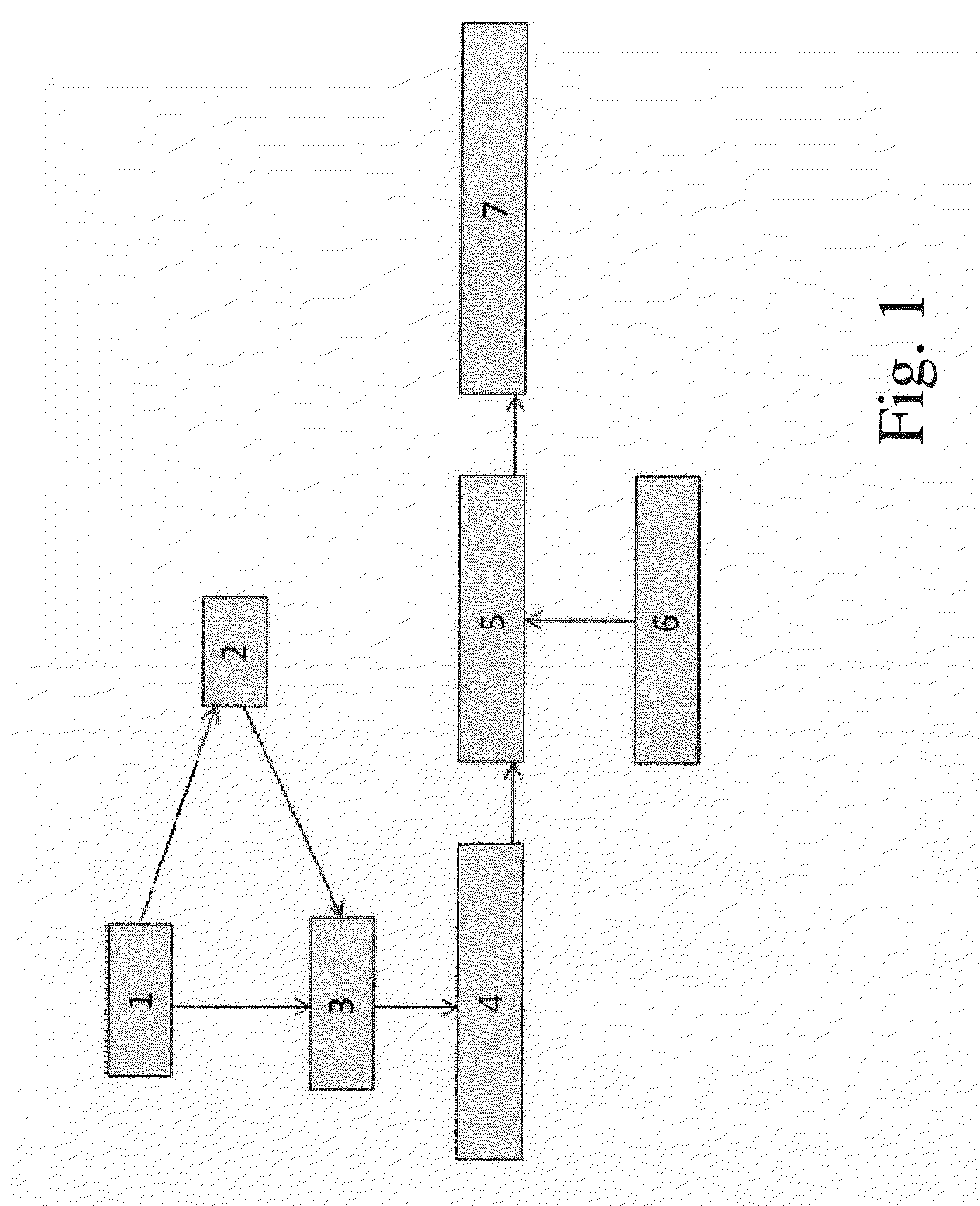
Systems, methods and devices for restoring or enhancing one or more motor functions of a patient are disclosed. The system comprises a biological interface apparatus and a joint movement device such as an exoskeleton device or FES device. The biological interface apparatus includes a sensor that detects the multicellular signals and a processing unit for producing a control signal based on the multicellular signals. Data from the joint movement device is transmitted to the processing unit for determining a value of a configuration parameter of the system. Also disclosed is a joint movement device including a flexible structure for applying force to one or more patient joints, and controlled cables that produce the forces required.
Owner:CYBERKINETICS NEUROTECH SYST
Multi-device patient ambulation system
InactiveUS20060206167A1Improve performanceImprove securityProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectrotherapyEngineeringProcessing element
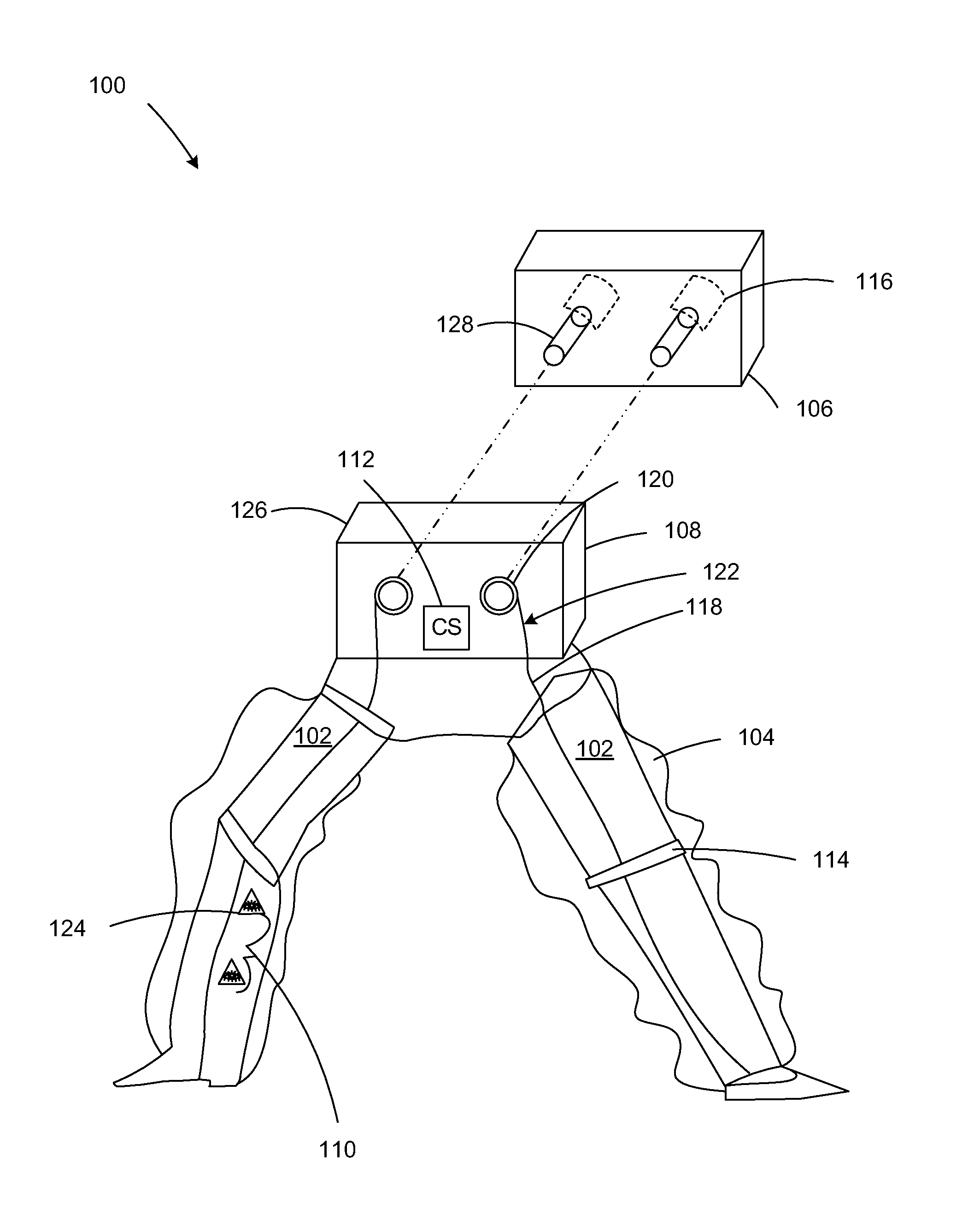
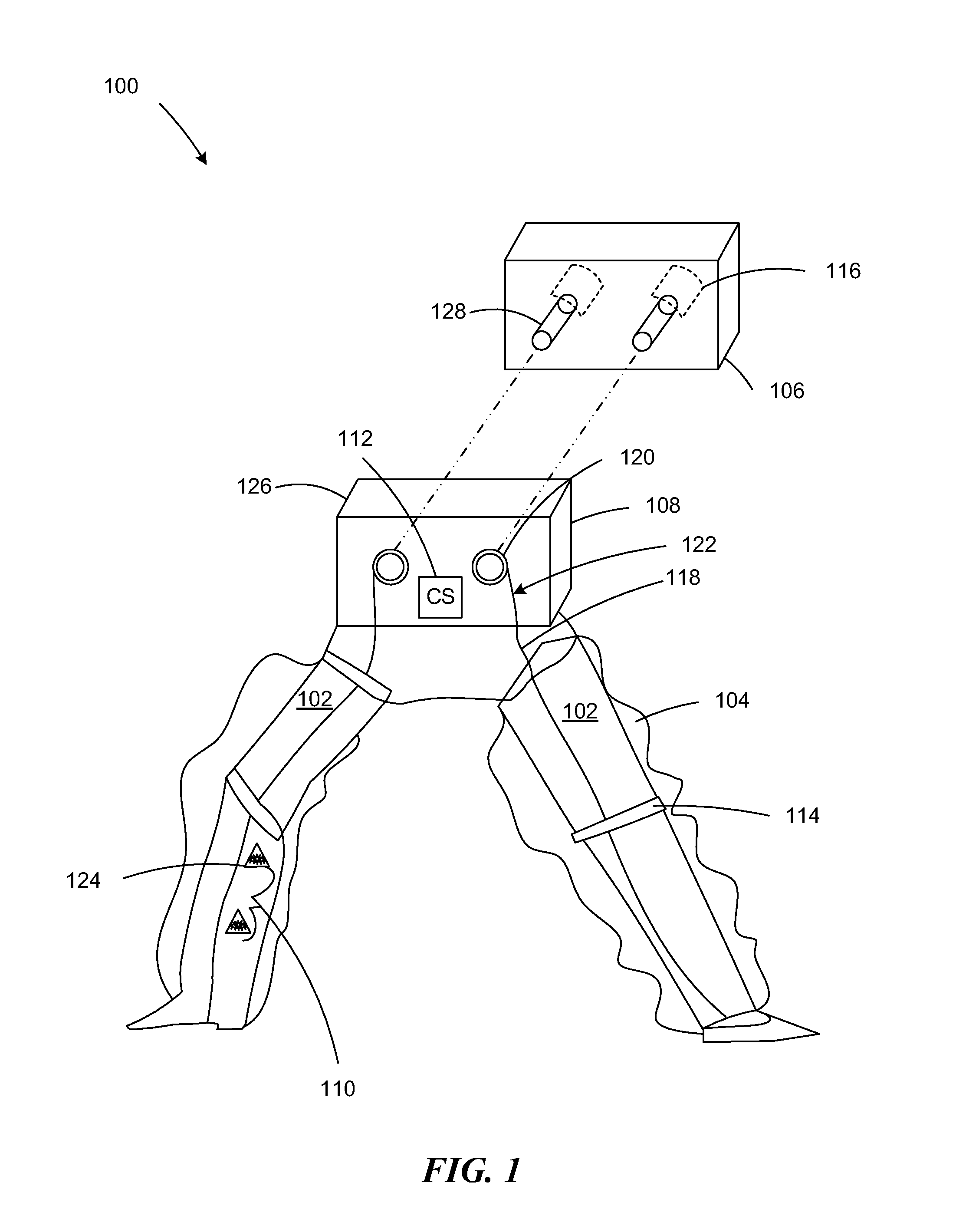
Various embodiments of an ambulation and movement assist system are disclosed. For example, an ambulation system for a patient may comprise an exoskeleton device attached to the patient, an FES device at least partially implanted in the patient, and a biological interface apparatus. The biological interface apparatus comprises a sensor having a plurality of electrodes for detecting multicellular signals, a processing unit configured to receive the multicellular signals from the sensor, process the multicellular signals to produce a processed signal, and transmit the processed signal to a controlled device. At least one of the exoskeleton device and the FES device is the controlled device of the biological interface apparatus.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD +1
Joint movement apparatus
Systems, methods and devices for restoring or enhancing one or more motor functions of a patient are disclosed. The system comprises a biological interface apparatus and a joint movement device such as an exoskeleton device or FES device. The biological interface apparatus includes a sensor that detects the multicellular signals and a processing unit for producing a control signal based on the multicellular signals. Data from the joint movement device is transmitted to the processing unit for determining a value of a configuration parameter of the system. Also disclosed is a joint movement device including a flexible structure for applying force to one or more patient joints, and controlled cables that produce the forces required.
Owner:CYBERKINETICS NEUROTECH SYST
Exoskeleton for gait assistance and rehabilitation
A method of operating an exoskeleton device includes: receiving sensor information; connecting a clutch system to a pulley system in; determining whether to engage a drive train gear to the clutch system based on the sensor information; engaging the drive train gear through the clutch system when determined to engage the drive train gear; and powering a first motor to drive the drive train gear for controlling a joint or segment of exoskeleton device.
Owner:LEONIS MEDICAL CORP
Wearable lower limb exoskeleton device
InactiveCN101589983AImprove consistencySmall coaxialityWalking aidsInvalid friendly devicesHuman bodyKnee Joint
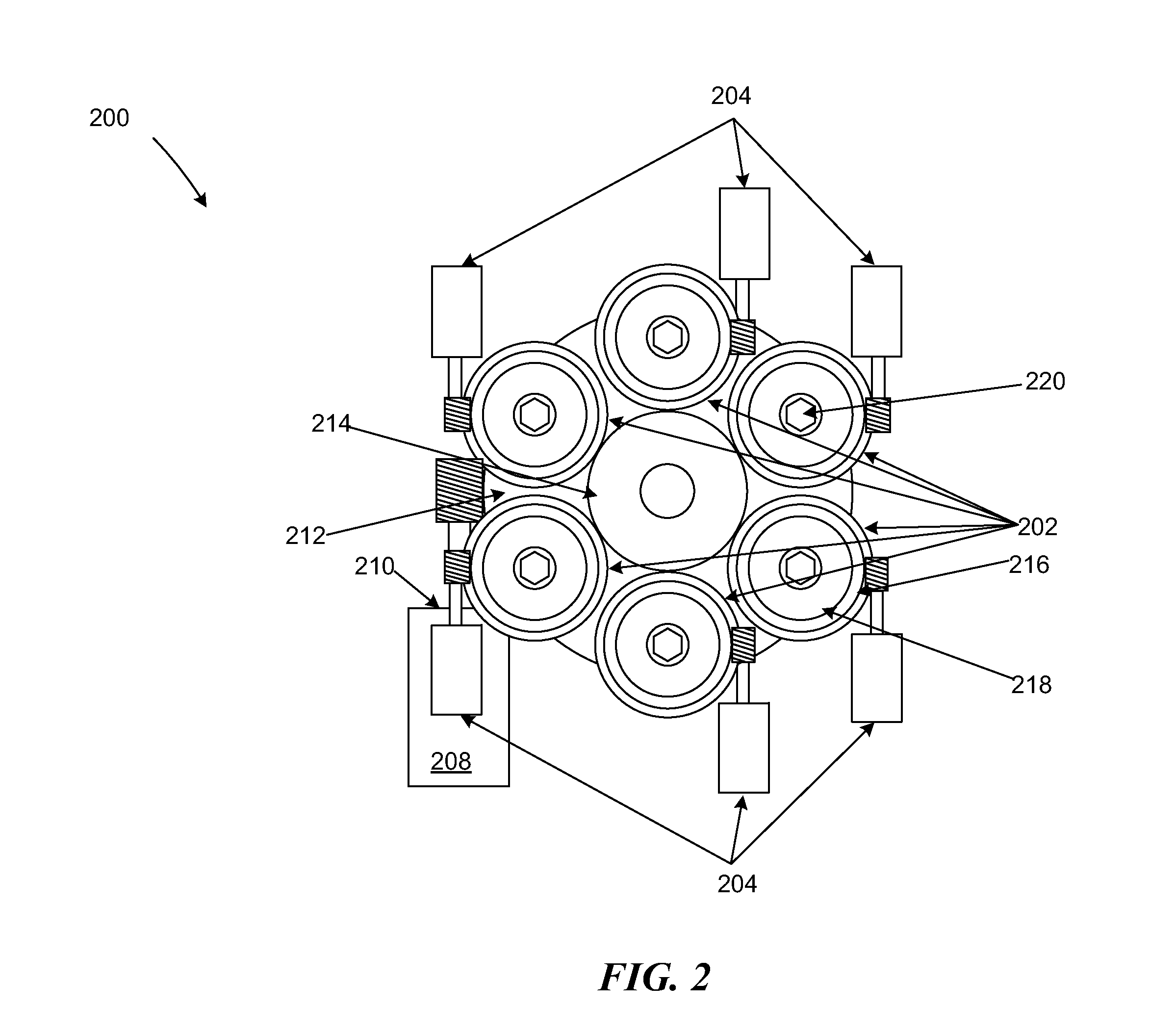
The invention discloses a wearable lower limb exoskeleton device, which comprises a waist supporting frame, a waist object carrier, an adjustable hip mechanism, a connecting rod adjustable knee joint mechanism, a connecting rod adjustable ankle joint mechanism, pressure detection shoes, a leg connecting rod, a constraint part and various connecting pieces. Both lower limbs have twelve rotational freedoms, the single lower limb has six degrees of freedom respectively, a hip has two degrees of freedom which finish bending and stretching as well as adduction and abduction movements of a hip joint, two joint axes always intersects at the center of the hip joint of a human body through the adjustment of the hip mechanism, and a knee joint has one degree of freedom which is coaxial with the knee joint of the human body and corresponds to the bending and stretching movement of the knee joint of the human body; and an ankle joint has three degrees of freedom. The device has good consistency of the movement of the hip joint and the movement of the human body during the walking of people; human-machine knee joints have small coaxality and position deviation; and the ankle joint has a compact structure. The device can be used for strengthening the abilities of walking with load and walking for a long time of wearers and detecting walking information of the wearers, and can also be used for helping people with slight obstacle of lower limb movement to normally walk and gradually rehabilitate.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
System and apparatus for robotic device and methods of using thereof
A robotic assembly control system is disclosed. The robotic assembly control system includes an exoskeleton apparatus adapted to be worn by a user, at least one robotic assembly, the at least one robotic assembly controlled by the user by way of the exoskeleton, and at least one mobile platform, the at least one mobile platform controlled by the user and wherein the at least one robotic assembly is attached to the at least one mobile platform.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Motorized exoskeleton unit
InactiveUS20130253385A1Programme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesEngineeringExoskeleton Device
A motorized exoskeleton device comprising: at least two segments, where one segment is superior to the other, the exoskeleton device configured to be coupled to a lower extremity of a user. The exoskeleton device further comprising at least two motorized joints for connecting the at least two segments and for providing relative angular movement between the at least two segments; and the motors coupled to the same superior segment of the exoskeleton device.
Owner:REWALK ROBOTICS LTD
Variable Impedance Mechanical Interface
ActiveUS20130282141A1Minimizing peak pressureMinimizing shear stressComputer aided designArtificial legsBiological bodyInterface impedance
A mechanical interface connecting a biological body segment, such as a limb, portion of a limb or other body segment, to a wearable device such as a prosthetic, orthotic or exoskeletal device, is fabricated by quantitatively mapping a characterized representation of the body segment to form a digital representation of the mechanical interface shape and mechanical interface impedance. The mechanical interface includes a continuous socket defining a contoured inside surface and a contoured outside surface, and includes a material having an intrinsic impedance that varies through the material, so that the intrinsic impedance varies along the contoured inside surface.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
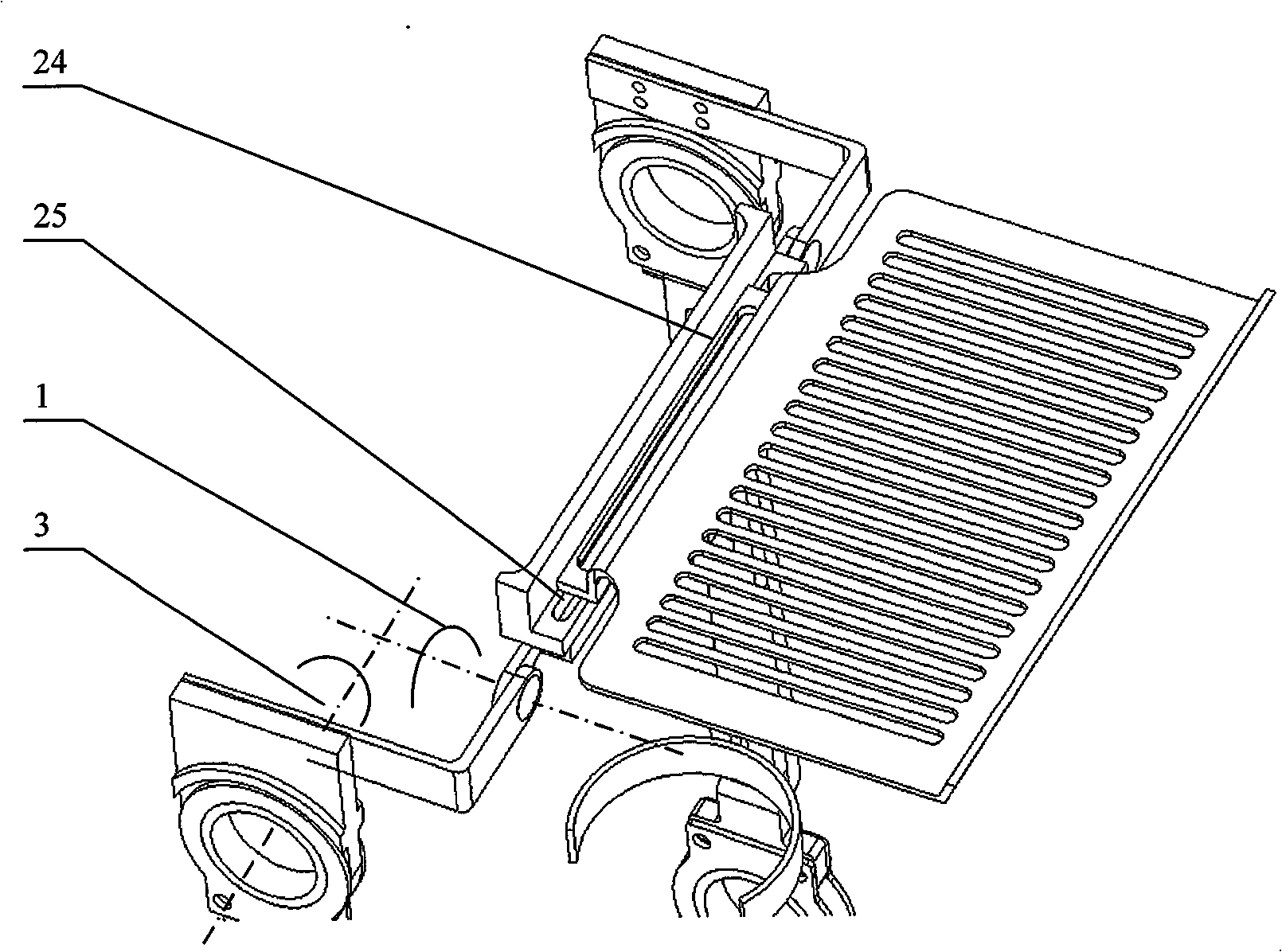
Transmission assembly for use in an exoskeleton apparatus
ActiveUS20140276261A1High mass moment of inertiaRelieve pressureChiropractic devicesWalking aidsEngineeringExoskeleton Device
An exoskeleton for a limb of a user wherein the limb has an upper portion that is pivotally mounted to another part of the exoskeleton about a pivot axis and the upper portion is drivingly connected to the exoskeleton by a force applied via a drive force transmission axis that is vertically offset from the pivot axis.
Owner:BIONIK LAB
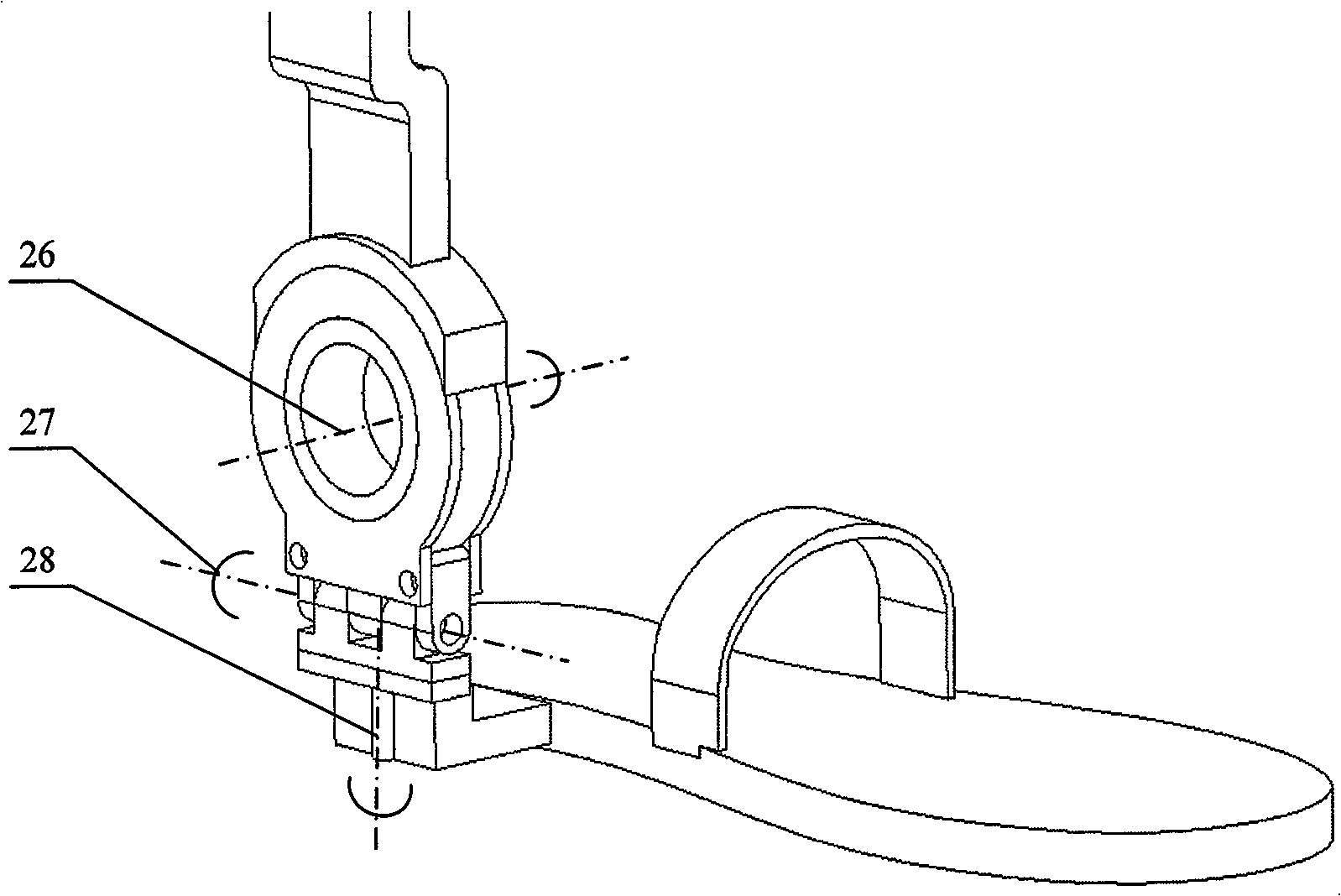
Foot plate assembly for use in an exoskeleton apparatus
ActiveUS20140276265A1High mass moment of inertiaRelieve pressureChiropractic devicesWalking aidsEngineeringExoskeleton Device
An exoskeleton for a leg of a user comprises a leg structure, a foot plate moveably mounted thereto, and a biasing member extending between the leg structure and the foot plate, the foot plate is moveably mounted to the leg structure between a first position in which the rearward portion extends downwardly and the forward portion extends upwardly and a second position in which the rearward portion extends upwardly and the forward portion extends downwardly and the foot plate is biased to the first position.
Owner:BIONIK LAB
Prosthetic, orthotic or exoskeleton device
ActiveUS20150127118A1Ease transition(s)Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsControl systemEngineering
A time-dependent decay behavior is incorporated into one or more joint actuator control parameters during operation of a lower-extremity, prosthetic, orthotic or exoskeleton device. These parameters may include joint equilibrium joint impedance (e.g., stiffness, damping) and / or joint torque components (e.g., gain, exponent). The decay behavior may be exponential, linear, piecewise, or may conform to any other suitable function. Embodiments presented herein are used in a control system that emulates biological muscle-tendon reflex response providing for a natural walking experience. Further, joint impedance may depend on an angular rate of the joint. Such a relationship between angular rate and joint impedance may assist a wearer in carrying out certain activities, such as standing up and ascending a ladder.
Owner:OTTO BOCK HEALTHCARE IP GMBH & CO KG
Robotic management system for limb rehabilitation
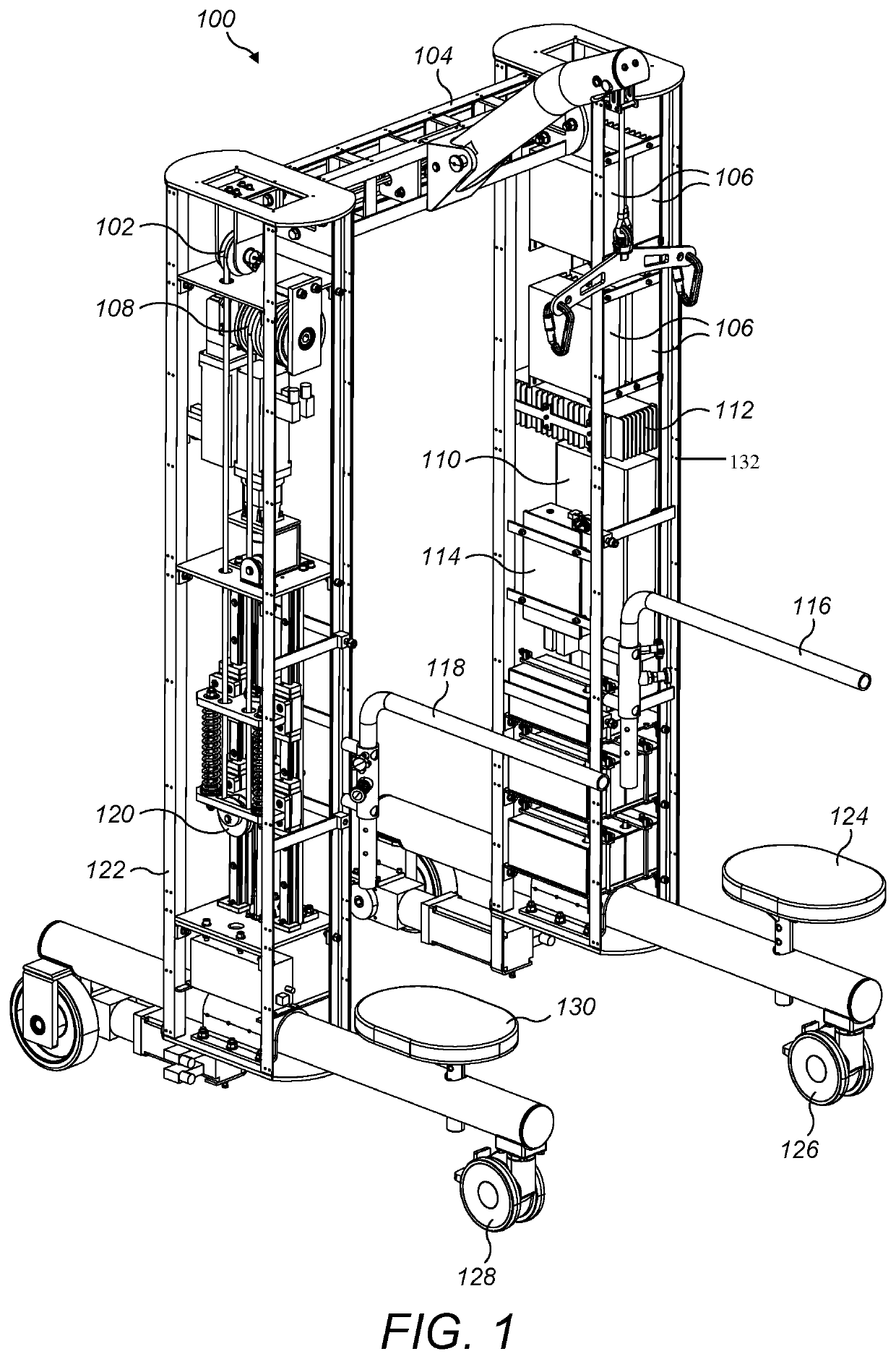
A robotic management system to control an apparatus that comprises of a mobile-frame, dynamic weight unloading mechanism and lower extremity exoskeleton device is disclosed. The fall safe apparatus receives the input from the doctors, users and therapist and the robotic management system automatically calculates the exercise routine using the robotic management system. An intelligent algorithm, embedded onto a dedicated processor, actuates various motors to execute the prescribed exercises, while the sensors provide dynamic feedback for corrective measures to control the exercise routine.
Owner:BIONIC YANTRA PTE LTD
Exoskeleton hand rehabilitation training device
The invention provides an exoskeleton hand rehabilitation training device for hand rehabilitation training of a stroke patient. The exoskeleton hand rehabilitation training device mainly comprises a finger driving device, a hand supporting assembly, a wrist supporting assembly and a motor driving device. The finger driving device is installed on the hand supporting assembly. The hand supporting assembly and the motor driving device are installed on the wrist supporting assembly. Power of a motor is transmitted to the finger driving device through a steel wire flexible shaft assembly, finger joints can move through gear transmission, the four fingers can be driven independently, the structure is simple and easy to obtain, and due to the rear motor driving device and the steel wire flexible shaft driving mode, the weight of the finger exoskeleton structure is lowered. Due to the fact that an arc track structure is arranged on the finger driving device, the rotation center of the exoskeleton device and the rotation center of the finger joints are kept consistent, and the finger driving device can adjust the length of the exoskeleton finger and replace a finger fixing ring according to the lengths and radiuses of fingers of the patient.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Hand exoskeleton device for rehabilitation training
ActiveCN105943308ASolve without mutual independenceFix the angle problemProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesLittle fingerEngineering
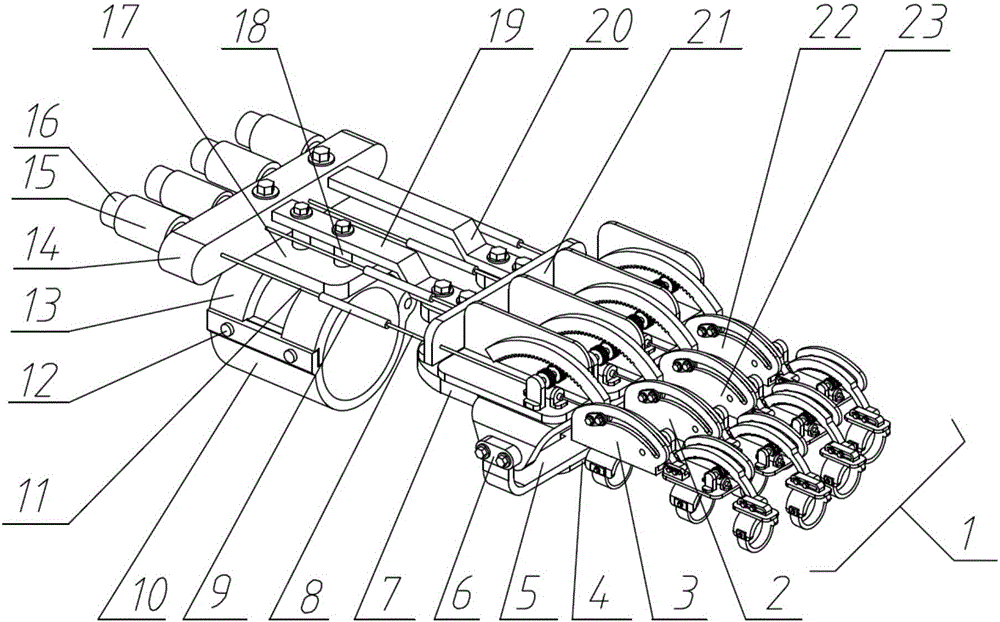
The invention discloses a hand exoskeleton device for rehabilitation training. The hand exoskeleton device comprises an opisthenar mechanism, a power source, an index finger exoskeleton, a middle finger exoskeleton, a ring finger exoskeleton, a little finger exoskeleton and a thumb exoskeleton. The opisthenar mechanism comprises an opisthenar platform, a motor support and a screw support. The power source comprises an index finger part, a middle finger part, a ring finger part and a little finger part. The index finger exoskeleton, the middle finger exoskeleton, the ring finger exoskeleton and the little finger exoskeleton each comprise a connecting rod, a far knuckle support, a transition connecting rod, a middle knuckle support, a transmission connecting rod, a driving connecting rod and a near knuckle support. The thumb exoskeleton comprises a thumb driving rod, a thumb transmission rod, a thumb connecting rod, a thumb near knuckle support, a thumb far knuckle support, a thumb motor, a thumb screw rod, a thumb sliding block, a thumb screw rod support, a thumb sliding block connecting rod, a thumb motor support and a thumb back platform. The whole device is light, low in cost and easy to assemble, and solves the problems that in an existing hand rehabilitation device, all fingers are not independent from one another, the bending angle is limited, fine actions are difficult to achieve, and cost is high.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Auxiliary training tool for comprehensive rehabilitation of cerebral palsy
The invention discloses an auxiliary training tool for comprehensive rehabilitation of cerebral palsy. The auxiliary training tool comprises a chassis, a lower limb exoskeleton device and a suspension device, wherein the chassis comprises universal casters with the locking function, a lower chassis, an upper chassis and an exoskeleton device inclination adjusting mechanism; the lower limb exoskeleton device is fixedly mounted on the chassis, and can realize rehabilitation training such as flexion / extension, adduction / abduction and pronation / supination of hip joints, flexion / extension of the knee joint, and dorsi-flexion / plantar-flexion, strephenopodia / strephexopodia and pronation ans supination of feet; the suspension device is fixedly mounted on the chassis, and plays a role in slinging, weight reduction and upper body posture correction of paitents. The auxiliary training tool can help patients with cerebral palsy to correct the abnormal posture of lower limbs, carry out the rehabilitation training on all joints of the lower limbs, promotes the development of all the joints of the lower limbs, and gradually establishes the normal standing and walking functions.
Owner:国家康复辅具研究中心
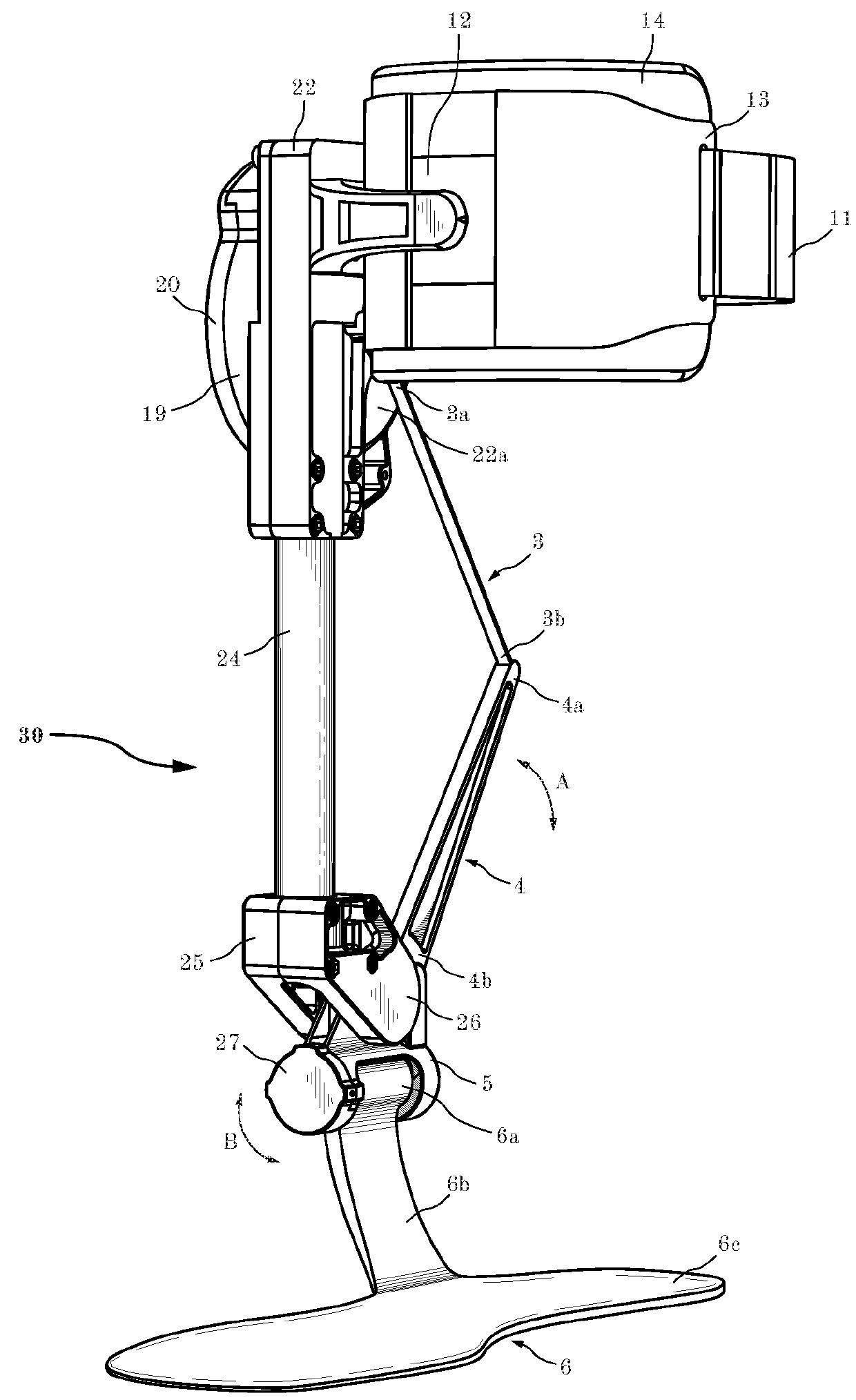
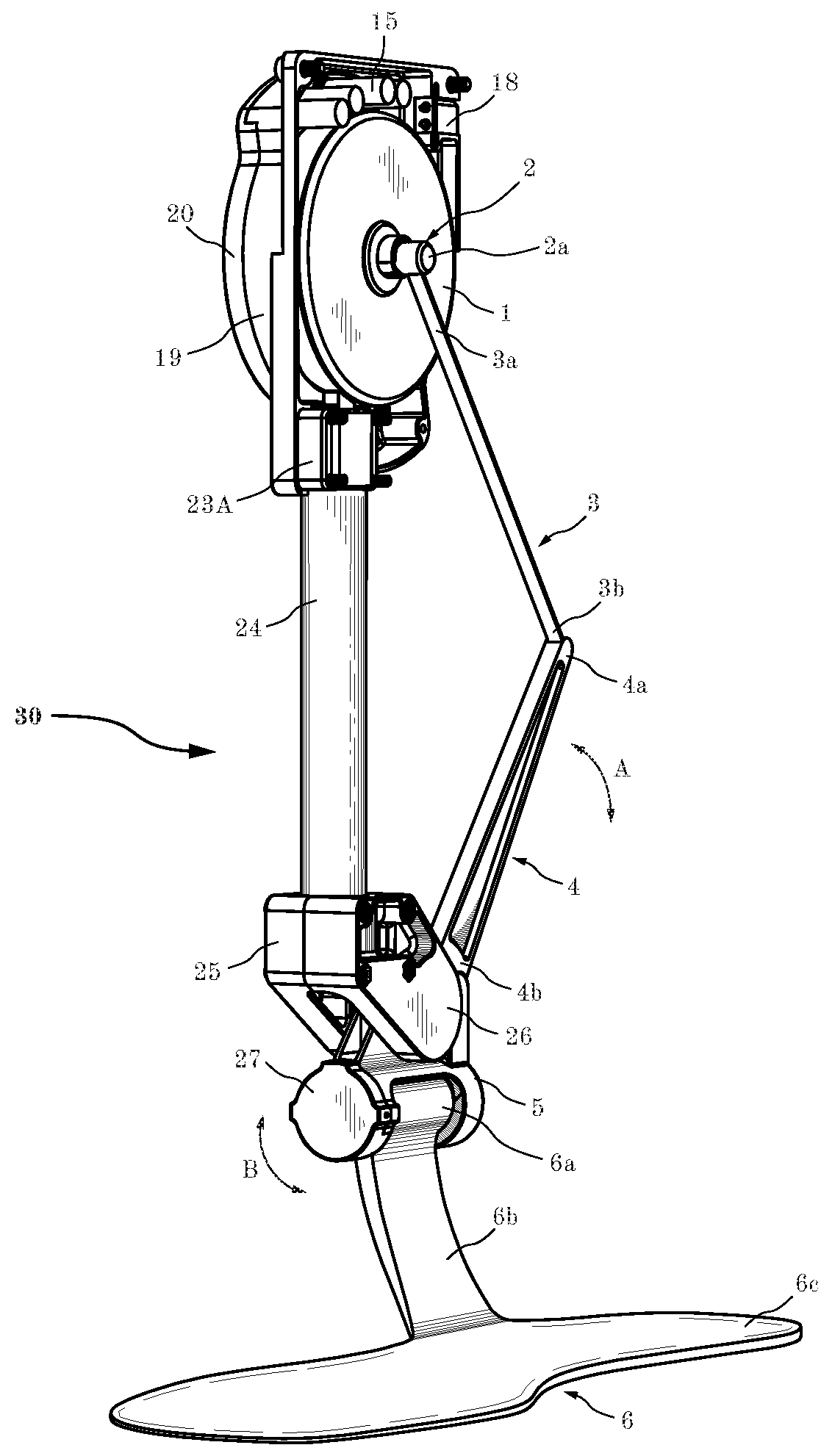
Unidirectional actuated exoskeleton device
ActiveUS20180104075A1Reduce manufacturing costPowerfulChiropractic devicesWalking aidsEngineeringCam
The present invention is directed to an autonomous exoskeleton device that includes one or more actuators, one or more controllers, one or more sensors with one or more unidirectional transmissions. The present invention provides a mechanical joint in parallel with a biological joint. The exoskeleton device preferably includes and electric motor and winch, chain, belt, cam transmission or other mechanism for providing unidirectional force to assist rotation about the biologic joint. Moreover, a controller, a motor angle sensor, joint angle sensor and / or force sensor may be used for additional control and monitoring of the device. The motor may be any type of motor, but is preferably brushless in configuration where its diameter is larger than its length to provide a compact and lightweight exoskeleton device.
Owner:DEPHY INC
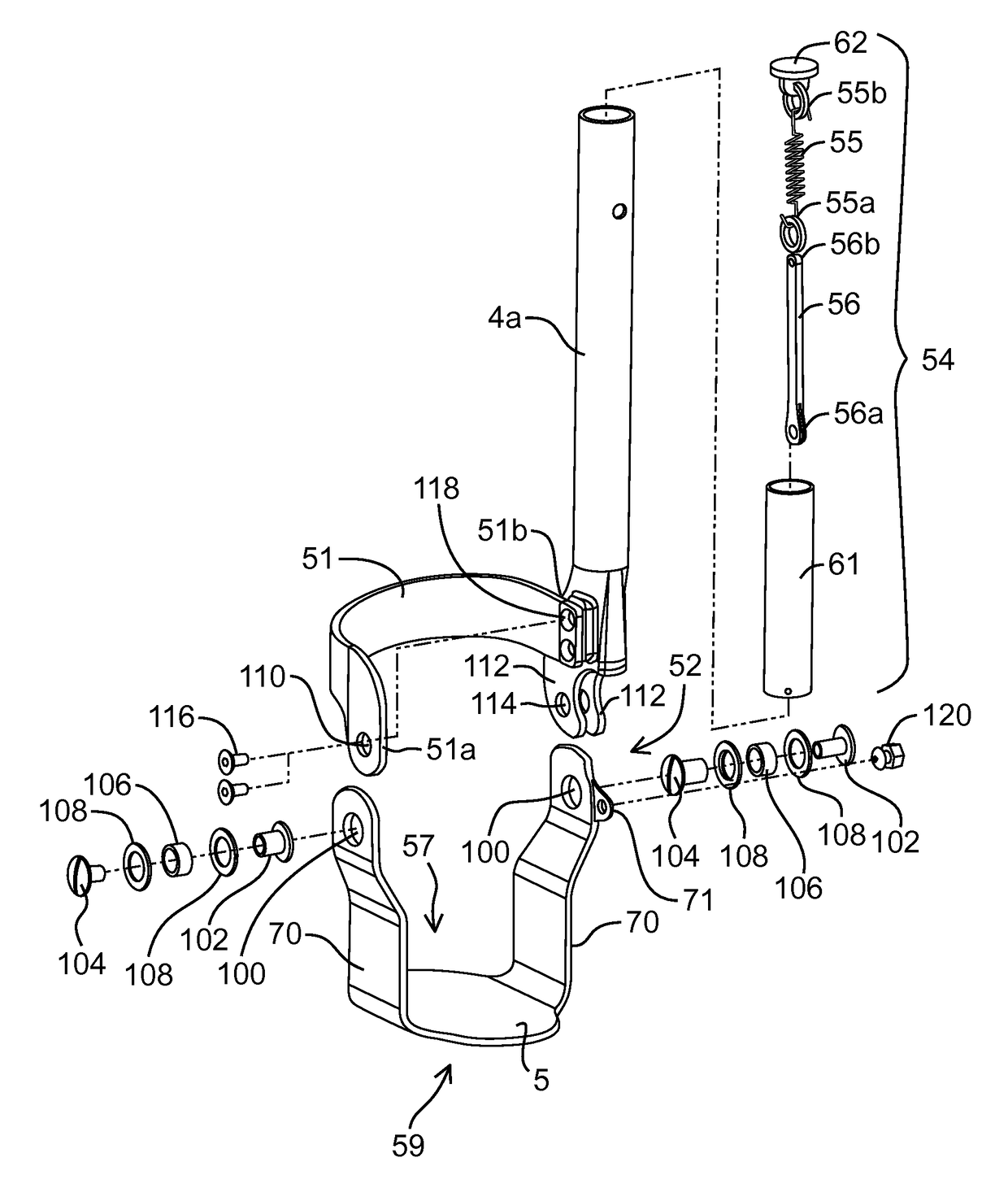
Hip-knee passive exoskeleton device based on clutch time-sharing control
ActiveUS20200085667A1Improve applicabilityImprove walking efficiencyChiropractic devicesWalking aidsThighKnee Joint
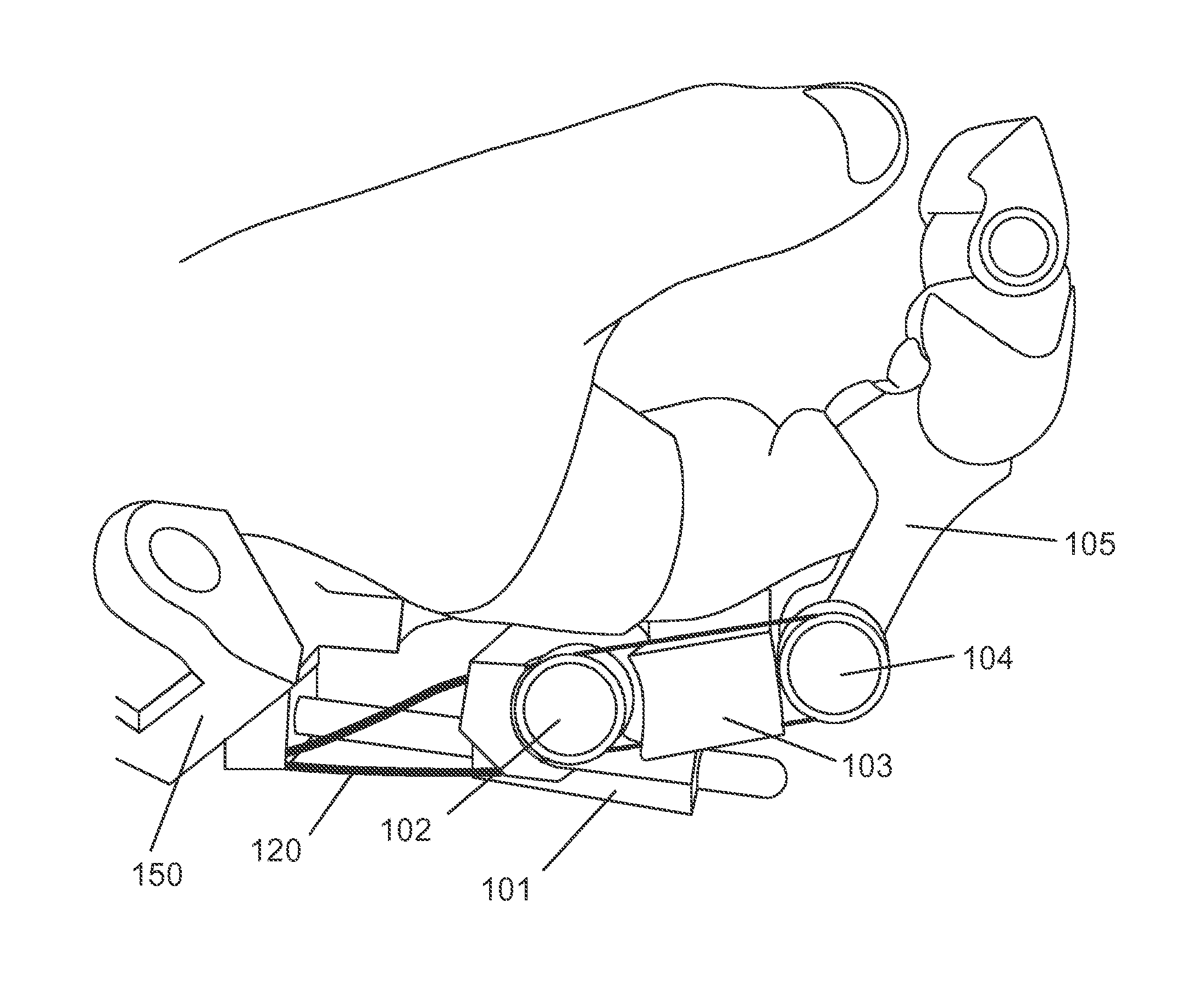
The disclosure belongs to the technical field of lower limb exoskeleton, and specifically discloses a hip-knee passive exoskeleton device based on clutch time-sharing control, comprising a waist support subassembly, connection subassemblies, thigh subassemblies, clutch subassemblies, shank subassemblies and elastic member subassemblies, the waist support subassembly is configured to be connected to the waist, the connection subassemblies are configured to include two connection subassemblies which are arranged in bilateral symmetry on two sides of the support subassembly, the thigh subassemblies are configured to include two thigh subassemblies which are respectively connected to the two connection subassemblies, the clutch subassemblies are configured to include two clutch subassemblies which are respectively mounted on the two thigh subassemblies, the shank subassemblies are configured to include two shank subassemblies which are arranged in bilateral symmetry below the two thigh subassemblies, the elastic member subassemblies are configured to include two elastic member subassemblies which are arranged in bilateral symmetry. The disclosure can assist the movements of the knee and hip joints, thereby improving the energy utilization efficiency and reducing the metabolic energy consumption of walking.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Hip joint passive exoskeleton device based on energy time-sharing regulation
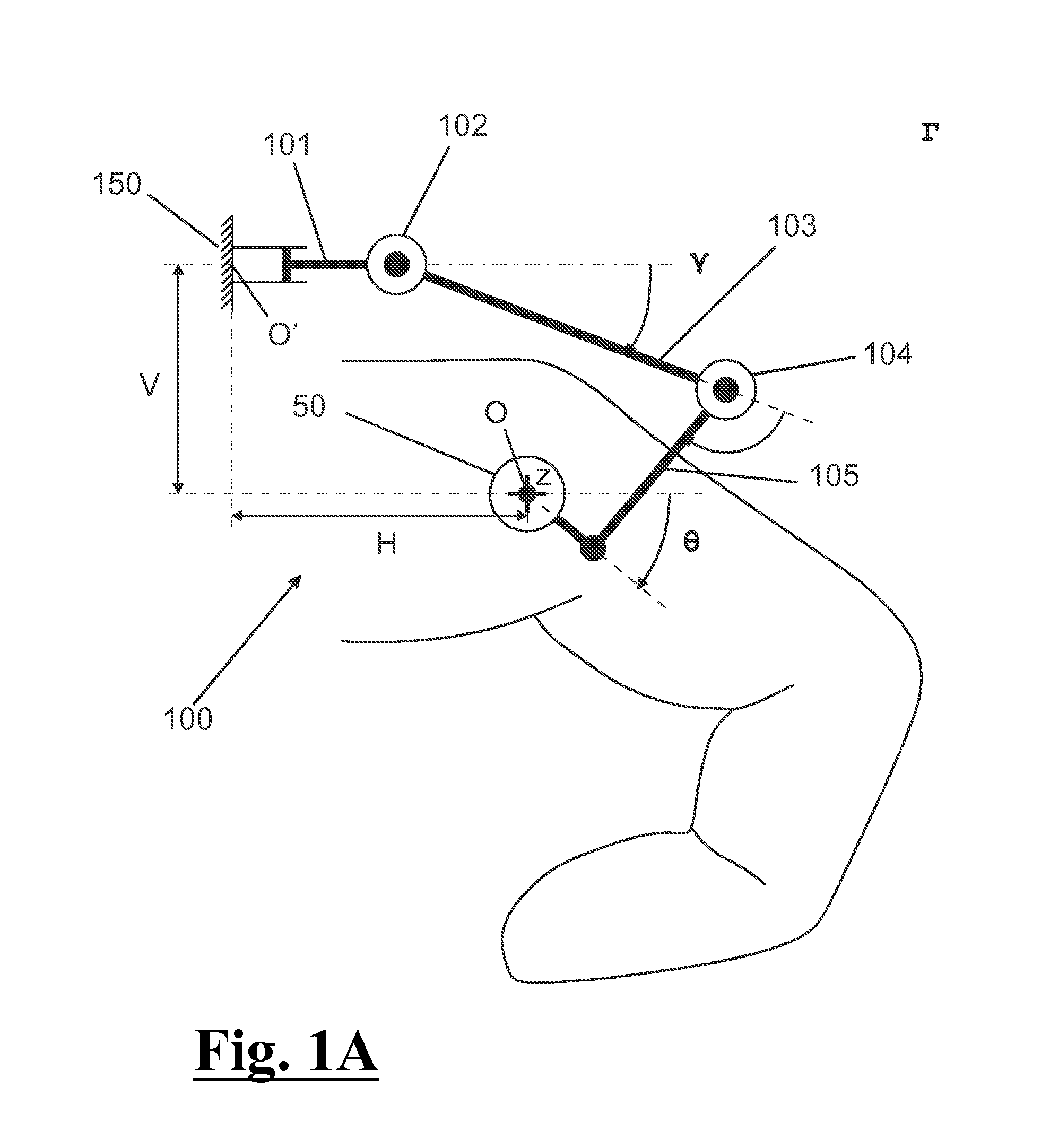
The invention belongs to the field of lower limb assisting exoskeletons, and discloses a hip joint passive exoskeleton device based on energy time-sharing regulation. The hip joint passive exoskeletondevice comprises a waist arc-shaped support assembly, hip joint assemblies, thigh assemblies and elastic component connecting assemblies, wherein the waist arc-shaped support assembly comprises surrounding support devices and flexible bandages; each hip joint assembly comprises a hip joint inwards folding and outward unfolding connector and a hip joint bending and stretching connector; each thighassembly comprises a thigh outer-side connecting rod, a thigh front hoop and a thigh rear hoop; each elastic component connecting assembly comprises an L-shaped cantilever, an force arm, a digging rope clutch, an extension spring and a flexible rope. For the hip joint passive exoskeleton device based on energy time-sharing regulation provided by the invention, through the digging rope clutches triggered along with the joint angle, the extension springs stretch for storing the mechanical energy of the human body when the human hip joint does negative work and contract for releasing the energywhen the human hip joint does positive work, so that the time-sharing regulation on the mechanical energy of the human body is realized finally, the movement of the hip joint is assisted, the metabolic energy consumption generated during walk is reduced, in addition, the hip joint passive exoskeleton device has the advantages that the structure is simple, the cost is low, the weight is small, andthe wearing is comfortable.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
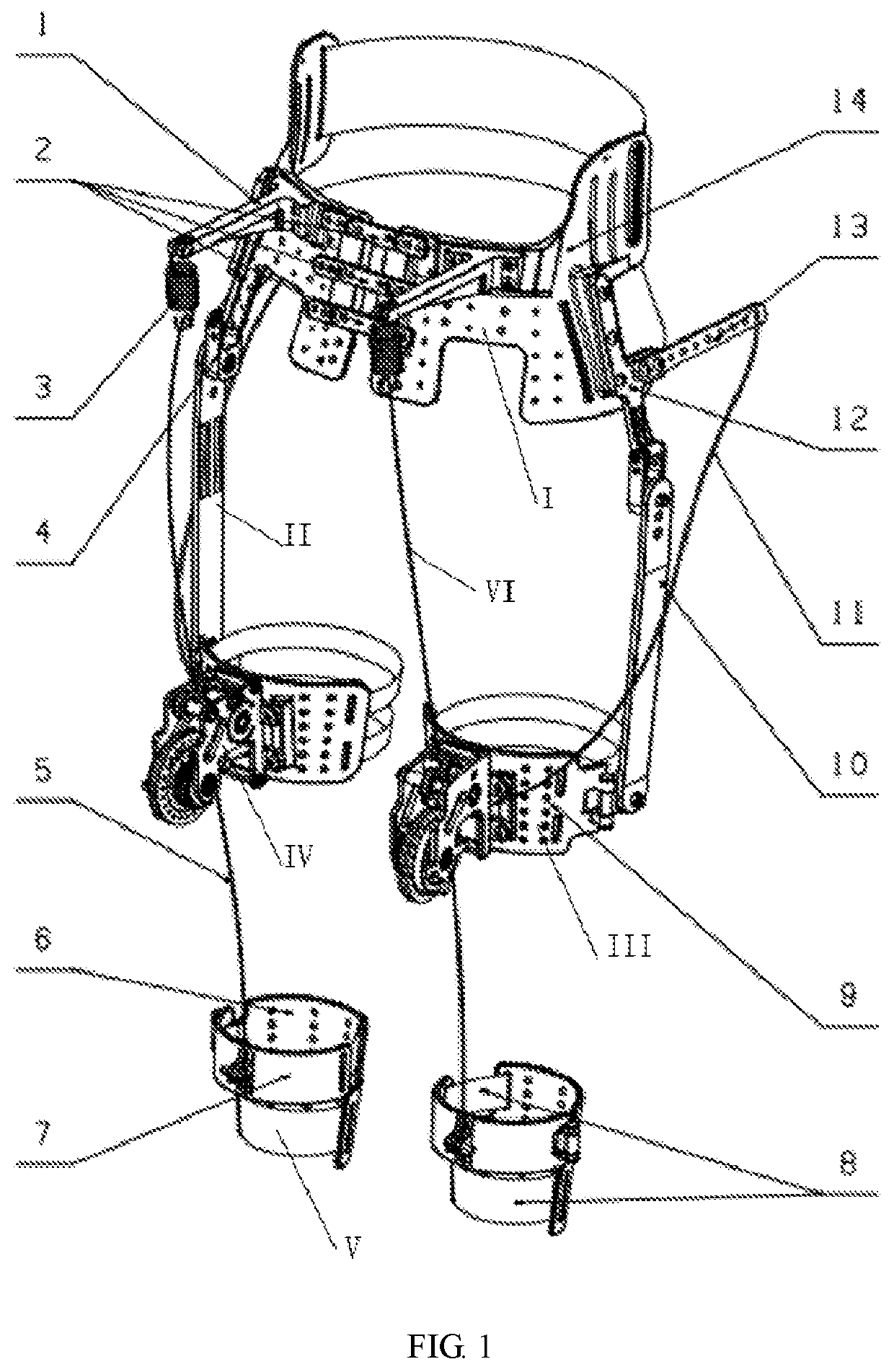
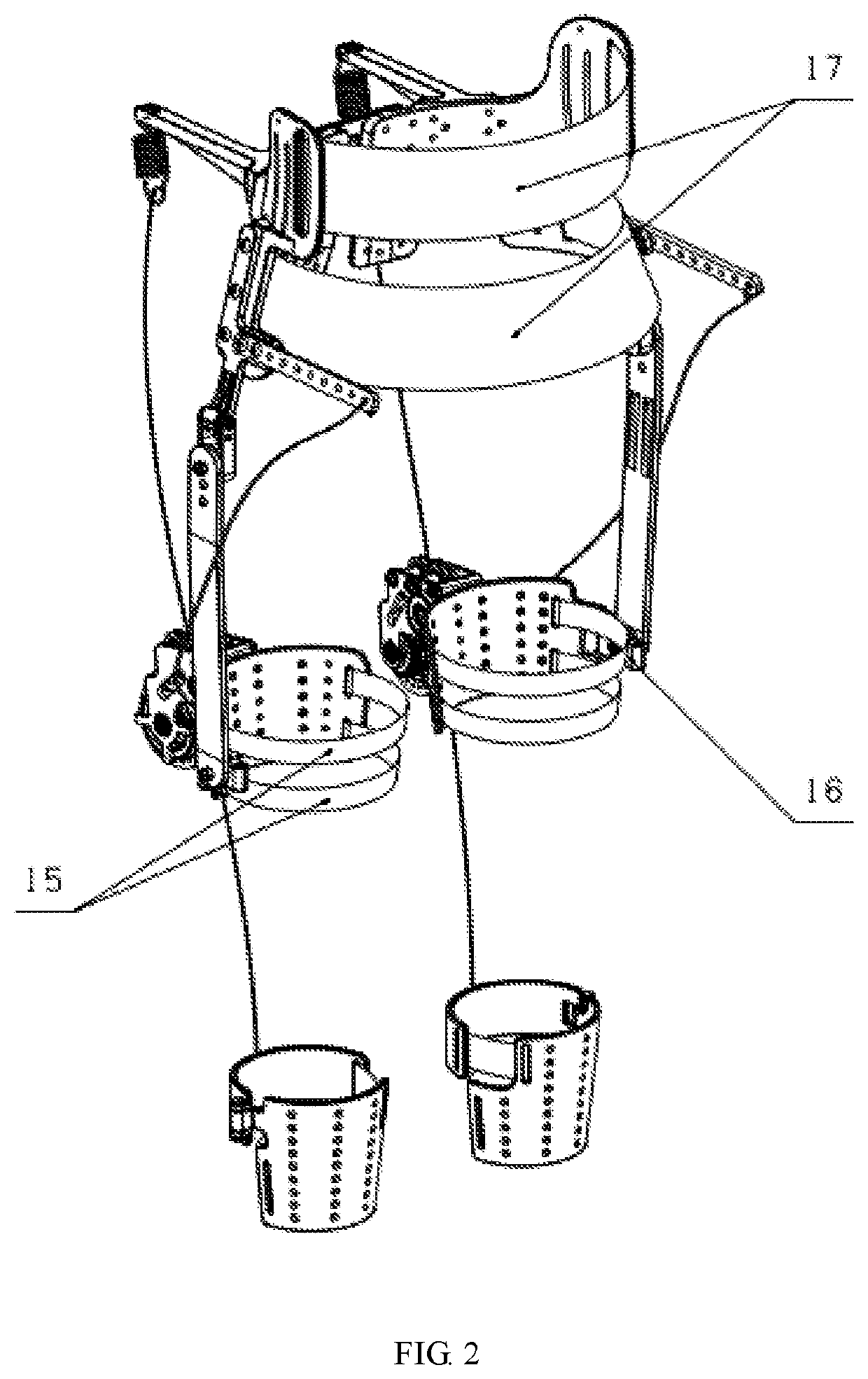
Artificial exoskeleton device or an orthotic device comprising an integrated hinge structure
InactiveUS20110009787A1Simple structureGood fit and functionalityNon-surgical orthopedic devicesMetal working apparatusRange of motionComputer-aided
A pivot or hinge structure integrated into the main body of an exoskeletal, e.g. orthotic device is described as well as methods for computer aided designing and making of these devices. Computer systems and software for carrying out the methods are also described.The integrated pivot or hinge structure has a specified axis of rotation, such as one coinciding or approximating with the natural rotation axis of the ankle, knee, elbow or any other relevant joint. Preferably the pivot or hinged structure is provided with a personalised resistance to rotation. The pivot or hinge structure is a pivot or hinge comprising at least two separate cylindrical parts that rotate with respect to each other, the axis of rotation being at the centre of the cylinder. The pivot or hinge can be placed to the optimal location and orientation in regard to the limb or anatomical features observed or measured from the patient thanks to the layered manufacturing technique. The range of motion can be structurally limited if needed. This enables more possibilities for adjustment when the exoskeletal device, e.g. orthotic device is fitted to the patient to ensure a better fit and functionality.
Owner:MATERIALISE NV
Wearable exoskeleton device for hand rehabilitation
ActiveUS20150223959A1Assisting the flexion/extension of the joints of a handChiropractic devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesProximal phalanxDistal phalange
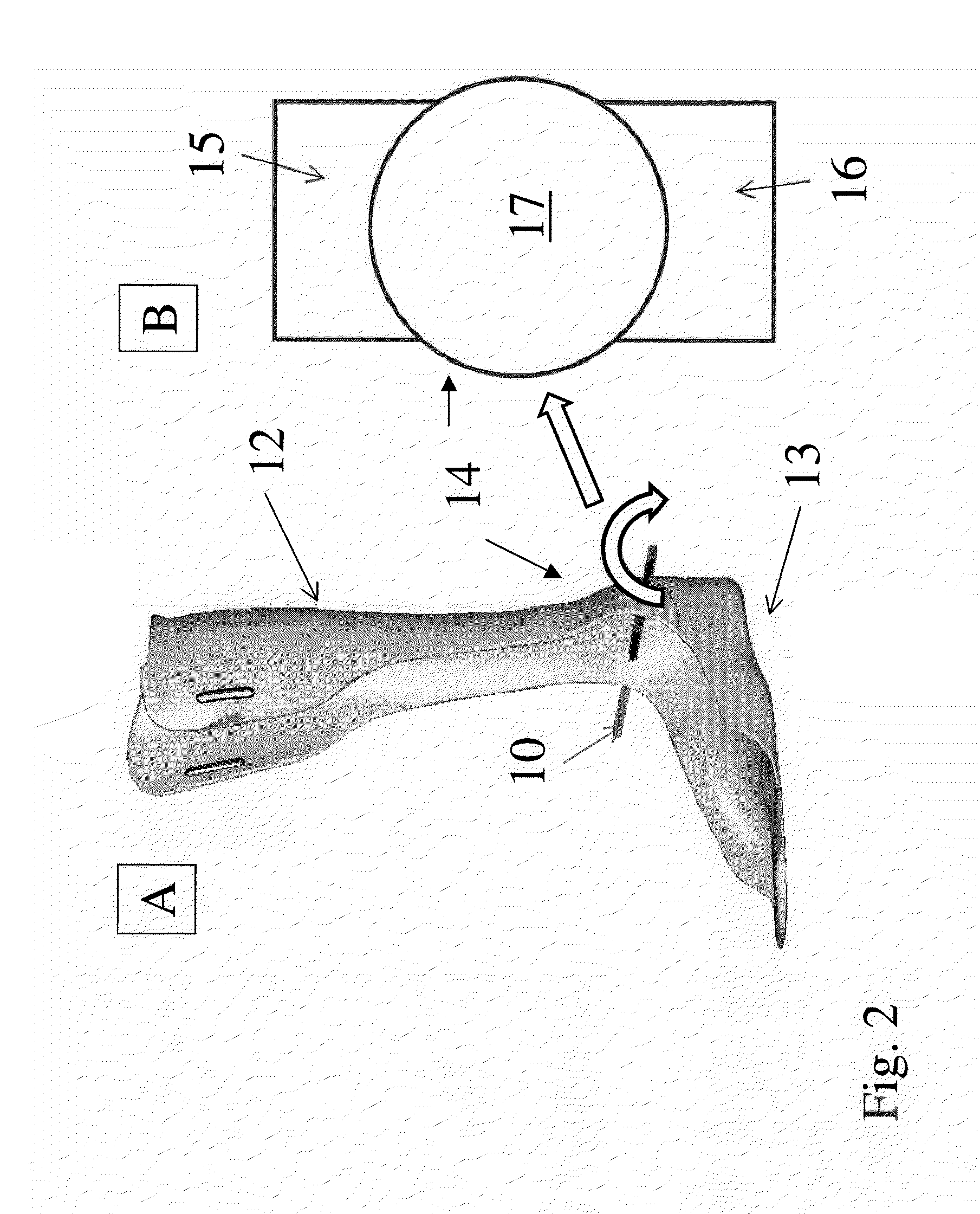
An exoskeleton device for assisting the movement of a metacarpal-phalangeal joint of a hand in a flexion / extension plane Γ of the joint, including a metacarpal support arranged integrally with a metacarpal portion of the hand, a phalangeal support having means for fastening to a proximal phalanx, a kinematical chain between the metacarpal support and the phalangeal support arranged to provide and carry out a rotation of the phalangeal support with respect to the metacarpal support.
Owner:SCUOLA SUPERIORE S ANNA
Apparatus and system for limb rehabilitation
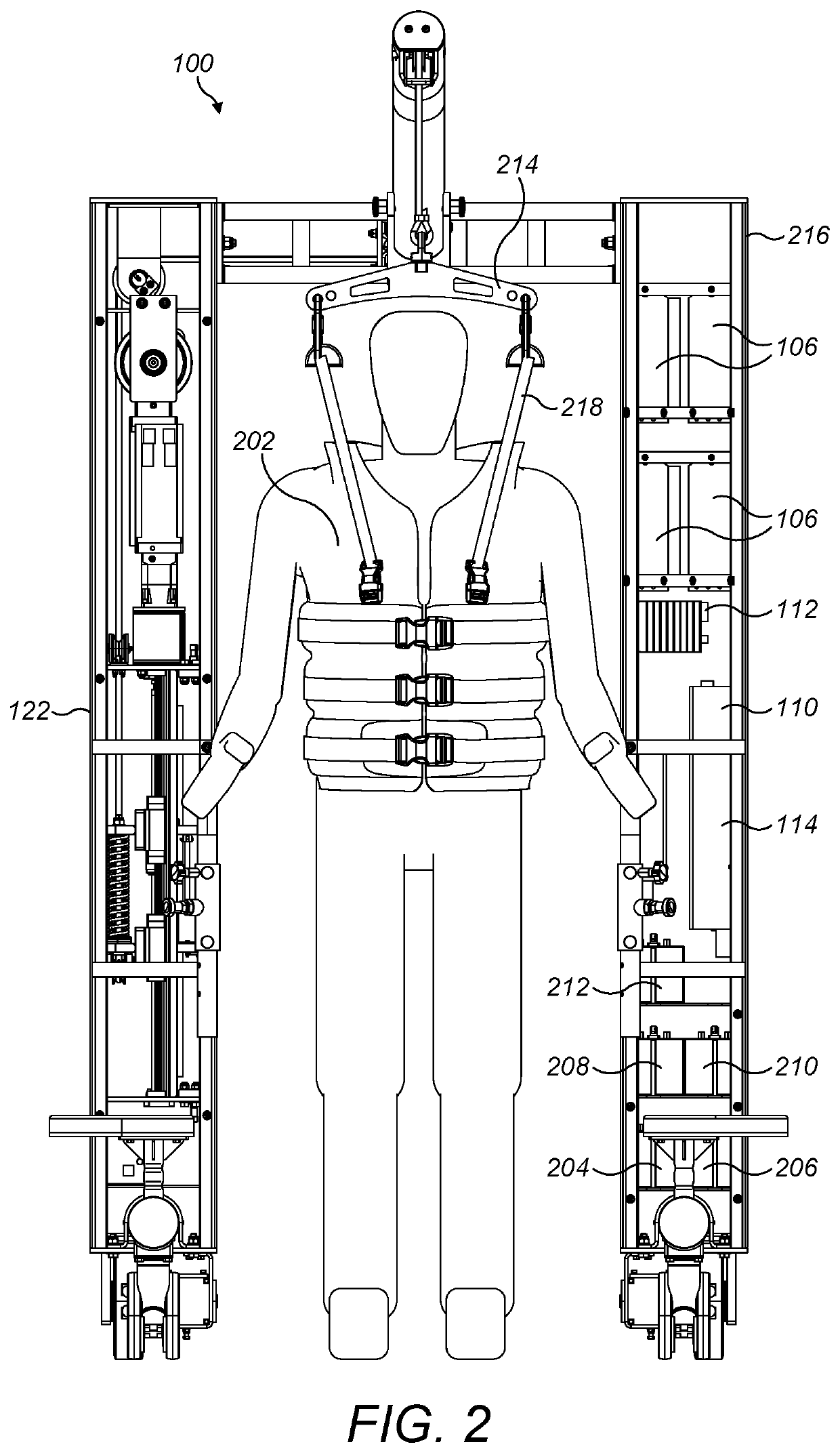
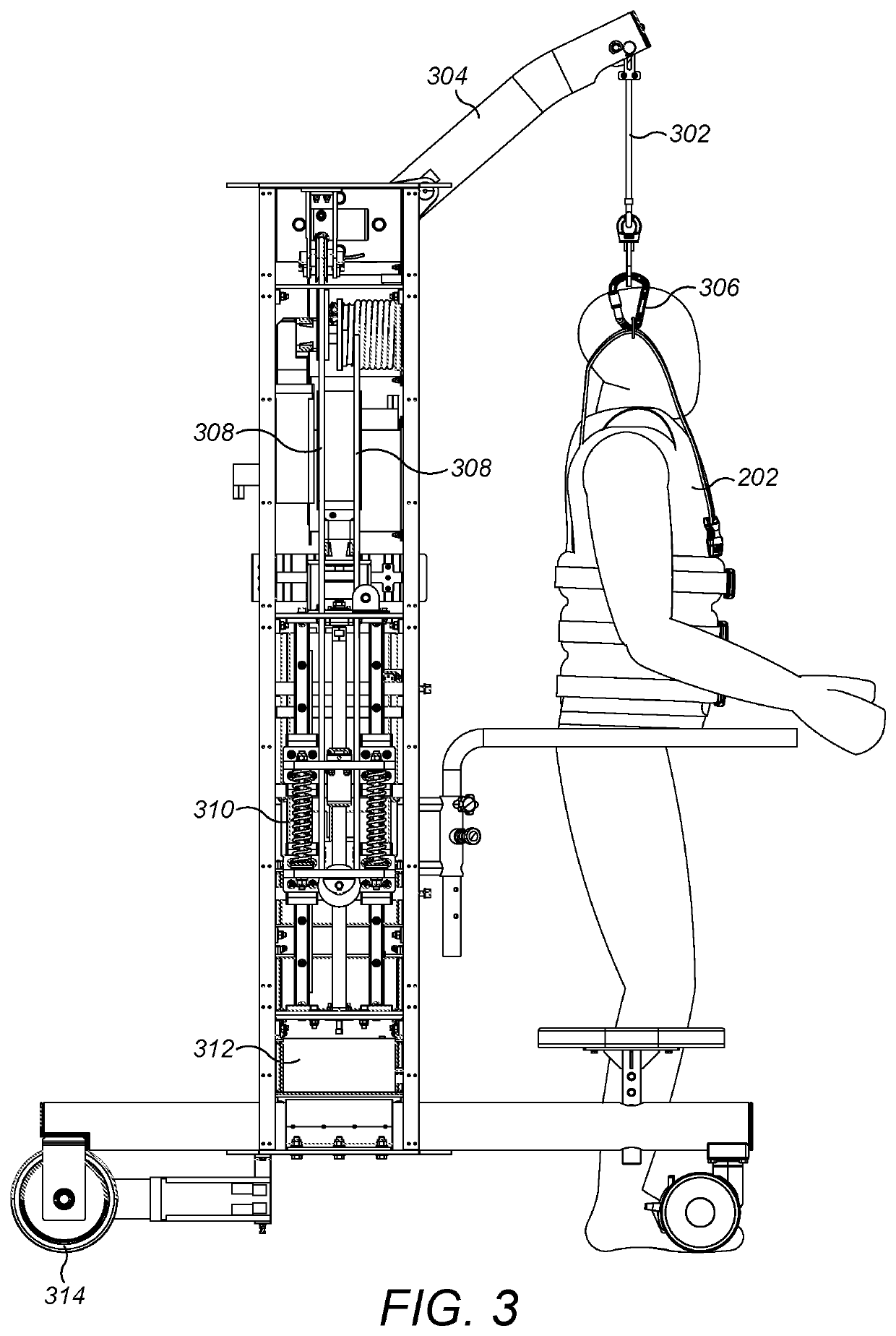
ActiveUS20190183715A1% fall safe limb rehabilitation100% fall safe limb rehabilitationPhysical therapies and activitiesDiagnosticsEngineeringIntelligent algorithms
A robotic limb rehabilitation apparatus and system for a lower limb in a human being is disclosed. The apparatus comprises of a mobile-frame, dynamic weight unloading mechanism and lower extremity exoskeleton device. The mobile-frame structure is constructed using first and second vertical structural support members connected by a horizontal cross bar / beam to which a boom arm assembly is attached. During the rehabilitation exercises the user is secured with a harness and lower extremity exoskeleton device for safe movements. An intelligent algorithm, embedded onto a dedicated processor, actuates various motors to execute the prescribed exercises, while the sensors provide dynamic feedback for corrective measures to control the exercise routine.
Owner:BIONIC YANTRA PTE LTD
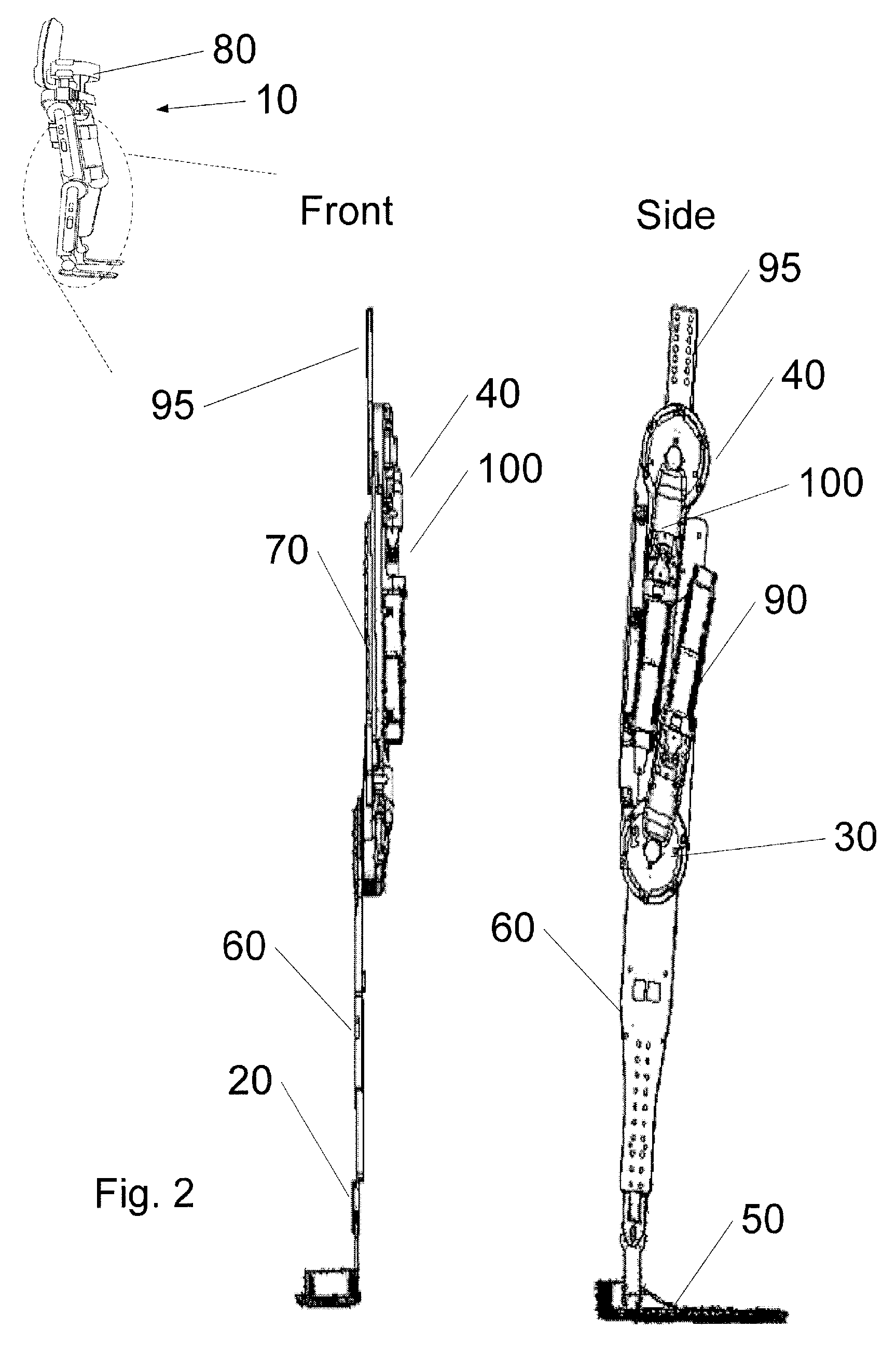
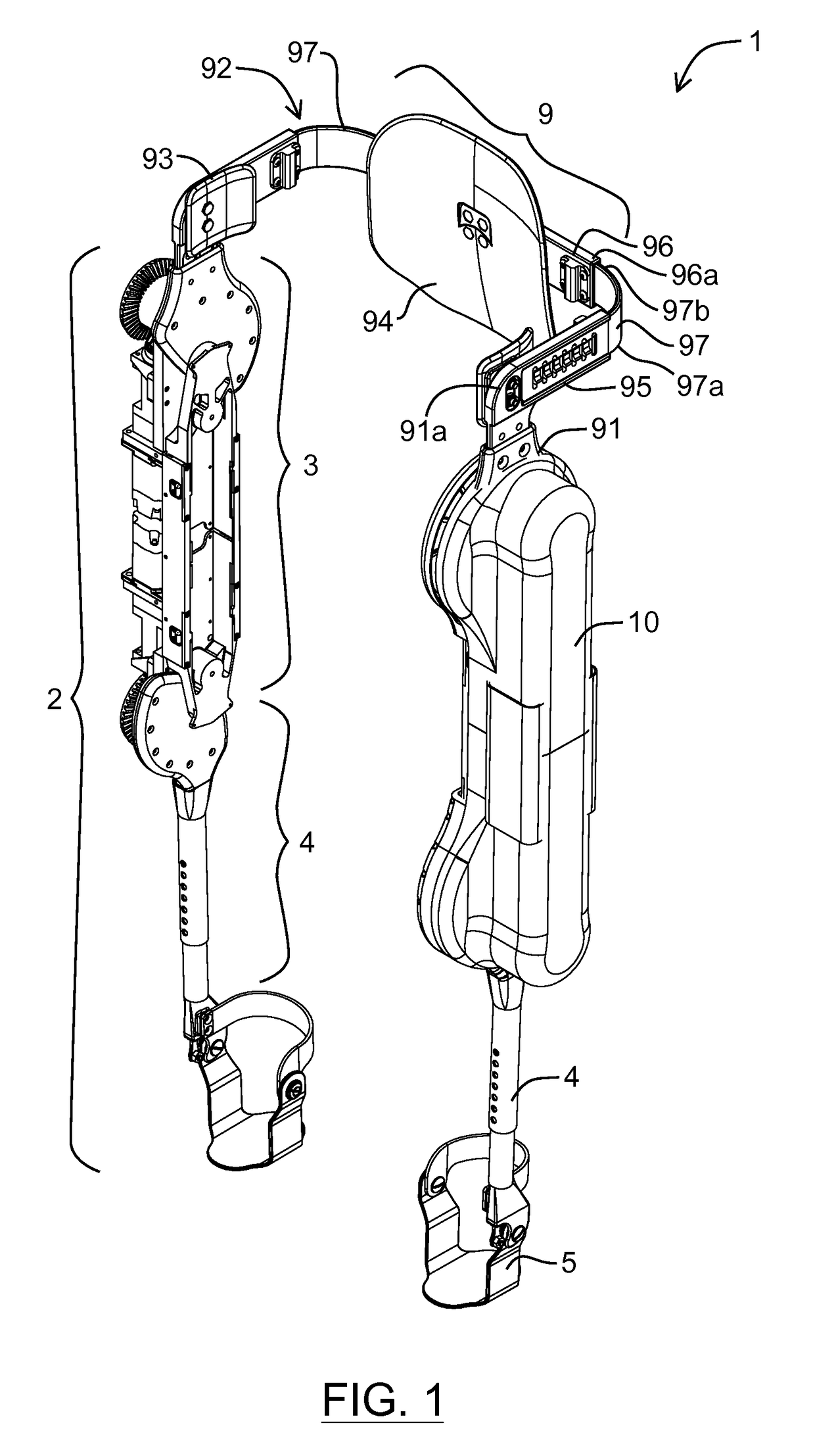
Exoskeleton device with sitting support and method of operation thereof
An exoskeleton device includes a plurality of braces that are each attachable to a part of a user. A plurality of joints connects adjacent braces. Each joint is controllable to bend or unbend so as to cause the exoskeleton device to change between an erect configuration and a sitting configuration. At least one support column is extendible from a brace. A length of the support column is adjustable. A controller is configured to adjust the length of the support column in coordination with the bending or unbending of a joint to provide support for the exoskeleton device when in the sitting configuration.
Owner:REWALK ROBOTICS LTD
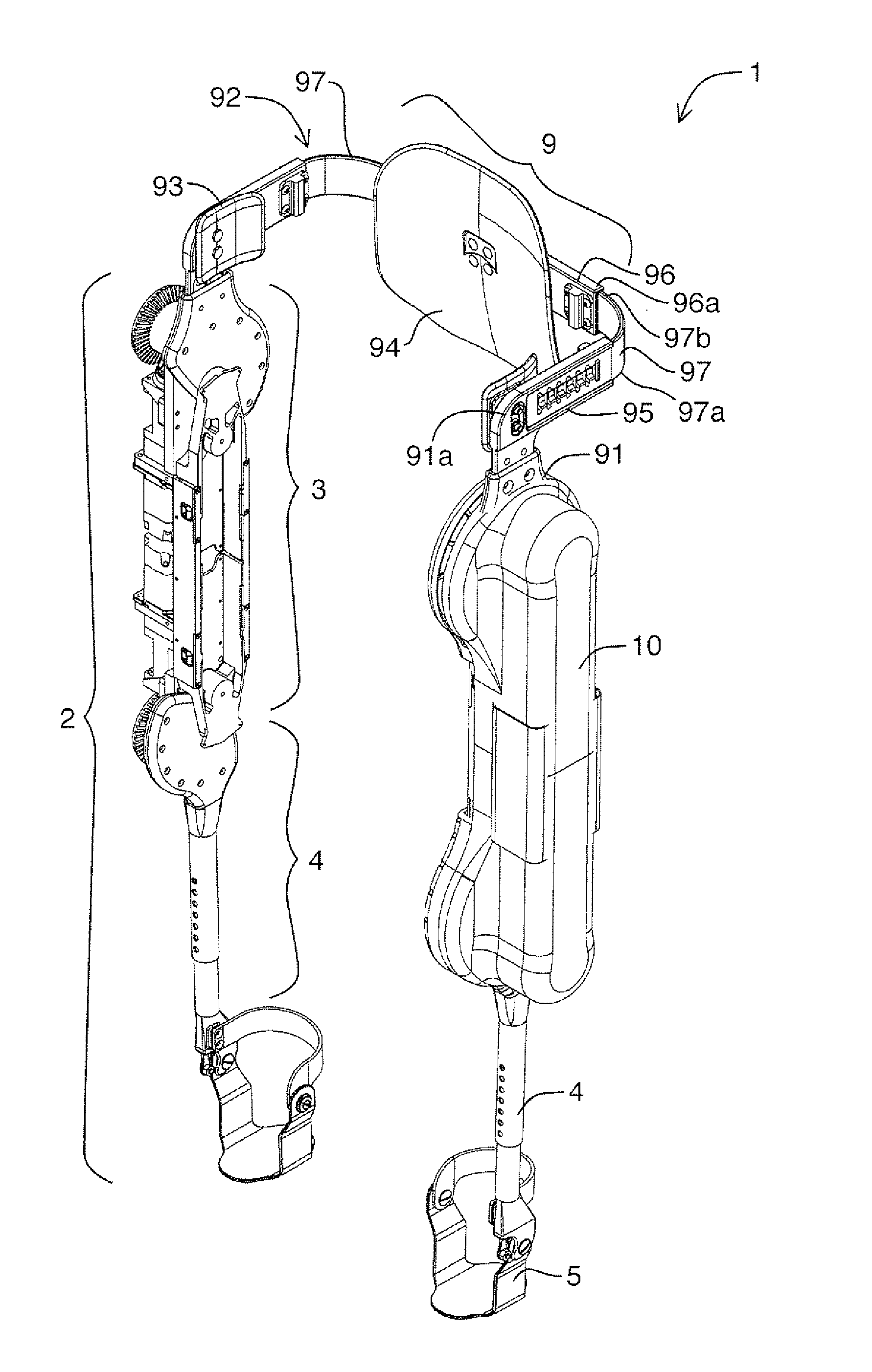
Airbag for exoskeleton device
A motorized exoskeleton system for facilitating locomotion for a user, the system including a motorized exoskeleton device, one or a plurality of sensors to sense one or a plurality of parameters indicative of a state in which a user of the motorized exoskeleton device is falling, and an airbag unit comprising one or a plurality of airbags configured to deploy in response to the sensed state.
Owner:REWALK ROBOTICS LTD
Safety monitoring and control system and methods for a legged mobility exoskeleton device
ActiveUS20190105777A1Avoid unnecessaryAvoid state transitionsProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorJoint componentElectronic controller
A method of controlling a mobility device and related device including at least one drive component that drives at least one joint component is described. The control method may include executing a control application with an electronic controller to perform: receiving sensor information from sensors corresponding to a state and / or mode of the mobility device; analyzing the sensor information and determining a control mode of operation based on the sensor information; generating a control signal to output an alert via electronic indicators corresponding to the determined control mode; and controlling at least one drive component of the mobility device to selectively configure and modulate at least one joint component in accordance with the determined control mode of operation. Different alerts may be outputted by the electronic indicators depending on the nature or severity of the alert condition, accompanied by respective device control operations in accordance with the alert condition.
Owner:EKSO BIONICS HLDG INC
Self adaptive support weight losing device for lower limb exoskeleton rehabilitation robot
ActiveCN104107131AEasy transferSimple structureChiropractic devicesMovement coordination devicesGravity centerEngineering
The invention discloses a self adaptive support weight losing device for a lower limb exoskeleton rehabilitation robot. The self adaptive support weight losing device comprises a gravity center following device arranged on the upper face of a lift platform moving plate and a lifting device arranged on the lower face of the lift platform moving plate and is characterized in that the gravity center following device comprises a slot type cam, a cam swing rod, a power exoskeleton support plate connected with a power exoskeleton device, one end of the cam swing rod is matched with an annular sliding slot of the slot type cam in a contacted mode through an idler wheel, the other end of the cam swing rod is connected with a parallelogram connecting rod structure, the rear edge of the parallelogram connecting rod structure is hinged to a stand column of the lift platform moving plate, and the front edge of the parallelogram connecting rod structure is hinged to a vertically moving mechanism which forms a sliding pair with the power exoskeleton support plate.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
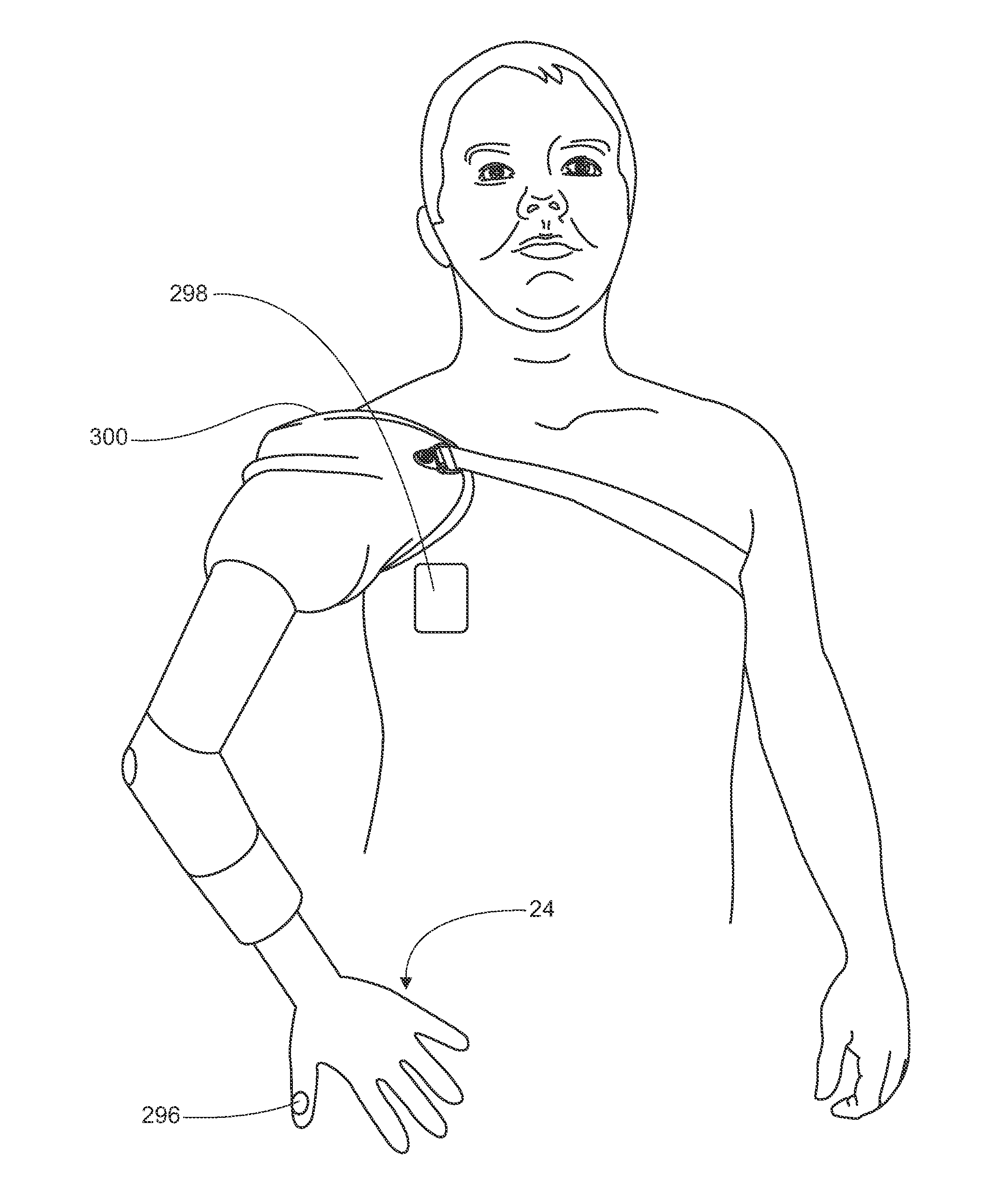
Wrist and forearm exoskeleton
InactiveUS20150359697A1Large range of motionMuscle strengthChiropractic devicesEye exercisersPronationsEngineering
An exoskeleton device and method of using the same is provided that helps rehabilitate limbs such has the lower arm. Embodiments of the exoskeleton device have multiple degrees of freedom so that a limb such as the lower arm may flex or rotate in multiple directions to establish or re-establish neural connections in the brain. With the lower arm example, a person may grasp a handle in the exoskeleton and then flex the lower arm about a pronation / supination axis, a flexion / extension axis, and / or an abductor / adductor axis. The exoskeleton device has several modes of operation where actuators can aid the person's motion, resist the person's motion, or passively allow free motion of the person's limb.
Owner:COLORADO SCHOOL OF MINES
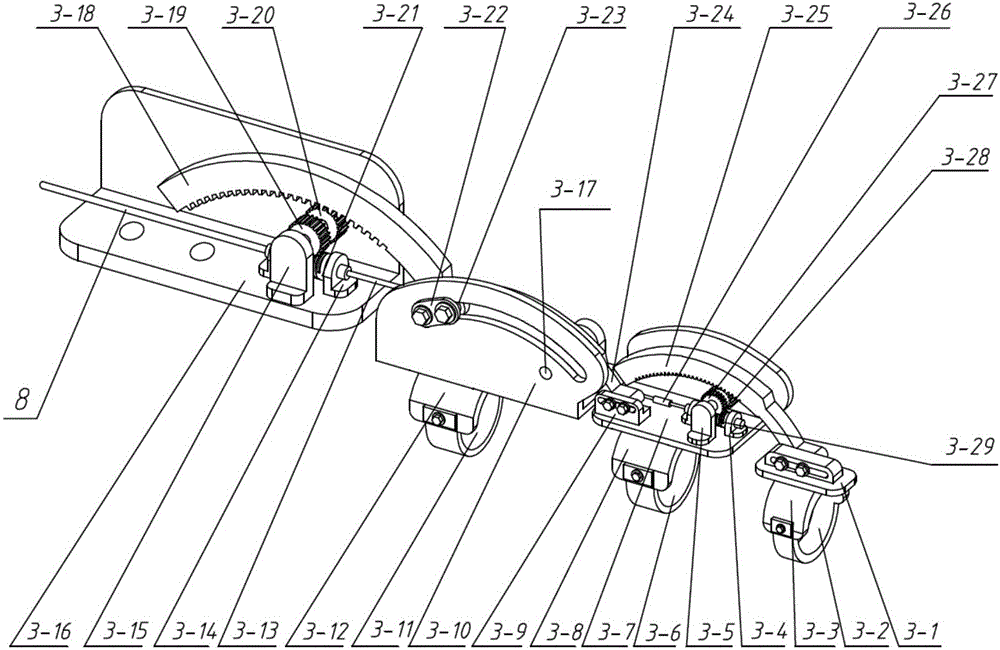
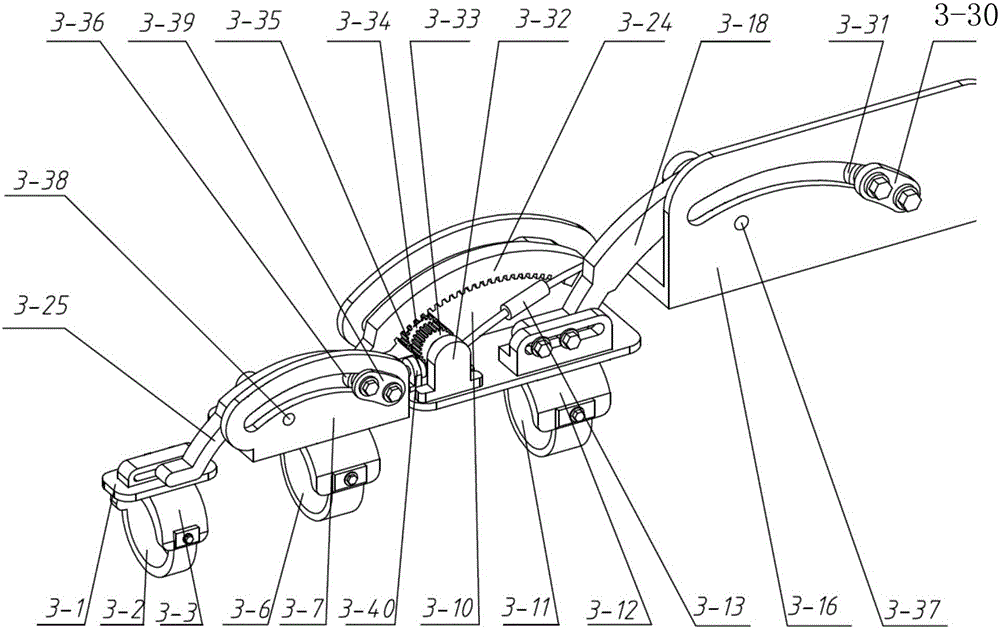
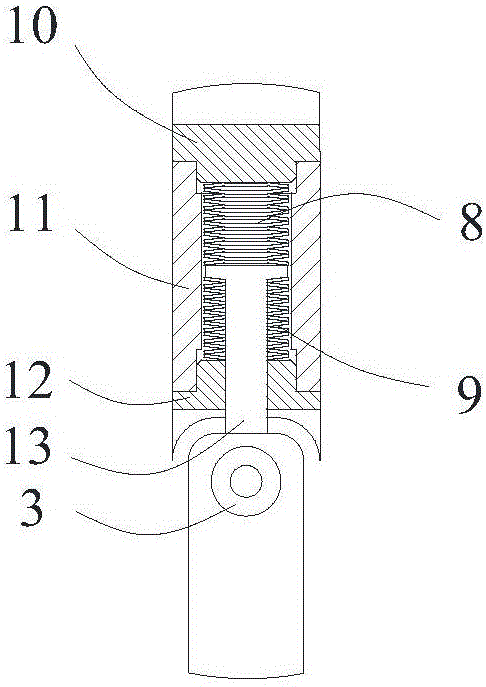
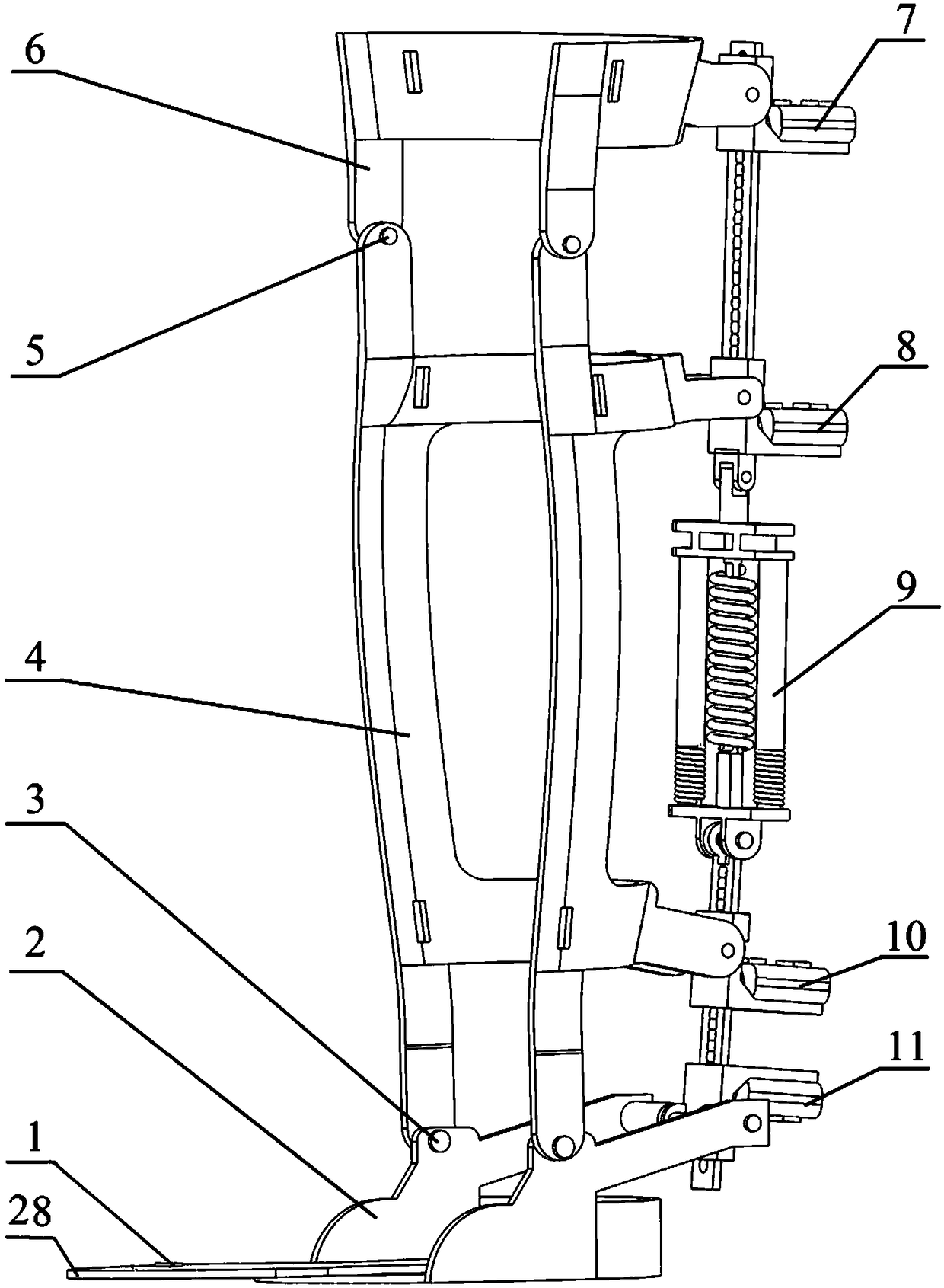
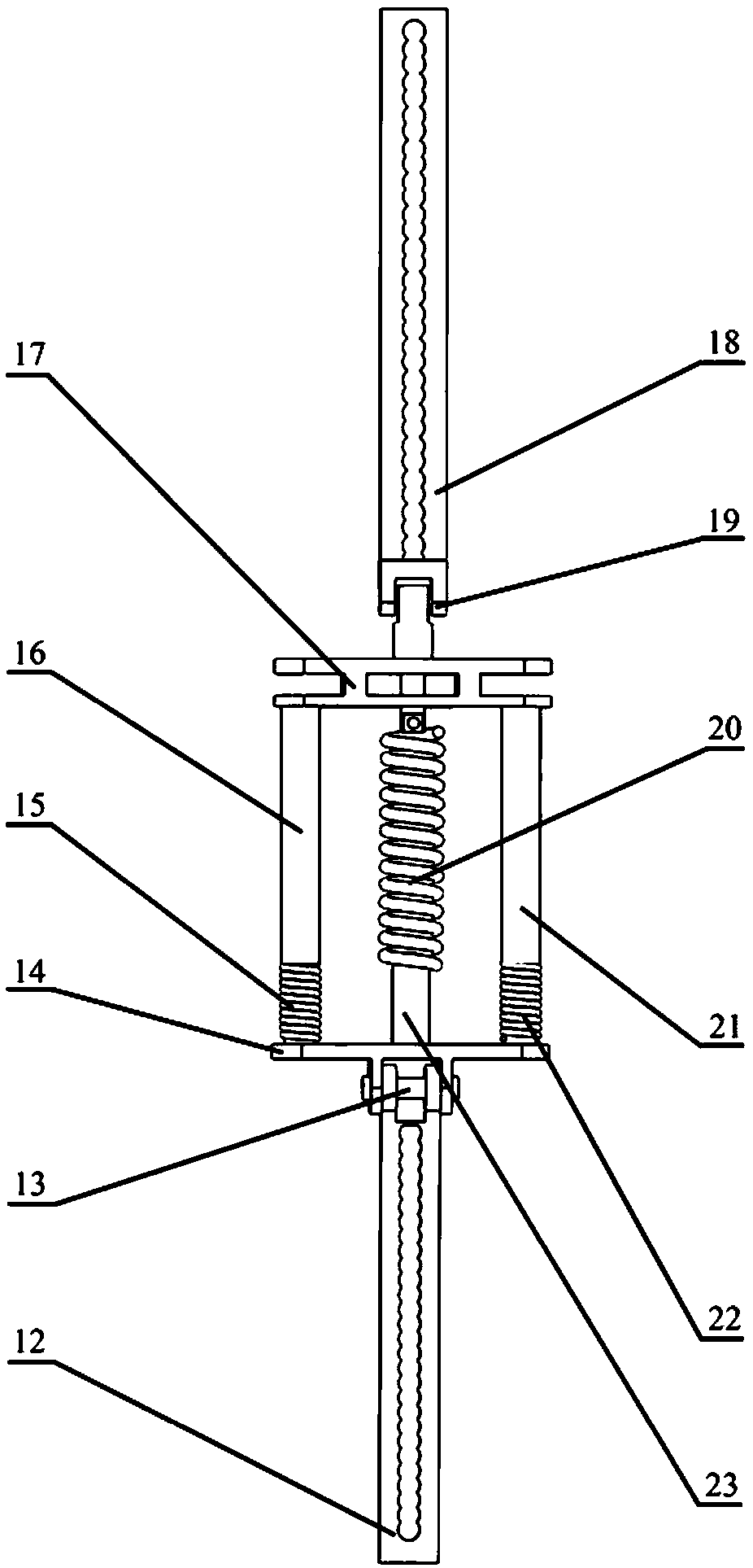
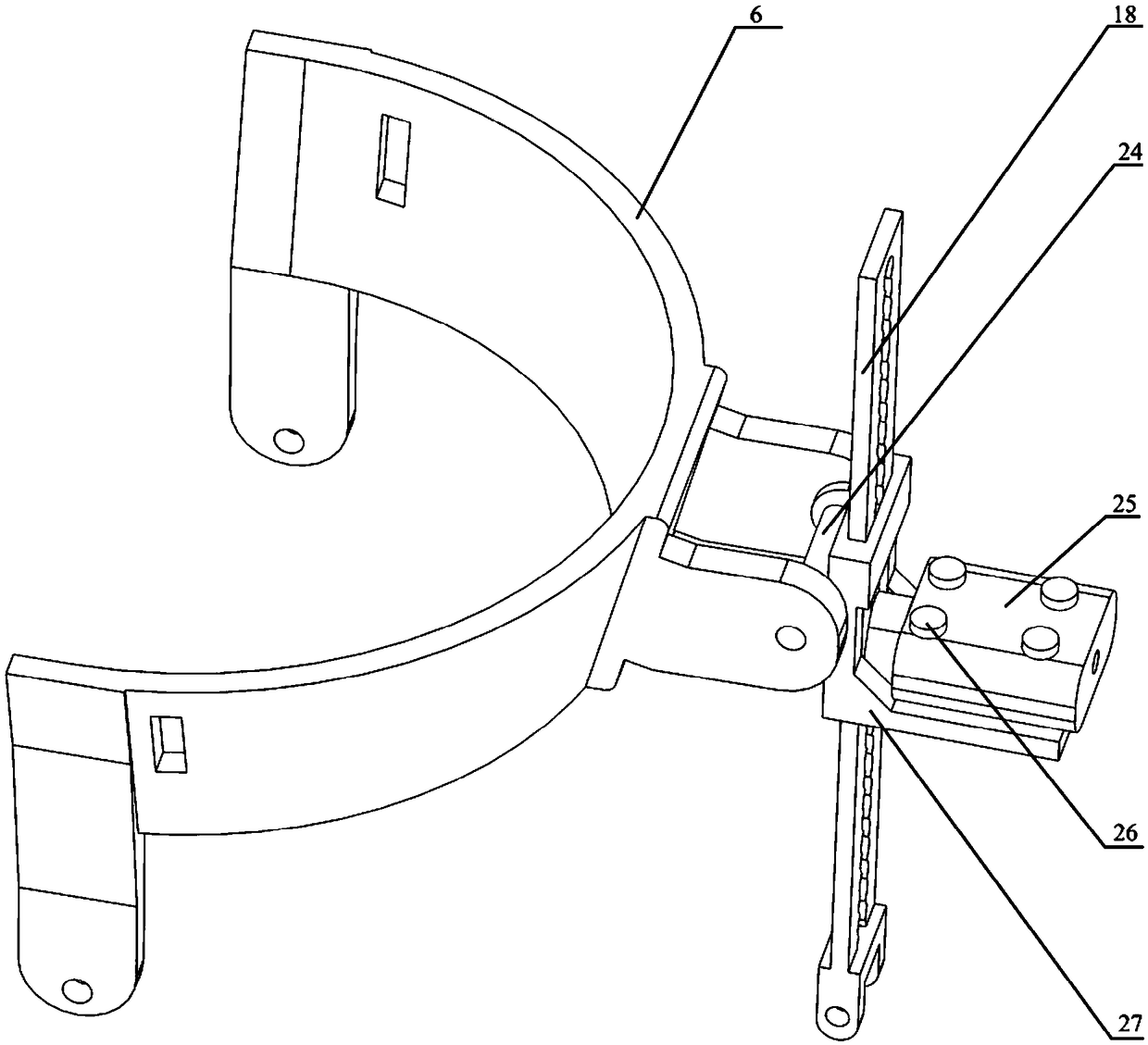
Self-adaptation flexible joint exoskeleton device
The invention discloses a self-adaptation flexible joint exoskeleton device. The self-adaptation flexible joint exoskeleton device is applied to bearing parts below the knee joint in a bionic human body cartilage tissue building structure. The self-adaptation flexible joint exoskeleton device comprises a thigh flexible power assisting mechanism (1), a shank connecting mechanism (2) hinged to the thigh flexible power assisting mechanism and a foot wearing force bearing mechanism hinged to the shank connecting mechanism. In the thigh flexible rotation power assisting mechanism (1), a tension and compression disc spring mechanism is formed by an upper tension and compression disc spring (8) and a lower tension and compression disc spring (9). A shank connecting rod (13) is a T-shaped rod piece. The upper tension and compression disc spring (8) is arranged on the upper side of the T-shaped head of the shank connecting rod, the lower tension and compression disc spring (9) is arranged on the lower side of the T-shaped head of the shank connecting rod, and the upper tension and compression disc spring (8) and the lower tension and compression disc spring (9) are fixed to the thigh of the human body through a knee joint rotation shaft connecting mechanism (11). The self-adaptation flexible joint exoskeleton device is flexible and is a buffering protection device achieving the joint motion freedom degree, and the self-adaptation flexible joint exoskeleton device is close to the human body physiology motion law, supports the motion of the human body and meets the requirement for bearing the load of the human body.
Owner:成都奥特为科技有限公司
Foot plate assembly for use in an exoskeleton apparatus
ActiveUS9808390B2Easy to walkAvoid obstaclesChiropractic devicesWalking aidsEngineeringExoskeleton Device
An exoskeleton for a leg of a user comprises a leg structure, a foot plate moveably mounted thereto, and a biasing member extending between the leg structure and the foot plate, the foot plate is moveably mounted to the leg structure between a first position in which the rearward portion extends downwardly and the forward portion extends upwardly and a second position in which the rearward portion extends upwardly and the forward portion extends downwardly and the foot plate is biased to the first position.
Owner:BIONIK LAB
Human wearable type decompression and assistance mechanical exoskeleton device
InactiveCN106112989ARelieve pressureWeight increaseProgramme-controlled manipulatorFoot supportsEngineering
The invention discloses a human wearable type decompression and assistance mechanical exoskeleton device. The human wearable type decompression and assistance mechanical exoskeleton device comprises shoulder joint exoskeleton multi-bar mechanisms, a vertebral column joint exoskeleton mechanism with dual six-axis platforms, hip joint exoskeleton multi-bar mechanisms and two shank foot supporting exoskeleton mechanisms which are sequentially connected from top to bottom; the structures of the shoulder joint exoskeleton multi-bar mechanisms are the same as those of the hip joint exoskeleton multi-bar mechanisms; the top and the bottom of the vertebral column joint exoskeleton mechanism with dual six-axis platforms are fixedly connected to the middle of the bottoms of the shoulder joint exoskeleton multi-bar mechanisms and the middle of the tops of the hip joint exoskeleton multi-bar mechanisms separately; and the upper end of each shank foot supporting exoskeleton mechanism is connected to the left side and the right side of the lower end of the corresponding hip joint exoskeleton multi-bar mechanism. According to the human wearable type decompression and assistance mechanical exoskeleton device disclosed by the invention, pressure of heavy objects carried on the back of the human is sufficiently relieved, good assistance is provided, and weight of heavy objects carried on the back is greatly increased, and therefore, the human wearable type decompression and assistance mechanical exoskeleton device is suitable for assisting the old to climb stairs and travel, and also can be used for rehabilitation on patients by virtue of medical apparatuses and instruments.
Owner:HUANGHE S & T COLLEGE
Passive lower limb exoskeleton device for achieving human body energy migration
InactiveCN108748099ARealize collection and storageLower metabolismProgramme-controlled manipulatorEnergy migrationKnee Joint
The invention discloses a passive lower limb exoskeleton device for achieving human body energy migration. The passive lower limb exoskeleton device comprises a sole pressure sensor assembly arrangedon an insole, a lower limb connecting assembly is arranged at the back end of the insole, a plurality of control switch assemblies in signal connection with the sole pressure sensor assembly are hinged to the back side of the lower limb connecting assembly, and a bionic spring assembly is in sliding connection to each control switch assembly and is matched with the control switch assembly in a clamped manner to achieve limitation; and sole pressure sensors are used for collecting signals, the signals are used for controlling switches, then the stretching / contracting states of the bionic springassemblies are controlled, energy generated when the knee joint does negative work in the human body walking process is converted into elastic potential energy to be collected and stored, and the energy is transferred to the ankle joint in the standing phase later period, and energy dissipation of muscle during positive work doing of the ankle joint is reduced. By means of the passive lower limbexoskeleton device, external connection energy resources are avoided, the structure is simple, the mass is small, and wearing is convenient.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com