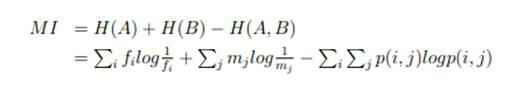Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
70 results about "Digital medicine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Within the field of digital health, digital medicine is a category of pharmaceuticals which combines a prescription medication with an ingestible sensor component. Digital medicines are designed to communicate to mobile and/or web-based applications that a patient has taken a specific dose of medication at a certain time.
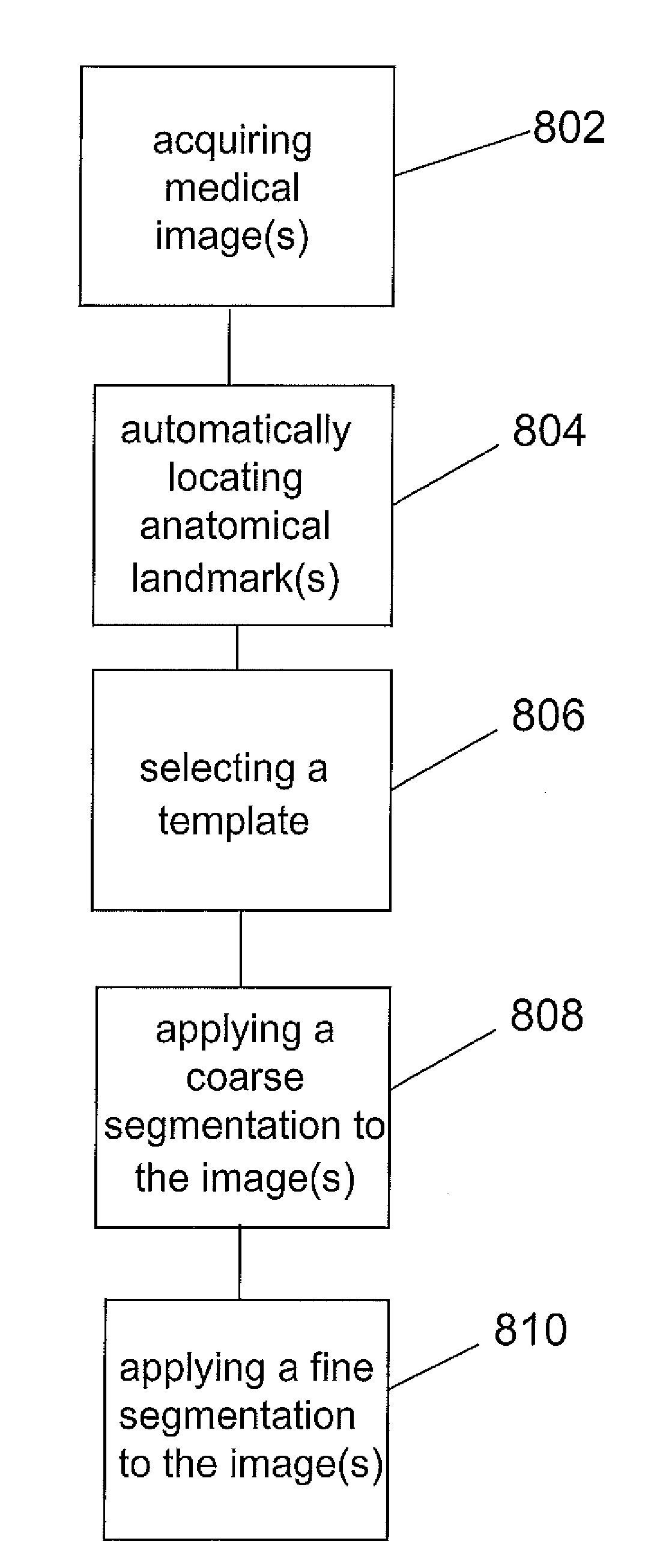
Enhanced image processing method for the presentation of digitally-combined medical images
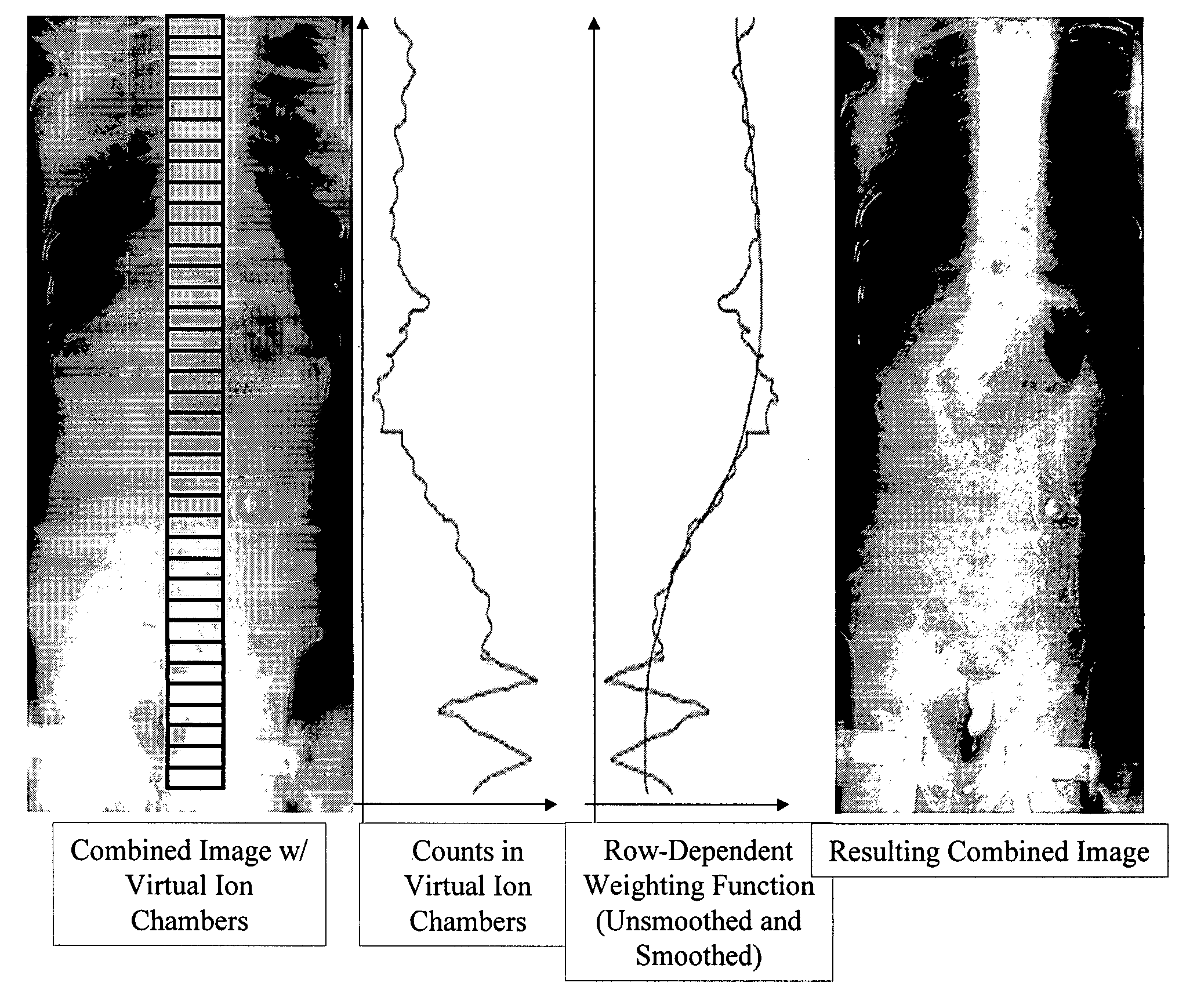
The present invention provides a method and associated system for processing a digital medical image. The method includes defining a plurality regions of an initial digital medical image, wherein the initial digital medical image is a combined initial digital medical image formed from the digital pasting of a plurality of individual initial digital medical images, and wherein the initial digital medical image is an exposure-normalized initial digital medical image; measuring an intensity for each of the plurality of regions of the initial digital medical image; deriving an intensity weighting function using the intensity measured for each of the plurality of regions of the initial digital medical image; and applying the intensity weighting function to the initial digital medical image to form a final digital medical image.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
System and method for geometric modeling of tubular structures
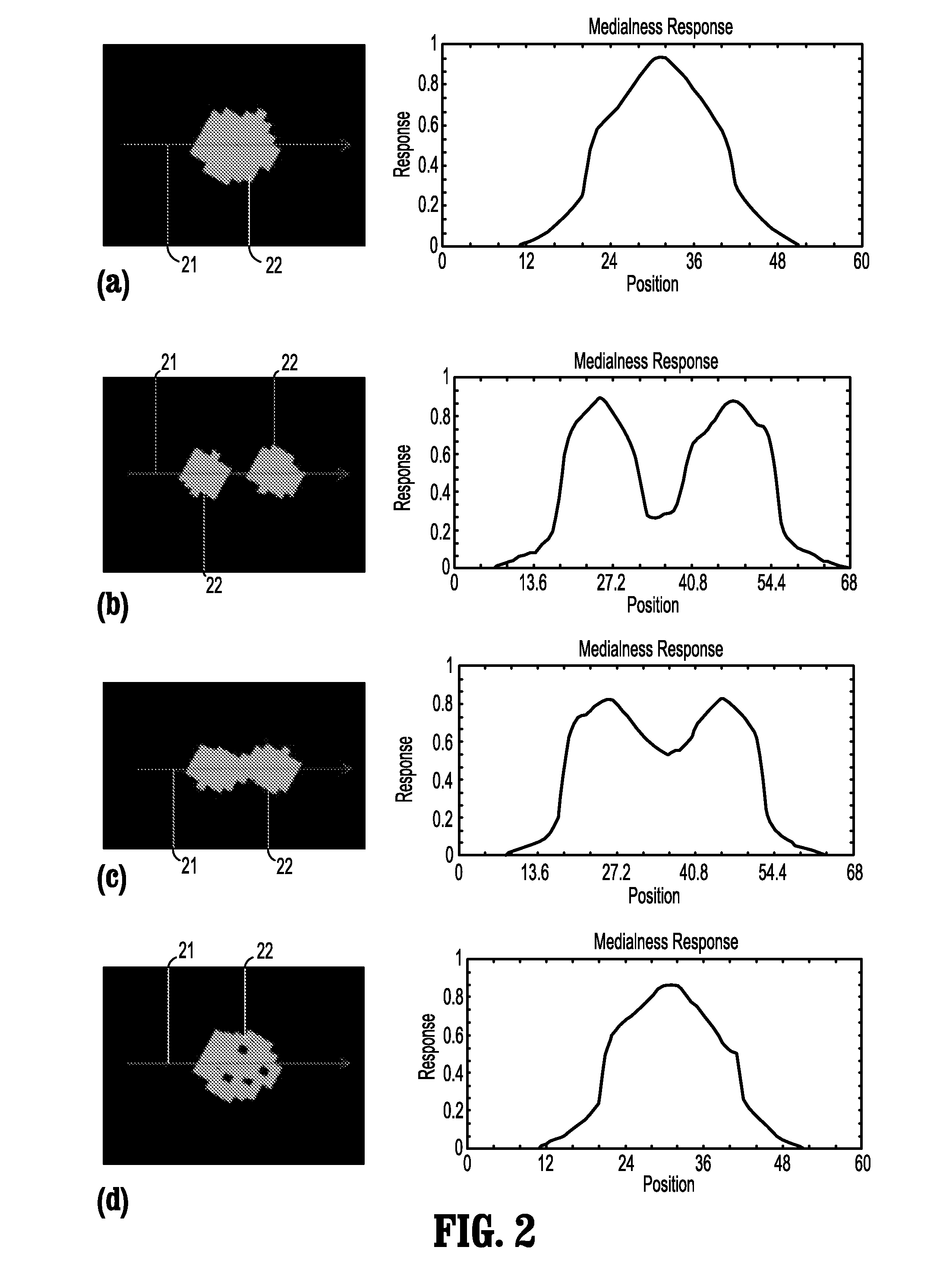
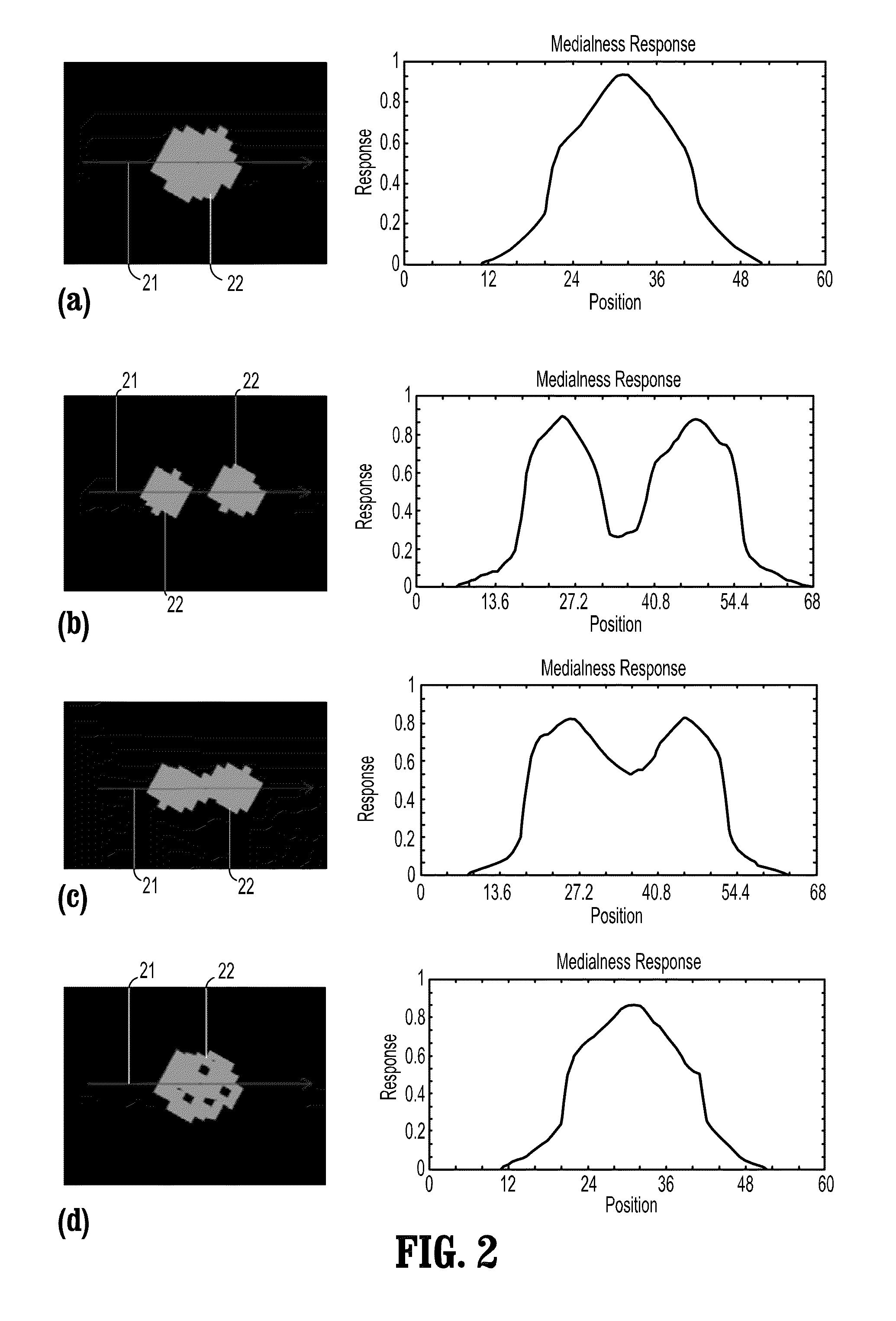
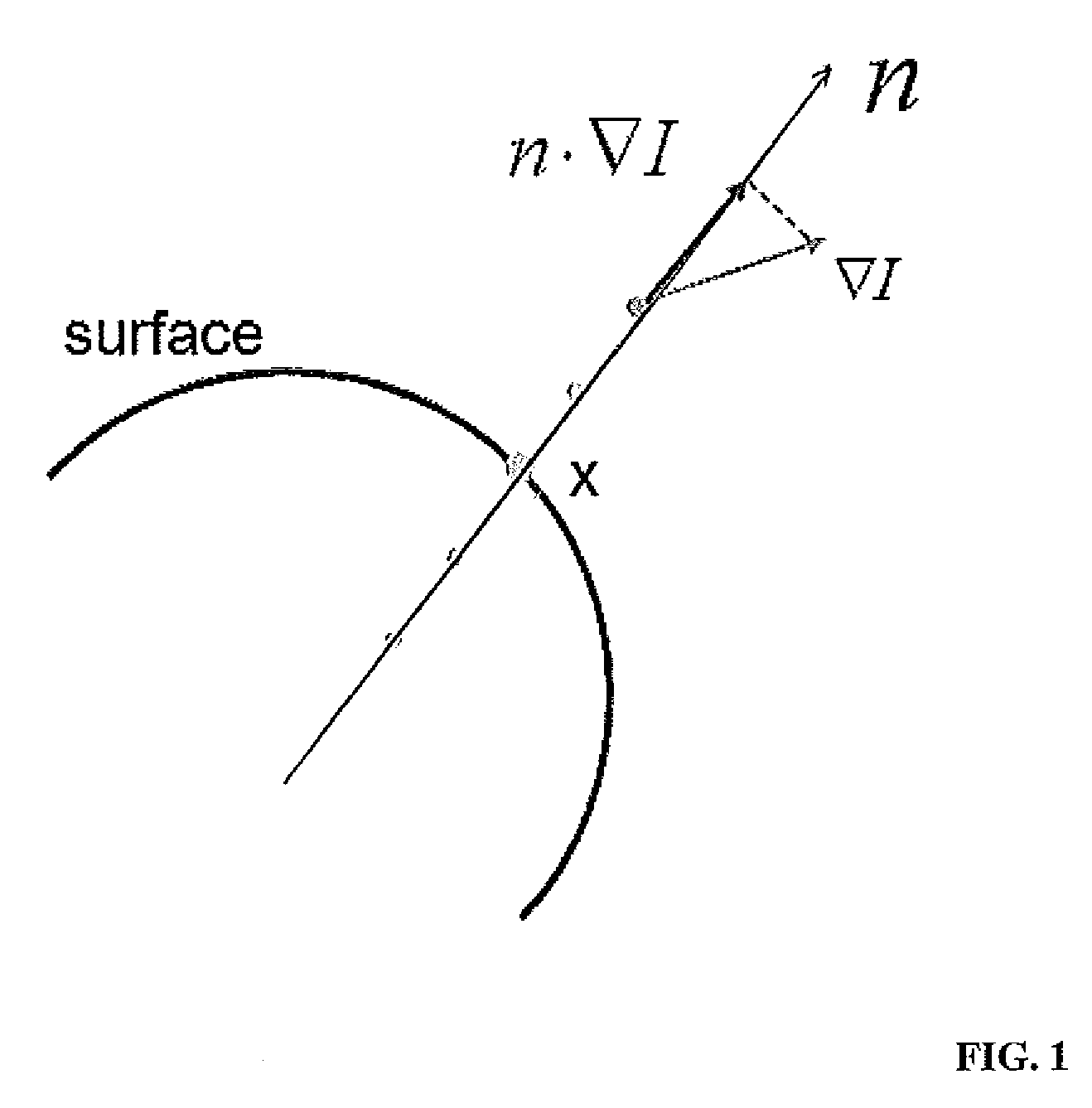
A method for extracting a centerline of a tubular structure in a digital medical image includes providing a 3-dimensional (3D) digitized medical image having a segmented tubular structure, finding a path in the image between a starting point and every other point in the tubular structure that minimizes an accumulative cost function, wherein the minimum accumulative cost φ(x) at a point x is a minimum of (φ(x′)+Px,x′) over all nearest neighbors x′ wherein Px,x′ is a cost of propagation obtained from the inverse of a medialness measure computed in a plane orthogonal to a line between x and x′ that is centered at a mid-point of the line, the medialness measure m(x) computed in a circular region C(x, R) centered at point x on the linr, with radius R, given bym(x)=maxR{1N∑i=0N-1f(x,Ru(2πi / N))},wherein {right arrow over (u)}(α)=sin(α){right arrow over (u)}1+cos(α){right arrow over (u)}2 and {right arrow over (u)}1 and {right arrow over (u)}2 define a 2D plane, and f(x0,R{right arrow over (u)}(α)) isf(xo,R)=max(1R∑x=x0x0+RI(x)-1M∑x=x0+R+1x0+R+1+MI(x)2,0).wherein M is the number of background points.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
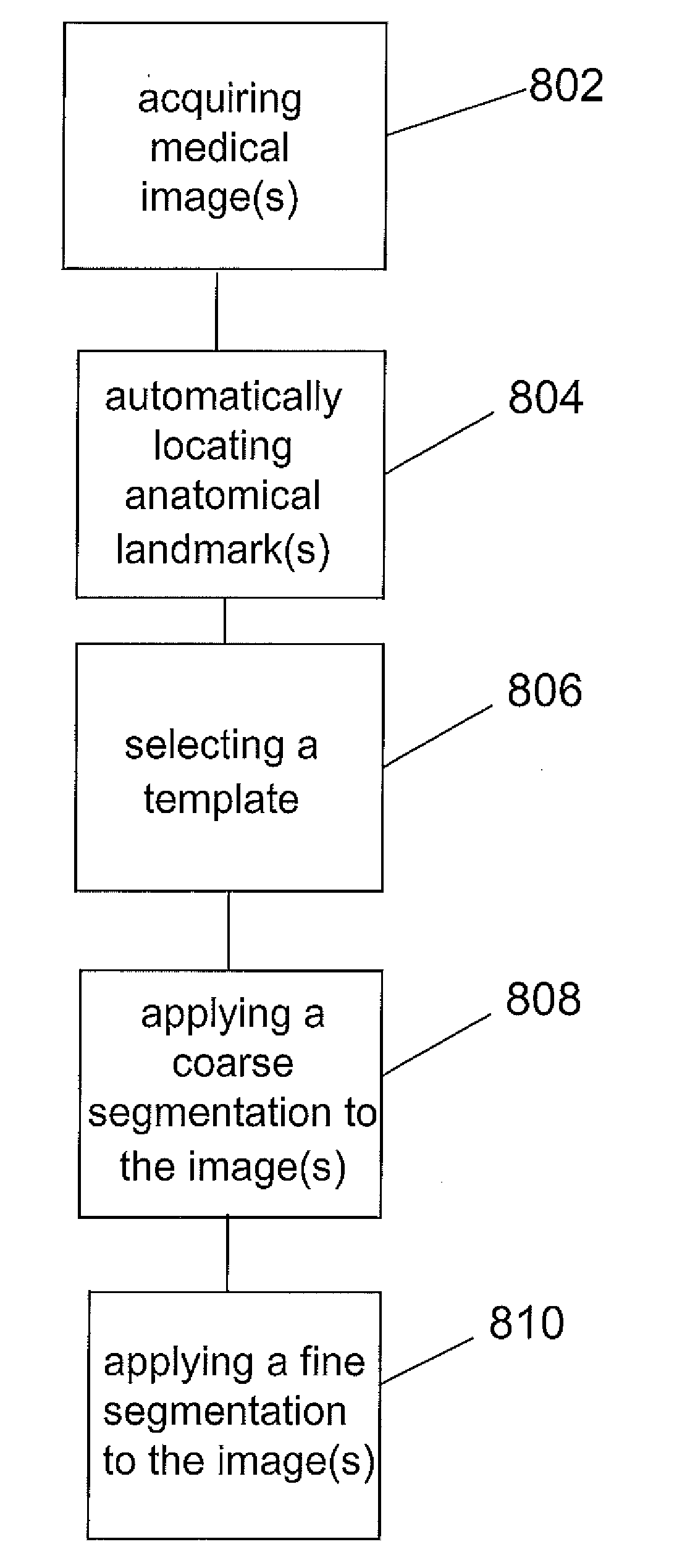
Systems and Methods for Automatic Vertebra Edge Detection, Segmentation and Identification in 3D Imaging
ActiveUS20110058720A1High fit responseImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionDigital medicine
Systems and methods for automatic accurate and efficient segmentation and identification of one or more vertebra in digital medical images using a coarse-to-fine segmentation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Virtual surgery simulation method and device thereof
InactiveCN103106348ARealize virtual displayStrong sense of immersionEducational modelsSpecial data processing applicationsBone tissueThree-dimensional space
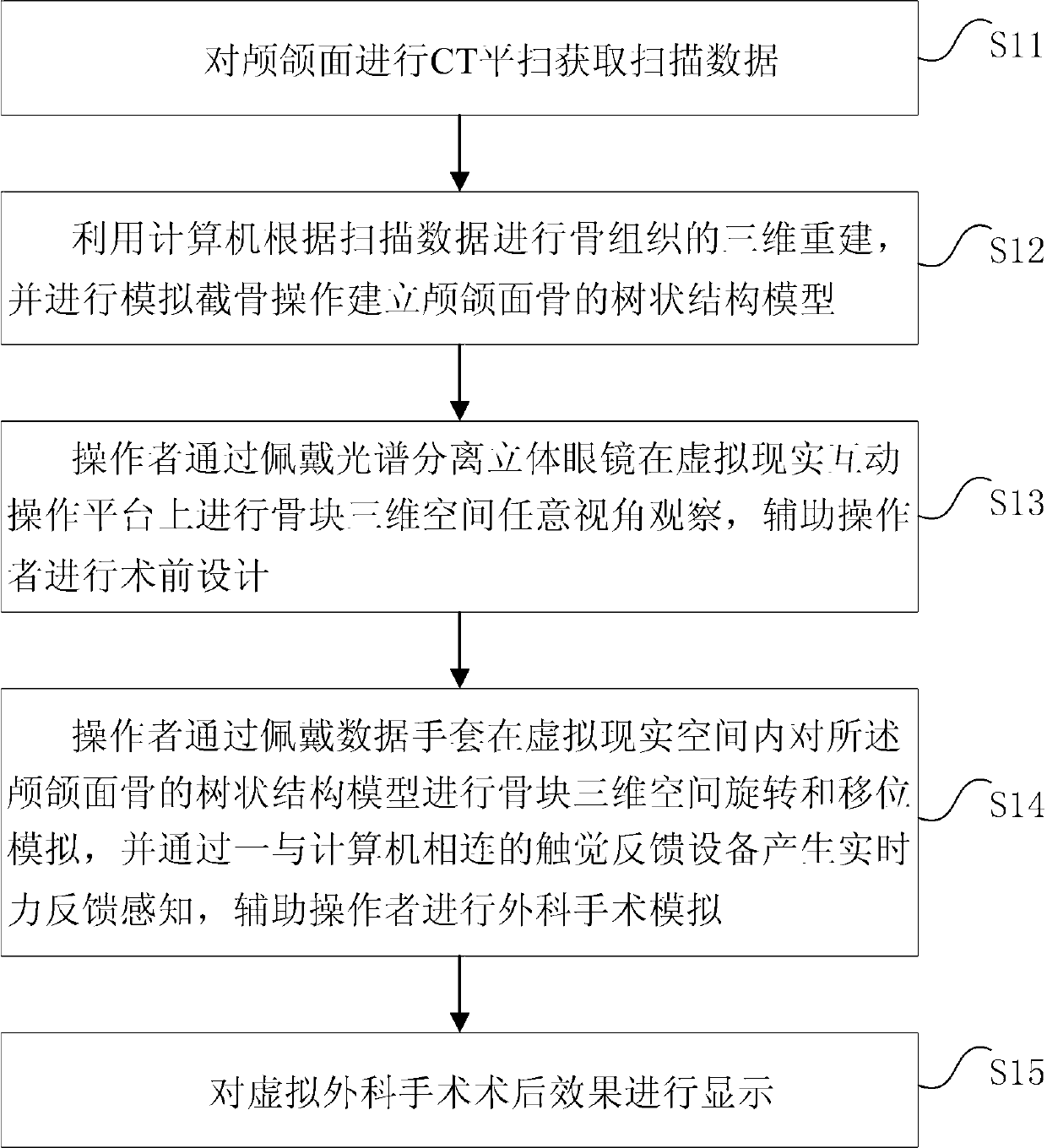
The invention relates to the fields of digital medicine and computer-assisted surgery, and provides a virtual surgery simulation method and a device of the virtual surgery simulation method. The virtual surgery simulation method comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out CT plain scanning on a craniomaxillofacial region to obtain scanned data; (2) carrying out three-dimensional reconstruction on bone tissue according to the scanned data by utilizing a computer, and simulating the operation of osteotomy to establish a dendritical structure model of a craniomaxillofacial bone; (3) carrying out bone block three-dimensional space observation at any angle of view on a virtual reality interactive operation platform by an operator who wears a pair of spectral separation stereo glasses to assist the operator in preoperative design; and (4) carrying out bone block three-dimensional space rotating and shifting simulation on the dendritical structure model of the craniomaxillofacial bone in a virtual reality space by the operator who wears a pair of data gloves, and producing real-time force feedback perception by a haptic feedback device which is connected with the computer to assist the operator in surgery simulation. The method and the device are strong in immersion and interaction, simple, efficient and easy to operate.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Spine image generating system based on ultrasonic rubbing technology and spine surgical navigation positioning system
ActiveCN107595387AAvoid damageAccurate intraoperative navigationImage enhancementImage analysisContour matchingSelf navigation
A spine image generating system based on an ultrasonic rubbing technology comprises a collecting unit and a processing unit. Ultrasonic rubbings are generated by the system based on ultrasonic imageswith two-dimensional spine surface structure characteristic outlines, and matched with a digital medical image outline, and thus a personalized spine surface topographic map which is consistent with an intraoperative position of a patient and updated in real time is obtained. A spine surgical navigation positioning system based on the spine image generating system comprises a navigation module andthe spine image generating system based on the ultrasonic rubbing technology. The spine surgical navigation positioning system can obtain the spine surface topographic map which is consistent with the intraoperative position of the patient and updated in real time, and can conduct real-time intraoperative navigation based on the spine surface topographic map. The spine image generating system based on the ultrasonic rubbing technology and the spine surgical navigation positioning system can greatly reduce the difficulty of a spinal operation, can achieve the operation auxiliary purposes of precise and nonradiative guided puncture, real-time navigation and being simple, convenient and reliable, and are particularly beneficial for application and popularization of a spinal minimally invasive surgery technology which is represented by a spine endoscopy to primary health care institutions.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
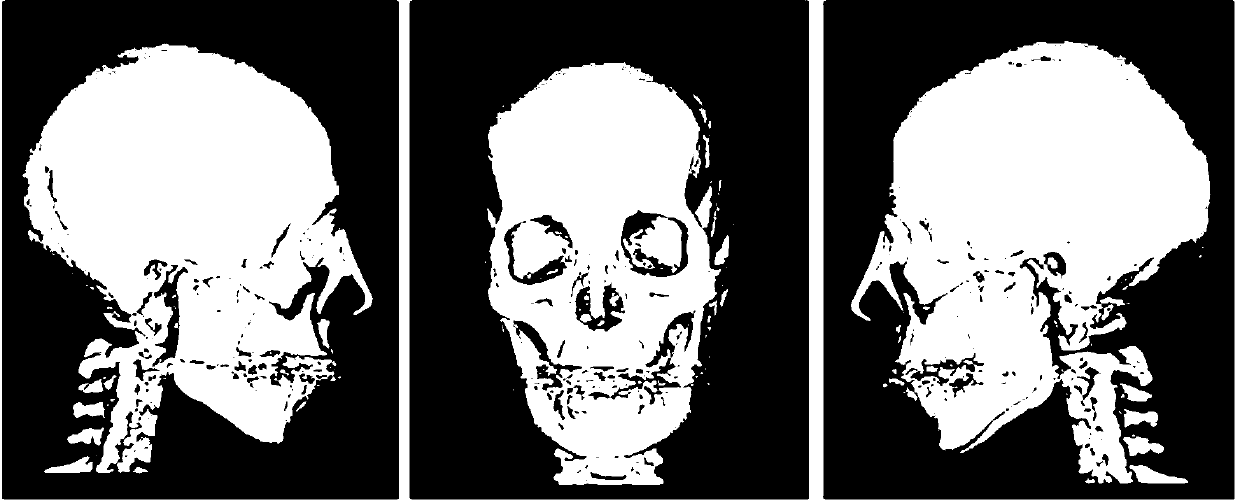
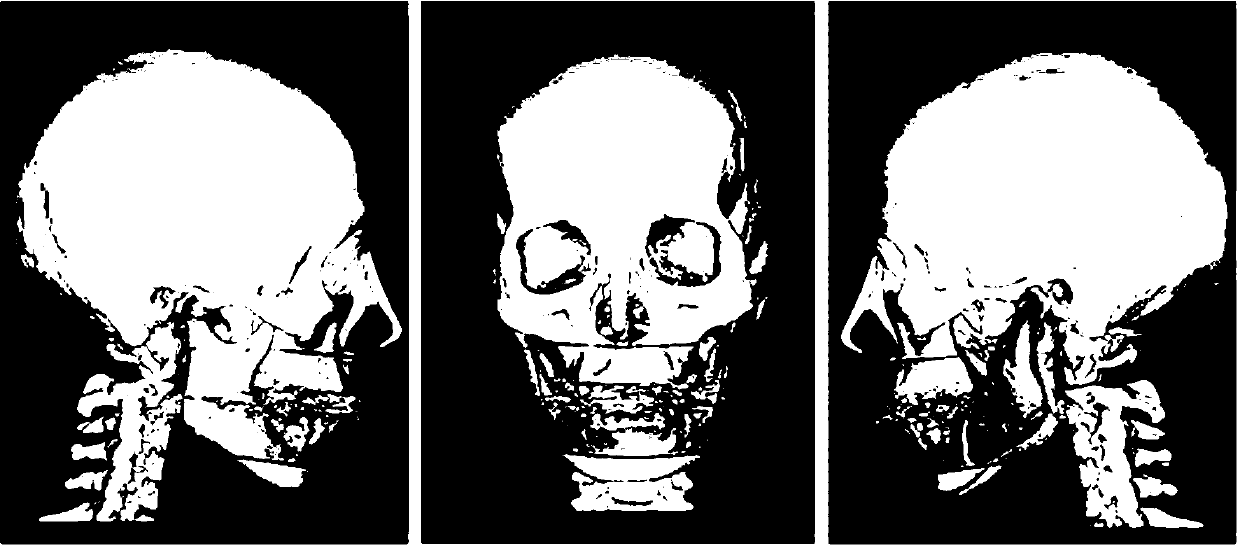
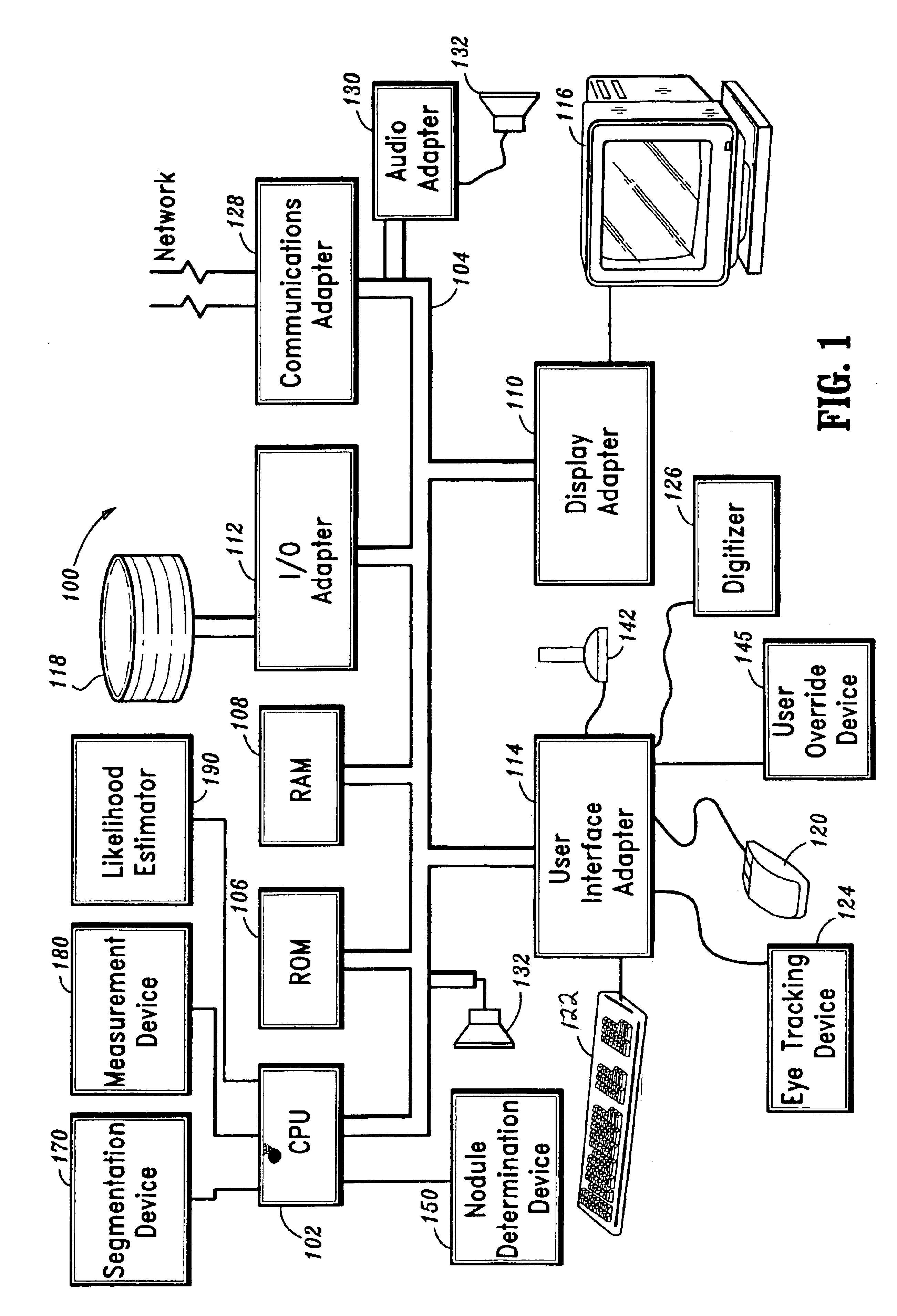
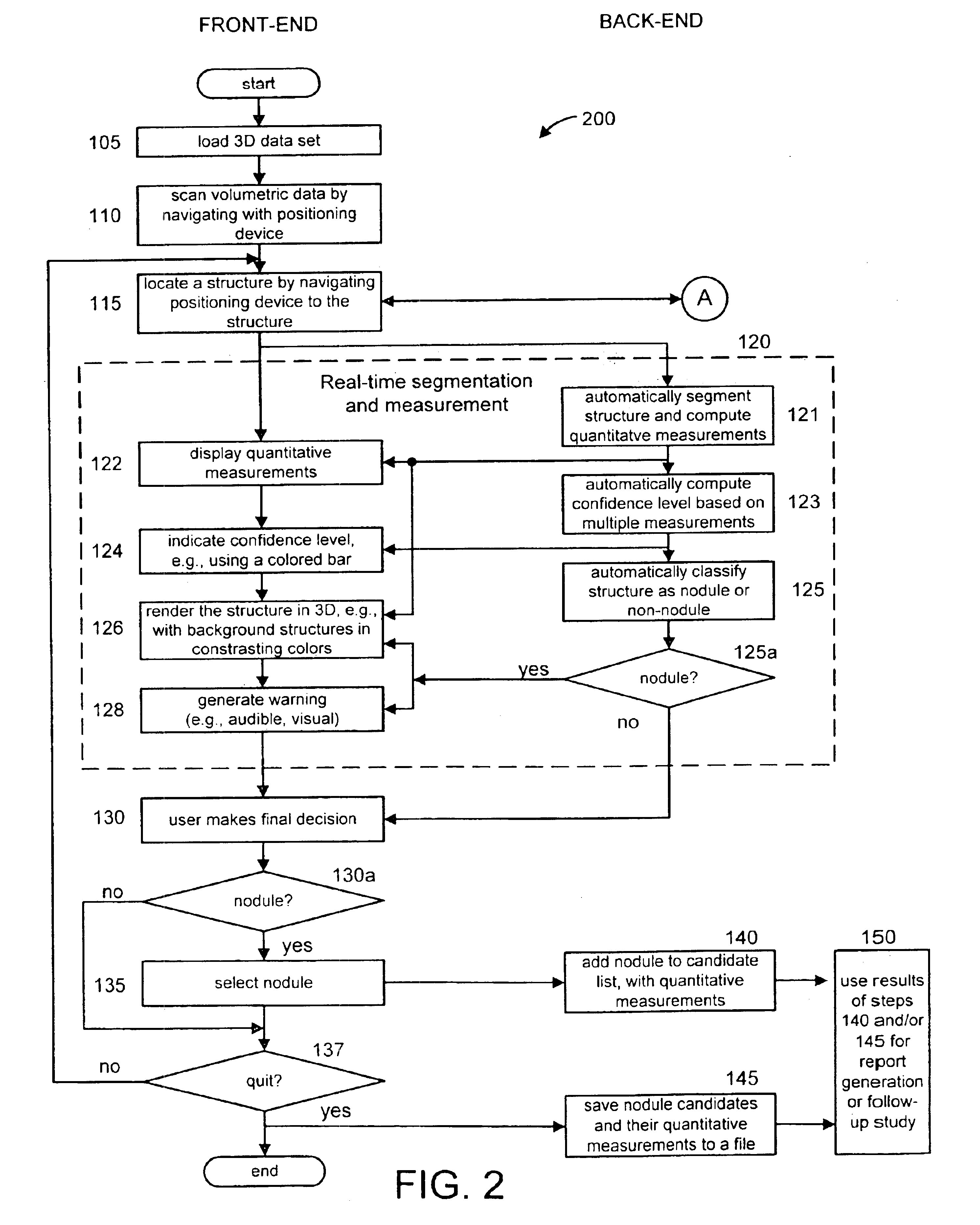
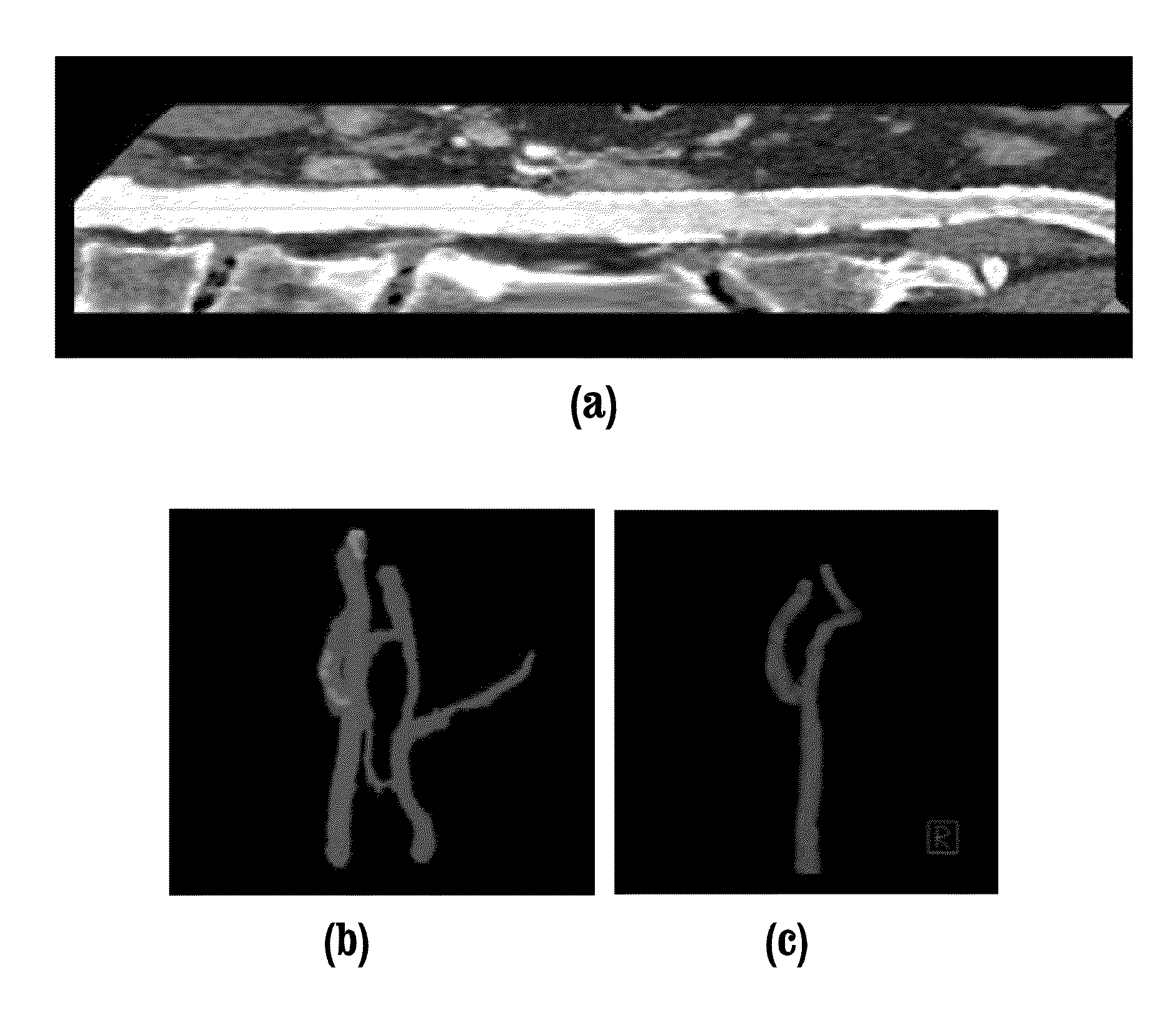
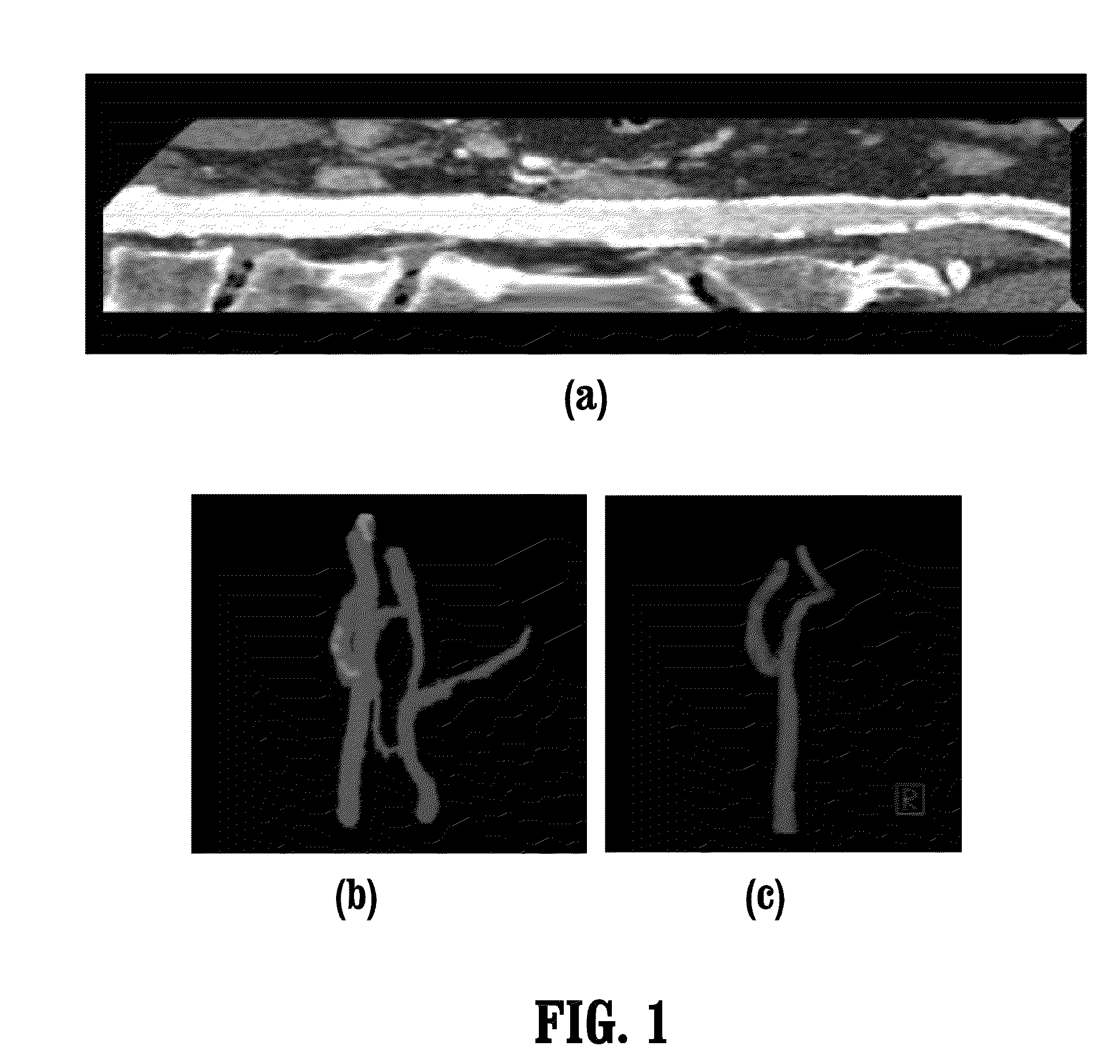
Interactive computer-aided diagnosis method and system for assisting diagnosis of lung nodules in digital volumetric medical images
InactiveUS6944330B2Fast computerHigh acceptanceImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresDiagnosis methods
A computer-assisted diagnosis method for assisting diagnosis of anatomical structures in a digital volumetric medical image of at least one lung includes identifying an anatomical structure of interest in the volumetric digital medical image. The anatomical structure of interest is automatically segmented, in real-time, in a predefined volume of interest (VOI). Quantitative measurements of the anatomical structure of interest are automatically computed, real-time. A result of the segmenting step and a result of the computing step are displayed, in real-time. A likelihood that the anatomical structure of interest corresponds to a disease or an area warranting further investigation is estimating, in real-time, based on predefined criteria and the quantitative measurements. A warning is generated, in real-time, when the likelihood is above a predefined threshold.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
System and method for in-context mpr visualization using virtual incision volume visualization
ActiveUS20070229500A1Layered productsRecord information storageComputer graphics (images)Observation point
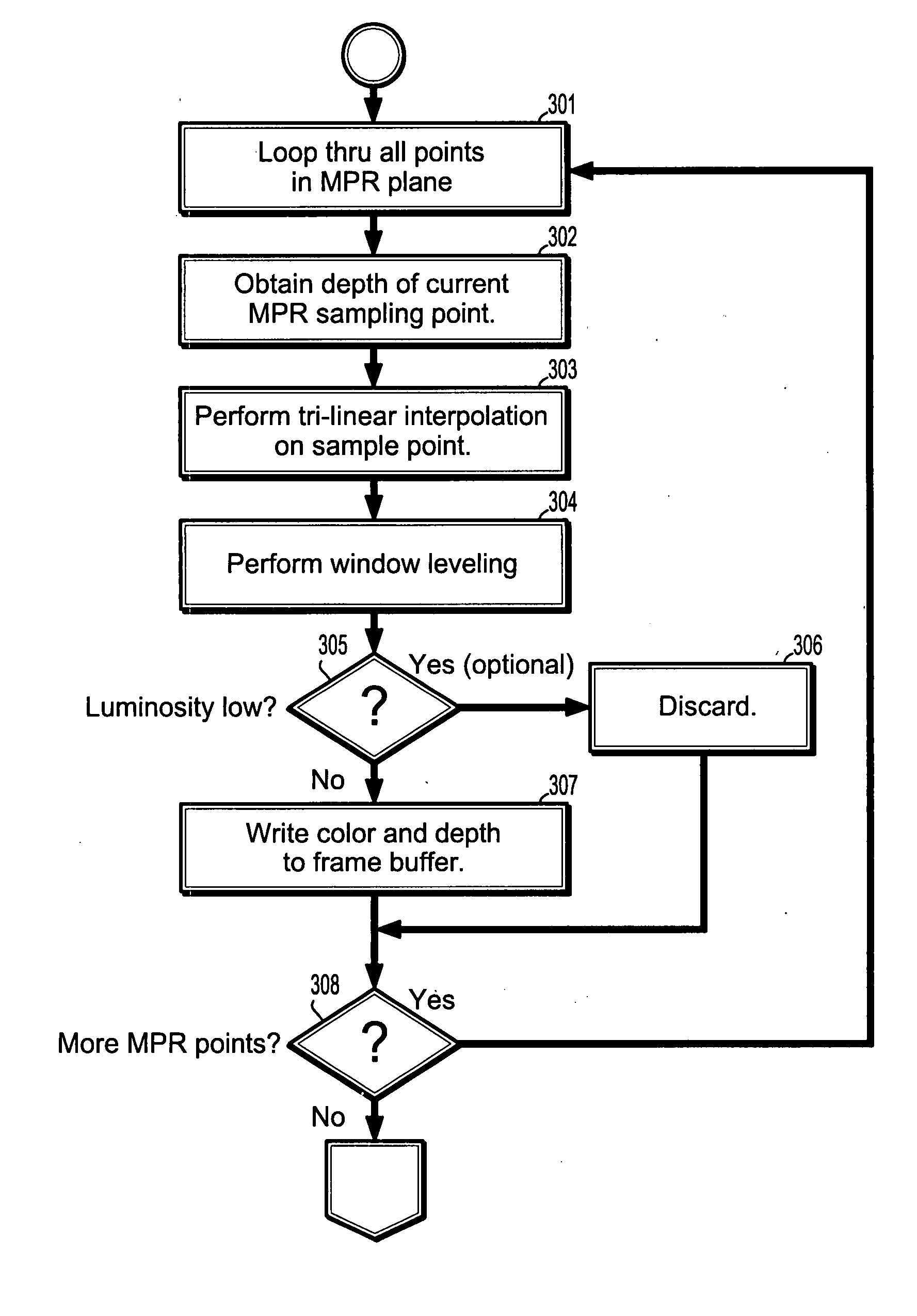
A method for multi-planar reconstruction of digitized medical images includes providing an image volume, sampling the neighborhood about each point in a planar region and saving a color value and a depth, providing a projection plane onto which rendering rays are projected from a viewing point through said image volume, advancing sampling points along rays through the image volume, computing depths of each sampling point, determining for sampling points on rays that penetrates the planar region if a depth of said sampling point is less than the buffer depth of a corresponding point in the planar region and sampling neighborhoods of points about such sampling points, determining if sampling points are near said planar region, applying first transfer function to sample values interpolated from first volume for sampling points close to or inside the planar region, and otherwise applying second transfer function to sample values interpolated from second volume.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
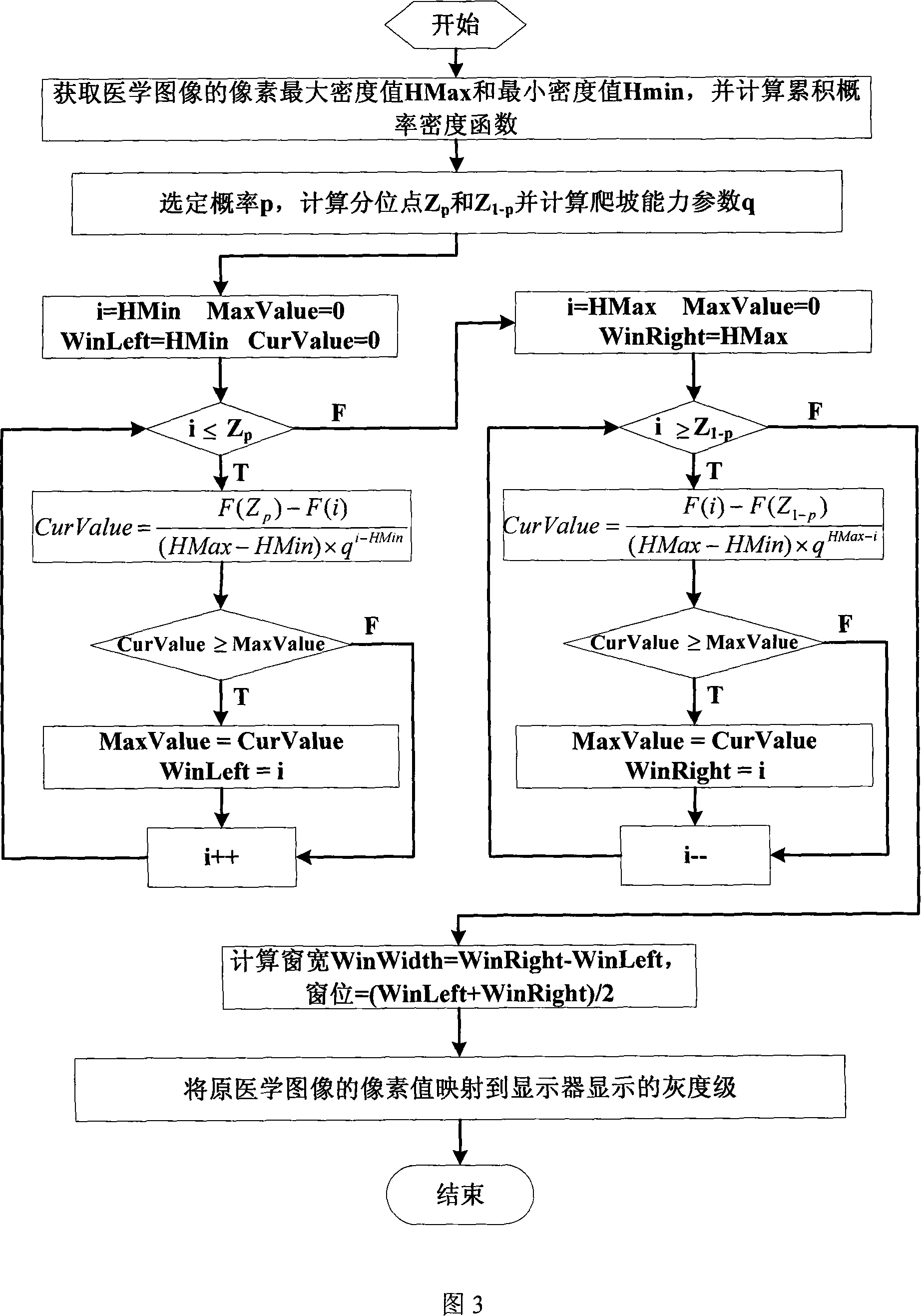
Medical image window parameter self-adaptive regulation method
InactiveCN101105862AImprove robustnessImprove the display effectImage enhancementDiagnosticsDisplay deviceRadiology
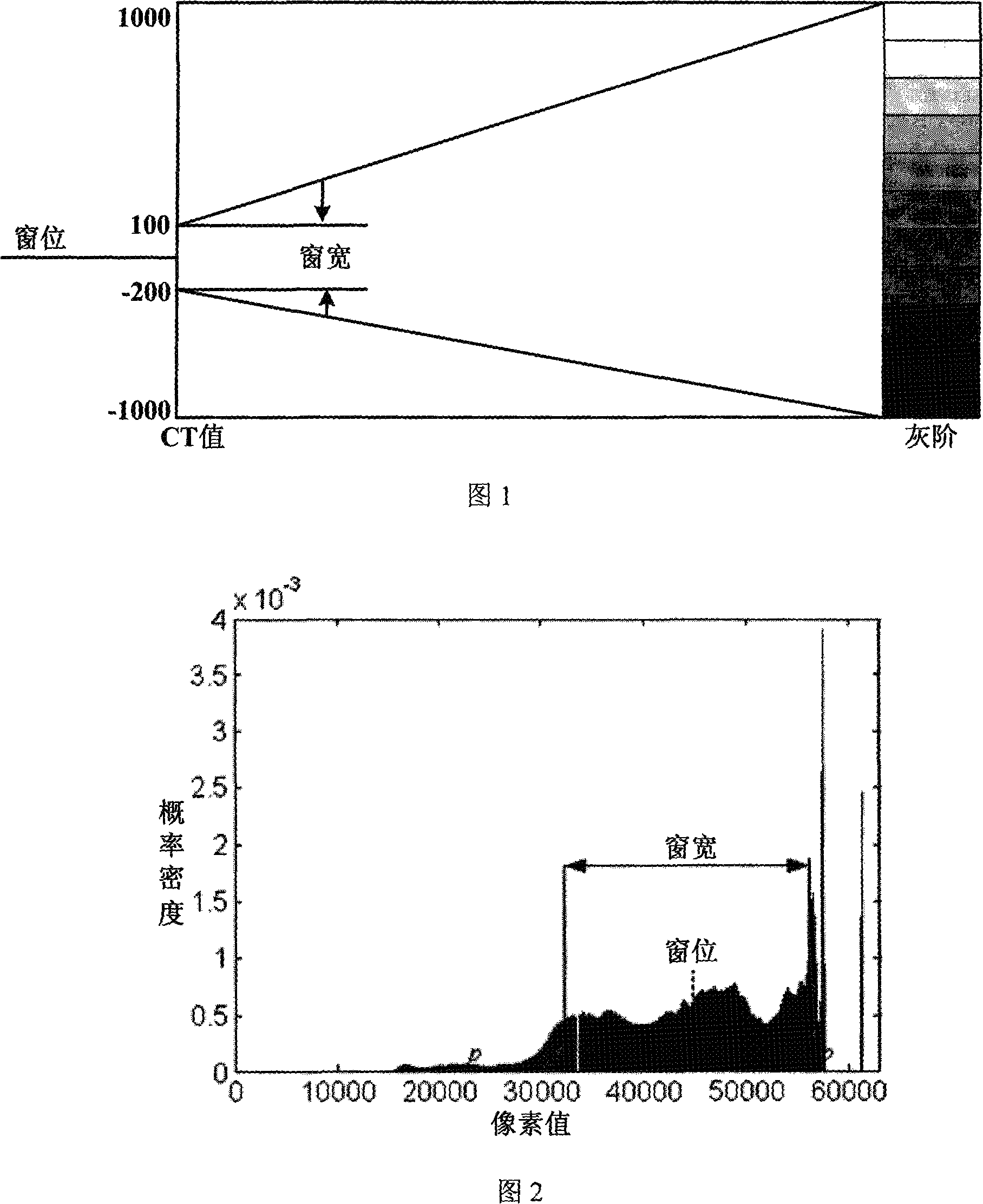
The invention discloses a self-adapting adjustment method for medical image window parameters. The method calculates the left boundary and right boundary of the window according to the accumulated probability intensity function of digital medical images, fractile of probability p, fractile of probability 1-p and climbing parameter q, so that position boundaries at major body of the image column diagram can be used to suitably determine the window parameter width and position of medical images, and then reflects the pixel value of digital medical images to the grey area in the grey stage range of the display. The invention has the advantages that through the automatic calculation of the optimum window width parameters through medical image information, users can obtain clear and satisfactory display images, thus having the high robustness; the window determined by the invention makes full use of the display gray stage of display, giving prominence to organization information useful for clinical diagnosis; the test and long-time clinical application prove that the invention is suitable for most of medical images and has the good display effect.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
System and Method For Myocardium Segmentation In Realtime Cardiac MR Data
A method for cardiac segmentation includes providing a plurality of digitized medical images, each image comprising a plurality of intensities corresponding to a domain of points on an 2-dimensional grid, the plurality of images forming a sequence of cardiac images acquired at different time points, filtering noise from the sequence of images, approximating the endocardium with a first circle, approximating the epicardium with a second circle, finding candidate points for the endocardium, finding candidate points for the epicardium, and interpolating gaps between points of the endocardium and between points of the epicardium wherein the myocardium is segmented.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
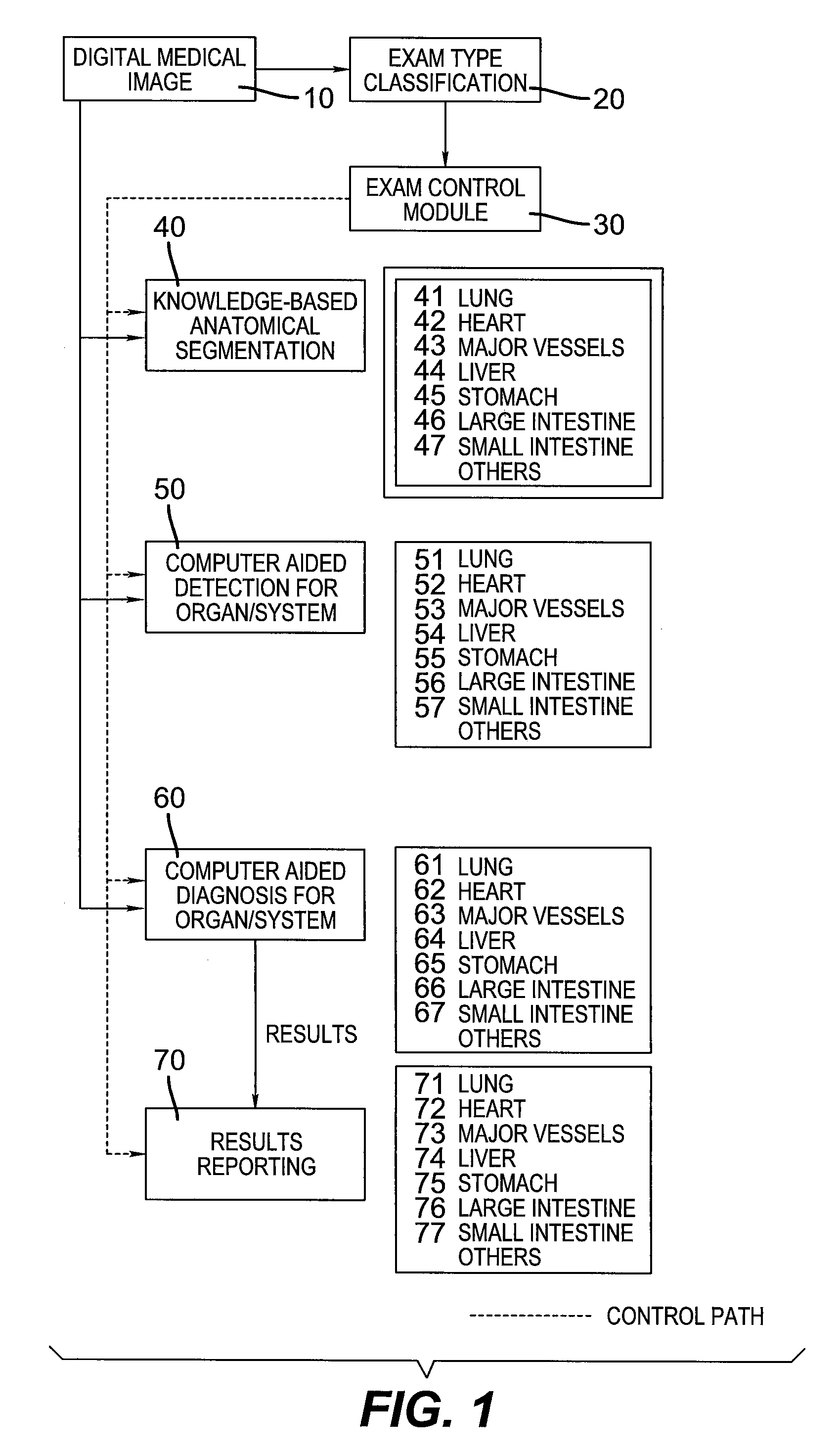
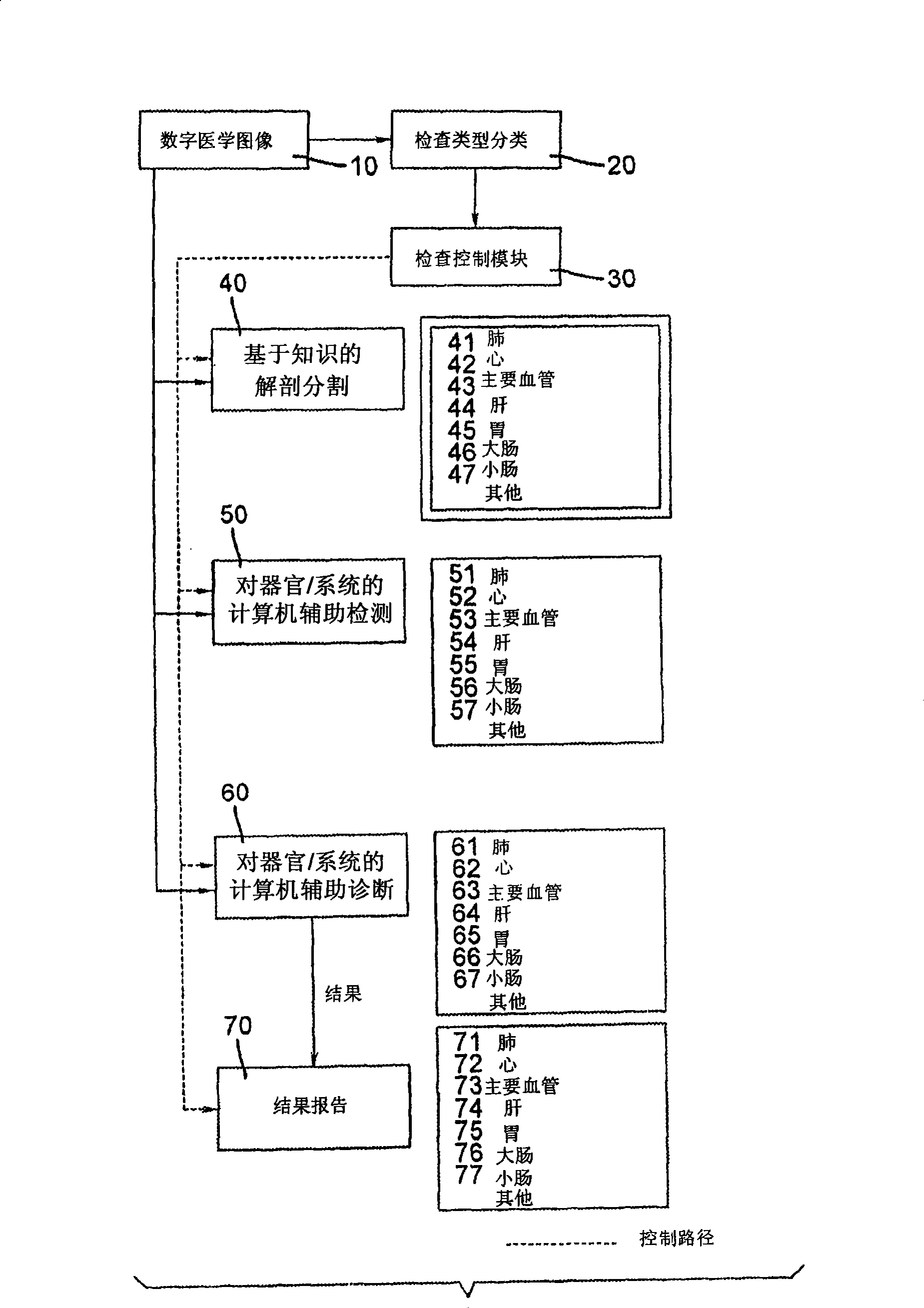
Computer aided disease detection system for multiple organ systems
ActiveUS7672497B2Shorten read timeImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionOrgan systemComputer-aided
A computer aided disease detection system and method for multiple organ systems. The method performs computer aided examination of digital medical images. A patient exam type of a digital medical image is determined. Based on the patient exam type, one or more of a plurality of knowledge based anatomical segmentation blocks are invoked, each block performing image segmentation for a single organ or organ system present in the image. Based on the patient exam type, for each successfully segmented organ or organ system, one or more of a plurality of knowledge based computer aided detection blocks are invoked, each block of which is designed to search for and locate potential disease foci in a particular organ or organ system.
Owner:PHILIPS HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS INC
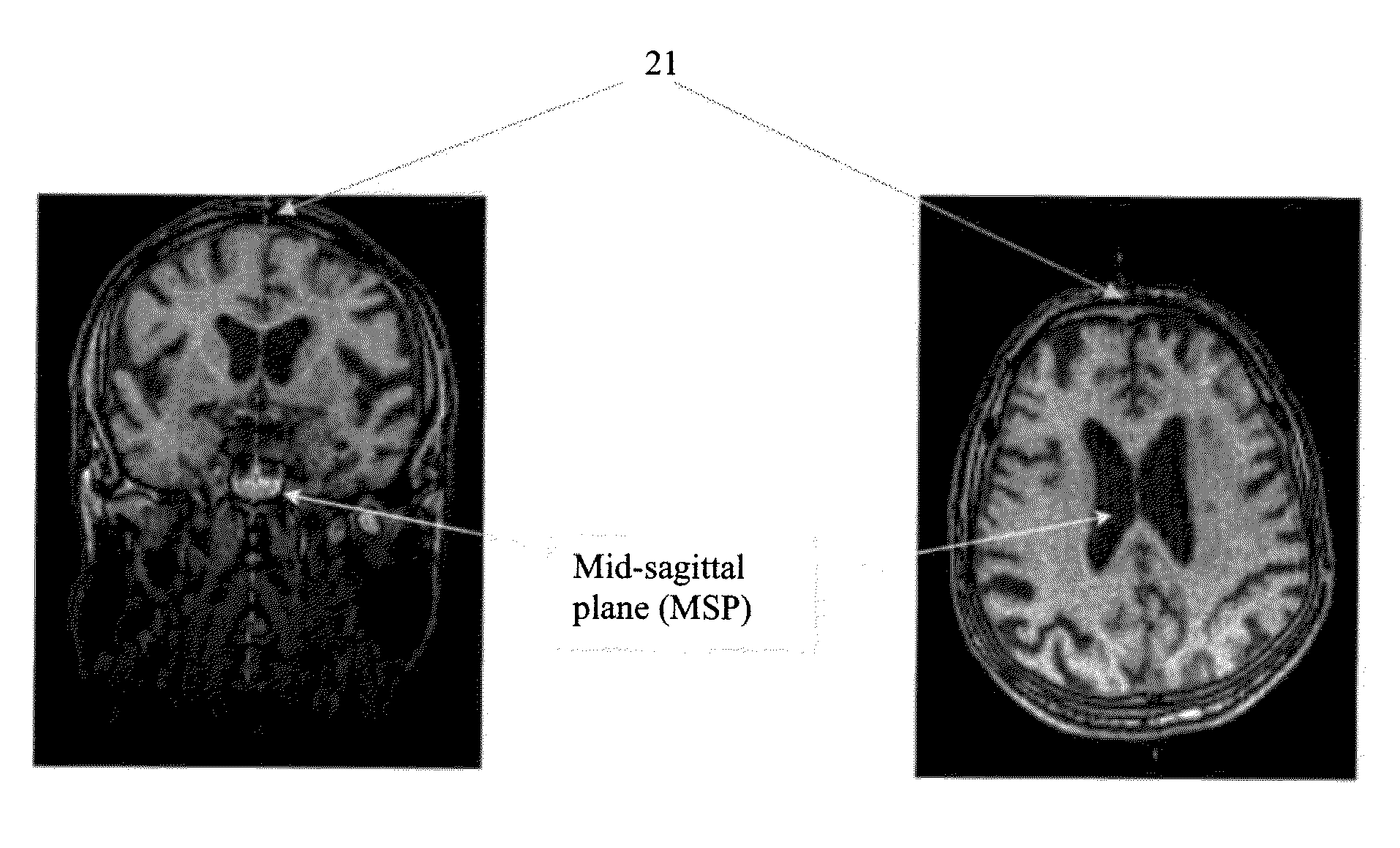
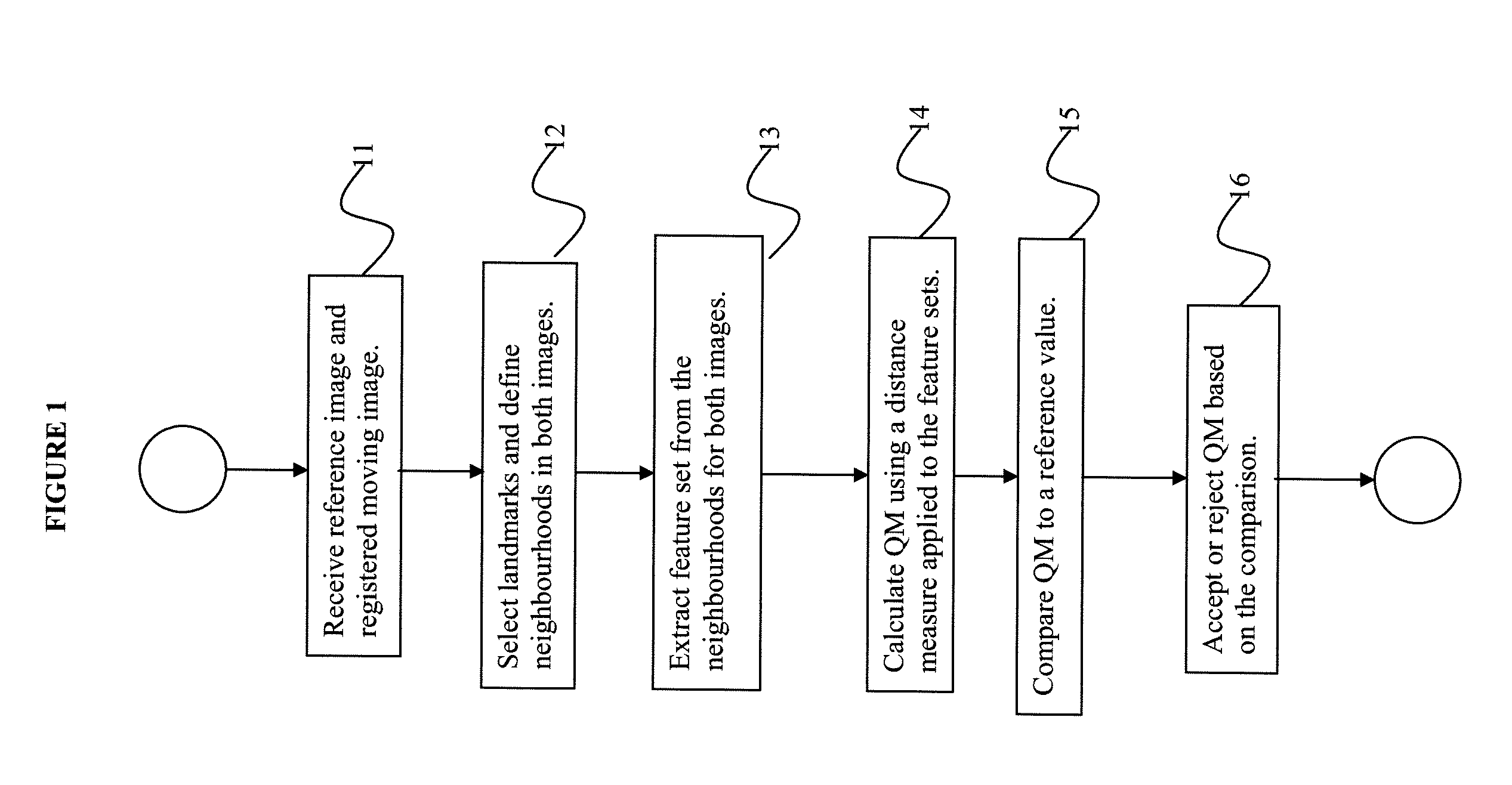
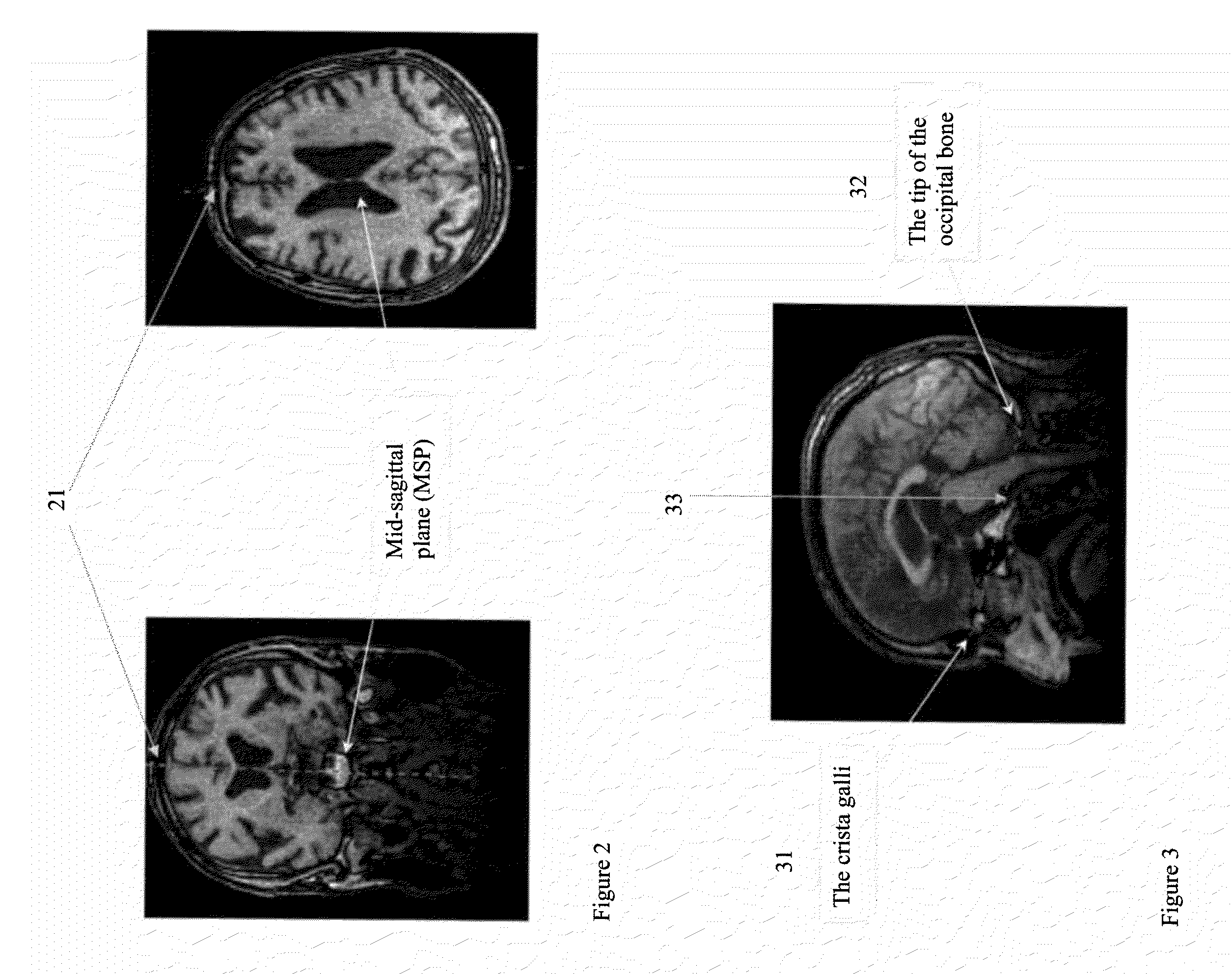
System and method for verifying registration accuracy in digital medical images
A method of verifying a registration of a digital image includes receiving a reference image and a moving image registered to the reference image representing the same object, selecting one or more landmarks in the images, defining a neighborhood in the domain of each image near each selected landmark, extracting feature sets from the neighborhoods for the reference image and the registered moving image, calculating a total quality measure of the registration of the moving image from a distance metric applied to the feature sets extracted from the neighborhoods of the reference image and the registered moving image, comparing the total quality measure to a threshold determined from a reference atlas for the object represented in the image, and determining whether to accept or reject the registration of the moving image based on the comparison result.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
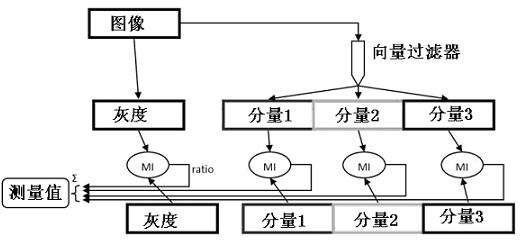
Gray scale and geometric information combined medical image registration method
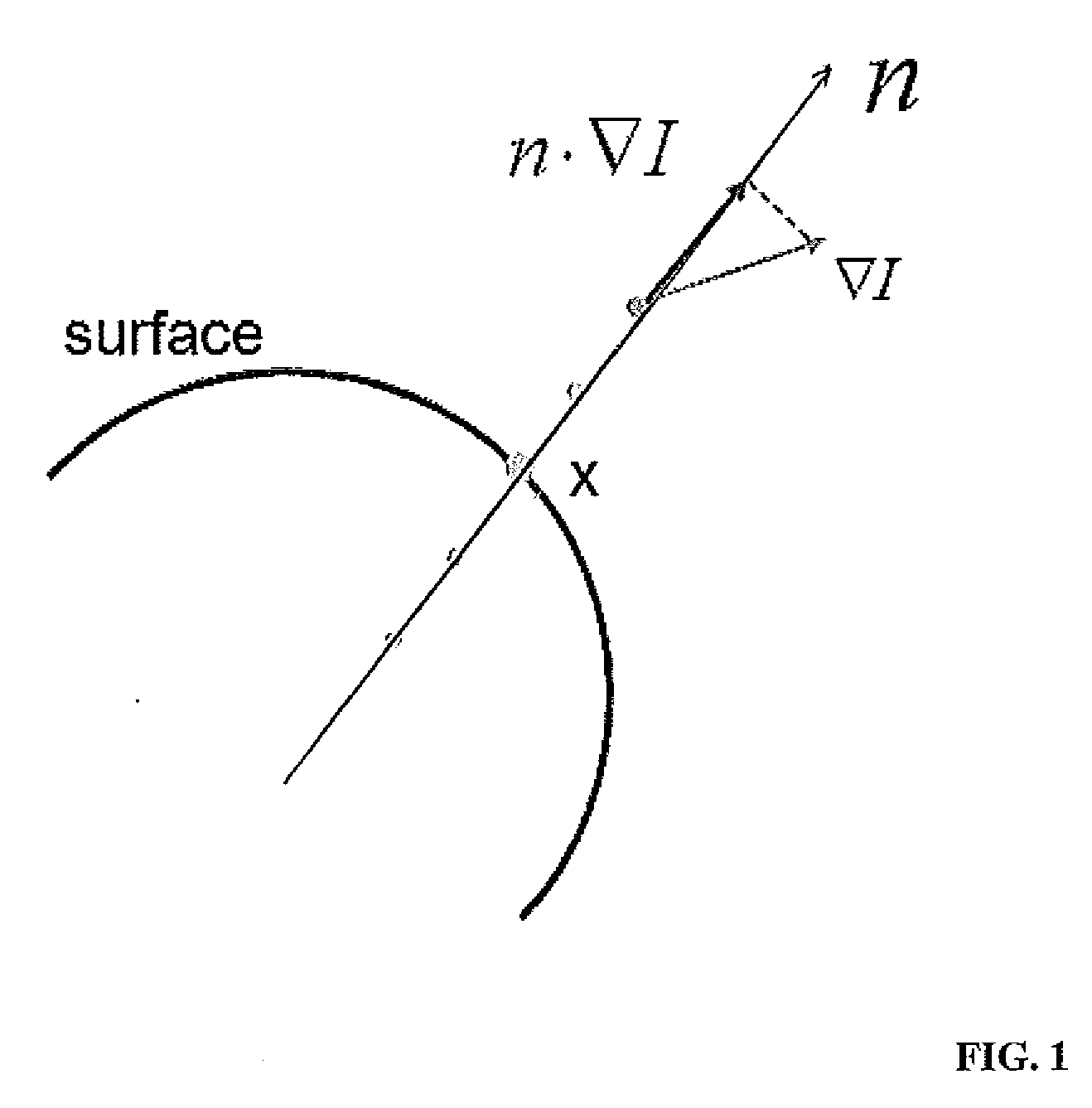
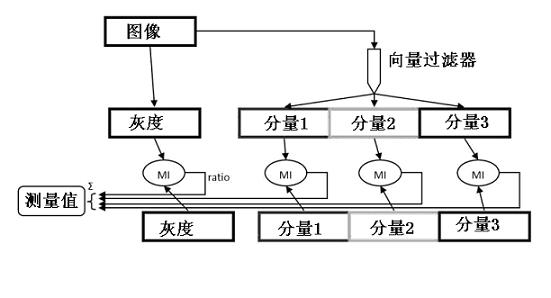
The invention provides a gray scale and geometric information combined medical image registration method and relates to the technical field of medical image processing. Grey scale values are the values on all pixels / voxels in digital medical images and distributed as image gray scale information; and normal vectors represent unit vectors of geometric normal of all points, represent the gray scale information of the medical images by adopting the grey scale value distribution, represent the geometric information of the medical images by adopting the image normal vector distribution, and finally measure the similarity between the gray scale and the geometric information quantity by adopting mutual information. According to the invention, the conventional mutual information method and gradient solution method are adopted, and the obtained mutual information values are added together, so that easy implementation can be realized in engineering application; the advantages of both the gray scale and the geometric information are fully utilized to ensure that less local extreme points fall in the registering process, and better robustness is achieved; and tests show that the method provided by the invention can acquire higher precision.
Owner:SUZHOU DIKAIER MEDICAL TECH
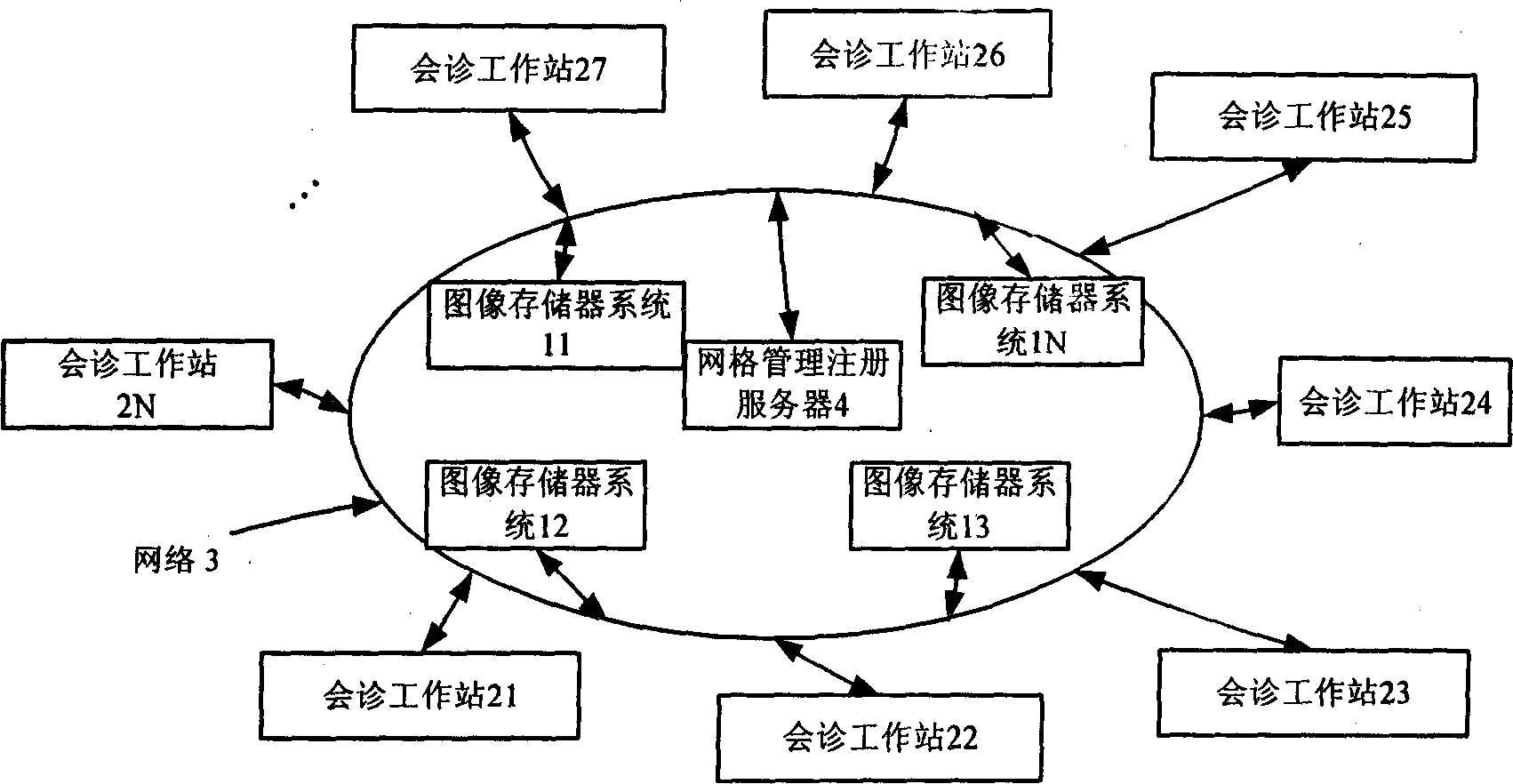
Method and system for realizing interactive network constitution of medicine image obtained by multipoint searching access
InactiveCN1787447AGuaranteed accuracyGet real timeSpecial service provision for substationCommunication interfaceDICOM
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
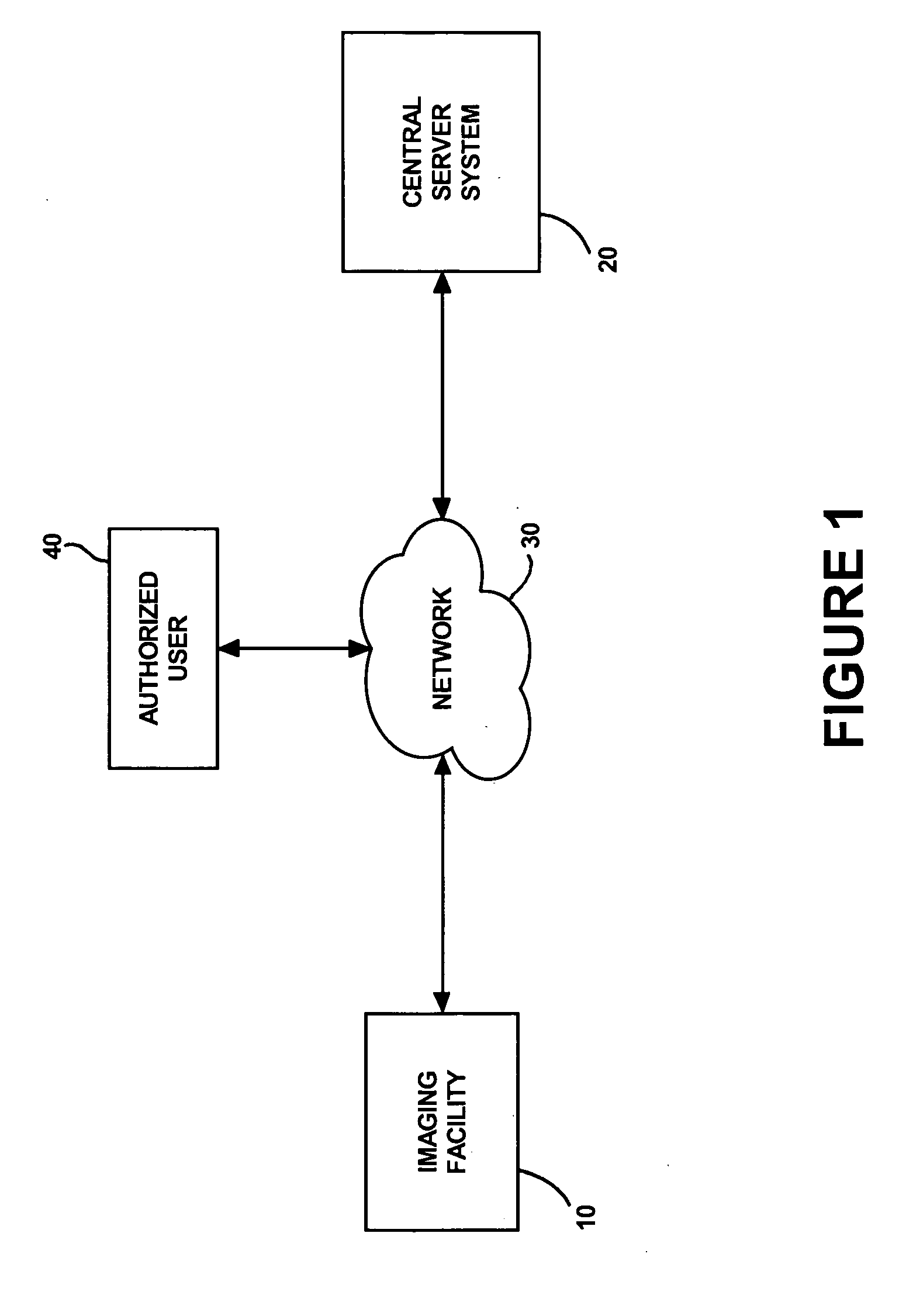
Method for payer access to medical image data
InactiveUS20050187787A1Low costRemove the burdenBuying/selling/leasing transactionsMedical imagesImaging equipmentComputer science
A business method provides access to digital medical image data generated by up to a plurality of imaging facilities to a payer. The business method includes receiving digital medical image data generated by the imaging facilities using a gateway at each imaging facility. The received-digital medical image data is transmitted from the gateway to a central server via a network and stored at the central server. The payer is then provided access to the stored digital medical image data via the network for a fee.
Owner:CANON USA
System and method for geometric modeling of tubular structures
A method for extracting a centerline of a tubular structure in a digital medical image includes providing a 3-dimensional (3D) digitized medical image having a segmented tubular structure, finding a path in the image between a starting point and every other point in the tubular structure that minimizes an accumulative cost function, wherein the minimum accumulative cost φ(x) at a point x is a minimum of (φ(x′)+Px,x′) over all nearest neighbors x′ wherein Px,x′ is a cost of propagation obtained from the inverse of a medialness measure computed in a plane orthogonal to a line between x and x′ that is centered at a mid-point of the line, the medialness measure m(x) computed in a circular region C(x, R) centered at point x on the line, with radius R, given bym(x)=maxR{1N∑i=0N-1f(x,Ru⟶(2πi / N))}, wherein {right arrow over (u)}(α)=sin(α){right arrow over (u)}1+cos(α){right arrow over (u)}2 and {right arrow over (u)}1 and {right arrow over (u)}2 define a 2D plane, and ƒ(x0,R{right arrow over (u)}(α)) isf(xo,R)=max(1R∑x=x0x0+RI(x)-1M∑x=x0+R+1x0+R+1+MI(x)2,0). wherein M is the number of background points.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and Method for Multiple Instance Learning for Computer Aided Detection
InactiveUS20070189602A1Extended run timeAlleviate challengeImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionBag of features
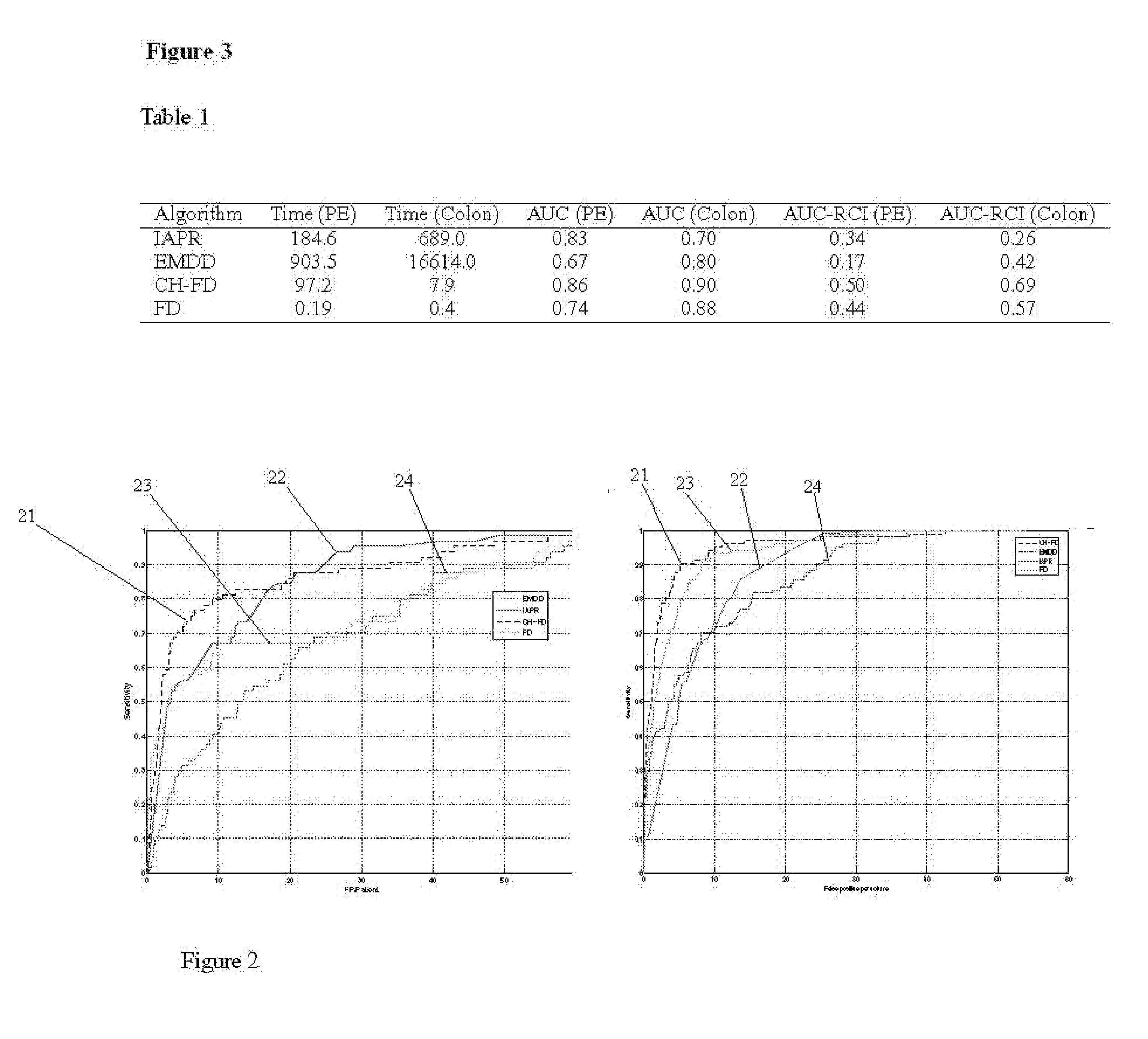
A method of training a classifier for computer aided detection of digitized medical images, includes providing a plurality of bags, each bag containing a plurality of feature samples of a single region-of-interest in a medical image, wherein said features include texture, shape, intensity, and contrast of said region-of-interest, wherein each region-of-interest has been labeled as either malignant or healthy, and training a classifier on said plurality of bags of feature samples, subject to the constraint that at least one point in a convex hull of each bag, corresponding to a feature sample, is correctly classified according to the labeled of the associated region-of-interest.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Cad detection system for multiple organ systems
A computer aided disease detection system and method for multiple organ systems. The method performs computer aided examination of digital medical images. A patient exam type of a digital medical image is determined. Based on the patient exam type, one or more of a plurality of knowledge based anatomical segmentation blocks are invoked, each block performing image segmentation for a single organ or organ system present in the image. Based on the patient exam type, for each successfully segmented organ or organ system, one or more of a plurality of knowledge based computer aided detection blocks are invoked, each block of which is designed to search for and locate potential disease foci in a particular organ or organ system.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
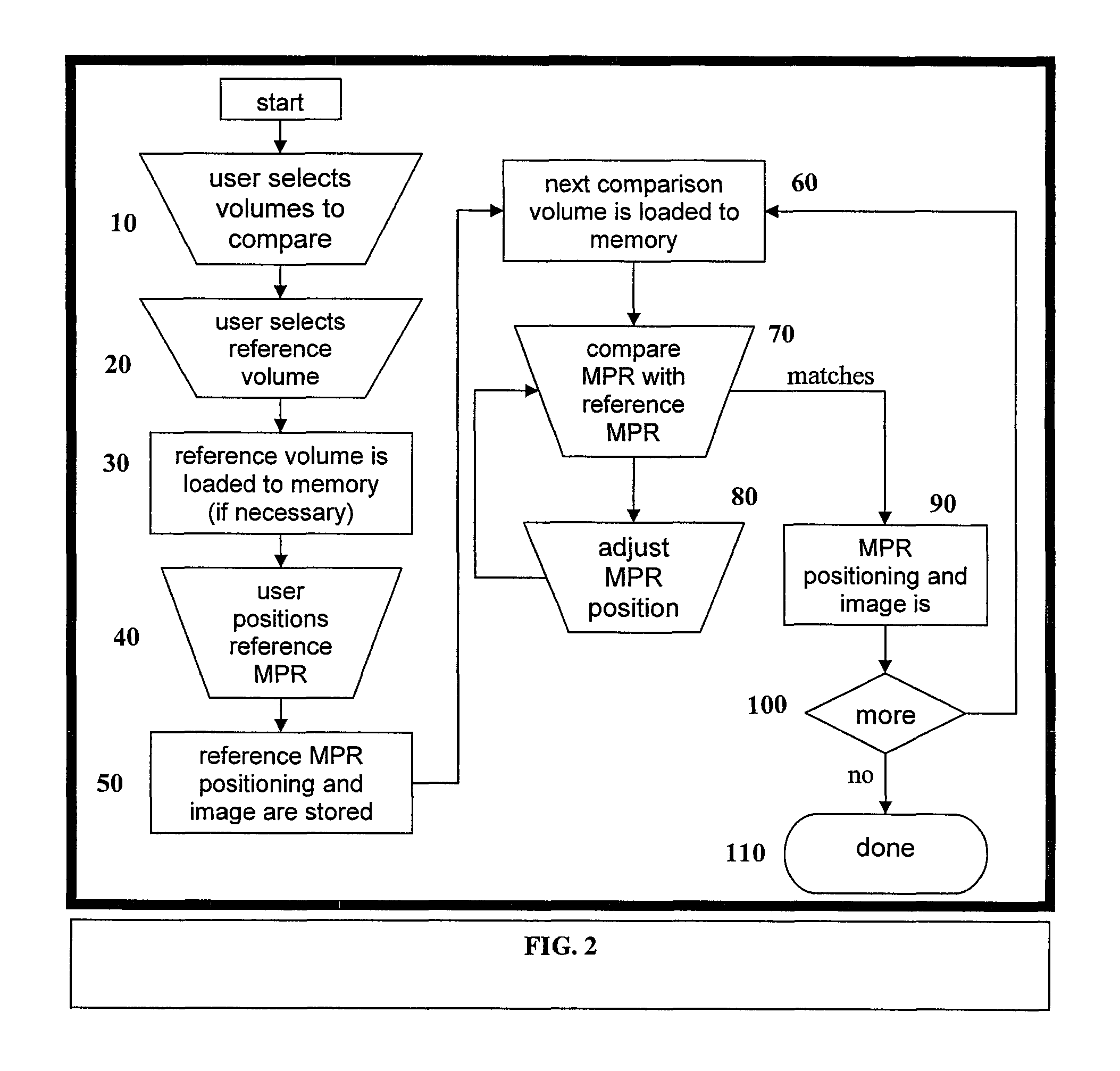
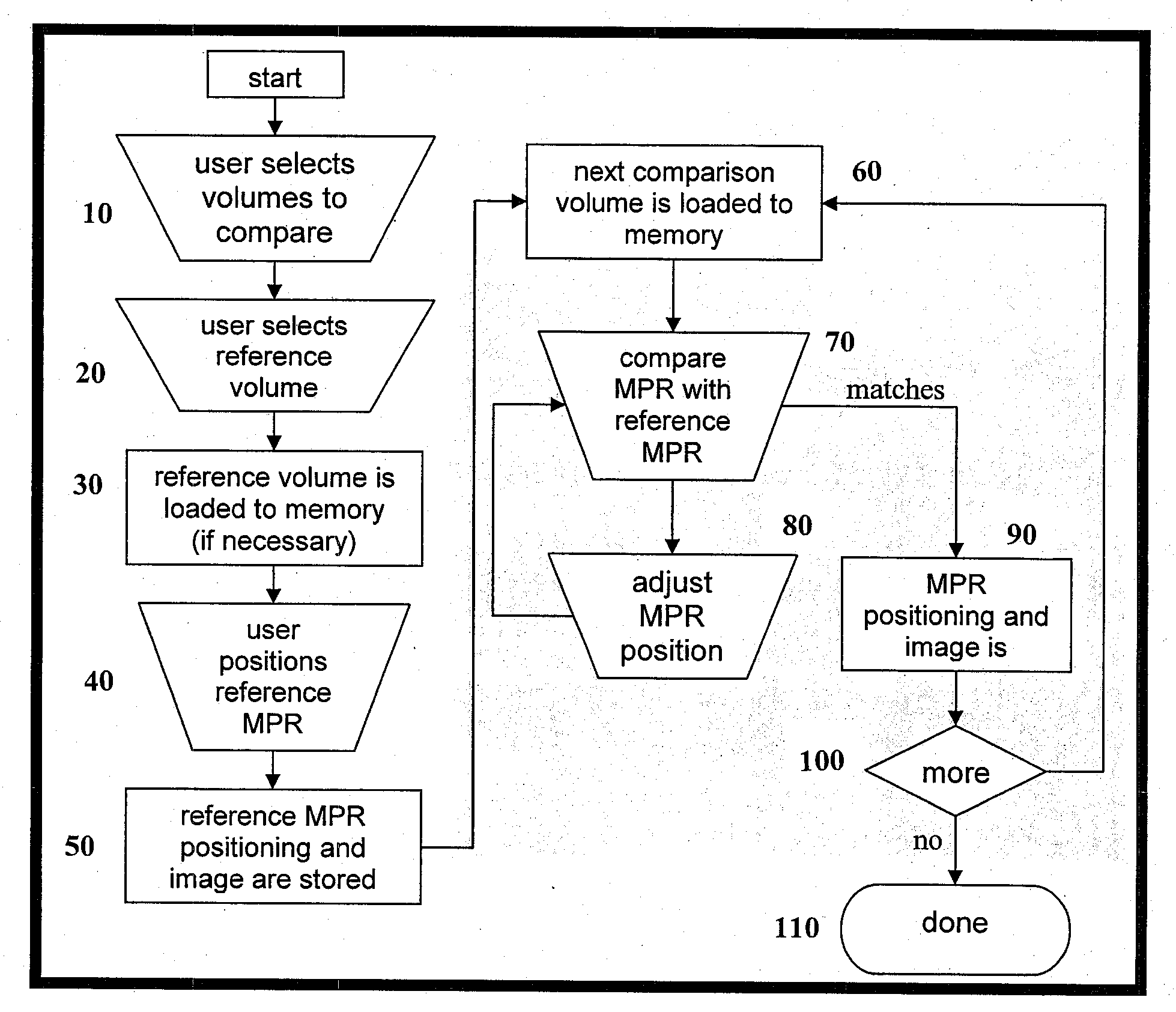
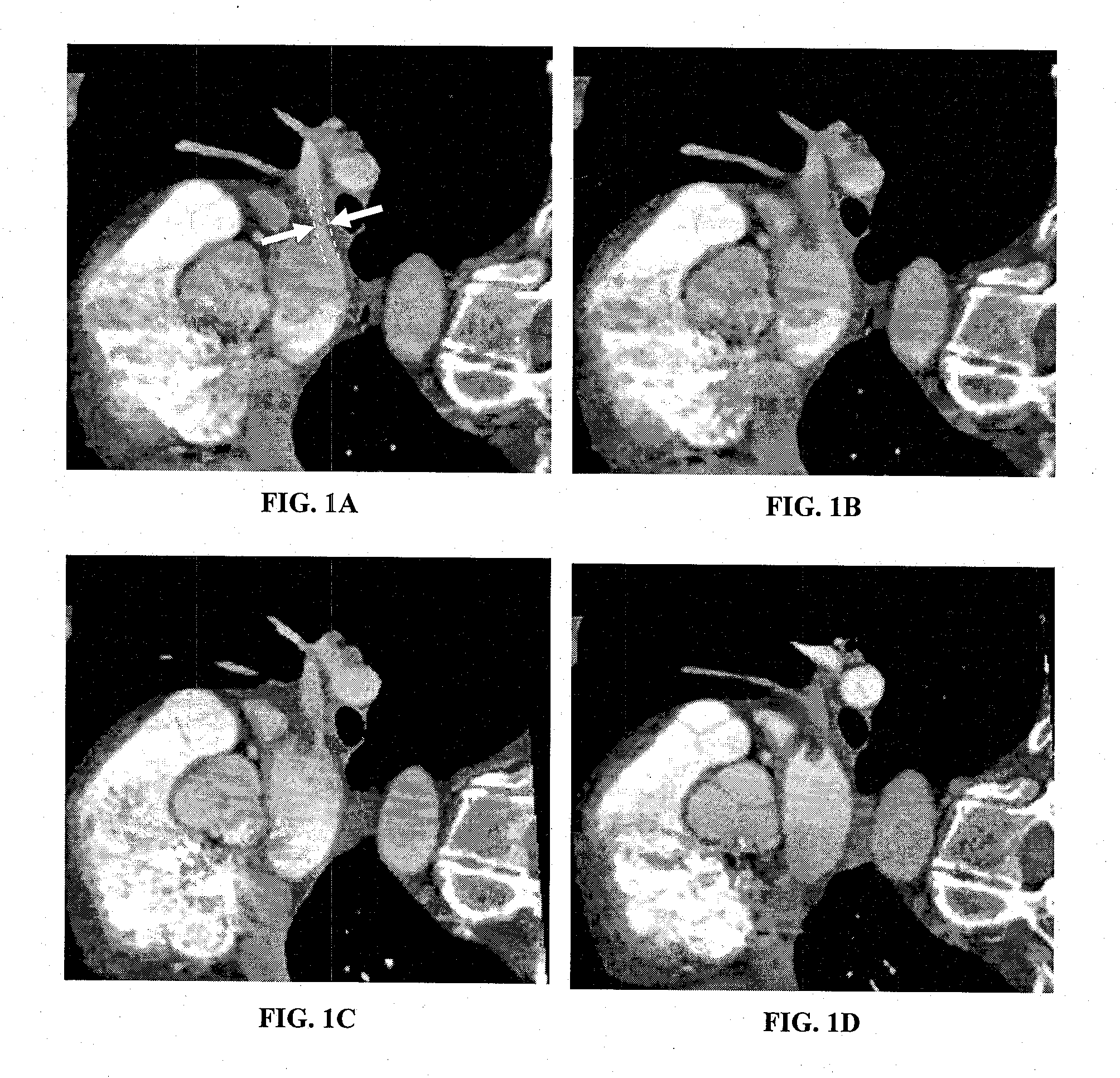
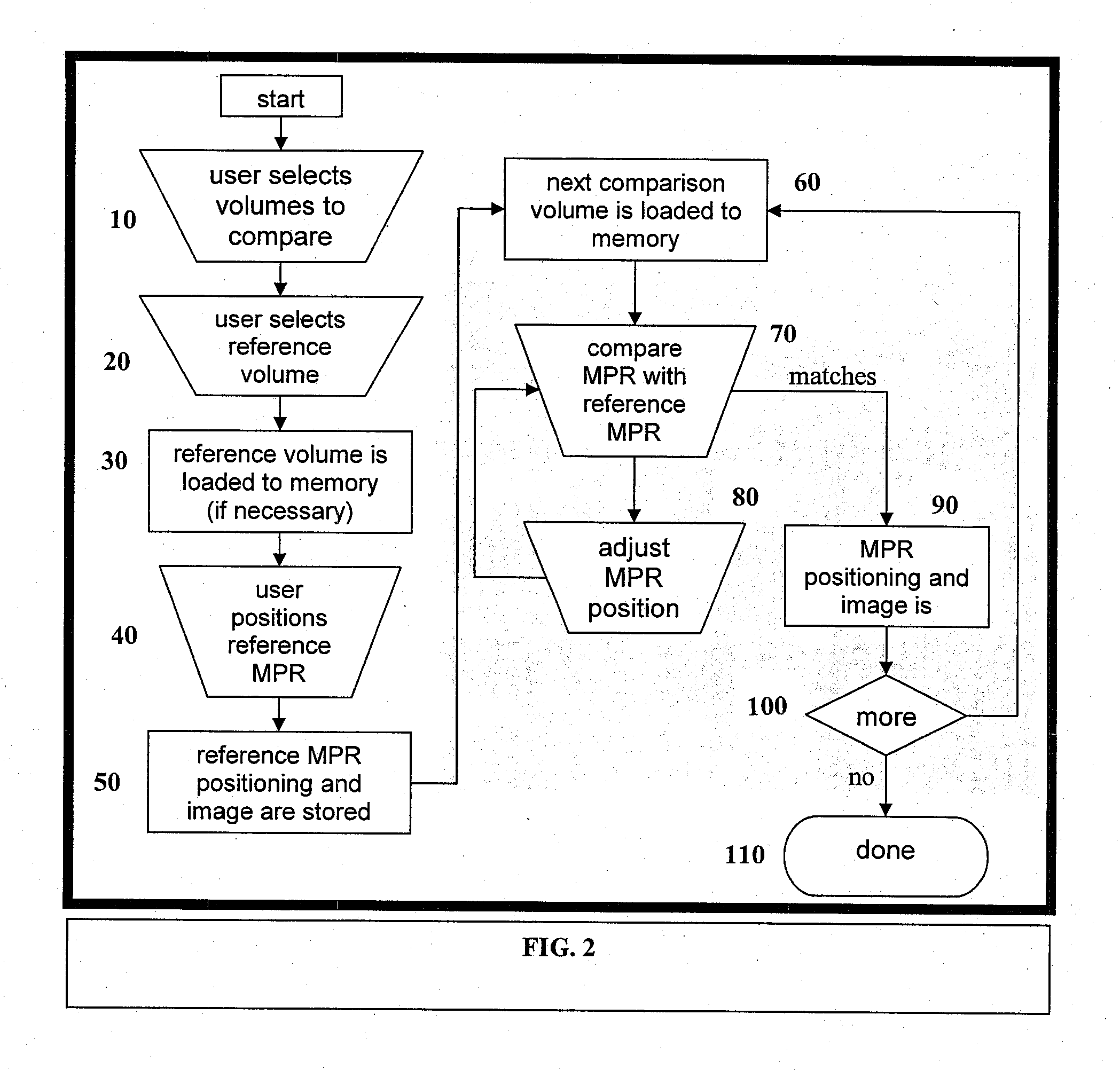
Automatic positioning of matching multi-planar image reformatting (MPR) views of multiple 3D medical images
A computer-implemented method is disclosed for comparing three dimensional (3D) digital medical images. The method uses a reference MPR to position subsequent MPRs in one or more other 3D digital medical images so their content matches the reference MPR. The matched MPRs may then be used by a medical professional to diagnose a patient condition. The ability to quickly and automatically position matching MPRs for multiple 3D images eases the medical staff workload and shortens diagnostics time. Matching MPRs provides an effective way to view the 3D volumes for anatomical changes over time and to monitor medical conditions such as stenosis and tumors.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
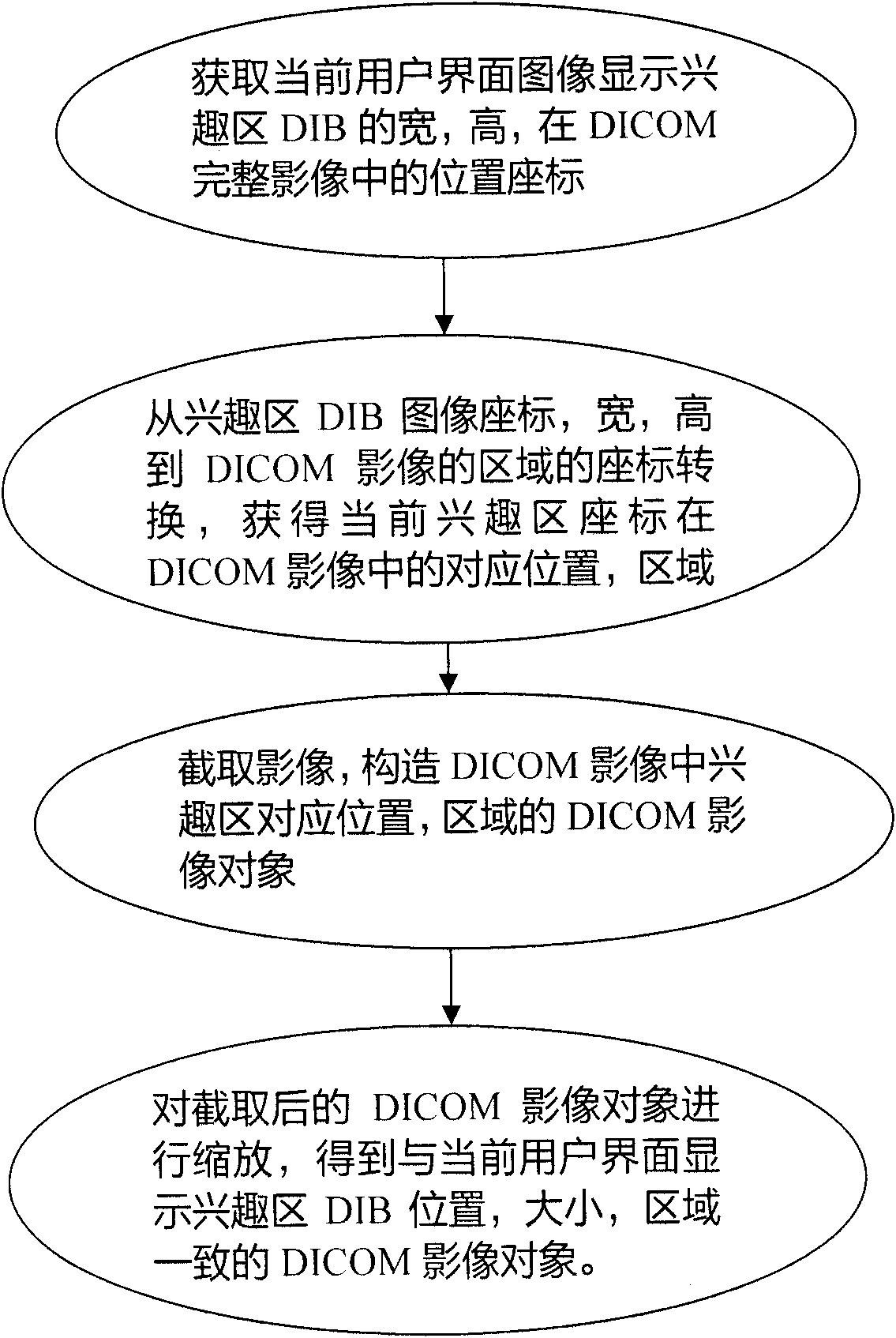
Window width and window level adjusting method for pixel set with large data volume
InactiveCN102104784AReduce window response frequencyReduce the response frequencyColor signal processing circuitsDICOMDigital imaging
The invention relates to a window width and window level adjusting method for a pixel set with large data volume, which comprises the following steps of: displaying a gray level image on an ordinary RGB (Red, Green and Blue) display in a window-adding manner through setting a DIB (Device Independent Bitmap) color contrast table aiming at a digital medical image of DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) format; during the process of adjusting the window width and the widow level of the image in real time, filtering a response frequency through modular arithmetic; intercepting and zooming an interest region of the image; establishing a window adjusting transformation rapid access table, and searching a pixel set in the traversal interest region of the window adjusting transformation rapid access table to obtain a method of displaying a gray level value and the like so as to reduce the amount of calculation during the window adjusting process of the pixel set, so that the window width and the window level can be adjusted continuously and smoothly in real time even for an image file with very large data volume.
Owner:梁威
Automatic positioning of matching multi-planar image reformatting (MPR) views of multiple 3D medical images
A computer-implemented method is disclosed for comparing three dimensional (3D) digital medical images. The method uses a reference MPR to position subsequent MPRs in one or more other 3D digital medical images so their content matches the reference MPR. The matched MPRs may then be used by a medical professional to diagnose a patient condition. The ability to quickly and automatically position matching MPRs for multiple 3D images eases the medical staff workload and shortens diagnostics time. Matching MPRs provides an effective way to view the 3D volumes for anatomical changes over time and to monitor medical conditions such as stenosis and tumors.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
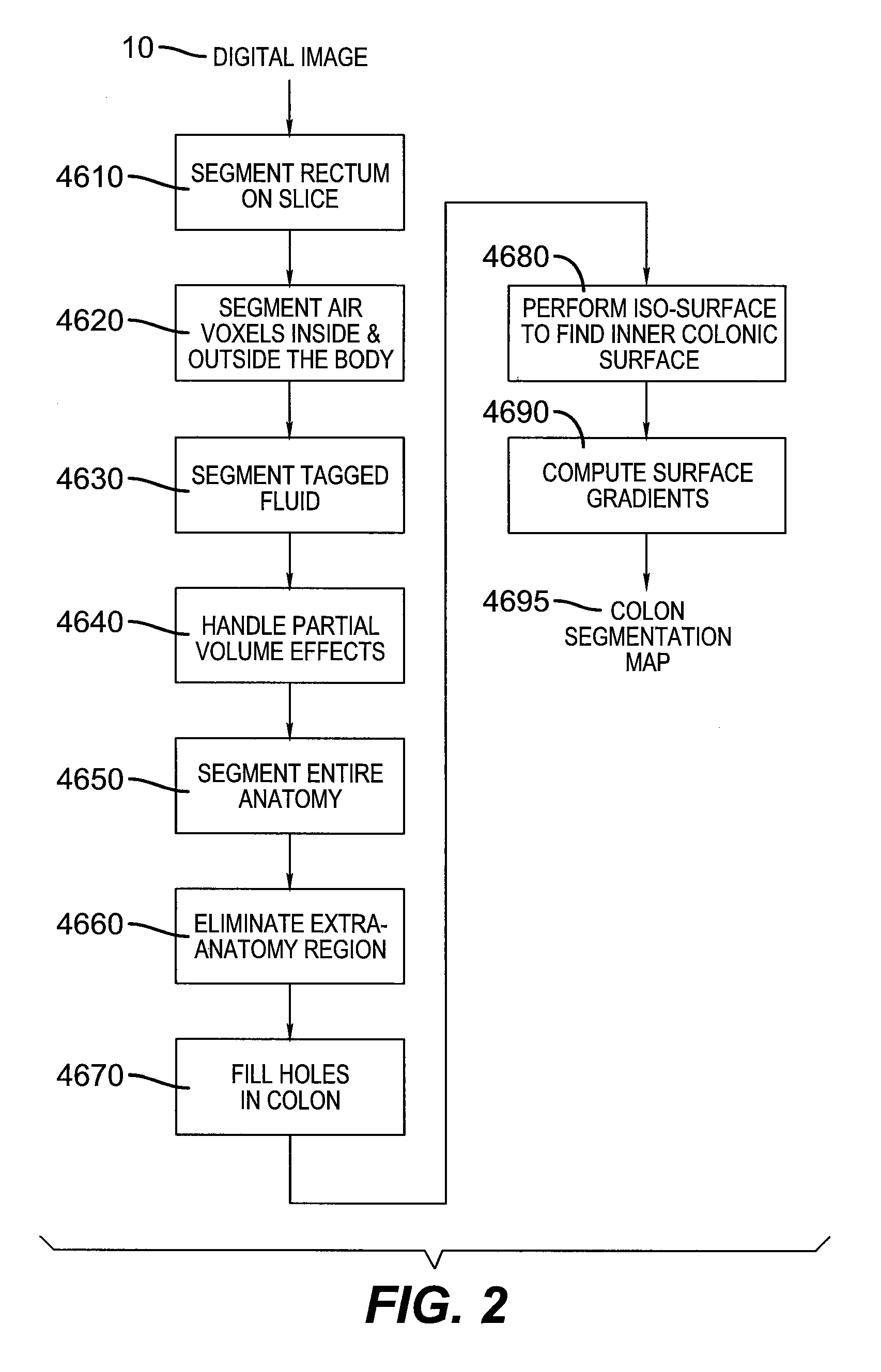
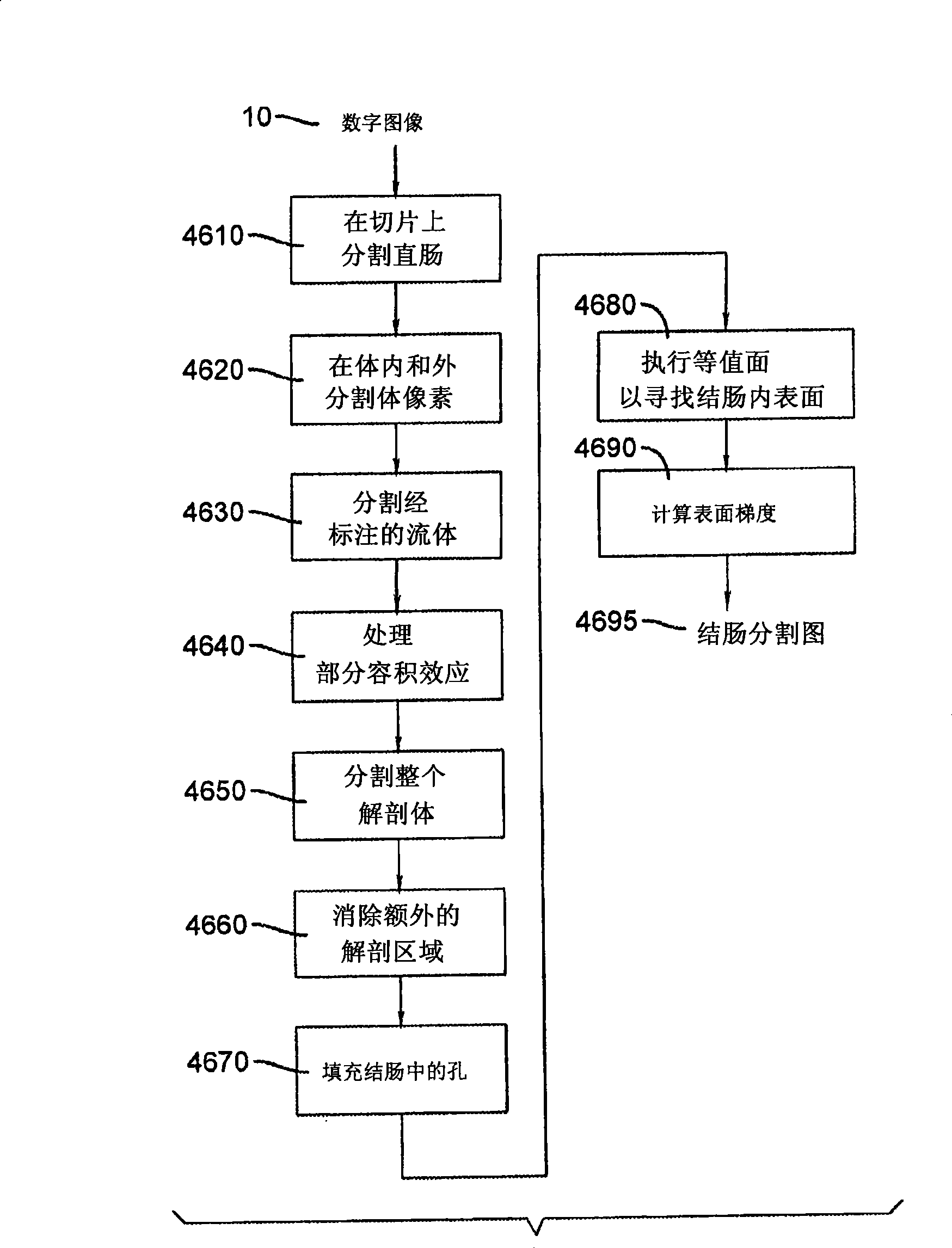
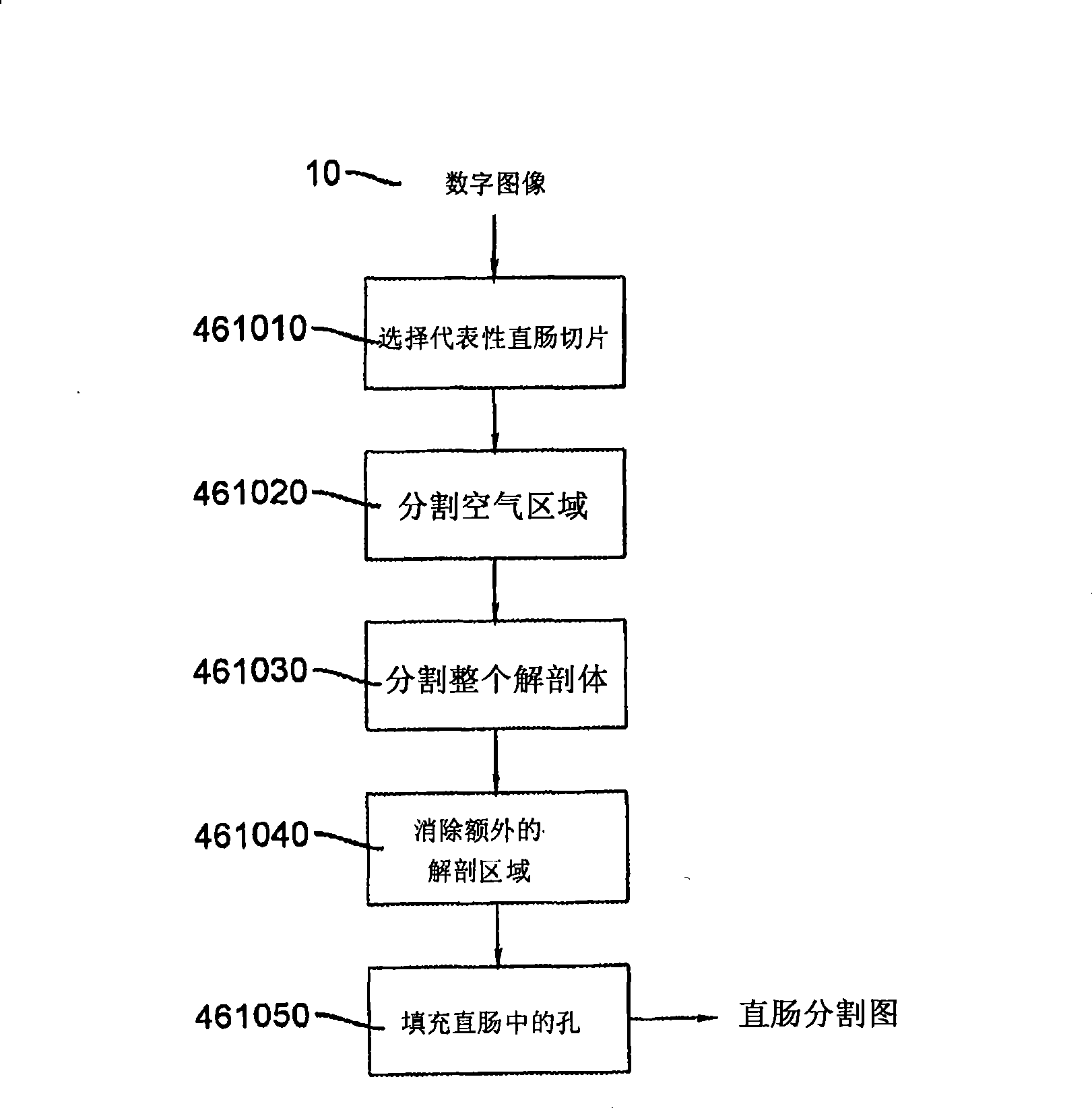
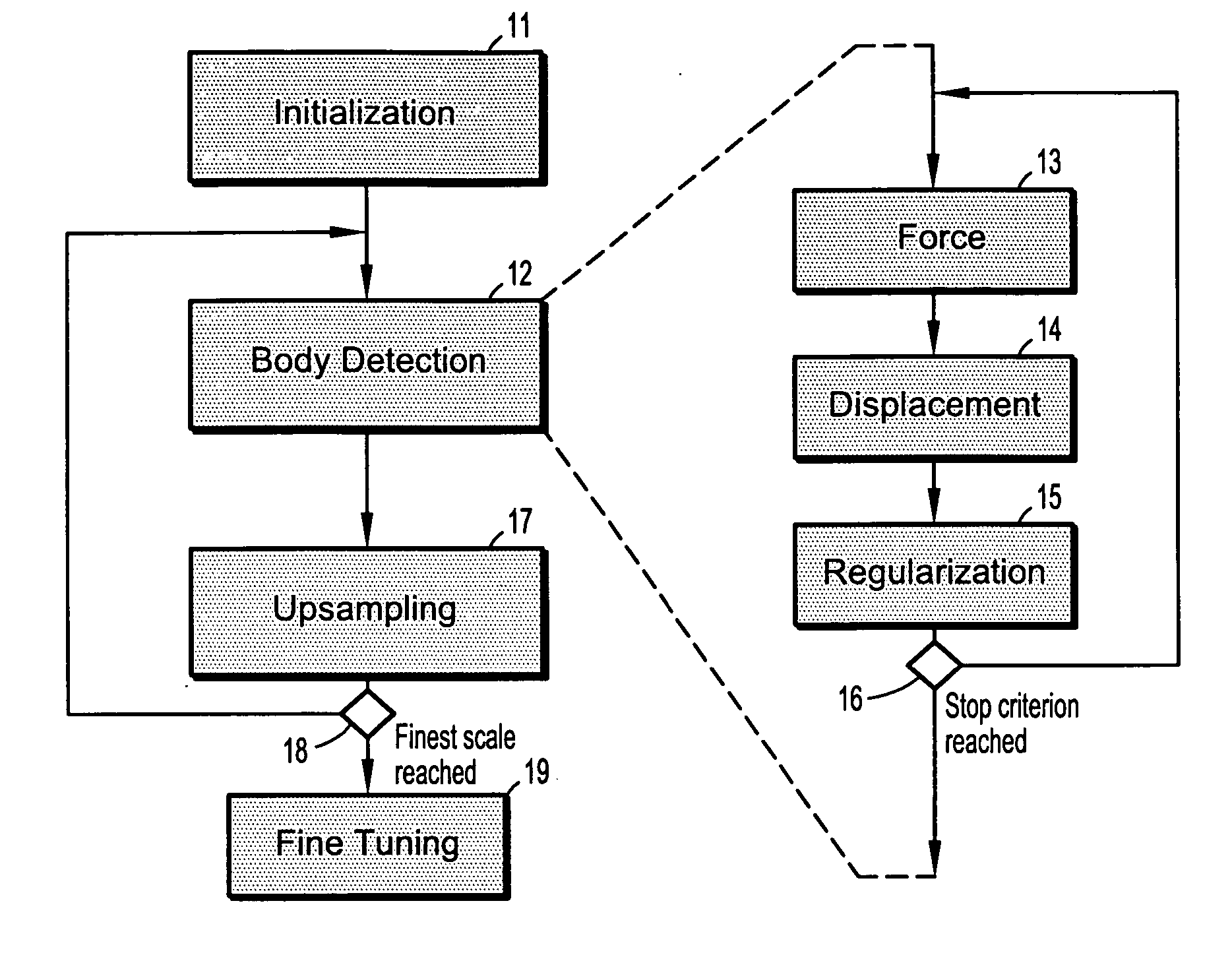
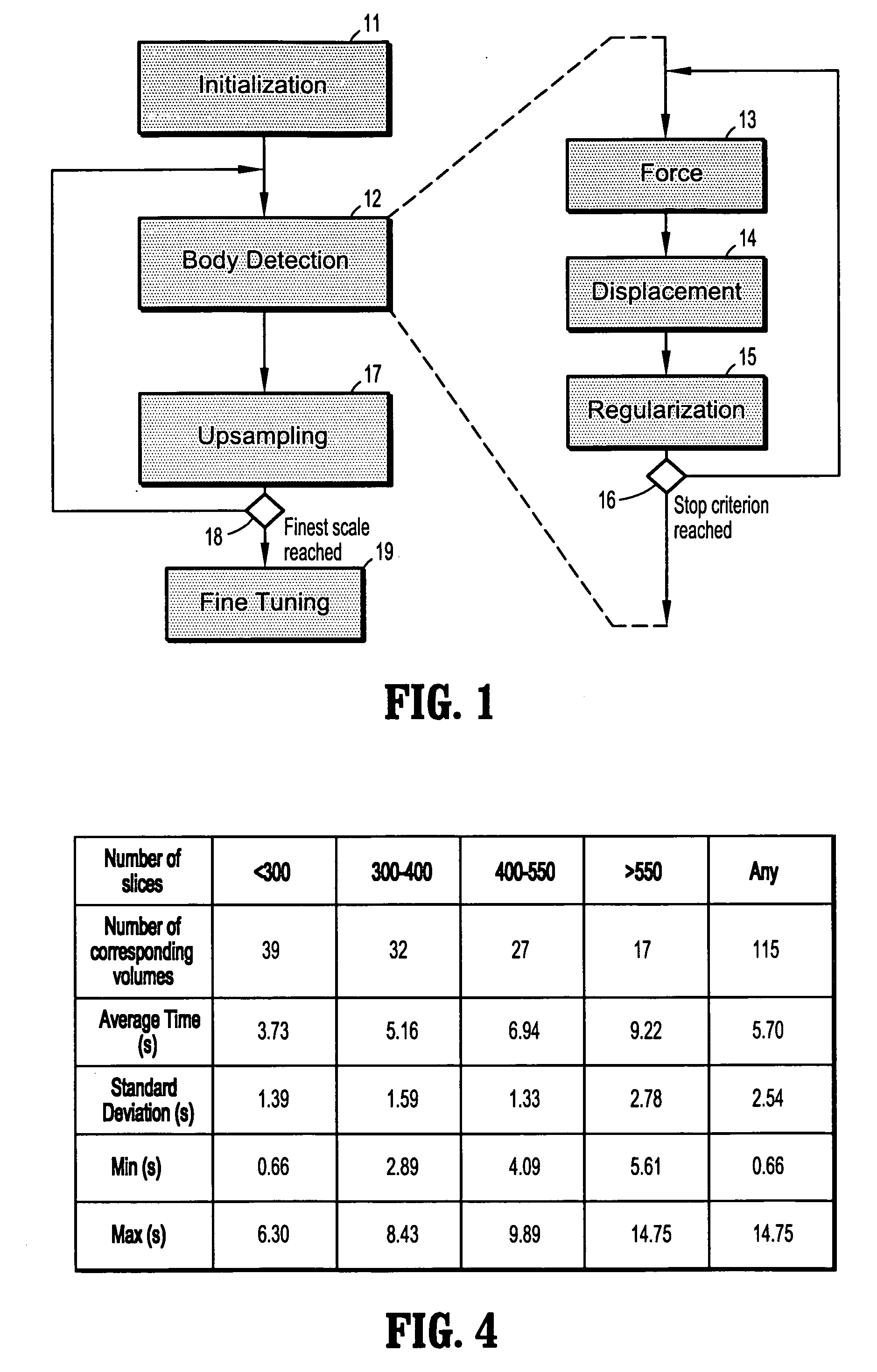
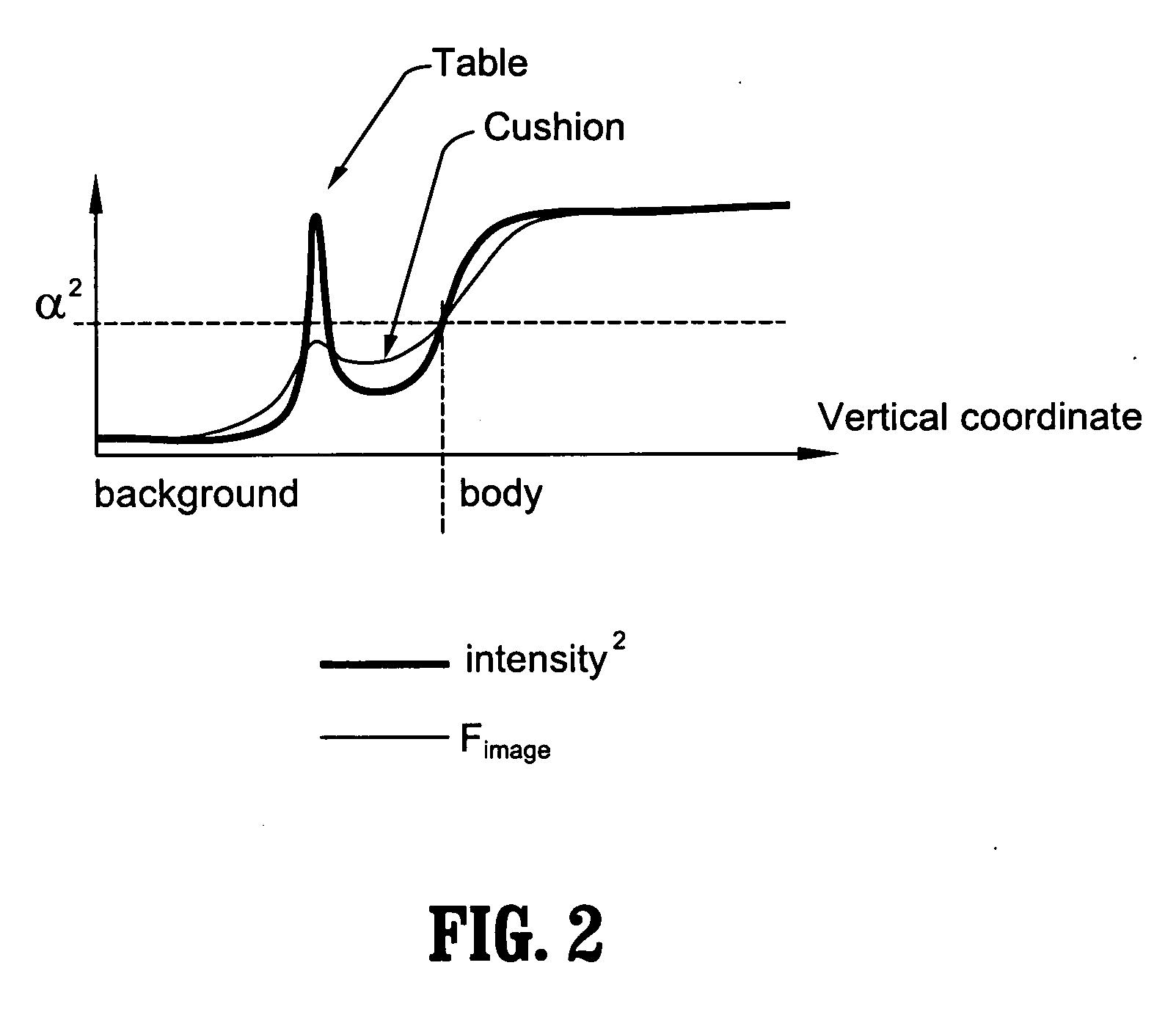
System and method for body extraction in medical image volumes
InactiveUS20070036411A1The result is accurateFast and reliableImage enhancementImage analysisDead bodyA domain
A method for identifying non-body structures in digitized medical images including the steps of providing a digitized image comprising a plurality of intensities corresponding to a domain of points on an N-dimensional grid, wherein said image includes a representation of a body and of non-body structures separate from said body, initializing a surface in said image on a side of said non-body structures opposite from said body, defining a plurality of forces acting on said surface, and displacing said surface through said non-body structures using said forces until said body is encountered.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
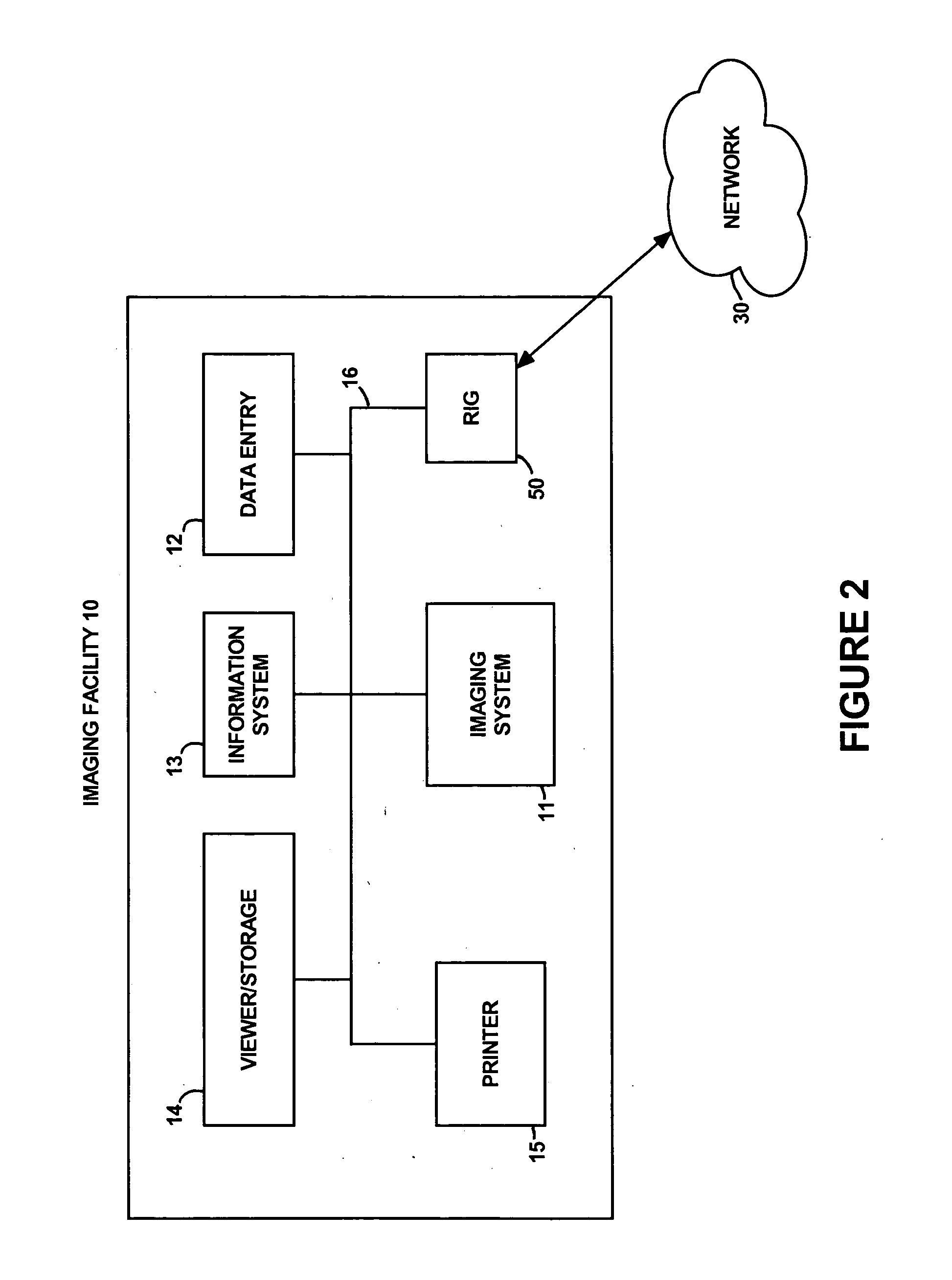
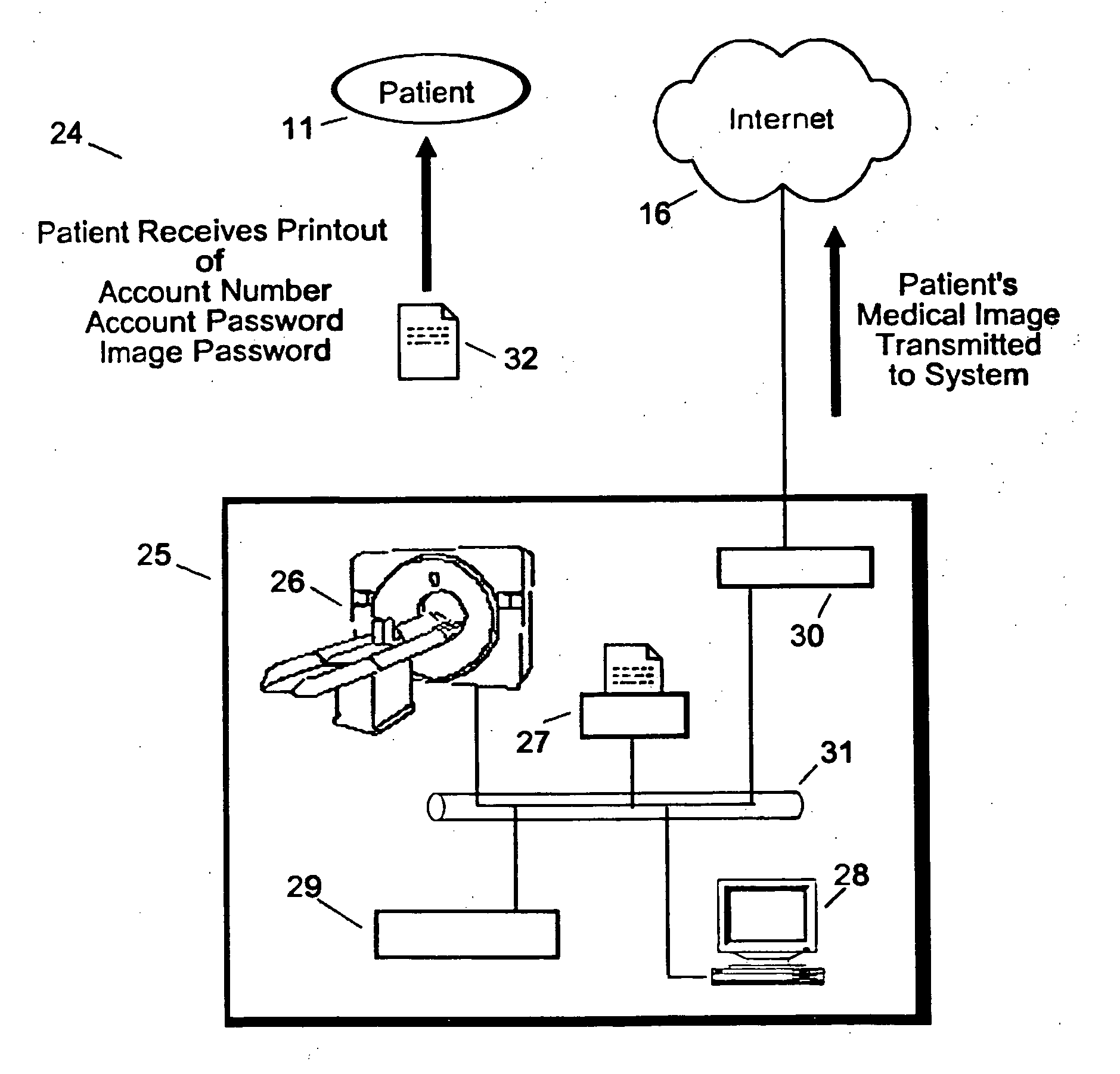
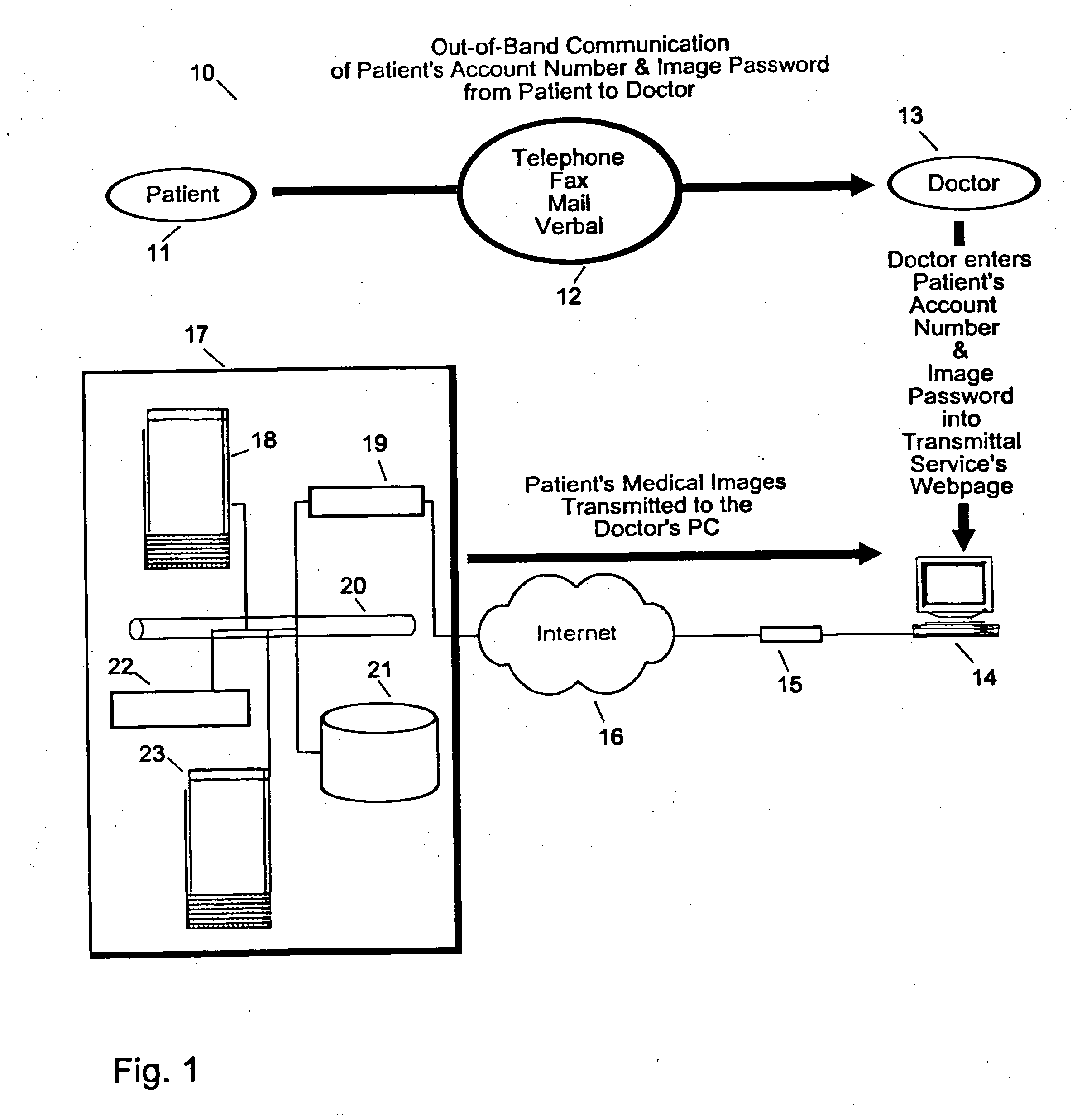
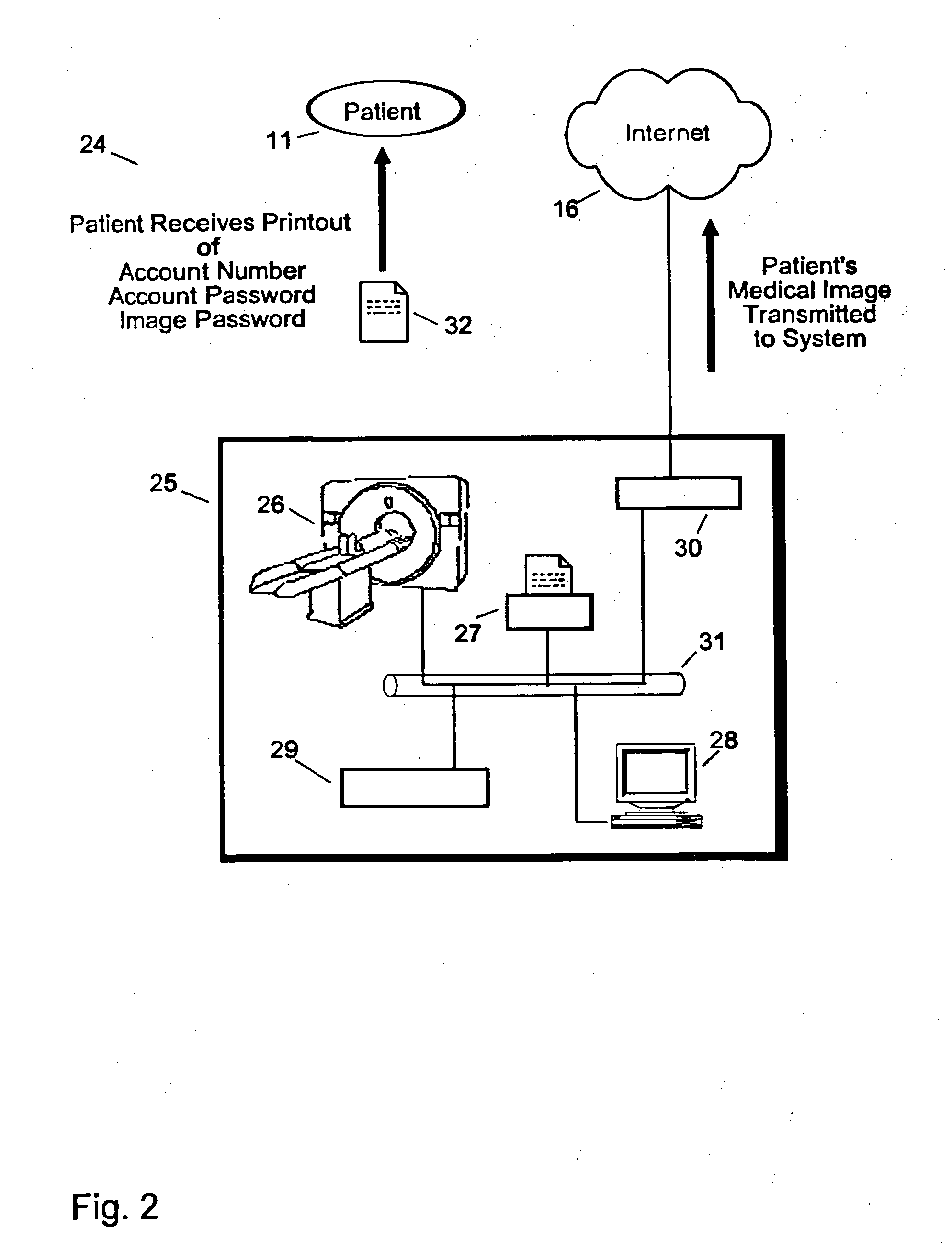
System and method for patient directed digital medical image transmittal device
The invention generally relates to a system and method for a digital medical image transmittal service that allows a patient, at the time of a medical imaging procedure, to choose to have a digital copy of their medical image acquired by the system (service). The system utilizes a patient account number with dual passwords for isolation of account information from the medical images. Subsequently, when a doctor requests the patient to provide their medical image or images, the patient provides the doctor with their account and password information using “out-of-band” communication which ensures patient privacy and control. This system and method are the functional equivalent of the patient bringing a film-based copy of their medical image to the doctor's office and handing the film to the doctor when asked for it. In effect, instead of handing the doctor a film the patient is handing the doctor a password that allows the image to be transmitted to the doctor's computer.
Owner:COTTHINGHAM HUGH V +2
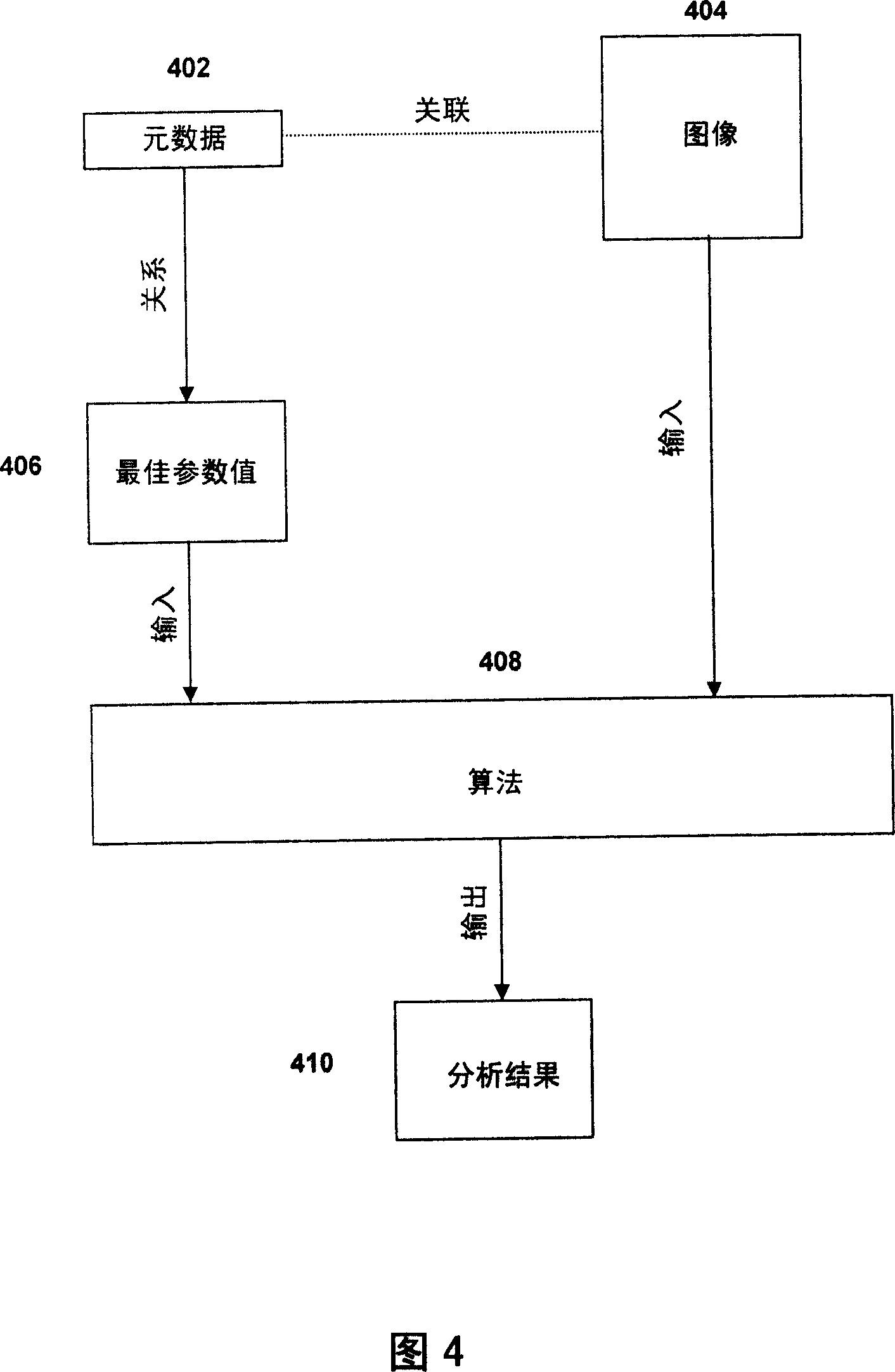
Digital medical image analysis
InactiveCN101084501AEase time constraintsAccurate Batch AnalysisImage enhancementImage analysisImaging analysisComputer science
A medical image (404) is analyzed using an algorithm (408) requiring input parameters (406), the values of which are derived from metadata (402) indicating properties of the image (404). The metadata may indicate the type of image acquisition device (102) or the settings used to create the image (404), and / or relate to the patient from whom the image (404) was taken. This allows optimum values to be selected for the parameters.
Owner:MEDICSIGHT
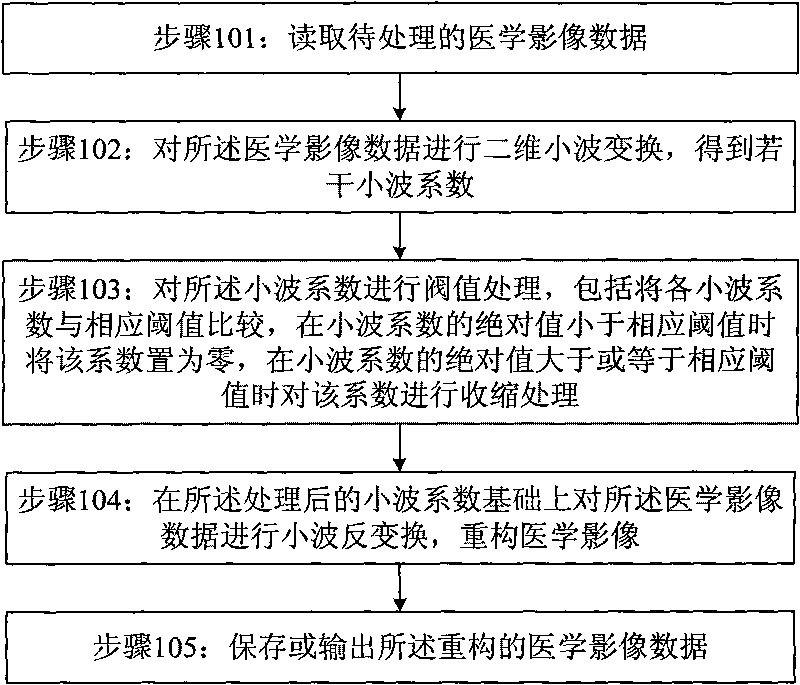
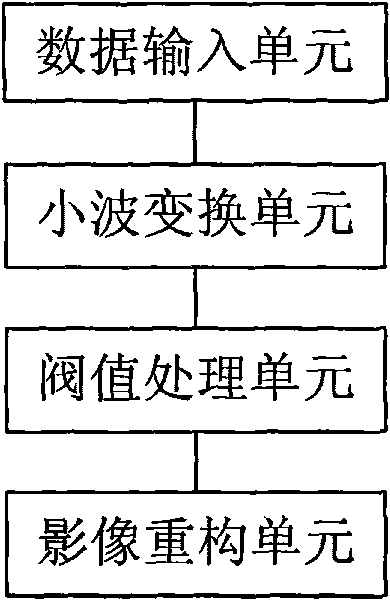
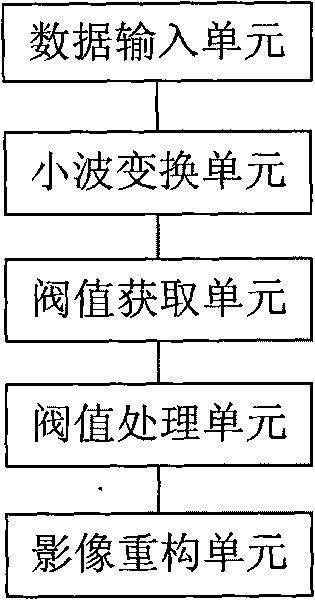
Method for de-noising wavelet in DR image processing
InactiveCN101739665AReduce the amplitudeEliminate noise pointsImage enhancementComputerised tomographsMedical imaging dataImaging processing
The invention discloses a method for de-noising a wavelet in DR image processing. The method comprises the following steps: reading medicinal image data to be processed; performing two-dimensional wavelet transformation on the medicinal image data to obtain a plurality of wavelet coefficients; performing threshold treatment on the wavelet coefficients, wherein the threshold treatment comprises comparing each wavelet coefficient with a corresponding threshold, setting the coefficient as zero when the absolute value of the wavelet coefficient is less than the corresponding threshold, and performing shrinkage processing on the coefficient when the absolute value of the wavelet coefficient is greater than or equal to the corresponding threshold; performing wavelet inverse transformation on the medicinal image data on the basis of the processed wavelet coefficients, and reconstructing a medicinal image; and storing or outputting the reconstructed medicinal image data. The method can effectively de-noise a digital medicinal image, and improve the diagnosis level of the medicinal image.
Owner:SHENZHEN ANGELL TECH
System and method for view-dependent cutout geometry for importance-driven volume rendering
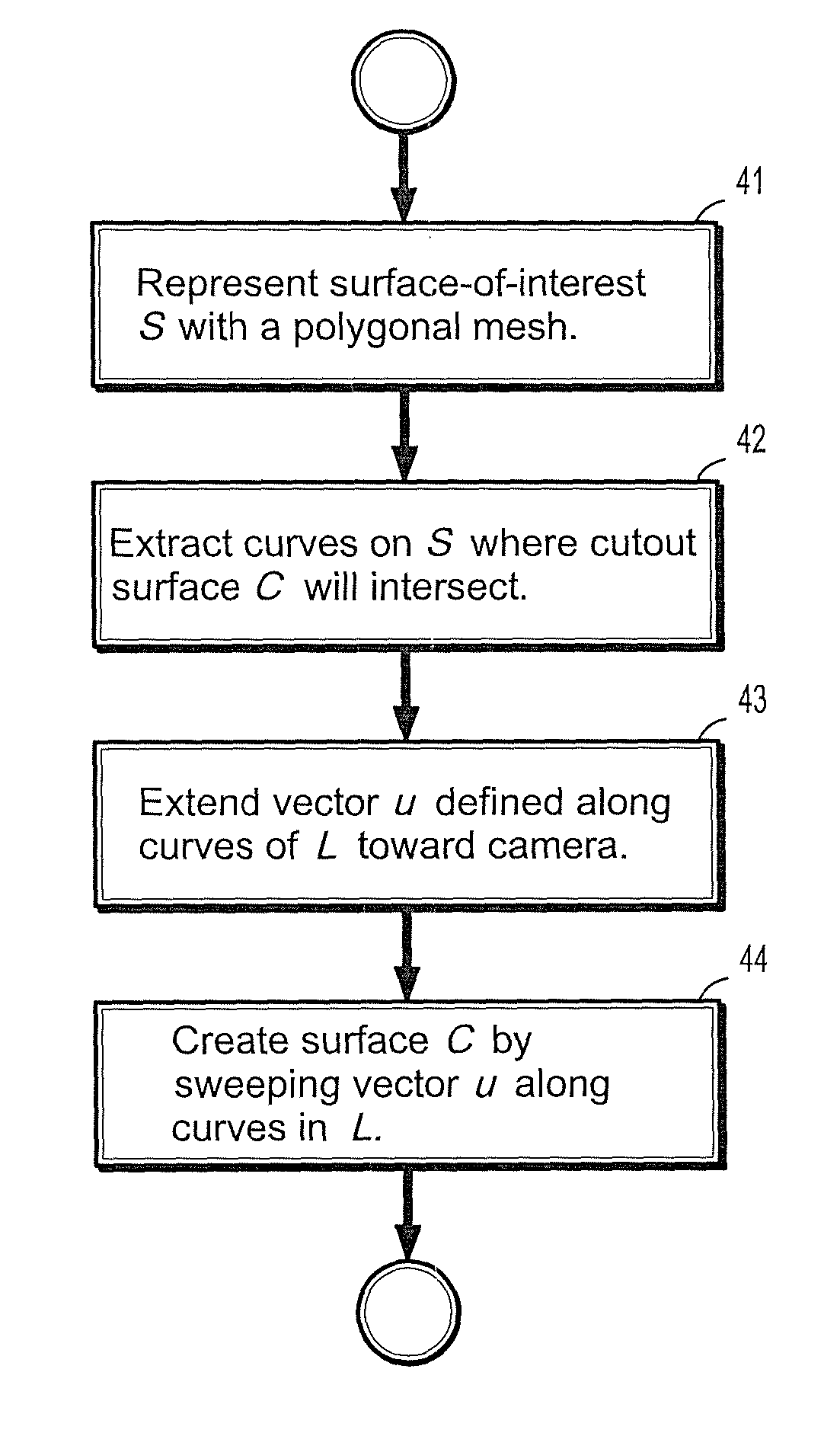
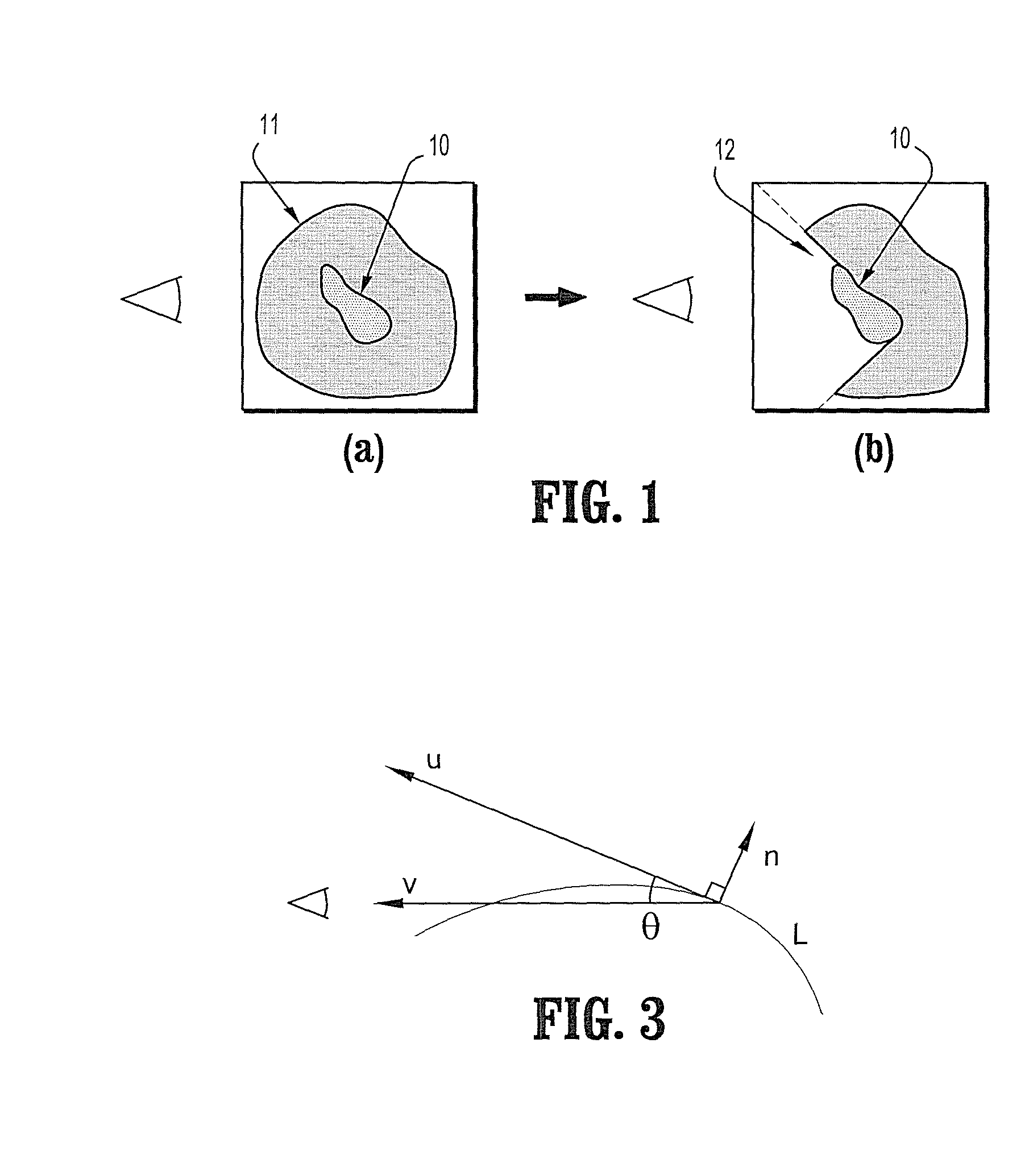
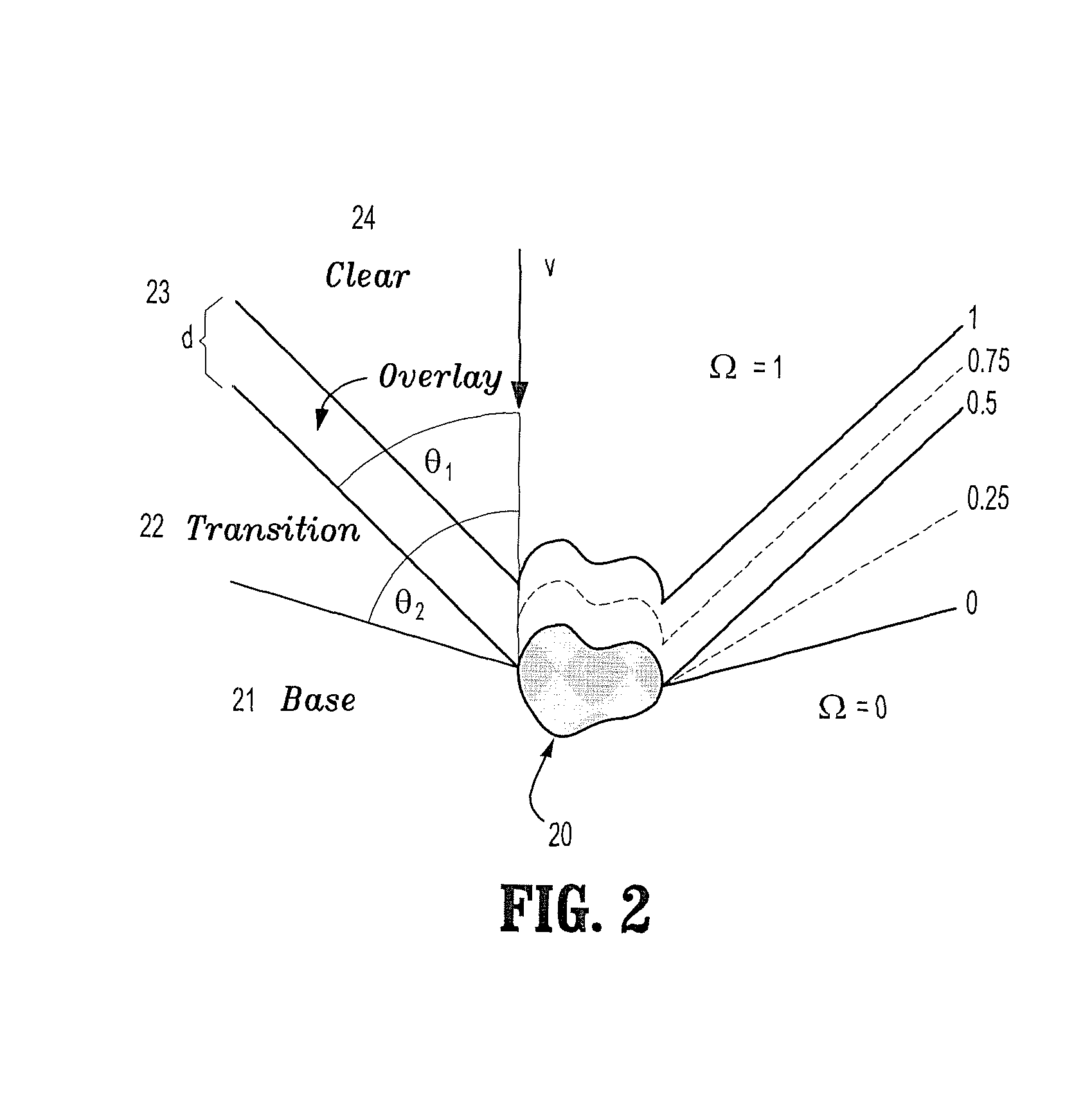
InactiveUS7952592B2Prevent renderingCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsPolygon meshView dependent
A method for creating a cutout surface for volume rendering includes providing a digitized medical image volume comprising a plurality of intensities corresponding to a 3-dimensional grid of points, identifying a surface of interest in said image volume, representing said surface-of-interest by a polygonal mesh, extracting a set of curves on said surface-of-interest where a cutout surface will intersect, extending a vector defined on one of said curves toward a viewing point, and sweeping said extended vector along said curve to create said cutout surface.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
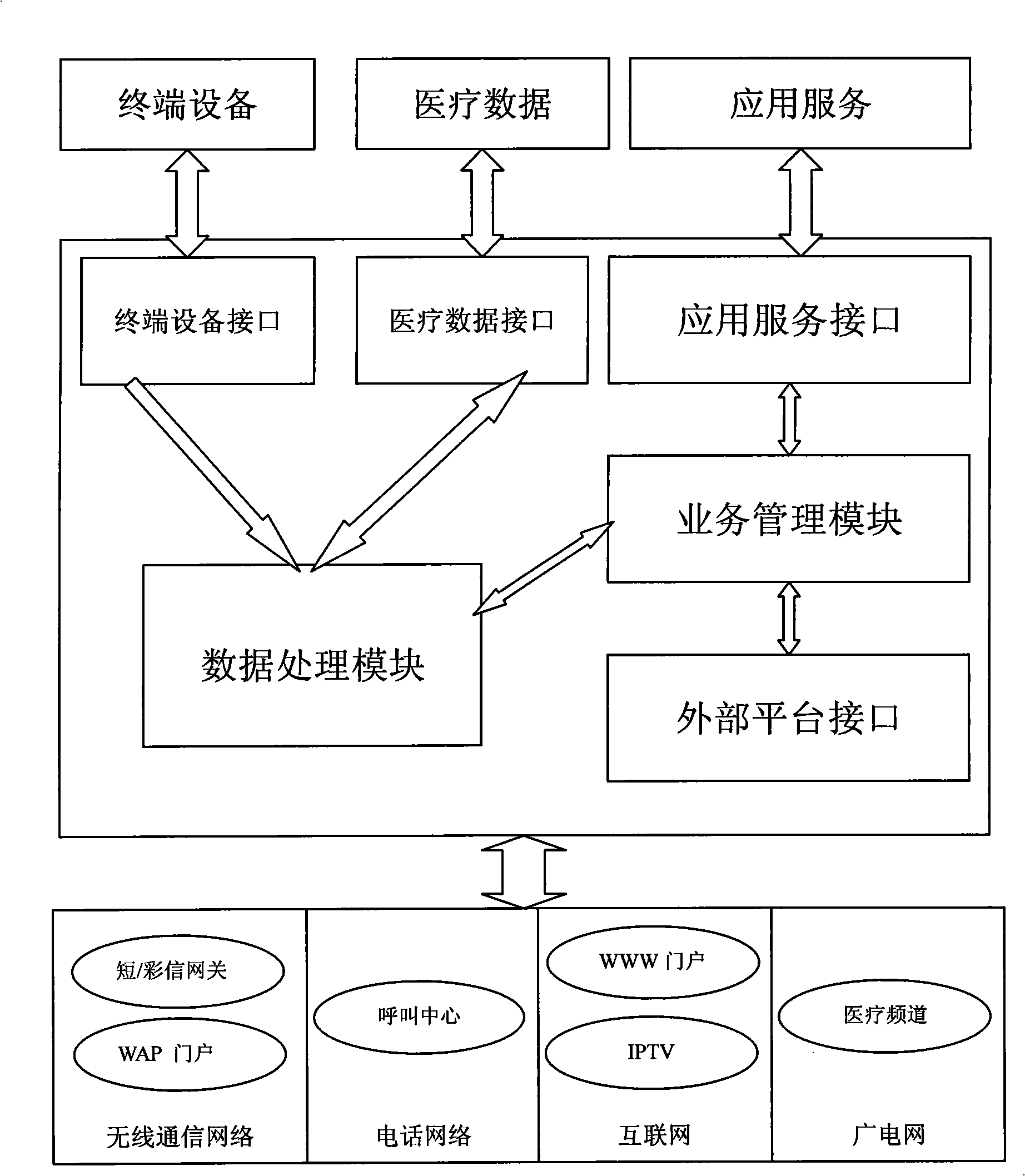
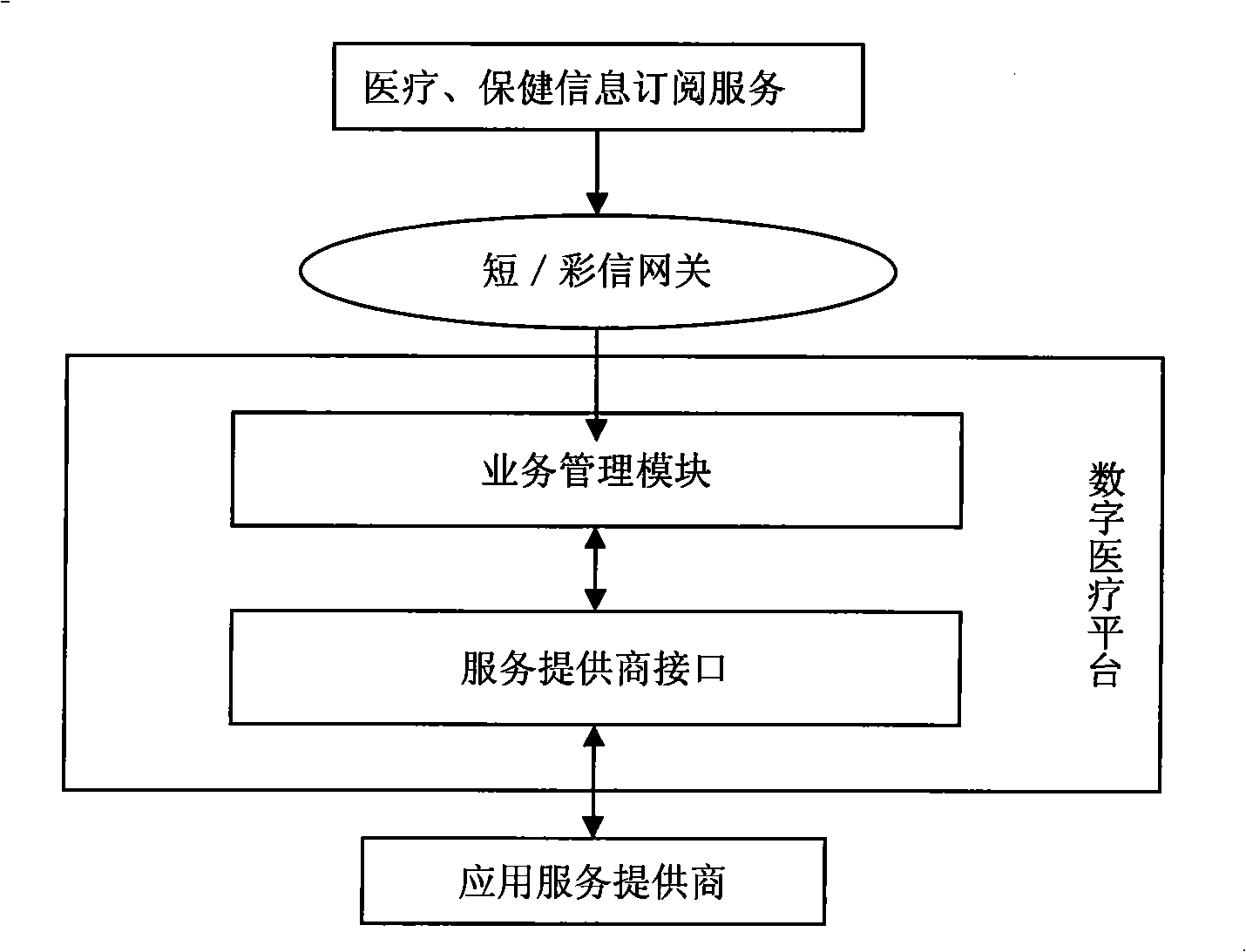
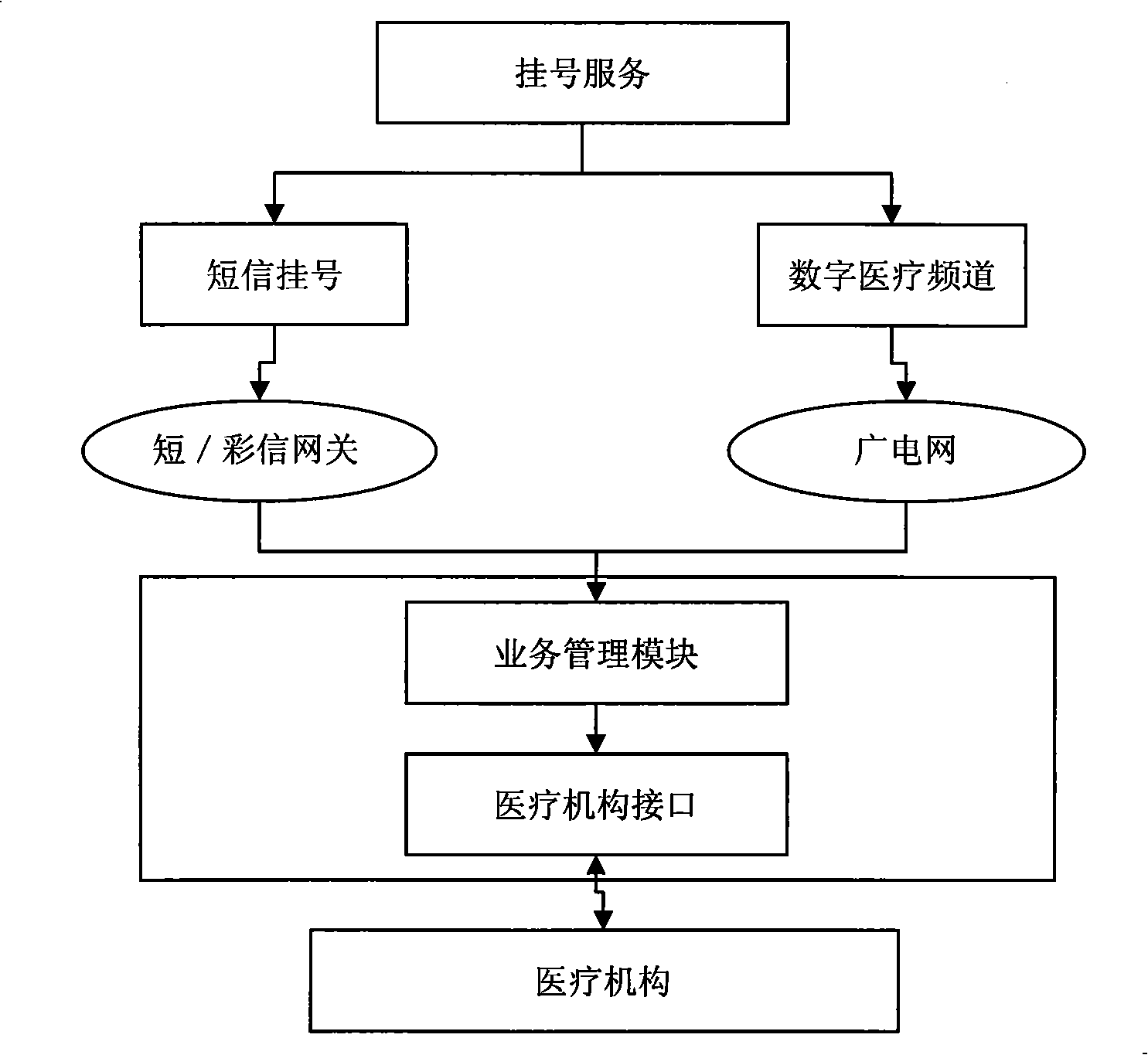
Service platform structure for digital medical treatment
InactiveCN101339586ALower the thresholdRealize medical digital servicesSpecial data processing applicationsMedical equipmentBusiness management
The invention provides a service platform framework applied for digital medicine, and the framework comprises a terminal equipment interface used for collecting medical equipment information and data, a medical data interface used for collecting medical institution information and data, an applied service interface used for releasing the information of the application service provider, a data processing module used for processing data format of the collected data, a business management module used for logically managing the platform business and an external platform interface used for realizing the resource sharing and business controlling between platforms. The framework causes the medical information to realize a rapid circulation, convenient sharing and guarantees the information safety, which is a service platform access framework for integrating the digital medicine functions of the medical institutions, the medical equipment providers and the applied service providers.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN IKER DIGITAL TECH +1
Systems and methods for automatic vertebra edge detection, segmentation and identification in 3D imaging
Systems and methods for automatic accurate and efficient segmentation and identification of one or more vertebra in digital medical images using a coarse-to-fine segmentation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
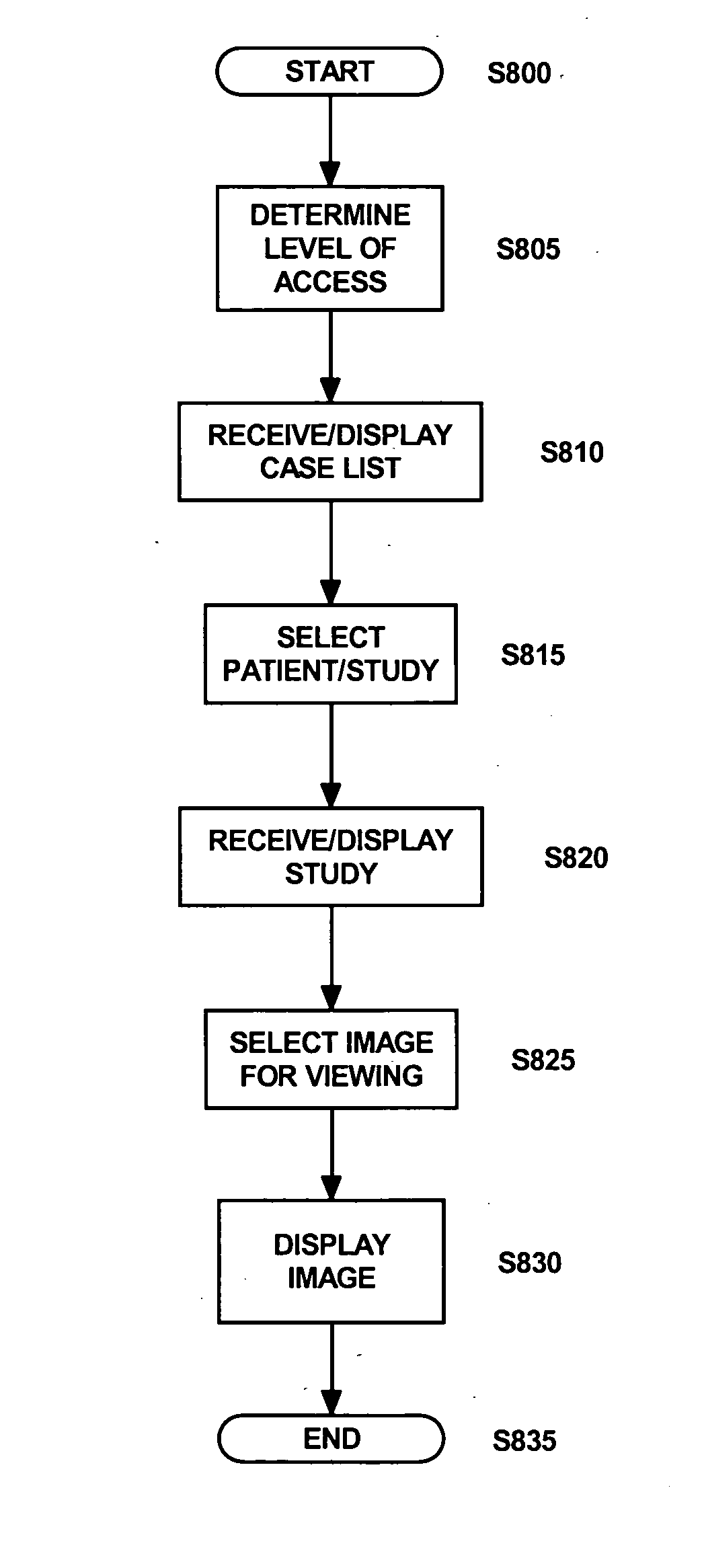
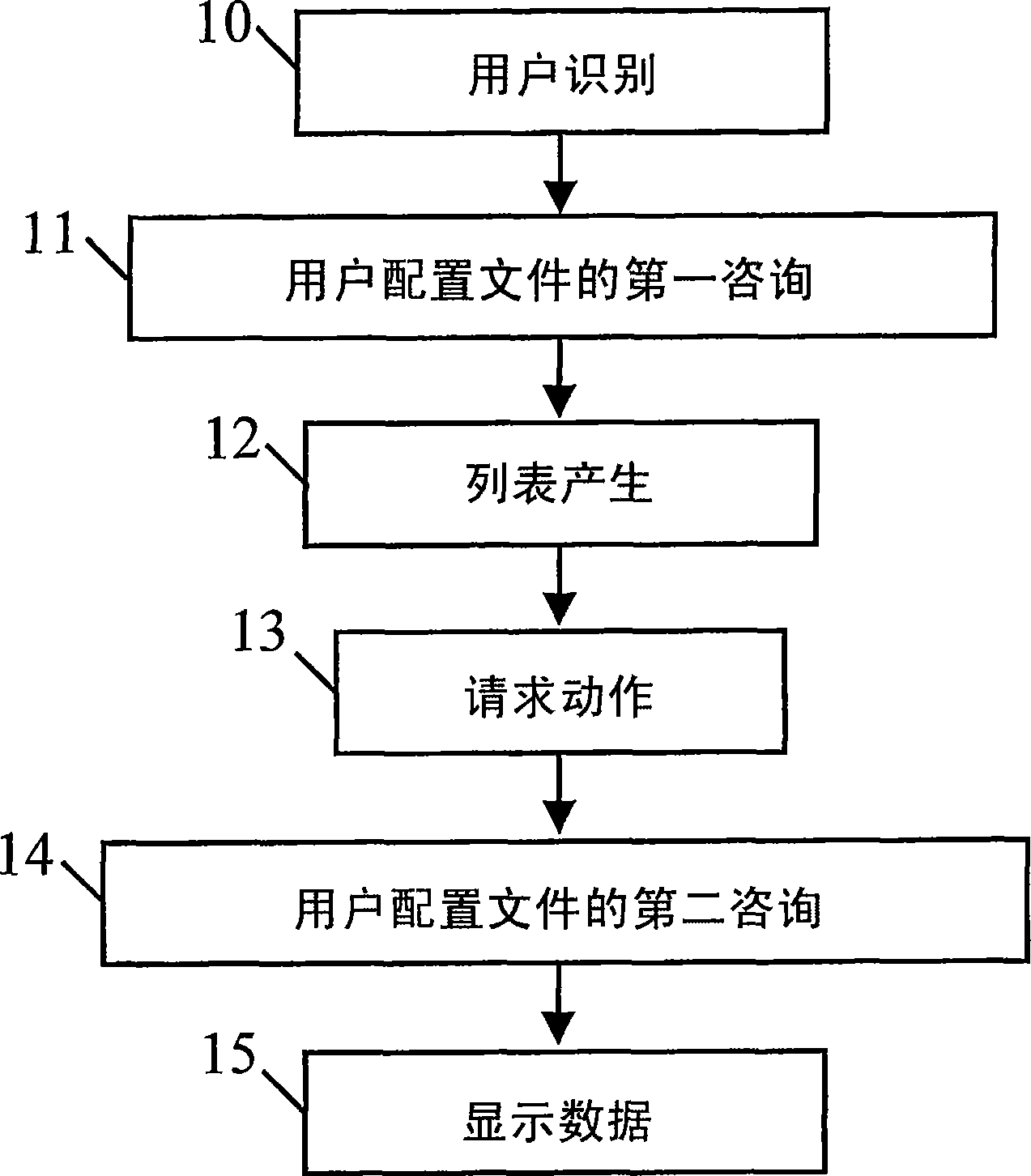
Method and system for direct and persistent access to digital medical data
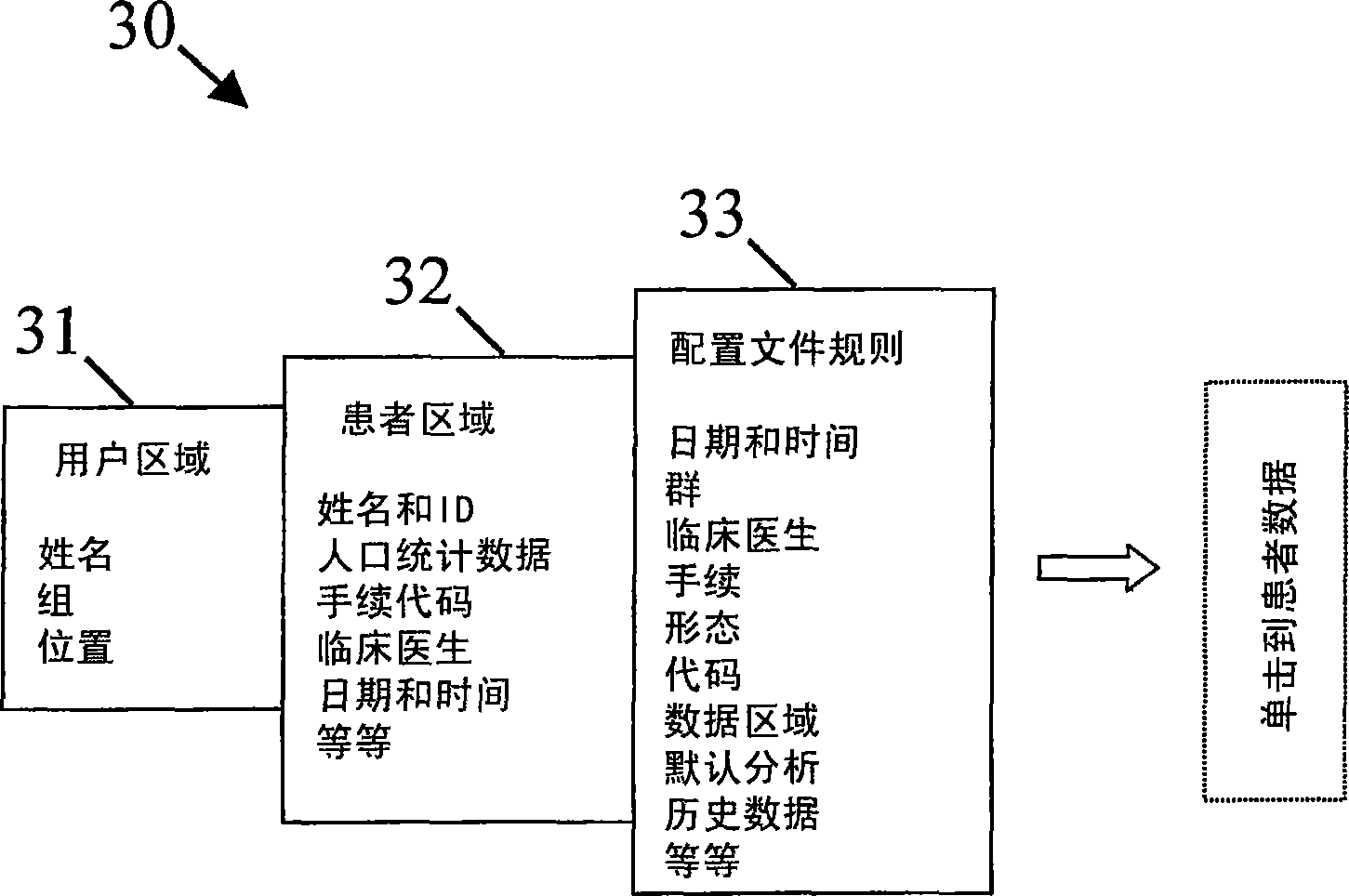
The invention provides direct and persistent access to digital data, in particular to digital medical data. Based upon the identity of the user (10), a list of relevant medical data is presented to the user (12) by accessing a repository of attributes relating to the digital medical data. In order to generate the list a user profile is consulted (11). The user profile dictates the items within the list on the basis of a rule-based comparison between the user profile and the attributes. The user selects from the list the medical data which should be presented, and the requested medical data is subsequently presented to the user (15).
Owner:MEDICAL INSIGHT
Data transmitting system of digital medical imaging device based on optical fiber communications
InactiveCN103705260AHigh resolutionResolve transmissionFibre transmissionRadiation diagnosticsX-rayData acquisition
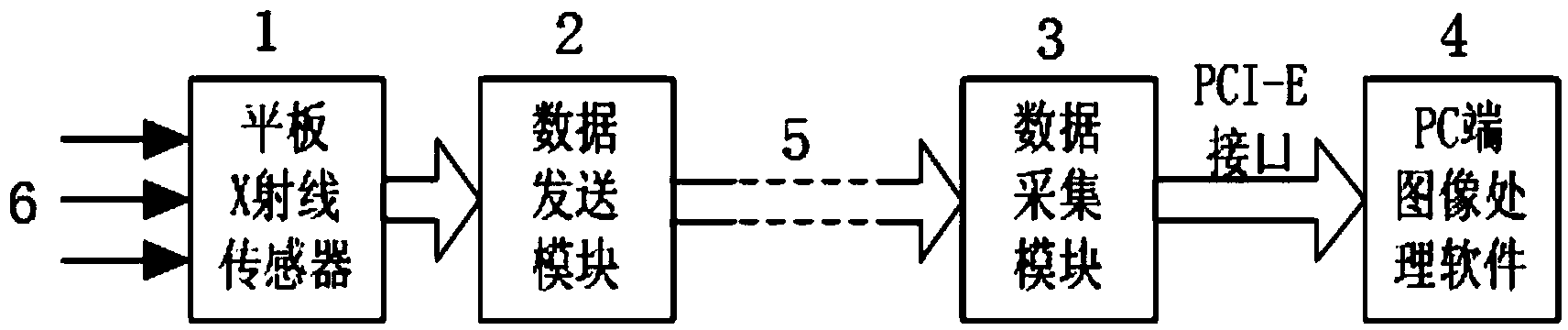
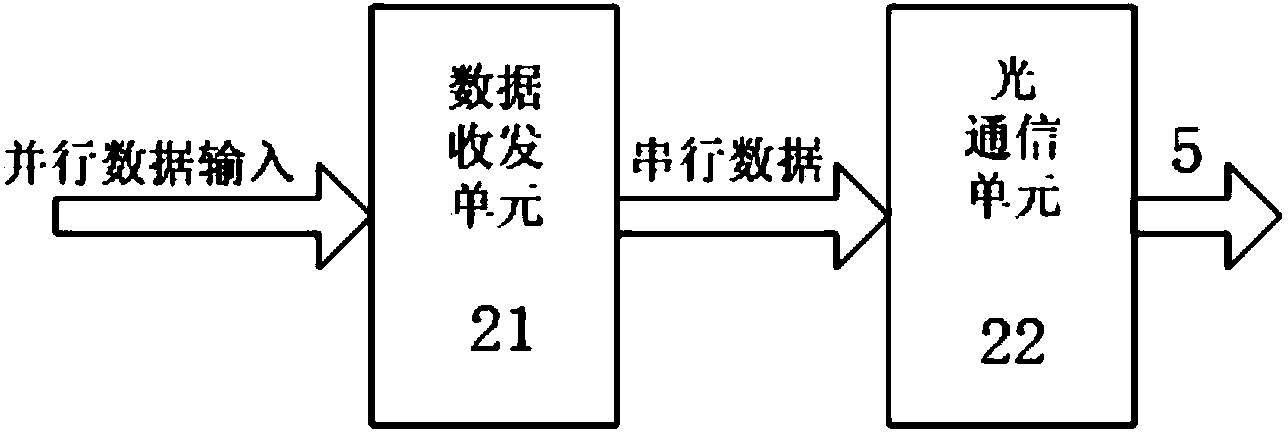
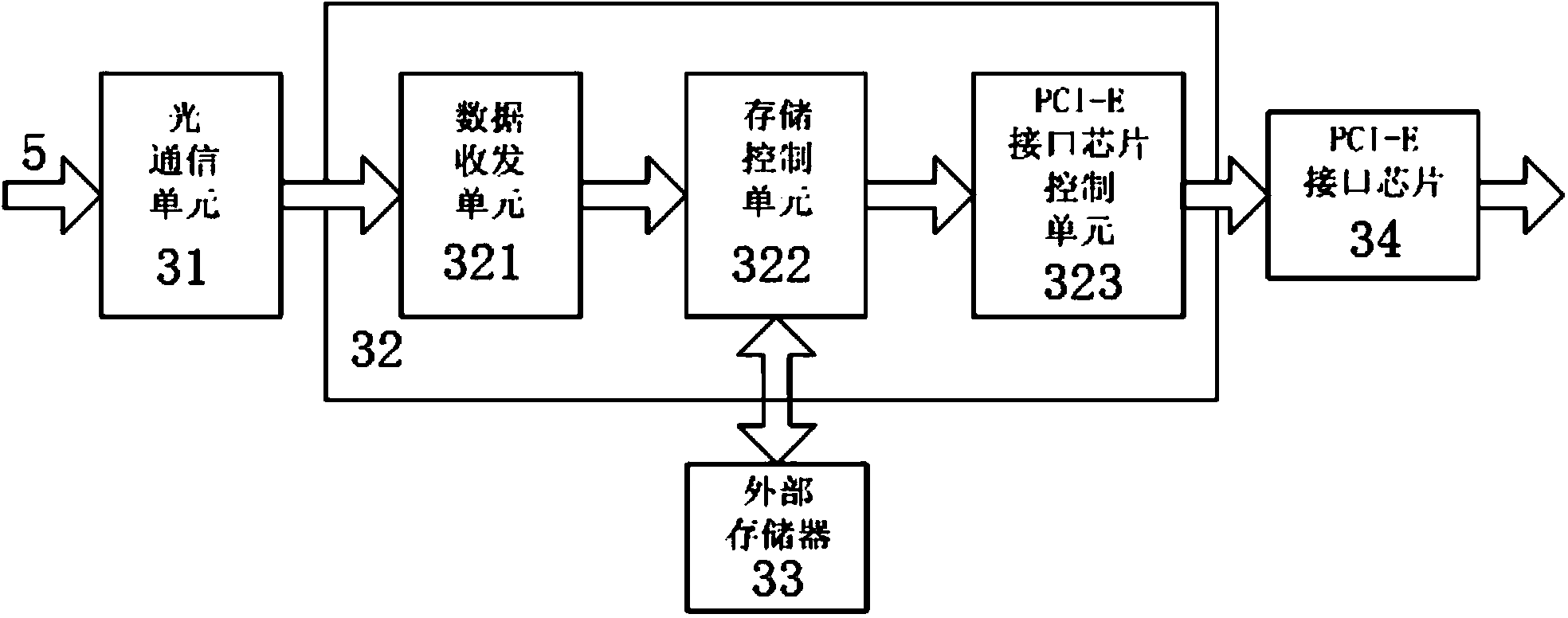
The invention discloses a data transmitting system of a digital medical imaging device based on optical fiber communications. The data transmitting system is provided with a panel X-ray sensor used for receiving X-rays, wherein the output end of the panel X-ray sensor is connected with a data sending module; the data sending module is connected with a data collection module through optical fibers; the data collection module is connected with a computer through a PCI-E interface. The data sending module is provided with a data receiving and sending unit and a first optical communication unit which are connected in sequence; the signal input end of the data receiving and sending unit is connected with the signal output end of the panel X-ray sensor; the signal output end of the first optical communication unit is connected with the data collection module through optical fibers. The data collection module is provided with a second communication unit, a data collection and storage unit, a PCI-E interface chip and an external storage which are connected in sequence; a storage and control unit is connected with the external storage. According to the data transmitting system of the digital medical imaging device based on the optical fiber communications, real-time and non-compression transmission of high-resolution-ratio digital medical images from an image sensor to a computer is achieved, and the real-time and high-speed non-compression data transmission between the medical imaging device and the external computer is achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
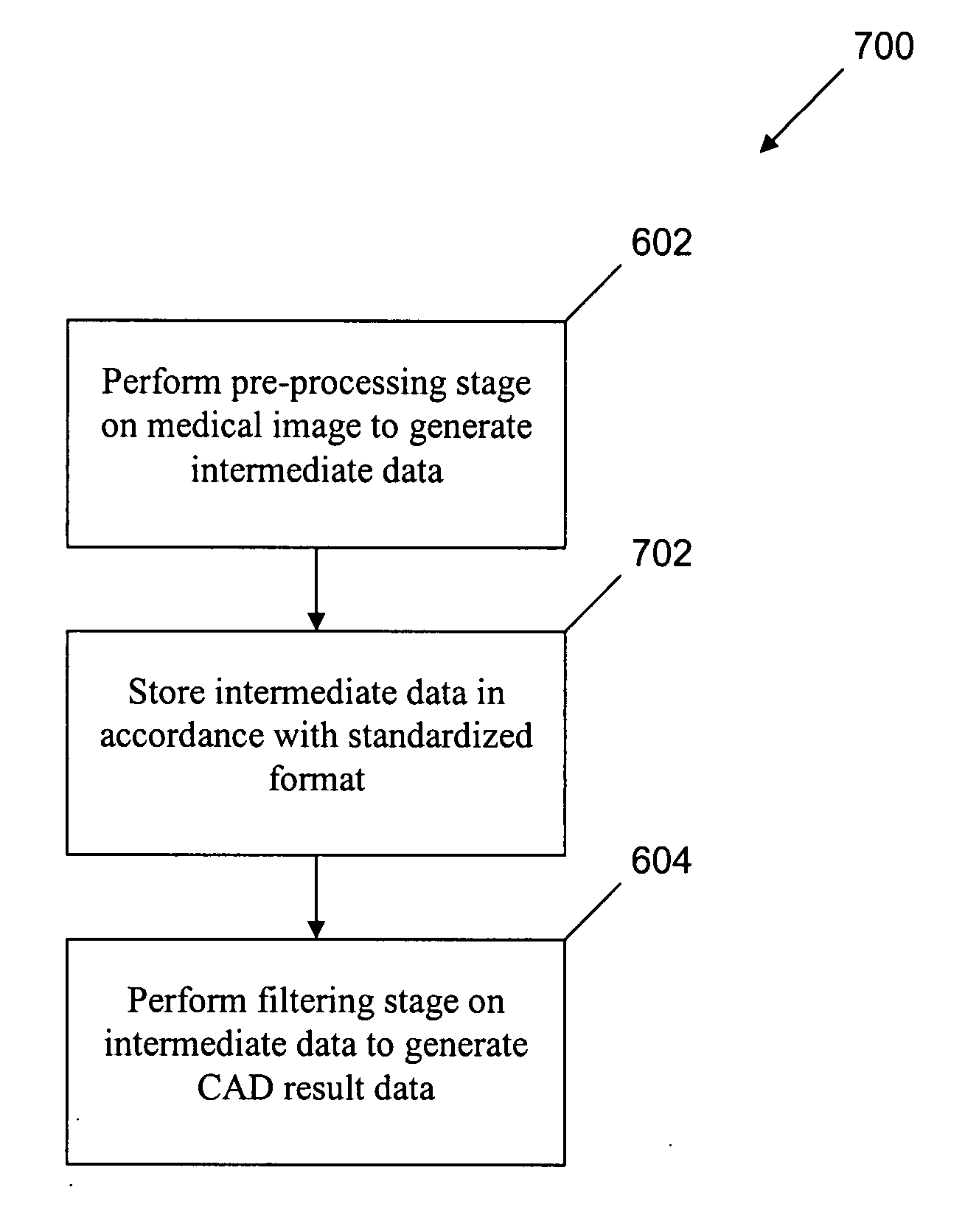
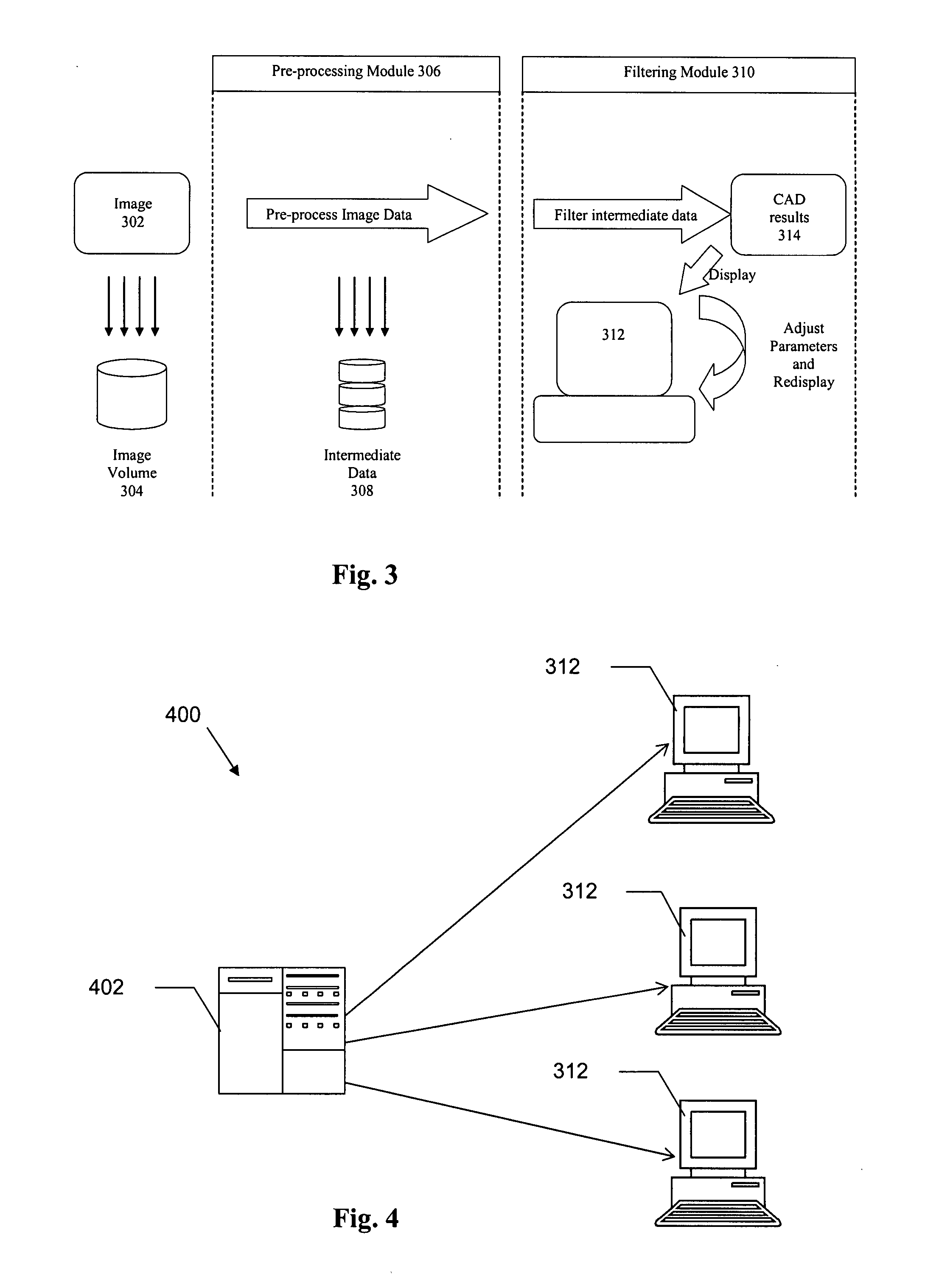
Digital medical image processing
In a method of performing CAD analysis of a medical image, the medical image volume is processed in a pre-processing module to generate intermediate data, and the intermediate data is processed by a filtering module to generate CAD result data. The different modules may be executed by different processing nodes or devices, enabling a variety of different system architectures. The intermediate data may be stored in accordance with a standard, such as the Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) standard. For instance, the intermediate data may be stored in accordance with the DICOM secondary capture image information object definition (SCI IOD) format. The CAD result data may be displayed on a viewer workstation, for example.
Owner:MEDICSIGHT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com