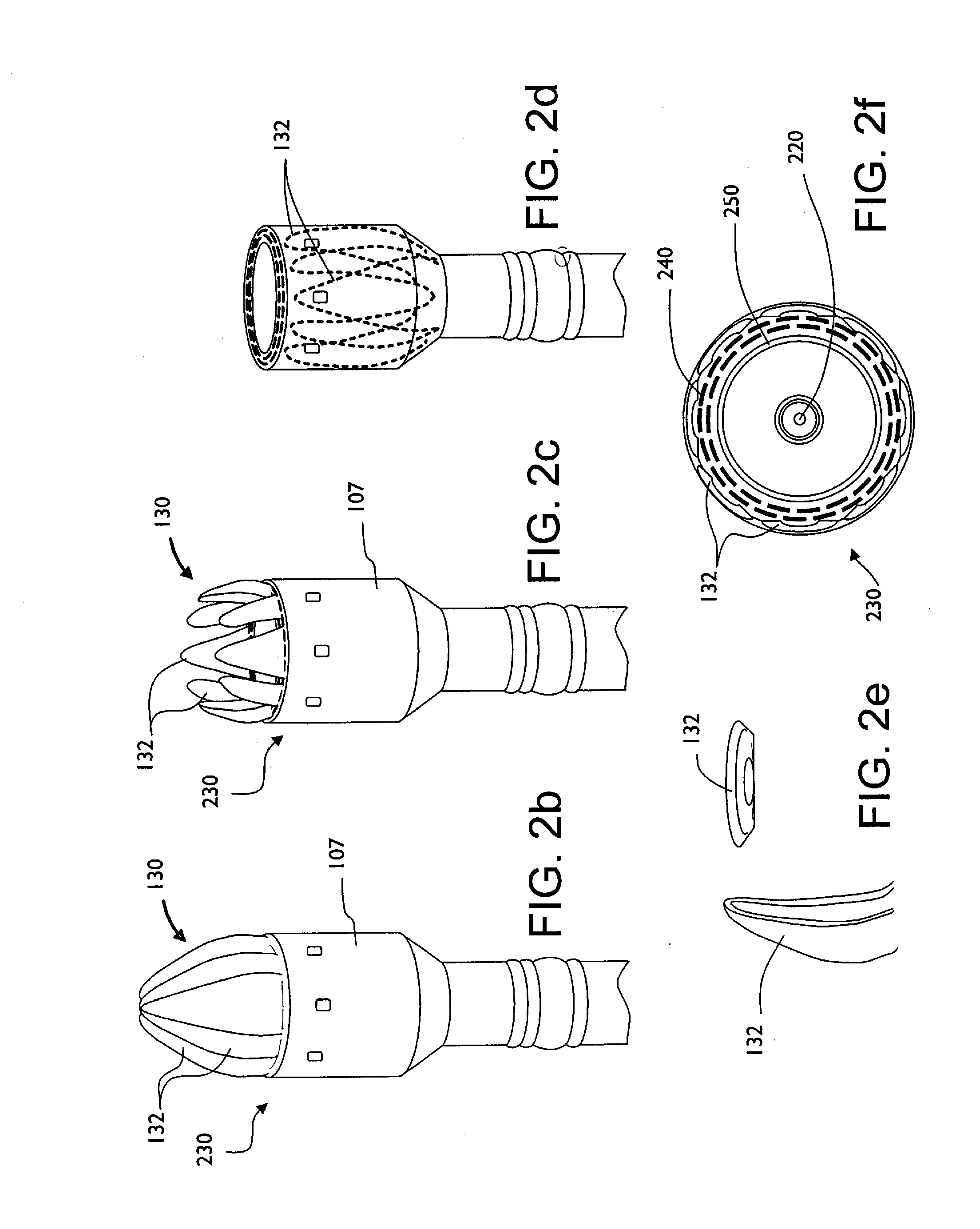
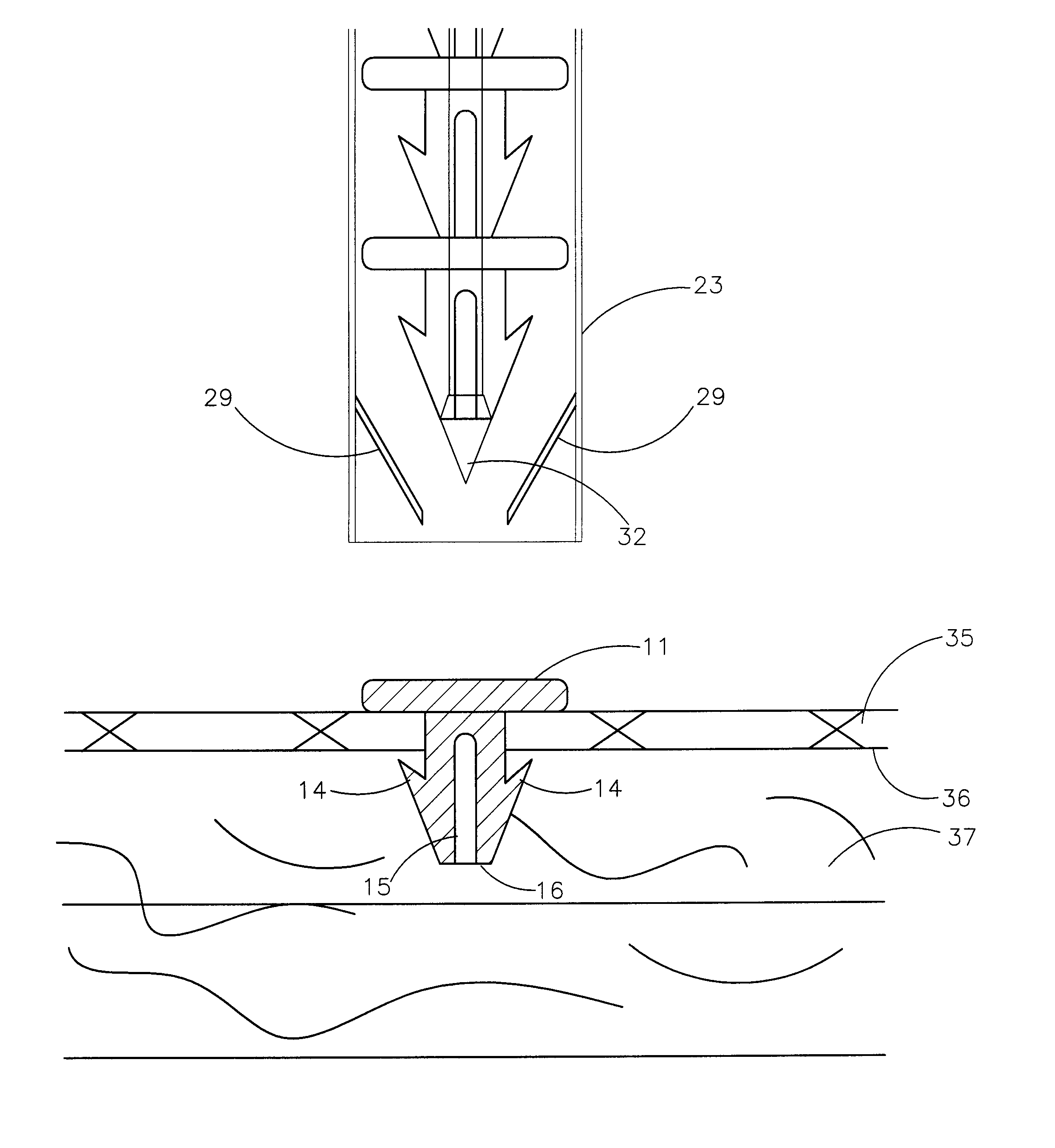
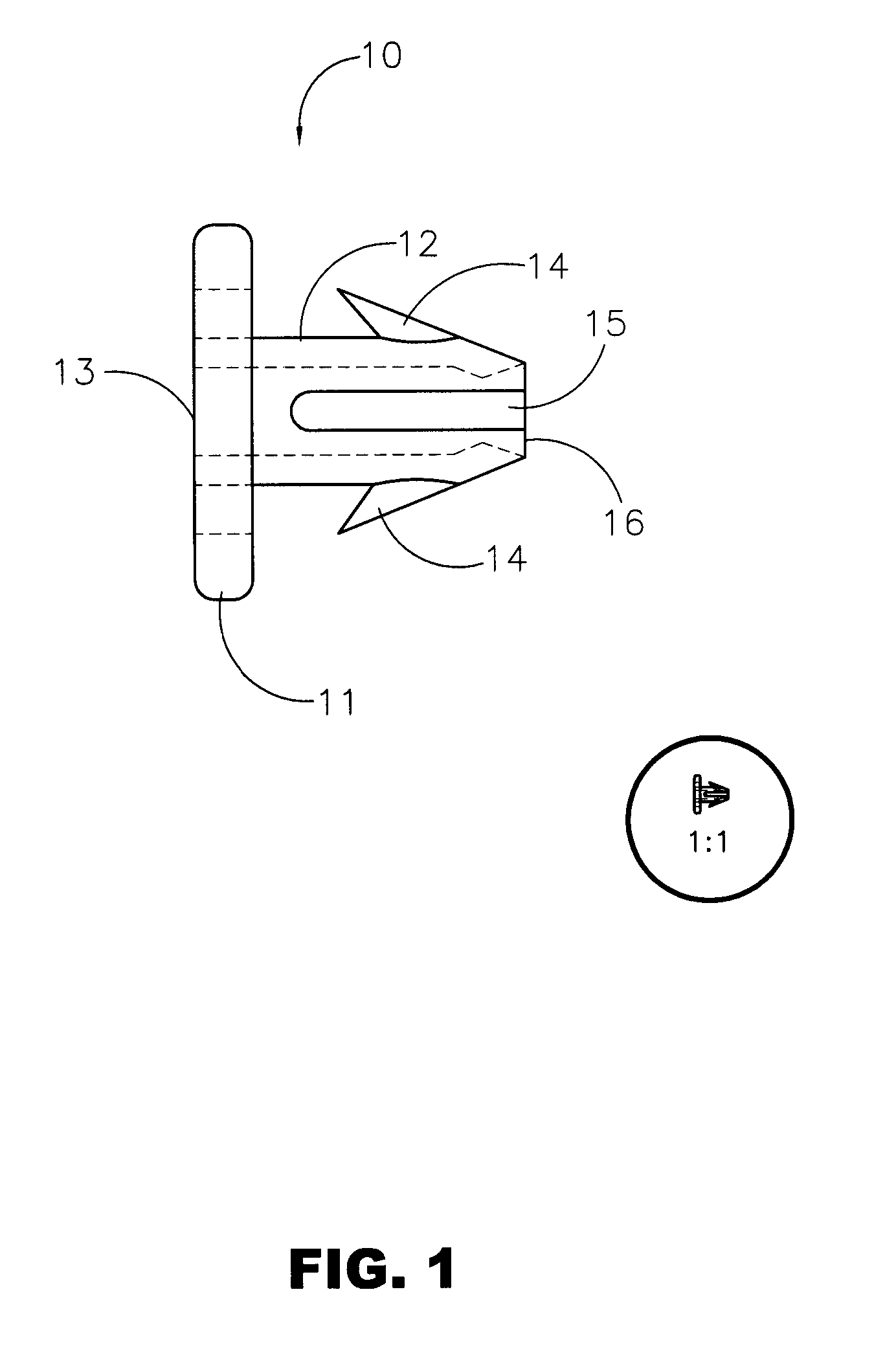
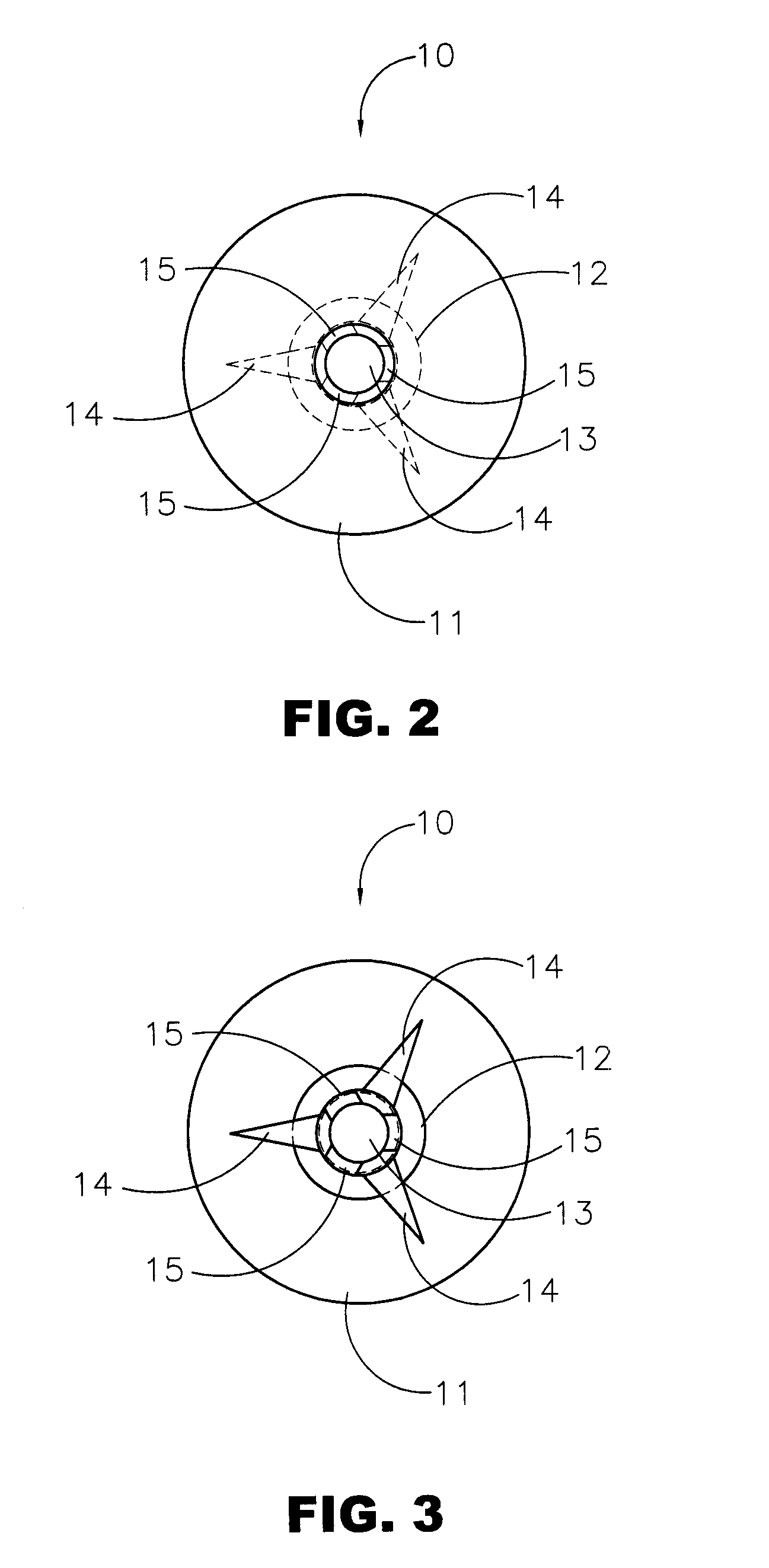
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3072 results about "Restorative surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
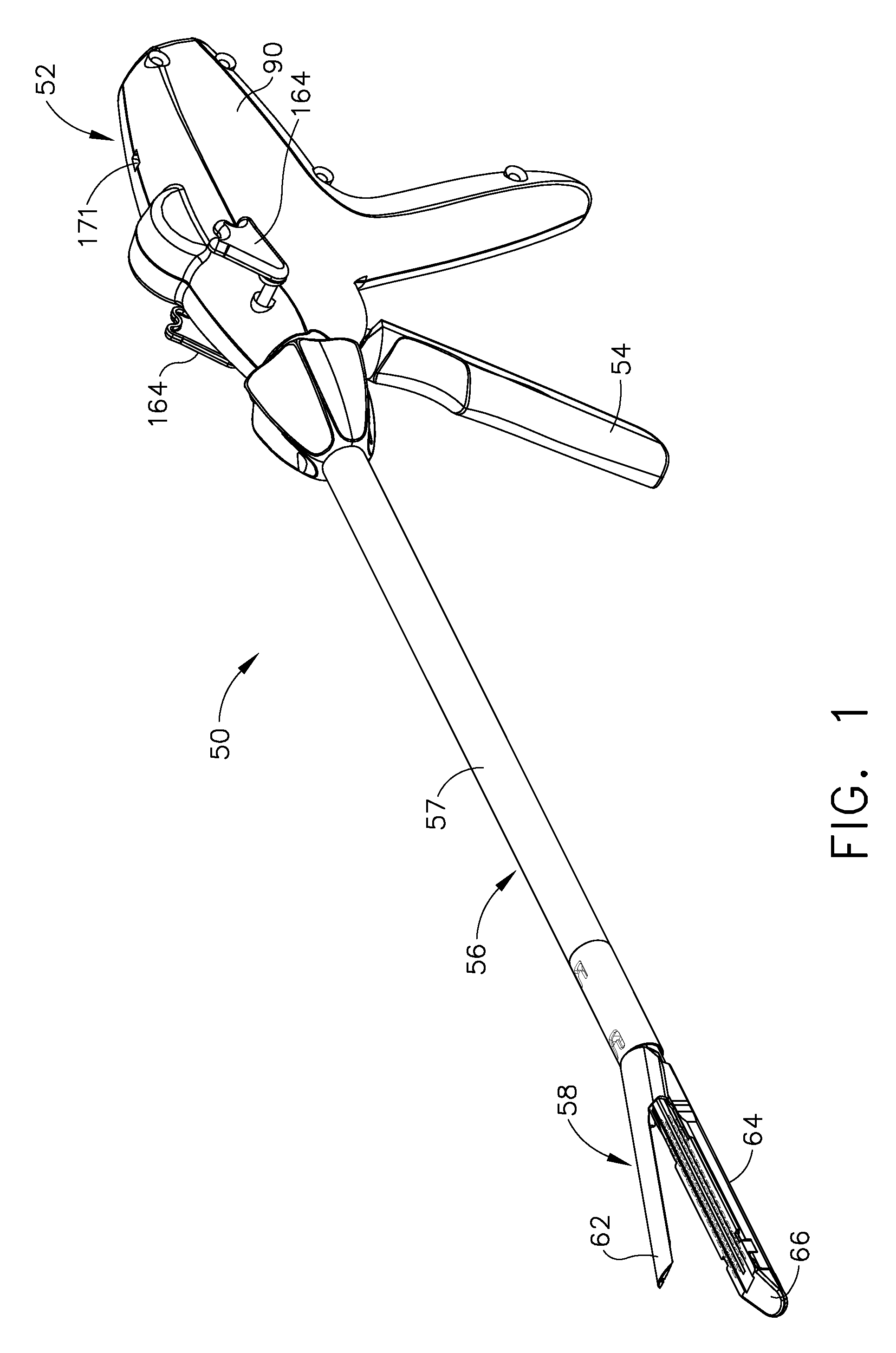
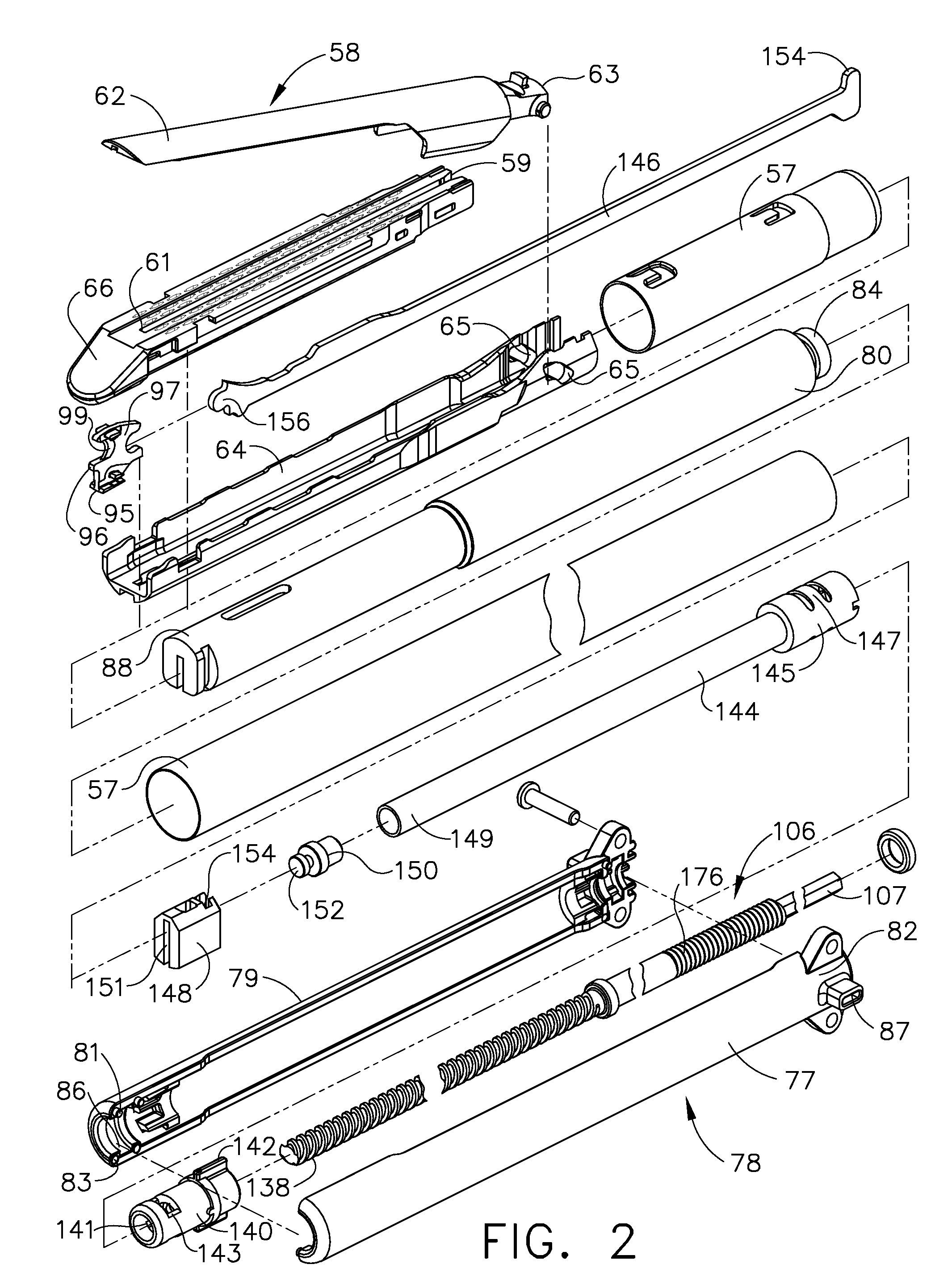
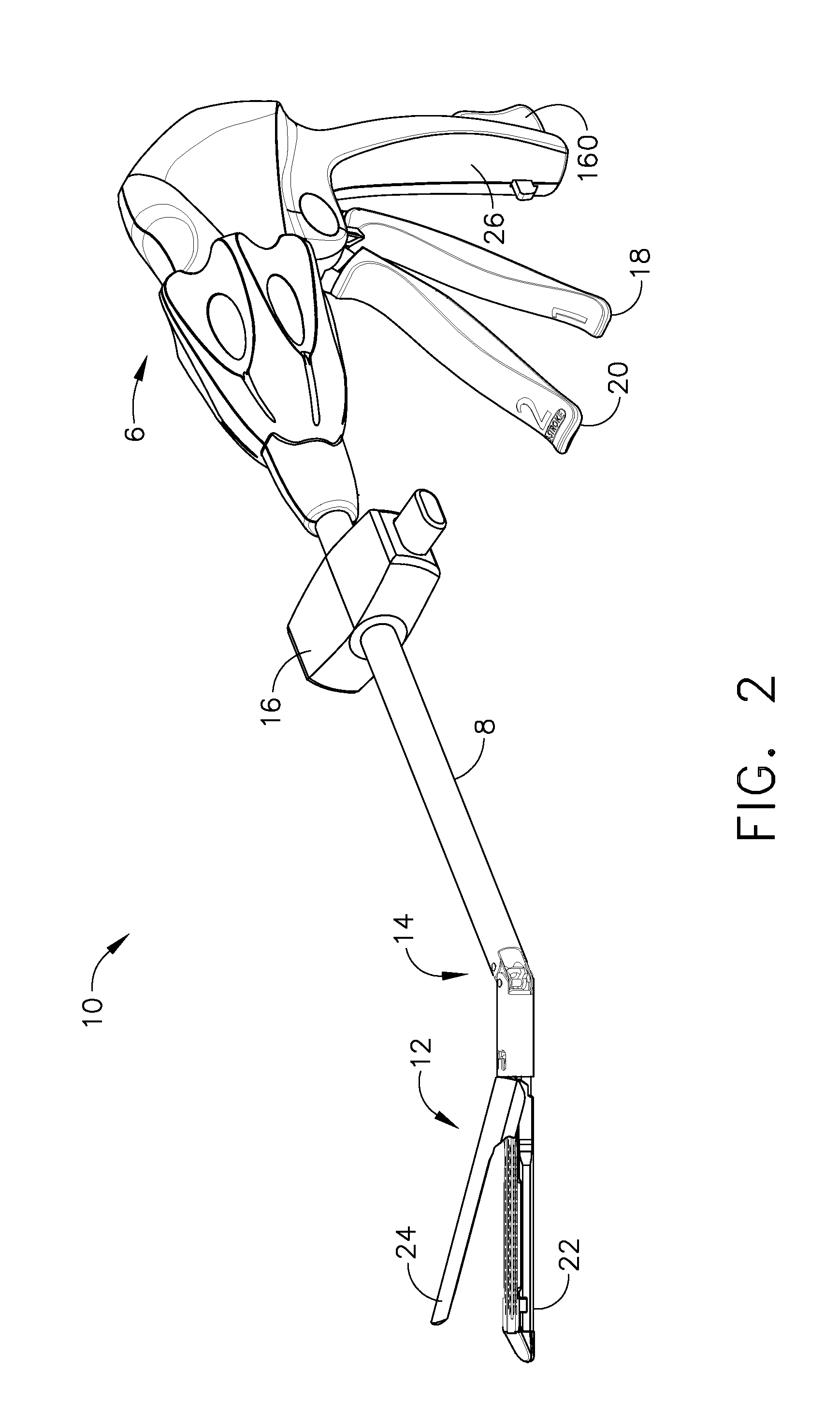
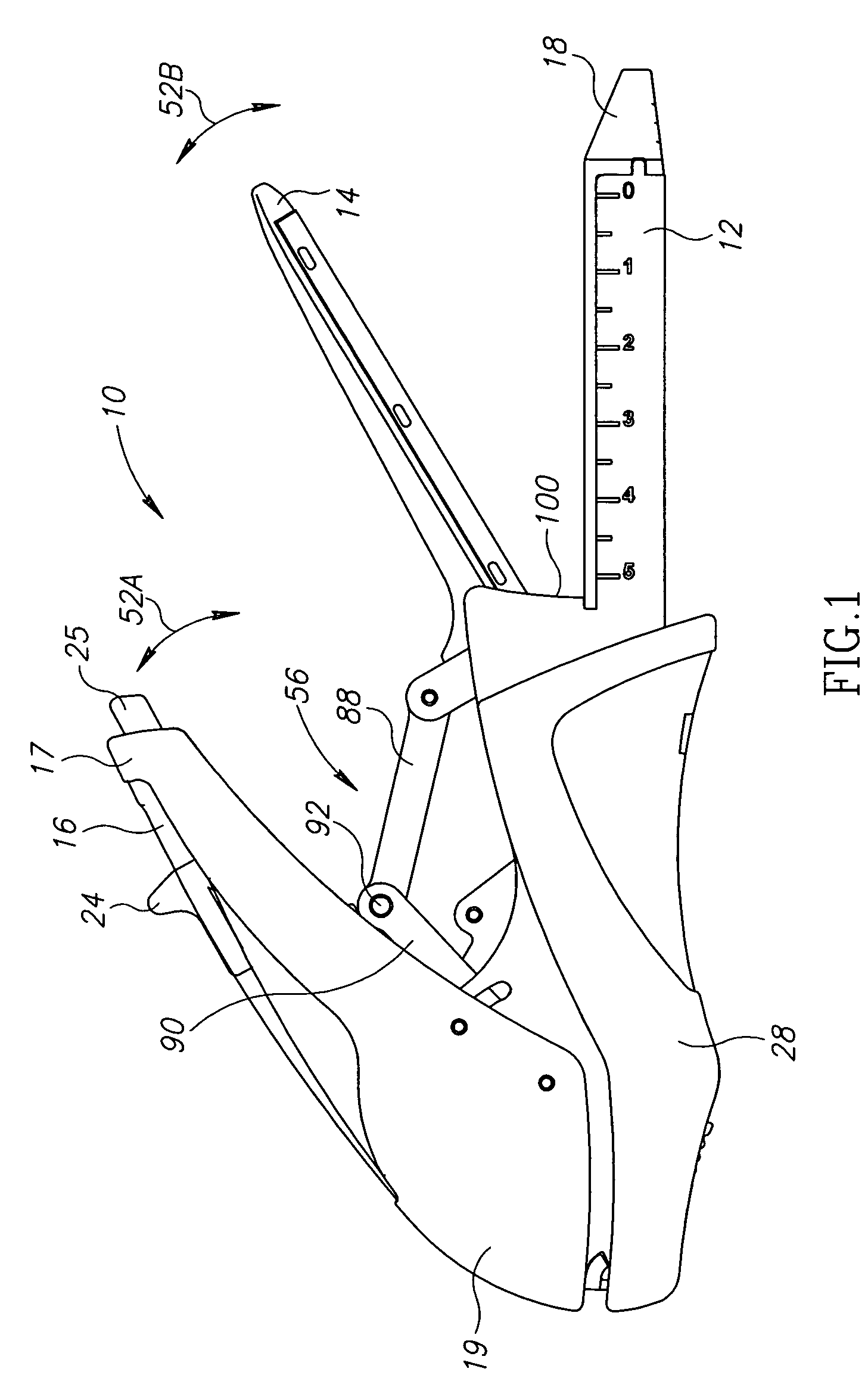
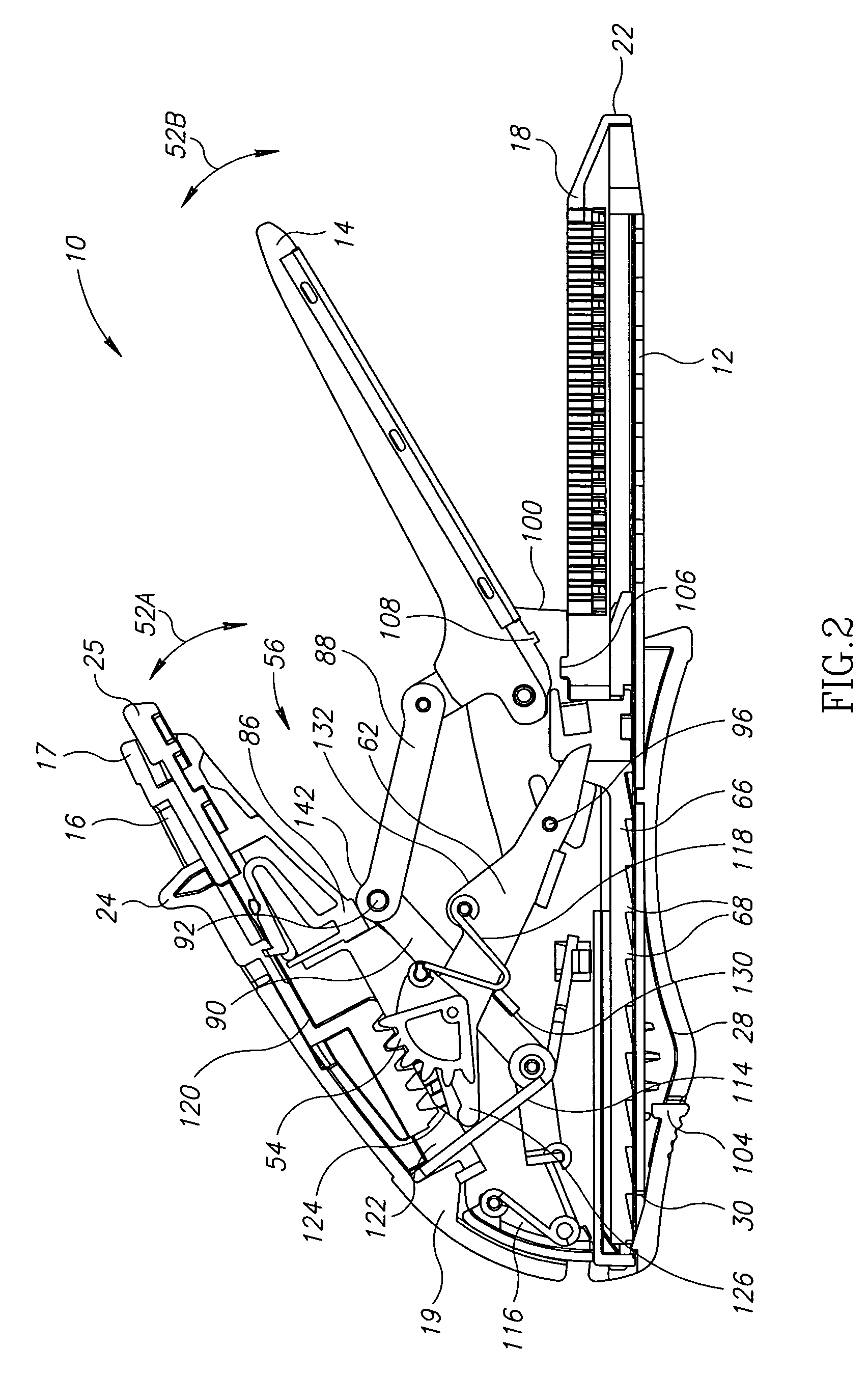
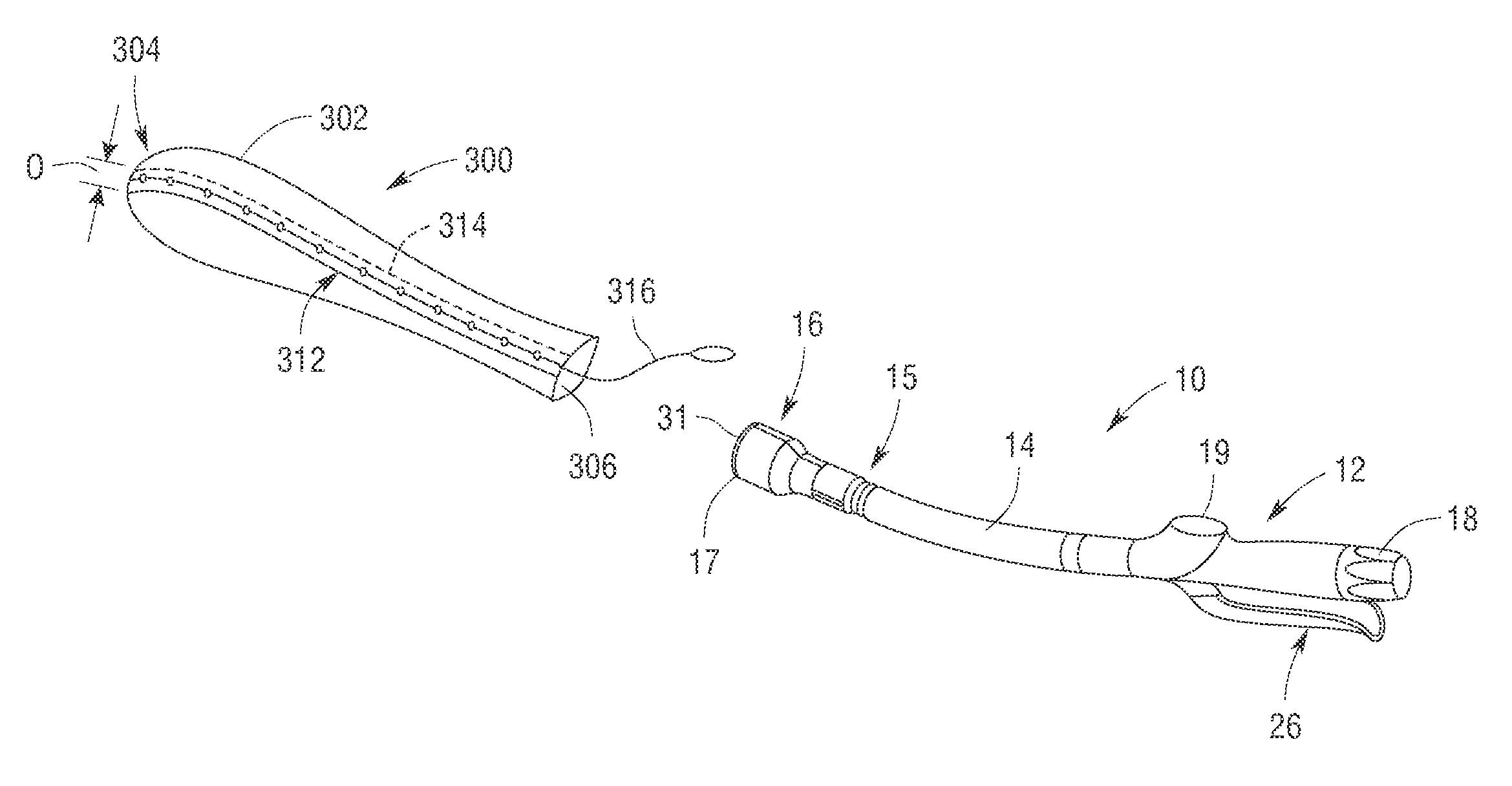
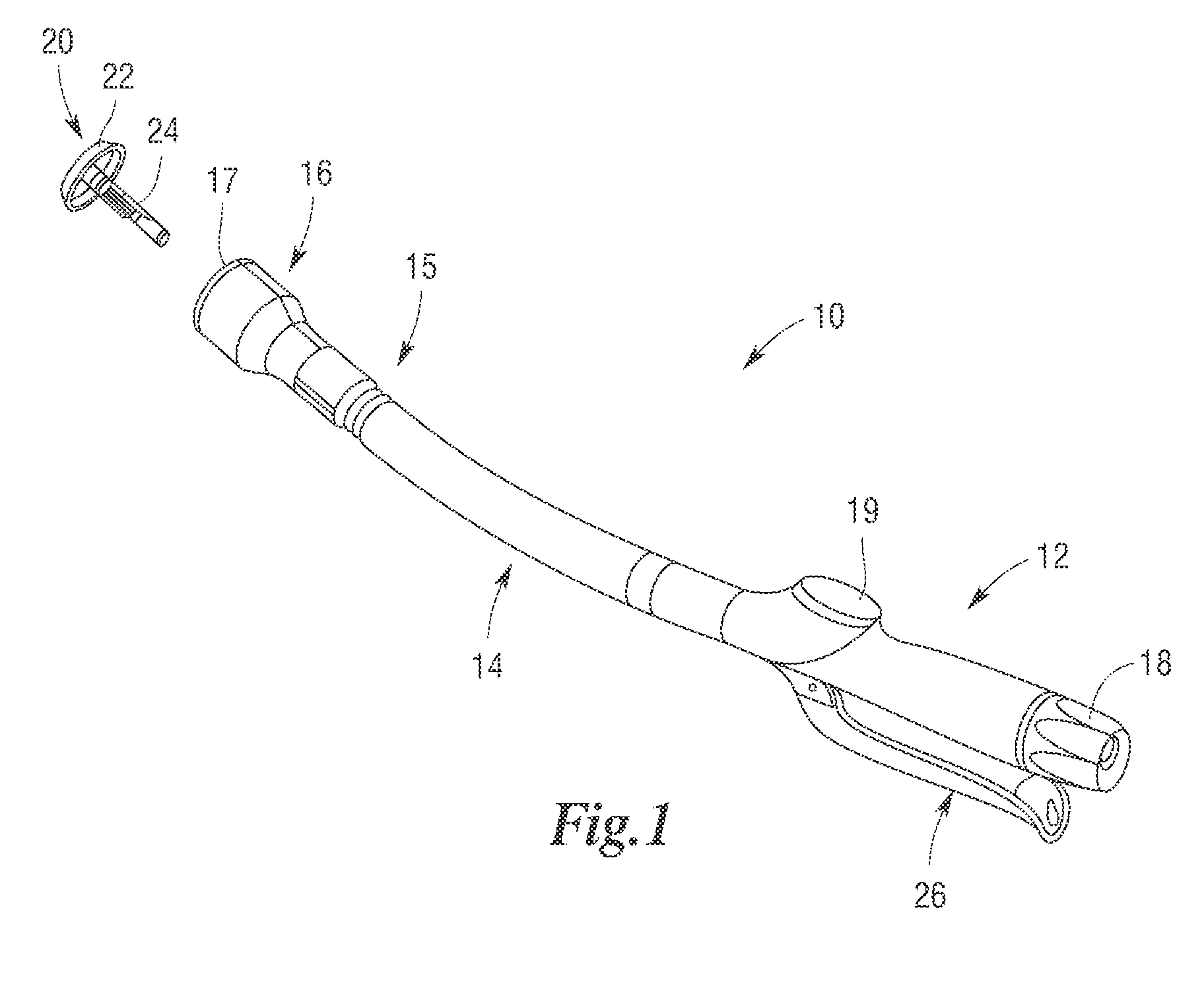
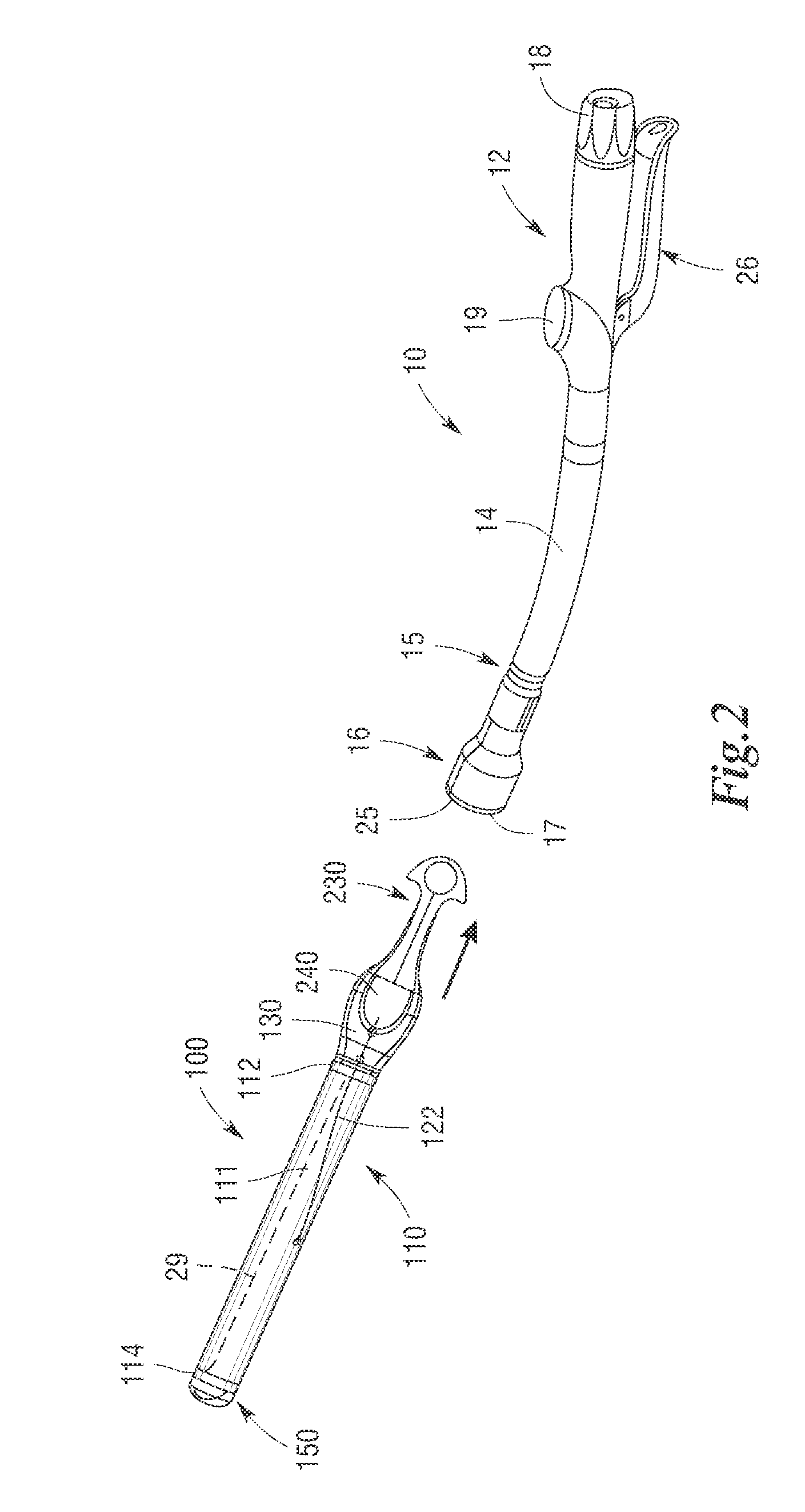
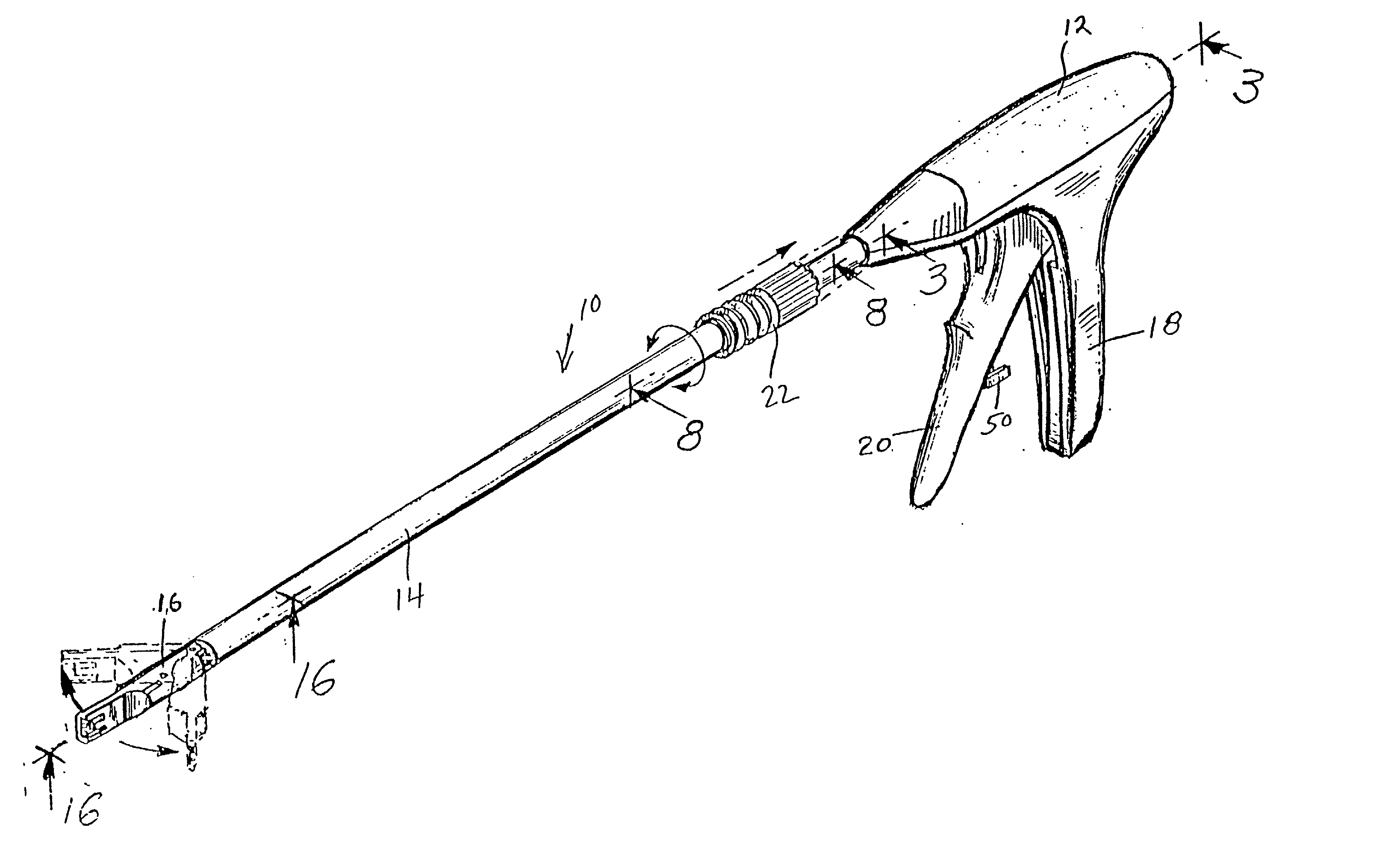
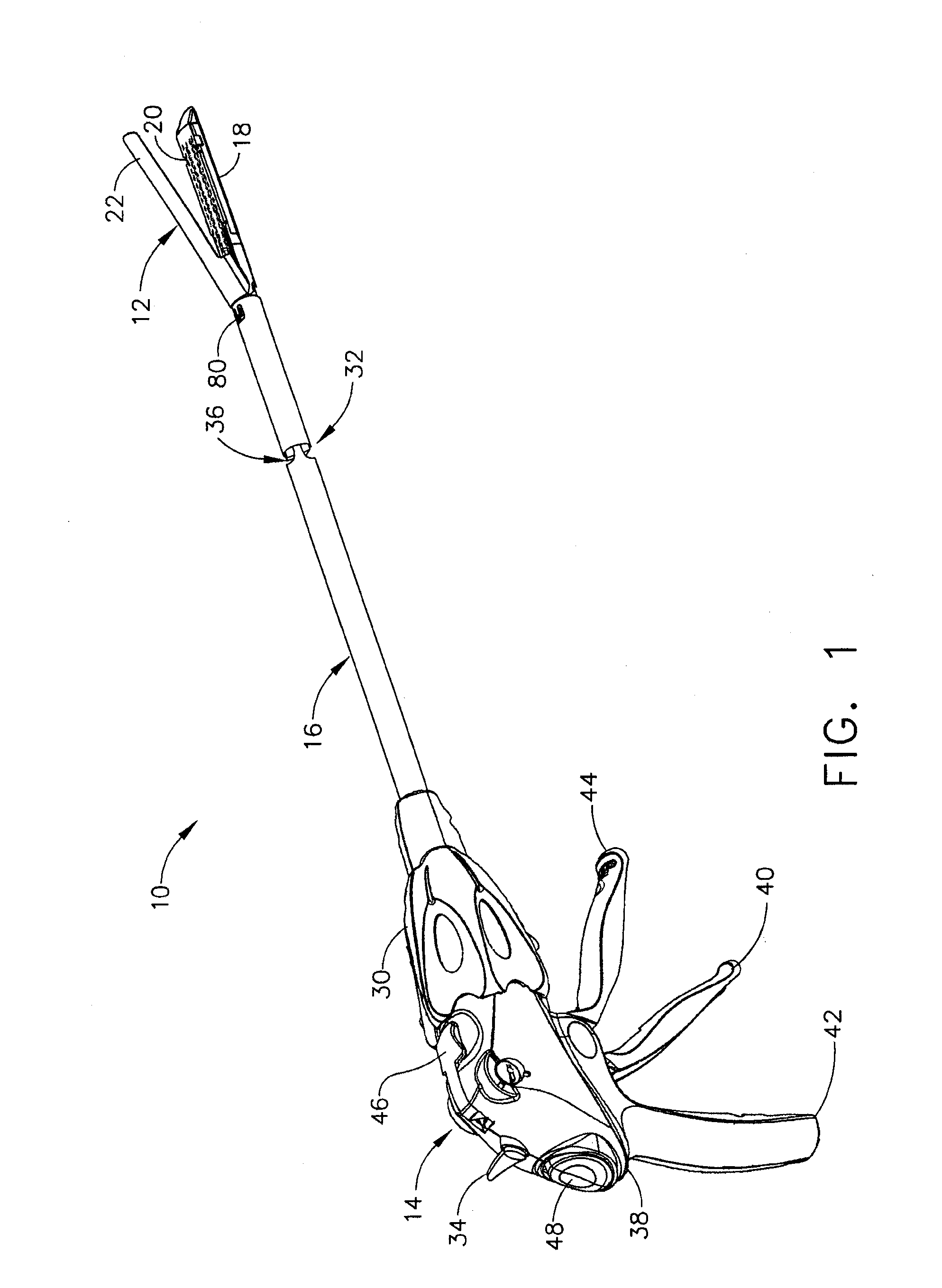
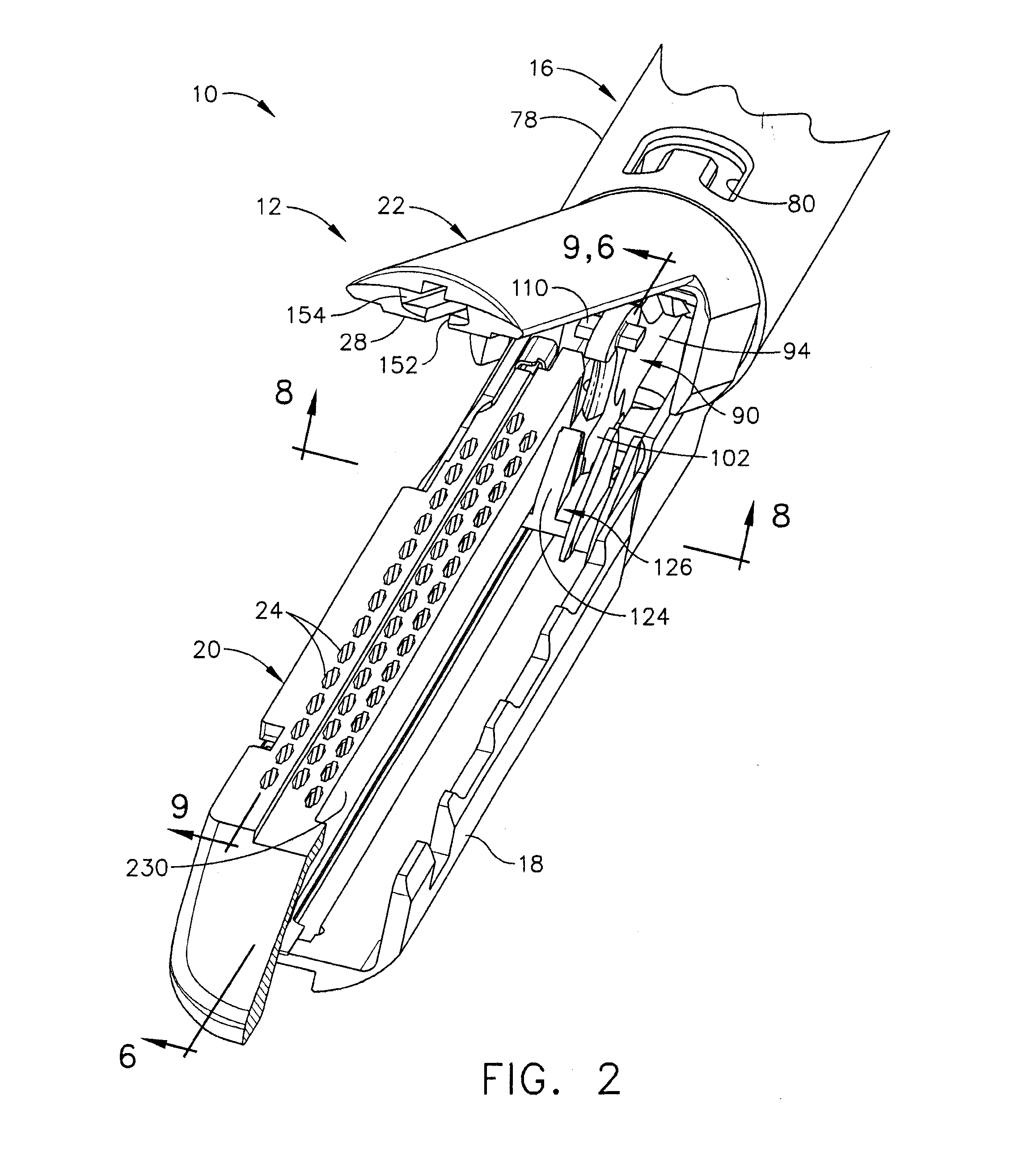
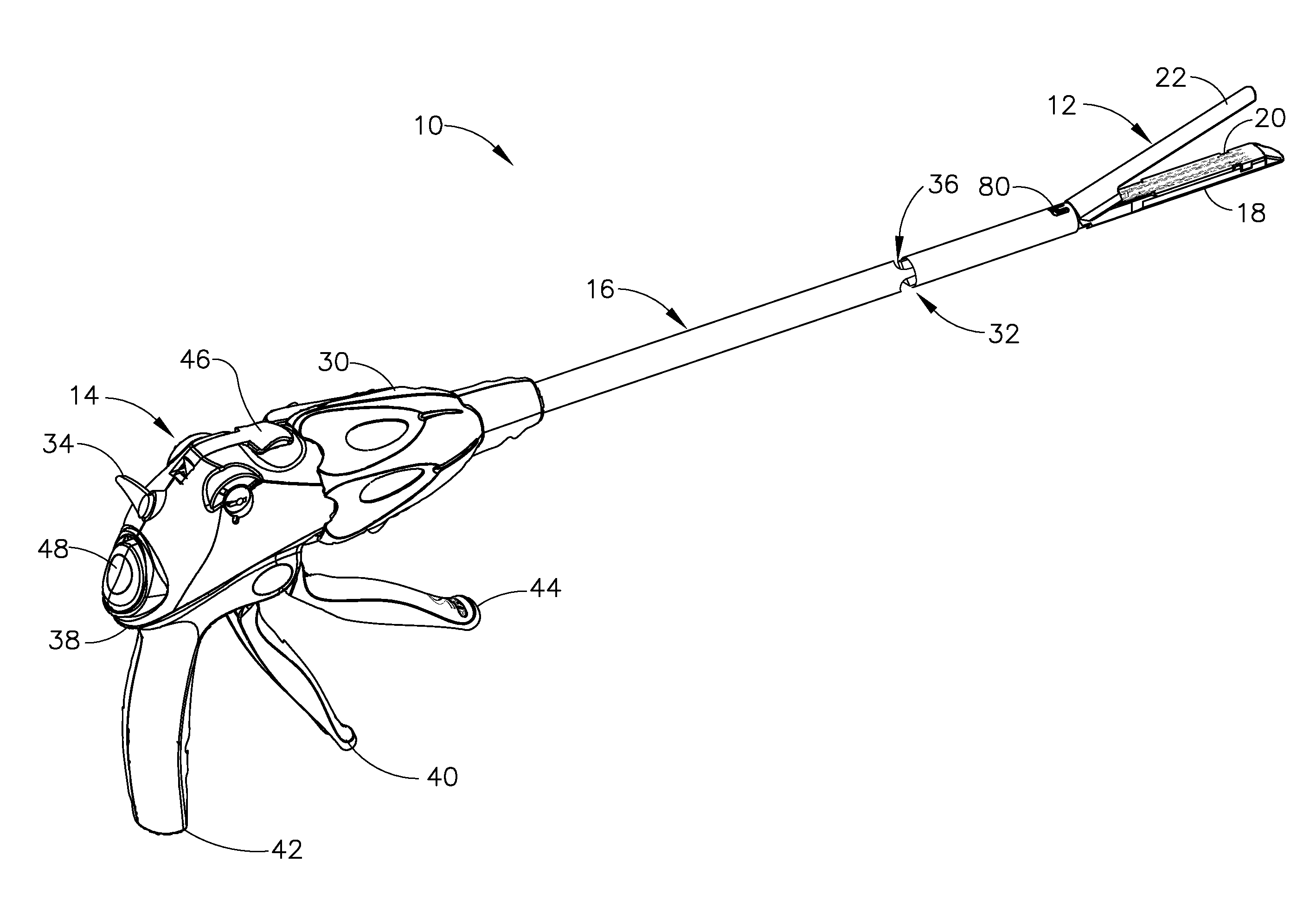
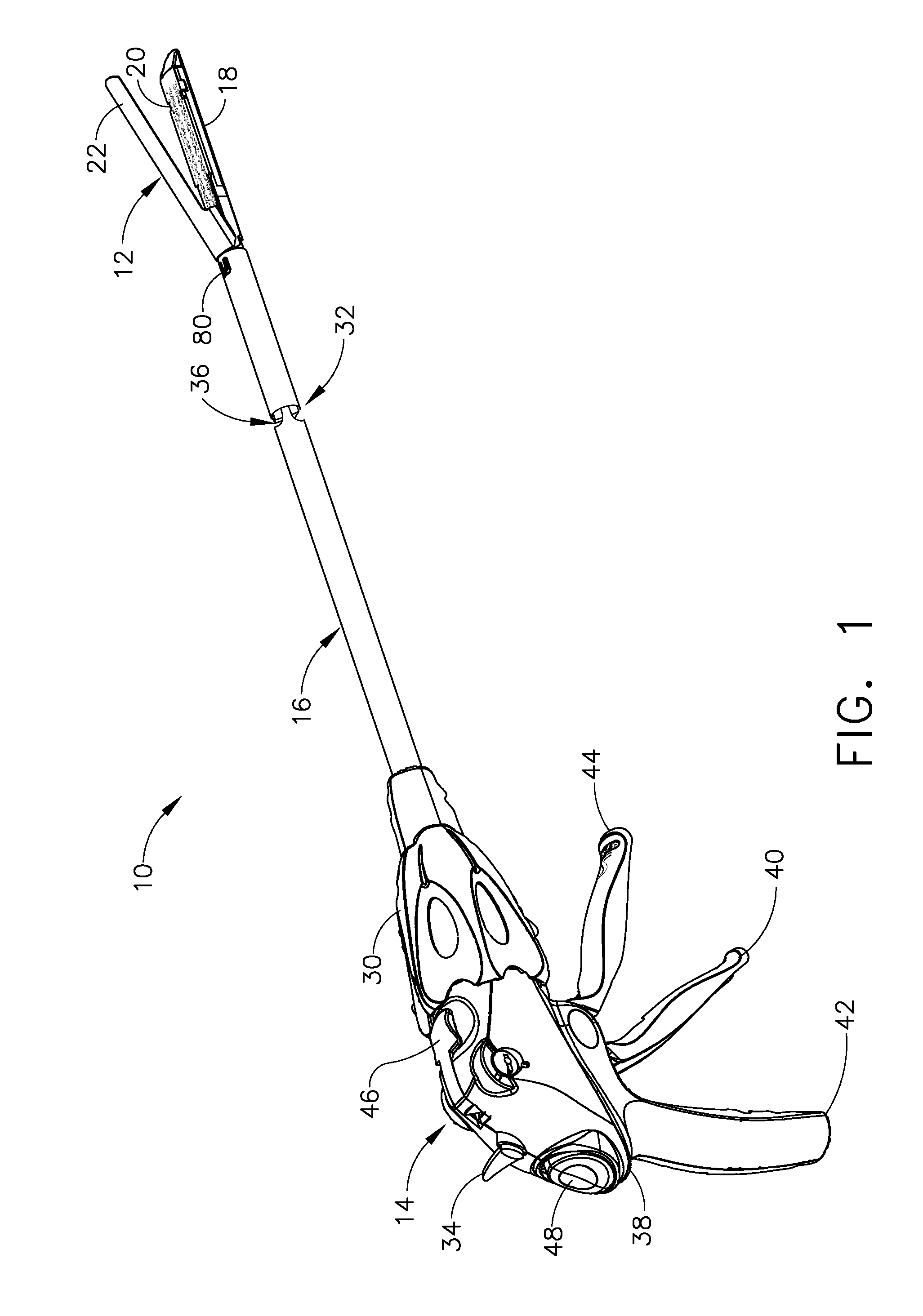
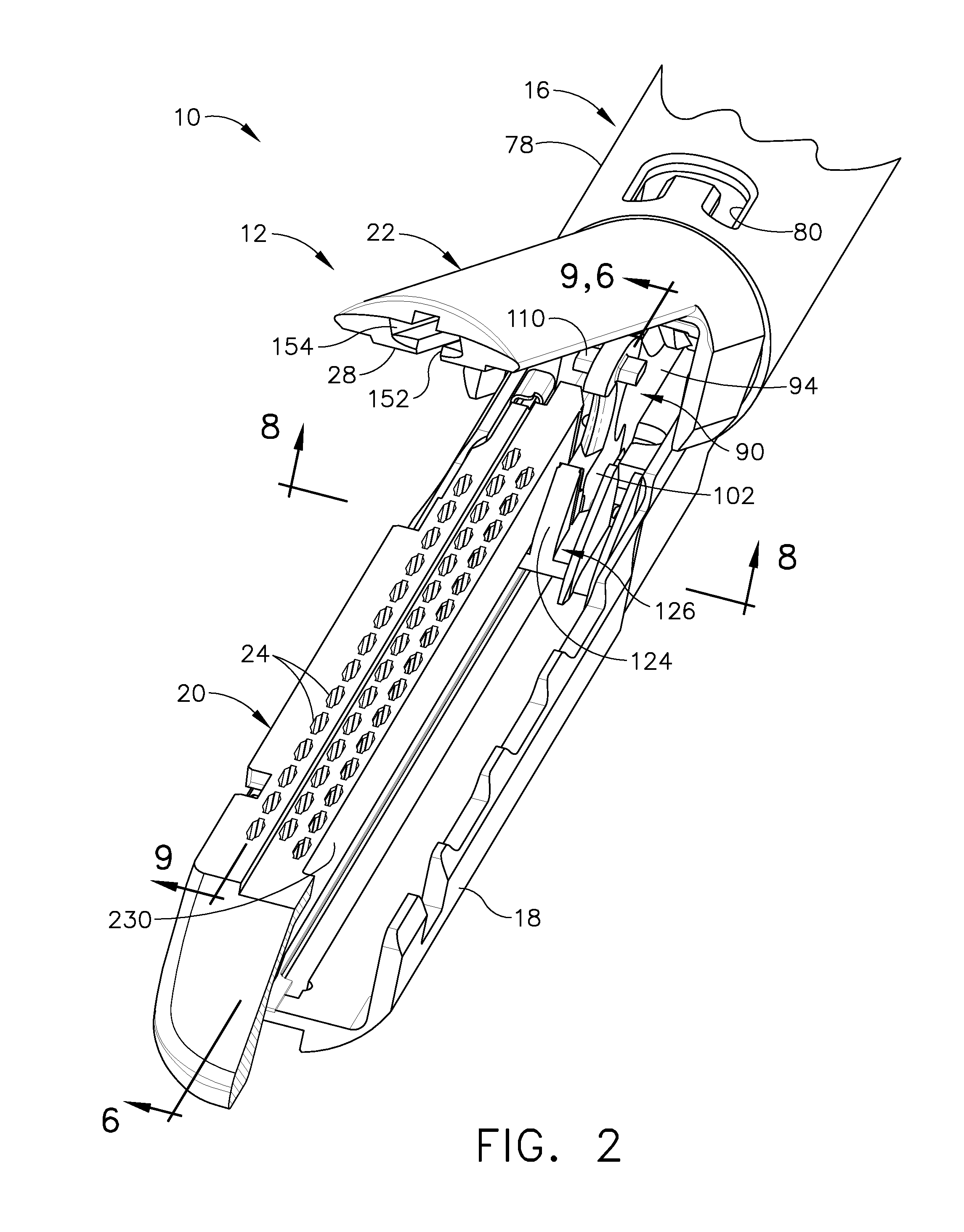
Robotic tool with wristed monopolar electrosurgical end effectors
ActiveUS7824401B2Avoid conductionSmall outer diameterDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingElectrical conductorBlood coagulations
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
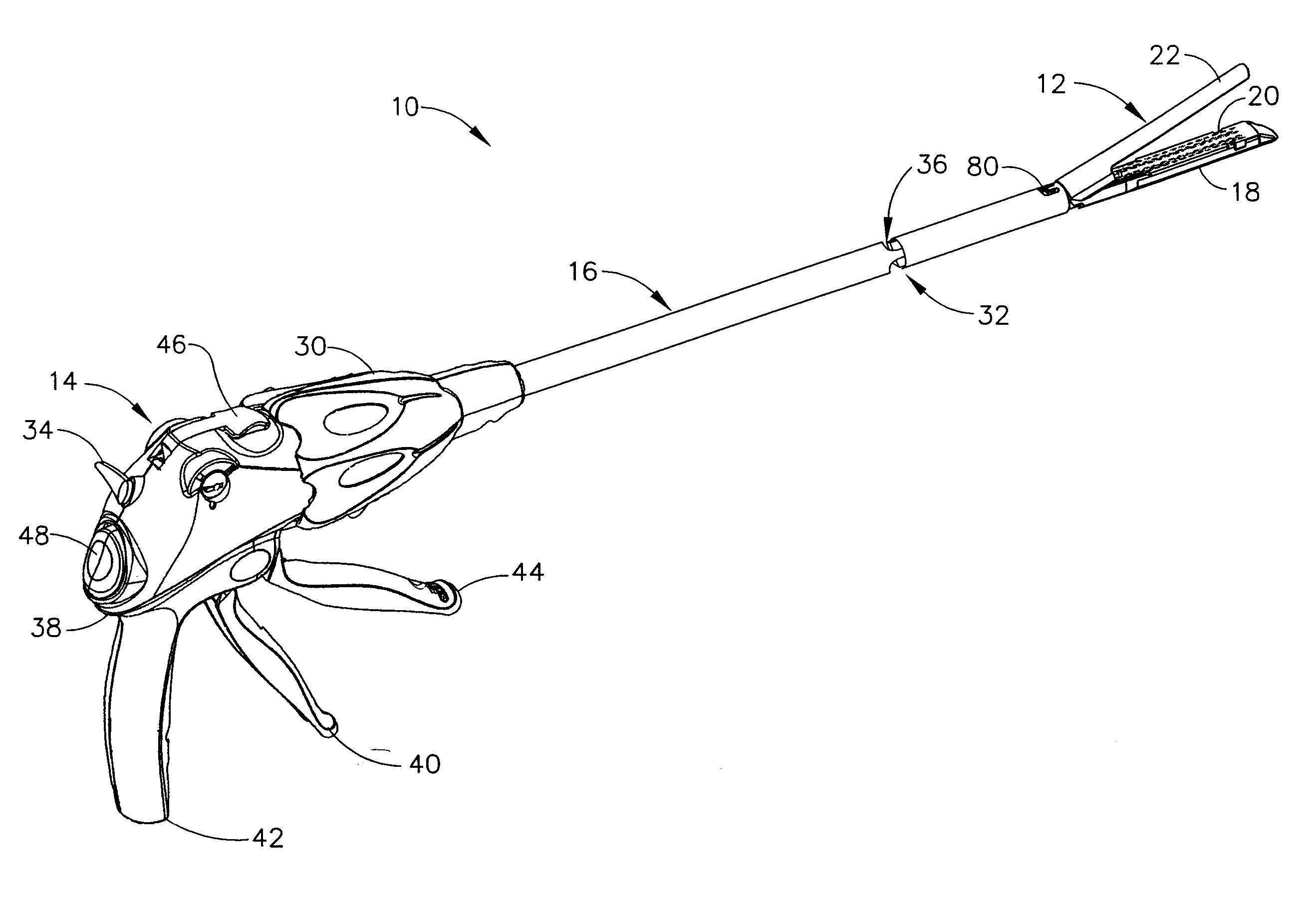
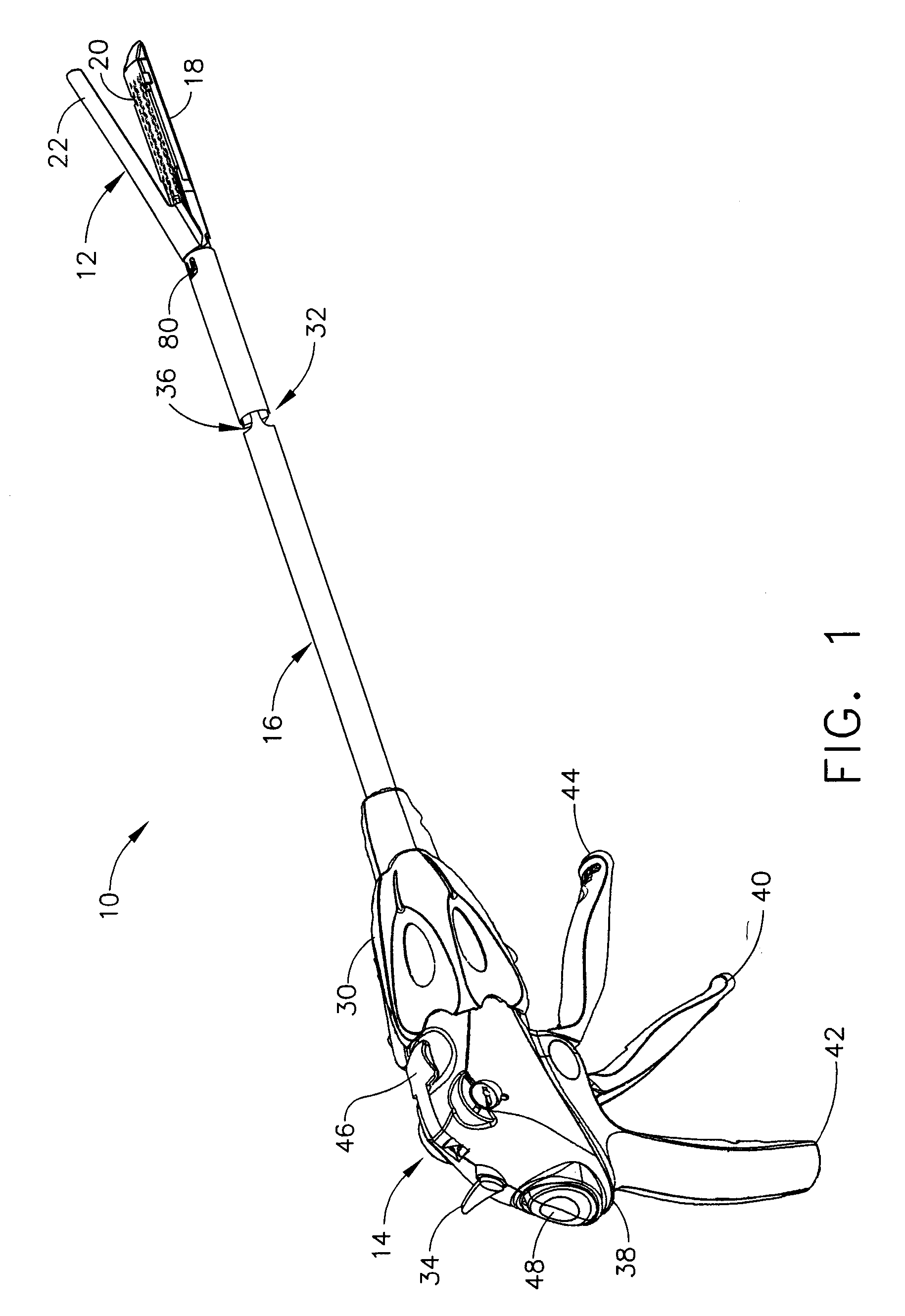
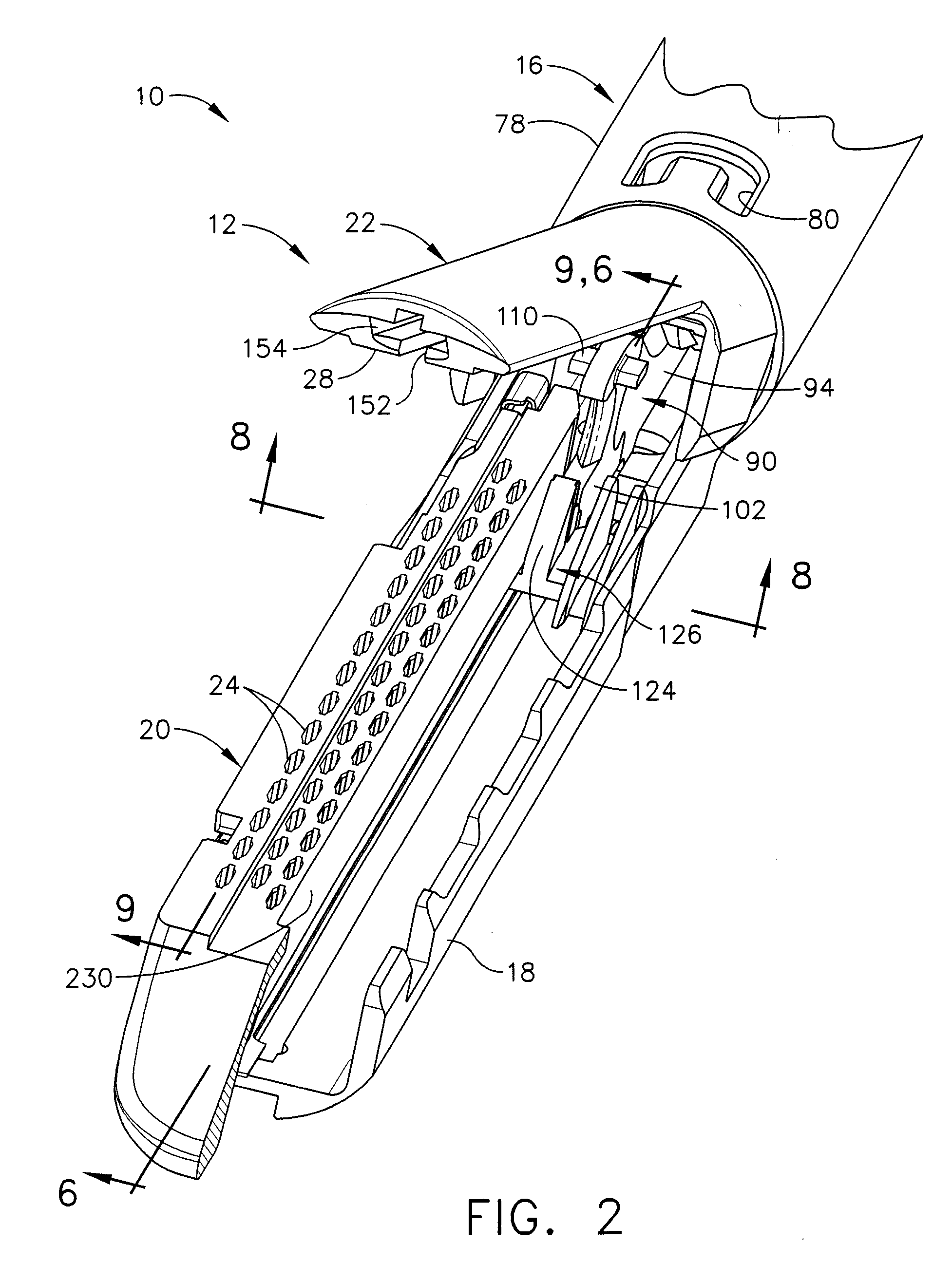
Surgical instrument having a directional switching mechanism
A surgical instrument including a switching mechanism which allows a surgeon to selectively advance or retract a staple driver and / or cutting member within a staple cartridge. In various embodiments, the surgical instrument can include a handle, a trigger operatively coupled to the handle, a firing drive, and an end effector. The firing drive can include a first ratchet assembly configured to advance a cutting member in the end effector and a second ratchet assembly configured to retract the cutting member. The trigger can include first and second pawls pivotably mounted thereon which are configured to be selectively engaged with the first and second ratchet assemblies, respectively. In at least one embodiment, the trigger can be configured to slide between a first position in which the first pawl is engaged with the first ratchet assembly and a second position in which the second pawl is engaged with the second ratchet assembly.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Powered surgical cutting and stapling apparatus with manually retractable firing system
In one general aspect, various embodiments of the present invention can include a motorized surgical cutting and fastening instrument having a drive shaft, a motor selectively engageable with the drive shaft, and a manual return mechanism configured to operably disengage the motor from the drive shaft and retract the drive shaft. In at least one embodiment, a surgeon, or other operator of the surgical instrument, can utilize the manual return mechanism to retract the drive shaft after it has been advanced, especially when the motor, or a power source supplying the motor, has failed or is otherwise unable to provide a force sufficient to retract the drive shaft.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Articulating surgical stapling instrument incorporating a two-piece e-beam firing mechanism
InactiveUS20070084897A1Solve the lack of spaceEasy to useSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleEngineering
A surgical severing and stapling instrument, suitable for laparoscopic and endoscopic clinical procedures, clamps tissue within an end effector of an elongate channel pivotally opposed by an anvil. An E-beam firing bar moves distally through the clamped end effector to sever tissue and to drive staples on each side of the cut. The E-beam firing bar affirmatively spaces the anvil from the elongate channel to assure properly formed closed staples, especially when an amount of tissue is clamped that is inadequate to space the end effector. In particular, an upper pin of the firing bar longitudinally moves through an anvil slot and a channel slot is captured between a lower cap and a middle pin of the firing bar to assure a minimum spacing. Forming the E-beam from a thickened distal portion and a thinned proximal strip enhances manufacturability and facilitates use in such articulating surgical instruments.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
End effector coupling arrangements for a surgical cutting and stapling instrument
InactiveUS20090206131A1Affected deploymentImprove the forceSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleDetent
In various embodiments, a surgical stapling instrument can include a handle, a shaft extending from the handle, wherein the shaft defines an axis, and a disposable loading unit which is assembled to the shaft in a direction which is transverse to the shaft axis. Such a connection between the disposable loading unit and the shaft can prevent, or at least inhibit, the disposable loading unit from being unintentionally displaced proximally and / or distally relative to the shaft of the surgical instrument. The surgical stapling instrument and / or disposable loading unit can further include a threaded collar and / or detent assembly configured to hold the disposable loading unit in place. In various embodiments, a disposable loading unit can include a lockout feature which can prevent, or at least inhibit, an expended disposable loading unit from being reassembled to the elongated body of the surgical instrument.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Palm-size surgical stapler for single hand operation
Owner:NITI SURGICAL SOLUTIONS
Articulating surgical stapling instrument incorporating a two-piece e-beam firing mechanism
InactiveUS20110147433A1Solve the lack of spaceEasy to useSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleEngineering
A surgical severing and stapling instrument, suitable for laparoscopic and endoscopic clinical procedures, clamps tissue within an end effector of an elongate channel pivotally opposed by an anvil. An E-beam firing bar moves distally through the clamped end effector to sever tissue and to drive staples on each side of the cut. The E-beam firing bar affirmatively spaces the anvil from the elongate channel to assure properly formed closed staples, especially when an amount of tissue is clamped that is inadequate to space the end effector. In particular, an upper pin of the firing bar longitudinally moves through an anvil slot and a channel slot is captured between a lower cap and a middle pin of the firing bar to assure a minimum spacing. Forming the E-beam from a thickened distal portion and a thinned proximal strip enhances manufacturability and facilitates use in such articulating surgical instruments.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Disposable loading units for a surgical cutting and stapling instrument
InactiveUS20090206137A1Affected deploymentImprove the forceSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical instrumentSurgical department
In various embodiments, a disposable loading unit for a surgical stapling instrument can include an anvil, a staple cartridge, a staple cartridge channel for operably supporting the staple cartridge, and a connector for removably attaching the disposable loading unit to the surgical instrument. In at least one embodiment, a first staple cartridge can be replaced with another staple cartridge after the first staple cartridge has been at least partially expended. In various embodiments, a staple cartridge can include a staple driver for deploying staples from the staple cartridge and a cutting member for incising tissue, wherein a new staple driver and a new cutting member can be provided with each new staple cartridge. The anvil can be removably attachable to the disposable loading unit such that a new anvil can be utilized with a new staple cartridge.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC +1
Circular stapler introducer with multi-lumen sheath
Owner:CILAG GMBH INTERNATIONAL +1
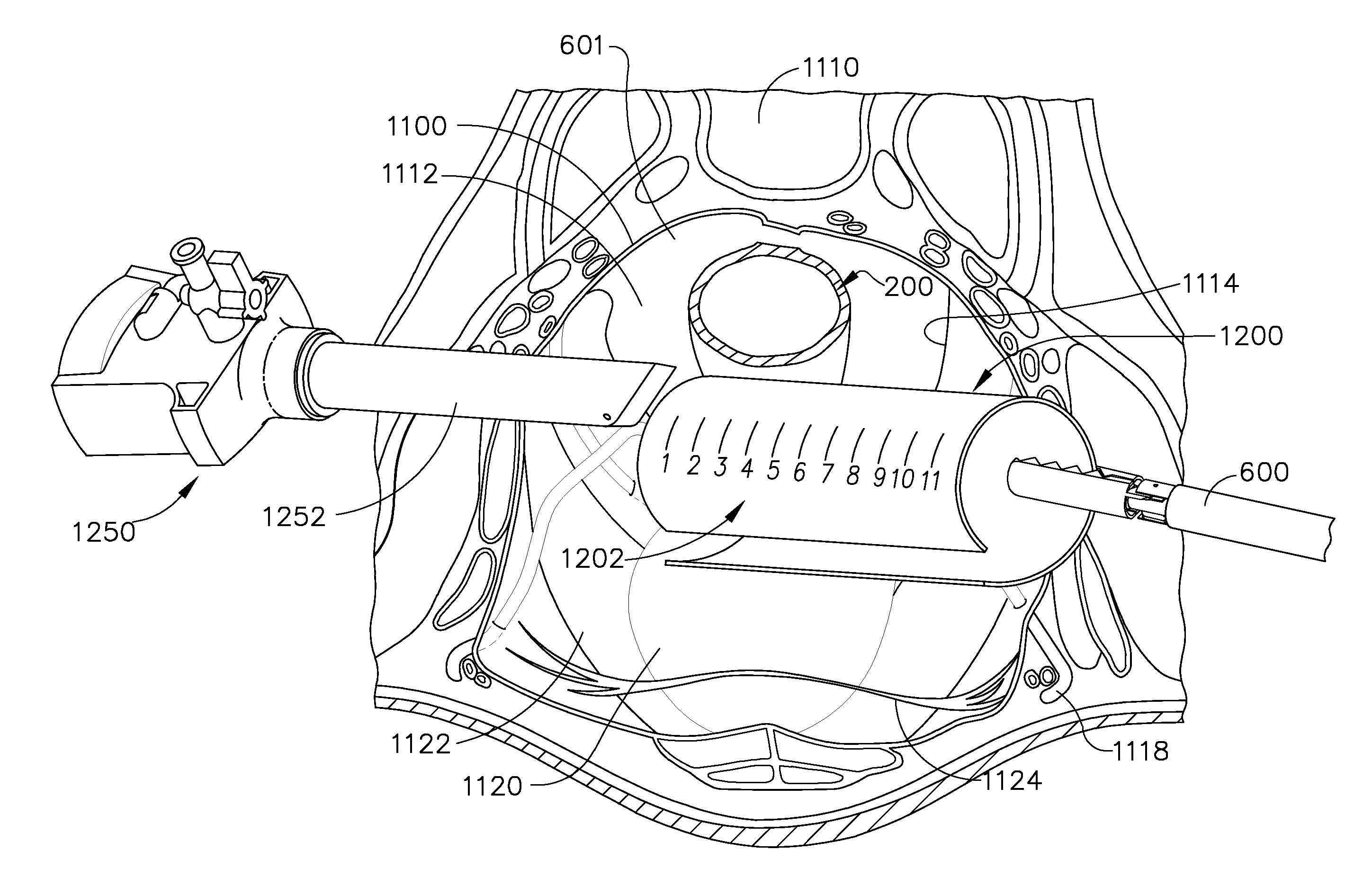
Apparatus and method for applying surgical staples to attach an object to body tissue
InactiveUS20020117534A1Avoid deformationSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSupporting systemSurgical staple
An apparatus is disclosed for endoscopic application of surgical staples adapted to attach surgical mesh to body tissue in laparoscopic hernia surgery. The apparatus includes a frame, and a generally elongated endoscopic section connected to the frame and extending distally therefrom. A staple storage cartridge is removably supported on a pivotal support system at the distal end portion of the endoscopic section with each staple being configured and adapted to attach the mesh to the body tissue. An elongated pusher system formed of several assembled components and extending from the frame to the endoscopic section is provided for individually advancing at least one staple at a time distally for positioning adjacent the surgical mesh and the body tissue. The pusher system also includes a trigger system to actuate the pusher. The trigger system is provided with perceptible tactile sensing means to indicate when the legs of the staple being advanced are exposed so as to be visible to the user for positioning and orientation purposes. Anvil means provides for individually closing each staple to encompass at least a portion of the surgical mesh and to penetrate the body tissue in a manner to attach the portion of the mesh to the body tissue. Projecting distally of the cartridge support system is a pair of legs which are dimensioned and configured to engage the staple during closure to prevent unwanted roll or deformation outside of the plane of the staple.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Bipolar cauterizing instrument
A bipolar surgical instrument that includes opposing grips that can engage the tissue. A current is delivered from an electrosurgical power source to electrodes disposed on the grips to cauterize the tissue. The electrode configurations provide efficient cauterization of the tissue. In some embodiments, the positive and negative electrodes will be offset from each other to prevent shorting and to provide a thin line of coagulation heating to the gripped tissue. In some embodiments the electrodes are removably coupled to the grips through nonconductive sleeves. In some embodiments, the first electrode is disposed in a groove and the second electrode is disposed on a boss.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Apparatus and methods for protecting adjacent structures during the insertion of a surgical instrument into a tubular organ
A device for protecting tissues and structures adjacent to a tubular organ during performance of a surgical procedure on a portion of the tubular organ. Various embodiments may comprise a member that may be deployed through a surgical instrument in a first configuration and expanded to a second configuration such that when in the second configuration, the protective member may extend substantially around an outer circumference of the portion of the tubular organ.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Surgery delivery device and mesh anchor
A delivery device for delivering a plurality of individual surgical anchors is disclosed. The delivery device includes a housing, a delivery tube, having a distal and a proximal end, an actuator, flexible anchor reaction members, a reciprocating anchor carrier, having a distal and a proximal end, the distal end terminating in a tissue penetrator. The device further includes at least one surgical anchor located in juxtaposition with the anchor carrier. Each of the surgical anchors has a penetration section and a head section. The surgical anchors are preferably made from an absorbable polymer. The actuator is connected to the anchor carrier and has at least two states. The first, or home state, is a position such that the surgical anchor is proximal the distal end of the tube. The second state is such that the penetrating section of the surgical anchor is exposed beyond the distal end of the delivery tube.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Surgical stapling instrument
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
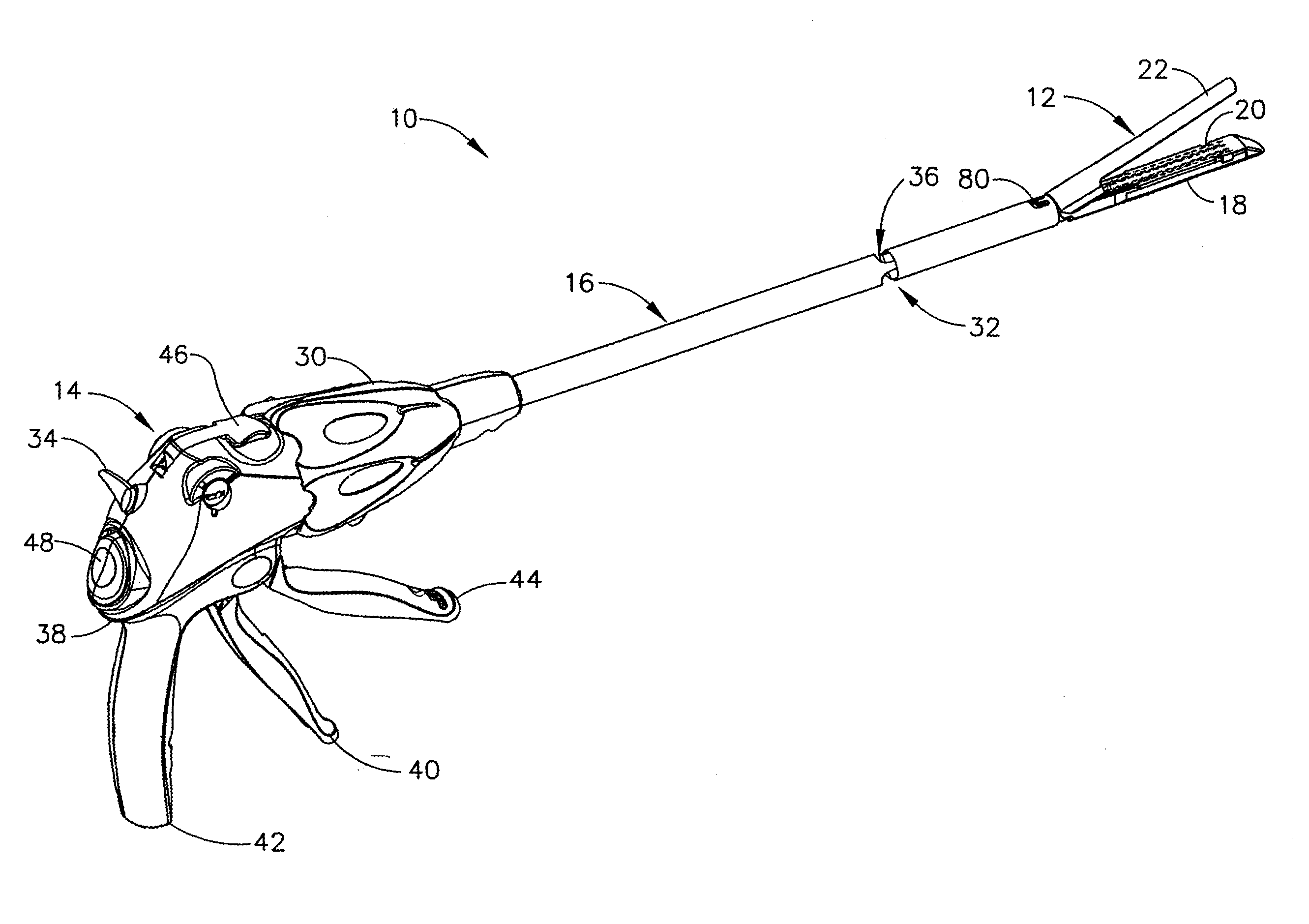
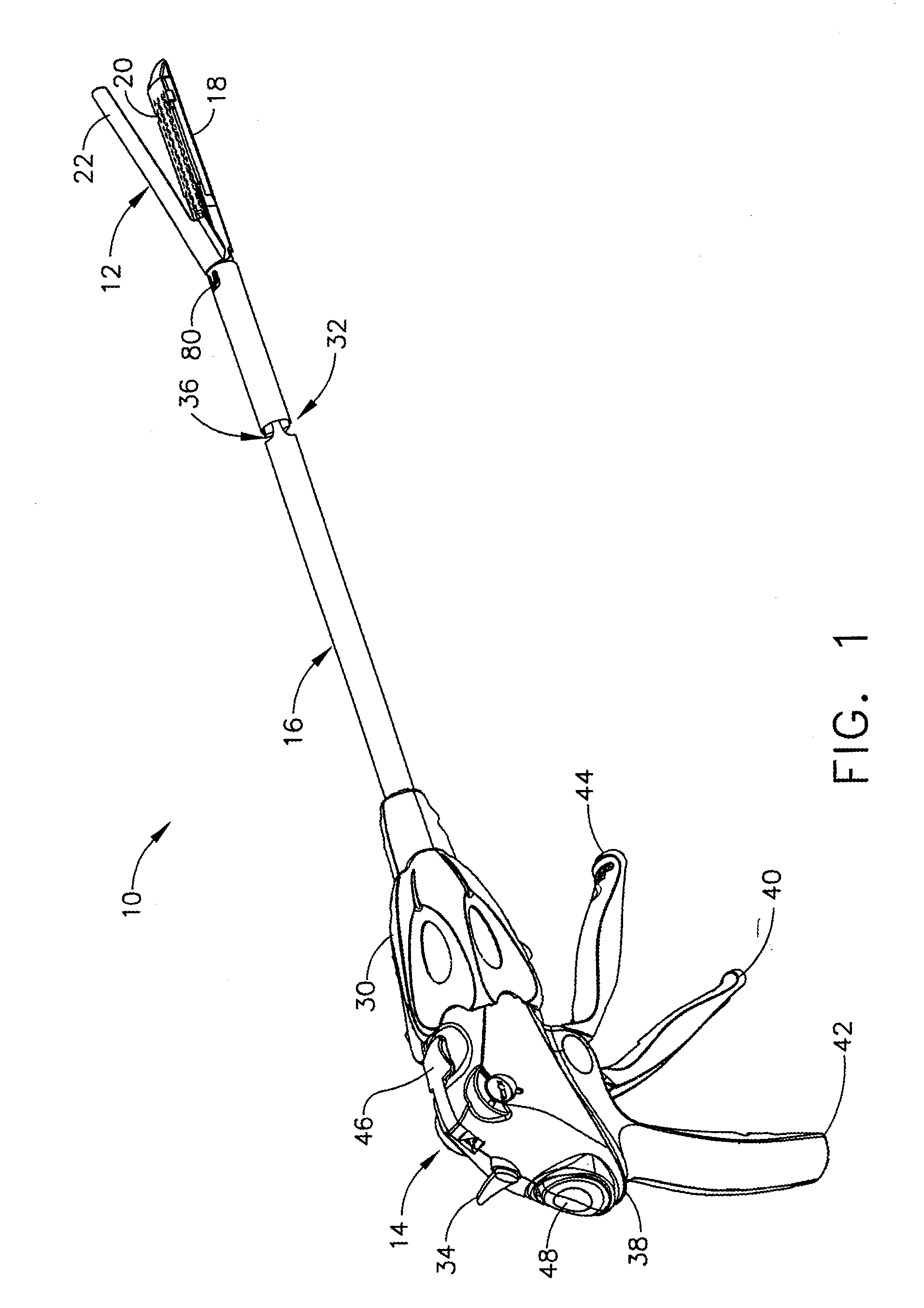
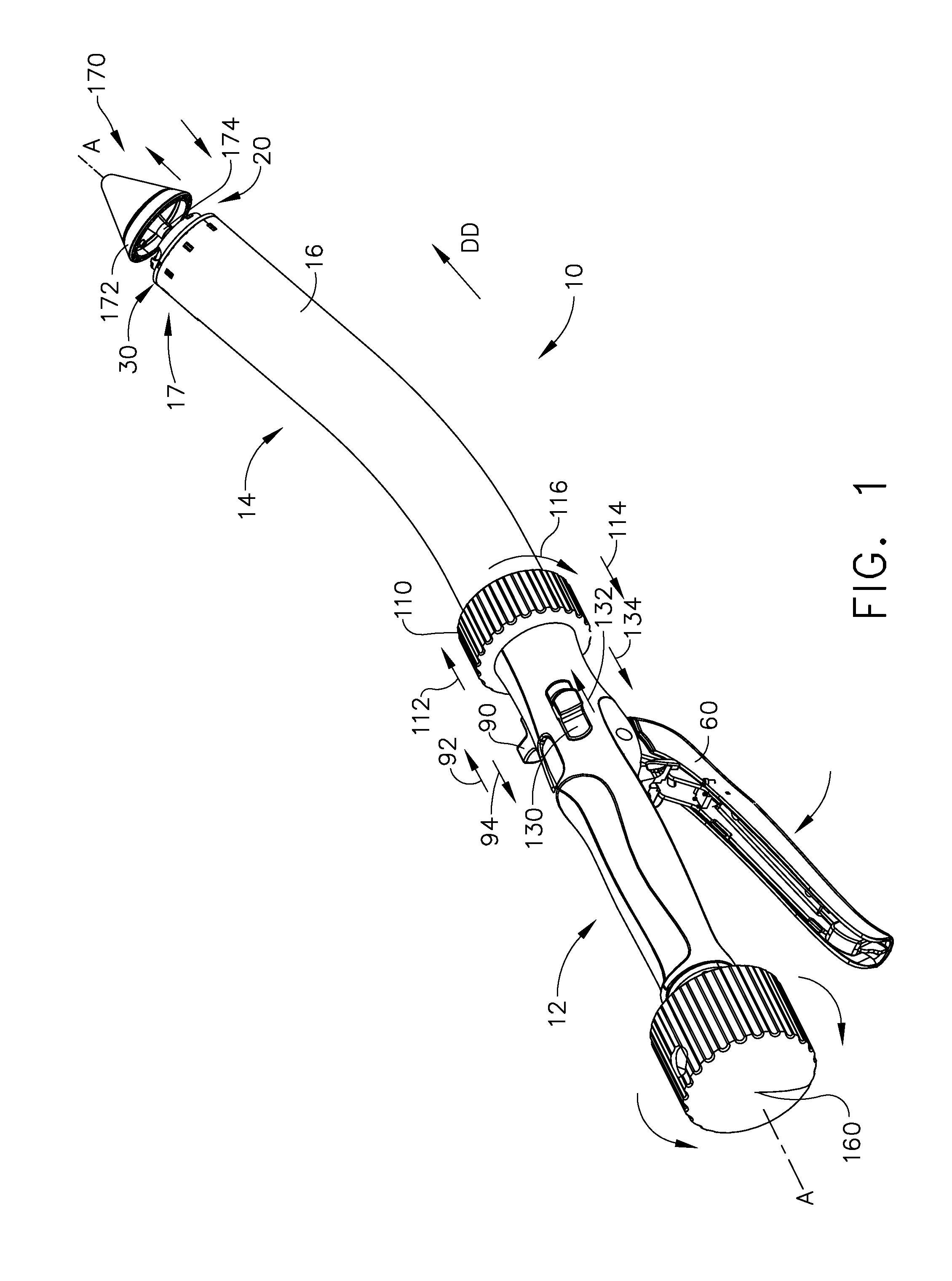
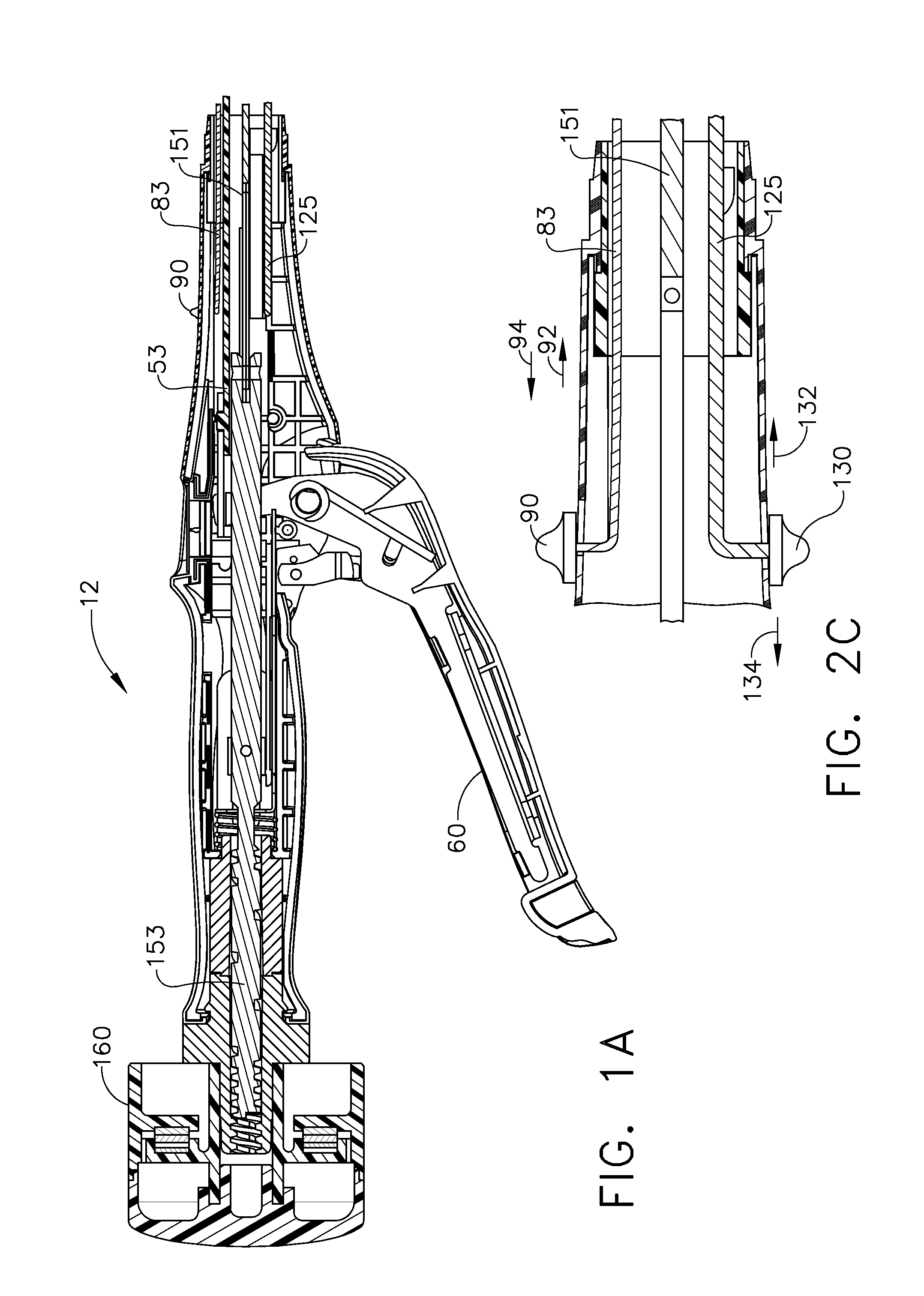
Articulating surgical device
An articulation mechanism for a surgical instrument includes an articulation assembly, a plurality of cables, and a trigger. The cables are coupled to the articulation assembly at a proximal end thereof and extend distally therefrom. The cables are configured to engage an end effector assembly of the surgical instrument at a distal end thereof. The trigger is coupled to the articulation assembly and is selectively moveable from a shipping position to a use position. In the shipping position, the cables are substantially un-tensioned. In the use position, the cables are disposed in an initial tensioned position. In the use position, the trigger is moveable between an unlocked position and a locked position. In the unlocked position, the cables are selectively tensionable to articulate the end effector assembly. In the locked position, the tensions on the cables are maintained to lock the end effector assembly in position.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method and force-limiting handle mechanism for a surgical instrument
A safety handle assembly for use with a surgical instrument having an operative distal end portion is disclosed. The handle assembly includes a handle housing and a drive element movably mounted within the handle housing and connected to an associated operative distal end portion. A drive assembly is positioned within the handle housing and is engageable with the drive element to move the drive element within the handle housing. An actuator is movably mounted on the handle housing and an adjustable force-limiting mechanism is interposed between the drive assembly and the actuator. A force-limiting mechanism releasably connects the actuator to the drive assembly. The force-limiting mechanism is adjustable to preset the force at which the actuator separates or breaks away from the drive assembly.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
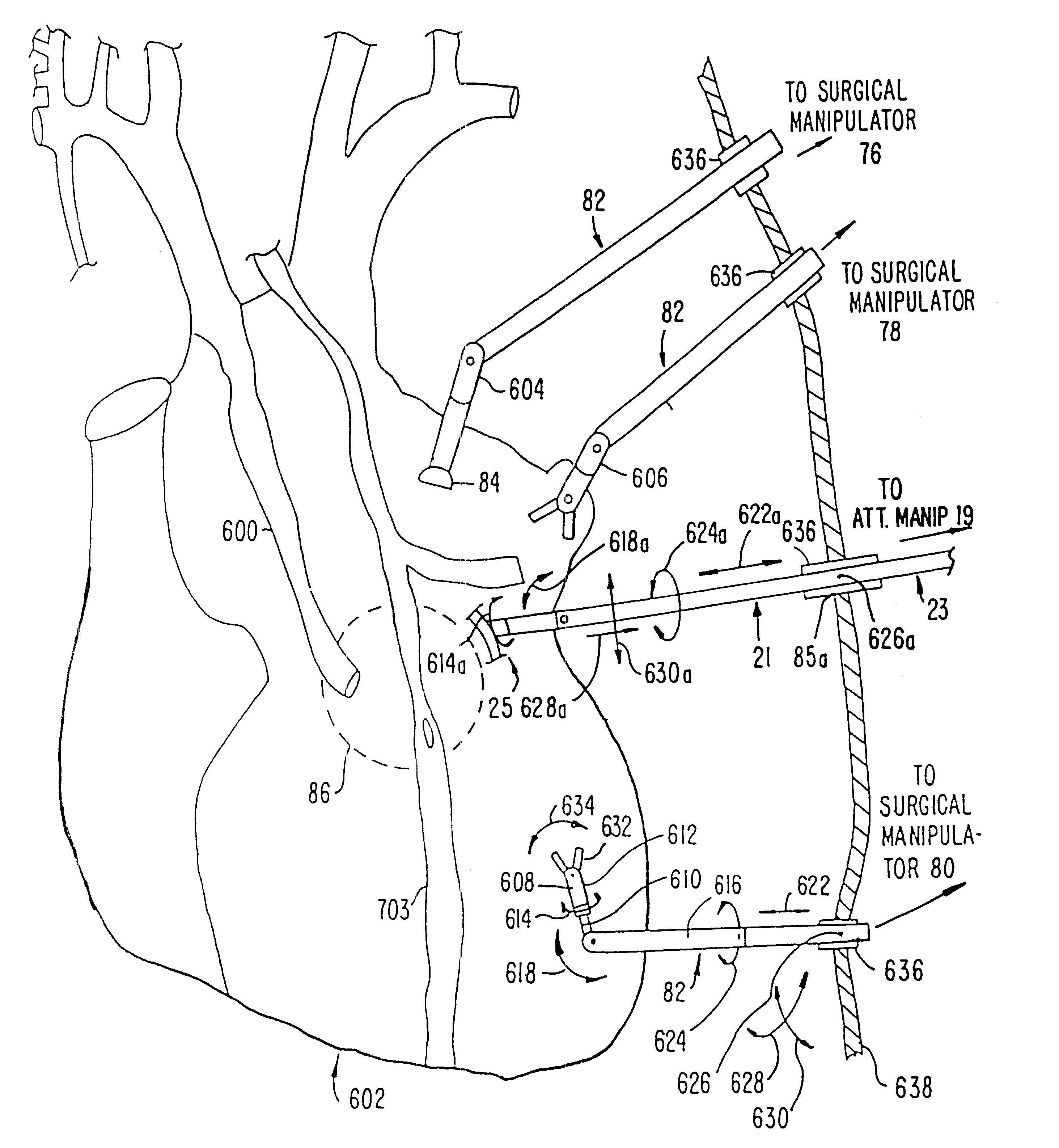
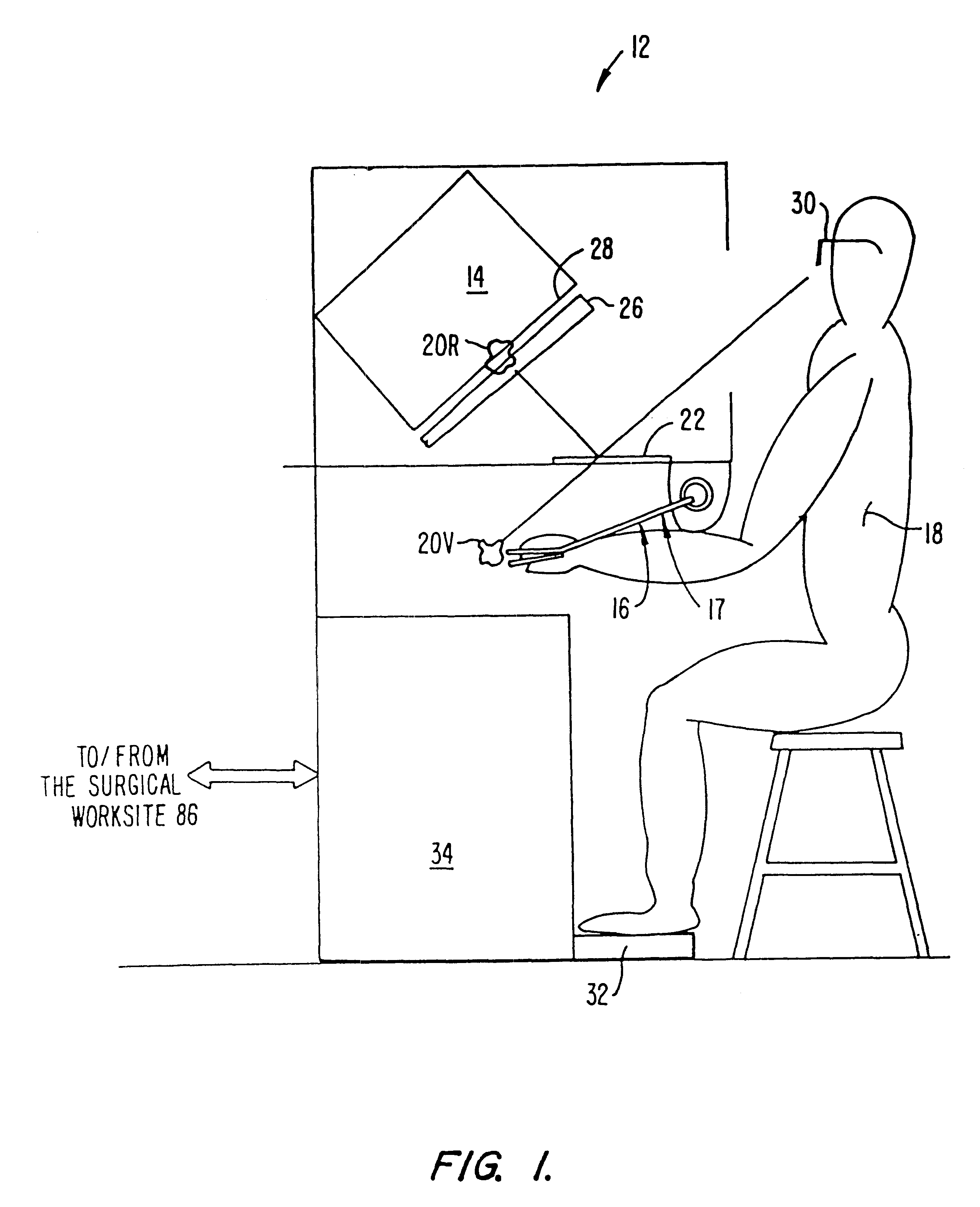
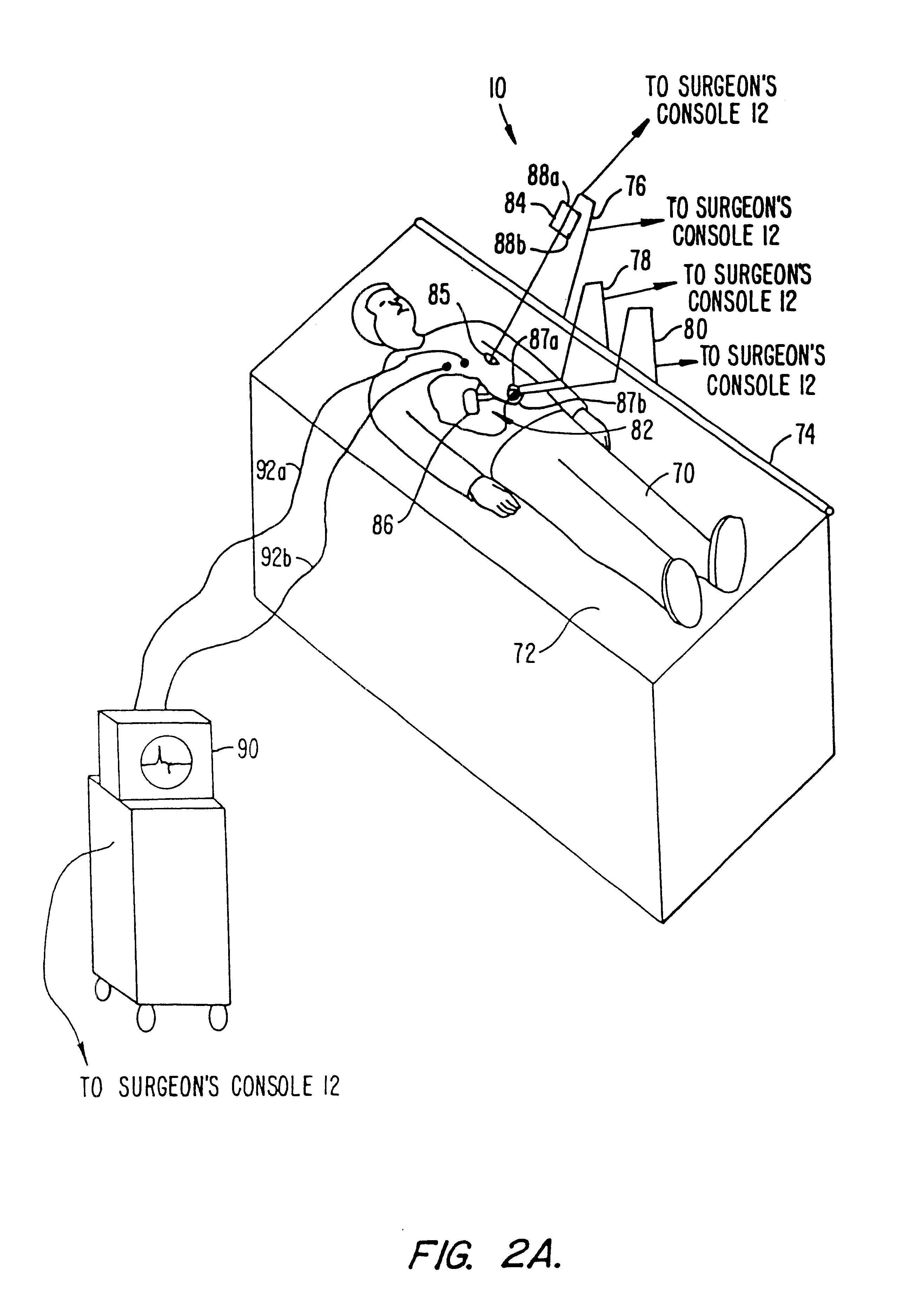
Performing cardiac surgery without cardioplegia
InactiveUS6468265B1Improve abilitiesEasy to controlSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsForcepsMotion tracking system
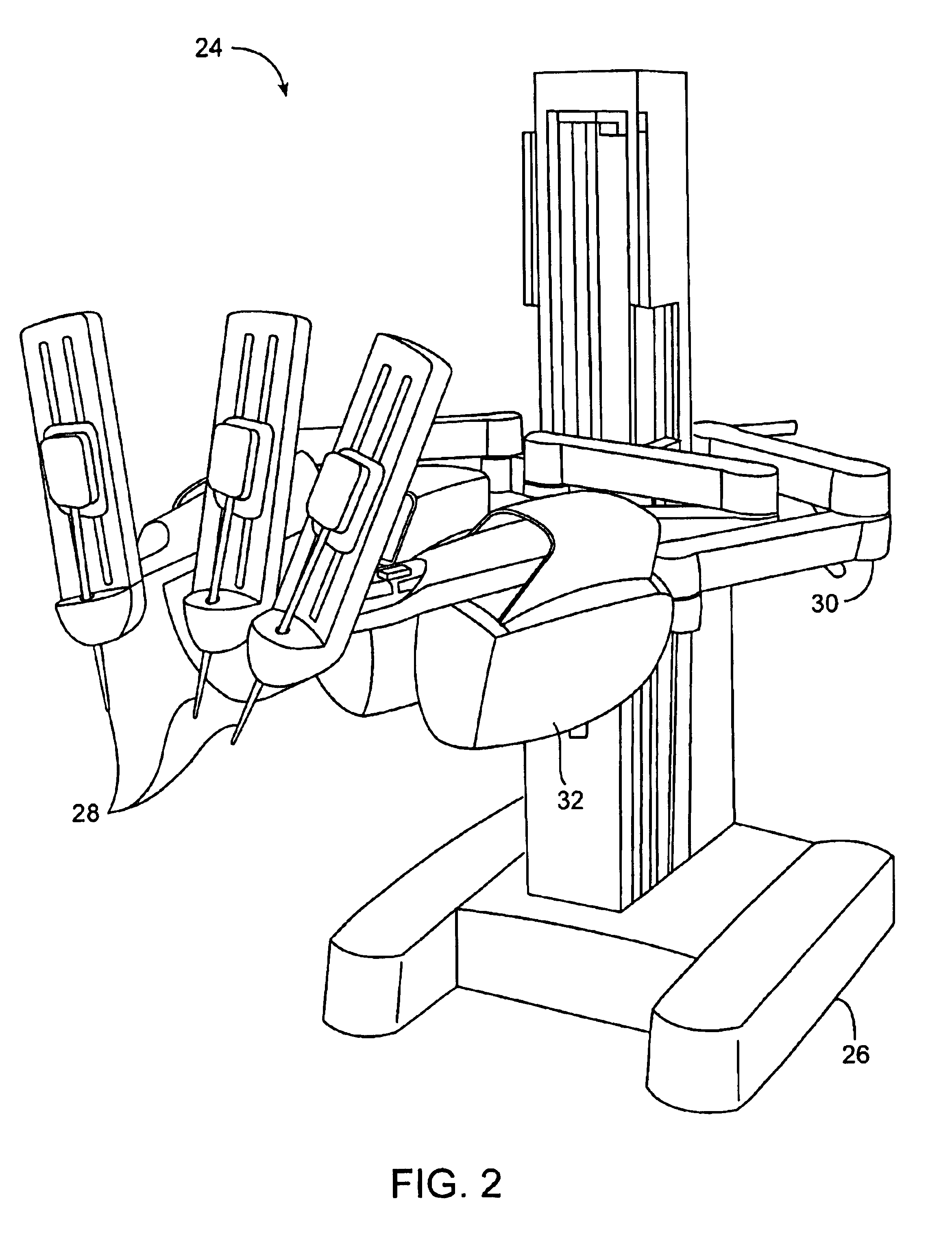
A surgical system or assembly for performing cardiac surgery includes a surgical instrument; a servo-mechanical system engaged to the surgical instrument for operating the surgical instrument; and an attachment assembly for removing at least one degree of movement from a moving surgical cardiac worksite to produce a resultant surgical cardiac worksite. The surgical system or assembly also includes a motion tracking system for gathering movement information on a resultant surgical cardiac worksite. A control computer is engaged to the attachment assembly and to the motion tracking system and to the servo-mechanical system for controlling movement of the attachment assembly and for feeding gathered information to the servo-mechanical system for moving the surgical instrument in unison with the resultant surgical cardiac worksite such that a relative position of the moving surgical instrument with respect to the resultant surgical cardiac worksite is generally constant. A video monitor is coupled to the control computer; and an input system is coupled to the servo-mechanical system and to the control computer for providing a movement of the surgical instrument. The video monitor displays movement of the surgical instrument while the resultant surgical cardiac worksite appears substantially stationary, and while a relative position of the surgical instrument moving in unison with the resultant surgical cardiac worksite, as a result from the movement information gathered by the motion tracking system, remains generally constant. A method of performing cardiac surgery without cardioplegia comprising removing at least one degree of movement freedom from a moving surgical cardiac worksite to produce at least a partially stationary surgical cardiac worksite while allowing a residual heart section, generally separate from the at least partially stationary surgical cardiac worksite, to move as a residual moving heart part. Cardiac surgery is performed on the at least partially stationary cardiac worksite with a surgical instrument such as needle drivers, forceps, blades and scissors.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Endoscopic surgical clip applier
An apparatus for application of surgical clips to body tissue has a handle portion with a body extending distally from the handle portion defining a longitudinal axis and a plurality of surgical clips disposed within the body. The apparatus also has a jaw assembly mounted adjacent a distal end portion of the body with the jaw assembly including first and second jaw portions movable between a spaced-apart and an approximated position. The apparatus further has a wedge plate longitudinally movable between the first and the second jaw portions, and a clip pusher configured to individually distally advance a surgical clip to the jaw assembly while the jaw portions are in the spaced apart position with an actuator. The actuator is at least partially disposed within the body and longitudinally movable in response to actuation of the handle portion and has a cam link. The apparatus also has a jaw closure member positioned adjacent the first and second jaw portions to move the jaw portions to the approximated position. The cam link longitudinally moves wedge plate between the first and the second jaw portions.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Shield for surgical stapler and method of use
InactiveUS20100163598A1Reduce traumaEasy to browseSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEngineeringSurgical department
A surgical stapler that may have a head assembly, a stapling assembly, a shield, a base head, a handle assembly, and a shaft assembly. A head assembly may have an anvil and anvil shaft, as well as a stapling assembly. A stapling assembly may have a trocar that can be removeably detachable with the anvil, a cannula extension, and a plurality of staples. A shield may be configured to retract from a first extended position where the shield generally covers the stapling assembly or the head assembly, to a second retracted position where the shield generally exposes the stapling assembly or the head assembly. The shield may be integral with the stapler, or provided after-market as an add-on. A surgical stapler may additionally or alternatively include an air or gas pump assembly that can be used to insufflate the rectum and intestinal tract during insertion and advancement of the stapler.
Owner:BELZER GEORGE E
Surgery delivery device and mesh anchor
A delivery device for delivering a plurality of individual surgical anchors is disclosed. The delivery device comprises a housing, a delivery tube, having a distal and a proximal end, an actuator, flexible anchor reaction members, a reciprocating anchor carrier, having a distal and a proximal end, the distal end terminating in a tissue penetrator. The device further includes at least one surgical anchor located in juxtaposition with the anchor carrier. Each of the surgical anchors has a penetration section and a head section. The surgical anchors are preferably made from an absorbable polymer. The actuator is connected to the anchor carrier and has at least two states. The first, or home state, comprises a position such that the surgical anchor is proximal the distal end of the tube. The second state is such that the penetrating section of the surgical anchor is exposed beyond the distal end of the delivery tube.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Robotically-driven surgical instrument with e-beam driver
ActiveUS20110290853A1Solve the lack of spaceEasy to useSuture equipmentsStapling toolsRobotic systemsSurgical instrumentation
A surgical severing and stapling instrument, suitable for laparoscopic and endoscopic clinical procedures, clamps tissue within an end effector of an elongate channel pivotally opposed by an anvil. Various embodiments are configured to be operably attached to a robotic system to receive actuation / control motions therefrom.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Robotically-controlled surgical end effector system
ActiveUS20120203247A1Solve the lack of spaceEasy to useSuture equipmentsStapling toolsRobotic systemsPERITONEOSCOPE
A surgical severing and stapling instrument, suitable for laparoscopic and endoscopic clinical procedures, clamps tissue within an end effector of an elongate channel pivotally opposed by an anvil. Various embodiments are configured to be operably attached to a robotic system to receive actuation / control motions therefrom.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Implantable joint prosthesis
InactiveUS20020035400A1Improve wear resistanceImprove tribological propertiesDiagnosticsJoint implantsRange of motionIntervertebral disc
The invention relates to a surgical implant that provides an artificial diarthroidal-like joint, suitable for use in replacing any joint, but particularly suitable for use as an intervertebral disc endoprosthesis. The invention contains two rigid opposing shells, each having an outer surface adapted to engage the surfaces of the bones of a joint in such a way that the shells are immobilized by friction between their outer surfaces and the surfaces of the bone. These outer surfaces are sufficiently rough that large frictional forces strongly resist any slippage between the outer surface and the bone surfaces in the joint. They may be convex, and when inserted into a milled concavity, are immediately mechanically stable. Desirably, the outer surfaces of the shells are adapted to allow for bony ingrowth, which further stabilizes the shells in place. The inner surfaces of the shells are relatively smooth, and adapted to slide easily across a portion of the outer surface of a central body disposed between the shells. The central body has a shape that cooperates with the shape of the inner surface of the shell so as to provide a range of motion similar to that provided by a healthy joint. A flexible sheath extends between edges of the opposing shells. The inner surface of this sheath, together with the inner surfaces of the rigid shells, defines a cavity encasing the central body. At least a portion of this cavity is filled with a fluid lubricant, further decreasing the frictional force between inner surfaces of the shell and the surface of the central body.
Owner:SPINAL DYNAMICS CORP
Method of internally potting or sealing a handheld medical device
The present disclosure provides a powered surgical instrument including a housing defining an inner cavity therein; at least one internal component disposed within the housing; and potting material injected into the inner cavity encapsulating at least a portion of the at least one internal component.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Ultrasonic surgical instruments
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Surgical staples with expandable backspan
A surgical staple includes a body having a first leg, a second leg, and a backspan. The first and second legs each have a first end portion and a second end portion. The backspan has a first portion, a second portion, and a third portion. The first portion of the backspan includes a looped member having a first end portion and a second end portion. The second portion of the backspan extends between the first end portion of the first leg and the first end portion of the looped member. The third portion of the backspan extends between the first end portion of the second leg and the second end portion of the looped member. The second portion of the backspan and the third portion of the backspan are in lateral contact.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Devices and methods for introducing a surgical circular stapling instrument into a patient
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical stapling device with firing indicator
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
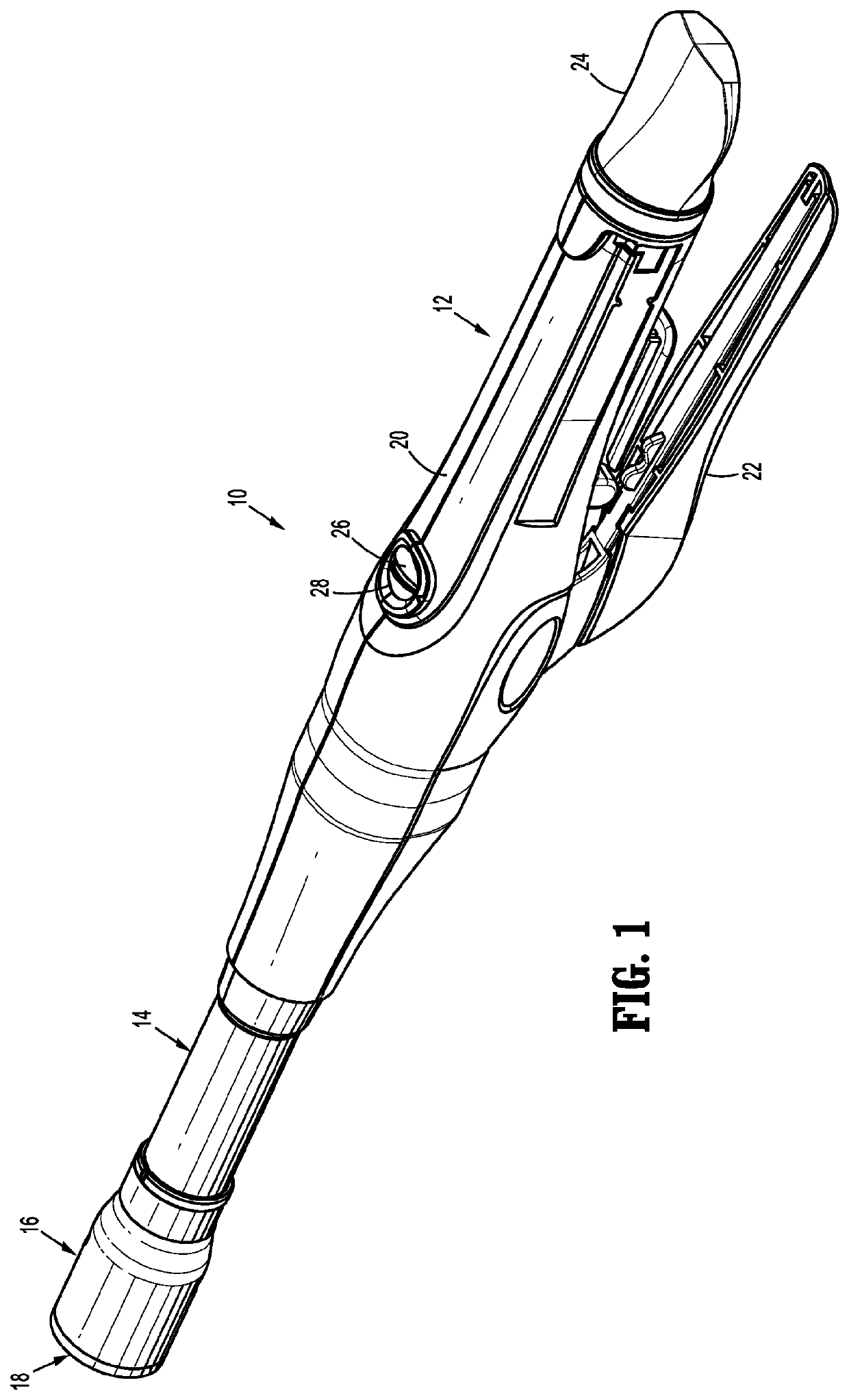
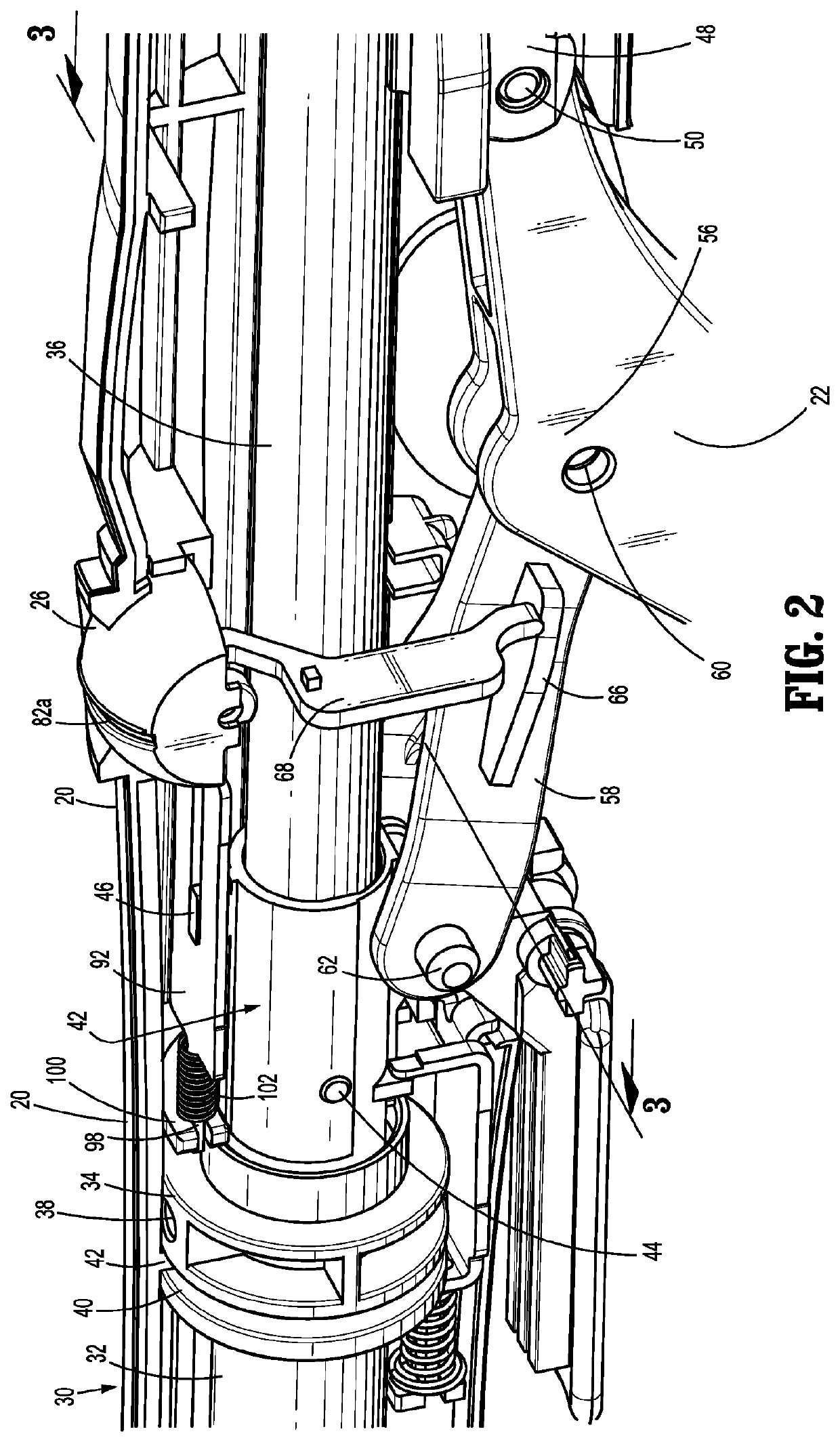
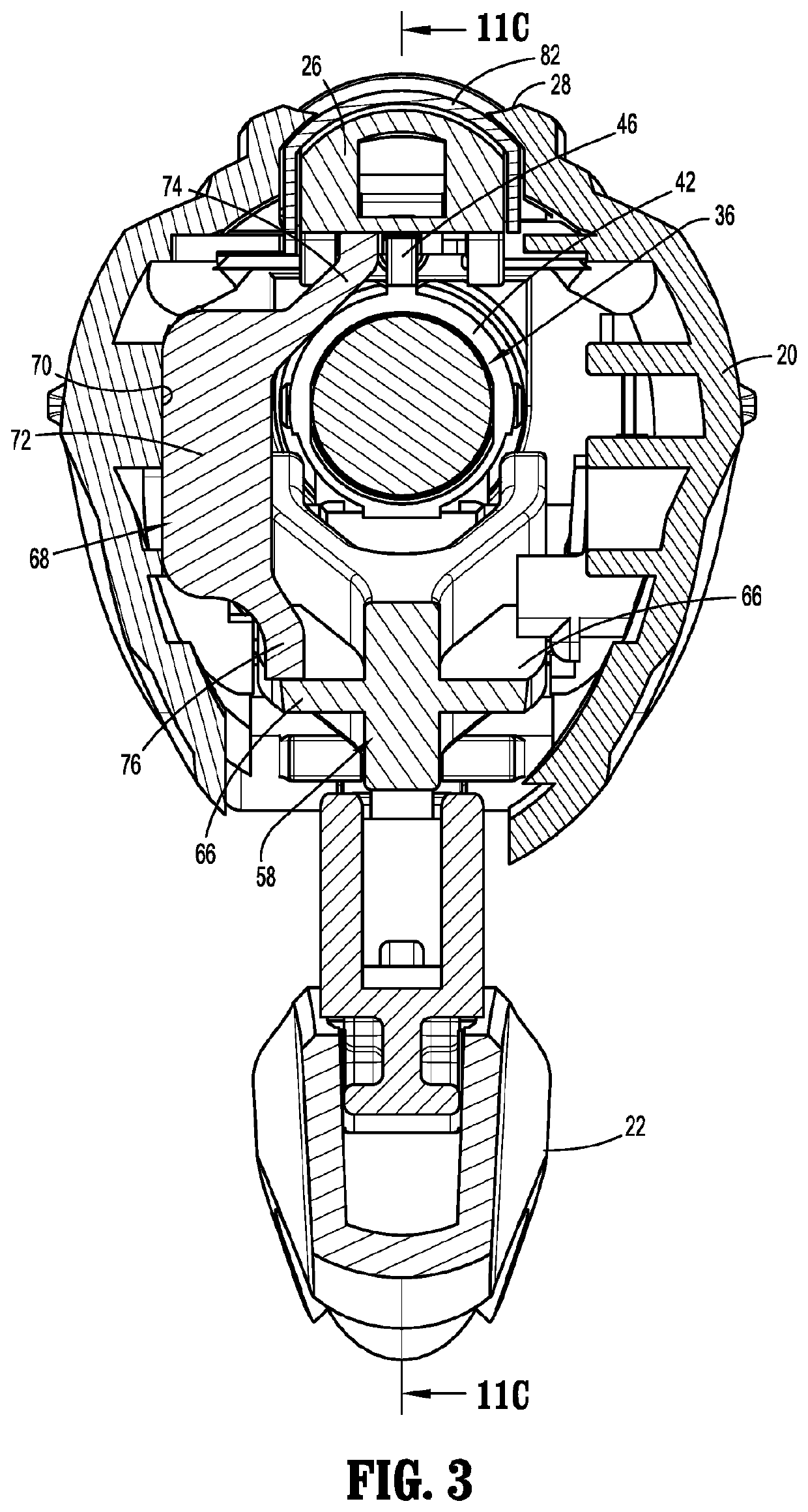
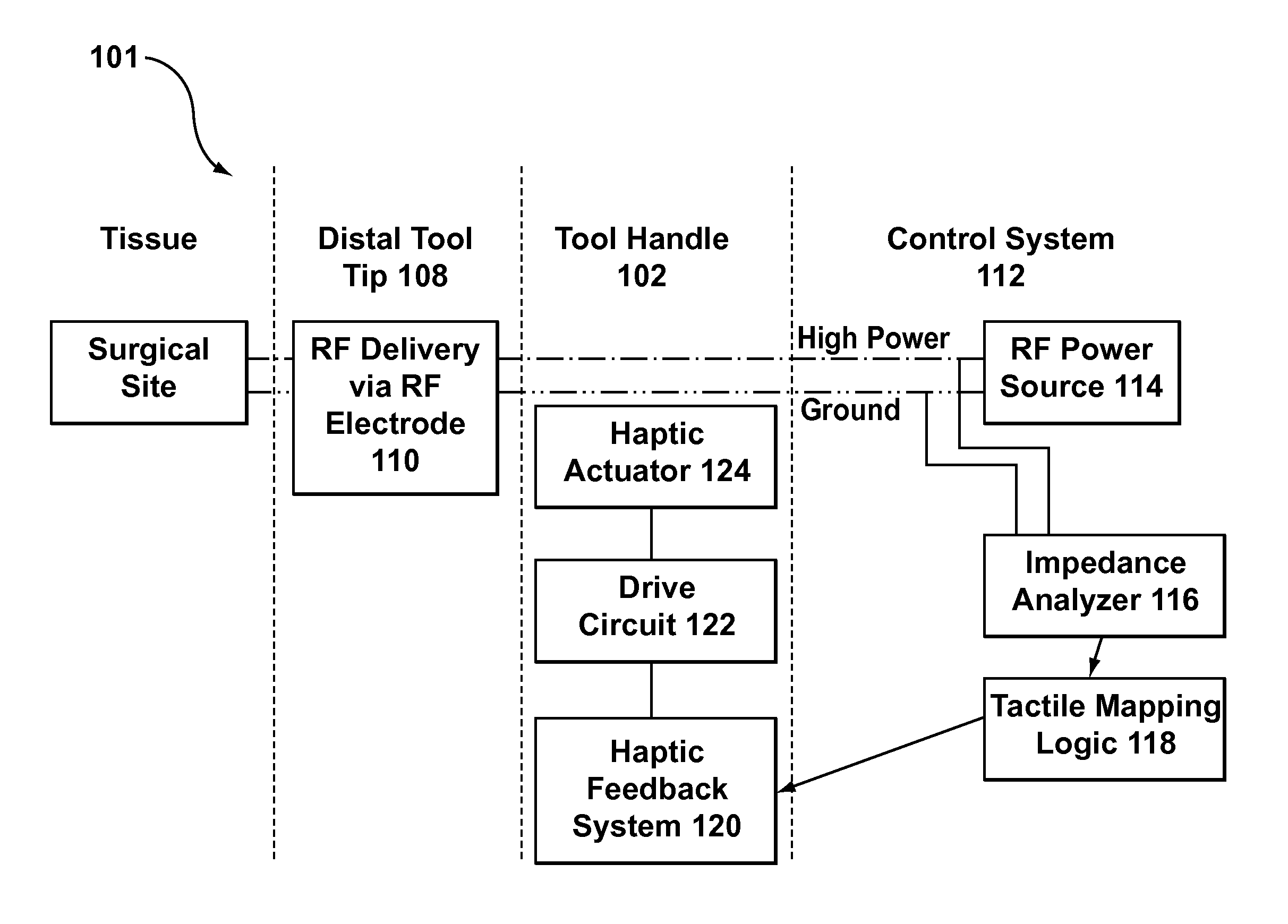
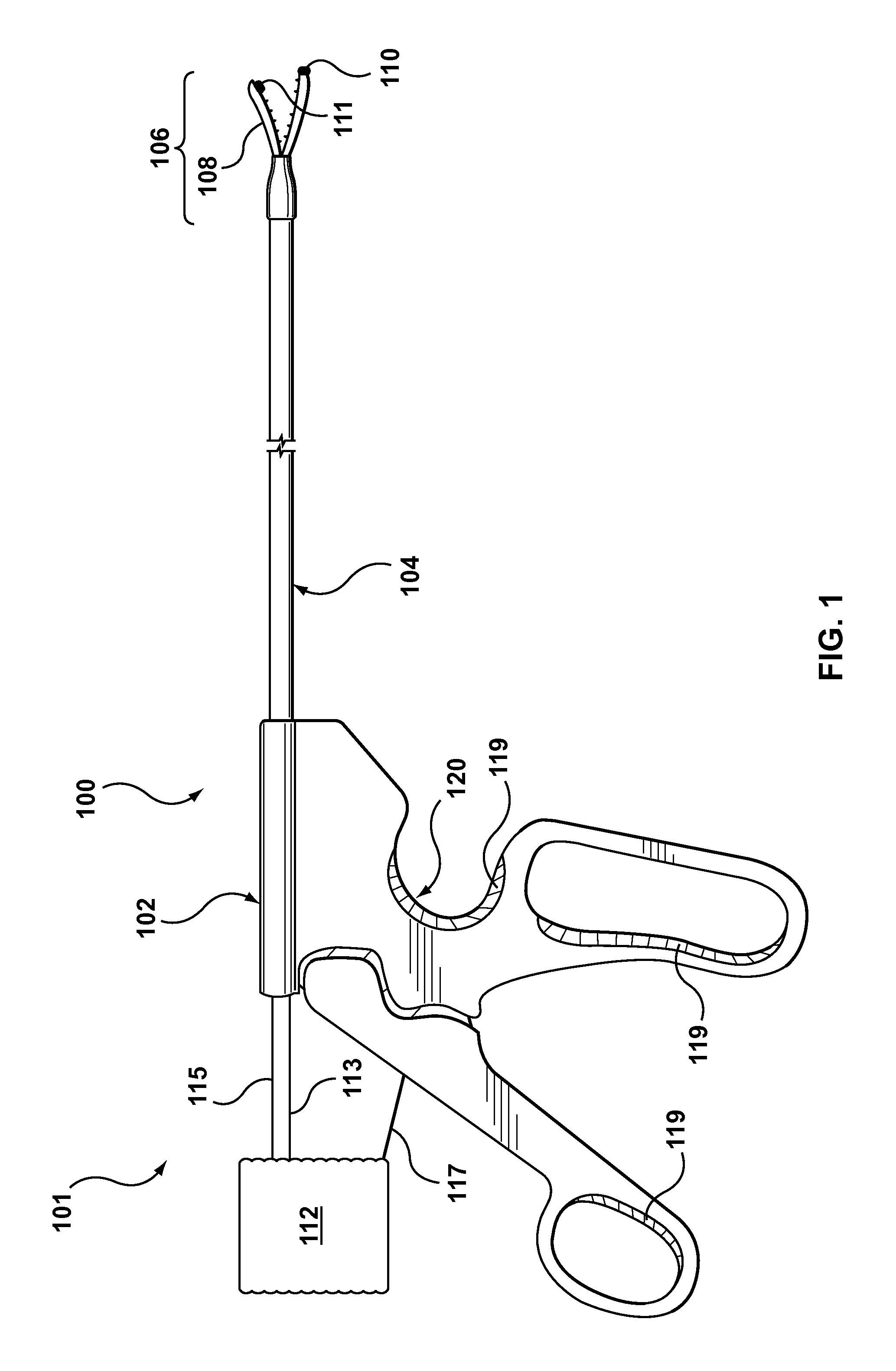
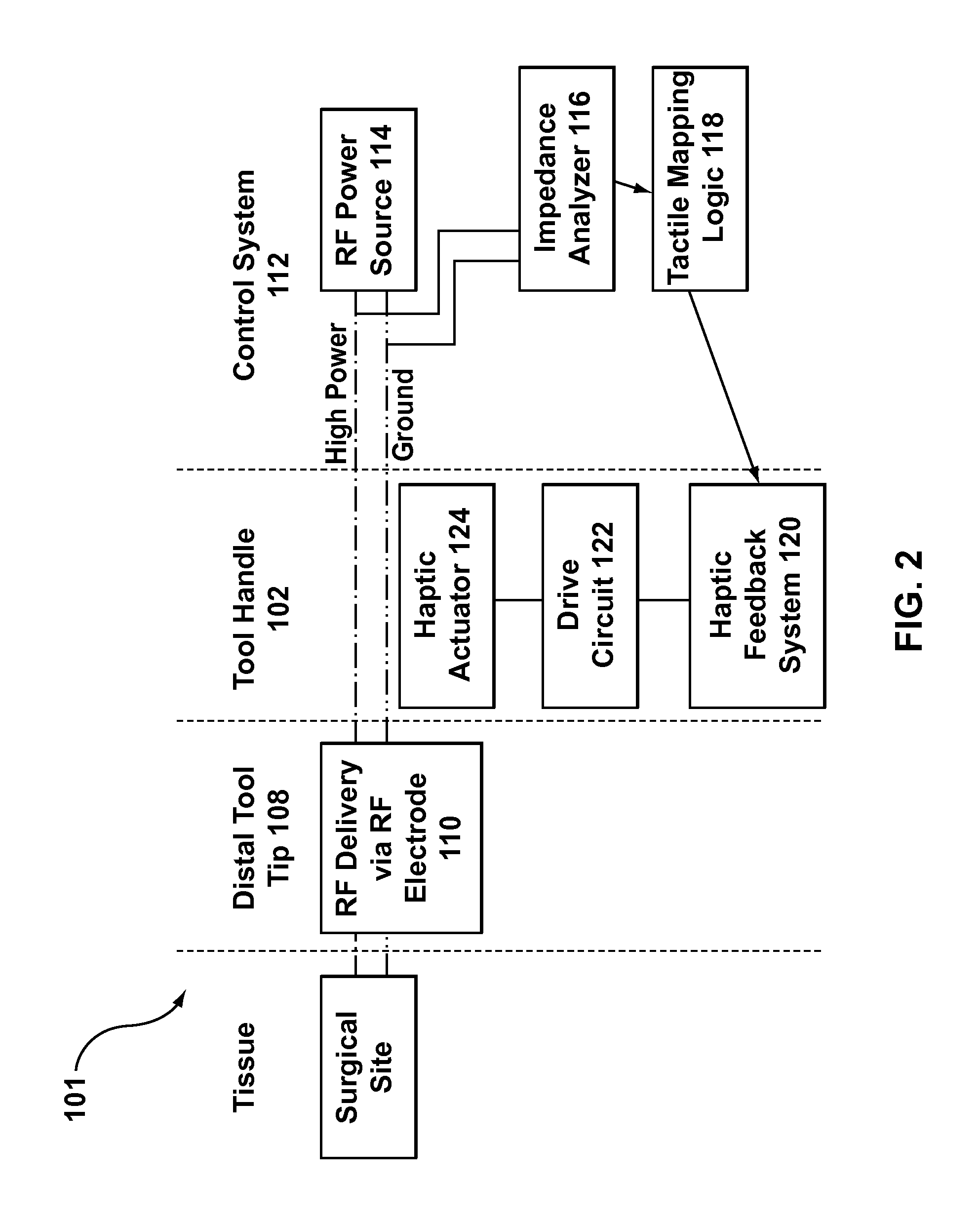
Electrosurgical tool having tactile feedback
InactiveUS9579143B2Mechanical features of instrumentSurgical instruments for heatingTactile sensationLaparoscopic treatment
A surgical tool system including a laparoscopic surgical tool for heating, ablating, sealing, and / or dissecting tissue, a control system for monitoring impedance of the tissue during treatment thereof, and a tactile feedback system integrated onto a handle of the tool that generates relevant feedback from the control system in at least the form of haptic effects to the user. The tactile feedback alerts the tool user of changes in tissue properties, i.e., when the impedance of the tissue indicates that the treatment procedure is complete. In addition, the tactile feedback provided may supply information relating to the operating status of the control system to the user.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Implantable joint prosthesis
ActiveUS20020128715A1Increased durabilityImprove stabilityDiagnosticsJoint implantsIntervertebral discSurgical implant
The invention relates to a surgical implant that provides an artificial diarthroidal-like joint, suitable for use in replacing any joint, but particularly suitable for use as an intervertebral disc endoprosthesis. The invention contains two rigid opposing shells, each having an outer surface adapted to engage the surfaces of the bones of a joint in such a way that the shells are immobilized by friction between their outer surfaces and the surfaces of the bone. These outer surfaces are sufficiently rough that large frictional forces strongly resist any slippage between the outer surface and the bone surfaces in the joint. They may be convex, and when inserted into a milled concavity, are immediately mechanically stable. Desirably, the outer surfaces of the shells are adapted to allow for bony ingrowth, which further stabilizes the shells in place. The inner surfaces of the shells are relatively smooth, and adapted to slide easily across a portion of the outer surface of a central body disposed between the shells. The central body has a shape that cooperates with the shape of the inner surface of the shell so as to provide a range of motion similar to that provided by a healthy joint. A flexible sheath extends between edges of the opposing shells. The inner surface of this sheath, together with the inner surfaces of the rigid shells, defines a cavity encasing the central body. At least a portion of this cavity is filled with a fluid lubricant, further decreasing the frictional force between inner surfaces of the shell and the surface of the central body.
Owner:COMPANION SPINE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com