Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
60 results about "View dependent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
To view the dependent’s information: Navigate to the Student Information page. 2. Click the dependent’s SEVIS ID in the Dependents section. The Student Information page with a Dependent Information section opens. The student’s information displays above the dependent’s information.
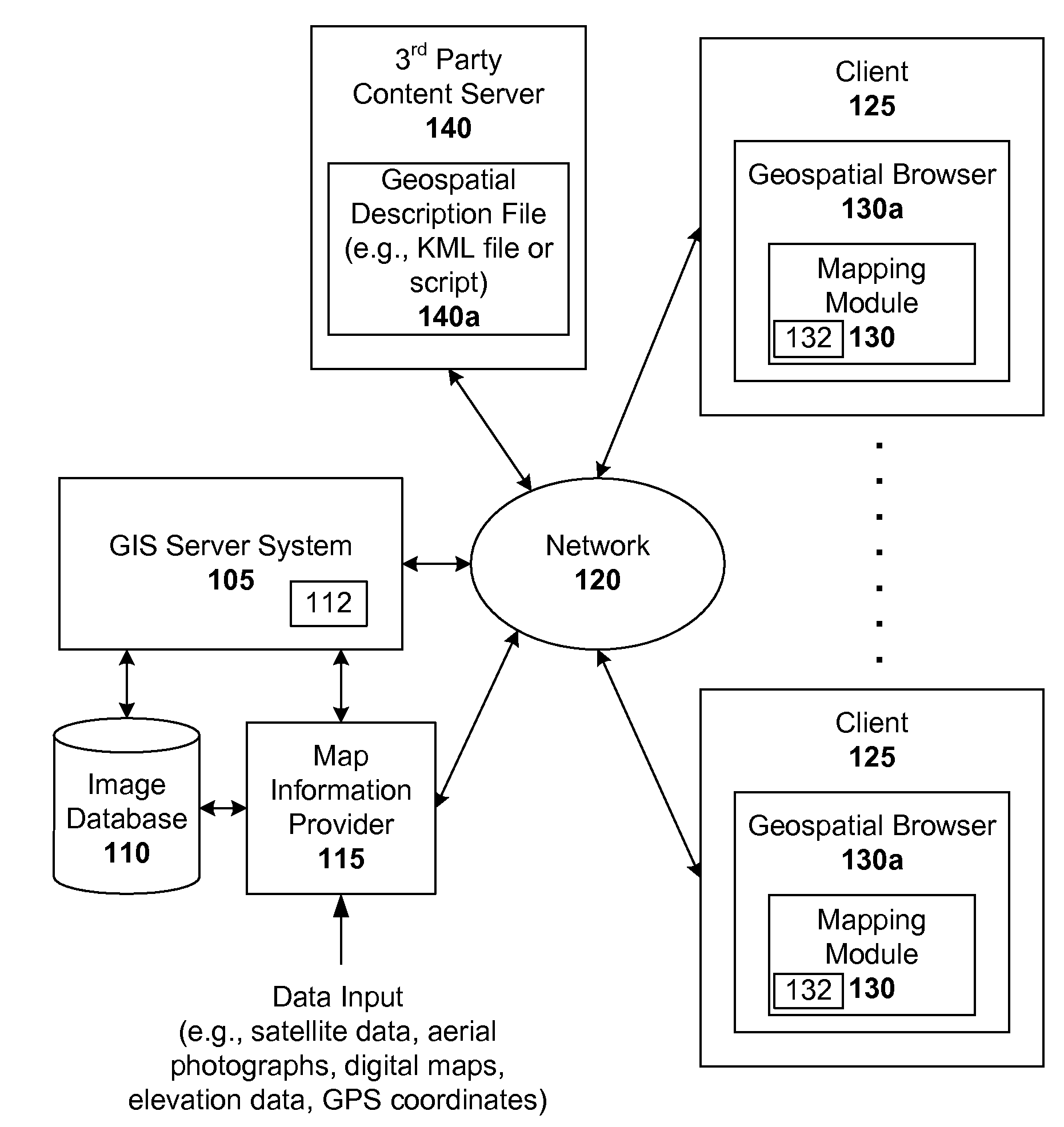
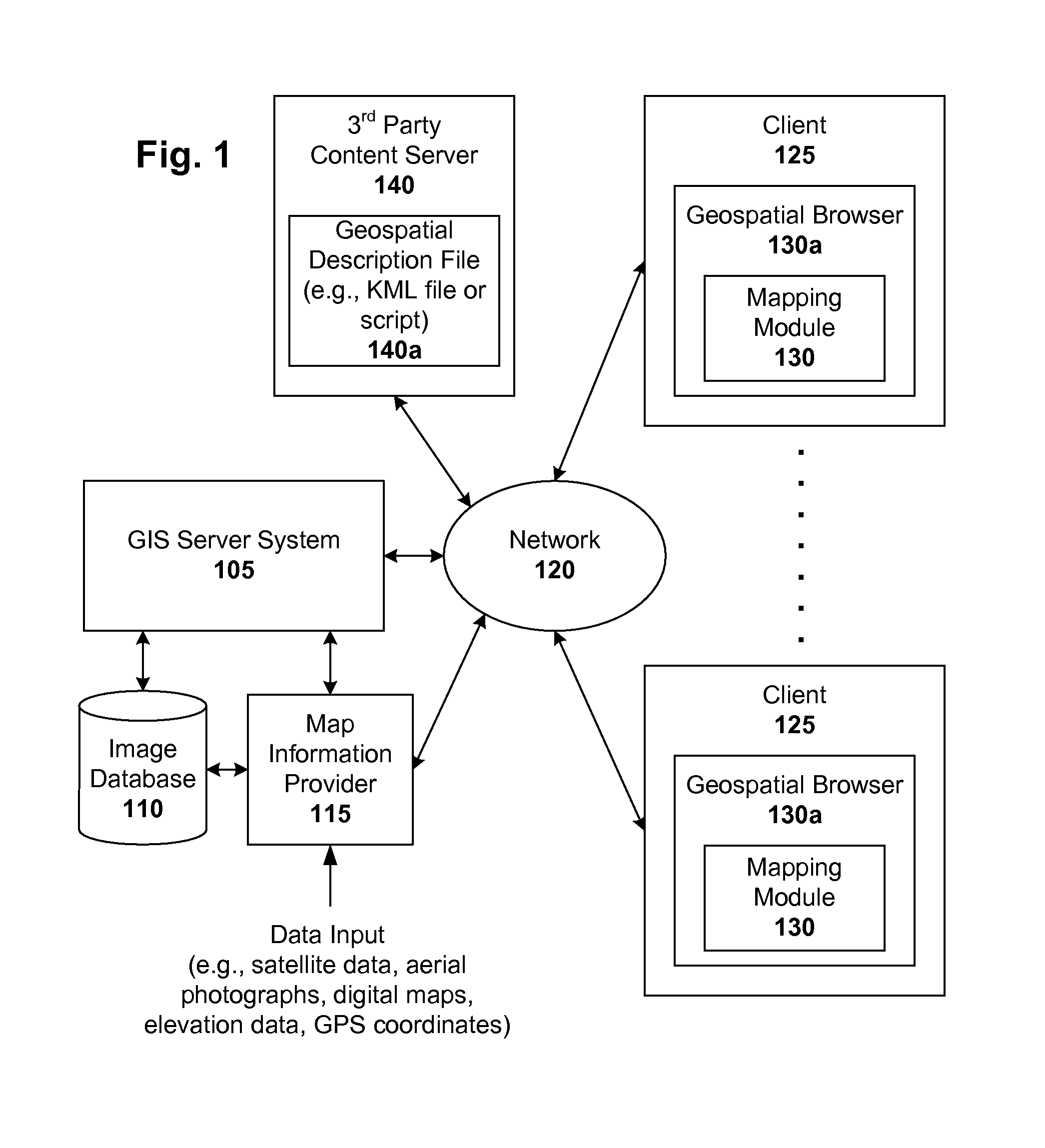
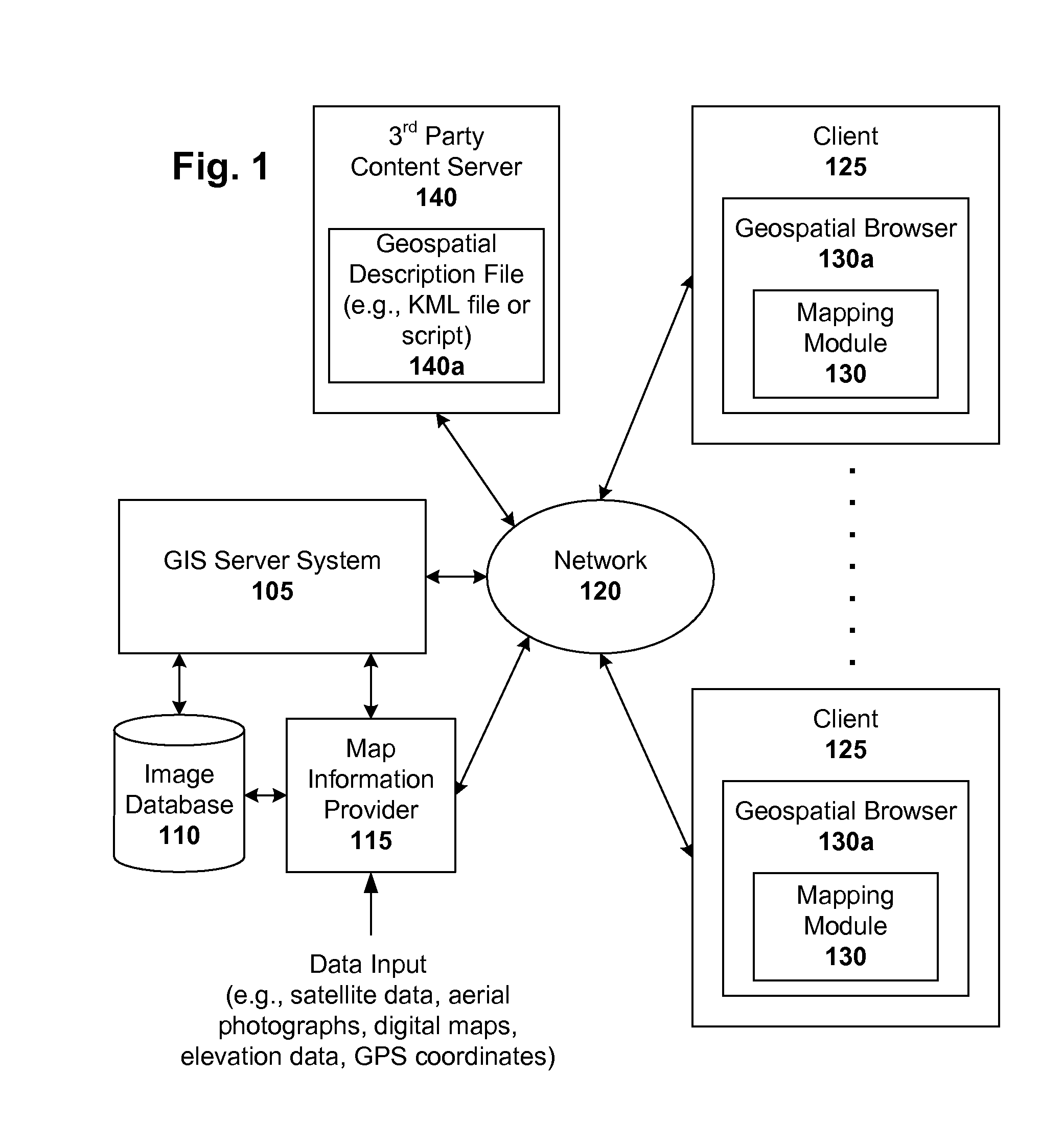
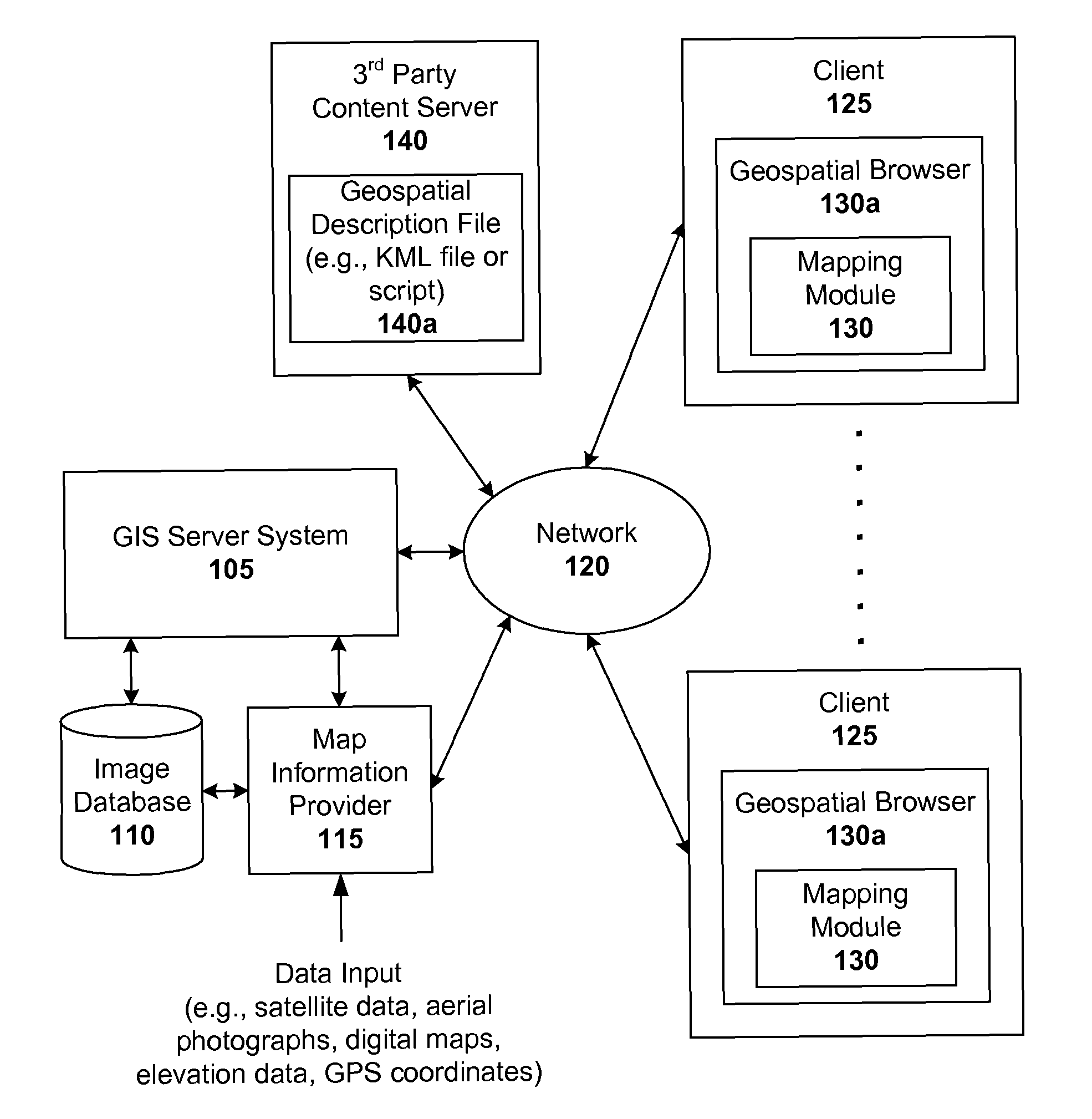
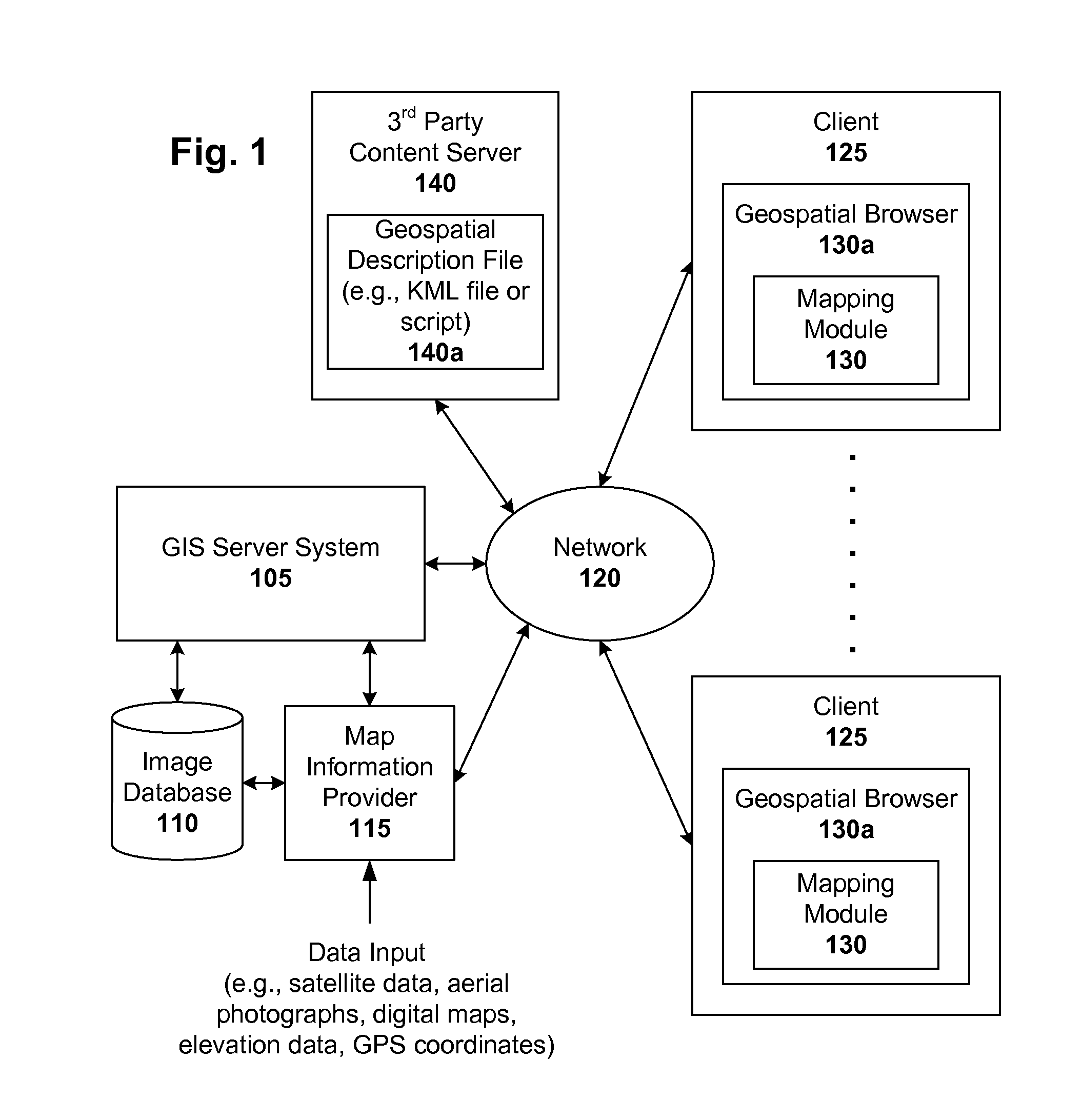
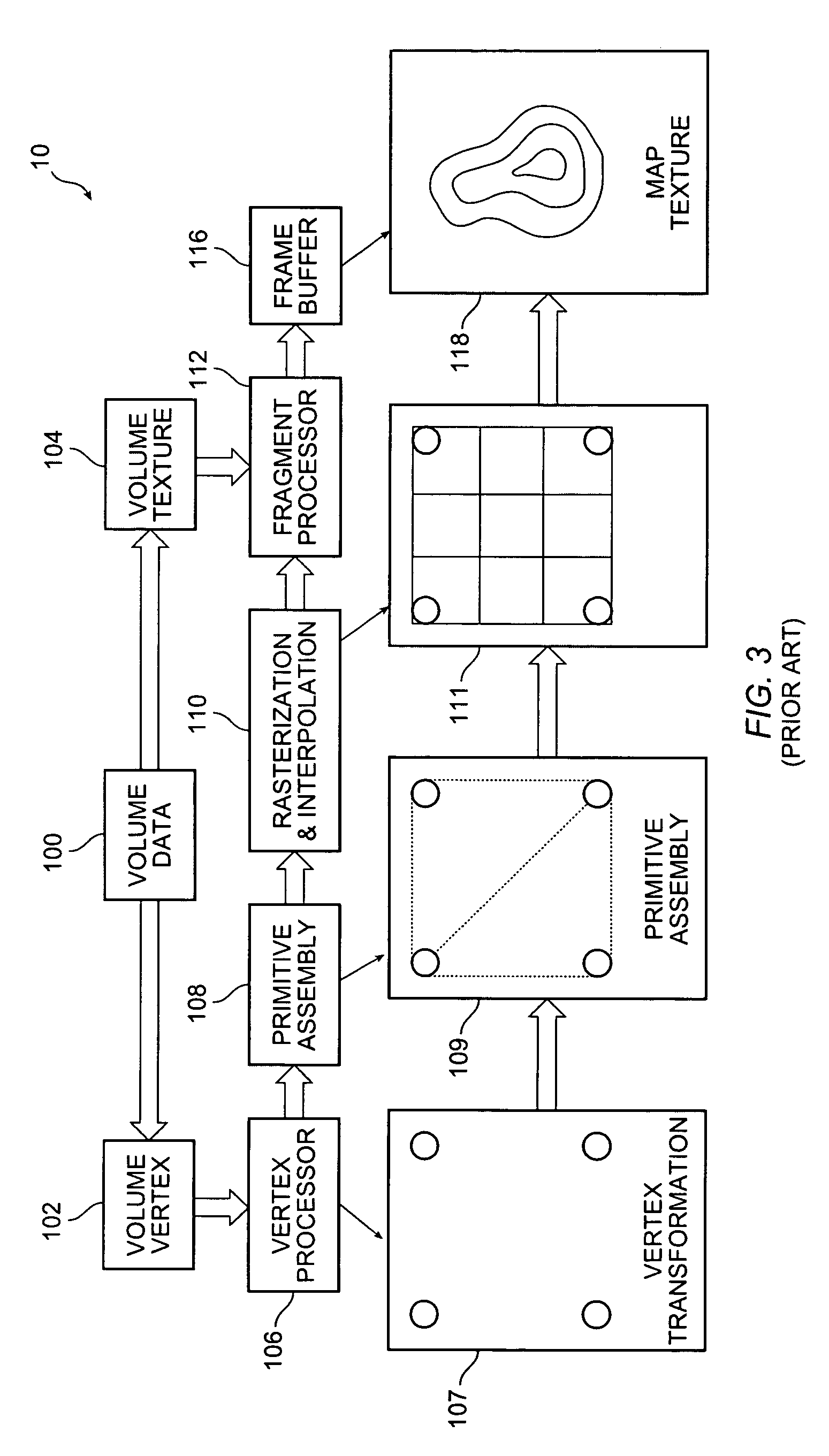
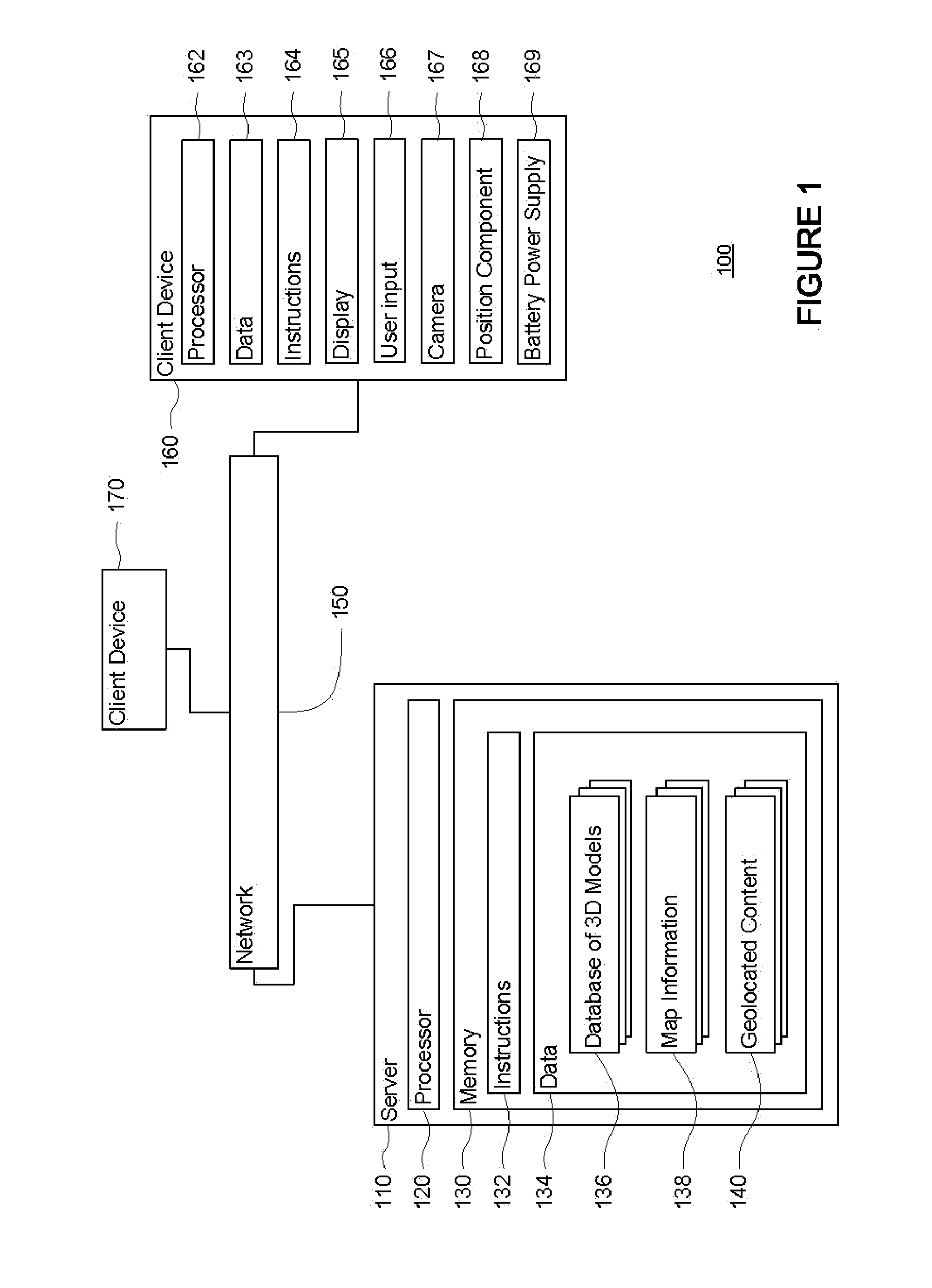
Markup language for an interactive geographic information system
ActiveUS7353114B1Natural language data processingNavigation instrumentsGeographic featureNetwork link
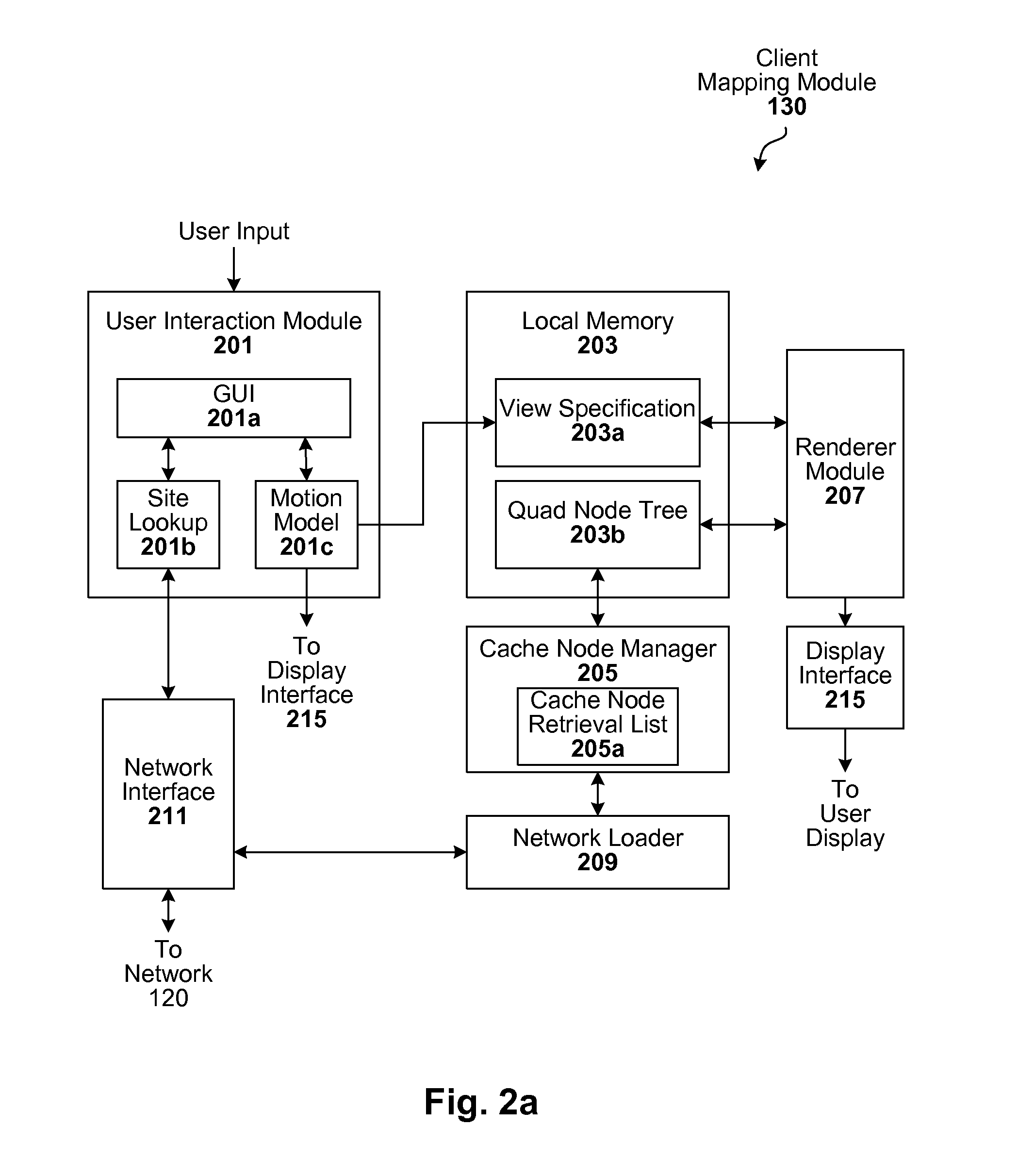
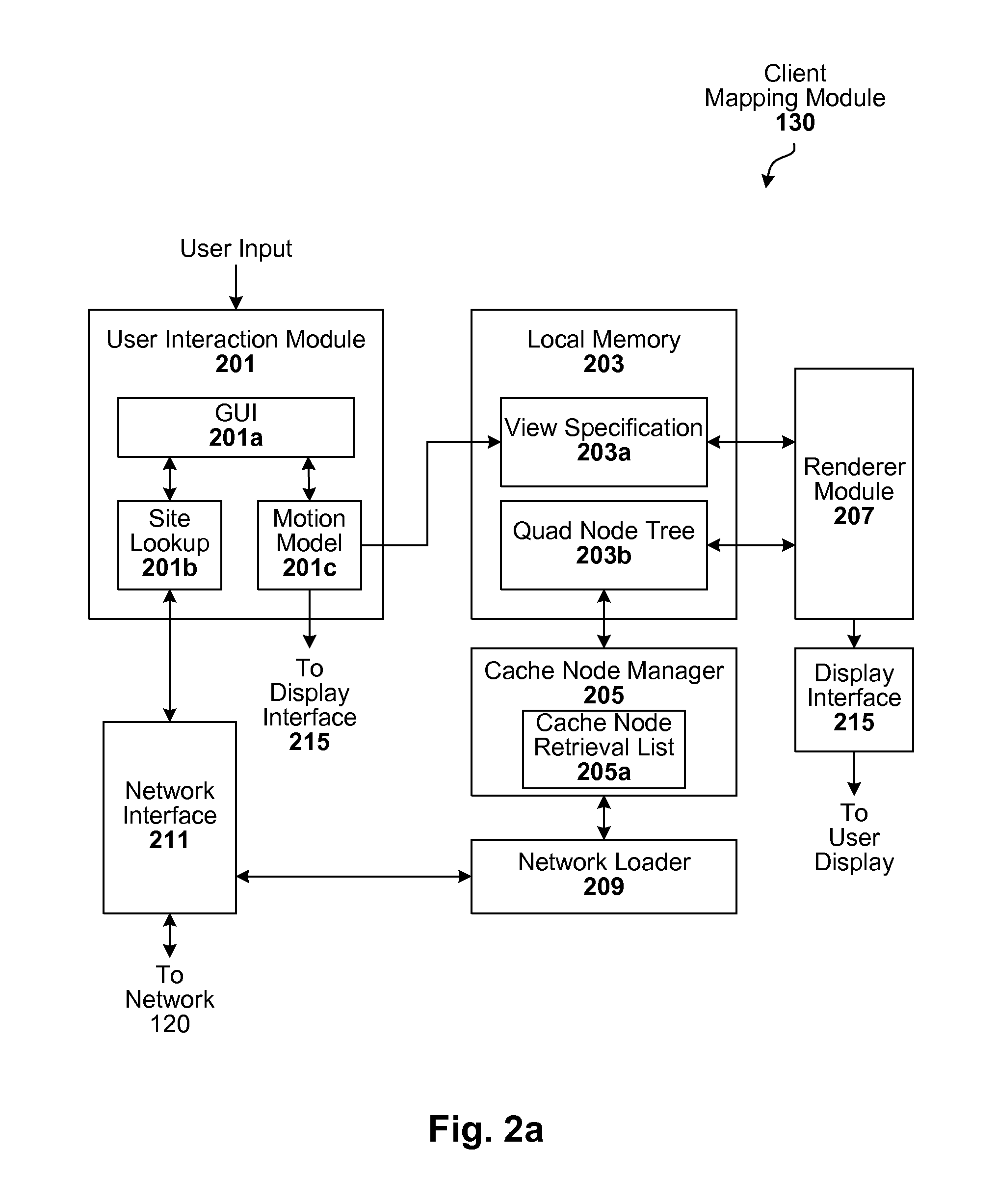
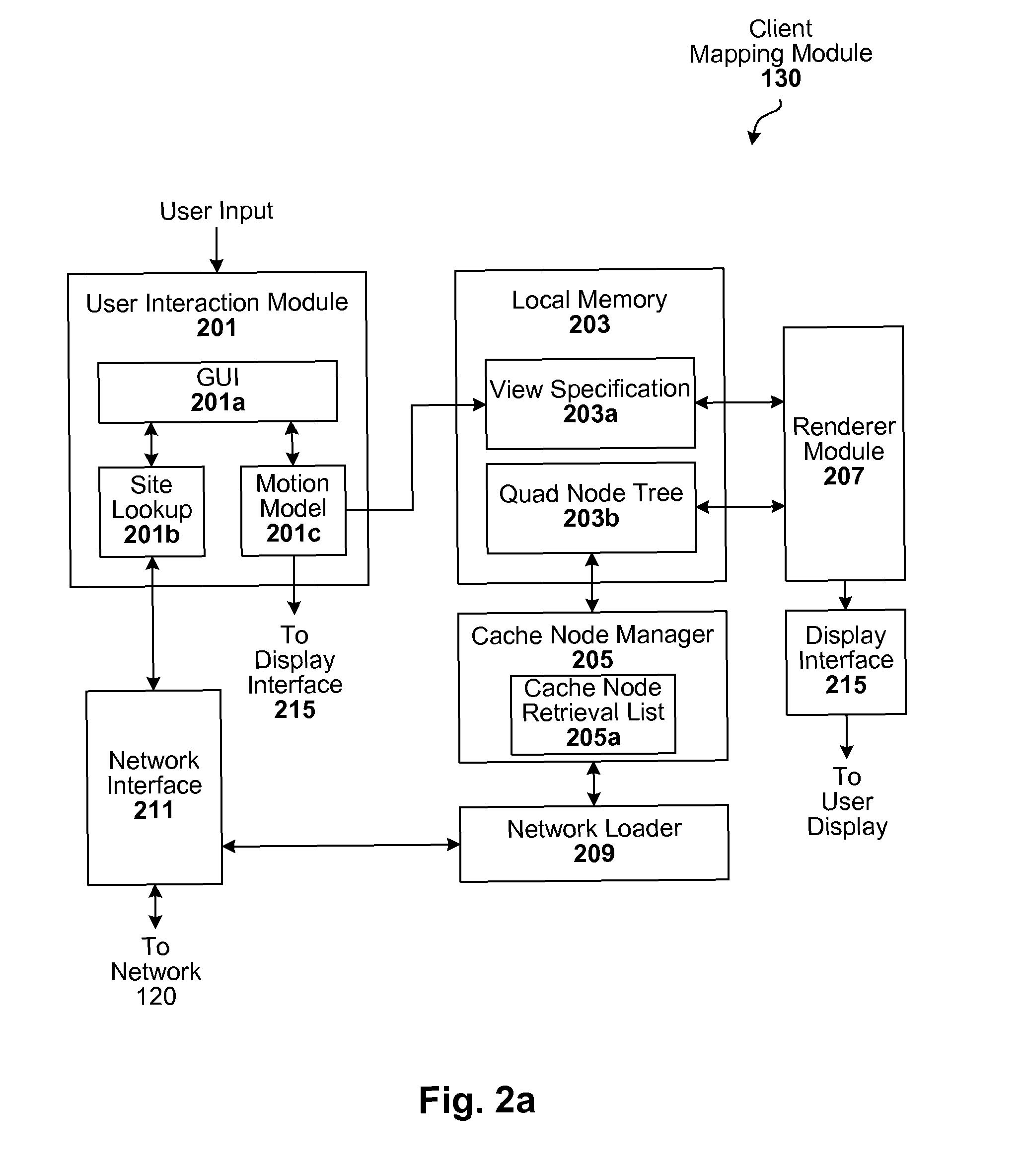
Interactive geographic information systems (GIS) and techniques are disclosed that provide users with a greater degree of flexibility, utility, and information. A markup language is provided that facilitates communication between servers and clients of the interactive GIS, which enables a number of GIS features, such as network links (time-based and view-dependent dynamic data layers), ground overlays, screen overlays, placemarks, 3D models, and stylized GIS elements, such as geometry, icons, description balloons, polygons, and labels in the viewer by which the user sees the target area. The markup language is used to describe a virtual camera view of a geographic feature. A compressed file format holds multiple files utilized to display a geographic feature in a single file.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Streaming and interactive visualization of filled polygon data in a geographic information system
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Network link for providing dynamic data layer in a geographic information system
A markup language is provided that facilitates communication between servers and clients of an interactive geographic information system (GIS, which enables a number of GIS features, such as network links (time-based and / or view-dependent dynamic data layers), ground overlays, screen overlays, placemarks, 3D models, and stylized GIS elements, such as geometry, icons, description balloons, polygons, and labels in the viewer by which the user sees the target area. Also, “virtual tours” of user-defined paths in the context of distributed geospatial visualization is enabled. Streaming and interactive visualization of filled polygon data are also enabled thereby allowing buildings and other such features to be provided in 3D. Also, techniques for enabling ambiguous search requests in a GIS are provided.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
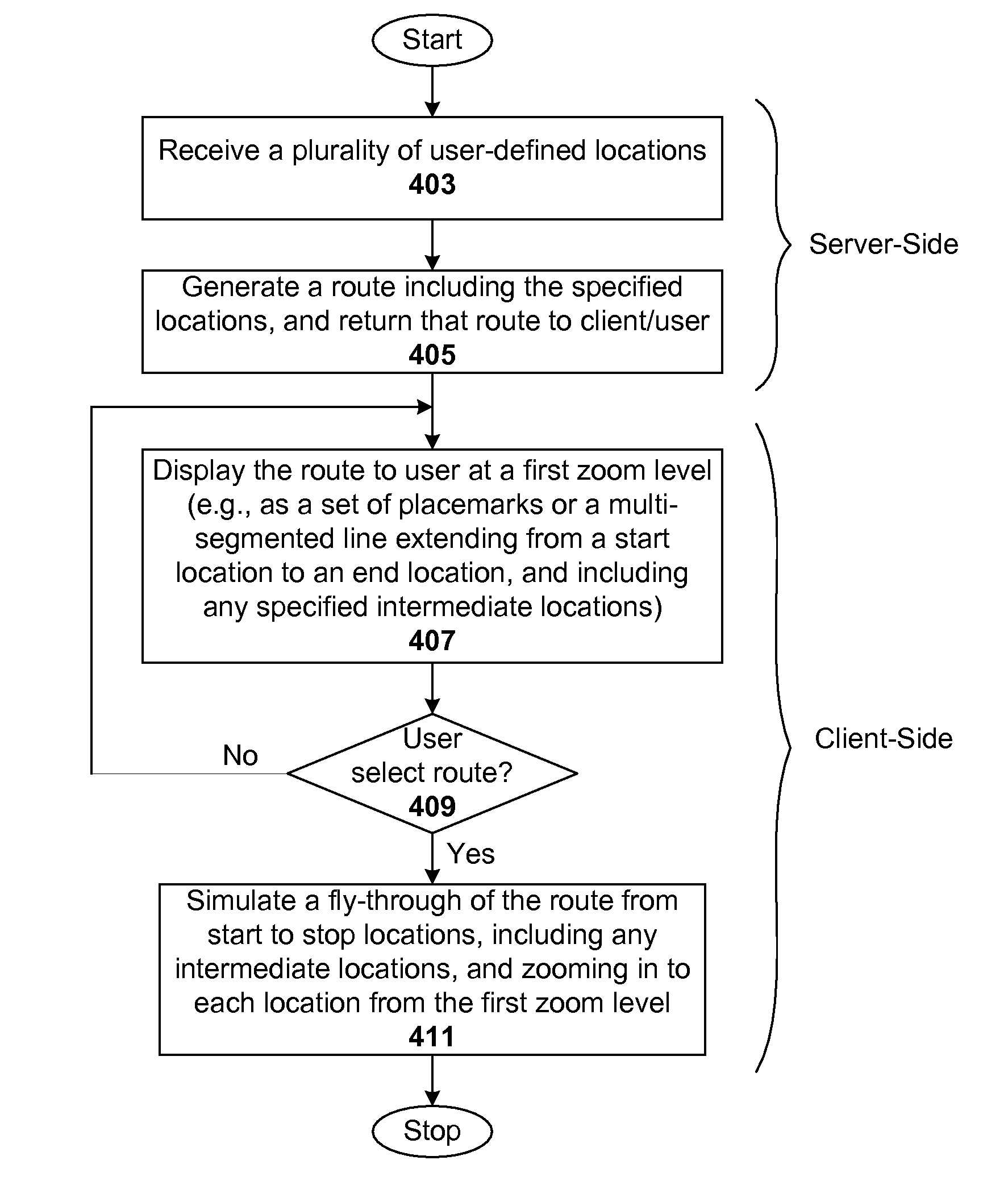
Virtual tour of user-defined paths in a geographic information system
Interactive geographic information systems (GIS) and techniques provide users with a greater degree of flexibility, utility, and information. A markup language facilitates communication between servers and clients of the interactive GIS, which enables a number of GIS features, such as network links (timebased and / or view-dependent dynamic data layers), ground overlays, screen overlays, placemarks, 3D models, and stylized GIS elements, such as geometry, icons, description balloons, polygons, and labels in the viewer by which the user sees the target area. Also, “virtual tours” of user-defined paths in the context of distributed geospatial visualization is enabled. Streaming and interactive visualization of filled polygon data are also enabled thereby allowing buildings and other such features to be provided in 3d. Also, techniques for enabling ambiguous search requests in a GIS are provided.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
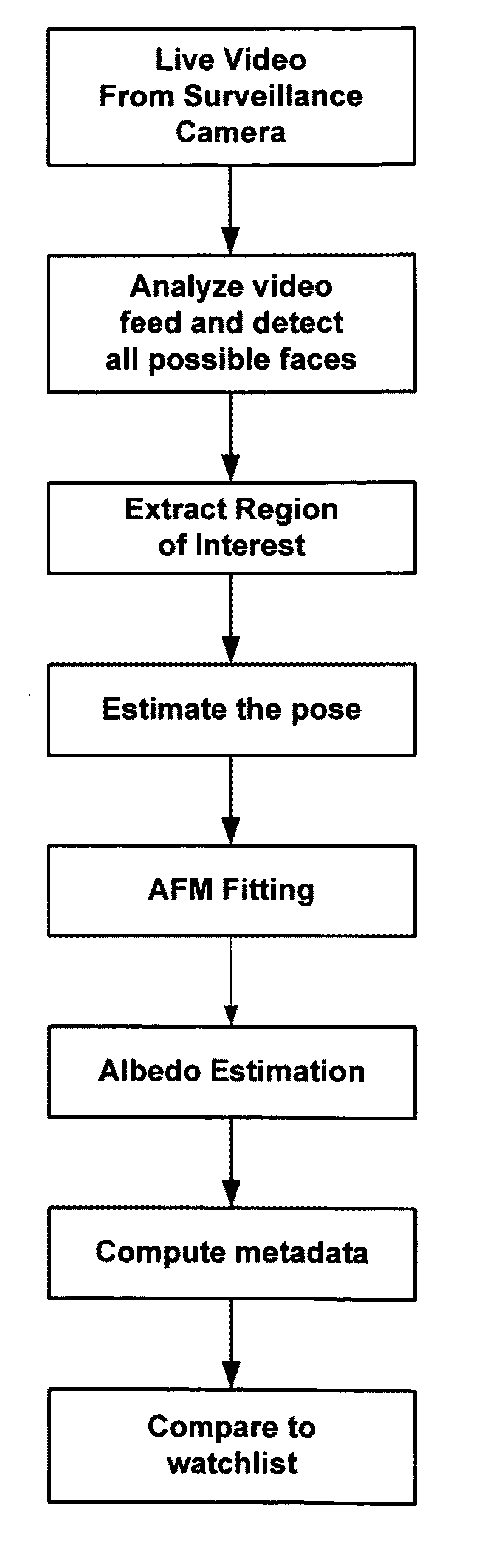
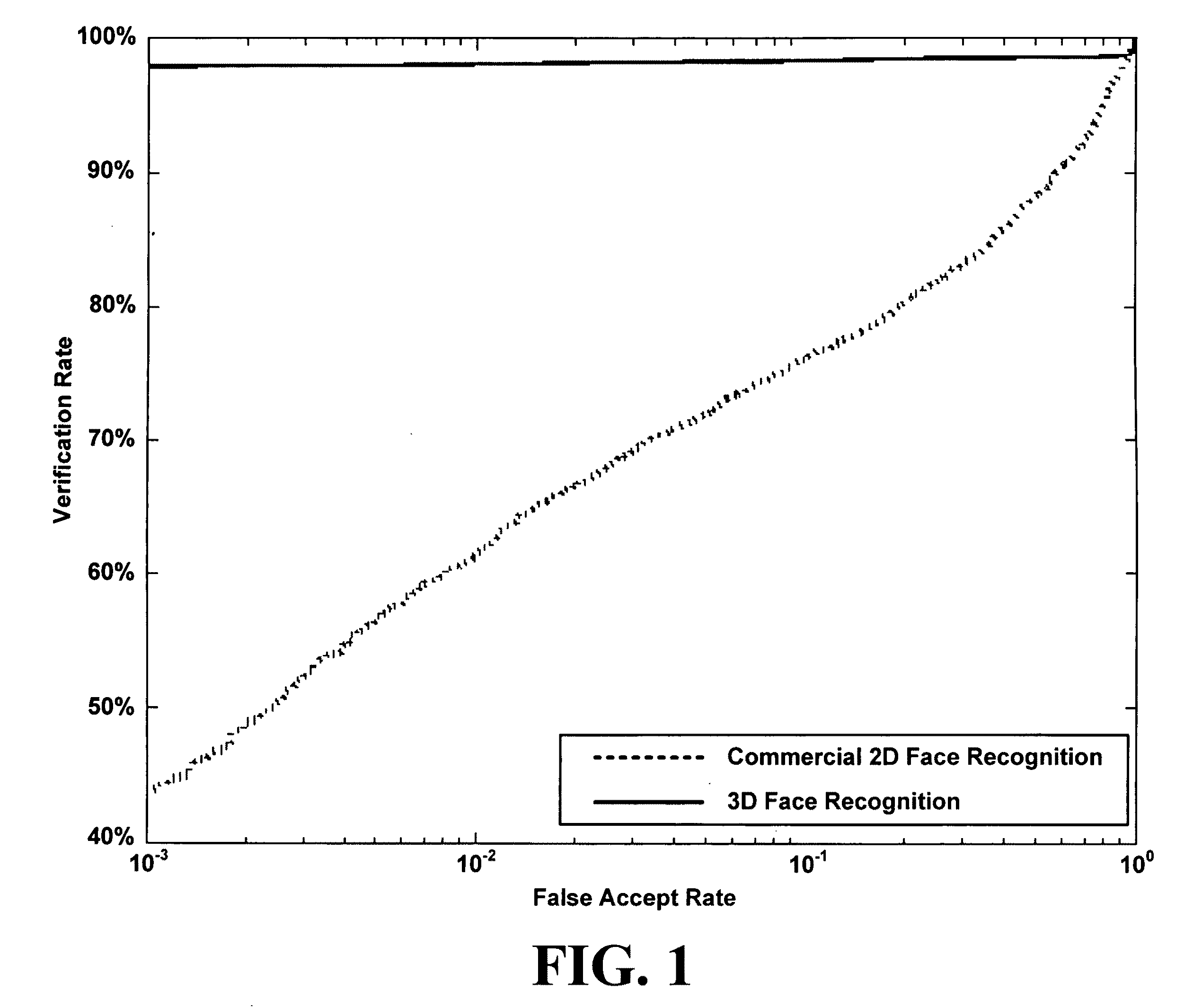
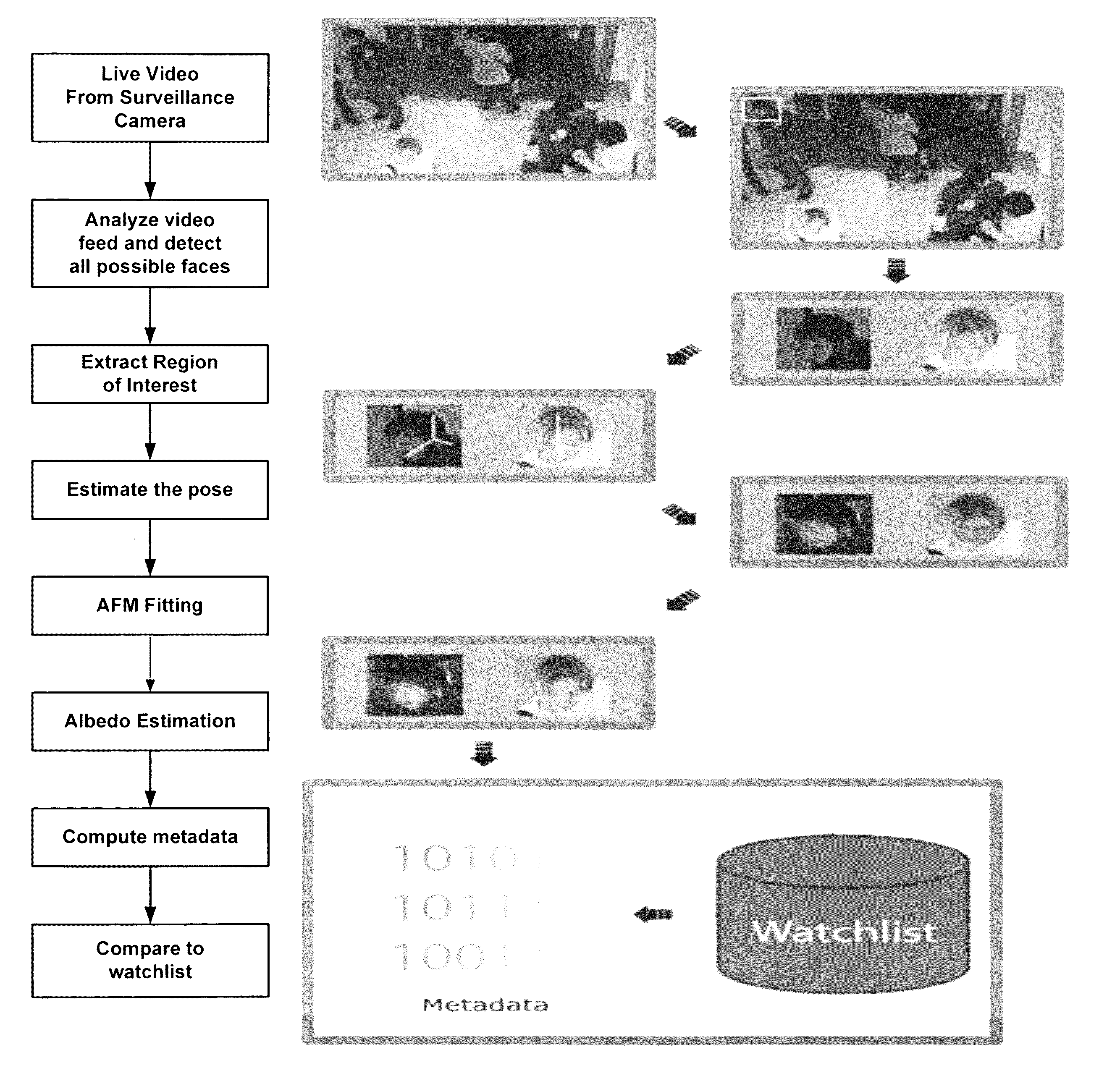
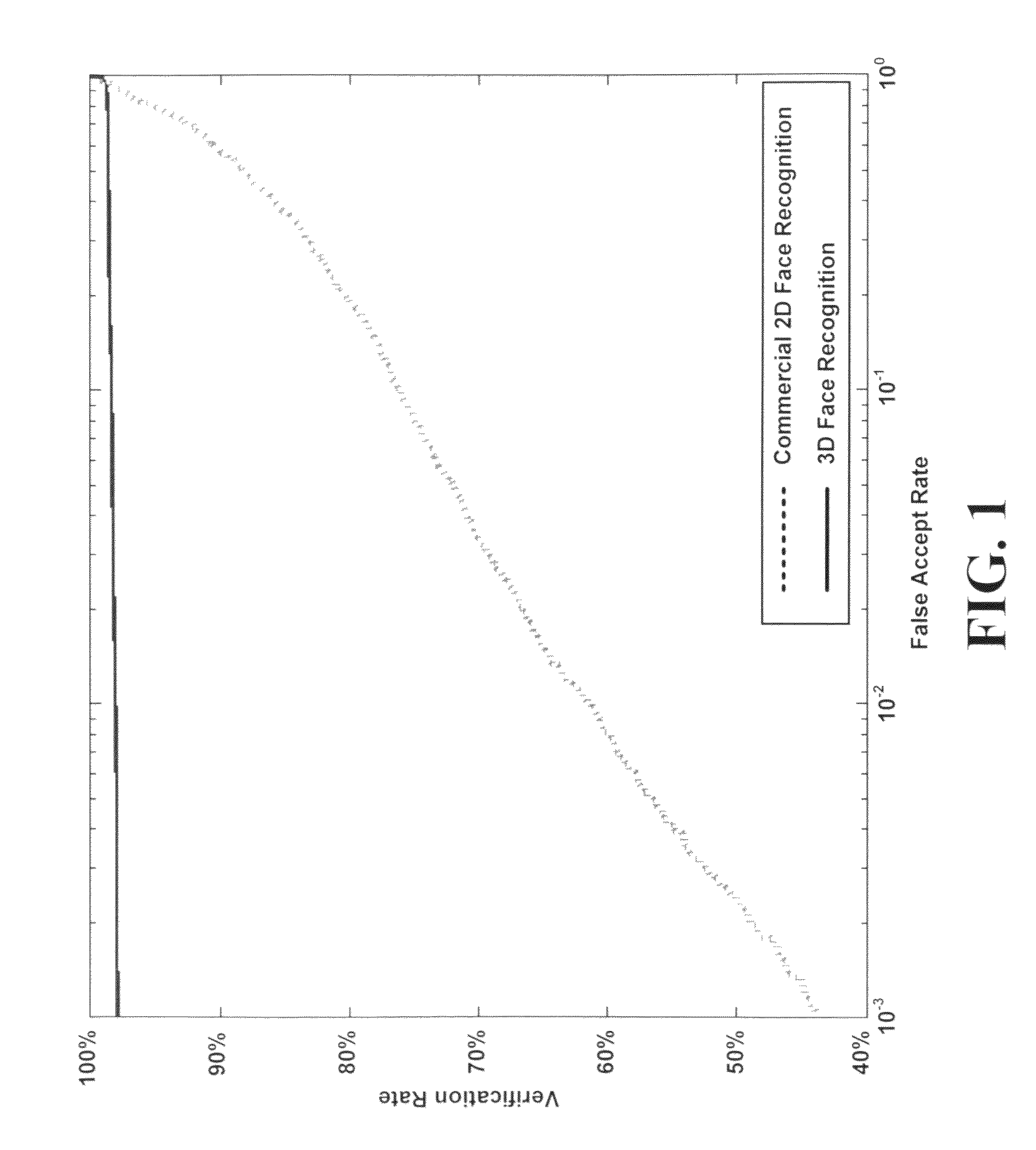
An automated method for human face modeling and relighting with application to face recognition
A novel method and system for 3d-aided-2D face recognition under large pose and illumination variations is disclosed. The method and system includes enrolling a face of a subject into a gallery database using raw 3D data. The method also includes verifying and / or identifying a target face form data produced by a 2D imagining or scanning device. A statistically derived annotated face model is fitted using a subdivision-based deformable model framework to the raw 3D data. The annotated face model is capable of being smoothly deformed into any face so it acts as a universal facial template. During authentication or identification, only a single 2D image is required. The subject specific fitted annotated face model from the gallery is used to lift a texture of a face from a 2D probe image, and a bidirectional relighting algorithm is employed to change the illumination of the gallery texture to match that of the probe. Then, the relit texture is compared to the gallery texture using a view-dependent complex wavelet structural similarity index metric.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
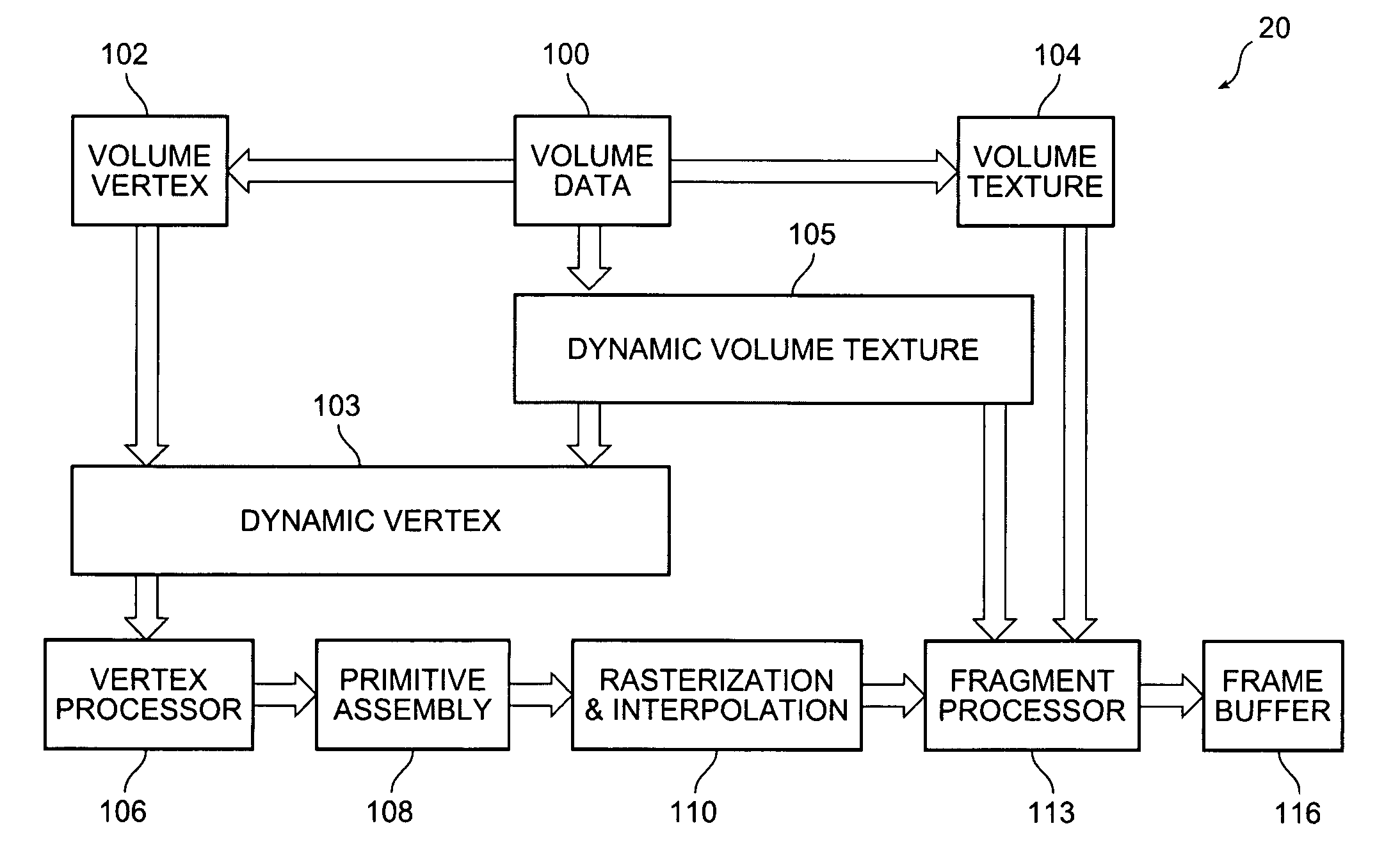
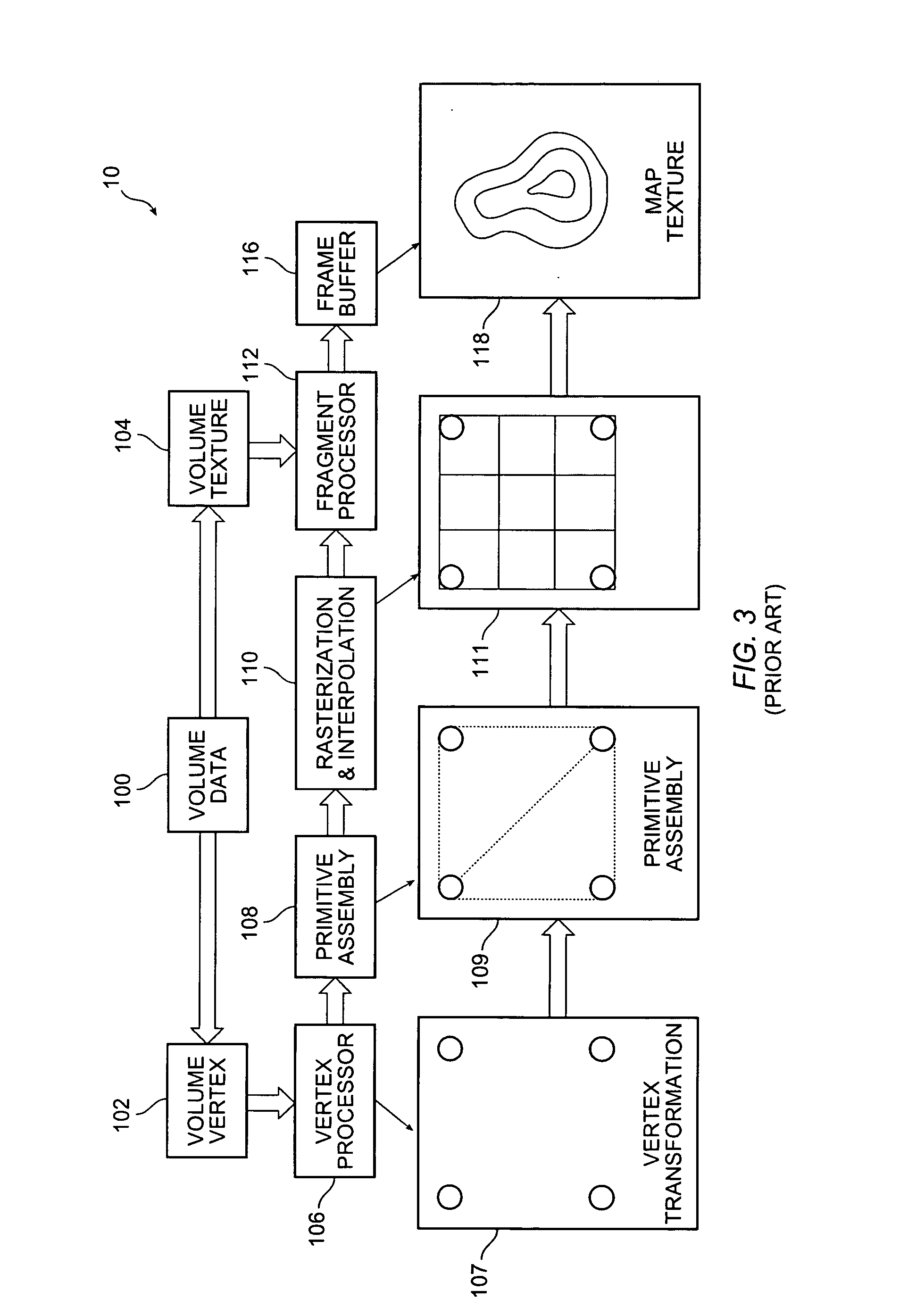
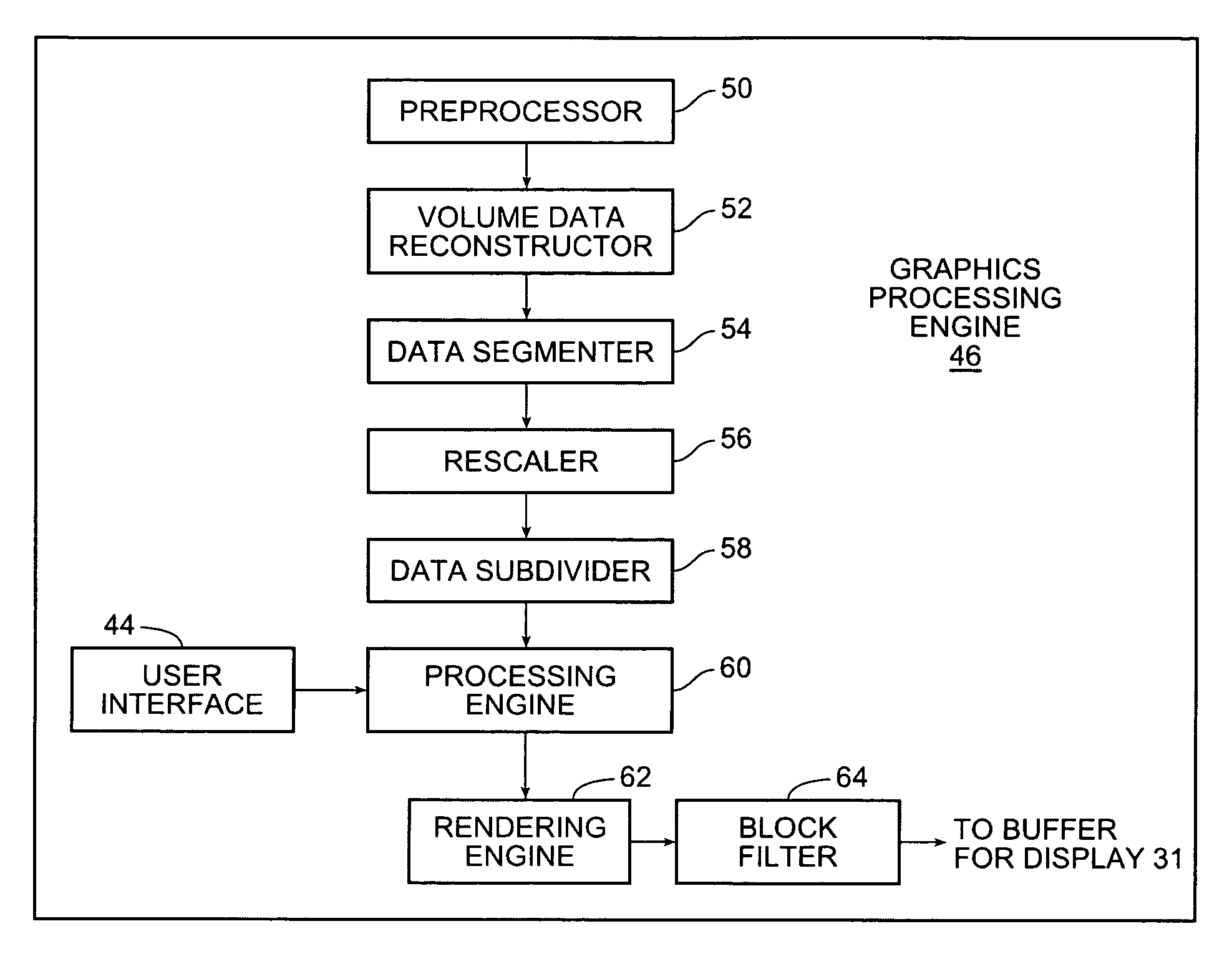
Block-based fragment filtration with feasible multi-GPU acceleration for real-time volume rendering on conventional personal computer
ActiveUS20050231503A1Reduce the burden onDetails involving 3D image dataCathode-ray tube indicatorsVoxelFiltration
A computer-based method and system for interactive volume rendering of a large volume data on a conventional personal computer using hardware-accelerated block filtration optimizing uses 3D-textured axis-aligned slices and block filtration. Fragment processing in a rendering pipeline is lessened by passing fragments to various processors selectively in blocks of voxels based on a filtering process operative on slices. The process involves generating a corresponding image texture and performing two-pass rendering, namely a virtual rendering pass and a main rendering pass. Block filtration is divided into static block filtration and dynamic block filtration. The static block filtration locates any view-independent unused signal being passed to a rasterization pipeline. The dynamic block filtration determines any view-dependent unused block generated due to occlusion. Block filtration processes utilize the vertex shader and pixel shader of a GPU in conventional personal computer graphics hardware. The method is for multi-thread, multi-GPU operation.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Adjustment of imaging property in view-dependent rendering
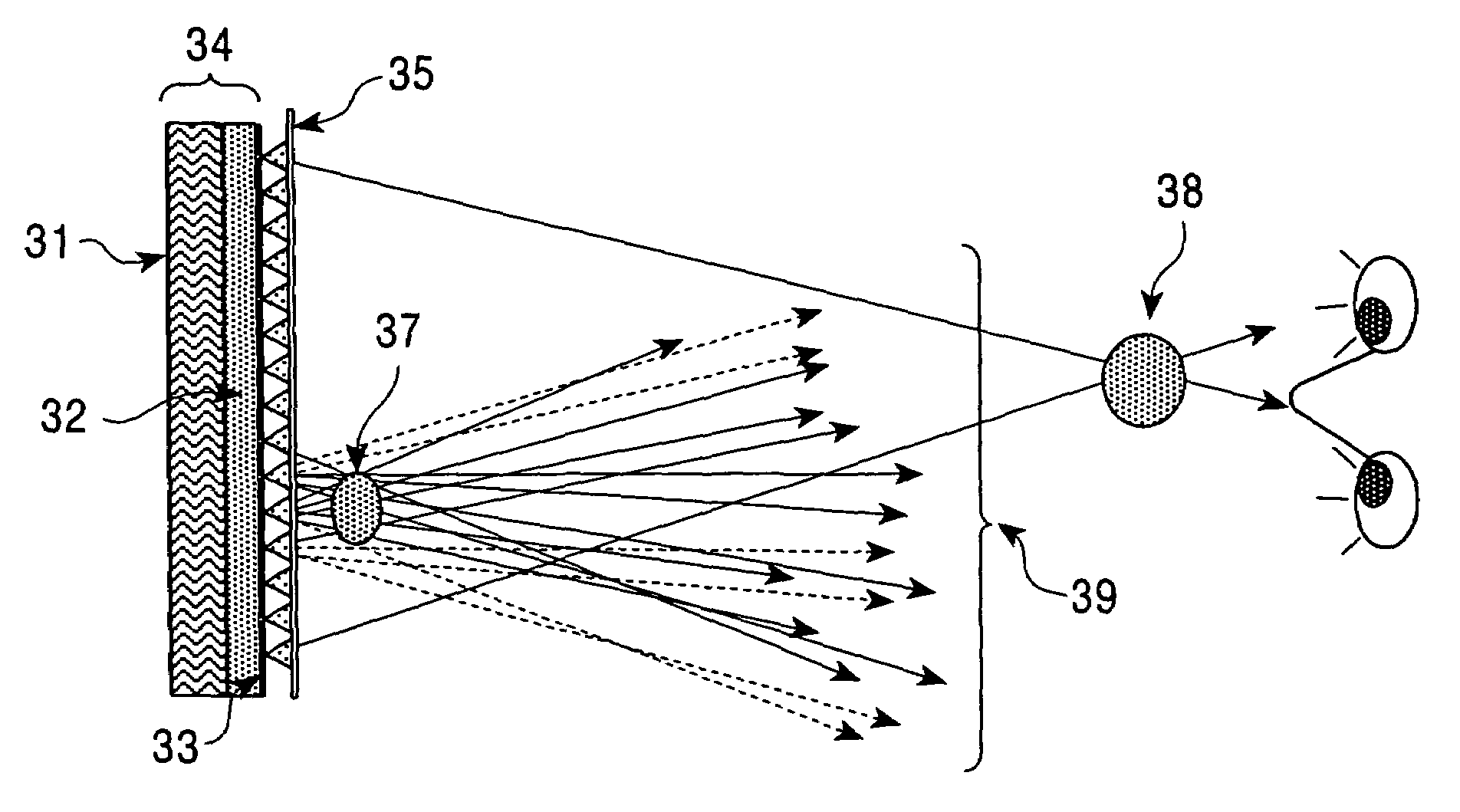
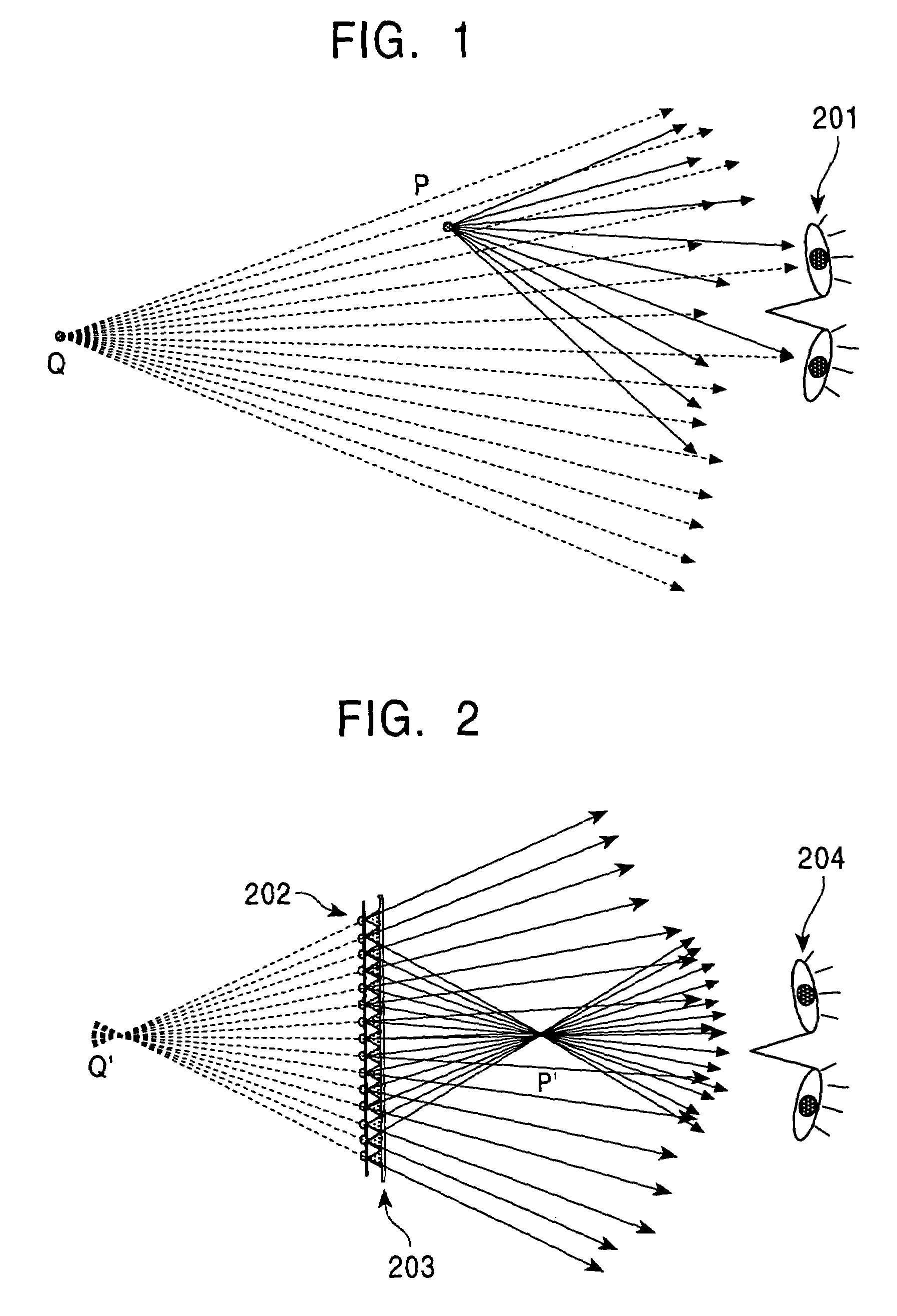
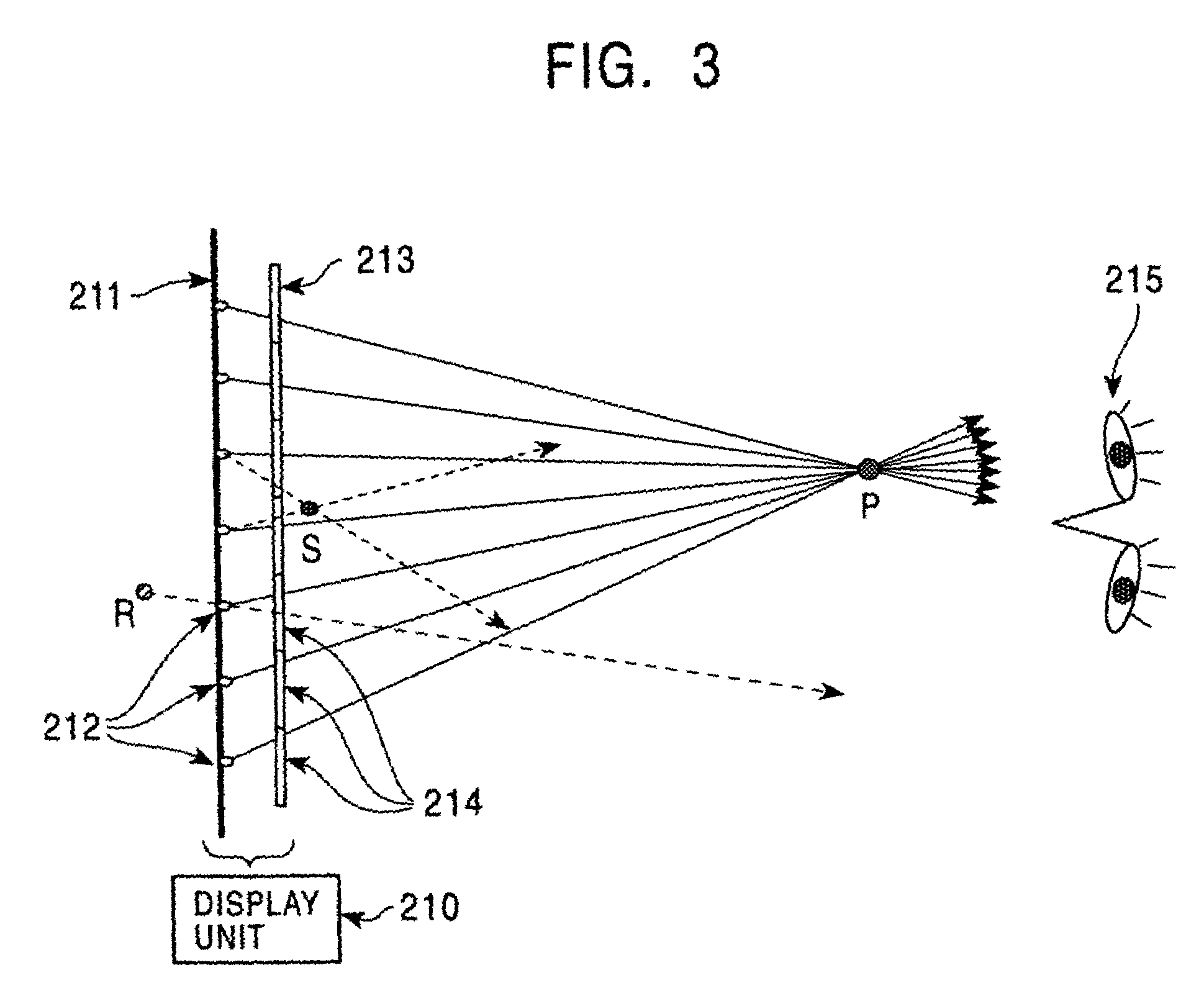
An image is displayed by determining a relative position and orientation of a display in relation to a viewer's head, and rendering an image based on the relative position and orientation. The viewer's eye movement relative to the rendered image is tracked, with at least one area of interest in the image to the viewer being determined based on the viewer's eye movement, and an imaging property of the at least one area of interest is adjusted.
Owner:CANON KK
Rendition of 3D content on a handheld device
InactiveUS20110285622A1Realistic visual interactionRealistic visual experienceCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage renderingComputer graphics (images)Display device
A handheld device having a display and a front-facing sensor and a back-facing sensor is able to render 3D content in a realistic and spatially correct manner using position-dependent rendering and view-dependent rendering. In one scenario, the 3D content is only computer-generated content and the display on the device is a typical, non-transparent (opaque) display. The position-dependent rendering is performed using either the back-facing sensor or a front-facing sensor having a wide-angle lens. In another scenario, the 3D content is composed of computer-generated 3D content and images of physical objects and the display is either a transparent or semi-transparent display where physical objects behind the device show through the display. In this case, position-dependent rendering is performed using a back-facing sensor that is actuated (capable of physical panning and tilting) or is wide-angle, thereby enabling virtual panning.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Preparing digital images for display utilizing view-dependent texturing
InactiveUS7348989B2Minimize polygonal loadHigh image fidelityCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsComputer graphics (images)
A computer program embodied on a computer-readable medium, a computer readable medium storing computer-executable instructions, and a computer data signal embodied in a carrier wave, all for providing a graphic image utilizing view-dependent texture data, including a graphic data code segment for providing data representing a graphic image and a texture data code segment in operational association with the graphic data code segment.
Owner:ARCHVISION
Automated method for human face modeling and relighting with application to face recognition
A novel method and system for 3d-aided-2D face recognition under large pose and illumination variations is disclosed. The method and system includes enrolling a face of a subject into a gallery database using raw 3D data. The method also includes verifying and / or identifying a target face form data produced by a 2D imagining or scanning device. A statistically derived annotated face model is fitted using a subdivision-based deformable model framework to the raw 3D data. The annotated face model is capable of being smoothly deformed into any face so it acts as a universal facial template. During authentication or identification, only a single 2D image is required. The subject specific fitted annotated face model from the gallery is used to lift a texture of a face from a 2D probe image, and a bidirectional relighting algorithm is employed to change the illumination of the gallery texture to match that of the probe. Then, the relit texture is compared to the gallery texture using a view-dependent complex wavelet structural similarity index metric.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
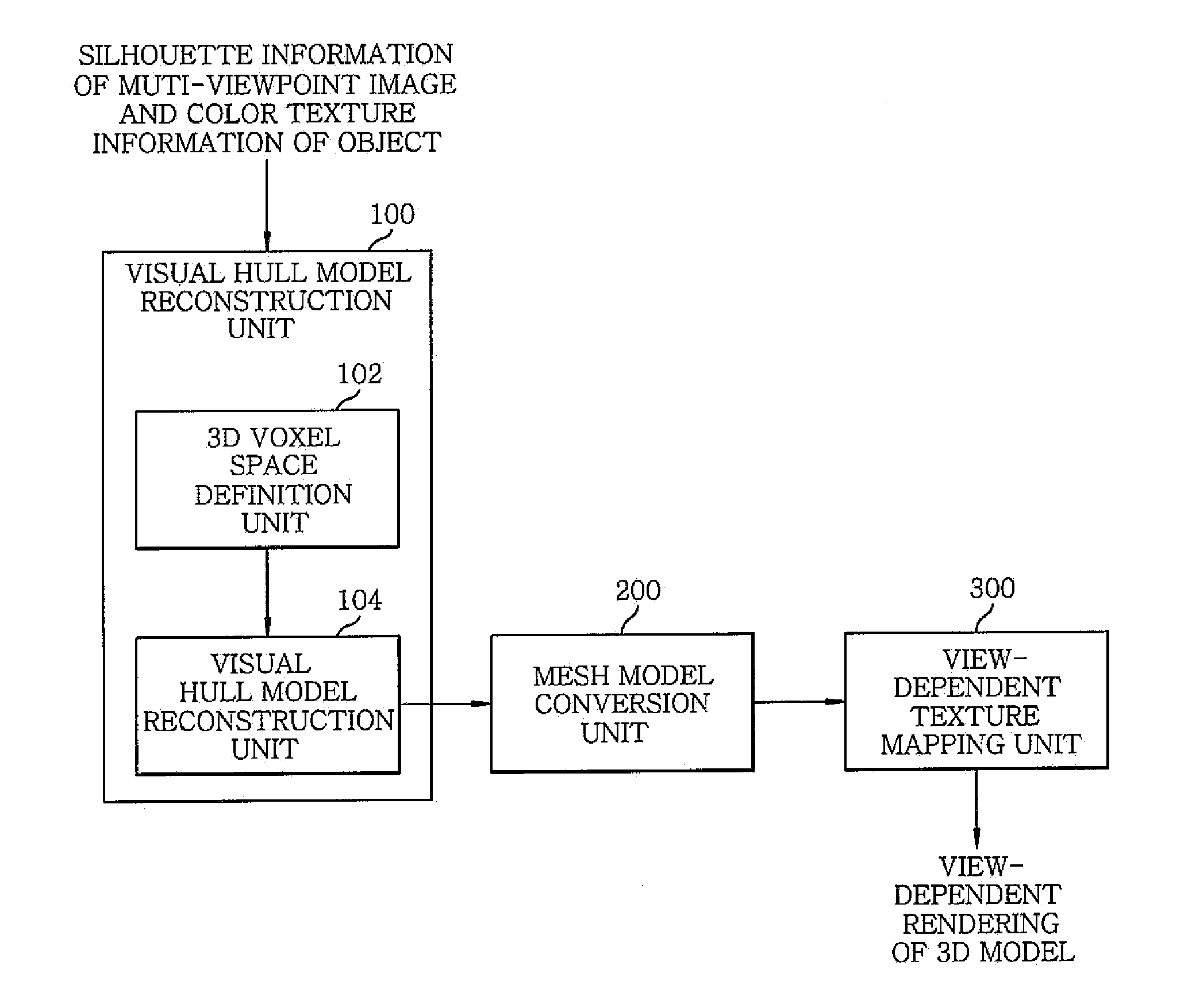
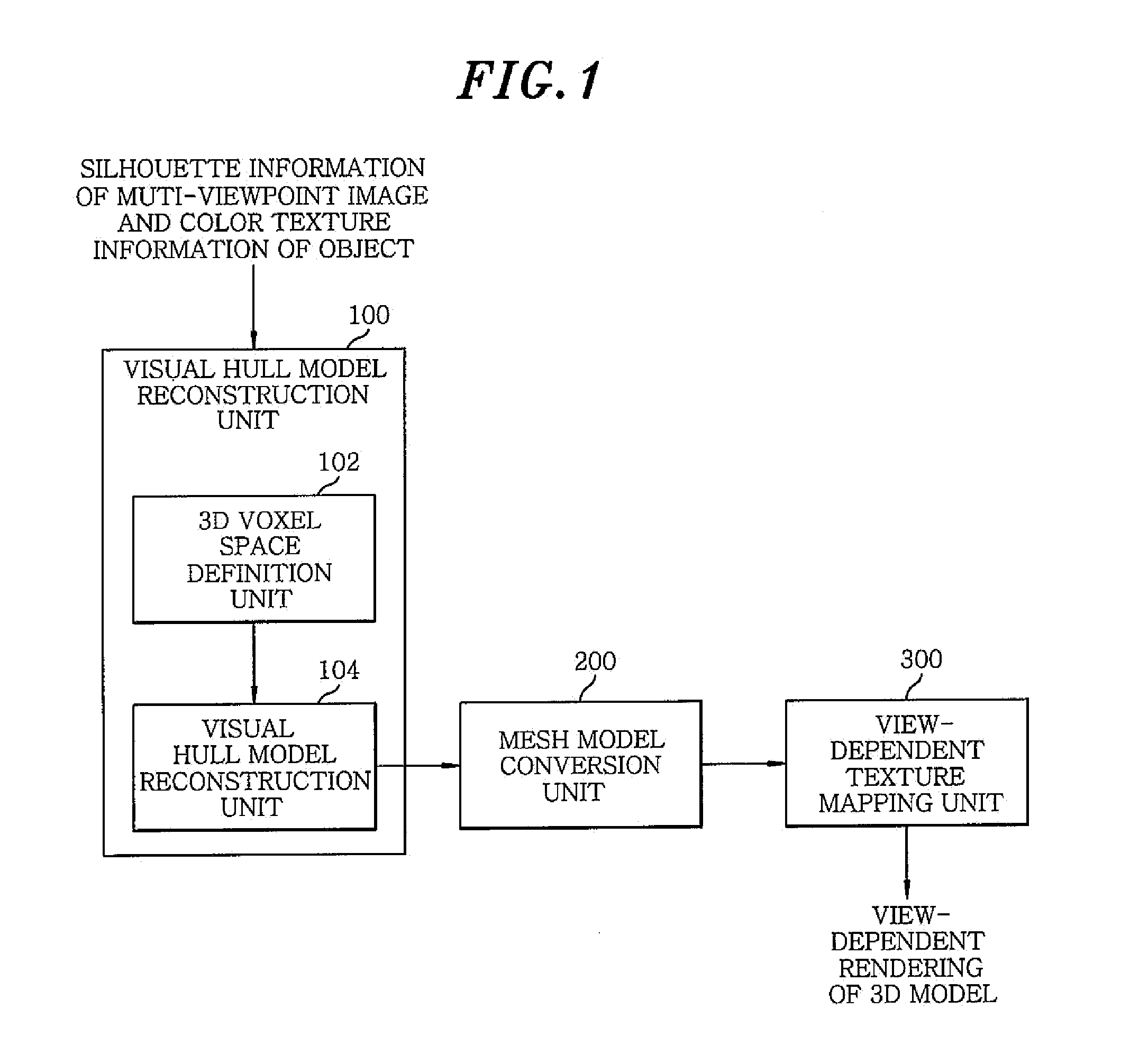
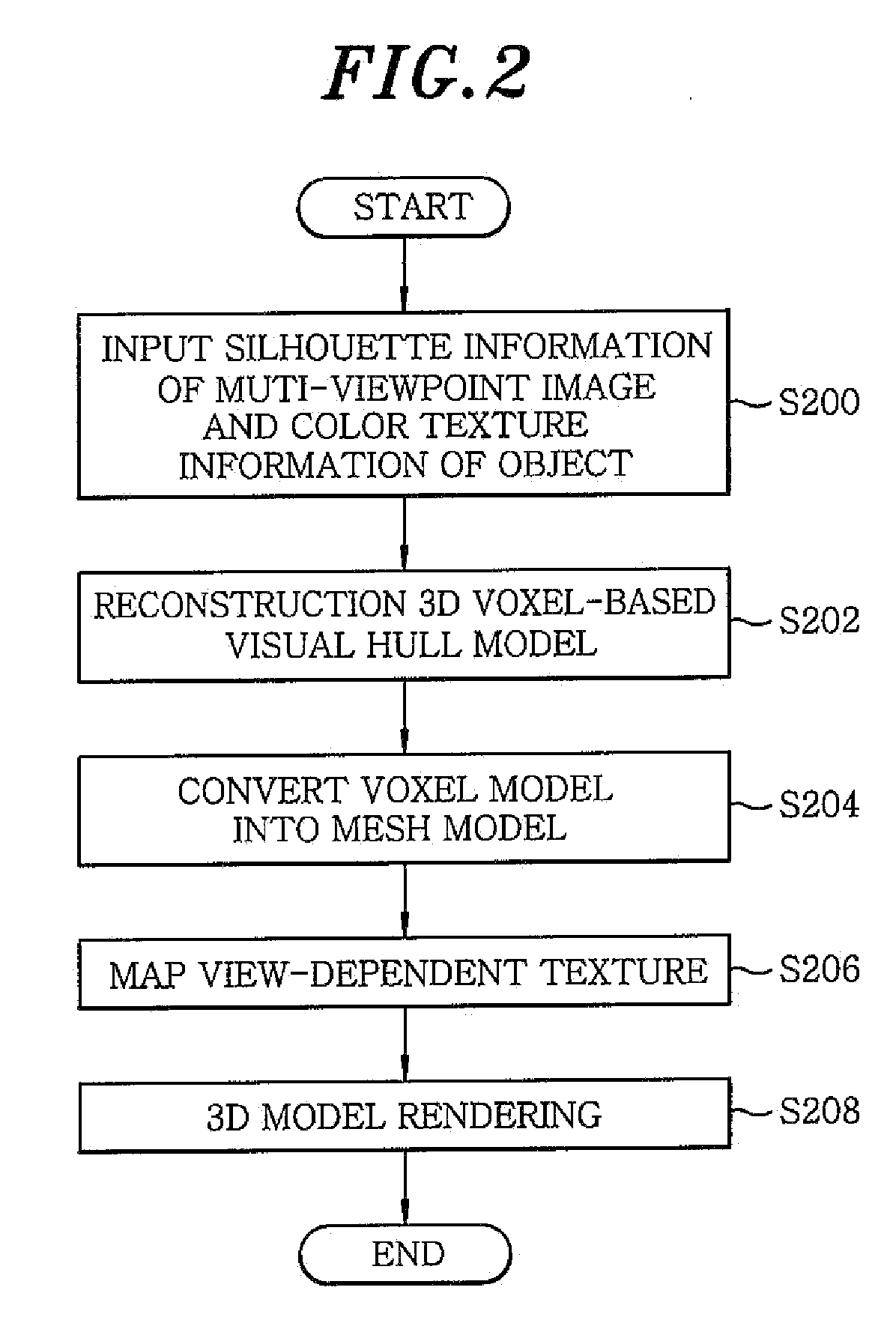
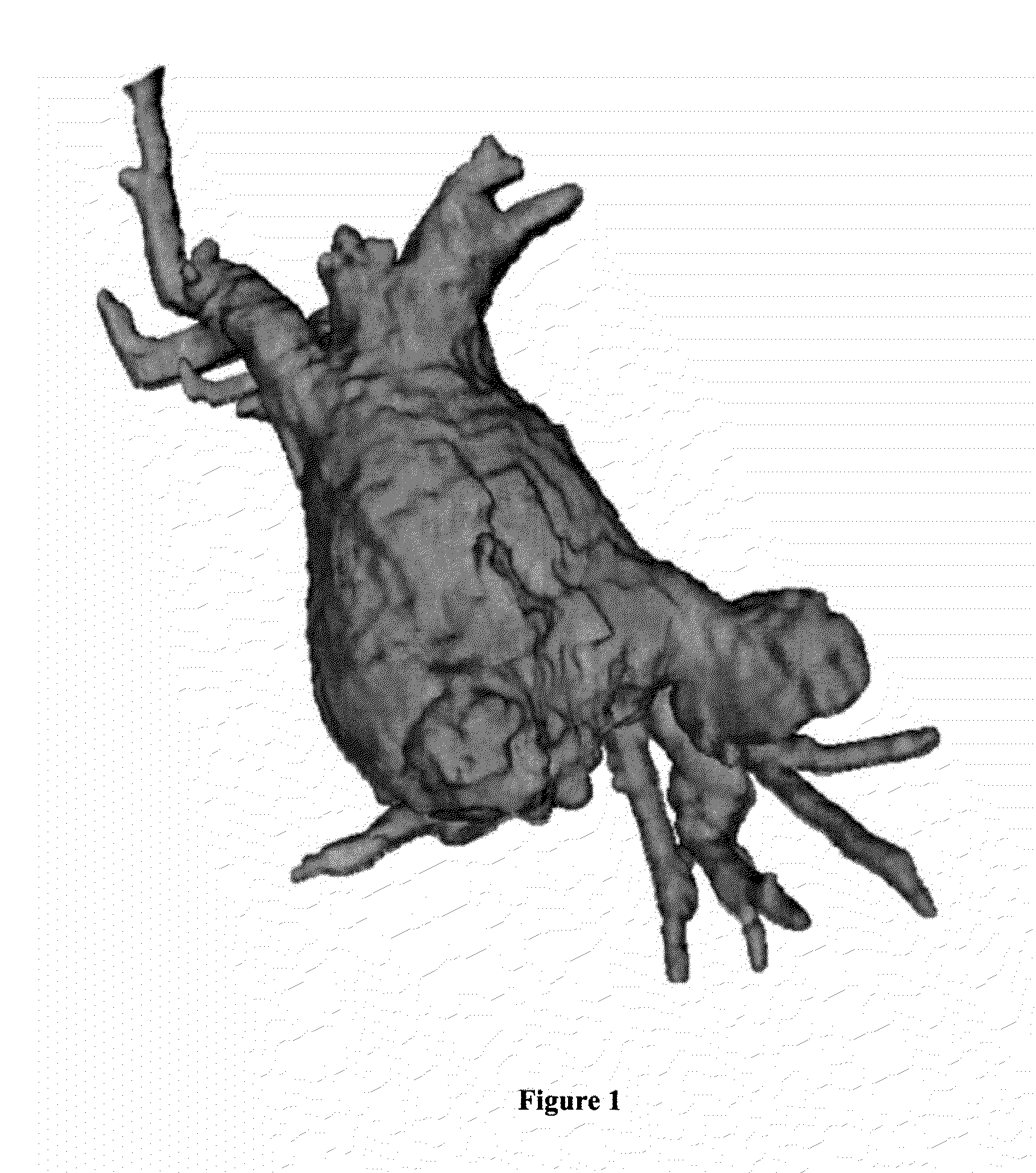
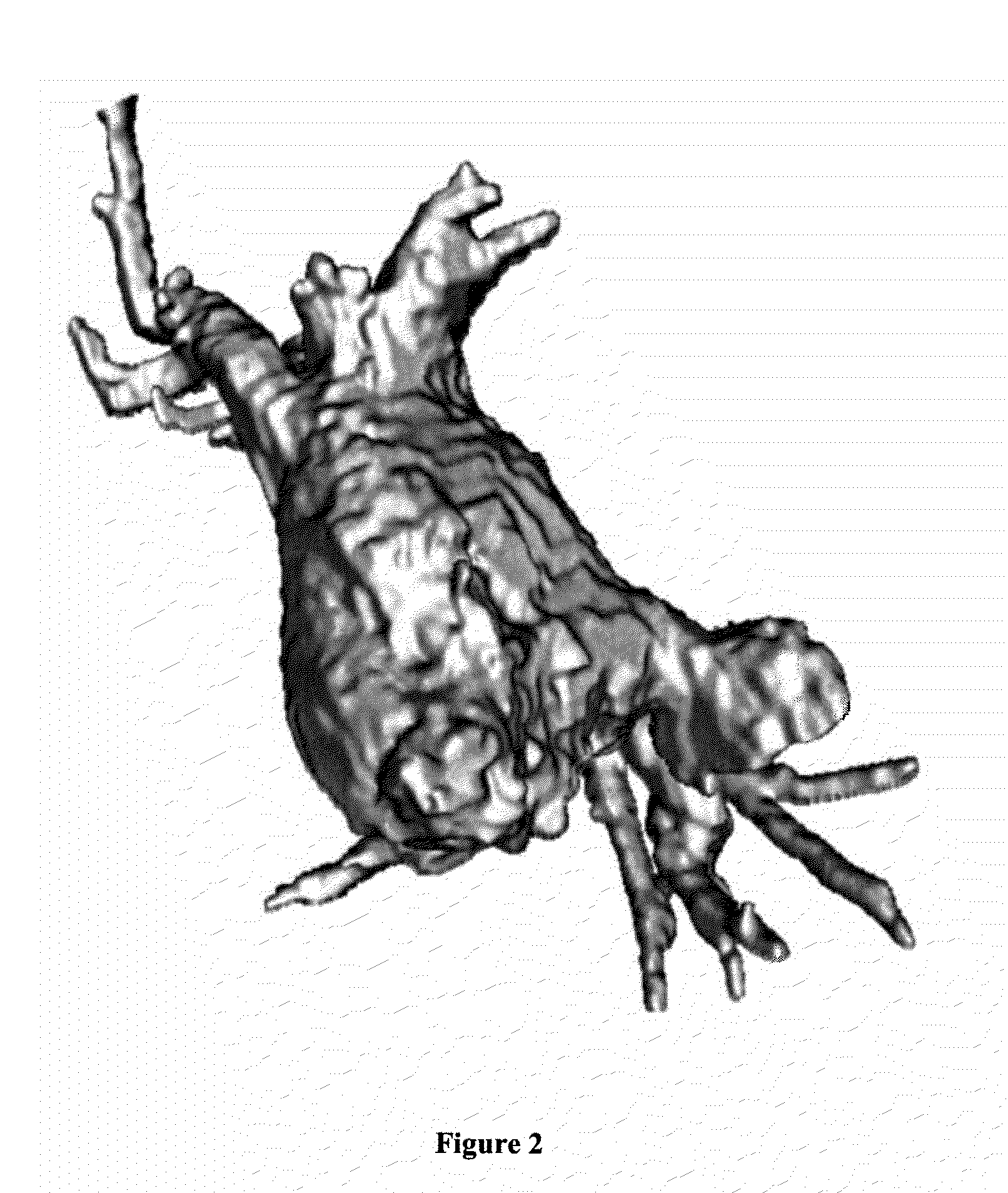
Method and apparatus for reconstructing 3D model
InactiveUS20100156901A1Loss can be compensatedEffective compensation3D-image rendering3D modellingView cameraVoxel
A method of reconstructing a 3D model includes reconstructing a 3D voxel-based visual hull model using input images of an object captured by a multi view camera; converting the 3D voxel-based visual hull model into a mesh model; and generating a result of view-dependent rendering of a 3D model by performing the view-dependent texture mapping on the mesh model obtained through the conversion. Further, the reconstructing includes defining a 3D voxel space to be reconstructed; and excluding voxels not belonging to the object from the defined 3D voxel space.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Block-based fragment filtration with feasible multi-GPU acceleration for real-time volume rendering on conventional personal computer
ActiveUS7154500B2Reduce the burden onDetails involving 3D image dataCathode-ray tube indicatorsVoxelFiltration
A computer-based method and system for interactive volume rendering of a large volume data on a conventional personal computer using hardware-accelerated block filtration optimizing uses 3D-textured axis-aligned slices and block filtration. Fragment processing in a rendering pipeline is lessened by passing fragments to various processors selectively in blocks of voxels based on a filtering process operative on slices. The process involves generating a corresponding image texture and performing two-pass rendering, namely a virtual rendering pass and a main rendering pass. Block filtration is divided into static block filtration and dynamic block filtration. The static block filtration locates any view-independent unused signal being passed to a rasterization pipeline. The dynamic block filtration determines any view-dependent unused block generated due to occlusion. Block filtration processes utilize the vertex shader and pixel shader of a GPU in conventional personal computer graphics hardware. The method is for multi-thread, multi-GPU operation.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
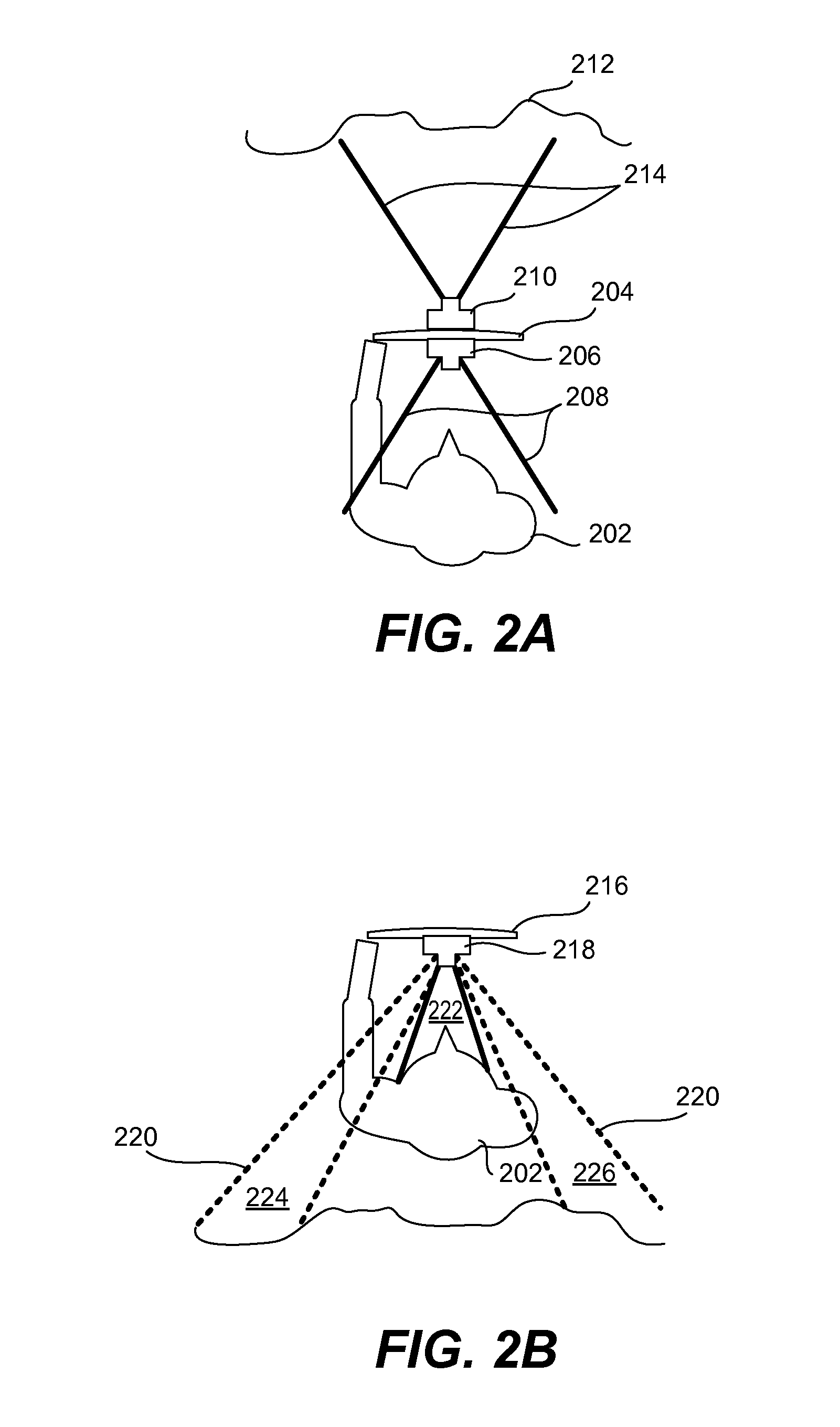
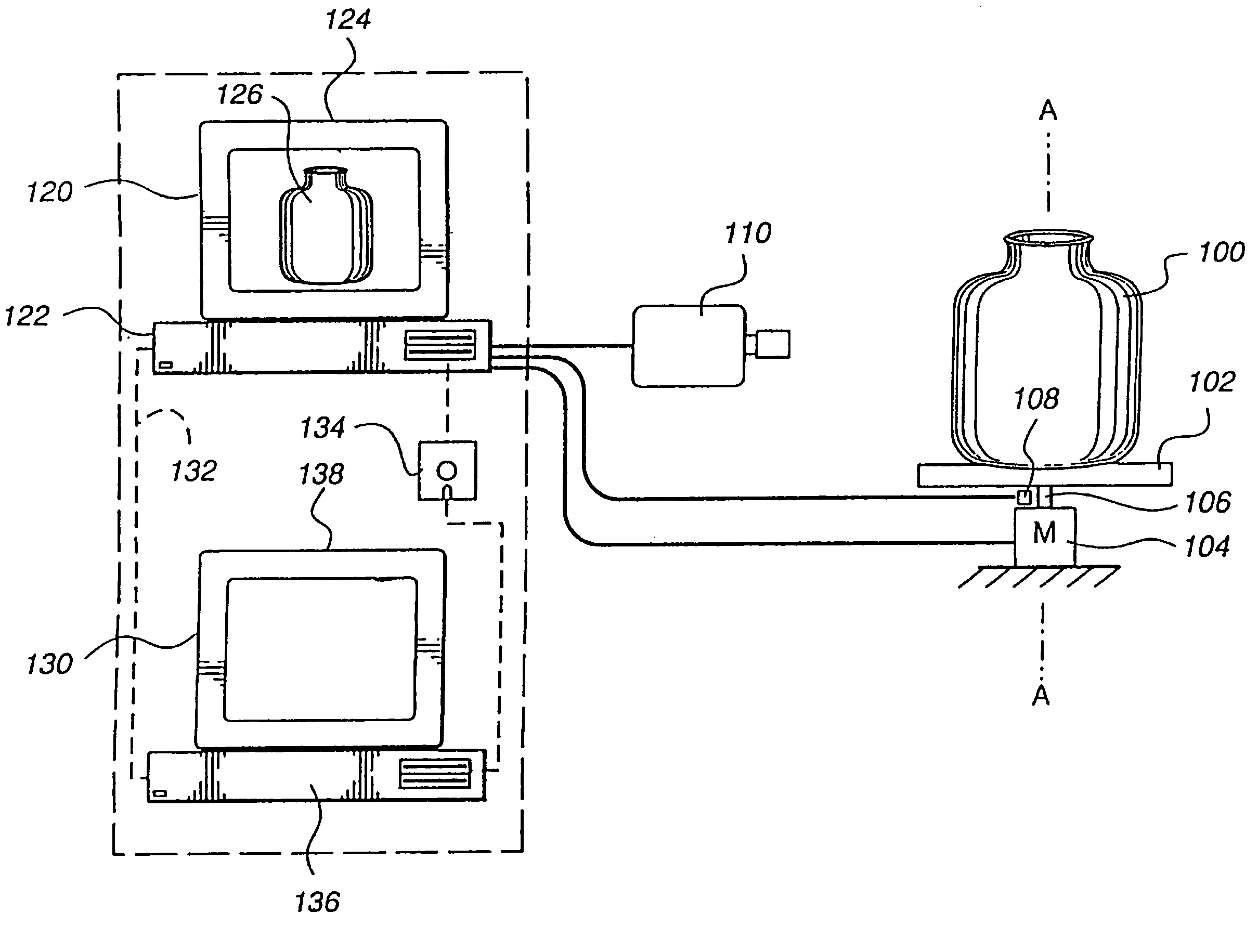
Calibration ring for developing and aligning view dependent image maps with 3-D surface data
InactiveUS7271377B2Improve accuracyImprove system accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisVisibilityData transmission
Apparatus and method for creating 3D imagery of an object using calibration means to transfer data to a reference frame and visibility analysis to determine and resolve occlusion.
Owner:MUELLER FREDERICK E
Method and system for culling view dependent visual data streams for a virtual environment
InactiveUS20050253872A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsData streamComputer graphics (images)
A method for culling visual data streams. Specifically, one embodiment of the present invention discloses a method for culling view dependent visual data streams for a virtual environment. The method begins by determining a view volume of a viewing participant within the virtual environment. The view volume determines a field-of-view of the viewing participant within the virtual environment. The embodiment of the method then determines a proximity of a representation of an observed object in the virtual environment to the view volume. Thereafter, the embodiment of the method processes a view dependent visual data stream of the observed object only when the representation is within a specified proximity to the view volume.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP +1
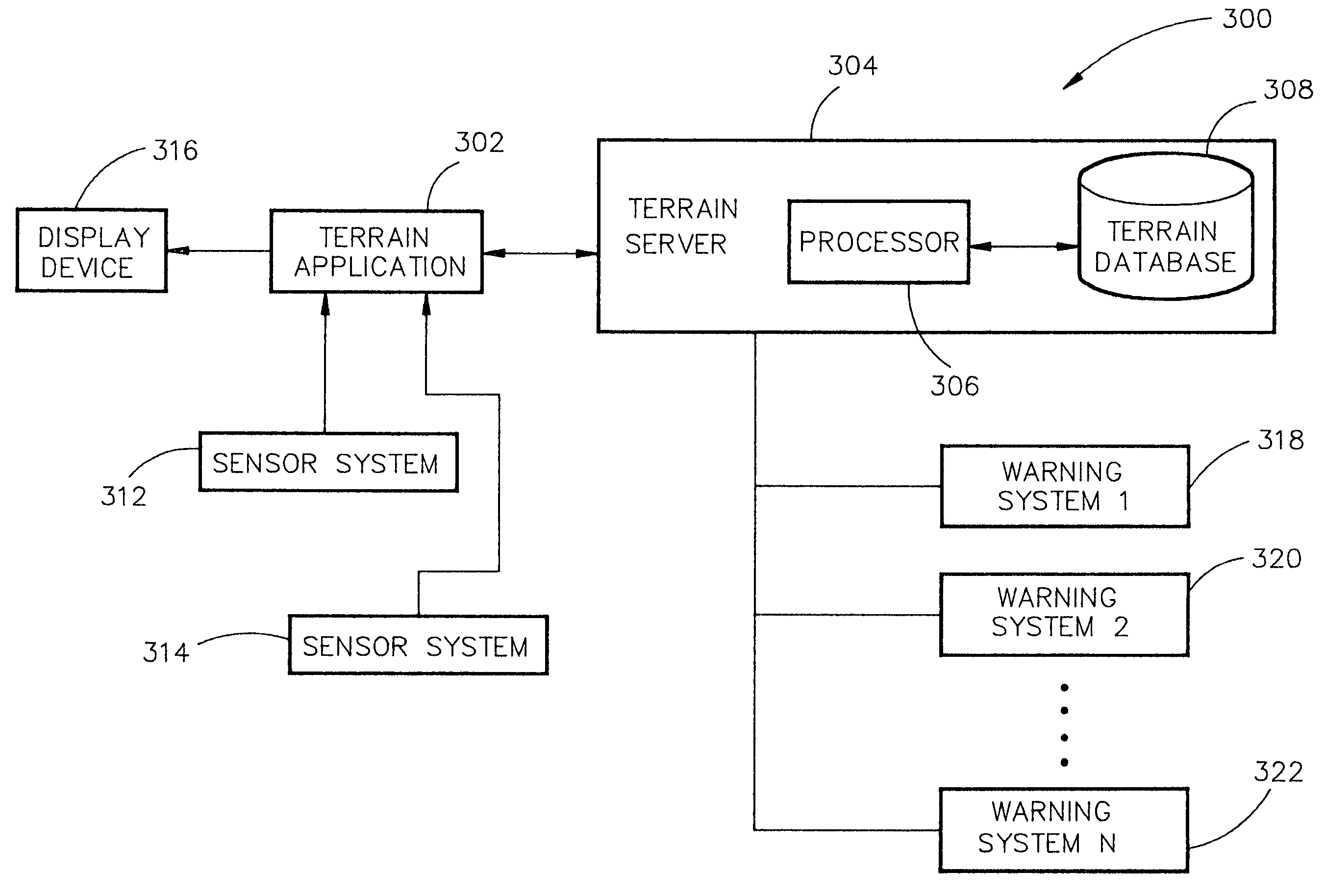
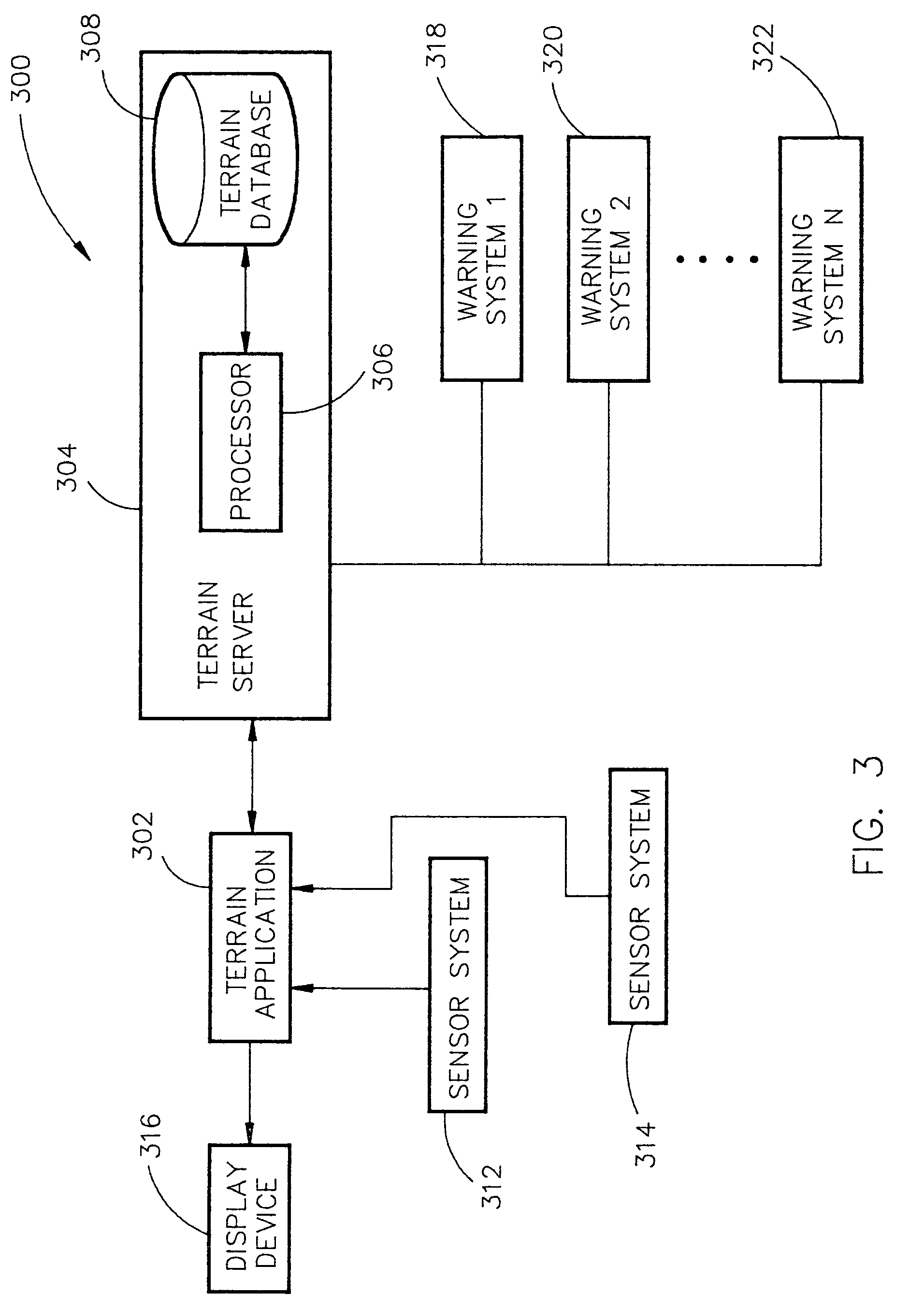
System and method for a safe depiction of terrain, airport and other dimensional data on a perspective flight display with limited bandwidth of data presentation
ActiveUS7262713B1Limited bandwidthReduce usageAnalogue computers for trafficNavigation instrumentsTerrainSystem capacity
The present invention is directed to a system and method for a safe flight display through increasing situation awareness by an optimal presentation, given limited capacity of the system. The system may determine which terrain area needs a detail representation and which area needs a coarse representation. A view-dependent visual error metric may be utilized to define and maintain an error bound and accurately minimize the amount of terrain data being depicted. By performing a breadth-first search on the terrain database, a user can determine amount of geometry to be displayed with limited bandwidth of data presentation. The user may be allowed to scale the application to his / her desired level of detail, given a capacity of the system. Therefore, the system may provide a safe flight display with an anticipated and graceful (all portions of the screen would be given an equal quality representation) degradation in performance upon the choice of the user.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Three-dimensional image display system
InactiveUS6999110B2Generation is preventedPrevent intrusionSteroscopic systemsOptical elementsParallaxLight beam
A three-dimensional image display system utilizing both a light beam reproducing method and a shadowgraph multi-view parallax method, including a color filter is disposed on an observer side of a white-color point light source array, and, in an area apart from the color filter and white point light source, light beams emitted from the white-color point light source are selectively colored by the color filter for generating an image of each point of an object, while in the region in the vicinity of the point light source and the color filter, the light beams are selectively colored by the color filter so that image data reaching the eye from the white-color point light source through the color filter performs a view-dependent parallax stereoscopic display operation not only laterally but also vertically, and in the intermediate region, these two operations are mixed, so that a stereoscopic image is continuously formed.
Owner:KOBAYASHI TETSURO
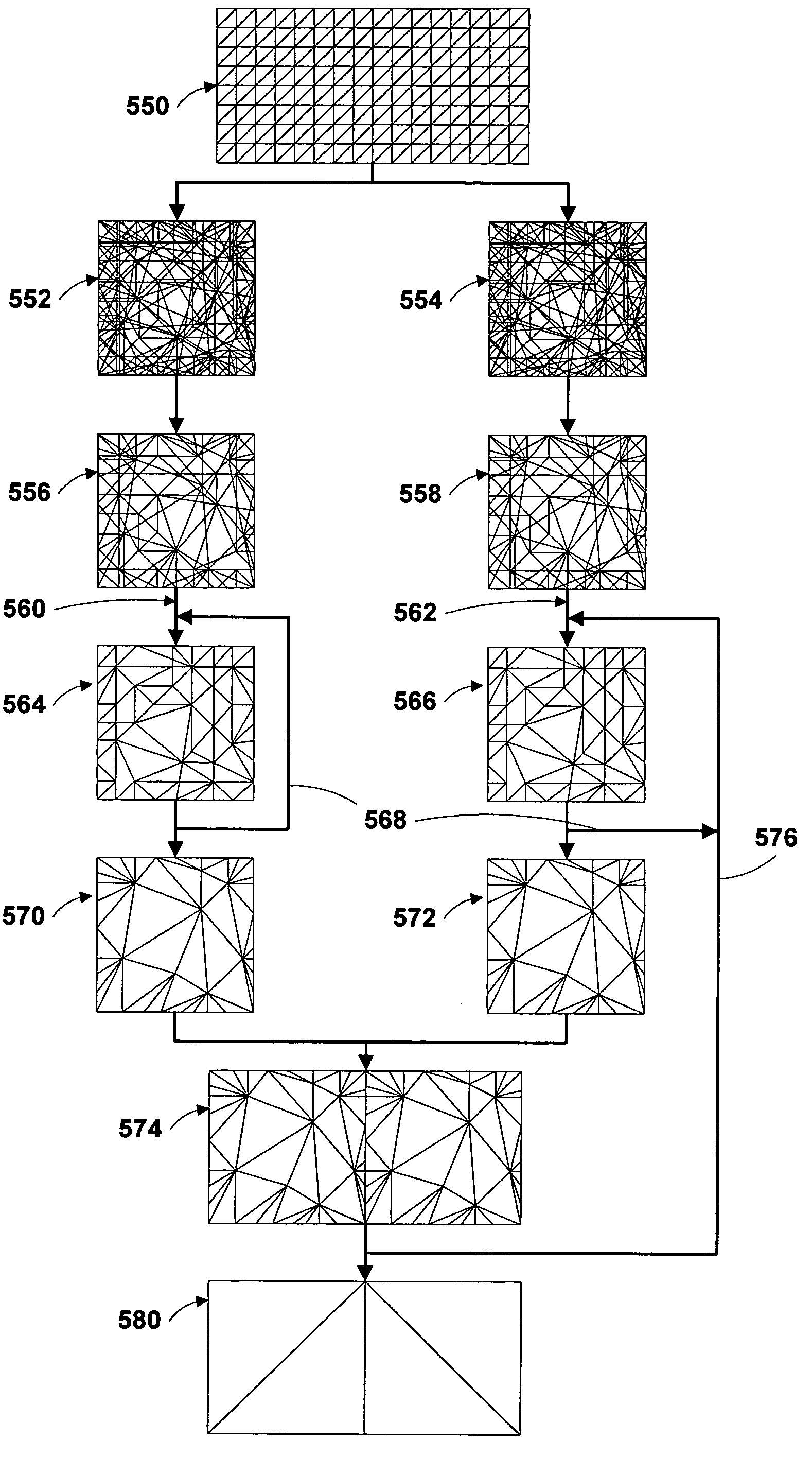
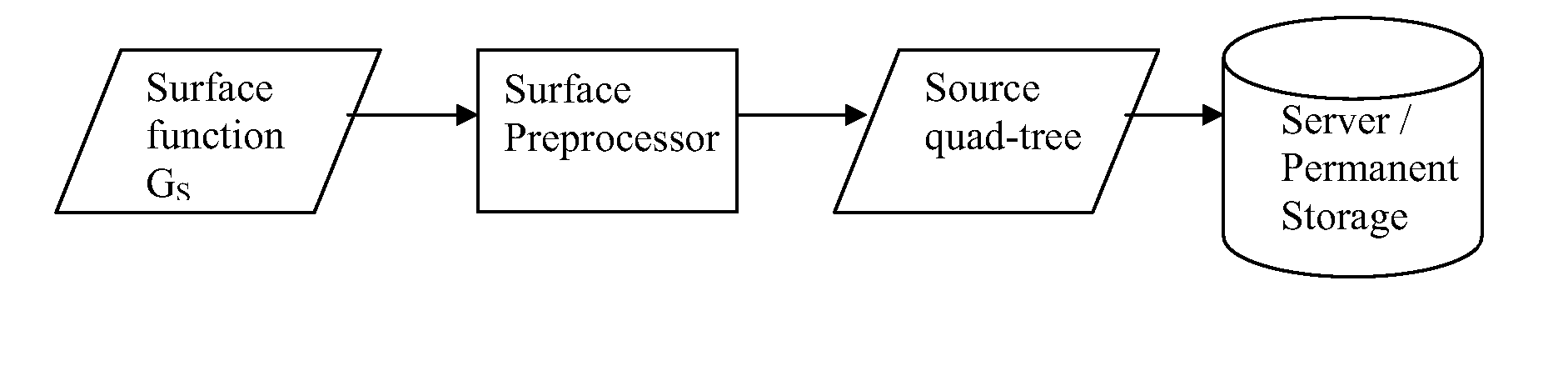
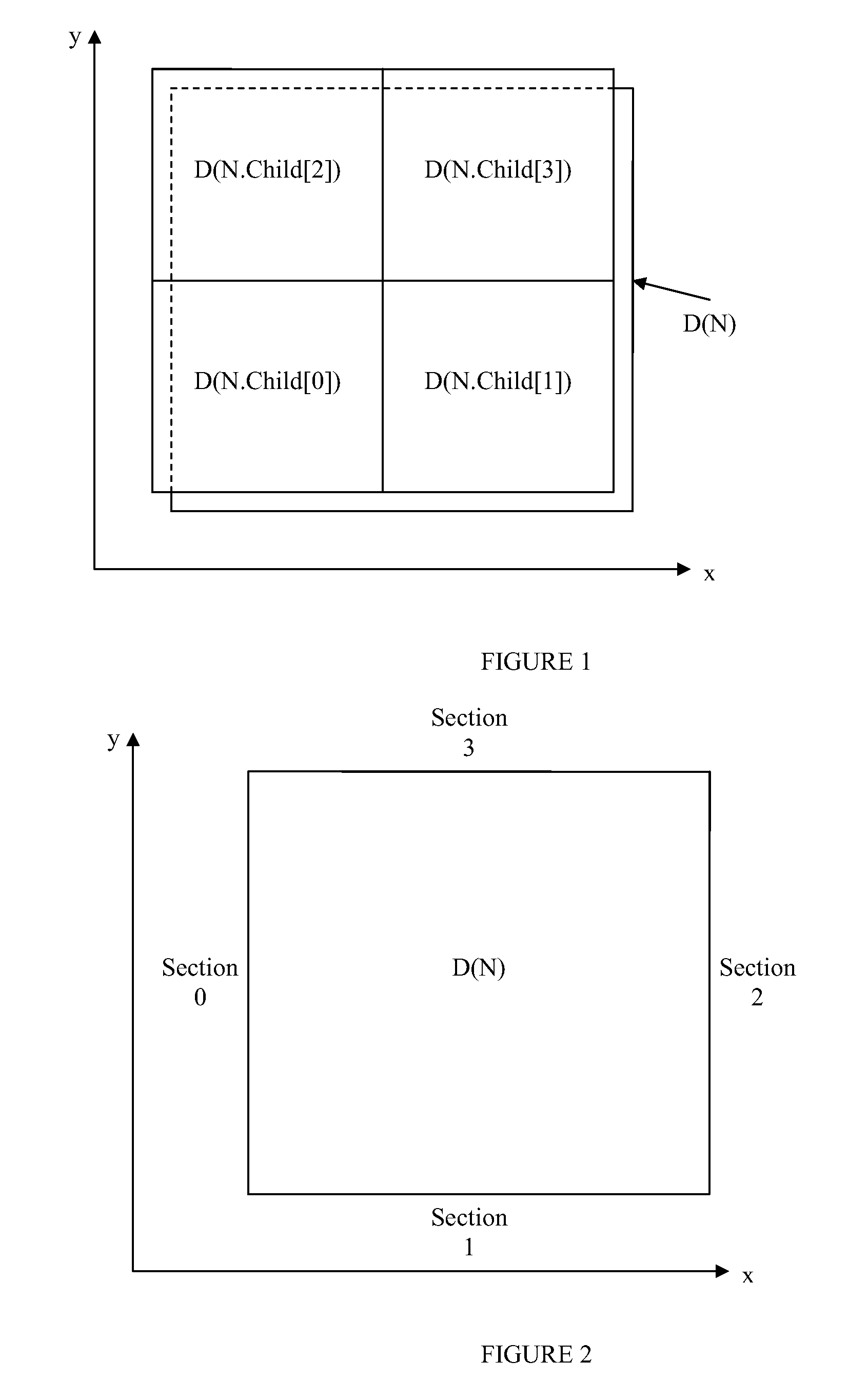
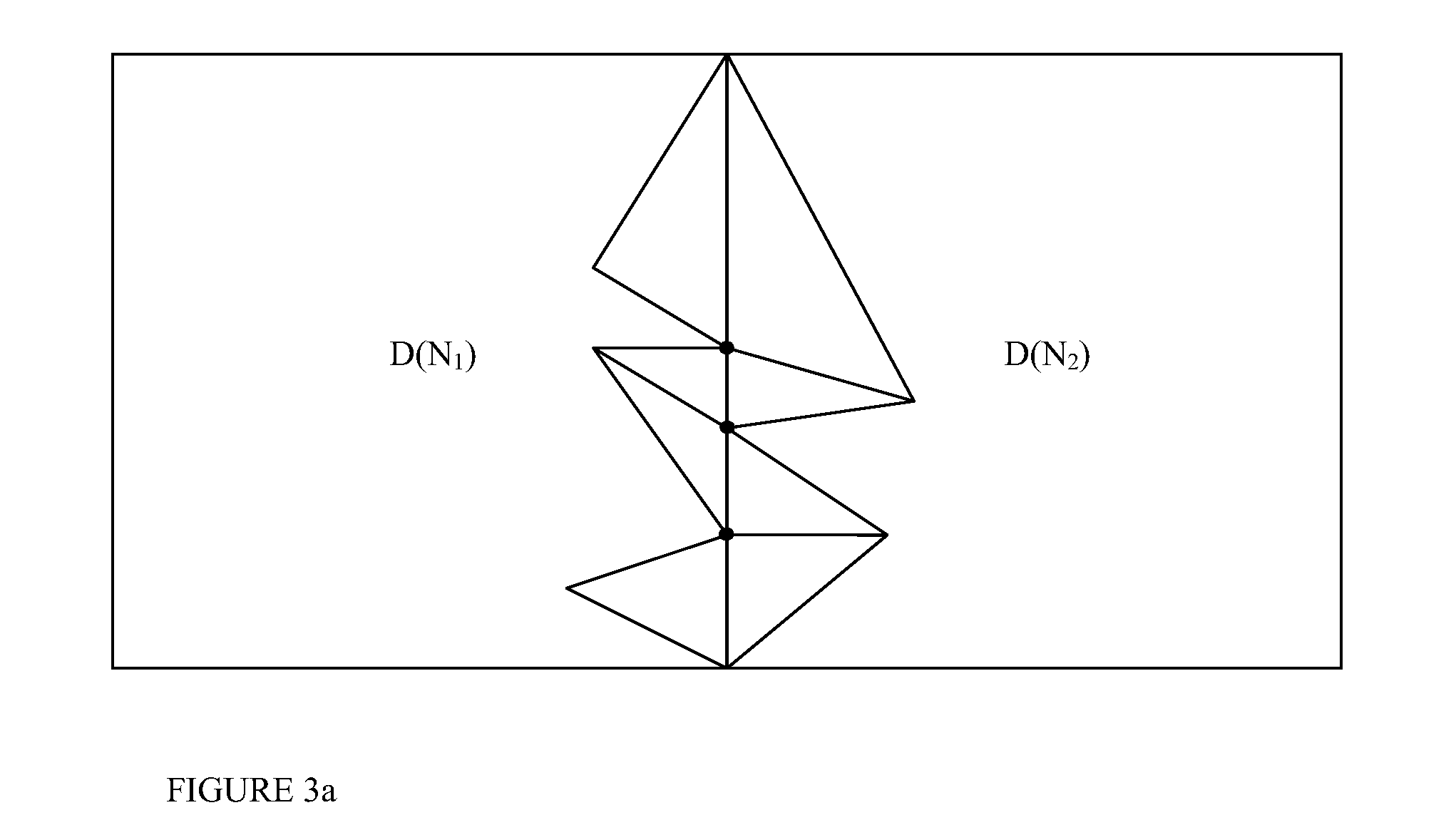
Regional progressive meshes
A regional progressive mesh provides support for real-time rendering of large-scale surfaces with locally adapting surface geometric complexity according to changing view parameters. The regional progressive mesh is constructed by subdividing an initial detailed mesh one or more times into multiple sub-regions as an iterative or recursive process. Each sub-region is separately simplified, and the localized transformations recorded in separate segments in a sequence of mesh refinement transformations that form the progressive mesh representation. The resulting regionalized organization of mesh refinement transformations reduces the working set of memory pages containing progressive mesh data needed for real-time view-dependent adaptation and rendering of the mesh surface. An exact approximate error measurement of a vertex split transformation also is defined as the maximum height deviation at enumerated vertices in the open neighborhood of the transformation relative to a regular triangulation of grid points, where the enumerated vertices include the grid points internal to the faces adjacent the split vertex and the grid line crossings internal to edges adjacent the split vertex.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Sideview Vision System Displaying A View Dependent Upon Transmission Selector
InactiveUS20100231715A1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsDriver/operatorDisplay device
A sideview vision system in a vehicle and a method for operating the system. The sideview vision system has a camera fixedly mounted to the vehicle for capturing an image alongside and extending rearward the vehicle, and a display for displaying a view to a driver of the vehicle. The method includes capturing an image using the camera, the image having a first portion and a second portion different from the first portion, displaying a first view corresponding to the first portion in response to the vehicle transmission being in a forward gear, and displaying a second view corresponding to the second portion in response to the transmission being in a reverse gear.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
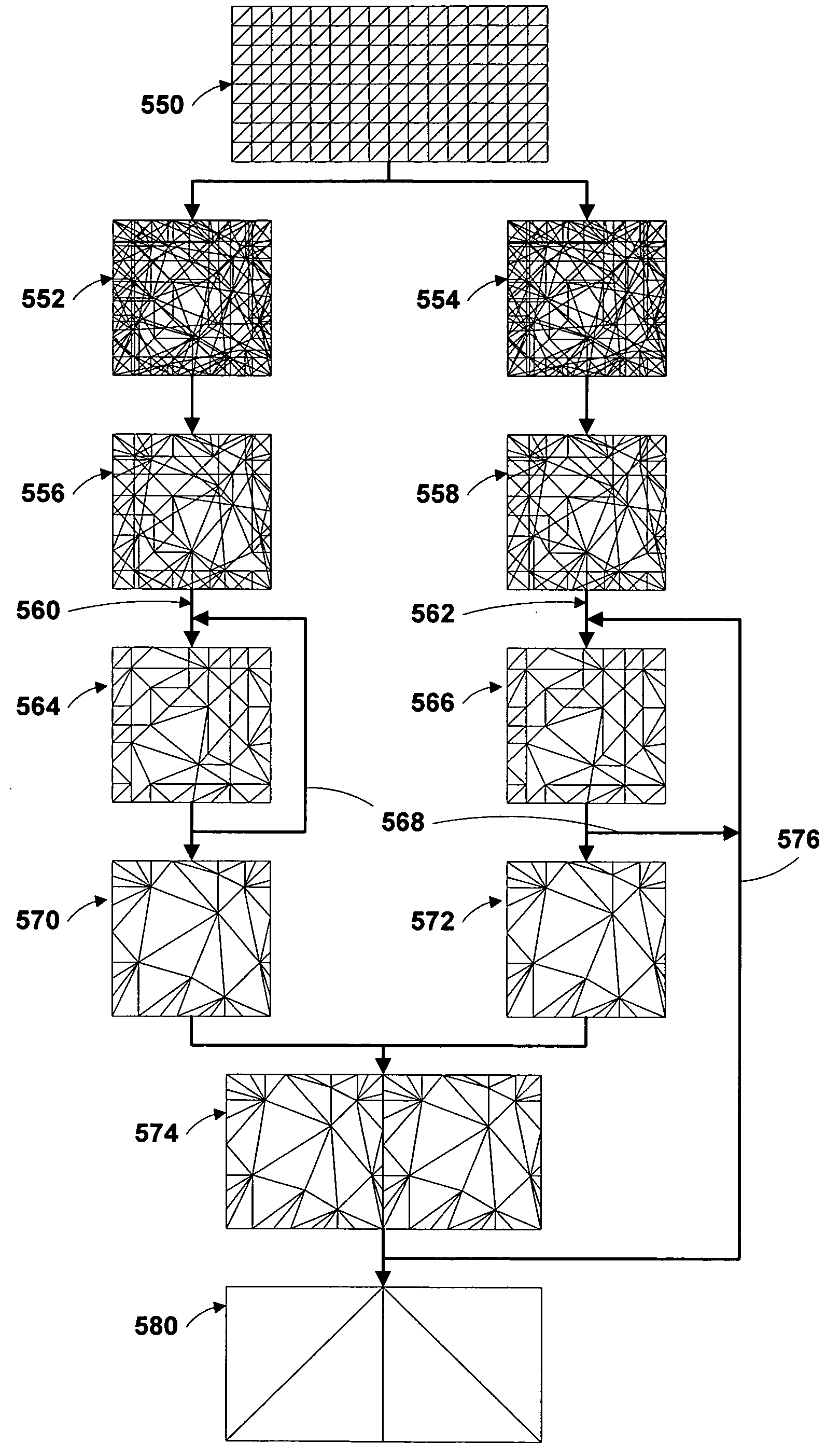
Adaptive Quadtree-based Scalable Surface Rendering
InactiveUS20070182734A1Excellent visible qualityExceptionally effectiveImage generation3D-image renderingLevel of detailGraphics accelerator
The present invention relates to computer graphics. This method allows efficient real-time 3D rendering of high-detail smooth surfaces. It is exceptionally effective with software rendering and low-end weaker graphics accelerators, and provides excellent visible quality per the amount of polygons used, while retaining low CPU processing overhead and high efficiency on graphics hardware. Also, it can be used under very restrictive memory requirements. In particular the invention relates to real time rendering of extremely detailed smooth surfaces with view-dependent tessellation using an improved level of detail approach. The invention utilizes a quad-tree map and geometric boundaries consisting of manifold non-self-intersecting surfaces. All cached fragments keep all of the information loaded from their corresponding source nodes in system memory, and additional information computed by the rendering system.
Owner:3DVU LTD 2000 ISRAEL +2
Regional progressive meshes
A regional progressive mesh provides support for real-time rendering of large-scale surfaces with locally adapting surface geometric complexity according to changing view parameters. The regional progressive mesh is constructed by subdividing an initial detailed mesh one or more times into multiple sub-regions as an iterative or recursive process. Each sub-region is separately simplified, and the localized transformations recorded in separate segments in a sequence of mesh refinement transformations that form the progressive mesh representation. The resulting regionalized organization of mesh refinement transformations reduces the working set of memory pages containing progressive mesh data needed for real-time view-dependent adaptation and rendering of the mesh surface. An exact approximate error measurement of a vertex split transformation also is defined as the maximum height deviation at enumerated vertices in the open neighborhood of the transformation relative to a regular triangulation of grid points, where the enumerated vertices include the grid points internal to the faces adjacent the split vertex and the grid line crossings internal to edges adjacent the split vertex.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Block-based fragment filtration with feasible multi-GPU acceleration for real-time volume rendering on conventional personal computer
A computer-based method and system for interactive volume rendering of a large volume data on a conventional personal computer using hardware-accelerated block filtration optimizing uses 3D-textured axis-aligned slices and block filtration. Fragment processing in a rendering pipeline is lessened by passing fragments to various processors selectively in blocks of voxels based on a filtering process operative on slices. The process involves generating a corresponding image texture and performing two-pass rendering, namely a virtual rendering pass and a main rendering pass. Block filtration is divided into static block filtration and dynamic block filtration. The static block filtration locates any view-independent unused signal being passed to a rasterization pipeline. The dynamic block filtration determines any view-dependent unused block generated due to occlusion. Block filtration processes utilize the vertex shader and pixel shader of a GPU in conventional personal computer graphics hardware. The method is for multi-thread, multi-GPU operation.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
View dependent techniques to determine user interest in a feature in a 3D application
InactiveUS20120162225A1Multiple digital computer combinationsGeographical information databasesRelevant informationApplication software
Aspects of the invention relate generally determining user interests and providing relevant information based on user interaction with 3D models. More specifically, a when a user interacts with a 3D model of an object, for example on a map or from a database of models, the user's view of the object along with the location of the interaction (or where the user clicked on the object) may be transmitted to a server. In response, based on the view and location of the click, the server identifies relevant content and transmits it to the user.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
System and method for view-dependent anatomic surface visualization
InactiveUS20110082667A1Improve understandingEasy to splitSpecial data processing applicationsImage generationComputer graphics (images)Euclidean vector
A method for simultaneous visualization of the outside and the inside of a surface model at a selected view orientation includes receiving a digitized representation of a surface of a segmented object, where the surface representation comprises a plurality of points, receiving a selection of a viewing direction for rendering the object, calculating an inner product image be calculating an inner product {right arrow over (n)}p·{right arrow over (d)} at each point on the surface mesh, where {right arrow over (n)}p is a normalized vector representing the normal direction of the surface mesh at a point p towards the exterior of the object and {right arrow over (d)} is a normalized vector representing the view direction, and rendering the object using an opacity that is a function of the denoised inner product image to yield a rendered object, where an interior of the object is rendered.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method and system for free-view relighting of dynamic scene based on photometric stereo
ActiveUS20110285822A1Reduce complexityEasily realizedImage enhancementImage analysisView cameraLuminosity
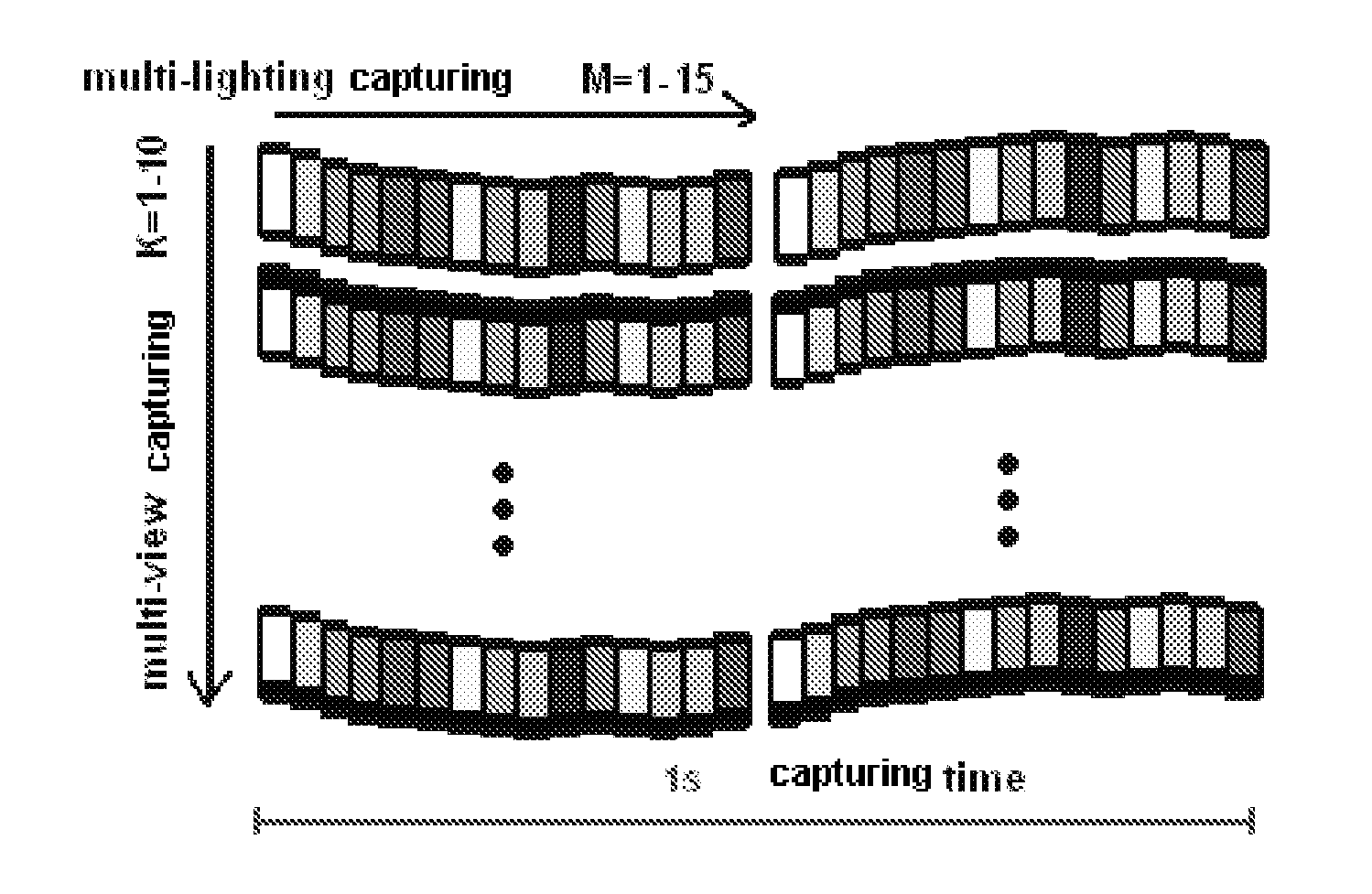
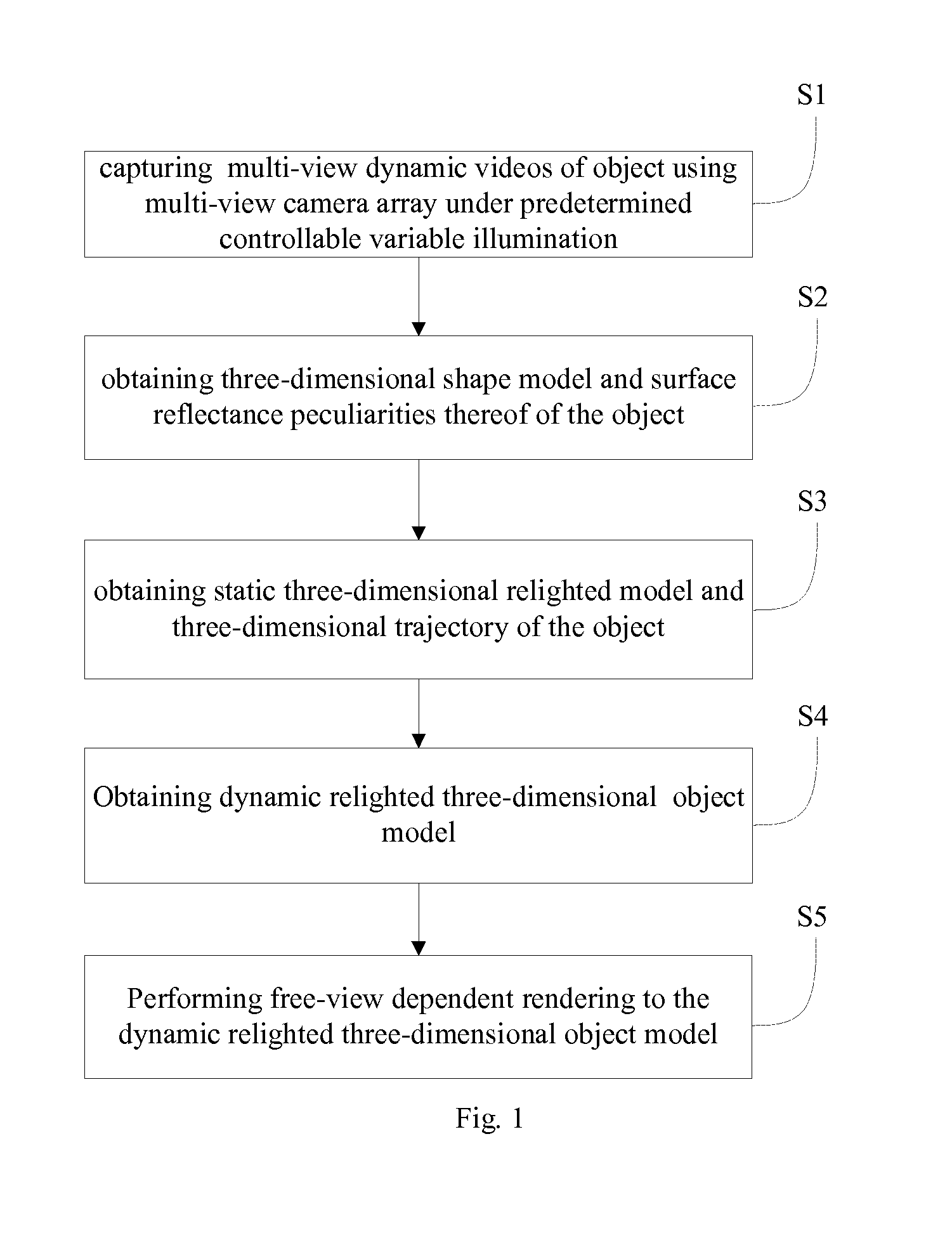
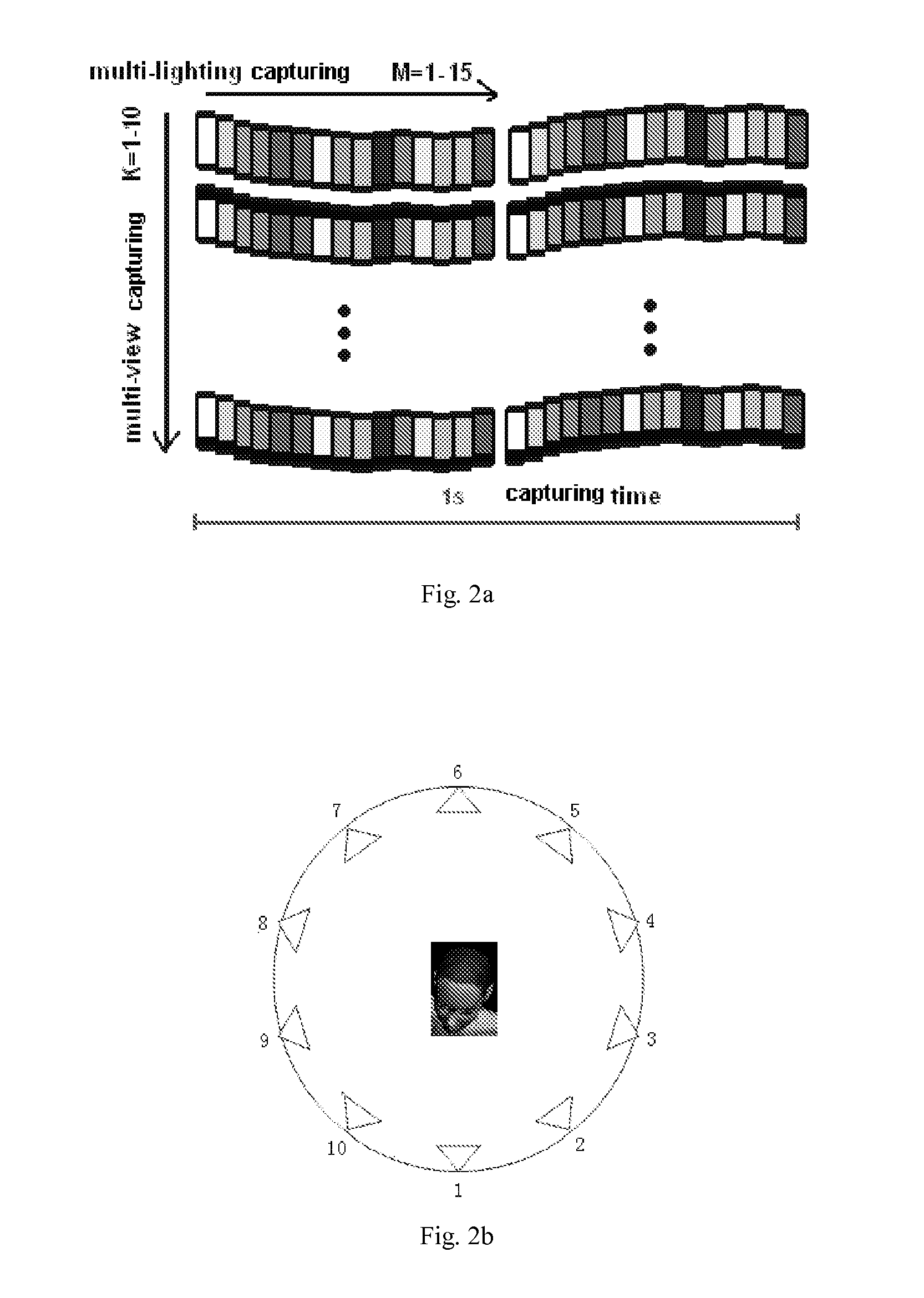
A method and a related system of free-view relighting for a dynamic scene based on photometric stereo, the method including the steps of: 1) performing multi-view dynamic videos of an object using a multi-view camera array under a predetermined controllable varying illumination; 2) obtaining a three-dimensional shape model and surface reflectance peculiarities of the object; 3) obtaining a static relighted three-dimensional model of the object and a three-dimensional trajectory of the object; 4) obtaining a dynamic relighted three-dimensional model; and 5) performing a free-view dependent rendering to the dynamic relighted three-dimensional model of the object.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
System and process for optimal texture map reconstruction from multiple views
InactiveUS20050285872A1Eliminate aliasingCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingImaging processingSynthesis methods
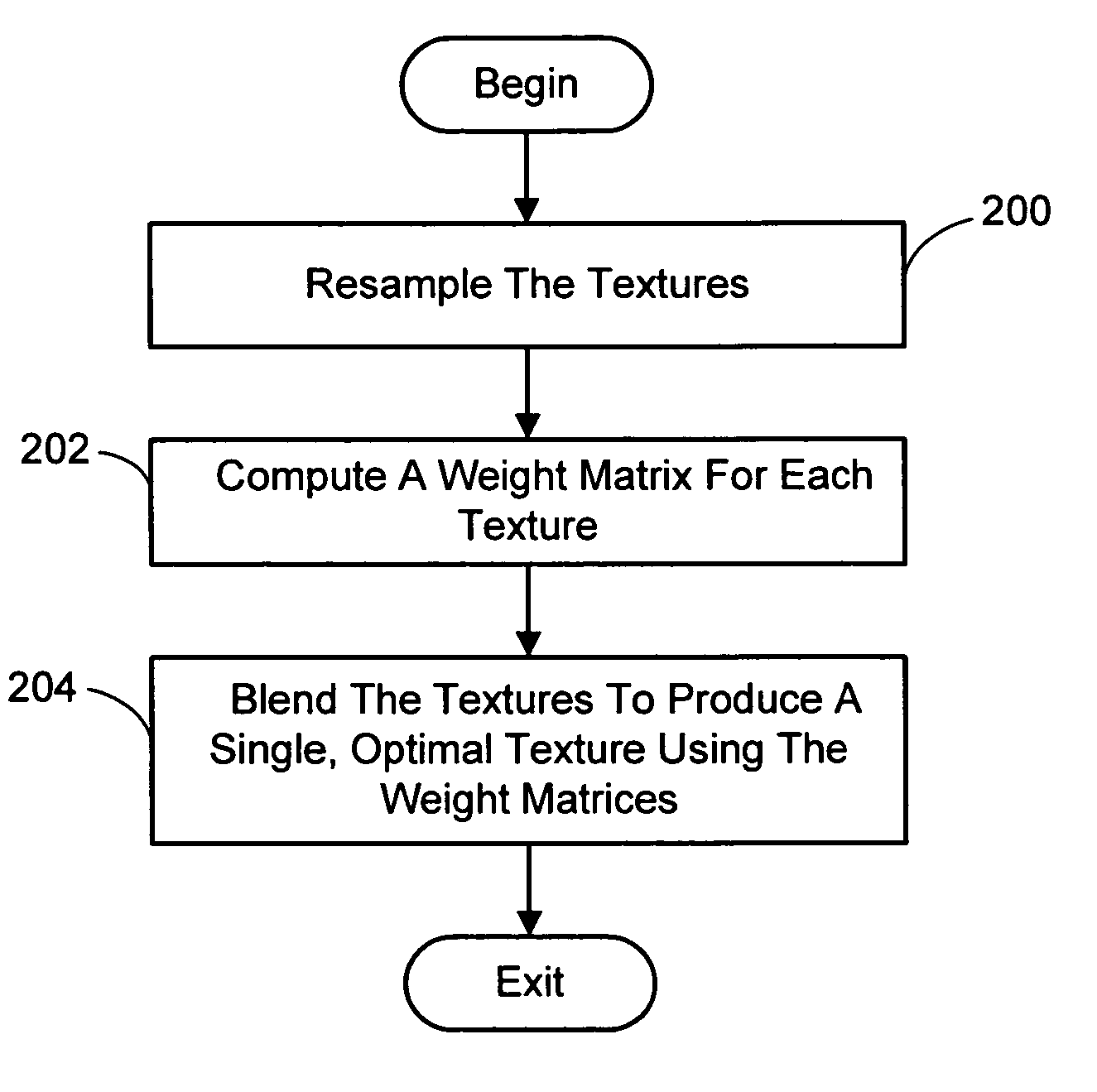
A system and process for reconstructing optimal texture maps from multiple views of a scene is described. In essence, this reconstruction is based on the optimal synthesis of textures from multiple sources. This is generally accomplished using basic image processing theory to derive the correct weights for blending the multiple views. Namely, the steps of reconstructing, warping, prefiltering, and resampling are followed in order to warp reference textures to a desired location, and to compute spatially-variant weights for optimal blending. These weights take into consideration the anisotropy in the texture projection and changes in sampling frequency due to foreshortening. The weights are combined and the computation of the optimal texture is treated as a restoration problem, which involves solving a linear system of equations. This approach can be incorporated in a variety of applications, such as texturing of 3D models, analysis by synthesis methods, super-resolution techniques, and view-dependent texture mapping.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Adaptive quadtree-based scalable surface rendering
InactiveUS7561156B2Exceptionally effectiveQuality improvementImage generation3D-image renderingLevel of detailGraphics accelerator
A 3D scalable surface renderer allows efficient real-time 3D rendering of high-detail smooth surfaces. The renderer is exceptionally effective with software rendering and low-end weaker graphics accelerators, and provides excellent visible quality per the amount of polygons used, while retaining low CPU processing overhead and high efficiency on graphics hardware. The 3D scalable surface renderer provides real time rendering of extremely detailed smooth surfaces with view-dependent tessellation using an improved level of detail approach.
Owner:3DVU LTD 2000 ISRAEL +2
System, program product and method of rendering a three dimensional image on a display
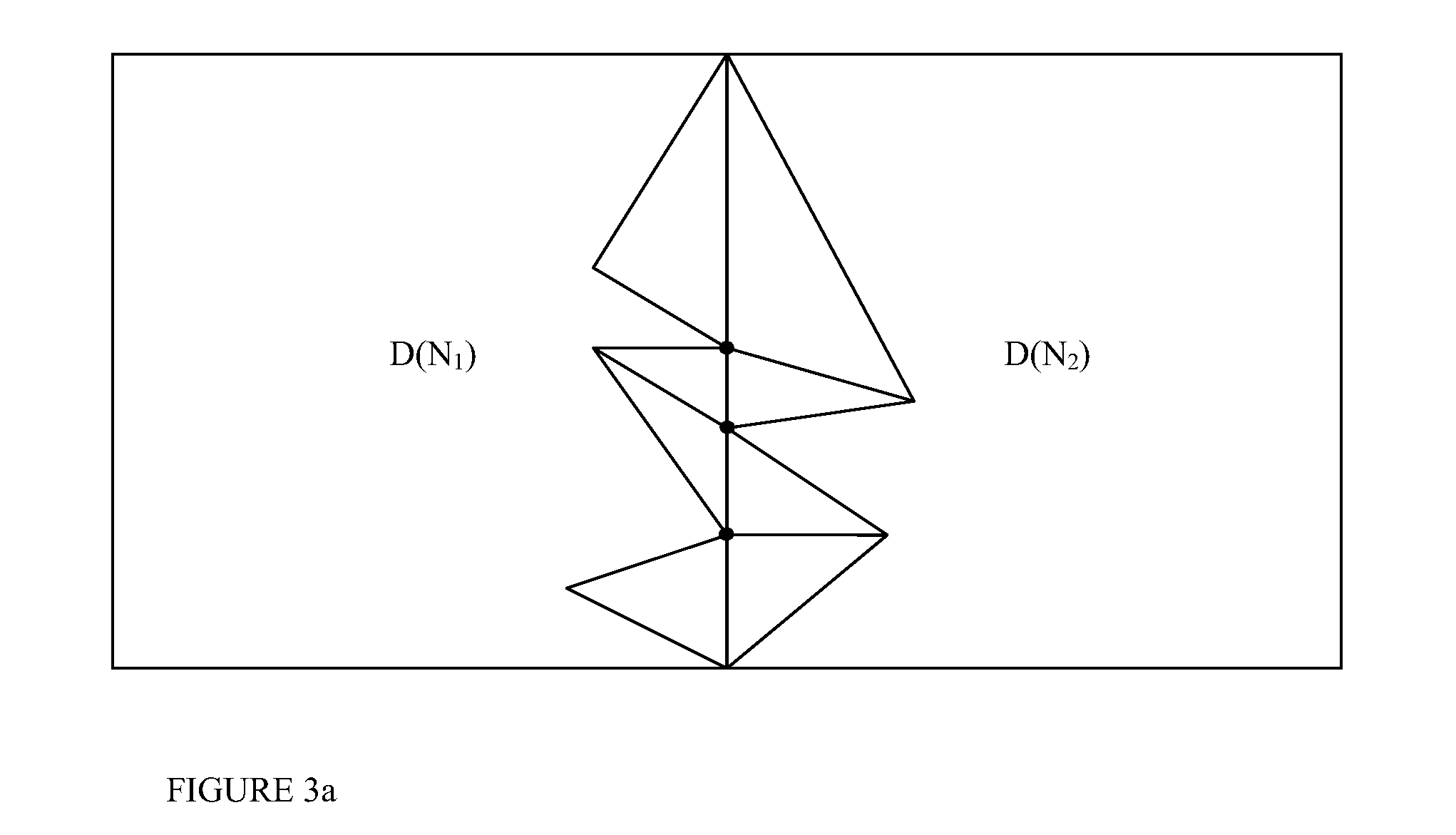
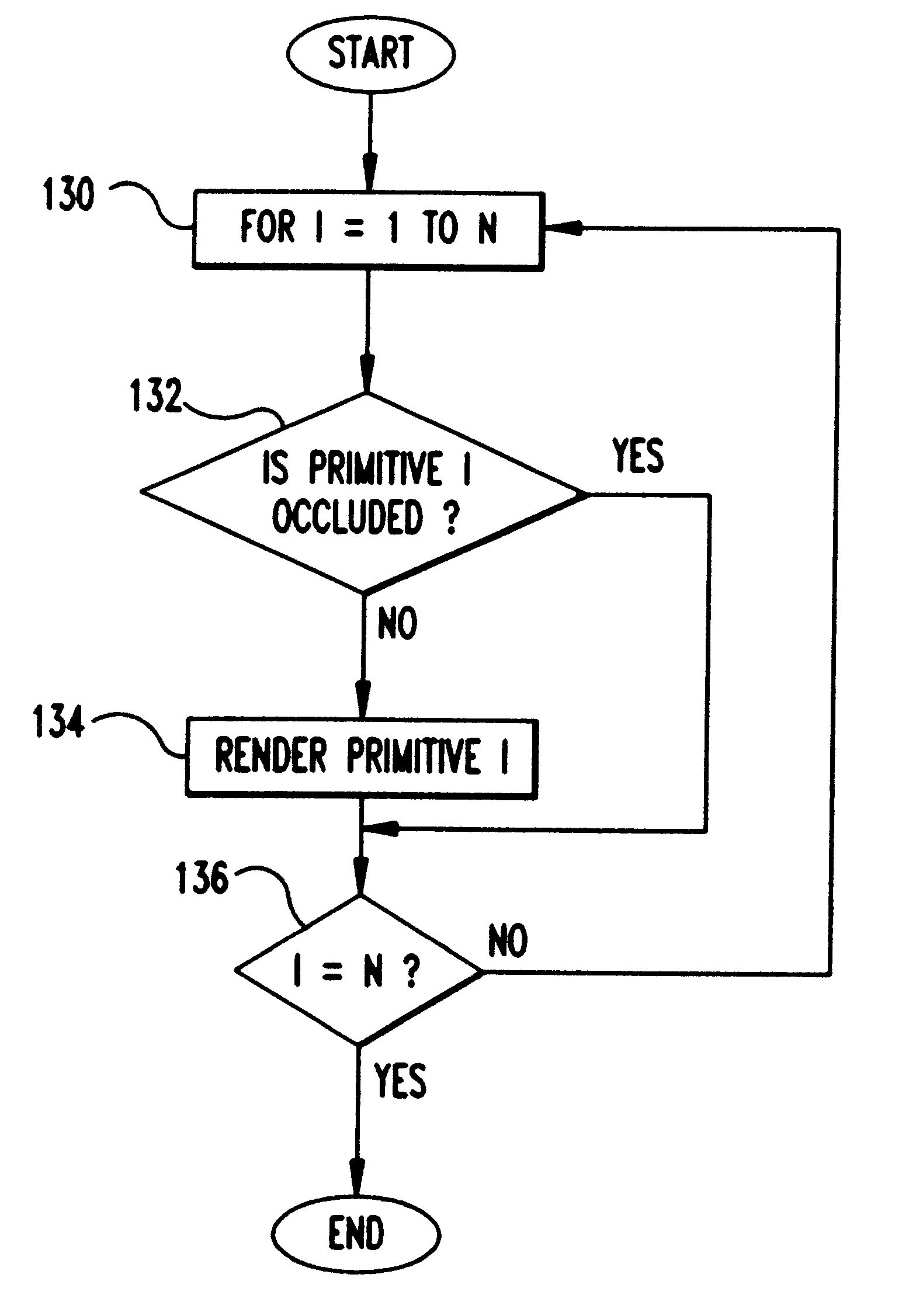
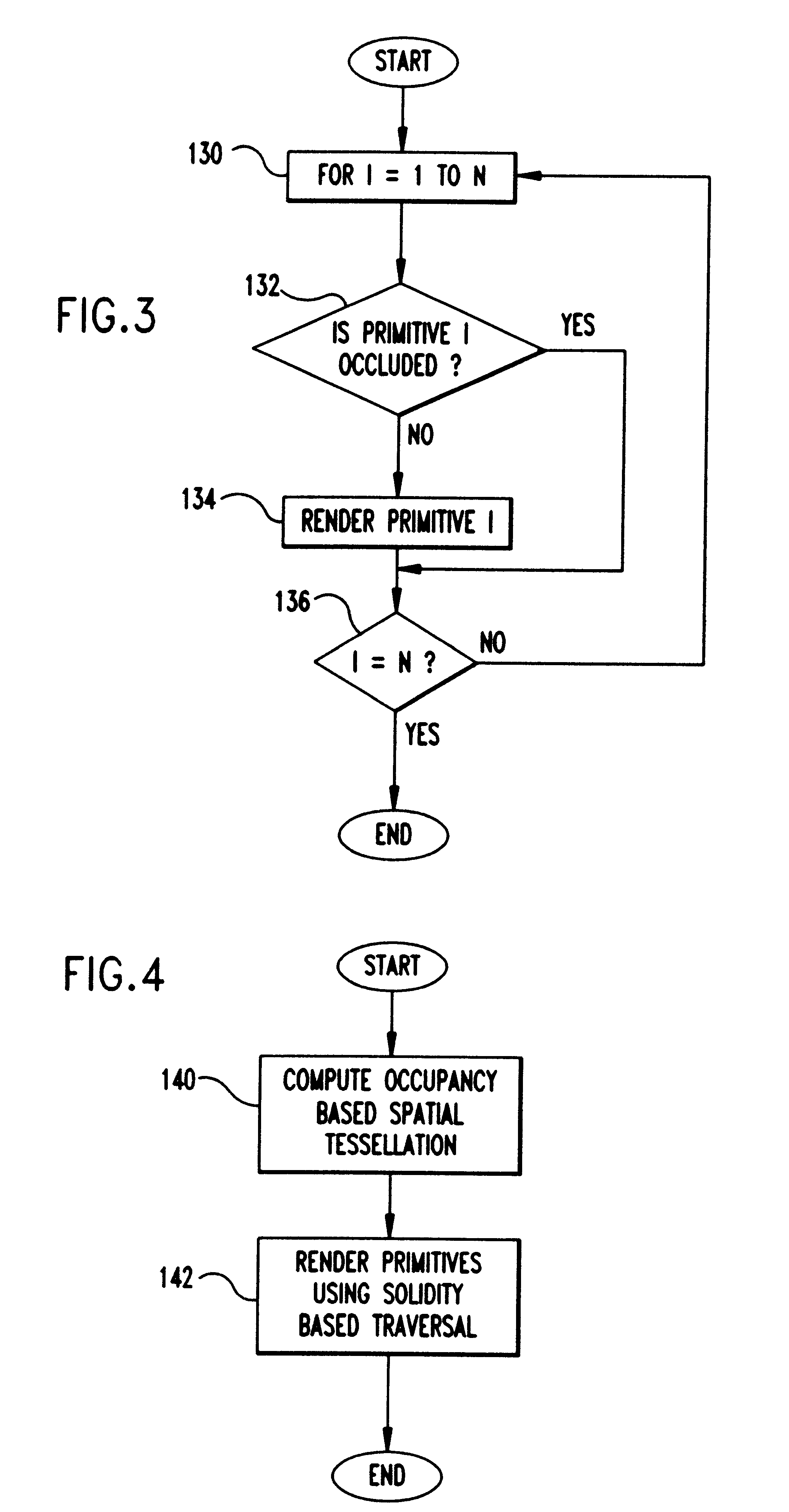
A Prioritized-Layered Projection (PLP) method and system for optimizing the rendering high-depth complexity scenes. Objects in each frame are prioritized with an estimation of the visible set within the rendered frame. A priority order for only the primitives in visible sets within the frame are computed "on demand" to maximize the likelihood of rendering visible primitives before rendering occluded ones. For a fixed budget, such as, time or number of triangles, rendering is constrained to a geometry budgeted priority. The method includes two main steps: an occupancy-based tessellation of space; and a solidity-based traversal algorithm. By first computing an occupancy-based tessellation of space, more cells result where there are more geometric primitives. In this spatial tessellation, each cell is assigned a "solidity" value directly proportional to its likelihood of occluding other cells. In its simplest form, a cell's solidity value is directly proportional to the number of primitives contained within the cell. Cells are marked for projection, and the geometric primitives contained within the marked cells are rendered. Cell solidity, and other view-dependent information determines the order cells are rendered.
Owner:IBM CORP
View dependent tiled textures
InactiveUS7071949B1Enhance detailsImprove realismCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingGraphicsView dependent
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for interactively rendering objects with surface light fields and view-dependent opacity
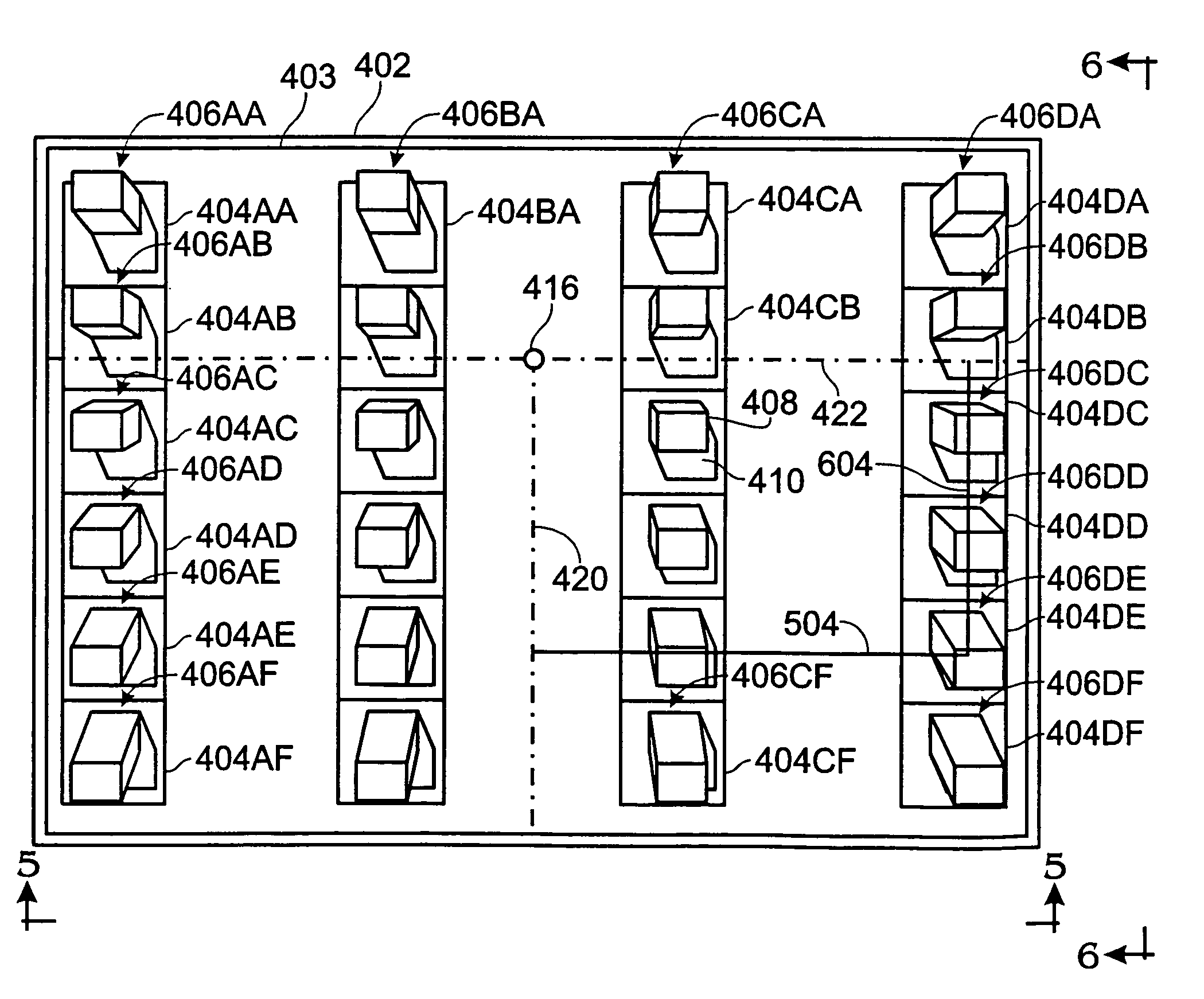
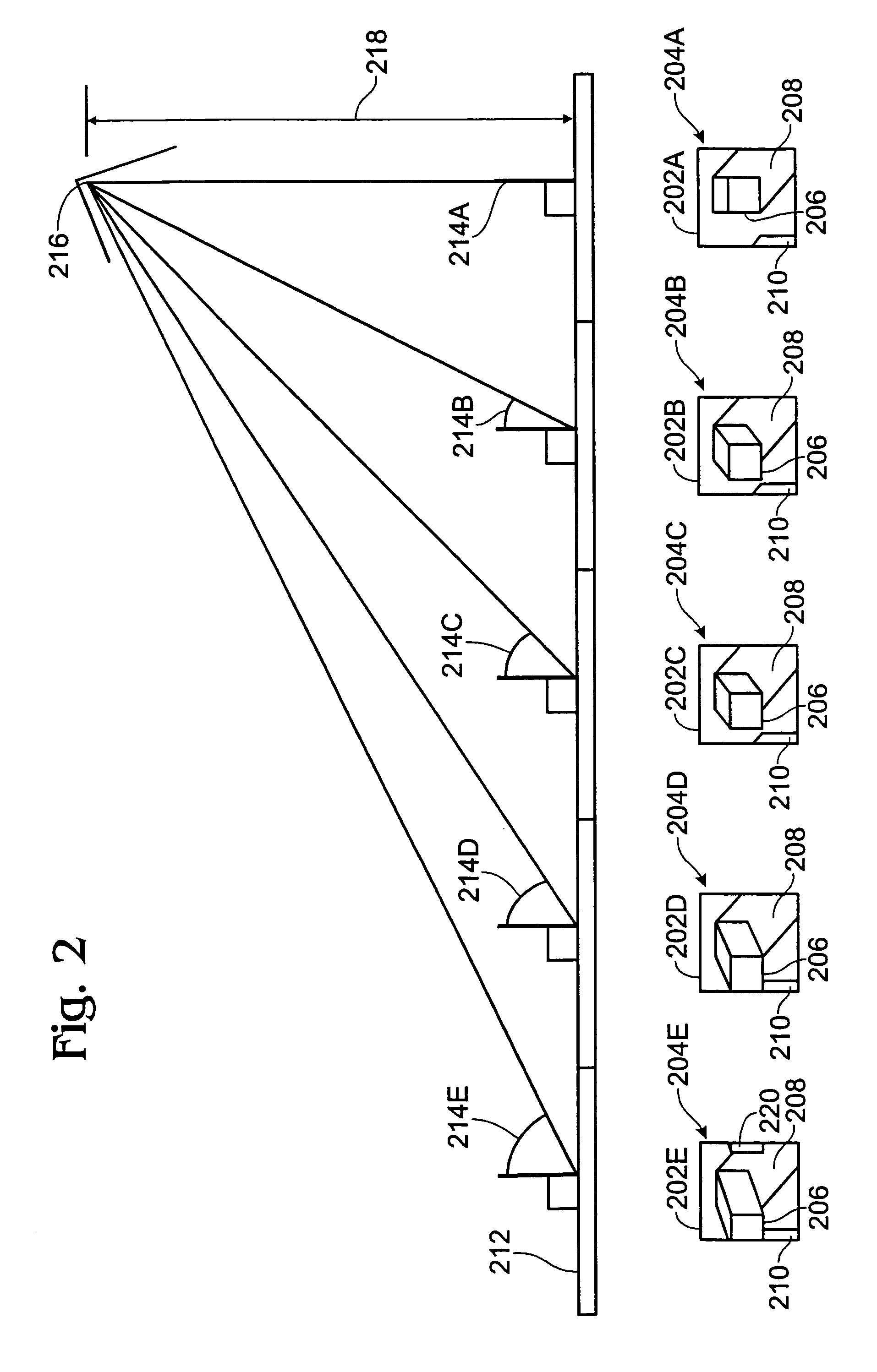
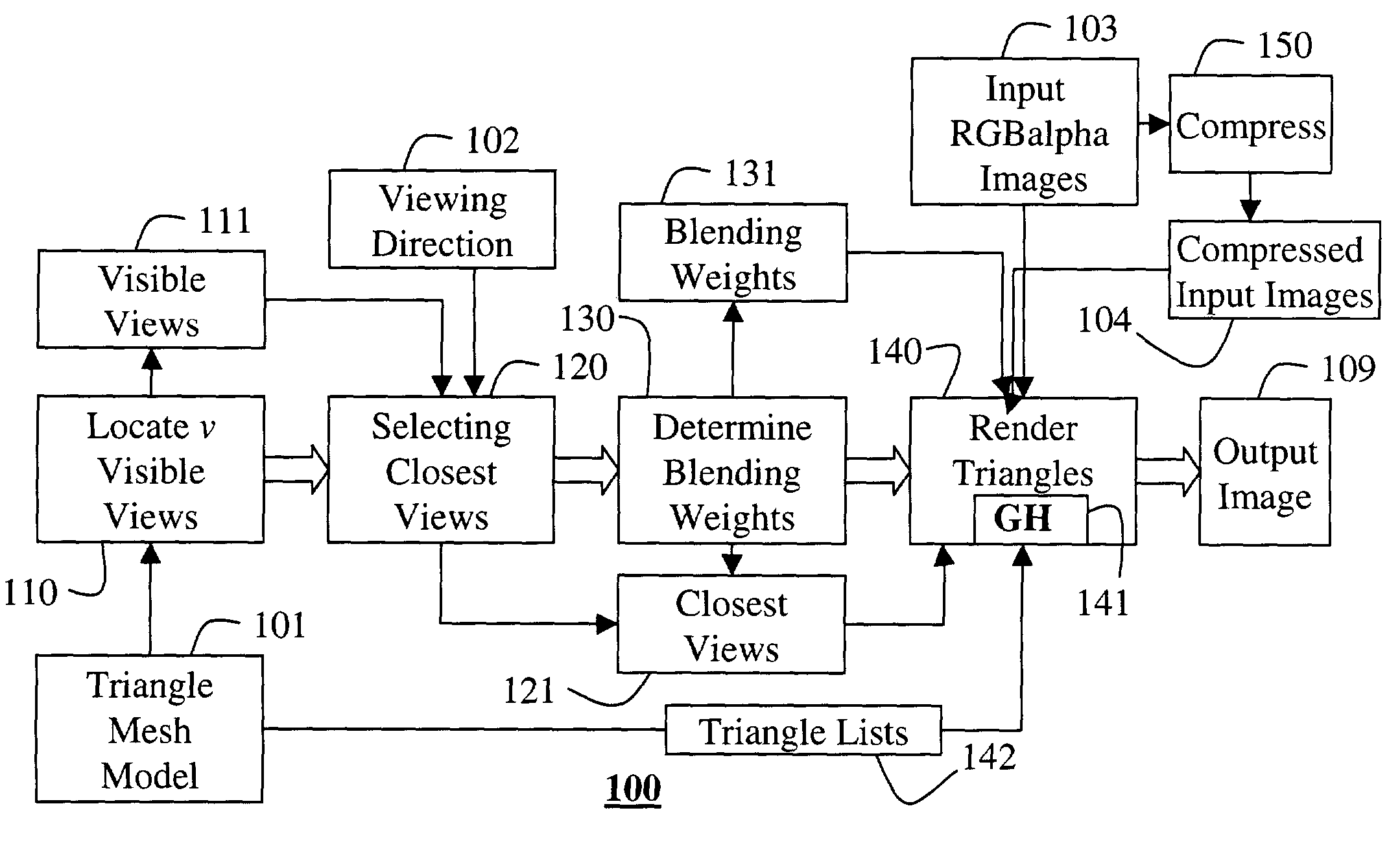
InactiveUS7194125B2Character and pattern recognition3D-image renderingVisibilityComputer graphics (images)
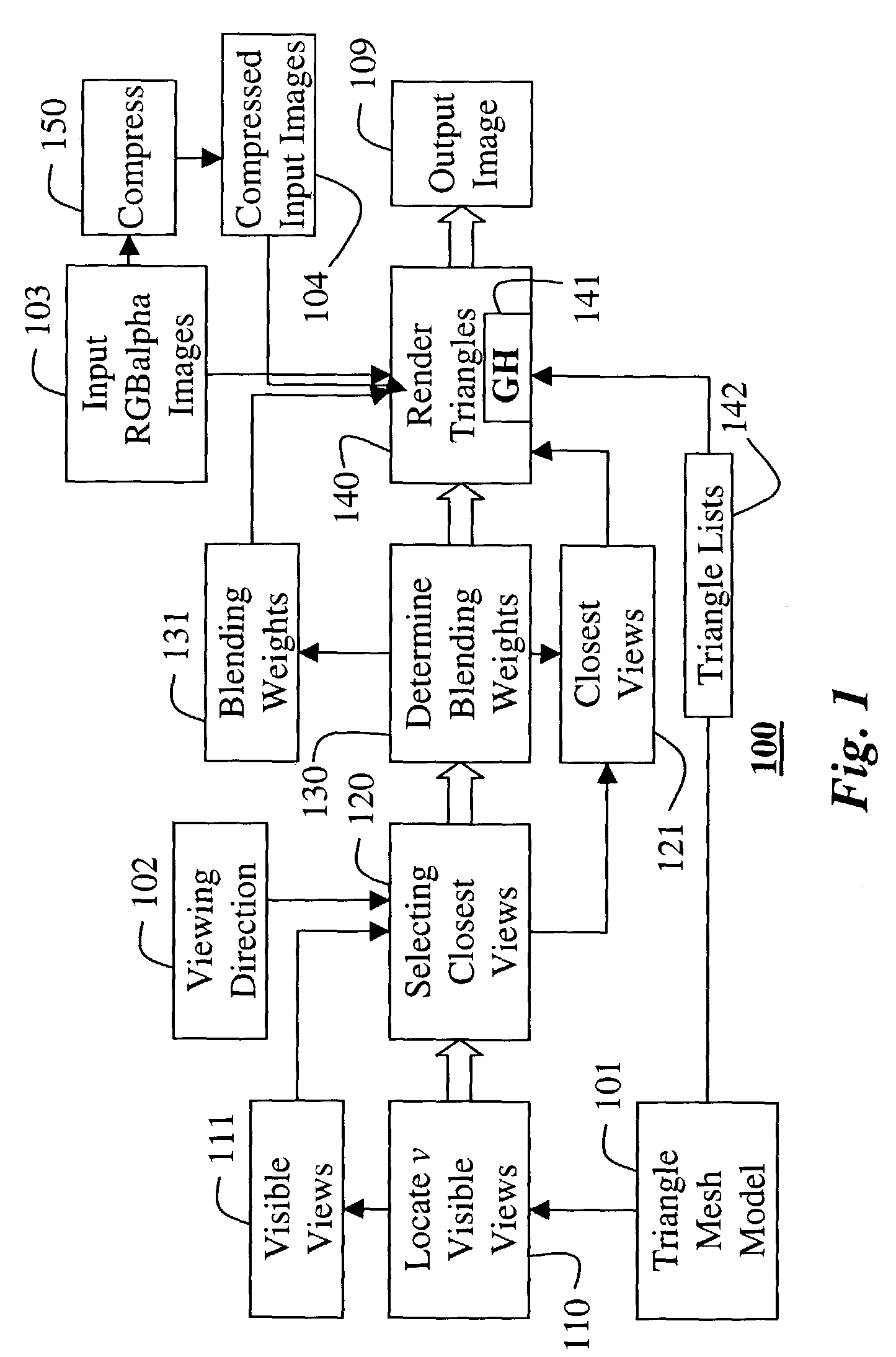
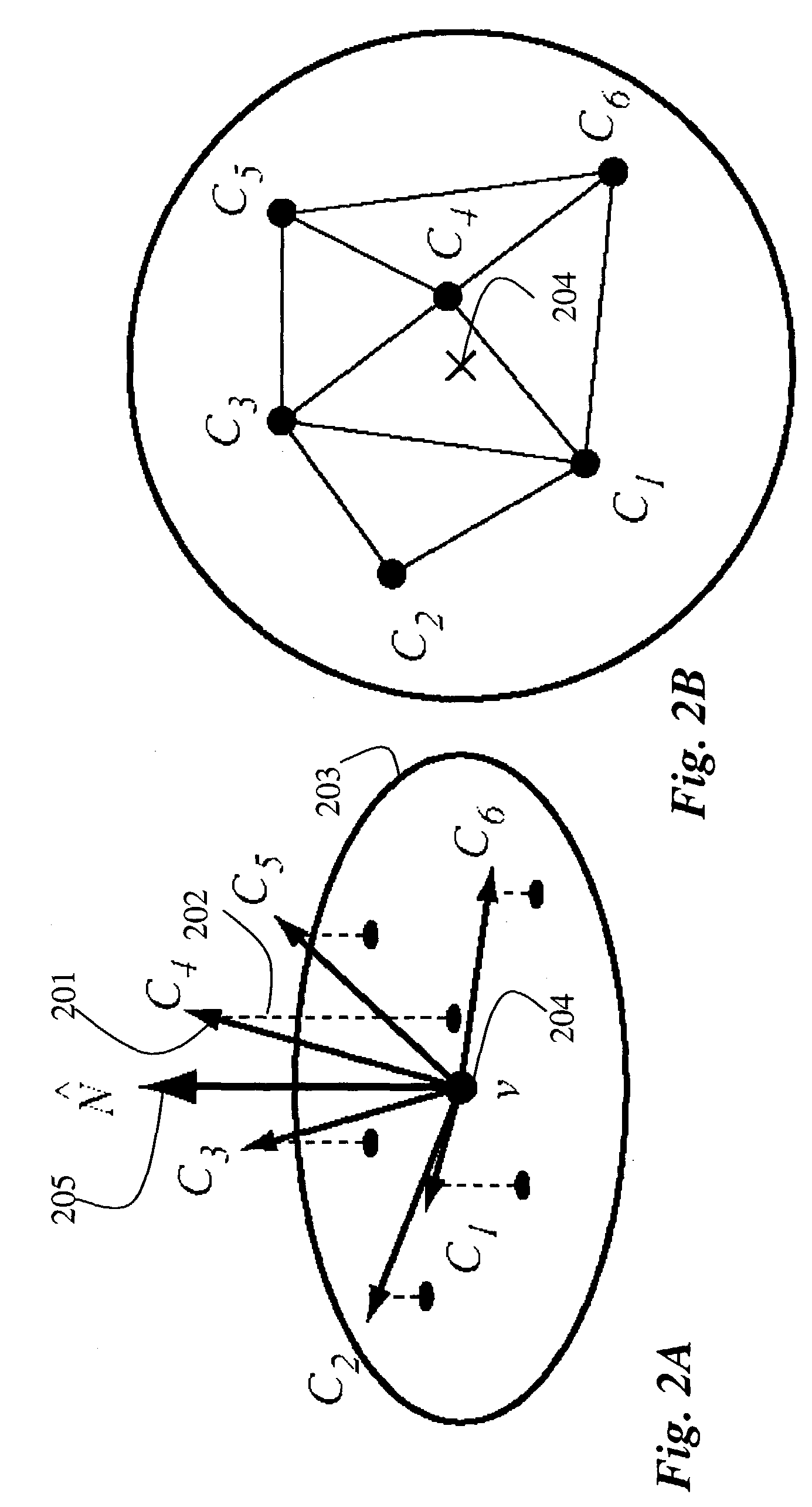
A method renders a model of a 3D object. A polygon model of the 3D object is generated, and a set of input images are acquired of the object. For each vertex of the polygon model, a set of visible views are located, and a set of closest views are selected from the visibility views. Blending weights are determined for each closest view. Then, the each polygon in the model is rendered into an output image. The rendering is performed by blending images of the set of input images corresponding to the set of closest views of each vertex of the polygon using the blending weights.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
View dependent displacement mapping
ActiveUS20050093857A1Quickly and efficiently employedCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingDisplacement mappingComputer graphics (images)
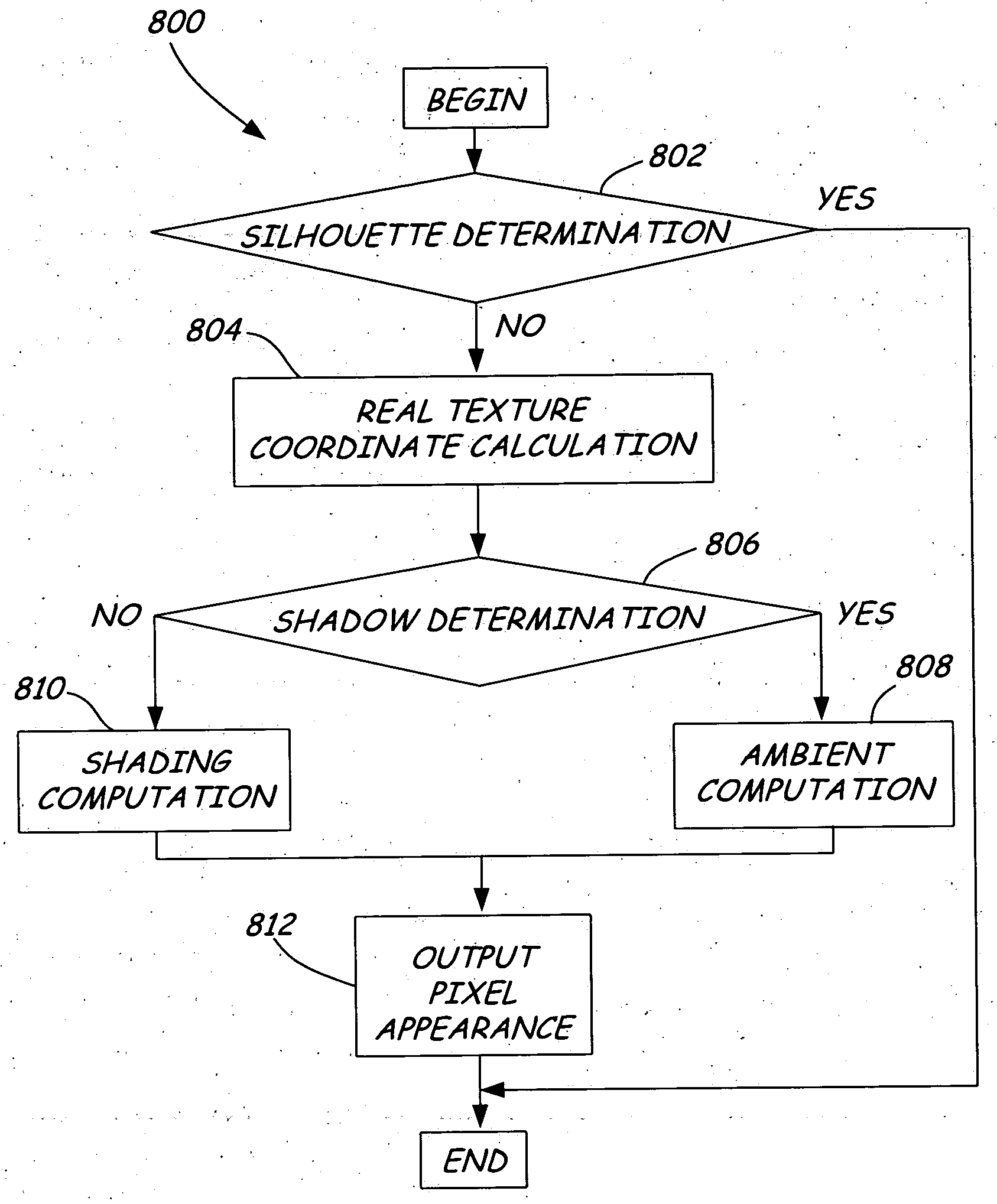
A computer implemented method for generating a representation of structure for use in rendering a synthesized image is provided. The representation is a view-dependent displacement mapping that represents displacements along a viewing direction. This view dependency allows the representation to be used to determine self shadows as well as shading, occlusion and silhouettes when used during rendering for synthesis.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com