Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
143 results about "Digital copy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
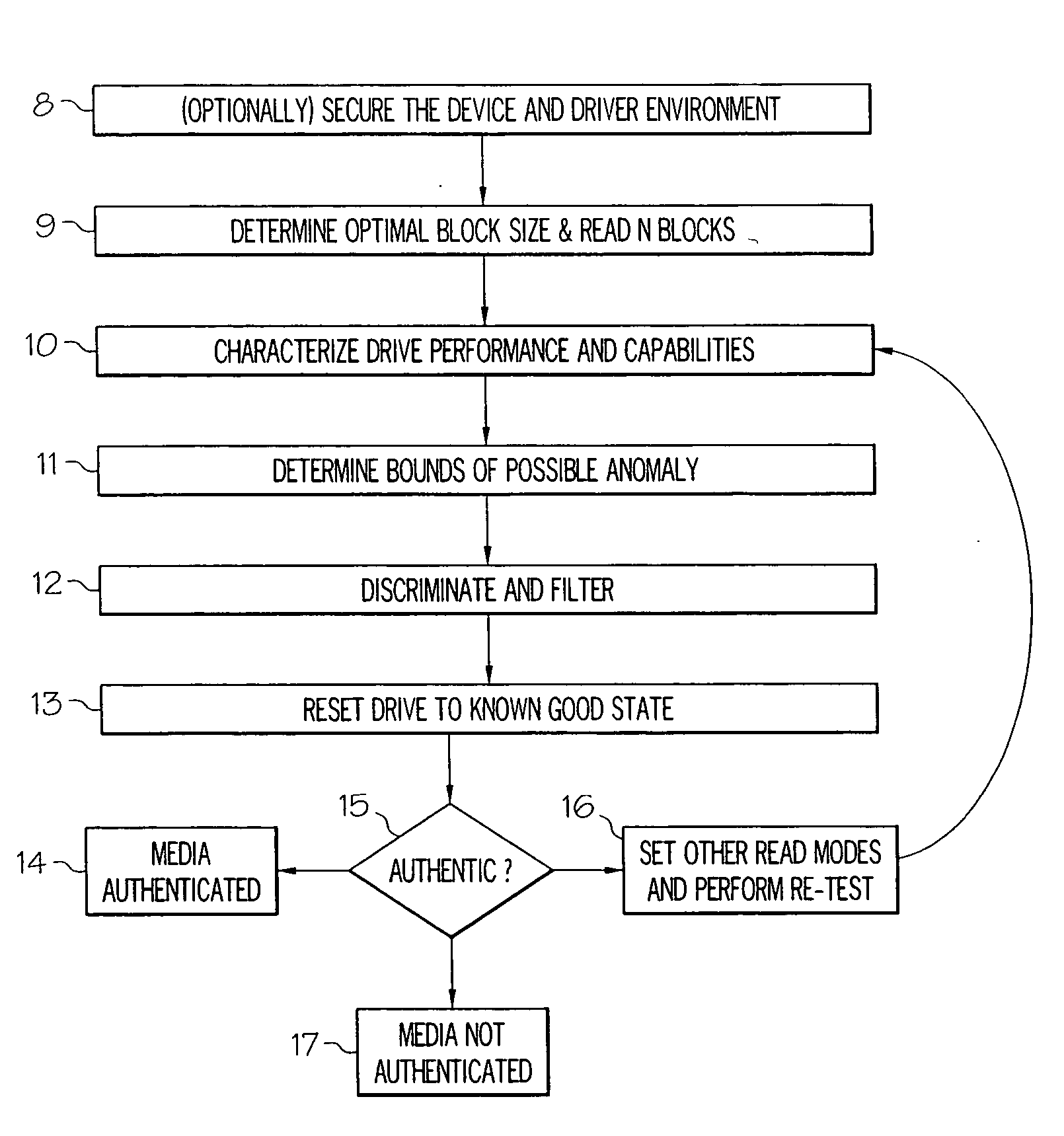
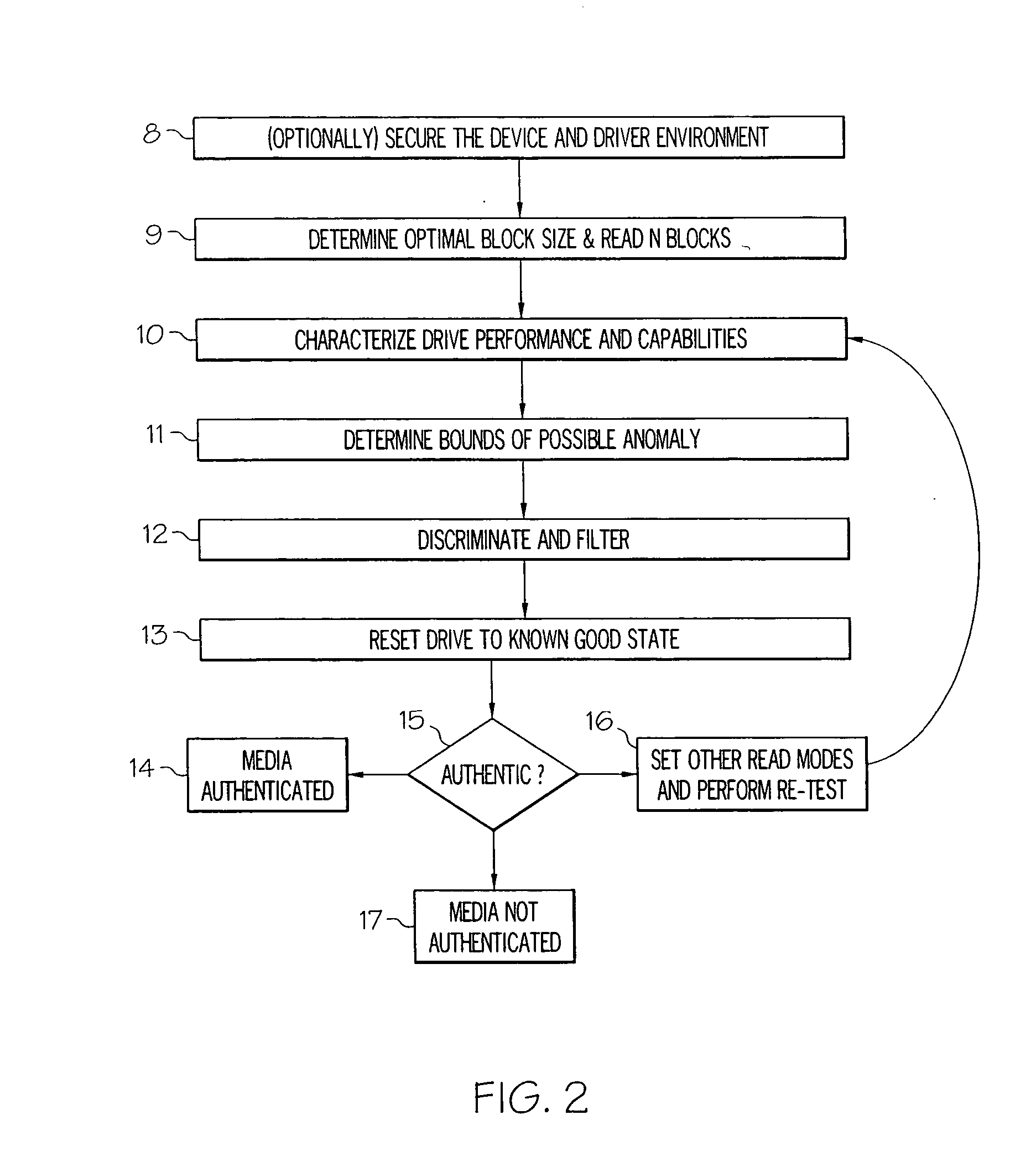
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
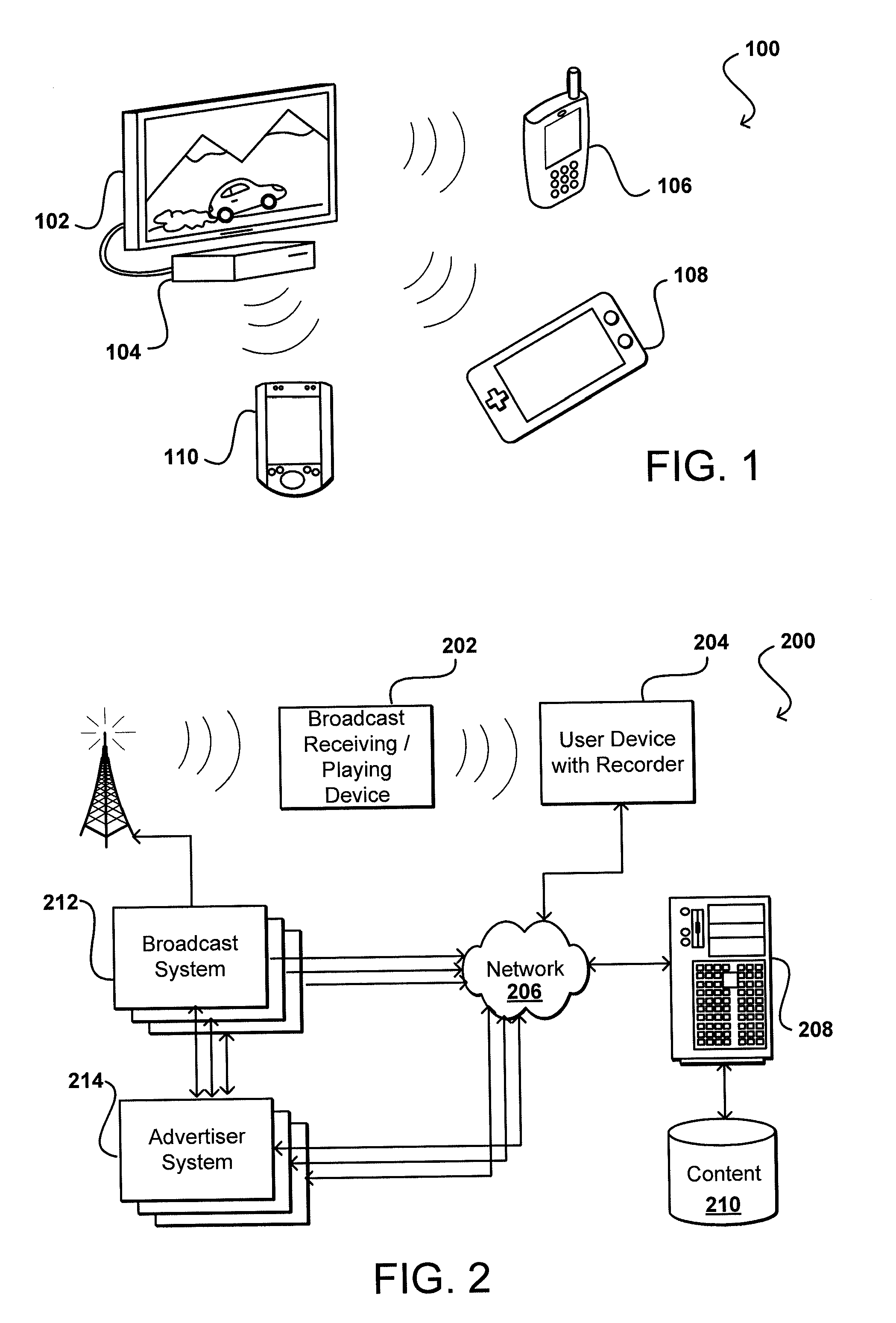
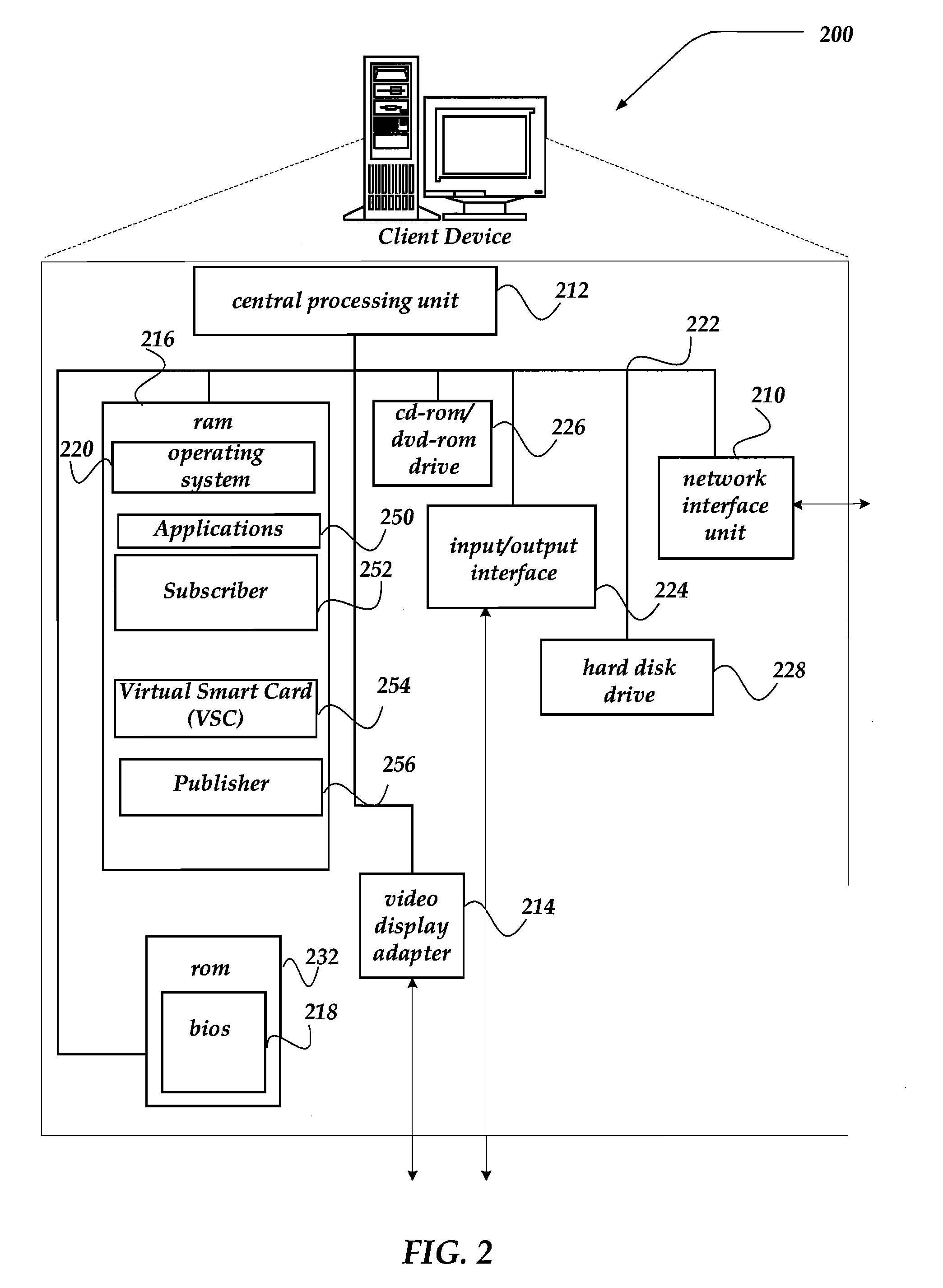
Personalized content processing and delivery system and media
ActiveUS20060123053A1Improve economyImprove utilizationDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsPersonalizationUser input
Owner:INSIGNIO TECH
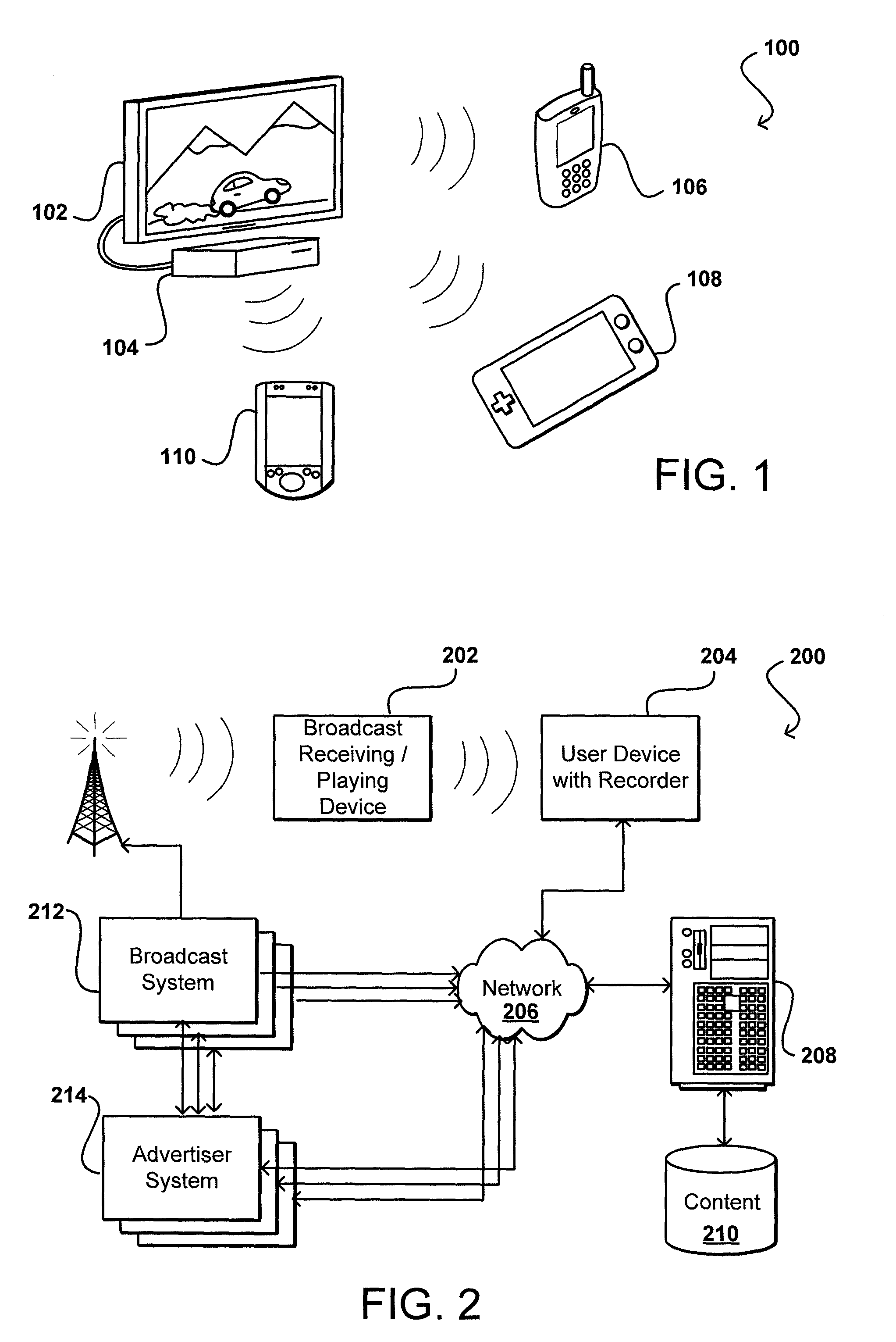
Media fingerprinting for content determination and retrieval
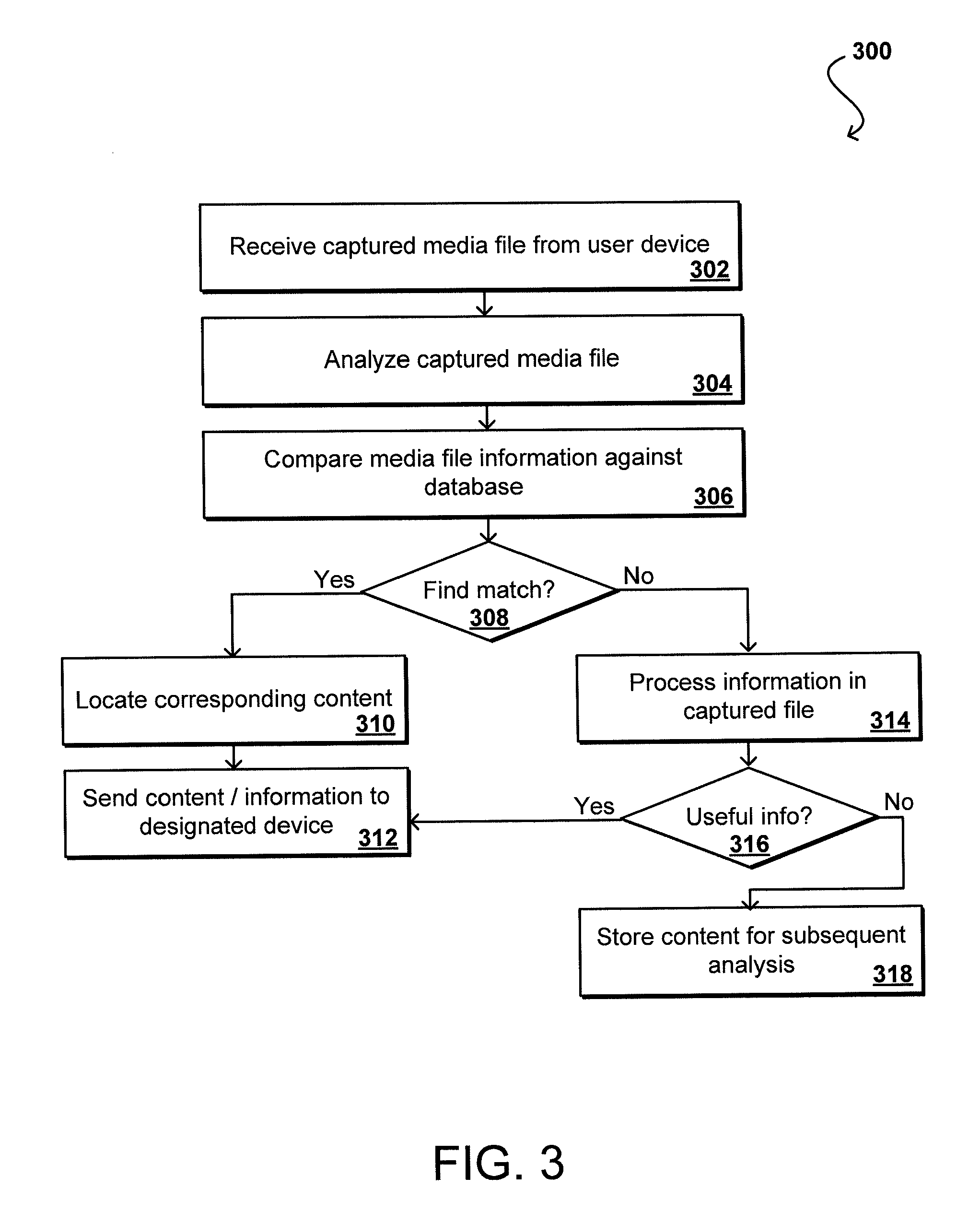
Audio fingerprinting and other media matching technologies can be used to identify broadcast media, such as television shows and radio broadcasts. A user device can record image, audio, and / or video information and upload information to a matching service that is able to use matching technology to identify the media and provide supplemental content or information to the user. The user might receive information identifying a product in an advertisement, identifying an actor on screen in a movie at a particular time, or other such information. In some embodiments, the user can receive access to a digital copy of the captured media, such as the ability to download a copy of a program in which a user expressed interest. Since a user might capture media information after the point of interest, a device can buffer a window of recently captured media in order to attempt to identify the intended media.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
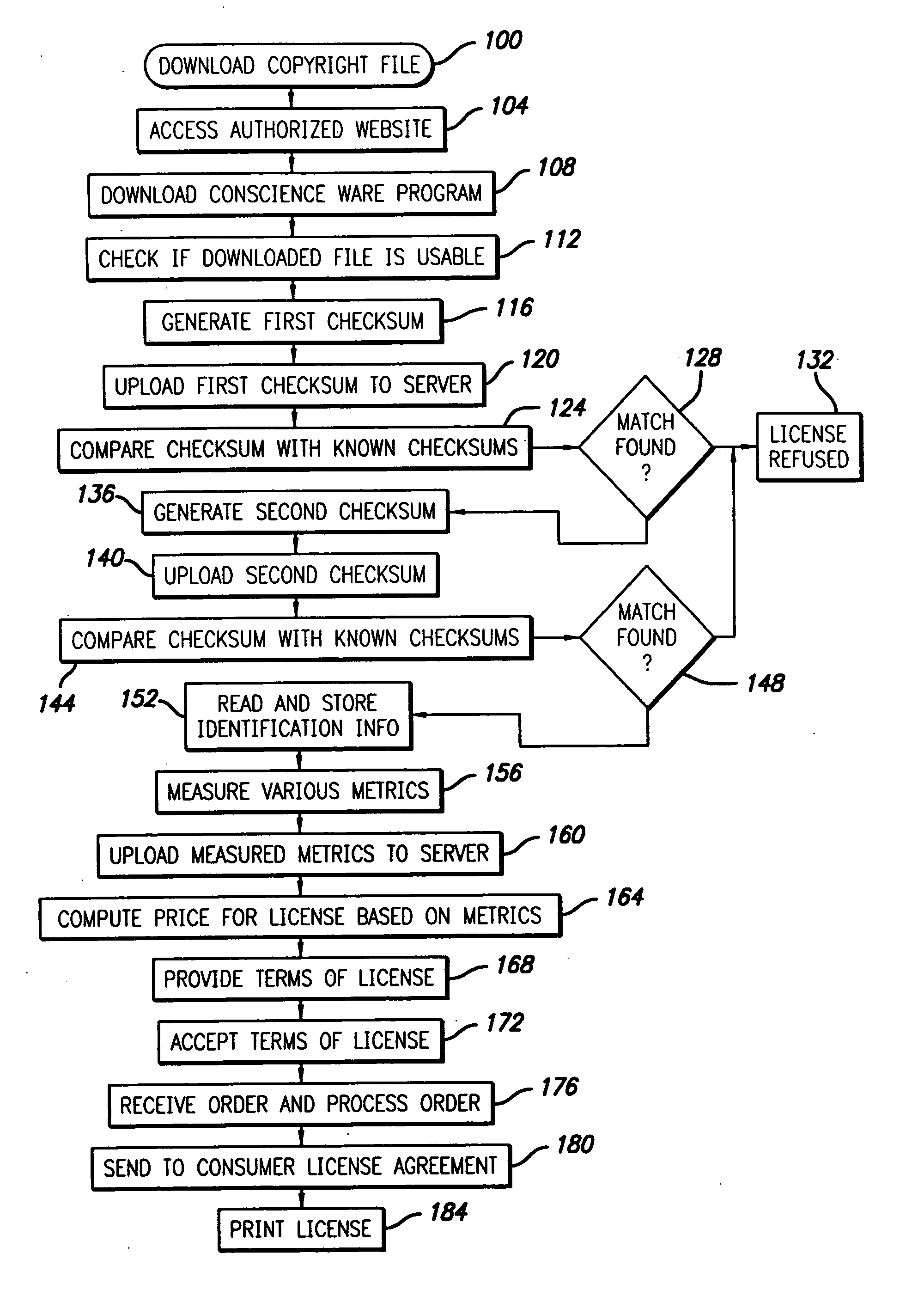
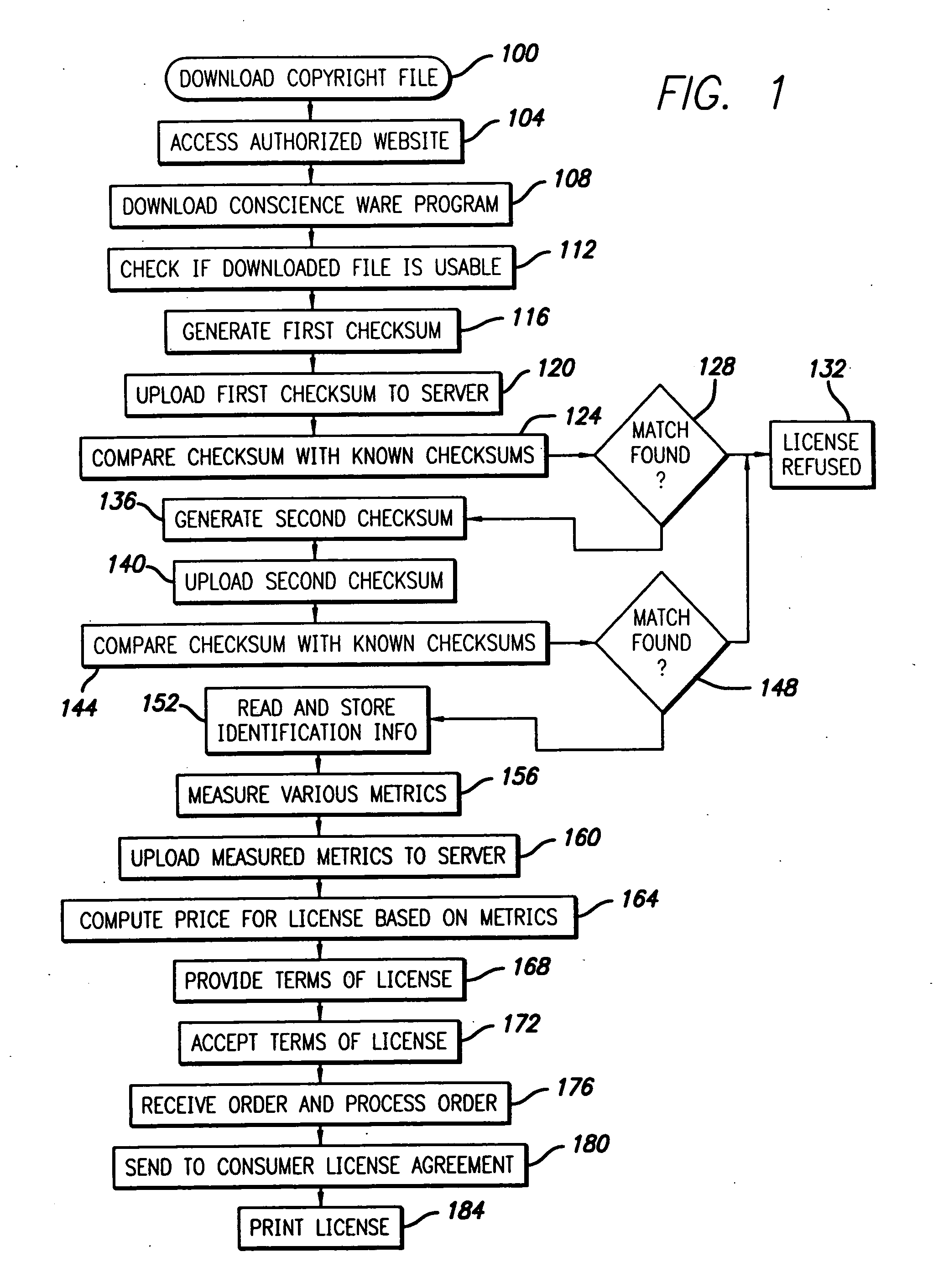
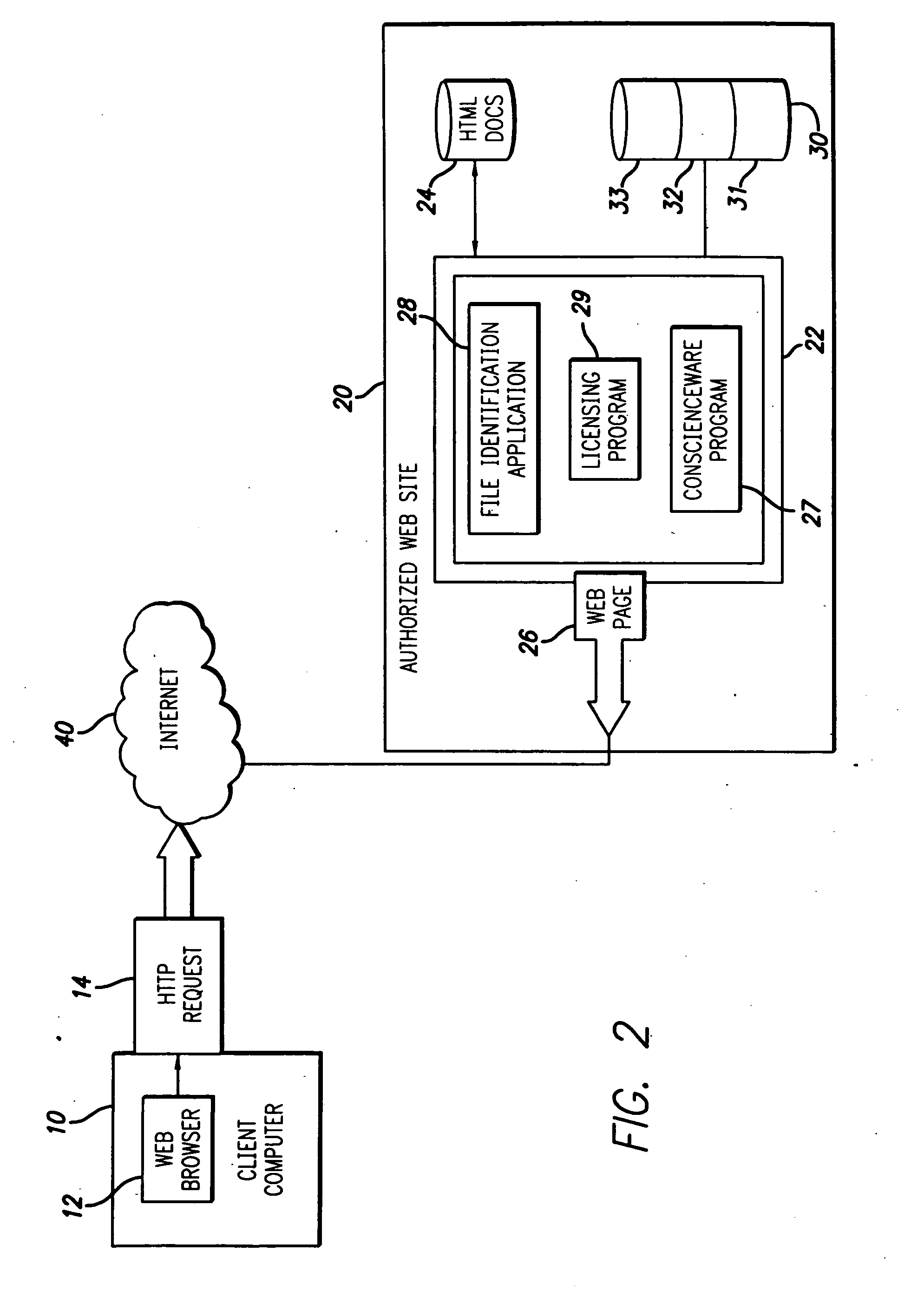
Digital work identification and licensing method
InactiveUS20050097059A1Low costEasy to buyComputer security arrangementsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsPaymentDigital copy
A method and system are provided for facilitating the purchase of a license for a downloaded file of a copyrighted work. In one embodiment, a method for licensing a digital copy of a copyrighted work includes determining an identity of the digital copy by using at least one computer program, calculating a fee for a license for the digital copy by the at least one computer program. The step of calculating includes the step of measuring at least one metric of the digital copy. A license is then provided for the copy after receiving payment of the fee.
Owner:KIOBA PROCESSING LLC
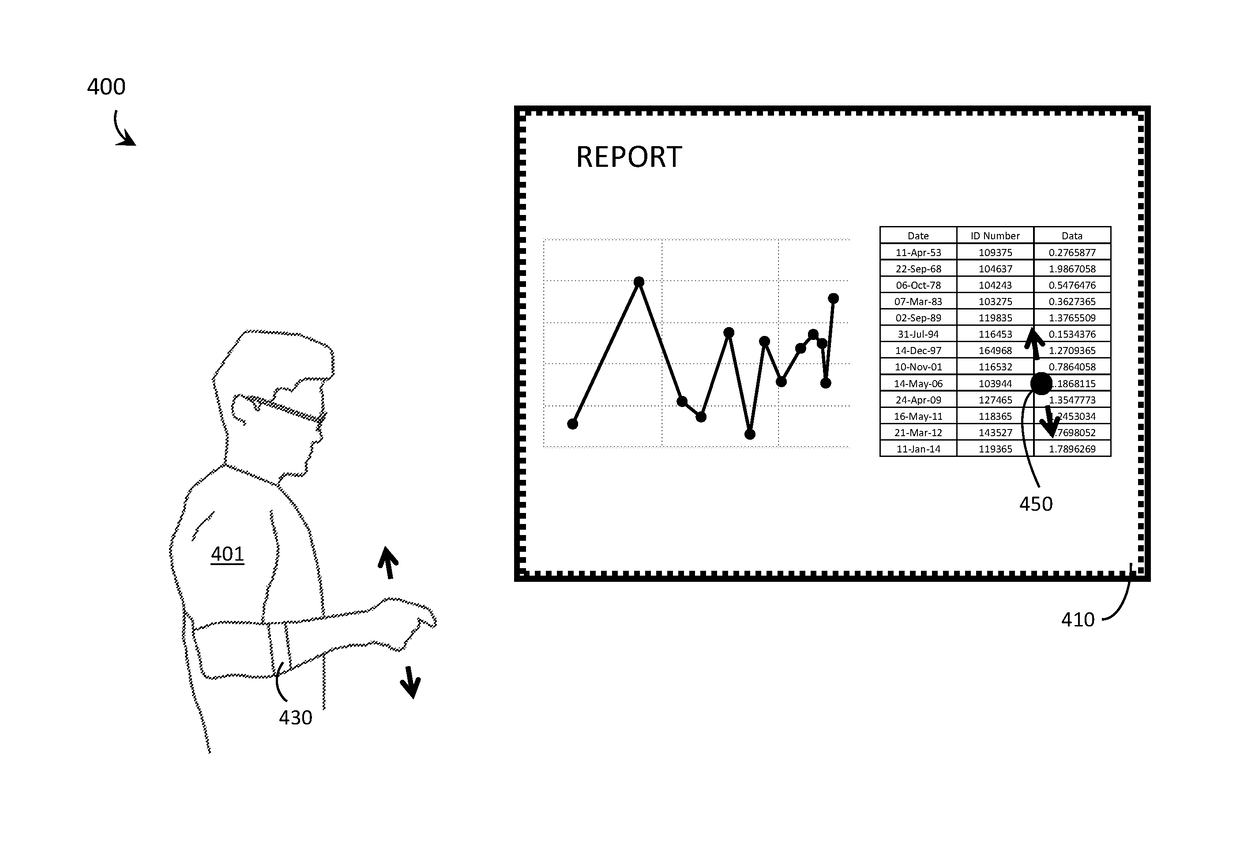
Systems, methods, and computer program products for interacting with electronically displayed presentation materials
ActiveUS20160313899A1Input/output for user-computer interactionGeometric image transformationComputer graphics (images)Digital copy
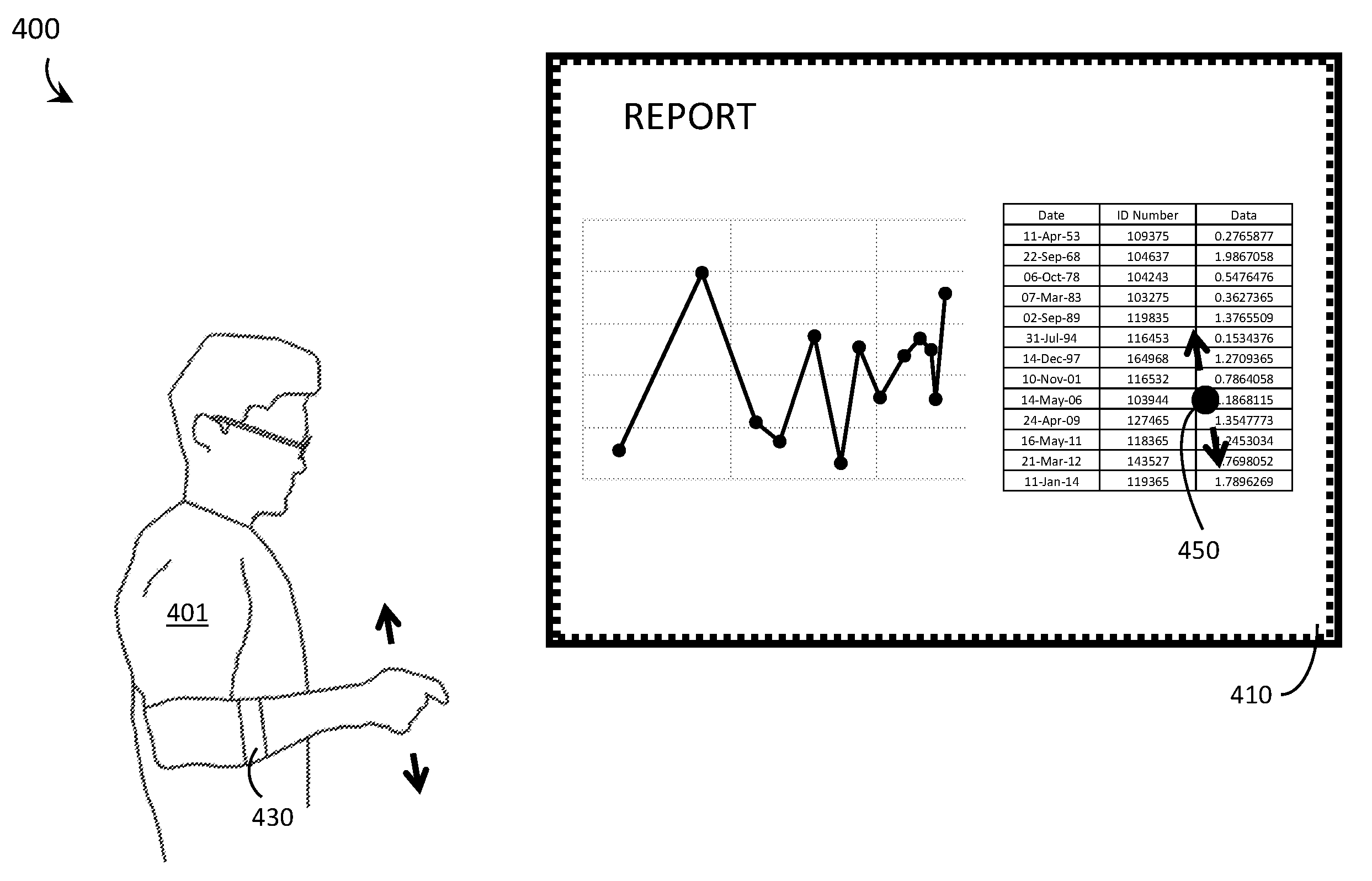
Systems, methods, and computer program products for interacting with electronically displayed presentation materials are described. A display system includes, at least, a digital processor, an electronic display, and a non-transitory processor-readable storage medium into which is loaded a computer program product that includes, at least, processor-executable instructions and / or data. The processor-executable instructions and / or data, when executed by the processor, cause the display system to respond to user inputs indicative of pointer commands and magnification setting commands. In response to such commands, the display system causes; i) a dynamic cursor to display over top of content on the electronic display; and ii) a digital copy image of the content to be displayed over top of the content on the electronic display, the digital copy image displayed at a greater magnification level than the content.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
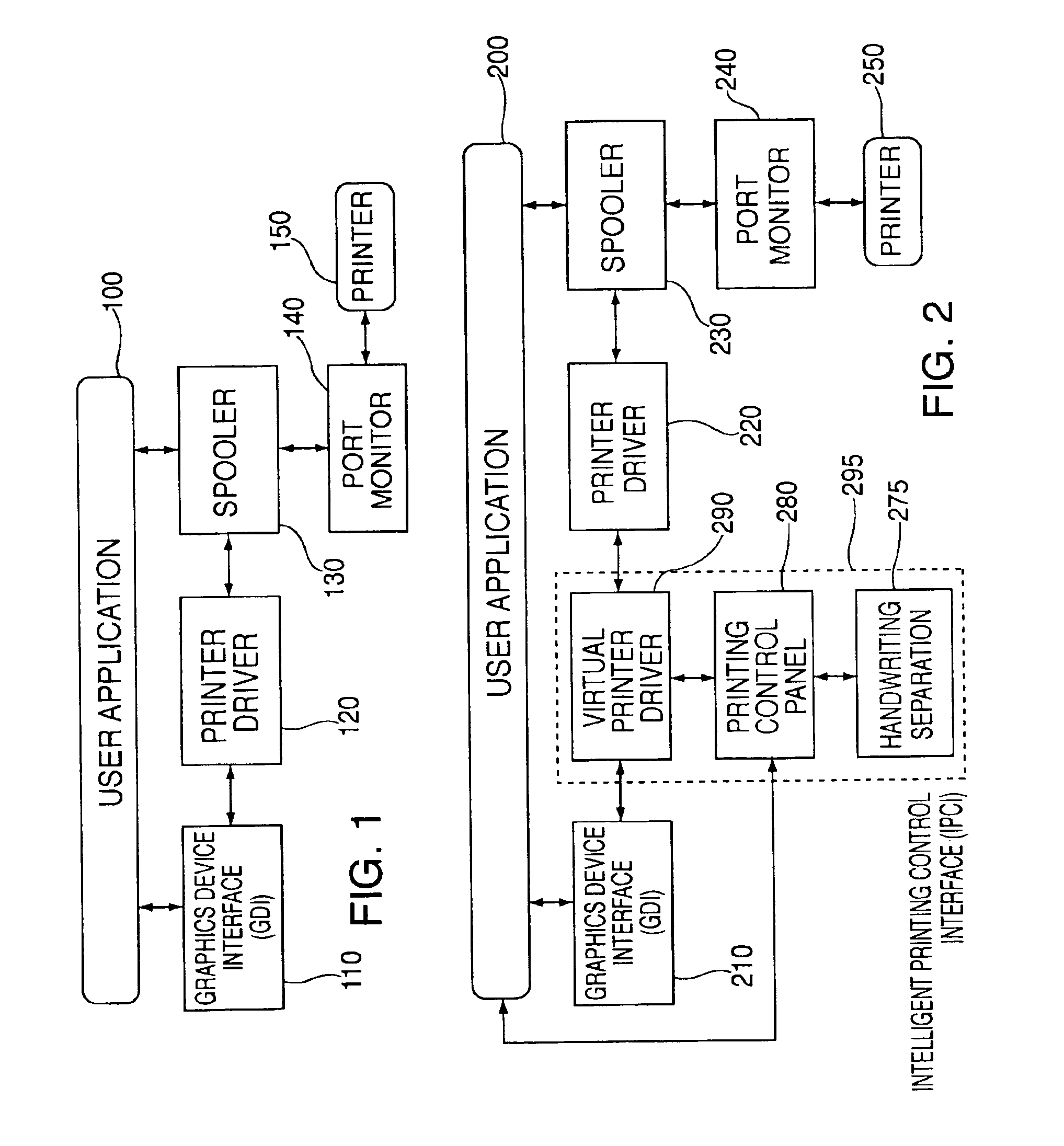
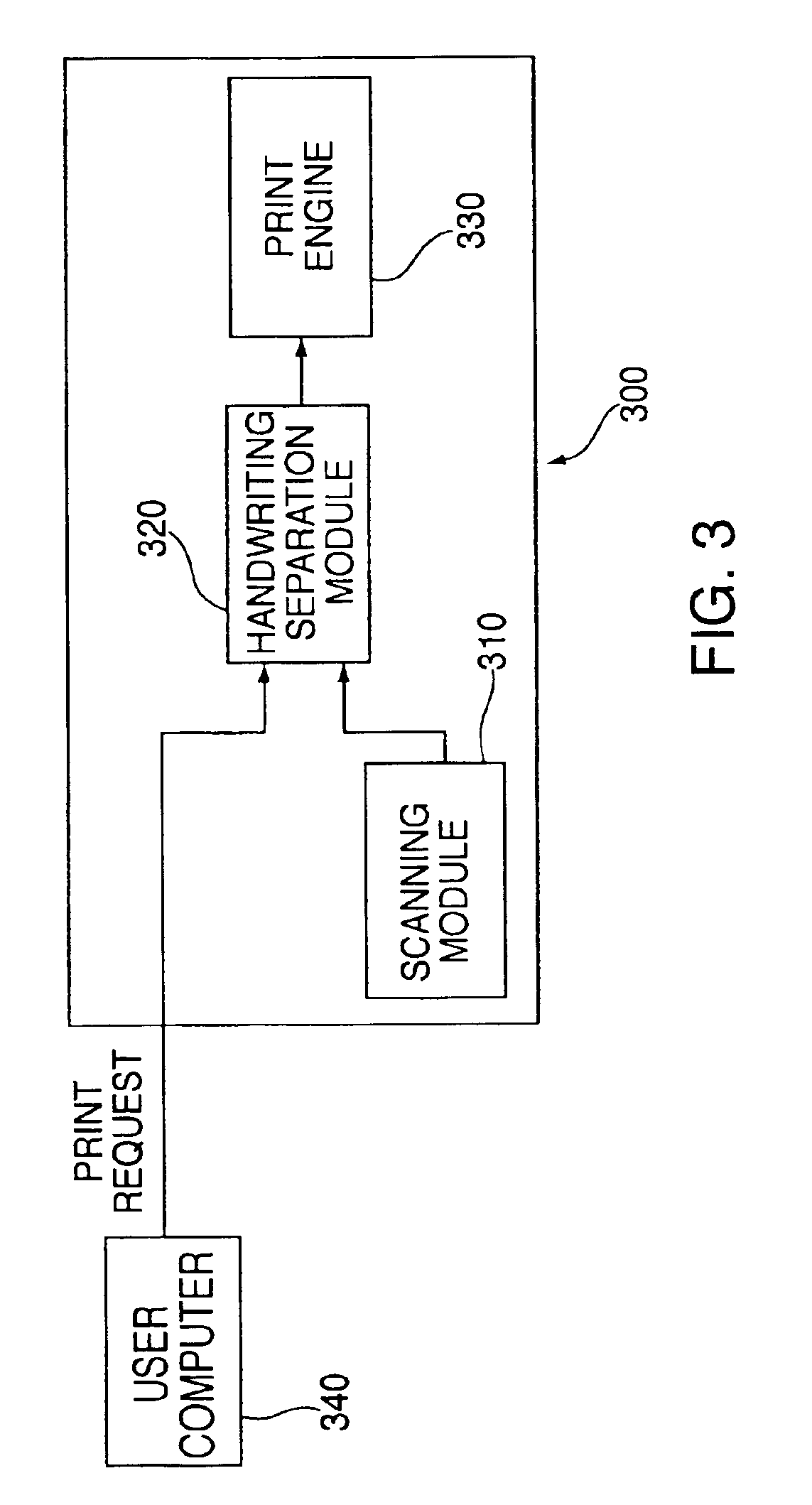
Printing control interface system and method with handwriting discrimination capability
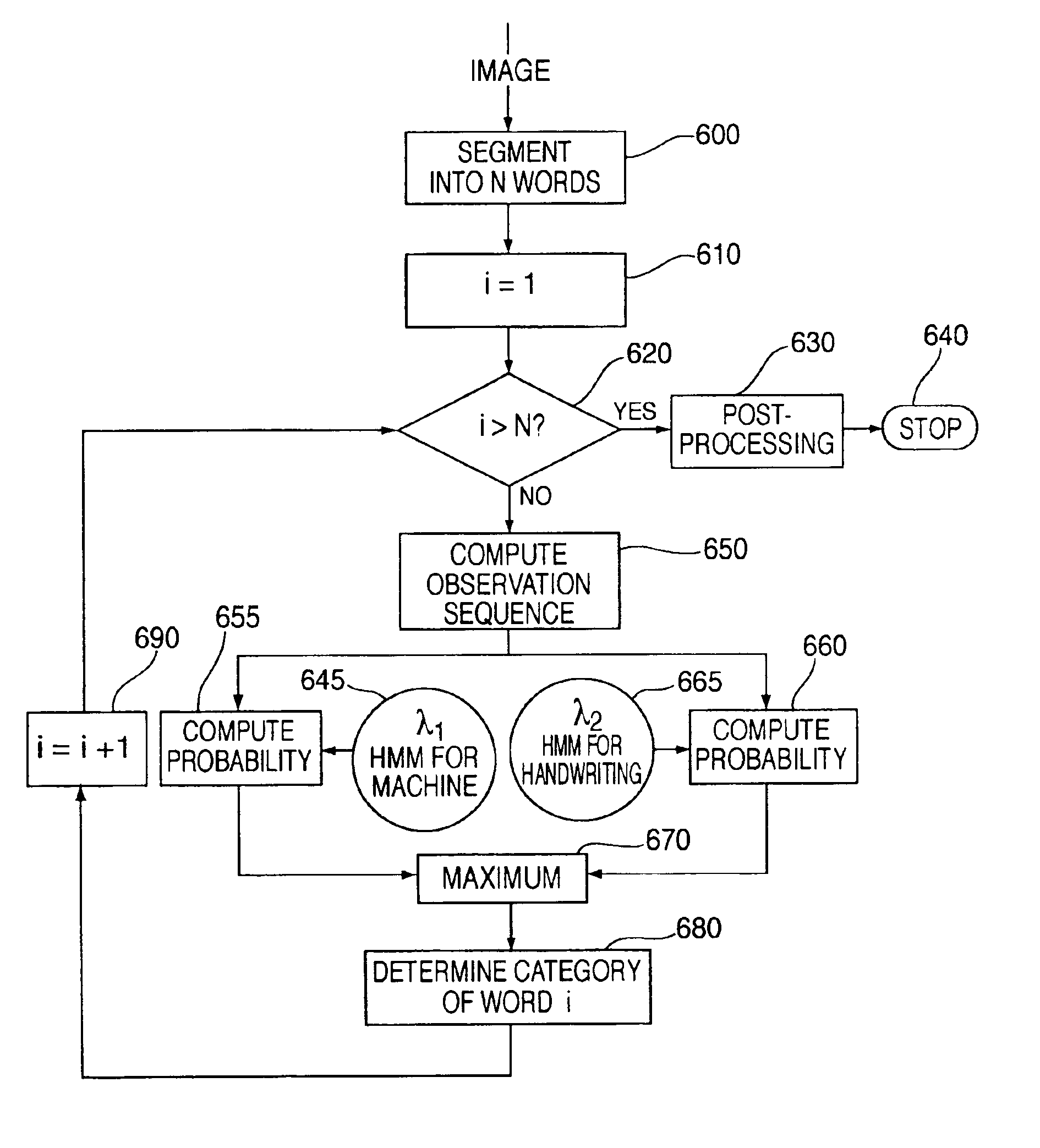
A system and method for identifying and separating handwritten text from machine printed text in a document having a combination of handwritten text and machine printed text. In one embodiment, the present invention is installed as an intelligent printing control interface in a conventional computer and allows any document generated by any application to be selectively processed to remove any handwritten text prior to printing of the document, under the control of the user. In an alternative embodiment, the present invention is installed as an intelligent printing control interface in a conventional digital copy machine, which allows any document being copied to be selectively processed to remove any handwritten text prior to printing of the document, under the control of the user. The present invention employs a handwriting separation method which uses Hidden Markov Models to identify regions as either handwritten text or machine printed text.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
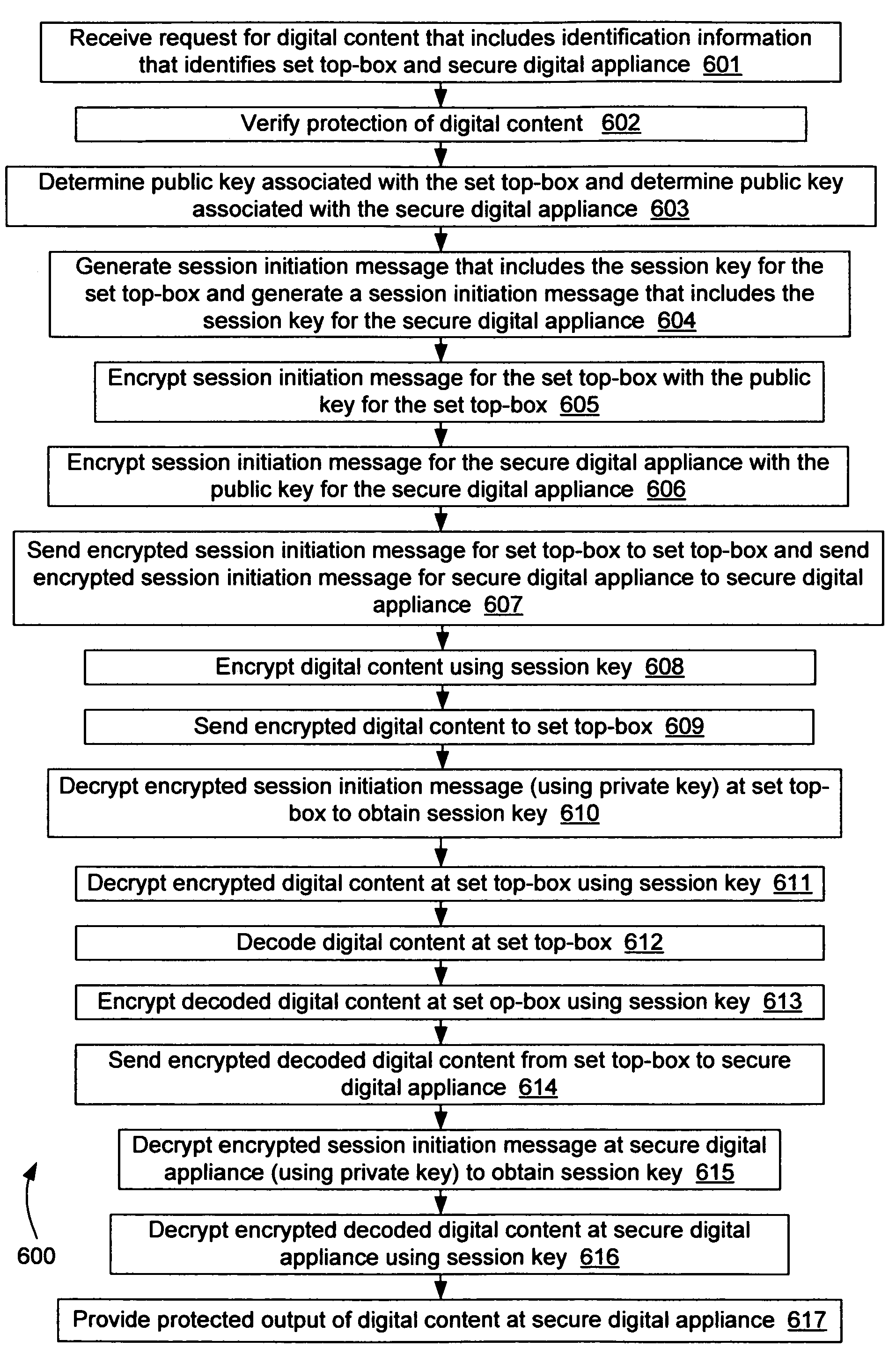
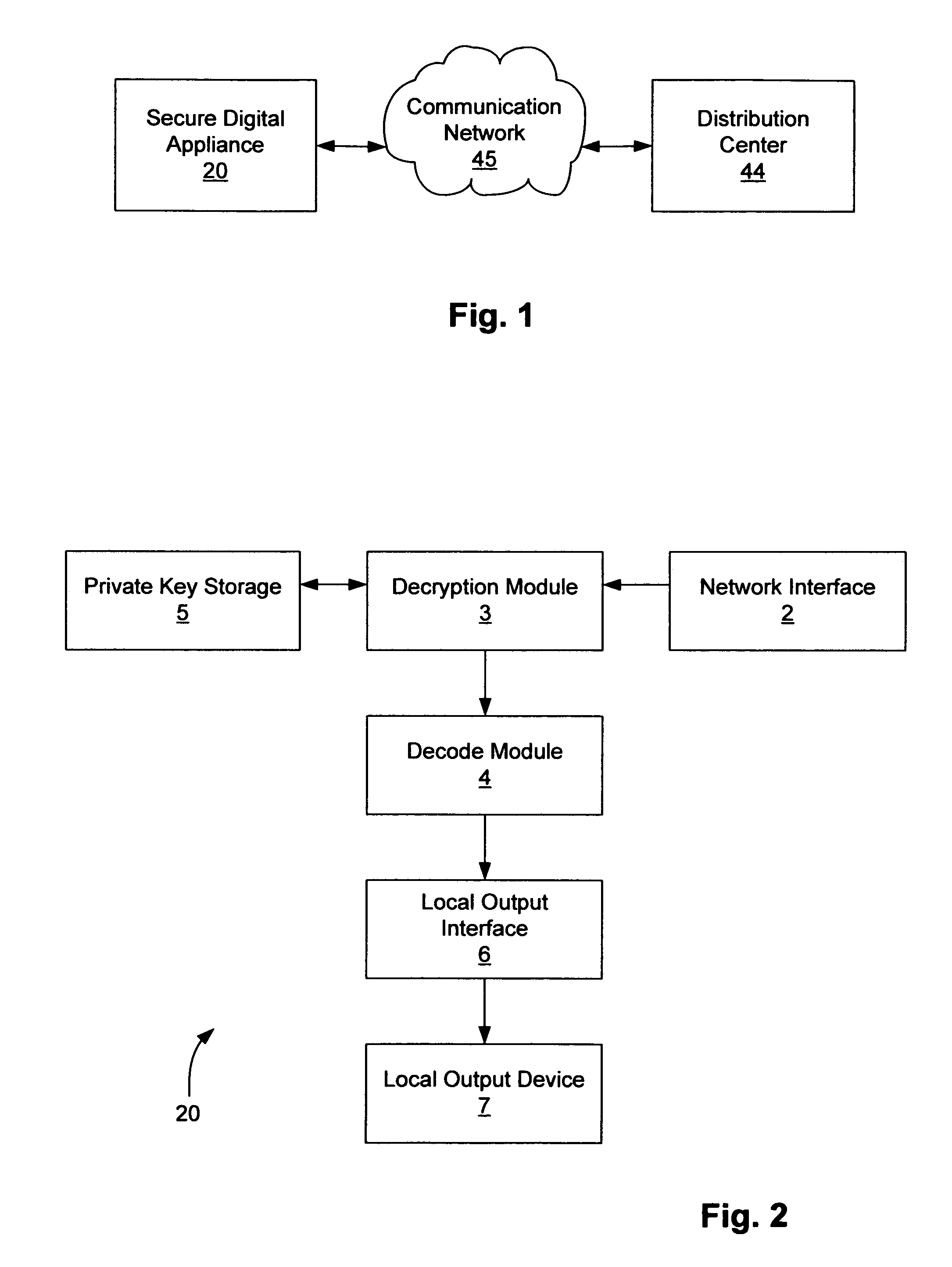
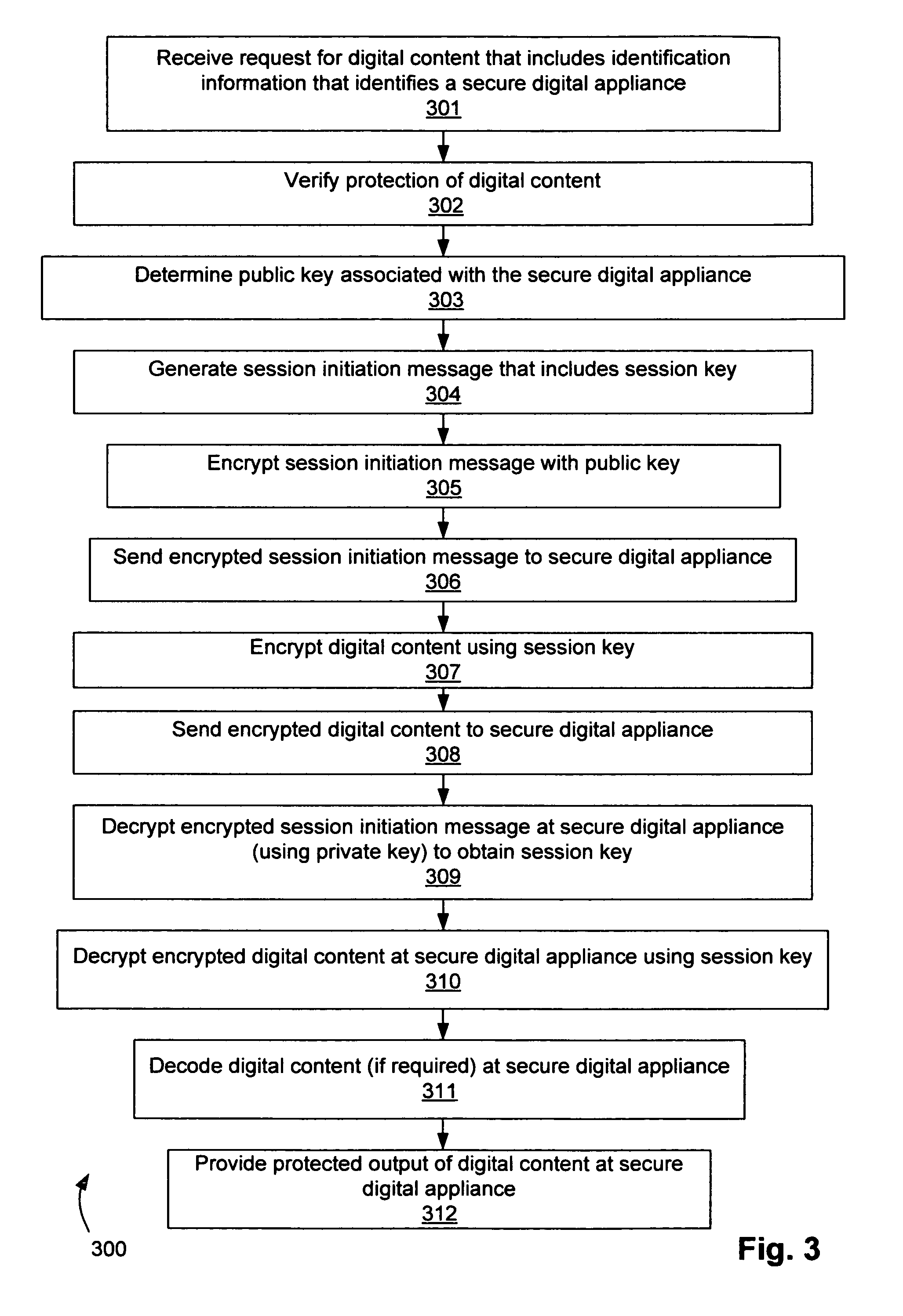
Secure digital appliance and method for protecting digital content
InactiveUS7062658B1Quality improvementSure easyData processing applicationsUnauthorized memory use protectionDigital contentDigital copy
A method and apparatus for protecting digital content. A secure digital appliance is disclosed for receiving communications coupled over a communication network. A private key of a private key and public key pair is stored in the secure digital appliance in such a way that the stored private key cannot be obtained by tampering with the secure digital appliance. Upon receipt of a session initiation message that is encrypted using the public key (of the private key and public key pair) the secure digital appliance decrypts the session initiation message using the stored private key to obtain a session key. The session key is then used to decrypt communications that include encrypted digital content. The secure digital appliance includes a local output device (e.g., a TV screen and / or speakers) that is operable to provide protected output of the digital content. The secure digital appliance does not contain any provision for output other than the protected output of digital content. Because the secure digital appliance does not allow for any output of the digital content other than the protected output, the end user cannot obtain a high quality digital copy of the digital content. Therefore, there is little chance that the security of digital content will be compromised.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
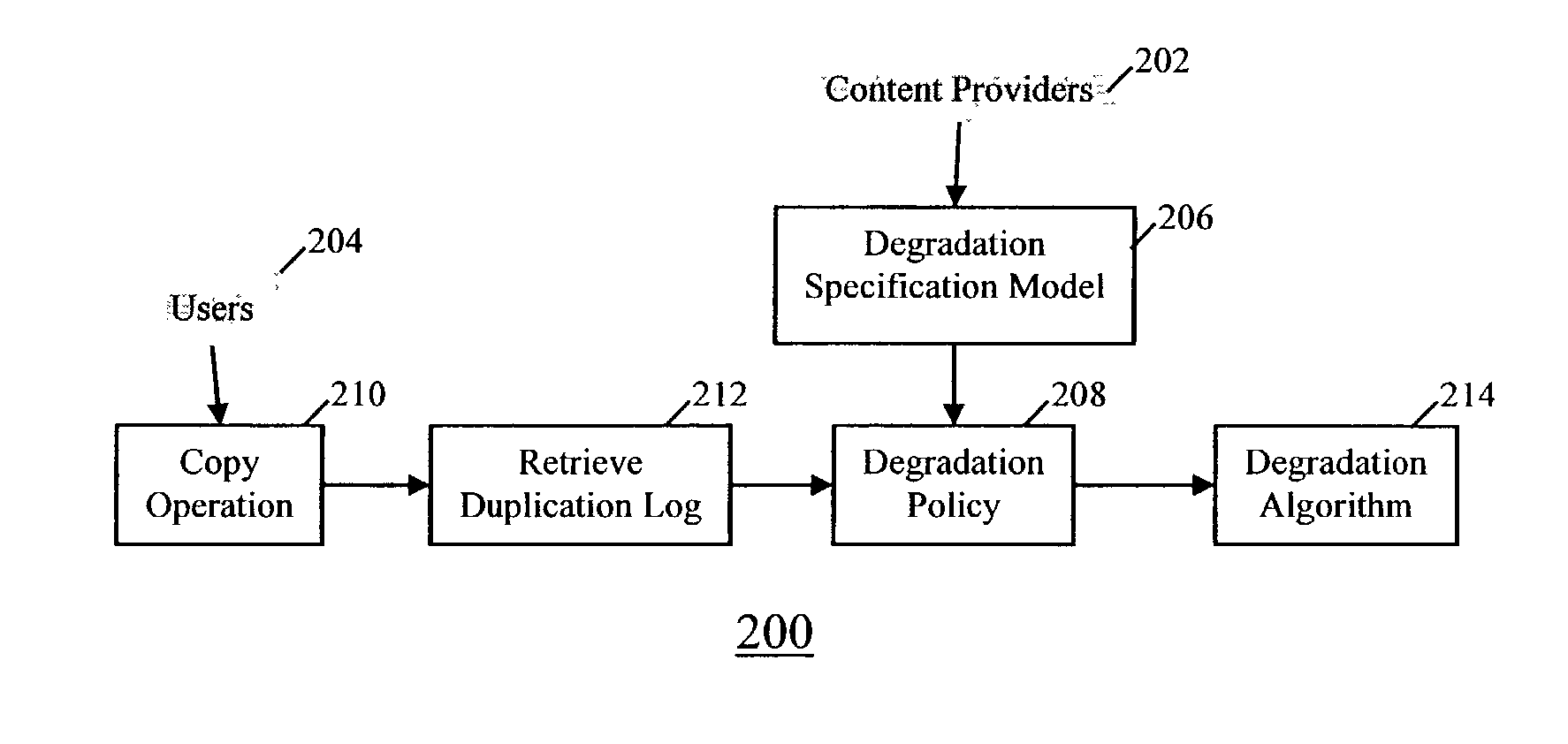
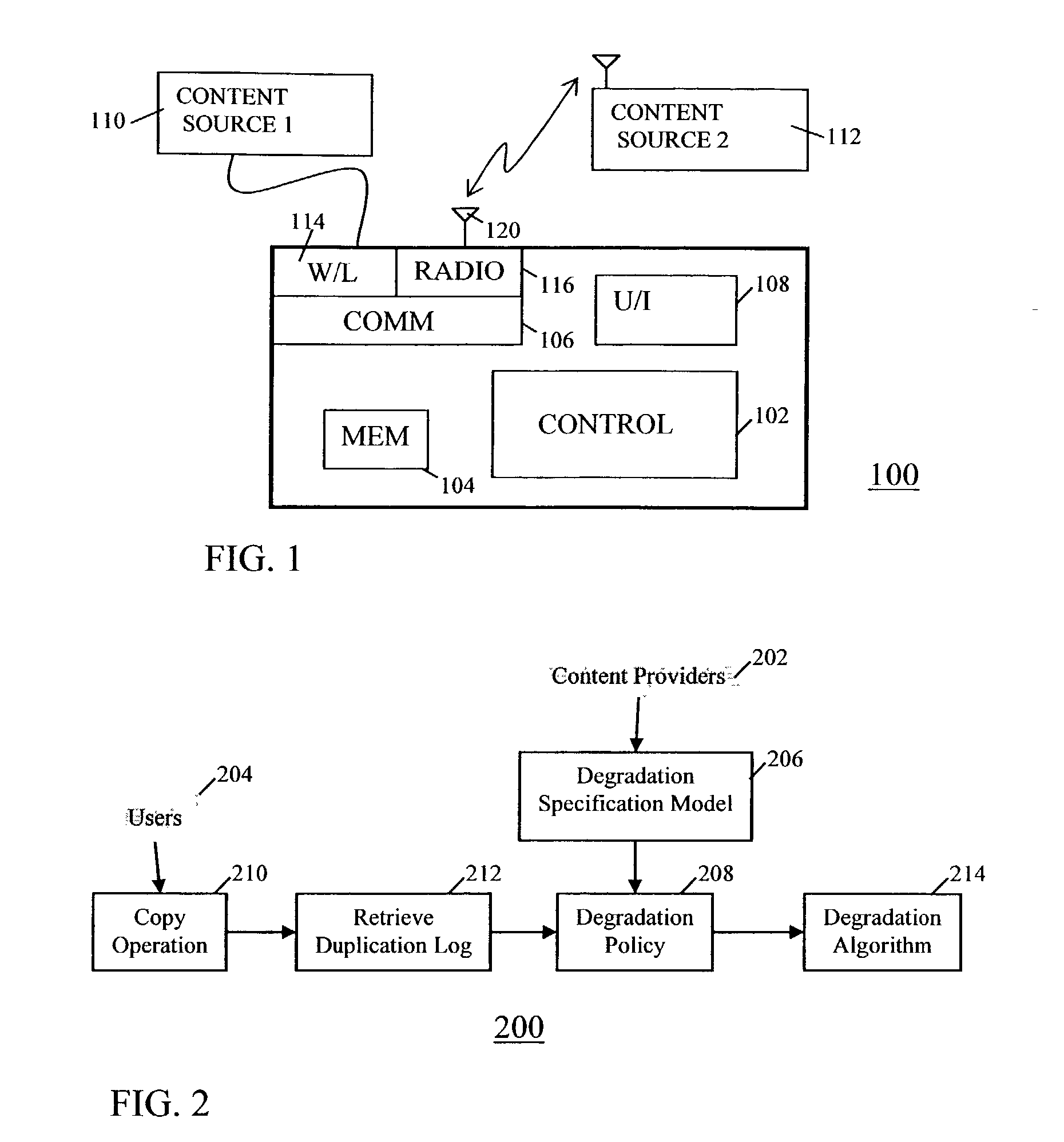
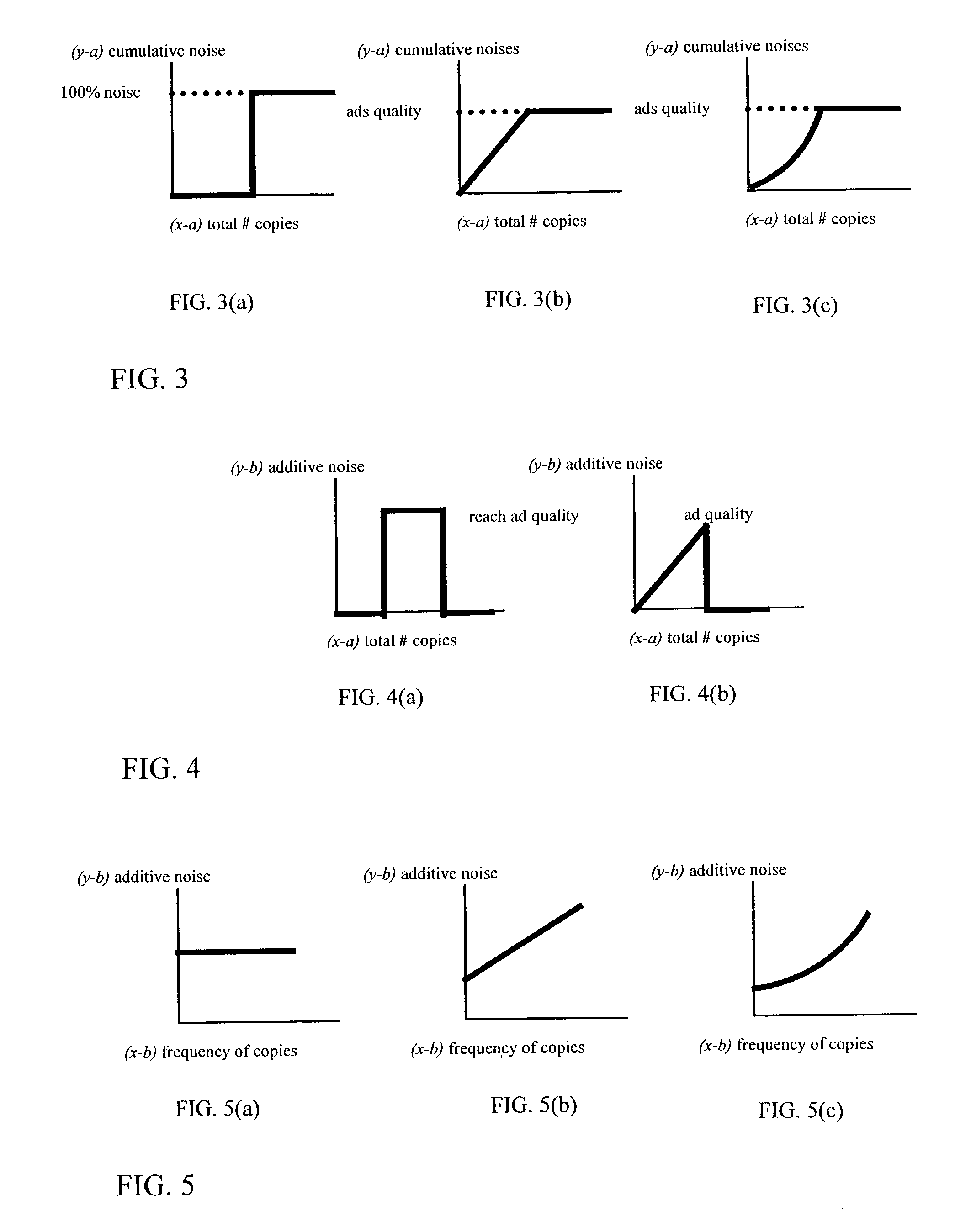
Method and apparatus for self-degrading digital data
InactiveUS20030216824A1Reducing decimal-place accuracyQuality is reduced and degradedData processing applicationsSpeech analysisDigital dataDigital copy
When copies of digital are made or after use of the digital data, the quality of the digital data is reduced or degraded. The degradation may be in any way suitable to the nature of the digital data. In one embodiment, the content provider which originates the digital data may specify a degradation policy or degradation specification model for the digital data. When the digital data is copied or moved, the copy is degraded according to this specified policy or model. In this manner, the content provider can control the extent to which the end user can copy the material. The end user can make copies limited in number only by the degradation of the digital data.
Owner:DOCOMO COMMUNICATIONS LABORATORIES USA INC
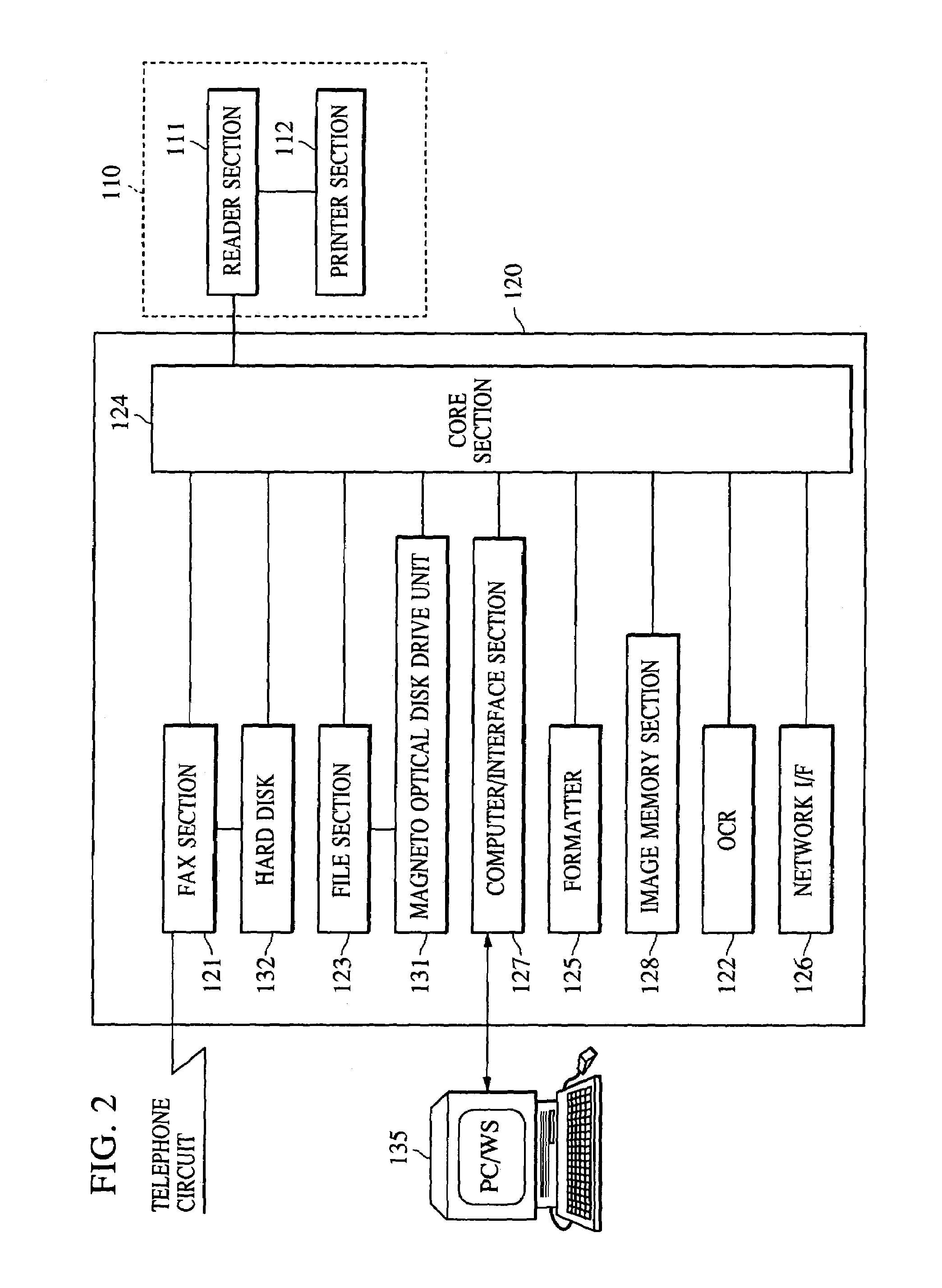
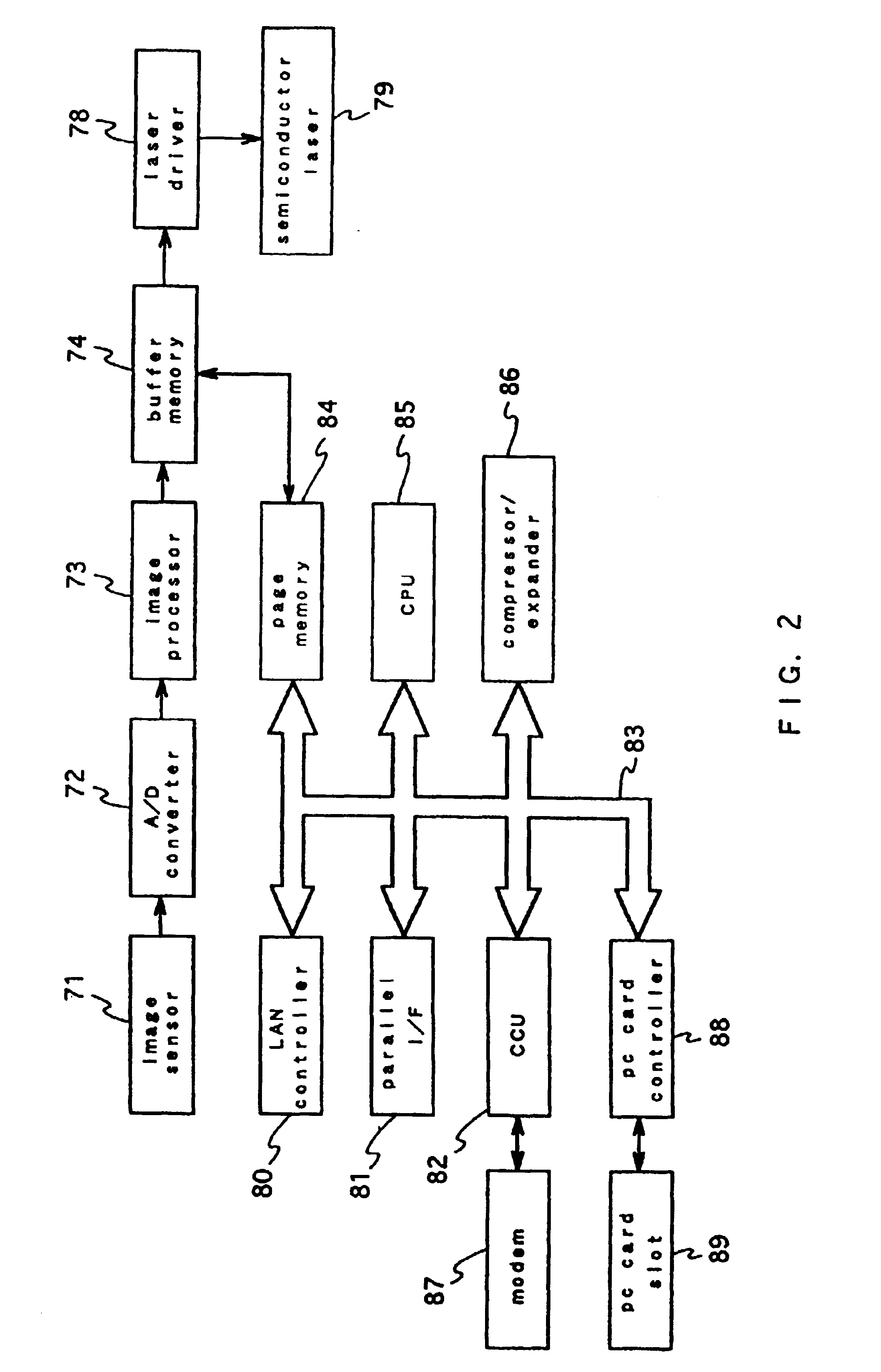
Image processing system that communicates with a portable device having user information
InactiveUS6871243B2Easy to useImprove securityDigital computer detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsImaging processingDigital copy
User information is acquired from a portable device and setting information of the user is acquired from a server based on the user information from the portable device to customize settings for each user. As a result, a digital copying machine having a user interface which is set to be easily customized for a user is provided.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
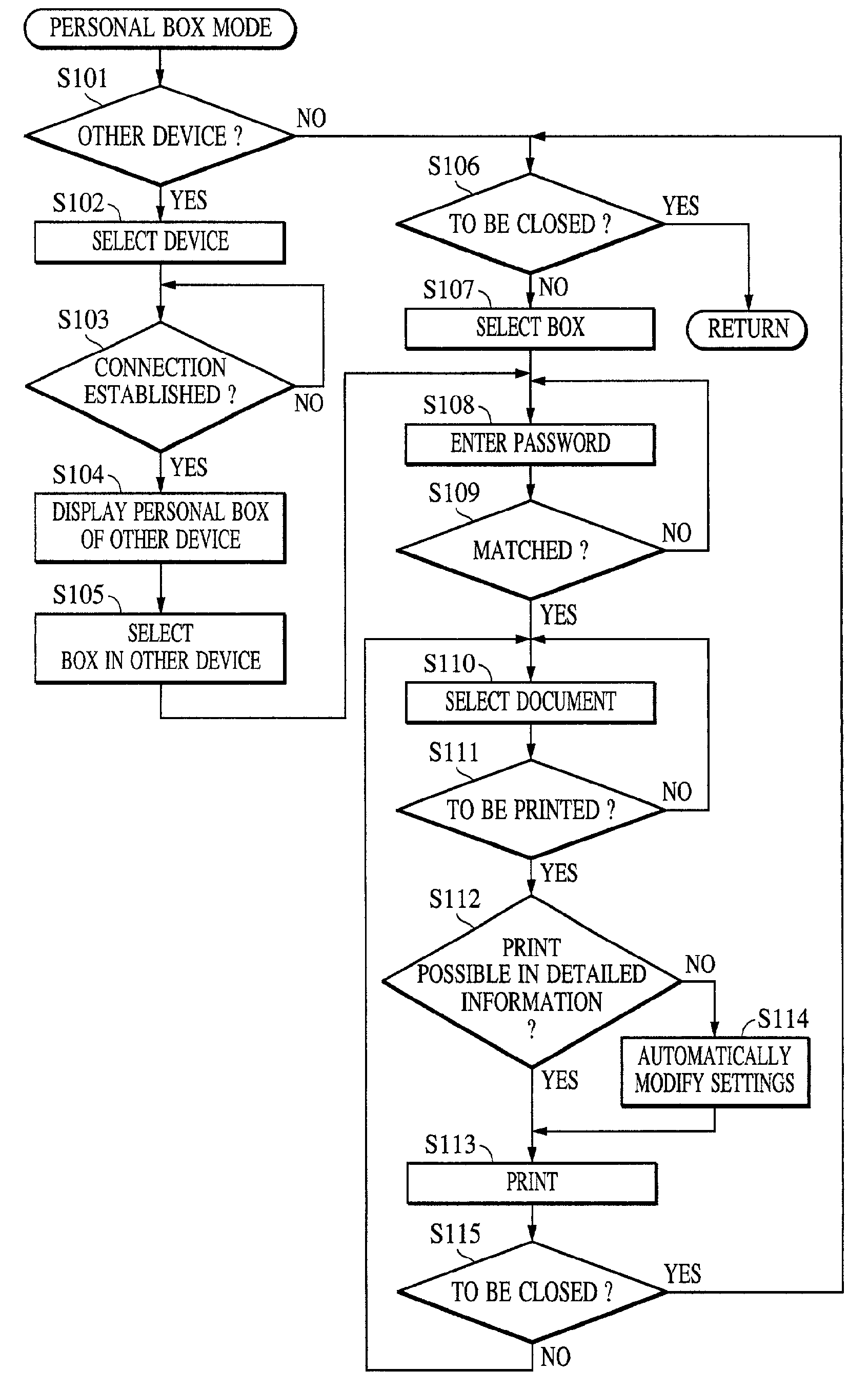
Image-forming system, control method therefor, image-forming apparatus, data processing method, and storage medium
InactiveUS7130069B1Improve usabilityDigitally marking record carriersPictoral communicationDigital copyImage formation
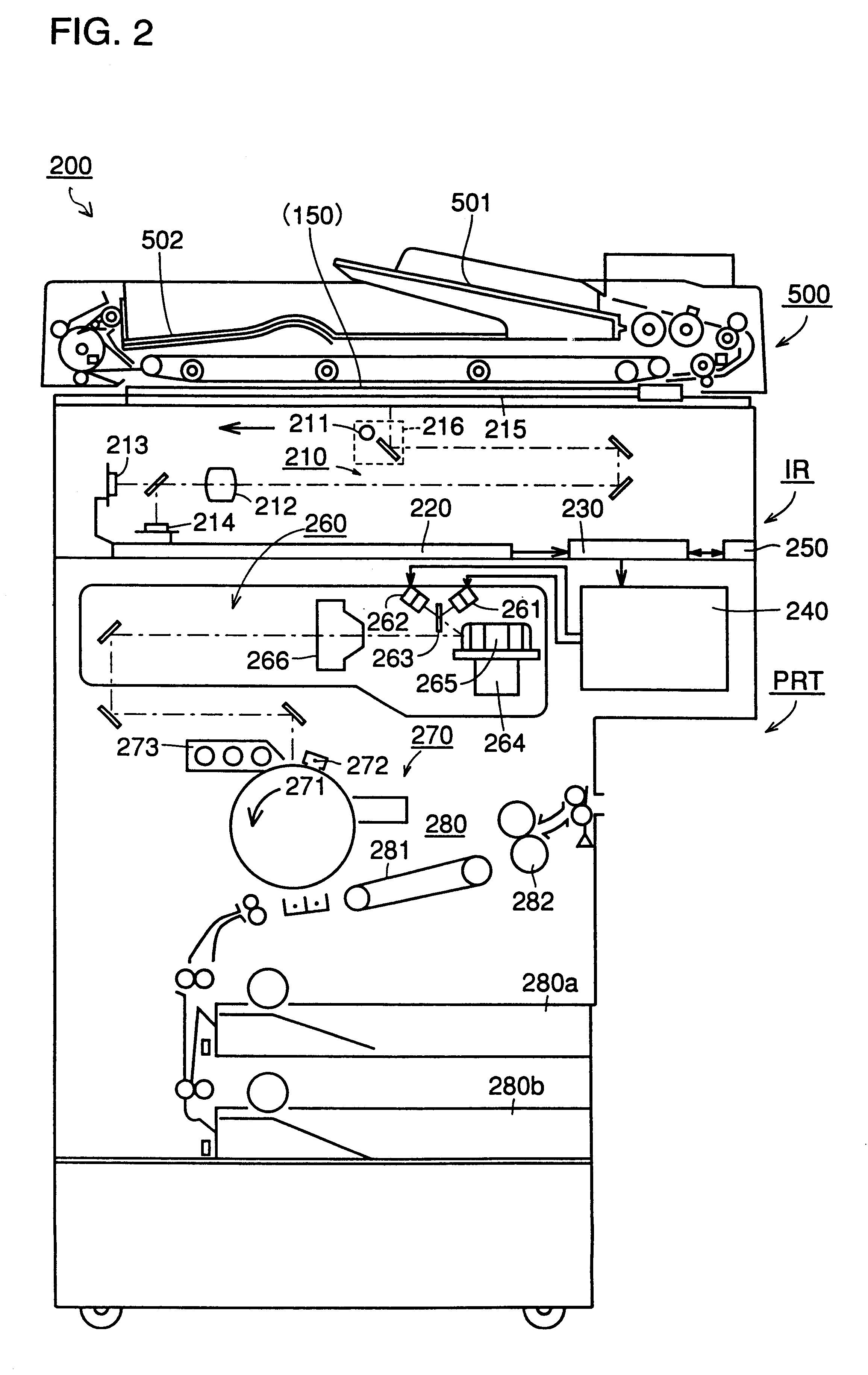
In an image-forming apparatus such as a digital copying apparatus, even when a digital copying apparatus having print data desired by a user is used by someone else or is in trouble, the apparatus outputs the print data desired by the user without any delay at any time convenient to the user and in an output form the user desires, and thus increases availability thereof. The digital copying apparatus includes an network interface communicating with an external host apparatus, and a memory for storing image data and operation mode data received through the network interface, and prints out the image data on a printer section. The digital copying apparatus receives image data and operation mode data from the other digital copying apparatus and prints out the image data on the printer section thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Tamper prevention and detection for video provided over a network to a client
A system, apparatus, and method are directed to providing digital copy protection of media using a subscriber / publisher architecture. In one embodiment, a publisher employs various dynamic and / or static tamper detection, including, filter graph change detectors, ICE detectors, screen scraping detectors, debugger detectors, pattern recognizers, or the like. When a tampering event is detected by one or more of the publishers, the tamper event may be published for access by a subscriber. Published tamper events may be pushed to or pulled by the subscribers. When one or more subscribers receive the tamper event, the subscriber(s) may perform one or more tamper response actions according to various business rules, and / or other core rules.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Systems, methods, and computer program products for interacting with electronically displayed presentation materials
ActiveUS10078435B2Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)User input
Systems, methods, and computer program products for interacting with electronically displayed presentation materials are described. A display system includes, at least, a digital processor, an electronic display, and a non-transitory processor-readable storage medium into which is loaded a computer program product that includes, at least, processor-executable instructions and / or data. The processor-executable instructions and / or data, when executed by the processor, cause the display system to respond to user inputs indicative of pointer commands and magnification setting commands. In response to such commands, the display system causes; i) a dynamic cursor to display over top of content on the electronic display; and ii) a digital copy image of the content to be displayed over top of the content on the electronic display, the digital copy image displayed at a greater magnification level than the content.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
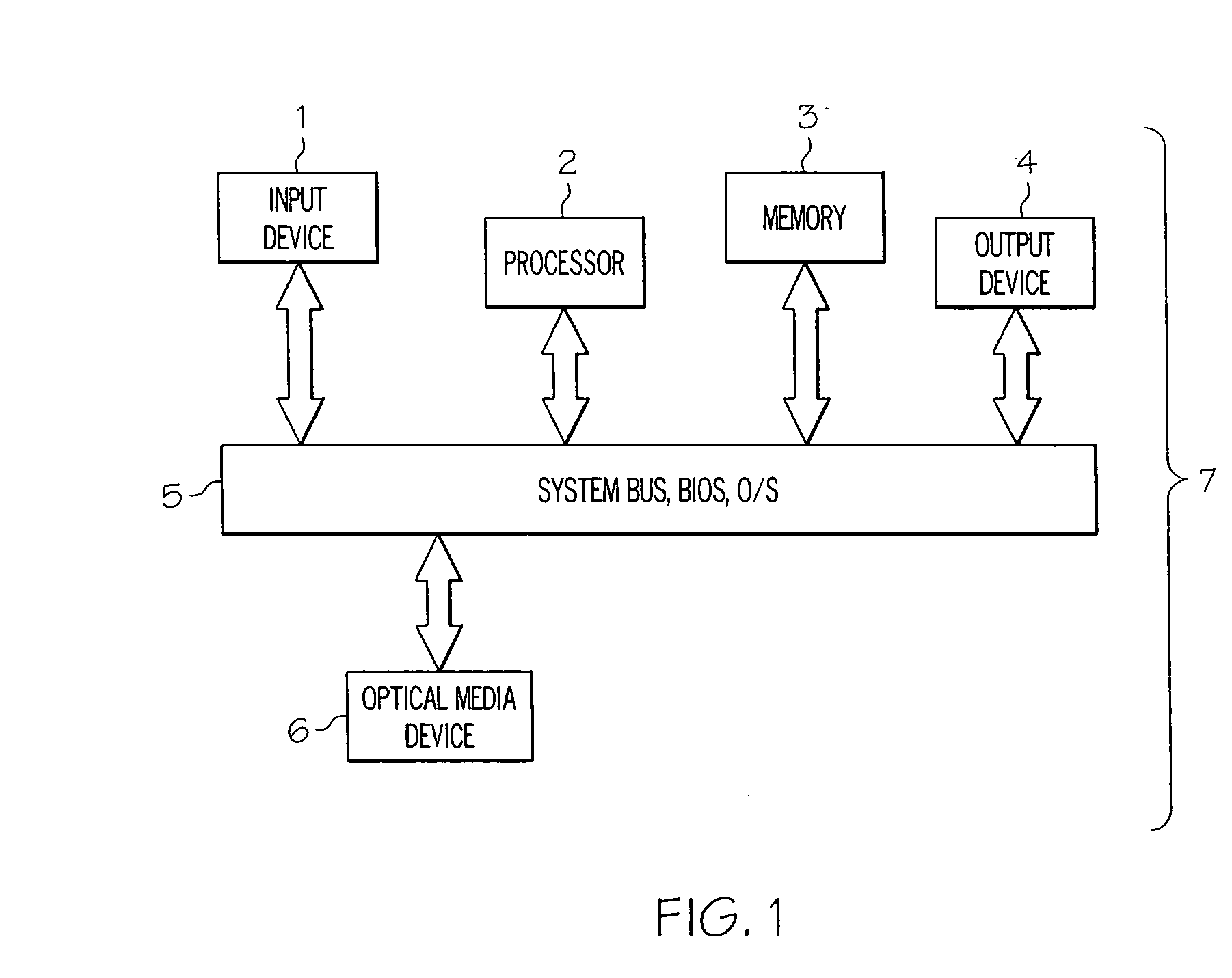
Systems and methods for media authentication
InactiveUS20050108538A1Inferior performanceDetection performanceFilamentary/web record carriersUser identity/authority verificationCompact discData segment
A method and system for authenticating a digital optical medium, such as a CD-ROM, determine whether the medium is an unauthorized copy, or the original. The original media is created, or altered, so as to contain anomalous locations from which the transfer of data is accomplished at different rates than a standard digital copy would exhibit. One implementation of the process involves timing analysis of the differences in data transfer rates. Another implementation involves the determination of digital signatures during multiple read operations performed on a data segment. The process can be employed in systems that control access to unauthorized copies, or may be used for other informative purposes. Theft, distribution, and piracy of digital content on optical media, such as computer software (also games, video, audio, e-book content), is often accomplished by copying it directly to another disc using commonly available copy tools and recordable optical media, or the replication of media to another mass manufactured disc. The present invention, which helps to irrefutably identify a unit of optical media as the original, and can correspondingly identify any copy made by any currently available means as such a copy, may prevent an unauthorized individual from making use of any unauthorized copies. This offers significant advantages to content creators who wish to protect their products.
Owner:IPLA HLDG
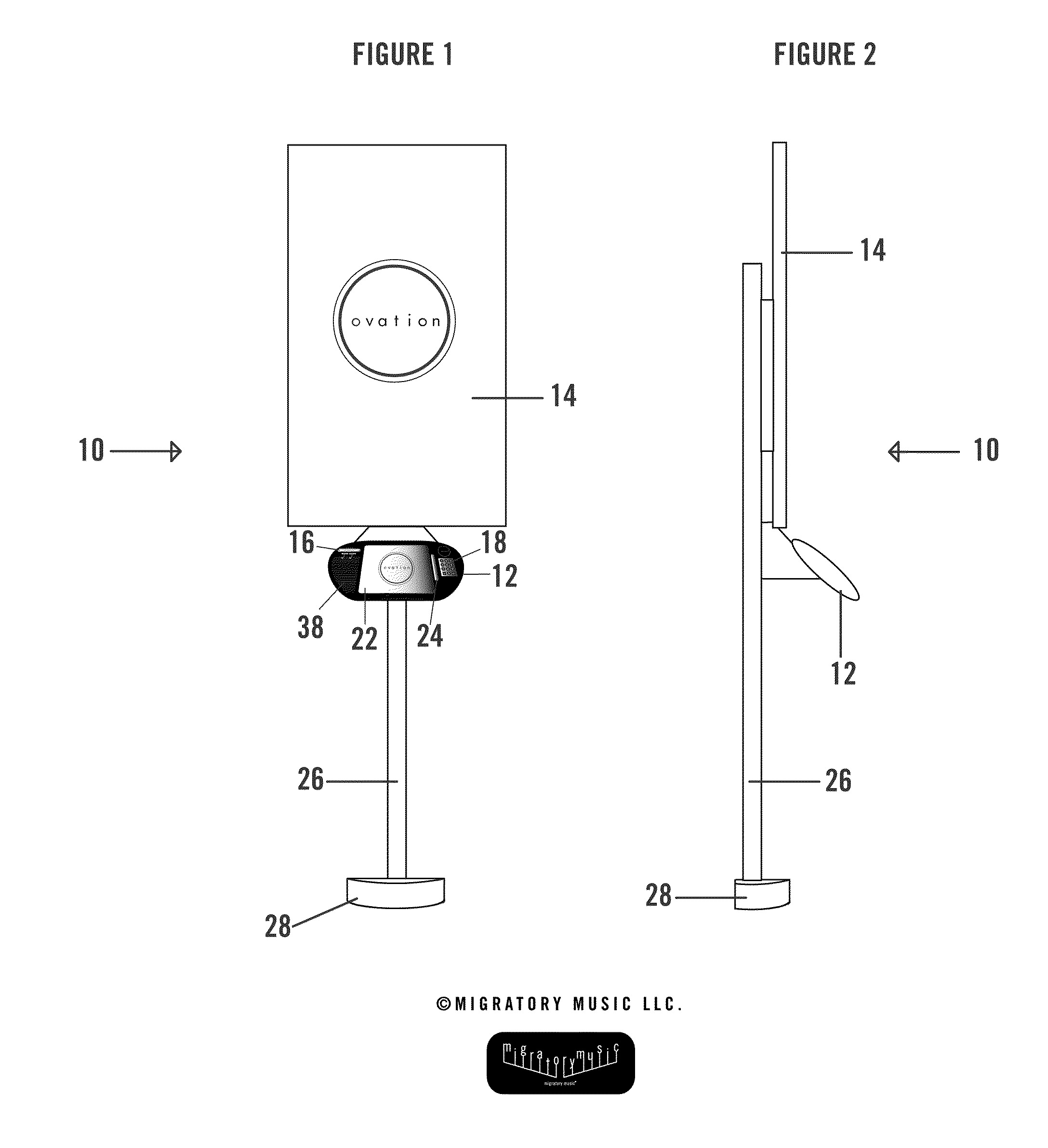
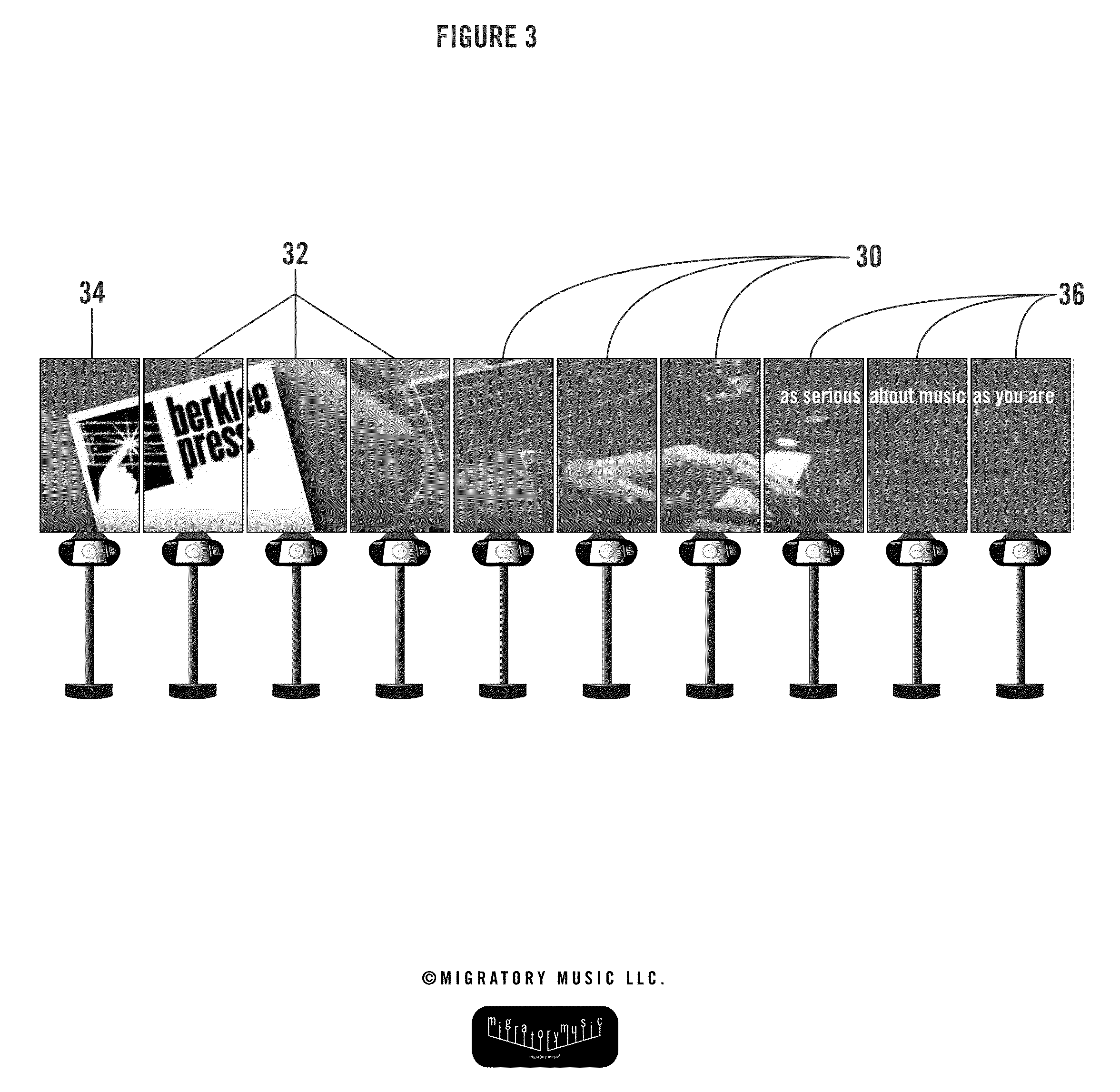
System and method for live music performance digital recording, distribution, and digital advertising
InactiveUS20110112913A1Heightens concert experienceAdvertisementsMultiple digital computer combinationsDigital copyDigital recording
The disclosure of the present application provides for a live music performance digital recording and distribution system as well as an advertising system that allows a consumer to purchase a digital copy of the live music performance immediately after the conclusion of the live music performance.
Owner:OVATION TECH LLC
Media fingerprinting for content determination and retrieval
Audio fingerprinting and other media matching technologies can be used to identify broadcast media, such as television shows and radio broadcasts. A user device can record image, audio, and / or video information and upload information to a matching service that is able to use matching technology to identify the media and provide supplemental content or information to the user. The user might receive information identifying a product in an advertisement, identifying an actor on screen in a movie at a particular time, or other such information. In some embodiments, the user can receive access to a digital copy of the captured media, such as the ability to download a copy of a program in which a user expressed interest. Since a user might capture media information after the point of interest, a device can buffer a window of recently captured media in order to attempt to identify the intended media.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
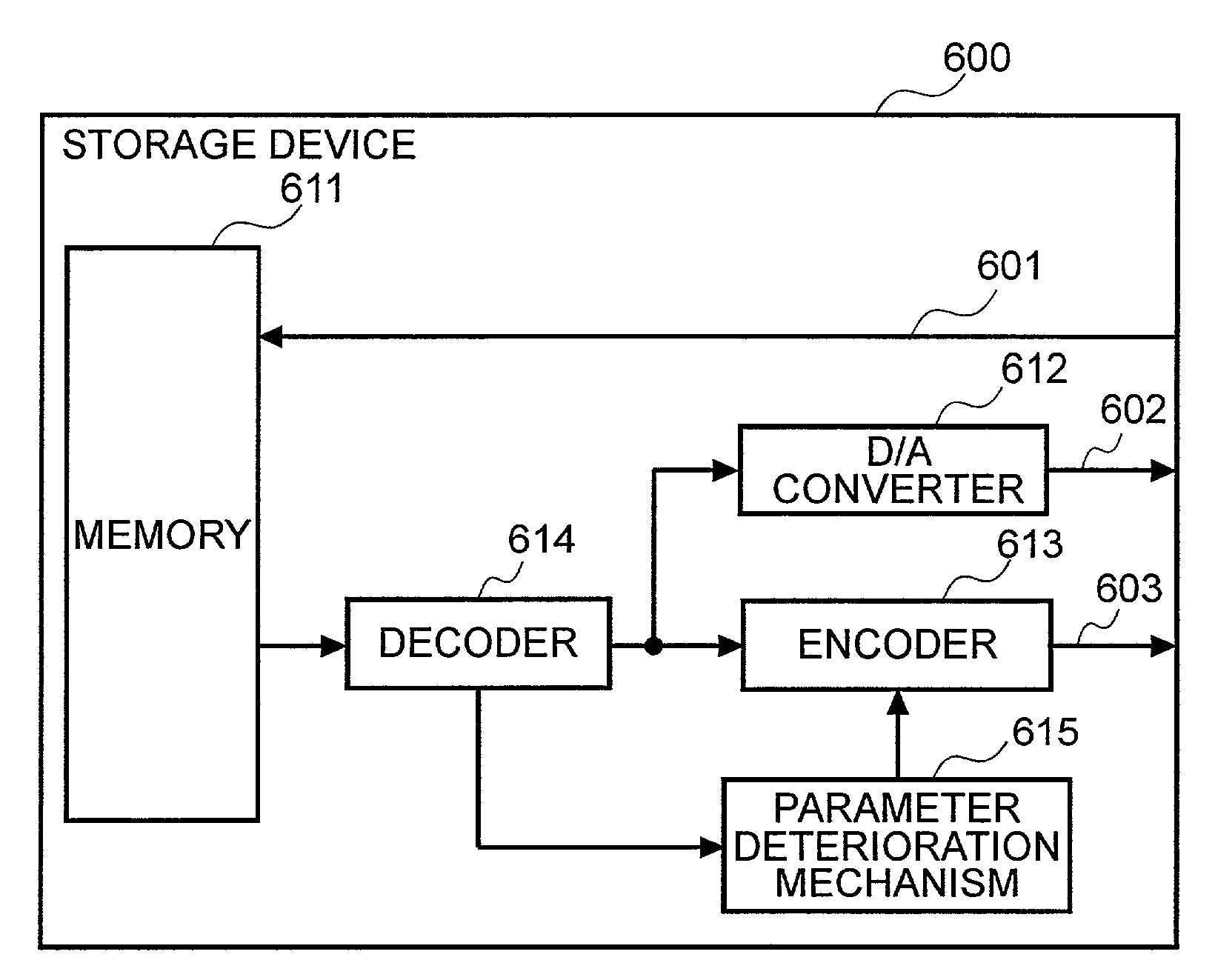
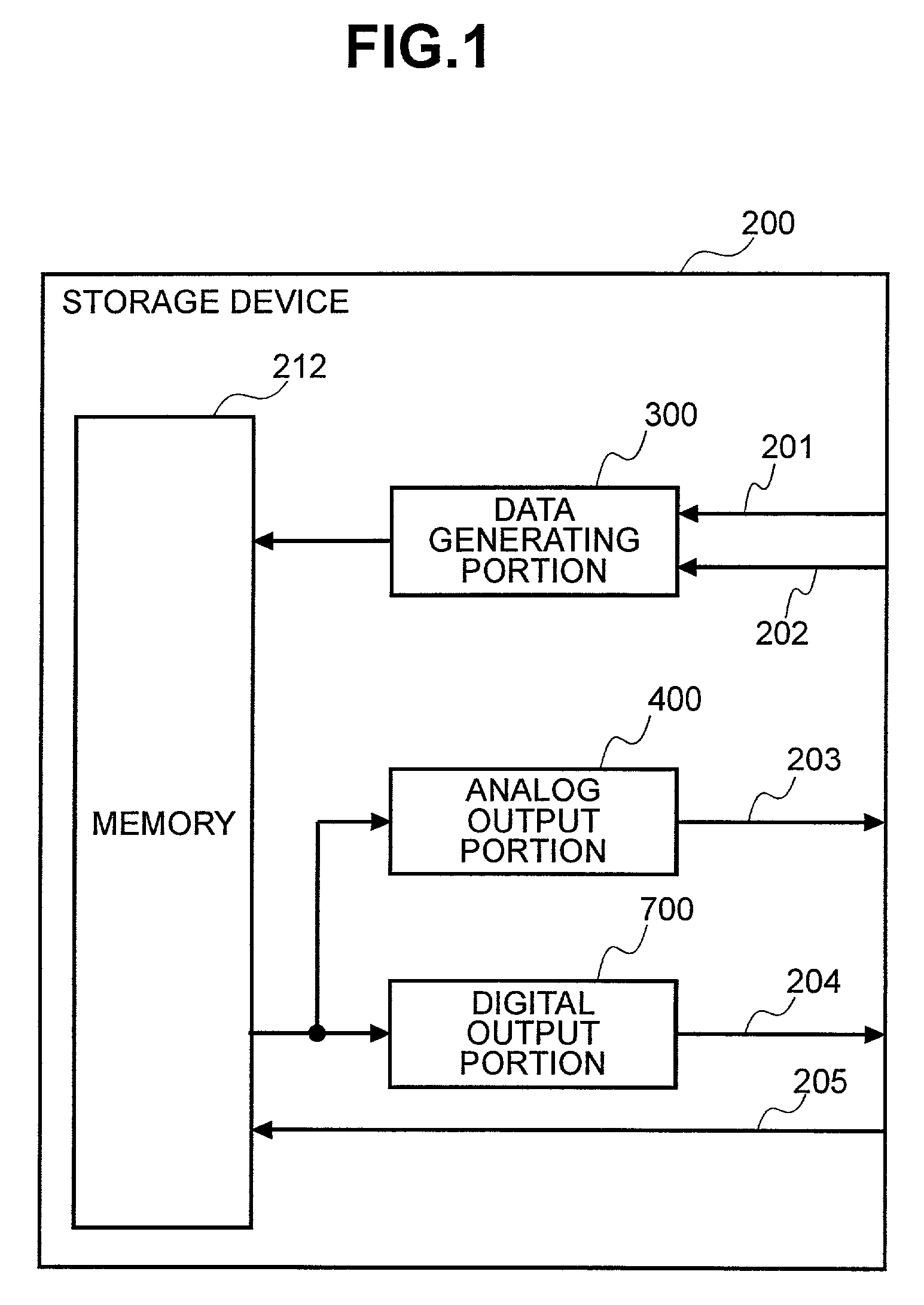
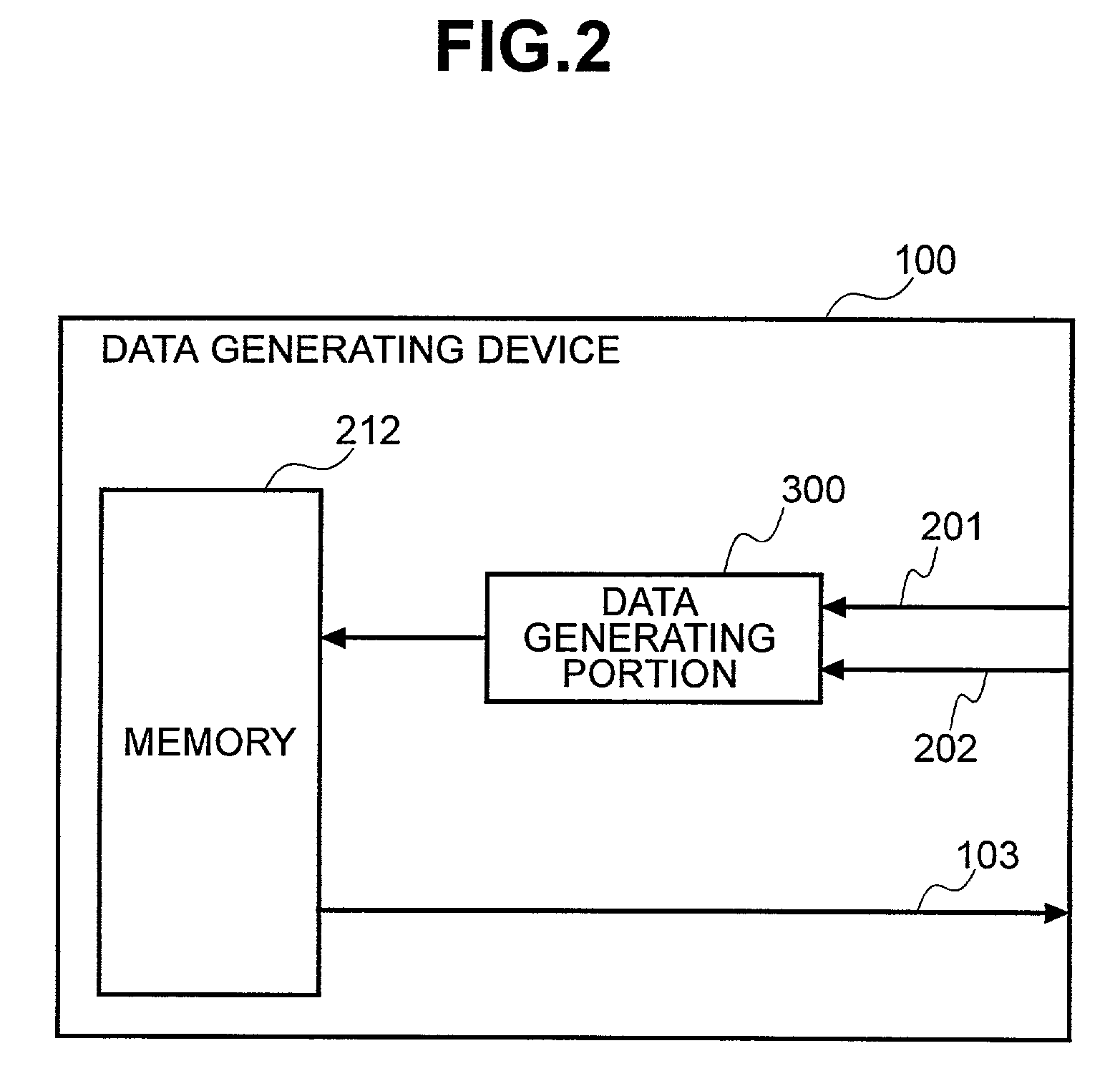
Digital copying method and storage device for digital content
InactiveUS7225340B2Degradation in quality levelTelevision system detailsUser identity/authority verificationDigital dataDigital content
The present invention provides a digital copying method for preventing complete copying by the use of digital copying. A data generating portion includes a storage device which generates a plurality of digital copies having mutually different amounts of effective information from original digital data, and stores the set of digital content having the digital copies encrypted different numbers of times in a memory. A digital output portion decrypts the set of digital content retrieved from the memory a prescribed number of times, making usable and outputting one of the digital copies in the set of digital content. An analog output portion extracts the digital copy that has been encrypted zero times from the set of digital content, converts that copy to analog data, and outputs that data.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Media fingerprinting for content determination and retrieval
Audio fingerprinting and other media matching technologies can be used to identify broadcast media, such as television shows and radio broadcasts. A user device can record image, audio, and / or video information and upload information to a matching service that is able to use matching technology to identify the media and provide supplemental content or information to the user. The user might receive information identifying a product in an advertisement, identifying an actor on screen in a movie at a particular time, or other such information. In some embodiments, the user can receive access to a digital copy of the captured media, such as the ability to download a copy of a program in which a user expressed interest. Since a user might capture media information after the point of interest, a device can buffer a window of recently captured media in order to attempt to identify the intended media.
Owner:SONY INTERACTIVE ENTERTAINMENT INC
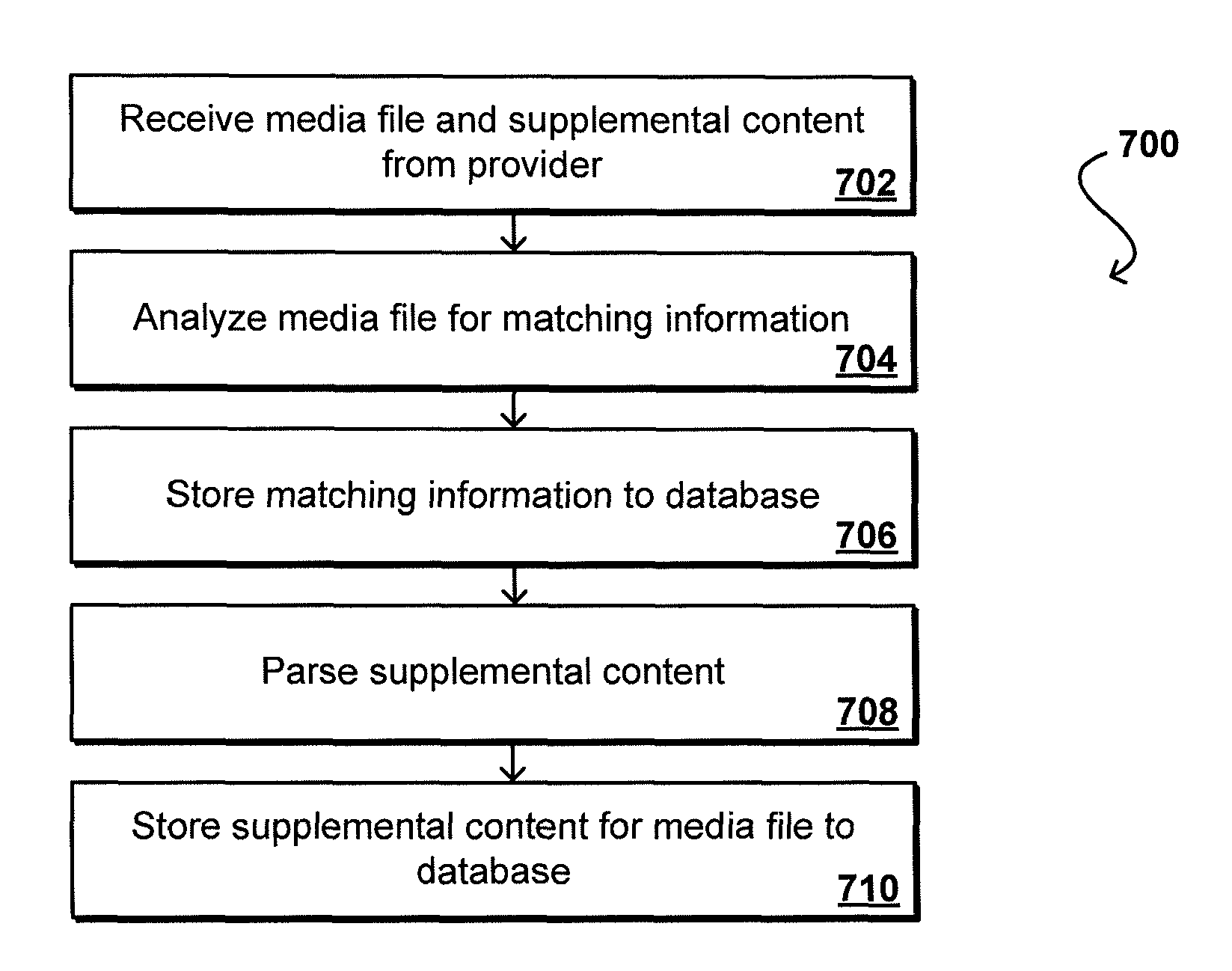
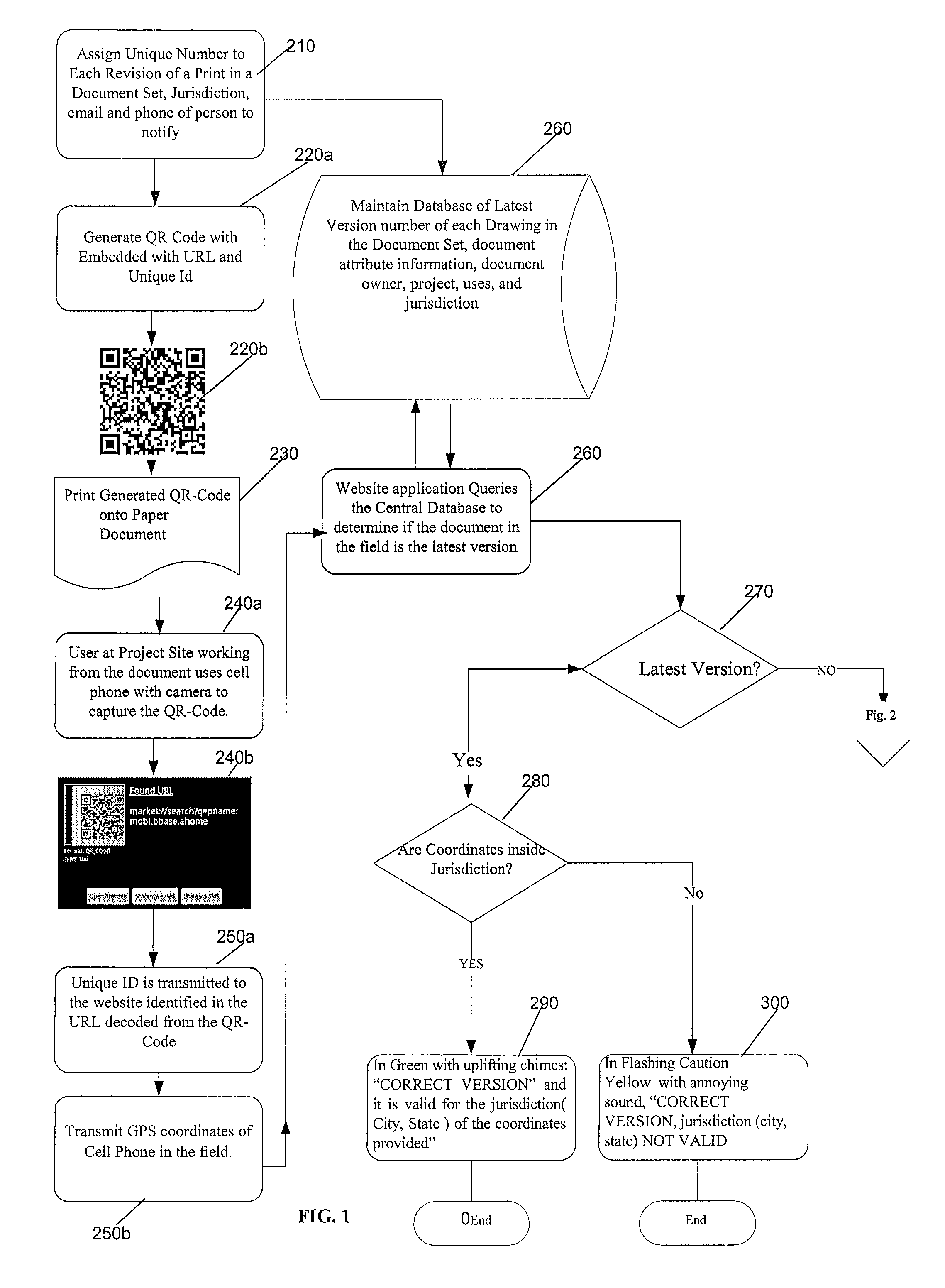
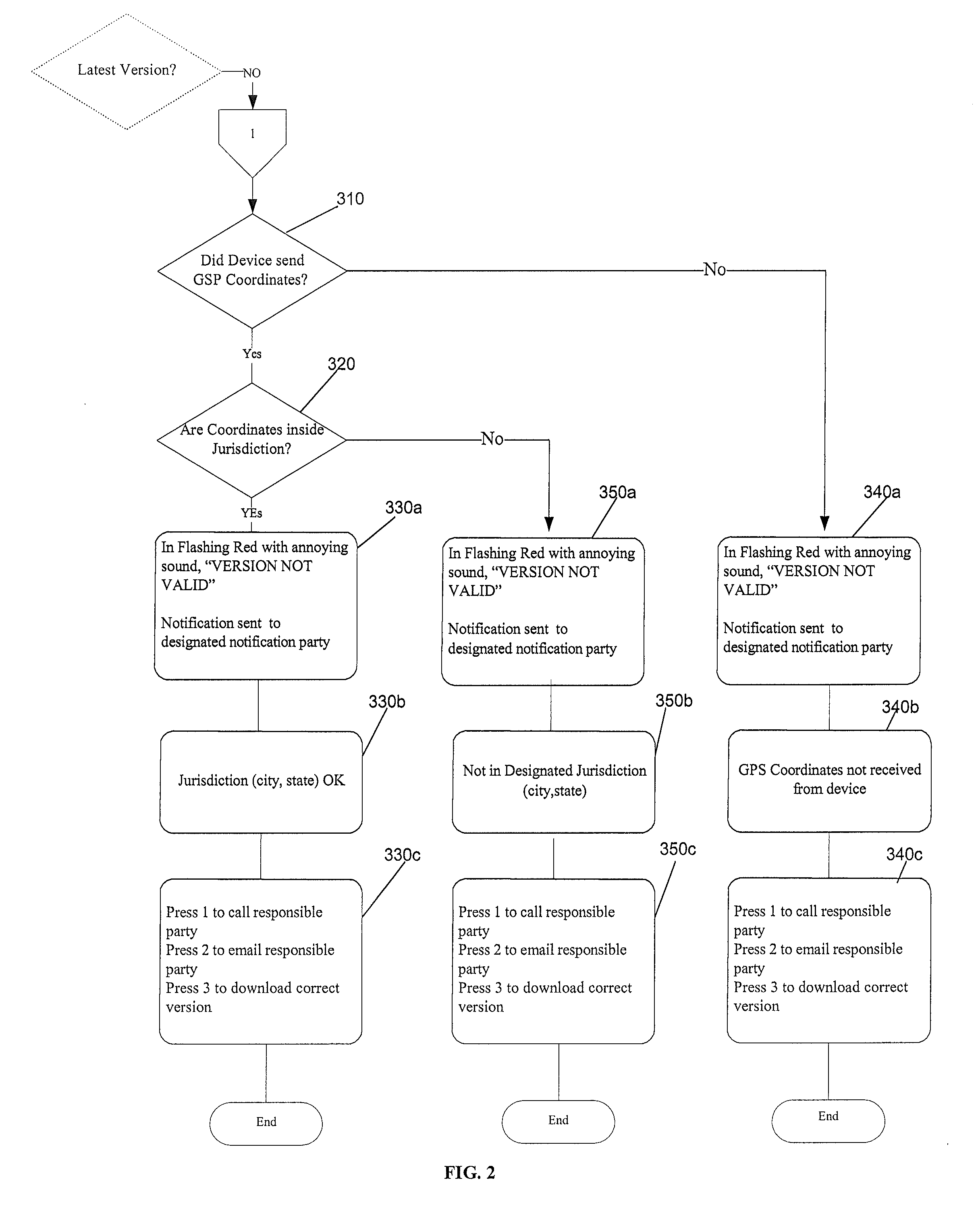
Method and system for document version management
A method of managing construction documents used on different on construction project sites includes storing digital copies of current and historical versions of the construction documents in a central document management server. A unique document version identifier and regulatory jurisdiction identifier is stored. When a paper document is printed, a matrix barcode is generated, encoded with the document version identifier, and printed on the paper document. The barcode is scanned at the project site. The central document server compares the document version identifier and regulatory jurisdiction identifier decoded from the matrix barcode to the identifiers stored in the central document server. The central document server then automatically communicates the result of the comparisons to a user of the printed document.
Owner:MONTCASTLE DEV
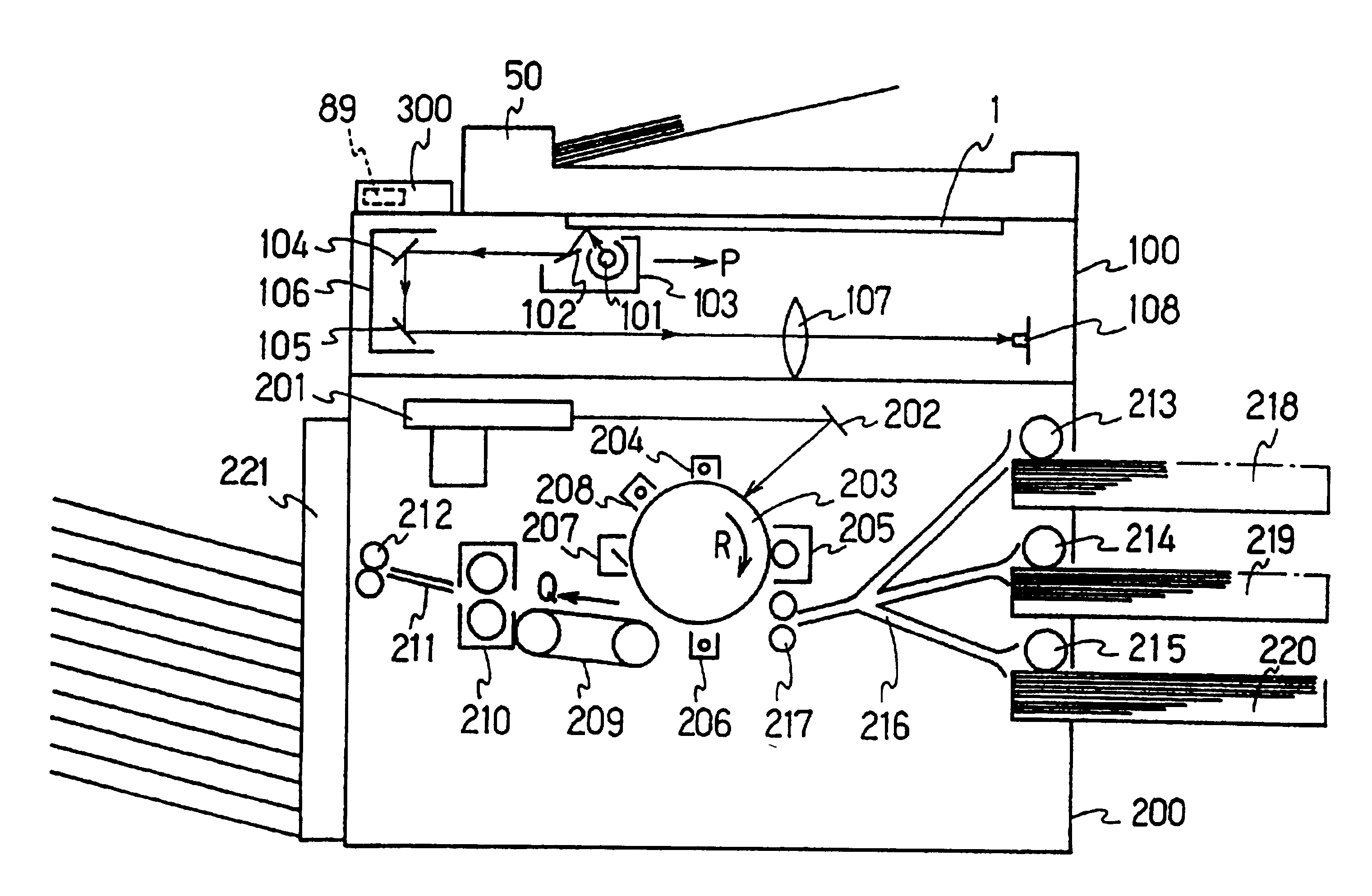
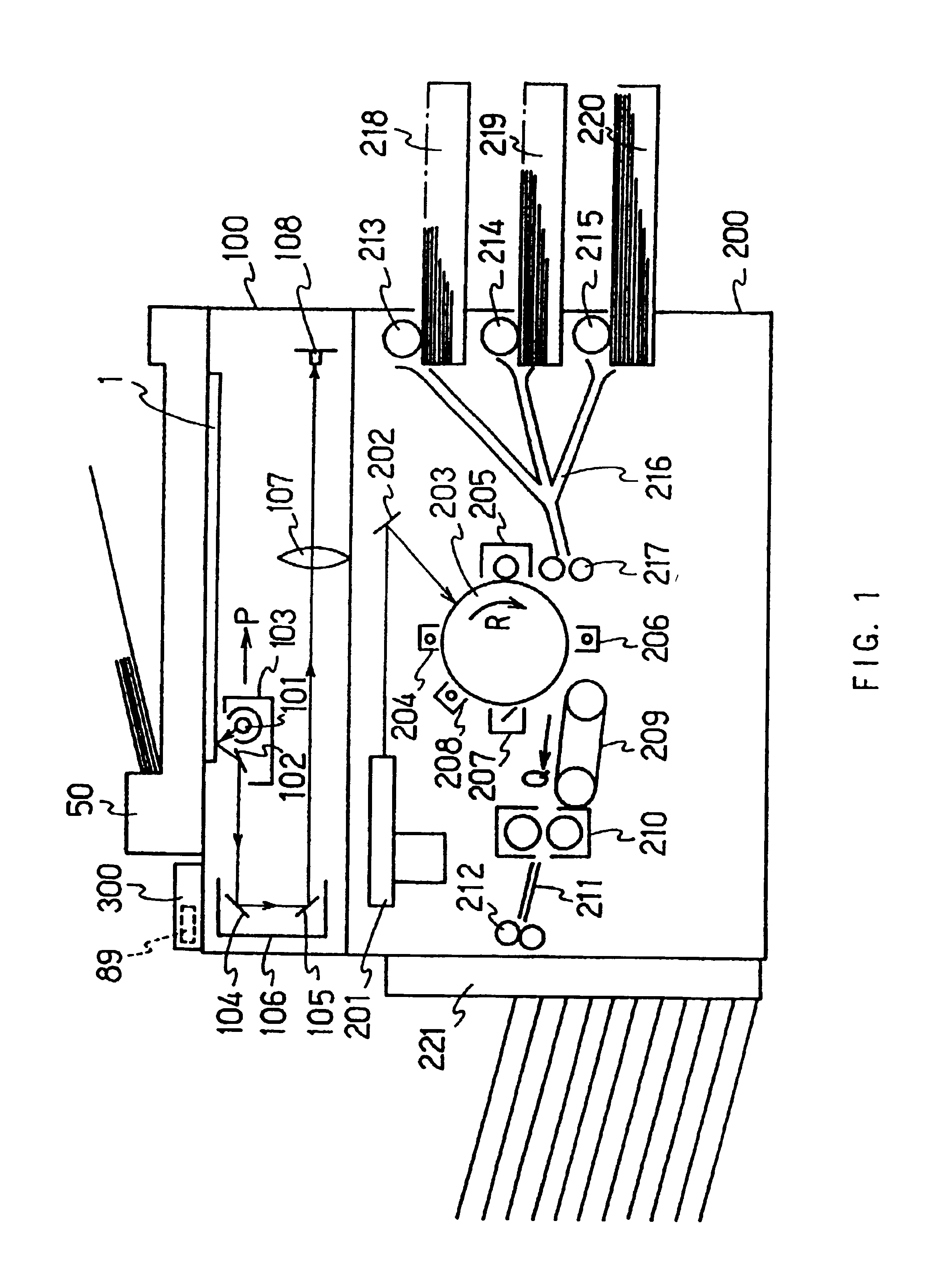
Image forming system and device, and control method and control program for controlling image forming device
ActiveUS7064854B2Improves power saving controlReduce the amount requiredElectrographic process apparatusVisual presentationEmbedded systemDigital copy
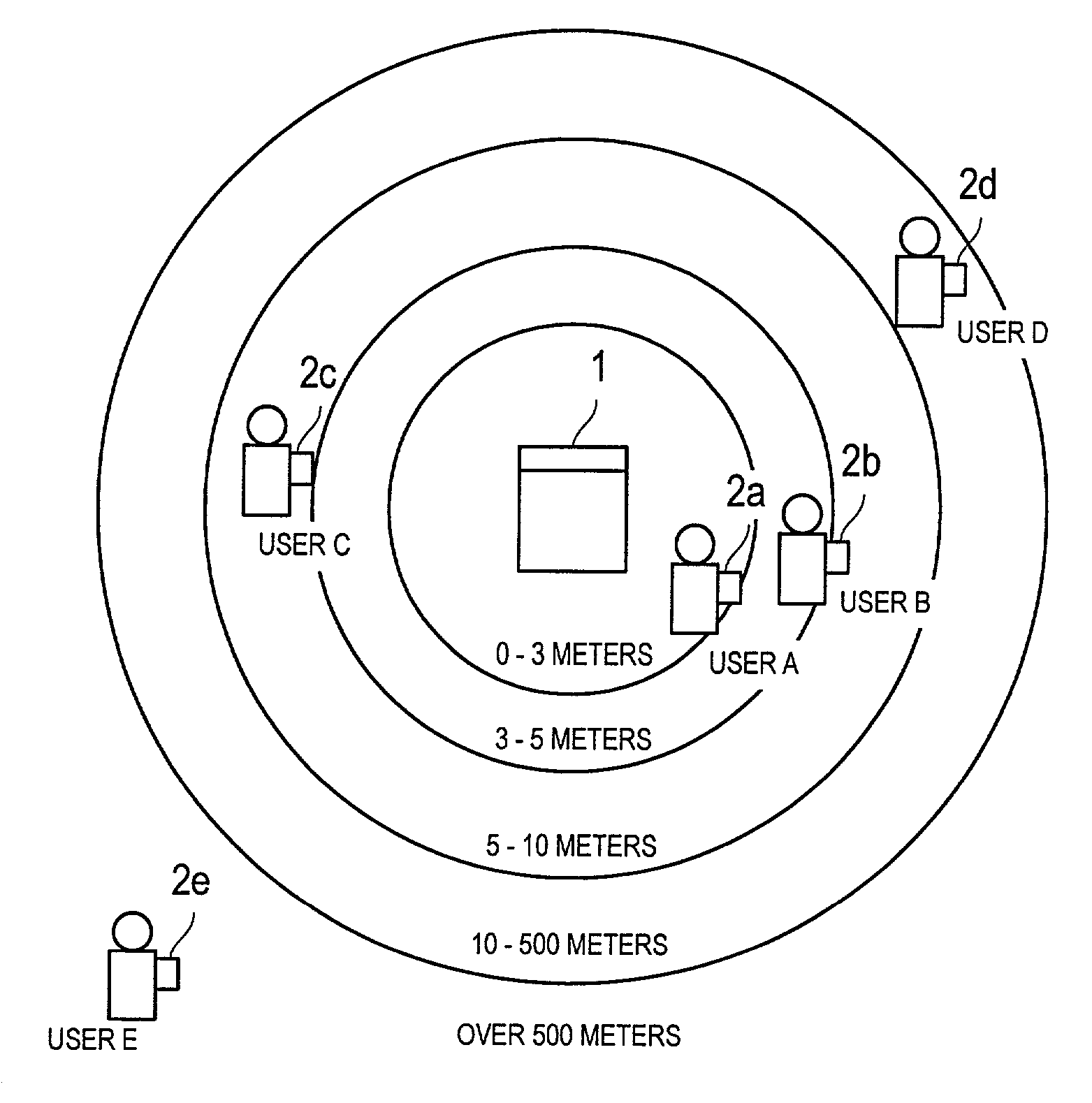
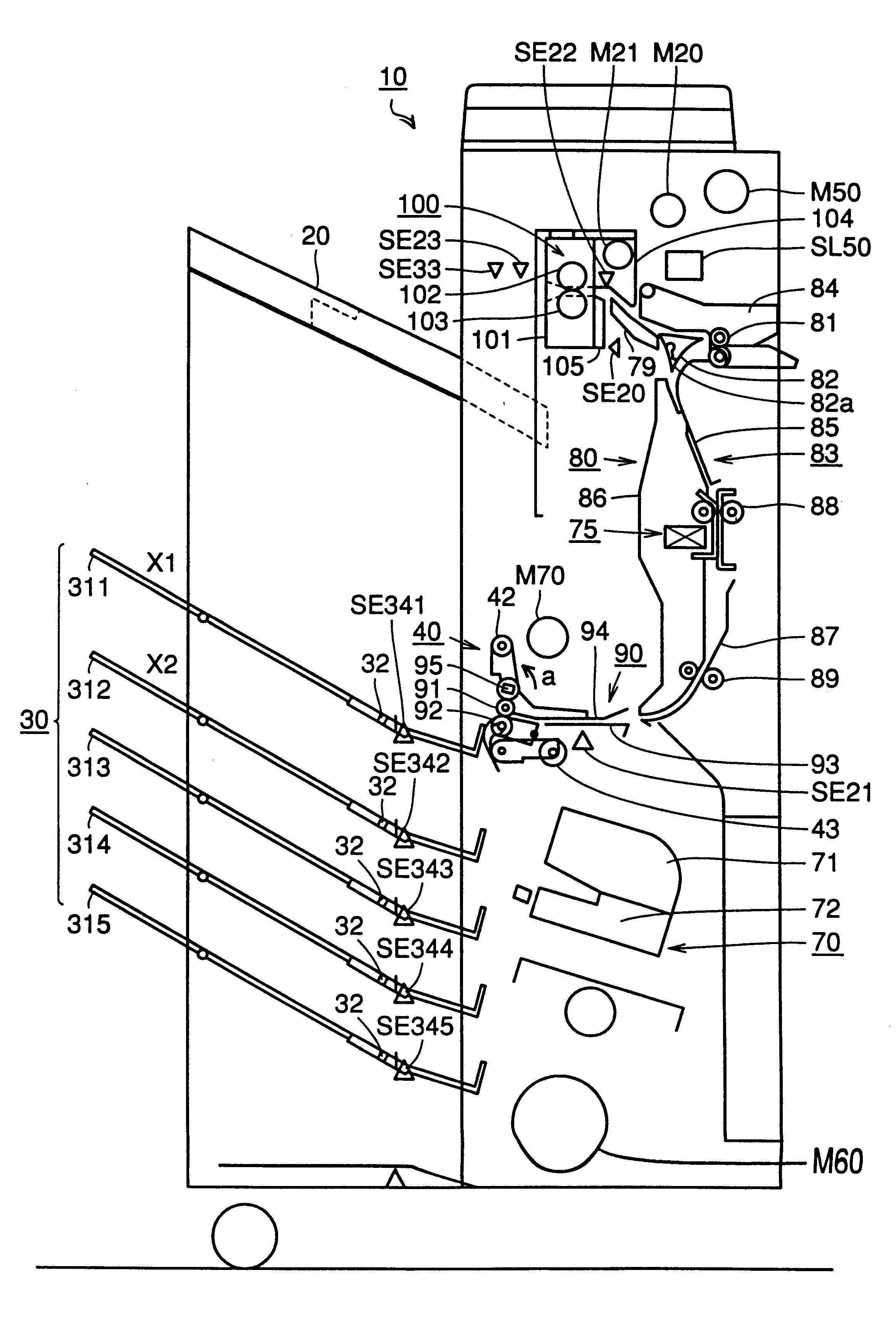
The image forming system includes a digital copying machine 1 and portable terminals 2. The digital copying machine 1 has a wireless communication unit 40, which is wirelessly communication with the portable terminals 2. The digital copying machine 1 identifies a portable terminal located closest to the digital copying machine 1 out of multiple portable terminals 2 that are in communicable conditions. As the distance between the identified portable terminal 2 and the digital copying machine 1 reduces, the temperature of heating rollers 31 is controlled to rise.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
Apparatus for retrieving document data
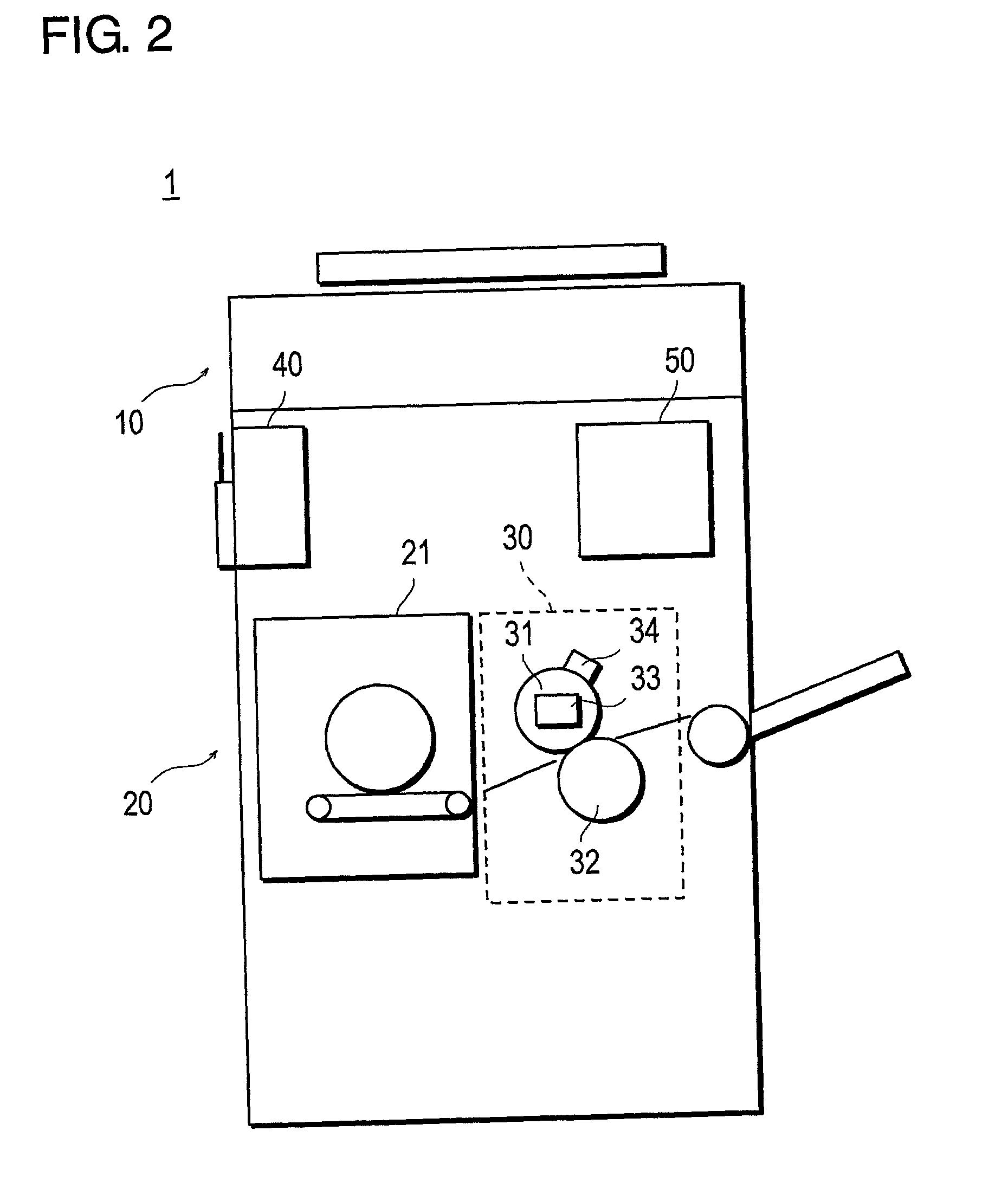
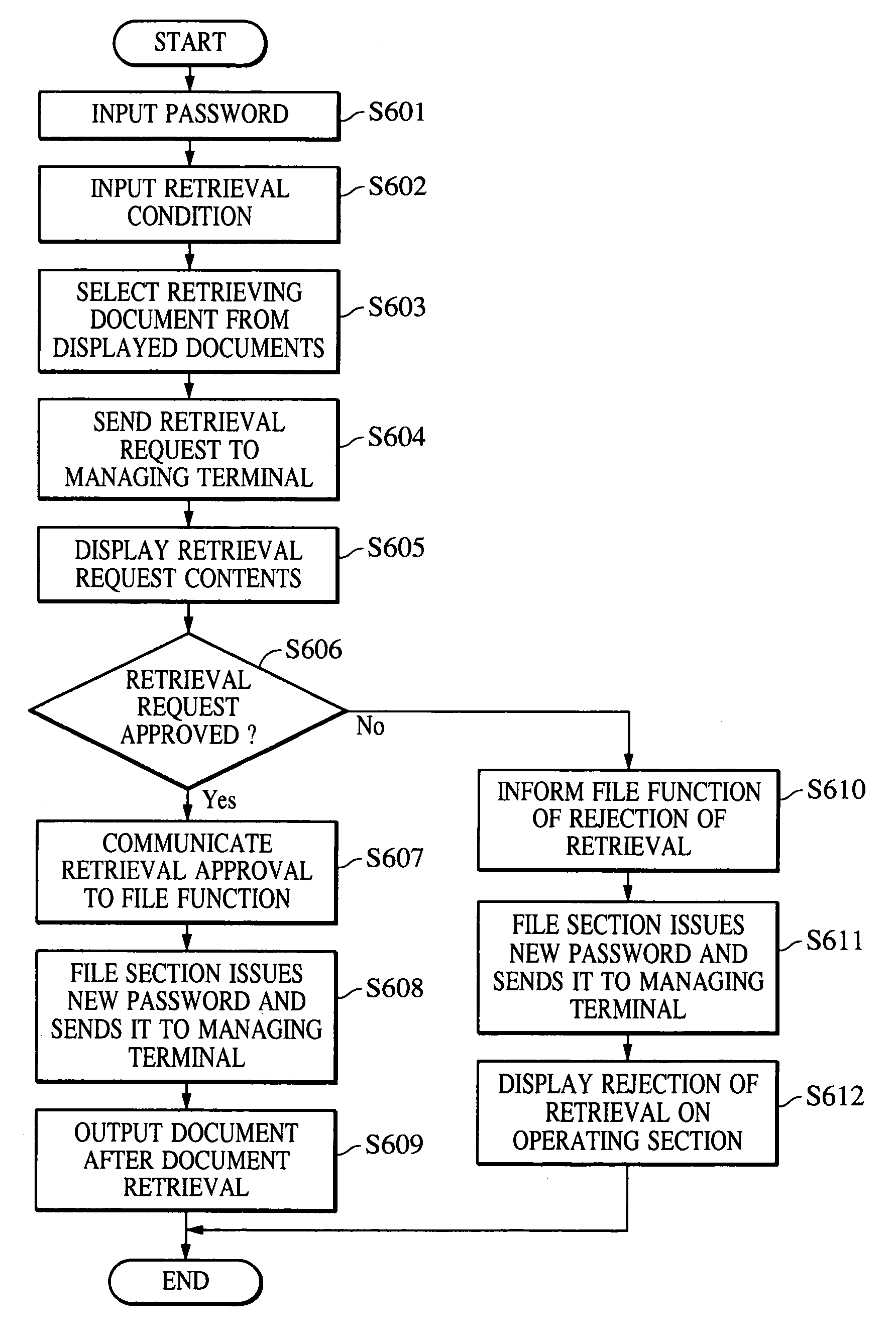
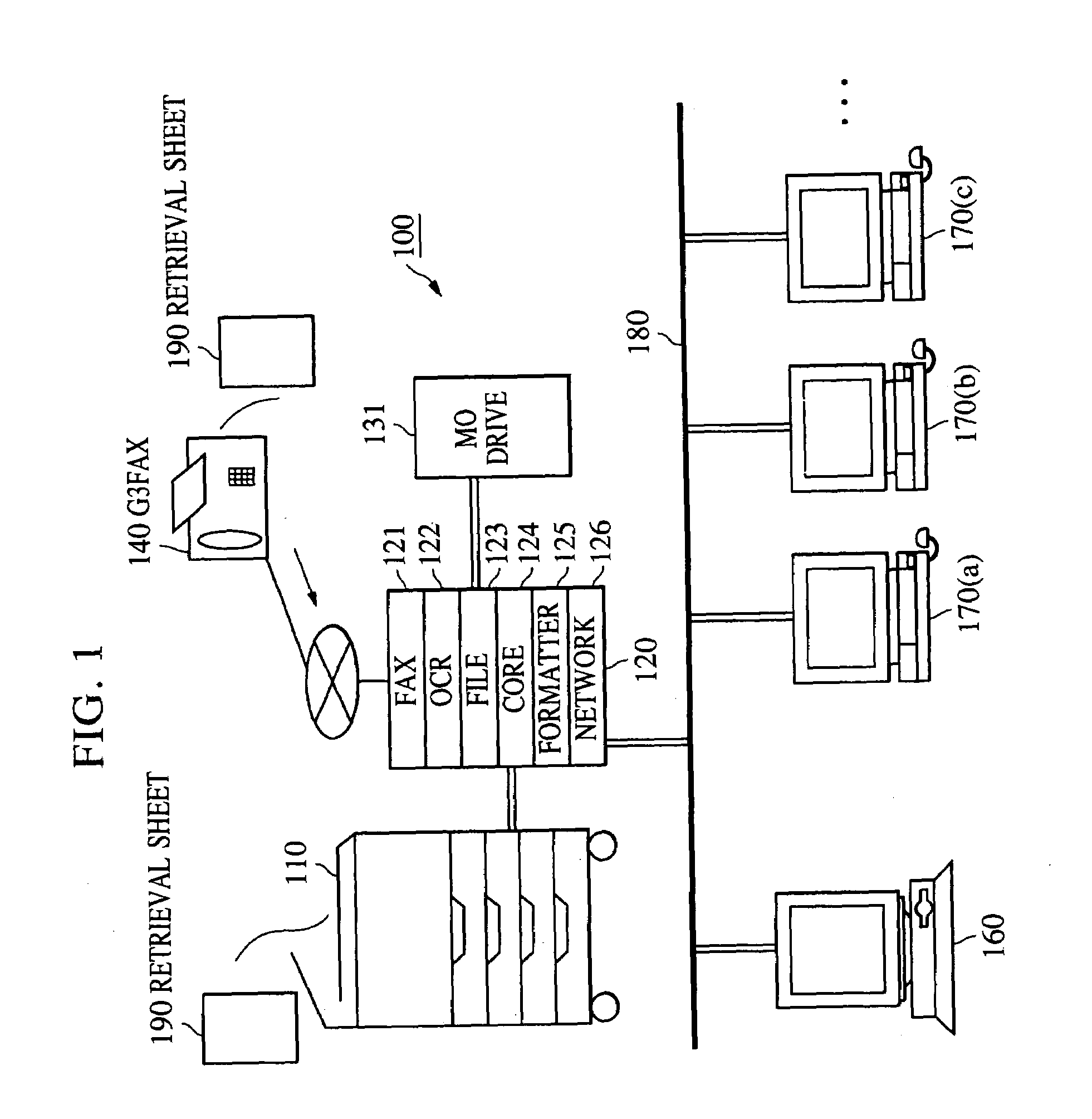
InactiveUS6950202B1Reliably preventing improper or illegal outward flowDrawback can be obviatedDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsPasswordDigital copy
An information input / output system capable of reliably preventing improper leakage of information and of keeping confidential information secret. The information input / output system provides a digital copying machine compositely having a plurality of functions, such as a filing function, an OCR function, a facsimile function and a network function. The digital copying machine performs an information retrieval on the basis of a password from a user in response to an information retrieval requirement (information retrieval request) made through its operating section, an information retrieval requirement made by a information retrieval sheet sent from the external through the use of a facsimile or an information retrieval requirement made through a personal computer on a network. After the completion of the information retrieval, the digital copying machine issues a new password (for example, at random) and makes the previously used password invalid.
Owner:CANON KK
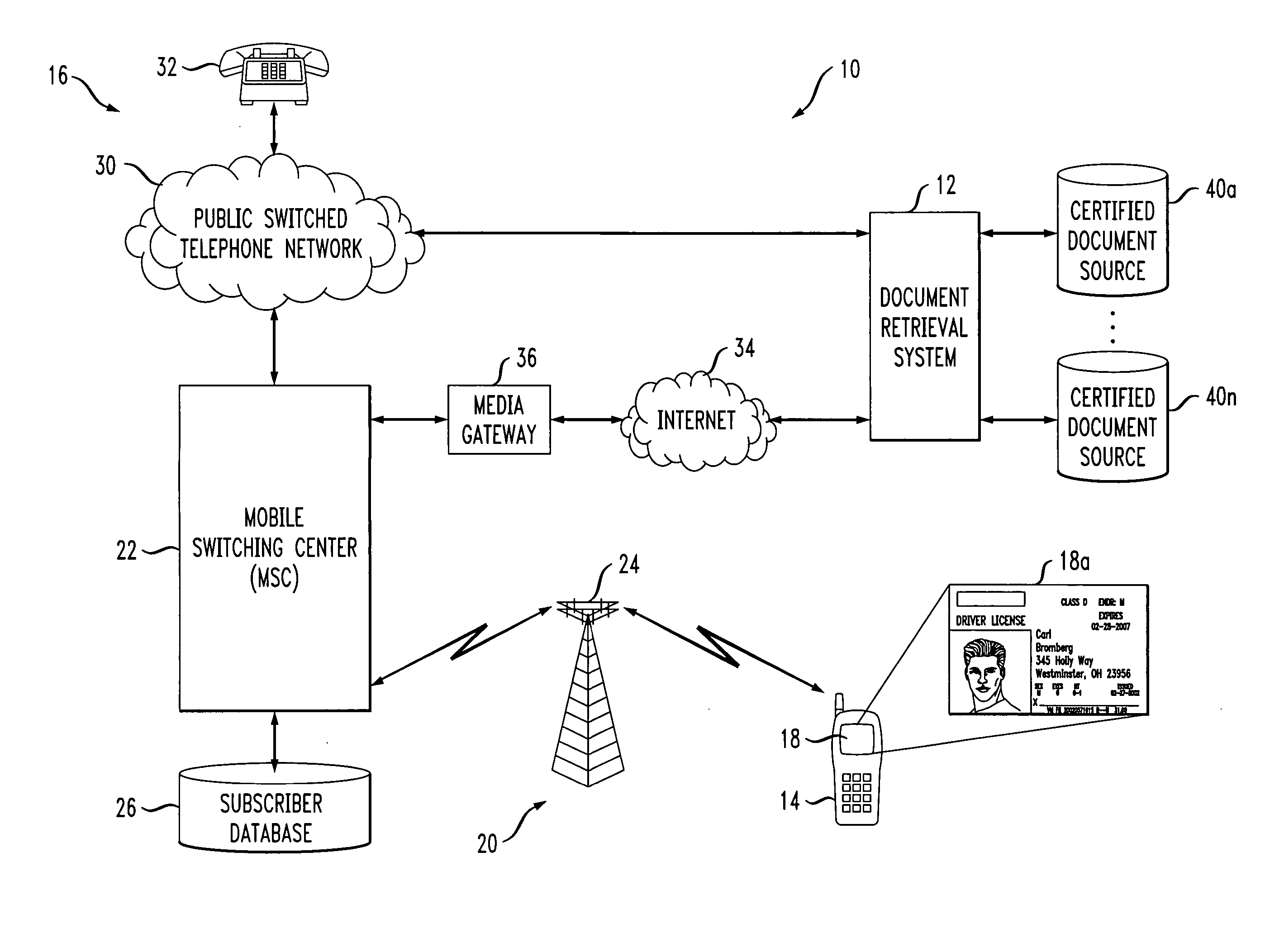
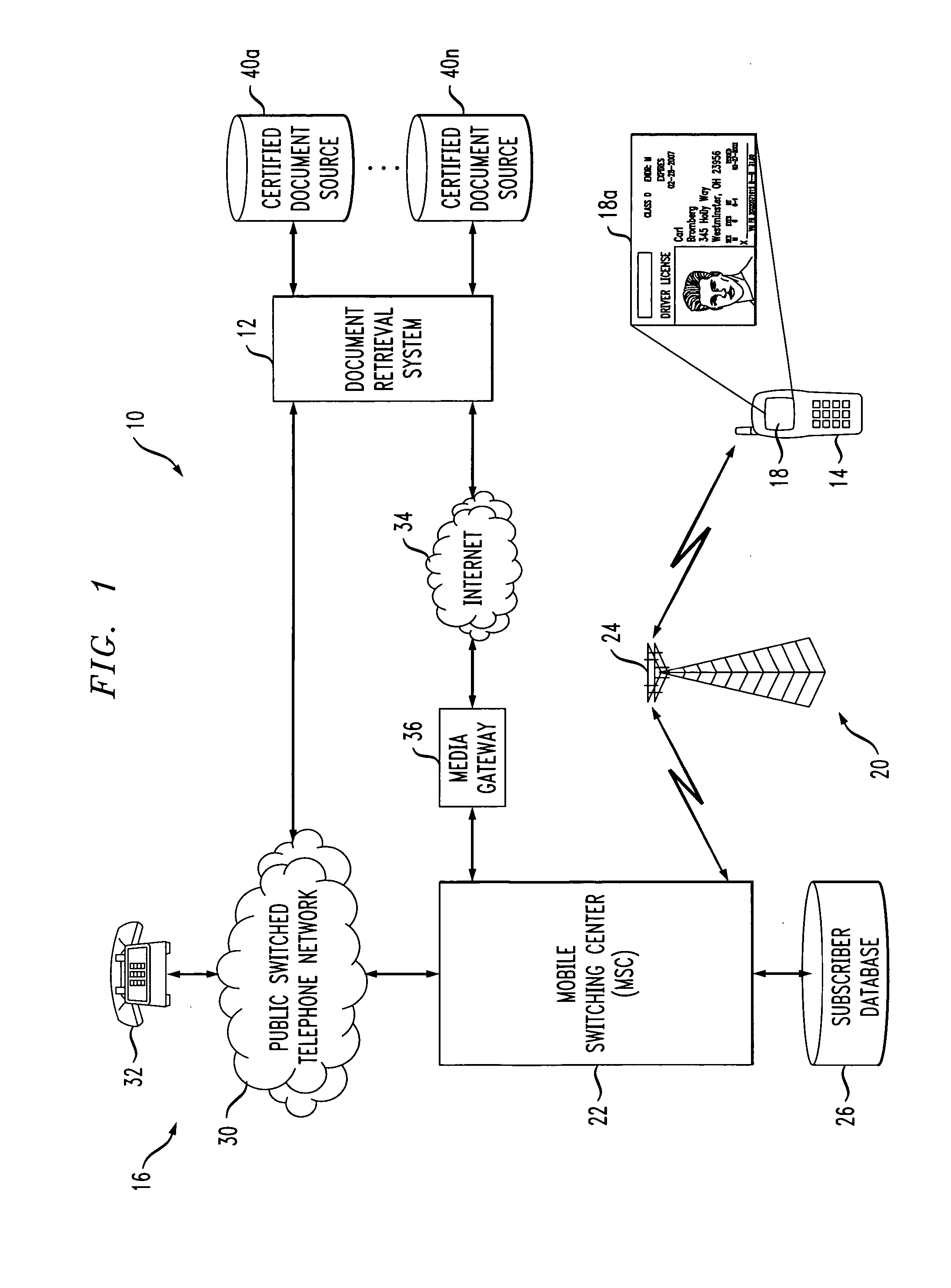
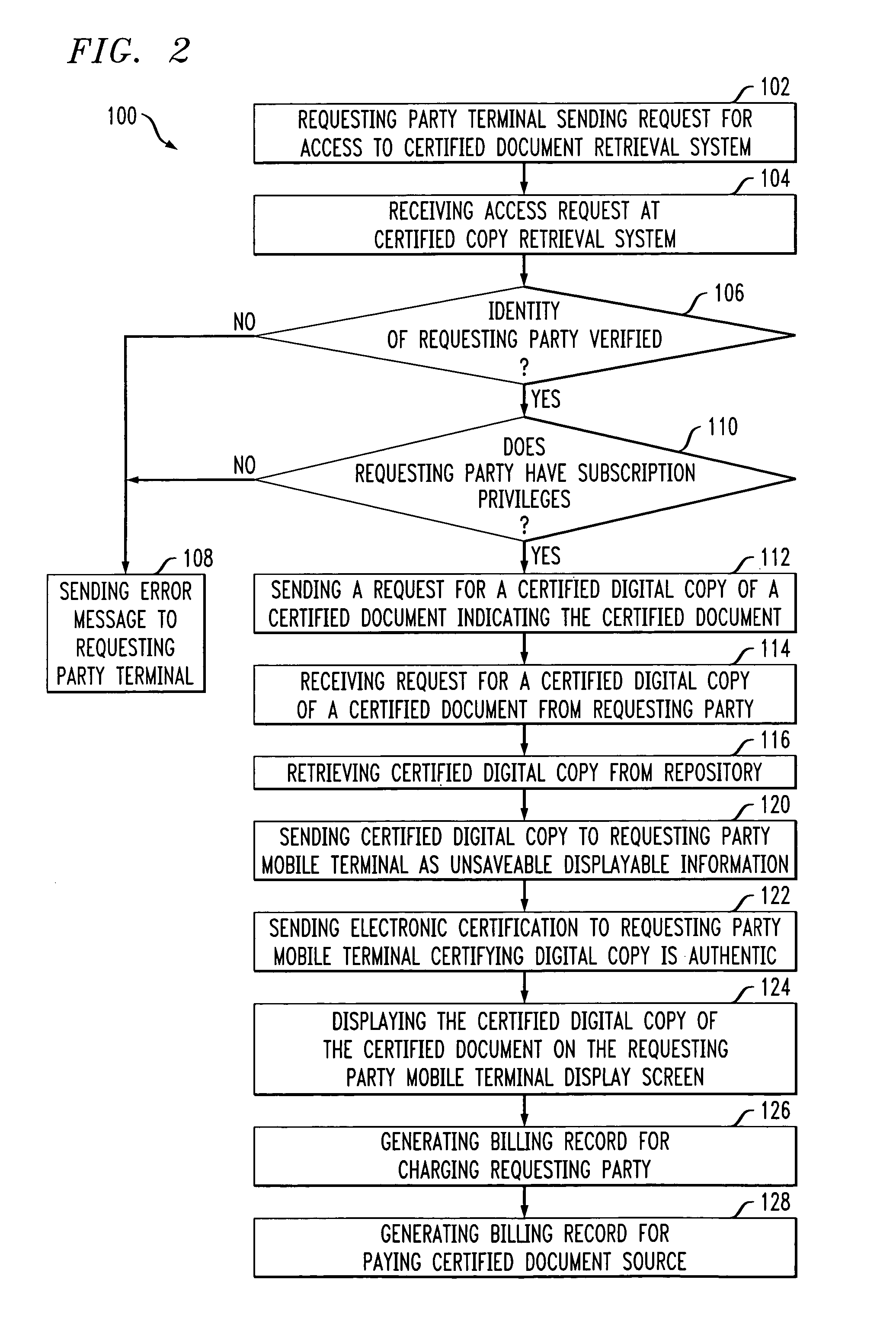
System and method of providing certified document retrieval
InactiveUS20060282661A1User identity/authority verificationComputer security arrangementsDigital copyPaper document
A method of providing a certified digital copy of a certified document for display on a requesting party mobile terminal display screen is provided. The method includes retrieving the certified digital copy from a repository, sending the certified digital copy to the requesting party mobile terminal as unsaveable displayable information for immediate display on the requesting party terminal display screen, wherein the unsaveable displayable information cannot be stored at the terminal, sending an electronic certification associated with the certified digital copy certifying the authenticity of the digital copy.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Image forming apparatus with highly operable sheet discharge device
InactiveUS6279892B1Easy to operateFunction indicatorsElectrographic process apparatusDigital copyImage formation
An image forming system includes a digital copy machine to form an image on a group of sheets from an image of a group of documents, and a staple sorter sorting and discharging copied sheets from the digital copy machine, According to the staple sorter, control is provided so that a sheet of a long left period of time is transported from the bin to a nonsort tray when all of a plurality of bins provided in the staple sorter are used during a print operation. The left time of a sheet is monitored even when a print operation is not carried out. When the left time exceeds a predetermined time, control is provided so that the sheet left in the bin is transferred to the nonsort tray. As a result, a sheet discharge device is provided improved in operability of sheet discharge.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
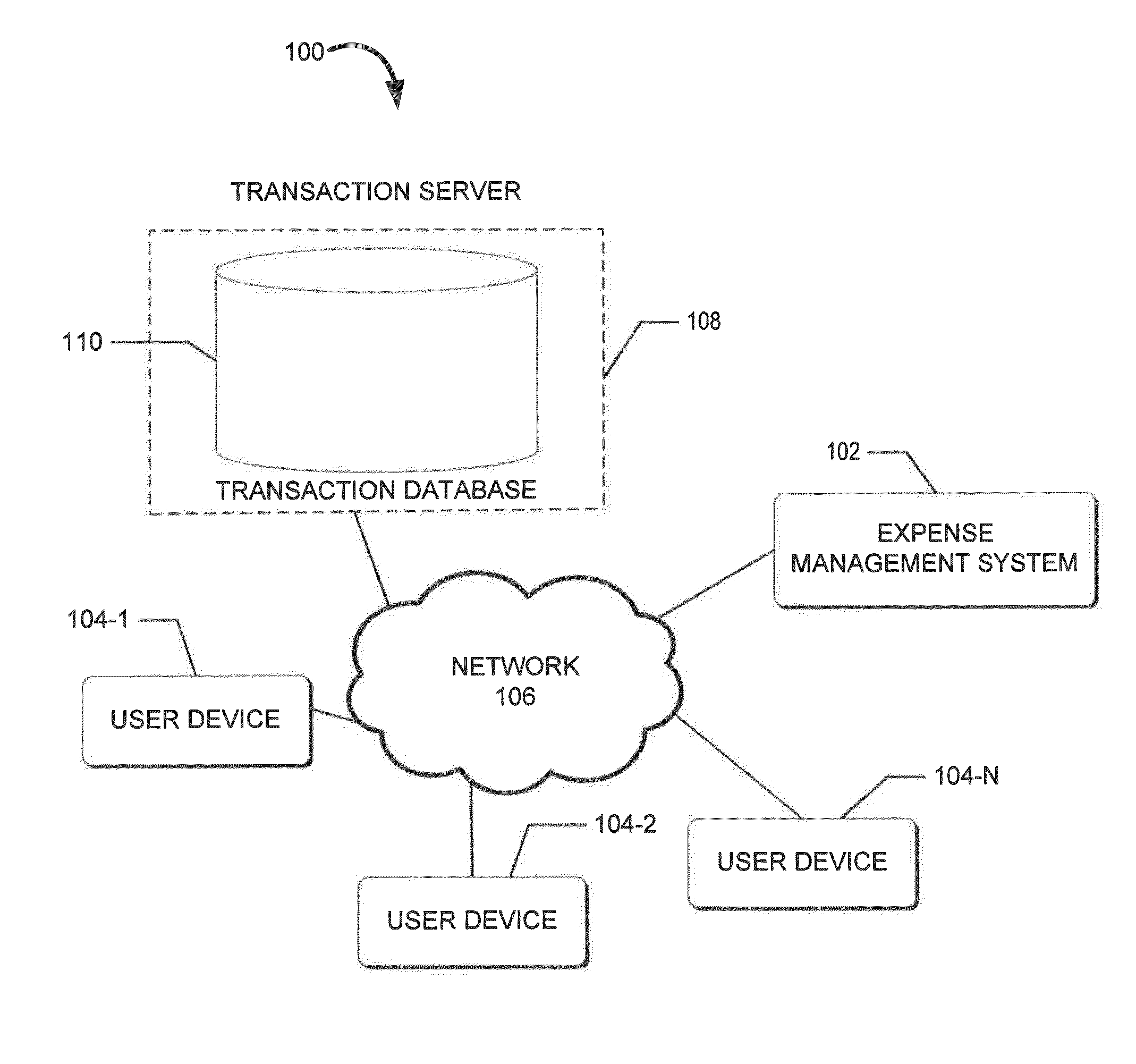
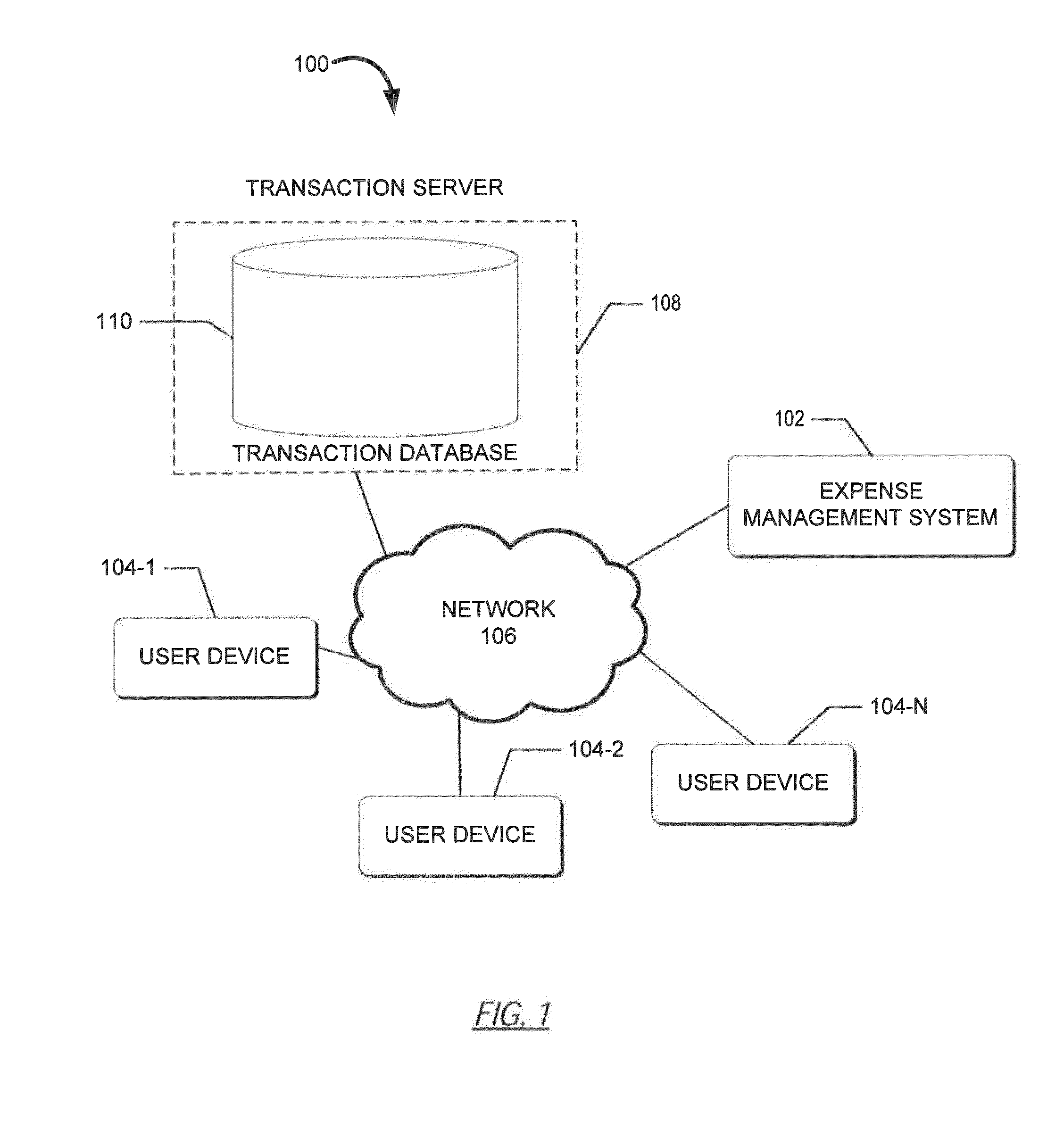
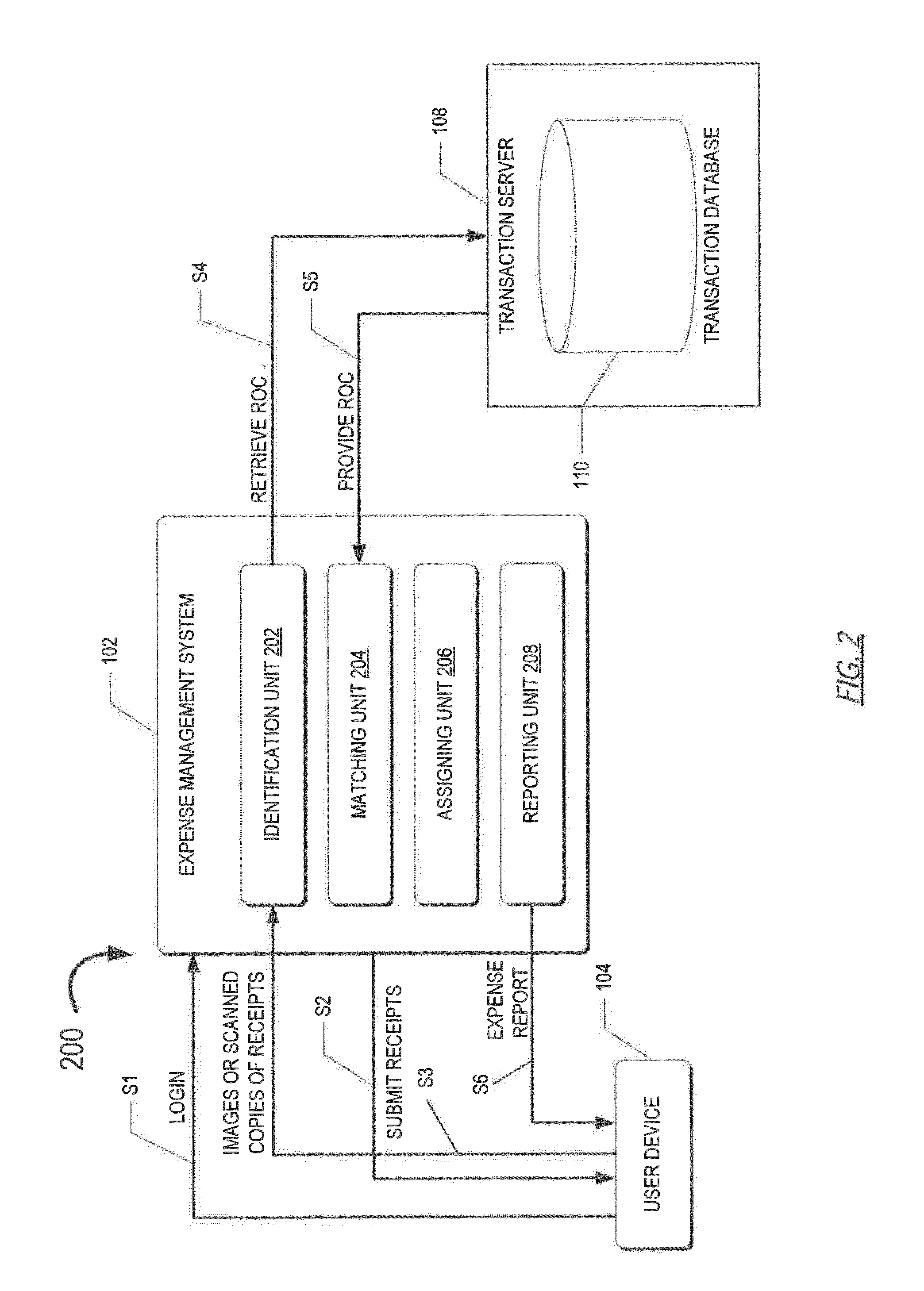
Systems and Methods for Expense Management
The present disclosure includes a system for expense management. The method may include authenticating a user to a user account, retrieving a unique id (GUID) associated with the user, receiving (from a user device associated with the user) a digital copy of a receipt, and associating the digital copy of the receipt with the GUID. The method may further comprise requesting a record of charge (ROC) associated with the GUID, receiving a record of charge (ROC) associated with a GUID, and / or matching, by the computer-based system, the image of the receipt to the ROC based upon the GUID and information acquired from the digital copy of the receipt.
Owner:AMERICAN EXPRESS TRAVEL RELATED SERVICES CO INC
Image outputting device from mobile storage medium
InactiveUS7423776B2Reduce necessityEasy to applyCosmetic preparationsDigitally marking record carriersDigital copyData file
An image output apparatus capable of offline printing or displaying image and text data automatically and efficiently to a digital copying machine, a printer, a facsimile, a liquid crystal projector, and a television set. Discrimination is conducted as to whether data in a data file to be printed, which is read out from a memory card by a memory card controller, is color or monochrome image data. As a result of the discrimination, when the data is color image data, print confirmation unit provided in the image output apparatus allows a user to confirm whether or not to print out monochrome image data, which is converted from the color image data by the color / monochrome conversion unit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
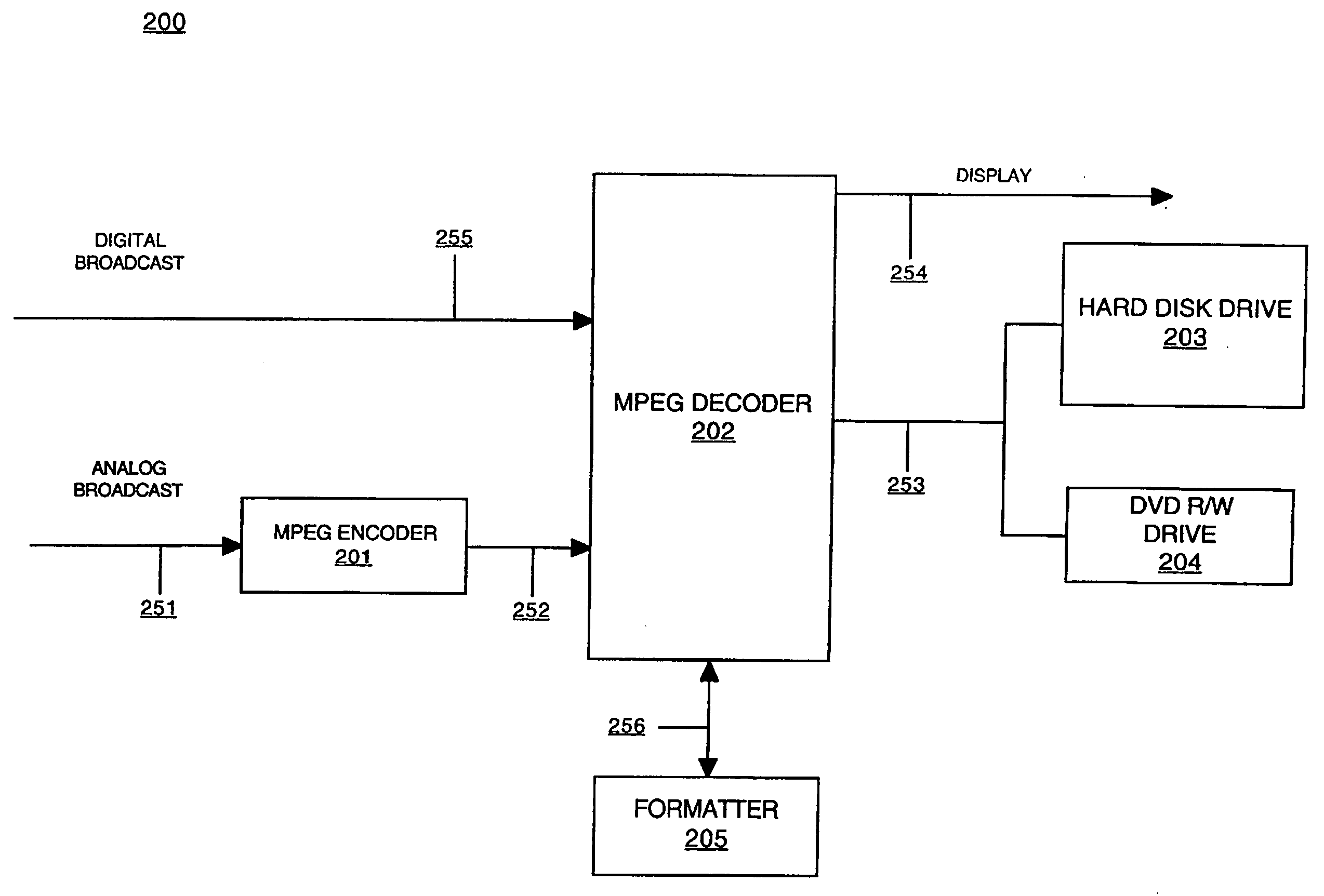
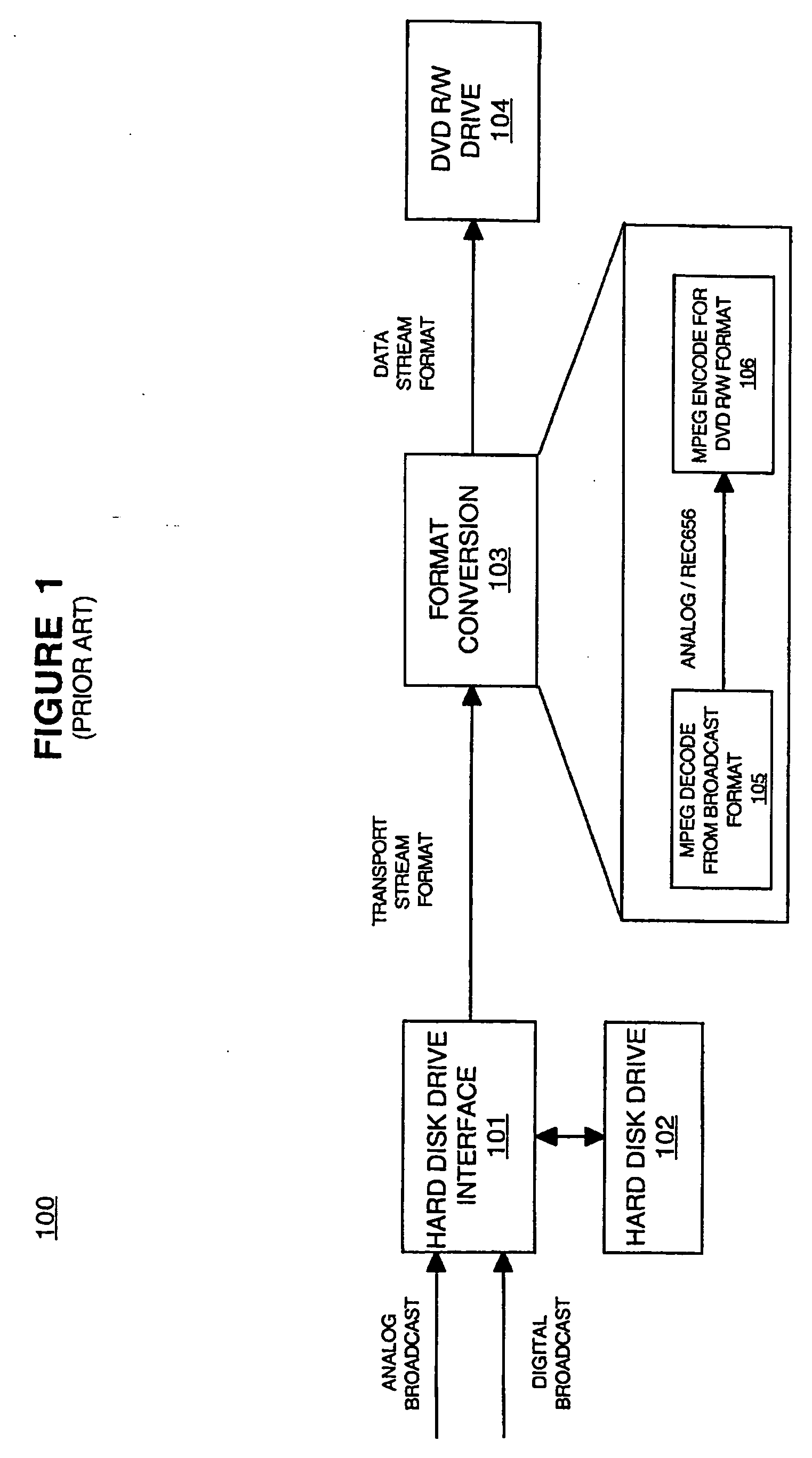
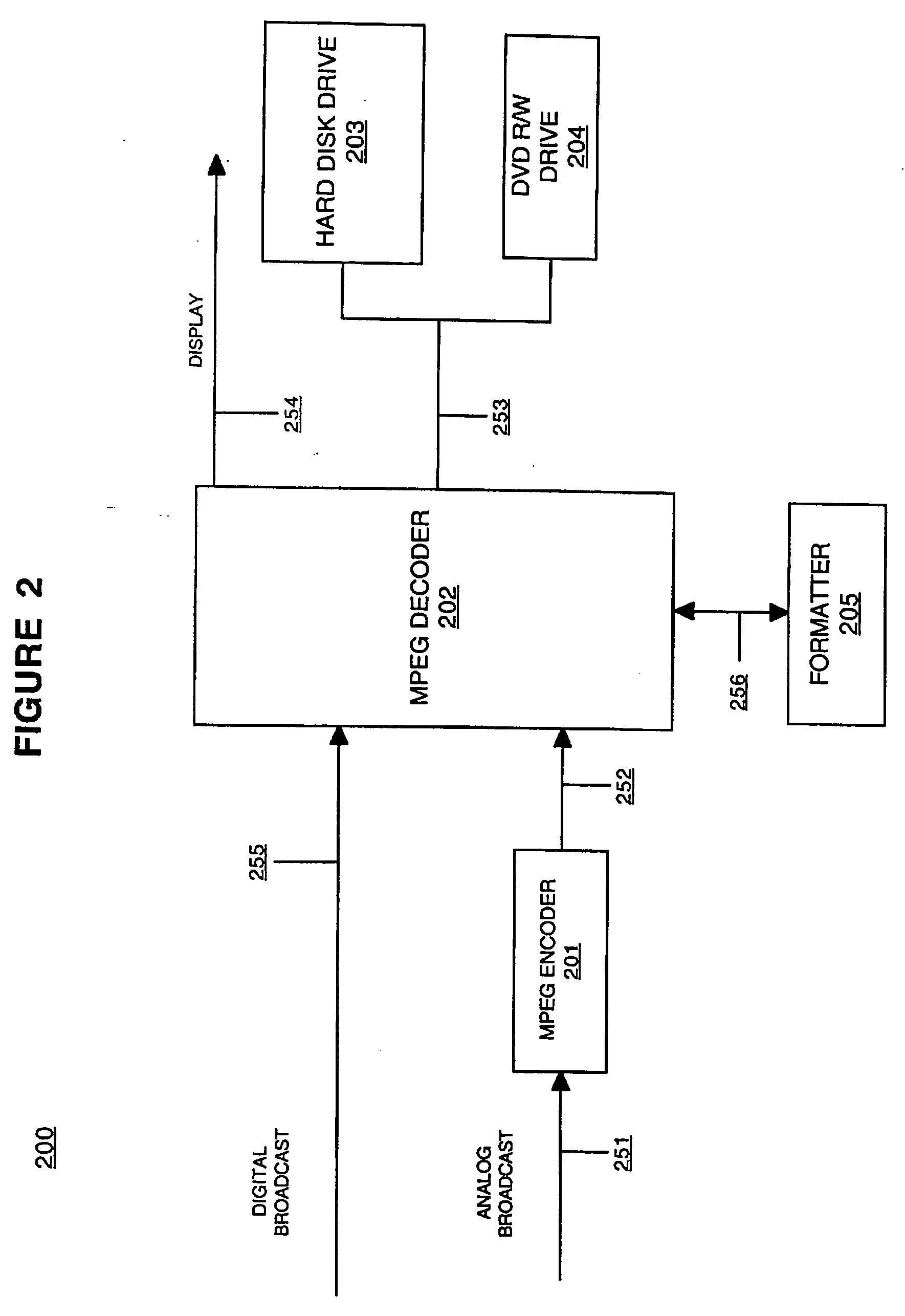
Method and system for digitally recording broadcast content
InactiveUS20060051060A1Few data errorImprove picture qualityTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsDigital copyMagnetic storage
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to a method and system for digitally recording broadcast content. In one embodiment, the broadcast content is received and a first digital copy of the broadcast content is stored (e.g., on a magnetic storage device). The first digital copy of the broadcast content is formatted to be displayed by a display device (e.g., encoded MPEG format). A second digital copy of the broadcast content is also made and stored on the magnetic storage device. The second digital copy of the broadcast content is formatted to be stored upon an optical media storage device. The second digital copy can be high-speed dubbed from the magnetic storage device to the optical media storage device.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
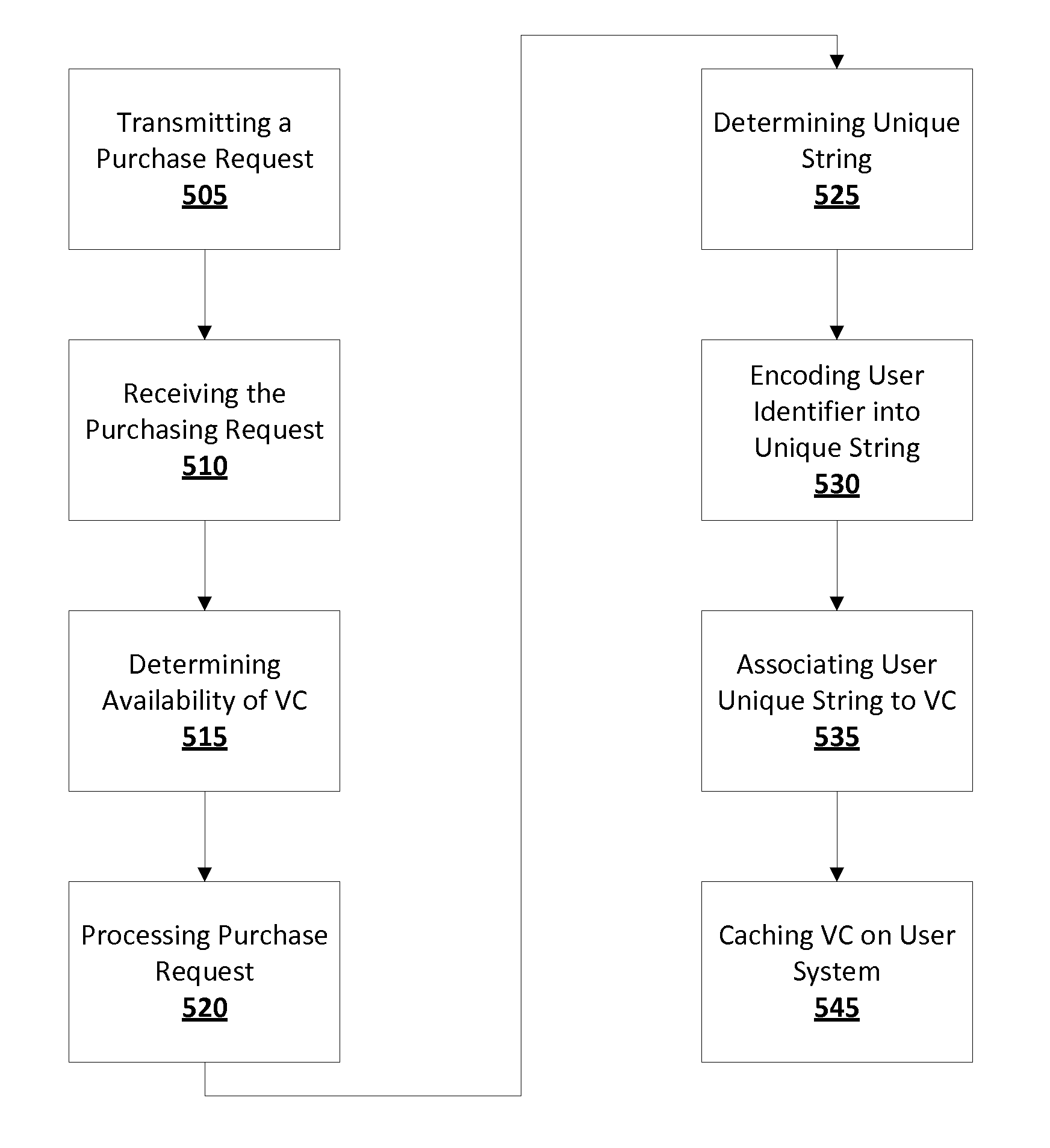
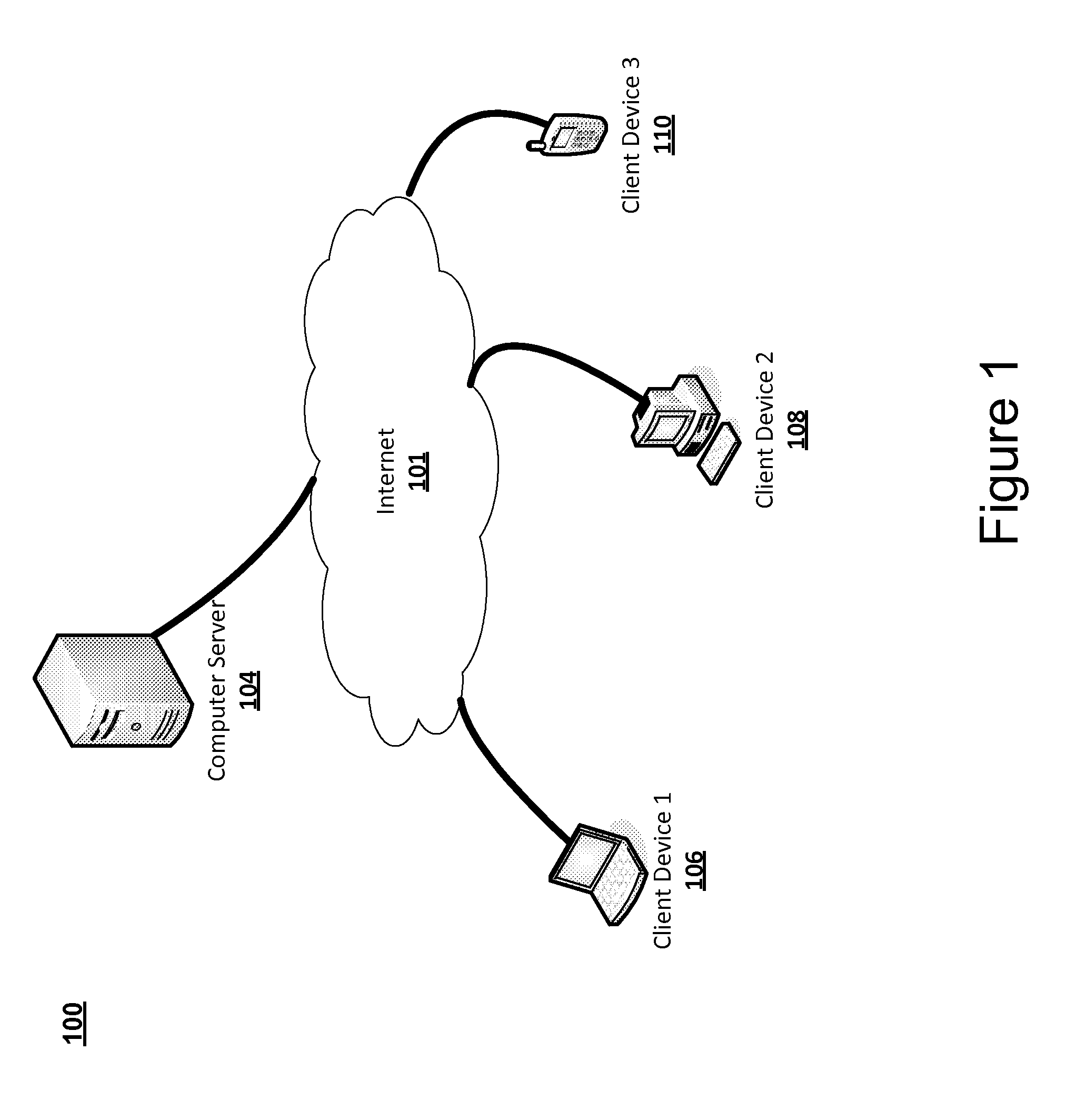
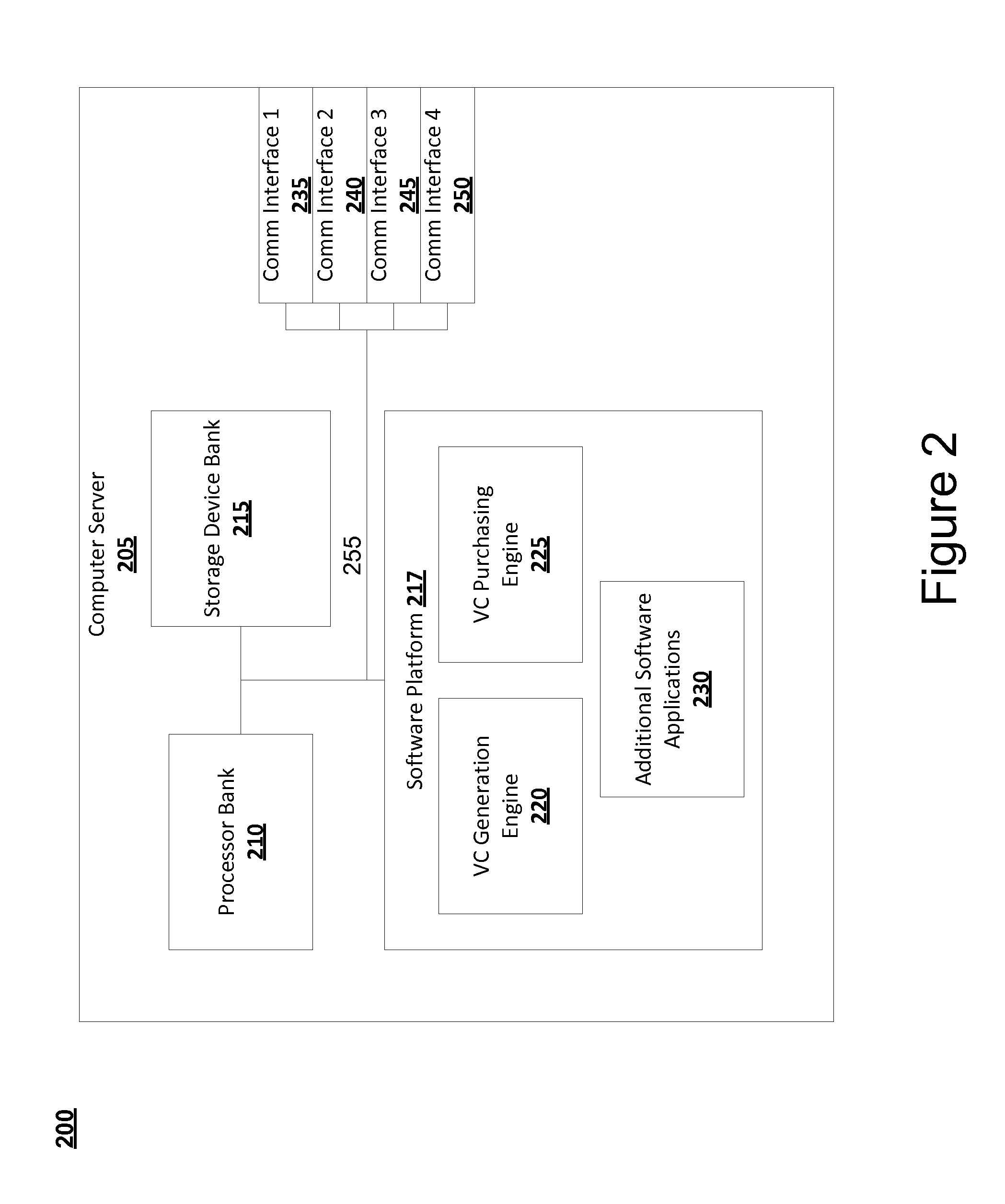
Systems, devices, and methods for virtual collectible generation, trading, purchasing, and management
InactiveUS20120316999A1Improve featuresDigital data processing detailsCommerceDigital copyThe Internet
Embodiments of the disclosure include systems, methods, and devices for generating, purchasing, and managing virtual collectibles (VCs) using a software platform. Embodiments take advantage of the capabilities of the Internet as a medium for users to exchange goods and couples the recent advancement in 3-D rendering technology to provide a virtual marketplace for collectors to purchase, sell, trade and manage (manipulate and control) VCs. Aspects of the disclosure include generating a VC by scanning a physical collectible, rendering a 3-D digital copy of the physical collectible, and enhancing virtual characteristics of the 3-D digital copy. A unique encrypted digital string may be generated based on the virtual characteristics. Also, unique digital string may be encoded into virtual characteristics such that the VC is the enhanced 3-D digital copy of the physical collectible encoded with the unique digital string.
Owner:HYBRID ORBITAL
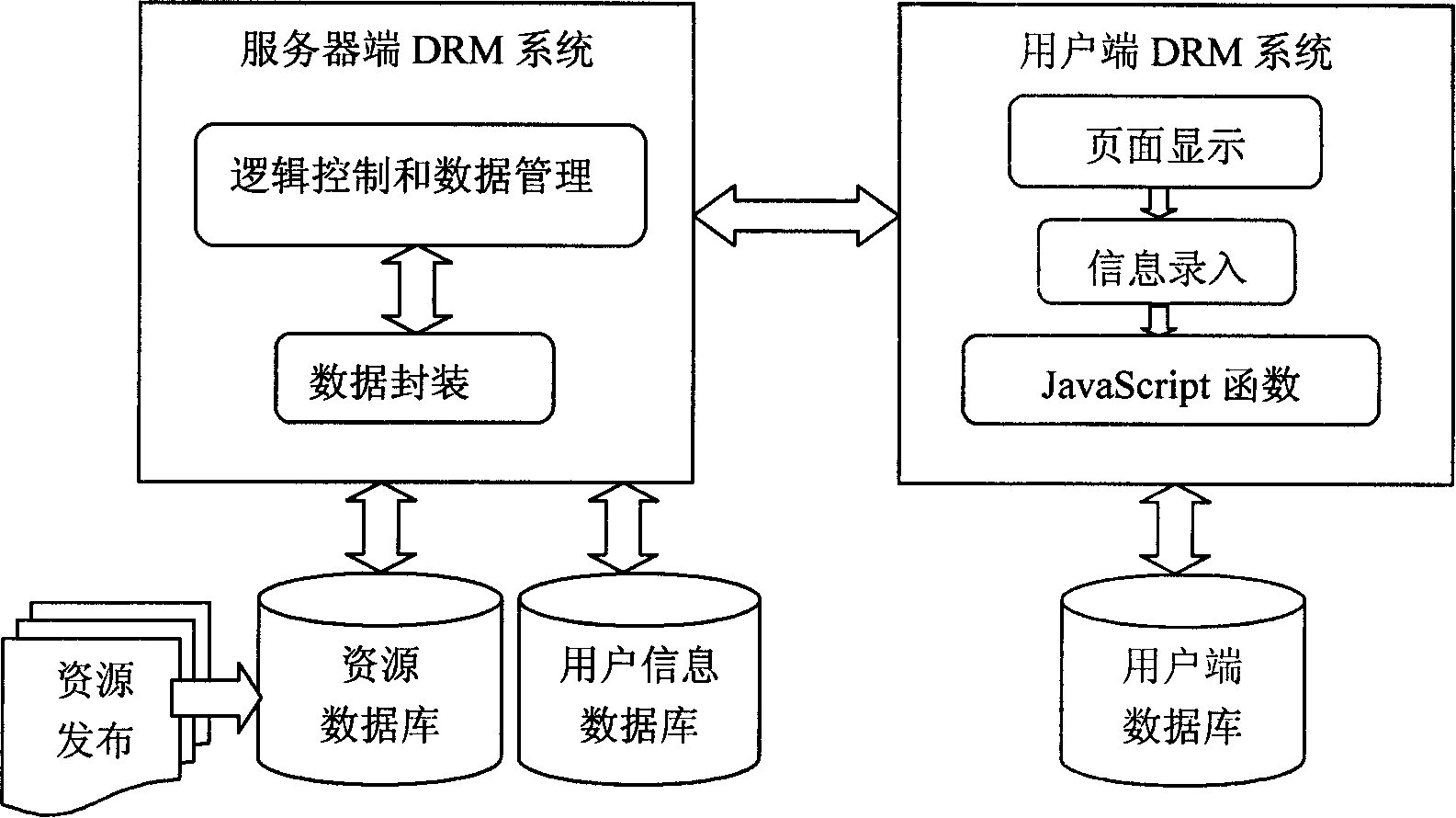
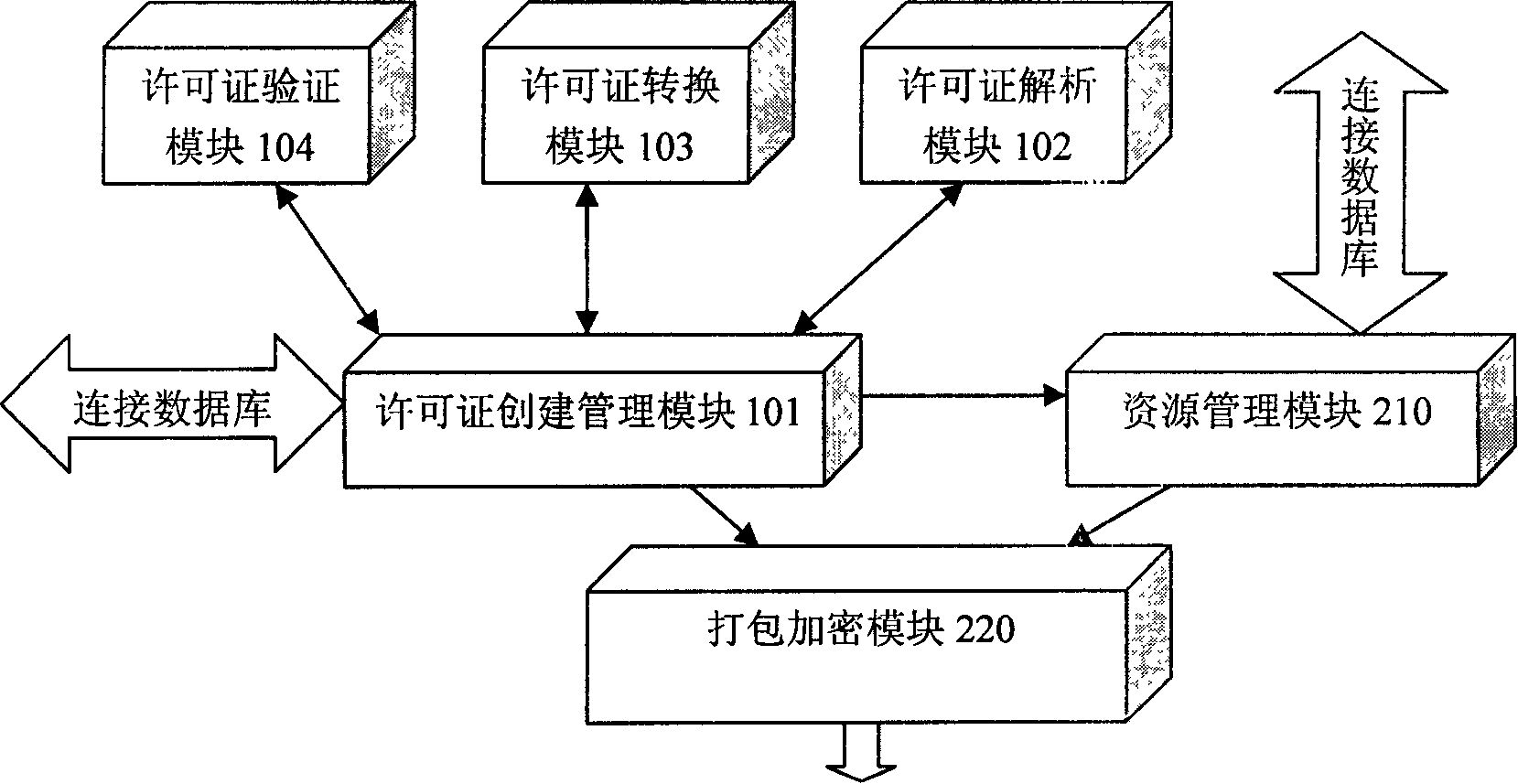
Digital resource copyright controller
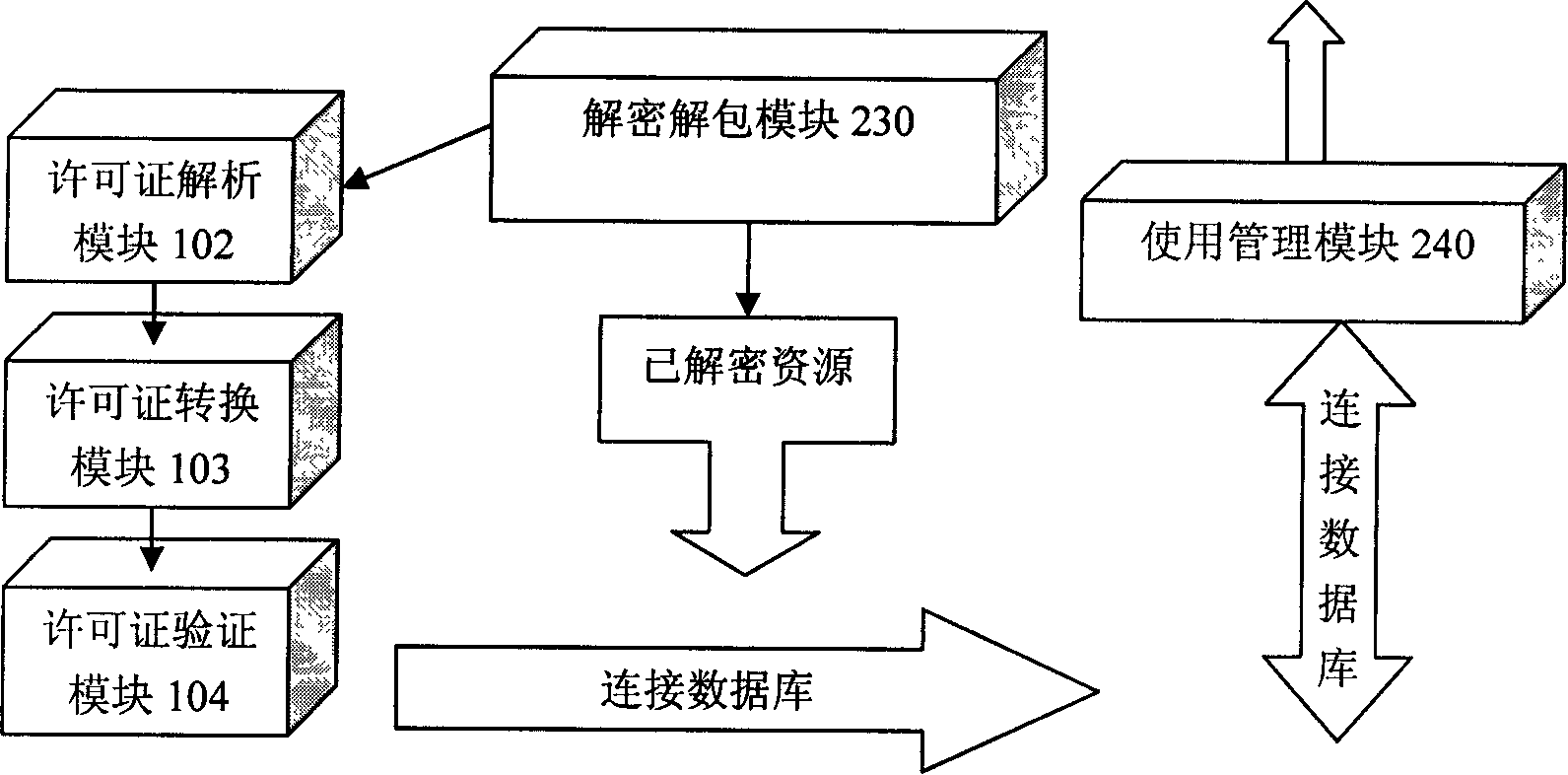
InactiveCN101158996ARealize synchronization managementConvenient queryProgram/content distribution protectionDigital rights managementDigital control
The invention relates to a device of digital resource copy right management to realize the real-time management and report of charges for using digital resources, pertaining to digital control equipment. The invention includes that: (1) a digital right management system on a server terminal takes charge of resource issuing, user authority and interaction with users; (2) a database on the server terminal comprises a resource database and a user information database, the resource database stores all digital resources available, and the user information database stores the information of user's previous use; (3) a digital right management system on user terminal takes charge of the concrete condition of user's using resources and the information interaction with the user's visual interface; (4) a database on user terminal stores the authorized resources and the use recorder of users. The invention fills the blank of the device of the prior digital resource copy right management, combines the user authority management and access control and the management and report of charges for user's using resources in real time and organically, and realizes the management and control of digital copy right in a real sense.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Image-forming system, control method therefor, image-forming apparatus, data processing method, and storage medium
InactiveUS7206092B2Improve usabilityVisual presentationPictoral communicationDigital copyImage formation
In an image-forming apparatus such as a digital copying apparatus, even when a digital copying apparatus having print data desired by a user is used by someone else or is in trouble, the apparatus outputs the print data desired by the user without any delay at any time convenient to the user and in an output form the user desires, and thus increases availability thereof. The digital copying apparatus includes an network interface communicating with an external host apparatus, and a memory for storing image data and operation mode data received through the network interface, and prints out the image data on a printer section. The digital copying apparatus receives image data and operation mode data from the other digital copying apparatus and prints out the image data on the printer section thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
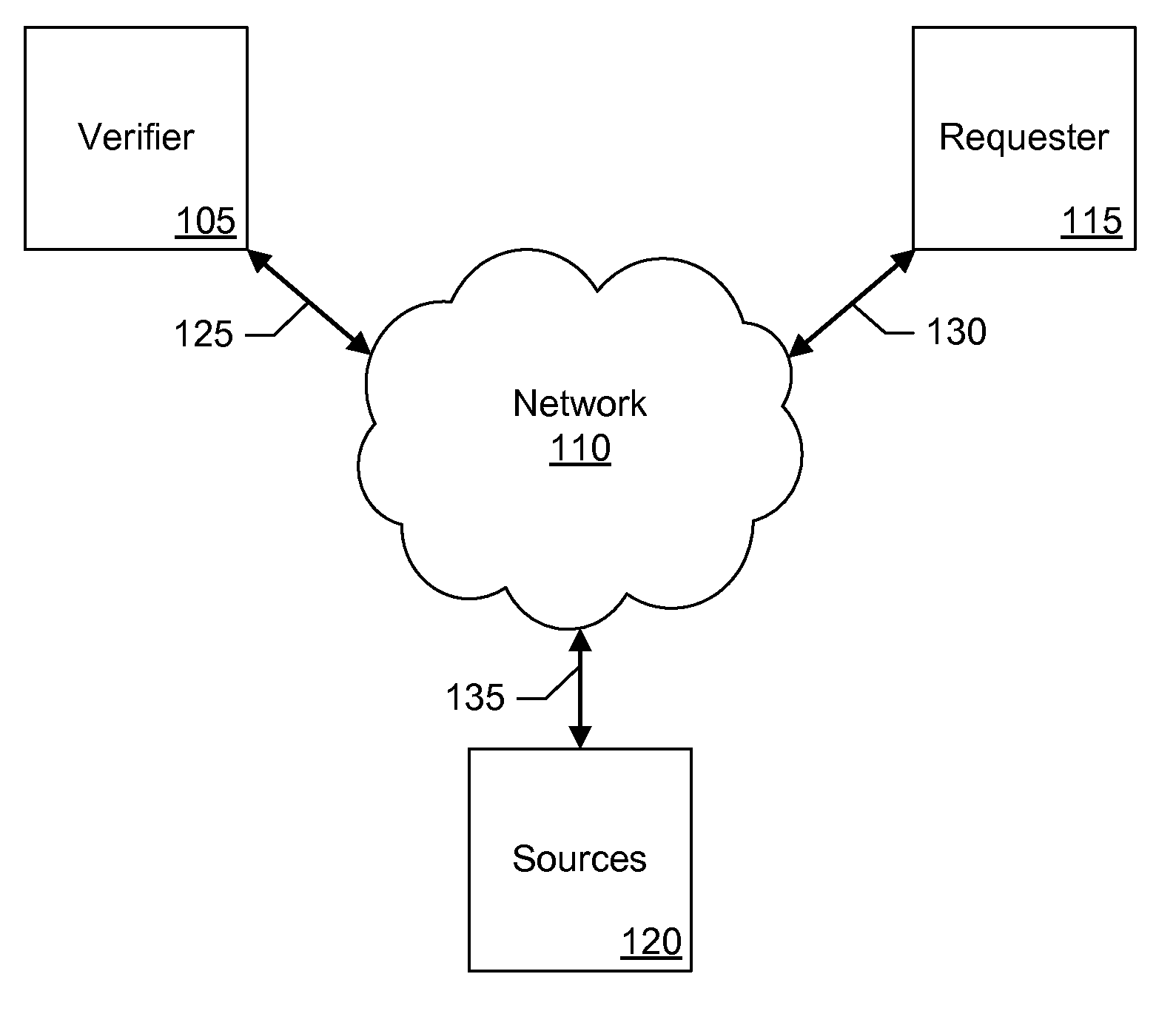
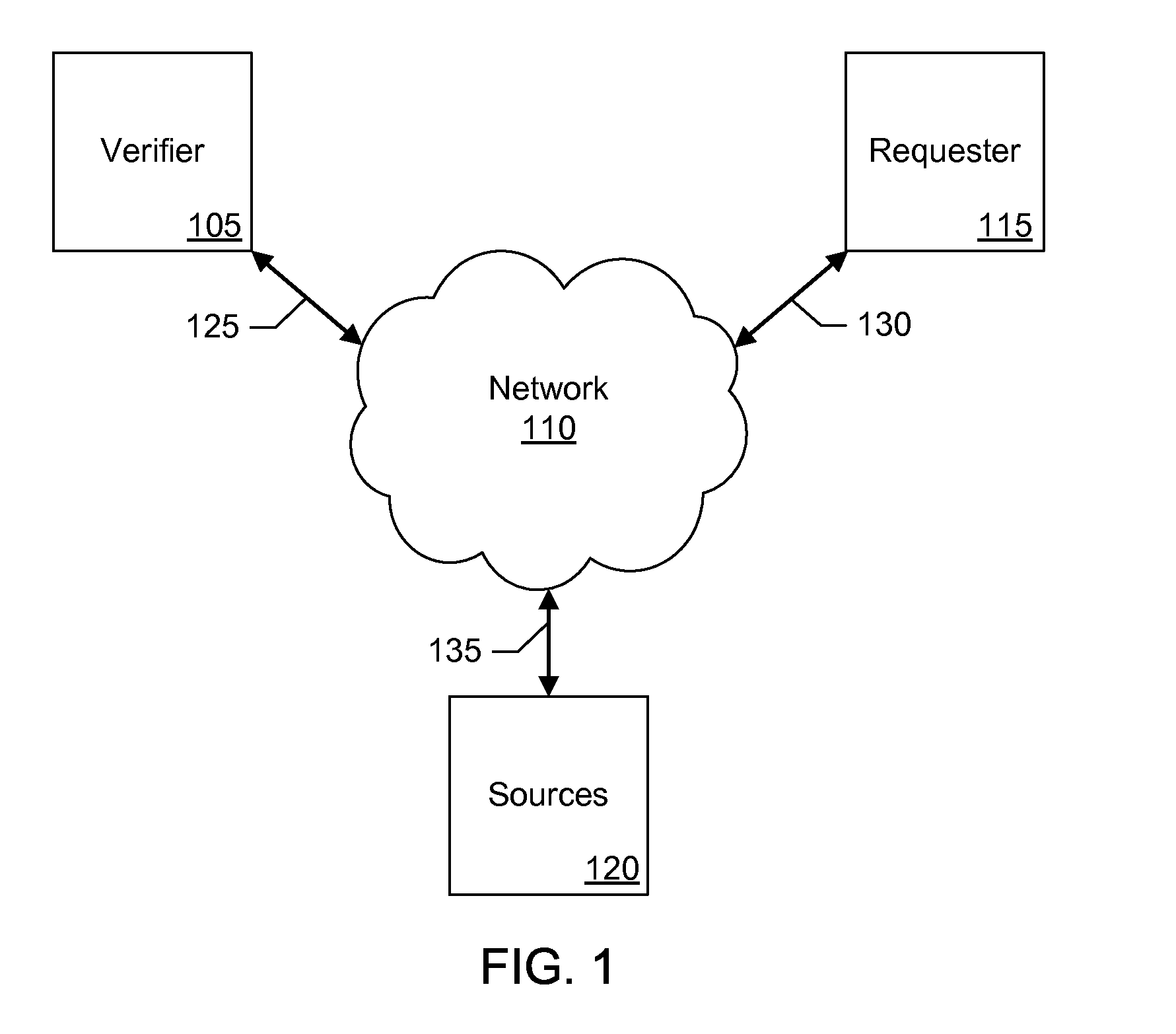
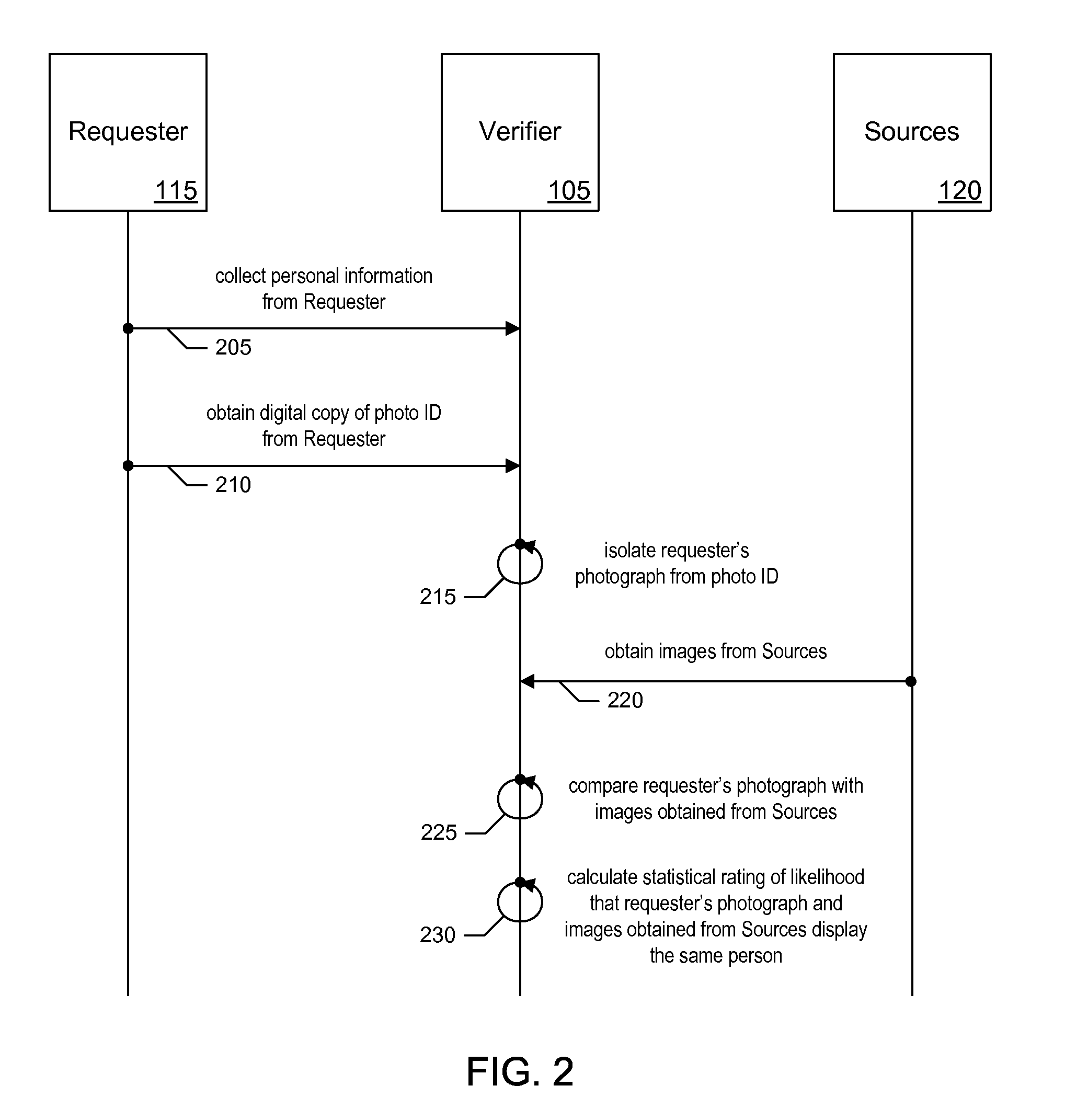
Methods for Person's Verification Using Photographs on Identification Documents
InactiveUS20120114196A1Character and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
One embodiment of a method of present invention provides for collecting personal information from a requester, obtaining a digital copy of a photo ID from the requester, isolating requester's photograph from the photo ID, obtaining images from computer network information sources, comparing requester's photograph with the images obtained from computer network information sources, and calculating a statistical rating of a likelihood that requester's photograph and images obtained from said one or more computer network information sources display the same person.
Owner:GO DADDY OPERATING
Offline print method using a printer apparatus and an external apparatus for printing out image data on a removable medium
InactiveUS6943906B2Easy to usePromote generationDigital computer detailsElectrographic process apparatusDigital copyControl data
A digital copying machine comprising an image scanner part for reading an original image to reproduce image data of the original image, a laser printer part for printing an image according to given image data, a removable memory card, and a reader / writer of the memory card is provided. For offline print, the image data of a document prepared in an external computer and output control data are stored into the memory card. By installing this memory card in the digital copying machine, the digital copying machine prints the image data read out from the memory card offline in a desired output form. For offline image input, read control data obtained by using an image scanner such as a read gradation level, a read size, density, and the degree of edge enhancement is stored in the removable memory card using software executed in an external computer. By installing this storage medium in the digital copying machine and setting an original to be read in the digital copying machine, the original image is read according to the read control data stored in the memory card, and the obtained image data is stored into the memory card.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
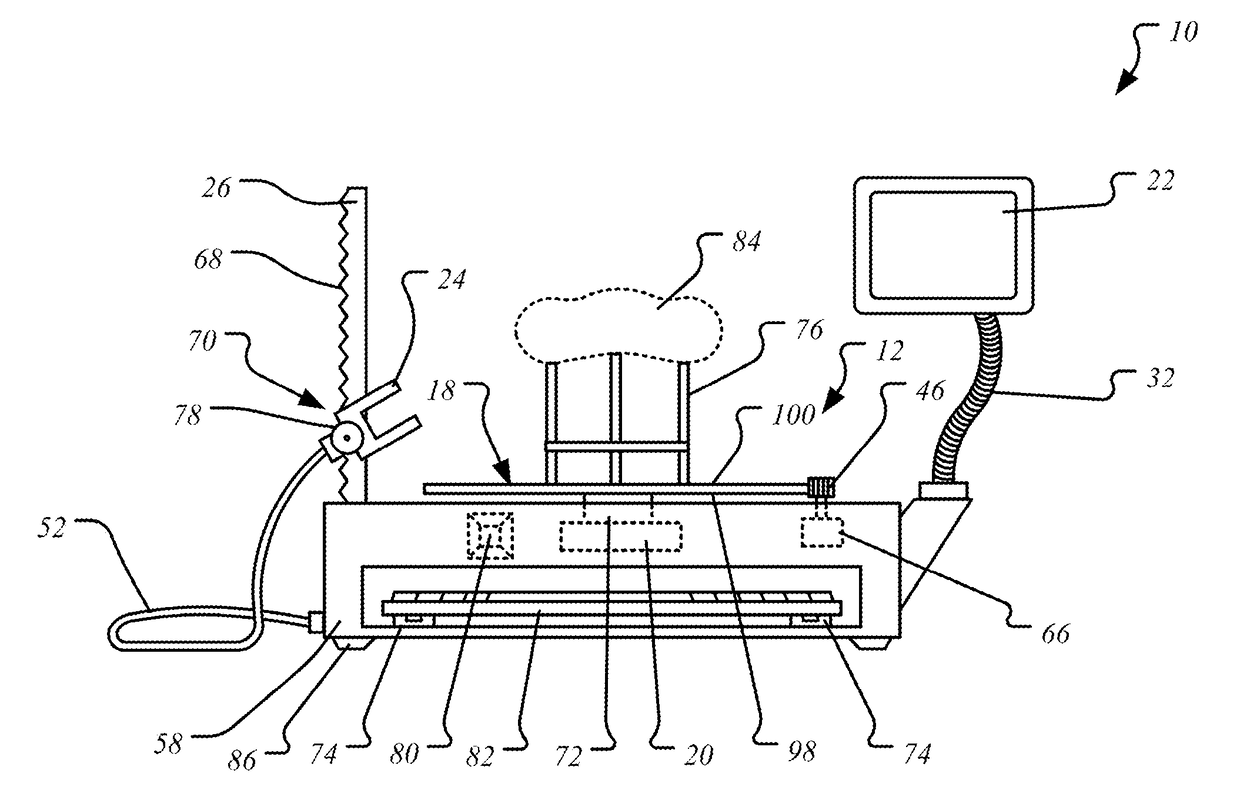
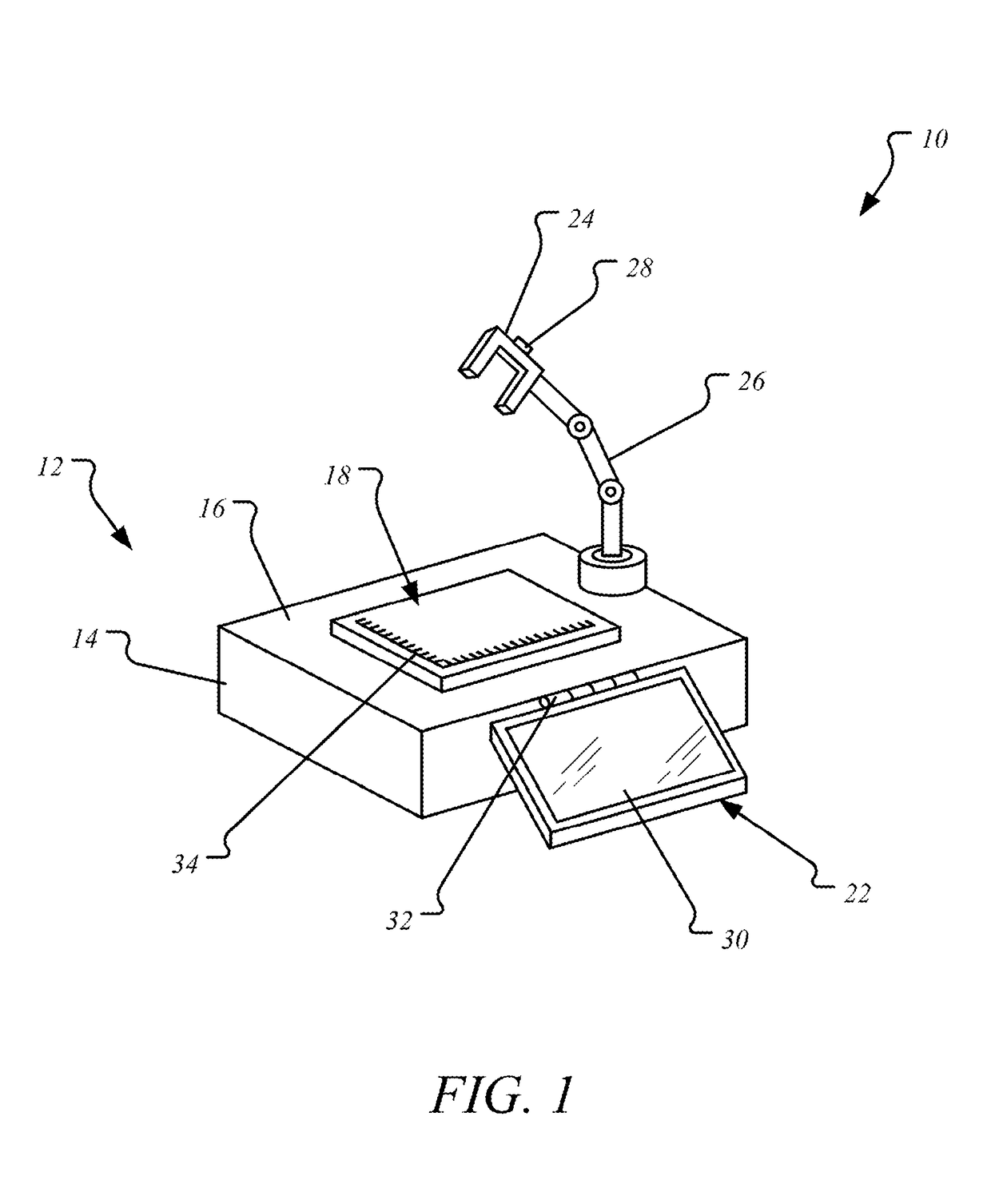
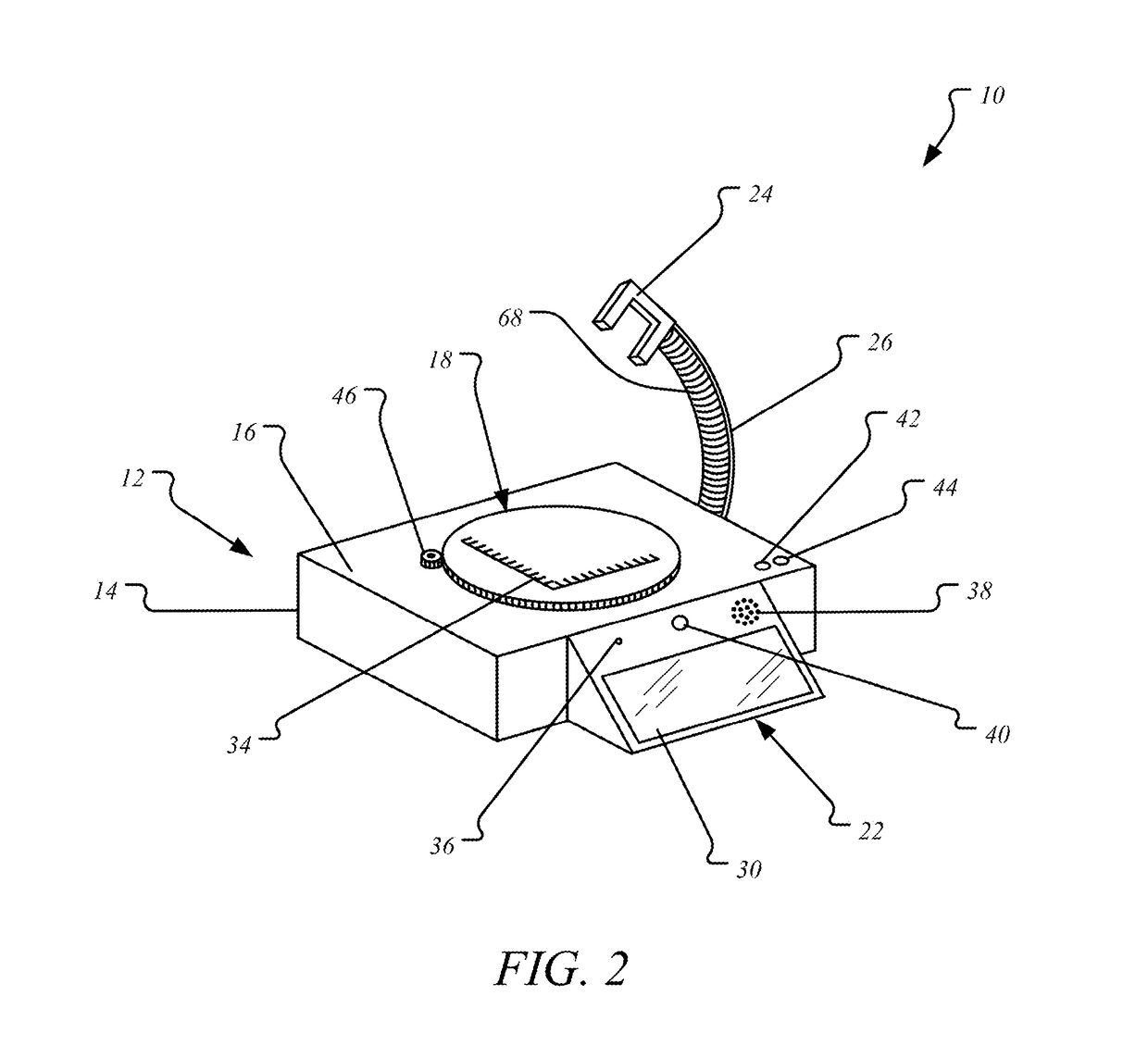
Grossing workstation with electronic scale
A grossing workstation comprising an electronic scale, screen, and camera holder is described. The camera holder may be mounted on a flexible or articulating arm in order to attach a digital camera for specimen imaging. A computing device in the scale may store digital copies of specimen images or measurements. The computing device may furthermore control movements of the balance pan and camera holder in order to automatically image a specimen at different view angles.
Owner:IMAM ABDULRAHRNAN BIN FAISAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com