Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Cross hybridization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
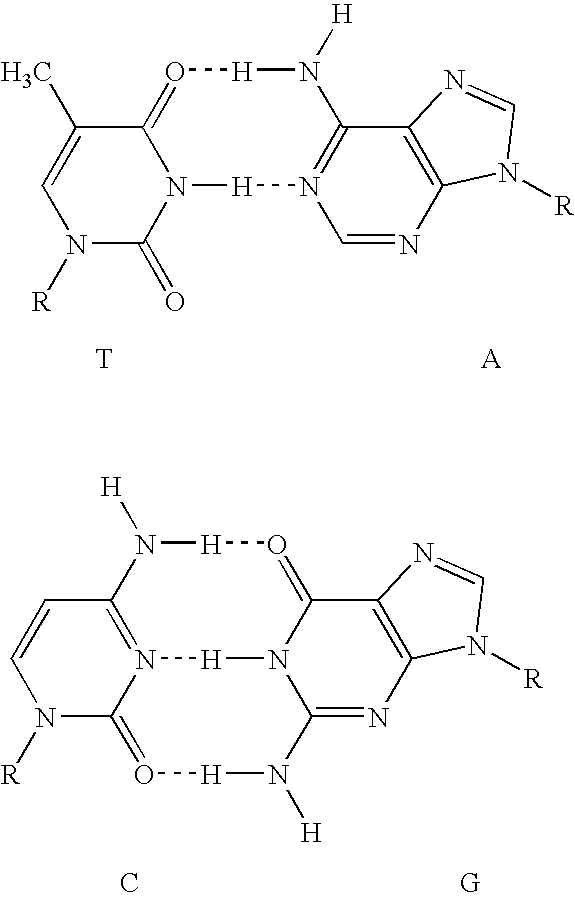
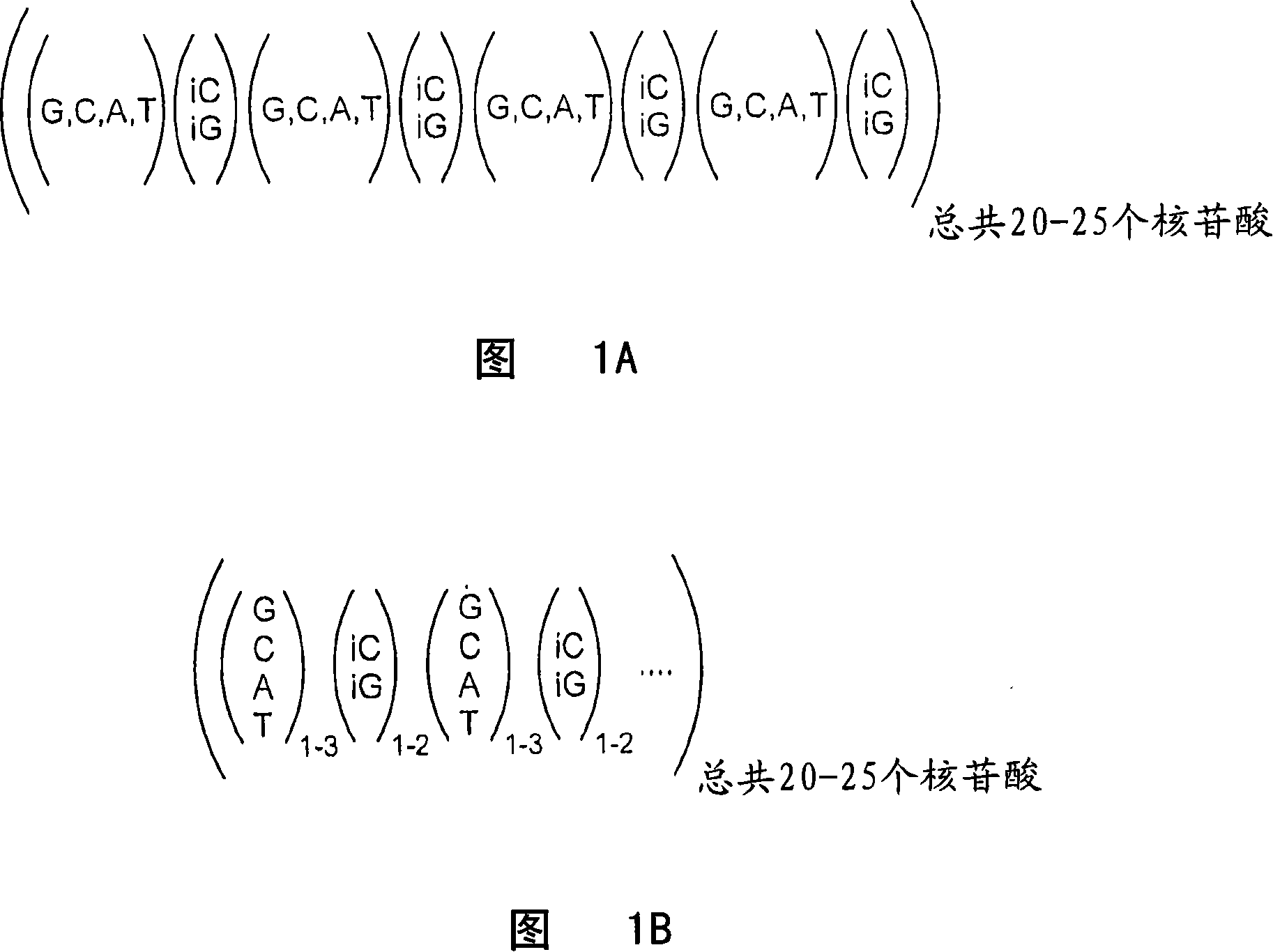
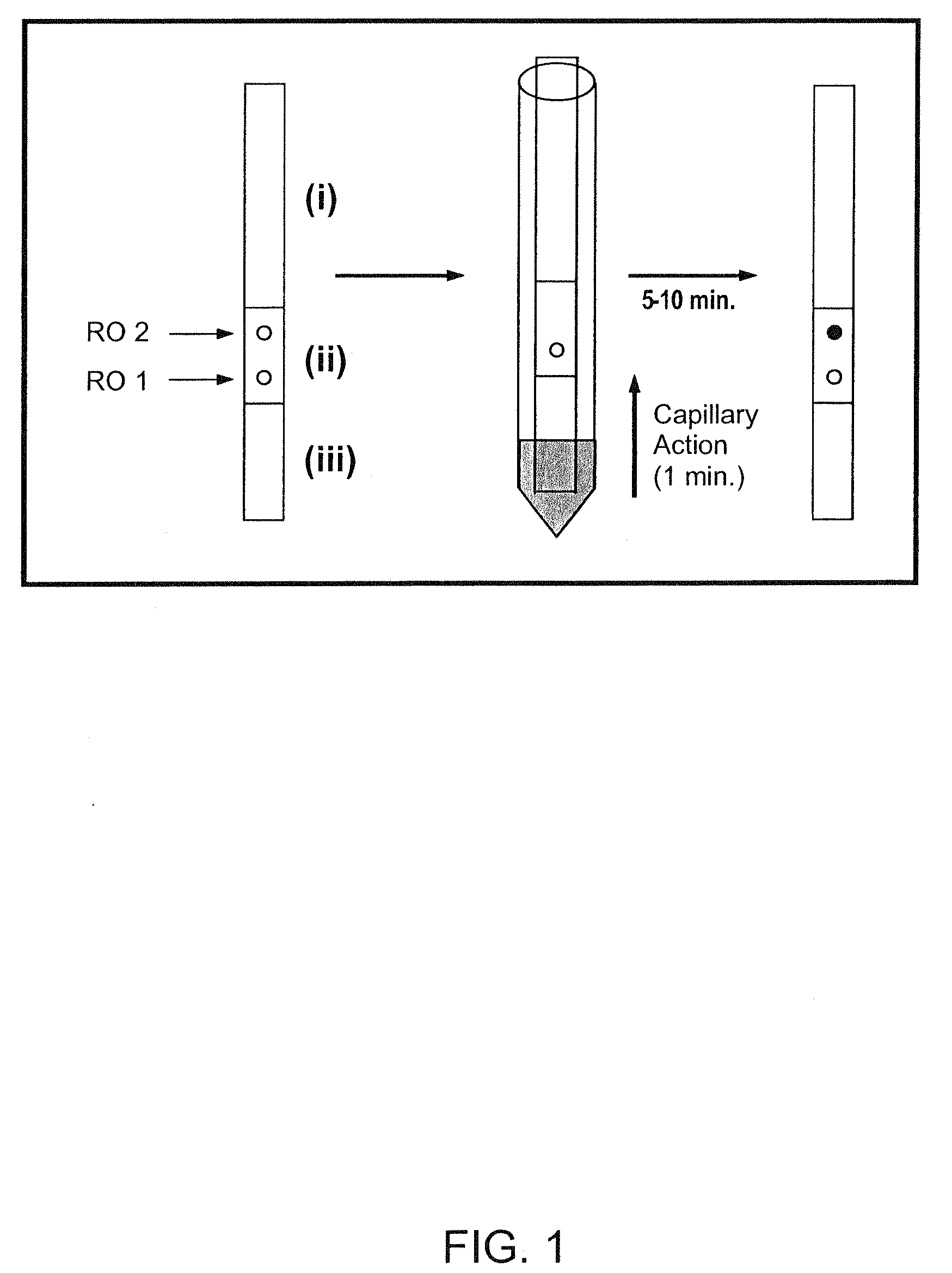
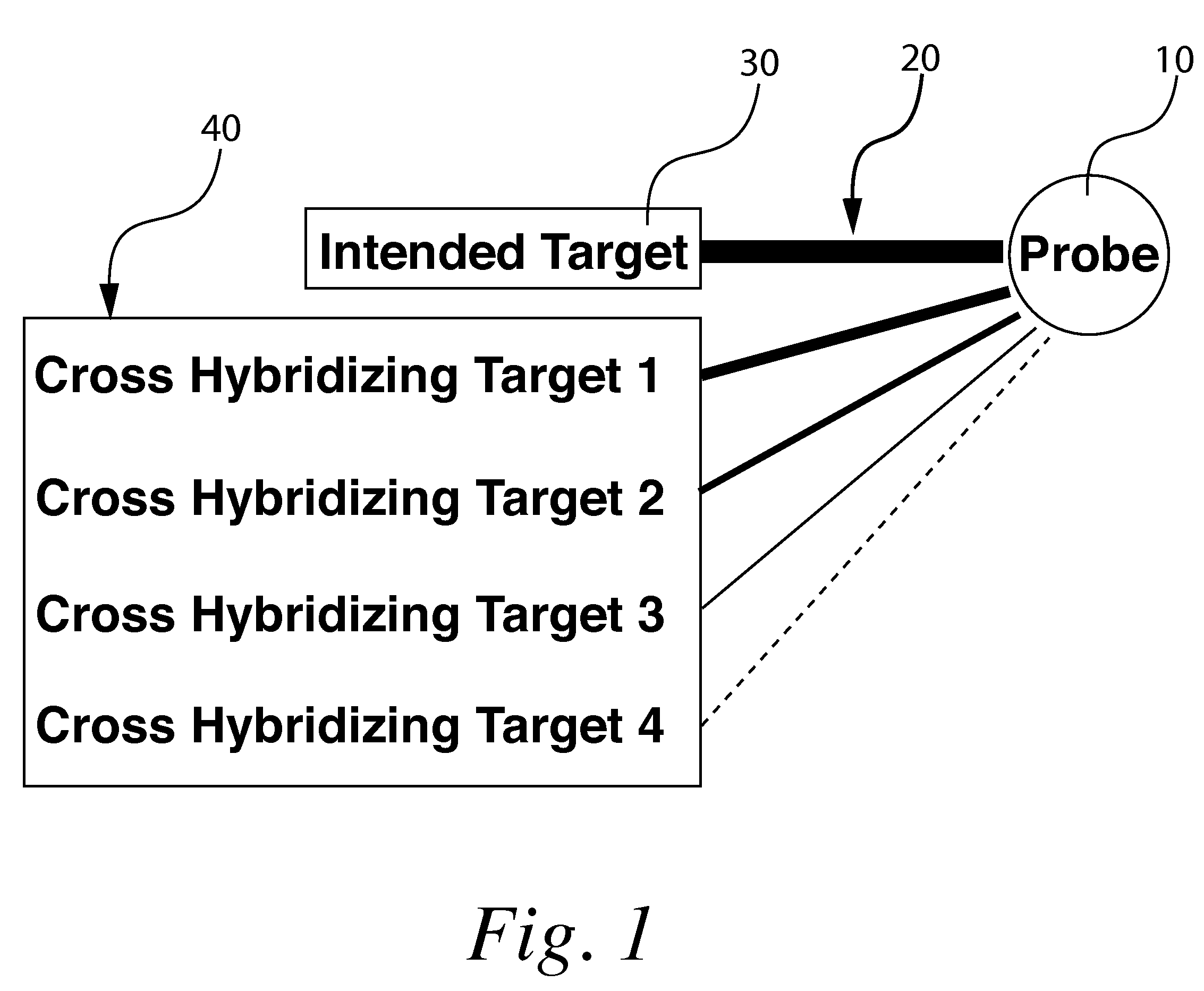
With respect to nucleic acids, "cross-hybridization" refers to the formation of double-stranded DNA, RNA, or DNA/RNA hybrids by complementary base pairing between two molecules that are not identical in sequence. Cross-hybridization may be observed between nucleic acids derived from orthologous or paralogous genes.
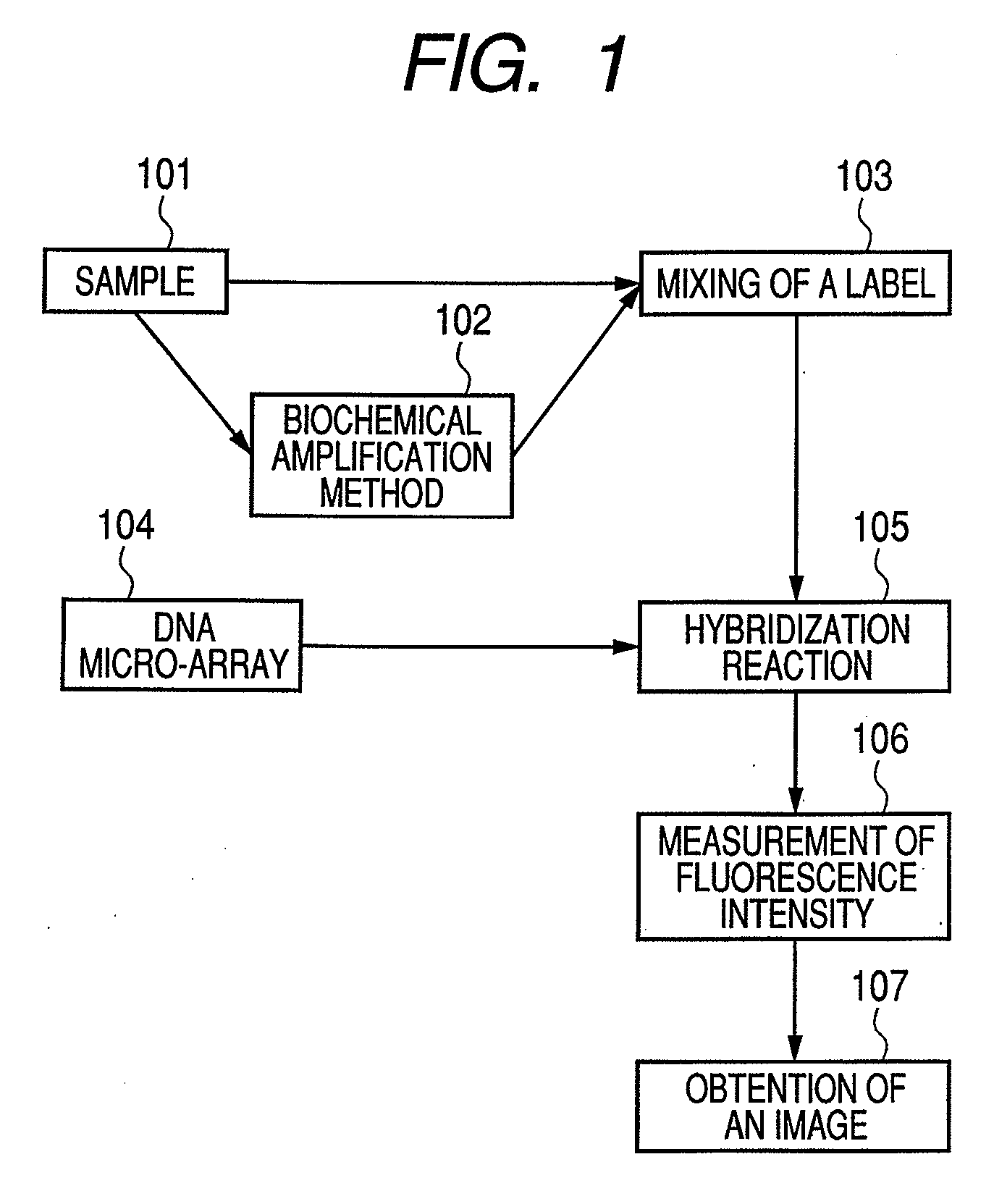
Methods for identifying biological samples
InactiveUS20060073506A1Efficient amplificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingCross hybridization
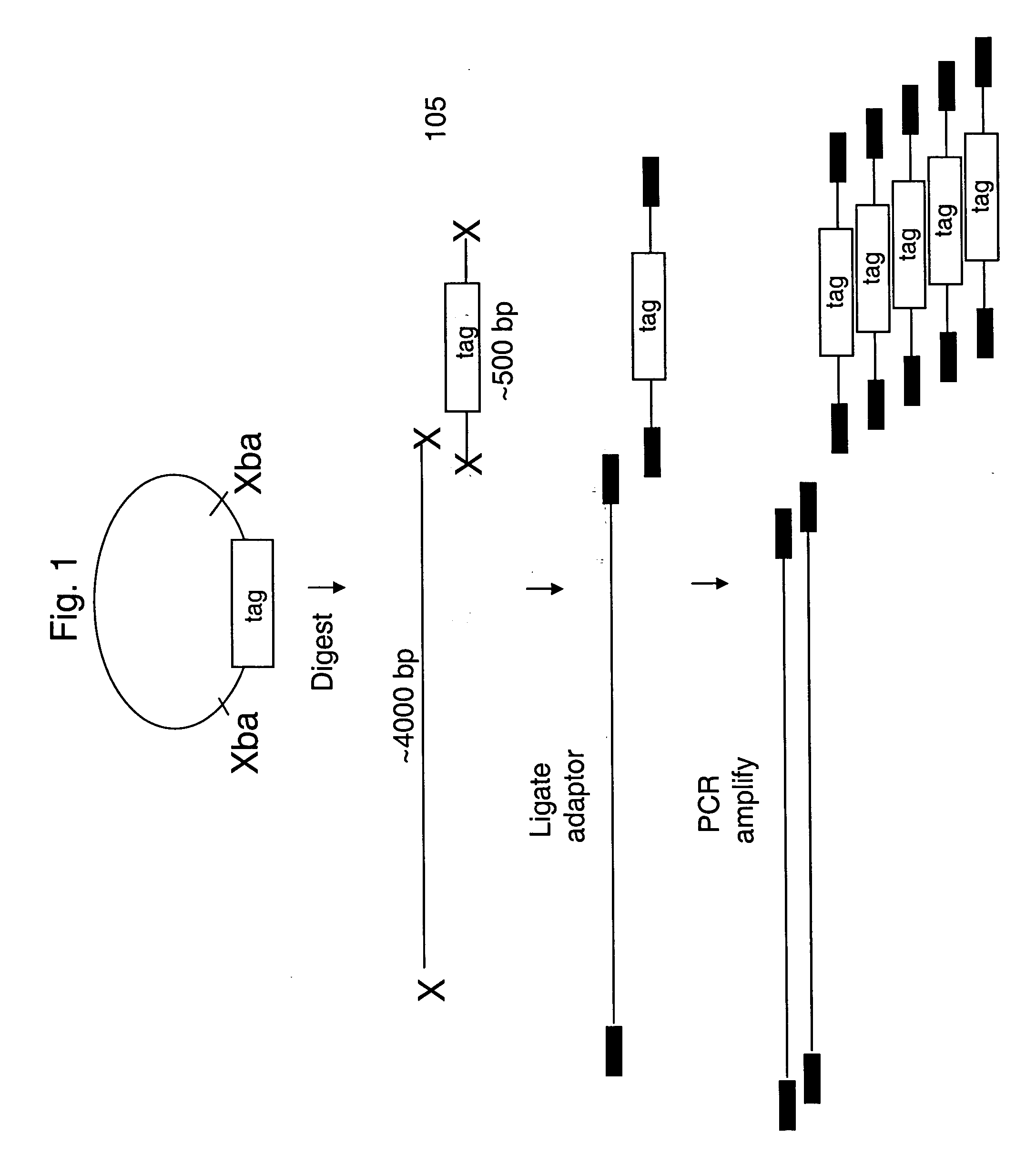
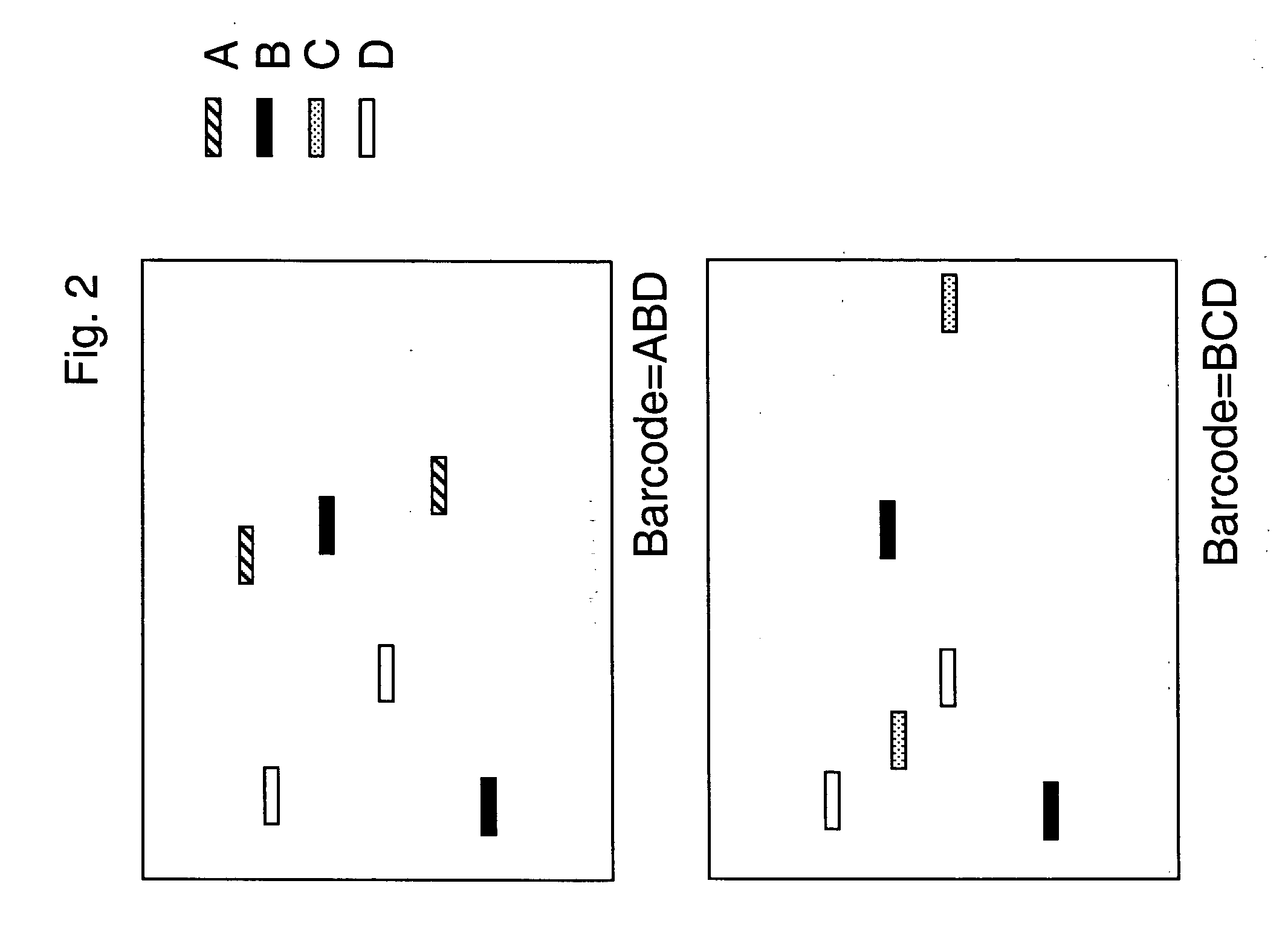
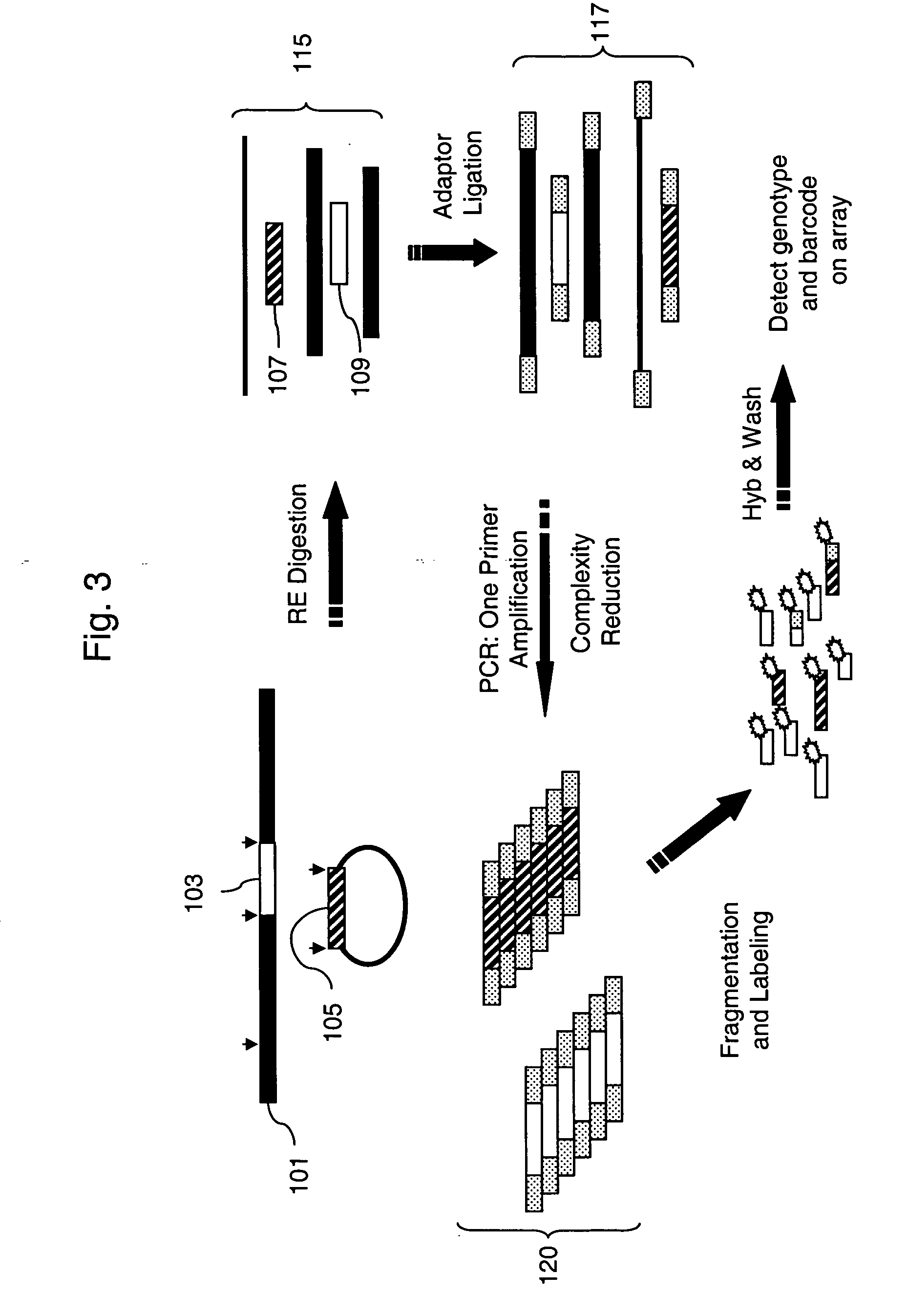
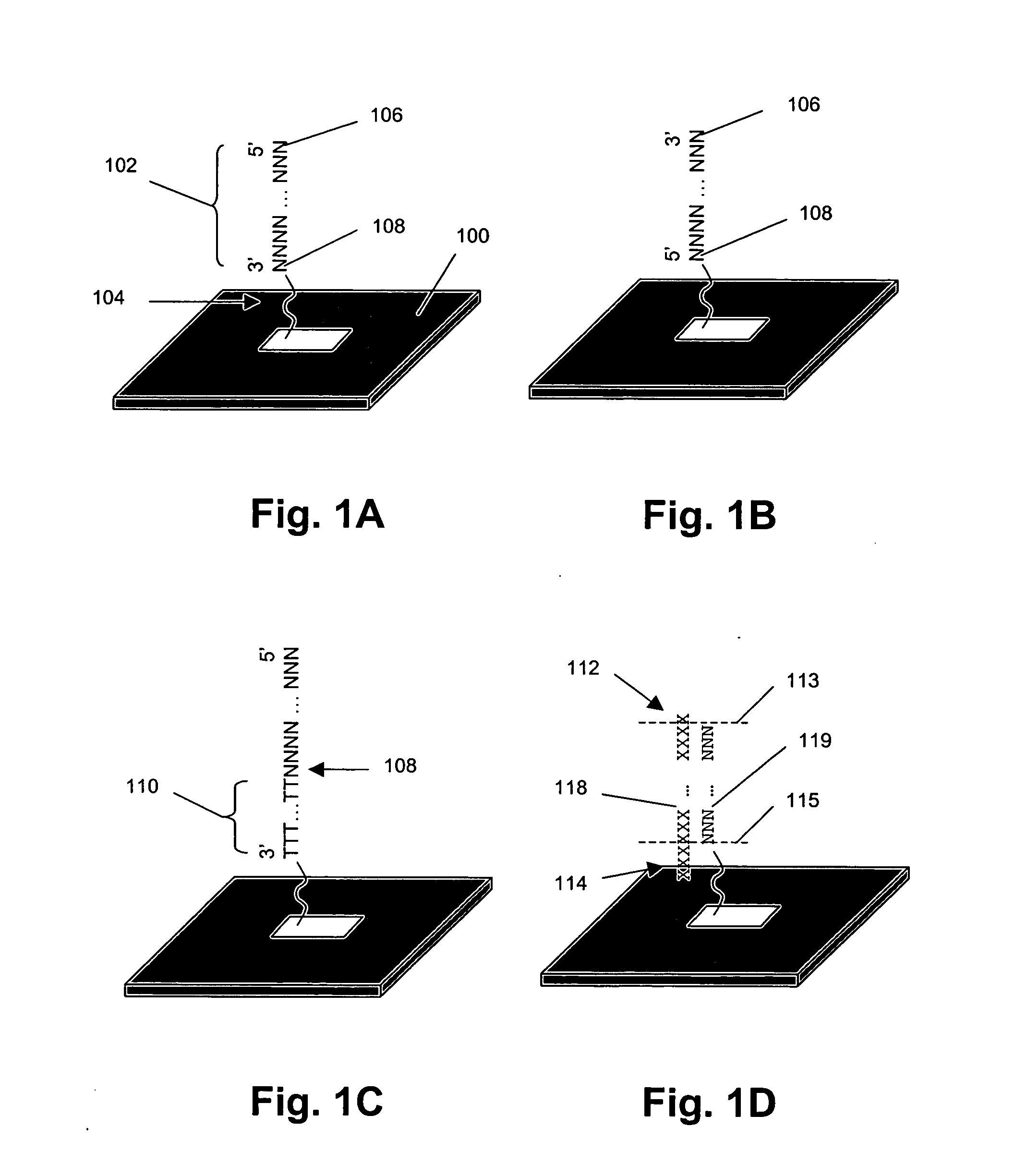
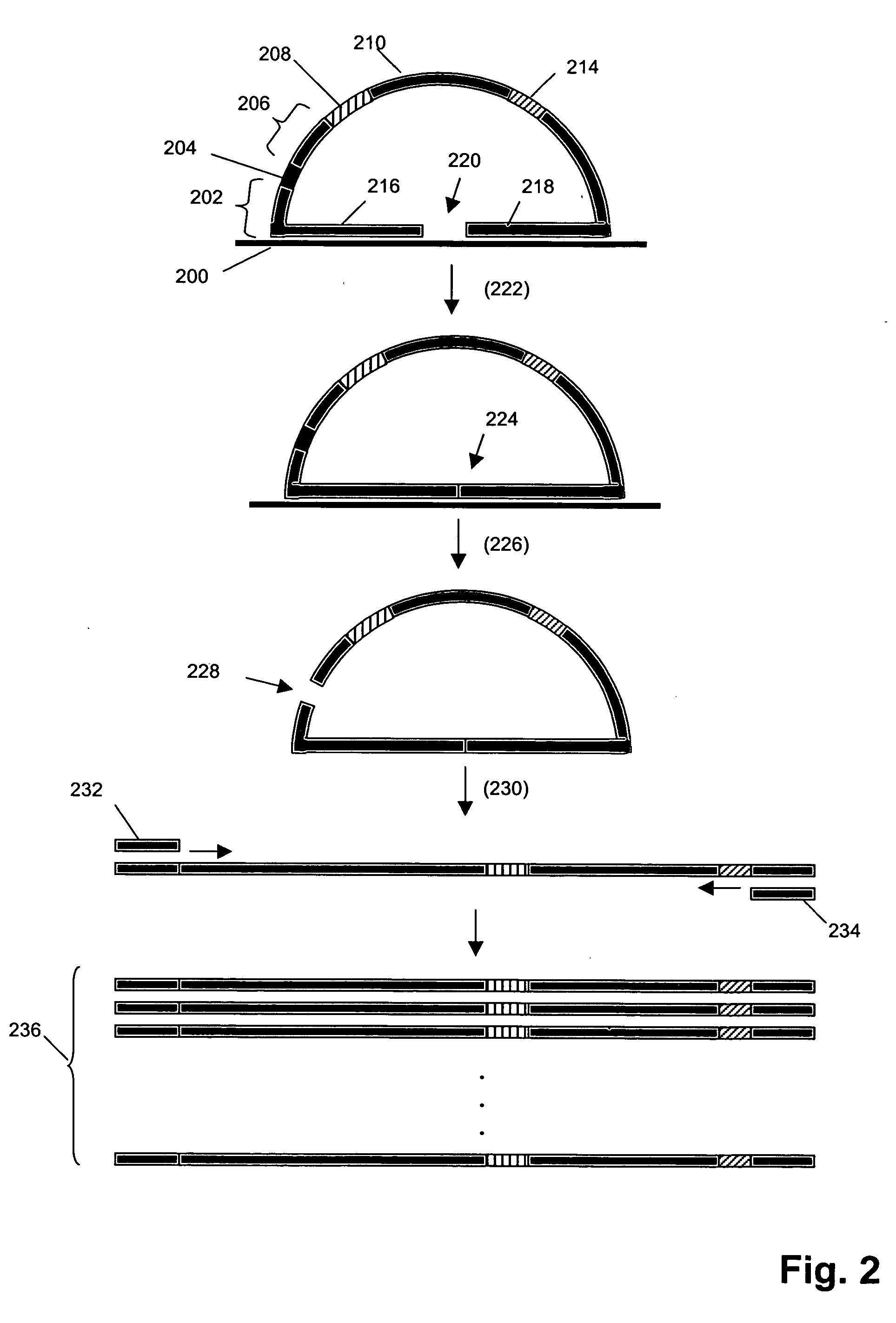
The present invention provides methods for marking nucleic acid samples with detectable markers by adding different combinations of marker molecules to each sample. Each sample may be marked with a different combination of two or more marker molecules each carrying a different tag nucleic acid sequences. The tag nucleic acid sequences may be random sequences that are not naturally occurring in the nucleic acid sample and do not cross hybridize to sequences naturally occurring in the nucleic acid sample. Methods of detecting the combination of tag sequences present in a sample, in parallel with methods of genetic analysis of the sample are disclosed. Kits containing marker molecules suitable for generating barcoded samples by mixing different combinations of marker molecules into each sample are also disclosed.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
System and methods for enhancing signal-to-noise ratios of microarray-based measurements
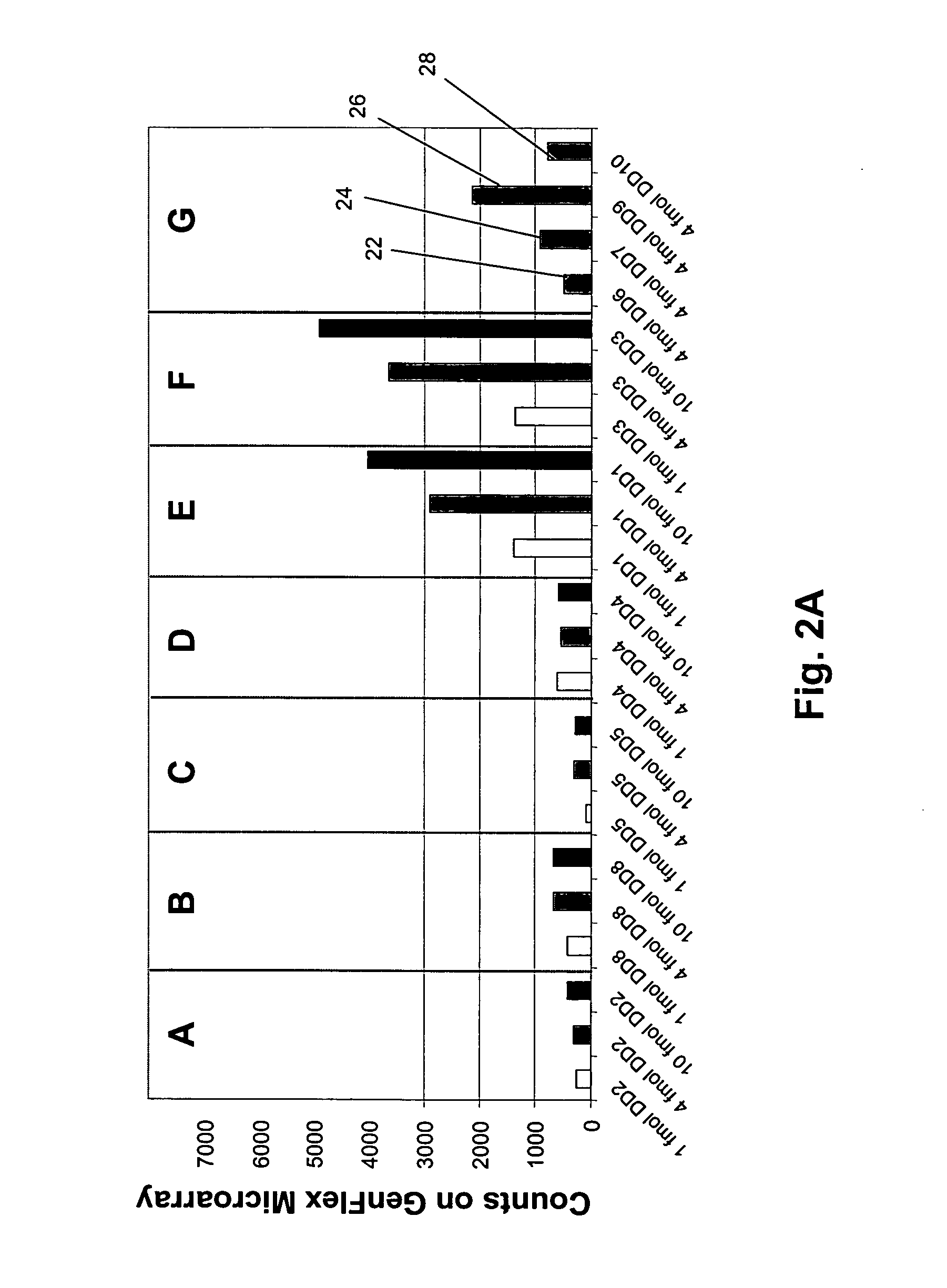
InactiveUS20050100939A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCross hybridizationPolynucleotide
The present invention provides systems and methods for large-scale genetic measurements by generating from a sample labeled target sequences whose length, orientation, label, and degree of overlap and complementarity are tailored to corresponding end-attached probes of a solid support so that signal-to-noise ratios of measurement from specifically hybridized labeled target sequences are maximized. Systems for implementing methods of the invention include a set of sample-interacting probes to produce amplicons that either each contain a segment of a target polynucleotide or an oligonucleotide tag that corresponds to a segment of a target polynucleotide, one or more solid phase supports that contain a plurality of end-attached probes, and methods of generating from sample-interacting probe amplicons from which labeled target sequences are tailored for hybridization to the solid phase supports, such as microarrays. In one aspect, labeled target sequences and end-attached probe of the solid phase supports comprise oligonucleotide tags and tag complements, respectively, selected from a minimally cross-hybridizing set.
Owner:PARALLELE BIOSCI
Polynucleotides for use as tags and tag complements, manufacture and use thereof
ActiveUS20050191625A1Simple processSimplify discussionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicineNucleotide
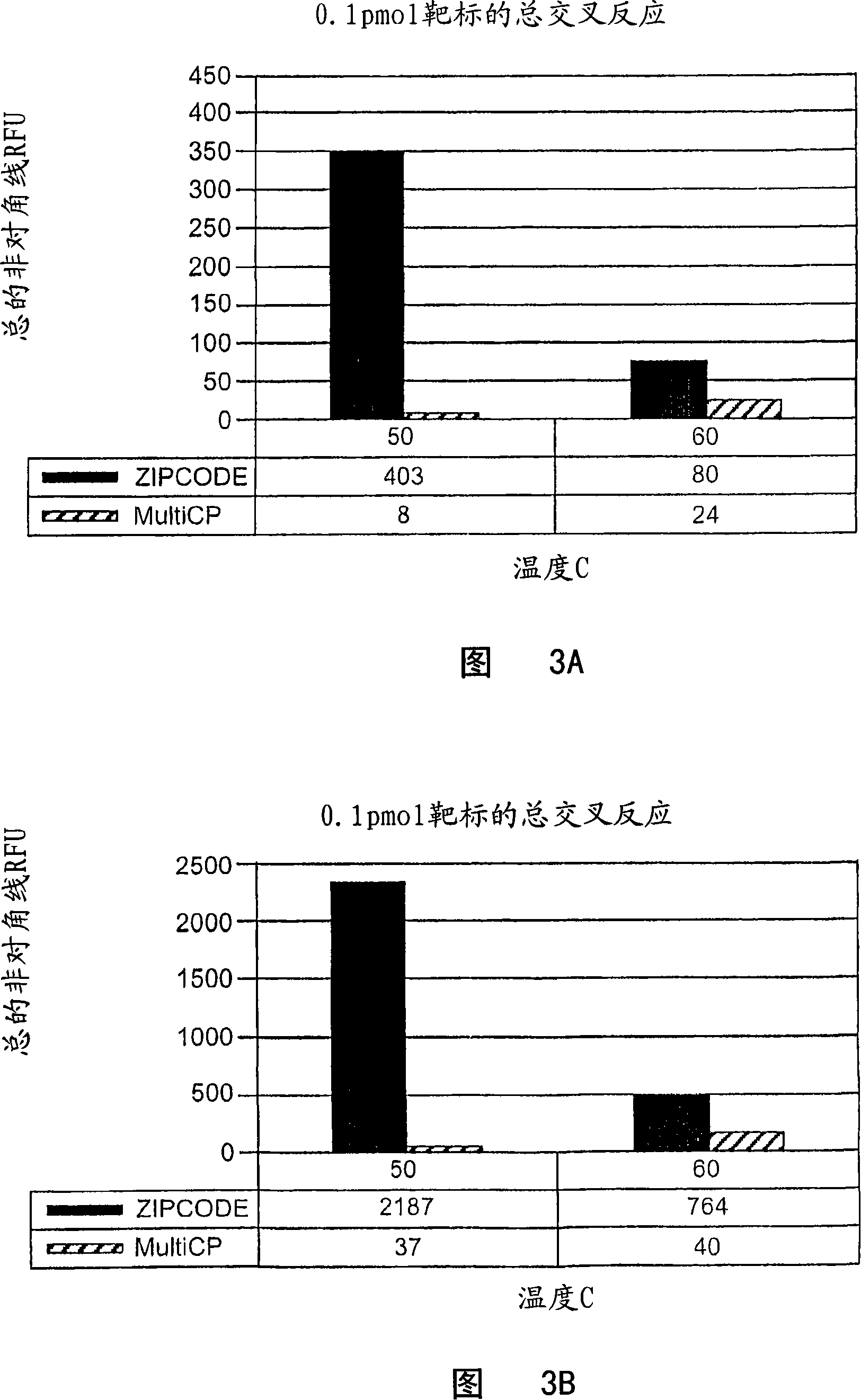
A family of minimally cross-hybridizing nucleotide sequences, methods of use, etc. A specific family of 1168 24mers is described.
Owner:LUMINEX MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS
Use of unstructured nucleic acids in assaying nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS7371580B2Reduce background signalHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein secondary structureCross hybridization
The present invention provides a system and methods for assaying nucleic acid molecules with reduced levels of background signal and enhanced specificity and sensitivity. In particular, the present invention provides a system and methods for detecting, sorting, tracking and characterizing nucleic acid molecules using hybridization assays with reduced levels of undesirable cross hybridization and reduced levels of intramolecular secondary structure.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Systems, tools and methods of assaying biological materials using spatially-addressable arrays
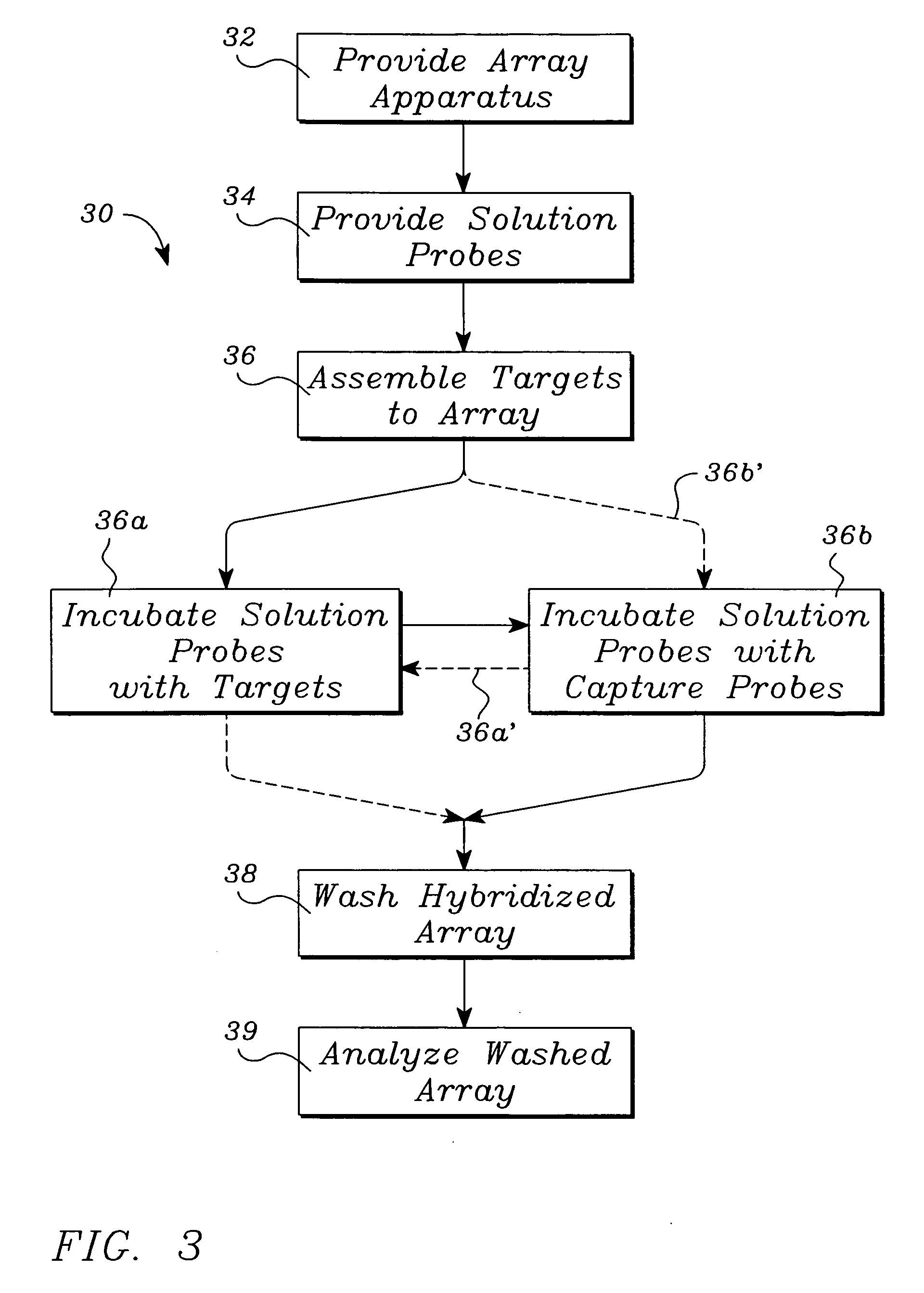
InactiveUS7052841B2Saving in cost timeSaving in turnaround timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMultiplexingNucleotide
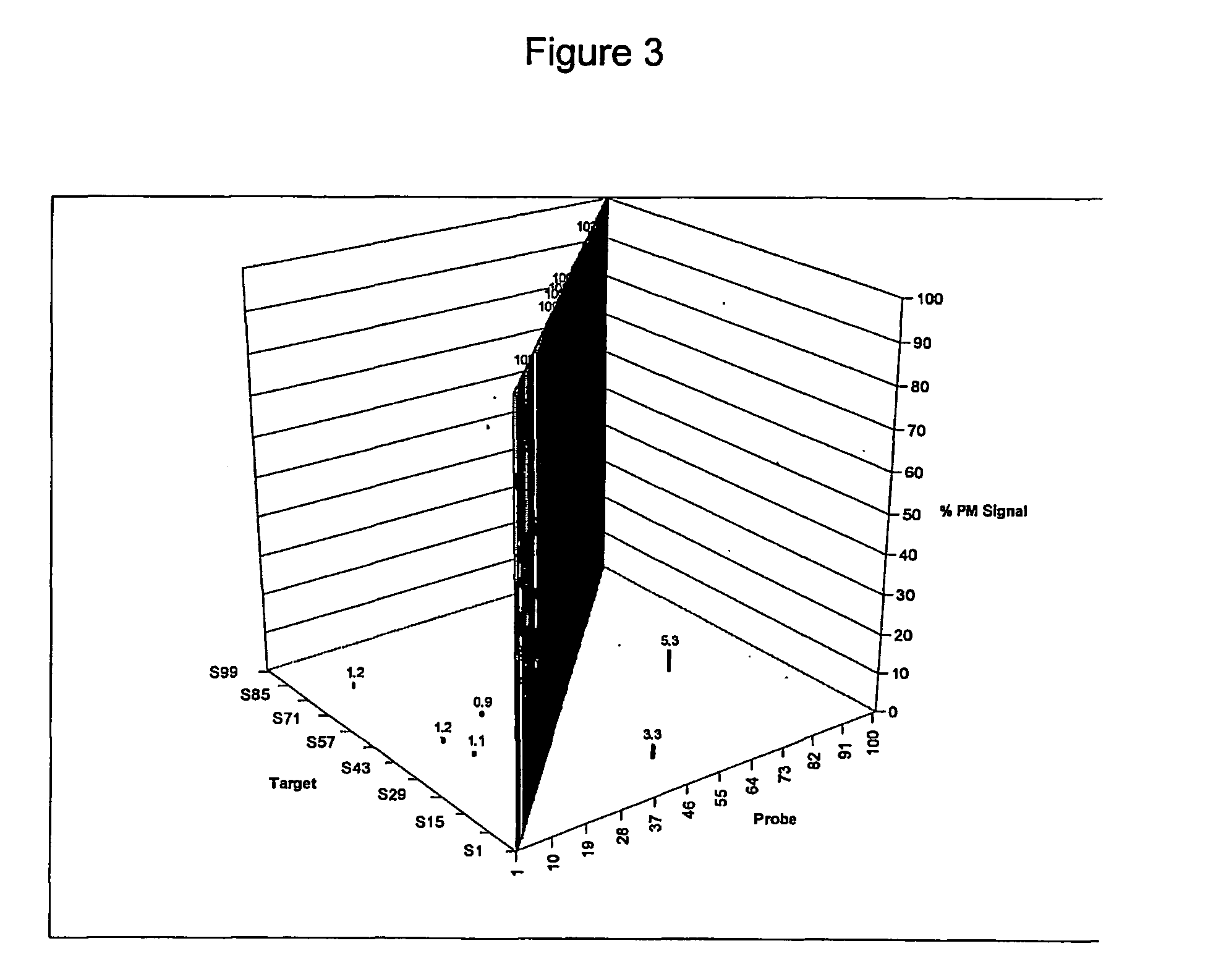
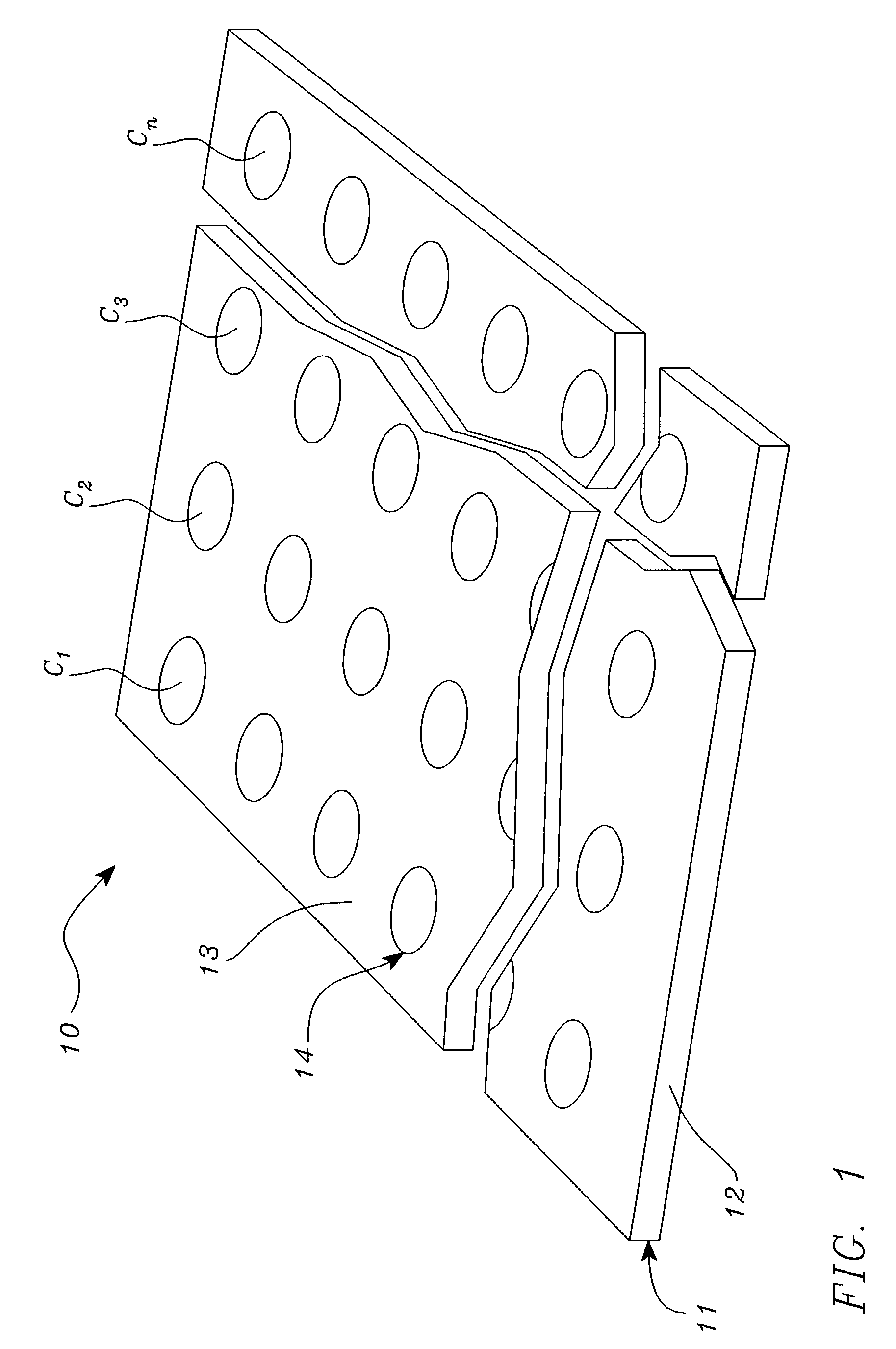
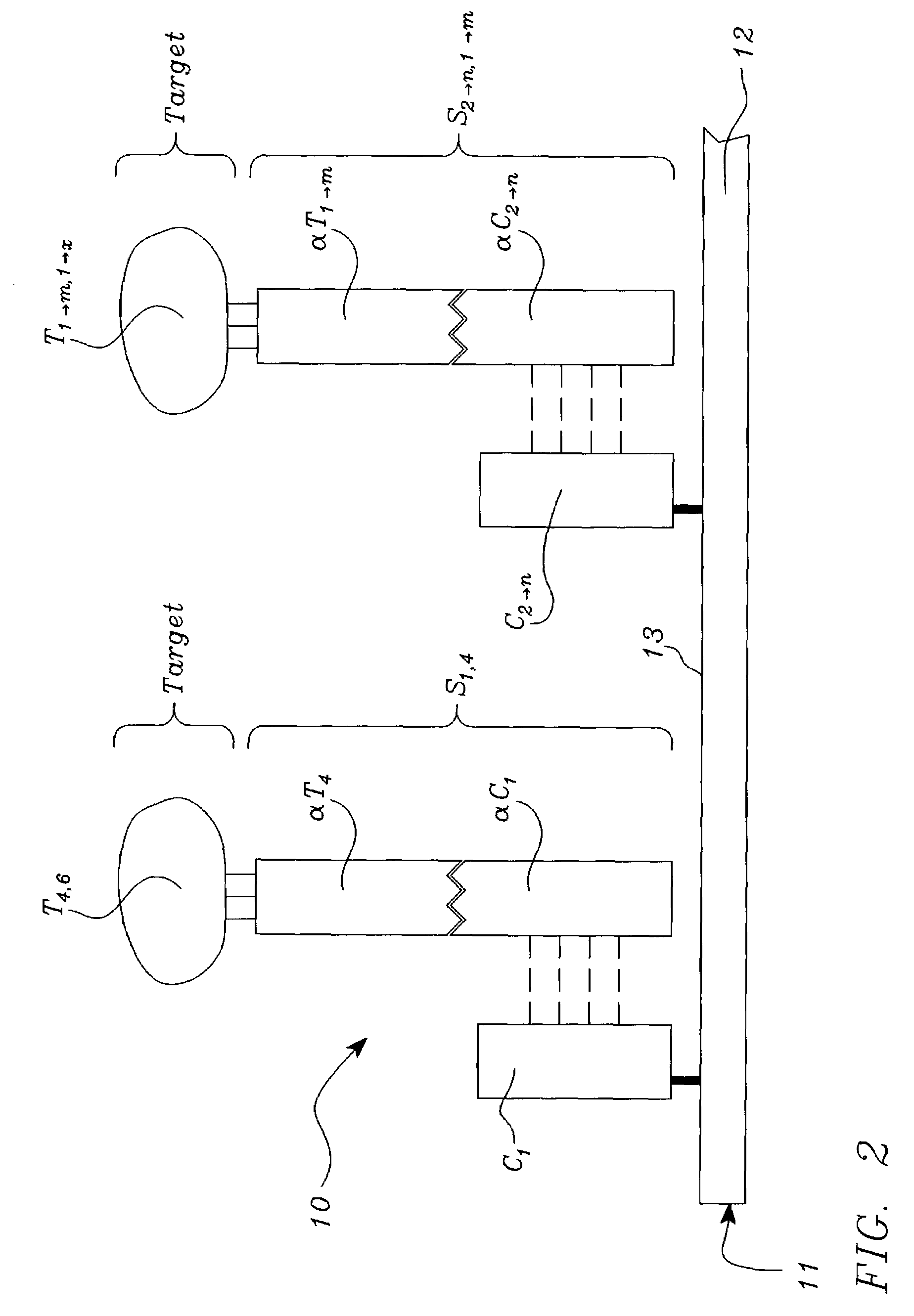
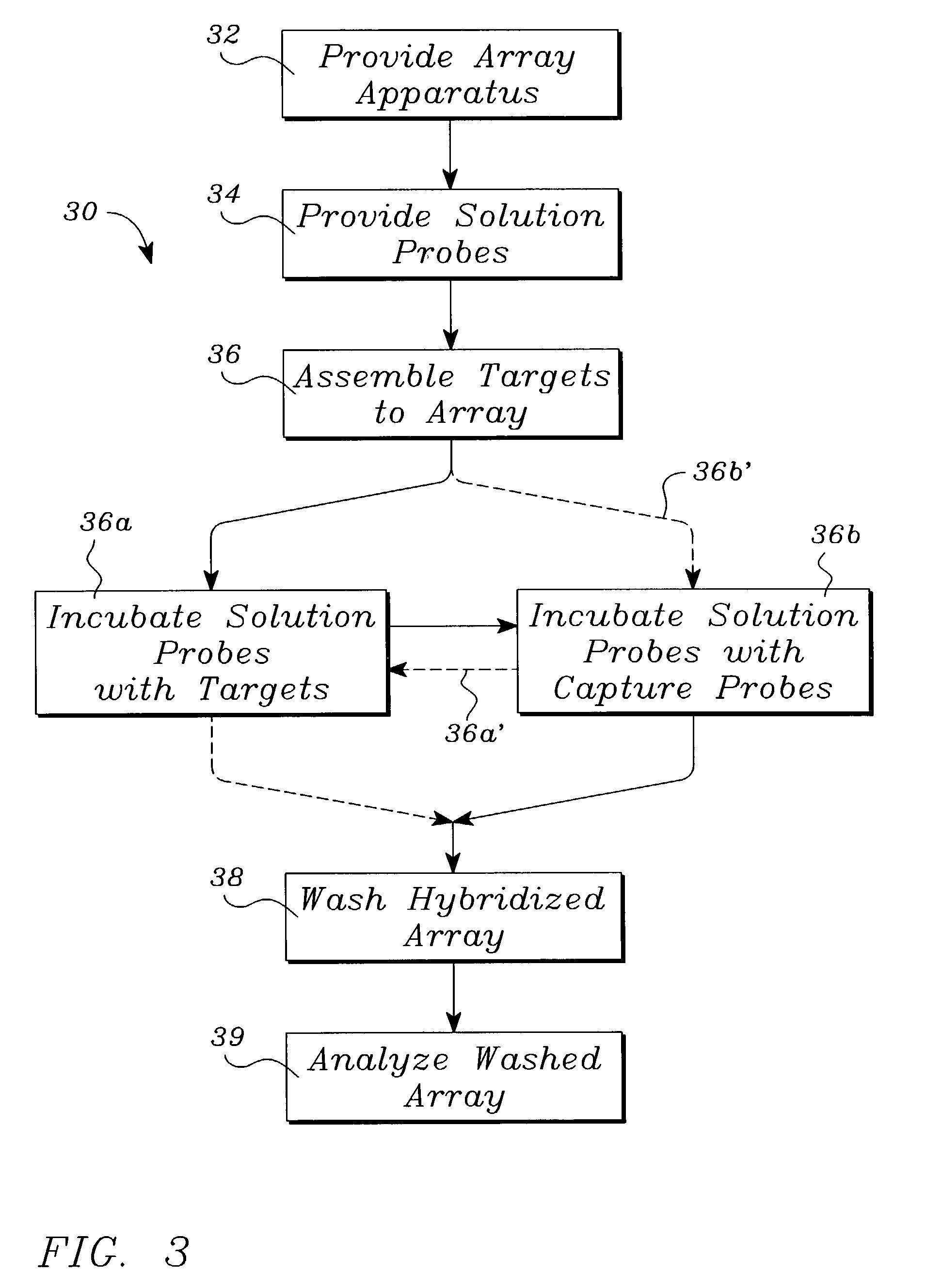
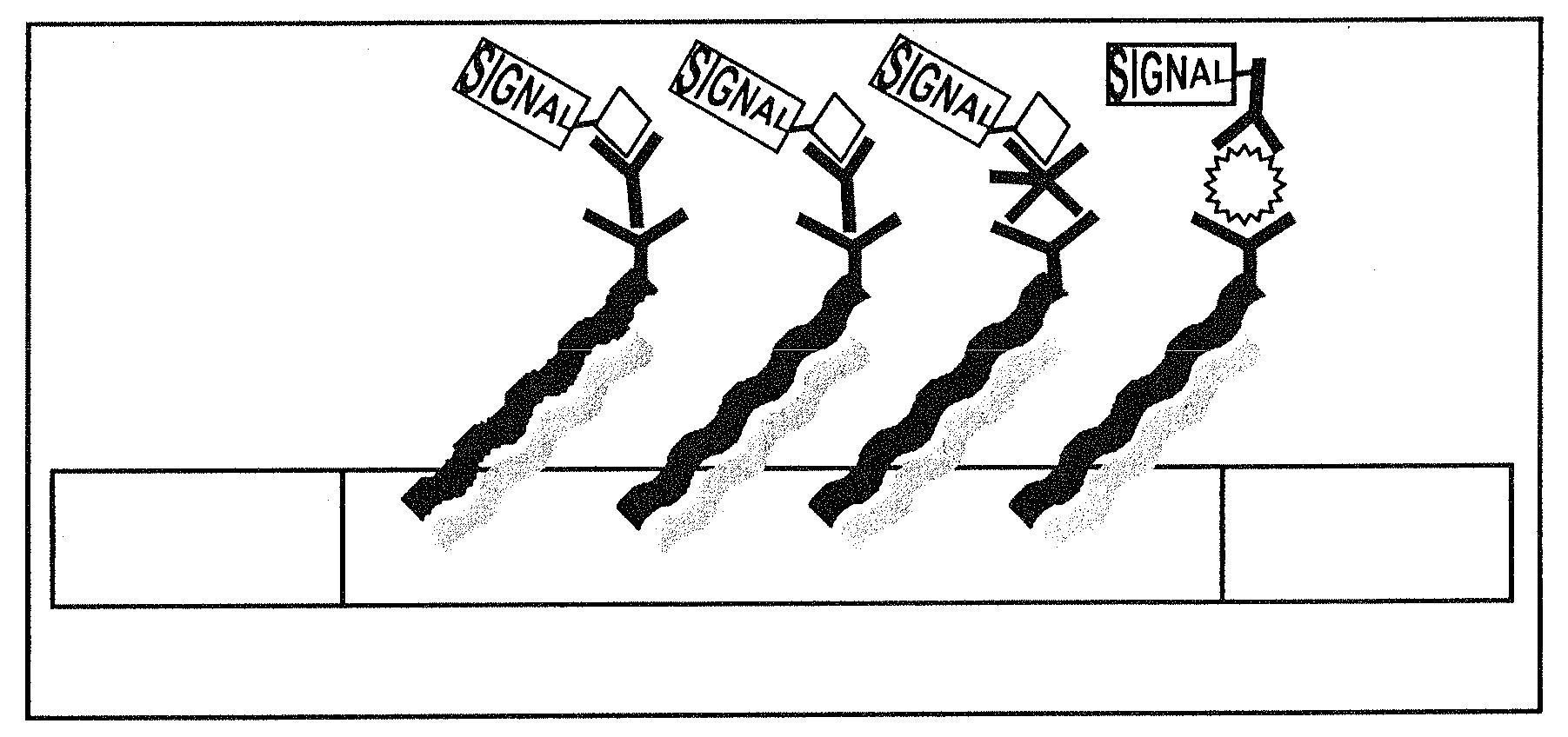
Systems, tools and methods of assaying biological material are used to perform complex sandwich hybridization assays. The tools used comprise biological solution probes that are customized for each assay. The solution probe comprises a first region for hybridizing to a probe, in a generic set of capture probes on a universal assay apparatus, and a second region for hybridizing to a target in a sample. The solution probe assembles the target to the assay apparatus by hybridizing the second region to the target and the first region to the capture probe. In array assays, one or more biological samples, having one or more targets per sample, can be multiplexed on the same universal array comprising the generic set of capture probes in an array pattern of features on the substrate. The customized solution probe addresses and assembles a predetermined target-sample combination onto the array at a corresponding capture probe address location. The systems, tools and methods have specificity and sensitivity by systematically providing a reduced likelihood of cross-hybridizations and intramolecular structures in the probes. Specificity and sensitivity of the assay are provided by the incorporation of a chemically modified monomer in the capture probe and a similarly modified monomer complement in the first region of the solution probe. The modified monomers preferentially hybridize with each other. When the probe and respective probe region are oligonucleotides, the complementary modified nucleotides have a reversed polarity relative to the polarity of the respective probe and probe region. The complementary reversed polarity nucleotides form a thermodynamically more stable hybridization to each other than a hybridization between the reversed polarity nucleotide and a complementary nucleotide whose polarity is not similarly reversed.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Highly orthogonal universal sequences for use in nucleic acid assays
ActiveUS20060172284A1Easy to analyzeDeletion increaseSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementThird generationOrthogonal sequence
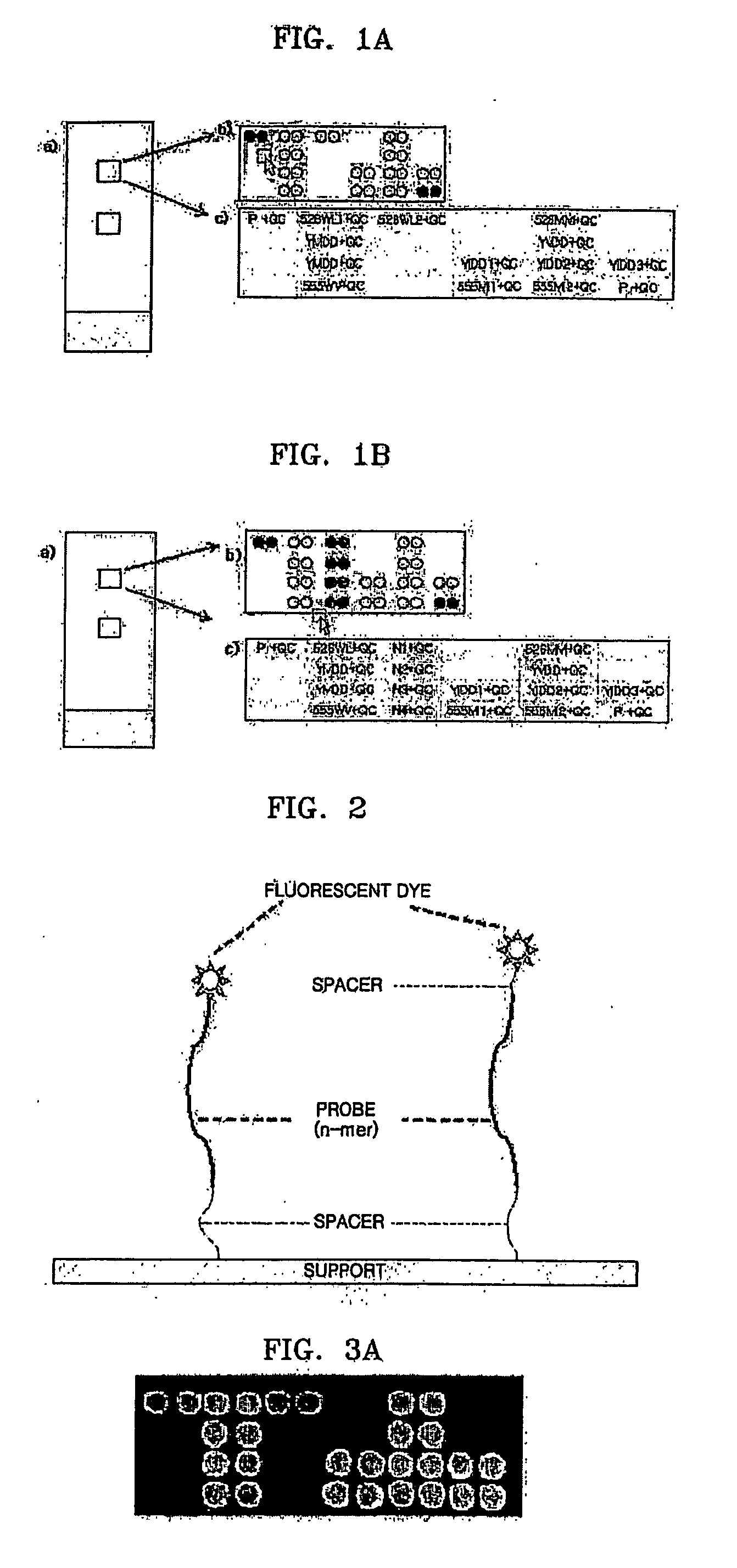
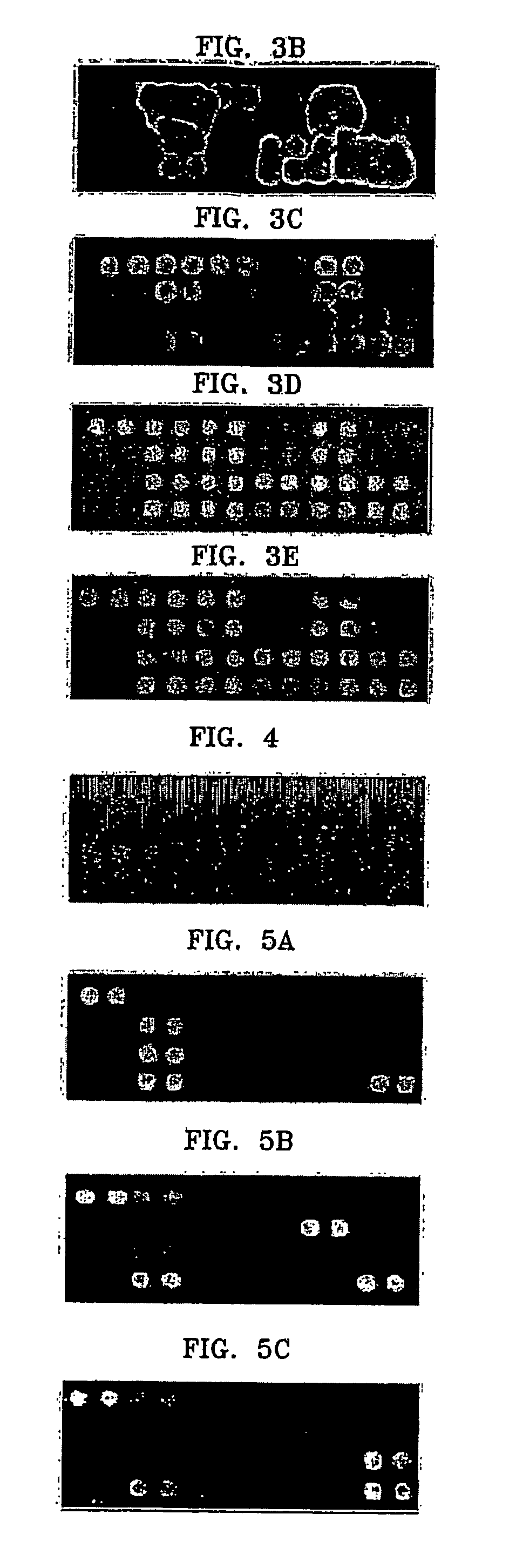
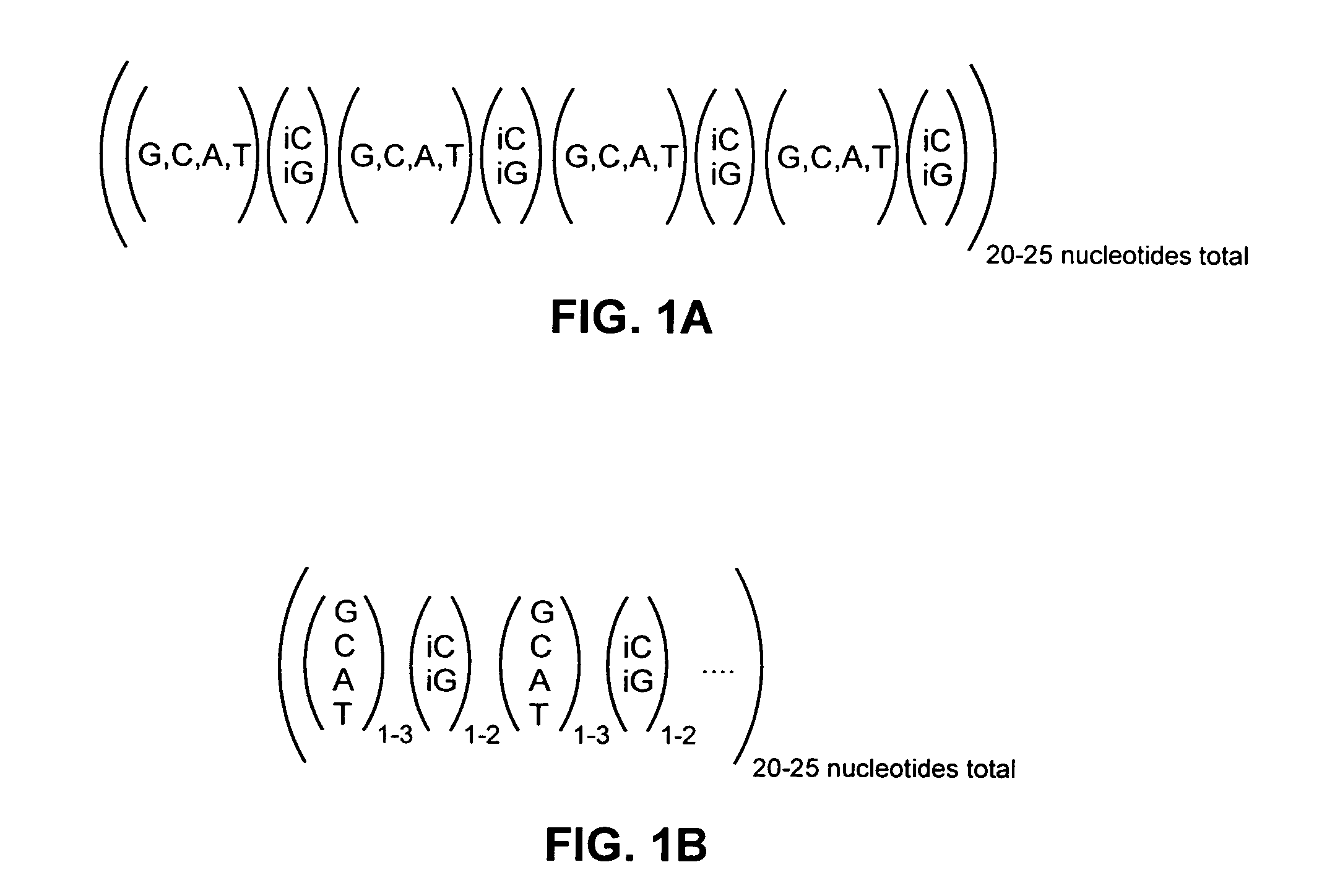
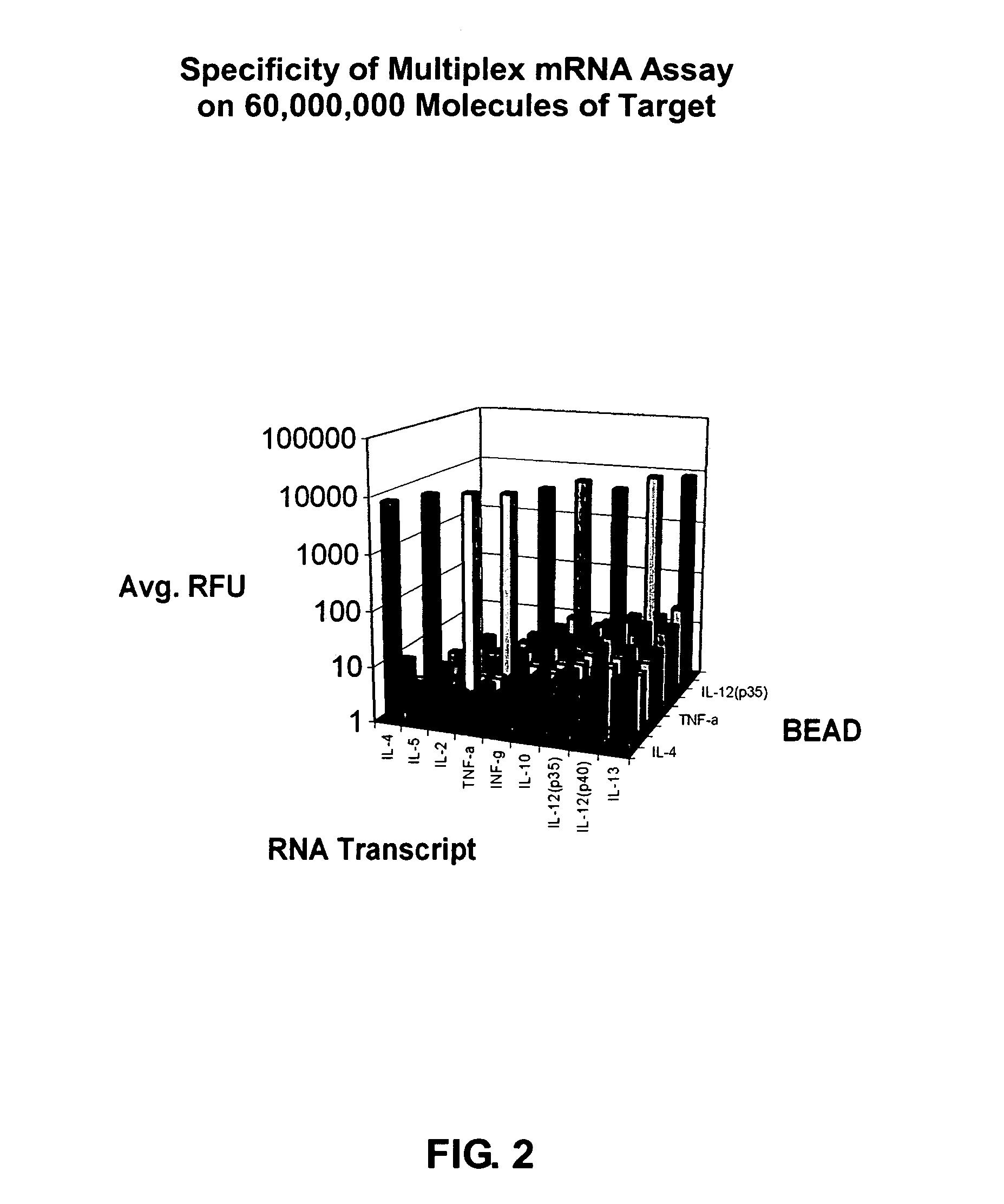
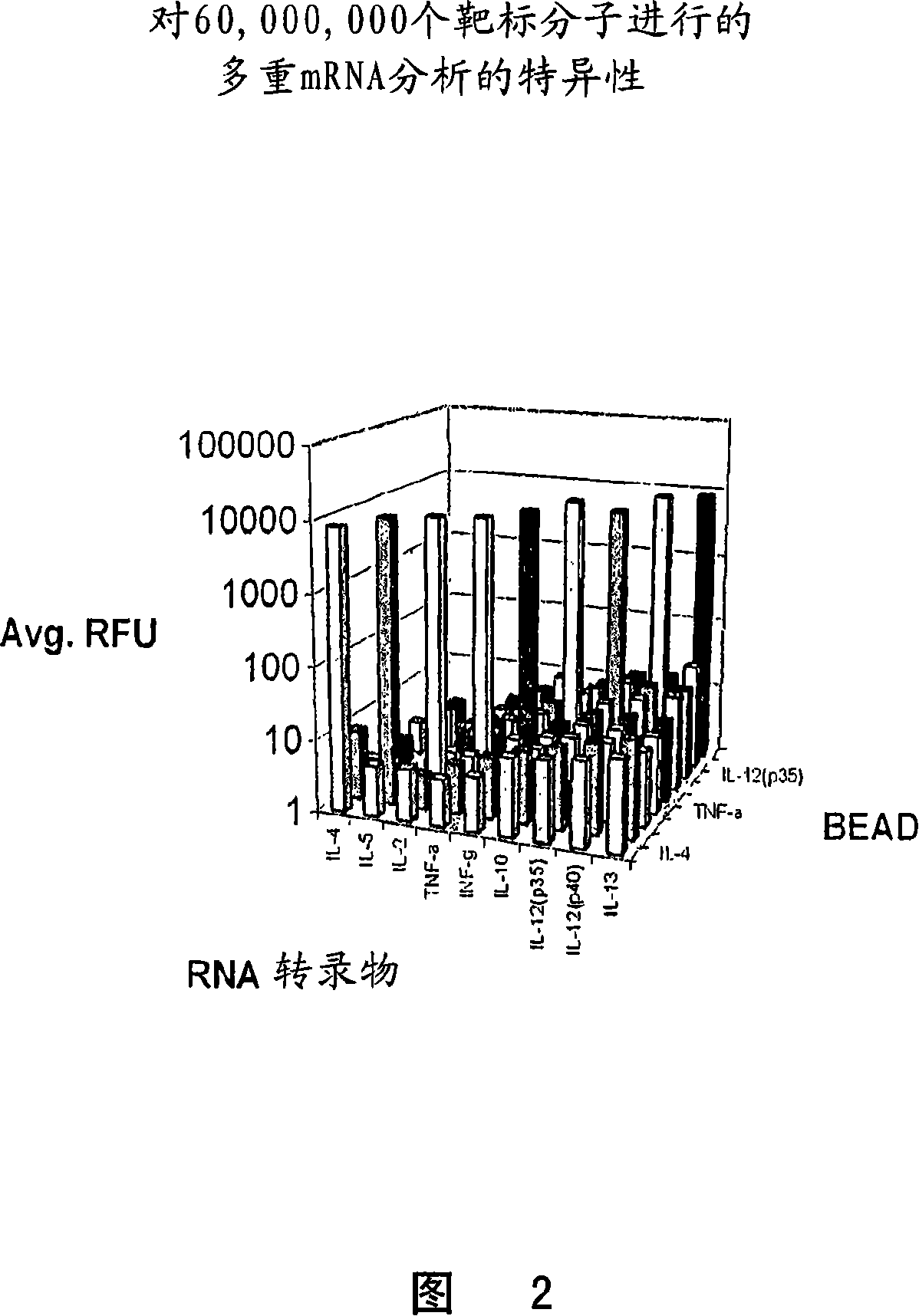
The invention provides a set of highly orthogonal six-code universal sequences for use in bDNA singleplex and multiplex nucleic acid hybridization assays. The six-code orthogonal sequences do not cross-hybridize and thus, minimize or eliminate the 3-mer cross-hybridization inherent in the second and third generation bDNA assays. The highly orthogonal universal sequences may be used in singleplex or multiplex bDNA assays quantitatively and qualitatively to determine mRNA levels in a sample; to screen for and genotype targets, such as viruses, that are present in low volumes in a sample; to screen for and genotype SNPs; and to measure changes in the amount of a gene in a sample such as when gene amplifications or deletions occur. The highly orthogonal universal sequences may also be used as universal capture probes to selectively bind assay components in a way that facilitates their further analysis.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Methods and compositions for utilizing changes of hybridization signals during approach to equilibrium
InactiveUS20050033520A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingHomopolynucleotideNucleic acid detection
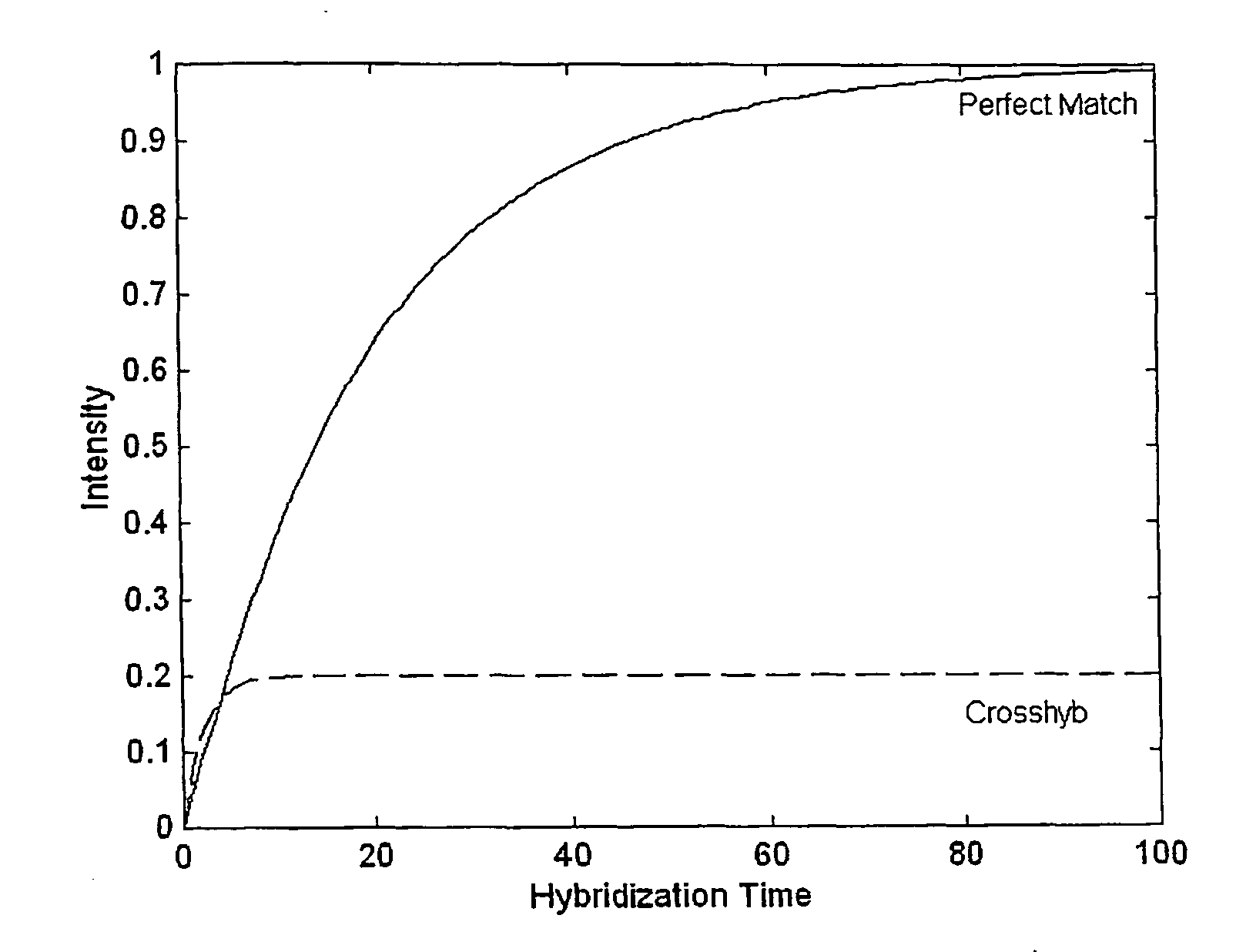
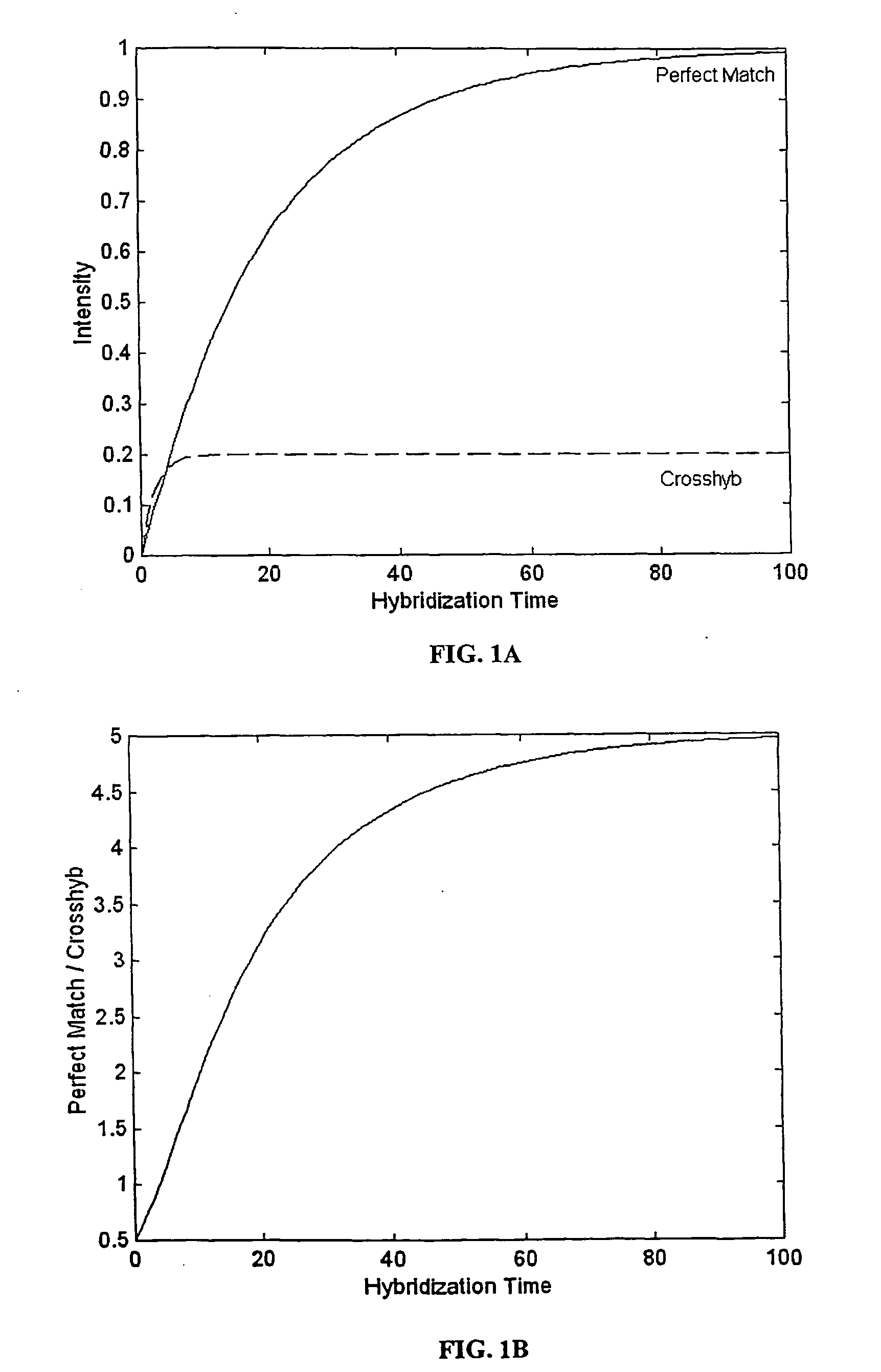
The present invention provides methods for utilizing the changes of hybridization levels in time during approach to equilibrium duplex formation for identifying specific hybridization to polynucleotide probes. In the invention, the changes of hybridization levels at one or more polynucleotide probes by a sample comprising a plurality of nucleic acid molecules having different sequences are monitored during their progress towards equilibrium and the continuing increase of hybridization signals beyond cross-hybridization is used as an indication of specific binding. The invention also provides methods of comparing specificities of different polynucleotides probes. The invention further provides methods for ranking and selecting polynucleotide probes that are specific to particular nucleic acids and methods for enhancing the detection of nucleic acids. The invention further provides methods for determining the orientation of nucleotide sequences.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Breeding method of new meat-type strain of small tailed han sheep
The invention discloses a breeding method of a new meat-type strain of small tailed han sheep. The small tailed han sheep are used as female parents, and white head Suffolk sheep are used as male parents for introductive hybridization to produce a second generation sheep flock to obtain a Sahan second generation sheep flock; then, first generation Duhan sheep produced by hybridizing white head Dorper sheep varieties with the small tailed han sheep are used as female patients; Australian white sheep are used as terminal male parents for producing Aoduhan second generation through hybridization; then, the sahan second generation female sheep are hybridized with the Aoduhan second generation male sheep to produce Saduaohan new strains; finally, through optimization combination and cross hybridization fixation, the new strain of meat-type small tailed han sheep is obtained through breeding. The obtained new strain has the advantages that the growth and development speed is high; both the meat and milk purposes can be achieved; the body shape is good; the hair in the whole body is white; the applicability is high; the polyembryony property of the small tailed han sheep is realized; the lambing percentage of the female sheep is 200 percent or above; the body weight of the adult male sheep reaches 100kg or higher; the body weight of the adult female sheep reaches 70kg or higher.
Owner:洛宁农本畜牧科技开发有限公司
Method for identifying and/or quantifying expression of nucleic acid molecules in a sample
InactiveUS6090548ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCross hybridizationDouble stranded
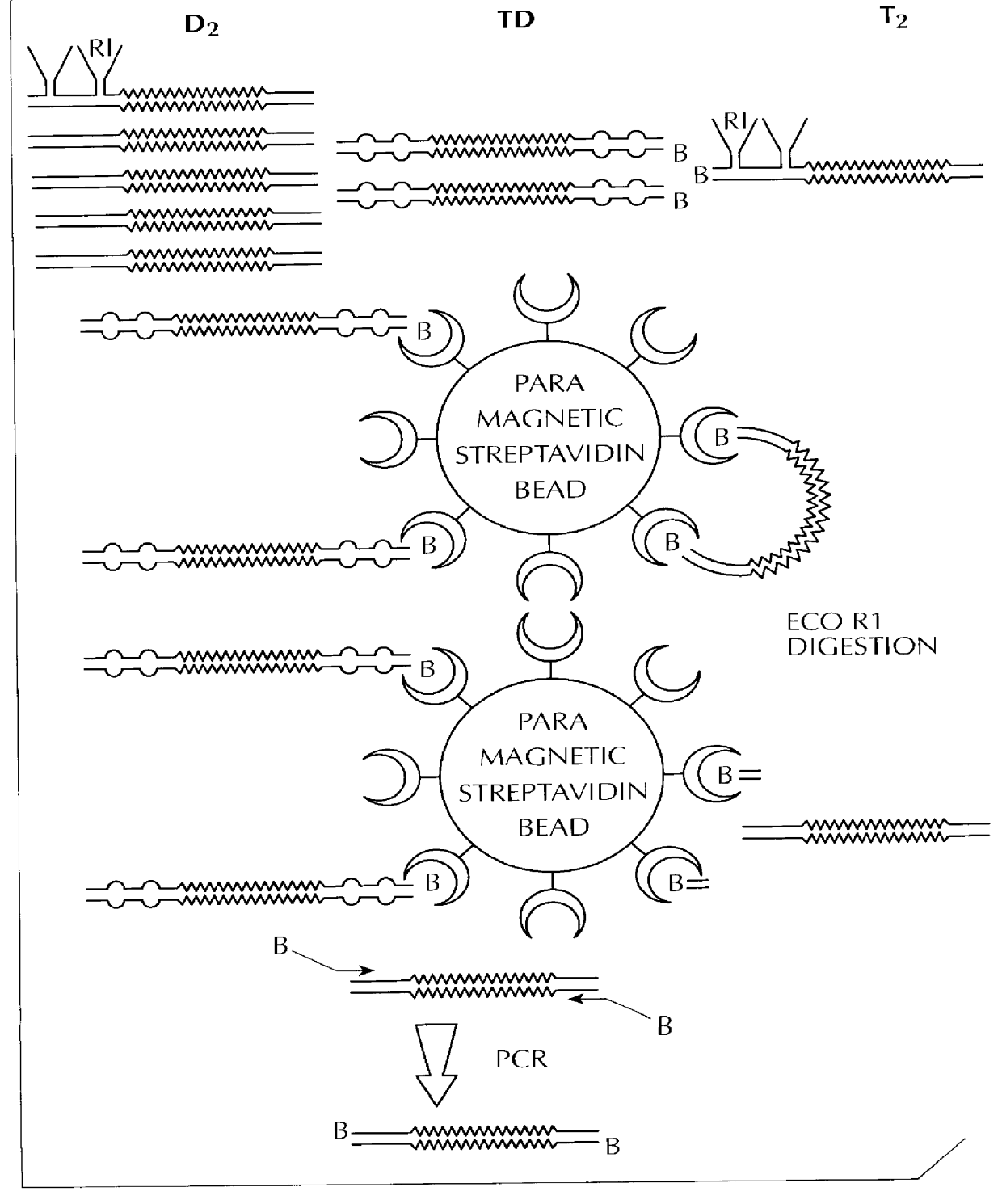
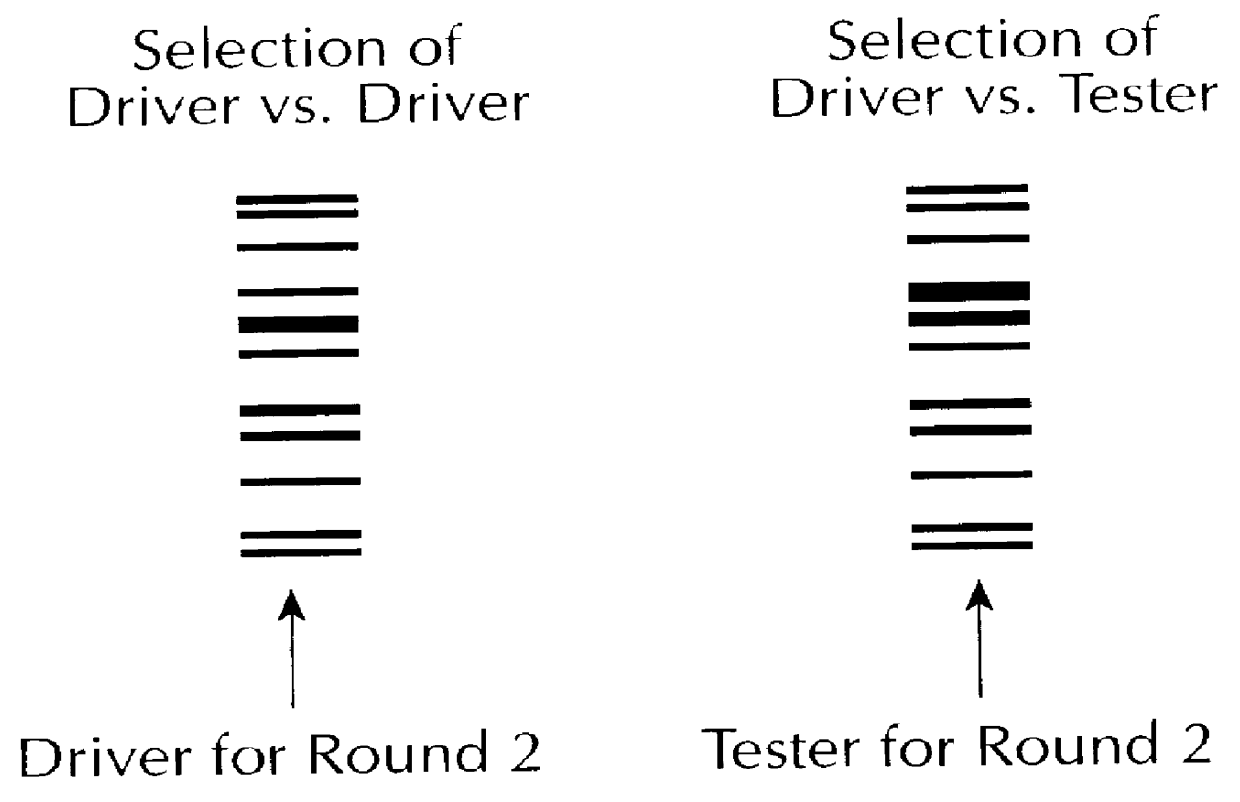
The invention involves methods for quantifying or identifying nucleic acid molecules in samples. The method involves using different, double stranded additions to nucleic acid molecules, followed by cross hybridization and identification of one type of molecule.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Method for cultivating highland high-quality black goat by virtue of hybridization of national and abroad goats
The invention discloses a method for cultivating highland high-quality black goat by virtue of hybridization of national and abroad goats. The method comprises the following steps: hybridizing an adventive Nubia goat used as a male parent with a Yunnan local Yunling mountain black goat used as a female parent, so as to obtain an F1-generation Nubia-Yunling hybrid black goat; performing grading hybridization on the Nubia goat used as the male parent and the F1-generation Nubia-Yunling hybrid black goat used as a female parent, so as to obtain an F2-generation Nubia-Yunling hybrid black goat; continuously performing grading hybridization on the Nubia goat used as the male parent and the F2-generation Nubia-Yunling hybrid black goat used as a female parent, so as to obtain an F3-generation Nubia-Yunling hybrid black goat; performing breeding and cross hybridization fixation on the F3-generation Nubia-Yunling hybrid black goat, so as to obtain a Nubia high-generation black goat variety applicable to growing in a high-altitude area. The Nubia high-generation black goat variety can be used for overcoming the defects of low general growth speed, low breeding rate, thick and hard flesh and the like of the Yunling black goat and has the advantages of cold resistance, coarse feed resistance, high farrowing rate, rapid growth speed, good flesh, high dressing percentage and the like.
Owner:王秋玉
New milk and meat dairy goat breeding method
ActiveCN104813981AStrong reproductive abilityStrong reproductive rateAnimal husbandryProduction rateCross hybridization
The invention discloses a new milk and meat dairy goat breeding method. The breeding method using excellent localized acclimatization Saanen dairy ewes in Puan as female parents and excellent localized acclimatization Nubian rams in Puan as male parents for grading crossing, selecting excellent first-filial generation ewes of the Nubian rams and the Saanen dairy ewes as female parents and excellent local Nubian goats as male parents for third-generation grading crossing, and selecting excellent filial generation rams and ewes of each grading crossing for cross hybridization fixing (combination) to breed and select the new milk and meat dairy goat having stable genetic nature. The new milk and meat dairy goat breeding method breeds the new milk and meat dairy goat by using the excellent filial generation of Nubian goats, which is high in resistance, large in physique, high in reproductive rate, fast in growth, good in meat quality, high in meat production rate and high in butter fat percentage.
Owner:普安县高棉乡六猫冲隆吉养殖场
Microarray comprising probes for drug-resistant hepatitis b virus detection, quality control and negative control, and method for detecting drug-resistant hepatitis b virus using the same
InactiveUS20060134792A1Easy to controlShorten diagnostic timeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingWild typeControl quality
Provided are a microarray manufactured using a mixture of target probes for drug-resistant HBV detection, quality control probes for controlling quality in probe hybridization and fabrication of microarrays, and negative control probes for determining the presence and ratio of more than one type, i.e., a wild type and a mutant in a codon, measuring a background of non-specific cross-hybridization, and discriminating homozygotes and heterozygotes, and a method of detecting a drug-resistant HBV, controlling the quality of a microarray, determining the presence and ratio of more than one type, and determining positive and false positive probes at the same time using the microarray. The microarray, which includes the target probes for drug-resistant HBV detection, the QC probes, and the negative control probes, can detect a drug-resistant HBV, control quality in fabrication of microarrays and hybridization, determine the presence and ratio of more than one type, i.e., a wild type and a mutant, determine positive and false positive probes by measuring a background of non-specific cross-hybridization, and discriminate homozygotes and heterozygotes. When a plurality of sets of probes, each set containing target probes, QC probes, and negative control probes, are immobilized on a support of the microarray, detection of resistance in HBV to multiple drugs, quality control, and determination as to the presence and ratio of a wild type and a mutant and whether each probe is positive or false positive can be rapidly and accurately performed.
Owner:JINYIN
Highly orthogonal universal sequences for use in nucleic acid assays
ActiveUS8063196B2Easy to analyzeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotypeOrthogonal sequence
The invention provides a set of highly orthogonal six-code universal sequences for use in bDNA singleplex and multiplex nucleic acid hybridization assays. The six-code orthogonal sequences do not cross-hybridize and thus, minimize or eliminate the 3-mer cross-hybridization inherent in the second and third generation bDNA assays. The highly orthogonal universal sequences may be used in singleplex or multiplex bDNA assays quantitatively and qualitatively to determine mRNA levels in a sample; to screen for and genotype targets, such as viruses, that are present in low volumes in a sample; to screen for and genotype SNPs; and to measure changes in the amount of a gene in a sample such as when gene amplifications or deletions occur. The highly orthogonal universal sequences may also be used as universal capture probes to selectively bind assay components in a way that facilitates their further analysis.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
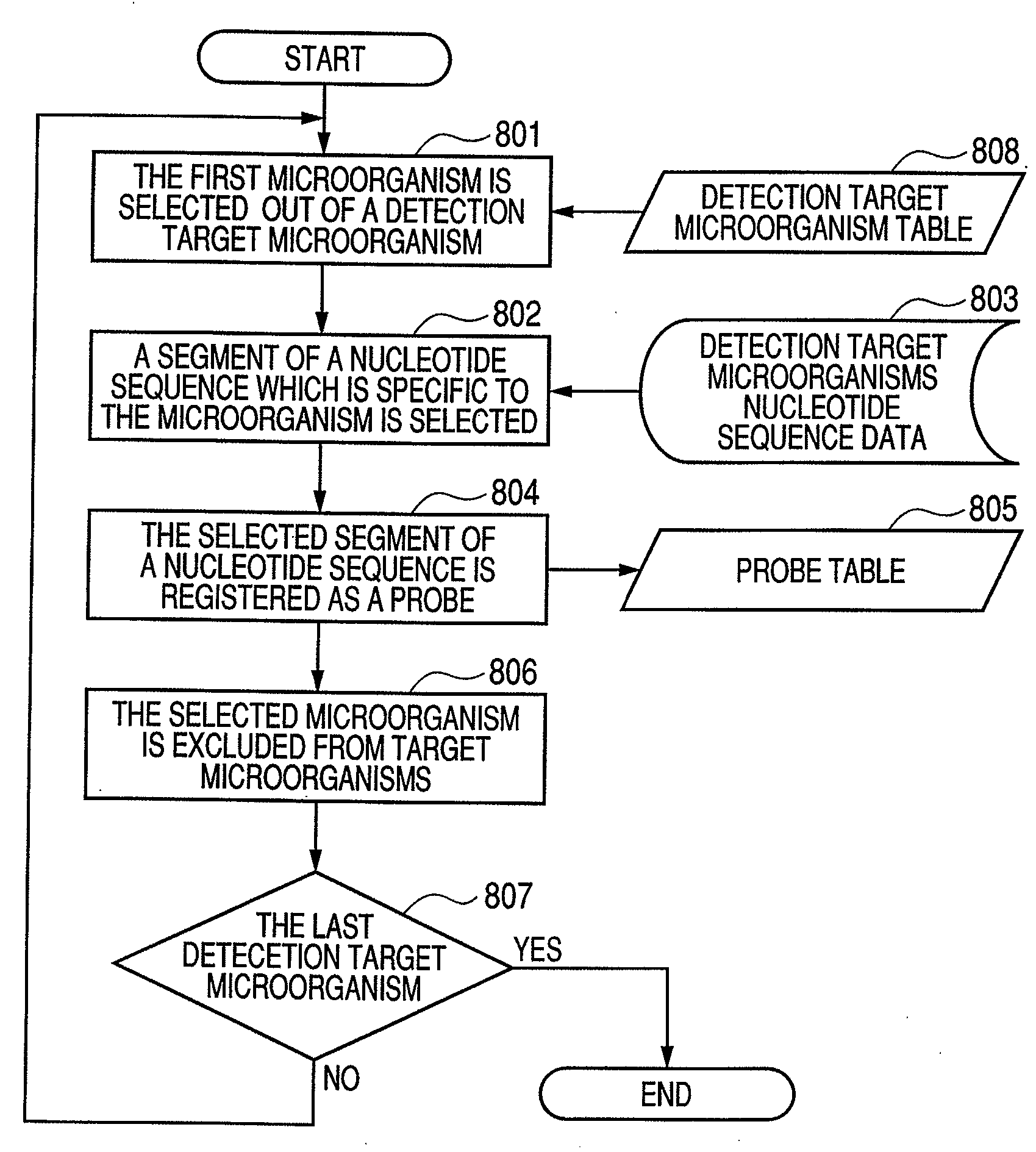
Method for detecting nucleic acid in sample, method for designing probes, system for designing probes therefor
InactiveUS20080254472A1Increase freedomEfficient discoveryMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationMicroorganismMicrobiology
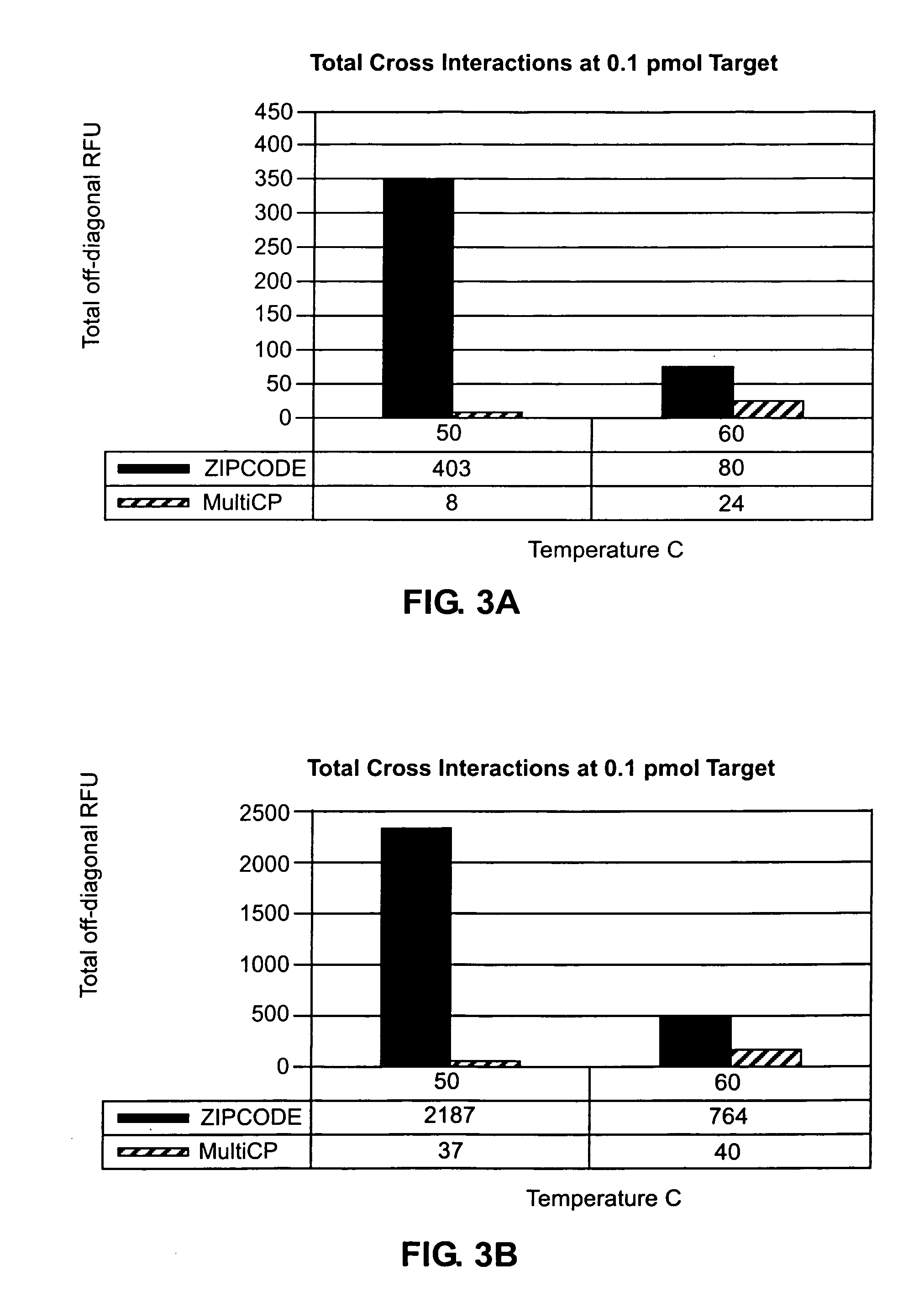
Accurate detection of a target microorganism from a sample, which may contain a plurality of microorganisms, is intended. This can be realized by eliminating a possibility of cross-hybridization of a microorganism with other probes, which can accelerate the designing speed, detecting microorganisms one-by-one in the designed order, and absorbing all the existing microorganisms.
Owner:CANON KK
MITIGATION OF Cot-1 DNA DISTORTION IN NUCLEIC ACID HYBRIDIZATION
InactiveUS20080050728A1Overcome problemsReduce signal distortionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesCross hybridization
A novel method of suppressing non-specific cross-hybridization between repetitive elements present in nucleic acid probes and corresponding repetitive elements in the target nucleic acid by using DNA synthesized to contain a plurality of repetitive elements while avoiding low and single copy sequences.
Owner:CHILDRENS MERCY HOSPITAL
High-yield corn planting method
The invention discloses a high-yield corn planting method belonging to the technical field of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, hunting, trapping and fishing, and particularly relates to a corn planting method. The invention provides the high-yield corn planting method which is high in yield and is green and pollution-free. The high-yield corn planting method comprises the following steps of (1) isolated planting: sowing by stages is carried out since sweet corn and waxy corn can be in out-crossing hybridization with common corn and grains of the sweet corn and the waxy corn can easily change into grains of the common corn; (2) seed preparation: elite hybrid seeds can be selected as the elite hybrid seeds have good yield-increasing potential and are the high-yield basis of corn; appropriate elite seeds can be selected by combining ecological types of different regions; (3) seed processing: appropriate seeds coated by a seed coating agent can be selected before seeding according to a local disease and pest occurrence regularity, or seed dressing processing can be carried out on seeds by selecting related pest killing agents, disinfecting agents, micro-element fertilizer and the like according to needs, so that the purposes of preventing diseases and pests and promoting the growth can be achieved; (4) land ploughing and land preparation: the appropriate tilling depth is 18 cm; the tilling depth can be up to 20 cm for the land which is high in soil fertility, thick in tilling layer and large in basic fertilizer application amount; otherwise, the tilling depth needs to be shallow; (5) seeding depth: generally, the appropriate seeding depth is 4 to 6 cm; but generally, the seeding depth is required not to exceed 8 cm. Attention, a great number of ineffective tillers can be generated during a seedling stage if the soil which is better in soil moisture content and better in fertility is subjected to too-shallow seeding.
Owner:牛玉琴
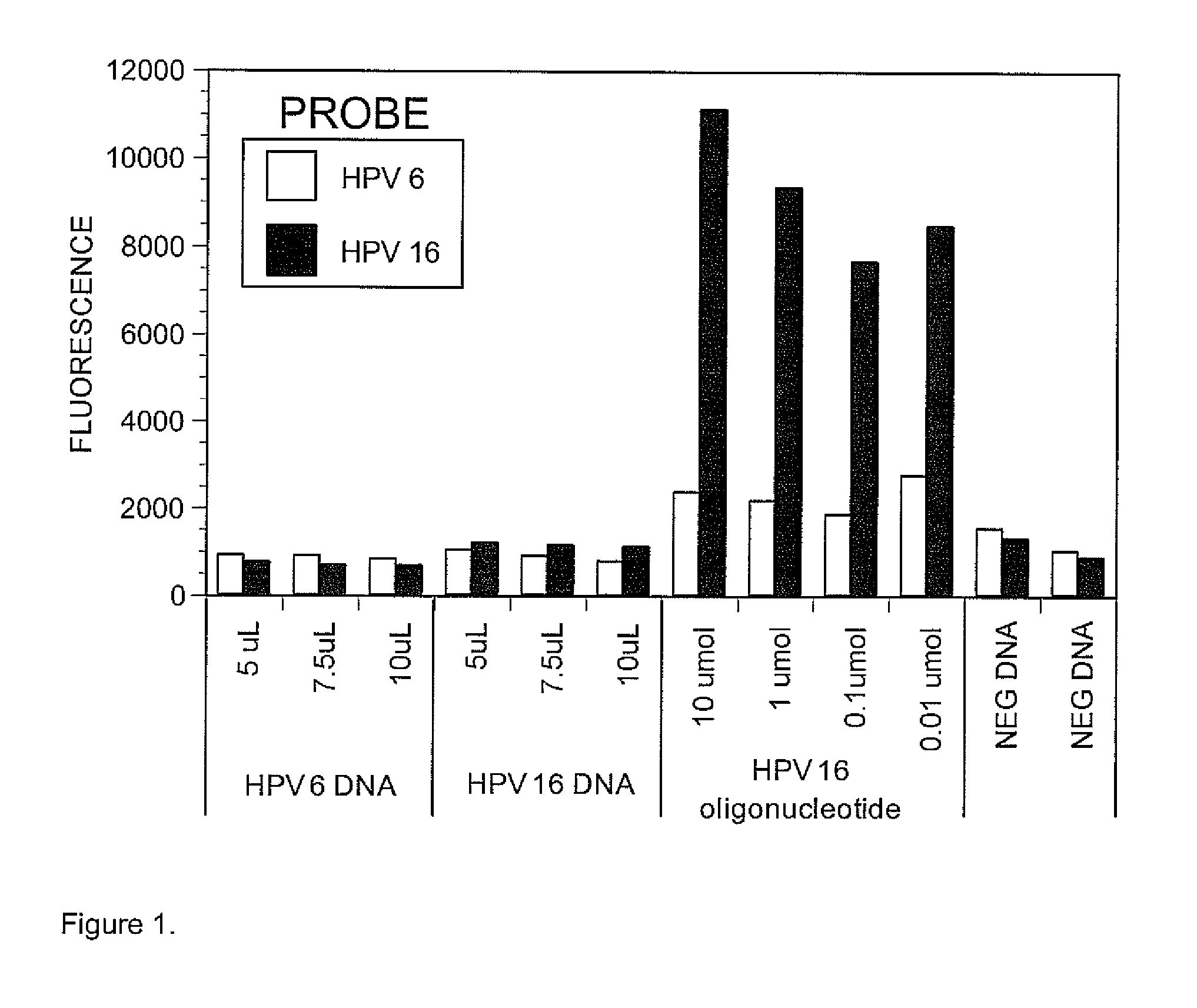
Set of Probes for the Detection and Typing of 46 Human Papillomavirus Mucosal Types
InactiveUS20130143751A1Accurate prevalence resultImprove automationNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman papillomavirusNorthern blot
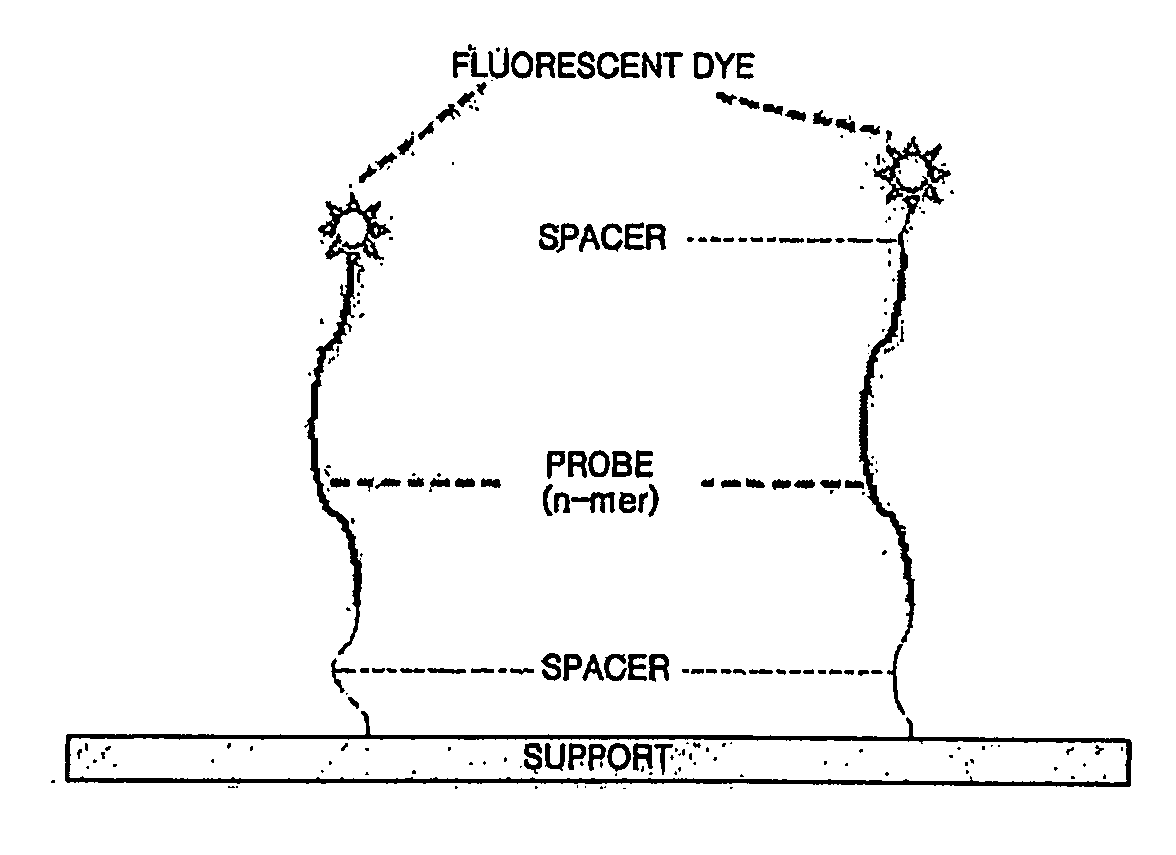
We have developed a set of probes to detect and identify 46 types of mucosal human papillomaviruses (HPV). These probes recognize the variable region comprised between the 2 conserved regions of the published GP5+ / GP6+ set of PCR primers. The example described in this application, called NML Luminex genotyping method, uses a multiplex assay based on nested PCR amplification and the Luminex xMAP technology. The 46 probes have been shown to hybridize, as intended, to the DNA derived from the following HPV types: 6, 11, 13, 16, 18, 26, 30, 31, 32, 33, 35, 39, 40, 42, 43, 44, 45, 51, 52, 53, 54, 56, 58, 59, 61, 62, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 89, 90, 91 and 97. The hybridization of each probe is specific for each type without any cross hybridization among types and it is sensitive enough to allow detection of PCR products for genotyping of HPV DNA contained in clinical samples. We also present a validation of the NML Luminex method against direct sequencing of HPV types and against the Roche Linear Array, a leading commercial method for HPV genotyping. The probes described here are suitable for use in other assays based on hybridization with labelled target HPV DNA, including, but not limited to, Southern and Northern blots, reverse line blot hybridization, DNA microarray, or ELISA.
Owner:SEVERINI ALBERTO +1
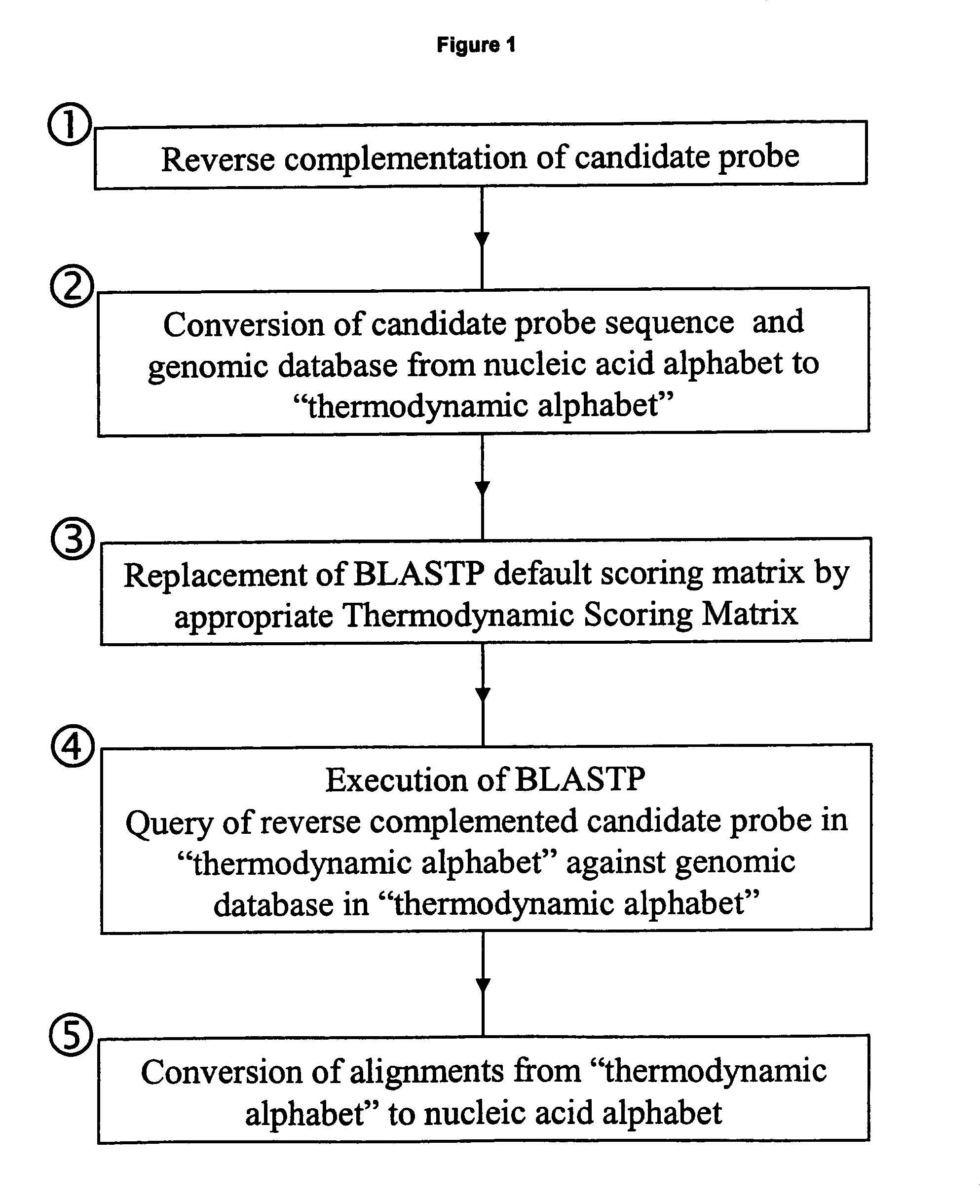
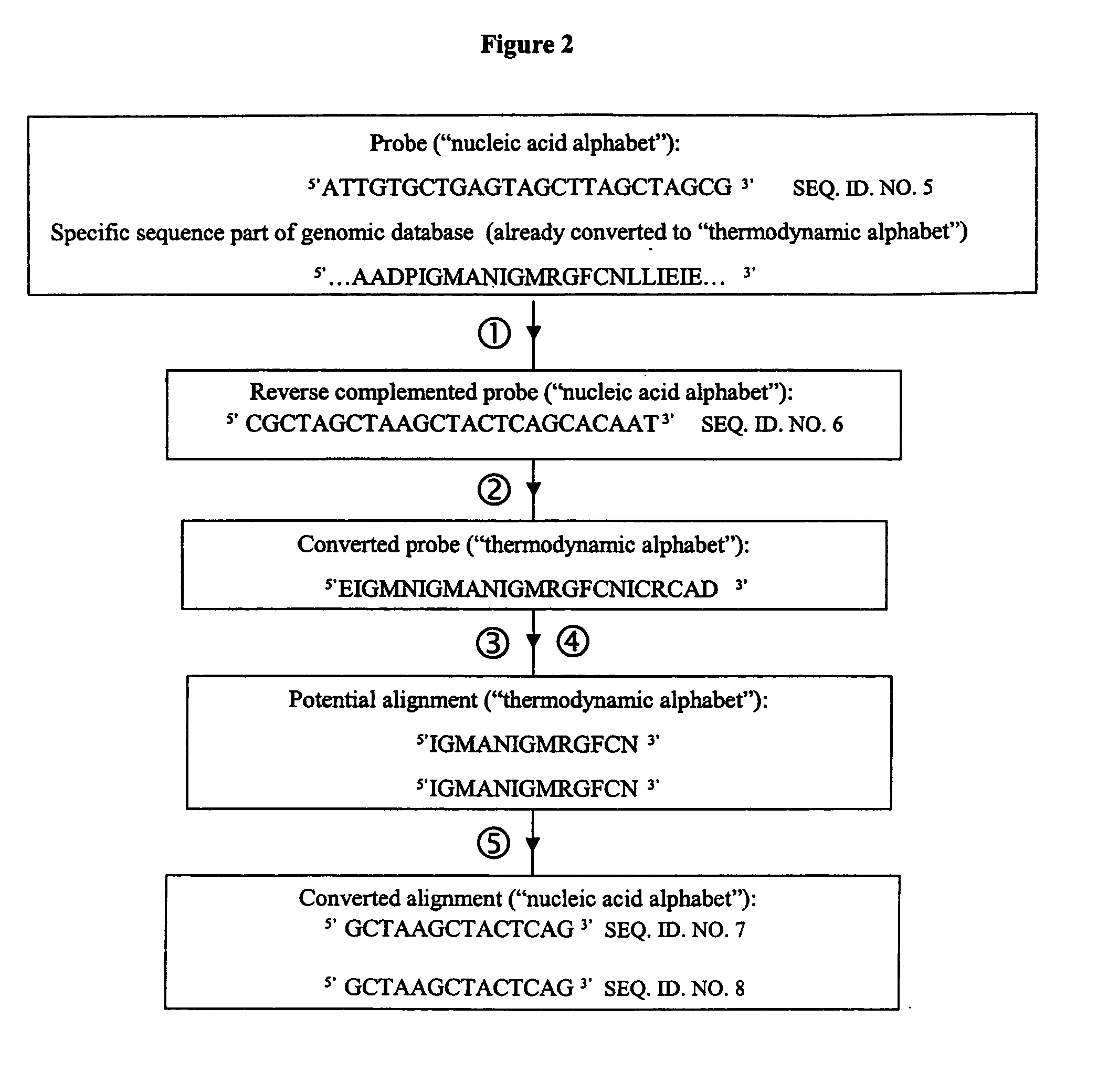
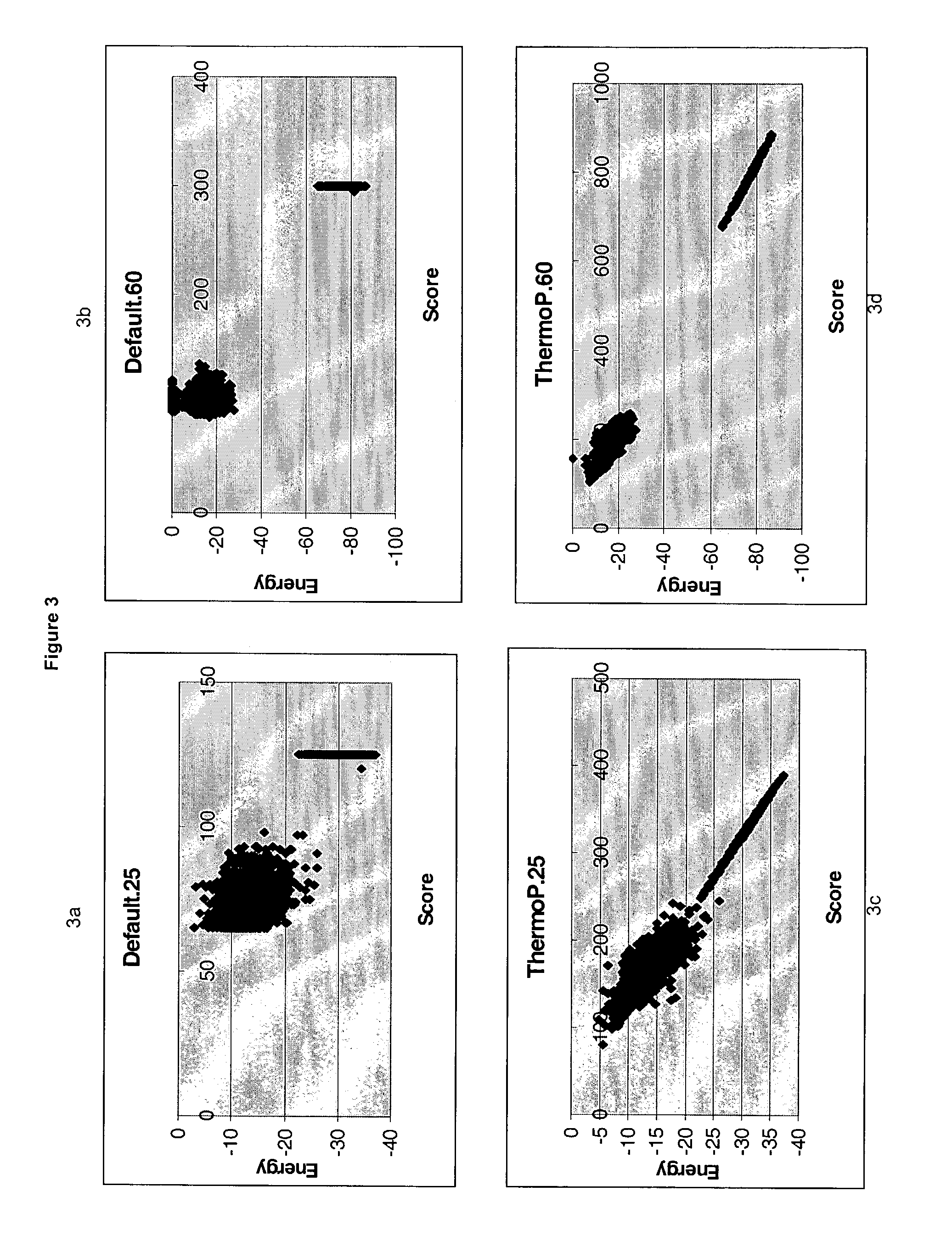
Methods for searching polynucleotide probe targets in databases
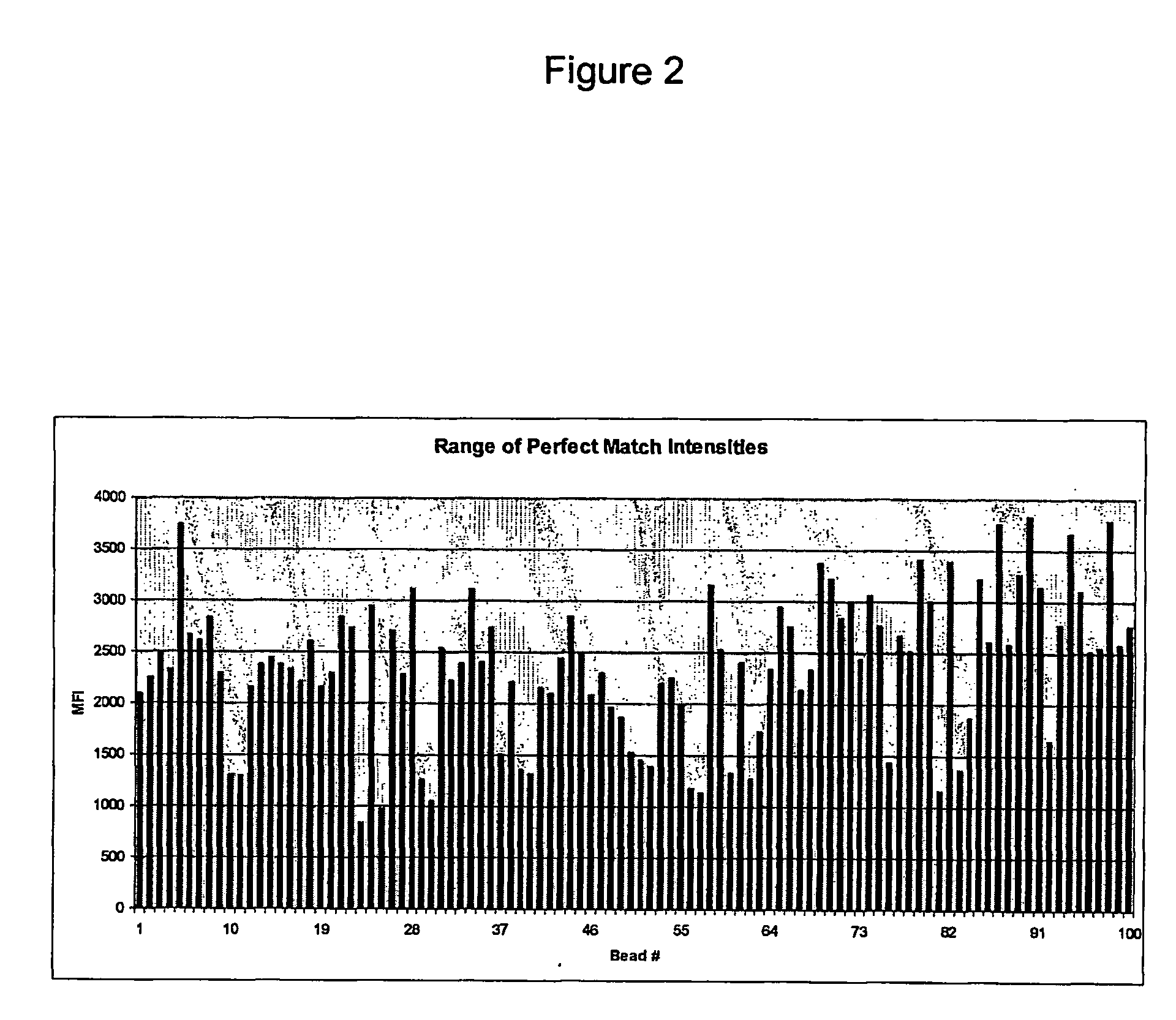
ActiveUS7085652B2Reduce in quantityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBinding siteCross hybridization
Methods for determining the binding affinity of a probe to a target or targets in a polynucleotide composite using an automated system. Such methods determine relative binding sites based on thermodynamic principles, using a thermodynamic alphabet and a thermodynamic scoring matrix, with appropriate computer software, such as BLASTP. The invention also provides methods for designing polynucleotide probes to be used in hybridization assays, and minimizing the occurrence of cross-hybridization.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Highly orthogonal universal sequences for use in nucleic acid assays
InactiveCN101111607AMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesGenotypeOrthogonal sequence
The invention provides a set of highly orthogonal six-code universal sequences for use in bDNA singleplex and multiplex nucleic acid hybridization assays. The six-code orthogonal sequences do not cross-hybridize and thus, minimize or eliminate the 3-mer cross-hybridization inherent in the second and third generation bDNA assays. The highly orthogonal universal sequences may be used in singleplex or multiplex bDNA assays quantitatively and qualitatively to determine mRNA levels in a sample; to screen for and genotype targets, such as viruses, that are present in low volumes in a sample; to screen for and genotype SNPs; and to measure changes in the amount of a gene in a sample such as when gene amplifications or deletions occur. The highly orthogonal universal sequences may also be used as universal capture probes to selectively bind assay components in a way that facilitates their further analysis.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Linear nucleic acid and sequence therefor
InactiveUS20080254999A1Low efficiencyReduce probabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionAnalyte
Nucleic acids and sequences therefor are disclosed that are characterized by a reduction or lack of internal secondary structure, are capable of hybridizing with a complementary nucleic acid and do not hybridise with non-complementary nucleic acids (eg. do not cross-hybridise or form dimers) under low stringency hybridisation conditions. In particular, the nucleotide sequences enable use of these nucleic acids, without reduction in target hybridisation efficiency with increasing nucleic acid length. The nucleic acids may be used with analyte capture systems, for example medical, veterinary and agricultural diagnostic applications. In particular, the nucleic acid may be used as irrelevant binding pairs in an analyte capture system, such as an array or lateral flow assay.
Owner:PANBIO
Systems, tools and methods of assaying biological materials using spatially-addressable arrays
InactiveUS20060246494A1Strong specificityReduce the possibilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMultiplexingElectrical polarity
Systems, tools and methods of assaying biological material are used to perform complex sandwich hybridization assays. The tools used comprise biological solution probes that are customized for each assay. The solution probe comprises a first region for hybridizing to a probe, in a generic set of capture probes on a universal assay apparatus, and a second region for hybridizing to a target in a sample. The solution probe assembles the target to the assay apparatus by hybridizing the second region to the target and the first region to the capture probe. In array assays, one or more biological samples, having one or more targets per sample, can be multiplexed on the same universal array comprising the generic set of capture probes in an array pattern of features on the substrate. The customized solution probe addresses and assembles a predetermined target-sample combination onto the array at a corresponding capture probe address location. The systems, tools and methods have specificity and sensitivity by systematically providing a reduced likelihood of cross-hybridizations and intramolecular structures in the probes. Specificity and sensitivity of the assay are provided by the incorporation of a chemically modified monomer in the capture probe and a similarly modified monomer complement in the first region of the solution probe. The modified monomers preferentially hybridize with each other. When the probe and respective probe region are oligonucleotides, the complementary modified nucleotides have a reversed polarity relative to the polarity of the respective probe and probe region. The complementary reversed polarity nucleotides form a thermodynamically more stable hybridization to each other than a hybridization between the reversed polarity nucleotide and a complementary nucleotide whose polarity is not similarly reversed.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
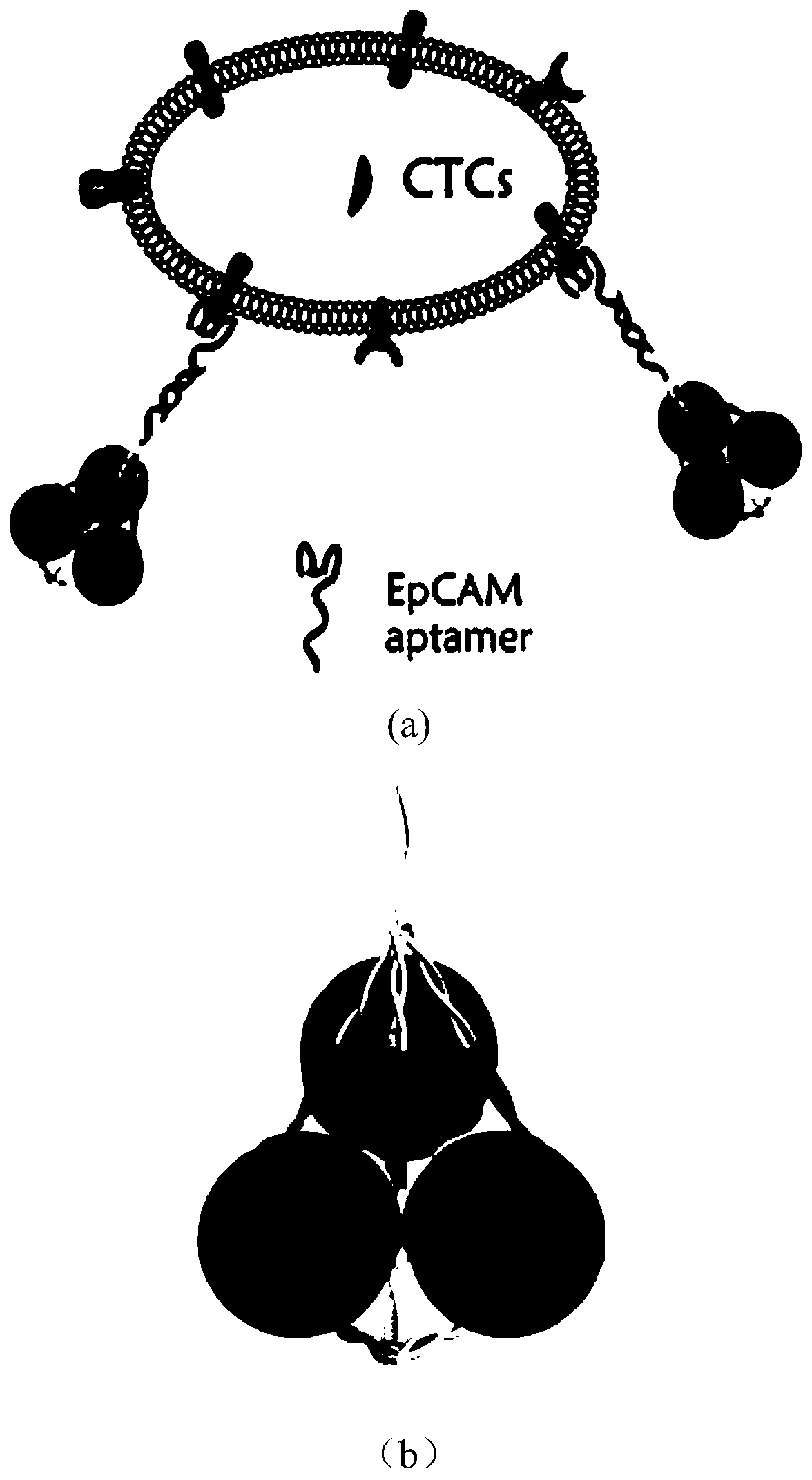
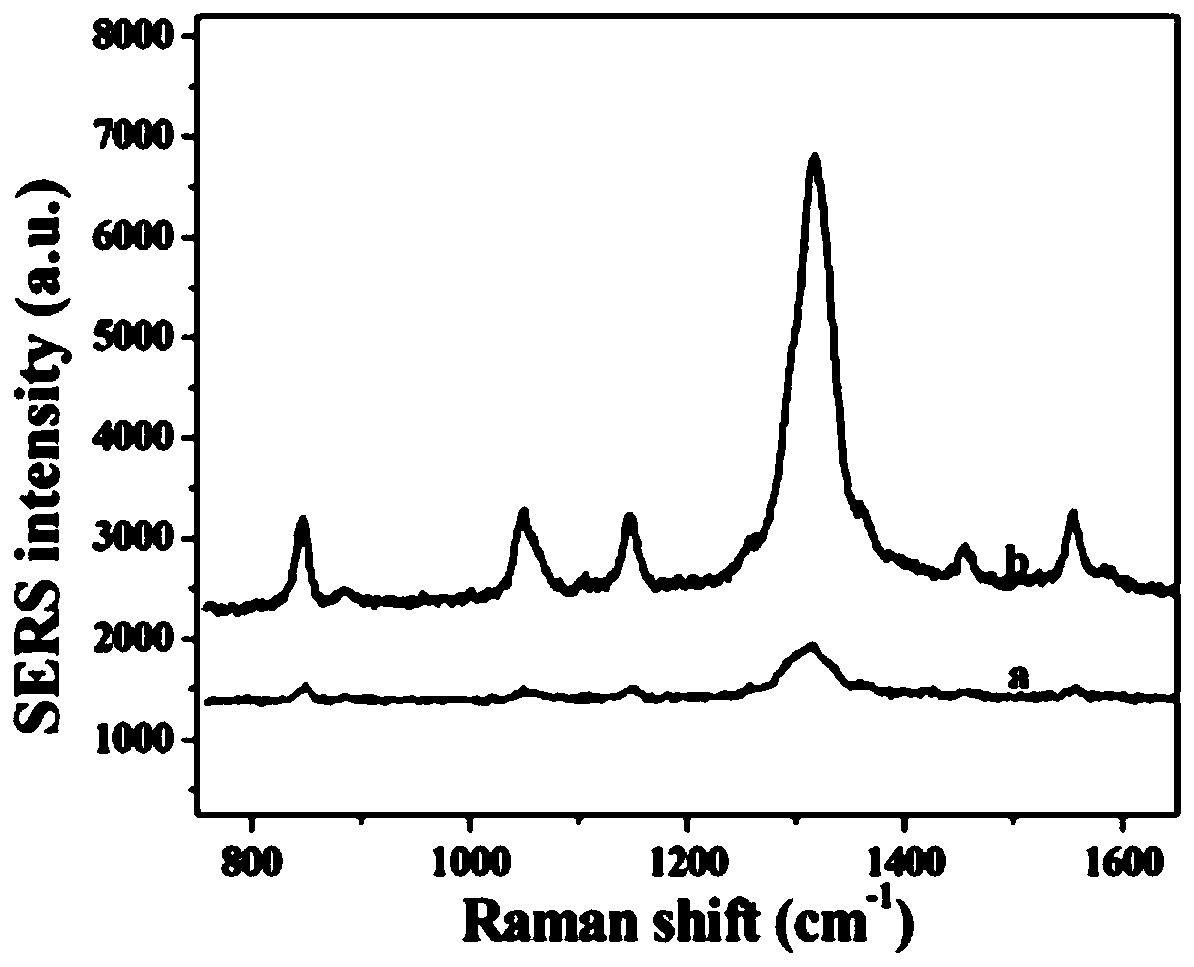
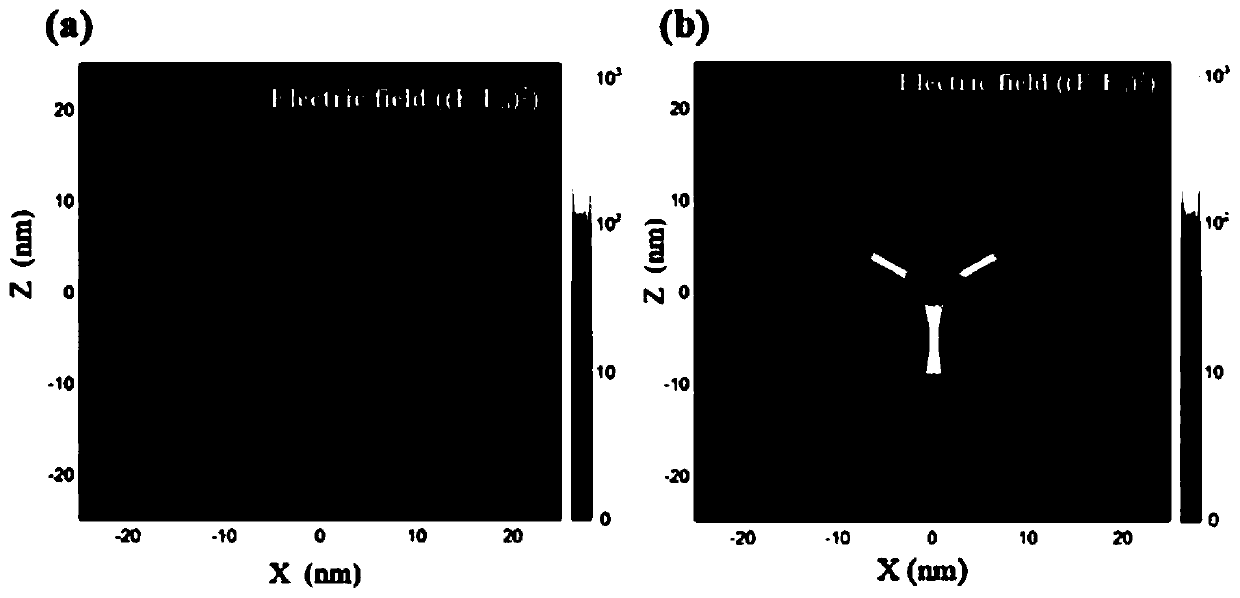
Novel Raman probe and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation and application of Raman probes, and discloses a novel Raman probe and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps of synthesizing a DNA triangular pyramid, and combining the DNA triangular pyramid with nanogold modified with quaternary ammonium salt under the electrostatic action; and combining a thiol-containing Raman probe 5,5'-dithio-bis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) with the nanogold to obtain the novel Raman probe. The probe is combined with an EpCAM aptamer chain, so that the detection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) can be realized. The detection of human breast cancer cells MCF-7 under the background of a large number of negative cells and the detection of the cells MCF-7 in a human peripheral blood environment are realized; and the problems that in the prior art, the probe is low in detection accuracy of the CTCs, poor in practicality and low in sensitivity of target detection, cannot avoid cross hybridization, is weak in repeatability, and is long in detection time and high in price due to enzymatic catalysis for signal amplification during detection are solved.
Owner:山东蓝鹏智能科技有限公司
Breeding goat selection method of crossbred Guizhou white goats
The invention discloses a breeding goat selection method of crossbred Guizhou white goats. The method includes the specific steps that Guizhou white goats and Boer white goats are mated to obtain a Boer first-filial generation, a first batch of basic goat flocks and a second batch of basic goat flocks are screened out, the first batch of basic goat flocks and the second batch of basic goat flocks are subjected to cross hybridization to obtain a Boer second-filial generation, the Boer second-filial generation and the Guizhou white goats are mated to obtain a Boer third-filial generation, then the Boer third-filial generation and the Guizhou white goats are mated to obtain the crossbred Guizhou white goats, and breeding goats are selected. The breeding goats, obtained through the method, of the crossbred Guizhou white goats keep the characteristics, such as high lambing rate, high diseases resistance, good skin toughness, tender meat quality, light goaty flavor and good taste, of the Guizhou white goats, have the advantages, like high growth speed and large size, of Boer goats, and can improve breeding economic benefits of farmers.
Owner:务川自治县宏牧羊业有限公司
Breeding method of a new strain of dairy goat with both milk and meat
ActiveCN104813981BImprove reproductive abilityStrong reproductive rateAnimal husbandryProduction rateCross hybridization
The invention discloses a new milk and meat dairy goat breeding method. The breeding method using excellent localized acclimatization Saanen dairy ewes in Puan as female parents and excellent localized acclimatization Nubian rams in Puan as male parents for grading crossing, selecting excellent first-filial generation ewes of the Nubian rams and the Saanen dairy ewes as female parents and excellent local Nubian goats as male parents for third-generation grading crossing, and selecting excellent filial generation rams and ewes of each grading crossing for cross hybridization fixing (combination) to breed and select the new milk and meat dairy goat having stable genetic nature. The new milk and meat dairy goat breeding method breeds the new milk and meat dairy goat by using the excellent filial generation of Nubian goats, which is high in resistance, large in physique, high in reproductive rate, fast in growth, good in meat quality, high in meat production rate and high in butter fat percentage.
Owner:普安县高棉乡六猫冲隆吉养殖场
Mitigation of Cot-1 DNA distortion in nucleic acid hybridization
InactiveUS7833713B2Suppressing cross-hybridizationReducing cross-hybridizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesCross hybridization
Owner:CHILDRENS MERCY HOSPITAL
Breeding method for a new strain of small tail cold mutton
The invention discloses a breeding method of a new meat-type strain of small tailed han sheep. The small tailed han sheep are used as female parents, and white head Suffolk sheep are used as male parents for introductive hybridization to produce a second generation sheep flock to obtain a Sahan second generation sheep flock; then, first generation Duhan sheep produced by hybridizing white head Dorper sheep varieties with the small tailed han sheep are used as female patients; Australian white sheep are used as terminal male parents for producing Aoduhan second generation through hybridization; then, the sahan second generation female sheep are hybridized with the Aoduhan second generation male sheep to produce Saduaohan new strains; finally, through optimization combination and cross hybridization fixation, the new strain of meat-type small tailed han sheep is obtained through breeding. The obtained new strain has the advantages that the growth and development speed is high; both the meat and milk purposes can be achieved; the body shape is good; the hair in the whole body is white; the applicability is high; the polyembryony property of the small tailed han sheep is realized; the lambing percentage of the female sheep is 200 percent or above; the body weight of the adult male sheep reaches 100kg or higher; the body weight of the adult female sheep reaches 70kg or higher.
Owner:洛宁农本畜牧科技开发有限公司
High-yield corn planting method
InactiveCN107343438AIncrease growth rateIncrease productionPlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsWaxy cornTrapping
A high-yield corn planting method belongs to the field of agriculture; forestry; animal husbandry; hunting; trapping; fishing technology, and particularly relates to a corn planting method. The invention provides a high-yield corn planting method with high yield, green and pollution-free. The high-yield corn planting method comprises the following steps. (1) Isolated planting, staged sowing due to the hybridization of sweet and waxy corn with common corn flour, the grains are easy to become common corn. (2) Seed preparation, selection of excellent hybrids: Excellent hybrids have good potential for increasing yield and are the basis for high yield of corn. The appropriate varieties should be selected in combination with the ecological types of various places. (4) Plowing and land preparation, the plowing depth should be 18cm. For high soil fertility, thick plowing layer, large amount of basal application, plowing depth can reach 20cm; otherwise, it should be shallow. (5) The sowing depth is generally 4 to 6 cm. But generally not more than 8cm. It should be noted that too shallow sowing in soil with better soil moisture and fertility will produce a large amount of ineffective tillers at the seedling stage.
Owner:周兰芝
Microarray Method
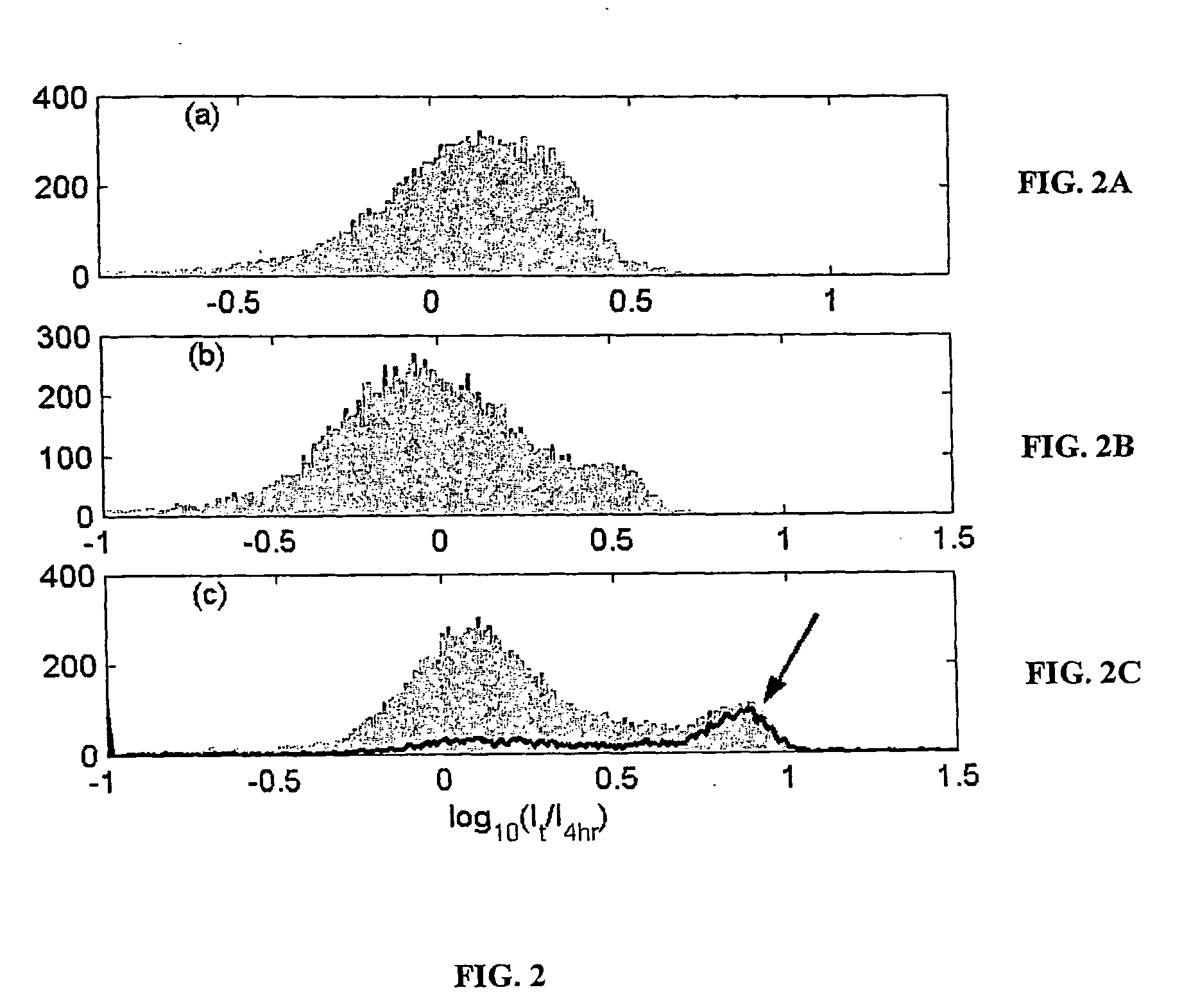
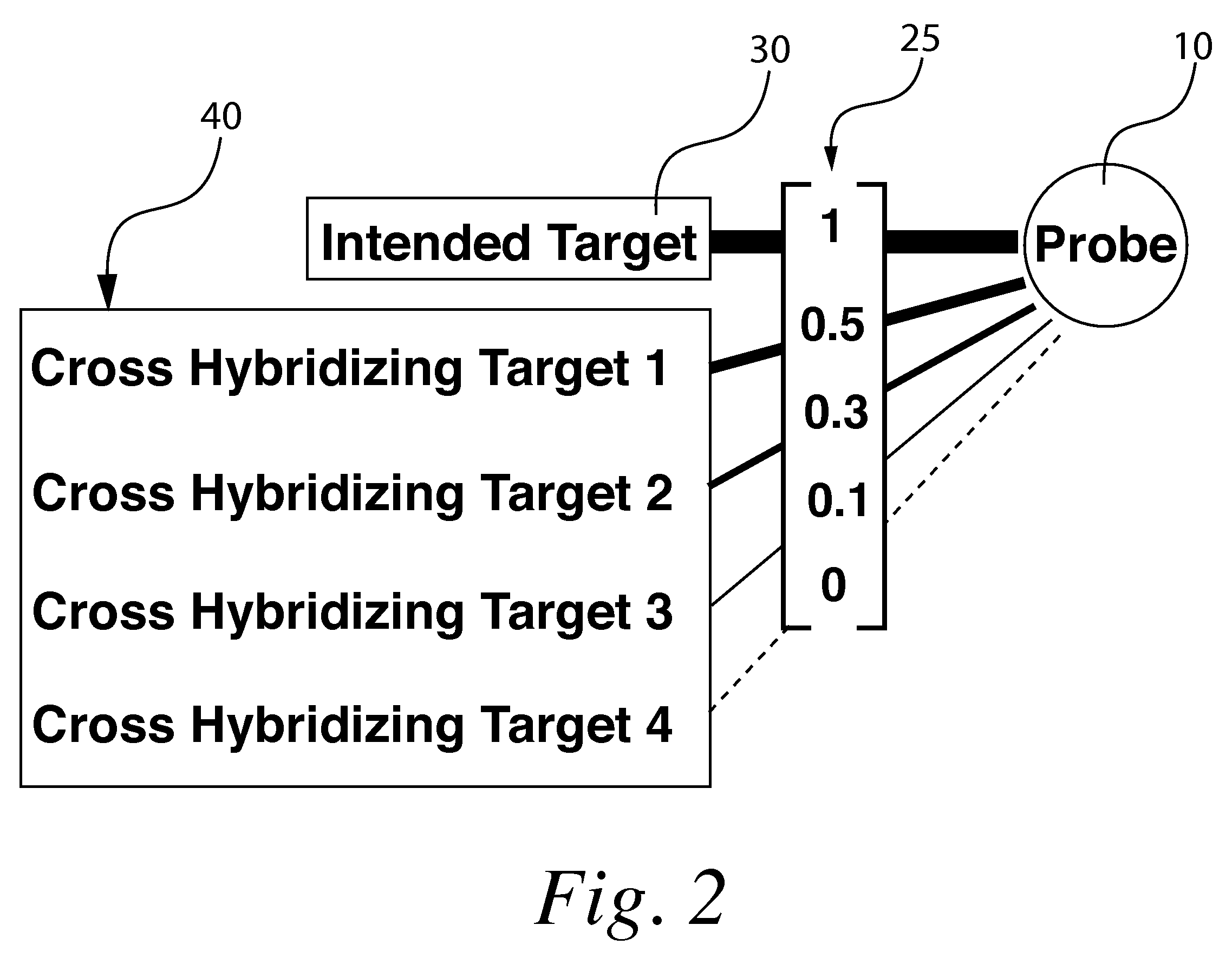
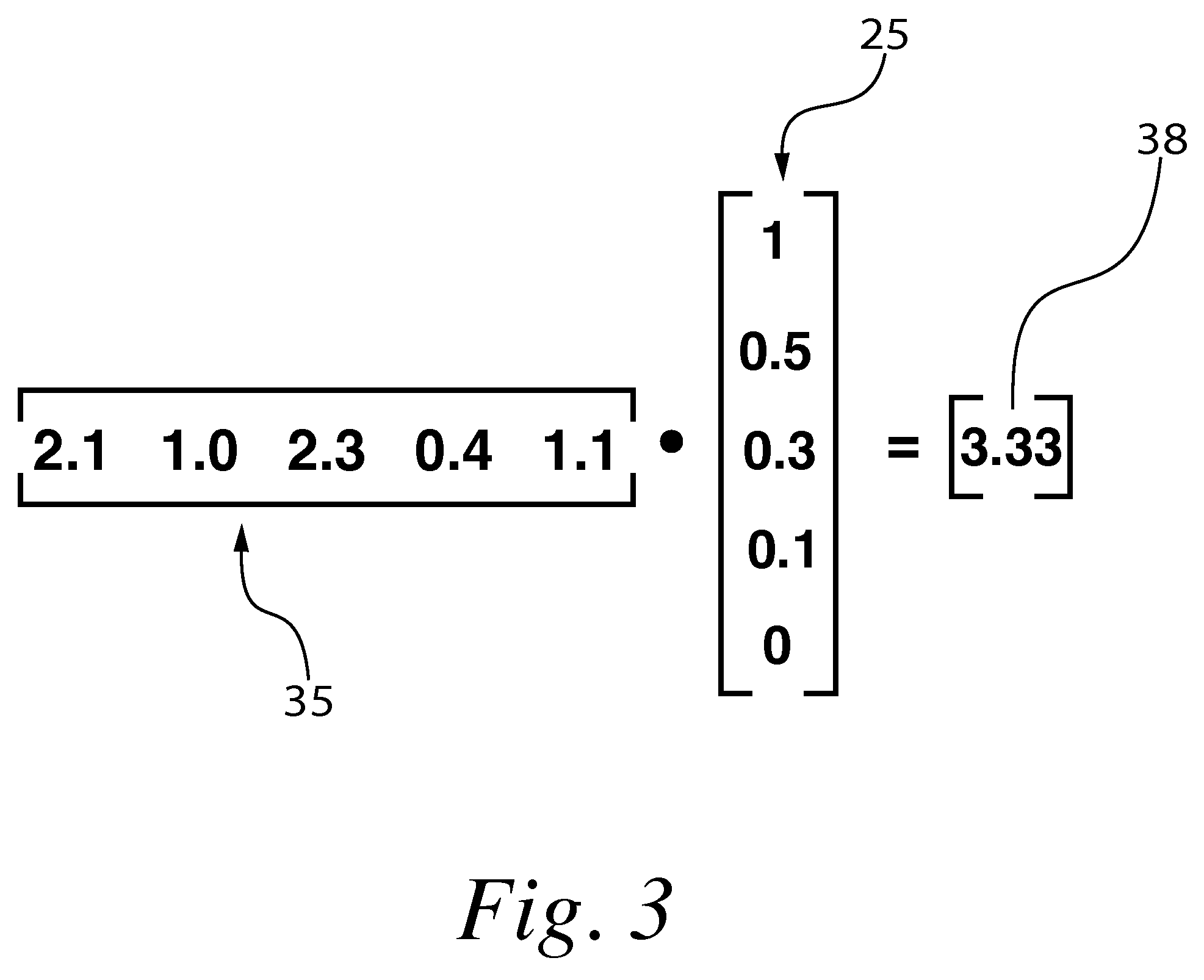
A method for correcting microarray data for the effects of cross-hybridization comprising multiplication of microarray probe hybridization intensities with the inverse or pseudoinverse of a matrix of cross-hybridization potentials between probes and targets. This matrix of cross-hybridization potentials may be determined experimentally by repeating a microarray experiment with each of the targeted genes individually present to determine the cross-hybridization of that targeted gene to each probe, or alternatively, computational models of hybridization may be employed. This represents a new paradigm for handling the problem of cross-hybridization and also can be used in probe-set design strategies.
Owner:DOTAN NATAN
Set of probes for the detection and typing of 46 human papillomavirus mucosal types
InactiveUS9096910B2Accurate prevalence resultImprove automationSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesHuman papillomavirusTyping
We have developed a set of probes to detect and identify 46 types of mucosal human papillomaviruses (HPV). These probes recognize the variable region comprised between the 2 conserved regions of the published GP5+ / GP6+ set of PCR primers. The 46 probes have been shown to hybridize, as intended, to the DNA derived from the following HPV types: 6, 11, 13, 16, 18, 26, 30, 31, 32, 33, 35, 39, 40, 42, 43, 44, 45, 51, 52, 53, 54, 56, 58, 59, 61, 62, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 89, 90, 91 and 97. The hybridization of each probe is specific for each type without any cross hybridization among types and it is sensitive enough to allow detection of PCR products for genotyping of HPV DNA contained in clinical samples.
Owner:SEVERINI ALBERTO +1
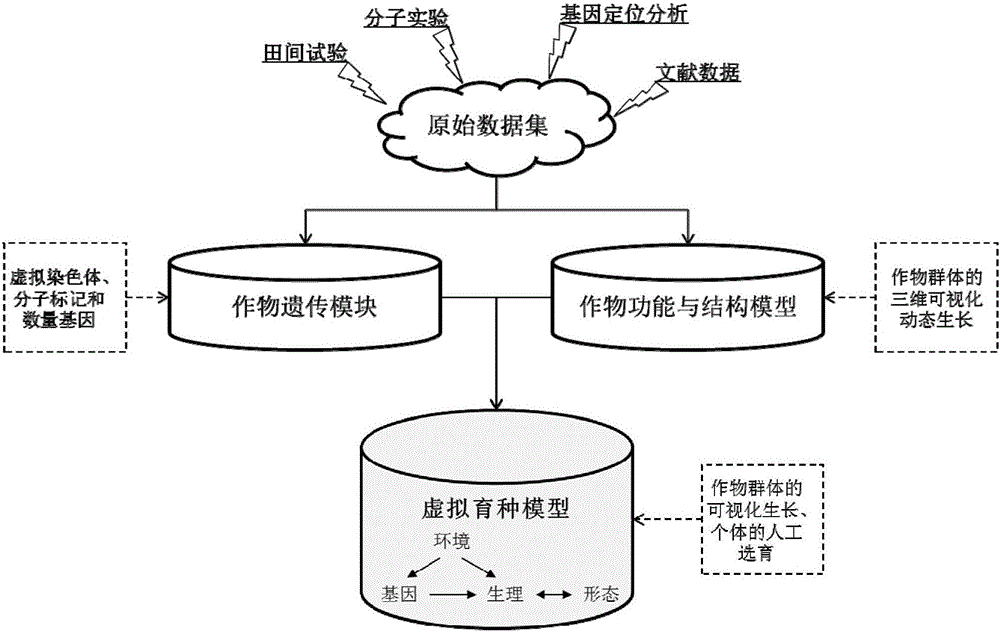
A Crop Virtual Breeding Method Based on Plant Function and Structure Model
ActiveCN104965997BRealize simulationComprehensive considerationPlant genotype modificationSpecial data processing applicationsData setOriginal data
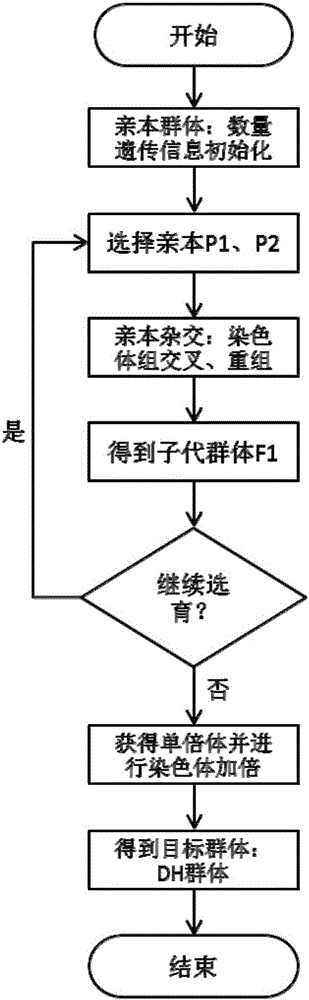
A crop virtual breeding method based on plant function and structure model. This method will combine the physiological and structural crop virtual growth model and quantitative genetic information to achieve the purpose of virtual breeding by simulating the growth and development process and reproduction process of the crop. The steps are: collecting physiological data, morphological data, and quantitative genetic data of the crop. Construct the original data set with the growth environment data; based on the original data, construct the crop function and structure model through the method of computer graphics and the principles of crop physiological ecology; construct the genetic module, including the quantitative genetic information, and establish the parameters from the quantitative genetic information to the relevant model connection; add the simulation of genetic operations such as crossover and recombination in the hybridization process, and realize the simulation of the crop reproduction process; through the selection and hybridization of individuals in the model, virtual breeding can be realized; the proposal of the present invention can use computer technology to realize crop breeding Virtual breeding, thus assisting and supporting traditional breeding processes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com