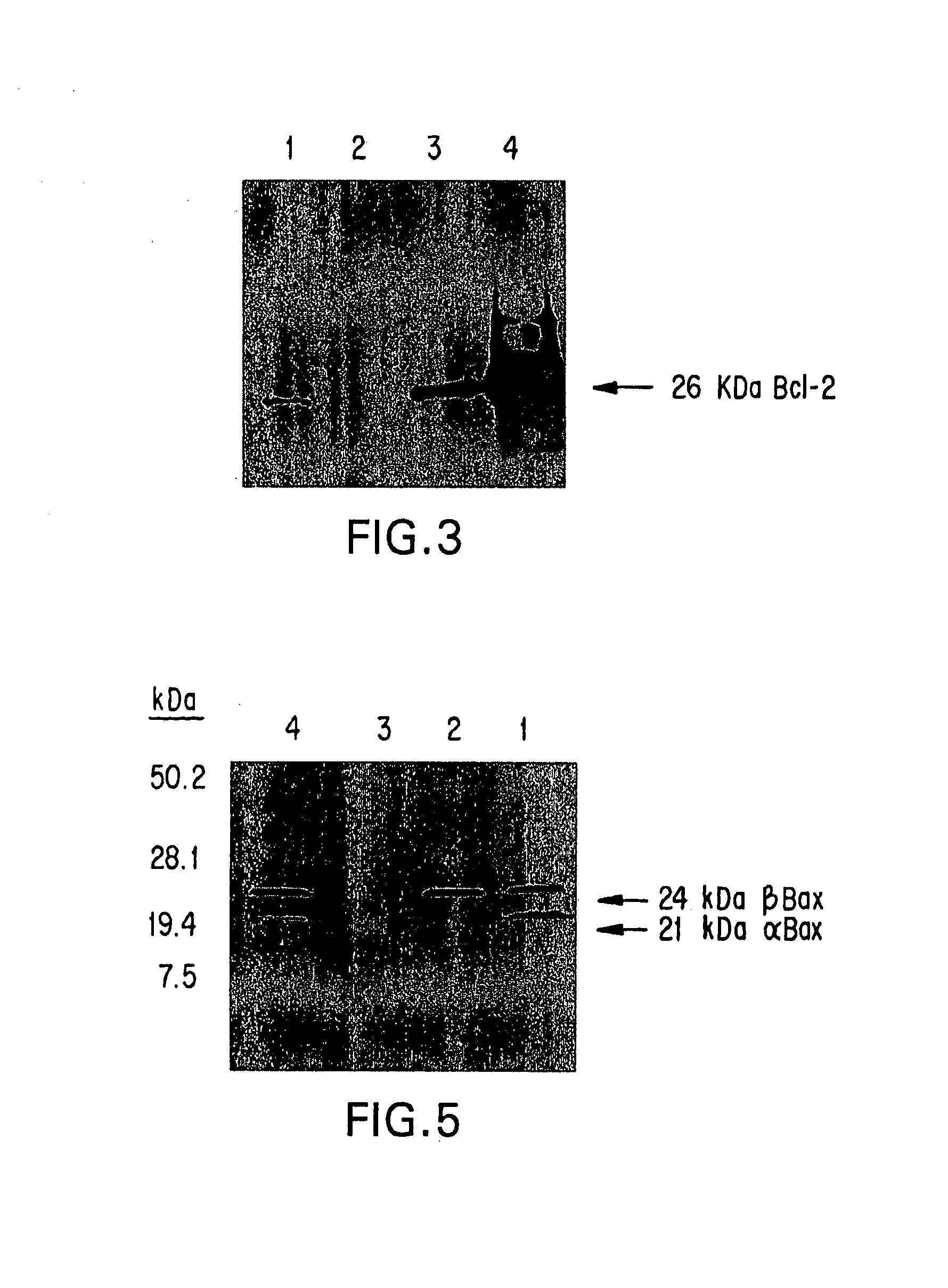
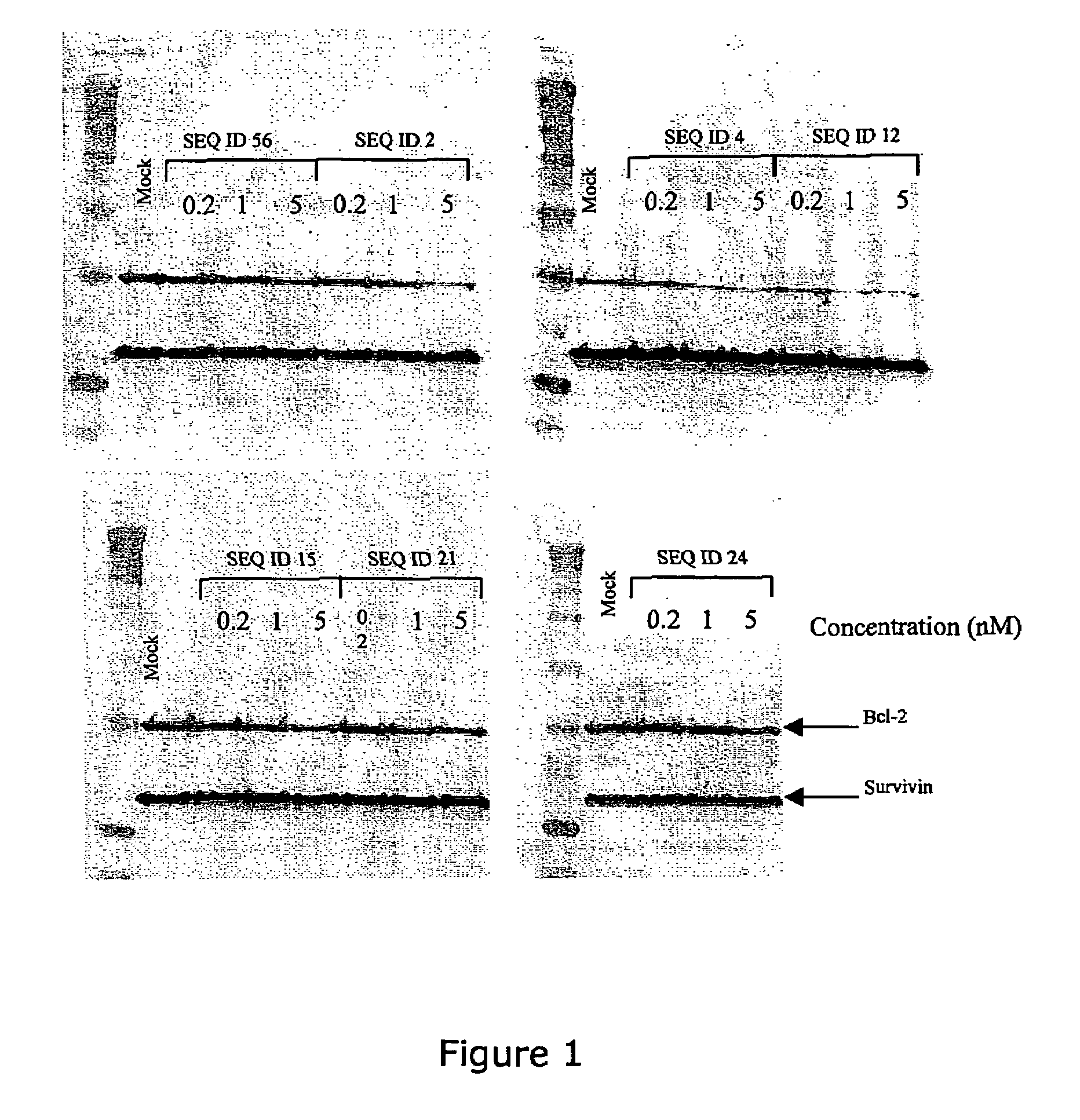
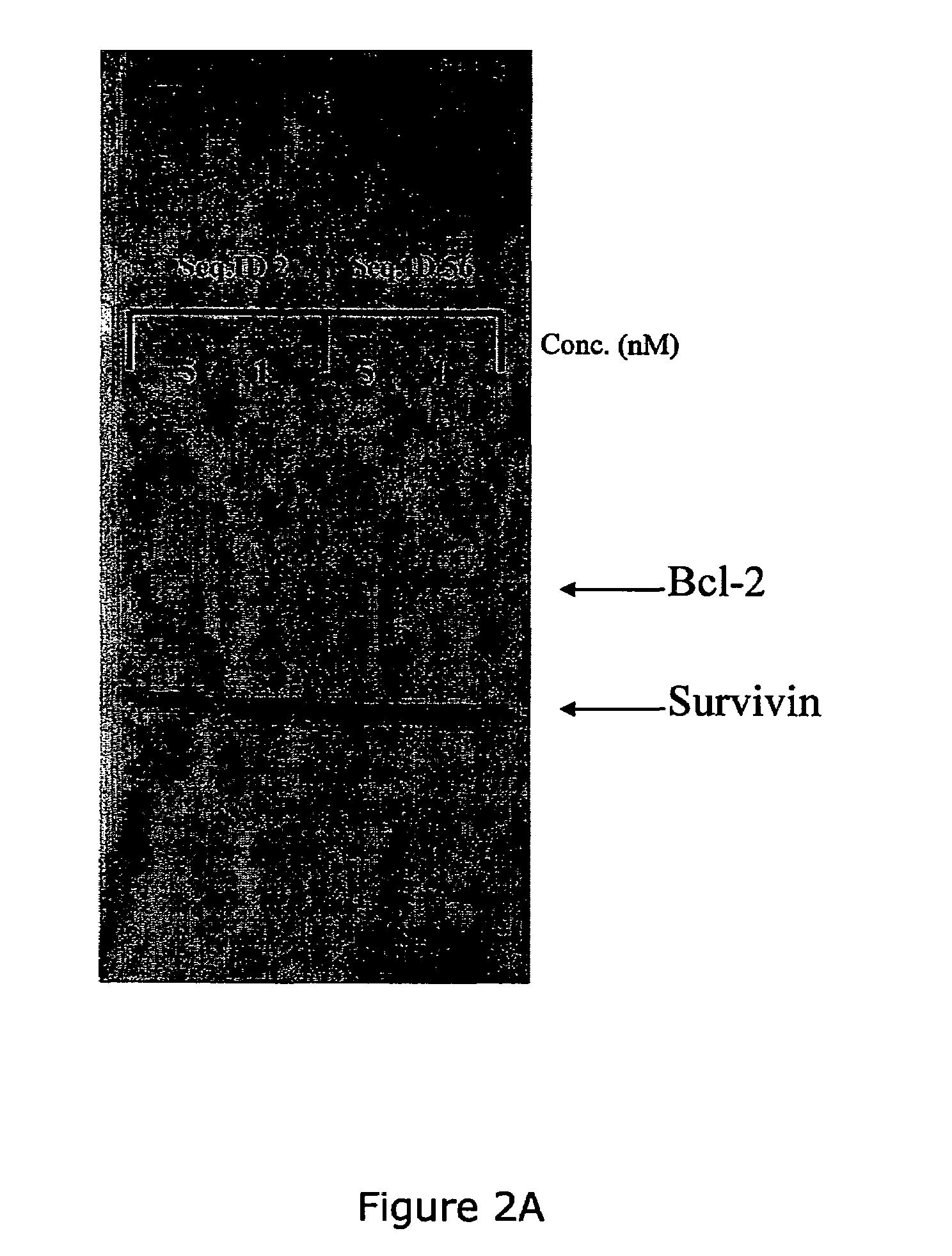
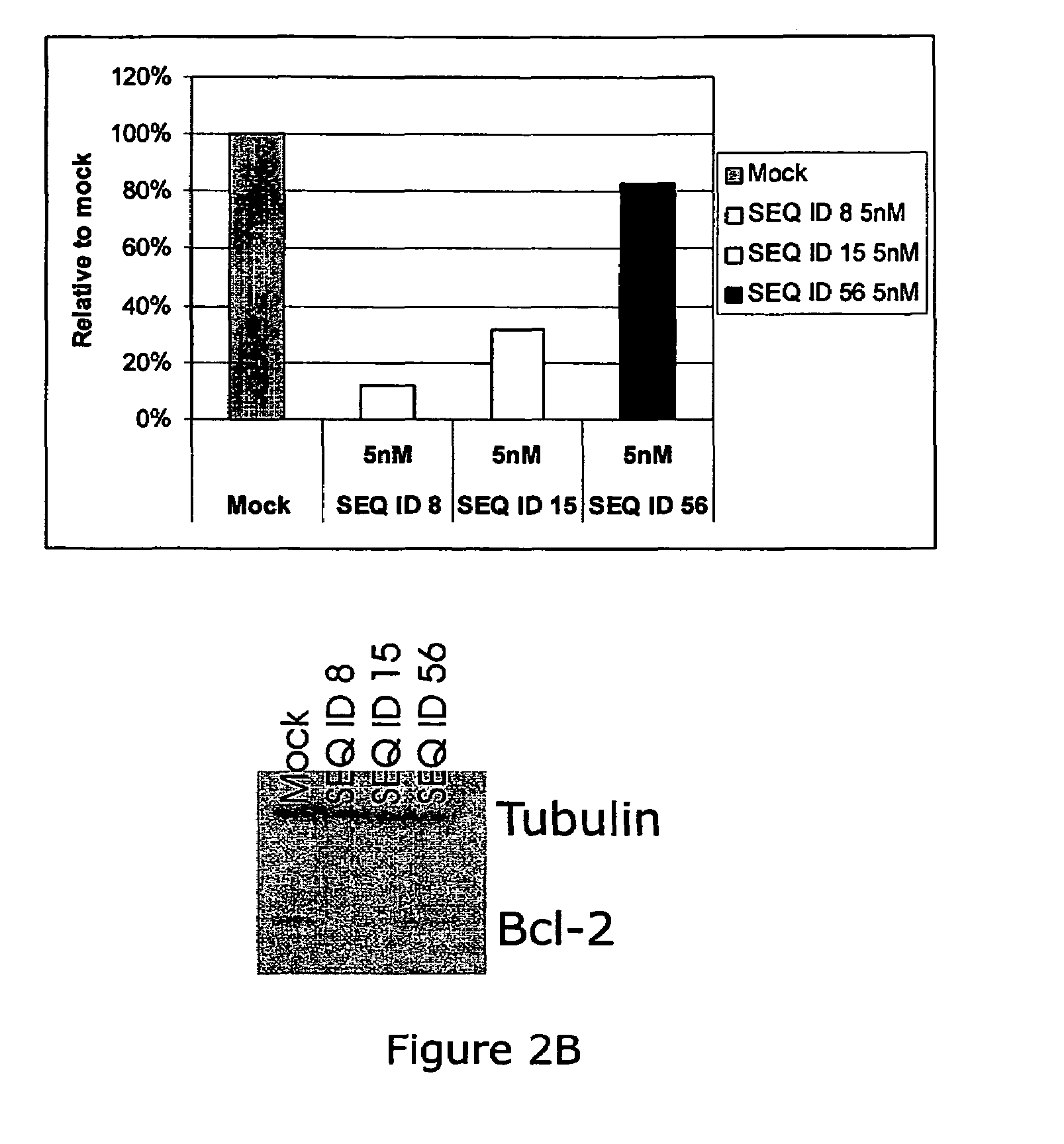
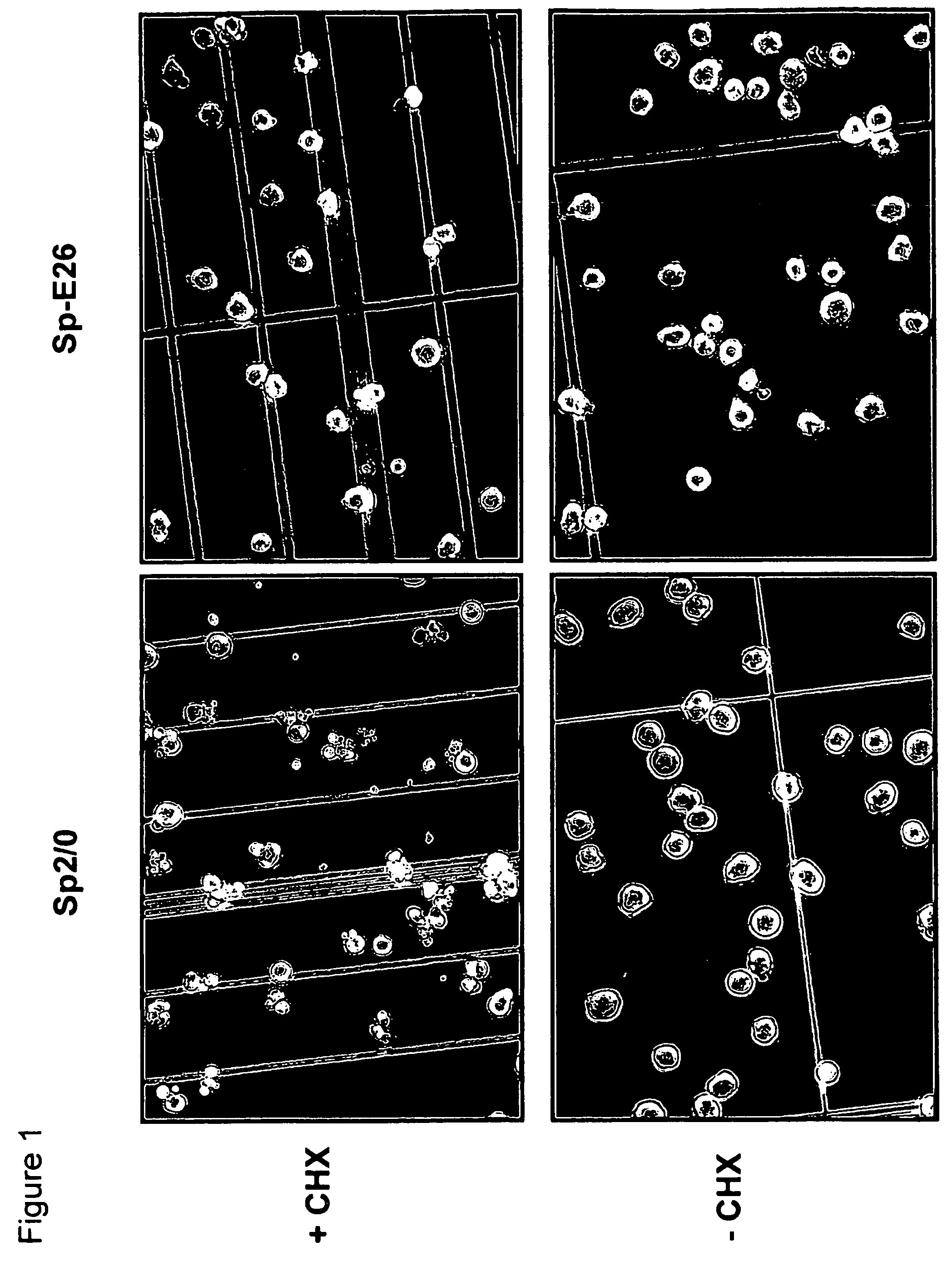
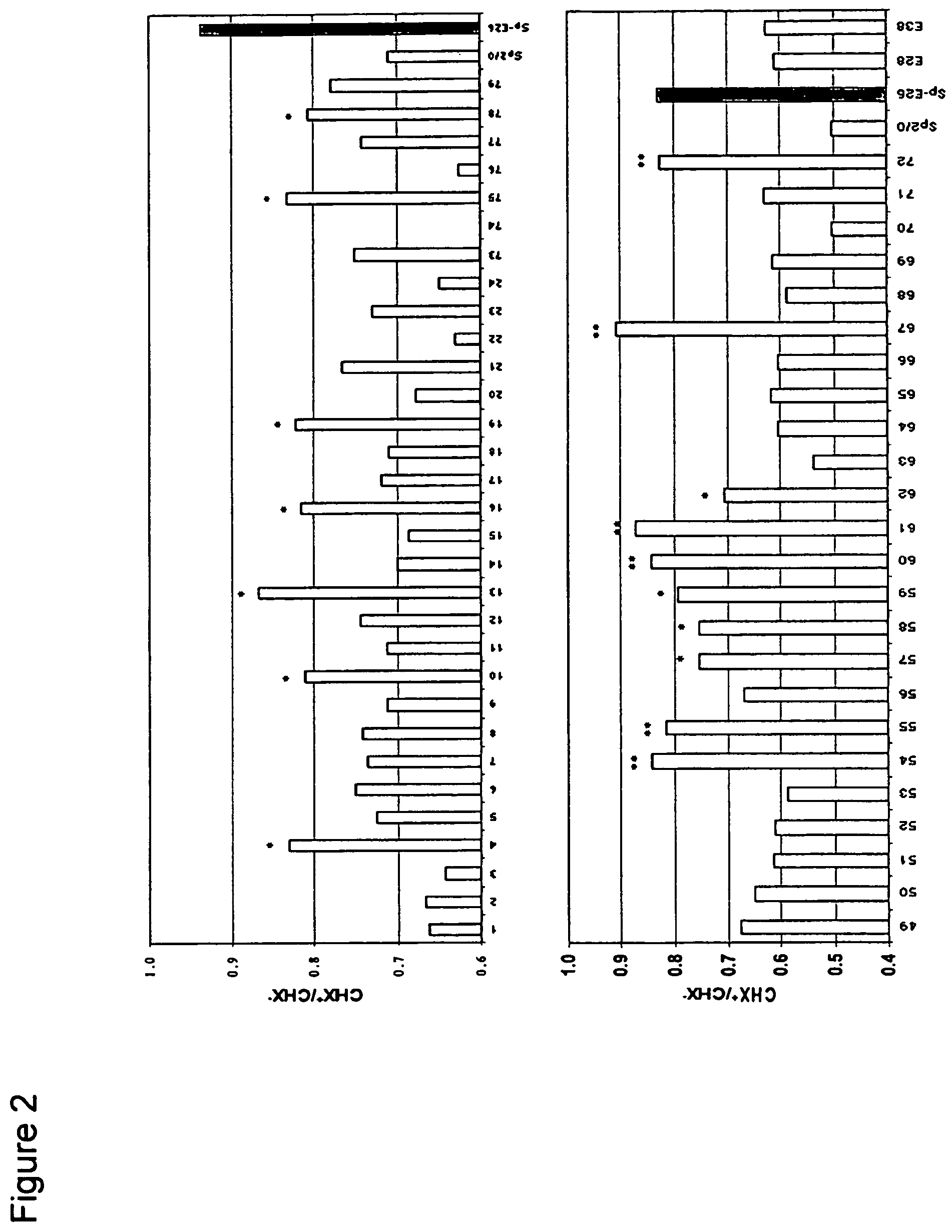
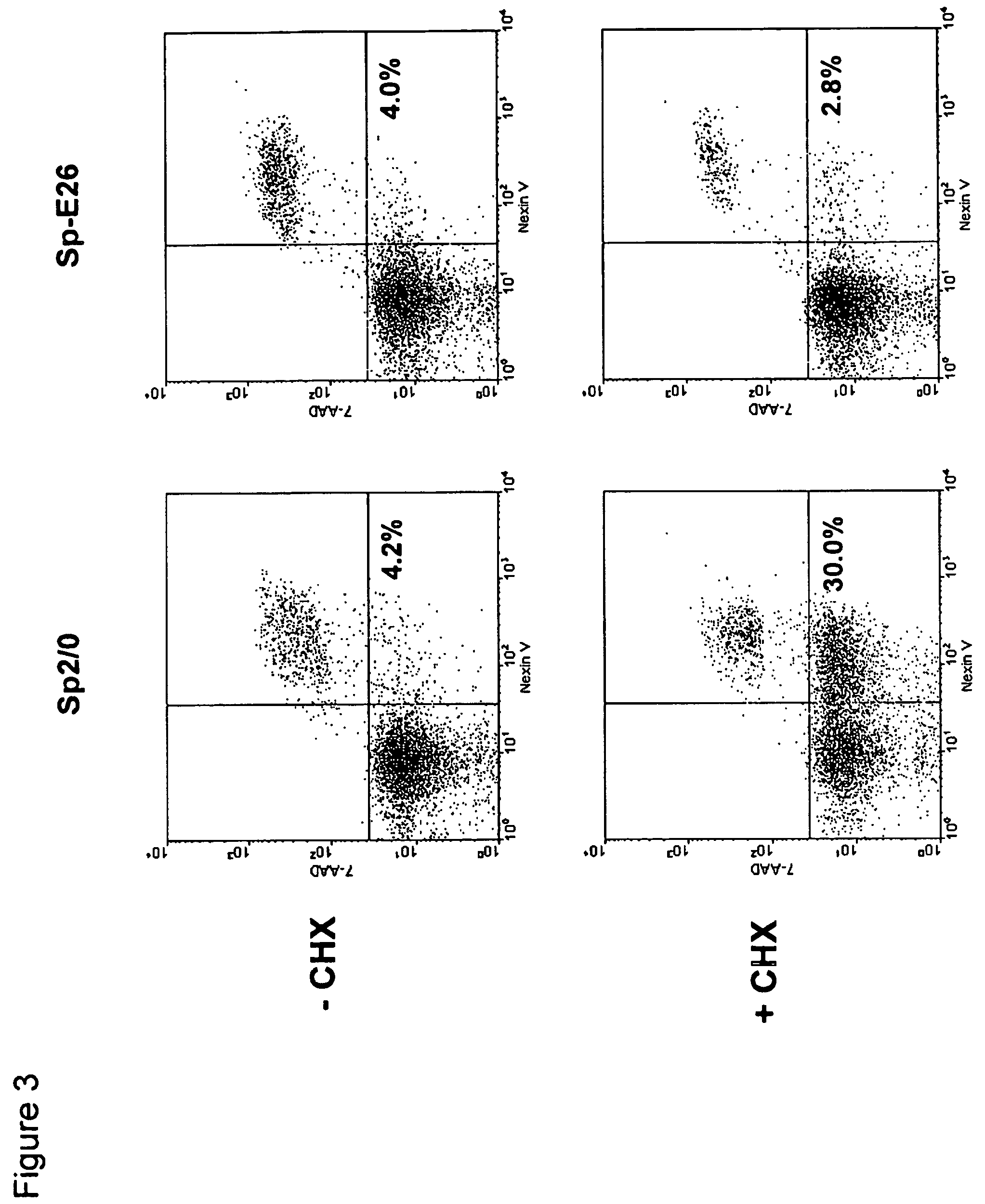
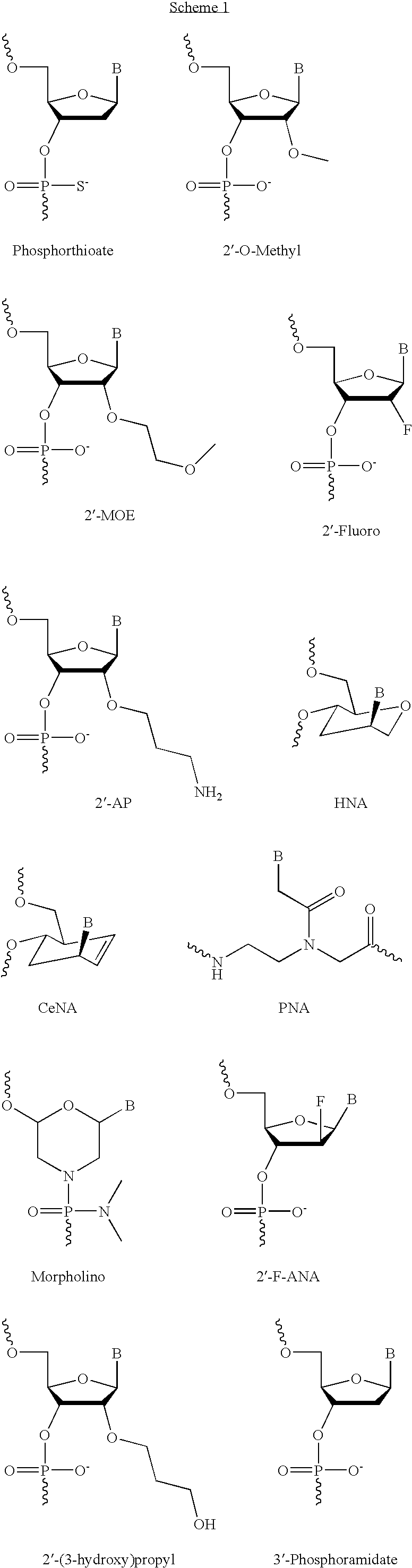
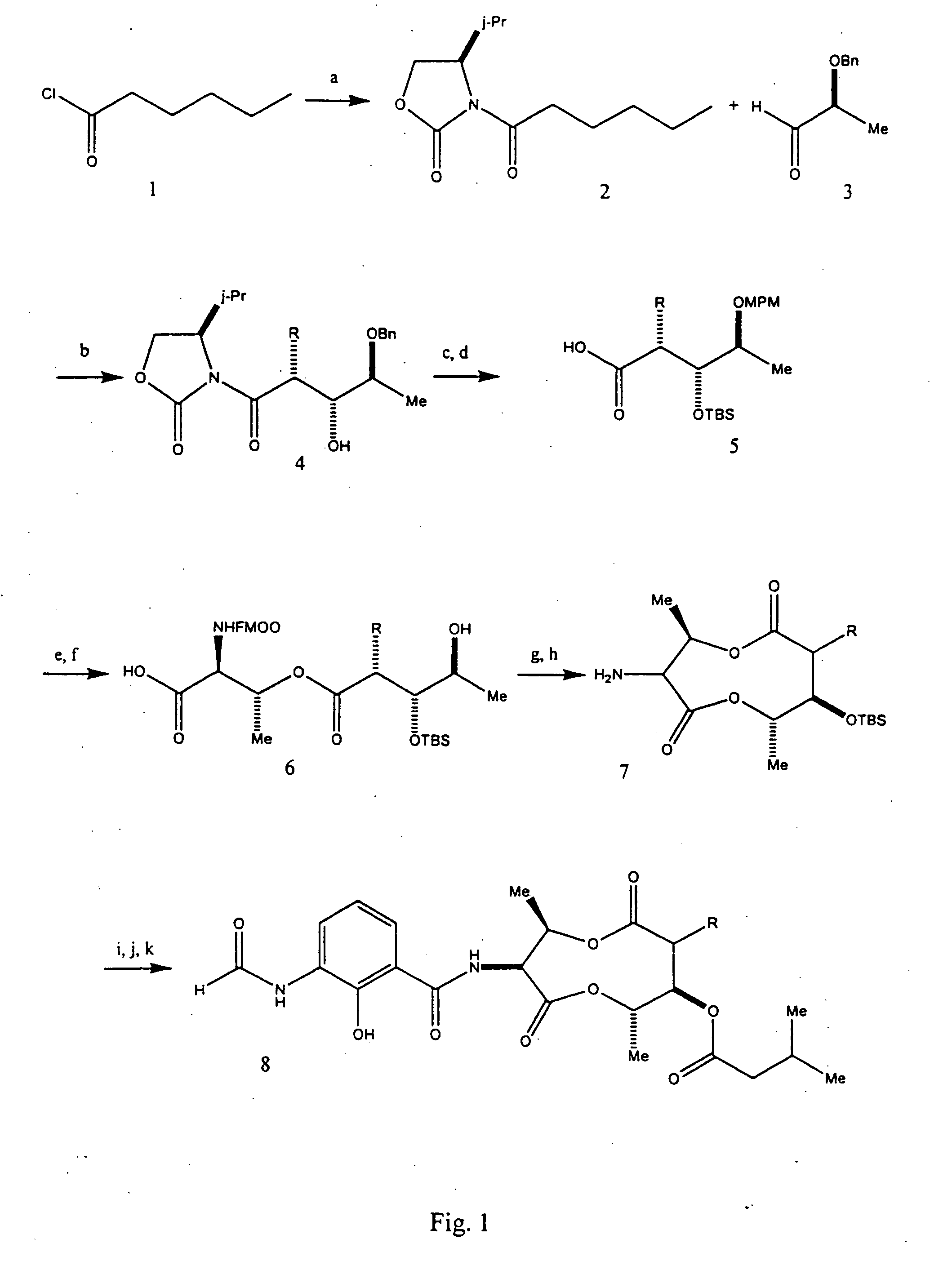
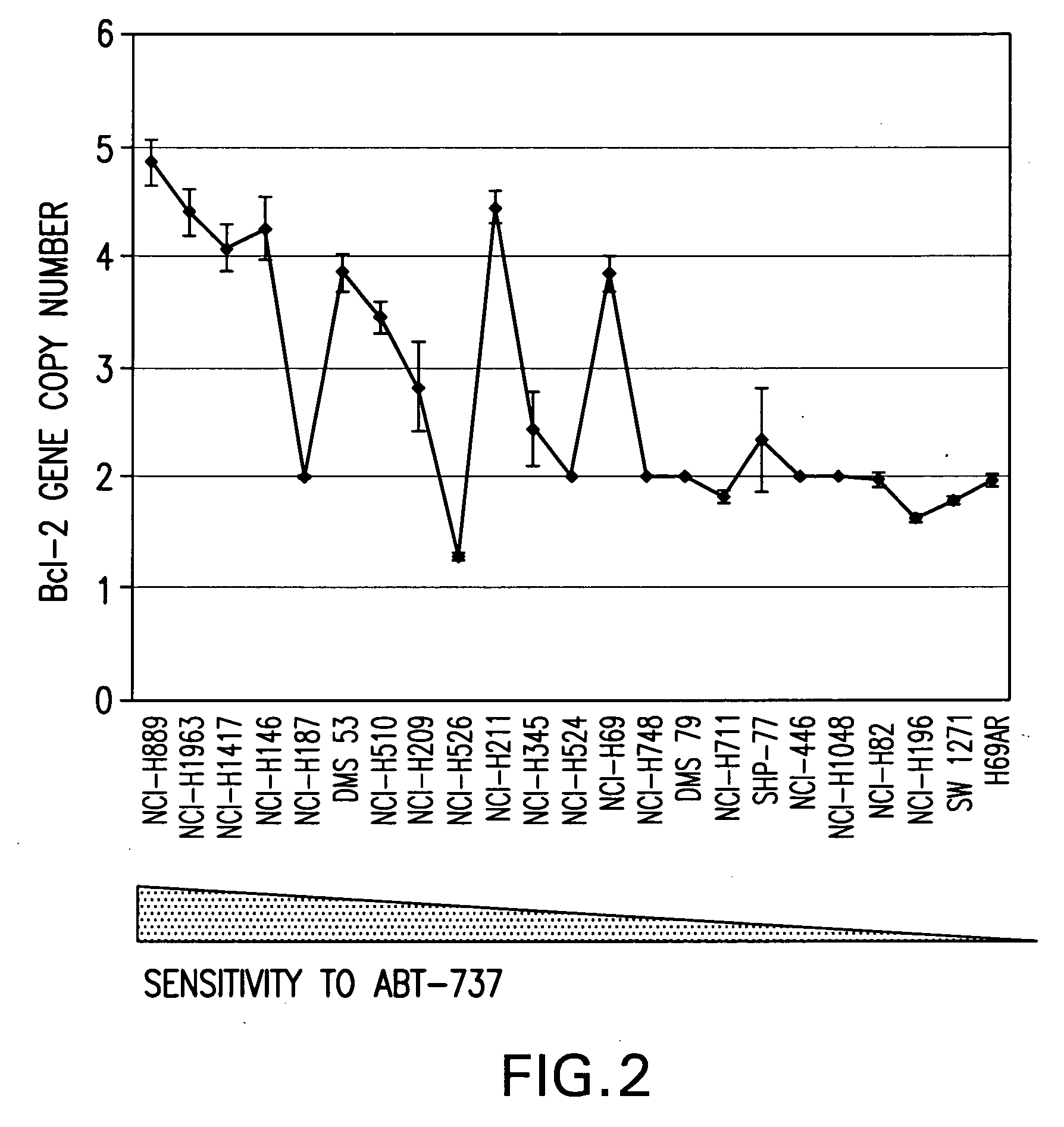
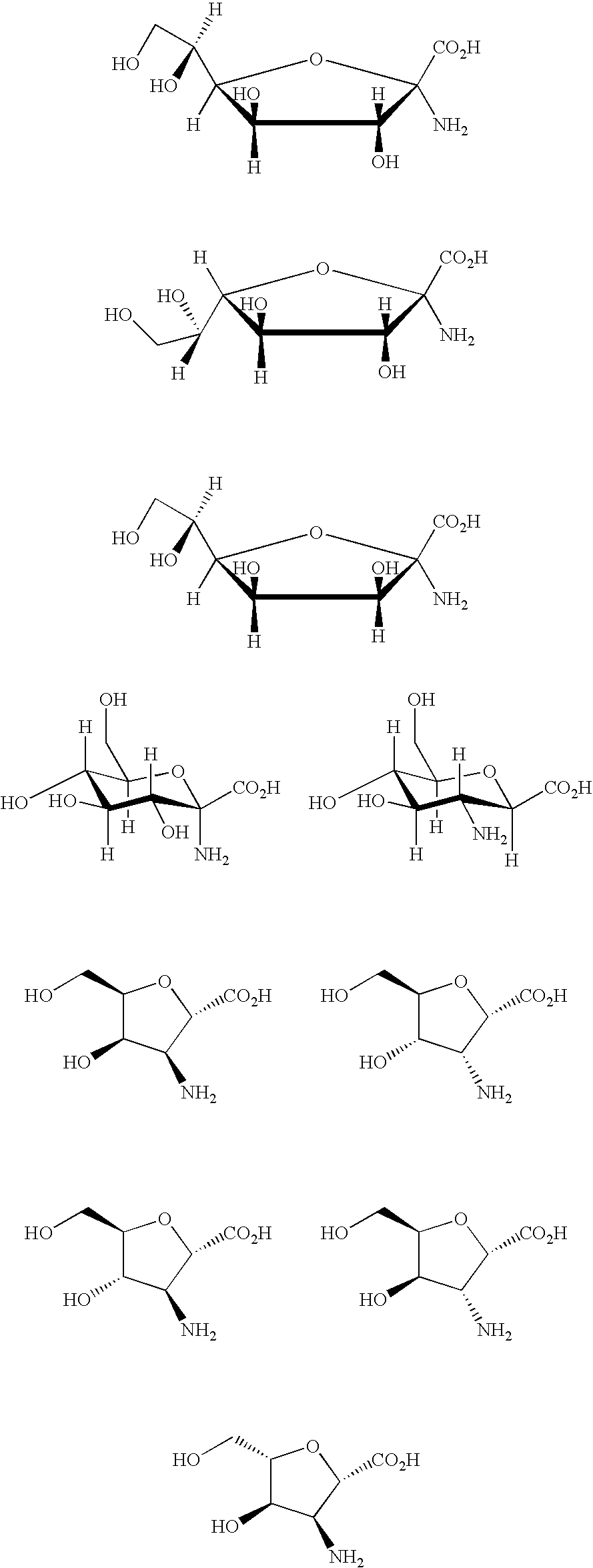
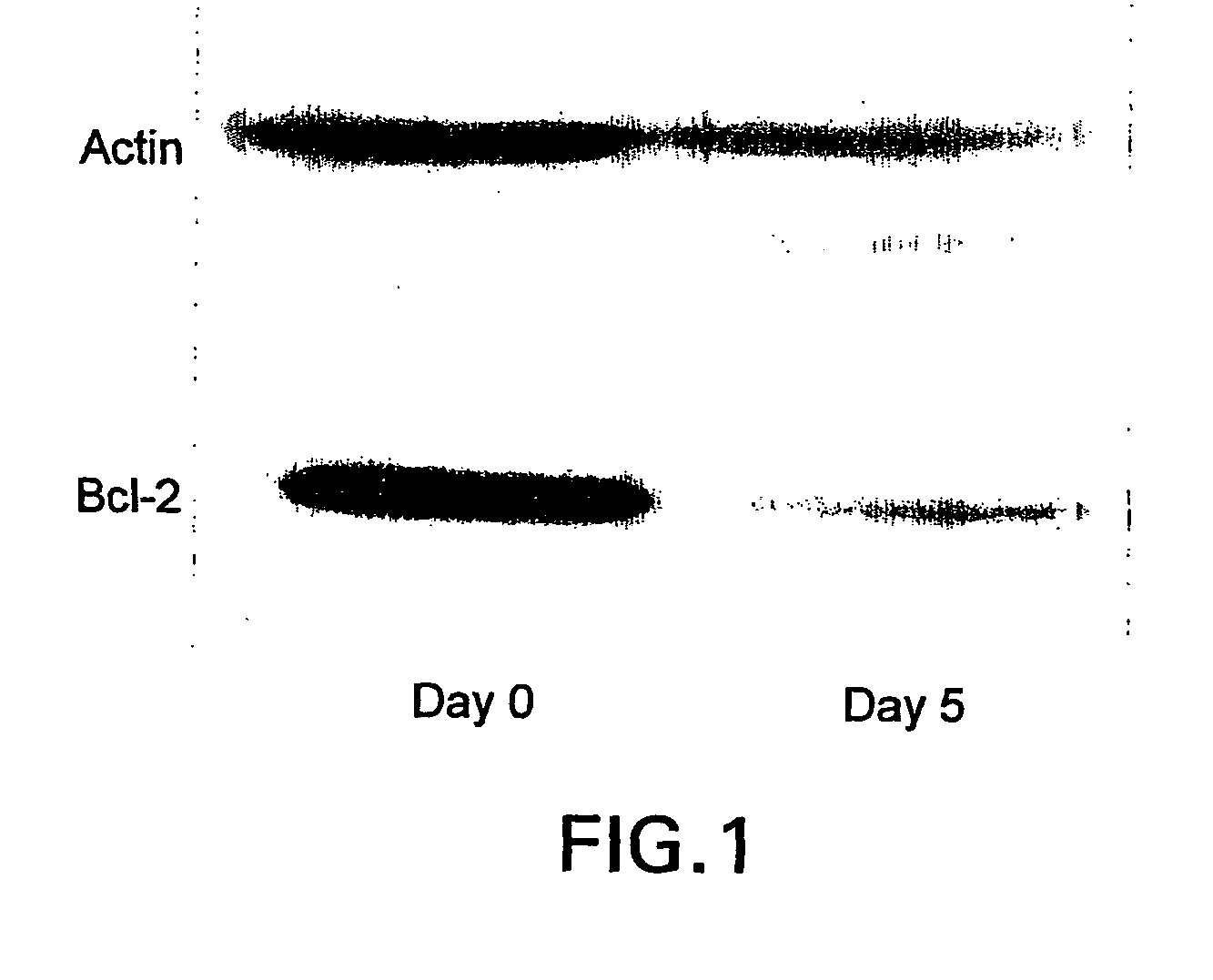
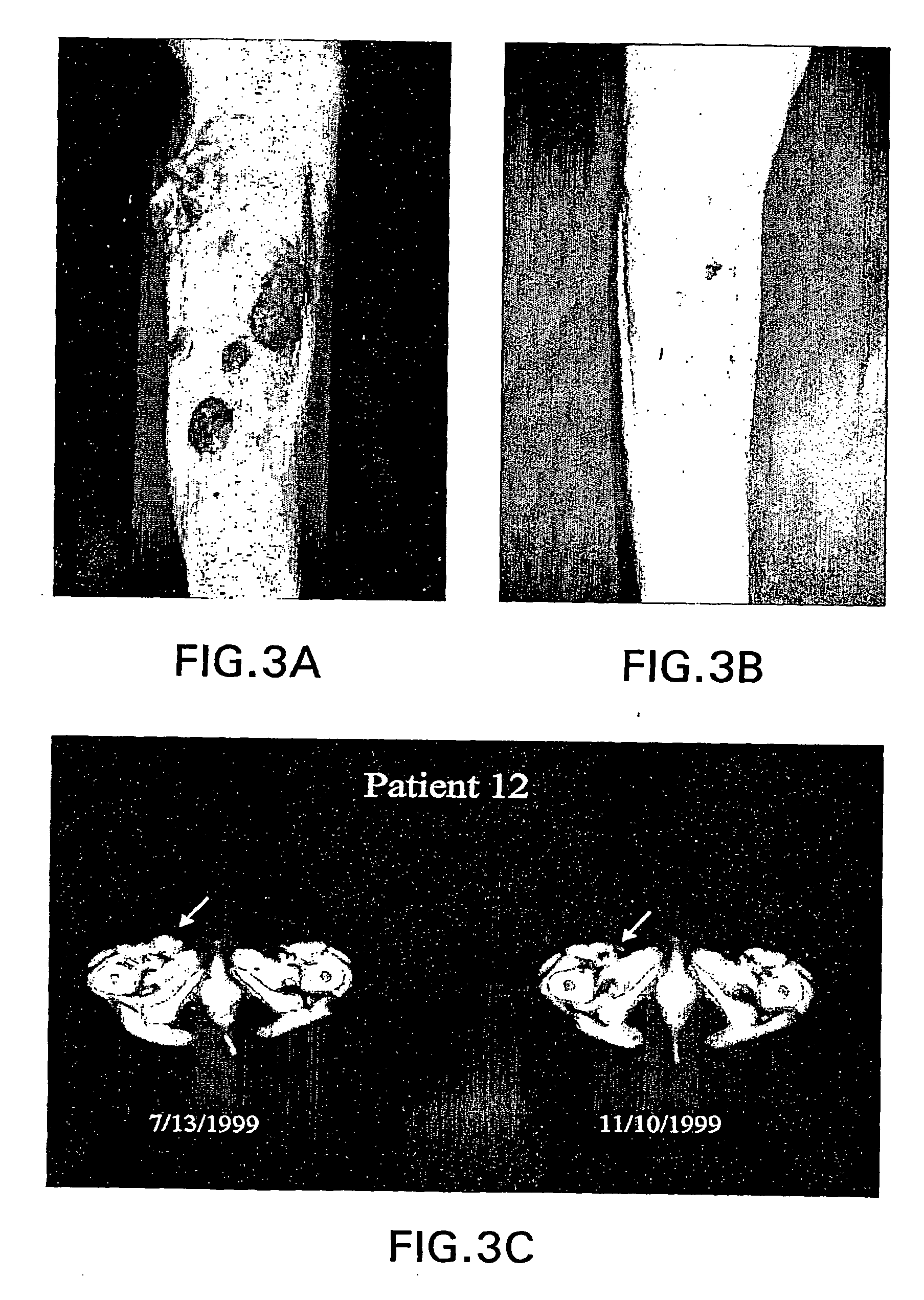
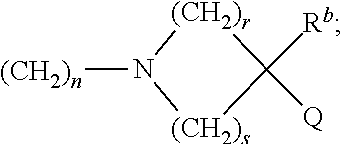
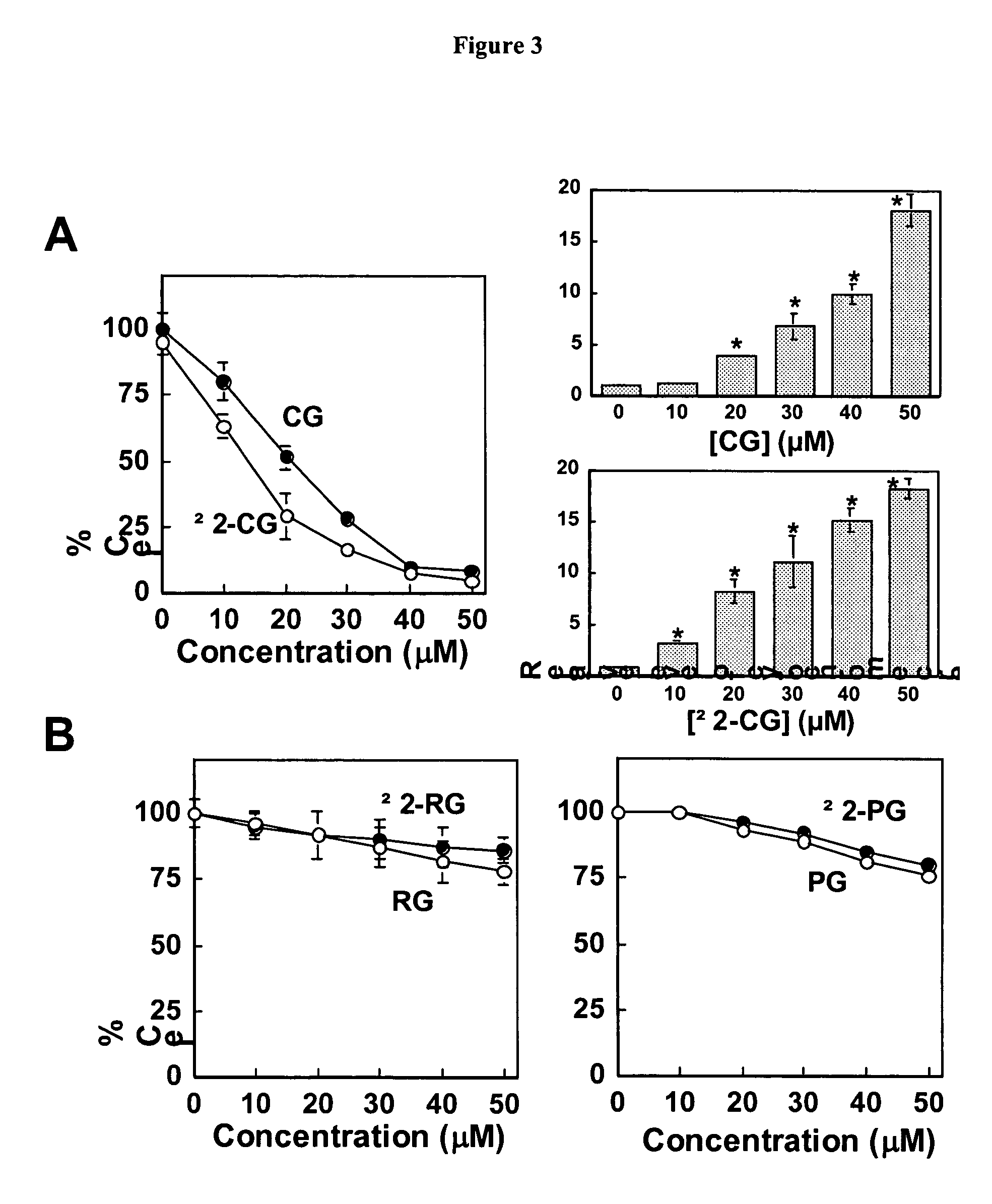
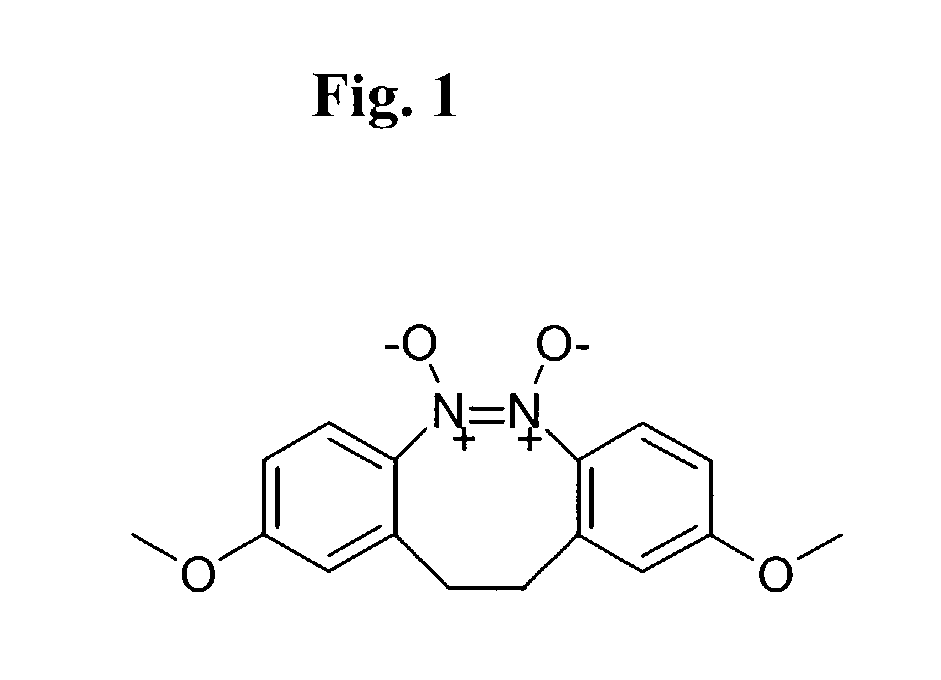
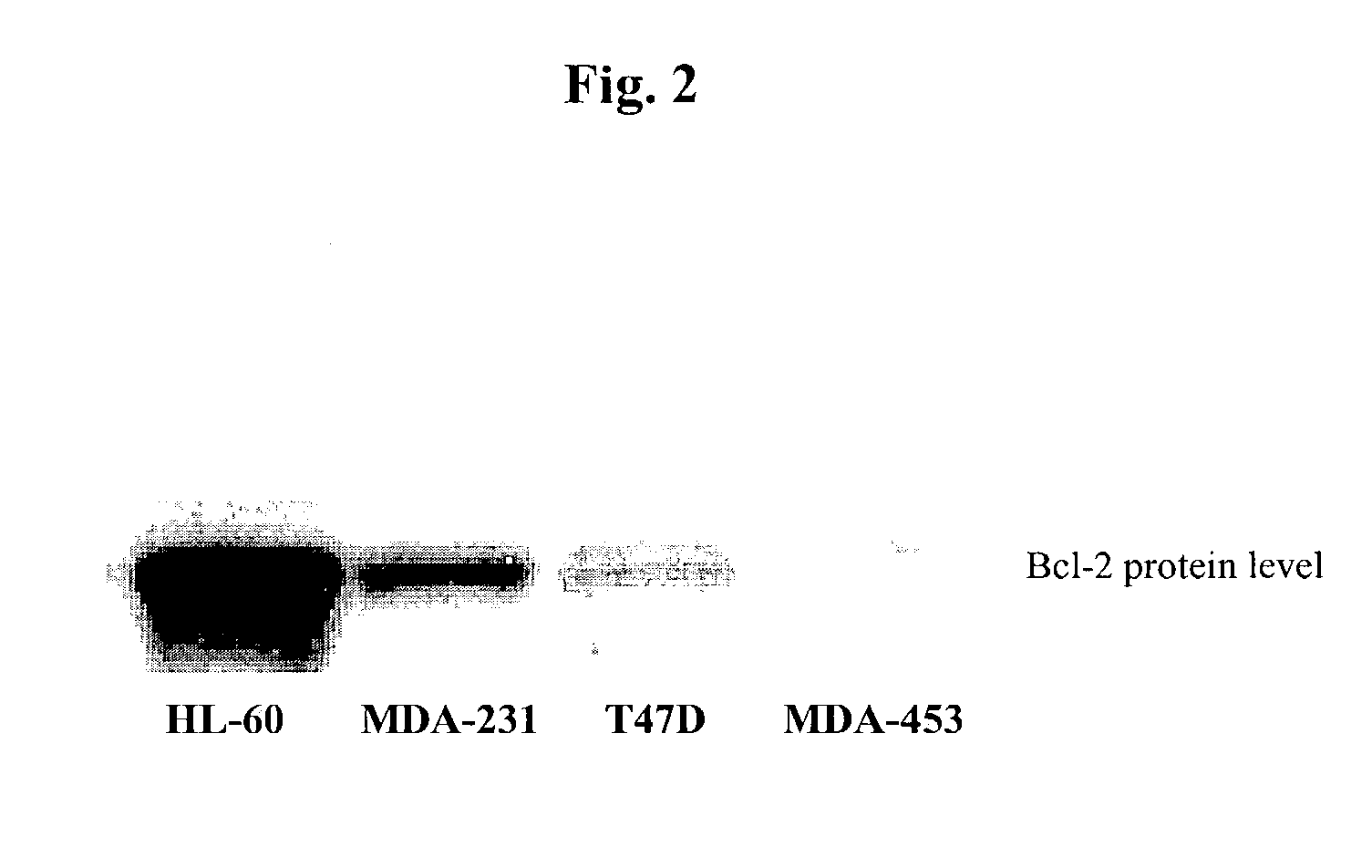
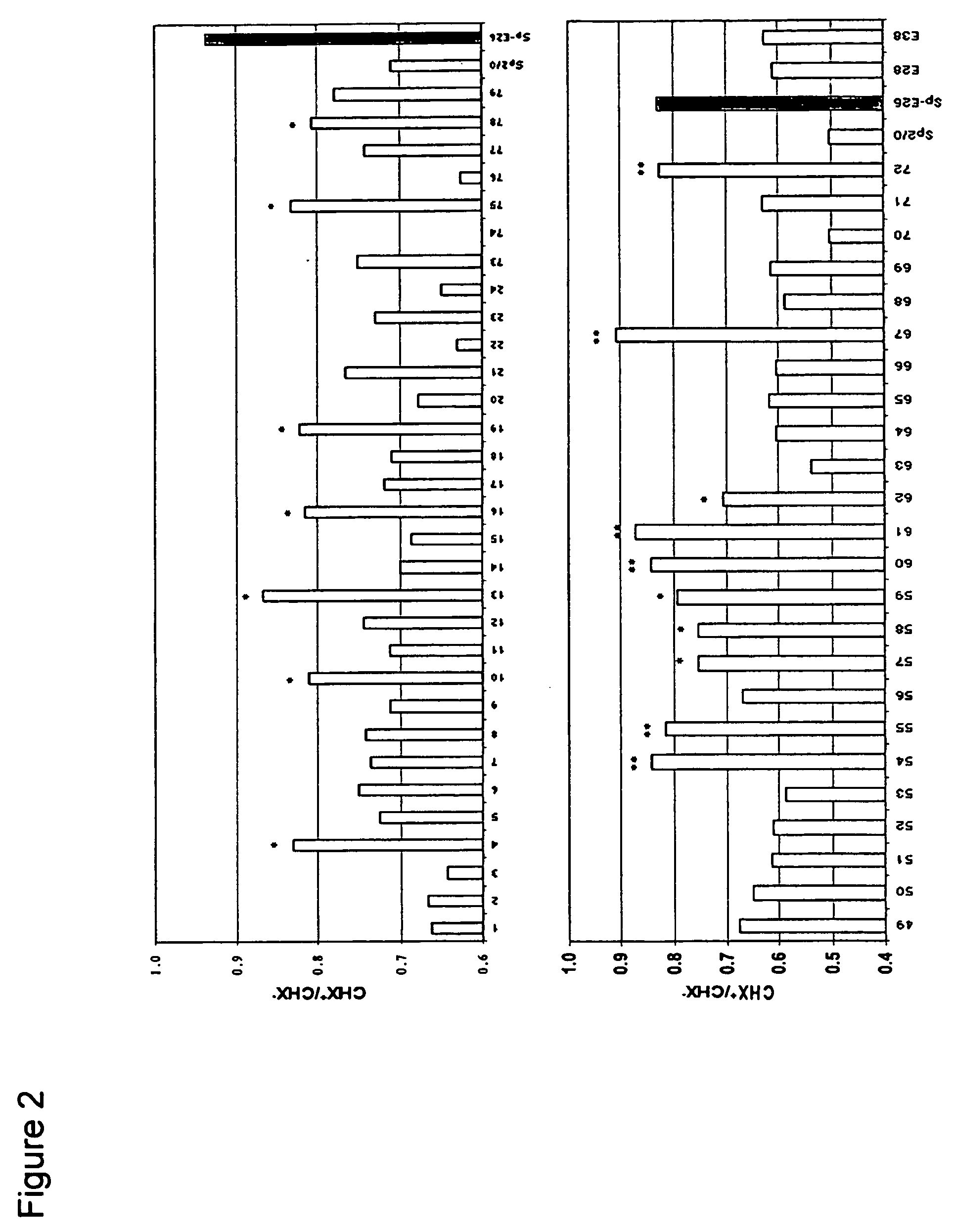
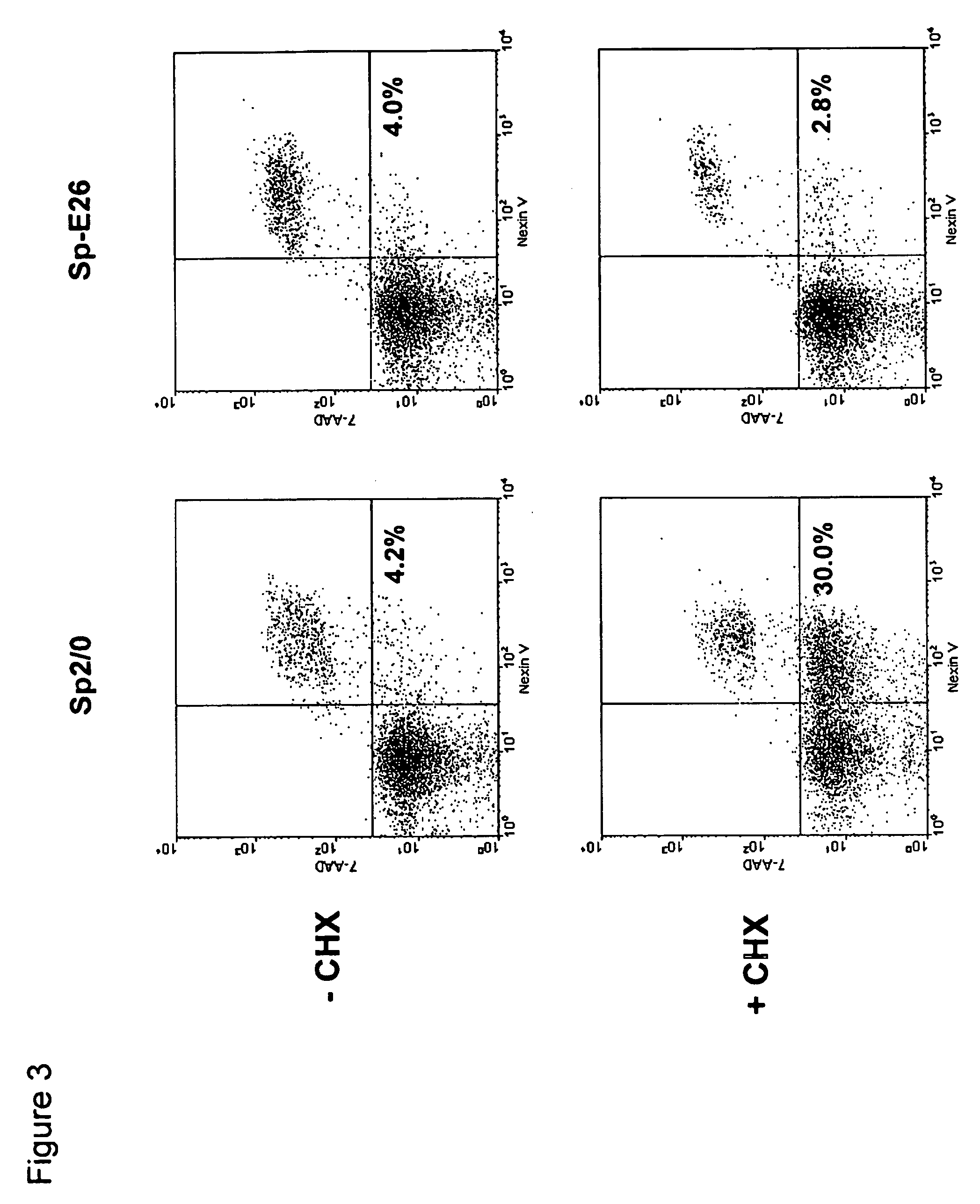
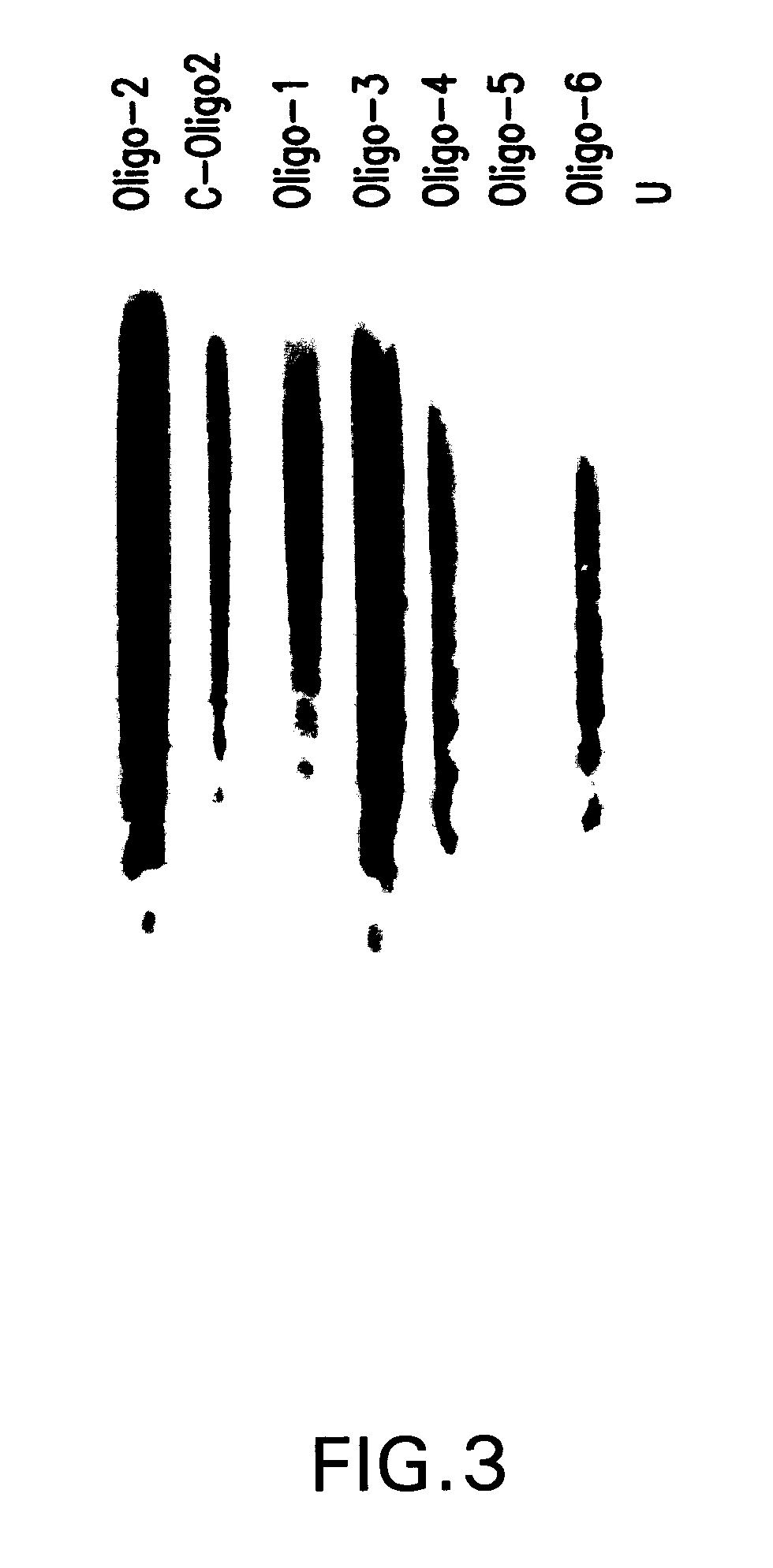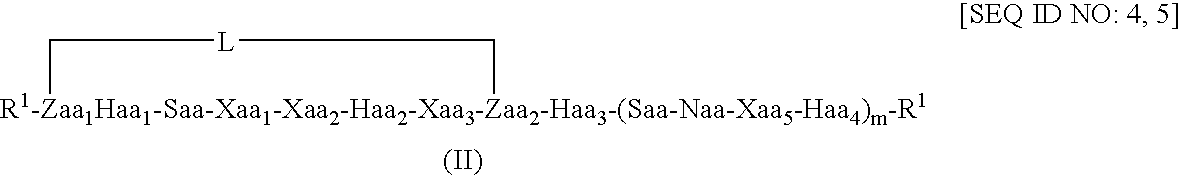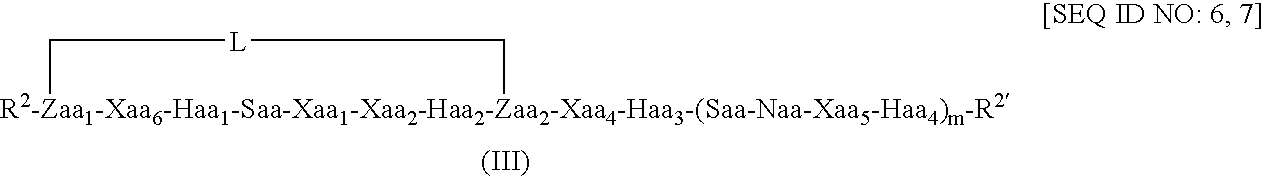Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
148 results about "Bcl-2 Genes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bcl-2 (B-cell lymphoma 2), encoded in humans by the BCL2 gene, is the founding member of the Bcl-2 family of regulator proteins that regulate cell death (apoptosis), by either inducing (pro-apoptotic) or inhibiting (anti-apoptotic) apoptosis.
RNA interference mediated inhibition of B-cell CLL/Lymphoma-2 (BCL-2) gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20050176025A1Improves various propertyImprove the immunityCompounds screening/testingSpecial deliveryAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating BCL2 gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. This invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating the expression and activity of other genes involved in pathways of BCL2 gene expression and / or activity by RNA interference (RNAi) using small nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of BCL2 genes (e.g., BCL2, BCL-XL, BCL2-L1, MCL-1 CED-9, BAG-1, E1B-194 and / or BCL-A1). The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of cancer, malignant blood disease, polycytemia vera, idiopathic myelofibrosis, essential thrombocythemia, myelodysplastic syndromes, autoimmune disease, viral infection, and proliferative diseases and conditions
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Regulation of BCL-2 gene expression
InactiveUS7022831B1High sensitivityIncreased chemosensitivitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsOligomerCancer cell
Owner:UCB SA
Inhibition of Bcl-2 protein expression by liposomal antisense oligodeoxynucleotides
InactiveUS7285288B1Lower the volumeIncrease the effective concentrationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseCancer cell
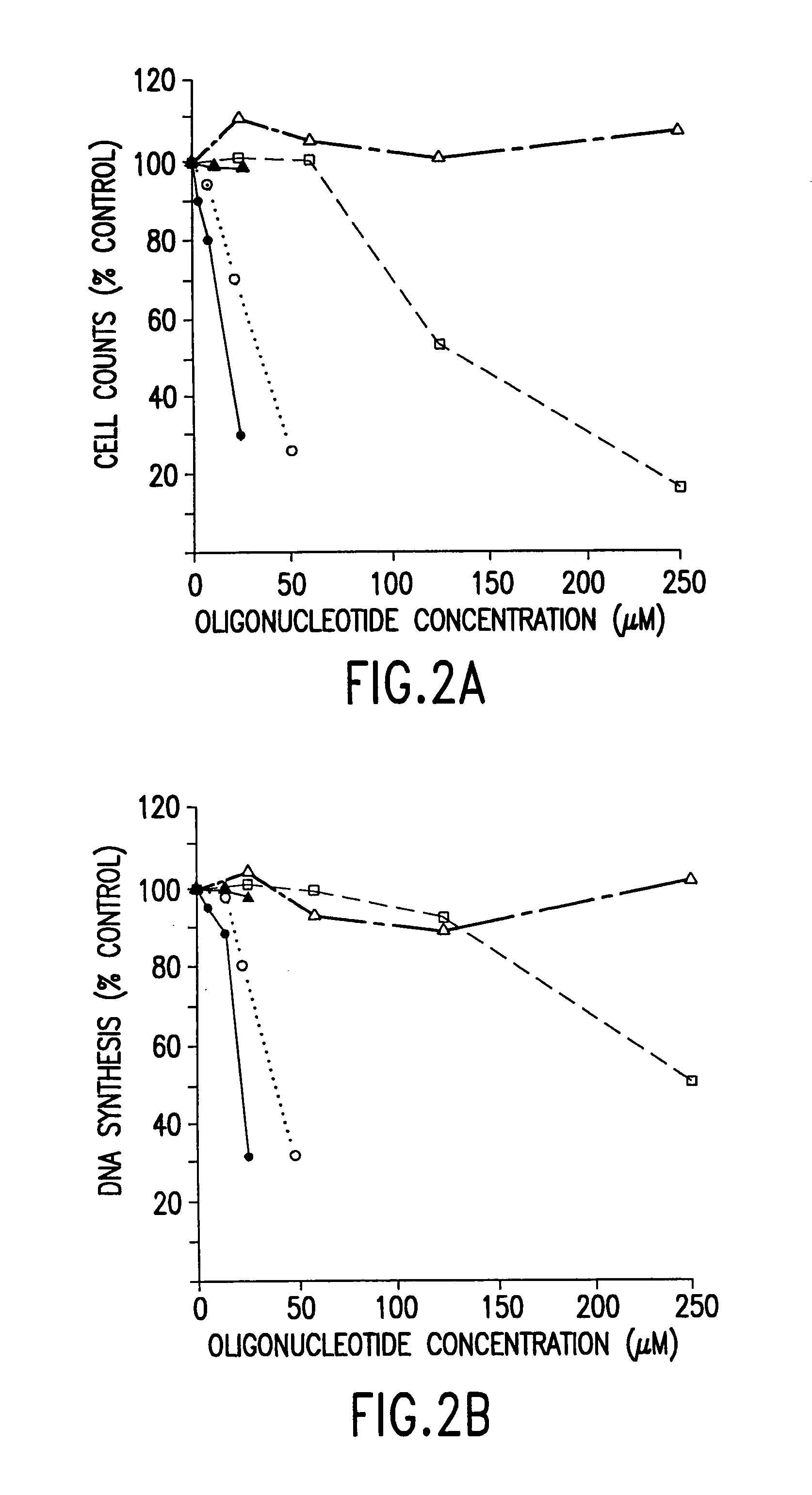
The present invention provides novel compositions and methods for use in the treatment of Bcl-2-associated diseases like cancer, specifically, in the treatment of follicular lymphoma (FL). The compositions contain antisense oligonucleotides that hybridize to Bcl-2 nucleic acids, the gene products of which are known to interact with the tumorigenic protein Bcl-2. Used alone, or in conjunction with other antisense oligonucleotides, these compositions inhibit the proliferation of FL cancer cells.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation of Bcl-2
InactiveUS7622453B2Comparable and enhanced biological effectInteresting biological propertiesBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseOligomer
The present invention provides improved oligomeric compound, in particular oligonucleotide compounds, and methods for modulating the expression of the Bcl-2 gene in humans. In particular, this invention relates to oligomeric compounds of 10-30 nucleobases in length which comprise a target binding domain that is specifically hybridizable to a region ranging from base position No. 1459 (5′) to No. 1476 (3′) of the human Bcl-2 mRNA, said target binding domain having the formula: 5′-[(DNA / RNA)0-1-(LNA / LNA*)2-7-(DNA / RNA / LNA*)4-14-(LNA / LNA*)2-7-(DNA / RNA)0-1]-3′ and said target binding domain comprising at least two LNA nucleotides or LNA analogue nucleotides linked by a phosphorothioate group (—O—P(O,S)—O—). In particular the oligo is predominantly or fully thiolated. The invention also provides the use of such oligomers or conjugates or chimera for the treatment of various diseases associated with the expression of the Bcl-2 gene, such as cancer.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
Mammalian cell lines for increasing longevity and protein yield from a cell culture
ActiveUS7537930B2Increase longevity and recombinant protein yieldIncreases lifespan and viabilityVirus peptidesApoptosis related proteinsSerum free mediaApoptosis
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation of Bcl-2
InactiveUS20050203042A1Comparable and enhanced biological effectInteresting biological propertiesBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseNucleobase
The present invention provides improved oligomeric compound, in particular oligonucleotide compounds, and methods for modulating the expression of the Bcl-2 gene in humans. In particular, this invention relates to oligomeric compounds of 10-30 nucleobases in length which comprise a target binding domain that is specifically hybridizable to a region ranging from base position No. 1459 (5′) to No. 1476 (3′) of the human Bcl-2 mRNA, said target binding domain having the formula: 5′-[(DNA / RNA)0-1-(LNA / LNA*)2-7-(DNA / RNA / LNA*)4-14-(LNA / LNA*)2-7-(DNA / RNA)0-1]-3 and said target binding domain comprising at least two LNA nucleotides or LNA analogue nucleotides linked by a phosphorothioate group (—O—P(O,S)—O—). In particular the oligo is predominantly or fully thiolated. The invention also provides the use of such oligomers or conjugates or chimera for the treatment of various diseases associated with the expression of the Bcl-2 gene, such as cancer.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
Methods for protein expression in mammalian cells in serum-free medium
ActiveUS7608425B2Increase longevity and recombinant protein yieldIncreases lifespan and viabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsApoptosis related proteinsSerum free mediaMammal
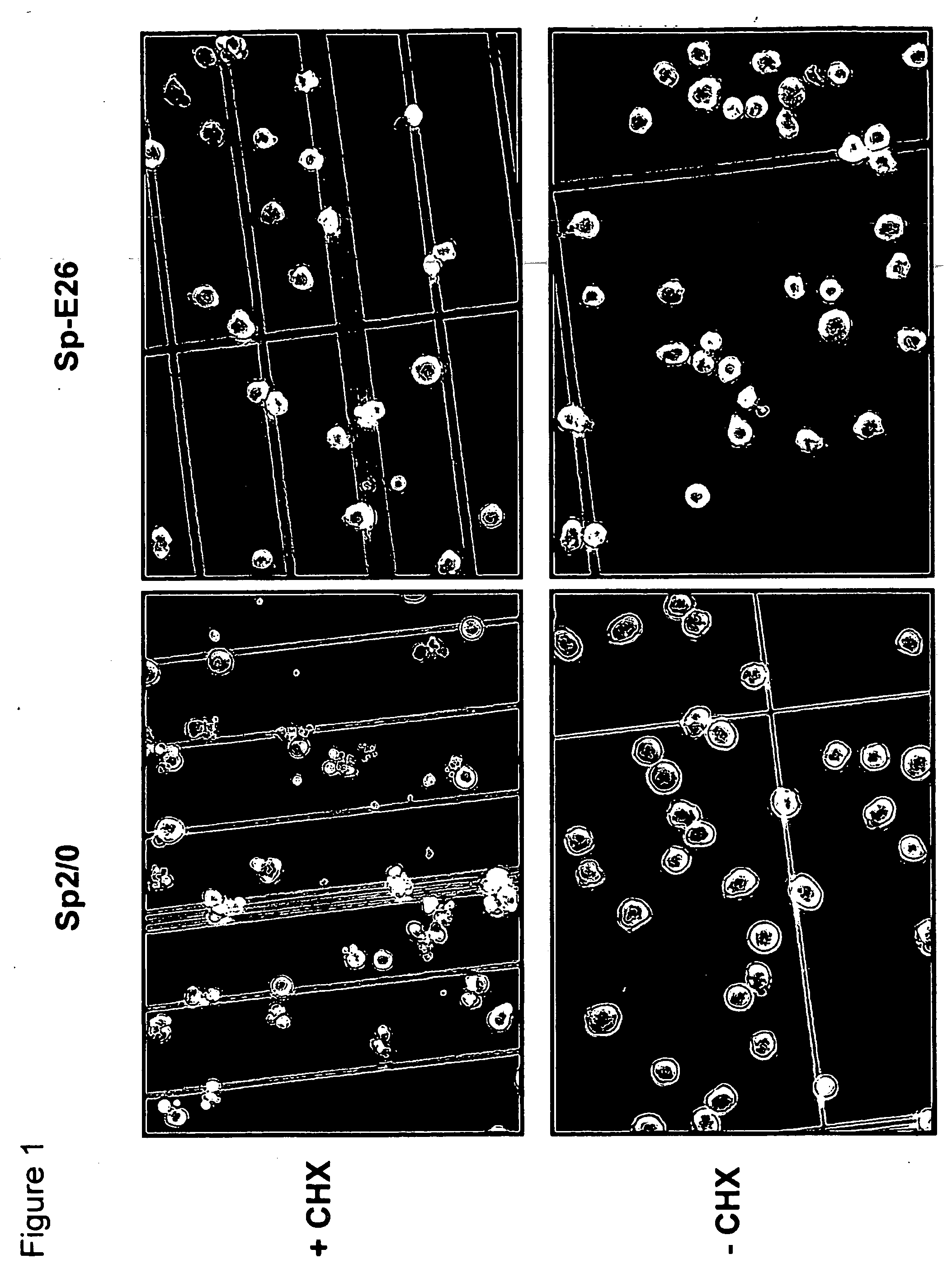
Disclosed are compositions and methods for increasing the longevity of a cell culture and permitting the increased production of proteins, preferably recombinant proteins, such as antibodies, peptides, enzymes, growth factors, interleukins, interferons, hormones, and vaccines. Cells transfected with an apoptosis-inhibiting gene or vector, such as a triple mutant Bcl-2 gene, can survive longer in culture, resulting in extension of the state and yield of protein biosynthesis. Such transfected cells exhibit maximal cell densities that equal or exceed the maximal density achieved by the parent cell lines. Transfected cells can also be pre-adapted for growth in serum-free medium, greatly decreasing the time required to obtain protein production in serum-free medium. In certain methods, the pre-adapted cells can be used for protein production following transfection under serum-free conditions. In preferred embodiments, the cells of use are SpESF or SpESF-X cells.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
2 Methoxy antimycin a derivatives and methods of use
InactiveUS20050239873A1Inhibitory activityInduce apoptosisBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBcl-2 GenesAntimycin A
Disclosed are 2-methoxy antimycin derivatives or analogs that modulate apoptosis by binding to the hydrophobic groove of a Bcl-2 family member protein (e.g., Bcl-2 or BCl-xL). The 2-methoxy antimycin derivatives or analogs are used in disclosed methods for treating apoptosis-associated diseases such as, for example, neoplastic disease (e.g., cancer) or other proliferative diseases associated with the over-expression of a Bcl-2 family member protein.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
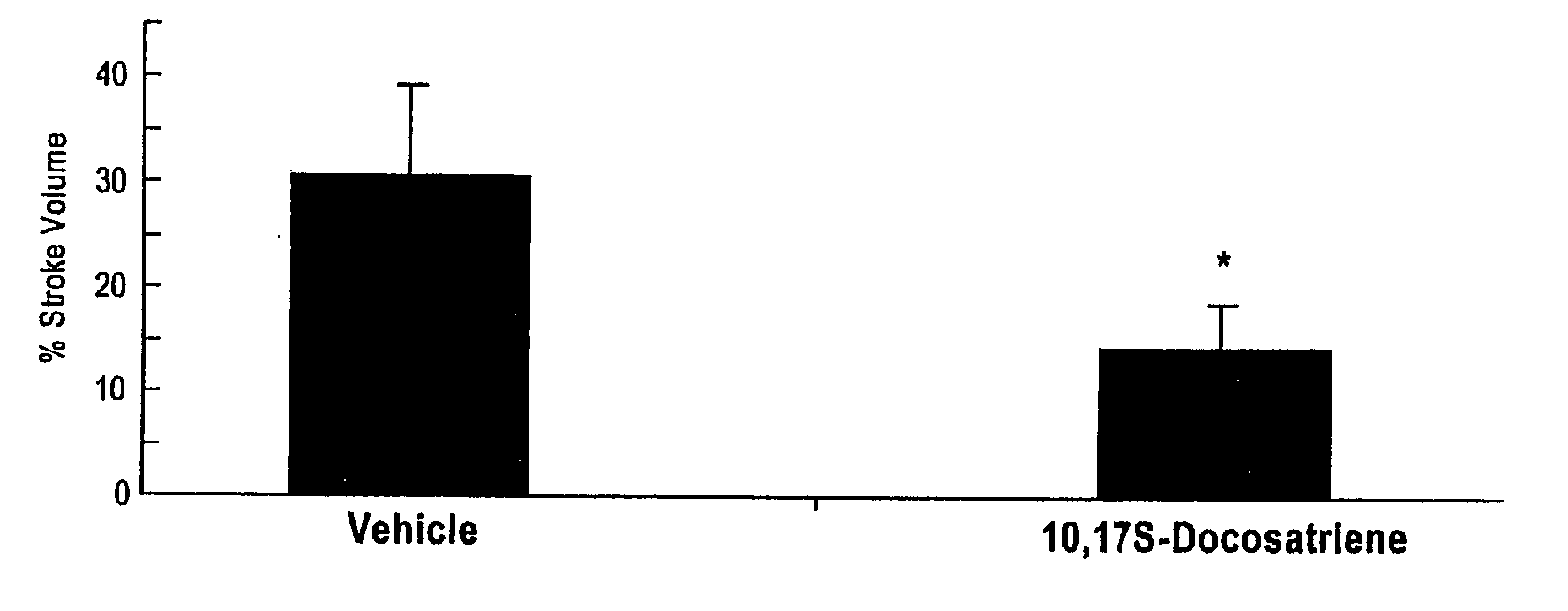
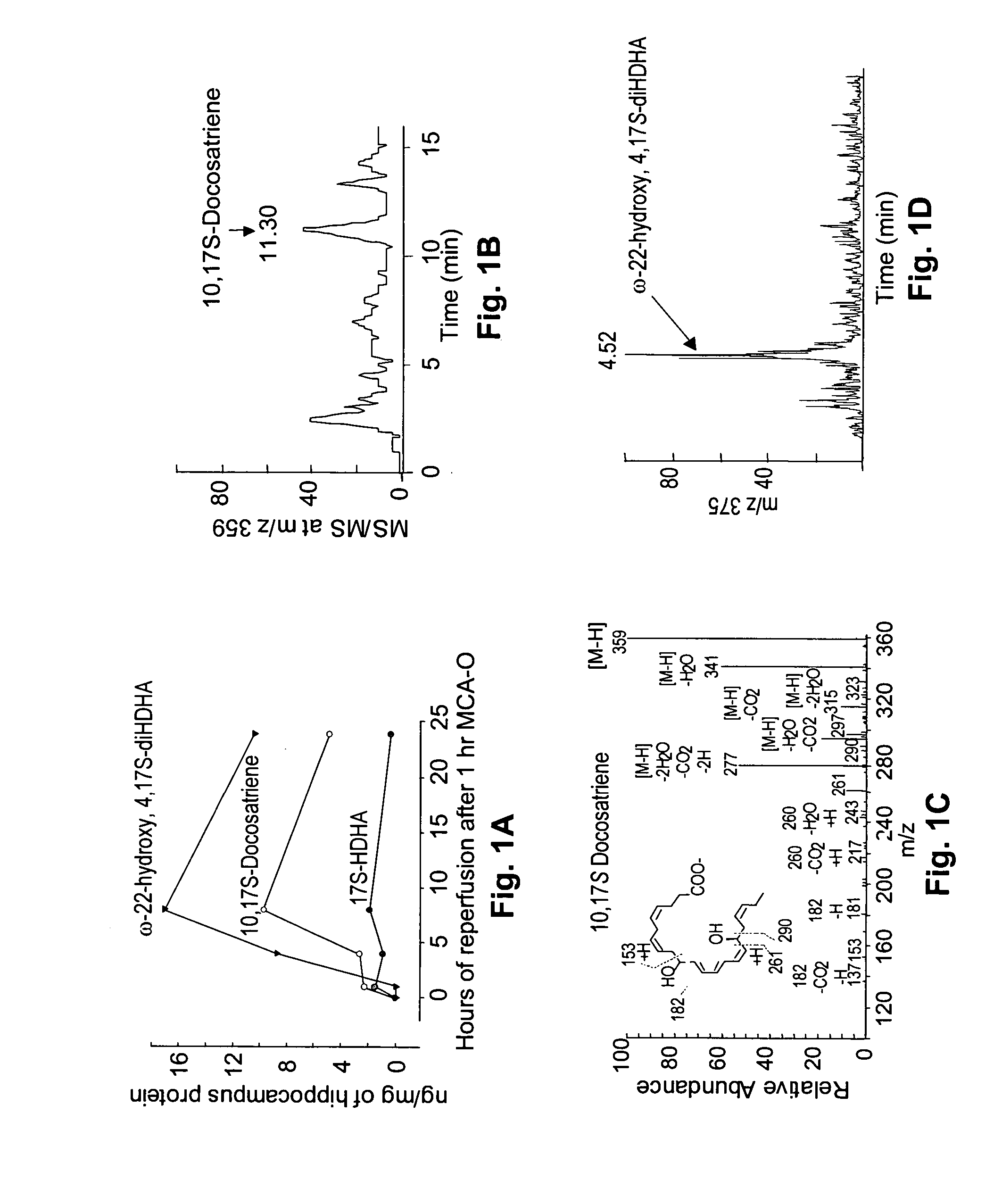
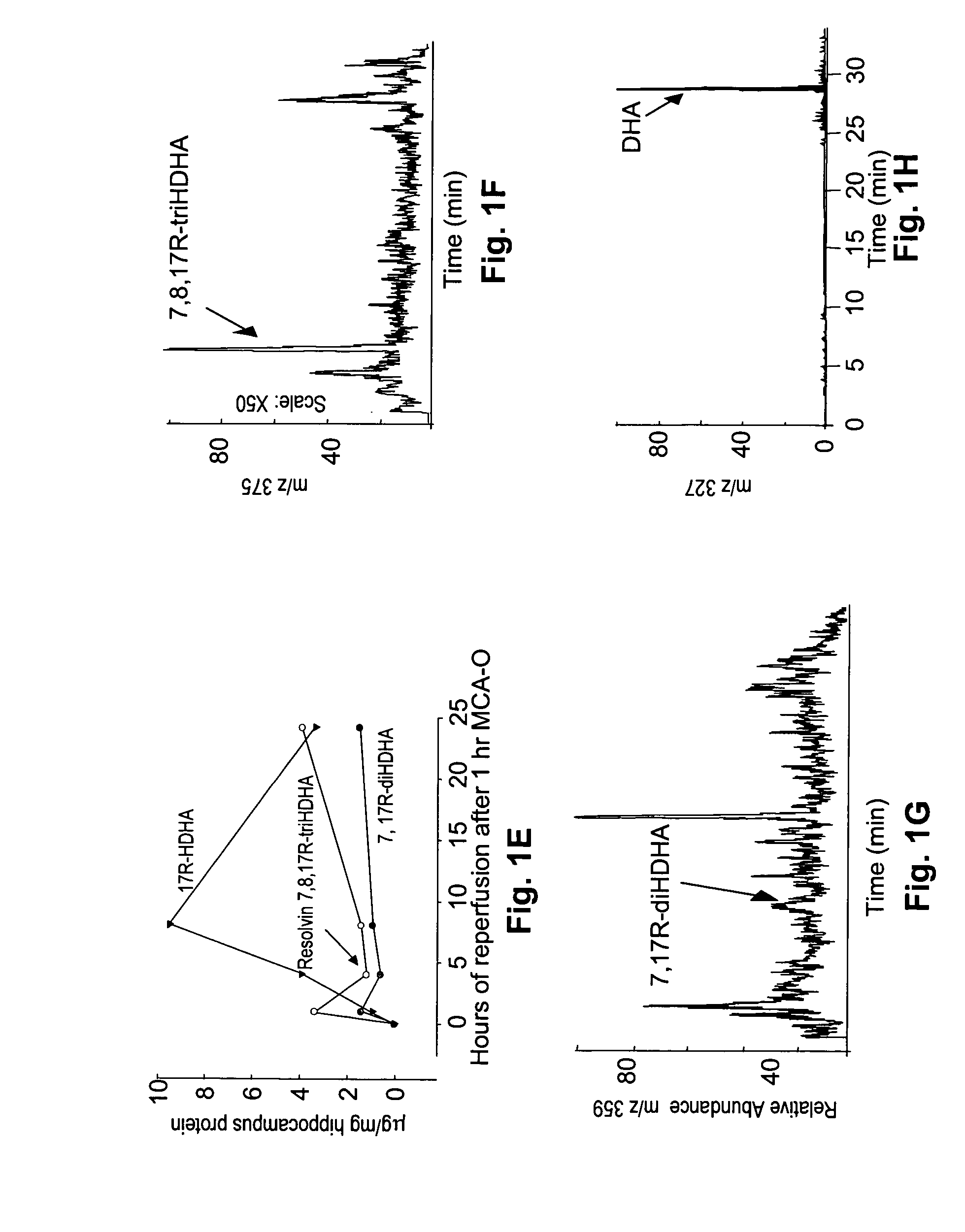
Neuroprotectin D1 protects against cellular apoptosis, stroke damage, alzheimer's disease and retinal diseases
InactiveUS20050075398A1Increase secretionReduce secretionBiocideSenses disorderRisk strokeRetinal pigment epithelial cell
A unique DHA product, 10, 17S-docosatriene (“Neuroprotectin D1” or “NPD1”), was found to provide surprisingly effective neuroprotection when administered right after an experimental stroke. Moreover, both nerve cells and retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells were found to synthesize 10,17S-docosatriene (NPD1) from DHA. NPD1 also potently counteracted H2O2 / TNFα oxidative stress-mediated cell apoptotic damage. Under the same oxidative-stress conditions, NPD1 up-regulated the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins, Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, and decreased expression of the pro-apoptotic proteins, Bad and Bax. Moreover, in RPE cells NPD1 inhibited oxidative stress-induced caspase-3 activation, IL-1β-stimulated human COX-2 promoter expression, and apoptosis due to N-retinylidene-N-retinylethanolamine (A2E). Overall, NPD1 protected both nerve and retinal pigment epithelial cells from cellular apoptosis and damage due to oxidative stress. NPD1 concentration in the brain of Alzheimer's patients was found to be significantly decreased from that of controls. In cultured human brain cells, NPD1 synthesis was up-regulated by neuroprotective soluble β amyloid, and NPD1 was found to inhibit secretion of toxic β amyloid peptides.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Small molecule antagonists of BCL-2 family proteins
InactiveUS20040214902A1Guaranteed long-term securityAntibacterial agentsBiocideChemical synthesisDisease
The present invention relates to naturally occurring and chemically synthesized small molecule antagonists of Bcl-2 family proteins. In particular, the present invention provides gossypol compounds (e.g., isomers, enantiomers, racemic compounds, metabolites, derivatives, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, in combination with acids or bases, and the like) and methods of using these compounds as antagonists of the anti-apoptotic effects of Bcl-2 family member proteins (e.g., Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, and the like). The present invention also provides compositions comprising gossypol compounds and optionally one or more additional therapeutic agents (e.g., anticancer / chemotherapeutic agents). The present invention also provides methods for treating diseases and pathologies (e.g., neoplastic diseases) comprising administering a composition comprising gossypol compounds and optionally one or more additional therapeutic agents (e.g., anticancer / chemotherapeutic agents) and / or techniques (e.g., radiation therapies, surgical interventions, and the like) to a subject or in vitro cells, tissues, and organs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Small molecule inhibitors of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members and the uses thereof
ActiveUS20060084647A1Great clinical benefitGreat tumor responseUrea derivatives preparationBiocideSensitized cellBcl-2 Genes
The invention relates to small molecules which function as inhibitors of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member proteins (e.g., Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL). The invention also relates to the use of these compounds for inducing apoptotic cell death and sensitizing cells to the induction of apoptotic cell death.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Peptides and therapeutic uses thereof
InactiveUS20070032417A1Significant pro-apoptotic activityImprove the immunityAntipyreticAnalgesicsMedicineBcl-2 Genes
Conformationally constrained peptides that mimic BH3-only proteins, compositions containing them and their use in the regulation of cell death are disclosed. The conformationally constrained peptides are capable of binding to and neutralising pro-survival Bcl-2 proteins. Processes for preparing the conformationally constrained peptides and their use in the treatment and / or prophylaxis of diseases or conditions associated with deregulation of cell death are also disclosed.
Owner:WALTER & ELIZA HALL INST OF MEDICAL RES
Companion diagnostic assays for cancer therapy
InactiveUS20080193943A1Promote stratificationParticular utilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhenacylOncology
A method for classifying cancer patients as eligible to receive cancer therapy with a small molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2 comprising determination of the presence or absence in a patient tissue sample of chromosomal copy number status at the chromosomal locus 13q14 comprising the microRNA's miR-15a and miR-16-1 or at the chromosomal locus 11q23.1 comprising the microRNA miR-34c. The classification of cancer patients based upon the presence or absence of 13q14 loss or gain allows better selection of patients to receive chemotherapy with a small molecule Bcl-2 inhibitor such as N-(4-(4-((2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5,5-dimethyl-1-cyclohex-1-en-1-yl) methyl)piperazin-1-yl)benzoyl)-4-(((1R)-3-(morpholin-4-yl)-1-((phenylsulfanyl) methyl)propyl)amino)-3-((trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl)benzenesulfonamide, and for monitoring patient response to this therapy.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Conjugates And Therapeutic Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20070197430A1Significant pro-apoptotic activityIncreased resistance to proteolysisBiocideAntipyreticBcl-2 GenesTreatment use
Conformationally constrained peptides that mimic BH3-only proteins and their conjugation to antibodies and other cell targeting compounds, compositions containing the conjugates and their use in the regulation of cell death are disclosed. The conformationally constrained peptides are capable of binding to and neutralising pro-survival Bcl-2 proteins. Processes for preparing the conformationally constrained peptides conjugated to antibodies and other cell targeting compounds and use of the conjugates in the treatment and / or prophylaxis of diseases or conditions associated with deregulation of cell death are also disclosed.
Owner:WALTER & ELIZA HALL INST OF MEDICAL RES
Methods of treatment of a bcl-2 disorder using bcl-2 antisense oligomers
InactiveUS20040147473A1Significant therapeutic responseLow toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseOligomer
The present invention is directed to the use of bcl-2 antisense oligomers to treat and prevent bcl-2 related disorders. These disorders include cancers, tumors, carcinomas and cell-proliferative related disorders. In one embodiment of the invention, a bcl-2 antisense oligomer is administered at high doses. The present invention is also directed to a method of preventing or treating a bcl-2 related disorder, in particular cancer, comprising administering a bcl-2 antisense oligomer for short periods of time. The present invention is further drawn to the use of bcl-2 antisense oligomers to increase the sensitivity of a subject to cancer therapeutics. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising one or more bcl-2 antisense oligomers, which may comprise one or more cancer therapeutic agents.
Owner:GENTA INC
Bcl-2/bcl-xl inhibitors and therapeutic methods using the same
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Bcl-2/bcl-xl inhibitors and therapeutic methods using the same
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Small molecule antagonists of Bcl-2 family proteins
InactiveUS7432304B2Inhibition of activationLoss of p53Antibacterial agentsBiocideChemical synthesisDisease
The present invention relates to naturally occurring and chemically synthesized small molecule antagonists of Bcl-2 family proteins. In particular, the present invention provides gossypol compounds (e.g., isomers, enantiomers, racemic compounds, metabolites, derivatives, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, in combination with acids or bases, and the like) and methods of using these compounds as antagonists of the anti-apoptotic effects of Bcl-2 family member proteins (e.g., Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, and the like). The present invention also provides compositions comprising gossypol compounds and optionally one or more additional therapeutic agents (e.g., anticancer / chemotherapeutic agents). The present invention also provides methods for treating diseases and pathologies (e.g., neoplastic diseases) comprising administering a composition comprising gossypol compounds and optionally one or more additional therapeutic agents (e.g., anticancer / chemotherapeutic agents) and / or techniques (e.g., radiation therapies, surgical interventions, and the like) to a subject or in vitro cells, tissues, and organs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Small molecule Bcl-xL/Bcl-2 binding inhibitors
Owner:OHIO STATE INNOVATION FOUND
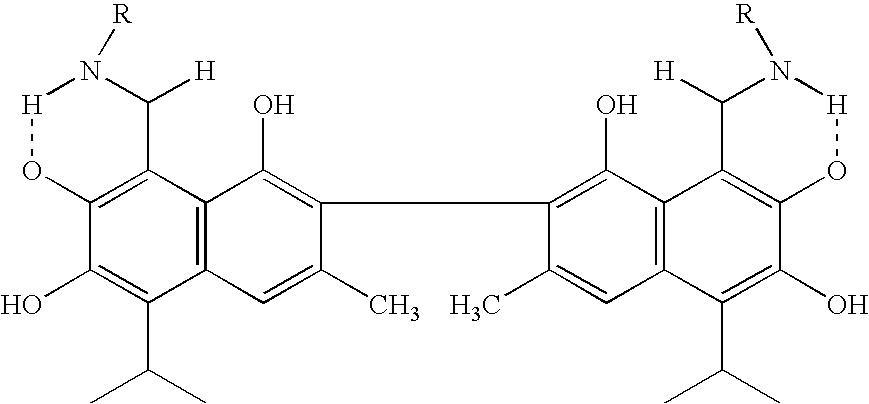
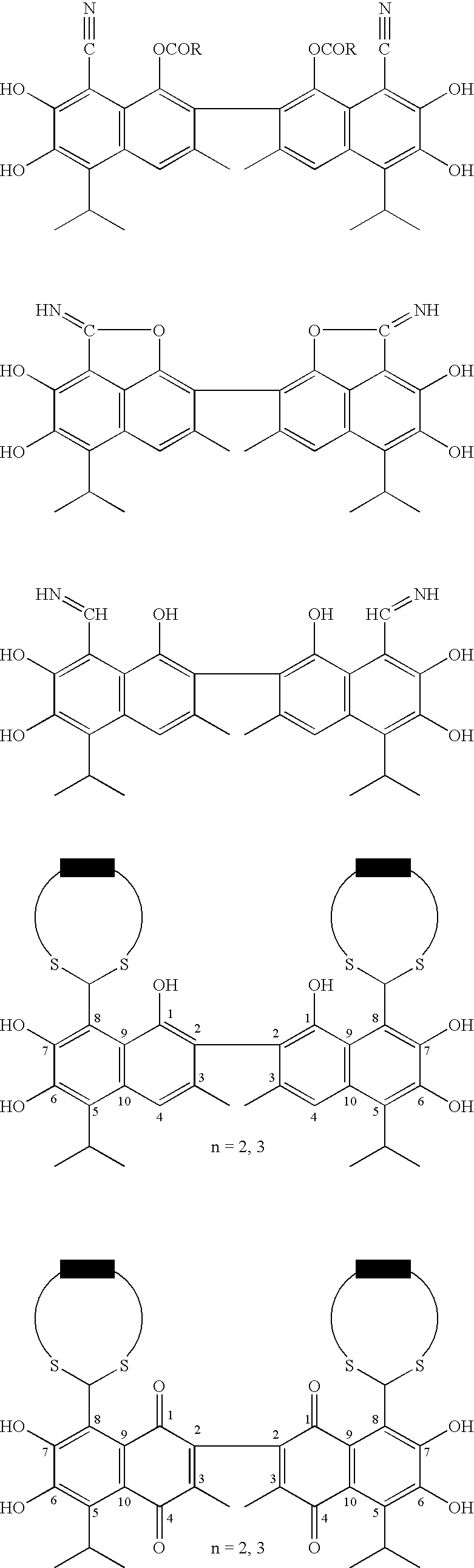
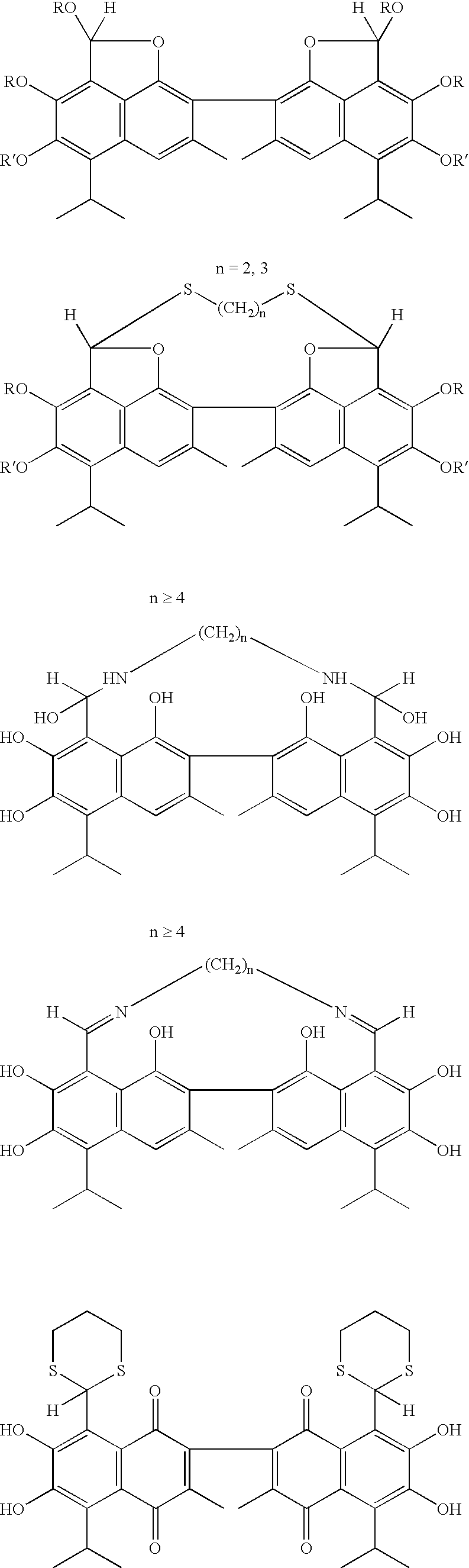
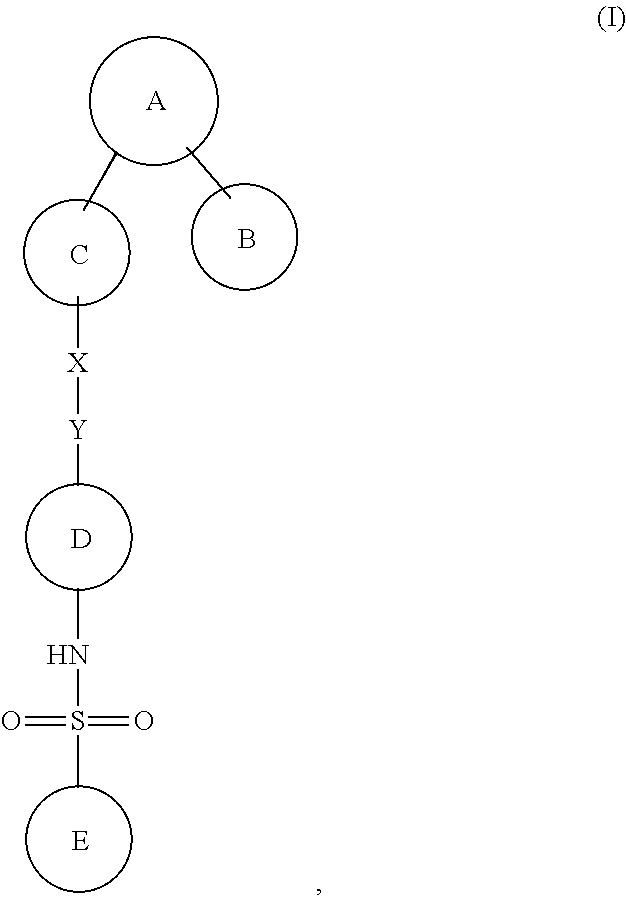
Chemical compounds
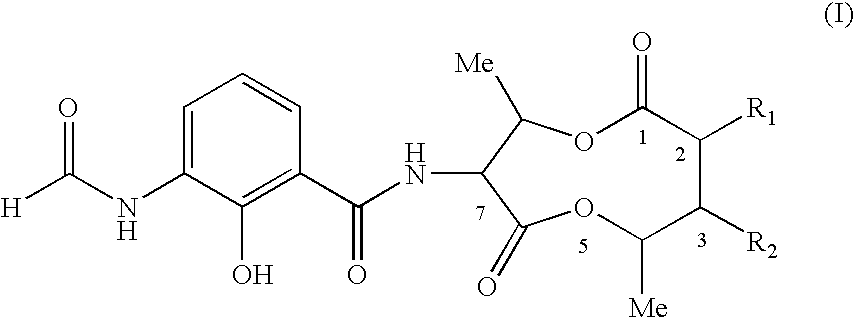
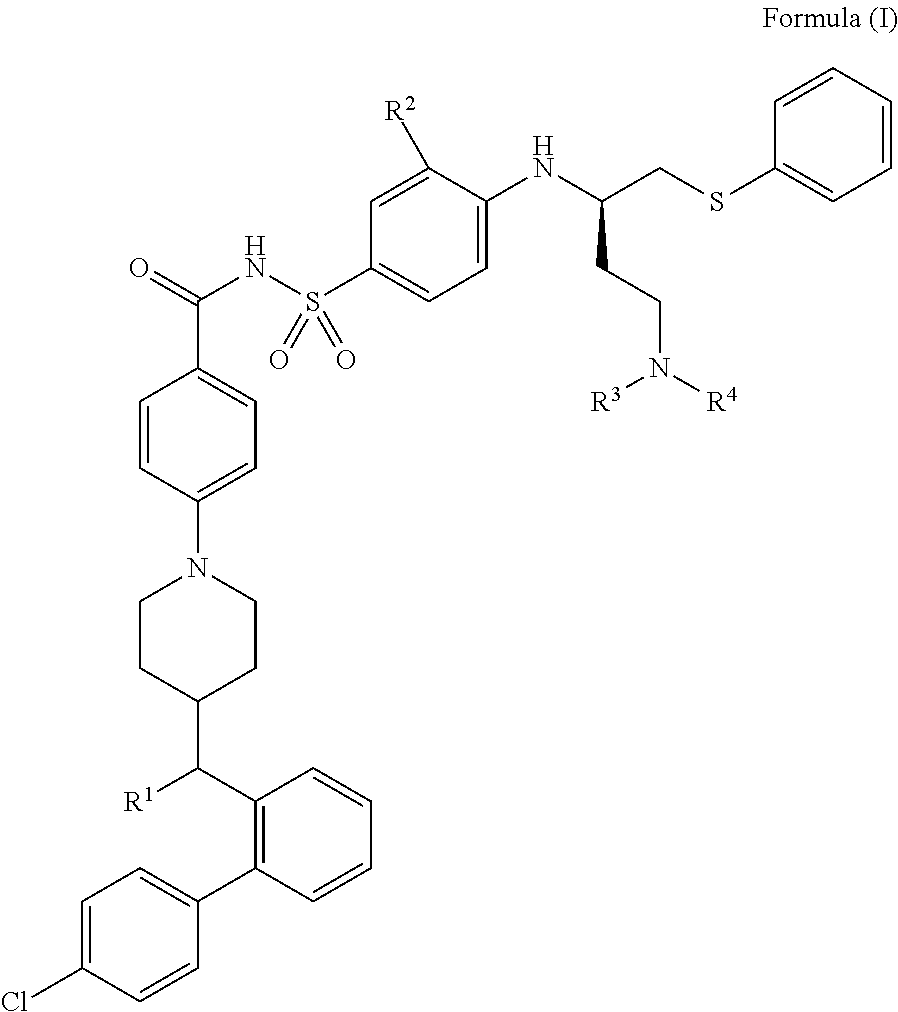
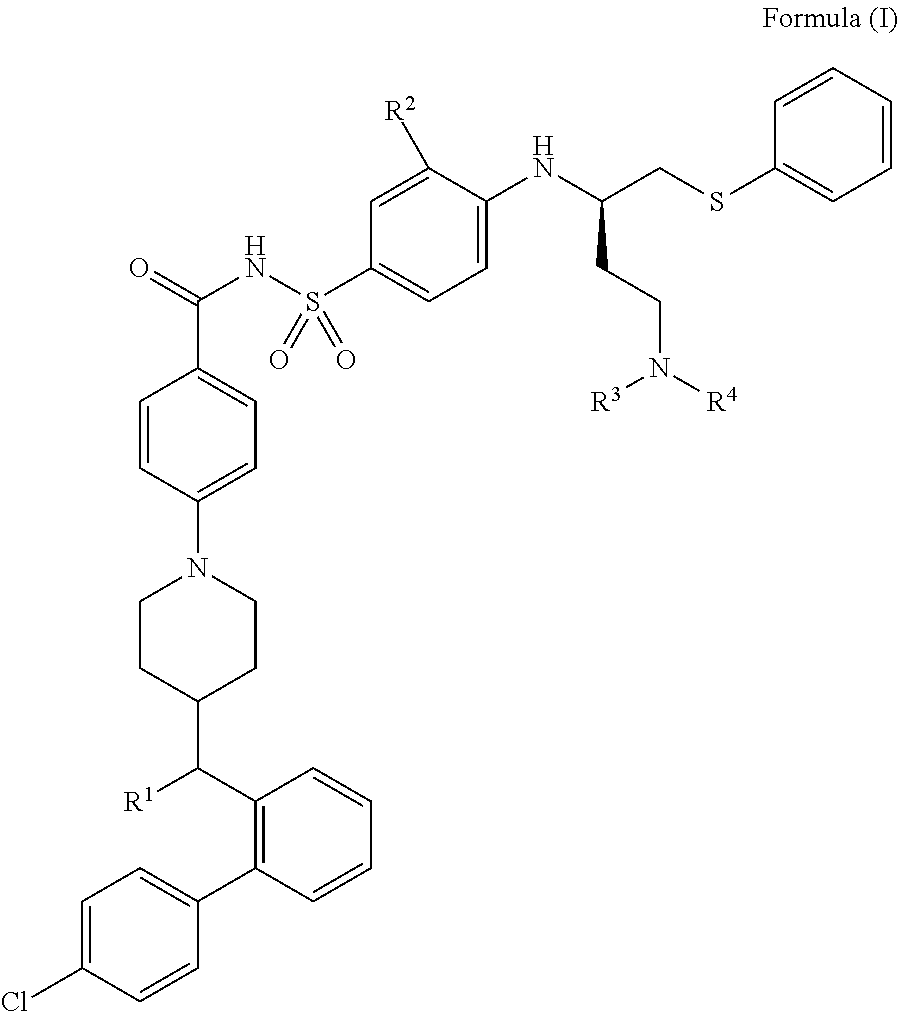
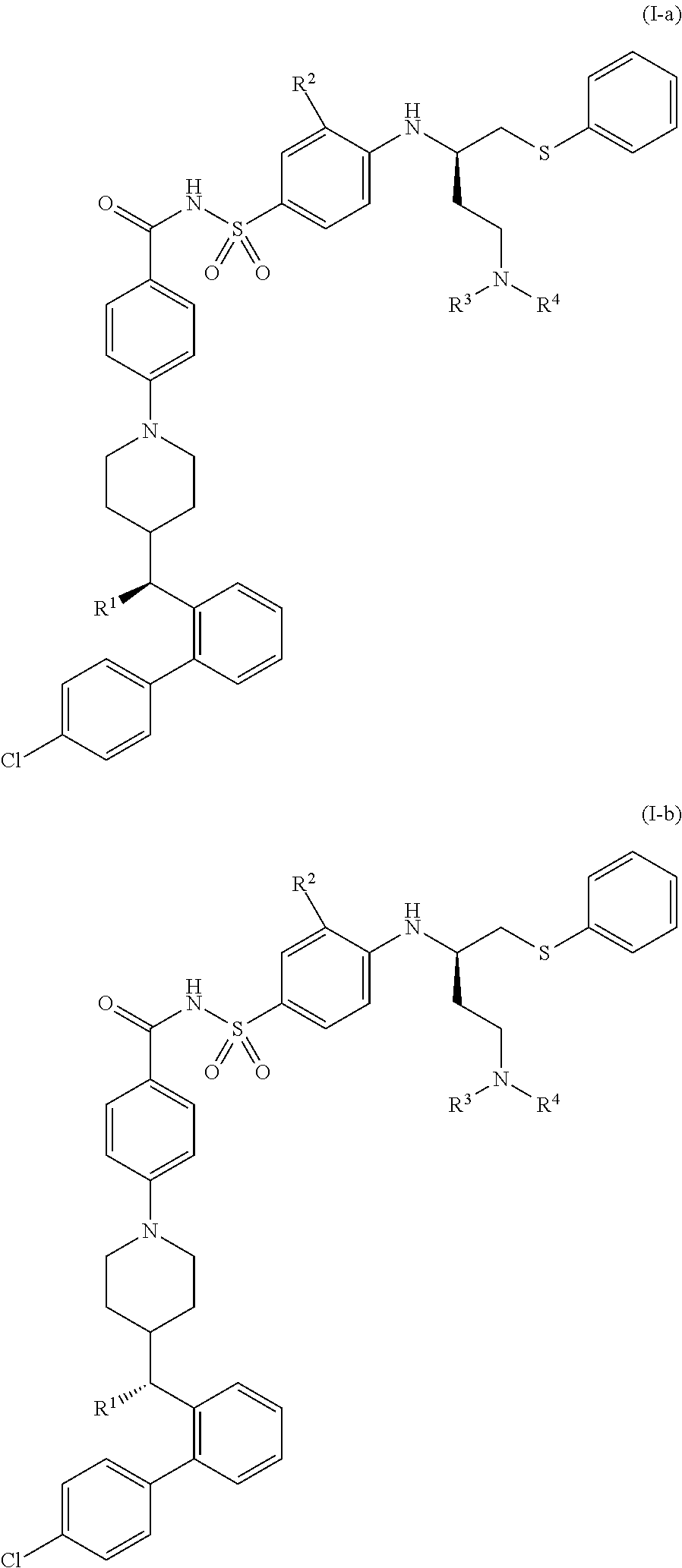
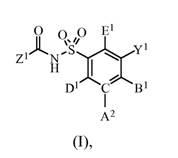
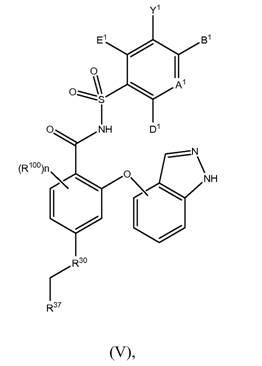
The present invention relates to compounds of Formula (I):and to their salts, pharmaceutical compositions, methods of use, and methods for their preparation. These compounds inhibit Bcl-2 and / or Bcl-XL activities and may be used for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Inhibition of Bcl-2 protein expression by liposomal antisense oligodeoxynucleotides
The present invention provides novel compositions and methods for use in the treatment of Bcl-2-associated diseases like cancer, specifically, in the treatment of follicular lymphoma (FL). The compositions contain antisense oligonucleotides that hybridize to Bcl-2 nucleic acids, the gene products of which are known to interact with the tumorigenic protein Bcl-2. Used alone, or in conjunction with other antisense oligonucleotides, these compositions inhibit the proliferation of FL cancer cells.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods and compositions for treating a cell-proliferative disorder using CRE decoy oligomers, BCL-2 antisense oligomers, and hybrid oligomers thereof
InactiveUS20030176376A1Hinder and prevent bindingModulate transcriptional activitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAbnormal tissue growth
The present invention is directed to hybrid oligomers comprising a cyclic AMP response element (CRE) sequence and a sequence that hybridizes to a bcl-2 pre-mRNA or mRNA, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising such hybrids. The present invention is also directed to the use of CRE decoy oligomers, comprising a CRE consensus sequence, and bcl-2 antisense oligomers in combination therapies, and the use of bcl-2 / CRE hybrid oligomers, to treat or prevent cell-proliferative related disorders, including hyperplasias, cancers, tumors and carcinomas. In one embodiment, the invention relates to therapeutic protocols comprising the administration of a CRE decoy oligomer and a bcl-2 antisense oligomer for the treatment of cell-proliferative related disorders. In another embodiment, the invention relates to therapeutic protocols comprising the administration of a bcl-2 antisense / CRE decoy (bcl-2 / CRE) hybrid oligomer for the treatment of cell-proliferative related disorders.
Owner:GENTA INC
Small molecule inhibitors targeted at Bcl-2
InactiveUS7354928B2Effective treatmentReduce overexpressionHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseCancer cell
The present invention relates to small molecule antagonists of Bcl-2 family proteins such as Bcl-2 and / or Bcl-XL. In particular, the present invention provides non-peptide cell permeable small molecules (e.g., tricyclo-dibenzo-diazocine-dioxides) that bind to a pocket in Bcl-2 / Bcl-XL that block the anti-apoptotic function of these proteins in cancer cells and tumor tissues exhibiting Bcl-2 protein overexpression. In preferred embodiments, the small molecules of the present invention are active at the BH3 binding pocket of Bcl-2 family proteins (e.g., Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, and Mcl-1). The compositions and methods of the present invention are useful therapeutics for cancerous diseases either alone or in combination with chemotherapeutic or other drugs.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV +1
Methods and compositions for increasing longevity and protein yield from a cell culture
ActiveUS20070015250A1Increased longevityIncrease recombinant protein yieldVirus peptidesApoptosis related proteinsSerum free mediaWhite blood cell
Disclosed are compositions and methods for increasing the longevity of a cell culture and permitting the increased production of proteins, preferably recombinant proteins, such as antibodies, peptides, enzymes, growth factors, interleukins, interferons, hormones, and vaccines. Cells transfected with an apoptosis-inhibiting gene or vector, such as a triple mutant Bcl-2 gene, can survive longer in culture, resulting in extension of the state and yield of protein biosynthesis. Such transfected cells exhibit maximal cell densities that equal or exceed the maximal density achieved by the parent cell lines. Transfected cells can also be pre-adapted for growth in serum-free medium, greatly decreasing the time required to obtain protein production in serum-free medium. In certain methods, the pre-adapted cells can be used for protein production following transformation under serum-free conditions. The method preferably involves eukaryotic cells, more preferably mammalian cells.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
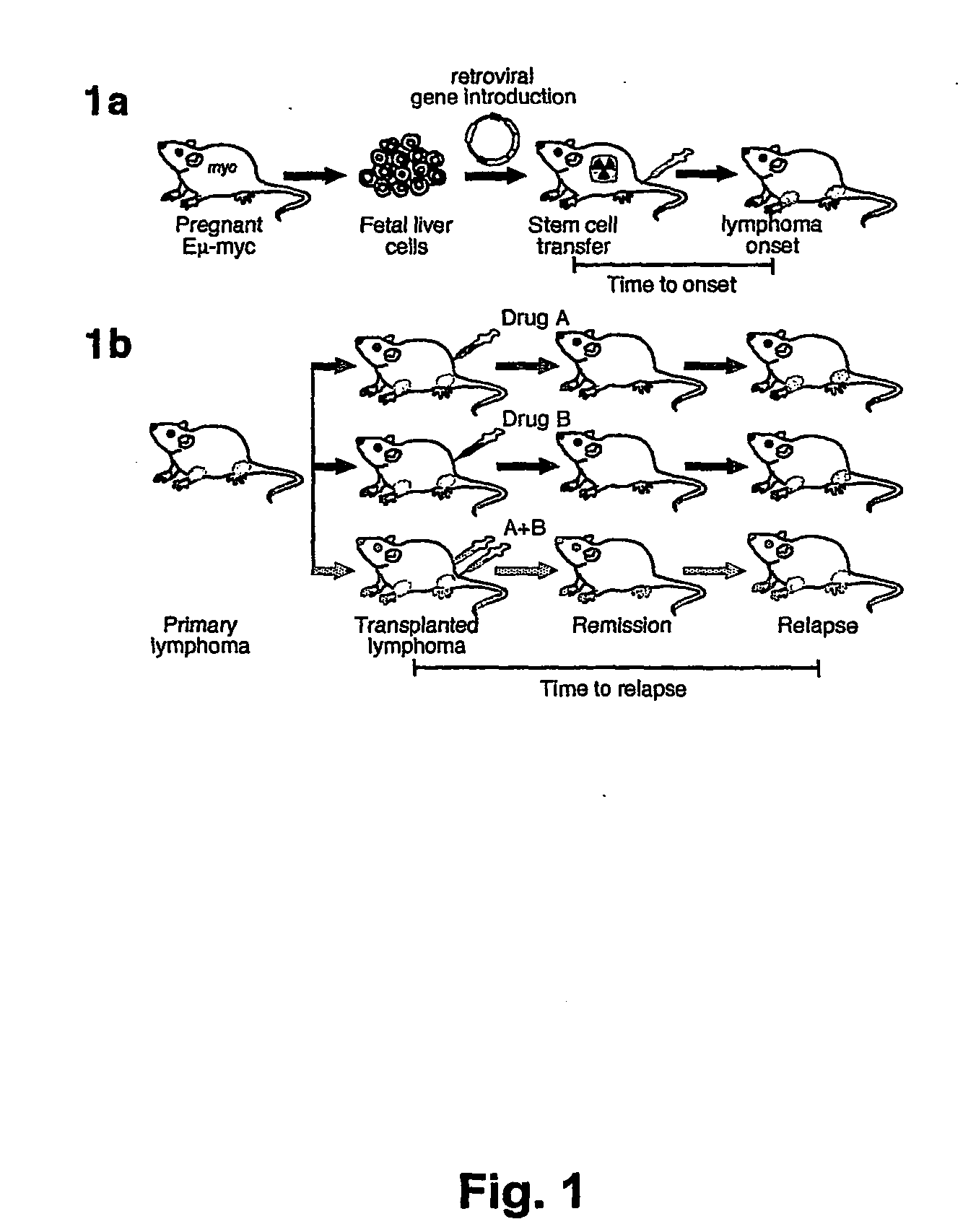
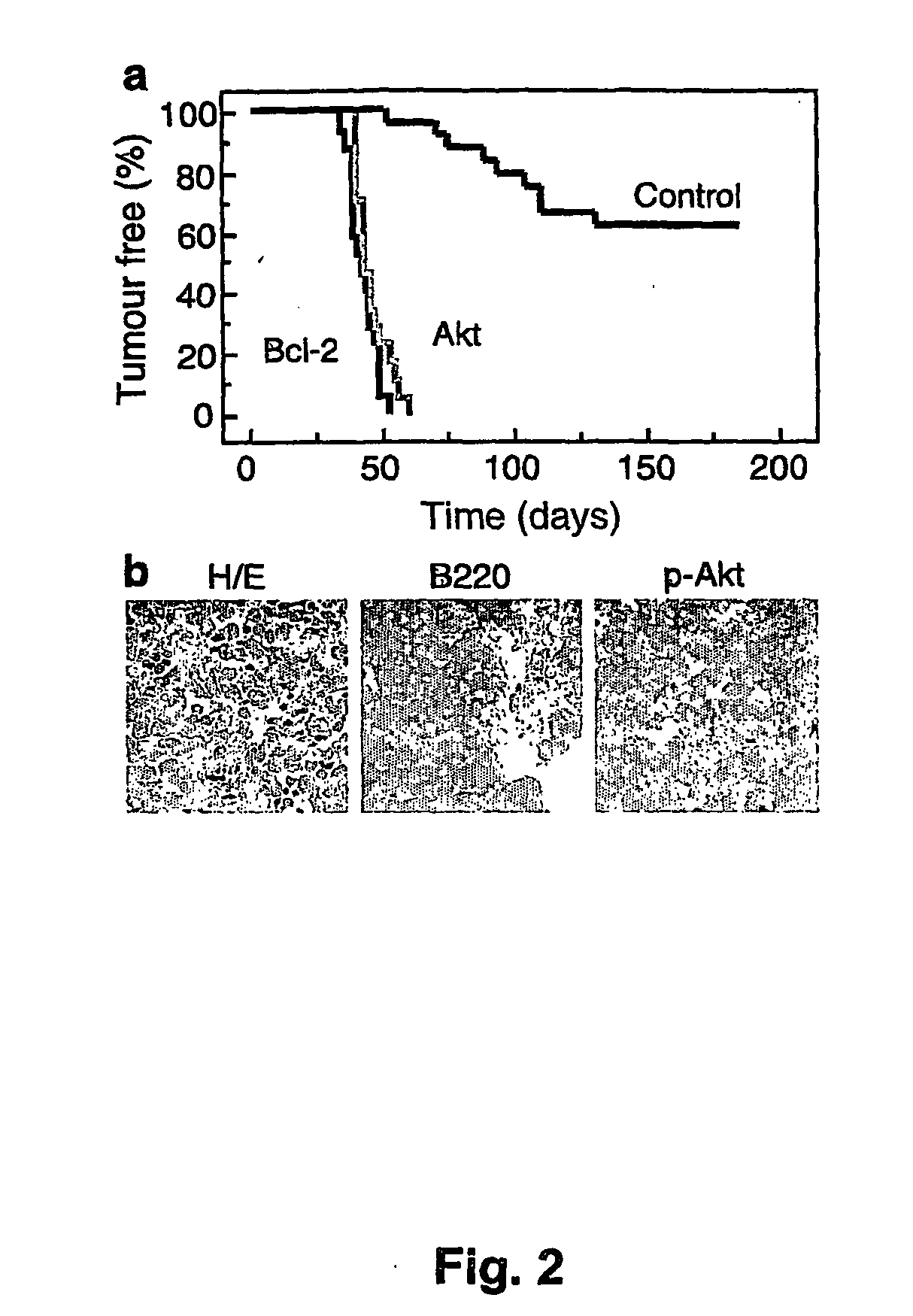
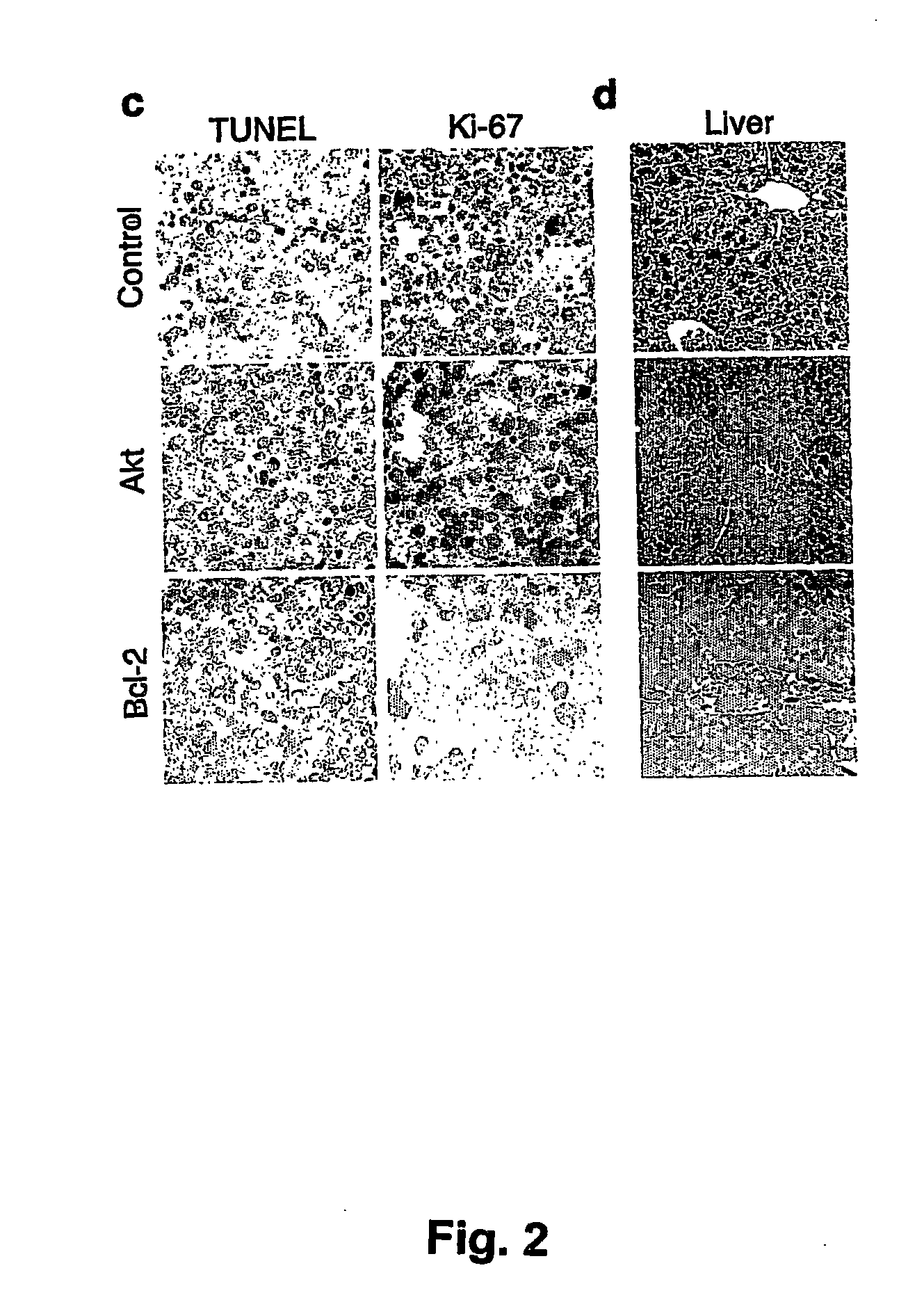
Model for studying the role of genes in tumor resistance to chemotherapy
The invention provides the components of in vivo and in vitro systems and methods which use them to study the effects of altered expression of a gene activity, such as the human akt, bcl-2, eIF4E or PTEN activities, on the descendants of stem cells that have been engineered to give rise to hematopoietic tumorigenic or tumor cells, such as lymphomas, with a high frequency. The present invention provides vectors, cells and mammals, and methods which in part depend on such products, useful for understanding tumorigenesis and its treatments, and in particular, for identifying and studying inhibitors and activators associated with tumor cell growth and growth inhibition, cell death through apoptotic pathways, and changes in apoptotic pathway components that affect drug sensitivity and resistance in tumorigenic cells. Methods for identifying molecular targets for drug screening, identifying interacting gene activities, for identifying therapeutic treatments and for identifying candidates for new therapeutic treatments are provided.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC +1
Vascularized human skin equivalent
InactiveUS20070207125A1Accelerated rate of vascularizationImprove clinical utilityBiocideEpidermal cells/skin cellsSkin equivalentIn vivo
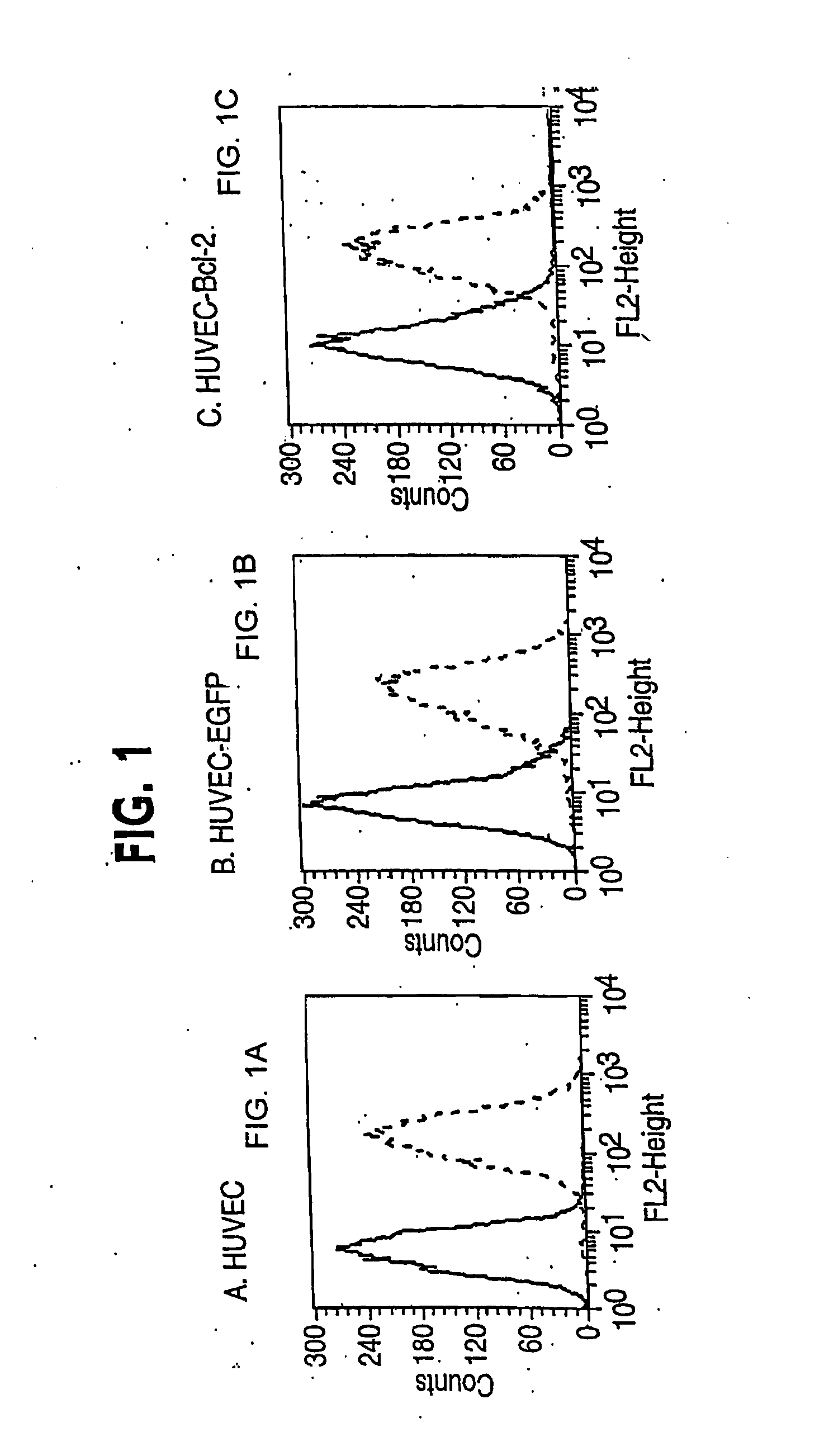
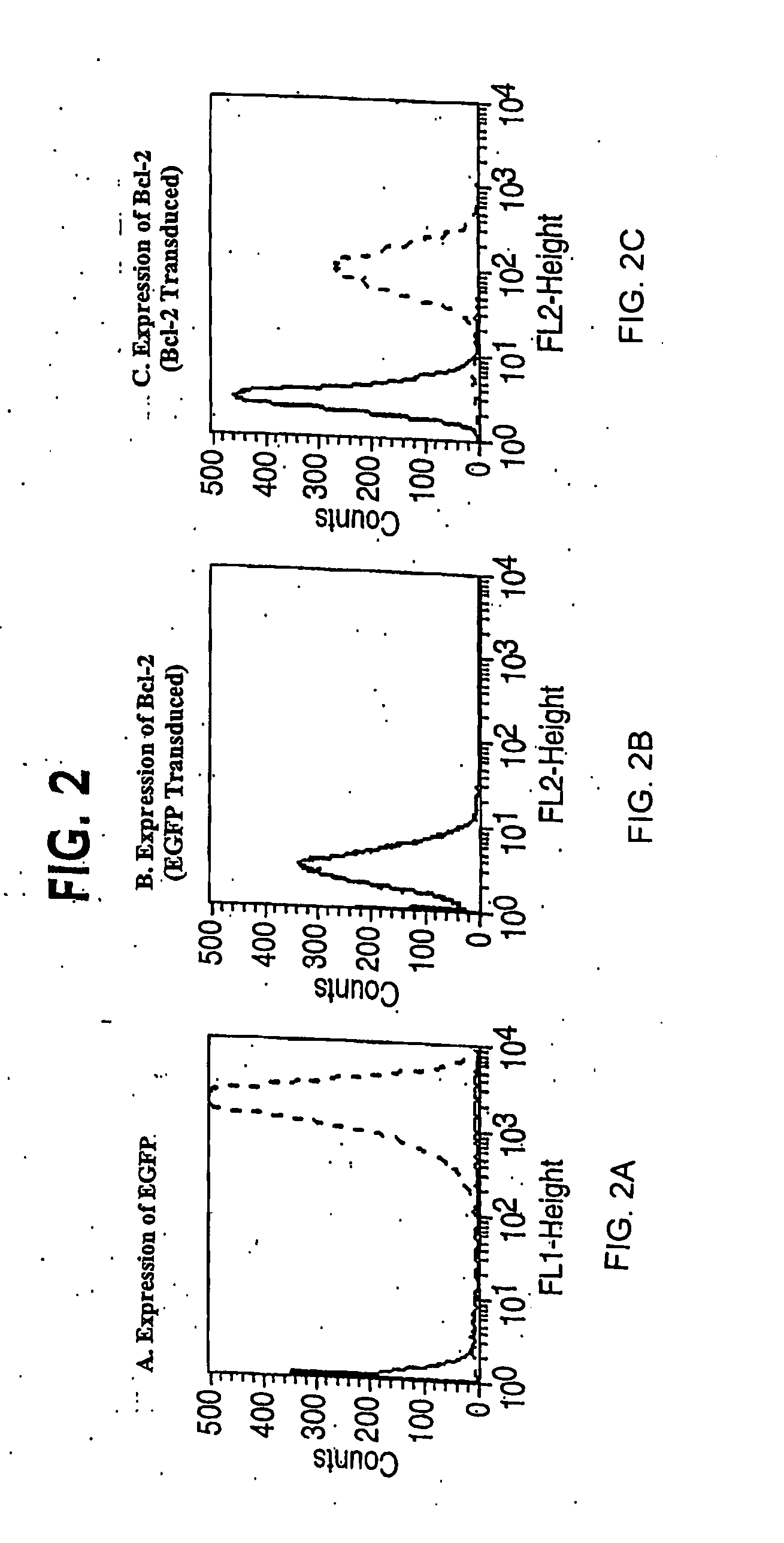
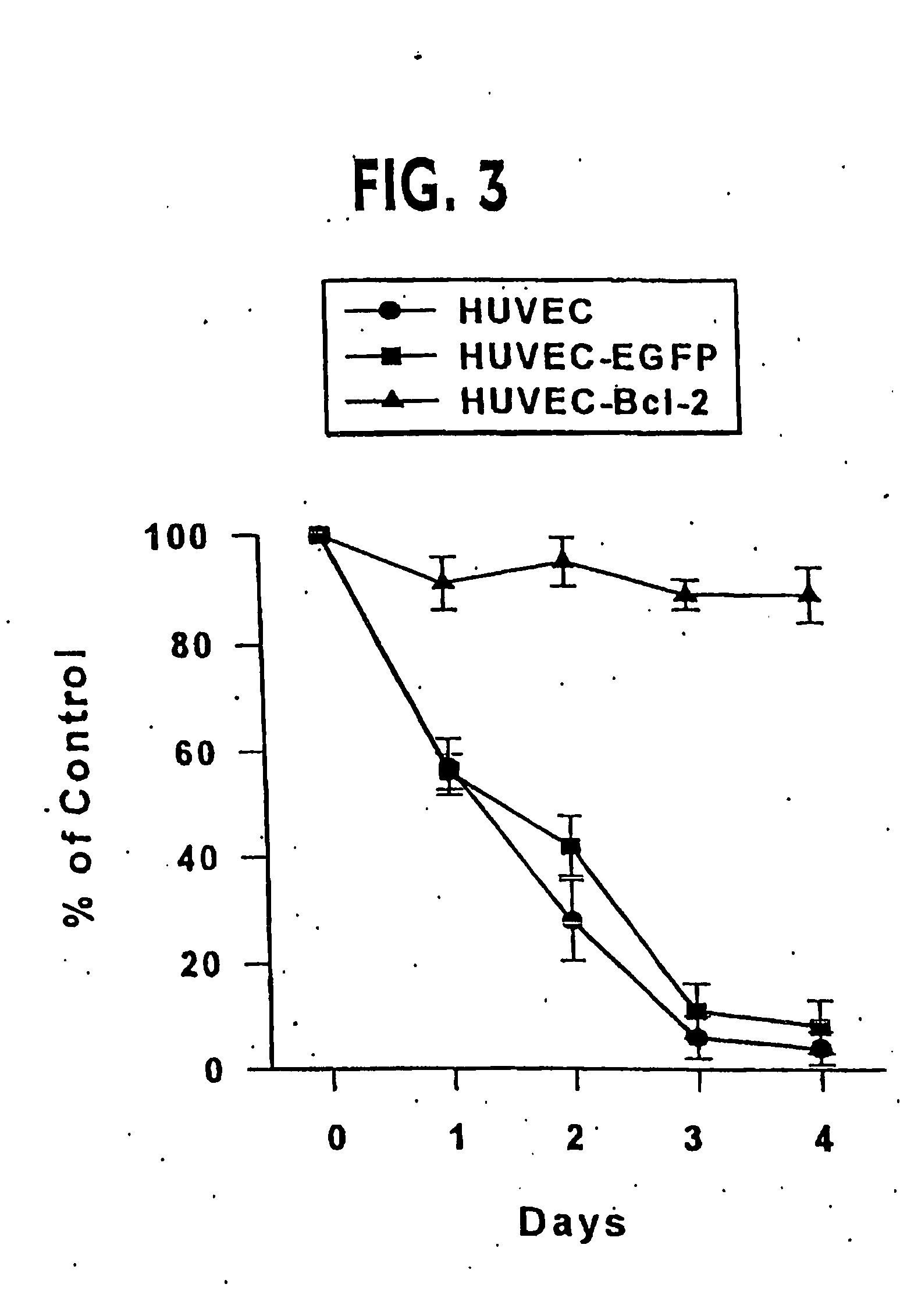
Clinical performance of currently available human skin equivalents is limited by failure to develop perfusion. To address this problem we have developed a method of endothelial cell transplantation that promotes vascularization of human skin equivalents in vivo. Living skin equivalents were constructed by sequentially seeding the apical and basal surfaces of acellular dermis with cultured human keratinocytes and Bcl-2 transduced HUVEC or umbilical cord cells sequentially. After orthotopic implantation of grafts comprising cultured human keratinocytes and Bcl-2 transduced HUVEC cells onto mice, the grafts displayed both a differentiated human epidermis and perfusion through the HUVEC-lined microvessels. These vessels, which showed evidence of progressive maturation, accelerated the rate of graft vascularization. Successful transplantation of such vascularized human skin equivalents should enhance clinical utility, especially in recipients with impaired angiogenesis.
Owner:YALE UNIV
BCL-2-selective apoptosis-inducing agents for the treatment of cancer and immune diseases
Disclosed are compounds which inhibit the activity of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL proteins, compositions containing the compounds and methods of treating diseases during which are expressed anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
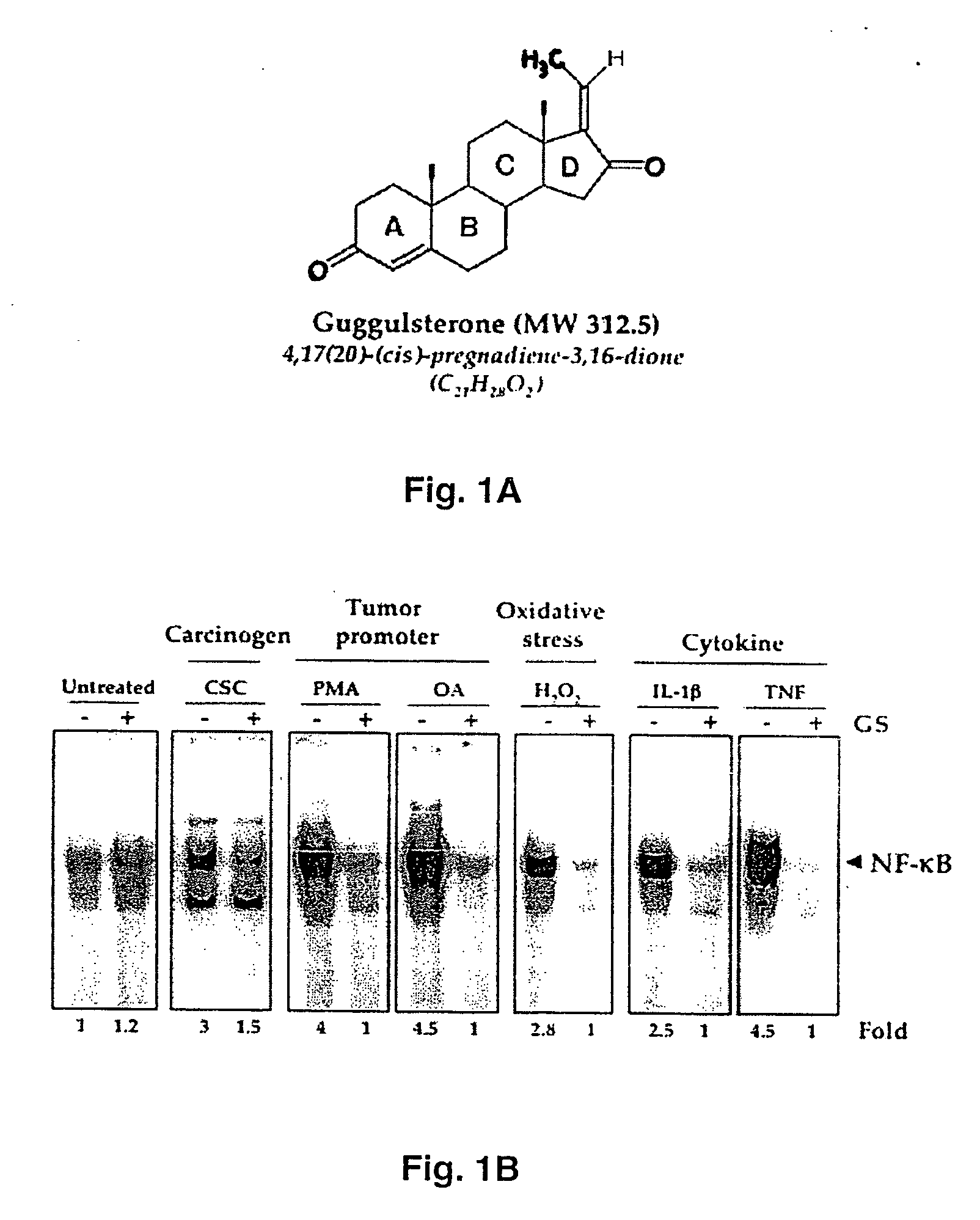
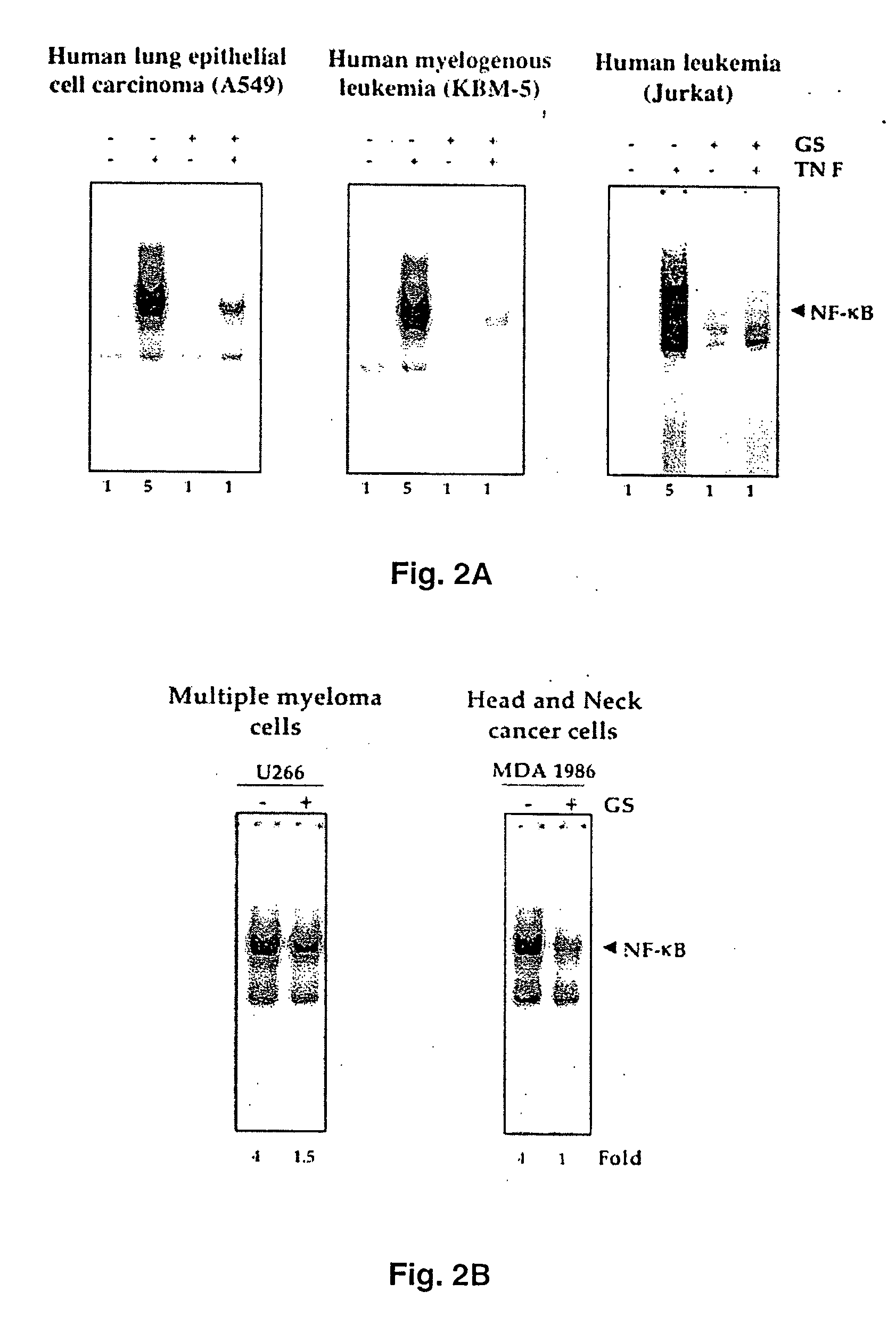
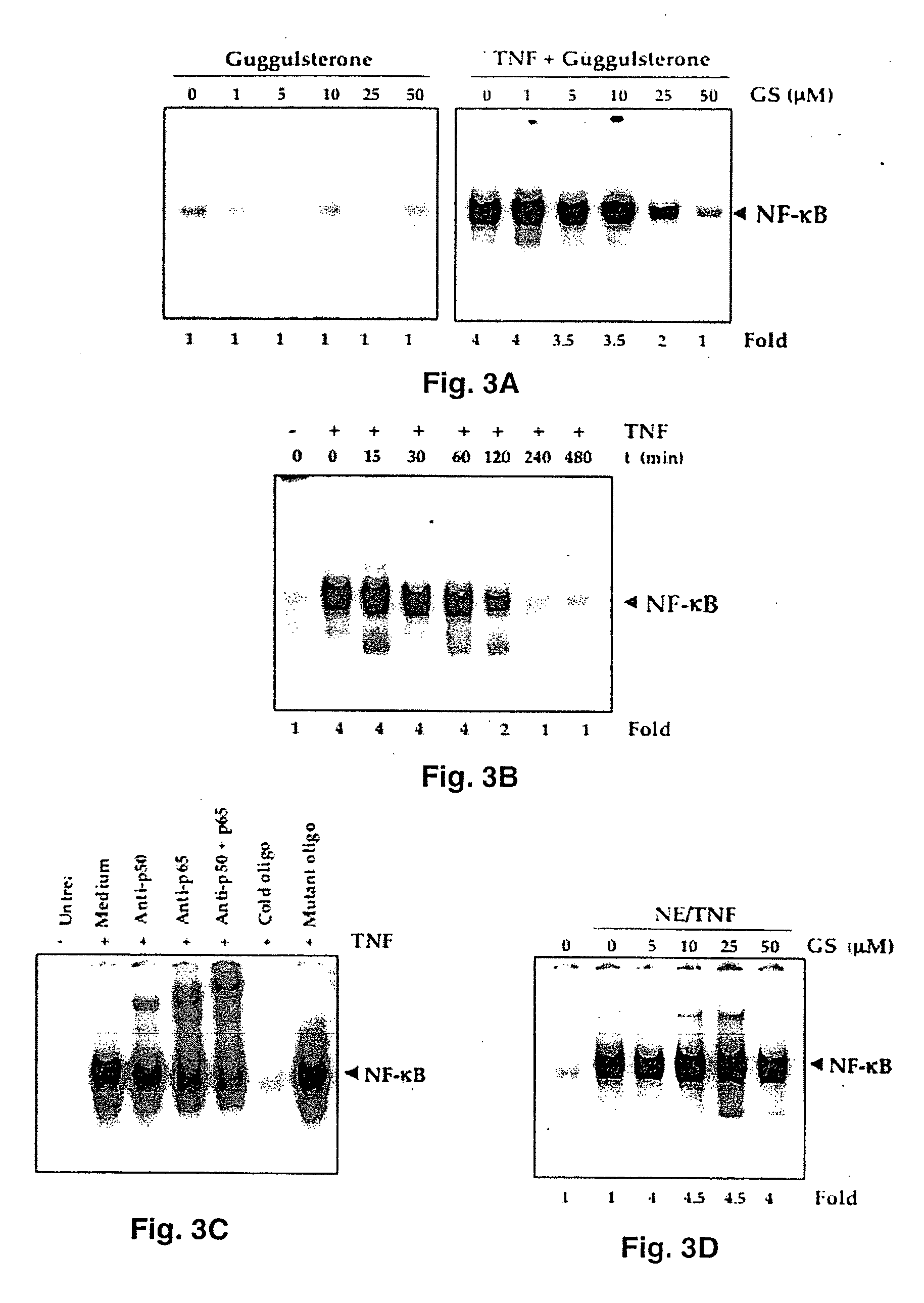
Guggulsterone: an inhibitor of nuclear factor - kappaB and IkappaBalpha kinase activation and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060019907A1Good effectHigh activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLymphatic SpreadCyclin D1
The present invention provides an inhibitor of NF-κB, guggulsterone and its analogs. Guggulsterone suppresses NF-κB activation induced by TNF, phorbol ester, okadaic acid, cigarette smoke, H2O2 and IL-1β, as well as constitutive NF-κB activation expressed in most tumor cells. One mechanism by which guggulsterone inhibits activation of NF-κB is through suppression of IκBα phosphorylation and IκBα degradation. NF-κB-dependent gene transcription is modulated by guggulsterone and its analogs. In particular, induction by TNF, TNFR1, TRADD, TRAF2, NIK and IKK, is modulated by guggulsterone and its analogs. In addition, guggulsterone decreased the expression of genes involved in anti-apoptosis (IAP1, XIAP, Bfl-1 / A1, bcl-2, cFLIP, survivin), proliferation (cyclin D1, c-myc) and metastasis (MMP-9, COX2 and VEGF).
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
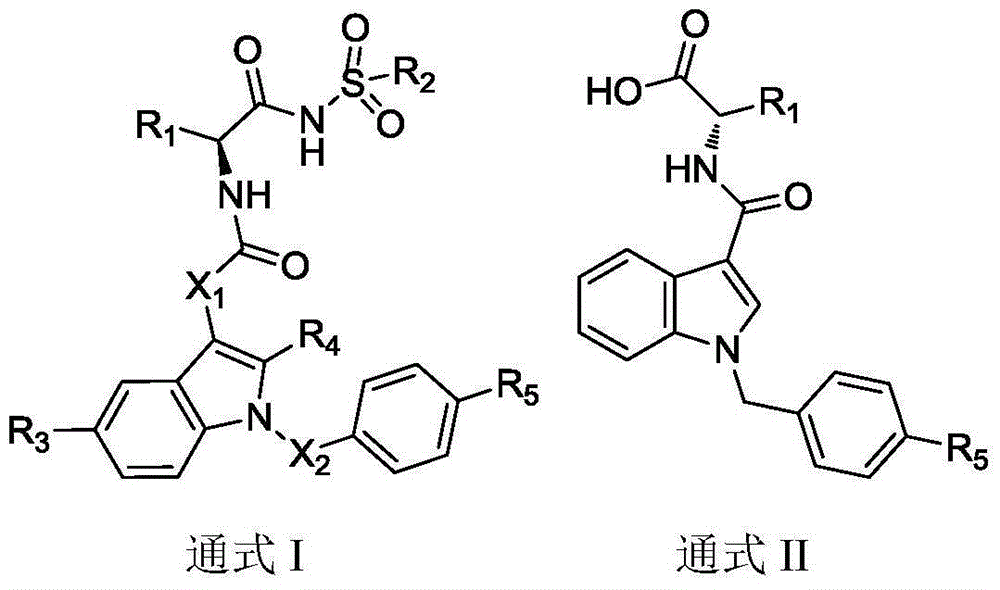
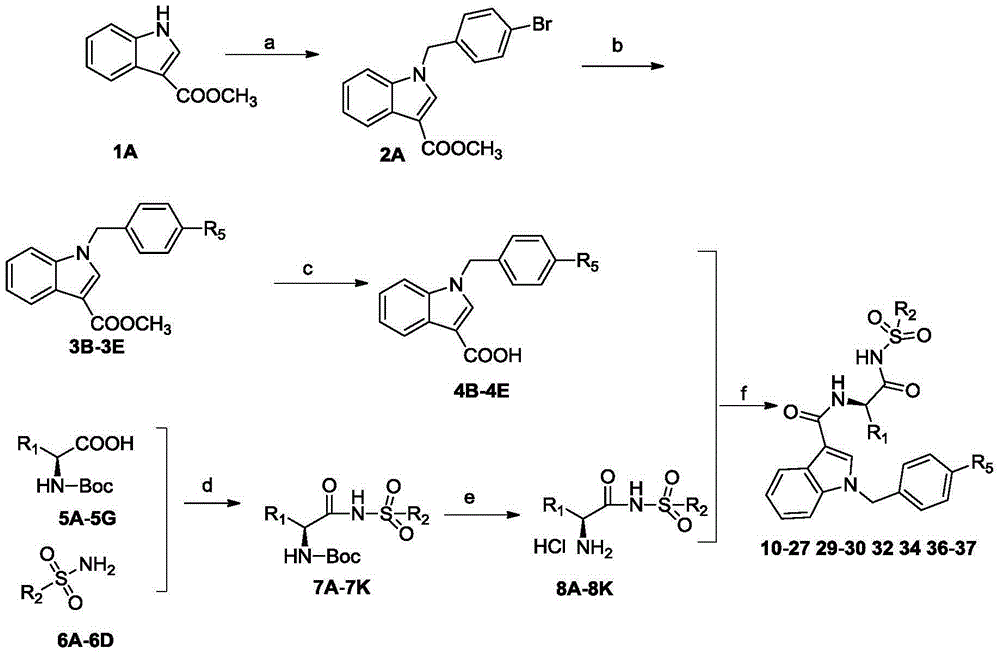
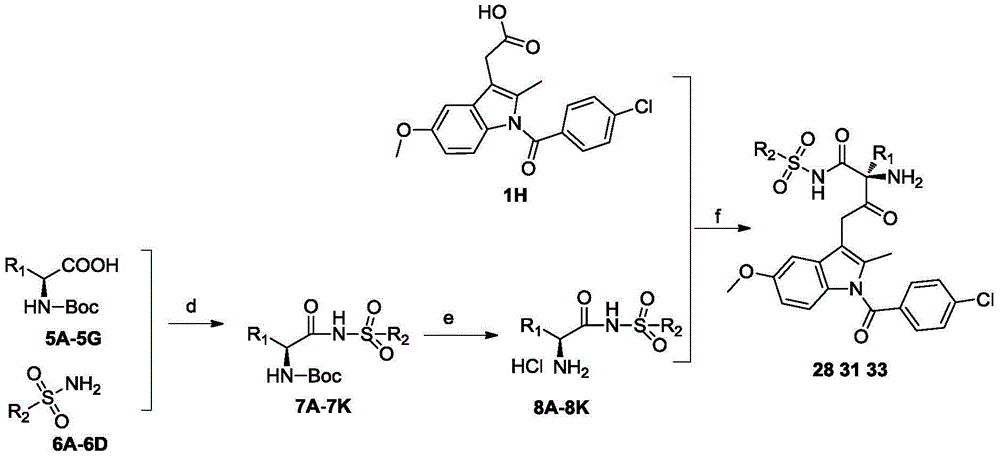
Substituted3-indole Bcl-2 protein inhibitor and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a substituted3-indole Bcl-2 protein inhibitor and a preparation method and an application thereof. The compound has a structure as shown in the general formula I or II. The compound of the invention has a strong inhibitory activity to Bcl-2 protein and can prevent or treat related mammalian diseases caused by abnormal expression of Bcl-2 protein. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical application of a compound of the compound having the structure as shown in the general formula I or II.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Methods and compositions for treating a cell-proliferative disorder using CRE decoy oligomers, BCL-2 antisense oligomers, and hybrid oligomers thereof
InactiveUS7060690B2Hinder and prevent bindingModulate transcriptional activitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAbnormal tissue growth
The present invention is directed to hybrid oligomers comprising a cyclic AMP response element (CRE) sequence and a sequence that hybridizes to a bcl-2 pre-mRNA or mRNA, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising such hybrids. The present invention is also directed to the use of CRE decoy oligomers, comprising a CRE consensus sequence, and bcl-2 antisense oligomers in combination therapies, and the use of bcl-2 / CRE hybrid oligomers, to treat or prevent cell-proliferative related disorders, including hyperplasias, cancers, tumors and carcinomas. In one embodiment, the invention relates to therapeutic protocols comprising the administration of a CRE decoy oligomer and a bcl-2 antisense oligomer for the treatment of cell-proliferative related disorders. In another embodiment, the invention relates to therapeutic protocols comprising the administration of a bcl-2 antisense / CRE decoy (bcl-2 / CRE) hybrid oligomer for the treatment of cell-proliferative related disorders.
Owner:GENTA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com