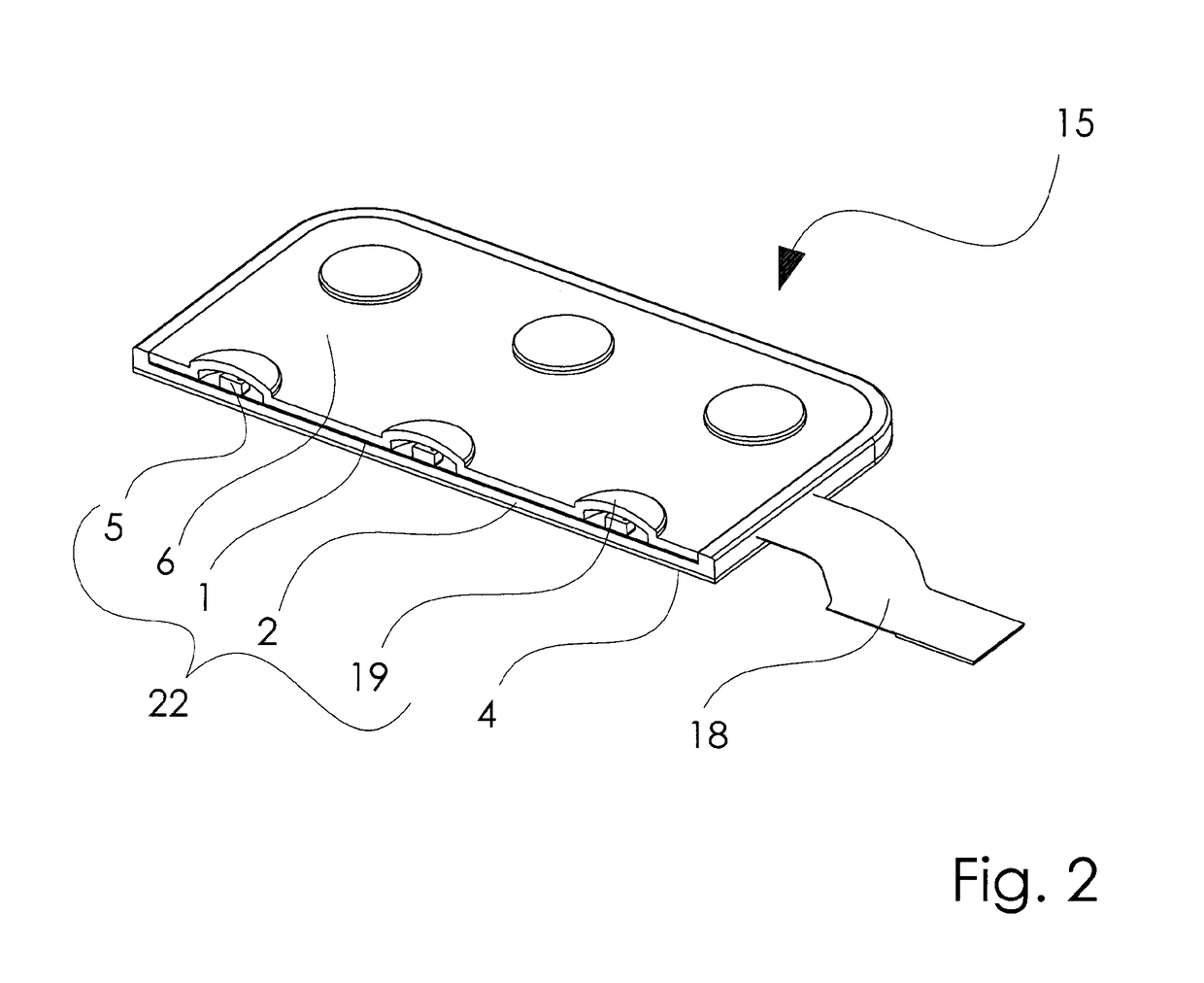
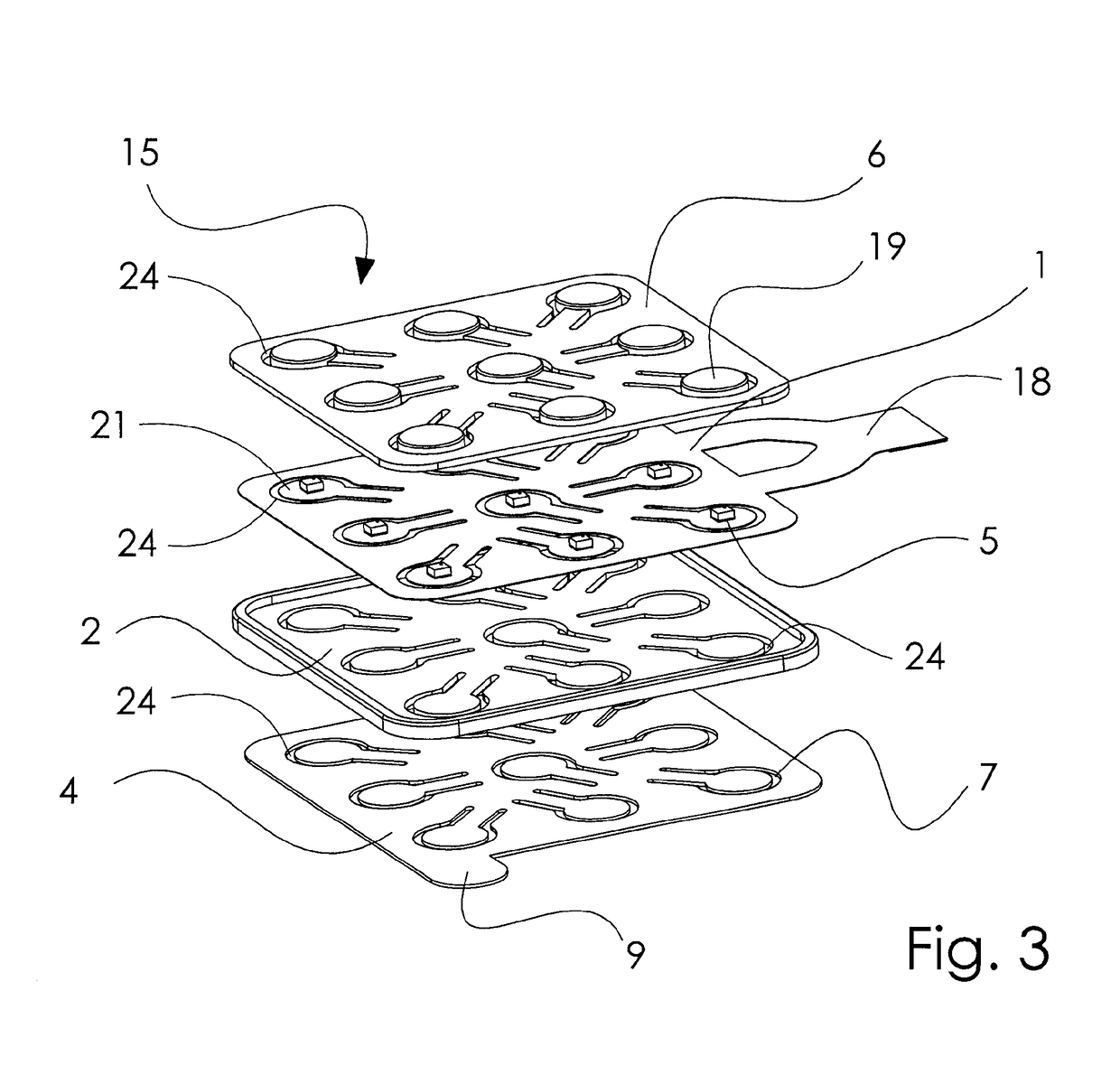
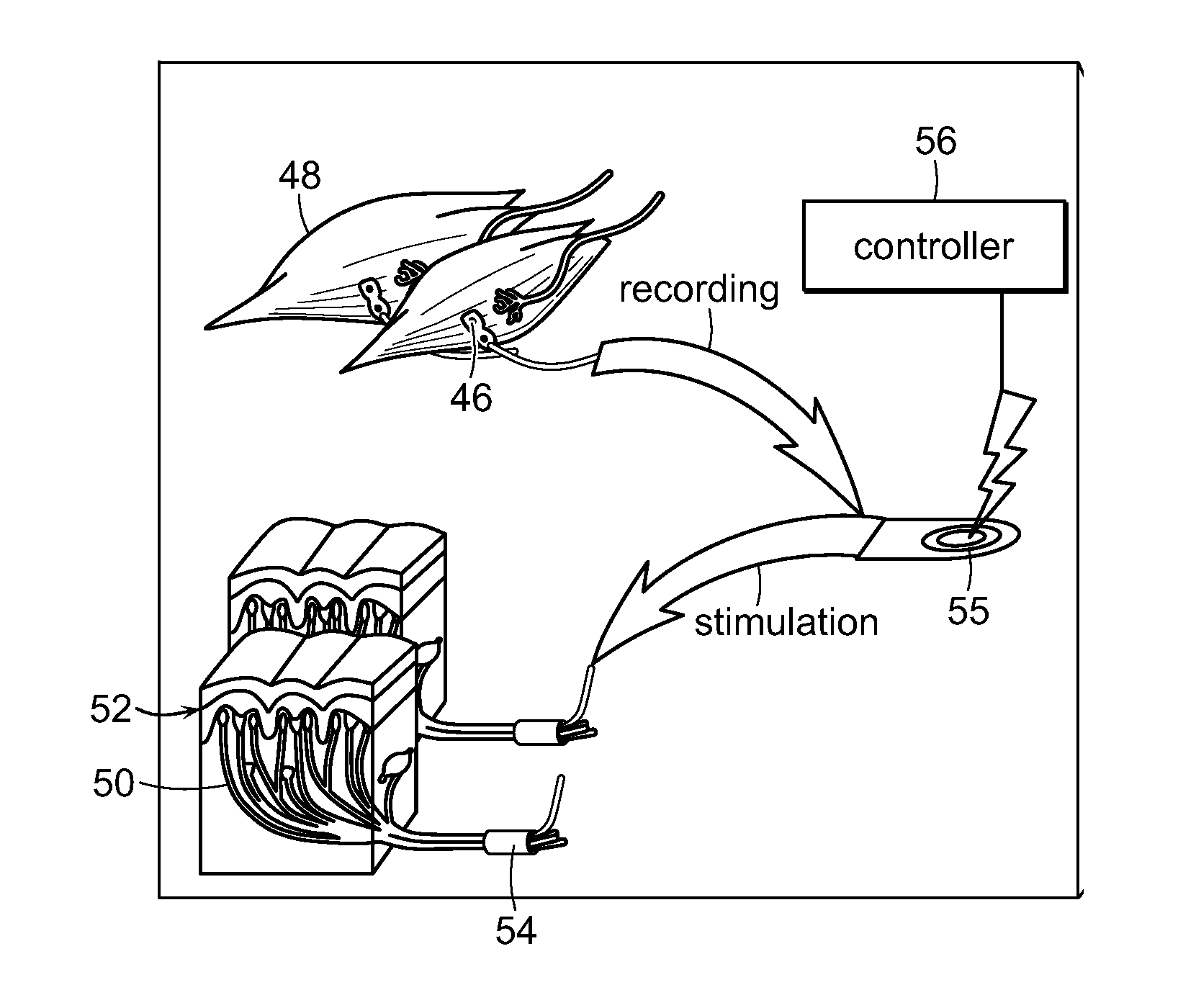
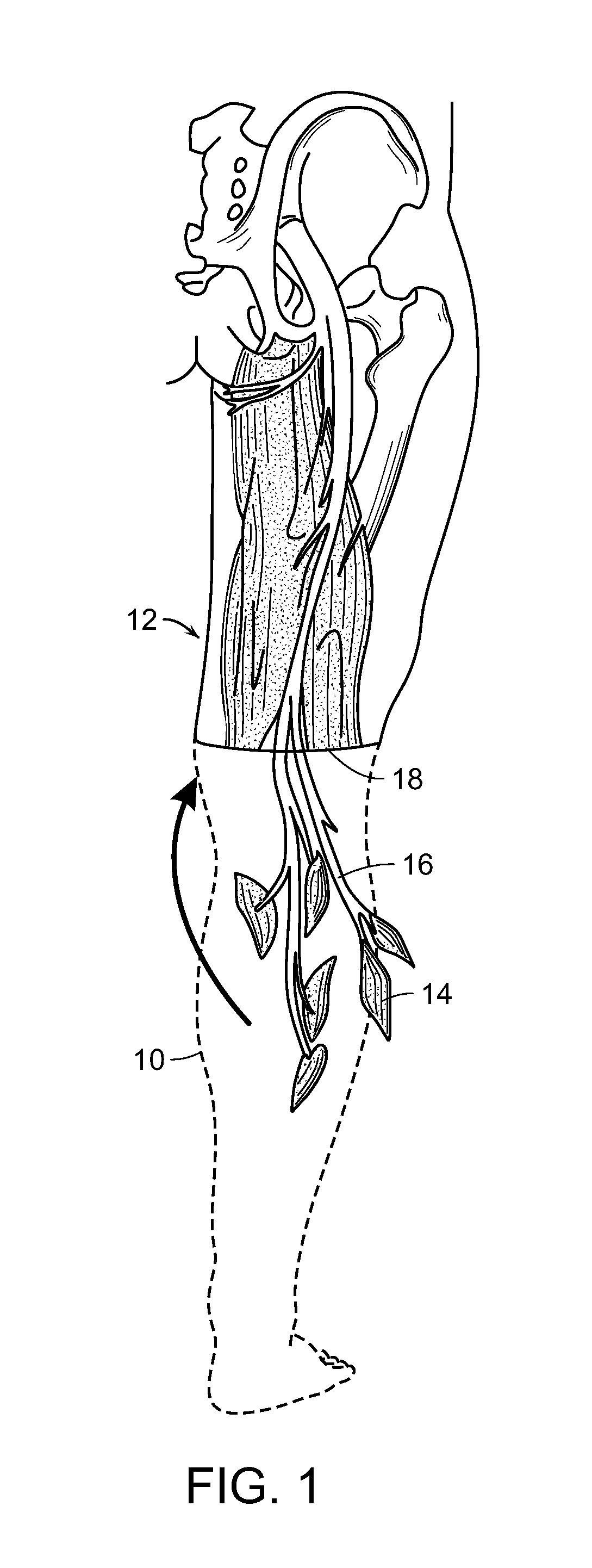
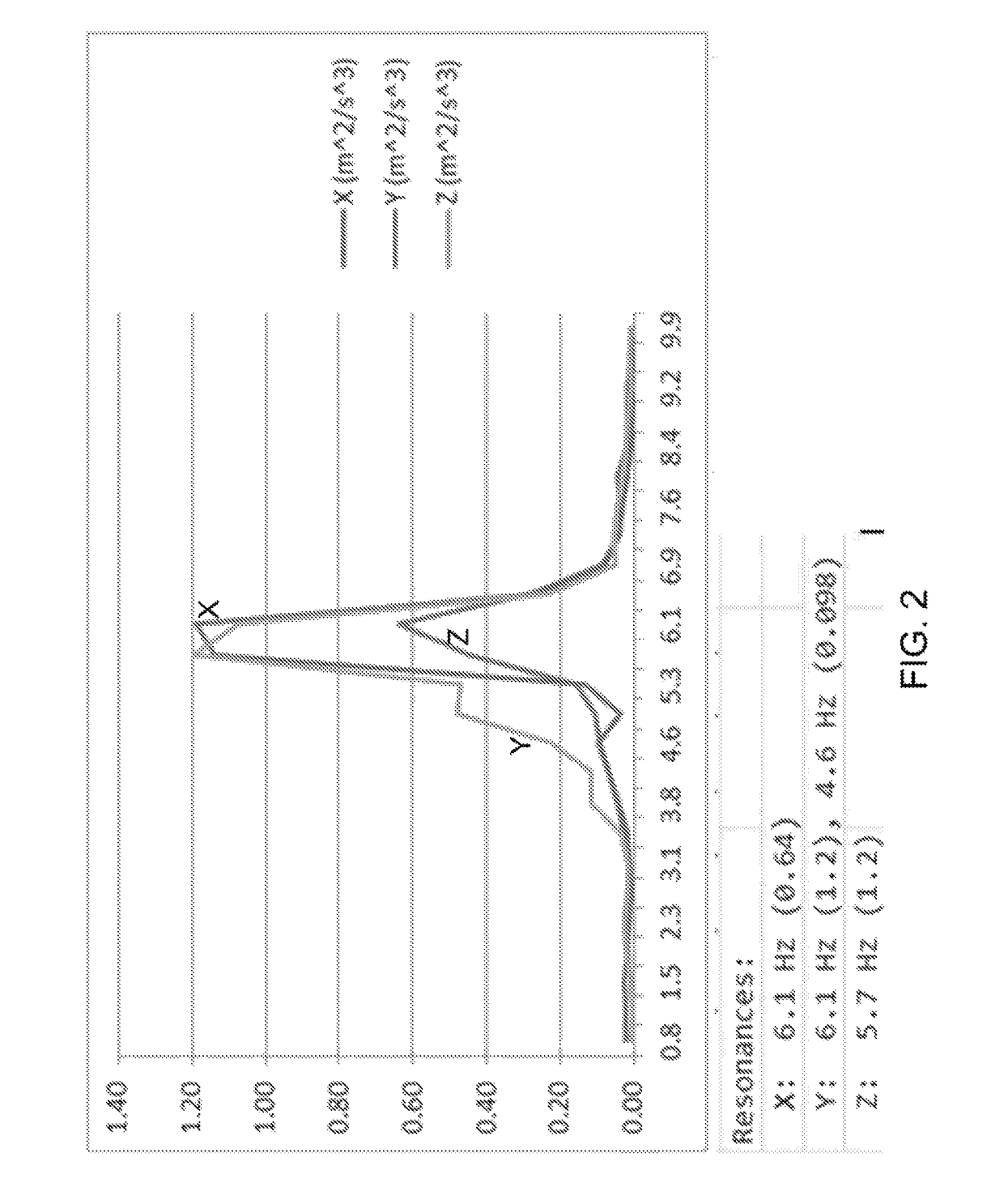
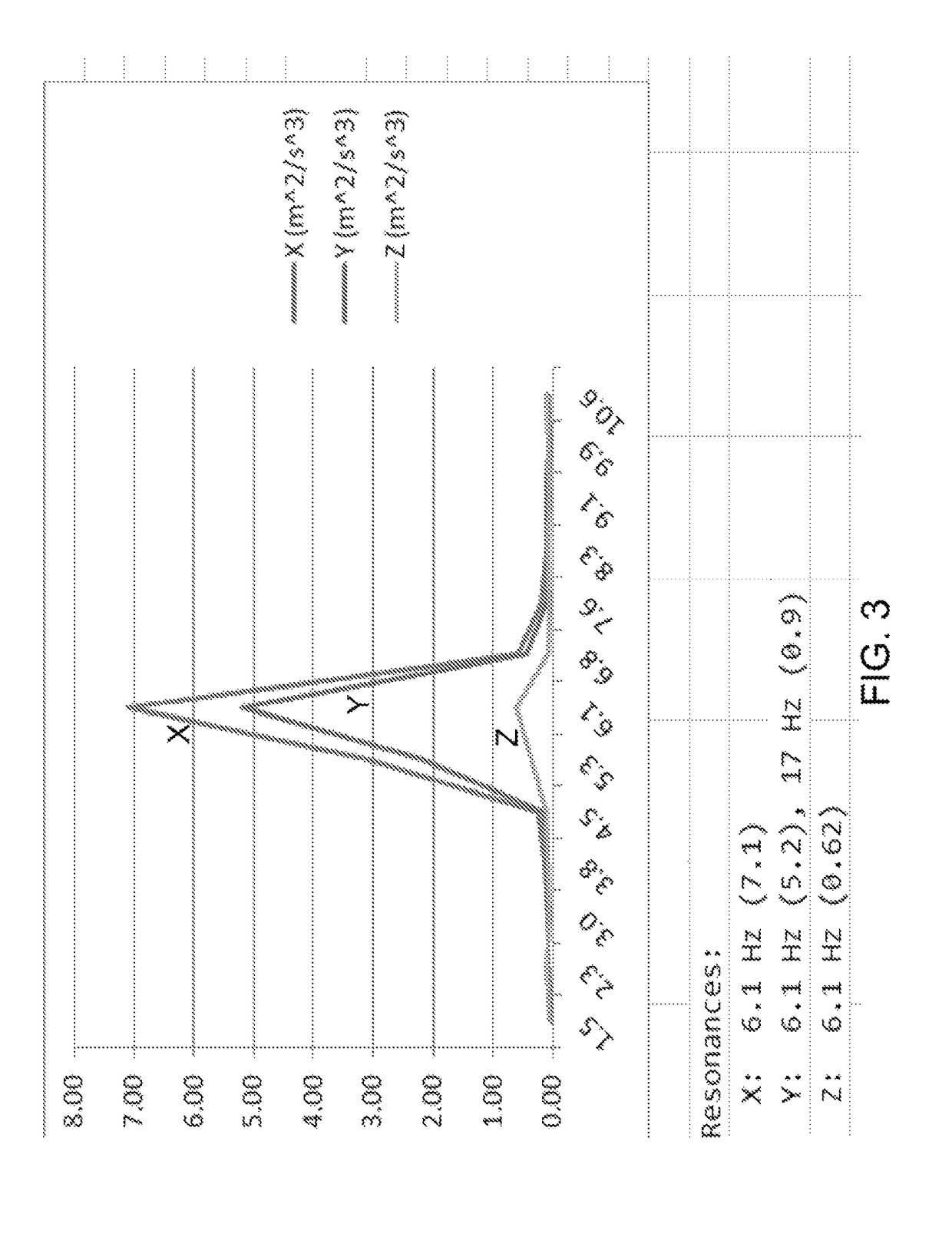
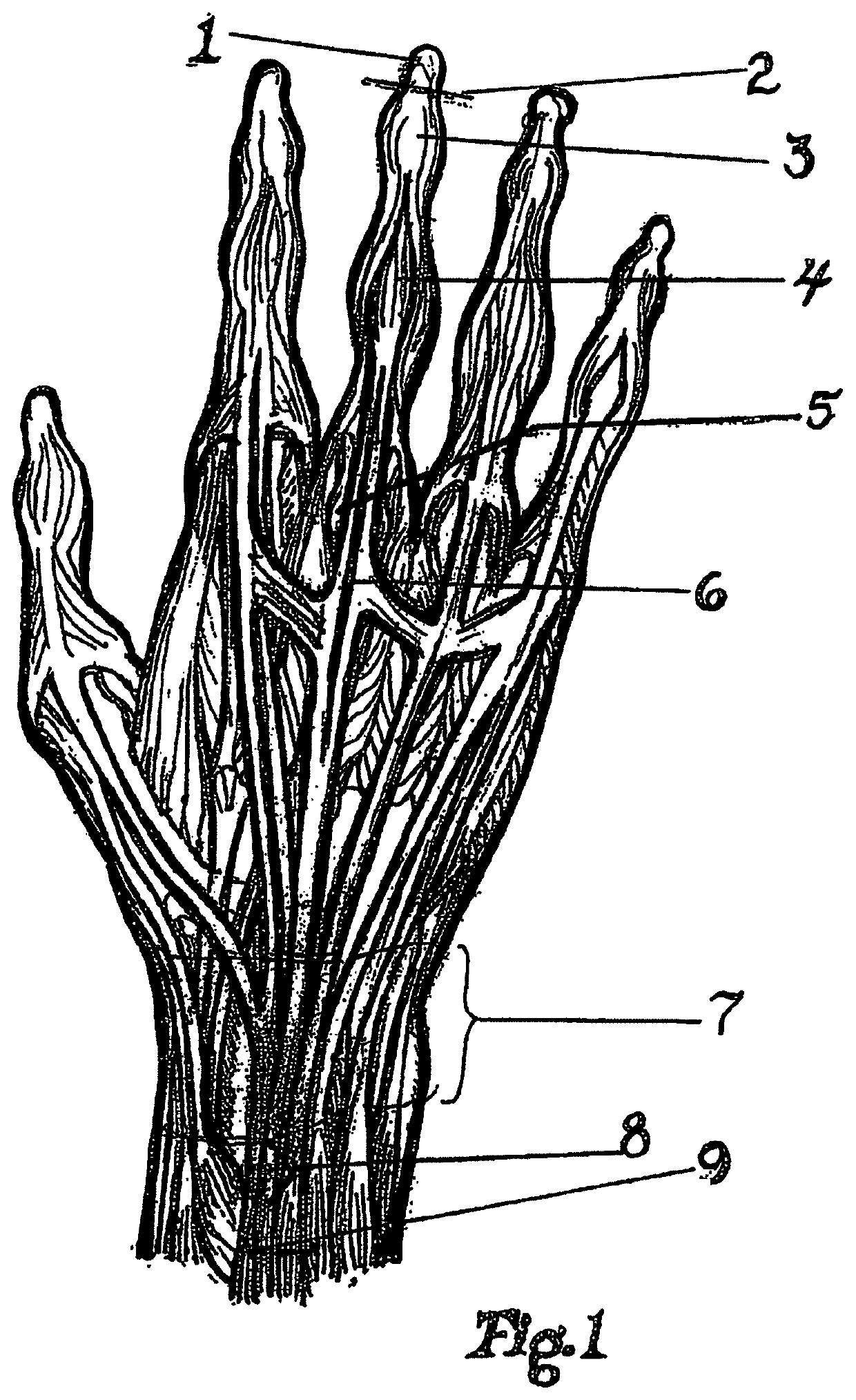
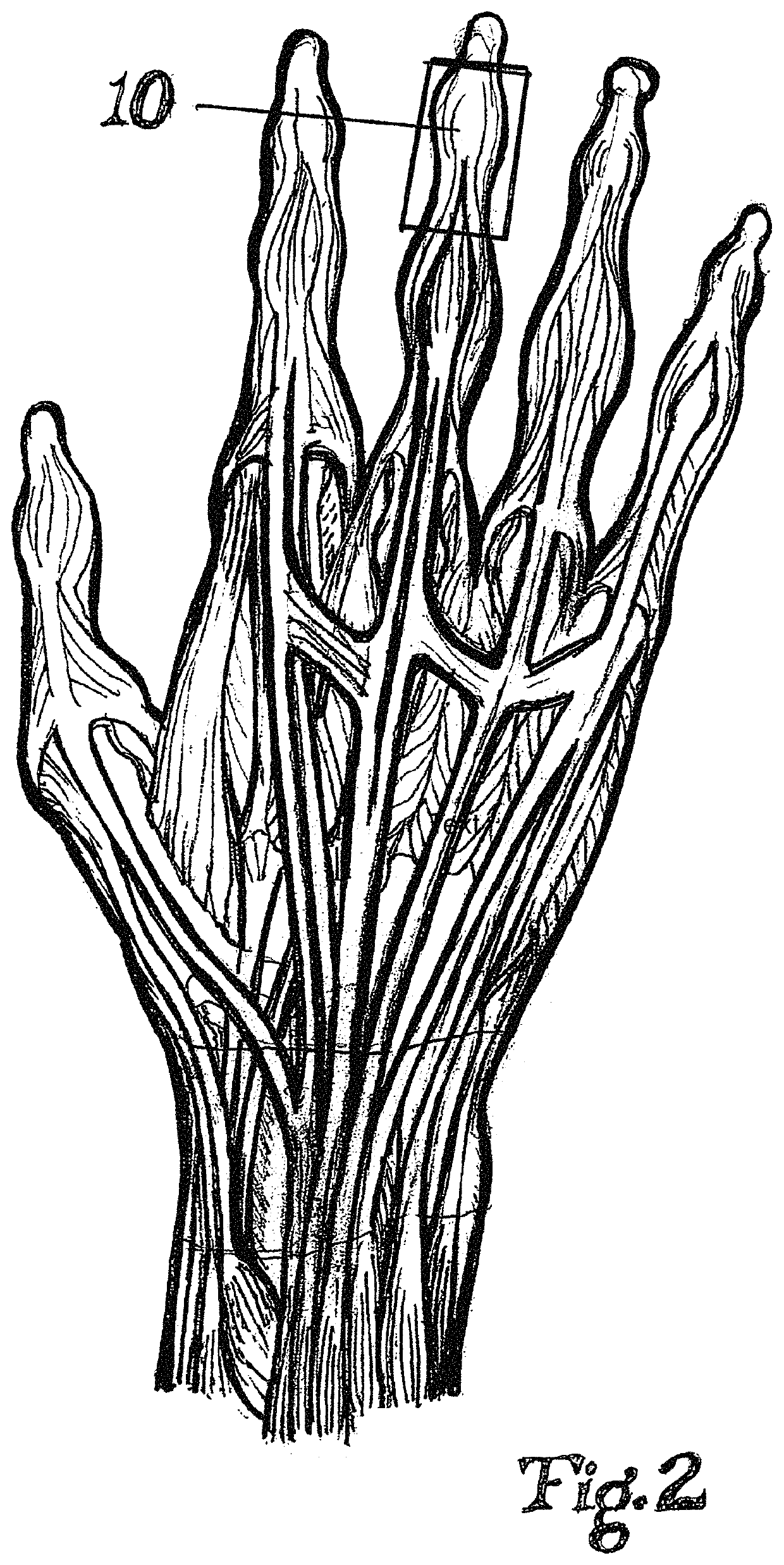
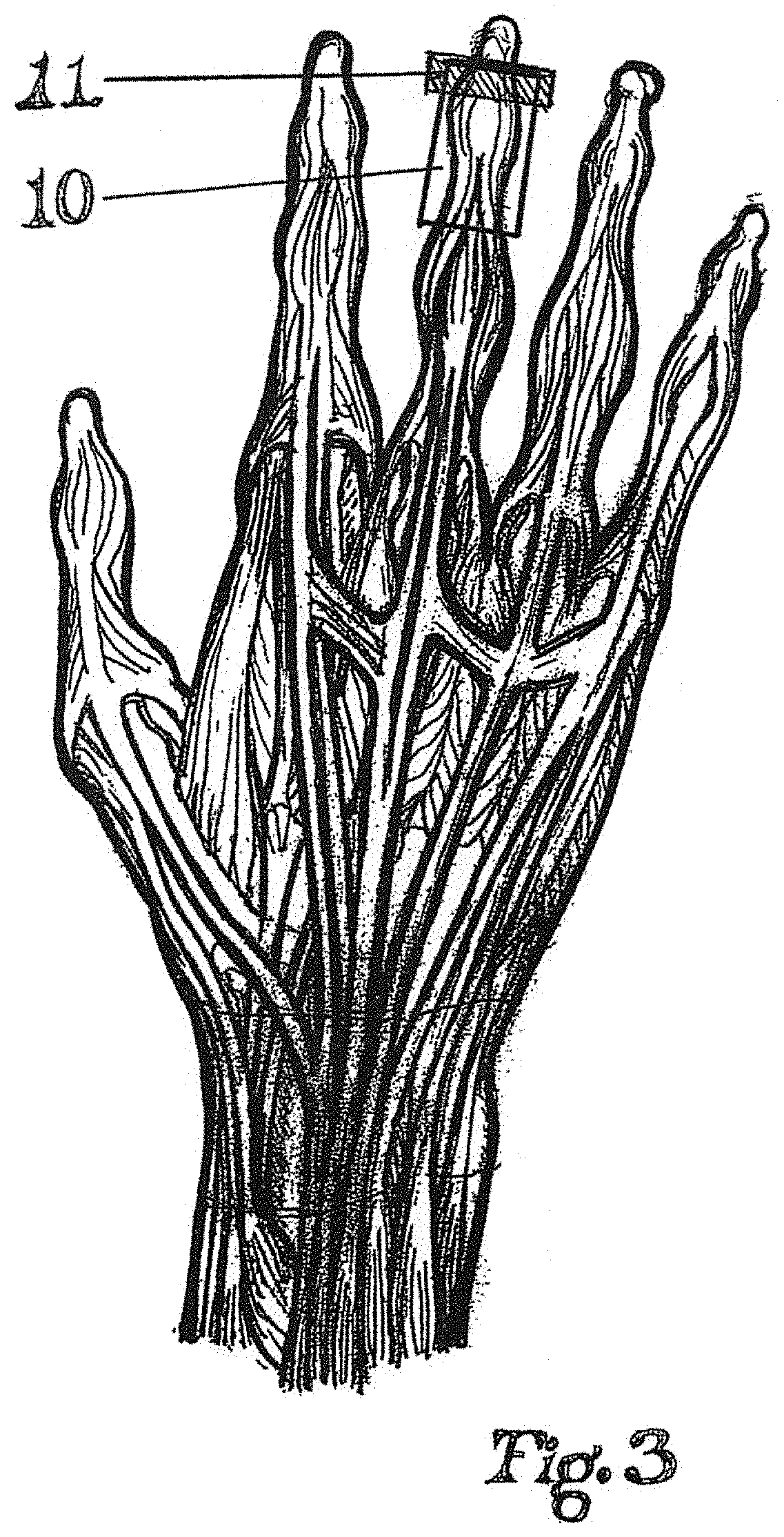
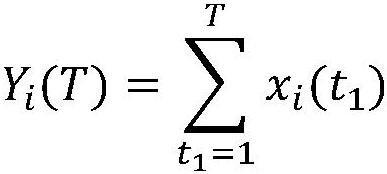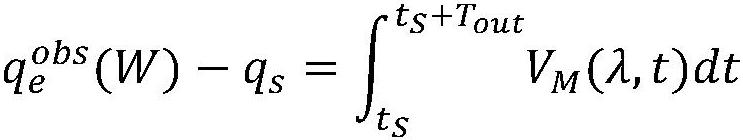Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Antagonist muscle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
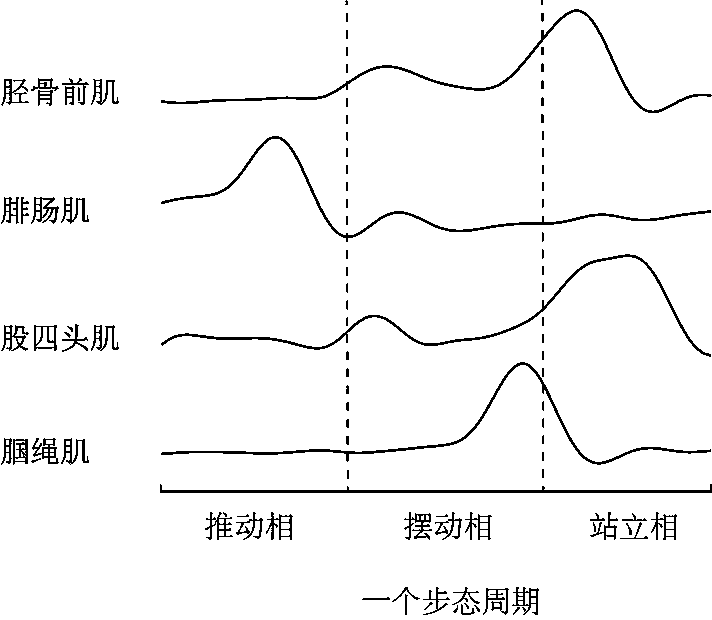
Your triceps is the antagonist muscle. If you reverse the motion, doing triceps extensions or press-downs against resistance, your triceps becomes the agonist muscle because it powers the motion, while your biceps becomes the antagonist muscle that passively lengthens so that your triceps can move the elbow joint.
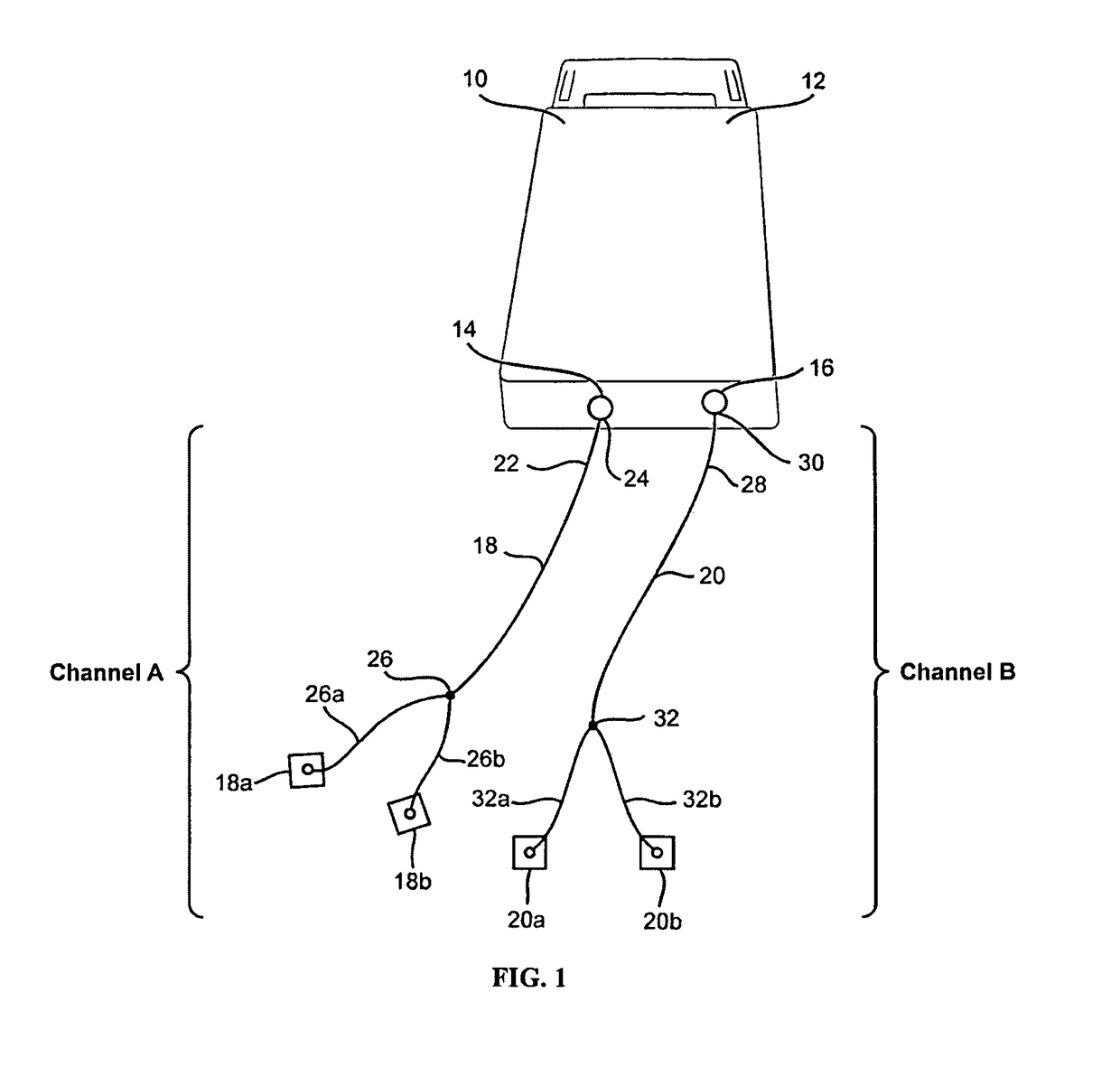
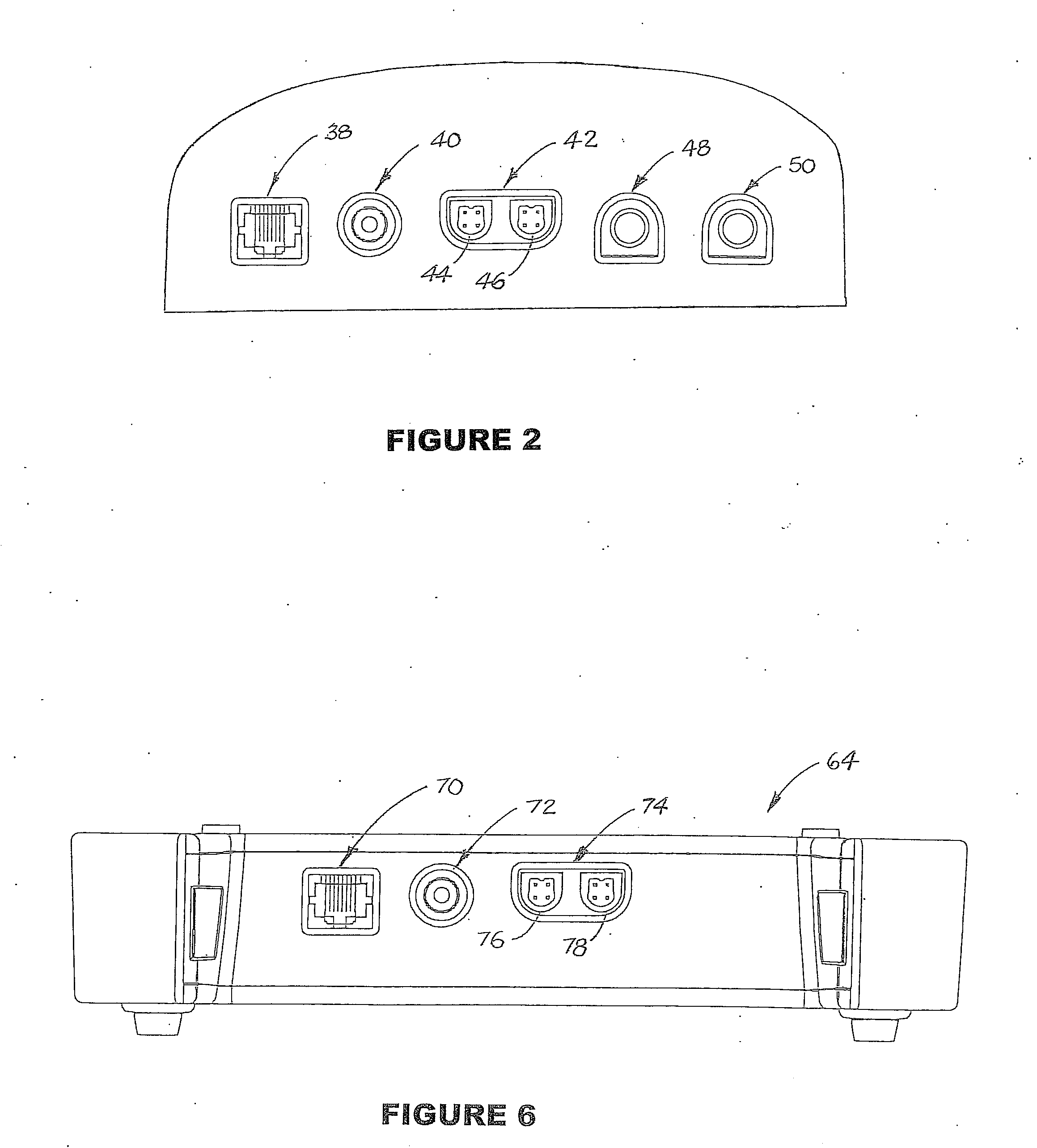
Electrical Stimulation Method for Treatment of Peripheral Neuropathy
ActiveUS20090326607A1Improve overall senseStiffer and more difficult it is to bendBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsElectricityPronations
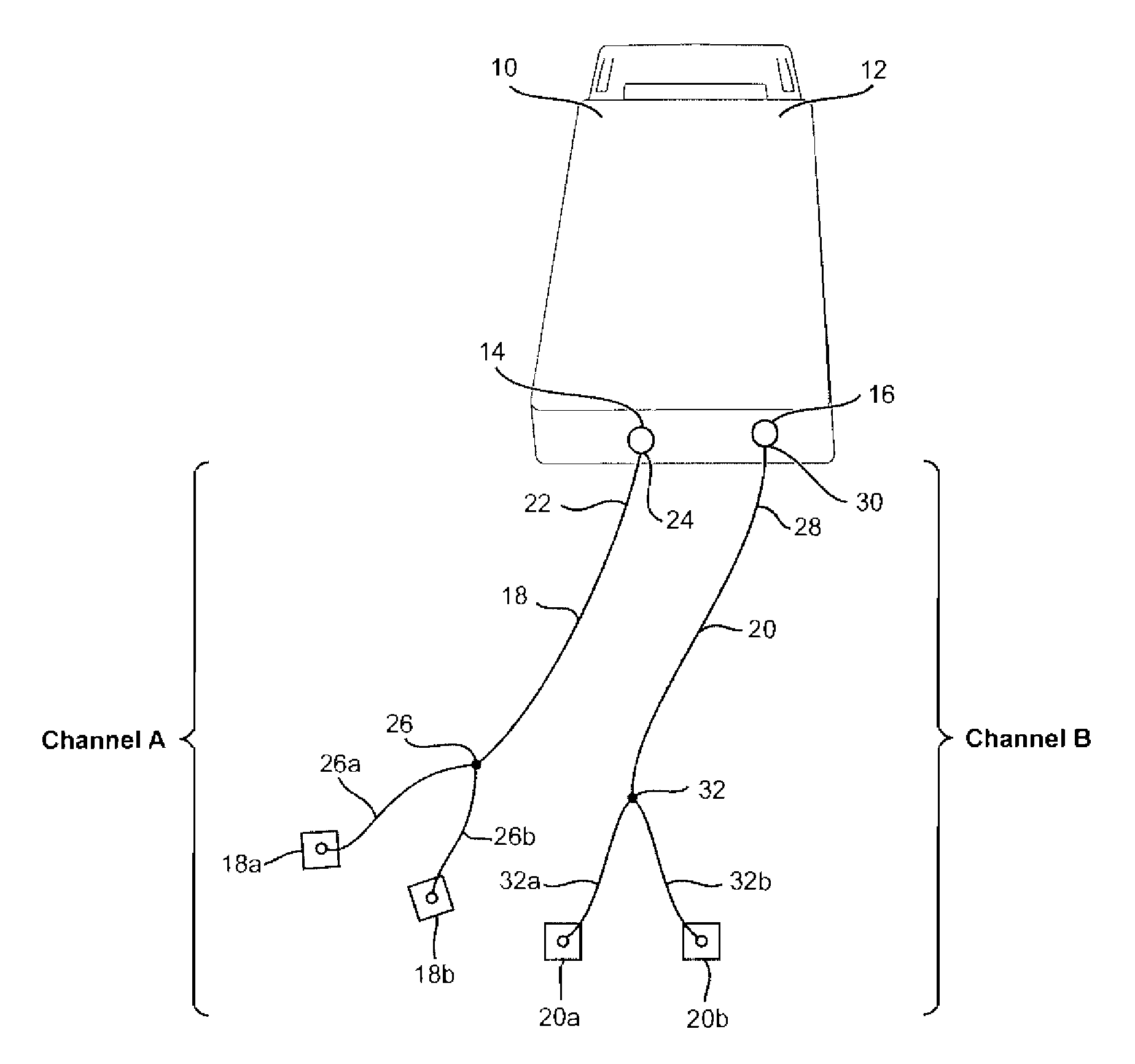
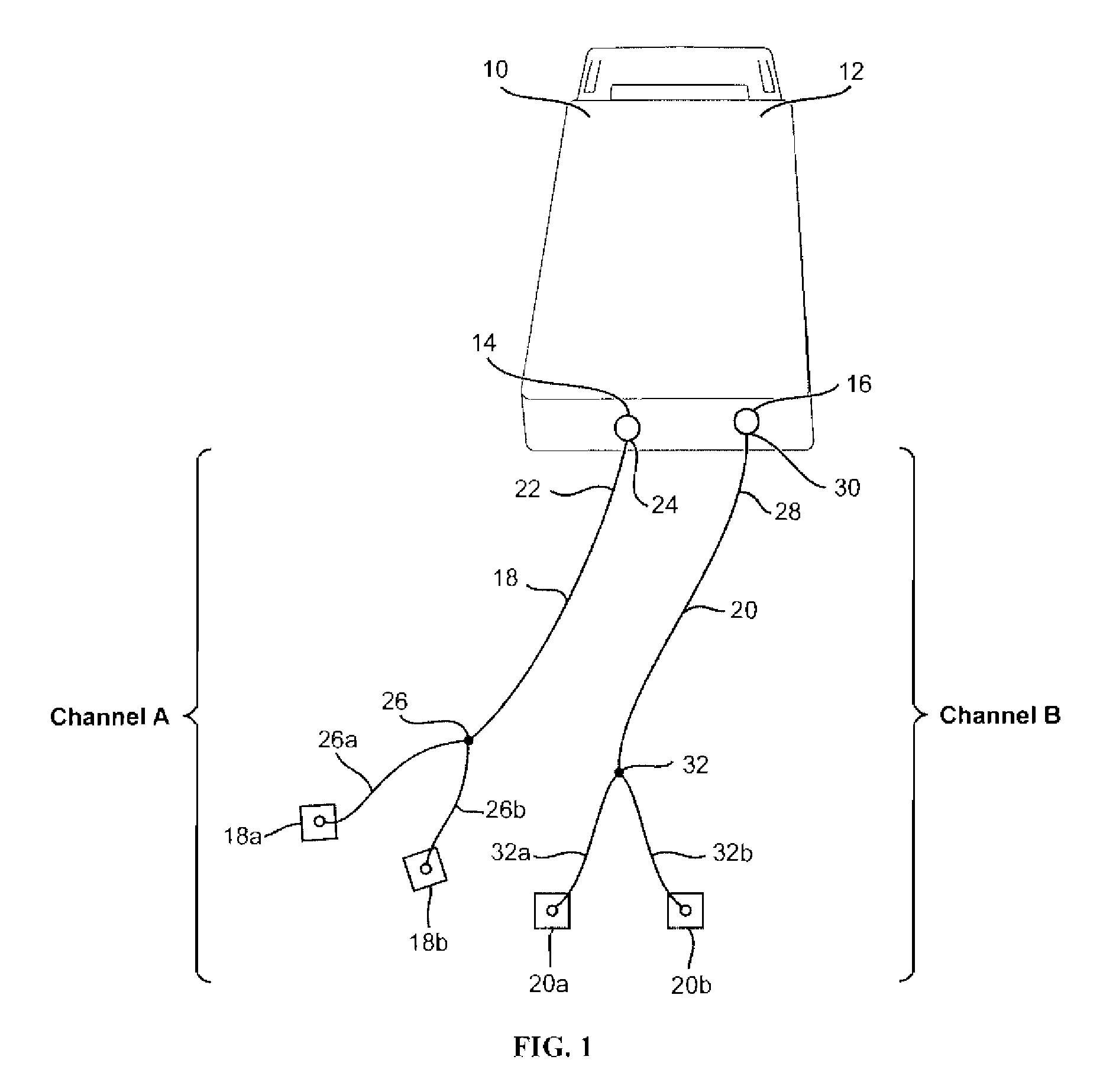
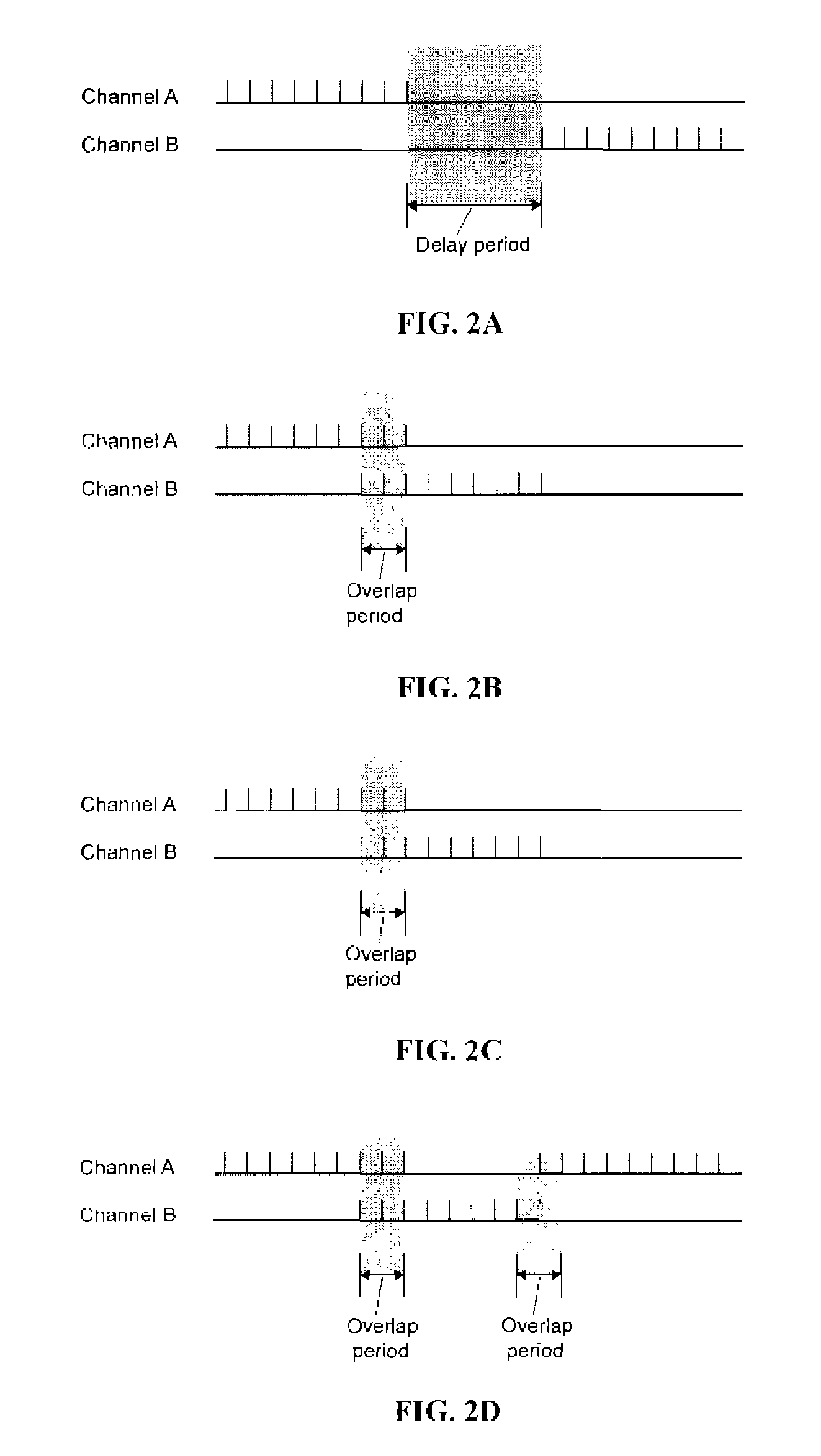
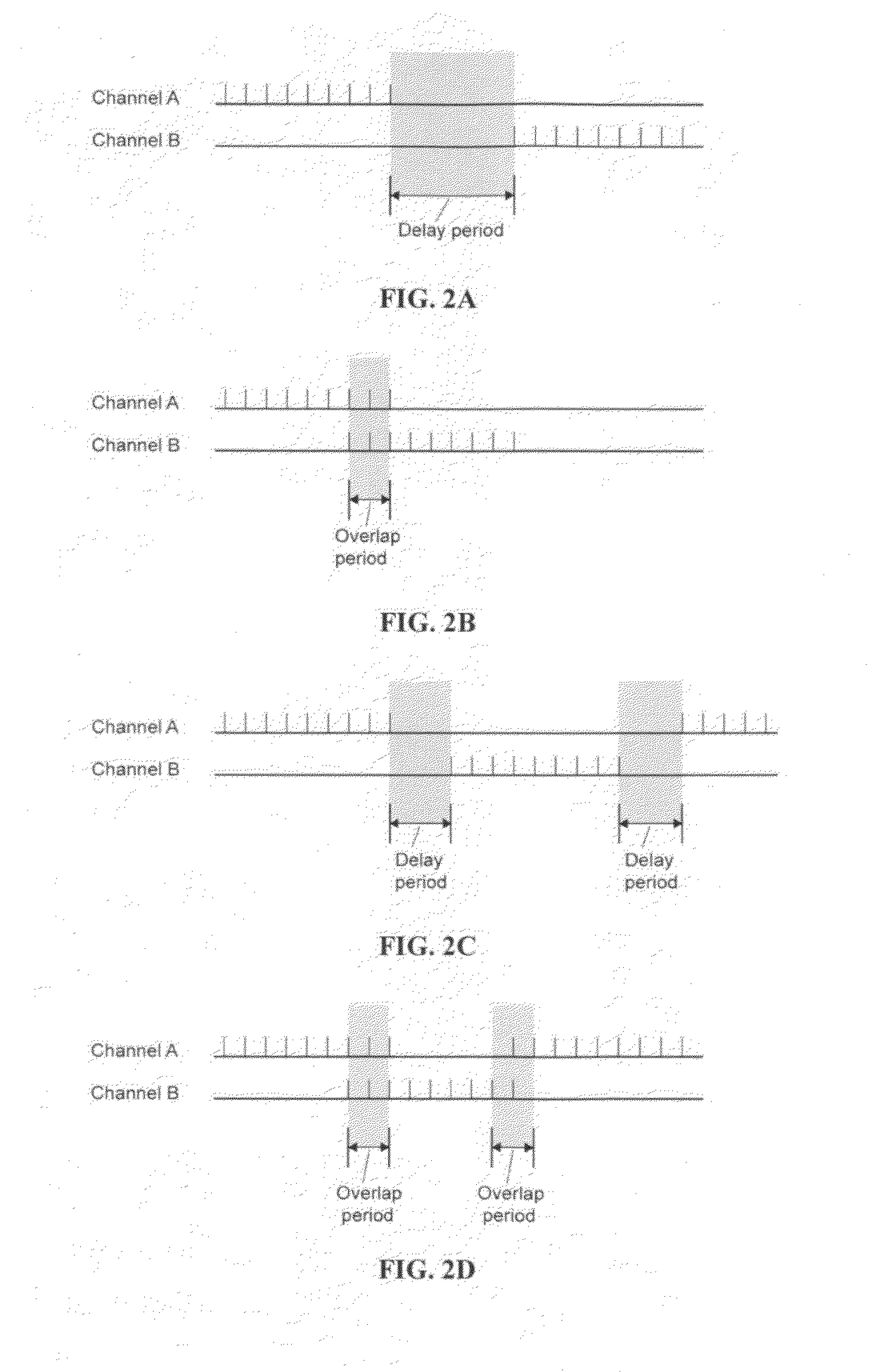
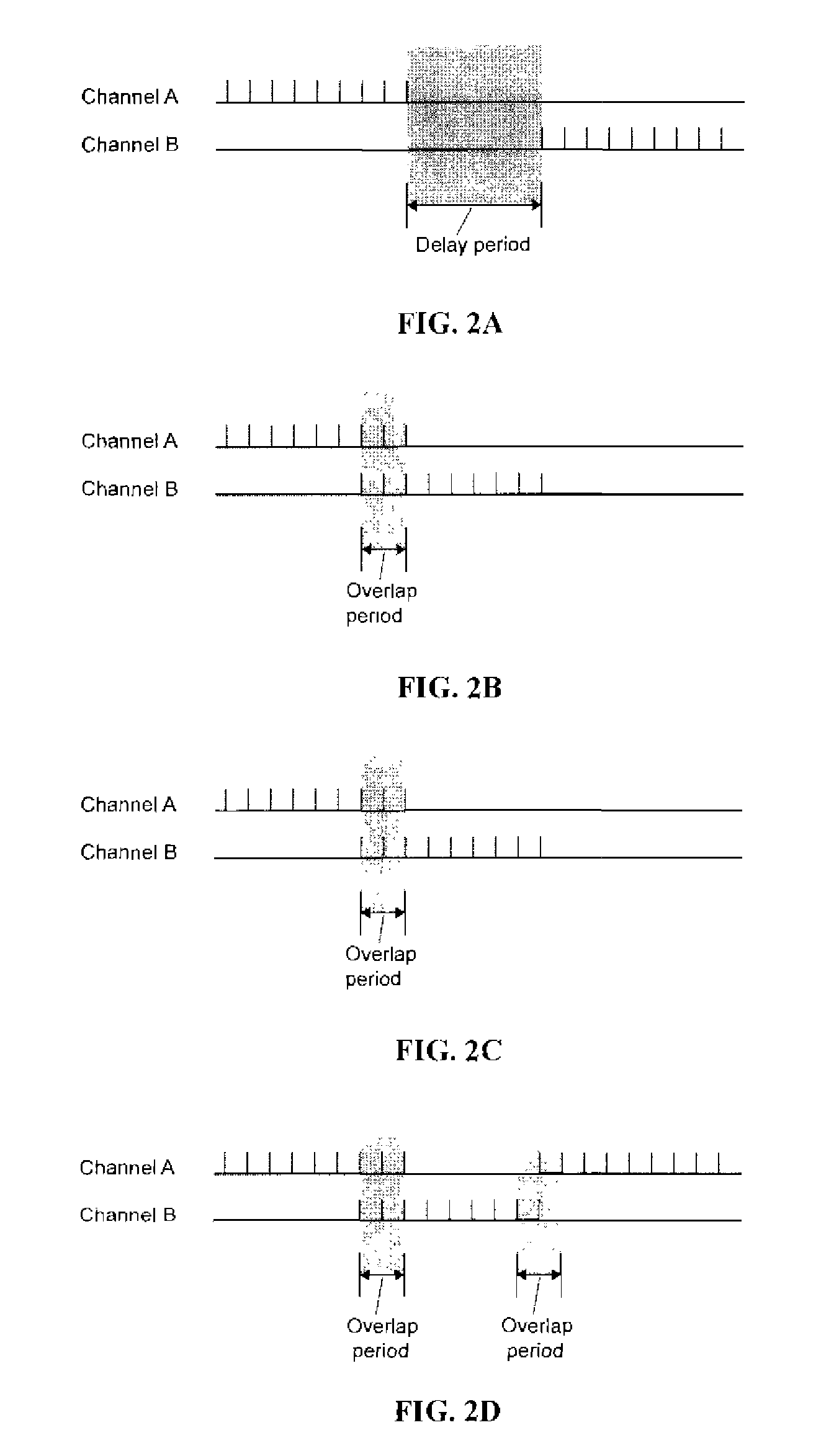
An electrical stimulation method for the treatment of peripheral neuropathy is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, the method utilizes an electrical stimulation device that includes a plurality of channels of electrodes each of which includes a first and second electrode positioned in electrical contact with tissue of a target region suffering from peripheral neuropathy. Agonist / antagonist muscles involved in abduction / adduction, flexion / extension, supination / pronation, protraction / retraction, and / or eversion / inversion in the peripheral body regions are stimulated with a patterned series of electrical pulses through channels of electrodes in accordance with a procedure for treating peripheral neuropathy. The patterned series of electrical pulses may comprise: a plurality of cycles of a biphasic sequential pulse train pattern; a plurality of cycles of a biphasic overlapping pulse train pattern; a plurality of cycles of a triphasic sequential pulse train pattern; and a plurality of cycles of a triphasic overlapping pulse train pattern.
Owner:ACCELERATED CARE PLUS CORP
Device and system to measure and assess superficial muscle contractile characteristics
InactiveUS20190022388A1Inertial sensorsDiagnostic recording/measuringAccelerometerMuscle contraction
The present invention relates to a device and system to measure and assess superficial skeletal muscle mechanical and neuromuscular contractile characteristics, and interpret the results to provide metrics with quantifiable and qualitative descriptors relating to muscle function. The present device provides a further type of mechanomyography and a new use for acceleromyography by measuring the mechanical muscle movement of an involuntary stimulated muscle from an automated electro-stimulation protocol to determine muscle contractile properties. Muscle twitch response during the latent, contraction and relaxation phase is measured using an array of multiple accelerometers on a sensor pad to assess and diagnose muscle. function from various measurements. This information is processed using algorithms to determine muscle function abnormalities, muscle activation patterns, muscle symmetry of lateral muscle pairs, muscle synchronization of antagonist muscle, muscle force, muscle acceleration, muscle speed, muscle tone, muscle fatigue, muscle power / torque and muscle efficiency.
Owner:QUANIMUS INC
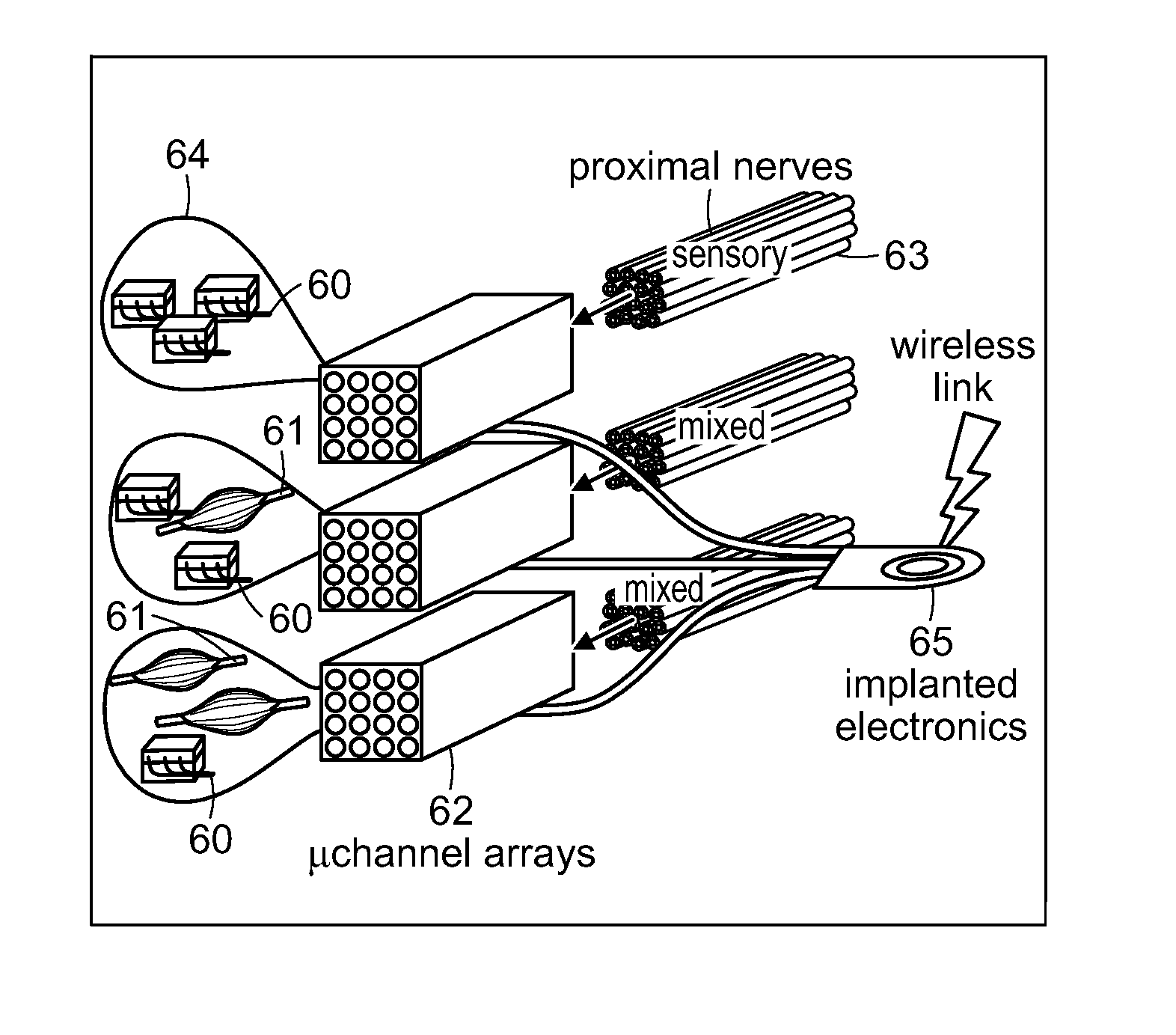
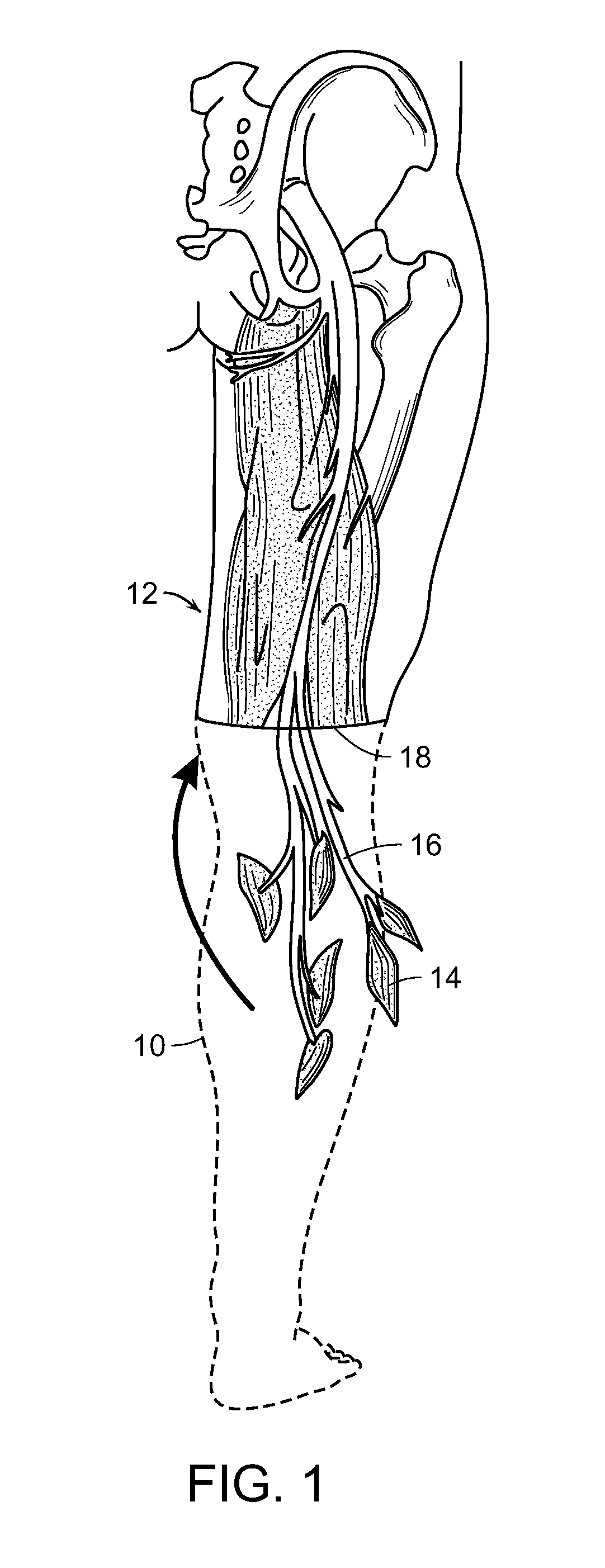
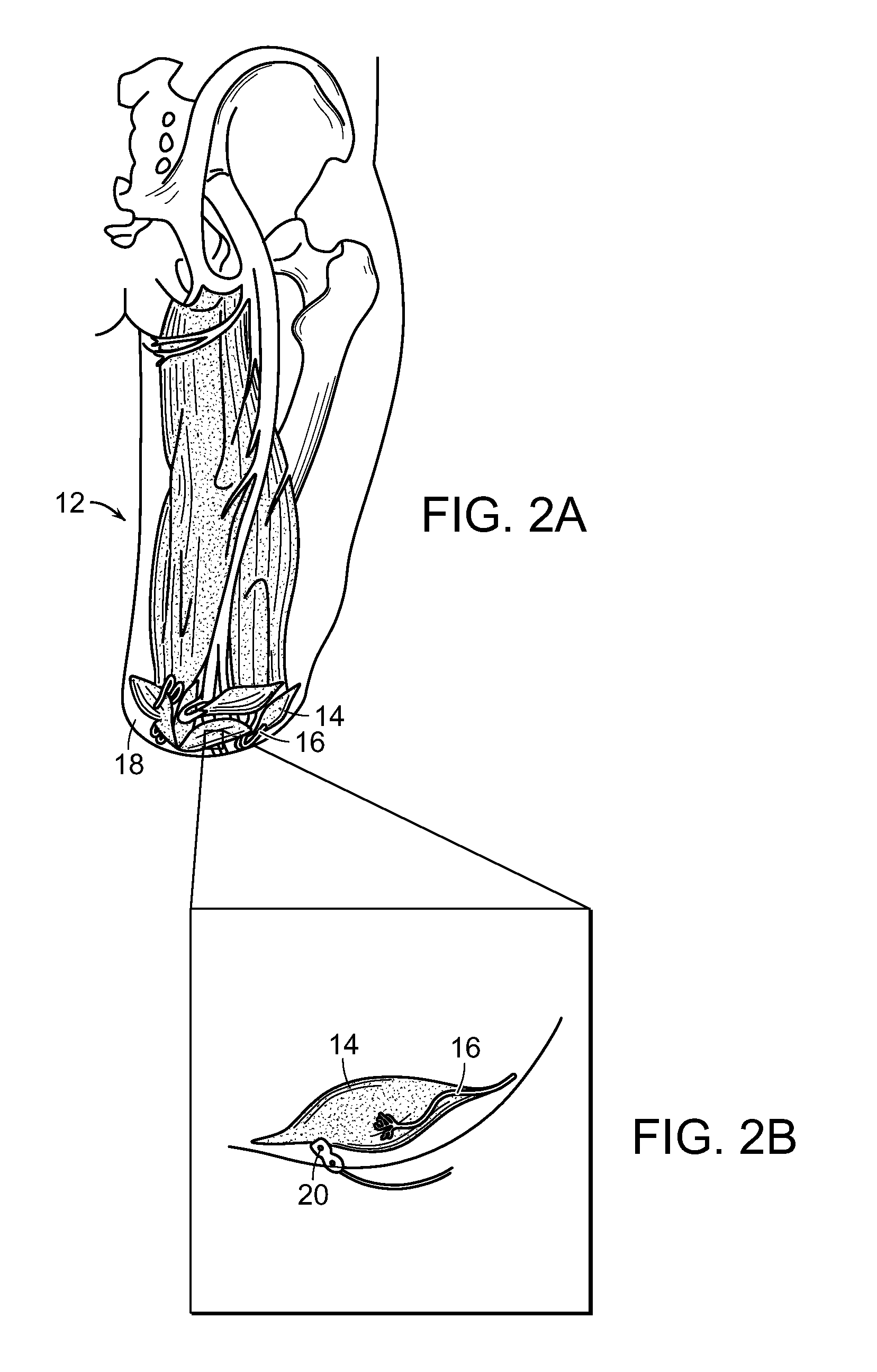
Peripheral Neural Interface Via Nerve Regeneration to Distal Tissues
ActiveUS20150173918A1Easy to controlRaise the potentialSpinal electrodesMusculoskeletal system evaluationSensory FeedbacksNeurulation
At least partial function of a human limb is restored by surgically removing at least a portion of an injured or diseased human limb from a surgical site of an individual and transplanting a selected muscle into the remaining biological body of the individual, followed by contacting the transplanted selected muscle, or an associated nerve, with an electrode, to thereby control a device, such as a prosthetic limb, linked to the electrode. Simulating proprioceptive sensory feedback from a device includes mechanically linking at least one pair of agonist and antagonist muscles, wherein a nerve innervates each muscle, and supporting each pair with a support, whereby contraction of the agonist muscle of each pair will cause extension of the paired antagonist muscle. An electrode is implanted in a muscle of each pair and electrically connected to a motor controller of the device, thereby simulating proprioceptive sensory feedback from the device.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for applying neuromuscular electrical stimulation
ActiveUS8620438B1Reduce the overall heightRegulate movementUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyElectricityNeuromuscular stimulation
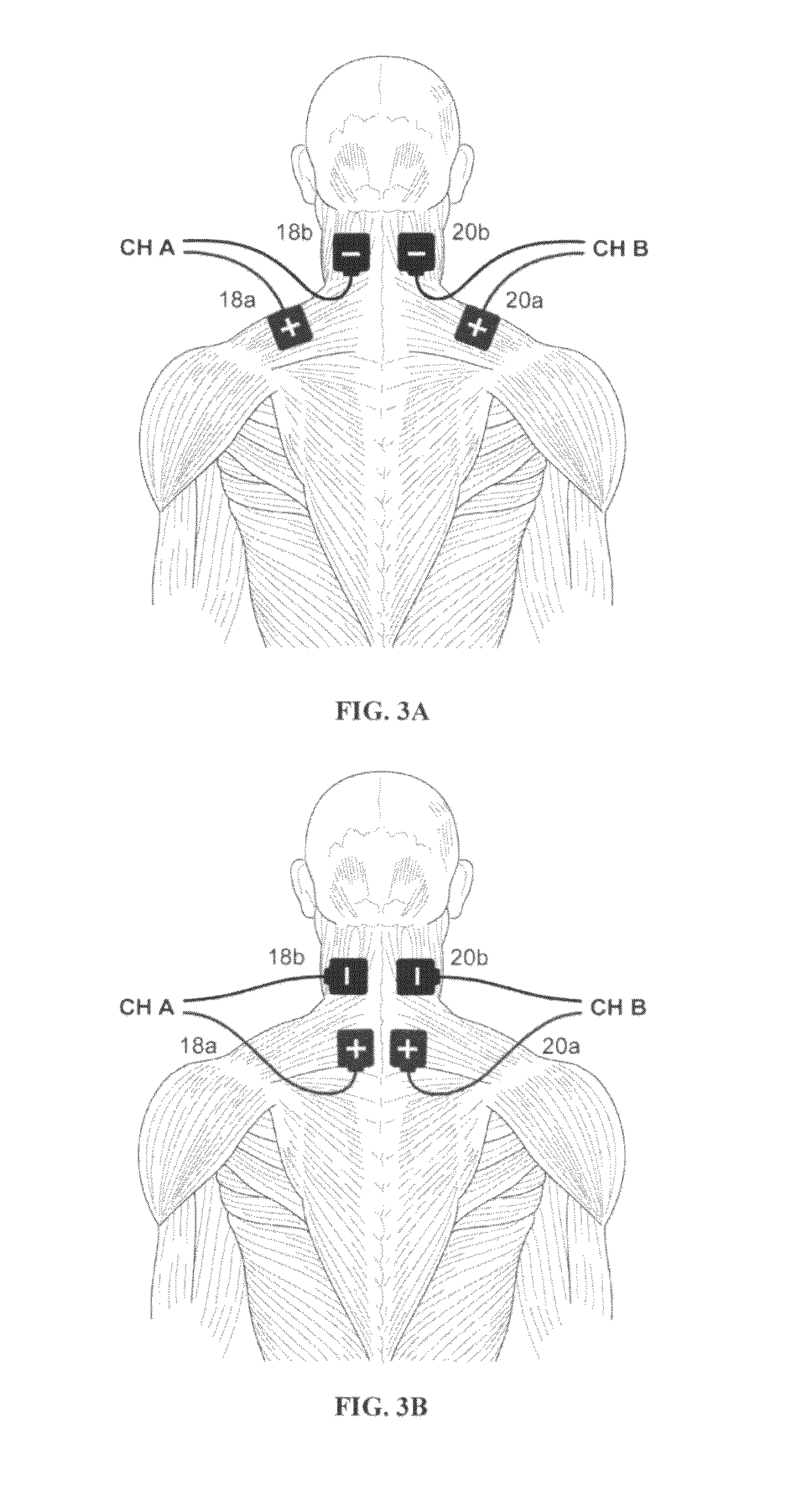
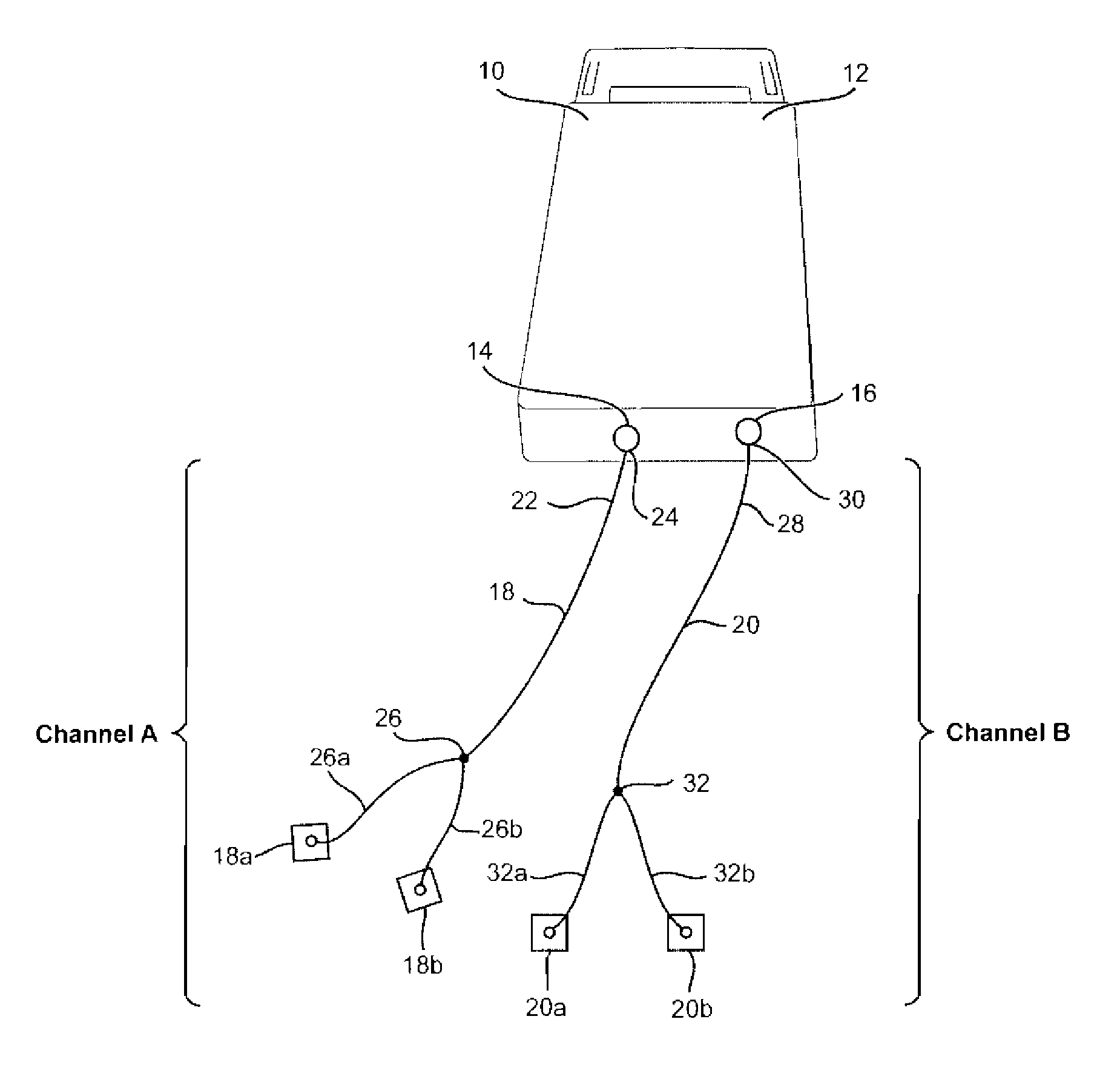
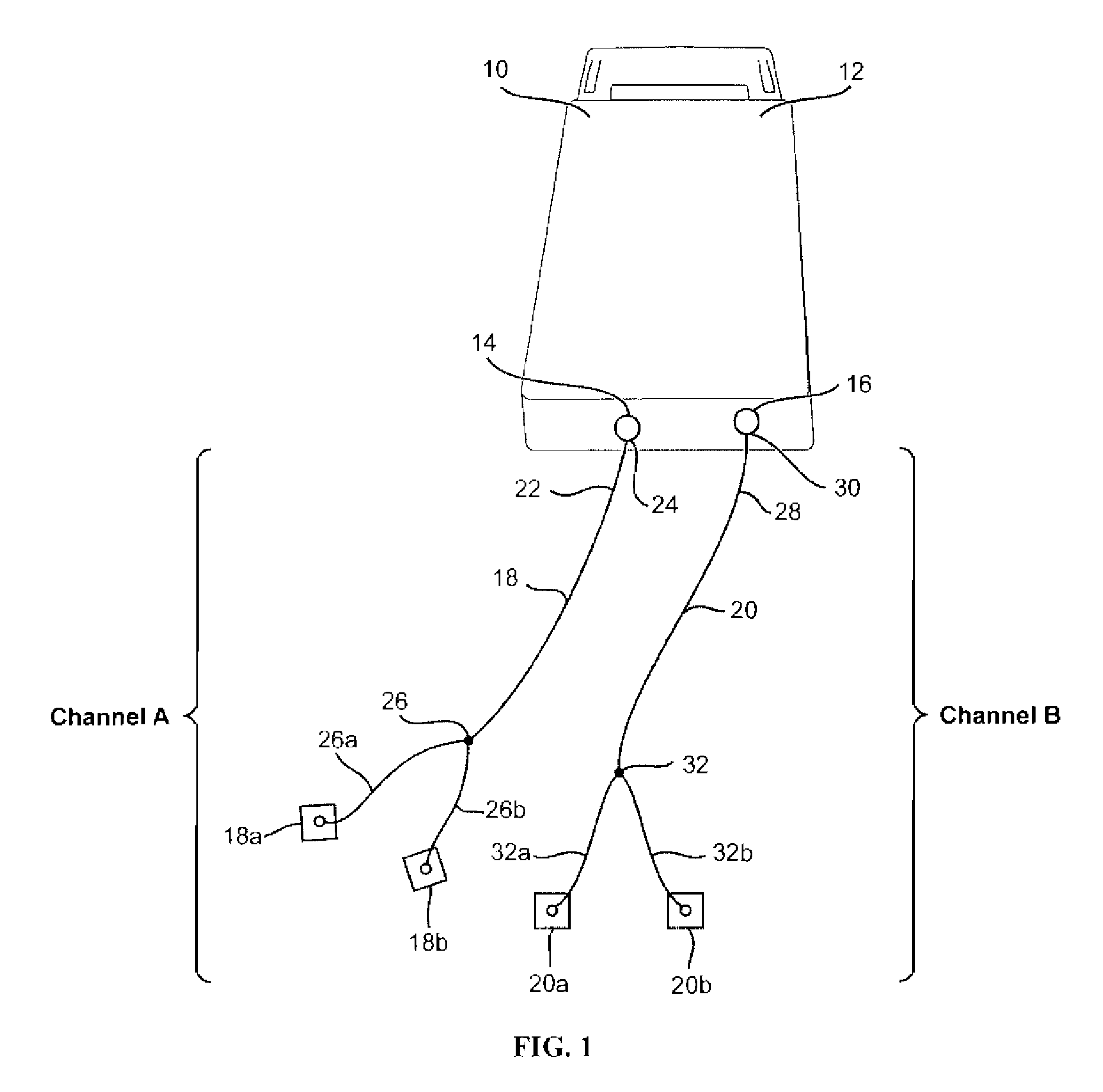
A method and apparatus for applying neuromuscular electrical stimulation to an agonist / antagonist muscle pair to move a limb about a joint includes generating a first pattern of neuromuscular electrical stimulation pulses for output through a first channel to a first pair of electrodes and generating a second pattern of neuromuscular stimulation pulses for output through a second channel to a second pair of electrodes. The first pair of electrodes are attached to the agonist muscle of the agonist / antagonist muscle pair, and the second pair of electrodes are attached to the antagonist muscle. A first pattern of electrical stimulation pulses is transmitted through the first pair of electrodes to the agonist muscle at a first intensity level to initiate contraction of the agonist muscle, and then at a second intensity level which is less than the first intensity level to continue contraction of the agonist muscle. A second pattern of electrical stimulation pulses is transmitted through the second pair of electrodes to the antagonist muscle at a first intensity level to reduce the acceleration of the limb, and then at a second intensity level which is less than the first intensity level to regulate the movement of the limb.
Owner:DJO
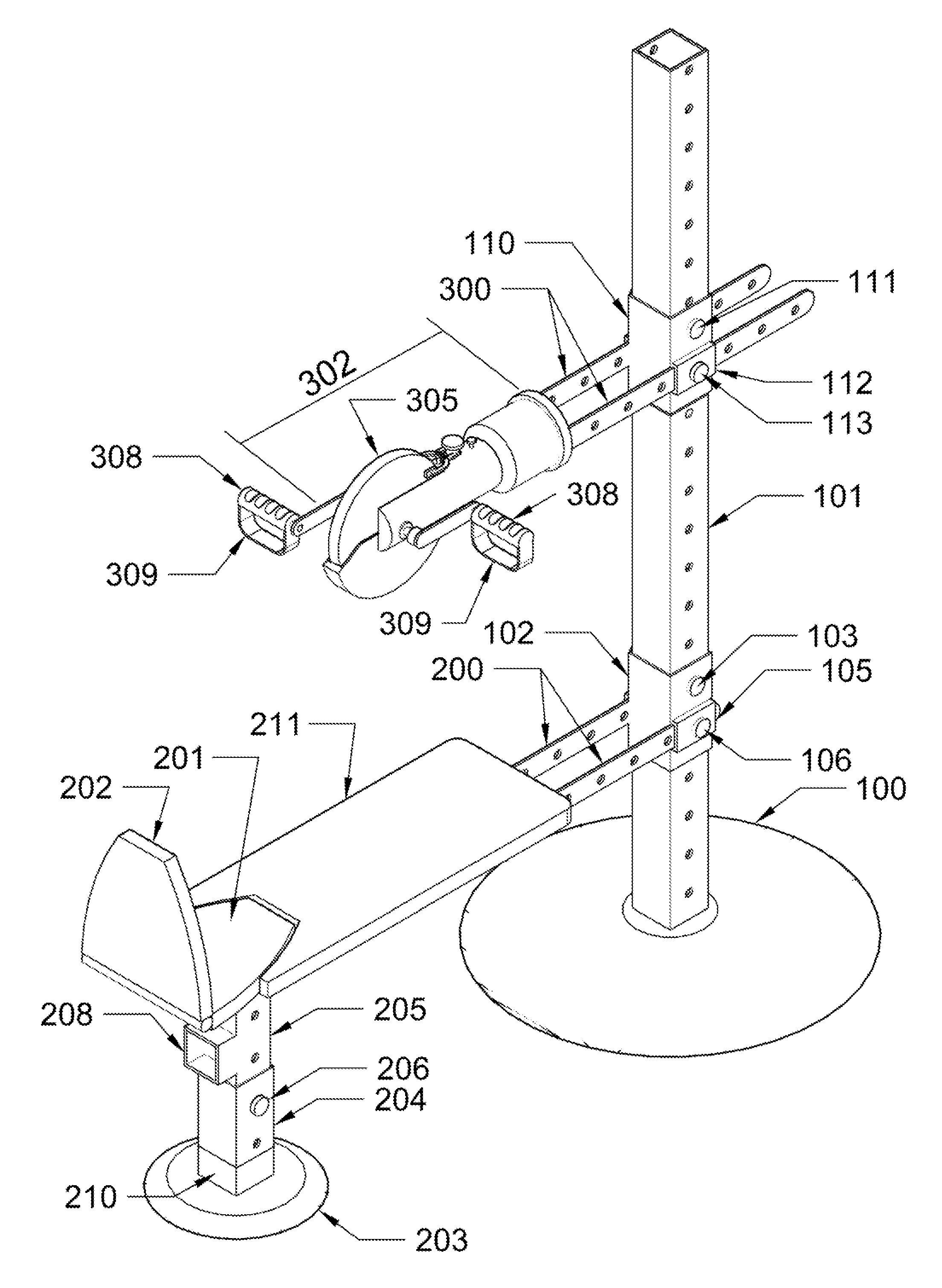
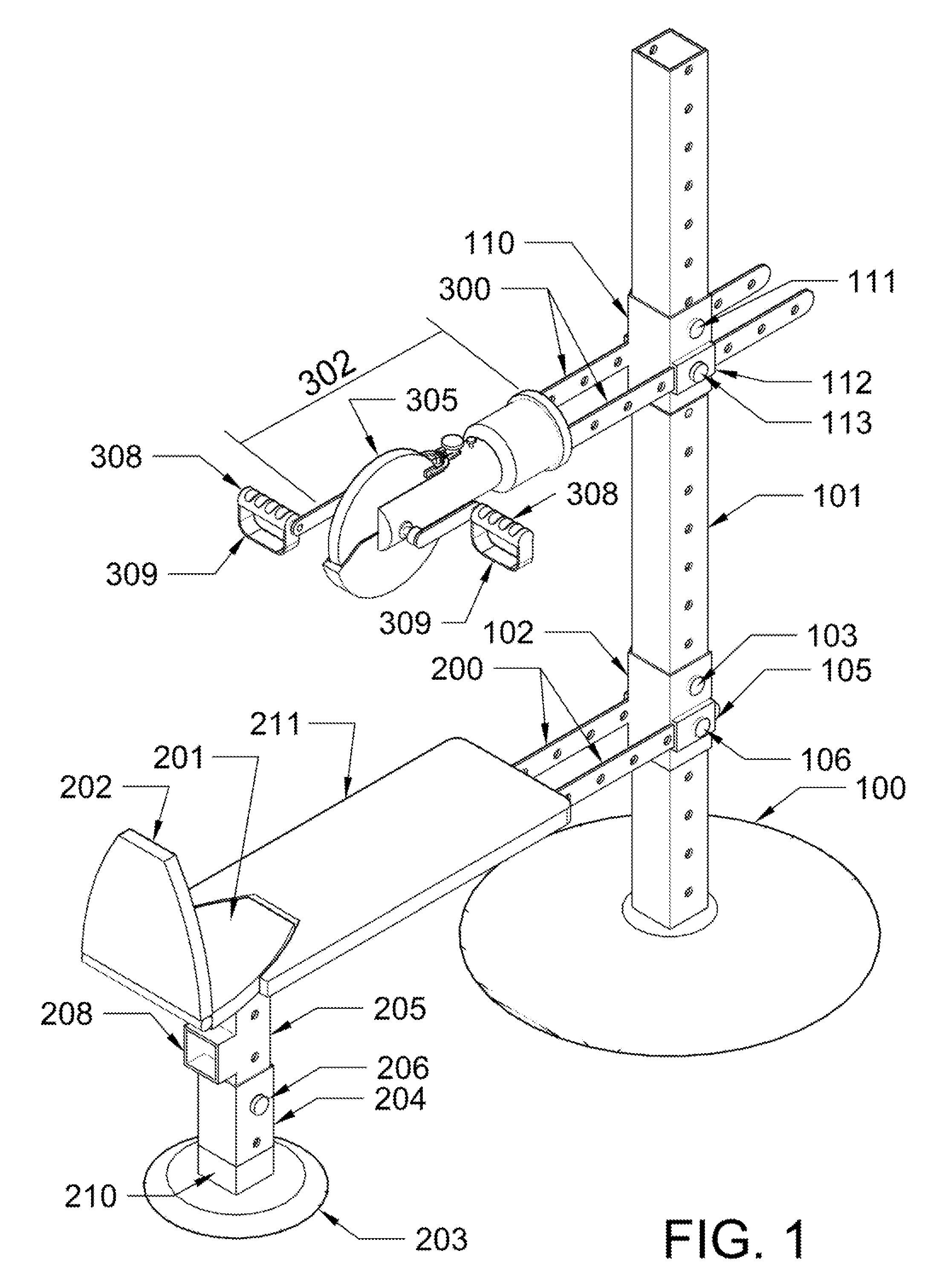
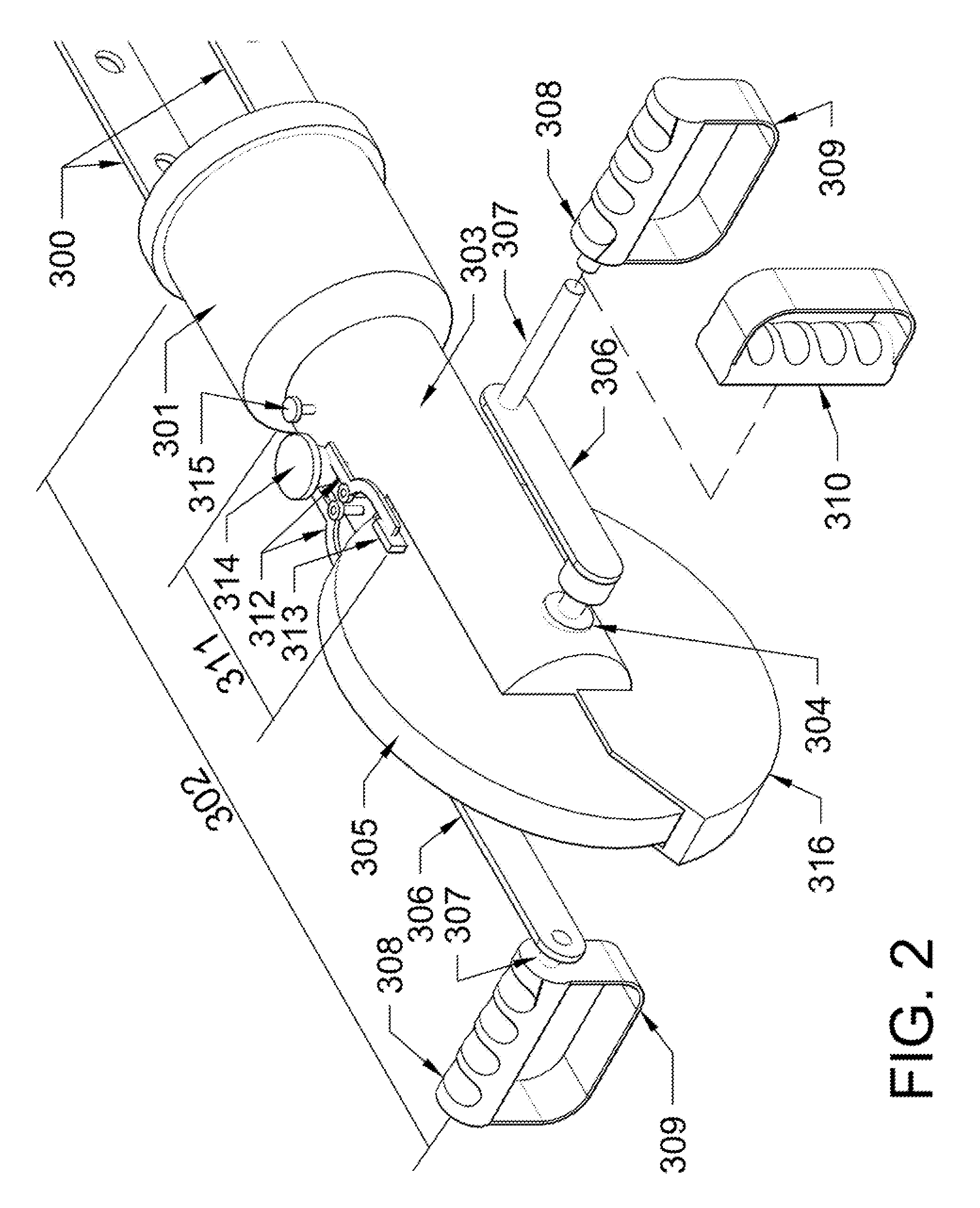
Rotary arm/leg exerciser
The present invention provides a compact, unitary exercise machine which may be rapidly reconfigured such that the user can perform a variety of exercise routines employing essentially the same rotary exercise movement, whether using the legs or the arms, while simultaneously exercising all the muscles of the subject extremity, including antagonistic muscles.
Owner:JAGUAN MAURO
Electrical stimulation method for reduction of joint compression
InactiveUS8473064B2Reduce compressionDecreased co-contractionExternal electrodesElectricityPronations
An electrical stimulation method for the reduction of joint compression utilizes an electrical stimulation device that includes a plurality of channels of electrodes each of which includes at least a first and second electrode positioned in electrical contact with tissue of at least two muscles crossing a joint. Agonist / antagonist muscles involved in abduction / adduction, flexion / extension, supination / pronation, protraction / retraction, and / or eversion / inversion of body regions via joint movement are stimulated with a patterned series of electrical pulses through channels of electrodes in accordance with a procedure for reducing joint compression. The patterned series of electrical pulses may comprise: a plurality of cycles of a biphasic sequential pulse train pattern; a plurality of cycles of a biphasic overlapping pulse train pattern; a plurality of cycles of a triphasic sequential pulse train pattern; and a plurality of cycles of a triphasic overlapping pulse train pattern.
Owner:ACCELERATED CARE PLUS CORP
Electrical stimulation method for treatment of peripheral neuropathy
ActiveUS8660651B2Improve overall senseStiffer and more difficult it is to bendElectrotherapyPeptide/protein ingredientsElectricityPronations
An electrical stimulation method for the treatment of peripheral neuropathy is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, the method utilizes an electrical stimulation device that includes a plurality of channels of electrodes each of which includes a first and second electrode positioned in electrical contact with tissue of a target region suffering from peripheral neuropathy. Agonist / antagonist muscles involved in abduction / adduction, flexion / extension, supination / pronation, protraction / retraction, and / or eversion / inversion in the peripheral body regions are stimulated with a patterned series of electrical pulses through channels of electrodes in accordance with a procedure for treating peripheral neuropathy. The patterned series of electrical pulses may comprise: a plurality of cycles of a biphasic sequential pulse train pattern; a plurality of cycles of a biphasic overlapping pulse train pattern; a plurality of cycles of a triphasic sequential pulse train pattern; and a plurality of cycles of a triphasic overlapping pulse train pattern.
Owner:ACCELERATED CARE PLUS CORP
Powered artificial knee with agonist-antagonist actuation
A knee prosthesis comprises an agonist-antagonist arrangement of two series- elastic actuators in parallel, including a knee joint, flexion and extension actuators connected to the joint in parallel with a leg member, and a controller for independently energizing the actuators to control the movement of the knee joint and leg. The flexion actuator comprises the series combination of a flexion motor and a flexion elastic element and the extension actuator comprises the series combination of an extension motor and an extension elastic element. Sensors provide feedback to the controller. The flexion actuator and the extension actuator may be unidirectional, with the flexion and extension elastic elements being series springs. The extension actuator may alternatively be bidirectional, with the extension elastic element being a set of pre-compressed series springs. Alternatively, the flexion elastic element may be a non-linear softening spring and the extension elastic element may be a non-linear hardening spring.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method And System For Providing Proprioceptive Feedback And Functionality Mitigating Limb Pathology
ActiveUS20190021883A1Enhance human physicalityRestores natural muscle control functionSpinal electrodesWalking aidsPartial lossControl system
Proprioceptive feedback is provided in a residual limb of a person that includes forming a linkage between a pair of agonist and antagonist muscles, forming a sliding surface over which the agonist and antagonist muscles slide. The sliding surface can include a synovial sleeve, a bridge formed between the distal ends of bones, or a fixture that is osseointegrated into the bone. The invention also includes a system for transdermal electrical communication in a person that includes a percutaneous access device, a sensory device that communicates signals between a muscle and the percutaneous device, and a stimulation device in communication with the percutaneous access device. In another embodiment, a closed-loop functional stimulation system restores lost functionality to a person that suffers from impairment of a neurological control system or at least partial loss of a limb.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Bi-directional resistance exercise machine
ActiveUS10596408B2Frictional force resistorsMovement coordination devicesTriceps brachii muscleResistance training
Owner:STEPANIAN ROBERT +1
Limb muscle function evaluation device
PendingCN112603322AComprehensive evaluation functionQuick responseSensorsMuscle exercising devicesMuscle contractionMuscle force
The invention discloses a limb muscle function evaluation device, which comprises a mechanical part, a control circuit part and upper computer software, wherein the mechanical part comprises an angle detection module, a muscle pressure measurement module and a muscle force resistance module; the angle detection module, the muscle pressure measurement module and the muscle force resistance module are controlled through the control circuit part and upper computer software, and the collected data are comprehensively analyzed, so that under the condition of three joint movement degrees, the muscle surface pressure of the active muscle and the antagonistic muscle in three states of relaxation, moderate and tension and the active resistance in two directions are measured. The limb muscle function evaluation device can be used for measuring the overall functions of muscles, including joint movement degree, muscle contraction capacity, muscle elasticity and muscle extension capacity, and has the advantages of comprehensive evaluation functions, high response speed, high adaptation degree, convenience in movement and the like.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
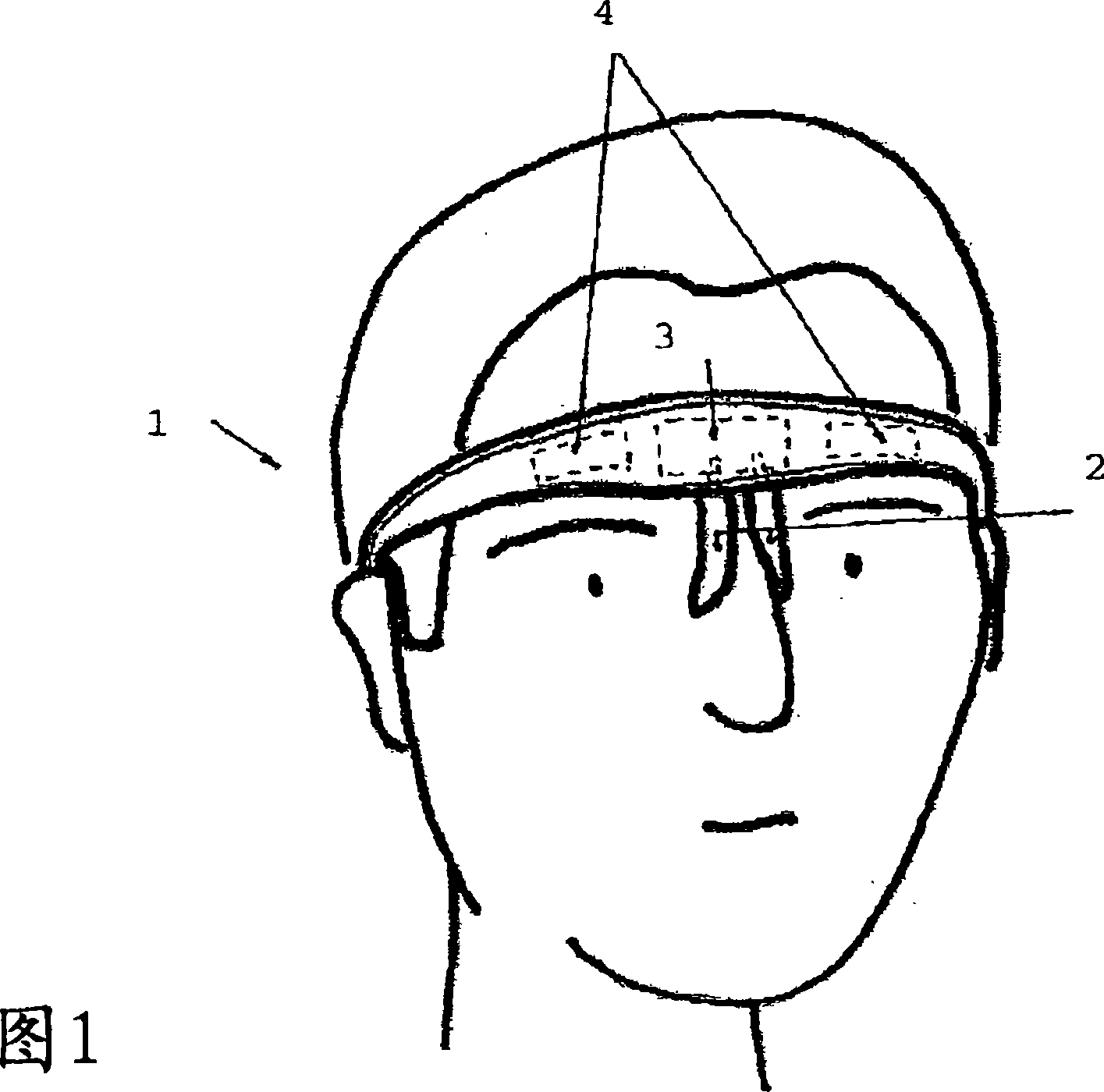
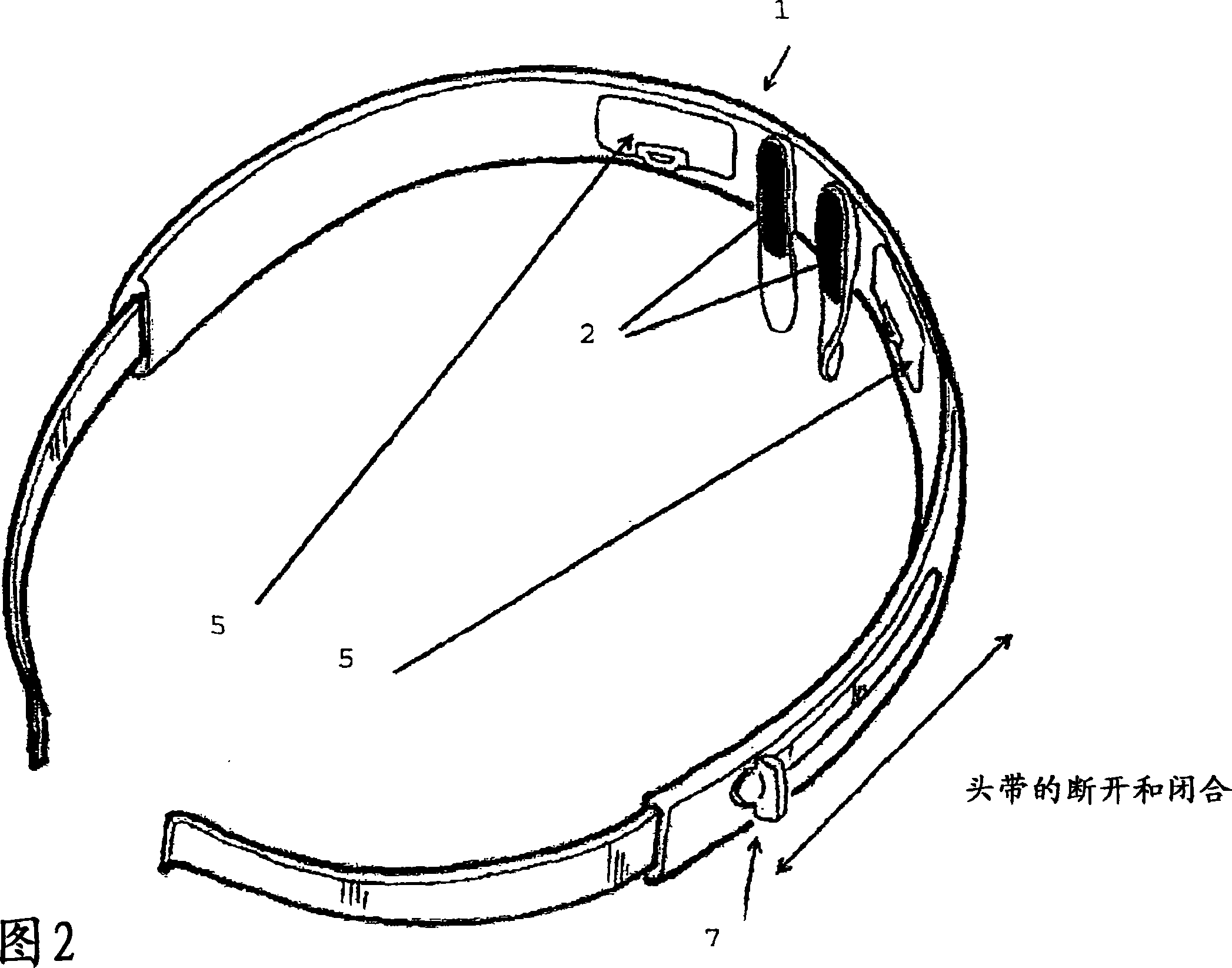
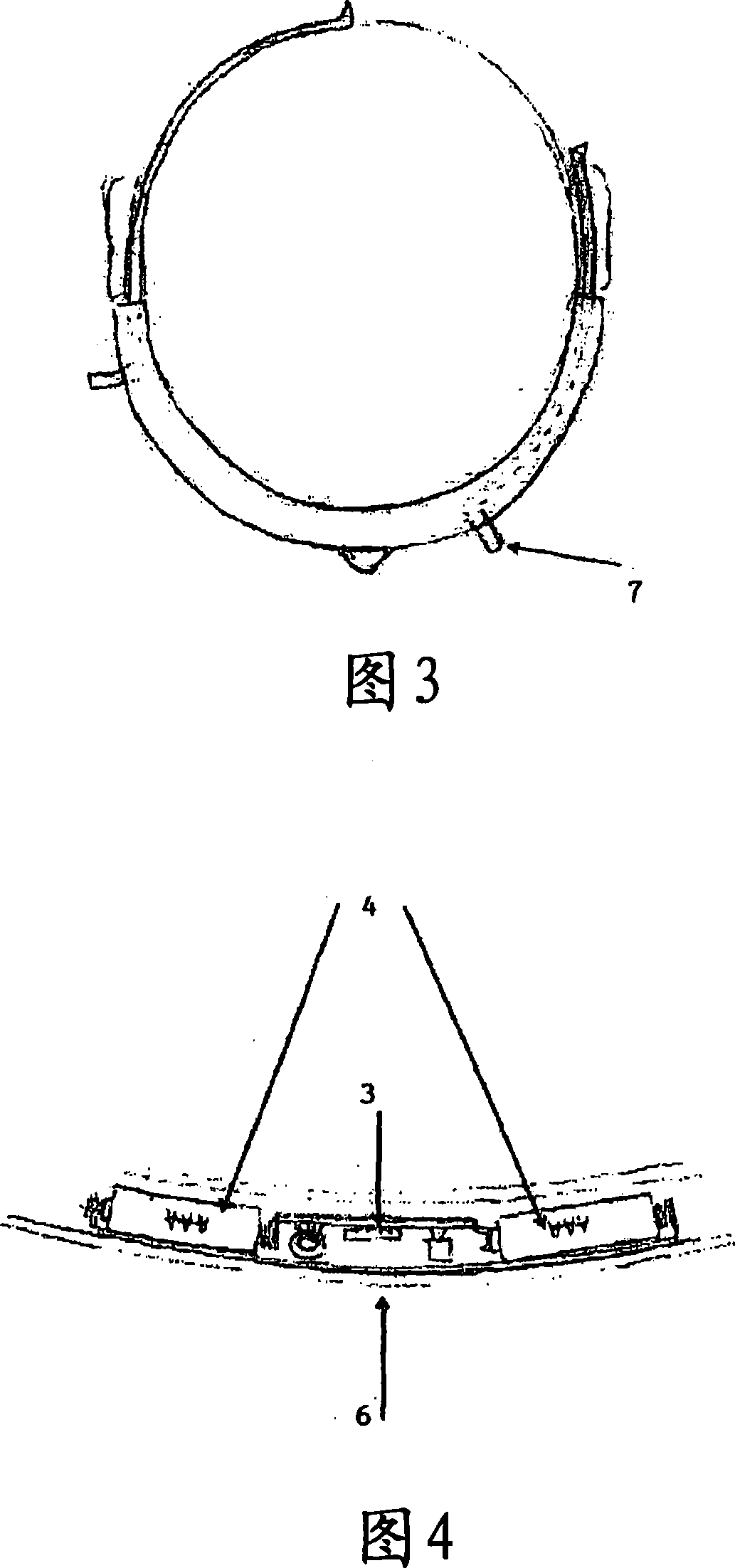
Apparatus for electrically inhibiting facial muscles
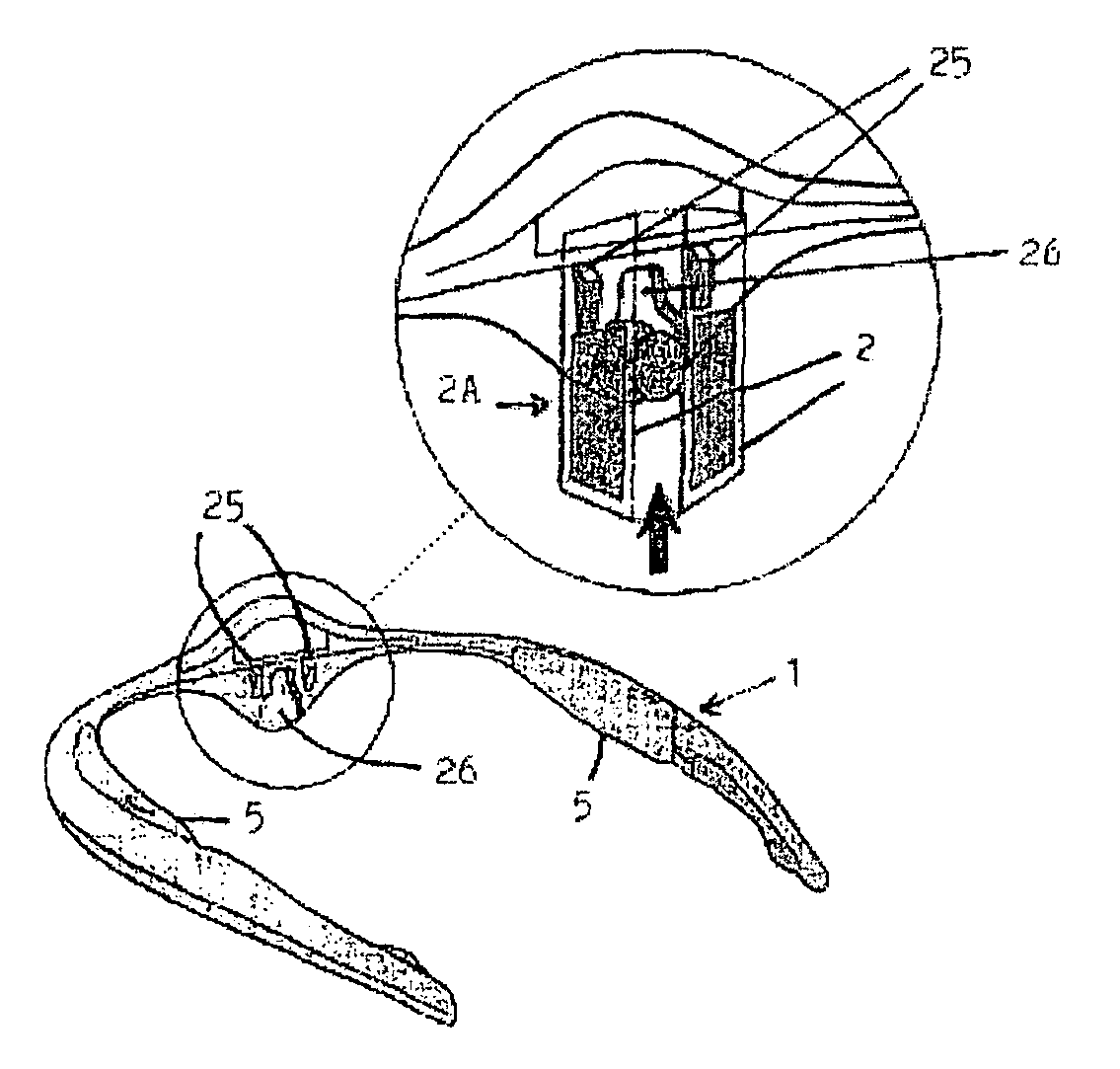
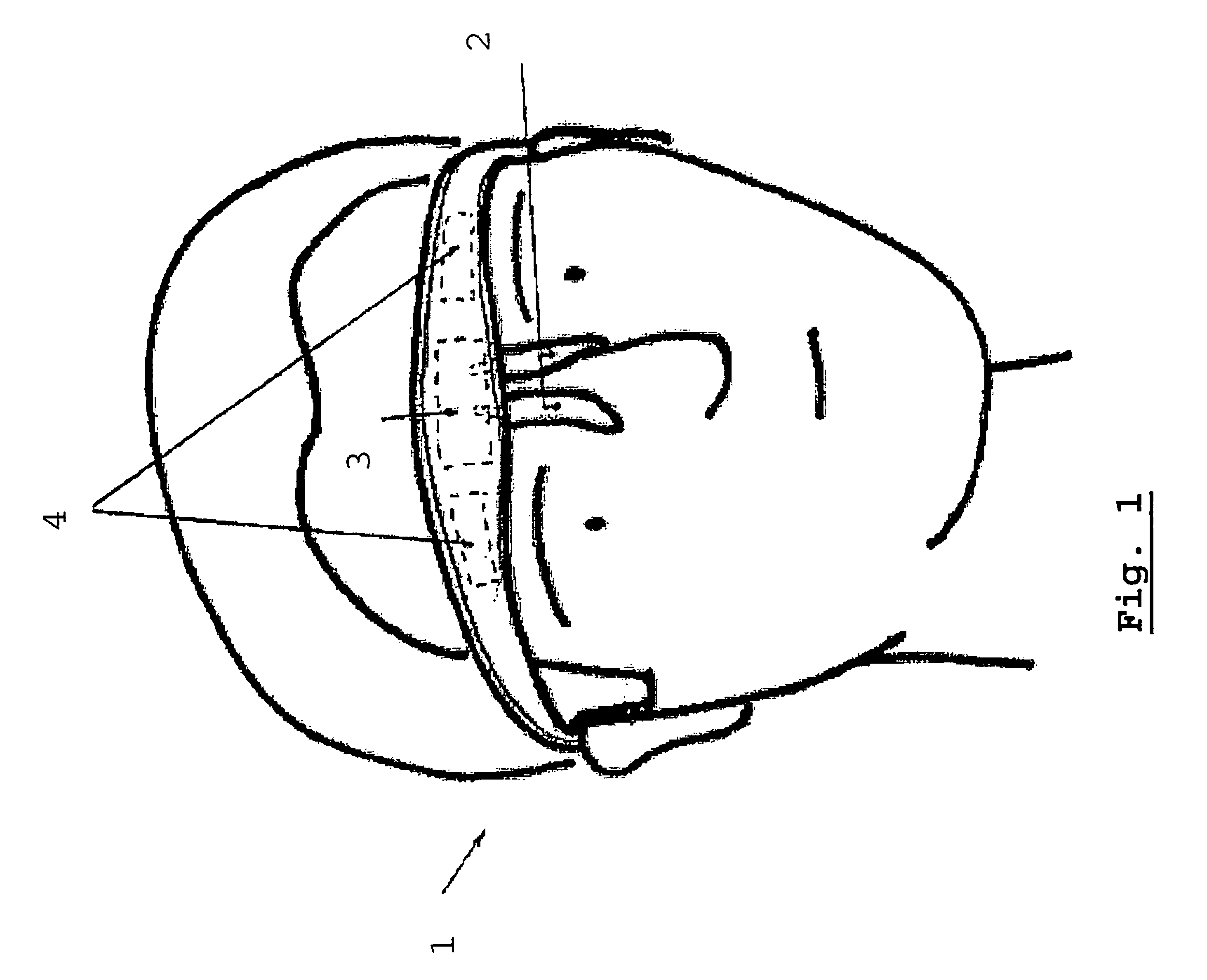
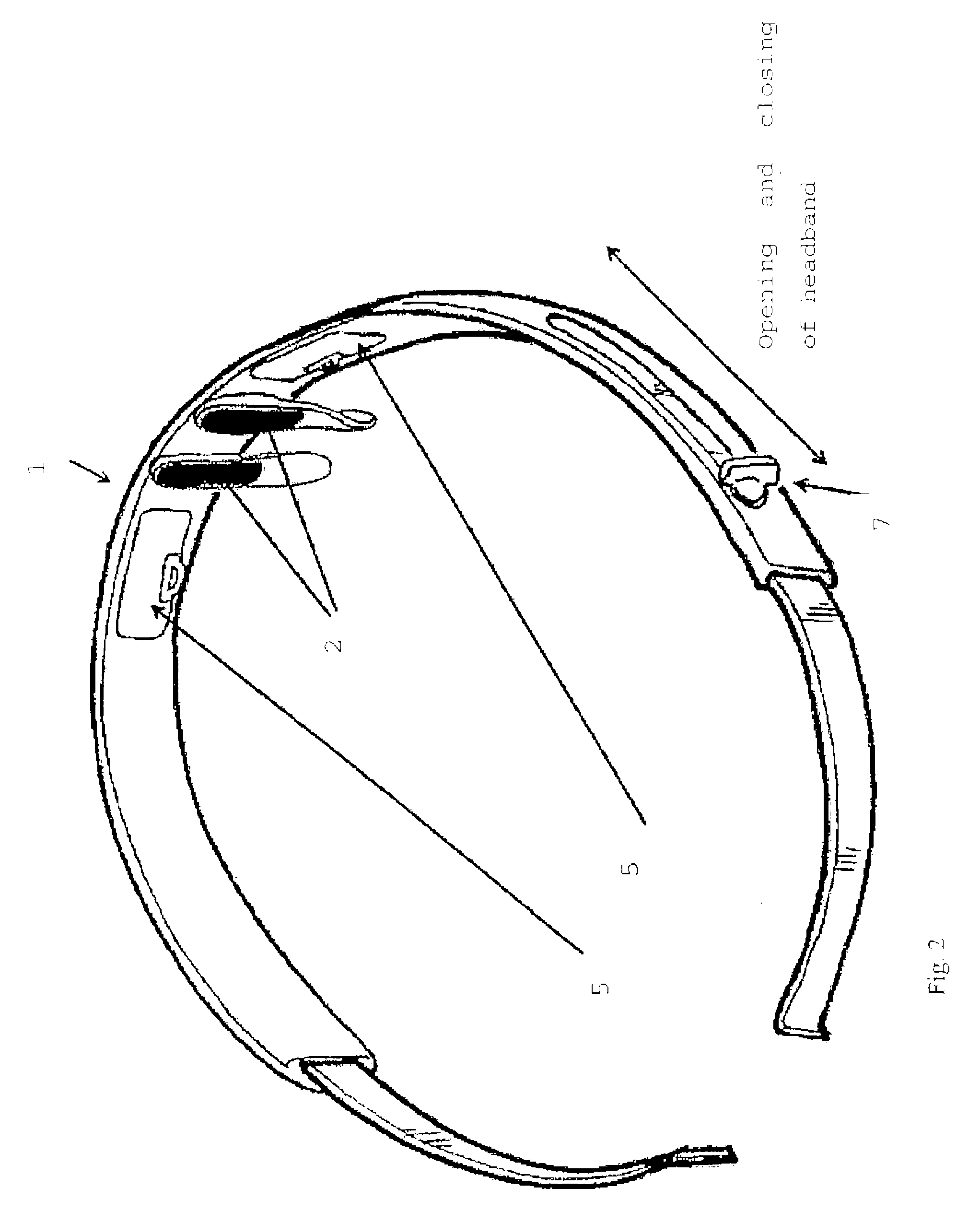
The invention concerns a method for performing an electric inhibition of the facial muscles for purely aesthetic purposes, using a device comprising a support at the head of a user (1), two contact electrodes (2), an electronic circuit (3) for generating low-voltage electric pulses at said electrodes (2), a direct current electric power supply (4) and means for fixing and locking (7) said components on the head. The invention is characterized in that it includes the following steps: placing the electrodes (2) on either side of the upper part of the nose, at the glabella; passing the electric pulses via the electrodes (2) through the pyramidal muscle of the nose so as to cause said pyramidal muscle of the nose to relax and hence its antagonist muscle, the forehead muscle and the double eyebrow muscle.
Owner:CEFALY TECH
Apparatus for electro-inhibition of facial muscles
The invention concerns a method for performing an electric inhibition of the facial muscles for purely aesthetic purposes, using a device comprising a support at the head of a user (1), two contact electrodes (2), an electronic circuit (3) for generating low-voltage electric pulses at said electrodes (2), a direct current electric power supply (4) and means for fixing and locking (7) said components on the head. The invention is characterized in that it includes the following steps: placing the electrodes (2) on either side of the upper part of the nose, at the glabella; passing the electric pulses via the electrodes (2) through the pyramidal muscle of the nose so as to cause said pyramidal muscle of the nose to relax and hence its antagonist muscle, the forehead muscle and the double eyebrow muscle.
Owner:ORSAN MEDICAL TECH
Multi-channel functional electrical stimulation output control method for lower limb rehabilitation of myoelectric modulation
InactiveCN108392737AAchieve motor function reconstructionConsistent shrinkage characteristicsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsKnee JointMuscle spasm
The invention relates to a multi-channel functional electrical stimulation output control method for lower limb rehabilitation of myoelectric modulation. Electromyographic signals of two pairs of antagonist muscles for controlling knee and ankle joint movement when a healthy person walks normally are collected offline, and the processed ectromyographic signals modulate multi-channel electrical stimulation output intensity enveloping lines to stimulate the two pairs of the antagonist muscles in the lower limbs of a patient. The method is applied to the lower limb rehabilitation training processof the apoplexy patient, can not only prevent muscle spasm, but also achieve multi-joint coordinated movement similar to normal people, and can achieve the rehabilitation training of a lower limb walking function, thereby achieving the purpose of lower limb functional reconstruction.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
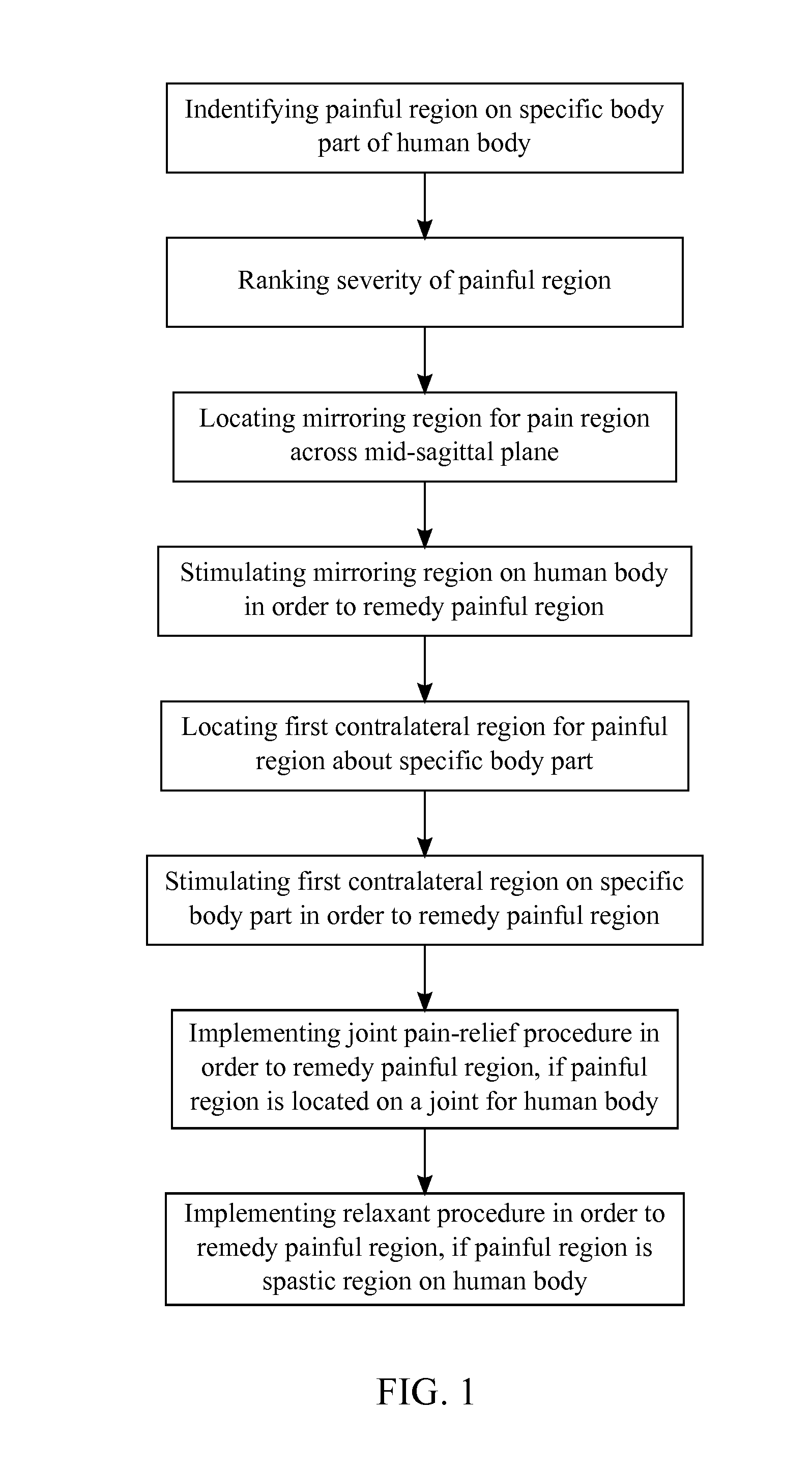
Therapeutic Method of Indirectly Relieving Localized Pain
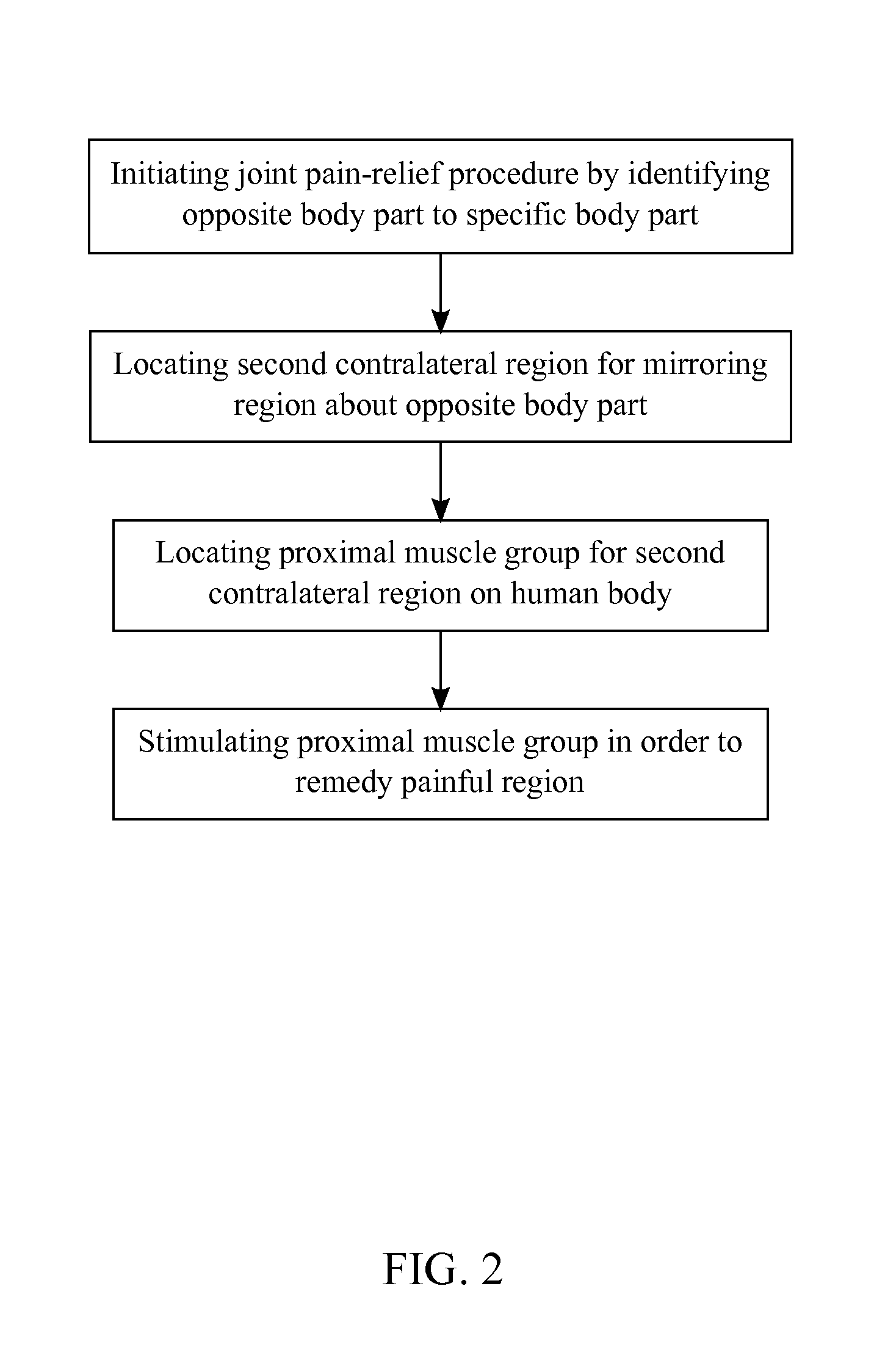
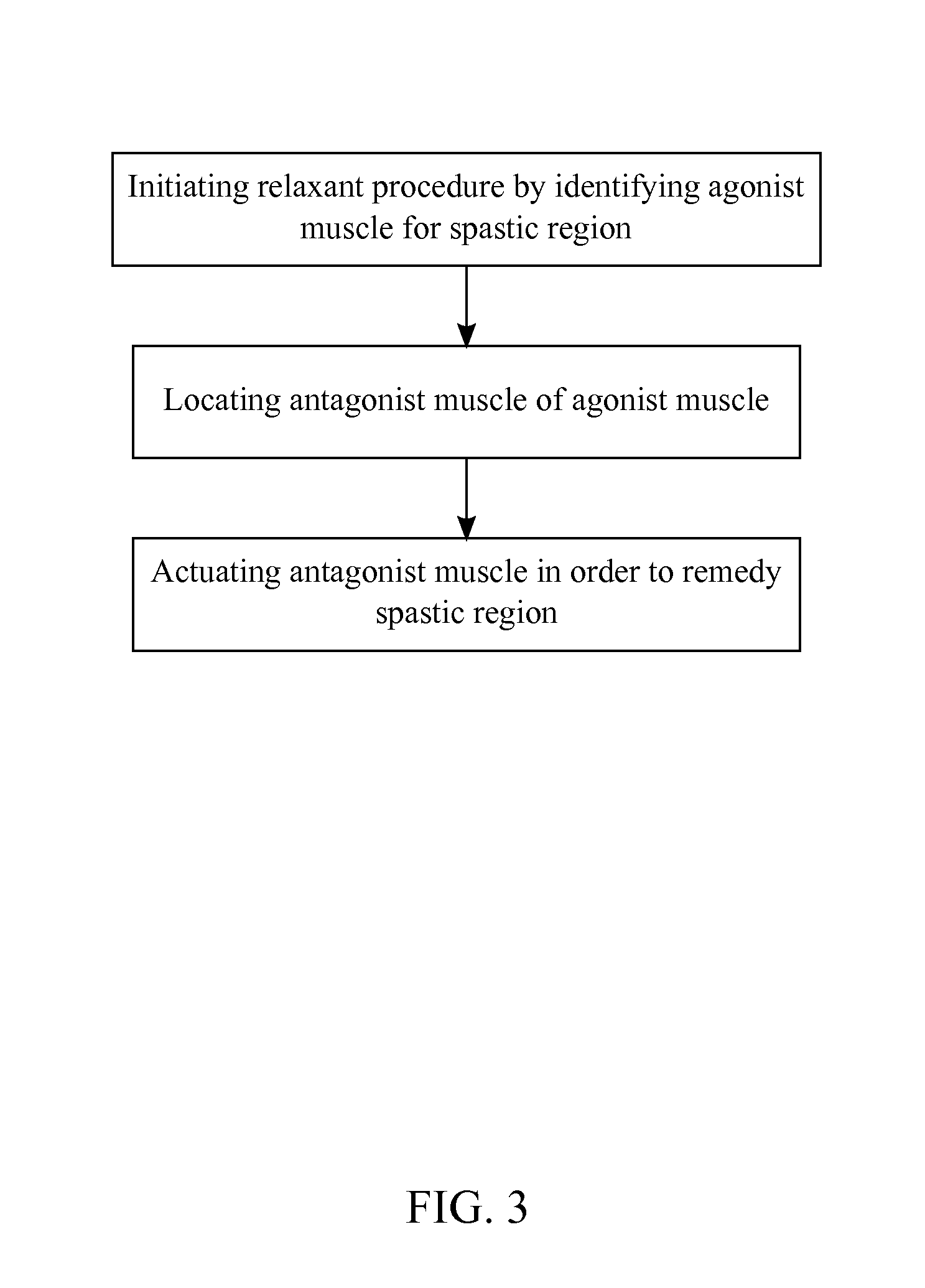
A therapeutic method that indirectly reliefs localized pain on a human body utilizes the neural circuitry that links agonist muscles to antagonist muscles and utilizes the neural circuitry that cross-links the left side of the body to the right side of the body. First, a practitioner of this method identifies the painful region on the human body and locates the mirroring region on the human body across the mid-sagittal plane. The practitioner will then stimulate the mirroring region to remedy the painful region. Second, the practitioner locates the contralateral region to the painful region about its respective body part. The practitioner will then stimulate the contralateral region in order to remedy the painful region.
Owner:BERG ERIC E
Neuromuscular plasticity apparatus and method using same
ActiveUS10195097B1Improve performanceIncrease demandChiropractic devicesVibration massageStretch reflexPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A portable motion control apparatus drives a user's extremity emulating the user's tremor. The driving motion entrains the tremor motion and stretches muscles evoking stretch reflexes in agonist and antagonist muscles used to maintain muscle tone. The motion applies a heightened and coordinated demand on the neuromuscular components of multiple stretch reflex circuits thereby effectuating neuromuscular plasticity; the retention of neuromuscular changes made to meet the heightened demands. Muscle tone is improved and tremor is suppressed for a protracted period.
Owner:CIMO GAETANO
Functional electrical stimulation system and method for regulating and controlling joint torque and rigidity
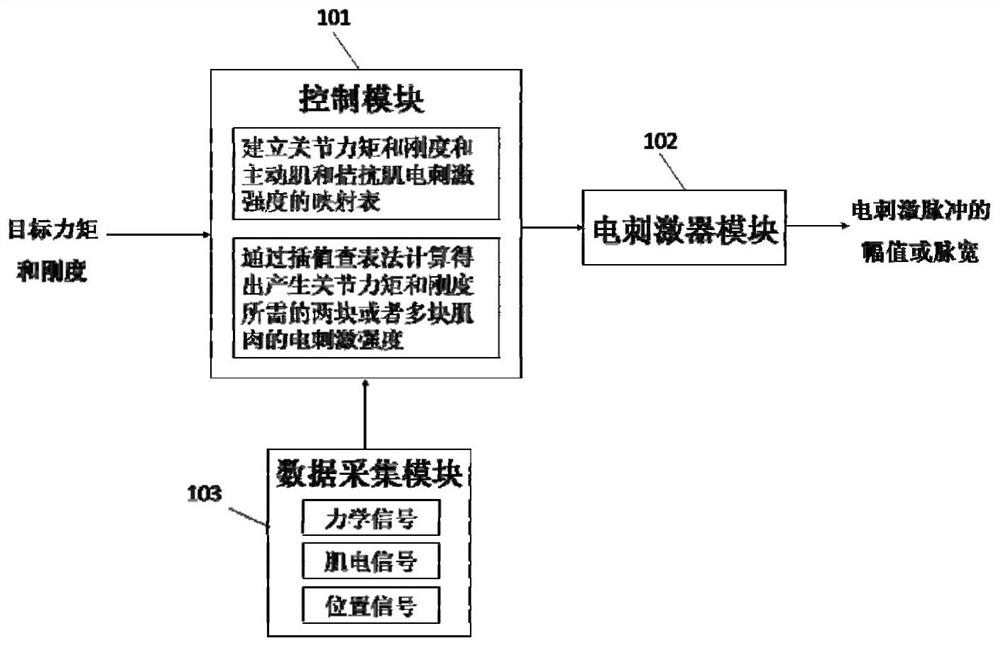
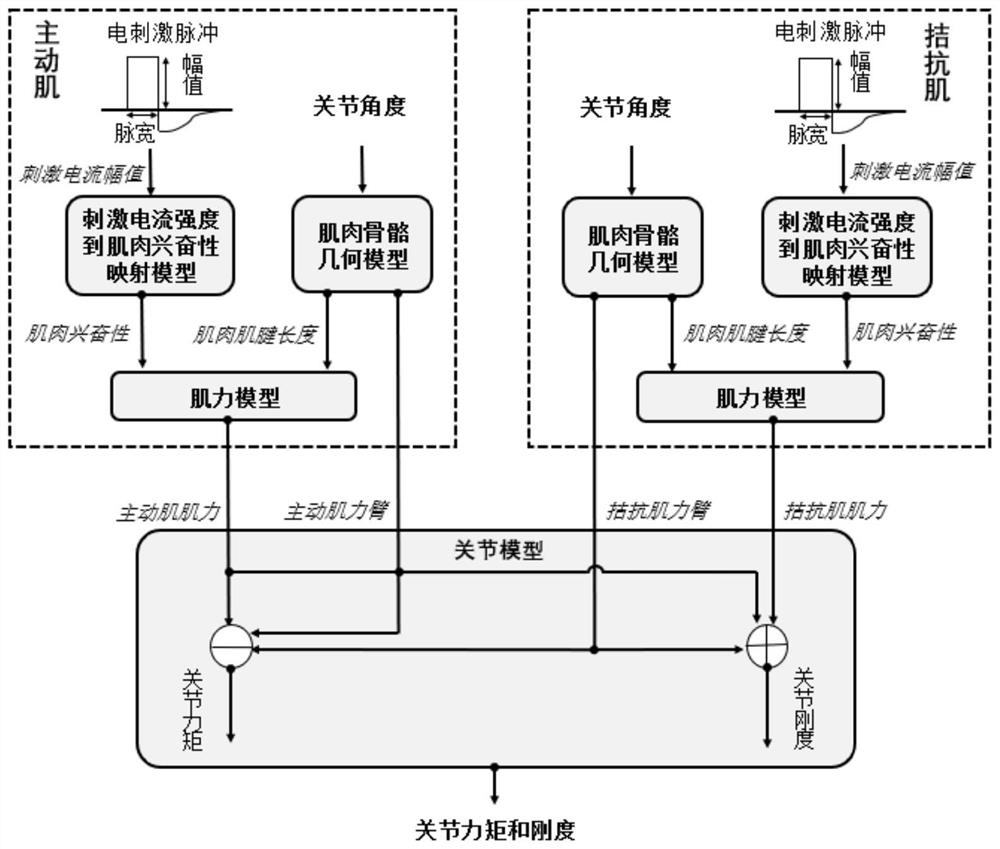
PendingCN113181550ASafe and reliable controlPrecise and stable controlElectrotherapyArtificial respirationData acquisitionPhysical therapy
The invention provides a functional electrical stimulation system and method for regulating and controlling joint torque and rigidity. The functional electrical stimulation system comprises a control module for sending an intensity signal to an electrical stimulator, an electrical stimulator module for generating electrical stimulation pulse current and a data acquisition module for acquiring mechanical, myoelectric and position signals. The data acquisition module transmits mechanical and position signals to the control module, the control module establishes a mapping table of joint torque and rigidity and electrical stimulation intensity of active muscles and antagonistic muscles, and the electrical stimulation intensity of two or more muscles required for generating the joint torque and rigidity is calculated through an interpolation look-up table method. The electrical stimulator module adjusts the amplitude or the pulse width of electrical stimulation pulses according to the required stimulation intensity, so that the torque and the rigidity of the joint are regulated and controlled.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
Adjustable elastic antagonist muscle replacement mechanism
The present invention is an anatomic system which uses the principle of applying higher elastic tonus than the rest tonus of the agonist muscles to provide the function of the antagonist muscles, and which is designed in a simplest way to provide the said purpose and which can be integrated to the body. The static mechanism of the invention is an elastic mechanism which applies a continuous stable tension in order to keep the joints open. The tension of the mechanism is calibrated by increasing or decreasing the amount of the liquid in a chamber which has flexible and elastic walls up to a certain via a port. In the dynamic mechanism of the invention, the tension applied by the elastic mechanism can be changed according to the motion the patient wants to perform.
Owner:ENGIN MURAT SINAN
Peripheral neural interface via nerve regeneration to distal tissues
ActiveUS9474634B2Raise the potentialSpinal electrodesMusculoskeletal system evaluationSensory FeedbacksBiological body
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for Relaxing Spasmed Muscles
The invention relates to medicine, and more particularly to physiotherapy, neurology, traumatology, orthopaedics, rehabilitation and sports medicine, and can be used for relaxing spasmed muscles when treating patients with different conditions of the musculoskeletal and nervous systems, and also for prophylaxis in the social sphere. For this purpose, relaxed antagonist muscles are subjected to a stimulating electric impulse effect at an impulse frequency of from 15 to 35 Hz, with an impulse signal duration of from 5 to 60 μs and a working signal level of from 5 to 75% of the strength of a signal at which the patient feels a vibration. Spasmed agonist muscles are subjected to a relaxing thermal effect at a temperature of from 42 to 60° C. In addition, the segments of the spinal cord responsible for innervating the agonist-antagonist muscle pairs undergoing treatment are subjected to a thermal effect at a temperature of from 42 to 60° C. The agonist-antagonist muscle pairs and the segments of the spinal cord responsible for innervating the agonist-antagonist muscle pairs can be acted on simultaneously and alternately. The stimulating electric impulse effect and the relaxing effect can be carried out on individual regions of the body or on all regions simultaneously. The method provides effective physiological relaxation of spasmed muscles by means of a synergistic effect resulting from a combination of effects which engage the central nervous system that regulates and alters the physiological state of the tissues of agonist-antagonist muscle pairs.
Owner:FESKOV GENNADY PETROVICH +1
Pneumatic humanoid robot system
InactiveCN112775943AAchieve movementHigh power/mass ratioProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsKnee JointUpper extremity joint
The invention relates to a pneumatic humanoid robot system. The pneumatic humanoid robot system uses pneumatic muscles to simulate human muscles to drive hip joints, knee joints, ankle joints, waist joints, shoulder joints, elbow joints and wrist joints to move and has the function of completely simulating human joint movement. The pneumatic humanoid robot system is mainly composed of pelvis, ribs, vertebrae, the pneumatic muscles, belt wheels, pneumatic claws, connecting pieces and a joint control system. Bones of the waist joints are constructed by vertebrae, ribs, chest structural members and pelvis, and long pneumatic muscles and short pneumatic muscles drive the waist joints to move together. In lower limb joints, single-joint pneumatic muscles and multi-joint pneumatic muscles are combined, and the multi-joint pneumatic muscles and the multi-joint pneumatic muscles are crosswise combined to drive the lower limb joints to move. Multi-joint pneumatic muscles in upper limb joints form antagonistic muscles to drive the shoulder joints and the elbow joints to move. The pneumatic humanoid robot system is driven by the pneumatic muscles, has the characteristics of being compact in structure, good in flexibility and diversified in pneumatic muscle state, and can be used for teaching and demonstration.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
Method and apparatus for applying neuromuscular electrical stimulation
A method and apparatus for applying neuromuscular electrical stimulation to an agonist / antagonist muscle pair to move a limb about a joint includes generating a first pattern of neuromuscular electrical stimulation pulses for output through a first channel to a first pair of electrodes and generating a second pattern of neuromuscular stimulation pulses for output through a second channel to a second pair of electrodes. The first pair of electrodes are attached to the agonist muscle of the agonist / antagonist muscle pair, and the second pair of electrodes are attached to the antagonist muscle. A first pattern of electrical stimulation pulses is transmitted through the first pair of electrodes to the agonist muscle at a first intensity level to initiate contraction of the agonist muscle, and then at a second intensity level which is less than the first intensity level to continue contraction of the agonist muscle. A second pattern of electrical stimulation pulses is transmitted through the second pair of electrodes to the antagonist muscle at a first intensity level to reduce the acceleration of the limb, and then at a second intensity level which is less than the first intensity level to regulate the movement of the limb.
Owner:DJO
Dynamic Taping Method for Inhibition and Elicitation of Skeletal Muscle Tone
ActiveUS20180168847A1Correct muscle imbalanceCorrect a muscle imbalanceFinger bandagesSuspensory bandagesHuman bodyMuscle tone
Is a taping method that follows a specific set of rules based on anatomical and physiological patterns in humans. This taping method causes a change in skeletal muscle tone in the human body, when tape is directly applied to the skin of the human body over targeted tendons and surrounding structures going over joints. This taping method will inhibit the muscle tone in the antagonist muscle of the opposing side of the joint where the tape is applied, while simultaneously eliciting the agonist of the muscle that are attached by the tendon of the joint where the tape is applied.
Owner:VACCA CHARISE
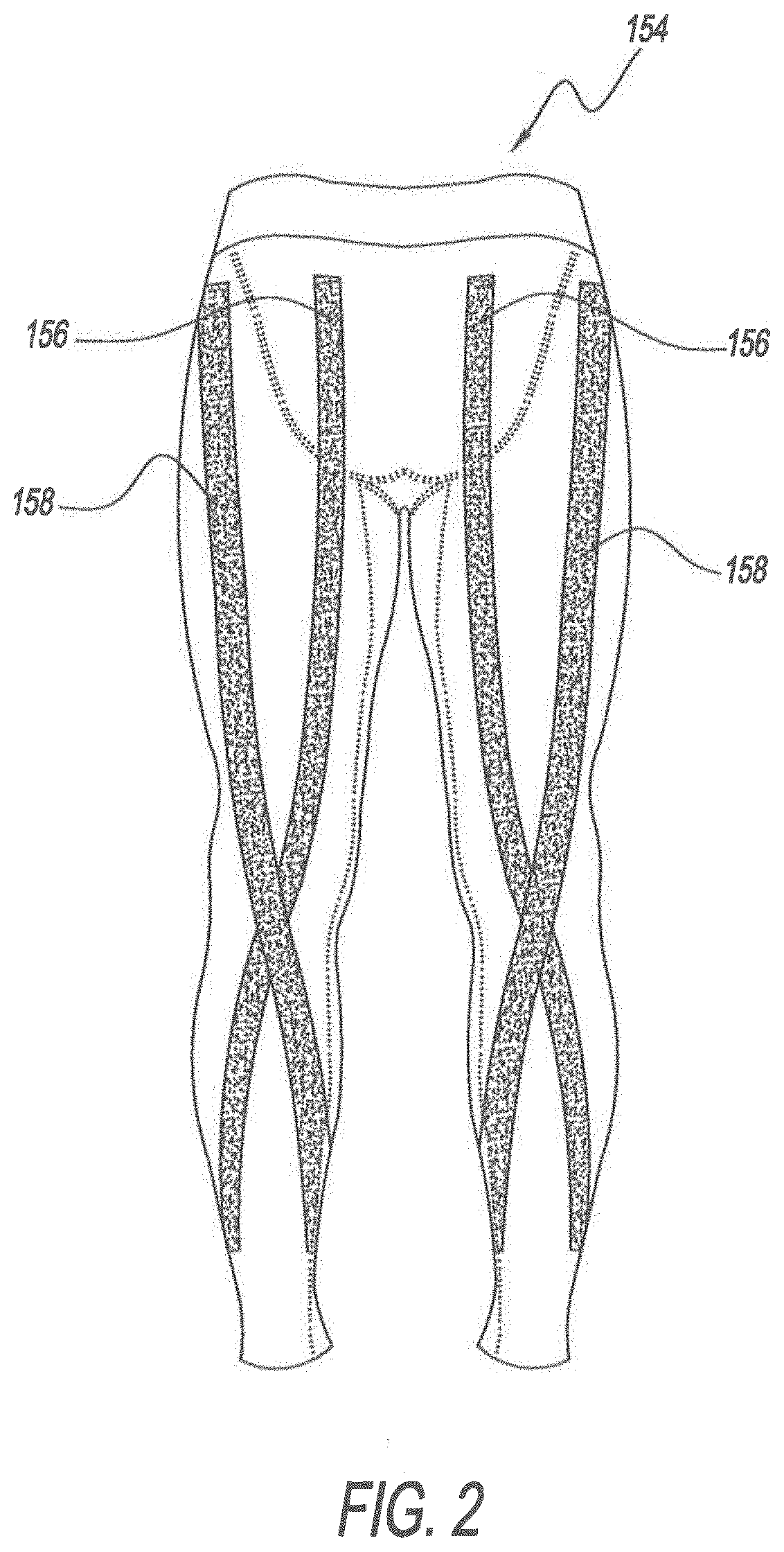
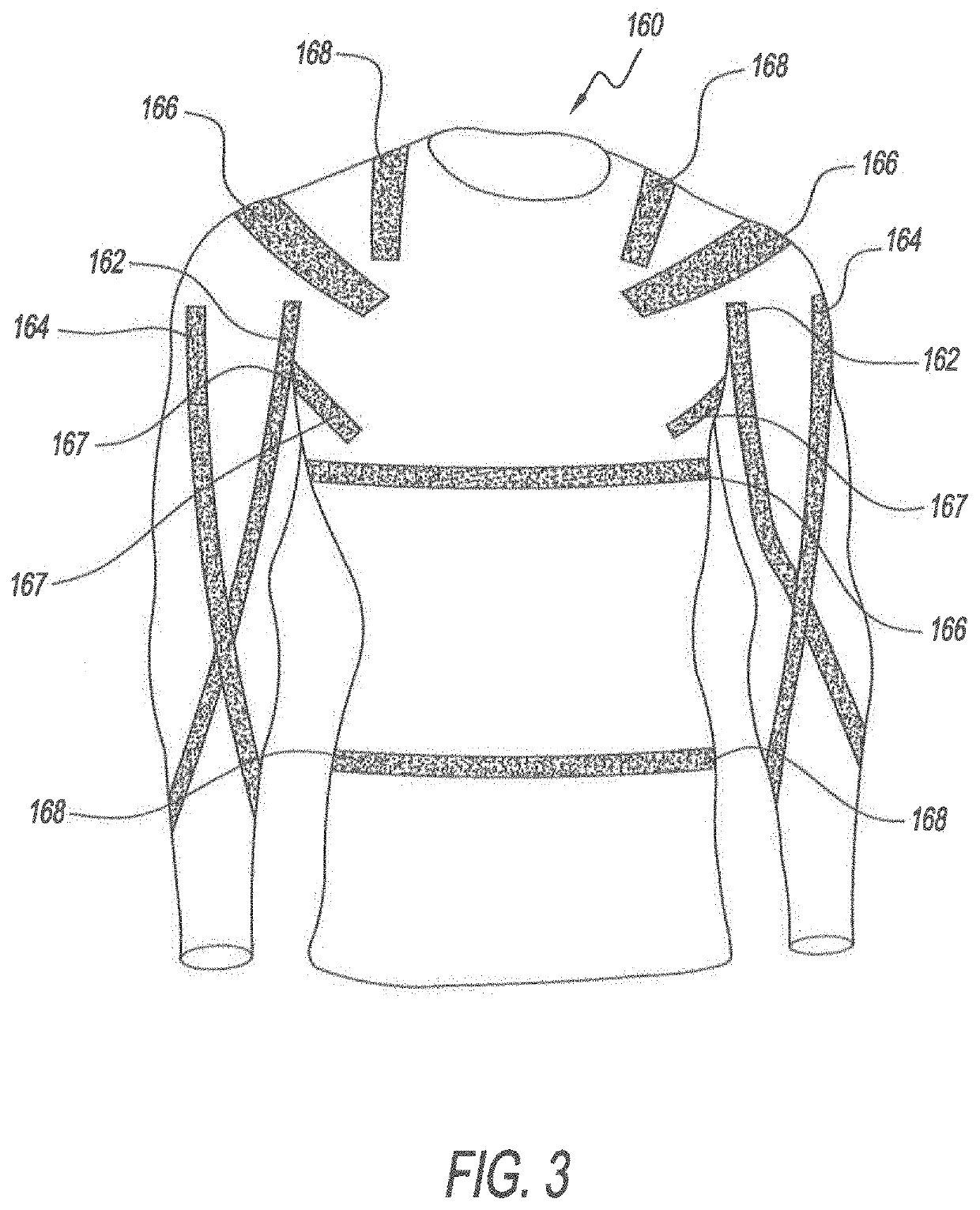
Method for Applying Resistance Through Exercise Clothing
ActiveUS20190364987A1Increase exerciseAssisted rehabilitationGarment special featuresProtective garmentHuman bodyAxial force
A method and apparatus for exercising a muscle in a given agonist and antagonist muscle pair of a user's human body by providing an elongated elastic band having a first length when no external forces are applied thereto, elongating the elastic band to a second length that is greater than the first length, securing the elastic band to a garment in a manner whereby when the elastic band is installed on the garment an axial force is imposed on the body of the user and the elastic band is disposed in aligned proximate relationship with at least one of the muscles in a given pair of muscles comprising an agonist muscle and antagonist muscle pair.
Owner:SHRIVER ENTERPRISES LLC
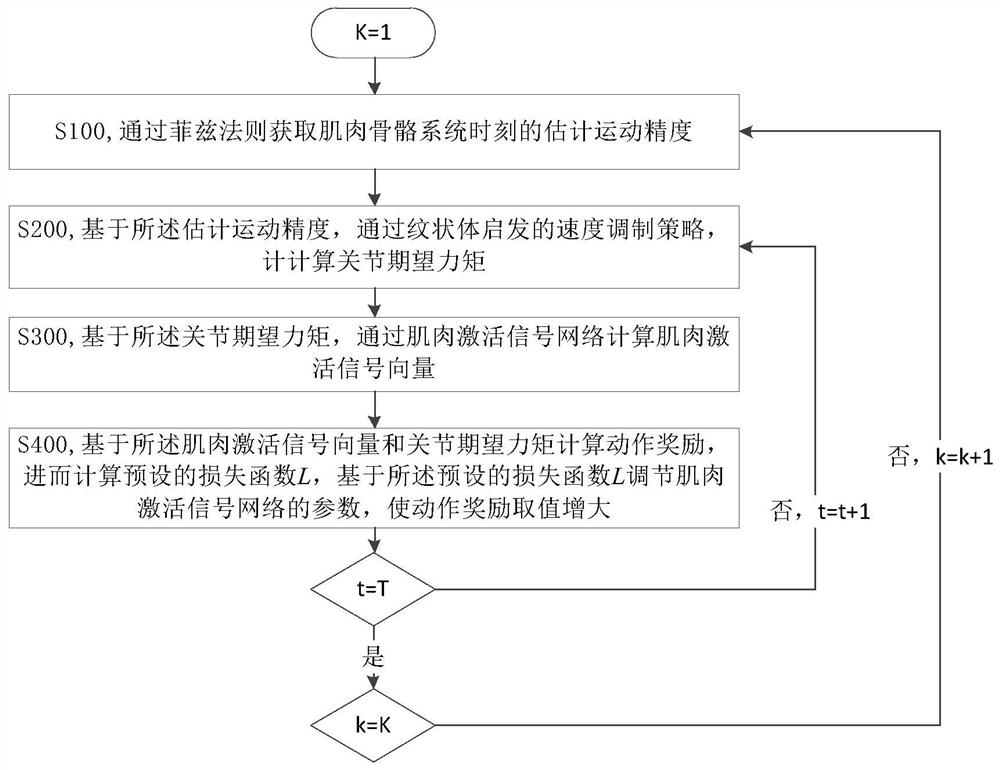
Musculoskeletal system control method and system based on speed precision balance and device
ActiveCN112757275AImprove adaptabilityEasy to controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSimulationRobot control
The invention belongs to the technical field of control, particularly relates to a musculoskeletal system control method and system based on speed precision balance and a device, and aims to solve the problem that an existing humanoid musculoskeletal robot control method cannot well perform antagonistic muscle collaborative contraction control. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring estimated motion precision of a musculoskeletal system through a Fitts' law; calculating a supervised item torque based on the estimated motion precision through a striatum inspired speed modulation strategy; calculating a muscle activation signal vector through a muscle activation signal network; and calculating an action award based on the muscle activation signal vector and the supervised item torque, then calculating a loss function, adjusting parameters of the muscle activation signal network based on the loss function, increasing the value of the action reward, and repeatedly iterating to obtain a muscle activation signal sequence required by control. According to the method, structural information of the musculoskeletal system is utilized, a universal antagonistic muscle cooperative contraction control strategy is constructed, and smooth movement is guaranteed.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dynamic taping method for inhibition and elicitation of skeletal muscle tone
ActiveUS11103384B2Correct muscle imbalanceCorrect a muscle imbalanceFinger bandagesSuspensory bandagesHuman bodyMuscle tone
Is a taping method that follows a specific set of rules based on anatomical and physiological patterns in humans. This taping method causes a change in skeletal muscle tone in the human body, when tape is directly applied to the skin of the human body over targeted tendons and surrounding structures going over joints. This taping method will inhibit the muscle tone in the antagonist muscle of the opposing side of the joint where the tape is applied, while simultaneously eliciting the agonist of the muscle that are attached by the tendon of the joint where the tape is applied.
Owner:VACCA CHARISE
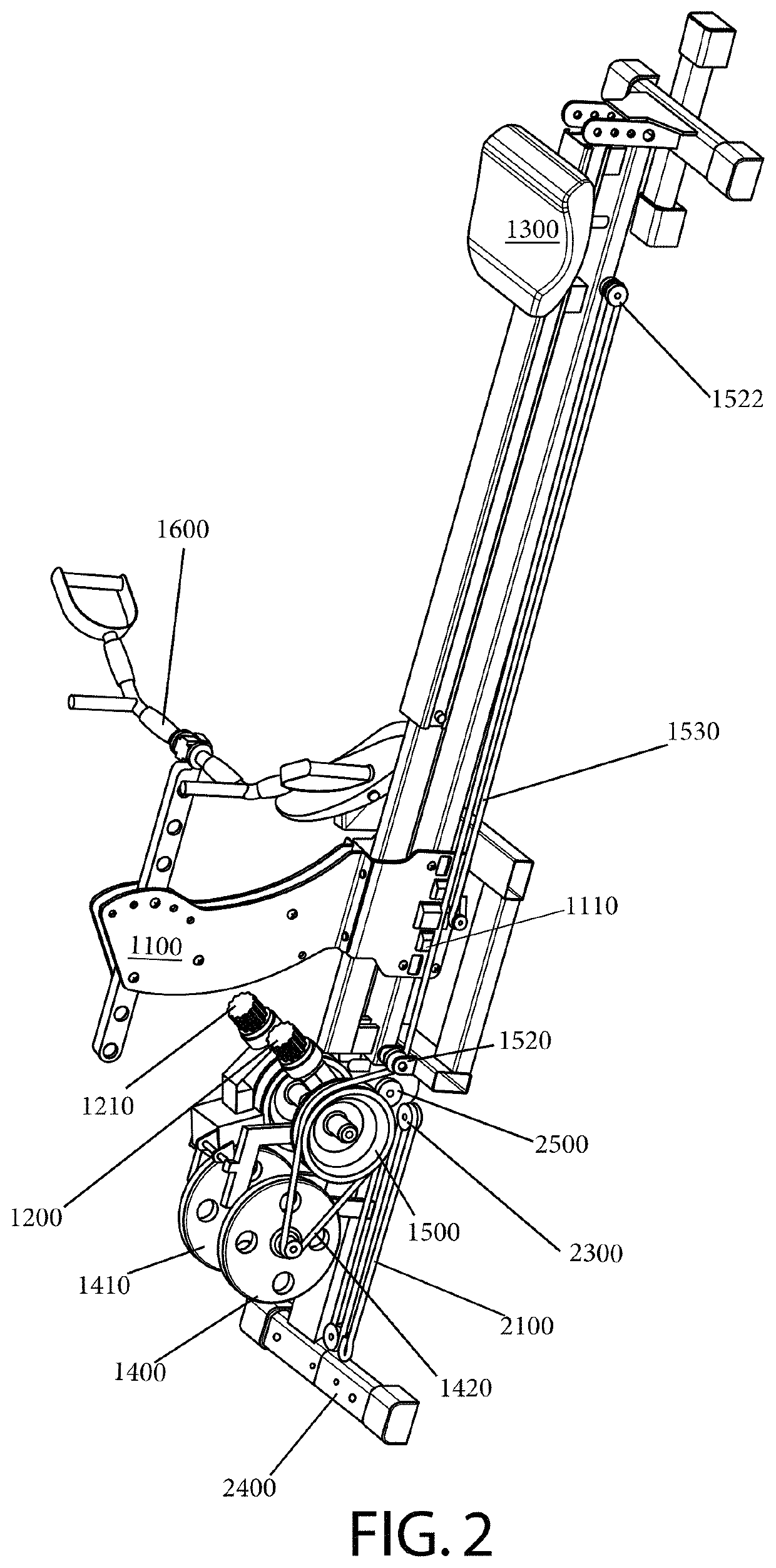
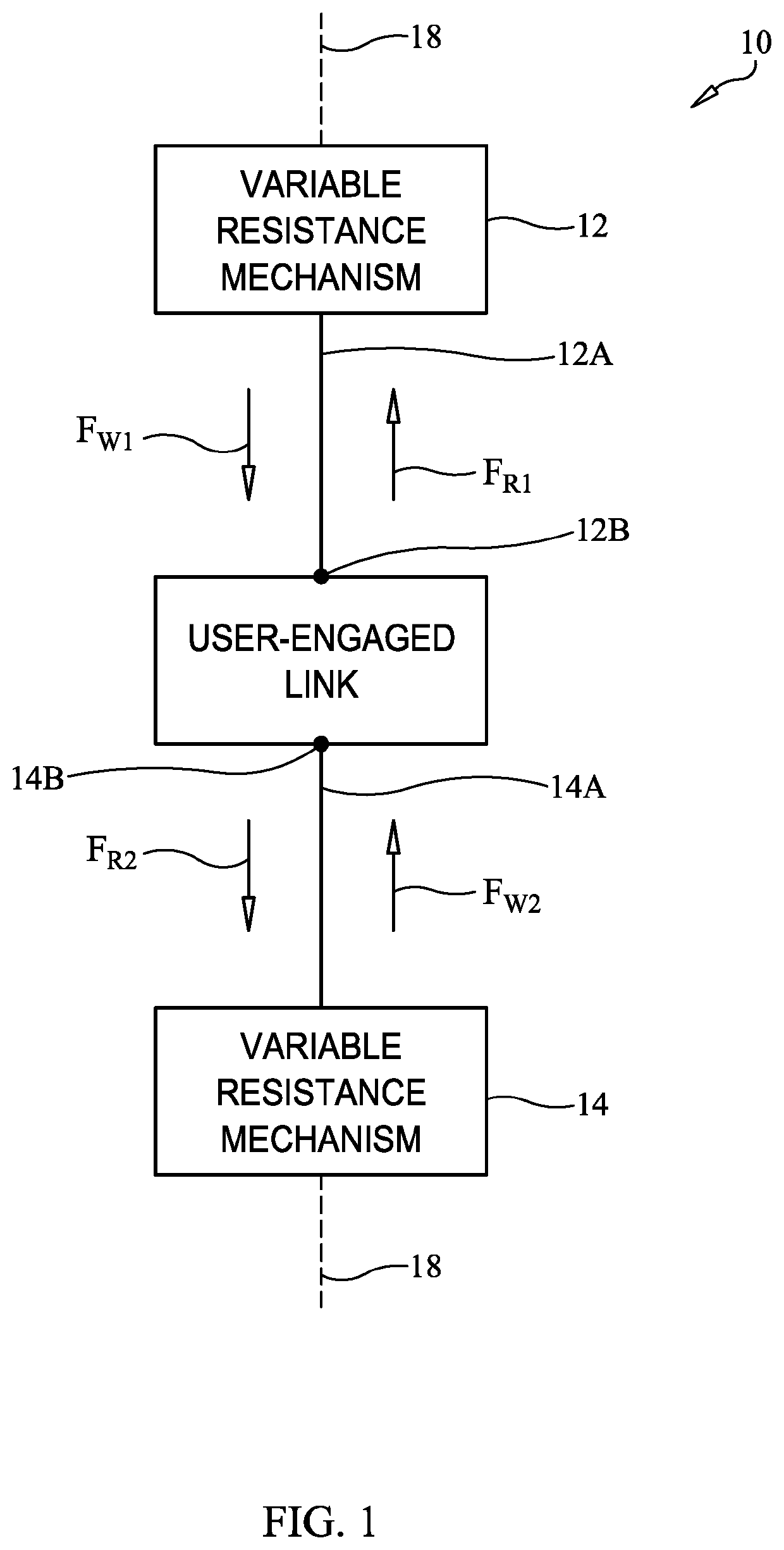
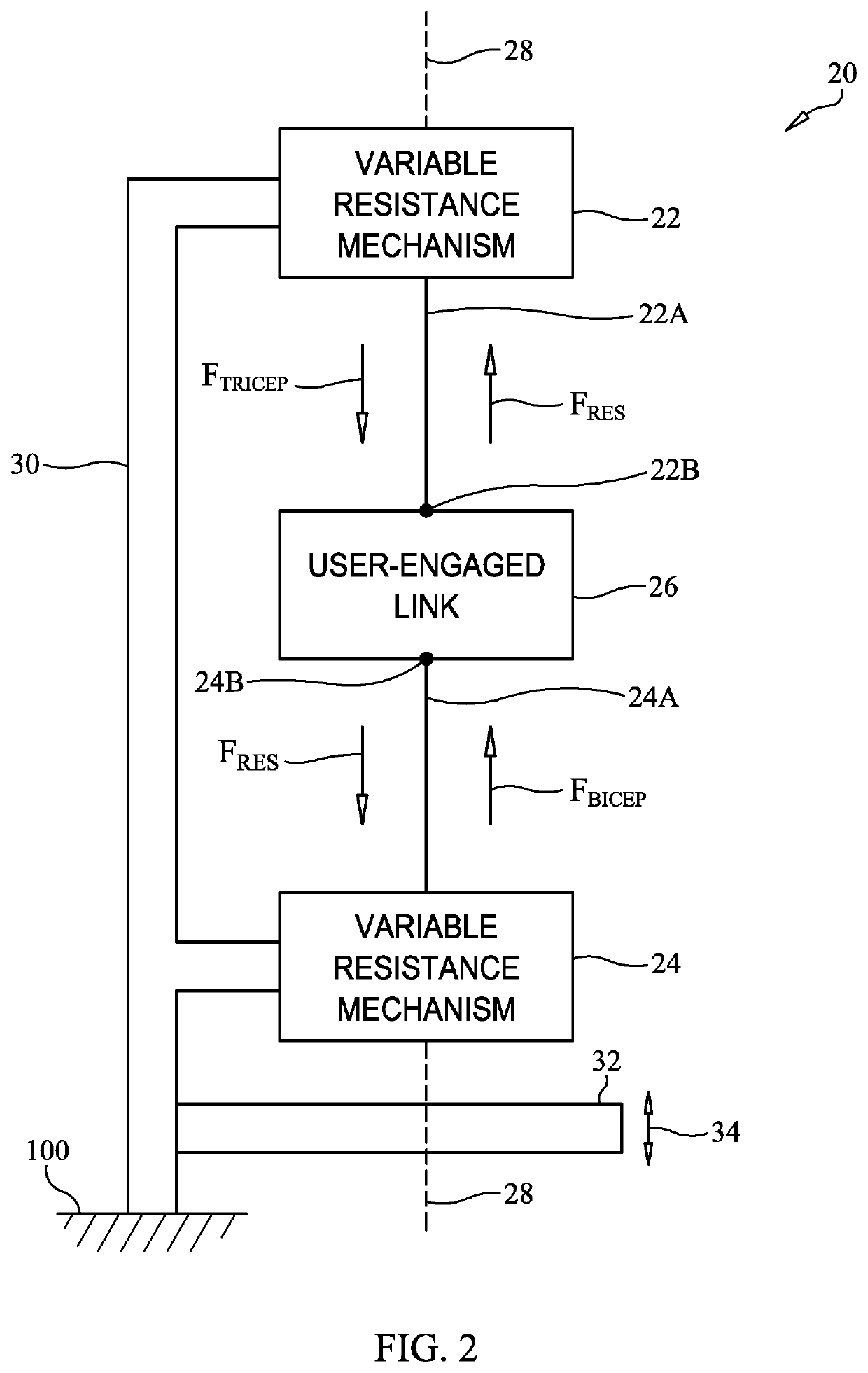
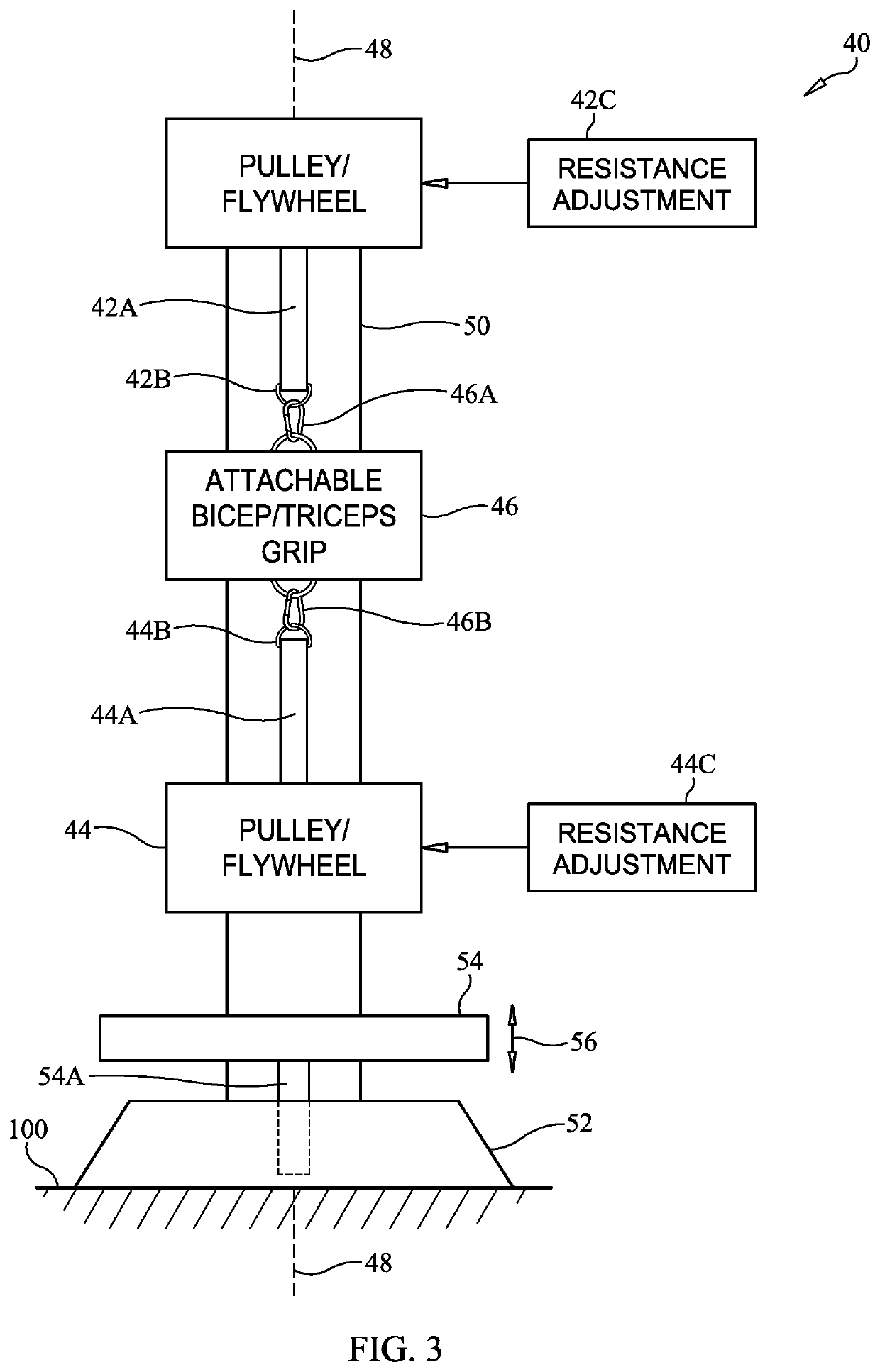
Exercise machine for fluent agonist-antagonist muscle training
An exercise machine is provided for agonist-antagonist muscle training. A first variable resistance mechanism has a first line extending therefrom, a second variable resistance mechanism has a second line extending therefrom, and a user-engaged link is coupled to the first line and second line with the first line, second line, and link being aligned along a common axis. When the user applies a first tensile force to the first line via the link, the first line extends from the first variable resistance mechanism against its resistance force while the second line retracts towards the second variable resistance mechanism under its restoring force. Then, when the user applies a second tensile force to the second line via the link, the second line extends from the second variable resistance mechanism against its resistance force while the first line retracts towards the first variable resistance mechanism under its restoring force.
Owner:SMITH III JAMES E
Method And System For Providing Proprioceptive Feedback And Functionality Mitigating Limb Pathology
PendingUS20220031479A1Enhance physical fitnessRecovery functionSpinal electrodesWalking aidsOsseointegrationResidual limb
Proprioceptive feedback is provided in a residual limb of a person that includes forming a linkage between a pair of agonist and antagonist muscles, forming a sliding surface over which the agonist and antagonist muscles slide. The sliding surface can include a synovial sleeve, a bridge formed between the distal ends of bones, or a fixture that is osseointegrated into the bone. The invention also includes a system for transdermal electrical communication in a person that includes a percutaneous access device, a sensory device that communicates signals between a muscle and the percutaneous device, and a stimulation device in communication with the percutaneous access device. In another embodiment, a closed-loop functional stimulation system restores lost functionality to a person that suffers from impairment of a neurological control system or at least partial loss of a limb.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Bionic robot based on pneumatic muscles
ActiveCN113146583AAchieve movementHigh power/mass ratioProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsEngineeringAnkle
The invention relates to a bionic robot based on pneumatic muscles. The pneumatic muscles are used for simulating human muscles to drive shoulder joints, elbow joints, wrist joints, a waist joint, hip joints, knee joints and ankle joints to move, and the function of completely simulating human joint movement is achieved. The bionic robot is mainly composed of sternum, vertebrae, ribs, pelvis, femur, fibula, connecting pieces, belt wheels, belts, bevel gears, the pneumatic muscles and control systems. The two groups of pneumatic muscles are driven in the form of antagonistic muscles, are transmitted through the belt wheels, the belts and the bevel gears, and simultaneously drive the shoulder joints, the elbow joints and the wrist joints to rotate. A plurality of groups of pneumatic muscles which are connected in series, in parallel and in series-parallel connection respectively start from the sternum or the pelvis and end at the ribs in the form of the outer layer, the middle layer and the inner layer. The robot is driven by the pneumatic muscles, has the characteristics of being compact in structure, good in flexibility and multiple in freedom degree, and can be used for teaching demonstration, medical diagnosis and athlete exercise training.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com