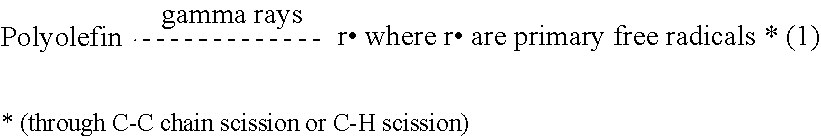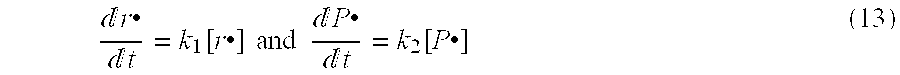Non-oxidizing polymeric medical implant
a medical implant and non-oxidizing technology, applied in the field of medical implants, can solve the problems of anti-oxidation, employ stabilizers, etc., and achieve the effect of preventing further oxidation and superior oxidation resistan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Two sets of 1-mm-thick UHMWPE sheets prepared by Methods A through D above were oven aged in air at 80° C. for 11 and 23 days respectively. After these sheets were cooled in room temperature, a thin film specimen of about 100 microns in thickness was cut from each of the 1-mm-thick aged UHMWPE sheets and placed in an IR window for a standard FTIR (A Nicolet 710 FTIR system was used) transmission run. A total of 32 spectra (scans) was collected and averaged. To determine the extent of oxidation, the IR absorption peaks in the frequency range of between 1660 and 1800 cm−1, corresponding to carbonyl (C—O) functional groups, were integrated for the peak area. The peak area is proportional to the amount of oxidized UHMWPE in the specimen. To correct for difference in specimen thickness, the integrated peak area was then normalized to the specimen thickness, by dividing by the area of the 1463 cm−1 (methyl) peak which is proportional to the specimen thickness. The obtained ratio was defi...
example 2
Two sets of 1-mm-thick UHMWPE sheets prepared by Methods B through D cited in the Sample Preparation were oven aged in air at 80° C. for 11 and 23 days respectively. After these sheets were cooled in room temperature, six tensile specimens with a dumbbell shape according to ASTM D638 (Type IV) were cut from each of the 1-mm-thick aged UHMWPE sheets. A standard tensile test was performed for each specimen at a speed of 2 inches / mm. Another set of 1-mm-thick UHMWPE sheets prepared by Methods B through D cited in the Sample Preparation, but without oven aging, were also evaluated by the same tensile test method for comparison. Tensile breaking strength results (average of six tests for each condition) are shown in Table 2:
TABLE 2Tensile BreakingSampleStrength, psiMethod B / not oven aged6510Method B / 11 day oven aging5227Method B / 23 day oven aging3192Method C / not oven aged6875Method C / 11 day oven aging6400Method C / 23 day oven aging6004Method D / not oven aged6941Method D / 11 day oven agin...
example 3
Two sets of 1-mm-thick UHMWPE sheets prepared by Methods B and Method D cited in the Sample Preparation were oven aged in air at 80° C. for 11 and 23 days respectively. After these sheets were cooled in room temperature, samples cut from sheets were characterized by a high temperature gel permeation chromatograph (GPC) column for molecular weight distribution. The samples were dissolved in hot trichlorobenzene (TCB). They were then run in the aforementioned solvent at 1.2 ml / mm. using a Jordi Gel Mixed Bed Column, 50 cm×10.0 mm ID., at a column oven temperature of 145° C. on the Waters 15° C. Chromatograph. The injection size was 250 uL of a 0.1% solution. An antioxidant (N-phenyl-2-naphthylamine) was added to all high temperature GPC samples to prevent polymer deterioration.
Prior to sample runs, the column was calibrated using narrow MW polystyrene standards. Since the samples were only partially soluble in the solvent due to cross-linking, the so-determined molecular weight dis...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com