Anti-coagulation hydrogel material for inducing NO release as well as preparation method and application thereof
A gel material and hydrogel technology, applied in anticoagulant treatment, gel preparation, colloid chemistry, etc. Repair the limited ability and other problems, achieve excellent coagulation performance, improve anticoagulation performance, and achieve remarkable results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Preparation of anticoagulant hydrogel materials that induce NO release
[0035](1) Graft heparin molecules at the end of six-armed polyethylene glycol to obtain an anticoagulant hydrogel material: in a 100mL single-mouth bottle, add 50mL of tetrahydrofuran solution, then add 10g of six-armed polyethylene glycol, fully Dissolve for 1h. Add 1 g of heparin and continue stirring for 10 min, then add 0.03 g of 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) and 0.2 g of 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) , treated in ice bath for 30 minutes, then stirred and reacted at room temperature for 12 hours, and then 50 mL of ice ethanol was added to produce precipitation after rotary evaporation to remove excess water, filtered by suction, and then dried in a vacuum drying oven to obtain heparin-modified six-armed polyethylene glycol hydrogel glue material.
[0036] (2) Graft selenocystamine on the heparin molecule to obtain an anticoagulant hydrogel materi...
Embodiment 2
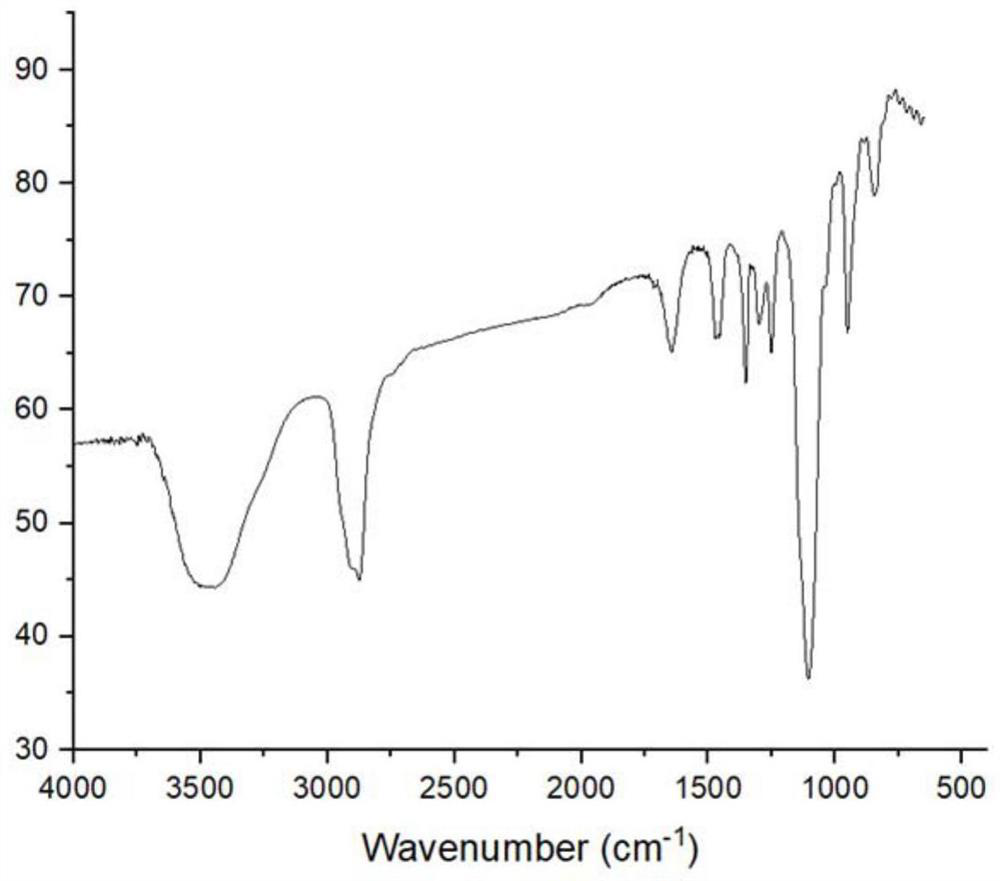
[0038] The anticoagulant hydrogel material that induces NO release obtained in Example 1 was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran solution to obtain a 10 mg / ml solution, which was prepared into a thin film material by solvent evaporation, and then the thin film material was subjected to infrared spectroscopy at normal temperature. The measuring range is 4000-400cm -1 , the result is as figure 1 as shown, figure 1 It is the infrared spectrogram of the anticoagulant hydrogel material, composed of figure 1 It can be seen that the wavelength of 3480cm -1 There is a broad hydroxyl absorption peak at a wavelength of 2910cm -1 and wavelength 2880cm -1 There are obvious methyl and methylene absorption peaks at a wavelength of 1650cm -1 and a wavelength of 1475cm -1 The absorption peak at is the absorption peak of the amide bond or the absorption peak of the ester group, and the wavelength is 1100cm -1 A strong absorption peak of the C-O group (mainly produced by the C-O in the PEG stru...
Embodiment 3
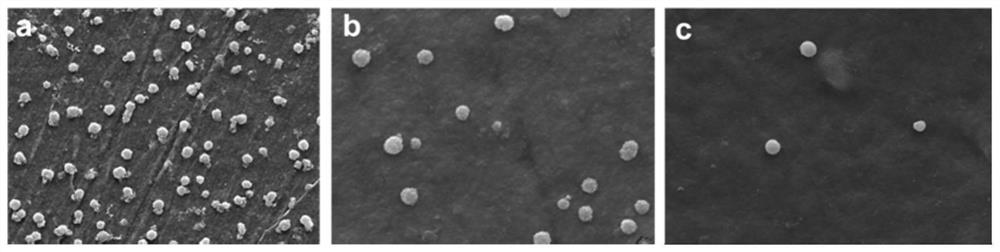
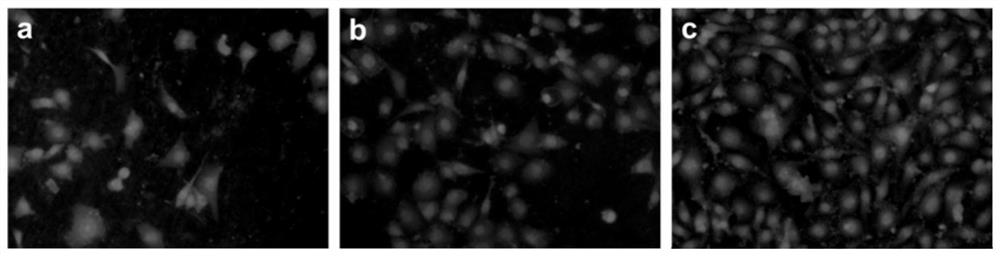
[0040] The anticoagulant hydrogel material that induced NO release obtained in Example 1 was fully dissolved in tetrahydrofuran solution to form a 20 mg / mL solution, and the hydrogel film material was obtained by solvent evaporation. In the absence of NO donor and the addition of 20 uL of NO donor (10 μM nitrosoglutathione and glutathione), polystyrene was used as the control material to conduct platelet adhesion experiments in vitro. Fresh human whole blood (provided by Huai'an Second People's Hospital) was centrifuged at 1500rpm for 15min to obtain platelet-rich plasma. 200 µL of platelet-rich plasma was dropped on each sample surface to cover the entire surface. After incubation at 37° C. for 2 h, the samples were washed with 0.1 M PBS buffer (pH=7.4). The adhered platelets were fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde in PBS solution for 24h, and then washed with PBS buffer. Then use 30%, 50%, 75%, 90%, 100% ethanol solution to dehydrate successively, each time for 10min, after de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com