Super-resolution stimulated Raman microimaging method and device for realizing near resonance enhancement
A stimulated Raman and microscopic imaging technology, which is applied in the fields of biomedicine and optical imaging, can solve the problems of inability to image fine structures, achieve the effects of reducing the effective spot volume, improving imaging sensitivity, and improving lateral resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0105] Example 1: High-resolution imaging of unlabeled neurons
[0106] For stimulated Raman imaging, when the frequency difference Δω of the two laser beams matches the molecular vibration frequency, the molecular transition rate is excited and the Raman signal is stimulated and amplified. By changing the excitation wavelength or spectral focusing method, etc., the imaging of different molecular bonds such as C-H bond and C=C bond can be realized. Taking the laser wavelength of 520nm & 450nm as an example, the spectral focusing technology can achieve 2800~3050cm -1 range of chemical imaging, including C-H 2 Molecular bond, C-H 3 Molecular bond, =C-H molecular bond.
[0107] Figure 8 (a) shows images of cultured osteosarcoma cells obtained by conventional near-infrared laser-based stimulated Raman microscopy. Figure 8 (b) shows the image of osteosarcoma cells obtained by the visible laser-based stimulated Raman microscope of the present invention, and the image has been...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Example 2: In situ three-dimensional hyperspectral imaging of unlabeled cells and tissues
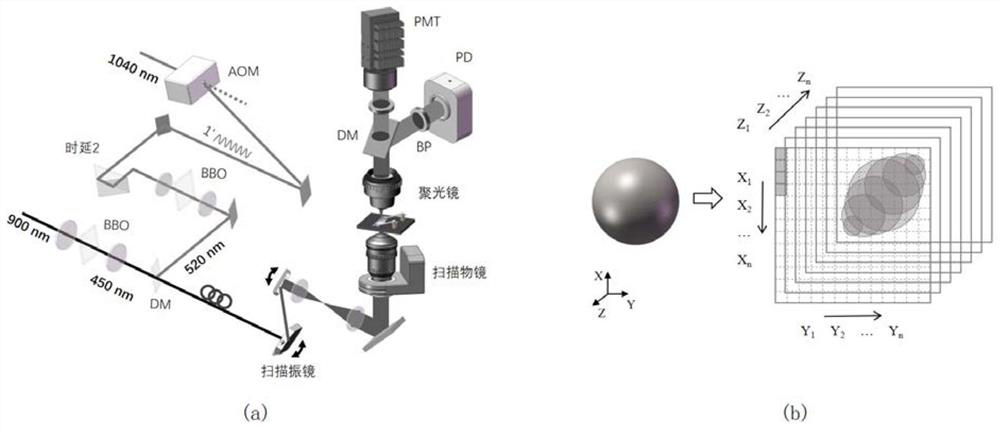
[0109] Based on nonlinear effects, stimulated Raman microscopy has natural optical section imaging capabilities. After collecting one XY plane through the galvanometer scanning, the Z-axis height of the objective lens is adjusted synchronously to image the next plane. Figure 9 (a) is the cross-section display at different heights in the high-resolution 3D image of human cervical cancer cells (HeLa cells). The three-dimensional structure of cell shape, nuclear membrane and nucleolus is clearly presented. Figure 9 (b) is a three-dimensional image of brain tissue, and the invention has the ability of direct tissue imaging.
[0110] The difference between the second embodiment and the first embodiment lies in the application of the three-dimensional imaging technology.
Embodiment 3
[0111] Example 3: Large-scale high-resolution hyperspectral stimulated Raman microscopic imaging of brain tissue
[0112] High-resolution imaging of intact tissue is very challenging for fluorescence microscopy due to the difficulty of eliminating out-of-focus fluorescence background, but this problem does not exist for stimulated Raman microscopy. Figure 10 Imaging results of unprocessed high-resolution C57 mouse brain tissue.
[0113] Figure 10 (b) with Figure 10 (c) Hyperspectral high-resolution SRS imaging of mouse brain tissue slices. Based on the improved resolution, the invention enables chemical analysis of samples in Figure 10 (d), the imaged strip area covers the cortex, hippocampus and other brain regions.
[0114] In visible light stimulated Raman imaging, the axon appears as a closed circle with a diameter of about 1 micron in the cross section, and two parallel curves in the longitudinal section. Such as Figure 10 (d), The neural network is composed of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com