Monascus industrial strain for traceless deletion of citrinin synthetic genes
A technology of citrinin and Monascus, which is applied in the field of preparation of Monascus strains, and can solve the problems of inability to completely eliminate citrinin, genetic instability and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
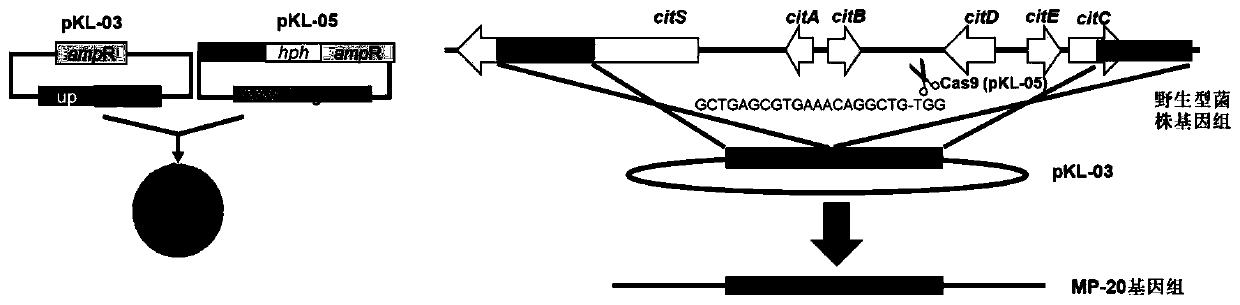
[0062] Example 1. Construction of CRISPR / Cas9 plasmid pKL-03 and donor plasmid pKL-05 that seamlessly deleted the Monascus citrin biosynthetic gene cluster
[0063] (1) Extraction of Monascus Genomic DNA
[0064] Take the PDA plate cultured by Monascus strain KL-001 for 7 days, place it in -80°C and freeze it for 20 minutes, scrape the surface hyphae after taking it out, wash it twice with sterile water, freeze-dry it and store it at -20°C. Grind the lyophilized mycelia into a fine powder using a liquid nitrogen precooled mortar, and resuspend in 500 μL of lysis buffer (40 μmol / L Tris-acetate, 20 μmol / L sodium acetate, 1 μmol / LEDTA, 1% w / v SDS, pH 7.8), pipette until the viscosity of the suspension decreases significantly and foam forms. Add RNase A and incubate at 37 °C for 5 min, then add 165 µL of 5 µmol / L NaCl solution and mix. Centrifuge at 13 000 rpm for 20 min, immediately transfer the supernatant to a new test tube, and add 400 μL of chloroform and 400 μL of phenol. ...
Embodiment 2
[0109] Embodiment 2, the complete deletion of Monascus citrin biosynthesis gene cluster
[0110] (1) Transformation of Monascus with pKL-03 and pKL-05 plasmids
[0111] The preparation method of Monascus protoplast is as follows:
[0112] a. Inoculate Monascus KL-001 onto a PDA plate and culture it in a 30°C incubator for 7 days.
[0113] b. Cut off the mycelium block with a sterile knife and inoculate into 200mL YEME liquid medium (yeast powder 3g / L, peptone 5g / L, malt extract 3g / L, glucose 10g / L, sucrose 130g / L and distilled water 1L ; Add MgCl after autoclaving 2 ·6H 2 O (2.5M) 2mL / L and glycine (10%) 100mL / L), cultured at 30°C for 30h.
[0114] c. Collect the hyphae in the culture medium by centrifugation at 10000×g, add 15 mL Osmotic Medium and wash 3 times.
[0115] d. Add 10mL of mixed enzymatic hydrolysis solution (100mg Lysing Enzyme, 30mg Yatalase, 30mg cellulase and 40mg helicase), culture in a shaker at 30°C and 80rpm, observe the enzymatic hydrolysis of mycel...
Embodiment 3
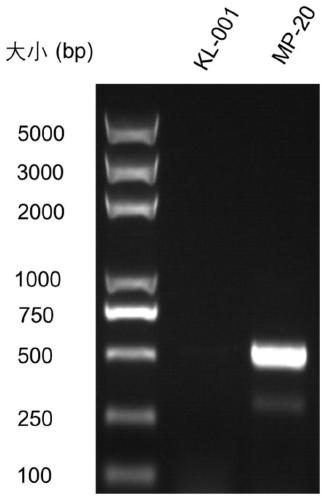
[0128] Embodiment 3, Monascus engineering strain MP-20 detects citrinin and pigment
[0129] (1) Detection of engineering strain MP-20 citrinin
[0130] The verified engineering strain MP-20 and the wild-type strain KL-001 were inoculated into PDB medium for fermentation, cultured on a shaker at 30°C and 200rpm for 7 days, and samples were taken.
[0131] Take 30 mL of fermentation broth, adjust the pH of the fermentation broth to 4.0 with HCl, extract the mycelium and supernatant with ethyl acetate for three times, and combine the organic phases. Rotary evaporate at 30°C until completely dry, add 300 μL methanol to dissolve. Filter through a 0.22 μm filter membrane, and detect citrinin by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS).
[0132] Citrinin LC-MS detection condition: carry out LC-MS analysis on Agilent-1200HPLC / 6520QTOFMS (USA) system, mobile phase is acetonitrile (v / v, 0.1% formic acid) and water (v / v, 0.1% formic acid), Flow rate 0.8mL / min. 0-15min, 5%-95%...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com