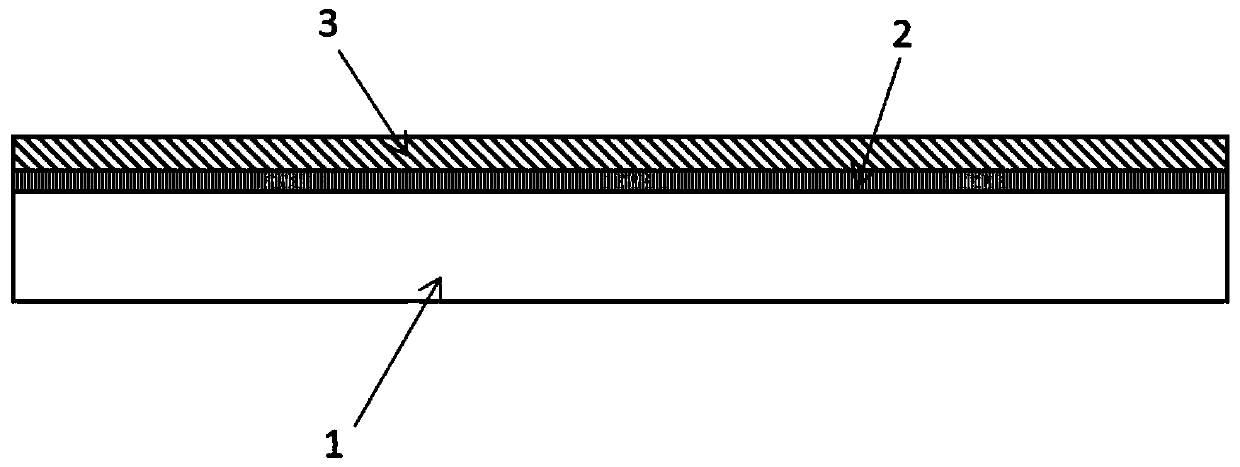
Antibacterial medical biological material and preparation method thereof
A technology of biomaterials and matrix materials, applied in the field of antibacterial medical biomaterials and its preparation, can solve problems such as chain complications, bacterial adhesion, infection, etc., and achieve the effect of improving moisturizing function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0049] Another aspect of the present invention provides a method for preparing an antibacterial medical biomaterial, comprising:
[0050] a) placing the acellular small intestinal submucosa matrix material in a sodium hydroxide solution containing sulfadiazine, controlling the pH of the solution to be between 7.1 and 13.0, and obtaining an intermediate material coated with sulfadiazine sodium on the surface and / or inside;
[0051] b) After the intermediate material obtained in step a is taken out from the solution, washed with sodium chloride solution, and dried, the intermediate material is soaked in silver nitrate solution, so that the sodium ions on the sodium sulfadiazine molecule are The silver ion substitution in silver nitrate is used to obtain the decellularized small intestinal submucosa matrix material loaded with silver sulfadiazine;
[0052] c) performing surface plasma treatment on the acellular small intestinal submucosa matrix material loaded with silver sulfadi...
Embodiment 1
[0075] A method for preparing an antibacterial medical biomaterial, comprising:
[0076] (1) Immerse the small intestinal submucosa tissue material on the pig body into normal saline for cleaning, put the cleaned small intestinal submucosa tissue material into a closed container, freeze-dry it in liquid nitrogen, seal it, and sterilize it For storage, the freeze-drying temperature is -75°C, and the freeze-drying time is 25 hours. The sterilization is to irradiate the sealed small intestinal submucosa tissue material with a radiation dose of 8000 rads and sterilize it through linear acceleration.
[0077] (2) Treat the small intestinal submucosa tissue material obtained in step a1 with decellularization solution in two ultrasonic frequency environments with different frequencies, and perform decellularization; wherein, the decellularization solution includes trypsin and PBS solution, and the decellularization solution The mass percent concentration of trypsin in the medium was ...
Embodiment 2
[0089] A method for preparing an antibacterial medical biomaterial, comprising:
[0090] (1) Immerse the small intestinal submucosa tissue material on the pig body into normal saline for cleaning, put the cleaned small intestinal submucosa tissue material into a closed container, freeze-dry it in liquid nitrogen, seal it, and sterilize it For storage, the freeze-drying temperature is -78°C, and the freeze-drying time is 25 hours. The sterilization is to sterilize the sealed small intestinal submucosa tissue material through linear acceleration and irradiation with a radiation dose of 8000 rads.
[0091] (2) Treat the small intestinal submucosa tissue material obtained in step a1 with decellularization solution in two ultrasonic frequency environments with different frequencies, and perform decellularization; wherein, the decellularization solution includes trypsin and PBS solution, and the decellularization solution The mass percent concentration of trypsin in the medium is 0....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com