A non-melting treatment device and method for highly active refractory metal polymer fibers
A refractory metal and processing device technology, applied in the field of ceramic fibers, can solve problems such as excessive tension and breakage, and achieve the effect of avoiding fusion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1: A non-melting treatment device for highly active refractory metal polymer fibers
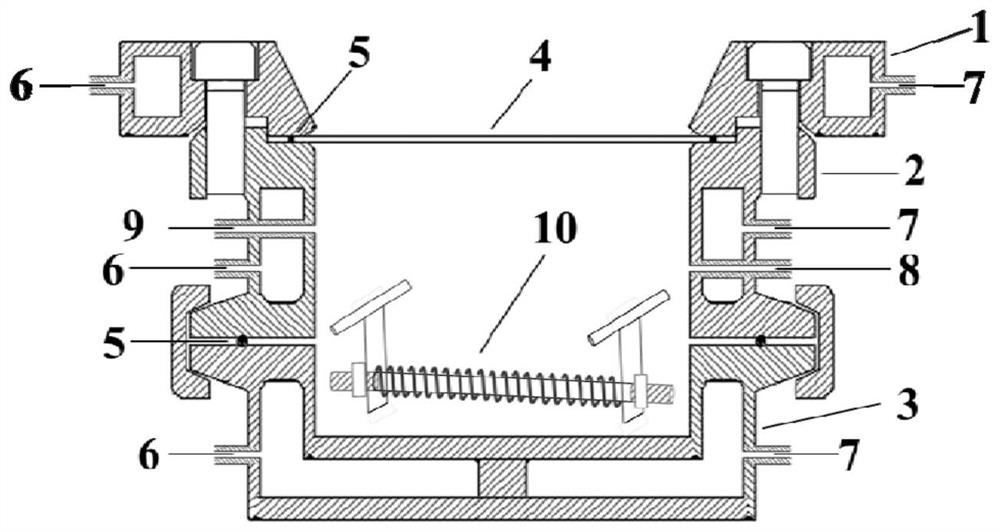
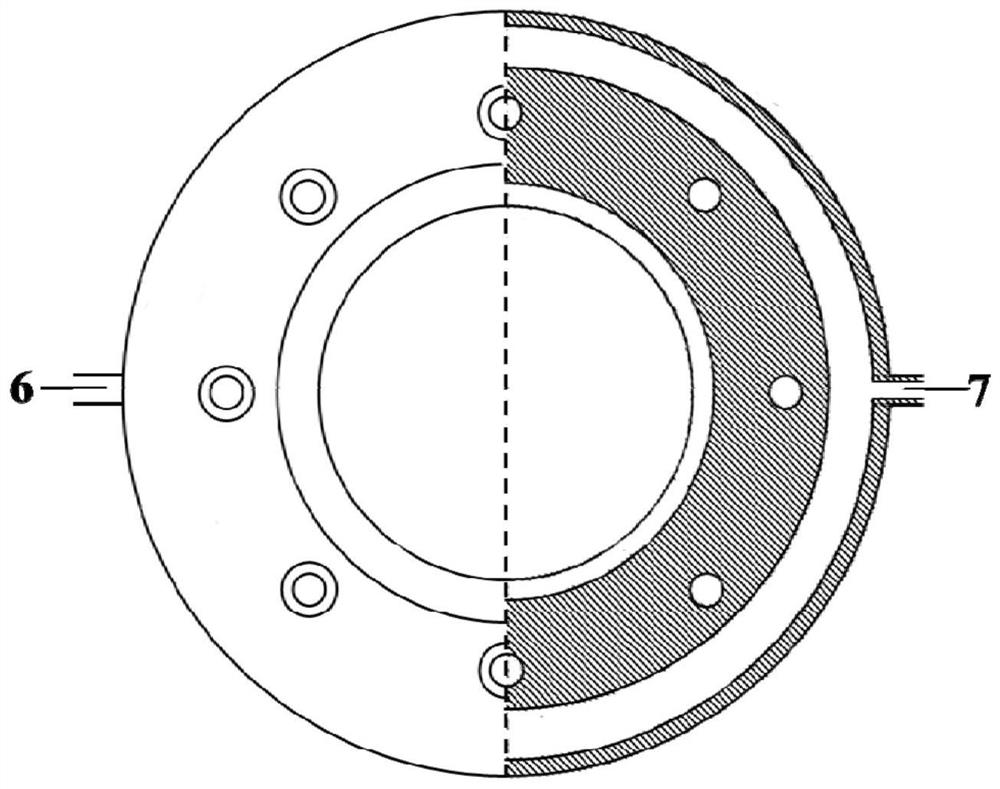
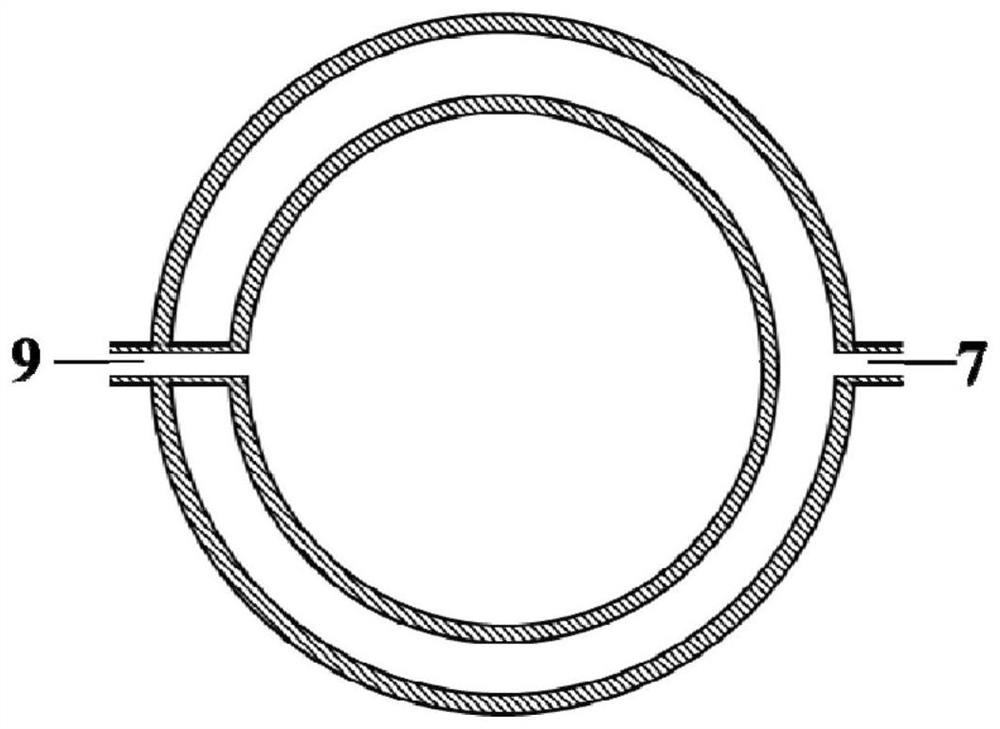
[0041] A non-melting treatment device for highly active refractory metal polymer fibers, the structure of which is as follows figure 1 , 2 , shown in 3, including casing 2, upper sealing cover 1 and lower sealing cover 3, receiving window 4, fiber tension control bracket 10, air inlet and air inlet valve 11, air outlet and air outlet valve 12; 2 is a round or square barrel shape with upper and lower ends open; the receiving window 4 is made of titanium metal material, and is arranged on the upper port of the box body 2 for the electron beam to penetrate and directly irradiate the inside of the box body 2. The upper sealing The cover 1 is used to fix the receiving window 4 on the upper opening of the box body 2 and seal the junction of the receiving window 4 and the box body 2; the lower sealing cover 3 is used to seal the lower port portion of the box body 2; the box body 2 an...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2: the preparation of polyhafnium azacarbane fiber
[0043] React 0.1 mol of hafnium tetrachloride and 0.1 mol of ethylenediamine in triethylamine at room temperature for 6 hours, then pass through excess methylamine, react at 100°C for 4 hours, then cool down to room temperature. The impurity was separated and removed by silica gel column chromatography, and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure to obtain polyhafnium azacarbane. The hafnium content in the polyhafiazacarbane is 46wt%, and the oxygen content is 0.3wt%. Polyhafiazacarbane was melt spun at 123° C. under the protection of an inert atmosphere to prepare polyhafiazacarbane fibers with an average fiber diameter of 18 μm.
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: non-melting treatment of polyhafiazacarbane fiber
[0045] Utilizing the non-melting treatment device of Example 1, under an inert atmosphere, the polyhafiazacarbane fiber prepared in Example 2 is placed on the fiber support in the non-melting device, and by adjusting the tension of the tow, the precursor fiber The shrinkage rate is controlled at 1%, the device is sealed, and the gas valve is closed. Then place the non-melting device under the electron beam for cross-linking at a dose rate of 10 3 Gy / s, the total dose is 18MGy, and the cooling water is used to cool down during the irradiation process to prevent the temperature from being too high during the crosslinking process. After the irradiation, the water inlet of the non-melting treatment device is fed with absolute ethanol to replace the residual moisture in the hollow structure, and then heated in the air to about 80°C to completely volatilize the ethanol in the hollow structure. Then put the no...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com