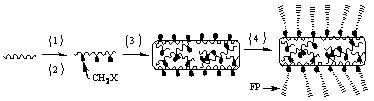
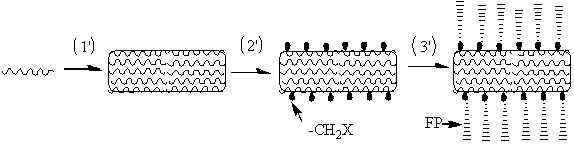
Method of producing aromatic polymer antifouling film
An aromatic polymer, polymer membrane technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, membrane technology, semi-permeable membrane separation, etc., can solve the problems of reduced protein retention rate, high cost and consumption of trimethylchlorosilane, and achieve reagent consumption. Volume reduction, wide availability, cost reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] 1) Pour 18 g of phenolphthalein type polyaryletherketone (PEK-C) into a round bottom flask, then add 2 g of polyethylene glycol (PEG-600) additives and 80 g of N-N, dimethylacetamide (DMAC) Solvent, stirred and dissolved rapidly at 60°C for 24 h to obtain a yellow transparent polymer solution; defoamed the polymer solution obtained above for 24 h in vacuum; slowly poured the obtained polymer solution on a clean glass plate, and adjusted the scraping film Speed up to 1.87 m / min, scrape out a film with a thickness of 150 μm (liquid film thickness), wait in the air for 8 s, then quickly put it into a deionized water coagulation bath at 15 °C, take it out after the film falls off automatically, and wash it It was soaked in deionized water for 24 h before use.
[0059] 2) Put the 2 cm2 PEK-C ultrafiltration membrane prepared by the phase inversion method above into the reactor, add 2.0 g of paraformaldehyde, 0.15 g of catalyst, and 30 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid. ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] After the polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane was prepared by the same phase inversion method as in Example 1, it was soaked in deionized water for 24 h before use.
[0064] 1) Put the polysulfone (PSF) ultrafiltration membrane prepared by the phase inversion method above into a reaction tube, add 1.5 g of paraformaldehyde, 0.05 g of catalyst, and 40 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid. The reaction temperature was set at 70°C, and the reaction time was 4 h. An ultrafiltration membrane grafted with chloromethyl groups was obtained. The prepared chloromethylated polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane was repeatedly washed with deionized water.
[0065] 2) The above-mentioned 2 square centimeter surface chloromethylated PSF ultrafiltration membrane, 0.0072g cuprous bromide powder, 0.0125 g 2,2-bipyridine and 1.68 g sulfobetaine and ultrafiltration grafted with chloromethyl Put the filter membrane into the polymerization tube, and add 4 ml of methanol and deionized water ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com