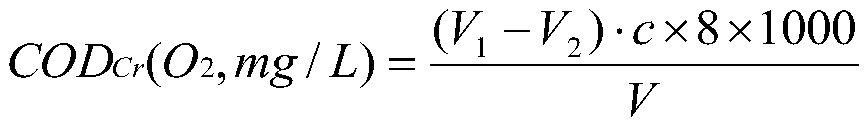An activation accelerator for improving the microbial treatment effect of daily chemical wastewater
A technology for activating accelerators and compound microbial inoculants, applied in the field of wastewater bio-enhanced treatment, can solve the problem of high cost of use, and achieve the effects of promoting growth, improving metabolic activity, and promoting ATP production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Embodiment 1: the influence of each additive on sewage treatment effect
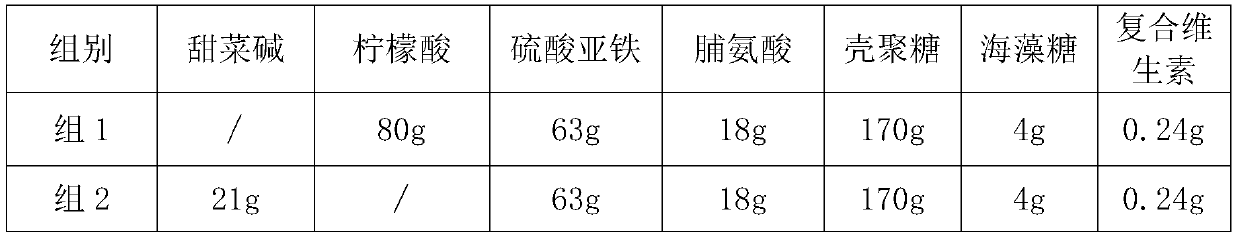
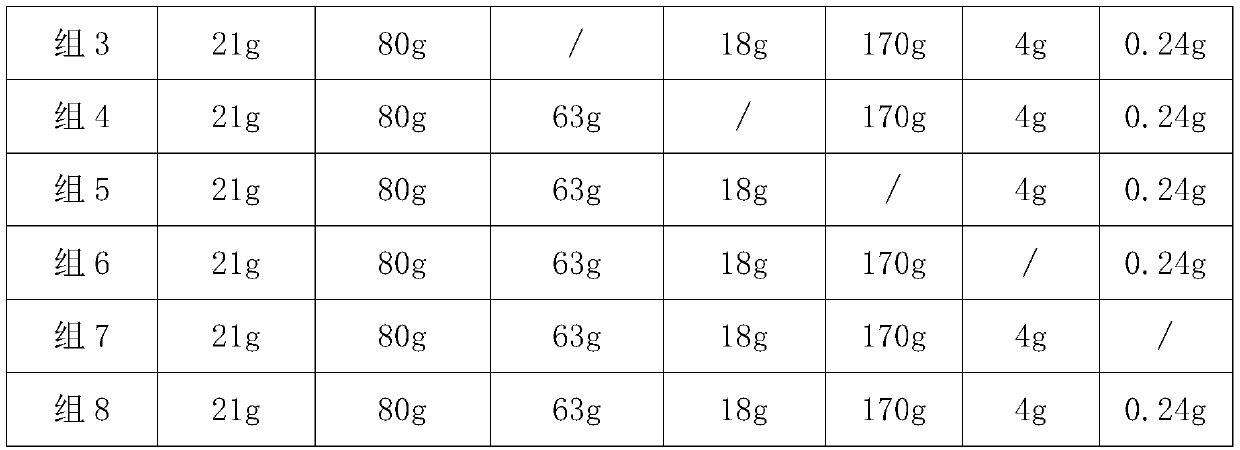
[0075] 1. The accelerator components of each group are shown in Table 1. At the same time, an equal amount of phosphate buffer solution was set as a control group.
[0076] Table 1 The list of accelerator ingredients in each group
[0077]
[0078]
[0079] 2, get the promotor of each group of equal amount step 1 respectively, the addition of microorganism activation promotor in every thousand liters of waste water is one liter, and initial surfactant concentration is about in the waste water of 1500mg COD / L, in the waste water, salt concentration ( NaCl) is 20~30g / L, then inoculated into the complex microbial bacterial agent, the inoculation amount is 20% (OD 600 =0.1~0.2), the working temperature is 20℃.
[0080] The microorganism activation accelerator prepared according to the technical scheme of the present invention can work well at 15-30° C., and for the convenience of operation, 2...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Embodiment 2: the impact of proline and citric acid on microbial treatment of wastewater under high-salt environment
[0087] 1. Preparation of accelerator:
[0088] (1) Positive control group: 18g of proline, 63g of ferrous sulfate, 270g of citric acid, 170g of chitosan, 21g of betaine, 4g of trehalose, and 0.24g of multivitamins were dissolved in 1L of water, mixed well, and made into microorganisms Activate the accelerator and keep it sealed.
[0089] (2) Blank control group: equal volume of phosphate buffer saline.
[0090] (3) The components of the test group are shown in Table 3.
[0091] Table 3 The components of the accelerator test group
[0092]
[0093] 2. Take the same amount of accelerators from each group in step 1, and add one liter of microbial activation accelerators per thousand liters of wastewater, add to 20°C, the initial concentration is 1500mgCOD / L, and the salt concentration is 20-30g / L In the waste water, then inoculated into the complex ...
Embodiment 3
[0098] Example 3: Effect of ferrous ions on microbial treatment of wastewater in a high-salt environment
[0099] 1. Preparation of accelerator:
[0100] (1) Positive control group: dissolve 18g of proline, 25g of ferrous sulfate, 80g of citric acid, 170g of chitosan, 21g of betaine, 4g of trehalose, and 0.24g of multivitamin in 1L of water, and mix well to prepare Microbial activation accelerator, sealed and stored.
[0101] (2) Blank control group: equal volume of phosphate buffer saline.
[0102] (3) Test group: each component is shown in Table 5. Dissolve each component in 1L of water, mix thoroughly to make a microorganism activation accelerator, and keep it sealed.
[0103] Table 5 Each component of the test group
[0104] group Betaine citric acid ferrous sulfate proline Chitosan Trehalose multi-vitamins group 1 21g 80g 50g 18g 170g 4g 0.24g group 2 21g 80g 58g 18g 170g 4g 0.24g group 3 21g 80g 70g 18g 170g 4...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com