Mass spectrometry probe for glutamate receptor as well as method for detecting spatial distribution rule of mass spectrometry probe in brain tissue
A glutamate receptor and spatial distribution technology, applied in the field of mass spectrometry imaging, can solve problems such as poor quantitative relationship of absolute mass spectrometry signals, different vaporization and ionization capabilities, and inability to solve quantitative comparison problems of different molecules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] For high-resolution molecular imaging of other endogenous substances in the mouse brain that has not been injected with mass spectrometry probes, the steps are as follows:
[0041] 1) Preparation of image acquisition film: (Bi 2 o 3 ) 0.07 (CoO) 0.03 (ZnO) 0.9 The nano-semiconductor material is placed on a conductive aluminum or copper strip, and an image acquisition film is made under a pressure of 10MPa. The prepared image acquisition film is attached and fixed to the metal sample target to avoid the generation of air bubbles;
[0042] 2) Prepare anesthesia solution and prepare tissue cleaning solution: use analytically pure diethyl ether as an anesthetic, weigh analytically pure NaCl, dissolve it in pure water, and obtain physiological saline, which is used as a cleaning solution for rat brain tissue blood stains, and refrigerate at -4°C for later use;
[0043] 3) After anesthetizing the mouse with the anesthetic prepared in step 2), the brain was removed, and th...
Embodiment 2
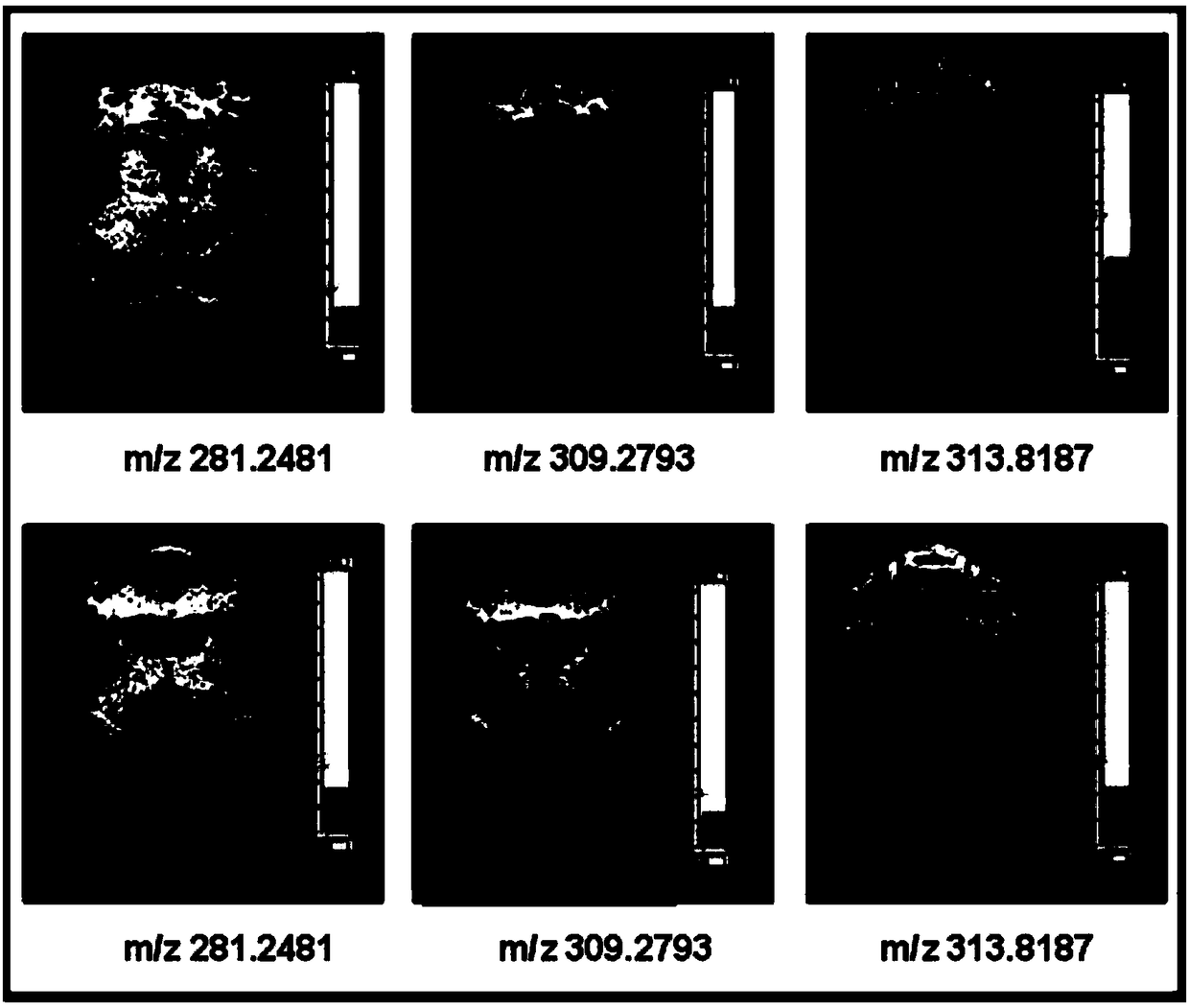
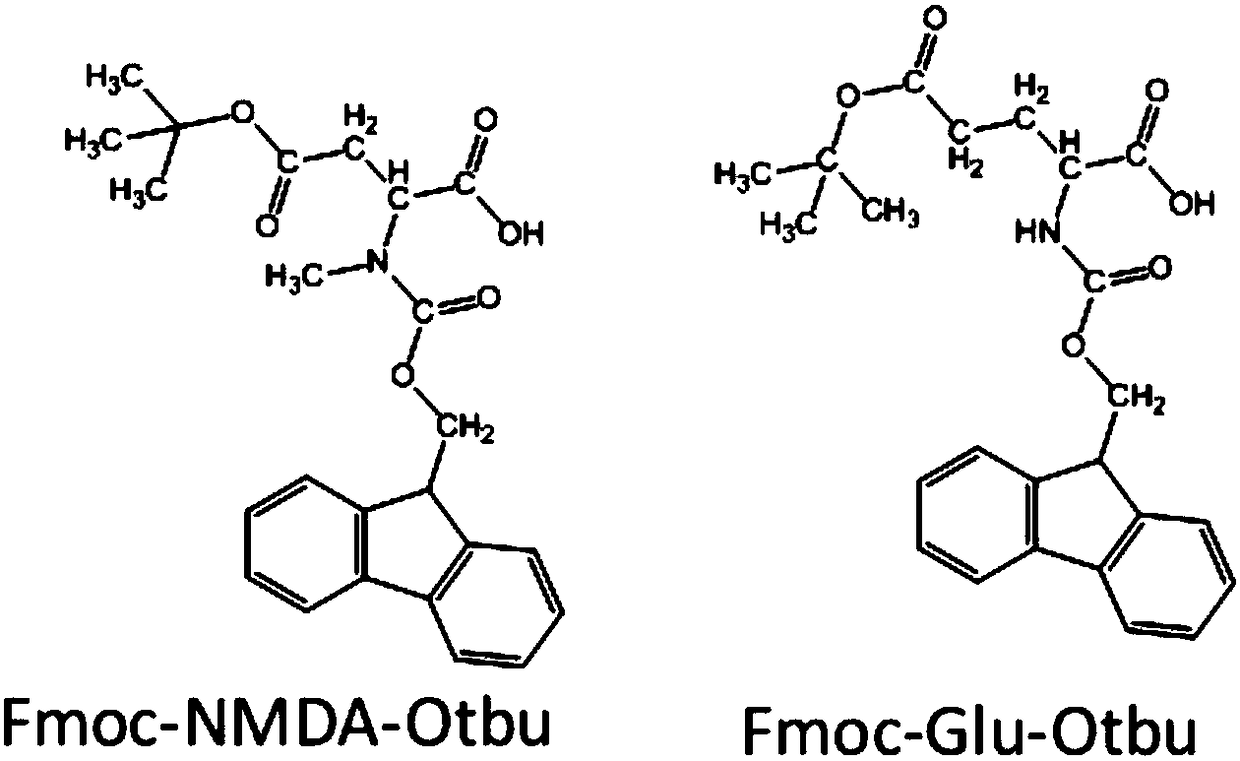
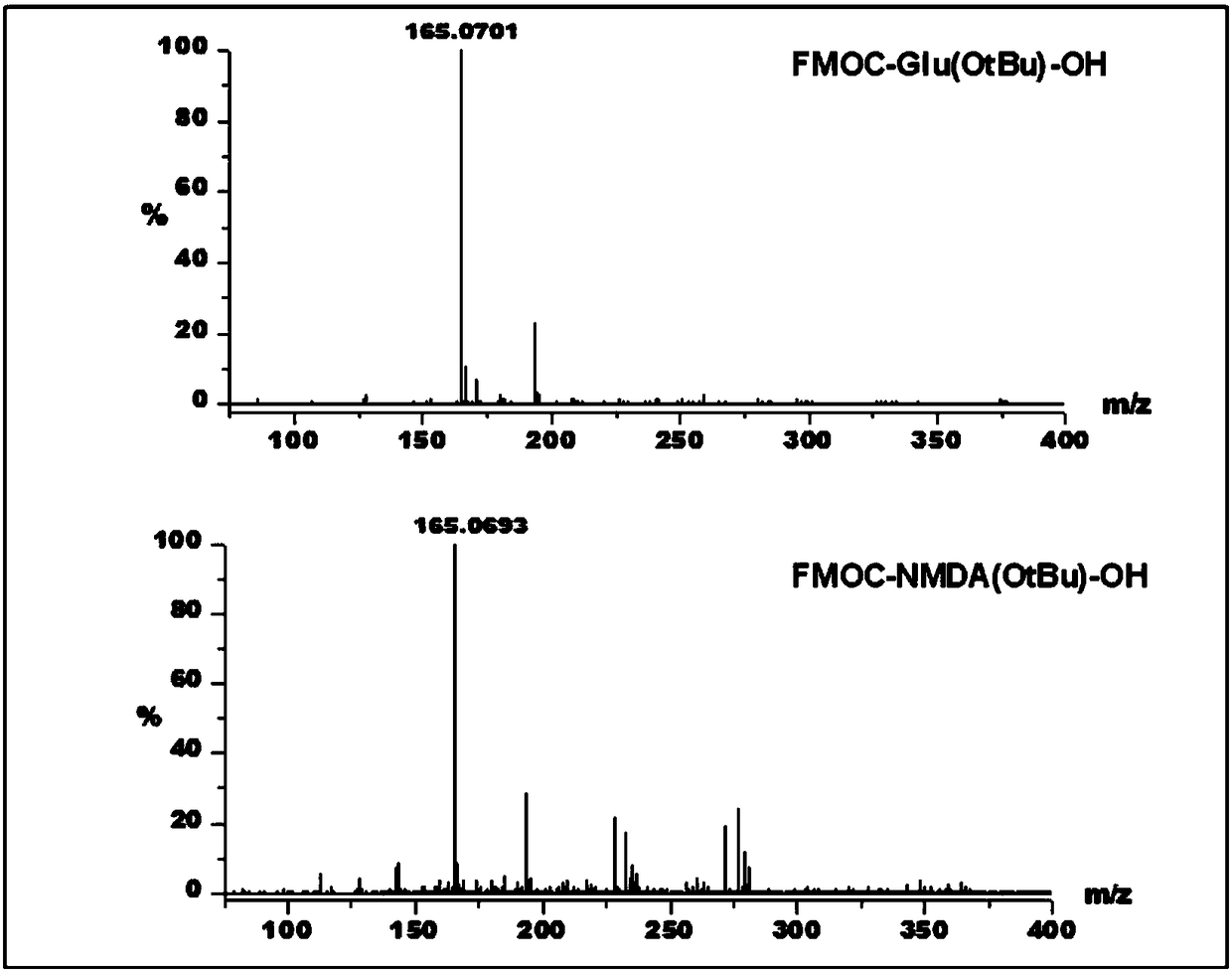
[0051] Spatialization of mass spectrometry probes (tert-butyl-protected glutamate conjugated to fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl group and tert-butyl-protected N-methyl-aspartic acid conjugated to fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl group) in the rat brain For distribution imaging, the operation steps are as follows:
[0052] 1) Prepare the probe molecule solution: Weigh the tert-butyl-protected glutamic acid combined with the fluorenyl moxycarbonyl group and the tert-butyl-protected N-methyl-aspartic acid combined with the fluorenyl moxycarbonyl group , dissolved in 50Mm NH 4 HCO 3 In normal saline, its concentration is 75mM;
[0053] 2) Place the solution obtained in step 1) on the surface of the image acquisition film with a pipette. After the solvent evaporates, put the sample target into the instrument for analysis, and adjust the voltage of the sample target, hexapod, extraction plate, and slit so that The voltage difference between the sample target and the slit is 20 volts;
[0054] ...
Embodiment 3
[0060] The spatial distribution imaging of mass spectrometry probe molecules (glutamic acid combined with fluorenyl moxycarbonyl group and N-methyl-aspartic acid combined with fluorenyl moxycarbonyl group) in the mouse brain, the operation steps are as follows :
[0061] 1) Prepare the probe molecule solution: Weigh the glutamic acid combined with the fluorenyl moxycarbonyl group and the N-methyl-aspartic acid combined with the fluorenyl methaneoxycarbonyl group, and dissolve them in 50Mm NH 4 HCO 3 In normal saline, its concentration is 75mM;
[0062] 2) Injecting the mass spectrometer probe solution obtained in step 1) into the mouse intravenously;
[0063] 3) The mouse brain obtained in step 2) was taken out and cleaned, and then cut into 20 micron thick tissue sections with a cryostat;
[0064] 4) Attach the tissue slice obtained in step 3) to the surface of the image acquisition film, put the sample target into the instrument for analysis, adjust the voltage of the sam...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com