A genetic modification method for introducing polyamine tags, soluble expression and biomimetic immobilization of lipase
A genetic modification, lipase technology, applied in the field of protein immobilization and genetic engineering, can solve the problems of reducing enzyme utilization, inactivation, insolubility, etc., and achieve simple immobilization methods, high immobilization efficiency, and high vitality recovery. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1: PCR method constructs and expresses the lipase gene 6His-CalB-10Lys with polyamine tag
[0047] Using PA1K-pPIC9K as a template, according to the known CalB gene sequence, design the upstream primer H6-CalB (F) (the underline is the NdeI restriction site) and the downstream primer CalB-K10 (R) (the underline is the XhoI restriction site ) sequence as follows:
[0048] H6-CalB(F):5'-ATATAT CATATG CACCACCCACCACCACCACCTACCTTCCGGTTCGGACCCTGC–3’
[0049] CalB-K10(R):5'-AATCGC CTCGAG TCATTTTTTTCTTTTTCTTTTTTTTCTTTTTCTTGGGGGTGACGATGCCG–3’
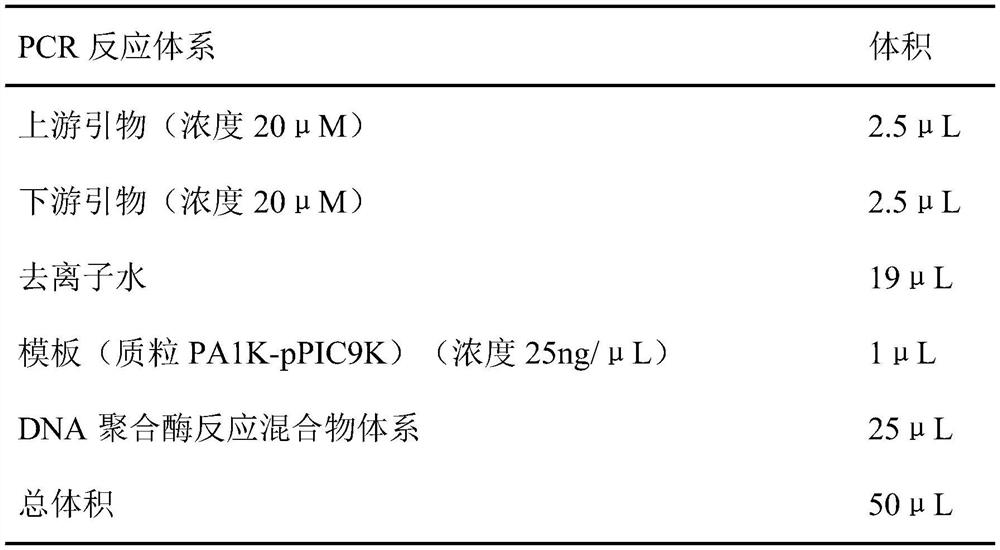
[0050] The plasmid PA1K-pPIC9K, upstream primers, downstream primers, deionized water, and DNA polymerase reaction mixture system were prepared according to the following volumes, and the lipase gene fragment 6His-CalB-10Lys rich in polyamine tags was amplified by PCR .
[0051]
[0052]
[0053] The PCR amplification program is: 94° C. for 2 min, 94° C. for 45 s, 55° C. for 45 s, and 72° C. for 2 min; a total of 35...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Embodiment 2: PCR method constructs and expresses the lipase gene 6His-CalB-10Arg with polyamine tag
[0058] The lipase CalB gene is derived from the plasmid PA1K-pPIC9K (Xiao Peiliang's master's thesis, the study of enzyme-catalyzed asymmetric synthesis of chiral caffeic acid derivatives), using PA1K-pPIC9K as a template, according to the known CAL-B gene sequence, design upstream primers The sequences of H6-CalB(F) (the underline is the NdeI restriction site) and the downstream primer CalB-R10(R) (the underline is the XhoI restriction site) are as follows:
[0059] H6-CalB(F):5'-ATATAT CATATG CACCACCCACCACCACCACCTACCTTCCGGTTCGGACCCTGC–3’
[0060] CalB-R10(R):5'-AATCGC CTCGAG TCAACGACGACGACGACGACGACGACGACGACGACGGGGGGTGACGATGCCG–3’
[0061] After the plasmid PA1K-pPIC9K, upstream primers, downstream primers, deionized water, and DNA polymerase reaction mixture system were prepared according to the following volumes, the polyamine-rich lipase gene fragment 6His-CalB-1...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Example 3: Expression plasmid transferred into BL21(DE3) competent cells for expression
[0068] The lipase expression plasmids 6His-CalB-10Lys-pET21a and 6His-CalB-10Arg-pET21a containing different polyamine tags prepared in Example 1 and Example 2 were respectively transferred into BL21 (DE3) competent cells, LB solid Medium plate, culture overnight, pick a single clone and inoculate it in LB liquid medium, cultivate to the logarithmic phase at 37°C; add 1mM IPTG, 16°C, 108rpm, cultivate for 14h, and obtain the expression strain BL21DE3 (6His-CalB-10Lys -pET21a) and the expression strain BL21DE3 (6His-CalB-10Arg-pET21a), induce the expression of the protein, that is, obtain the lipase containing the polyamine tag.
[0069] The amino acid sequence of 6His-CalB-10Lys lipase is:
[0070] MHHHHHHLPSGSDPAFSQPKSVLDAGLTCQGASPSSVSKPILLVPGTGTTGPQSFDSNWIPLSTQLGYTPCWISPPPFMLNDTQVNTEYMVNAITALYAGSGNNKLPVLTWSQGGLVAQWGLTFFPSIRSKVDRLMAFAPDYKGTVLAGPLDALAVSAPSVWQQTTGSALTTALRNAGGLTQIVP...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com