Preparation method and application of nanometer zero-valent ion composite material
A technology of nano-zero-valent iron and composite materials, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of loss of nano-characteristics, reduced reactivity, strong reactivity, etc., and achieve improved removal rate , solve the effect of agglomeration and activity reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
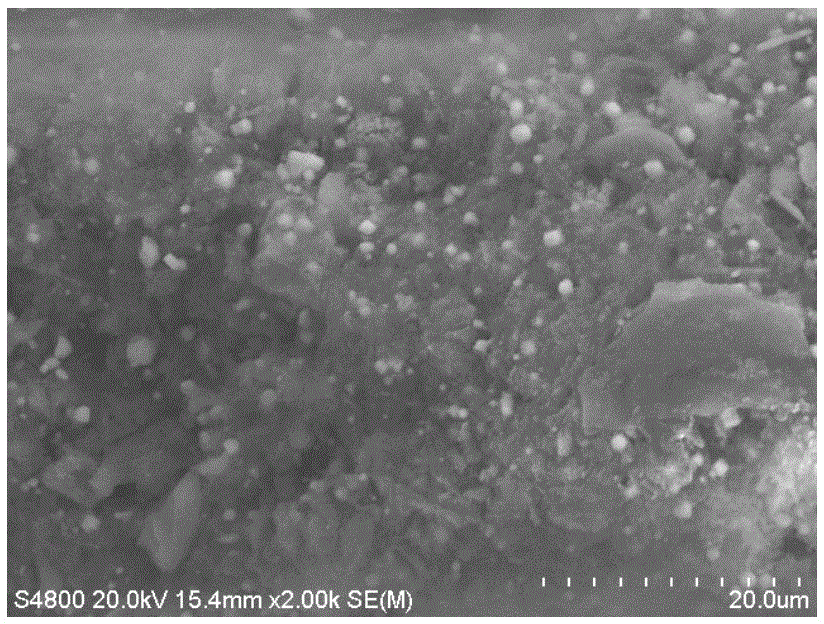
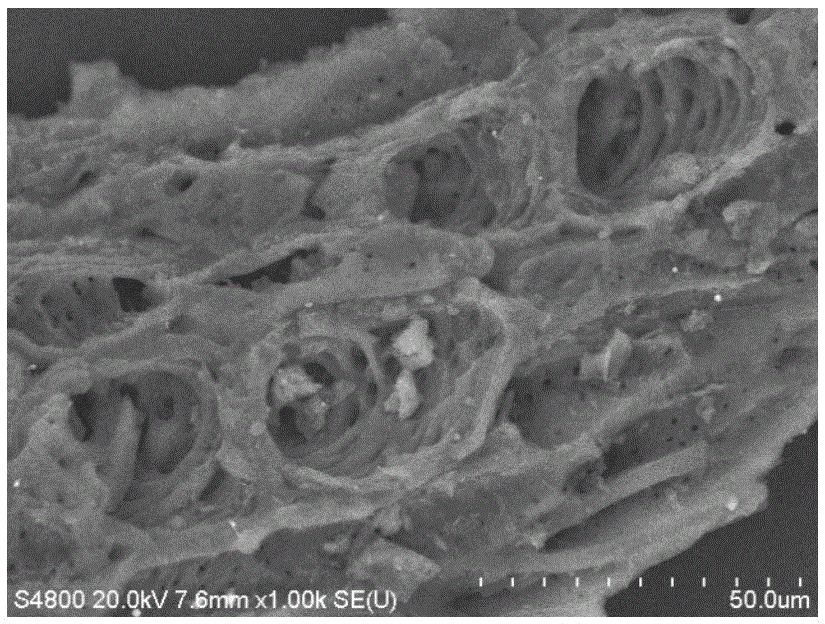
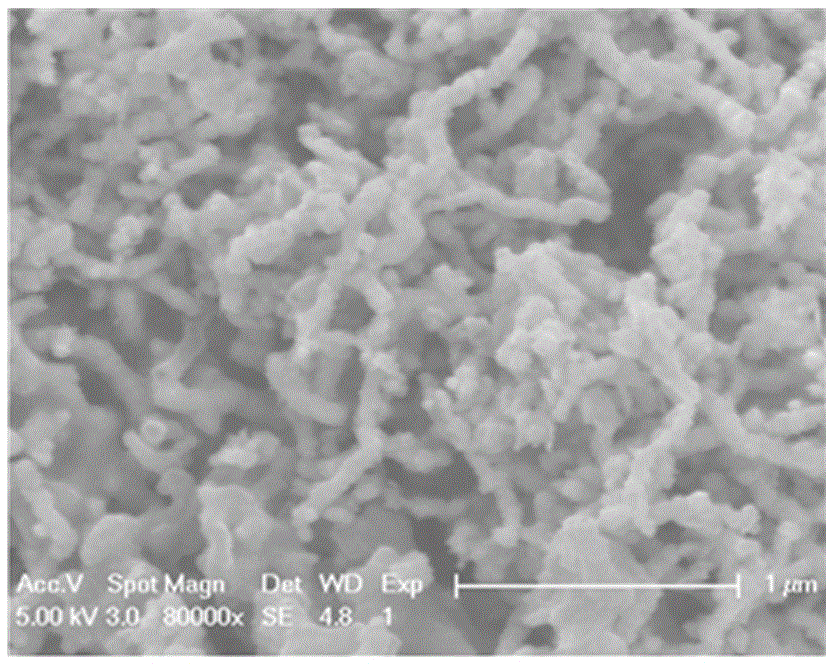
[0027] Because the nano zero-valent iron particles are easy to agglomerate, the particle size becomes larger, loses many nano-characteristics based on small size, and reduces the reactivity. Many studies at home and abroad have loaded nano-zero-valent iron on montmorillonite, bentonite, activated carbon, resin and other carriers to enhance its dispersion, but there are few reports on using biochar as a carrier, especially in the application of removing lead ions in water. has not been reported yet. Biochar (biochar) refers to the stable, highly aromatic carbon-rich solid material produced by high-temperature slow pyrolysis (usually <700 °C) of raw materials such as biomass and fossil fuels under oxygen-limited conditions. From the microstructure point of view, most biochars are composed of tightly packed and highly twisted aromatic ring sheets, with remarkable porosity. Compared with other carriers, biochar has a tubular porous structure and a larger specific surface area, wh...
Embodiment 1
[0041] Clean the corn stalks, dry them in an oven at 80°C for 48 hours, crush them, and set aside;
[0042] The crushed corn stalks were put into a crucible, placed in an anaerobic tube furnace, and fed with nitrogen for 30 minutes. Carbonize at 100°C for 1 hour, and carbonize at 400°C for 3 hours (heating rate is 10°C / min). After pyrolysis and cooling, take out the carbonized material, grind and pulverize it with a mortar, pass through an 80-mesh sieve, and make powdery biochar;
[0043] Under the condition of 85°C, modify the powdery biochar with 10% nitric acid solution for 8 hours, wash it with ultrapure water until neutral, dry it at 80°C, put it into a brown bottle and put it in a desiccator for later use;
[0044] 1gFeSO 4 •7H 2 O dissolved in 100mL ethanol solution (V 水 :V 乙醇 =1:4), ultrasonically oscillated for 5 minutes to make ferrous sulfate ethanol solution. The prepared ferrous sulfate solution and 1g of biochar powder were placed in a 500mL three-necked fl...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Clean the corn stalks, dry them in an oven at 80°C for 48 hours, crush them, and set aside;
[0049] The crushed corn stalks were put into a crucible, placed in an anaerobic tube furnace, and fed with nitrogen for 30 minutes. Carbonize at 100°C for 1 hour, and carbonize at 400°C for 3 hours (heating rate is 10°C / min). After pyrolysis and cooling, take out the carbonized material, grind and pulverize it with a mortar, pass through an 80-mesh sieve, and make powdery biochar;
[0050] Under the condition of 85°C, modify the powdery biochar with 20% nitric acid solution for 8 hours, wash it with ultrapure water until neutral, dry it at 80°C, put it into a brown bottle and put it in a desiccator for later use;
[0051] 1gFeSO 4 •7H 2 O dissolved in 100mL ethanol solution (V 水 :V 乙醇 =1:4), ultrasonically oscillated for 5 minutes to make ferrous sulfate ethanol solution. The prepared ferrous sulfate solution and 1g of biochar powder were placed in a 500mL three-necked fl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com