Mucosal vaccine composition
一种疫苗组合物、粘膜的技术,应用在药物组合、微生物、药物输送等方向,能够解决不明确、难以防御感染自身等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
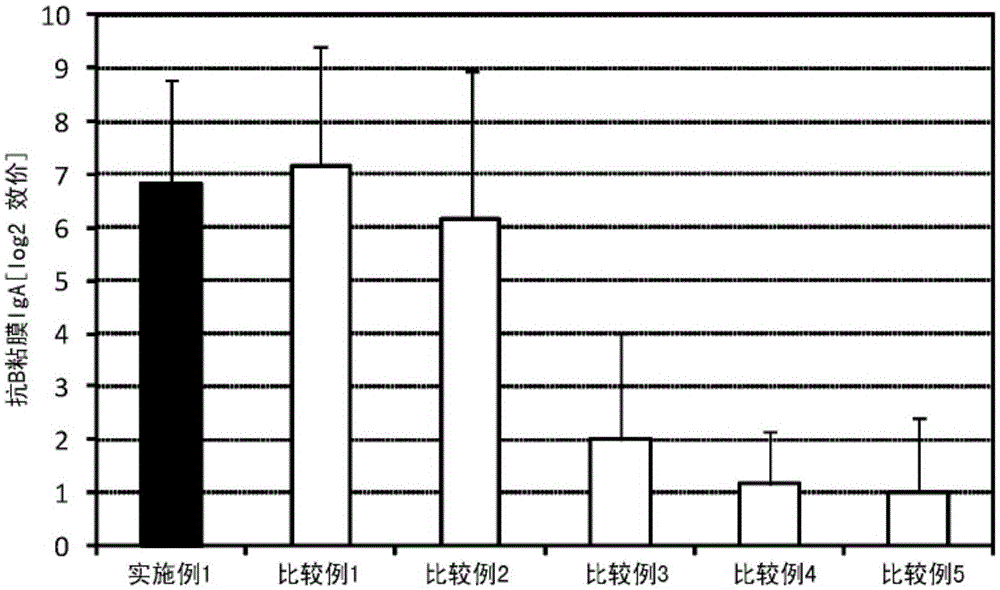
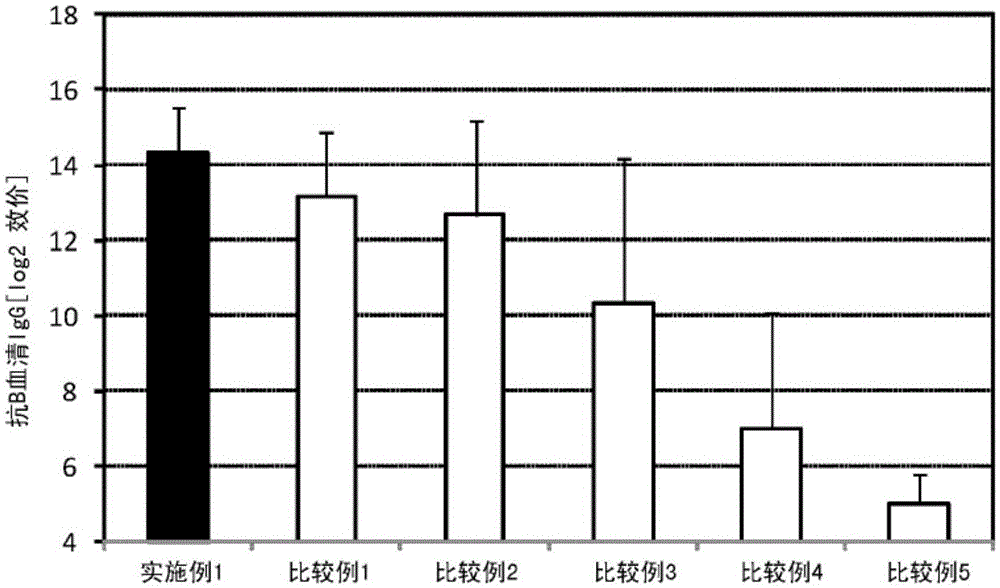
[0117] 2.25 μL (445 μg / mL) of a solution containing influenza vaccine antigen (B / Wisconsin / 1 / 2010, manufactured by Osaka University Institute of Microbial Diseases) and lipopolysaccharide derived from Pantoea agglomerans (NACALAITESQUE, INC. Phosphate buffer (manufactured by NACALAITESQUE, INC.) was added to 5 μL (2 mg / mL) of the solution to prepare 300 μL of a mucosal vaccine composition.
[0118] Six mice (8-week-old female BALB / C mice, Japan SLC, Inc.) were anesthetized, and 30 μL of the prepared vaccine composition was sublingually administered to each mouse. One week after the administration, the mice were anesthetized again, and 30 μL of the prepared vaccine composition was sublingually administered to each mouse. After the second administration and one week later, the serum and nasal cavity washing fluid of the mice were collected, and for the titer of influenza HA (type B)-specific IgG in the serum and the specific IgA of influenza HA (type B) in the nasal cavity washing...
Embodiment 2
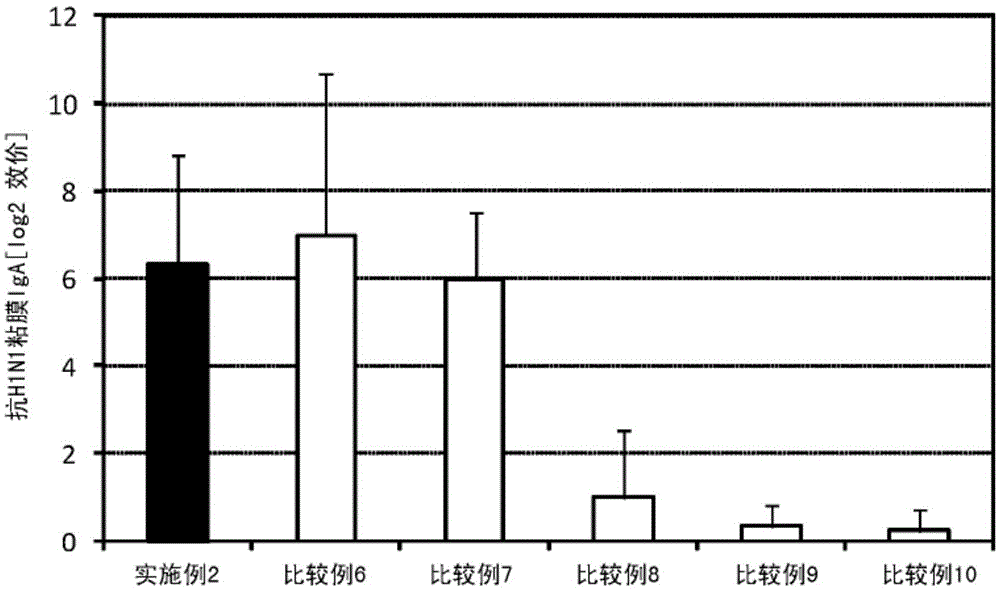
[0124] Add 1.25 μL (801 μg / mL) of a solution containing influenza vaccine antigen (A / California / 07 / 2009 (H1N1), manufactured by Osaka University Institute of Microbial Diseases) and lipopolysaccharide (NACALAITESQUE , INC.) was added to 5 μL (2 mg / mL) of a phosphate buffer solution (NACALAITESQUE, INC.) to prepare a 300 μL mucosal vaccine composition.
[0125] Six mice (8-week-old female BALB / C mice, Japan SLC, Inc.) were anesthetized, and 30 μL of the prepared mucosal vaccine composition was sublingually administered to each mouse. One week after the administration, the mice were anesthetized again, and 30 μL of the prepared mucosal vaccine composition was sublingually administered to each mouse. After the second administration and one week later, the serum and nasal cavity washing fluid of the mice were collected, and the influenza HA (H1N1) specific IgG titer in the serum and the influenza HA (H1N1) specific IgA titer in the nasal cavity washing fluid were collected. The d...
reference example 1
[0131] A sample containing the same antigen and immunostimulant as in the sample administered in Example 1, and the same (antigen / immunostimulant) as in Example 1 was produced, and its safety was evaluated. That is, 225 μL (445 μg / mL) of a solution containing influenza vaccine antigen (B / Wisconsin / 1 / 2010, manufactured by Osaka University Institute of Microbial Diseases) and lipopolysaccharide derived from Pantoea agglomerans (NACALAITESQUE, INC .) solution (2 mg / mL) was added to 500 μL (2 mg / mL) of phosphate buffer (NACALAITESQUE, INC.) to prepare 1000 μL of vaccine composition.
[0132] Eight mice (8-week-old female BALB / C mice, Japan SLC, Inc.) were anesthetized, and 100 μL of the prepared vaccine composition was subcutaneously administered to each mouse. The mice were followed up to 72 hours after the administration, and the survival rate was observed.
[0133] (Refer to Comparative Examples 1 and 2)
[0134] Instead of the lipopolysaccharide derived from Pantoea agglomer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com